«Щелкунчик»:
путешествие во времени
Долгая история самого новогоднего балета
Уже больше 125 лет балет «Щелкунчик» живет на театральной сцене — и все это время балетмейстеры продолжают искать новые подходы к музыке Петра Чайковского, а сказка Эрнста Гофмана раз за разом получает новые оригинальные воплощения.
В специальном проекте портала «Культура.РФ» вы узнаете, как рождался самый новогодний русский балет и что скрывал Чайковский от коллег-композиторов, а также услышите легендарную музыку из «Щелкунчика» в редких записях фирмы «Мелодия» и увидите старинные фотографии первых постановок балета, которые сохранились в ГЦТМ им. А.А. Бахрушина.
Уже больше 125 лет балет «Щелкунчик» живет на театральной сцене — и все это время балетмейстеры продолжают искать новые подходы к музыке Петра Чайковского, а сказка Эрнста Гофмана раз за разом получает новые оригинальные воплощения.
В специальном проекте портала «Культура.РФ» вы узнаете, как рождался самый новогодний русский балет и что скрывал Чайковский от коллег-композиторов, а также услышите легендарную музыку из «Щелкунчика» в редких записях фирмы «Мелодия» и увидите старинные фотографии первых постановок балета, которые сохранились в ГЦТМ им. А.А. Бахрушина.
Уже больше 125 лет балет «Щелкунчик» живет на театральной сцене — и все это время балетмейстеры продолжают искать новые подходы к музыке Петра Чайковского, а сказка Эрнста Гофмана раз за разом получает новые оригинальные воплощения.
В специальном проекте портала «Культура.РФ» вы узнаете, как рождался самый новогодний русский балет и что скрывал Чайковский от коллег-композиторов, а также услышите легендарную музыку из «Щелкунчика» в редких записях фирмы «Мелодия» и увидите старинные фотографии первых постановок балета, которые сохранились в ГЦТМ им. А.А. Бахрушина.
Секреты новой постановки «Щелкунчика» в МАМТе
Портал «Культура.РФ» и МАМТ представляют серию коротких видео в VK Клипах о новой постановке балета «Щелкунчик». Пользователи узнают, как создавался спектакль — от задумки до постановки на сцене. Официальный хештег проекта — #СекретыЩелкунчика.
Идея сказочного балета
В 1890 году Петр Чайковский получил от дирекции Императорских театров заказ на одноактную оперу и двухактный балет. Композитор, находившийся тогда на пике популярности после успешных премьер балета «Спящая красавица» и оперы «Пиковая дама», должен был написать музыку для так называемого сборного спектакля: оперу и балет планировали представить в один вечер в декабре 1891 года.
Для оперы Чайковский сам выбрал полюбившийся ему сюжет драмы датского писателя Генрика Герца — «Дочь короля Рене». А создать балет по сказке Гофмана «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король» ему предложили директор Императорских театров Иван Всеволожский и знаменитый балетмейстер Мариус Петипа. У последнего уже был примерный сценарий постановки, который, правда, сильно изменился в процессе работы.
Для оперы Чайковский сам выбрал полюбившийся ему сюжет драмы датского писателя Генрика Герца — «Дочь короля Рене». А создать балет по сказке Гофмана «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король» ему предложили директор Императорских театров Иван Всеволожский и знаменитый балетмейстер Мариус Петипа. У последнего уже был примерный сценарий постановки, который, правда, сильно изменился в процессе работы.
Чайковский согласился, поскольку со сказкой Гофмана был уже знаком. Сохранилось письмо, в котором композитор благодарил музыкального критика Сергея Флёрова, приславшего ему издание «Щелкунчика и Мышиного короля» на русском языке, и отзывался о книге как о «превосходнейшем переводе превосходной сказки».
Петр Чайковский. Балет «Щелкунчик»
Исполняет Государственный симфонический оркестр СССР, дирижер Евгений Светланов
1988 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
«Щелкунчик» и мотивы со всего света
По задумке Мариуса Петипа, новогодняя «пряничная» сказка про волшебный город Конфитюренбург должна была стать совершенно не такой, какой мы ее знаем. На создание либретто балетмейстера вдохновила тема Великой французской революции, столетие которой отмечали в 1889 году. Судя по записям Петипа, во втором акте балета должны были звучать популярные французские революционные песни — «Карманьола» и «Добрый путь, милый дю Молле!». Однако балет на революционную тематику в царской России конца XIX века поставить было невозможно, и многие идеи Петипа остались только на бумаге. Хотя мотив из песни «Добрый путь, милый дю Молле!» Чайковский по просьбе балетмейстера в партитуре сохранил.
Тамара Старженецкая. Эскиз декорации «Занавес» к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». 1978 год
Изображение: tchaikovskyhome.ru
Ирина Старженецкая. Эскиз декорации II акта к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». 1969 год
Изображение: tchaikovskyhome.ru
Тамара Старженецкая. Эскиз декорации «Бой мышей» к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». 1978 год
Изображение: tchaikovskyhome.ru
Ирина Старженецкая. Эскиз декорации I акта к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». 1969 год
Изображение: tchaikovskyhome.ru
Валерий Доррер. Эскиз декорации II акта к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». 1947 год
Изображение: tchaikovskyhome.ru
Музыка к «Щелкунчику» в целом богата на цитаты. Например, арабский танец «Кофе» из второго акта балета основан на традиционной грузинской колыбельной песне. Ее мелодию Чайковский лично слышал в Грузии: его брат Анатолий был вице-губернатором Тбилиси, и композитор несколько раз бывал у него в гостях.
В танце родителей и гостей звучит немецкая мелодия «Grossvater Tanz» («Танец дедушки»), которую до этого использовал в одном из своих произведений Роберт Шуман — один из любимых композиторов Чайковского. Мелодия «Grossvater Tanz» появилась в XVII веке, однако до сих пор доподлинно неизвестно, был ли этот танец народным или принадлежал авторству Карла Готлиба Геринга. На протяжении несколько веков лирический «Grossvater Tanz» исполняли в конце свадебной церемонии.
Петр Чайковский. Балет «Щелкунчик»
Большой симфонический оркестр Центрального телевидения и Всесоюзного радио, дирижер Владимир Федосеев
1986 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
Приключения челесты в России

В партитуре «Щелкунчика» Чайковский использовал новые для русской музыки второй половины XIX века инструменты. Внимание композитора привлекла французская челеста — клавишный металлофон. Ее Чайковский услышал на премьере драмы «Буря» Эрнеста Шоссона и остался очарован сказочным звучанием инструмента. О неожиданной находке он написал в 1891 году музыкальному издателю Петру Юргенсону:
«Я открыл в Париже новый оркестровый инструмент, нечто среднее между маленьким фортепиано и глокеншпилем, с божественно чудным звуком… Называется он Celesta Mustel и стоит тысячу двести франков. Купить его можно только в Париже у господина Мюстэля… Так как инструмент этот нужен будет в Петербурге раньше, чем в Москве, то желательно, чтобы его послали из Парижа к Осипу Ивановичу. Но при этом я желал бы, чтобы его никому не показывали, ибо боюсь, что Римский-Корсаков и Глазунов пронюхают и раньше меня воспользуются его необыкновенными эффектами».
Челеста звучит в знаменитом «Танце феи Драже». Она, как было указано в либретто Мариуса Петипа, подражает «звуку падающих капель».
Петр Чайковский. Балет «Щелкунчик»
Оркестр Большого театра СССР, дирижер Геннадий Рождественский
1960 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
«Главное — отделаться от балета»
Вскоре после начала работы над постановкой «Щелкунчика» от нее отказался Мариус Петипа, и балет передали второму балетмейстеру Мариинского театра Льву Иванову, который ранее ставил «Половецкие пляски» в «Князе Игоре» Александра Бородина и танцы в опере-балете Николая Римского-Корсакова «Млада».
Чайковскому работа над «Щелкунчиком» тоже давалась непросто: он долгое время не понимал, как соединить сложную симфоническую музыку и балет, второй акт которого представлял собой довольно наивный дивертисмент — набор танцев без сквозного сюжета и драматургии. По просьбе композитора премьеру постановки перенесли на год, а директор Императорских театров Всеволожский даже несколько раз извинялся перед Чайковским за то, что привлек его к столь «несерьезному» проекту. В 1891 году композитор писал: «Я работаю изо всей мочи, начинаю примиряться с сюжетом балета». Он мечтал: «Главное — отделаться от балета».
Партитуру балета Чайковский завершил в 1892 году. В премьерной постановке «Щелкунчика» было два акта и три картины. Первая показывала праздник в доме родителей Мари, вторая — сон девочки, в котором Щелкунчик воевал с крысиным войском и в финале превращался в прекрасного принца, а третья — сказочный город, куда попадали Мари и Щелкунчик.
Почему в балете в качестве антагонистов выступали крысы, а не мыши, как в сказке Гофмана, до сих пор остается загадкой. В рабочих материалах Петипа сохранилась лишь запись «Появляются крысы с мышиным царем» без каких-либо пояснений.
-
«Иногда мы безобидно и незаметно для зрителя шутим. Во втором акте есть проходка восьми мышей по заднику. Бывало, если в последней кулисе сидела девочка в роли Снежинки и переодевала пуанты, мыши хватали эту Снежинку на руки и, закрывая ее от зрителя спинами, перебегали по сцене в противоположную кулису. Зритель никогда такого озорства не замечал, ведь артисты работали опытные».
Петр Чайковский. Фрагменты из балета «Щелкунчик»
Академический симфонический оркестр Ленинградской государственной филармонии,
дирижер Евгений Мравинский
1981 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
«Невообразимая по безвкусию постановка»
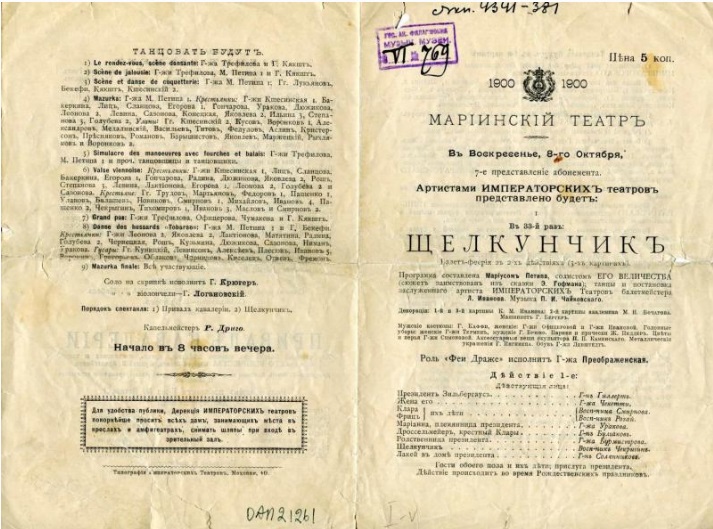
В декабре 1892 года «Щелкунчик» предстал перед публикой на сцене Мариинского театра, который входил в состав Императорских театров России. Критика была разгромной. Уровень искусства театральной постановки не соответствовал сложной симфонической музыке Чайковского, да и талант композитора рецензенты подвергли сомнению.
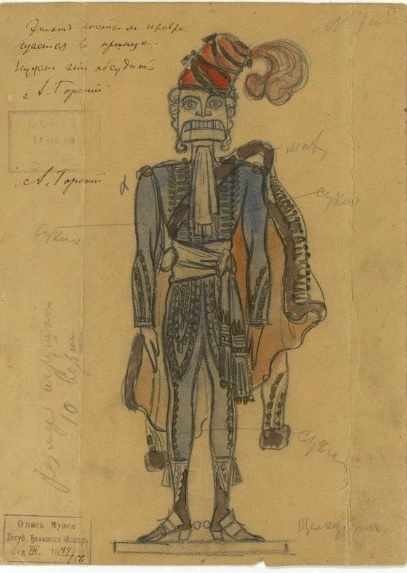
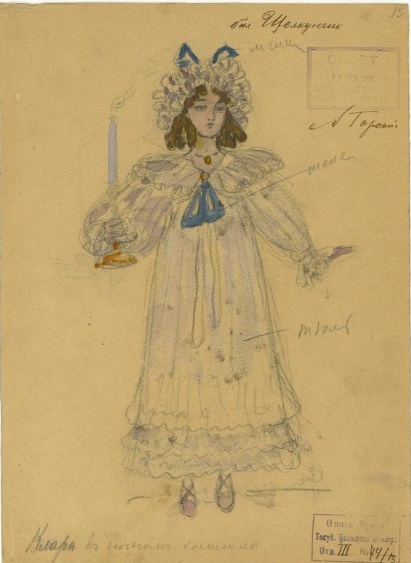
Иван Всеволожский. Эскиз костюмов Клары и ее брата Фрица. 1892 год
Изображение: sorokastore.com
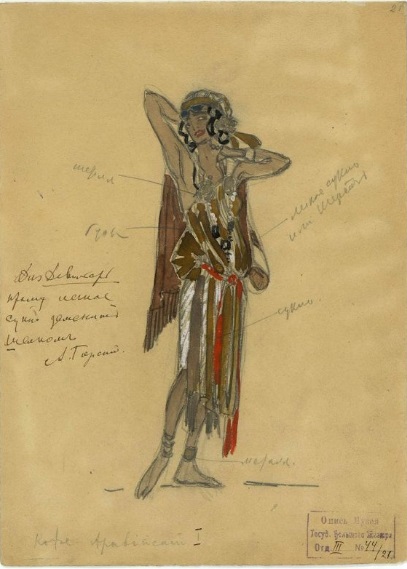
Иван Всеволожский. Эскиз костюмов феи Драже и Принца Коклюша
Изображение: sorokastore.com
Иван Всеволожский. Эскизы костюмов для балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик»
Изображение: sorokastore.com
Иван Всеволожский. Эскиз костюмов Клары и ее брата Фрица. 1892 год
Изображение: sorokastore.com
Иван Всеволожский. Эскиз костюмов феи Драже и Принца Коклюша
Изображение: sorokastore.com
Иван Всеволожский. Эскизы костюмов для балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик»
Изображение: sorokastore.com
«Вообще «Щелкунчик» поставлен преимущественно для детей — для танцовщиц в нем было весьма мало, для искусства — ровно ничего. Даже музыка оказалась довольно слабою», — писал Константин Скальковский в «Биржевой газете».
«Трудно представить себе что-нибудь скучнее и бессмысленнее «Щелкунчика», — отзывался Николай Безобразов из «Петербургской газете».
Но самый известный критик той эпохи дал балету положительный отзыв. Александр Бенуа писал брату Анатолию о генеральной репетиции «Щелкунчика»: «Государь был в восхищении, призывал в ложу и наговорил массу сочувственных слов. Постановка… великолепна и в балете даже слишком великолепна — глаза устают от этой роскоши».
Партию Мари исполнила Станислава Белинская, а Щелкунчика — Сергей Легат. Оба танцовщика на тот момент еще учились на балетном отделении Петербургского театрального училища: Легату было 17 лет, а Белинской — всего 12. Критики были беспощадны и к ним.
Но самый известный критик той эпохи дал балету положительный отзыв. Александр Бенуа писал брату Анатолию о генеральной репетиции «Щелкунчика»: «Государь был в восхищении, призывал в ложу и наговорил массу сочувственных слов. Постановка… великолепна и в балете даже слишком великолепна — глаза устают от этой роскоши».
Партию Мари исполнила Станислава Белинская, а Щелкунчика — Сергей Легат. Оба танцовщика на тот момент еще учились на балетном отделении Петербургского театрального училища: Легату было 17 лет, а Белинской — всего 12. Критики были беспощадны и к ним.
Сам Чайковский в письмах друзьям и родным отмечал, что даже внешне балет выглядел аляповато и безвкусно, вспоминал, что ему было сложно смотреть на сцену.
«После ряда удачных постановок, как «Пиковая дама» и «Спящая красавица», появилась невообразимая по безвкусию постановка балета Чайковского «Щелкунчик», в последней картине которого некоторые балетные артистки были одеты сдобными бриошами из булочной Филиппова», — писал будущий директор Императорских театров Владимир Теляковский.
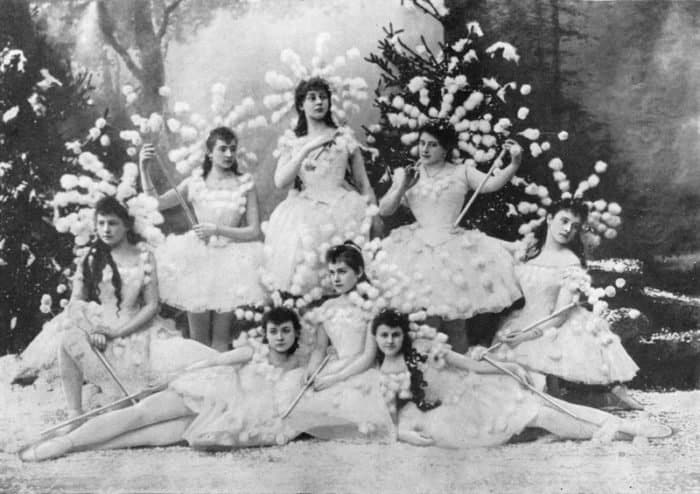
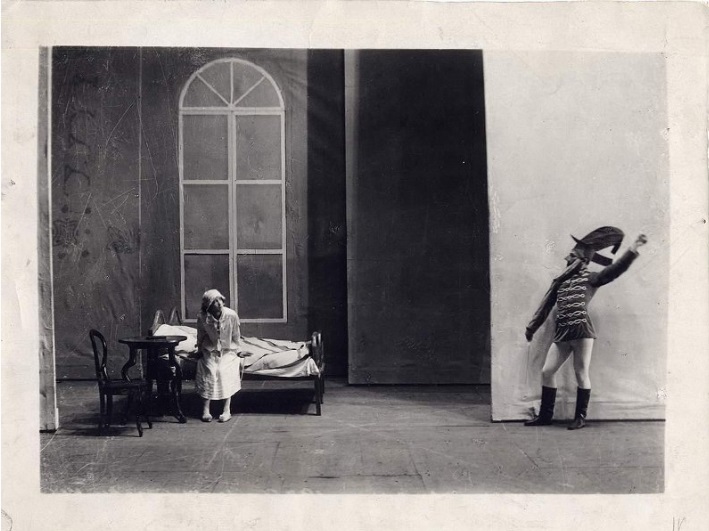
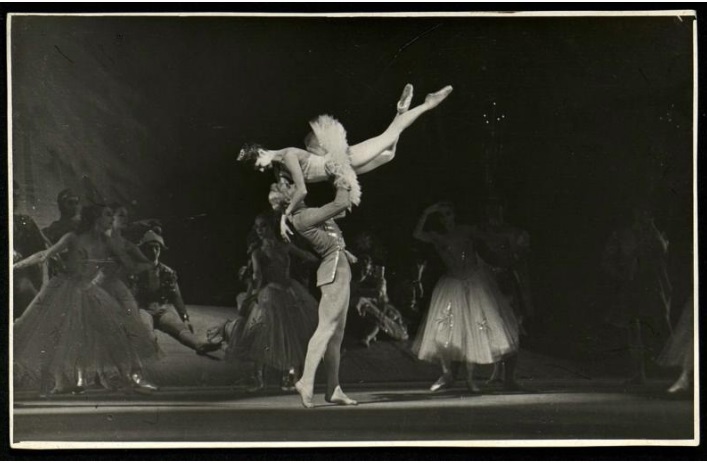
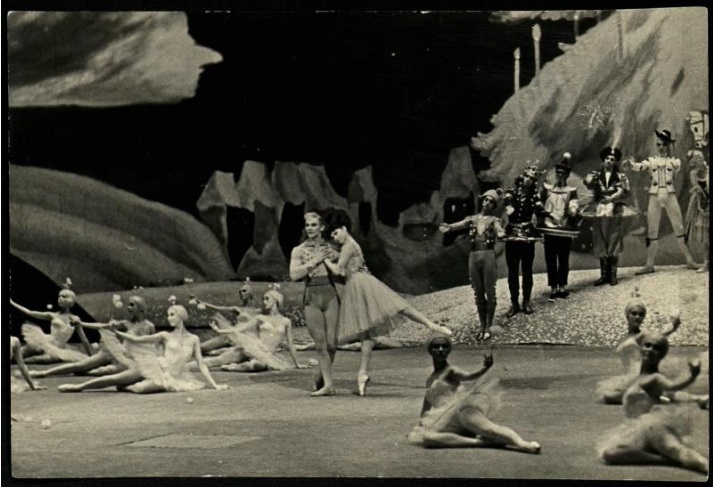
Балет «Щелкунчик». Дорина в роли
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Дорина в роли. Обратная сторона фотографии
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
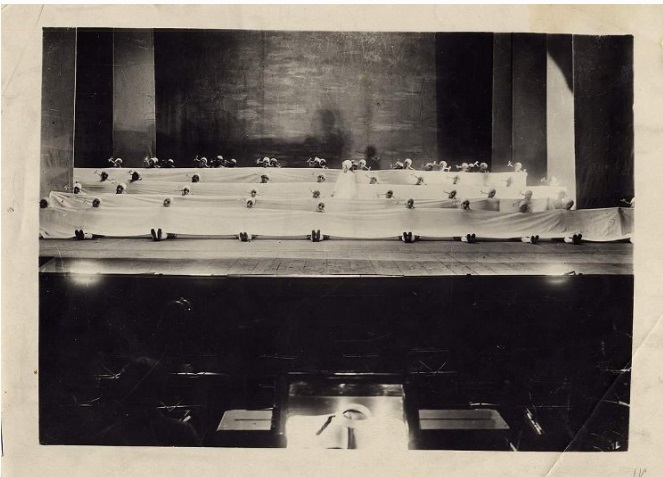
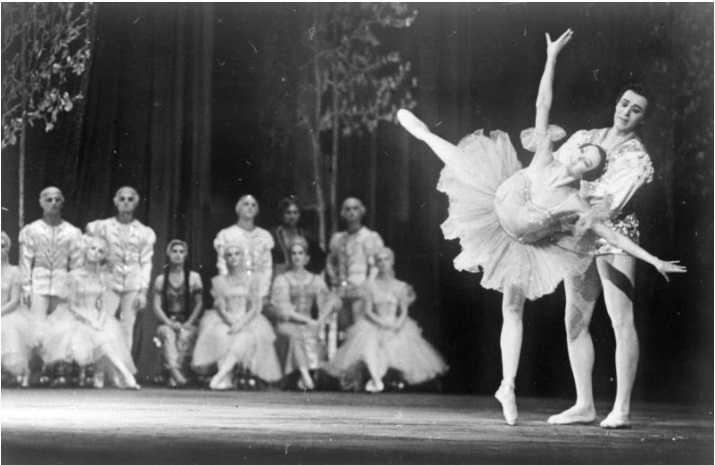
Балет «Щелкунчик». Ольга Преображенская и Сергей Легат в ролях. 1900 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Дорина в роли
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Дорина в роли. Обратная сторона фотографии
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Ольга Преображенская и Сергей Легат в ролях. 1900 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Впрочем, несмотря на оглушительный провал, «Щелкунчик» продержался в репертуаре Мариинского театра более 30 лет.
-
«В детстве я ни разу не видел полномасштабный классический балет. Спектакль «Щелкунчик» я увидел, уже будучи учеником МГАХ. С тех пор этот спектакль так устойчиво закрепился в моей артистической жизни, что Новый год для меня ассоциируется именно с «Щелкунчиком».
Петр Чайковский. Сюита из балета «Щелкунчик»
Государственный симфонический оркестр СССР, дирижер Евгений Светланов
1987 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
«Щелкунчик» в России и за рубежом
-
В 1919 году по-новому интерпретировать «Щелкунчика» решился балетмейстер Александр Горский на сцене московского Большого театра. Постановка, появившаяся в разгар революционных событий, прожила недолго.
1919 год
-
В 1923 году в Петербурге появилась новая версия спектакля от балетмейстера Федора Лопухова. На сцене царил авангард: декорации представляли собой восемь разноцветных щитов на колесиках. Спектакль показали всего девять раз.
1923 год
-
В 1934 году «Щелкунчик» снова предстал на сцене Мариинки. Вернуть его в репертуар поручили балетмейстеру Василию Вайнонену. В целом постановка была похожа на первоначальную версию Петипа — Иванова, но оказалась более удачной. Главные партии на премьере исполнили Галина Уланова и Константин Сергеев. На родной сцене «Щелкунчик» Вайнонена идет до сих пор — уже более 80 лет.
1934 год
-
В 1934 году «Щелкунчика» впервые реконструировали за границей. Свою версию балета в Лондоне представил Николай Сергеев, эмигрировавший после Октябрьской революции.
1934 год
-
Воспитанник Мариинки Джордж Баланчин поставил «Щелкунчика» в Нью-Йорке в 1954 году. Его версия целиком и полностью опиралась на сценарий Петипа, в который постановщик добавил новые танцы и мизансцены. Балет уже больше полувека с постоянным успехом идет каждую зиму на нью-йоркской сцене. В экранизации его постановки 1993 года главную партию танцевал ученик балетной школы Баланчина — Маколей Калкин, тогда уже снявшийся в известном фильме «Один дома».
1954 год
-
В 1967 году в Англию «Щелкунчика» вернул Рудольф Нуреев в 1967 году. Сперва новый балет показали на сцене Королевской шведской оперы в Стокгольме, а потом постановка Нуреева обосновалась в лондонском Ковент-Гардене. Еще через несколько лет балет смогли увидеть зрители миланского театра Ла Скала. Став директором балетной труппы Парижской оперы, Нуреев поставил «Щелкунчика» и там. В его версии сказка стала ближе к оригиналу Гофмана: менее «пряничной» и куда более готичной.
1967 год
-
Свою версию «Щелкунчика» на сцене нью-йоркского Американского театра балета в 1976 году представил Михаил Барышников. Главную партию в балете он исполнил сам. Премьера «Щелкунчика» Барышникова прошла с успехом, но, когда в 1989 году он ушел из Американского театра балета, его постановки убрали из репертуара. Зато видеоверсия спектакля сохранилась до наших дней.
1976 год
-
«Я пересматривал большое количество видеозаписей с артистами старшего поколения и должен признать, что многое почерпнул для своей роли в плане нюансов, манеры, настроений. Однако передо мной не стояла задача подражать кому-то из великих, я пытался создать своего Принца. При этом я не забываю, что моего Принца придумывает в своем воображении Маша, в её голове я идеален. А знаете, как непросто соответствовать ожиданиям опытных прим-балерин Большого?!»
Петр Чайковский. Сюита из балета «Щелкунчик»
Оркестр Ленинградского академического театра им. С. Кирова, дирижер Валерий Гергиев
1988 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
Современная сценография
В 1966 году в Большом театре появилась постановка Юрия Григоровича, которую историки театра считают почти идеальным решением партитуры Чайковского. Взяв за основу сценарий Петипа, Григорович создал сквозной сюжет всего спектакля. Второй акт из дивертисмента превратился в сказочное путешествие героев по елке, которое завершалось венчанием Маши и Щелкунчика.
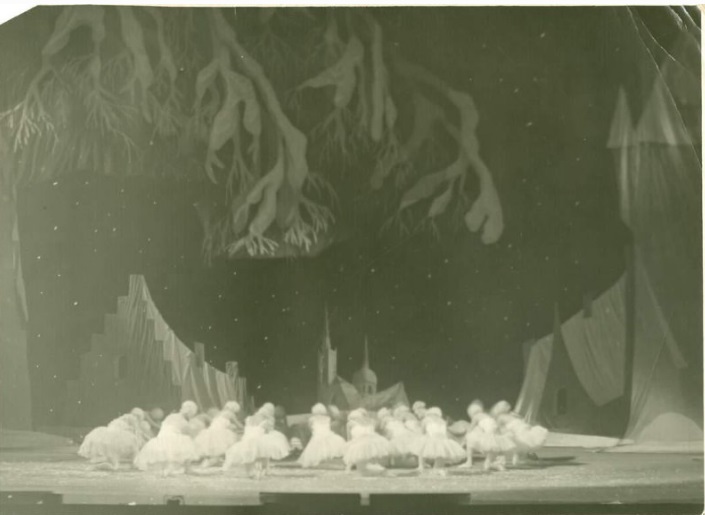
Балет «Щелкунчик». Екатерина Максимова в роли Маши и Владимир Васильев в роли Принца. Государственный Большой театр оперы и балета, Москва. 1966 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Александр Рубашкин, Галина Уланова, Екатерина Максимова в роли Маши и Владимир Васильев в роли Принца на поклонах. Юбилей Галины Улановой. 1980 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Галина Уланова в роли Маши. Государственный академический театр оперы и балета, Москва. 1934 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Екатерина Максимова в роли Маши и Владимир Васильев в роли Принца. Государственный Большой театр оперы и балета, Москва. 1966 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Александр Рубашкин, Галина Уланова, Екатерина Максимова в роли Маши и Владимир Васильев в роли Принца на поклонах. Юбилей Галины Улановой. 1980 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Балет «Щелкунчик». Галина Уланова в роли Маши. Государственный академический театр оперы и балета, Москва. 1934 год
Государственный центральный театральный музей им. А.А. Бахрушина, Москва
Сам балетмейстер еще во время учебы в Ленинградском хореографическом училище в 1930-х годах танцевал в «Щелкунчике» Вайнонена. «Мы, дети, очень любили этот балет и хорошо знали, что когда закончим танцевать и подойдем к накрытому на сцене праздничному столу, то обязательно найдем на нем приготовленные для нас настоящие сладости», — вспоминал Григорович.
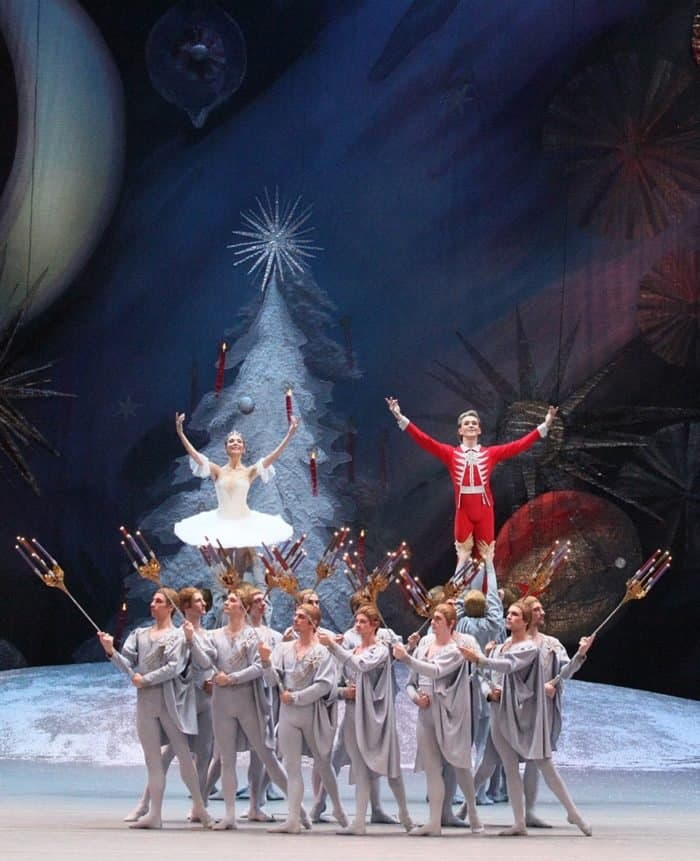
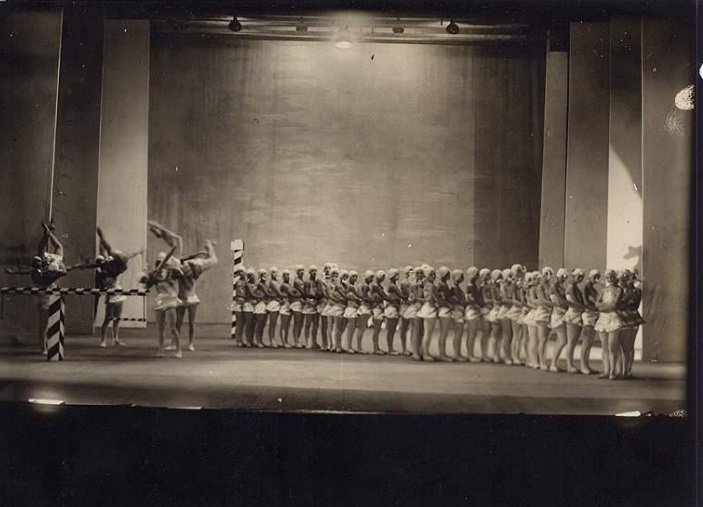
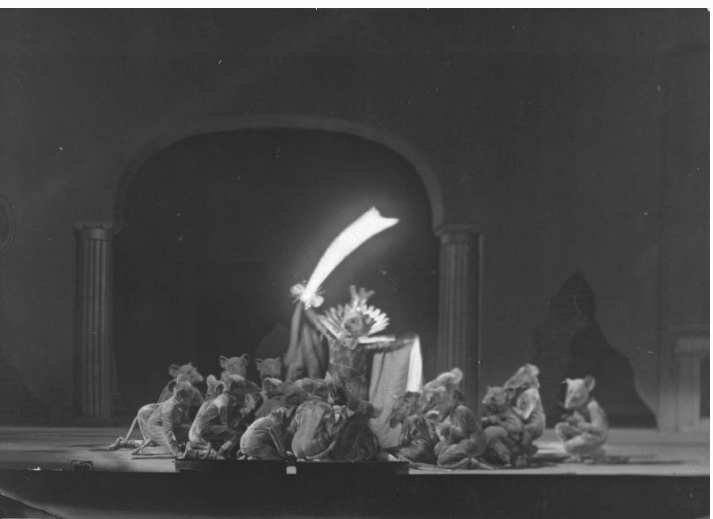
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Московский государственный академический детский музыкальный театр им. Н.И. Сац, Москва
Фотография: Елена Лапина / teatr-sats.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Большой театр России, Москва
Фотография: theatrehd.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Большой театр России, Москва
Фотография: theatrehd.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Большой театр России, Москва
Фотография: theatrehd.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
В постановке Григоровича танцевала главная пара советского балета тех лет — Владимир Васильев и Екатерина Максимова. Именно эта версия «Щелкунчика» идет и в наши дни на сцене Большого театра.
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Академия Русского балета им. А.Я. Вагановой, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Большой театр России, Москва
Фотография: coolconnections.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Большой театр России, Москва
Фотография: theatrehd.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Большой театр России, Москва
Фотография: theatrehd.ru
Сцена из балета Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
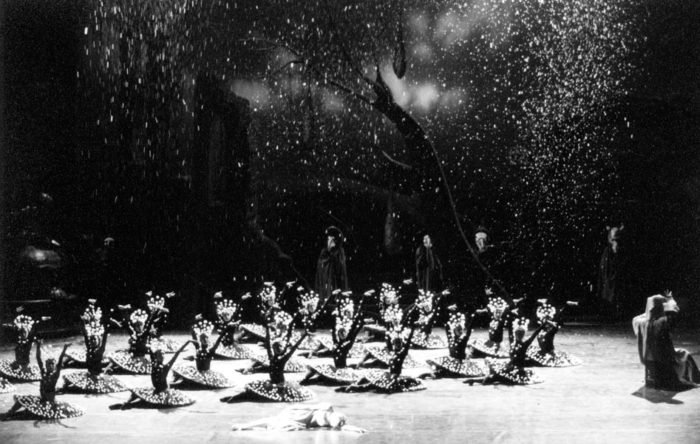
В 2001 году на второй сцене Мариинского театра появилась одна из самых необычных вариаций «Щелкунчика». Либретто Мариуса Петипа переработал Михаил Шемякин, значительно «гофманизировав» спектакль. Хореограф добавил в знакомую сказку множество фантасмагорических образов, гротескных персонажей и совсем не детских тем.
Михаил Шемякин. Эскиз костюма к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Крысенок в головке сыра. 2000 год
Изображение: artchive.ru
Эскиз костюма к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Крыс-ветеран. 2000 год
Изображение: artchive.ru
Михаил Шемякин. Эскиз костюма к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Мухолов. 2000 год
Изображение: artchive.ru
Михаил Шемякин. Эскиз костюма к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Крысенок в головке сыра. 2000 год
Изображение: artchive.ru
Эскиз костюма к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Крыс-ветеран. 2000 год
Изображение: artchive.ru
Михаил Шемякин. Эскиз костюма к балету Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик». Мухолов. 2000 год
Изображение: artchive.ru
Шемякин писал, что в центре его балета — история одинокой девочки в чуждом для нее мире, который она не может и не хочет принять. Маша в этой версии «Щелкунчика» предстает нелюбимой дочерью, которую не принимают ни родители, ни сверстники. Поэтому в финале она превращается в сахарную фигурку на торте, чтобы никогда не возвращаться в безрадостный реальный мир.
Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Валерия Мартынюк в роли Маши и Алексей Недвига в роли Щелкунчика-куклы. Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Действие первое. Сцена «Панорама». Маша и Щелкунчик отправляются в путешествие в дедушкином башмаке. Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Действие первое. Сцена вторая. «Рождественский праздник». Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Действие первое. Сцена третья «Баталия». Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Вальс цветов. Вальс цветов. Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Pas de trois пчелок. Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
Анастасия Петушкова в роли Королевы снежинок. Балет Петра Чайковского «Щелкунчик» в постановке Михаила Шемякина. Государственный академический Мариинский театр, Санкт-Петербург
Фотография: mariinsky.ru
-
«Спектакль «Щелкунчик» Григоровича я впервые увидел, когда уже был приглашен в Большой театр. У меня ни один другой спектакль не пробуждает такие чувства и мысли о волшебстве. Мы, взрослые, которые, как нам кажется, знают эту жизнь с ее цинизмом и неурядицами, вдруг погружаемся в атмосферу, где создается магия. Здесь мы снова превращаемся в детей с их чистыми мечтами и искренней верой в чудеса. Здесь можно загадывать желания, которые исполняются».
Петр Чайковский. Концертная сюита из балета «Щелкунчик»
Переложение для фортепиано Михаила Плетнева
Михаил Плетнев, фортепиано
1978 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
«Щелкунчик» на слух
Слушайте литературно-музыкальную композицию «Щелкунчик» и беседу о балете от фирмы «Мелодия».
Петр Чайковский. Балет «Щелкунчик»
Беседа о музыке для общеобразовательных школ
1968 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
Музыкально-литературная композиция
по балету Петра Чайковского и сказке Эрнста Гофмана
1966 год, запись из архива Фирмы «Мелодия»
Постановки «Щелкунчика» в российских театрах
Смотрите две видеоверсии спектакля в постановке Юрия Григоровича — главные партии в них исполнили Владимир Васильев и Екатерина Максимова. А еще знакомьтесь с другими интерпретациями классического балета. Государственный Московский Театр балета классической хореографии создал на его основе детское представление, а режиссер Петр Базарон из екатеринбургского театра «Щелкунчик» перенес действие спектакля в современность.
-
«Щелкунчик»
Государственный академический Большой театр России
1966 год -
«Щелкунчик»
Государственный академический Большой театр России
1977 год -
«Щелкунчик»
Муниципальный театр балета «Щелкунчик»
2019 год -
«Щелкунчик»
Московский театр балета классической хореографии
2020 год
-
«Щелкунчик»
Государственный академический Большой театр России
1966 год -
«Щелкунчик»
Государственный академический Большой театр России
1977 год -
«Щелкунчик»
Муниципальный театр балета «Щелкунчик»
2019 год -
«Щелкунчик»
Московский театр балета классической хореографии
2020 год
Автор текста: Полина Пендина
Автор проекта: Екатерина Тарасова
Верстка: Кристина Мацевич
The Nutcracker (Russian: Щелкунчик[a], tr. Shchelkunchik listen (help·info)) is an 1892 two-act «fairy ballet» (Russian: балет-феерия, balet-feyeriya) set on Christmas Eve at the foot of a Christmas tree in a child’s imagination. The music is by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky, his Opus 71. The plot is an adaptation of E. T. A. Hoffmann’s 1816 short story The Nutcracker and the Mouse King. The ballet’s first choreographer was Marius Petipa, with whom Tchaikovsky had worked three years earlier on The Sleeping Beauty, assisted by Lev Ivanov. Although the complete and staged The Nutcracker ballet was not as successful as the 20-minute Nutcracker Suite Tchaikovsky had premiered nine months earlier, The Nutcracker soon became popular.
Since the late 1960s, it has been danced by countless ballet companies, especially in North America.[1] Major American ballet companies generate around 40% of their annual ticket revenues from performances of The Nutcracker.[2][3] The ballet’s score has been used in several film adaptations of Hoffmann’s story.
Tchaikovsky’s score has become one of his most famous compositions. Among other things, the score is noted for its use of the celesta, an instrument the composer had already employed in his much lesser known symphonic ballad The Voyevoda (1891).
Composition[edit]
After the success of The Sleeping Beauty in 1890, Ivan Vsevolozhsky, the director of the Imperial Theatres, commissioned Tchaikovsky to compose a double-bill program featuring both an opera and a ballet. The opera would be Iolanta. For the ballet, Tchaikovsky would again join forces with Marius Petipa, with whom he had collaborated on The Sleeping Beauty. The material Vsevolozhsky chose was an adaptation of E. T. A. Hoffmann’s story «The Nutcracker and the Mouse King», by Alexandre Dumas called «The Story of a Nutcracker».[4] The plot of Hoffmann’s story (and Dumas’ adaptation) was greatly simplified for the two-act ballet. Hoffmann’s tale contains a long flashback story within its main plot titled «The Tale of the Hard Nut», which explains how the Prince was turned into the Nutcracker. This had to be excised for the ballet.[5]
Petipa gave Tchaikovsky extremely detailed instructions for the composition of each number, down to the tempo and number of bars.[4] The completion of the work was interrupted for a short time when Tchaikovsky visited the United States for twenty-five days to conduct concerts for the opening of Carnegie Hall.[6] Tchaikovsky composed parts of The Nutcracker in Rouen, France.[7]
History[edit]
Saint Petersburg premiere[edit]
(Left to right) Lydia Rubtsova as Marianna, Stanislava Belinskaya as Clara and Vassily Stukolkin as Fritz, in the original production of The Nutcracker (Imperial Mariinsky Theatre, Saint Petersburg, 1892)
Varvara Nikitina as the Sugar Plum Fairy and Pavel Gerdt as the Cavalier, in a later performance in the original run of The Nutcracker, 1892
The first performance of The Nutcracker was not deemed a success.[8] The reaction to the dancers themselves was ambivalent. While some critics praised Dell’Era on her pointework as the Sugar Plum Fairy (she allegedly received five curtain-calls), one critic called her «corpulent» and «podgy». Olga Preobrajenskaya as the Columbine doll was panned by one critic as «completely insipid» and praised as «charming» by another.[9]
Alexandre Benois described the choreography of the battle scene as confusing: «One can not understand anything. Disorderly pushing about from corner to corner and running backwards and forwards – quite amateurish.»[9]
The libretto was criticized as «lopsided»[10] and for not being faithful to the Hoffmann tale. Much of the criticism focused on the featuring of children so prominently in the ballet,[11] and many bemoaned the fact that the ballerina did not dance until the Grand Pas de Deux near the end of the second act (which did not occur until nearly midnight during the program).[10] Some found the transition between the mundane world of the first scene and the fantasy world of the second act too abrupt.[4] Reception was better for Tchaikovsky’s score. Some critics called it «astonishingly rich in detailed inspiration» and «from beginning to end, beautiful, melodious, original, and characteristic».[12] But this also was not unanimous, as some critics found the party scene «ponderous» and the Grand Pas de Deux «insipid».[13]
Subsequent productions[edit]
In 1919, choreographer Alexander Gorsky staged a production which eliminated the Sugar Plum Fairy and her Cavalier and gave their dances to Clara and the Nutcracker Prince, who were played by adults instead of children. This was the first production to do so. An abridged version of the ballet was first performed outside Russia in Budapest (Royal Opera House) in 1927, with choreography by Ede Brada.[14][unreliable source?] In 1934, choreographer Vasili Vainonen staged a version of the work that addressed many of the criticisms of the original 1892 production by casting adult dancers in the roles of Clara and the Prince, as Gorsky had. The Vainonen version influenced several later productions.[4]
The first complete performance outside Russia took place in England in 1934,[8] staged by Nicholas Sergeyev after Petipa’s original choreography. Annual performances of the ballet have been staged there since 1952.[15] Another abridged version of the ballet, performed by the Ballet Russe de Monte Carlo, was staged in New York City in 1940,[16] Alexandra Fedorova – again, after Petipa’s version.[8] The ballet’s first complete United States performance was on 24 December 1944 by the San Francisco Ballet, staged by its artistic director, Willam Christensen, and starring Gisella Caccialanza as the Sugar Plum Fairy, and Jocelyn Vollmar as the Snow Queen.[17][8] After the enormous success of this production, San Francisco Ballet has presented Nutcracker every Christmas Eve and throughout the winter season, debuting new productions in 1944, 1954, 1967, and 2004. The original Christensen version continues in Salt Lake City, where Christensen relocated in 1948. It has been performed every year since 1963 by the Christensen-founded Ballet West.[18]
The New York City Ballet gave its first annual performance of George Balanchine’s reworked staging of The Nutcracker in 1954.[8] The performance of Maria Tallchief in the role of the Sugar Plum Fairy helped elevate the work from obscurity into an annual Christmas classic and the industry’s most reliable box-office draw. Critic Walter Terry remarked that «Maria Tallchief, as the Sugar Plum Fairy, is herself a creature of magic, dancing the seemingly impossible with effortless beauty of movement, electrifying us with her brilliance, enchanting us with her radiance of being. Does she have any equals anywhere, inside or outside of fairyland? While watching her in The Nutcracker, one is tempted to doubt it.»[19]
Since Gorsky, Vainonen and Balanchine’s productions, many other choreographers have made their own versions. Some institute the changes made by Gorsky and Vainonen while others, like Balanchine, utilize the original libretto. Some notable productions include Rudolf Nureyev’s 1963 production for the Royal Ballet, Yury Grigorovich for the Bolshoi Ballet, Mikhail Baryshnikov for the American Ballet Theatre, Fernand Nault for Les Grands Ballets Canadiens starting in 1964, Kent Stowell for Pacific Northwest Ballet starting in 1983, and Peter Wright for the Royal Ballet and the Birmingham Royal Ballet. In recent years, revisionist productions, including those by Mark Morris, Matthew Bourne, and Mikhail Chemiakin have appeared; these depart radically from both the original 1892 libretto and Vainonen’s revival, while Maurice Béjart’s version completely discards the original plot and characters. In addition to annual live stagings of the work, many productions have also been televised or released on home video.[1]
Roles[edit]
The following extrapolation of the characters (in order of appearance) is drawn from an examination of the stage directions in the score.[20]
Act I[edit]
- Herr Stahlbaum
- His wife
- His children, including:
- Clara, his daughter, sometimes known as Marie or Masha
- Fritz, his son
- Louise, his daughter
- Children Guests
- Parents dressed as incroyables
- Herr Drosselmeyer
- His nephew (in some versions) who resembles the Nutcracker Prince and is played by the same dancer
- Dolls (spring-activated, sometimes all three dancers instead):
- Harlequin and Columbine, appearing out of a cabbage (1st gift)
- Vivandière and a Soldier (2nd gift)
- Nutcracker (3rd gift, at first a normal-sized toy, then full-sized and «speaking», then a Prince)
- Owl (on clock, changing into Drosselmeyer)
- Mice
- Sentinel (speaking role)
- The Bunny
- Soldiers (of the Nutcracker)
- Mouse King
- Snowflakes (sometimes Snow Crystals, sometimes accompanying a Snow Queen and King)
Act II[edit]
Ivan Vsevolozhsky’s original costume sketch for The Nutcracker (1892)
- Angels and/or Fairies
- Sugar Plum Fairy
- Clara/Marie
- The Nutcracker Prince
- 12 Pages
- Eminent members of the court
- Spanish dancers (Chocolate)
- Arabian dancers (Coffee)
- Chinese dancers (Tea)
- Russian dancers (Candy Canes)
- Danish shepherdesses / French mirliton players (Marzipan)
- Mother Ginger
- Polichinelles (Mother Ginger’s Children)
- Dewdrop
- Flowers
- Sugar Plum Fairy’s Cavalier
Plot [edit]
Below is a synopsis based on the original 1892 libretto by Marius Petipa. The story varies from production to production, though most follow the basic outline. The names of the characters also vary. In the original Hoffmann story, the young heroine is called Marie Stahlbaum and Clara (Klärchen) is her doll’s name. In the adaptation by Dumas on which Petipa based his libretto, her name is Marie Silberhaus.[5] In still other productions, such as Baryshnikov’s, Clara is Clara Stahlbaum rather than Clara Silberhaus.
Act I[edit]
Scene 1: The Stahlbaum Home
Konstantin Ivanov’s original sketch for the set of The Nutcracker (1892)
The ballet is set on Christmas Eve, where family and friends have gathered in the parlor to decorate the beautiful Christmas tree in preparation for the party. Once the tree is finished, the children are summoned. They stand in awe of the tree sparkling with candles and decorations.
The party begins.[21] A march is played.[22] Presents are given out to the children. Suddenly, as the owl-topped grandfather clock strikes eight, a mysterious figure enters the room. It is Drosselmeyer— a local councilman, magician, and Clara’s godfather. He is also a talented toymaker who has brought with him gifts for the children, including four lifelike dolls who dance to the delight of all.[23] He then has them put away for safekeeping.
Clara and her brother Fritz are sad to see the dolls being taken away, but Drosselmeyer has yet another toy for them: a wooden nutcracker carved in the shape of a little man, which the other children ignore. Clara immediately takes a liking to it, but Fritz accidentally breaks it. Clara is heartbroken, but Drosselmeyer fixes the nutcracker, much to everyone’s relief.
During the night, after everyone else has gone to bed, Clara returns to the parlor to check on her beloved nutcracker. As she reaches the little bed, the clock strikes midnight and she looks up to see Drosselmeyer perched atop it. Suddenly, mice begin to fill the room and the Christmas tree begins to grow to dizzying heights. The nutcracker also grows to life size. Clara finds herself in the midst of a battle between an army of gingerbread soldiers and the mice, led by their king. The mice begin to eat the gingerbread soldiers.
The nutcracker appears to lead the soldiers, who are joined by tin soldiers, and by dolls who serve as doctors to carry away the wounded. As the seven-headed Mouse King advances on the still-wounded nutcracker, Clara throws her slipper at him, distracting him long enough for the nutcracker to stab him.[24]
Scene 2: A Pine Forest
The mice retreat and the nutcracker is transformed into a handsome Prince.[25] He leads Clara through the moonlit night to a pine forest in which the snowflakes dance around them, beckoning them on to his kingdom as the first act ends.[26][27]
Act II[edit]
The Land of Sweets
Ivan Vsevolozhsky’s original costume designs for Mother Gigogne and her Polichinelle children, 1892
Clara and the Prince travel to the beautiful Land of Sweets, ruled by the Sugar Plum Fairy in the Prince’s place until his return. He recounts for her how he had been saved from the Mouse King by Clara and transformed back into himself.
In honor of the young heroine, a celebration of sweets from around the world is produced: chocolate from Spain, coffee from Arabia,[28][29] tea from China,[30] and candy canes from Russia[31] all dance for their amusement; Danish shepherdesses perform on their flutes;[32] Mother Ginger has her children, the Polichinelles, emerge from under her enormous hoop skirt to dance; a string of beautiful flowers perform a waltz.[33][34] To conclude the night, the Sugar Plum Fairy and her Cavalier perform a dance.[35][36]
A final waltz is performed by all the sweets, after which the Sugar Plum Fairy ushers Clara and the Prince down from their throne. He bows to her, she kisses Clara goodbye, and leads them to a reindeer-drawn sleigh. It takes off as they wave goodbye to all the subjects who wave back.
In the original libretto, the ballet’s apotheosis «represents a large beehive with flying bees, closely guarding their riches».[37] Just like Swan Lake, there have been various alternative endings created in productions subsequent to the original.
Musical sources and influences[edit]
The Nutcracker is one of the composer’s most popular compositions. The music belongs to the Romantic period and contains some of his most memorable melodies, several of which are frequently used in television and film. (They are often heard in TV commercials shown during the Christmas season.[38])
Tchaikovsky is said to have argued with a friend who wagered that the composer could not write a melody based on a one-octave scale in sequence. Tchaikovsky asked if it mattered whether the notes were in ascending or descending order and was assured it did not. This resulted in the Adagio from the Grand pas de deux, which, in the ballet, nearly always immediately follows the «Waltz of the Flowers». A story is also told that Tchaikovsky’s sister Alexandra (9 January 1842 — 9 April 1891[39]) had died shortly before he began composition of the ballet and that his sister’s death influenced him to compose a melancholy, descending scale melody for the adagio of the Grand Pas de Deux.[40] However, it is more naturally perceived as a dreams-come-true theme because of another celebrated scale use, the ascending one in the Barcarolle from The Seasons.[41]
Danse de la Fée-Dragée (Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy) is the third pas de deux in Act II
Tchaikovsky was less satisfied with The Nutcracker than with The Sleeping Beauty. (In the film Fantasia, commentator Deems Taylor observes that he «really detested» the score.) Tchaikovsky accepted the commission from Vsevolozhsky but did not particularly want to write the ballet[42] (though he did write to a friend while composing it, «I am daily becoming more and more attuned to my task»).[43]
Instrumentation[edit]
The music is written for an orchestra with the following instrumentation.
Musical scenes[edit]
From the Imperial Ballet’s 1892 program[edit]
Titles of all of the numbers listed here come from Marius Petipa’s original scenario as well as the original libretto and programs of the first production of 1892. All libretti and programs of works performed on the stages of the Imperial Theatres were titled in French, which was the official language of the Imperial Court, as well as the language from which balletic terminology is derived.
Casse-Noisette. Ballet-féerie in two acts and three tableaux with apotheosis.
|
Act I
|
Act II
Grand divertissement—
|
Structure[edit]
List of acts, scenes (tableaux) and musical numbers, along with tempo indications. Numbers are given according to the original Russian and French titles of the first edition score (1892), the piano reduction score by Sergei Taneyev (1892), both published by P. Jurgenson in Moscow, and the Soviet collected edition of the composer’s works, as reprinted Melville, New York: Belwin Mills [n.d.][44]
| Scene | No. | English title | French title | Russian title | Tempo indication | Notes | Listen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Act I | |||||||
| Miniature Overture | Ouverture miniature | Увертюра | Allegro giusto | ||||
| Tableau I | 1 | Scene (The Christmas Tree) | Scène (L’arbre de Noël) | Сцена (Сцена украшения и зажигания ёлки) | Allegro non troppo – Più moderato – Allegro vivace | scene of decorating and lighting the Christmas tree | |
| 2 | March (also March of the Toy Soldiers) | Marche | Марш | Tempo di marcia viva | |||
| 3 | Children’s Gallop and Dance of the Parents | Petit galop des enfants et Entrée des parents | Детский галоп и вход (танец) родителей | Presto – Andante – Allegro | |||
| 4 | Dance Scene (Arrival of Drosselmeyer) | Scène dansante | Сцена с танцами | Andantino – Allegro vivo – Andantino sostenuto – Più andante – Allegro molto vivace – Tempo di Valse – Presto | Drosselmeyer’s arrival and distribution of presents | ||
| 5 | Scene and Grandfather Waltz | Scène et danse du Gross-Vater | Сцена и танец Гросфатер | Andante – Andantino – Moderato assai – Andante – L’istesso tempo – Tempo di Gross-Vater – Allegro vivacissimo | |||
| 6 | Scene (Clara and the Nutcracker) | Scène | Сцена | Allegro semplice – Moderato con moto – Allegro giusto – Più allegro – Moderato assai | departure of the guests | ||
| 7 | Scene (The Battle) | Scène | Сцена | Allegro vivo | |||
| Tableau II | 8 | Scene (A Pine Forest in Winter) | Scène | Сцена | Andante | a.k.a. «Journey through the Snow» | |
| 9 | Waltz of the Snowflakes | Valse des flocons de neige | Вальс снежных хлопьев | Tempo di Valse, ma con moto – Presto | |||
| Act II | |||||||
| Tableau III | 10 | Scene (The Magic Castle in the Land of Sweets) | Scène | Сцена | Andante | introduction | |
| 11 | Scene (Clara and Nutcracker Prince) | Scène | Сцена | Andante con moto – Moderato – Allegro agitato – Poco più allegro – Tempo precedente | arrival of Clara and the Prince | ||
| 12 | Divertissement | Divertissement | Дивертисмент | ||||
| a. Chocolate (Spanish Dance) | a. Le chocolat (Danse espagnole) | a. Шоколад (Испанский танец) | Allegro brillante | ||||
| b. Coffee (Arabian Dance) | b. Le café (Danse arabe) | b. Кофе (Арабский танец) | Commodo | ||||
| c. Tea (Chinese Dance) | c. Le thé (Danse chinoise) | c. Чай (Китайский танец) | Allegro moderato | ||||
| d. Trepak (Russian Dance) | d. Trépak (Danse russe) | d. Трепак (русский танец, карамельная трость)[45] | Tempo di Trepak, Presto | ||||
| e. Dance of the Reed Flutes | e. Les Mirlitons (Danse des Mirlitons) | e. Танец пастушков (Датский марципан)[45] | Andantino | ||||
| f. Mother Ginger and the Polichinelles | f. La mère Gigogne et les polichinelles | f. Полишинели | Allegro giocoso – Andante – Allegro vivo | ||||
| 13 | Waltz of the Flowers | Valse des fleurs | Вальс цветов | Tempo di Valse | |||
| 14 | Pas de Deux | Pas de deux | Па-де-дё | ||||
| a. Intrada (Sugar Plum Fairy and Her Cavalier) | a. La Fée-Dragée et le Prince Orgeat | a. Танец принца Оршада и Феи Драже | Andante maestoso | ||||
| b. Variation I: Tarantella | b. Variation I: Tarantelle (Pour le danseur) | b. Вариация I: Тарантелла | Tempo di Tarantella | ||||
| c. Variation II: Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy | c. Variation II: Danse de la Fée-Dragée (Pour la danseuse) | c. Вариация II: Танец Феи Драже | Andante ma non troppo – Presto | ||||
| d. Coda | d. Coda | d. Кода | Vivace assai | ||||
| 15 | Final Waltz and Apotheosis | Valse finale et Apothéose | Финальный вальс и Апофеоз | Tempo di Valse – Molto meno |
Concert excerpts and arrangements[edit]
Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker Suite, Op. 71a[edit]
Tchaikovsky made a selection of eight of the numbers from the ballet before the ballet’s December 1892 première, forming The Nutcracker Suite, Op. 71a, intended for concert performance. The suite was first performed, under the composer’s direction, on 19 March 1892 at an assembly of the Saint Petersburg branch of the Musical Society.[46] The suite became instantly popular, with almost every number encored at its premiere,[47] while the complete ballet did not begin to achieve its great popularity until after the George Balanchine staging became a hit in New York City.[48] The suite became very popular on the concert stage, and was excerpted in Disney’s Fantasia, omitting the two movements prior to the Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy . The outline below represents the selection and sequence of the Nutcracker Suite made by the composer:
- Miniature Overture
- Characteristic Dances
- March
- Dance of the Sugar-Plum Fairy [ending altered from ballet version]
- Russian Dance (Trepak)
- Arabian Dance (coffee)
- Chinese Dance (tea)
- Dance of the Reed Flutes (Mirlitons)
- Waltz of the Flowers
Grainger: Paraphrase on Tchaikovsky’s Flower Waltz, for solo piano[edit]
The Paraphrase on Tchaikovsky’s Flower Waltz is a successful piano arrangement from one of the movements from The Nutcracker by the pianist and composer Percy Grainger.
Pletnev: Concert suite from The Nutcracker, for solo piano[edit]
The pianist and conductor Mikhail Pletnev adapted some of the music into a virtuosic concert suite for piano solo:
- March
- Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy
- Tarantella
- Intermezzo (Journey through the Snow)
- Russian Trepak
- Chinese Dance
- Andante maestoso (Pas de Deux)
Contemporary arrangements[edit]
- In 1942, Freddy Martin and his orchestra recorded The Nutcracker Suite for Dance Orchestra on a set of 4 10-inch 78-RPM records. An arrangement of the suite that lay between dance music and jazz, it was released by RCA Victor.[49]
- In 1947, Fred Waring and His Pennsylvanians recorded «The Nutcracker Suite» on a two-part Decca Records 12-inch 78 RPM record with one part on each side as Decca DU 90022,[50] packaged in a picture sleeve. This version had custom lyrics written for Waring’s chorus by among others, Waring himself. The arrangements were by Harry Simeone.
- In 1952, the Les Brown big band recorded a version of the Nutcracker Suite, arranged by Frank Comstock, for Coral Records.[51] Brown rerecorded the arrangement in stereo for his 1958 Capitol Records album Concert Modern.
- In 1960, Duke Ellington and Billy Strayhorn composed jazz interpretations of pieces from Tchaikovsky’s score, recorded and released on LP as The Nutcracker Suite.[52] In 1999, this suite was supplemented with additional arrangements from the score by David Berger for The Harlem Nutcracker, a production of the ballet by choreographer Donald Byrd (born 1949) set during the Harlem Renaissance.[53]
- In 1960, Shorty Rogers released The Swingin’ Nutcracker, featuring jazz interpretations of pieces from Tchaikovsky’s score.
- In 1962, American poet and humorist Ogden Nash wrote verses inspired by the ballet,[54] and these verses have sometimes been performed in concert versions of the Nutcracker Suite. It has been recorded with Peter Ustinov reciting the verses, and the music is unchanged from the original.[55]
- In 1962 a novelty boogie piano arrangement of the «Marche», titled «Nut Rocker», was a No.1 single in the UK, and No.21 in the USA. Credited to B. Bumble and the Stingers, it was produced by Kim Fowley and featured studio musicians Al Hazan (piano), Earl Palmer (drums), Tommy Tedesco (guitar) and Red Callender (bass). «Nut Rocker» has subsequently been covered by many others including The Shadows, Emerson, Lake & Palmer, The Ventures, Dropkick Murphys, The Brian Setzer Orchestra, and the Trans-Siberian Orchestra. The Ventures’ own instrumental rock cover of «Nut Rocker», known as «Nutty», is commonly connected to the NHL team, the Boston Bruins, from being used as the theme for the Bruins’ telecast games for over two decades, from the late 1960s. In 2004, The Invincible Czars arranged, recorded, and now annually perform the entire suite for rock band.
- The Trans-Siberian Orchestra’s first album, Christmas Eve and Other Stories, includes an instrumental piece titled «A Mad Russian’s Christmas», which is a rock version of music from The Nutcracker.
- On the other end of the scale is the comedic Spike Jones version released in December 1945 as «Spike Jones presents for the Kiddies: The Nutcracker Suite (With Apologies to Tchaikovsky)», featuring humorous lyrics by Foster Carling and additional music by Joe «Country» Washburne. An abridged version was released in 1971 as part of the long play record Spike Jones is Murdering the Classics, one of the rare comedic pop records to be issued on the prestigious RCA Red Seal label.
- International choreographer Val Caniparoli has created several versions of The Nutcracker ballet for Louisville Ballet, Cincinnati Ballet, Royal New Zealand Ballet, and Grand Rapids Ballet.[56] While his ballets remain classically rooted, he has contemporarized them with changes such as making Marie an adult instead of a child, or having Drosselmeir emerges through the clock face during the overture making «him more humorous and mischievous.»[57] Caniparoli has been influenced by his simultaneous career as a dancer, having joined San Francisco Ballet in 1971 and performing as Drosselmeir and other various Nutcracker roles ever since that time.[58]
- The Disco Biscuits, a trance-fusion jam band from Philadelphia, have performed «Waltz of the Flowers» and «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on multiple occasions.
- The Los Angeles Guitar Quartet (LAGQ) recorded the Suite arranged for four acoustic guitars on their CD recording Dances from Renaissance to Nutcracker (1992, Delos).
- In 1993, guitarist Tim Sparks recorded his arrangements for acoustic guitar on The Nutcracker Suite.
- The Shirim Klezmer Orchestra released a klezmer version, titled «Klezmer Nutcracker,» in 1998 on the Newport label. The album became the basis for a December 2008 production by Ellen Kushner, titled The Klezmer Nutcracker and staged off-Broadway in New York City.[59]
- In 2002, The Constructus Corporation used the melody of Sugar Plum Fairy for their track «Choose Your Own Adventure».
- In 2009, Pet Shop Boys used a melody from «March» for their track «All Over the World», taken from their album Yes.
- In 2012, jazz pianist Eyran Katsenelenbogen released his renditions of Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy, Dance of the Reed Flutes, Russian Dance and Waltz of the Flowers from the Nutcracker Suite.
- In 2014, Pentatonix released an a cappella arrangement of «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on the holiday album That’s Christmas to Me and received a Grammy Award on 16 February 2016 for best arrangement.
- In 2016, Jennifer Thomas included an instrumental version of «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on her album Winter Symphony.
- In 2017, Lindsey Stirling released her version of «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on her holiday album Warmer in the Winter.[60]
- In 2018, Pentatonix released an a cappella arrangement of «Waltz of the Flowers» on the holiday album Christmas Is Here!.
- In 2019, Madonna sampled a portion on her song «Dark Ballet» from her Madame X album.[61]
- In 2019, Mariah Carey released a normal and an a cappella version of ‘Sugar Plum Fairy’ entitled the ‘Sugar Plum Fairy Introlude’ to open and close her 25th Deluxe Anniversary Edition of Merry Christmas.[62]
- In 2020, Coone made a hardstyle cover version titled «The Nutcracker».[63]
Selected discography[edit]
Many recordings have been made since 1909 of the Nutcracker Suite, which made its initial appearance on disc that year in what is now historically considered the first record album.[64] This recording was conducted by Herman Finck and featured the London Palace Orchestra.[65] But it was not until the LP album was developed that recordings of the complete ballet began to be made. Because of the ballet’s approximate hour and a half length when performed without intermission, applause, or interpolated numbers, it fits very comfortably onto two LPs. Most CD recordings take up two discs, often with fillers. An exception is the 81-minute 1998 Philips recording by Valery Gergiev that fits onto one CD because of Gergiev’s somewhat brisker speeds.
- In 1954, the first complete recording of the ballet was released, a 2-LP set in mono sound released by Mercury Records. The cover design was by George Maas with illustrations by Dorothy Maas.[66] The music was performed by the Minneapolis Symphony Orchestra, conducted by Antal Doráti. Doráti later re-recorded the complete ballet in stereo, with the London Symphony Orchestra in 1962 for Mercury and with the Amsterdam Concertgebouw Orchestra in 1975 for Philips Classics. According to Mercury Records, the 1962 recording was made on 35mm magnetic film rather than audio tape, and used album cover art identical to that of the 1954 recording.[67][68] Dorati is the only conductor so far to have made three different recordings of the complete ballet. Some have hailed the 1975 recording as the finest ever made of the complete ballet.[69] It is also faithful to the score in employing a boys’ choir in the Waltz of the Snowflakes. Many other recordings use an adult or mixed choir.
- In 1956, Artur Rodziński and the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra made a complete recording of the ballet in stereo for Westminster Records.
- In 1959, the first stereo LP album set of the complete ballet, with Ernest Ansermet conducting the Orchestre de la Suisse Romande, appeared on Decca Records in the UK and London Records in the US.
- The first complete stereo Nutcracker with a Russian conductor and a Russian orchestra appeared in 1960, when Gennady Rozhdestvensky’s recording of it, with the Bolshoi Theatre Orchestra, was issued first in the Soviet Union on Melodiya, then imported to the U.S. on Columbia Masterworks. It was also Columbia Masterworks’ first complete Nutcracker.[70]
With the advent of the stereo LP coinciding with the growing popularity of the complete ballet, many other complete recordings of it have been made. Notable conductors who have done so include Maurice Abravanel, André Previn, Michael Tilson Thomas, Mariss Jansons, Seiji Ozawa, Richard Bonynge, Semyon Bychkov, Alexander Vedernikov, Ondrej Lenard, Mikhail Pletnev, and most recently, Simon Rattle.[71] A CD of excerpts from the Tilson Thomas version had as its album cover art a painting of Mikhail Baryshnikov in his Nutcracker costume; perhaps this was due to the fact that the Tilson Thomas recording was released by CBS Masterworks, and CBS had first telecast the Baryshnikov «Nutcracker».[72]
- The soundtrack of the 1977 television production with Mikhail Baryshnikov and Gelsey Kirkland, featuring the National Philharmonic Orchestra conducted by Kenneth Schermerhorn, was issued in stereo on a CBS Masterworks 2 LP-set, but it has not appeared on CD. The LP soundtrack recording was, for a time, the only stereo version of the Baryshnikov Nutcracker available, since the show was originally telecast only in mono, and it was not until recently that it began to be telecast with stereo sound. The sound portion of the DVD is also in stereo.
- The first complete recording of the ballet in digital stereo was issued in 1985, on a two-CD RCA set featuring Leonard Slatkin conducting the St. Louis Symphony Orchestra. This album originally had no «filler», but it has recently been re-issued on a multi-CD set containing complete recordings of Tchaikovsky’s two other ballets, Swan Lake and The Sleeping Beauty. This three-ballet album has now gone out of print.
There have been two major theatrical film versions of the ballet, made within seven years of each other, and both were given soundtrack albums.
- The first theatrical film adaptation, made in 1985, is of the Pacific Northwest Ballet version, and was conducted by Sir Charles Mackerras. The music is played in this production by the London Symphony Orchestra. The film was directed by Carroll Ballard, who had never before directed a ballet film (and has not done so since). Patricia Barker played Clara in the fantasy sequences, and Vanessa Sharp played her in the Christmas party scene. Wade Walthall was the Nutcracker Prince.
- The second film adaptation was a 1993 film of the New York City Ballet version, titled George Balanchine’s The Nutcracker, with David Zinman conducting the New York City Ballet Orchestra. The director was Emile Ardolino, who had won the Emmy, Obie, and Academy Awards for filming dance, and was to die of AIDS later that year. Principal dancers included the Balanchine muse Darci Kistler, who played the Sugar Plum Fairy, Heather Watts, Damian Woetzel, and Kyra Nichols. Two well-known actors also took part: Macaulay Culkin appeared as the Nutcracker/Prince, and Kevin Kline served as the offscreen narrator. The soundtrack features the interpolated number from The Sleeping Beauty that Balanchine used in the production, and the music is heard on the album in the order that it appears in the film, not in the order that it appears in the original ballet.[73]
- Notable albums of excerpts from the ballet, rather than just the usual Nutcracker Suite, were recorded by Eugene Ormandy conducting the Philadelphia Orchestra for Columbia Masterworks, and Fritz Reiner and the Chicago Symphony Orchestra for RCA Victor. Arthur Fiedler and the Boston Pops Orchestra (for RCA), as well as Erich Kunzel and the Cincinnati Pops Orchestra (for Telarc) have also recorded albums of extended excerpts. The original edition of Michael Tilson Thomas’s version with the Philharmonia Orchestra on CBS Masterworks was complete, but is out of print;[74] the currently available edition is abridged.[75]
Neither Ormandy, Reiner, nor Fiedler ever recorded a complete version of the ballet; however, Kunzel’s album of excerpts runs 73 minutes, containing more than two-thirds of the music. Conductor Neeme Järvi has recorded act 2 of the ballet complete, along with excerpts from Swan Lake. The music is played by the Royal Scottish National Orchestra.[76]
- Many famous conductors of the twentieth century made recordings of the suite, but not of the complete ballet. These include Arturo Toscanini, Sir Thomas Beecham, Claudio Abbado, Leonard Bernstein, Herbert von Karajan, James Levine, Sir Neville Marriner, Robert Shaw, Mstislav Rostropovich, Sir Georg Solti, Leopold Stokowski, Zubin Mehta, and John Williams.
- In 2007, Josh Perschbacher recorded an organ transcription of the Nutcracker Suite.
Ethnic stereotypes and US activism[edit]
In 2013, Dance Magazine printed the opinions of three directors. Ronald Alexander of Steps on Broadway and The Harlem School of the Arts said the characters in some of the dances were «borderline caricatures, if not downright demeaning». He also said some productions had made changes to improve this. In the Arabian dance, for example, it was not necessary to portray a woman as a «seductress», showing too much skin. Alexander tried a more positive portrayal of the Chinese, but this was replaced by the more traditional version, despite positive reception. Stoner Winslett of the Richmond Ballet said The Nutcracker was not racist and that her productions had a «diverse cast». Donald Byrd of Spectrum Dance Theater saw the ballet as Eurocentric and not racist.[77] Chloe Angyal, in Feministing, referred to «unbelievably offensive racial and ethnic stereotypes». Some people who have performed in productions of the ballet do not see a problem because they are continuing what is viewed as «a tradition».[78] According to George Balanchine, «Coffee» was a sensuous belly dance intended for the fathers, not the children.[79]
In The New Republic in 2014, Alice Robb described white people wearing «harem pants and a straw hat, eyes painted to look slanted» and «wearing chopsticks in their black wigs» in the Chinese dance. The Arabian dance, she said, has a woman who «slinks around the stage in a belly shirt, bells attached to her ankles».[78] One of the problems, Robb said, was the use of white people to play ethnic roles, because of the directors’ desire for everyone to look the same.[78]
Among the attempts to change the dances were Austin McCormick making the Arabian dance into a pole dance, and San Francisco Ballet and Pittsburgh Ballet Theater changing the Chinese dance to a dragon dance.[78]
Alastair Macaulay of The New York Times defended Tchaikovsky, saying he «never intended his Chinese and Arabian music to be ethnographically correct».[80] He said, «their extraordinary color and energy are far from condescending, and they make the world of ‘The Nutcracker’ larger.»[80] To change anything is to «unbalance The Nutcracker» with music the author did not write. If there were stereotypes, Tchaikovsky also used them in representing his own country of Russia.[80] Moreover, the Votkinsk-born composer is perceived as a part of cultural heritage of Finnic peoples (non-Indo-European).[81][82][failed verification]
University of California, Irvine professor Jennifer Fisher said in 2018 that a two-finger salute[which?] used in the Chinese dance was not a part of the culture. Though it might have had its source in a Mongolian chopstick dance, she called it «heedless insensitivity to stereotyping». She also complained about the use in the Chinese dance of «bobbing, subservient ‘kowtow’ steps, Fu Manchu mustaches, and … yellowface» makeup, compared to blackface. One concern she had was that dancers believed they were learning about Asian culture, when they were really experiencing a cartoon version.[83]
Fisher went on to say some ballet companies were recognizing that change had to happen. Georgina Pazcoguin of the New York City Ballet and former dancer Phil Chan started the «Final Bow for Yellowface» movement and created a web site which explained the history of the practices and suggested changes. One of their points was that only the Chinese dance made dancers look like an ethnic group other than the one they belonged to. The New York City Ballet went on to drop geisha wigs and makeup and change some dance moves. Some other ballet companies followed.[83]
In popular culture[edit]
Film[edit]
Several films having little or nothing to do with the ballet or the original Hoffmann tale have used its music:
- The 1940 Disney animated film Fantasia features a segment using The Nutcracker Suite. This version was also included both as part of the 3-LP soundtrack album of Fantasia (since released as a 2-CD set), and as a single LP, with Dance of the Hours, another Fantasia segment, on the reverse side.[84][85]
- The Spirit of Christmas, a 1950 marionette made-for-TV featurette in color narrated by Alexander Scourby, utilizes the poem A Visit from St. Nicholas, and this sequence also includes music from The Nutcracker.
- A 1951 thirty-minute short, Santa and the Fairy Snow Queen, issued on DVD by Something Weird Video, features several dances from The Nutcracker.[86]
- The Nutcracker (1973) features a nameless girl (slightly similar to Clara) who works as a maid. She befriends and falls in love with a nutcracker ornament, who was a young prince cursed by the three headed Mouse King.
- Sanrio released a stop-motion adaptation of The Nutcracker entitled Nutcracker Fantasy in 1979.
- In 1988, Care Bears Nutcracker Suite was produced by the Canadian animation studio Nelvana and featured the Care Bears characters.
- A 1990 animated film titled The Nutcracker Prince was released and distributed by Warner Brothers Pictures and uses cuts of the music throughout and its story is based heavily on that of the ballet.
- A 1999 animated film titled The Nuttiest Nutcracker featured the voices of Cheech Marin, Jim Belushi, and Phyllis Diller, and followed a group of anthropomorphic fruits and vegetables.
- In 2001, Barbie appeared in her first film, Barbie in the Nutcracker. It used excerpts by Tchaikovsky, which were performed by the London Symphony Orchestra. Though it heavily altered the story, it still made use of ballet sequences which had been rotoscoped using real ballet dancers.[87]
- In 2007, Tom and Jerry: A Nutcracker Tale also used The Nutcracker excerpts, which were performed by the Chamber Orchestra of Philadelphia.
- Disney announced that a remake of The Nutcracker would be directed by Robert Zemeckis through the use of motion capture, a technique that was used in The Polar Express, Monster House, Beowulf, and A Christmas Carol. The film was cancelled following the box office disappointment of Mars Needs Moms.
- In 2010, The Nutcracker in 3D with Elle Fanning abandoned the ballet and most of the story, retaining much of Tchaikovsky’s music with lyrics by Tim Rice. The $90 million film became the year’s biggest box office bomb.
- In 2016, the Hallmark Channel presented A Nutcracker Christmas; a tele-film that contains a number of selected scenes of the 1892 two-act Nutcracker ballet.
- In 2017, the Athens State Orchestra in collaboration with Cinecreed productions (former name: 1895 cinematic creations) presented «A Different Nutcracker» animation film, directed by Yiorgos Molvalis. At the premiere (Chr. Lamprakis, Athens Concert Hall, December 26, 2017) as Silent animation, the film was recorded live by the Athens State Orchestra. In 2020 the official recording was integrated in to the film marking its completion and making it available for screenings without the need to have the orchestra present.
- In 2018, the Disney live-action film The Nutcracker and the Four Realms was released with Lasse Hallström and Joe Johnston as directors and a script by Ashleigh Powell.[88][89]
Television[edit]
- A 1954 Christmas episode of General Electric Theater featured Fred Waring and his choral group, the Pennsylvanians, singing excerpts from The Nutcracker with specially written lyrics. While the music was being sung, the audience saw ballet dancers performing.[90] The episode was hosted by Ronald Reagan.
- The 1987 true crime miniseries Nutcracker: Money, Madness and Murder opens every episode with the first notes of the ballet amid scenes of Frances Schreuder’s daughter dancing to it in ballet dress.
- «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» plays in the gabian dubbing version of El Chapulín Colorado episode «El Mistério Del Hombre De Las Nieves» while Chapolin and his friends Carlos and Florinda use sleeping bags for themselves to sleep at home until the music is interrupted after a fake yeti invades the house to scare them.
- Garfield and Friends episode, «Caped Avenger», «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» plays briefly while a shadow kidnaps Pooky.
- The «Toon TV» episode of Tiny Toon Adventures features an arcade-themed song called «Video Game Blues», set to «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» and «The Russian Dance».
- Batman: The Animated Series episode, «Christmas with the Joker», The Joker plays, «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy», and later, «The Russian Dance» on a record player to distract Batman and Robin.
- A 1996 episode of The Magic School Bus («Holiday Special», season 3, episode 39), Wanda is planning to see a performance of The Nutcracker. Some of the music for this episode was based on the score of the ballet.[91]
- The Mickey Mouse Works «MouseTales» segment, the House of Mouse episode, «Pete’s Christmas Caper», and the feature film, Mickey’s Magical Christmas: Snowed in at the House of Mouse, with Mickey Mouse playing the role of the Nutcraker, Minnie Mouse as Maria, Donald Duck as the King Mouse, Goofy as the Magical Snow Fairy, and Ludwig Von Drake as Godpapa Drosselmeyer.
- The Barney & Friends TV Christmas episode features its own version of the Nutcracker with Barney the Dinosaur as the narrator, dressed up in a tuxedo vest and matching cuffs.
- Princess Tutu, a 2002 anime series that uses elements from many ballets as both music and as part of the storyline, uses the music from The Nutcracker in many places throughout its run, including using an arranged version of the overture as the theme for the main character. Both the first and last episodes feature The Nutcracker as their ‘theme’, and one of the main characters is named Drosselmeyer.
- An arrangement of this the Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy can be heard in Episode 8 of Girls und Panzer.
- Arrangements of the Waltz of the flowers can be heard in Episode 7 of Guilty Crown.
- The 2015 Canadian television film The Curse of Clara: A Holiday Tale, based on an autobiographical short story by onetime Canadian ballet student Vickie Fagan, centres on a young ballet student preparing to dance the role of Clara in a production of The Nutcracker.
Video games[edit]
- In the NES version of Tetris, the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» is available as background music (referred to in the settings as «Music 1»), and the same arrangement was later remixed for the Game Boy Advance version of Tetris Worlds.
- In the NES game Winter Games, «Waltz of the Flowers» is used as the music for the figure skating event.
- In the game BioShock, the main character Jack meets an insane musician named Sander Cohen who tasks Jack with killing and photographing four of Sander’s ex-disciples. When the third photograph is given to Sander, in a fit of pique he unleashes waves of splicer enemies to attack Jack while playing «Waltz of the Flowers» from speakers in the area.
- In the original Lemmings «Dance of the Reed Flutes» and «Miniature Overture» is used in several levels.
- In Weird Dreams, there is also a plus sized ballerina dancing to the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» in the Hall of Tubes.
- In the Baby Bowser levels of Yoshi’s Story, a variation of the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» is used as the background music.
- In Mega Man Legends, the «Waltz of the Flowers» can be heard in the Balloon Fantasy minigame.
- In Crash Tag Team Racing, the «Trepak» are the background themes played during Tire & Ice track as a part with «Kalinka» and «Hungarian Dance No. 5».
- In the Wii version of Mario & Sonic at the Olympic Winter Games, «Waltz of the Flowers» is used as optional background music for the figure skating event. In the Nintendo DS version, the «Marche» and «Trepak» are used.[92]
- In Kingdom Hearts 3D: Dream Drop Distance the «Waltz of Flowers», «The Arabian Dance», «The Russian Dance», «The Dance of the Reed Flutes» and «The Chinese Dance» are the background themes that play when Riku is in the world based on Disney’s Fantasia.
- In Hatoful Boyfriend, the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» is used as the character theme for Iwamine Shuu.
- In a TV advertisement for Army Men: Sarge’s Heroes 2, the plastic army men work together using a train playset to move a firecracker under the Christmas tree and place it between the Nutcracker doll’s legs, while «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» plays.
- In Fantasia: Music Evolved, a medley of «The Nutcracker» is listed and consists of the «Marche», «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy», and «Trepak»; besides the original mix, there is also the «D00 BAH D00» mix and the «DC Breaks» mix.
- In Dynamite Headdy, the «March» is used in the Mad Dog boss battle.
- In Grand Theft Auto V one of the classical horns, that can be bought for cars, plays the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy».[93]
- The «Waltz of the Flowers» appears during a baby’s death scene in What Remains of Edith Finch.
- In the game «Cell to Singularity,» «Waltz of the Flowers» is heard in the background when new creatures are created.
- In LittleBigPlanet 3, a remix of «Waltz of the Flowers» is used as background music in the level «Tutu Tango» and is an unlockable music track in Create Mode.
- The «Kids Mode» of Just Dance 2021 and Just Dance 2022 features the song «Dance of the Mirlitons» on the soundtrack.
Children’s recordings[edit]
There have been several recorded children’s adaptations of the E.T.A. Hoffmann story (the basis for the ballet) using Tchaikovsky’s music, some quite faithful, some not. One that was not was a version titled The Nutcracker Suite for Children, narrated by Metropolitan Opera announcer Milton Cross, which used a two-piano arrangement of the music. It was released as a 78-RPM album set in the 1940s.[94] For the children’s label Peter Pan Records, actor Victor Jory narrated a condensed adaptation of the story with excerpts from the score. It was released on one side of a 45-RPM disc.[95] A later version, titled The Nutcracker Suite, starred Denise Bryer and a full cast, was released in the 1960s on LP and made use of Tchaikovsky’s music in the original orchestral arrangements. It was quite faithful to Hoffmann’s story The Nutcracker and the Mouse King, on which the ballet is based, even to the point of including the section in which Clara cuts her arm on the glass toy cabinet, and also mentioning that she married the Prince at the end. It also included a less gruesome version of «The Tale of the Hard Nut», the tale-within-a-tale in Hoffmann’s story. It was released as part of the Tale Spinners for Children series.[96]
Spike Jones produced a 78 rpm record set «Spike Jones presents for the kiddies The Nutcracker Suite (with Apologies to Tchaikovsky)» in 1944. It includes the tracks: «The Little Girl’s Dream», «Land of the Sugar Plum Fairy», «The Fairy Ball», «The Mysterious Room», «Back to the Fairy Ball» and «End of the Little Girl’s Dream». This is all done in typical Spike Jones style, with the addition of choruses and some swing music. The entire recording is available at archive.com [97]
Journalism[edit]
- In 2009, Pulitzer Prize–winning dance critic Sarah Kaufman wrote a series of articles for The Washington Post criticizing the primacy of The Nutcracker in the American repertory for stunting the creative evolution of ballet in the United States:[98][99][100]
That warm and welcoming veneer of domestic bliss in The Nutcracker gives the appearance that all is just plummy in the ballet world. But ballet is beset by serious ailments that threaten its future in this country… companies are so cautious in their programming that they have effectively reduced an art form to a rotation of over-roasted chestnuts that no one can justifiably croon about… The tyranny of The Nutcracker is emblematic of how dull and risk-averse American ballet has become. There were moments throughout the 20th century when ballet was brave. When it threw bold punches at its own conventions. First among these was the Ballets Russes period, when ballet—ballet—lassoed the avant-garde art movement and, with works such as Michel Fokine’s fashionably sexy Scheherazade (1910) and Léonide Massine’s Cubist-inspired Parade (1917), made world capitals sit up and take notice. Afraid of scandal? Not these free-thinkers; Vaslav Nijinsky’s rough-hewn, aggressive Rite of Spring famously put Paris in an uproar in 1913… Where are this century’s provocations? Has ballet become so entwined with its «Nutcracker» image, so fearfully wedded to unthreatening offerings, that it has forgotten how eye-opening and ultimately nourishing creative destruction can be?[99]
- In 2010, Alastair Macaulay, dance critic for The New York Times (who had previously taken Kaufman to task for her criticism of The Nutcracker[101]) began The Nutcracker Chronicles, a series of blog articles documenting his travels across the United States to see different productions of the ballet.[102]
Act I of The Nutcracker ends with snow falling and snowflakes dancing. Yet The Nutcracker is now seasonal entertainment even in parts of America where snow seldom falls: Hawaii, the California coast, Florida. Over the last 70 years this ballet—conceived in the Old World—has become an American institution. Its amalgam of children, parents, toys, a Christmas tree, snow, sweets and Tchaikovsky’s astounding score is integral to the season of good will that runs from Thanksgiving to New Year… I am a European who lives in America, and I never saw any Nutcracker until I was 21. Since then I’ve seen it many times. The importance of this ballet to America has become a phenomenon that surely says as much about this country as it does about this work of art. So this year I’m running a Nutcracker marathon: taking in as many different American productions as I can reasonably manage in November and December, from coast to coast (more than 20, if all goes well). America is a country I’m still discovering; let The Nutcracker be part of my research.[103]
- In 2014, Ellen O’Connell, who trained with the Royal Ballet in London, wrote, in Salon (website), on the darker side of The Nutcracker story. In E.T.A. Hoffmann’s original story, the Nutcracker and Mouse King, Marie’s (Clara’s), journey becomes a fevered delirium that transports her to a land where she sees sparkling Christmas Forests and Marzipan Castles, but in a world populated with dolls.[104] Hoffmann’s tales were so bizarre, Sigmund Freud wrote about them in The Uncanny.[105][106]
E.T.A. Hoffmann’s 1816 fairy tale, on which the ballet is based, is troubling: Marie, a young girl, falls in love with a nutcracker doll, whom she only sees come alive when she falls asleep. …Marie falls, ostensibly in a fevered dream, into a glass cabinet, cutting her arm badly. She hears stories of trickery, deceit, a rodent mother avenging her children’s death, and a character who must never fall asleep (but of course does, with disastrous consequences). While she heals from her wound, the mouse king brainwashes her in her sleep. Her family forbids her from speaking of her «dreams» anymore, but when she vows to love even an ugly nutcracker, he comes alive and she marries him.
Popular music[edit]
- The song «Dance Mystique» (track B1) on the studio album Bach to the Blues (1964) by the Ramsey Lewis Trio is a jazz adaptation of Coffee (Arabian Dance).
- The song «Fall Out» by English band Mansun from their 1998 album Six heavily relies on the celesta theme from the Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy.
- The song «Dark Ballet» by American singer-songwriter Madonna samples the melody of Dance of the Reed Flutes (Danish Marzipan) which is often mistaken for Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy. The song also relied on the lesser-known harp cadenza from Waltz of the Flowers. The same Tchaikovsky sample was earlier used in internationally famous 1992 ads for Cadbury Dairy Milk Fruit & Nut with ‘Madonna’ as the singing chocolate bar (in Russian version the subtitles «‘This Is Madonna'» (Russian: Это Мадонна, tr. Eto Madonna) were displayed on a screen.[107]
See also[edit]
- Parade of the Wooden Soldiers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Щелкунчикъ in Russian pre-revolutionary script.
References[edit]
- ^ a b Fisher, J. (2003). Nutcracker Nation: How an Old World Ballet Became a Christmas Tradition in the New World. New Haven: Yale University Press.
- ^ Agovino, Theresa (23 December 2013). «The Nutcracker brings big bucks to ballet companies». Crain’s New York Business. Retrieved 3 November 2017.
- ^ Wakin, Daniel J. (30 November 2009). «Coming Next Year: Nutcracker Competition». The New York Times.
- ^ a b c d Anderson, J. (1958). The Nutcracker Ballet, New York: Mayflower Books.
- ^ a b Hoffmann, E. T. A., Dumas, A., Neugroschel, J. (2007). Nutcracker and Mouse King, and the Tale of the Nutcracker, New York
- ^ Rosenberg, Donald (22 November 2009). «Tchaikovsky’s ‘Nutcracker’ a rite of winter thanks to its glorious music and breathtaking dances». Cleveland.com. Cleveland. Retrieved 4 November 2010.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky». Balletalert.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2012. Retrieved 10 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Nutcracker History». Balletmet.org. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 18 December 2008.
- ^ a b Fisher 2003, p. 15
- ^ a b Fisher 2003, p. 16
- ^ Fisher 2003, pp. 14–15.
- ^ Fisher 2003, p. 17.
- ^ Wiley, Roland John (1991). Tchaikovsky’s Ballets: Swan Lake, The Sleeping Beauty, The Nutcracker. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- ^ «Ballet Talk [Powered by Invision Power Board]». Ballettalk.invisionzone.com. 26 November 2008. Archived from the original on 17 September 2009. Retrieved 7 January 2009.
- ^ Craine, Debra (8 December 2007). «Christmas cracker». The Times. London.
- ^ «Ballet Russe de Monte Carlo. Ballet Russe de Monte Carlo records, 1935–1968 (MS Thr 463): Guide». Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 3 February 2013.
- ^ «Remembering Jocelyn Vollmar (1925-2018): SF Ballet’s 1st Snow Queen sparkled on- and offstage».
- ^ «About : Ballet West».
- ^ «Maria Tallchief». The Kennedy Center. The John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ Soviet ed., where they are printed in the original French with added Russian translation in editorial footnotes
- ^ Maximova, Yekaterina; Vasiliev, Vladimir (1967). Nutcracker Suite Performed By The Bolshoi (1967). Moscow, Russia: British Pathé.
- ^ The Nutcracker at the Royal Ballet: «March of the Toy Soldiers». London: Playbill Video. 1967. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Moscow Ballet (2017). Doll Dance. Moscow, Russia: Moscow Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Moscow Ballet (2017). The Rat King Appears. Moscow, Russia: Moscow Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the SemperOperBallett (2016). Snow Pas de Deux. Dresden, Germany: SemperOperBallett. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Bolshoi Ballet (2015). The Nutcracker (Casse-Noisette) – Bolshoi Ballet in Cinema (Preview 1). Moscow, Russia: Pathé Live. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Perm Opera Ballet Theatre (2017). Вальс снежинок из балета «Щелкунчик». Russia: Perm Opera Ballet Theatre. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the SemperOperBallett. The Nutcracker – Arabian Divertissement. Dresden, Germany: SemperOperBallett. Archived from the original on 15 January 2020.
- ^ Cecilia Iliesiu (2017). Arabian Coffee/Peacock. Pacific Northwest Ballet.
- ^ Dancers of the Mariinsky ballet (2012). The Nutcracker – Tea (Chinese Dance). Mariinsky Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Boston Ballet (2017). SPOTLIGHT The Nutcracker’s Russian Dance. Boston Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the SemperOperBallett. The Nutcracker – Mirlitons Divertissement. Dresden, Germany: SemperOperBallett.
- ^ Kyra Nichols and the NYCB Corps de Ballet (2015). New York City Ballet: Waltz of the Flowers. New York City: Lincoln Center.
- ^ PNB dancers. Nutcracker Flowers Excerpt. Pacific Northwest Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Alina Somova & Vladimir Shklyarov (2012). Sugarplum and Cavalier variations. St Petersburg, Russia: Ovation.
- ^ Darci Kistler. Dance of the Sugarplum Fairy. New York City: Ovation. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Wiley 1991, p. 220.
- ^ Schwarm, Betsy. «The Nutcracker, OP. 71». Encyclopaedia Britannica. The Music Alliance. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- ^ «Tchaikovskaya (Davydova) Alexandra Ilinichna». chaiklib.permculture.ru (in Russian). Chaykovsky Centralized Library System. Archived from the original on 24 October 2020. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ^ Jennifer Fisher (2004). ‘Nutcracker’ Nation: How an Old World Ballet Became a Christmas Tradition in the New World. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-10599-5.
- ^ «Шесть шедевров Чайковского, сделанных из обычной гаммы» [Six masterpieces by Tchaikovsky created from the usual scale]. kultspargalka.ru (in Russian). 4 April 2020. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
1. June. Barcarole from The Seasons 2. ‘Adagio’ from The Nutcracker 3. Lensky’s aria from Eugene Onegin 4. Serenade for Strings Waltz 5. ‘Melodrama’ from the music to the play by A. Ostrovsky The Snow Maiden 6. Yeletsky’s aria from The Queen of Spades
- ^ Tchaikovsky By David Brown W. W. Norton & Company, 1992 page 332
- ^ Appleford, David (19 December 2008). «The KEZ Christmas Countdown: Day 19 – The Nutcracker». Kfyi.com. Archived from the original on 12 January 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Tchaikovsky, P. (2004). The Nutcracker: Complete Score, Dover Publications.
- ^ a b «Ballet and Food». art-eda.ru (in Russian). Artoteka of Food. 21 November 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
Russian trepak «Candy Cane» and dance of sugar shepherds «Danish Marzipan»
- «Russian Seasons in Monaco». rusmonaco.fr (in Russian). Monaco and Cote D’Azur (printed Russian-language newspaper and magazine in Monaco and France). Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- «П.Чайковский. Щелкунчик. Дивертисмент. Большой театр. Tchaikovsky. The Nutcracker (1980)». YouTube. Official channel «Soviet Television» by the State TV and Radio Fund of Russia. 11 December 2018. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
The second title is «Датский марципан» – Danish marzipan. In the Grigorovich version for Bolshoi Theatre the idea of Europe is represented by dance with a marzipan sheep on wheels; Russian dance «Cancy Cane» combines the colors of candy canes and folklore heroes Ivan Tsarevich and Vasilisa the Wise
- ^ Alexander Poznansky, Tchaikovsky: The Quest for the Inner Man, p. 544
- ^ Brown, David. Tchaikovsky: The Final Years, 1885-1893. London, 1991; corrected edition 1992: p. 386
- ^ «The Nutcracker Profile: The History of The Nutcracker». Classicalmusic.about.com. 11 June 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Freddy Martin And His Orchestra – Tschaikowsky’s Nutracker Suite In Dance Tempo». Discogs.
- ^ «Fred Waring & the Pennsylvanians – Nutcracker Suite«. Discogs.
- ^ «Discography of American Historical Recordings, s.v. «Decca matrix L 6763. Nutcracker suite, part 1 / Les Brown and his Band of Renown,» accessed December 19, 2020″.
- ^ «A Duke Ellington Panorama». Depanorama.net. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «The Harlem Nutcracker». Susan Kuklin. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ The New Nutcracker Suite and Other Innocent Verses: Ogden Nash, Ivan Chermayeff. Little, Brown and Company. January 1962 – via Amazon.com.
- ^ Ogden Nash. «The New Nutcracker Suite & Other Innocent Verses». Kirkus Reviews.
- ^ Cooper, Antonio. «Nutcracker Brings Magic to DeVos». The Oakland Press. Retrieved 1 October 2019.
- ^ Scher, Avichai (3 December 2018). «What’s it like to choreograph Nutcracker four different times». Dance Magazine. Dance Magazine. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- ^ Merrell, Sue (30 November 2017). ««Nutcracker» Choreographer Makes GR Stop Ahead of Opening». grand rapids magazine. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ «blogcritics.org». blogcritics.org. Archived from the original on 11 July 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Lindsey Stirling Talks Joining ‘Dancing With the Stars’ & Shares First Holiday Album Track: Premiere». Billboard. 14 September 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Alexeyev, Alexander (5 August 2019). «Баян для Мадонны. Чайковский в новом альбоме Madame X» [Bayan [also a slang word for anything related to media content: videos, pictures, news, and an old post as fresh news] for Madonna. Tchaikovsky on the new Madame X album] (in Russian). Rossiyskaya Gazeta. Archived from the original on 2 September 2019. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ Van Horn, Charisse (19 November 2019). «Mariah Carey Shows Off Her Whistle Register In New Sugar Plum Fairy Acapella Rendition». celebrityinsider.org. Celebrity Insider. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ «Ho Ho, whatever! Got some jolly news for you… Proud to be part of the @smashthehouse Christmas album dropping 27/12. Swipe left to witness «The Nutcracker»!». Twitter. Retrieved 26 November 2020.
- ^ «Recording Technology History». History.sandiego.edu. Archived from the original on 12 March 2010. Retrieved 18 December 2008.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (31 December 2010). «‘The Nutcracker’ Chronicles: Listening to the Score».
- ^ «Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete Ballet); Serenade for Strings – Credits on MSN Music». Music.msn.com. Archived from the original on 8 June 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Pyotr Il’yich Tchaikovsky, Antal Dorati, Harold Lawrence, London Symphony Orchestra, Philharmonia Hungarica, London Symphony Orchestra Chorus – Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete Ballet); Serenade in C Major – Amazon.com Music». Amazon.
- ^ Styrous® (10 December 2012). «The Styrous® Viewfinder».
- ^ «Nutcracker». Classicalcdreview.com. Retrieved 18 December 2008.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky, Gennady Rozhdestvensky, Bolshoi Theater Orchestra – Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete) – Amazon.com Music». Amazon.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky: the Nutcracker: Sir Simon Rattle, Tchaikovsky, Berliner Philharmoniker: Music». Amazon. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Peter Ilyich Tchaikovsky, Michael Tilson Thomas, The Philharmonia Orchestra, Ambrosian Singers – Tchaikovsky: Music From The Nutcracker (Highlights) – Amazon.com Music». Amazon.
- ^ «The Nutcracker (1993 Motion Picture Soundtrack): Pyotr Il’yich Tchaikovsky, David Zinman, New York City Ballet Orchestra: Music». Amazon. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Archived copy» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ «Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete): Music». Amazon. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky: Nutcracker, Act II/ Swan Lake». AllMusic.
- ^ «Burning Question: Is Nutcracker Racist?». Dance Magazine. 1 December 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ a b c d Robb, Alice (24 December 2014). «Sorry, ‘The Nutcracker’ Is Racist». The New Republic. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ Dunning, Jennifer (26 November 2004). «Staying on Their Toes for ‘The Nutcracker,’ Show After Show». The New York Times. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ a b c Macaulay, Alastair (6 September 2012). «Stereotypes in Toeshoes». The New York Times. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky Museum-Estate» (in Russian). Finno-Ugric World. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ^ «Udmurtia to Host a Conference ‘Tchaikovsky: a Son of Udmurtia, the Genius of Man!’» (in Russian). Regnum. 5 October 2007. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ^ a b Fisher, Jennifer (11 December 2018). «Op-Ed: ‘Yellowface’ in ‘The Nutcracker’ isn’t a benign ballet tradition, it’s racist stereotyping». Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ «Disney (All) The Nutcracker Suite/Dance of the Hours – Sealed USA LP RECORD (284287)». Eil.com. 21 April 2004. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky’s The Nutcracker Suite Also Ponchielli’s Dance of the Hours Philadelphia Orchestra Leopold Stokowski Conducting: Leopold Stokowski: Music». Amazon. 9 September 2009. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Santa and the Fairy Snow Queen : A Sid Davis Production : Free Download & Streaming : Internet Archive». 10 March 2001. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ daflauta (2 October 2001). «Barbie in the Nutcracker (Video 2001)». IMDb.
- ^ Kit, Borys (4 March 2016). «Lasse Hallstrom to Direct Live-Action ‘Nutcracker’ for Disney». The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ «The Nutcracker and the Four Realms (2018)». Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved 1 November 2018.
- ^ ««General Electric Theater» Music for Christmas (TV Episode 1954)». IMDb. 19 December 1954.
- ^ ««The Magic School Bus» The Family Holiday Special (TV Episode 1996)». IMDb. 25 December 1996.
- ^ «Super Mario Wiki/Figure Skating». Mariowiki.com. 10 September 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «GTA5 Classical horn 3». youtube.com. 8 May 2015. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- ^ «Week 50». Kiddierecords.com. Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «11 The Nutcracker Suite : Victor Jory». SoundCloud.
- ^ «Tale Spinners for Children». Artsreformation.com. 14 May 2008. Archived from the original on 13 August 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ Spike Jones and his City Slickers. «Spike Jones presents for the kiddies The Nutcracker Suite with Apologies to Tchaikovsky«. archive.org. Retrieved 29 December 2022.
- ^ Kaufman, Sarah (13 September 2009). «Here Come Those Sugar Plums and Chestnuts». The Washington Post. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ a b Kaufman, Sarah (22 November 2009). «Breaking pointe: ‘The Nutcracker’ takes more than it gives to world of ballet». The Washington Post. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ Itzkoff, Dave (14 December 2009). «Sugar Plum Overdose: The Case Against ‘The Nutcracker’«. The Washington Post. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (16 November 2010). «A ‘Nutcracker’ Lover Explains Himself». The New York Times. Retrieved 20 November 2010.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (10 November 2010). «The ‘Nutcracker’ Chronicles: The Marathon Begins». The New York Times. Retrieved 15 November 2010.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (10 November 2010). «The Sugarplum Diet». The New York Times. Retrieved 15 November 2010.
- ^ O’Connell, Ellen (25 December 2014). ««The Nutcracker’s» disturbing origin story: Why this was once the world’s creepiest ballet». Solon. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Freud, Sigmund (1919). «The Uncanny» (PDF).
- ^ «Nutcracker Ballet 101». Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ «Reklamka Vimto i Frut’n’Nuts (1994)» (in Russian). YouTube channel «towaroved». Retrieved 24 September 2019.
External links[edit]
- The Nutcracker (ballet): Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- The Nutcracker (suite): Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- Tchaikovsky Research
- The Nutcracker ballet
The Nutcracker (Russian: Щелкунчик[a], tr. Shchelkunchik listen (help·info)) is an 1892 two-act «fairy ballet» (Russian: балет-феерия, balet-feyeriya) set on Christmas Eve at the foot of a Christmas tree in a child’s imagination. The music is by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky, his Opus 71. The plot is an adaptation of E. T. A. Hoffmann’s 1816 short story The Nutcracker and the Mouse King. The ballet’s first choreographer was Marius Petipa, with whom Tchaikovsky had worked three years earlier on The Sleeping Beauty, assisted by Lev Ivanov. Although the complete and staged The Nutcracker ballet was not as successful as the 20-minute Nutcracker Suite Tchaikovsky had premiered nine months earlier, The Nutcracker soon became popular.
Since the late 1960s, it has been danced by countless ballet companies, especially in North America.[1] Major American ballet companies generate around 40% of their annual ticket revenues from performances of The Nutcracker.[2][3] The ballet’s score has been used in several film adaptations of Hoffmann’s story.
Tchaikovsky’s score has become one of his most famous compositions. Among other things, the score is noted for its use of the celesta, an instrument the composer had already employed in his much lesser known symphonic ballad The Voyevoda (1891).
Composition[edit]
After the success of The Sleeping Beauty in 1890, Ivan Vsevolozhsky, the director of the Imperial Theatres, commissioned Tchaikovsky to compose a double-bill program featuring both an opera and a ballet. The opera would be Iolanta. For the ballet, Tchaikovsky would again join forces with Marius Petipa, with whom he had collaborated on The Sleeping Beauty. The material Vsevolozhsky chose was an adaptation of E. T. A. Hoffmann’s story «The Nutcracker and the Mouse King», by Alexandre Dumas called «The Story of a Nutcracker».[4] The plot of Hoffmann’s story (and Dumas’ adaptation) was greatly simplified for the two-act ballet. Hoffmann’s tale contains a long flashback story within its main plot titled «The Tale of the Hard Nut», which explains how the Prince was turned into the Nutcracker. This had to be excised for the ballet.[5]
Petipa gave Tchaikovsky extremely detailed instructions for the composition of each number, down to the tempo and number of bars.[4] The completion of the work was interrupted for a short time when Tchaikovsky visited the United States for twenty-five days to conduct concerts for the opening of Carnegie Hall.[6] Tchaikovsky composed parts of The Nutcracker in Rouen, France.[7]
History[edit]
Saint Petersburg premiere[edit]
(Left to right) Lydia Rubtsova as Marianna, Stanislava Belinskaya as Clara and Vassily Stukolkin as Fritz, in the original production of The Nutcracker (Imperial Mariinsky Theatre, Saint Petersburg, 1892)
Varvara Nikitina as the Sugar Plum Fairy and Pavel Gerdt as the Cavalier, in a later performance in the original run of The Nutcracker, 1892
The first performance of The Nutcracker was not deemed a success.[8] The reaction to the dancers themselves was ambivalent. While some critics praised Dell’Era on her pointework as the Sugar Plum Fairy (she allegedly received five curtain-calls), one critic called her «corpulent» and «podgy». Olga Preobrajenskaya as the Columbine doll was panned by one critic as «completely insipid» and praised as «charming» by another.[9]
Alexandre Benois described the choreography of the battle scene as confusing: «One can not understand anything. Disorderly pushing about from corner to corner and running backwards and forwards – quite amateurish.»[9]
The libretto was criticized as «lopsided»[10] and for not being faithful to the Hoffmann tale. Much of the criticism focused on the featuring of children so prominently in the ballet,[11] and many bemoaned the fact that the ballerina did not dance until the Grand Pas de Deux near the end of the second act (which did not occur until nearly midnight during the program).[10] Some found the transition between the mundane world of the first scene and the fantasy world of the second act too abrupt.[4] Reception was better for Tchaikovsky’s score. Some critics called it «astonishingly rich in detailed inspiration» and «from beginning to end, beautiful, melodious, original, and characteristic».[12] But this also was not unanimous, as some critics found the party scene «ponderous» and the Grand Pas de Deux «insipid».[13]
Subsequent productions[edit]
In 1919, choreographer Alexander Gorsky staged a production which eliminated the Sugar Plum Fairy and her Cavalier and gave their dances to Clara and the Nutcracker Prince, who were played by adults instead of children. This was the first production to do so. An abridged version of the ballet was first performed outside Russia in Budapest (Royal Opera House) in 1927, with choreography by Ede Brada.[14][unreliable source?] In 1934, choreographer Vasili Vainonen staged a version of the work that addressed many of the criticisms of the original 1892 production by casting adult dancers in the roles of Clara and the Prince, as Gorsky had. The Vainonen version influenced several later productions.[4]
The first complete performance outside Russia took place in England in 1934,[8] staged by Nicholas Sergeyev after Petipa’s original choreography. Annual performances of the ballet have been staged there since 1952.[15] Another abridged version of the ballet, performed by the Ballet Russe de Monte Carlo, was staged in New York City in 1940,[16] Alexandra Fedorova – again, after Petipa’s version.[8] The ballet’s first complete United States performance was on 24 December 1944 by the San Francisco Ballet, staged by its artistic director, Willam Christensen, and starring Gisella Caccialanza as the Sugar Plum Fairy, and Jocelyn Vollmar as the Snow Queen.[17][8] After the enormous success of this production, San Francisco Ballet has presented Nutcracker every Christmas Eve and throughout the winter season, debuting new productions in 1944, 1954, 1967, and 2004. The original Christensen version continues in Salt Lake City, where Christensen relocated in 1948. It has been performed every year since 1963 by the Christensen-founded Ballet West.[18]
The New York City Ballet gave its first annual performance of George Balanchine’s reworked staging of The Nutcracker in 1954.[8] The performance of Maria Tallchief in the role of the Sugar Plum Fairy helped elevate the work from obscurity into an annual Christmas classic and the industry’s most reliable box-office draw. Critic Walter Terry remarked that «Maria Tallchief, as the Sugar Plum Fairy, is herself a creature of magic, dancing the seemingly impossible with effortless beauty of movement, electrifying us with her brilliance, enchanting us with her radiance of being. Does she have any equals anywhere, inside or outside of fairyland? While watching her in The Nutcracker, one is tempted to doubt it.»[19]
Since Gorsky, Vainonen and Balanchine’s productions, many other choreographers have made their own versions. Some institute the changes made by Gorsky and Vainonen while others, like Balanchine, utilize the original libretto. Some notable productions include Rudolf Nureyev’s 1963 production for the Royal Ballet, Yury Grigorovich for the Bolshoi Ballet, Mikhail Baryshnikov for the American Ballet Theatre, Fernand Nault for Les Grands Ballets Canadiens starting in 1964, Kent Stowell for Pacific Northwest Ballet starting in 1983, and Peter Wright for the Royal Ballet and the Birmingham Royal Ballet. In recent years, revisionist productions, including those by Mark Morris, Matthew Bourne, and Mikhail Chemiakin have appeared; these depart radically from both the original 1892 libretto and Vainonen’s revival, while Maurice Béjart’s version completely discards the original plot and characters. In addition to annual live stagings of the work, many productions have also been televised or released on home video.[1]
Roles[edit]
The following extrapolation of the characters (in order of appearance) is drawn from an examination of the stage directions in the score.[20]
Act I[edit]
- Herr Stahlbaum
- His wife
- His children, including:
- Clara, his daughter, sometimes known as Marie or Masha
- Fritz, his son
- Louise, his daughter
- Children Guests
- Parents dressed as incroyables
- Herr Drosselmeyer
- His nephew (in some versions) who resembles the Nutcracker Prince and is played by the same dancer
- Dolls (spring-activated, sometimes all three dancers instead):
- Harlequin and Columbine, appearing out of a cabbage (1st gift)
- Vivandière and a Soldier (2nd gift)
- Nutcracker (3rd gift, at first a normal-sized toy, then full-sized and «speaking», then a Prince)
- Owl (on clock, changing into Drosselmeyer)
- Mice
- Sentinel (speaking role)
- The Bunny
- Soldiers (of the Nutcracker)
- Mouse King
- Snowflakes (sometimes Snow Crystals, sometimes accompanying a Snow Queen and King)
Act II[edit]
Ivan Vsevolozhsky’s original costume sketch for The Nutcracker (1892)
- Angels and/or Fairies
- Sugar Plum Fairy
- Clara/Marie
- The Nutcracker Prince
- 12 Pages
- Eminent members of the court
- Spanish dancers (Chocolate)
- Arabian dancers (Coffee)
- Chinese dancers (Tea)
- Russian dancers (Candy Canes)
- Danish shepherdesses / French mirliton players (Marzipan)
- Mother Ginger
- Polichinelles (Mother Ginger’s Children)
- Dewdrop
- Flowers
- Sugar Plum Fairy’s Cavalier
Plot [edit]
Below is a synopsis based on the original 1892 libretto by Marius Petipa. The story varies from production to production, though most follow the basic outline. The names of the characters also vary. In the original Hoffmann story, the young heroine is called Marie Stahlbaum and Clara (Klärchen) is her doll’s name. In the adaptation by Dumas on which Petipa based his libretto, her name is Marie Silberhaus.[5] In still other productions, such as Baryshnikov’s, Clara is Clara Stahlbaum rather than Clara Silberhaus.
Act I[edit]
Scene 1: The Stahlbaum Home
Konstantin Ivanov’s original sketch for the set of The Nutcracker (1892)
The ballet is set on Christmas Eve, where family and friends have gathered in the parlor to decorate the beautiful Christmas tree in preparation for the party. Once the tree is finished, the children are summoned. They stand in awe of the tree sparkling with candles and decorations.
The party begins.[21] A march is played.[22] Presents are given out to the children. Suddenly, as the owl-topped grandfather clock strikes eight, a mysterious figure enters the room. It is Drosselmeyer— a local councilman, magician, and Clara’s godfather. He is also a talented toymaker who has brought with him gifts for the children, including four lifelike dolls who dance to the delight of all.[23] He then has them put away for safekeeping.
Clara and her brother Fritz are sad to see the dolls being taken away, but Drosselmeyer has yet another toy for them: a wooden nutcracker carved in the shape of a little man, which the other children ignore. Clara immediately takes a liking to it, but Fritz accidentally breaks it. Clara is heartbroken, but Drosselmeyer fixes the nutcracker, much to everyone’s relief.
During the night, after everyone else has gone to bed, Clara returns to the parlor to check on her beloved nutcracker. As she reaches the little bed, the clock strikes midnight and she looks up to see Drosselmeyer perched atop it. Suddenly, mice begin to fill the room and the Christmas tree begins to grow to dizzying heights. The nutcracker also grows to life size. Clara finds herself in the midst of a battle between an army of gingerbread soldiers and the mice, led by their king. The mice begin to eat the gingerbread soldiers.
The nutcracker appears to lead the soldiers, who are joined by tin soldiers, and by dolls who serve as doctors to carry away the wounded. As the seven-headed Mouse King advances on the still-wounded nutcracker, Clara throws her slipper at him, distracting him long enough for the nutcracker to stab him.[24]
Scene 2: A Pine Forest
The mice retreat and the nutcracker is transformed into a handsome Prince.[25] He leads Clara through the moonlit night to a pine forest in which the snowflakes dance around them, beckoning them on to his kingdom as the first act ends.[26][27]
Act II[edit]
The Land of Sweets
Ivan Vsevolozhsky’s original costume designs for Mother Gigogne and her Polichinelle children, 1892
Clara and the Prince travel to the beautiful Land of Sweets, ruled by the Sugar Plum Fairy in the Prince’s place until his return. He recounts for her how he had been saved from the Mouse King by Clara and transformed back into himself.
In honor of the young heroine, a celebration of sweets from around the world is produced: chocolate from Spain, coffee from Arabia,[28][29] tea from China,[30] and candy canes from Russia[31] all dance for their amusement; Danish shepherdesses perform on their flutes;[32] Mother Ginger has her children, the Polichinelles, emerge from under her enormous hoop skirt to dance; a string of beautiful flowers perform a waltz.[33][34] To conclude the night, the Sugar Plum Fairy and her Cavalier perform a dance.[35][36]
A final waltz is performed by all the sweets, after which the Sugar Plum Fairy ushers Clara and the Prince down from their throne. He bows to her, she kisses Clara goodbye, and leads them to a reindeer-drawn sleigh. It takes off as they wave goodbye to all the subjects who wave back.
In the original libretto, the ballet’s apotheosis «represents a large beehive with flying bees, closely guarding their riches».[37] Just like Swan Lake, there have been various alternative endings created in productions subsequent to the original.
Musical sources and influences[edit]
The Nutcracker is one of the composer’s most popular compositions. The music belongs to the Romantic period and contains some of his most memorable melodies, several of which are frequently used in television and film. (They are often heard in TV commercials shown during the Christmas season.[38])
Tchaikovsky is said to have argued with a friend who wagered that the composer could not write a melody based on a one-octave scale in sequence. Tchaikovsky asked if it mattered whether the notes were in ascending or descending order and was assured it did not. This resulted in the Adagio from the Grand pas de deux, which, in the ballet, nearly always immediately follows the «Waltz of the Flowers». A story is also told that Tchaikovsky’s sister Alexandra (9 January 1842 — 9 April 1891[39]) had died shortly before he began composition of the ballet and that his sister’s death influenced him to compose a melancholy, descending scale melody for the adagio of the Grand Pas de Deux.[40] However, it is more naturally perceived as a dreams-come-true theme because of another celebrated scale use, the ascending one in the Barcarolle from The Seasons.[41]
Danse de la Fée-Dragée (Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy) is the third pas de deux in Act II
Tchaikovsky was less satisfied with The Nutcracker than with The Sleeping Beauty. (In the film Fantasia, commentator Deems Taylor observes that he «really detested» the score.) Tchaikovsky accepted the commission from Vsevolozhsky but did not particularly want to write the ballet[42] (though he did write to a friend while composing it, «I am daily becoming more and more attuned to my task»).[43]
Instrumentation[edit]
The music is written for an orchestra with the following instrumentation.
Musical scenes[edit]
From the Imperial Ballet’s 1892 program[edit]
Titles of all of the numbers listed here come from Marius Petipa’s original scenario as well as the original libretto and programs of the first production of 1892. All libretti and programs of works performed on the stages of the Imperial Theatres were titled in French, which was the official language of the Imperial Court, as well as the language from which balletic terminology is derived.
Casse-Noisette. Ballet-féerie in two acts and three tableaux with apotheosis.
|
Act I
|
Act II
Grand divertissement—
|
Structure[edit]
List of acts, scenes (tableaux) and musical numbers, along with tempo indications. Numbers are given according to the original Russian and French titles of the first edition score (1892), the piano reduction score by Sergei Taneyev (1892), both published by P. Jurgenson in Moscow, and the Soviet collected edition of the composer’s works, as reprinted Melville, New York: Belwin Mills [n.d.][44]
| Scene | No. | English title | French title | Russian title | Tempo indication | Notes | Listen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Act I | |||||||
| Miniature Overture | Ouverture miniature | Увертюра | Allegro giusto | ||||
| Tableau I | 1 | Scene (The Christmas Tree) | Scène (L’arbre de Noël) | Сцена (Сцена украшения и зажигания ёлки) | Allegro non troppo – Più moderato – Allegro vivace | scene of decorating and lighting the Christmas tree | |
| 2 | March (also March of the Toy Soldiers) | Marche | Марш | Tempo di marcia viva | |||
| 3 | Children’s Gallop and Dance of the Parents | Petit galop des enfants et Entrée des parents | Детский галоп и вход (танец) родителей | Presto – Andante – Allegro | |||
| 4 | Dance Scene (Arrival of Drosselmeyer) | Scène dansante | Сцена с танцами | Andantino – Allegro vivo – Andantino sostenuto – Più andante – Allegro molto vivace – Tempo di Valse – Presto | Drosselmeyer’s arrival and distribution of presents | ||
| 5 | Scene and Grandfather Waltz | Scène et danse du Gross-Vater | Сцена и танец Гросфатер | Andante – Andantino – Moderato assai – Andante – L’istesso tempo – Tempo di Gross-Vater – Allegro vivacissimo | |||
| 6 | Scene (Clara and the Nutcracker) | Scène | Сцена | Allegro semplice – Moderato con moto – Allegro giusto – Più allegro – Moderato assai | departure of the guests | ||
| 7 | Scene (The Battle) | Scène | Сцена | Allegro vivo | |||
| Tableau II | 8 | Scene (A Pine Forest in Winter) | Scène | Сцена | Andante | a.k.a. «Journey through the Snow» | |
| 9 | Waltz of the Snowflakes | Valse des flocons de neige | Вальс снежных хлопьев | Tempo di Valse, ma con moto – Presto | |||
| Act II | |||||||
| Tableau III | 10 | Scene (The Magic Castle in the Land of Sweets) | Scène | Сцена | Andante | introduction | |
| 11 | Scene (Clara and Nutcracker Prince) | Scène | Сцена | Andante con moto – Moderato – Allegro agitato – Poco più allegro – Tempo precedente | arrival of Clara and the Prince | ||
| 12 | Divertissement | Divertissement | Дивертисмент | ||||
| a. Chocolate (Spanish Dance) | a. Le chocolat (Danse espagnole) | a. Шоколад (Испанский танец) | Allegro brillante | ||||
| b. Coffee (Arabian Dance) | b. Le café (Danse arabe) | b. Кофе (Арабский танец) | Commodo | ||||
| c. Tea (Chinese Dance) | c. Le thé (Danse chinoise) | c. Чай (Китайский танец) | Allegro moderato | ||||
| d. Trepak (Russian Dance) | d. Trépak (Danse russe) | d. Трепак (русский танец, карамельная трость)[45] | Tempo di Trepak, Presto | ||||
| e. Dance of the Reed Flutes | e. Les Mirlitons (Danse des Mirlitons) | e. Танец пастушков (Датский марципан)[45] | Andantino | ||||
| f. Mother Ginger and the Polichinelles | f. La mère Gigogne et les polichinelles | f. Полишинели | Allegro giocoso – Andante – Allegro vivo | ||||
| 13 | Waltz of the Flowers | Valse des fleurs | Вальс цветов | Tempo di Valse | |||
| 14 | Pas de Deux | Pas de deux | Па-де-дё | ||||
| a. Intrada (Sugar Plum Fairy and Her Cavalier) | a. La Fée-Dragée et le Prince Orgeat | a. Танец принца Оршада и Феи Драже | Andante maestoso | ||||
| b. Variation I: Tarantella | b. Variation I: Tarantelle (Pour le danseur) | b. Вариация I: Тарантелла | Tempo di Tarantella | ||||
| c. Variation II: Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy | c. Variation II: Danse de la Fée-Dragée (Pour la danseuse) | c. Вариация II: Танец Феи Драже | Andante ma non troppo – Presto | ||||
| d. Coda | d. Coda | d. Кода | Vivace assai | ||||
| 15 | Final Waltz and Apotheosis | Valse finale et Apothéose | Финальный вальс и Апофеоз | Tempo di Valse – Molto meno |
Concert excerpts and arrangements[edit]
Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker Suite, Op. 71a[edit]
Tchaikovsky made a selection of eight of the numbers from the ballet before the ballet’s December 1892 première, forming The Nutcracker Suite, Op. 71a, intended for concert performance. The suite was first performed, under the composer’s direction, on 19 March 1892 at an assembly of the Saint Petersburg branch of the Musical Society.[46] The suite became instantly popular, with almost every number encored at its premiere,[47] while the complete ballet did not begin to achieve its great popularity until after the George Balanchine staging became a hit in New York City.[48] The suite became very popular on the concert stage, and was excerpted in Disney’s Fantasia, omitting the two movements prior to the Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy . The outline below represents the selection and sequence of the Nutcracker Suite made by the composer:
- Miniature Overture
- Characteristic Dances
- March
- Dance of the Sugar-Plum Fairy [ending altered from ballet version]
- Russian Dance (Trepak)
- Arabian Dance (coffee)
- Chinese Dance (tea)
- Dance of the Reed Flutes (Mirlitons)
- Waltz of the Flowers
Grainger: Paraphrase on Tchaikovsky’s Flower Waltz, for solo piano[edit]
The Paraphrase on Tchaikovsky’s Flower Waltz is a successful piano arrangement from one of the movements from The Nutcracker by the pianist and composer Percy Grainger.
Pletnev: Concert suite from The Nutcracker, for solo piano[edit]
The pianist and conductor Mikhail Pletnev adapted some of the music into a virtuosic concert suite for piano solo:
- March
- Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy
- Tarantella
- Intermezzo (Journey through the Snow)
- Russian Trepak
- Chinese Dance
- Andante maestoso (Pas de Deux)
Contemporary arrangements[edit]
- In 1942, Freddy Martin and his orchestra recorded The Nutcracker Suite for Dance Orchestra on a set of 4 10-inch 78-RPM records. An arrangement of the suite that lay between dance music and jazz, it was released by RCA Victor.[49]
- In 1947, Fred Waring and His Pennsylvanians recorded «The Nutcracker Suite» on a two-part Decca Records 12-inch 78 RPM record with one part on each side as Decca DU 90022,[50] packaged in a picture sleeve. This version had custom lyrics written for Waring’s chorus by among others, Waring himself. The arrangements were by Harry Simeone.
- In 1952, the Les Brown big band recorded a version of the Nutcracker Suite, arranged by Frank Comstock, for Coral Records.[51] Brown rerecorded the arrangement in stereo for his 1958 Capitol Records album Concert Modern.
- In 1960, Duke Ellington and Billy Strayhorn composed jazz interpretations of pieces from Tchaikovsky’s score, recorded and released on LP as The Nutcracker Suite.[52] In 1999, this suite was supplemented with additional arrangements from the score by David Berger for The Harlem Nutcracker, a production of the ballet by choreographer Donald Byrd (born 1949) set during the Harlem Renaissance.[53]
- In 1960, Shorty Rogers released The Swingin’ Nutcracker, featuring jazz interpretations of pieces from Tchaikovsky’s score.
- In 1962, American poet and humorist Ogden Nash wrote verses inspired by the ballet,[54] and these verses have sometimes been performed in concert versions of the Nutcracker Suite. It has been recorded with Peter Ustinov reciting the verses, and the music is unchanged from the original.[55]
- In 1962 a novelty boogie piano arrangement of the «Marche», titled «Nut Rocker», was a No.1 single in the UK, and No.21 in the USA. Credited to B. Bumble and the Stingers, it was produced by Kim Fowley and featured studio musicians Al Hazan (piano), Earl Palmer (drums), Tommy Tedesco (guitar) and Red Callender (bass). «Nut Rocker» has subsequently been covered by many others including The Shadows, Emerson, Lake & Palmer, The Ventures, Dropkick Murphys, The Brian Setzer Orchestra, and the Trans-Siberian Orchestra. The Ventures’ own instrumental rock cover of «Nut Rocker», known as «Nutty», is commonly connected to the NHL team, the Boston Bruins, from being used as the theme for the Bruins’ telecast games for over two decades, from the late 1960s. In 2004, The Invincible Czars arranged, recorded, and now annually perform the entire suite for rock band.
- The Trans-Siberian Orchestra’s first album, Christmas Eve and Other Stories, includes an instrumental piece titled «A Mad Russian’s Christmas», which is a rock version of music from The Nutcracker.
- On the other end of the scale is the comedic Spike Jones version released in December 1945 as «Spike Jones presents for the Kiddies: The Nutcracker Suite (With Apologies to Tchaikovsky)», featuring humorous lyrics by Foster Carling and additional music by Joe «Country» Washburne. An abridged version was released in 1971 as part of the long play record Spike Jones is Murdering the Classics, one of the rare comedic pop records to be issued on the prestigious RCA Red Seal label.
- International choreographer Val Caniparoli has created several versions of The Nutcracker ballet for Louisville Ballet, Cincinnati Ballet, Royal New Zealand Ballet, and Grand Rapids Ballet.[56] While his ballets remain classically rooted, he has contemporarized them with changes such as making Marie an adult instead of a child, or having Drosselmeir emerges through the clock face during the overture making «him more humorous and mischievous.»[57] Caniparoli has been influenced by his simultaneous career as a dancer, having joined San Francisco Ballet in 1971 and performing as Drosselmeir and other various Nutcracker roles ever since that time.[58]
- The Disco Biscuits, a trance-fusion jam band from Philadelphia, have performed «Waltz of the Flowers» and «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on multiple occasions.
- The Los Angeles Guitar Quartet (LAGQ) recorded the Suite arranged for four acoustic guitars on their CD recording Dances from Renaissance to Nutcracker (1992, Delos).
- In 1993, guitarist Tim Sparks recorded his arrangements for acoustic guitar on The Nutcracker Suite.
- The Shirim Klezmer Orchestra released a klezmer version, titled «Klezmer Nutcracker,» in 1998 on the Newport label. The album became the basis for a December 2008 production by Ellen Kushner, titled The Klezmer Nutcracker and staged off-Broadway in New York City.[59]
- In 2002, The Constructus Corporation used the melody of Sugar Plum Fairy for their track «Choose Your Own Adventure».
- In 2009, Pet Shop Boys used a melody from «March» for their track «All Over the World», taken from their album Yes.
- In 2012, jazz pianist Eyran Katsenelenbogen released his renditions of Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy, Dance of the Reed Flutes, Russian Dance and Waltz of the Flowers from the Nutcracker Suite.
- In 2014, Pentatonix released an a cappella arrangement of «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on the holiday album That’s Christmas to Me and received a Grammy Award on 16 February 2016 for best arrangement.
- In 2016, Jennifer Thomas included an instrumental version of «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on her album Winter Symphony.
- In 2017, Lindsey Stirling released her version of «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» on her holiday album Warmer in the Winter.[60]
- In 2018, Pentatonix released an a cappella arrangement of «Waltz of the Flowers» on the holiday album Christmas Is Here!.
- In 2019, Madonna sampled a portion on her song «Dark Ballet» from her Madame X album.[61]
- In 2019, Mariah Carey released a normal and an a cappella version of ‘Sugar Plum Fairy’ entitled the ‘Sugar Plum Fairy Introlude’ to open and close her 25th Deluxe Anniversary Edition of Merry Christmas.[62]
- In 2020, Coone made a hardstyle cover version titled «The Nutcracker».[63]
Selected discography[edit]
Many recordings have been made since 1909 of the Nutcracker Suite, which made its initial appearance on disc that year in what is now historically considered the first record album.[64] This recording was conducted by Herman Finck and featured the London Palace Orchestra.[65] But it was not until the LP album was developed that recordings of the complete ballet began to be made. Because of the ballet’s approximate hour and a half length when performed without intermission, applause, or interpolated numbers, it fits very comfortably onto two LPs. Most CD recordings take up two discs, often with fillers. An exception is the 81-minute 1998 Philips recording by Valery Gergiev that fits onto one CD because of Gergiev’s somewhat brisker speeds.
- In 1954, the first complete recording of the ballet was released, a 2-LP set in mono sound released by Mercury Records. The cover design was by George Maas with illustrations by Dorothy Maas.[66] The music was performed by the Minneapolis Symphony Orchestra, conducted by Antal Doráti. Doráti later re-recorded the complete ballet in stereo, with the London Symphony Orchestra in 1962 for Mercury and with the Amsterdam Concertgebouw Orchestra in 1975 for Philips Classics. According to Mercury Records, the 1962 recording was made on 35mm magnetic film rather than audio tape, and used album cover art identical to that of the 1954 recording.[67][68] Dorati is the only conductor so far to have made three different recordings of the complete ballet. Some have hailed the 1975 recording as the finest ever made of the complete ballet.[69] It is also faithful to the score in employing a boys’ choir in the Waltz of the Snowflakes. Many other recordings use an adult or mixed choir.
- In 1956, Artur Rodziński and the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra made a complete recording of the ballet in stereo for Westminster Records.
- In 1959, the first stereo LP album set of the complete ballet, with Ernest Ansermet conducting the Orchestre de la Suisse Romande, appeared on Decca Records in the UK and London Records in the US.
- The first complete stereo Nutcracker with a Russian conductor and a Russian orchestra appeared in 1960, when Gennady Rozhdestvensky’s recording of it, with the Bolshoi Theatre Orchestra, was issued first in the Soviet Union on Melodiya, then imported to the U.S. on Columbia Masterworks. It was also Columbia Masterworks’ first complete Nutcracker.[70]
With the advent of the stereo LP coinciding with the growing popularity of the complete ballet, many other complete recordings of it have been made. Notable conductors who have done so include Maurice Abravanel, André Previn, Michael Tilson Thomas, Mariss Jansons, Seiji Ozawa, Richard Bonynge, Semyon Bychkov, Alexander Vedernikov, Ondrej Lenard, Mikhail Pletnev, and most recently, Simon Rattle.[71] A CD of excerpts from the Tilson Thomas version had as its album cover art a painting of Mikhail Baryshnikov in his Nutcracker costume; perhaps this was due to the fact that the Tilson Thomas recording was released by CBS Masterworks, and CBS had first telecast the Baryshnikov «Nutcracker».[72]
- The soundtrack of the 1977 television production with Mikhail Baryshnikov and Gelsey Kirkland, featuring the National Philharmonic Orchestra conducted by Kenneth Schermerhorn, was issued in stereo on a CBS Masterworks 2 LP-set, but it has not appeared on CD. The LP soundtrack recording was, for a time, the only stereo version of the Baryshnikov Nutcracker available, since the show was originally telecast only in mono, and it was not until recently that it began to be telecast with stereo sound. The sound portion of the DVD is also in stereo.
- The first complete recording of the ballet in digital stereo was issued in 1985, on a two-CD RCA set featuring Leonard Slatkin conducting the St. Louis Symphony Orchestra. This album originally had no «filler», but it has recently been re-issued on a multi-CD set containing complete recordings of Tchaikovsky’s two other ballets, Swan Lake and The Sleeping Beauty. This three-ballet album has now gone out of print.
There have been two major theatrical film versions of the ballet, made within seven years of each other, and both were given soundtrack albums.
- The first theatrical film adaptation, made in 1985, is of the Pacific Northwest Ballet version, and was conducted by Sir Charles Mackerras. The music is played in this production by the London Symphony Orchestra. The film was directed by Carroll Ballard, who had never before directed a ballet film (and has not done so since). Patricia Barker played Clara in the fantasy sequences, and Vanessa Sharp played her in the Christmas party scene. Wade Walthall was the Nutcracker Prince.
- The second film adaptation was a 1993 film of the New York City Ballet version, titled George Balanchine’s The Nutcracker, with David Zinman conducting the New York City Ballet Orchestra. The director was Emile Ardolino, who had won the Emmy, Obie, and Academy Awards for filming dance, and was to die of AIDS later that year. Principal dancers included the Balanchine muse Darci Kistler, who played the Sugar Plum Fairy, Heather Watts, Damian Woetzel, and Kyra Nichols. Two well-known actors also took part: Macaulay Culkin appeared as the Nutcracker/Prince, and Kevin Kline served as the offscreen narrator. The soundtrack features the interpolated number from The Sleeping Beauty that Balanchine used in the production, and the music is heard on the album in the order that it appears in the film, not in the order that it appears in the original ballet.[73]
- Notable albums of excerpts from the ballet, rather than just the usual Nutcracker Suite, were recorded by Eugene Ormandy conducting the Philadelphia Orchestra for Columbia Masterworks, and Fritz Reiner and the Chicago Symphony Orchestra for RCA Victor. Arthur Fiedler and the Boston Pops Orchestra (for RCA), as well as Erich Kunzel and the Cincinnati Pops Orchestra (for Telarc) have also recorded albums of extended excerpts. The original edition of Michael Tilson Thomas’s version with the Philharmonia Orchestra on CBS Masterworks was complete, but is out of print;[74] the currently available edition is abridged.[75]
Neither Ormandy, Reiner, nor Fiedler ever recorded a complete version of the ballet; however, Kunzel’s album of excerpts runs 73 minutes, containing more than two-thirds of the music. Conductor Neeme Järvi has recorded act 2 of the ballet complete, along with excerpts from Swan Lake. The music is played by the Royal Scottish National Orchestra.[76]
- Many famous conductors of the twentieth century made recordings of the suite, but not of the complete ballet. These include Arturo Toscanini, Sir Thomas Beecham, Claudio Abbado, Leonard Bernstein, Herbert von Karajan, James Levine, Sir Neville Marriner, Robert Shaw, Mstislav Rostropovich, Sir Georg Solti, Leopold Stokowski, Zubin Mehta, and John Williams.
- In 2007, Josh Perschbacher recorded an organ transcription of the Nutcracker Suite.
Ethnic stereotypes and US activism[edit]
In 2013, Dance Magazine printed the opinions of three directors. Ronald Alexander of Steps on Broadway and The Harlem School of the Arts said the characters in some of the dances were «borderline caricatures, if not downright demeaning». He also said some productions had made changes to improve this. In the Arabian dance, for example, it was not necessary to portray a woman as a «seductress», showing too much skin. Alexander tried a more positive portrayal of the Chinese, but this was replaced by the more traditional version, despite positive reception. Stoner Winslett of the Richmond Ballet said The Nutcracker was not racist and that her productions had a «diverse cast». Donald Byrd of Spectrum Dance Theater saw the ballet as Eurocentric and not racist.[77] Chloe Angyal, in Feministing, referred to «unbelievably offensive racial and ethnic stereotypes». Some people who have performed in productions of the ballet do not see a problem because they are continuing what is viewed as «a tradition».[78] According to George Balanchine, «Coffee» was a sensuous belly dance intended for the fathers, not the children.[79]
In The New Republic in 2014, Alice Robb described white people wearing «harem pants and a straw hat, eyes painted to look slanted» and «wearing chopsticks in their black wigs» in the Chinese dance. The Arabian dance, she said, has a woman who «slinks around the stage in a belly shirt, bells attached to her ankles».[78] One of the problems, Robb said, was the use of white people to play ethnic roles, because of the directors’ desire for everyone to look the same.[78]
Among the attempts to change the dances were Austin McCormick making the Arabian dance into a pole dance, and San Francisco Ballet and Pittsburgh Ballet Theater changing the Chinese dance to a dragon dance.[78]
Alastair Macaulay of The New York Times defended Tchaikovsky, saying he «never intended his Chinese and Arabian music to be ethnographically correct».[80] He said, «their extraordinary color and energy are far from condescending, and they make the world of ‘The Nutcracker’ larger.»[80] To change anything is to «unbalance The Nutcracker» with music the author did not write. If there were stereotypes, Tchaikovsky also used them in representing his own country of Russia.[80] Moreover, the Votkinsk-born composer is perceived as a part of cultural heritage of Finnic peoples (non-Indo-European).[81][82][failed verification]
University of California, Irvine professor Jennifer Fisher said in 2018 that a two-finger salute[which?] used in the Chinese dance was not a part of the culture. Though it might have had its source in a Mongolian chopstick dance, she called it «heedless insensitivity to stereotyping». She also complained about the use in the Chinese dance of «bobbing, subservient ‘kowtow’ steps, Fu Manchu mustaches, and … yellowface» makeup, compared to blackface. One concern she had was that dancers believed they were learning about Asian culture, when they were really experiencing a cartoon version.[83]
Fisher went on to say some ballet companies were recognizing that change had to happen. Georgina Pazcoguin of the New York City Ballet and former dancer Phil Chan started the «Final Bow for Yellowface» movement and created a web site which explained the history of the practices and suggested changes. One of their points was that only the Chinese dance made dancers look like an ethnic group other than the one they belonged to. The New York City Ballet went on to drop geisha wigs and makeup and change some dance moves. Some other ballet companies followed.[83]
In popular culture[edit]
Film[edit]
Several films having little or nothing to do with the ballet or the original Hoffmann tale have used its music:
- The 1940 Disney animated film Fantasia features a segment using The Nutcracker Suite. This version was also included both as part of the 3-LP soundtrack album of Fantasia (since released as a 2-CD set), and as a single LP, with Dance of the Hours, another Fantasia segment, on the reverse side.[84][85]
- The Spirit of Christmas, a 1950 marionette made-for-TV featurette in color narrated by Alexander Scourby, utilizes the poem A Visit from St. Nicholas, and this sequence also includes music from The Nutcracker.
- A 1951 thirty-minute short, Santa and the Fairy Snow Queen, issued on DVD by Something Weird Video, features several dances from The Nutcracker.[86]
- The Nutcracker (1973) features a nameless girl (slightly similar to Clara) who works as a maid. She befriends and falls in love with a nutcracker ornament, who was a young prince cursed by the three headed Mouse King.
- Sanrio released a stop-motion adaptation of The Nutcracker entitled Nutcracker Fantasy in 1979.
- In 1988, Care Bears Nutcracker Suite was produced by the Canadian animation studio Nelvana and featured the Care Bears characters.
- A 1990 animated film titled The Nutcracker Prince was released and distributed by Warner Brothers Pictures and uses cuts of the music throughout and its story is based heavily on that of the ballet.
- A 1999 animated film titled The Nuttiest Nutcracker featured the voices of Cheech Marin, Jim Belushi, and Phyllis Diller, and followed a group of anthropomorphic fruits and vegetables.
- In 2001, Barbie appeared in her first film, Barbie in the Nutcracker. It used excerpts by Tchaikovsky, which were performed by the London Symphony Orchestra. Though it heavily altered the story, it still made use of ballet sequences which had been rotoscoped using real ballet dancers.[87]
- In 2007, Tom and Jerry: A Nutcracker Tale also used The Nutcracker excerpts, which were performed by the Chamber Orchestra of Philadelphia.
- Disney announced that a remake of The Nutcracker would be directed by Robert Zemeckis through the use of motion capture, a technique that was used in The Polar Express, Monster House, Beowulf, and A Christmas Carol. The film was cancelled following the box office disappointment of Mars Needs Moms.
- In 2010, The Nutcracker in 3D with Elle Fanning abandoned the ballet and most of the story, retaining much of Tchaikovsky’s music with lyrics by Tim Rice. The $90 million film became the year’s biggest box office bomb.
- In 2016, the Hallmark Channel presented A Nutcracker Christmas; a tele-film that contains a number of selected scenes of the 1892 two-act Nutcracker ballet.
- In 2017, the Athens State Orchestra in collaboration with Cinecreed productions (former name: 1895 cinematic creations) presented «A Different Nutcracker» animation film, directed by Yiorgos Molvalis. At the premiere (Chr. Lamprakis, Athens Concert Hall, December 26, 2017) as Silent animation, the film was recorded live by the Athens State Orchestra. In 2020 the official recording was integrated in to the film marking its completion and making it available for screenings without the need to have the orchestra present.
- In 2018, the Disney live-action film The Nutcracker and the Four Realms was released with Lasse Hallström and Joe Johnston as directors and a script by Ashleigh Powell.[88][89]
Television[edit]
- A 1954 Christmas episode of General Electric Theater featured Fred Waring and his choral group, the Pennsylvanians, singing excerpts from The Nutcracker with specially written lyrics. While the music was being sung, the audience saw ballet dancers performing.[90] The episode was hosted by Ronald Reagan.
- The 1987 true crime miniseries Nutcracker: Money, Madness and Murder opens every episode with the first notes of the ballet amid scenes of Frances Schreuder’s daughter dancing to it in ballet dress.
- «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» plays in the gabian dubbing version of El Chapulín Colorado episode «El Mistério Del Hombre De Las Nieves» while Chapolin and his friends Carlos and Florinda use sleeping bags for themselves to sleep at home until the music is interrupted after a fake yeti invades the house to scare them.
- Garfield and Friends episode, «Caped Avenger», «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» plays briefly while a shadow kidnaps Pooky.
- The «Toon TV» episode of Tiny Toon Adventures features an arcade-themed song called «Video Game Blues», set to «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» and «The Russian Dance».
- Batman: The Animated Series episode, «Christmas with the Joker», The Joker plays, «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy», and later, «The Russian Dance» on a record player to distract Batman and Robin.
- A 1996 episode of The Magic School Bus («Holiday Special», season 3, episode 39), Wanda is planning to see a performance of The Nutcracker. Some of the music for this episode was based on the score of the ballet.[91]
- The Mickey Mouse Works «MouseTales» segment, the House of Mouse episode, «Pete’s Christmas Caper», and the feature film, Mickey’s Magical Christmas: Snowed in at the House of Mouse, with Mickey Mouse playing the role of the Nutcraker, Minnie Mouse as Maria, Donald Duck as the King Mouse, Goofy as the Magical Snow Fairy, and Ludwig Von Drake as Godpapa Drosselmeyer.
- The Barney & Friends TV Christmas episode features its own version of the Nutcracker with Barney the Dinosaur as the narrator, dressed up in a tuxedo vest and matching cuffs.
- Princess Tutu, a 2002 anime series that uses elements from many ballets as both music and as part of the storyline, uses the music from The Nutcracker in many places throughout its run, including using an arranged version of the overture as the theme for the main character. Both the first and last episodes feature The Nutcracker as their ‘theme’, and one of the main characters is named Drosselmeyer.
- An arrangement of this the Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy can be heard in Episode 8 of Girls und Panzer.
- Arrangements of the Waltz of the flowers can be heard in Episode 7 of Guilty Crown.
- The 2015 Canadian television film The Curse of Clara: A Holiday Tale, based on an autobiographical short story by onetime Canadian ballet student Vickie Fagan, centres on a young ballet student preparing to dance the role of Clara in a production of The Nutcracker.
Video games[edit]
- In the NES version of Tetris, the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» is available as background music (referred to in the settings as «Music 1»), and the same arrangement was later remixed for the Game Boy Advance version of Tetris Worlds.
- In the NES game Winter Games, «Waltz of the Flowers» is used as the music for the figure skating event.
- In the game BioShock, the main character Jack meets an insane musician named Sander Cohen who tasks Jack with killing and photographing four of Sander’s ex-disciples. When the third photograph is given to Sander, in a fit of pique he unleashes waves of splicer enemies to attack Jack while playing «Waltz of the Flowers» from speakers in the area.
- In the original Lemmings «Dance of the Reed Flutes» and «Miniature Overture» is used in several levels.
- In Weird Dreams, there is also a plus sized ballerina dancing to the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» in the Hall of Tubes.
- In the Baby Bowser levels of Yoshi’s Story, a variation of the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» is used as the background music.
- In Mega Man Legends, the «Waltz of the Flowers» can be heard in the Balloon Fantasy minigame.
- In Crash Tag Team Racing, the «Trepak» are the background themes played during Tire & Ice track as a part with «Kalinka» and «Hungarian Dance No. 5».
- In the Wii version of Mario & Sonic at the Olympic Winter Games, «Waltz of the Flowers» is used as optional background music for the figure skating event. In the Nintendo DS version, the «Marche» and «Trepak» are used.[92]
- In Kingdom Hearts 3D: Dream Drop Distance the «Waltz of Flowers», «The Arabian Dance», «The Russian Dance», «The Dance of the Reed Flutes» and «The Chinese Dance» are the background themes that play when Riku is in the world based on Disney’s Fantasia.
- In Hatoful Boyfriend, the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» is used as the character theme for Iwamine Shuu.
- In a TV advertisement for Army Men: Sarge’s Heroes 2, the plastic army men work together using a train playset to move a firecracker under the Christmas tree and place it between the Nutcracker doll’s legs, while «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy» plays.
- In Fantasia: Music Evolved, a medley of «The Nutcracker» is listed and consists of the «Marche», «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy», and «Trepak»; besides the original mix, there is also the «D00 BAH D00» mix and the «DC Breaks» mix.
- In Dynamite Headdy, the «March» is used in the Mad Dog boss battle.
- In Grand Theft Auto V one of the classical horns, that can be bought for cars, plays the «Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy».[93]
- The «Waltz of the Flowers» appears during a baby’s death scene in What Remains of Edith Finch.
- In the game «Cell to Singularity,» «Waltz of the Flowers» is heard in the background when new creatures are created.
- In LittleBigPlanet 3, a remix of «Waltz of the Flowers» is used as background music in the level «Tutu Tango» and is an unlockable music track in Create Mode.
- The «Kids Mode» of Just Dance 2021 and Just Dance 2022 features the song «Dance of the Mirlitons» on the soundtrack.
Children’s recordings[edit]
There have been several recorded children’s adaptations of the E.T.A. Hoffmann story (the basis for the ballet) using Tchaikovsky’s music, some quite faithful, some not. One that was not was a version titled The Nutcracker Suite for Children, narrated by Metropolitan Opera announcer Milton Cross, which used a two-piano arrangement of the music. It was released as a 78-RPM album set in the 1940s.[94] For the children’s label Peter Pan Records, actor Victor Jory narrated a condensed adaptation of the story with excerpts from the score. It was released on one side of a 45-RPM disc.[95] A later version, titled The Nutcracker Suite, starred Denise Bryer and a full cast, was released in the 1960s on LP and made use of Tchaikovsky’s music in the original orchestral arrangements. It was quite faithful to Hoffmann’s story The Nutcracker and the Mouse King, on which the ballet is based, even to the point of including the section in which Clara cuts her arm on the glass toy cabinet, and also mentioning that she married the Prince at the end. It also included a less gruesome version of «The Tale of the Hard Nut», the tale-within-a-tale in Hoffmann’s story. It was released as part of the Tale Spinners for Children series.[96]
Spike Jones produced a 78 rpm record set «Spike Jones presents for the kiddies The Nutcracker Suite (with Apologies to Tchaikovsky)» in 1944. It includes the tracks: «The Little Girl’s Dream», «Land of the Sugar Plum Fairy», «The Fairy Ball», «The Mysterious Room», «Back to the Fairy Ball» and «End of the Little Girl’s Dream». This is all done in typical Spike Jones style, with the addition of choruses and some swing music. The entire recording is available at archive.com [97]
Journalism[edit]
- In 2009, Pulitzer Prize–winning dance critic Sarah Kaufman wrote a series of articles for The Washington Post criticizing the primacy of The Nutcracker in the American repertory for stunting the creative evolution of ballet in the United States:[98][99][100]
That warm and welcoming veneer of domestic bliss in The Nutcracker gives the appearance that all is just plummy in the ballet world. But ballet is beset by serious ailments that threaten its future in this country… companies are so cautious in their programming that they have effectively reduced an art form to a rotation of over-roasted chestnuts that no one can justifiably croon about… The tyranny of The Nutcracker is emblematic of how dull and risk-averse American ballet has become. There were moments throughout the 20th century when ballet was brave. When it threw bold punches at its own conventions. First among these was the Ballets Russes period, when ballet—ballet—lassoed the avant-garde art movement and, with works such as Michel Fokine’s fashionably sexy Scheherazade (1910) and Léonide Massine’s Cubist-inspired Parade (1917), made world capitals sit up and take notice. Afraid of scandal? Not these free-thinkers; Vaslav Nijinsky’s rough-hewn, aggressive Rite of Spring famously put Paris in an uproar in 1913… Where are this century’s provocations? Has ballet become so entwined with its «Nutcracker» image, so fearfully wedded to unthreatening offerings, that it has forgotten how eye-opening and ultimately nourishing creative destruction can be?[99]
- In 2010, Alastair Macaulay, dance critic for The New York Times (who had previously taken Kaufman to task for her criticism of The Nutcracker[101]) began The Nutcracker Chronicles, a series of blog articles documenting his travels across the United States to see different productions of the ballet.[102]
Act I of The Nutcracker ends with snow falling and snowflakes dancing. Yet The Nutcracker is now seasonal entertainment even in parts of America where snow seldom falls: Hawaii, the California coast, Florida. Over the last 70 years this ballet—conceived in the Old World—has become an American institution. Its amalgam of children, parents, toys, a Christmas tree, snow, sweets and Tchaikovsky’s astounding score is integral to the season of good will that runs from Thanksgiving to New Year… I am a European who lives in America, and I never saw any Nutcracker until I was 21. Since then I’ve seen it many times. The importance of this ballet to America has become a phenomenon that surely says as much about this country as it does about this work of art. So this year I’m running a Nutcracker marathon: taking in as many different American productions as I can reasonably manage in November and December, from coast to coast (more than 20, if all goes well). America is a country I’m still discovering; let The Nutcracker be part of my research.[103]
- In 2014, Ellen O’Connell, who trained with the Royal Ballet in London, wrote, in Salon (website), on the darker side of The Nutcracker story. In E.T.A. Hoffmann’s original story, the Nutcracker and Mouse King, Marie’s (Clara’s), journey becomes a fevered delirium that transports her to a land where she sees sparkling Christmas Forests and Marzipan Castles, but in a world populated with dolls.[104] Hoffmann’s tales were so bizarre, Sigmund Freud wrote about them in The Uncanny.[105][106]
E.T.A. Hoffmann’s 1816 fairy tale, on which the ballet is based, is troubling: Marie, a young girl, falls in love with a nutcracker doll, whom she only sees come alive when she falls asleep. …Marie falls, ostensibly in a fevered dream, into a glass cabinet, cutting her arm badly. She hears stories of trickery, deceit, a rodent mother avenging her children’s death, and a character who must never fall asleep (but of course does, with disastrous consequences). While she heals from her wound, the mouse king brainwashes her in her sleep. Her family forbids her from speaking of her «dreams» anymore, but when she vows to love even an ugly nutcracker, he comes alive and she marries him.
Popular music[edit]
- The song «Dance Mystique» (track B1) on the studio album Bach to the Blues (1964) by the Ramsey Lewis Trio is a jazz adaptation of Coffee (Arabian Dance).
- The song «Fall Out» by English band Mansun from their 1998 album Six heavily relies on the celesta theme from the Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy.
- The song «Dark Ballet» by American singer-songwriter Madonna samples the melody of Dance of the Reed Flutes (Danish Marzipan) which is often mistaken for Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy. The song also relied on the lesser-known harp cadenza from Waltz of the Flowers. The same Tchaikovsky sample was earlier used in internationally famous 1992 ads for Cadbury Dairy Milk Fruit & Nut with ‘Madonna’ as the singing chocolate bar (in Russian version the subtitles «‘This Is Madonna'» (Russian: Это Мадонна, tr. Eto Madonna) were displayed on a screen.[107]
See also[edit]
- Parade of the Wooden Soldiers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Щелкунчикъ in Russian pre-revolutionary script.
References[edit]
- ^ a b Fisher, J. (2003). Nutcracker Nation: How an Old World Ballet Became a Christmas Tradition in the New World. New Haven: Yale University Press.
- ^ Agovino, Theresa (23 December 2013). «The Nutcracker brings big bucks to ballet companies». Crain’s New York Business. Retrieved 3 November 2017.
- ^ Wakin, Daniel J. (30 November 2009). «Coming Next Year: Nutcracker Competition». The New York Times.
- ^ a b c d Anderson, J. (1958). The Nutcracker Ballet, New York: Mayflower Books.
- ^ a b Hoffmann, E. T. A., Dumas, A., Neugroschel, J. (2007). Nutcracker and Mouse King, and the Tale of the Nutcracker, New York
- ^ Rosenberg, Donald (22 November 2009). «Tchaikovsky’s ‘Nutcracker’ a rite of winter thanks to its glorious music and breathtaking dances». Cleveland.com. Cleveland. Retrieved 4 November 2010.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky». Balletalert.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2012. Retrieved 10 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Nutcracker History». Balletmet.org. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 18 December 2008.
- ^ a b Fisher 2003, p. 15
- ^ a b Fisher 2003, p. 16
- ^ Fisher 2003, pp. 14–15.
- ^ Fisher 2003, p. 17.
- ^ Wiley, Roland John (1991). Tchaikovsky’s Ballets: Swan Lake, The Sleeping Beauty, The Nutcracker. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- ^ «Ballet Talk [Powered by Invision Power Board]». Ballettalk.invisionzone.com. 26 November 2008. Archived from the original on 17 September 2009. Retrieved 7 January 2009.
- ^ Craine, Debra (8 December 2007). «Christmas cracker». The Times. London.
- ^ «Ballet Russe de Monte Carlo. Ballet Russe de Monte Carlo records, 1935–1968 (MS Thr 463): Guide». Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 3 February 2013.
- ^ «Remembering Jocelyn Vollmar (1925-2018): SF Ballet’s 1st Snow Queen sparkled on- and offstage».
- ^ «About : Ballet West».
- ^ «Maria Tallchief». The Kennedy Center. The John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ Soviet ed., where they are printed in the original French with added Russian translation in editorial footnotes
- ^ Maximova, Yekaterina; Vasiliev, Vladimir (1967). Nutcracker Suite Performed By The Bolshoi (1967). Moscow, Russia: British Pathé.
- ^ The Nutcracker at the Royal Ballet: «March of the Toy Soldiers». London: Playbill Video. 1967. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Moscow Ballet (2017). Doll Dance. Moscow, Russia: Moscow Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Moscow Ballet (2017). The Rat King Appears. Moscow, Russia: Moscow Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the SemperOperBallett (2016). Snow Pas de Deux. Dresden, Germany: SemperOperBallett. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Bolshoi Ballet (2015). The Nutcracker (Casse-Noisette) – Bolshoi Ballet in Cinema (Preview 1). Moscow, Russia: Pathé Live. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Perm Opera Ballet Theatre (2017). Вальс снежинок из балета «Щелкунчик». Russia: Perm Opera Ballet Theatre. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the SemperOperBallett. The Nutcracker – Arabian Divertissement. Dresden, Germany: SemperOperBallett. Archived from the original on 15 January 2020.
- ^ Cecilia Iliesiu (2017). Arabian Coffee/Peacock. Pacific Northwest Ballet.
- ^ Dancers of the Mariinsky ballet (2012). The Nutcracker – Tea (Chinese Dance). Mariinsky Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the Boston Ballet (2017). SPOTLIGHT The Nutcracker’s Russian Dance. Boston Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Dancers of the SemperOperBallett. The Nutcracker – Mirlitons Divertissement. Dresden, Germany: SemperOperBallett.
- ^ Kyra Nichols and the NYCB Corps de Ballet (2015). New York City Ballet: Waltz of the Flowers. New York City: Lincoln Center.
- ^ PNB dancers. Nutcracker Flowers Excerpt. Pacific Northwest Ballet. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Alina Somova & Vladimir Shklyarov (2012). Sugarplum and Cavalier variations. St Petersburg, Russia: Ovation.
- ^ Darci Kistler. Dance of the Sugarplum Fairy. New York City: Ovation. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021.
- ^ Wiley 1991, p. 220.
- ^ Schwarm, Betsy. «The Nutcracker, OP. 71». Encyclopaedia Britannica. The Music Alliance. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- ^ «Tchaikovskaya (Davydova) Alexandra Ilinichna». chaiklib.permculture.ru (in Russian). Chaykovsky Centralized Library System. Archived from the original on 24 October 2020. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ^ Jennifer Fisher (2004). ‘Nutcracker’ Nation: How an Old World Ballet Became a Christmas Tradition in the New World. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-10599-5.
- ^ «Шесть шедевров Чайковского, сделанных из обычной гаммы» [Six masterpieces by Tchaikovsky created from the usual scale]. kultspargalka.ru (in Russian). 4 April 2020. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
1. June. Barcarole from The Seasons 2. ‘Adagio’ from The Nutcracker 3. Lensky’s aria from Eugene Onegin 4. Serenade for Strings Waltz 5. ‘Melodrama’ from the music to the play by A. Ostrovsky The Snow Maiden 6. Yeletsky’s aria from The Queen of Spades
- ^ Tchaikovsky By David Brown W. W. Norton & Company, 1992 page 332
- ^ Appleford, David (19 December 2008). «The KEZ Christmas Countdown: Day 19 – The Nutcracker». Kfyi.com. Archived from the original on 12 January 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Tchaikovsky, P. (2004). The Nutcracker: Complete Score, Dover Publications.
- ^ a b «Ballet and Food». art-eda.ru (in Russian). Artoteka of Food. 21 November 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
Russian trepak «Candy Cane» and dance of sugar shepherds «Danish Marzipan»
- «Russian Seasons in Monaco». rusmonaco.fr (in Russian). Monaco and Cote D’Azur (printed Russian-language newspaper and magazine in Monaco and France). Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- «П.Чайковский. Щелкунчик. Дивертисмент. Большой театр. Tchaikovsky. The Nutcracker (1980)». YouTube. Official channel «Soviet Television» by the State TV and Radio Fund of Russia. 11 December 2018. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
The second title is «Датский марципан» – Danish marzipan. In the Grigorovich version for Bolshoi Theatre the idea of Europe is represented by dance with a marzipan sheep on wheels; Russian dance «Cancy Cane» combines the colors of candy canes and folklore heroes Ivan Tsarevich and Vasilisa the Wise
- ^ Alexander Poznansky, Tchaikovsky: The Quest for the Inner Man, p. 544
- ^ Brown, David. Tchaikovsky: The Final Years, 1885-1893. London, 1991; corrected edition 1992: p. 386
- ^ «The Nutcracker Profile: The History of The Nutcracker». Classicalmusic.about.com. 11 June 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Freddy Martin And His Orchestra – Tschaikowsky’s Nutracker Suite In Dance Tempo». Discogs.
- ^ «Fred Waring & the Pennsylvanians – Nutcracker Suite«. Discogs.
- ^ «Discography of American Historical Recordings, s.v. «Decca matrix L 6763. Nutcracker suite, part 1 / Les Brown and his Band of Renown,» accessed December 19, 2020″.
- ^ «A Duke Ellington Panorama». Depanorama.net. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «The Harlem Nutcracker». Susan Kuklin. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ The New Nutcracker Suite and Other Innocent Verses: Ogden Nash, Ivan Chermayeff. Little, Brown and Company. January 1962 – via Amazon.com.
- ^ Ogden Nash. «The New Nutcracker Suite & Other Innocent Verses». Kirkus Reviews.
- ^ Cooper, Antonio. «Nutcracker Brings Magic to DeVos». The Oakland Press. Retrieved 1 October 2019.
- ^ Scher, Avichai (3 December 2018). «What’s it like to choreograph Nutcracker four different times». Dance Magazine. Dance Magazine. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- ^ Merrell, Sue (30 November 2017). ««Nutcracker» Choreographer Makes GR Stop Ahead of Opening». grand rapids magazine. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ «blogcritics.org». blogcritics.org. Archived from the original on 11 July 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Lindsey Stirling Talks Joining ‘Dancing With the Stars’ & Shares First Holiday Album Track: Premiere». Billboard. 14 September 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Alexeyev, Alexander (5 August 2019). «Баян для Мадонны. Чайковский в новом альбоме Madame X» [Bayan [also a slang word for anything related to media content: videos, pictures, news, and an old post as fresh news] for Madonna. Tchaikovsky on the new Madame X album] (in Russian). Rossiyskaya Gazeta. Archived from the original on 2 September 2019. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ Van Horn, Charisse (19 November 2019). «Mariah Carey Shows Off Her Whistle Register In New Sugar Plum Fairy Acapella Rendition». celebrityinsider.org. Celebrity Insider. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ «Ho Ho, whatever! Got some jolly news for you… Proud to be part of the @smashthehouse Christmas album dropping 27/12. Swipe left to witness «The Nutcracker»!». Twitter. Retrieved 26 November 2020.
- ^ «Recording Technology History». History.sandiego.edu. Archived from the original on 12 March 2010. Retrieved 18 December 2008.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (31 December 2010). «‘The Nutcracker’ Chronicles: Listening to the Score».
- ^ «Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete Ballet); Serenade for Strings – Credits on MSN Music». Music.msn.com. Archived from the original on 8 June 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Pyotr Il’yich Tchaikovsky, Antal Dorati, Harold Lawrence, London Symphony Orchestra, Philharmonia Hungarica, London Symphony Orchestra Chorus – Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete Ballet); Serenade in C Major – Amazon.com Music». Amazon.
- ^ Styrous® (10 December 2012). «The Styrous® Viewfinder».
- ^ «Nutcracker». Classicalcdreview.com. Retrieved 18 December 2008.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky, Gennady Rozhdestvensky, Bolshoi Theater Orchestra – Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete) – Amazon.com Music». Amazon.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky: the Nutcracker: Sir Simon Rattle, Tchaikovsky, Berliner Philharmoniker: Music». Amazon. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Peter Ilyich Tchaikovsky, Michael Tilson Thomas, The Philharmonia Orchestra, Ambrosian Singers – Tchaikovsky: Music From The Nutcracker (Highlights) – Amazon.com Music». Amazon.
- ^ «The Nutcracker (1993 Motion Picture Soundtrack): Pyotr Il’yich Tchaikovsky, David Zinman, New York City Ballet Orchestra: Music». Amazon. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Archived copy» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ «Tchaikovsky: The Nutcracker (Complete): Music». Amazon. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky: Nutcracker, Act II/ Swan Lake». AllMusic.
- ^ «Burning Question: Is Nutcracker Racist?». Dance Magazine. 1 December 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ a b c d Robb, Alice (24 December 2014). «Sorry, ‘The Nutcracker’ Is Racist». The New Republic. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ Dunning, Jennifer (26 November 2004). «Staying on Their Toes for ‘The Nutcracker,’ Show After Show». The New York Times. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ a b c Macaulay, Alastair (6 September 2012). «Stereotypes in Toeshoes». The New York Times. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky Museum-Estate» (in Russian). Finno-Ugric World. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ^ «Udmurtia to Host a Conference ‘Tchaikovsky: a Son of Udmurtia, the Genius of Man!’» (in Russian). Regnum. 5 October 2007. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ^ a b Fisher, Jennifer (11 December 2018). «Op-Ed: ‘Yellowface’ in ‘The Nutcracker’ isn’t a benign ballet tradition, it’s racist stereotyping». Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ «Disney (All) The Nutcracker Suite/Dance of the Hours – Sealed USA LP RECORD (284287)». Eil.com. 21 April 2004. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Tchaikovsky’s The Nutcracker Suite Also Ponchielli’s Dance of the Hours Philadelphia Orchestra Leopold Stokowski Conducting: Leopold Stokowski: Music». Amazon. 9 September 2009. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «Santa and the Fairy Snow Queen : A Sid Davis Production : Free Download & Streaming : Internet Archive». 10 March 2001. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ daflauta (2 October 2001). «Barbie in the Nutcracker (Video 2001)». IMDb.
- ^ Kit, Borys (4 March 2016). «Lasse Hallstrom to Direct Live-Action ‘Nutcracker’ for Disney». The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ «The Nutcracker and the Four Realms (2018)». Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved 1 November 2018.
- ^ ««General Electric Theater» Music for Christmas (TV Episode 1954)». IMDb. 19 December 1954.
- ^ ««The Magic School Bus» The Family Holiday Special (TV Episode 1996)». IMDb. 25 December 1996.
- ^ «Super Mario Wiki/Figure Skating». Mariowiki.com. 10 September 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «GTA5 Classical horn 3». youtube.com. 8 May 2015. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- ^ «Week 50». Kiddierecords.com. Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ «11 The Nutcracker Suite : Victor Jory». SoundCloud.
- ^ «Tale Spinners for Children». Artsreformation.com. 14 May 2008. Archived from the original on 13 August 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ Spike Jones and his City Slickers. «Spike Jones presents for the kiddies The Nutcracker Suite with Apologies to Tchaikovsky«. archive.org. Retrieved 29 December 2022.
- ^ Kaufman, Sarah (13 September 2009). «Here Come Those Sugar Plums and Chestnuts». The Washington Post. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ a b Kaufman, Sarah (22 November 2009). «Breaking pointe: ‘The Nutcracker’ takes more than it gives to world of ballet». The Washington Post. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ Itzkoff, Dave (14 December 2009). «Sugar Plum Overdose: The Case Against ‘The Nutcracker’«. The Washington Post. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (16 November 2010). «A ‘Nutcracker’ Lover Explains Himself». The New York Times. Retrieved 20 November 2010.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (10 November 2010). «The ‘Nutcracker’ Chronicles: The Marathon Begins». The New York Times. Retrieved 15 November 2010.
- ^ Macaulay, Alastair (10 November 2010). «The Sugarplum Diet». The New York Times. Retrieved 15 November 2010.
- ^ O’Connell, Ellen (25 December 2014). ««The Nutcracker’s» disturbing origin story: Why this was once the world’s creepiest ballet». Solon. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Freud, Sigmund (1919). «The Uncanny» (PDF).
- ^ «Nutcracker Ballet 101». Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ «Reklamka Vimto i Frut’n’Nuts (1994)» (in Russian). YouTube channel «towaroved». Retrieved 24 September 2019.
External links[edit]
- The Nutcracker (ballet): Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- The Nutcracker (suite): Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- Tchaikovsky Research
- The Nutcracker ballet
П.И. Чайковский балет «Щелкунчик»
Самое волшебное и новогоднее произведение П.И. Чайковского, известное по всему миру – балет «Щелкунчик». Зачастую в классических операх или балетах есть один или несколько известных номеров, которые становятся знаковыми для произведения и горячо любимыми публикой. О «Щелкунчике» этого не скажешь, потому что весь балет состоит из таких «хитов»! Пожалуй, это самое узнаваемое произведение во всем мире. Чего только стоит завораживающий Танец феи Драже, нежнейший Вальс Цветов, череда танцев: Шоколад, Кофе, Чай и многие другие. Да и кто из детей, в конце концов, не мечтал оказаться на месте Мари и Щелкунчика в этом сказочном месте из шоколада, карамели, зефира и прочих вкусностей?!
Краткое содержание балета Чайковского «Щелкунчик» и множество интересных фактов об этом произведении читайте на нашей странице.
|
Действующие лица |
Описание |
| Штальбаум | советник медицины, именно в его доме разворачиваются все события |
| Мари | дочка Штальбаума, получившая в подарок Щелкунчика |
| Фриц | брат Мари, сломавший Щелкунчика на празднике |
| Дроссельмейер | крестный Мари, подаривший ей Щелкунчика и рассказавший о чудесном городе |
| Щелкунчик | заколдованный принц |
| Фея Драже | правительница в волшебном городе Конфитюренбурге |
| Принц Коклюш | принц из сказочного города, встречающий девочку и Щелкунчика |
| Король мышей | злой повелитель враждебной армии мышей, напавший на Щелкунчика |
Краткое содержание «Щелкунчика»
Основные события в балете разворачиваются накануне большого и светлого праздника — Рождества.
В доме Штальбаума собрались гости и крестный Мари, который пришел с кучей подарков для детей. Среди них заметно выделяется кукла, предназначенная для колки орехов – Щелкунчик. Довольно неуклюжая игрушка с широкой улыбкой сразу понравилась девочке Мари. Уже все дети ушли спать, а она все не могла расстаться с Щелкунчиком.
Девочка так заигралась, что не заметила, как вокруг все стало меняться. Елка стала огромных размеров и послышался странный шорох. В комнате появилась армия мышей, а сам Щелкунчик внезапно ожил, превратившись в прекрасного юношу. Он тут же собрал себе армию из солдатиков и отправился на врага, но их силы были неравны. Мари, увидев это, решила помочь Щелкунчику и кинула своим башмачком в Короля мышей. Враги испугались внезапной атаки и разбежались.
Когда Мари очнулась, перед ней оказался ее крестный – Дроссельмейер, представший в образе волшебника. Он рассказал об удивительном сказочном мире, в который достаточно непросто попасть, преодолевая снежную бурю. Но Мари вместе с Щелкунчиком отправляются в эту страну. Они оказываются в чудесном городе Конфитюренбурге, где кругом много сладостей и гостей, встречающих их. Фея Драже устраивает пышный бал в их честь и Мари становится настоящей принцессой, после того, как Щелкунчик рассказал, как она спасла его. Когда торжество заканчивается, волшебник помогает Мари вернуться домой из своего чудесного путешествия.
| Продолжительность спектакля | |
| I Акт | II Акт |
| 50 мин. | 50 мин. |
Фото:


Интересные факты о Щелкунчике
- Сохранились сведения, что на первом представлении балета в Мариинском театре (декабрь 1892 года) публика была необычайно удивлена именно силой звучания оркестра. В особенности привлек их внимание музыкальный инструмент челеста.
- Начиная с постановок «Щелкунчика», появилась традиция отдавать второстепенные роли ученикам хореографических училищ.
- Танец «Кофе» основан на народной грузинской колыбельной.
- Согласно содержанию немецкой легенды, щелкунчики приносят удачу и оберегают дом. Поэтому эти деревянные механические куклы были популярны как рождественские подарки для детей.
- Елка, которую устанавливают обычно на сцене в первом акте, весит около тонны.
- Во время нежного танца снежинок на сцену падает конфетти, общая масса которого около 20 кг.
- За весь спектакль на сцене демонстрируется около 150 различных костюмов.
- Для полноценной работы всего оборудования, нанесения грима и смены костюмов за кулисами во время выступления должно находится около 60 человек.
- Для освещения балета применяется обычно до 700 осветительных приборов.
- На одну пачку Феи Драже уходит 7 слоев тюля.
- Существует некая путаница в именах девочки (Мари, Маша или Клара). На самом деле, как указано в первоисточнике, Клара – это всего лишь кукла девочки, которую зовут Марихен. На французский манер ее имя звучит как Мари, именно такая версия досталась директору Императорских театров Всеволжскому. В советских постановках, начиная с 1930 года, балет русифицировался и девочка Мари получила имя Мария, а ее брат стал Мишей. Также праздник Рождество заменили на Новый Год.
- Перед тем как приступить к написанию балета, Чайковский сначала полностью написал сюжет со слов Всеволжского и уже после принялся сочинять музыку.
- Волшебный город Конфитюренберг из второго акта так же придумал Всеволжский.
- Самый большой шелкунчик был сделан в Германии и имел высоту более 10 метров.
- Франк Рассел Гэли исполнил партию Щелкунчика в рекордном возрасте, на тот момент ему было 74 года и 101 день.
- Первоисточником знаменитого спектакля стала немецкая сказка Э.Т.А. Гофмана «Щелкунчик и мышиный король», вышедшая в свет в 1816 году.
Популярные номера «Щелкунчика»
Вальс цветов (слушать)
Марш из I действия (слушать)
Танец Феи Драже (слушать)
Вальс снежных хлопьев (слушать)
Па-де-де Феи Драже и Принца Оршада-Коклюша — адажио (слушать)
Музыка
Петр Ильич воплощает уже известную ему тематику в балете – преодоление враждебных сил благодаря силе любви. Музыка насыщается новыми выразительными образами. Интересно наблюдать за тем, как совмещается здесь выразительность с изобразительностью, яркая театральность и глубочайший психологизм.
Музыкальная ткань балета очень яркая и насыщена сильными, запоминающимися номерами. Так, перед сценой роста елки из первого акта звучит необычайная по выразительности музыка. Начинается она призрачно, передавая мышиную суету. Постепенно она приобретает более широкий размах, трансформируясь в разворачивающуюся мелодию.
Чайковский постарался, чтобы музыка очень тонко передавала всё содержание сказки, происходящее на сцене: барабанный бой, фанфары или писк мышей. Особенно любим у публики Дивертисмент II акта, который заключает в себе череду танцев на балу в сказочной стране. Это и яркий испанский танец – Шоколад, волнующий восточный – Кофе, характерный китайский – Чай, а также необычайно яркий и живой – Трепак. Далее идет изящный танец пастушков, Матушка Жигонь и жемчужина Дивертисмента – Вальс цветов с его завораживающей мелодией. Танец Феи Драже привлекает своей изысканностью, а настоящей лирической и драматической кульминацией смело можно назвать адажио.
История создания «Щелкунчика»
В 1890 году Петру Ильичу Чайковскому предложили сочинить оперу, состоящую из одного акта и балет. По замыслу эти произведения должны были исполняться в один вечер. Работать над балетом он начал вместе с Мариусом Петипа. Примечательно, что при написании партитуры Чайковский постоянно советовался с ним, даже по поводу музыки. Работа протекала достаточно быстро, однако, весной 1891 года, Петр Ильич вынужден был сделать паузу. Причина была уважительной – он отправился в США, где проходило долгожданное открытие знаменитого Карнеги-холла. Сохранились сведения, что Чайковский умудрялся сочинять даже в дороге на пароходе, так как боялся не успеть к сроку.
Несмотря на все свои старания, композитор был вынужден послать Всеволжскому письмо из Парижа и попросить немного перенести премьеру. Как только Чайковский вернулся, работа пошла гораздо продуктивнее. Так, к февралю 1892 года он полностью закончил свой спектакль. Премьера сюиты из «Щелкунчика» состоялась в Русском музыкальном обществе под управлением автора. Публика восторженно встретила новое произведение композитора. В этом время Петипа тяжело заболевает и роль балетмейстера теперь уже исполняет Л. Иванов, который как раз заканчивал свою карьеру танцовщика и ранее попробовал себя в роли хореографа. Так как Петипа не мог уже работать над либретто, его созданием продолжил заниматься брат композитора Модест Чайковский. Работа в театре над постановкой началась осенью 1892 года, премьера же была назначена на декабрь этого же года.
Литературная основа балета «Щелкунчик»
Первоисточником знаменитого спектакля стала немецкая сказка Э.Т.А. Гофмана «Щелкунчик и мышиный король», вышедшая в свет в 1861 году. По сюжету Марихен Штальбаум получает от своего крестного в подарок на Рождество небольшую куклу, предназначенную для колки орешков. Этой же ночью Щелкунчик чудесным образом оживает и вступает в сильнейшую и неравную борьбу с отрядом коварных мышей. Утром крестный Дроссельмейер поведал девочке одну интересную историю про своего племянника, заколдованного злобным королем мышей. И ночью Марихен, вместе со своей куклой Кларой и Щелкунчиком снова были атакованы врагами. Сумев одолеть коварное войско, они все вместе направились в сказочное царство, где девочку избрали принцессой.
Эта сказка была переведена литератором Эмилем Лабедолльером на французский язык в 1838 году. Именно этот перевод и достался знаменитому писателю Александру Дюма. Любопытно, что он решил создать уже свой вариант произведения. Эта немного измененная версия сказки с некоторыми отступлениями и попалась И.А. Всеволжскому, решившему создать балет.
Постановки «Щелкунчика»
Впервые постановка «Щелкунчик» вместе с оперой «Иоланта» состоялась в декабре 1892 года в Мариинском театре. Разработкой костюмов занимался сам Всеволжский, за дирижерским пультом стоял Р. Дриго. Успех был широчайшим, хотя и сохранились сведения о том, что опера публике понравилась поначалу больше. Несмотря на то, что единого действа не получилось, как планировал директор театров, по отдельности это были замечательные спектакли и в одной программе они больше не использовались. Работу Л. Иванова признали великолепной, особенно критики отметили созданный им танец воздушных снежинок. После своей премьеры балет оставался в репертуаре театра еще на протяжении 30 лет. В 1923 году балетмейстер Ф. Лопухов вновь обратился к спектаклю Чайковского, и в 1929 вышла обновленная версия «Щелкунчика». После этого балет еще неоднократно был поставлен на разных мировых сценах. Среди наиболее ярких постановок можно отметить версию балетмейстера Джорджа Баланчина, осуществленную в 1954 году в Нью-Йорке. Причем эта постановка вот уже более 50 лет ежегодно собирает все больше восторженных зрителей. Наряду с театральными постановками, балет также неоднократно был экранизирован.
На музыку «Щелкунчика» обратили внимание и многие мультипликаторы. В 1940 году на студии Уолта Диснея вышел мультфильм «Фантазия», в котором представлены некоторые фрагменты из балета. В советское время Борис Степанцев создал свой знаменитый мультфильм по сказке Гофмана, также с музыкой Чайковского. Подробнее познакомиться с этими версиями, можно в специальном разделе «Музыка из мультфильмов».
К необычным постановкам можно отнести версию Мэтью Боурна – британского хореографа. Она не имеет ничего общего с классической версией балета, тем не менее, хорошо отражает музыку. В частности, он дал другую интерпретацию Па-де-де из второго акта. События перенесены в приют для беспризорных детей, где за ними присматривает доктор Дросс. Сон главной героини оказывается совсем не таким, как в первоначальной версии. В нем все неустойчиво и любые объекты внезапно превращаются в различные вещи, иногда даже зловещие. А сами герои разлучаются из-за соперницы Мари, причем сам Щелкунчик и вовсе теряет память.
Вполне заслуженно спектакль является настоящей жемчужиной мирового балета. Со времен первой премьеры он с успехом ставится на всех известных мировых сценах. Музыку из «Щелкунчика» можно услышать в кино, в разнообразных мультфильмах и даже в компьютерных играх. Современные хореографы с удовольствием используют этот балет, привнося в него новшества, изменяя сюжет, место действия, вводя современные танцы. Лишь одно остается нетронутым – это удивительно прекрасная, завораживающая слушателей буквально с первых волшебных звуков музыка Чайковского.
Понравилась страница? Поделитесь с друзьями:
Пётр Ильич Чайковский «Щелкунчик»
Приблизительное время чтения: 10 мин.
Что это такое
Один из самых известных русских балетов. Рассказанная музыкой история о том, что в мире бюргеров 1 есть место чуду. Гофмановская сказка о любви доброй девочки и заколдованного юноши усилиями композитора Петра Чайковского (1840–1893) и либреттиста Мариуса Петипа 2 превратилась в балет-сновидение. «Щелкунчик» разделил историю балета на «до» и «после», став к тому же самым известным балетом на тему Рождества.
Литературная основа
Сказка Эрнста Теодора Амадея Гофмана «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король» была опубликована в 1816 году. Позже она вошла во второй раздел первого тома гофмановского сборника «Серапионовы братья» (1819–1921). В этой книге рассказчиком сказки о Щелкунчике писатель сделал одного из членов литературного «братства» — Лотара, прототипом которого обычно считают литератора Фридриха де ла Мотт Фуке, автора знаменитой сказочной повести «Ундина».
Описанный в сказке Щелкунчик — это одновременно игрушка и столовая утварь для колки орехов. Такие фигурки под названием Nussknacker были распространены в Германии и Австрии с XVIII века.
Гофмановская манера причудливо соединять в одном тексте два мира — реальный и фантастический — проявилась и в «Щелкунчике»: старший советник суда Дроссельмейер оказывается придворным часовщиком из полусказочного Нюрнберга, а деревянный щелкунчик — принцем Марципанового замка. В отличие от других гофмановских сказок («Золотой горшок», «Крошка Цахес», «Повелитель блох»), в «Щелкунчике» практически не звучат иронические мотивы в адрес главных героев — это один из самых поэтичных текстов в творчестве Гофмана.
Первые два русских перевода «Щелкунчика» появились практически одновременно, оба — в 1835 году. Однако основой для балетного либретто послужили вовсе не они. В 1844 году гофмановскую сказку по-своему пересказал Александр Дюма («История Щелкунчика»). Он освободил причудливую гофмановскую фантазию от множества сюжетных деталей, а принца-щелкунчика сделал лихим рыцарем, в чём-то похожим на героев собственных романов. Именно версию Дюма и навязал Чайковскому и балетмейстеру Мариусу Петипа директор императорских театров Иван Всеволожский. За либретто 3 принялся Петипа.
Либретто
На первом этапе Петипа задумал ввести в балет революционную тематику, даже использовать в одном из фрагментов мелодию «Карманьолы» 4. Шел 1891 год, буквально только что было столетие Великой французской революции. Из планов Петипа к «Щелкунчику»: «Толпа полишинелей. Карманьола. Станцуем карманьолу! Да здравствует гул пушек! Паспье королевы. В добрый путь, милый дю Молле». Последнее — слова из детской песенки, намекающие на бегство Карла Х в Англию после Июльской революции 1830 года во Франции.
Мариус Петипа в партии Таора. 1862 г.
Но мы-то помним, что сюжет о Щелкунчике пришёл к Петипа из дирекции императорских театров. Балету с революционной тематикой доступ на императорскую сцену был бы закрыт. Так что из окончательного сценария Петипа все революционные мотивы были изгнаны.
Сюжет Гофмана-Дюма также пострадал: из сказки выпала вся предыстория заколдованного юноши. Зато общая канва истории стала компактной и стройной. В первом действии главная героиня получает в подарок Щелкунчика, который с наступлением ночи вместе с оловянными солдатиками ведет бой против мышей во главе с Мышиным королем. В конце первого действия девочка спасает Щелкунчика, он превращается в прекрасного принца и ведет девочку за собой в сказочную страну. В финале она просыпается — это был всего лишь сон.
Сцена из балета «Щелкунчик». Мариинский театр, 1892
Многие мотивы из либретто Петипа проходят мимо большинства постановок «Щелкунчика». Так, например, снежная буря, которая обрушивается на главных героев (ведь счастья можно добиться, только пройдя через испытания), обычно превращается в безобидный «вальс снежных хлопьев». Исчезает игрушечный трамплин, выталкивающий на сцену оловянных солдатиков, готовых к бою с мышами. Знаменитое Адажио в оригинале танцуют не главная героиня и Принц, как можно подумать, а Фея Драже и принц Оршад 5, которого уже на премьере переименовали в принца Коклюша (в переводе с французского — «любимчик»).
В сказке Гофмана имя главной героини — Мари, а одну из её кукол зовут Кларой. Петипа назвал Кларой саму девочку. На этом сложности с именем не закончились: в советские времена возникла традиция звать главную героиню русифицированным именем Маша. Потом героиню стали называть и по-гофмановски — Мари. Аутентичным следует считать имя Клара, которое фигурирует в сценарии Петипа и в партитуре Чайковского.
Музыка
Музыка сочинялась тяжело. В феврале 1891 года Чайковский сообщает брату: «Я работаю изо всей мочи, начинаю примиряться с сюжетом балета». В марте: «Главное — отделаться от балета». В апреле: «Я тщательно напрягал все силы для работы, но ничего не выходило, кроме мерзости». Ещё позже: «А вдруг окажется, что… ‘’Щелкунчик’’ — гадость…»
П. И. Чайковский, 1893
Начало 1890-х стали для композитора временем размышлений о жизни и смерти. В 1891 году умирает его сестра Александра Давыдова-Чайковская, и ее смерть он воспринял очень болезненно. Впереди были самые трагические сочинения композитора — «Пиковая дама» и Шестая симфония. В музыковедении последних лет высказывается идея, что «Щелкунчик» — это сочинение из того же ряда, балет о смерти и бессмертии, а всё, что случается с героиней, происходит в некоем ином мире. Возможно, снежная буря — метафора перехода из земной жизни в другое состояние, а Конфитюренбург — это рай. В Вальсе снежных хлопьев и в знаменитом Адажио есть, кстати, музыка весьма страшная, даром что мажорная.
Первая часть балета — это действие в чистом виде. Второе же, за исключением финала, представляет собой обычный для балета того времени дивертисмент 6. Идея кондитерского дивертисмента в Конфитюренбурге, городе сладостей, не слишком нравилась самому Чайковскому; впрочем, с поставленной задачей он справился блестяще.
Александра Ильинична Давыдова, сестра Петра Ильича Чайковского
В музыке «Щелкунчика» есть несколько пластов. Есть сцены детские и взрослые, фантастические и романтические, есть танцы дивертисмента. В музыке много аллюзий на культуру XVIII века: это, например, и галантный Танец пастушков, и Китайский танец, который, скорее, псевдокитайский (есть такой термин «шинуазри», то есть «китайщина»). А романтические фрагменты, наиболее связанные с эмоциональной сферой, становятся для композитора поводом для личных, очень интимных высказываний. Их суть непросто разгадать и очень интересно интерпретировать.
На пути симфонизации музыки композитор зашёл очень далеко даже по сравнению с «Лебединым озером» (1876) и «Спящей красавицей» (1889). Композитор обрамляет дивертисмент, который требовал от него балетмейстер, музыкой, насыщенной подлинным драматизмом. Сцена роста елки в первом акте сопровождается музыкой симфонического размаха: из тревожного, «ночного» звучания вырастает прекрасная, бесконечно льющаяся мелодия. Кульминацией всего балета стало Адажио, которое по замыслу Петипа танцевали Фея Драже и принц Оршад.
В марте 1892 года публике была представлена сюита из балета 7. Она имела большой успех: из шести номеров пять по требованию публики были повторены.
Первая трактовка
«Щелкунчик» и Петипа разминулись. Считается, что хореограф, пребывая в депрессии после смерти дочери, переложил всю работу на своего ассистента Льва Иванова. В сотрудничестве с ним Чайковский и заканчивал свой балет.
Впоследствии, уже после премьеры, газеты сообщали, что Петипа намерен представить его новую версию. Однако этим замыслам не суждено было осуществиться: балетмейстер так и не вернулся к своему проекту.
Премьера балета состоялась 6 декабря (18 декабря по новому стилю) 1892 года в Мариинском театре в Санкт-Петербурге в один вечер с оперой «Иоланта». Роли Клары и Фрица исполняли дети, учащиеся петербургского Императорского театрального училища.
Фрагмент спектакля «Щелкунчик» в постановке Императорского Мариинского театра, 1892
Вопрос о том, сколько идей Петипа перешло в хореографию Иванова, дискуссионный. Иванов в основном иллюстрировал сюжет, не обращая внимания на драматические возможности партитуры. Именно у него снежная буря и превратилась в безобидный вальс снежных хлопьев. Второе действие балета критики назвали вульгарным: балетные артистки, одетые сдобными булочками-бриошами, были восприняты как вызов хорошему вкусу. Сам Чайковский также остался недоволен постановкой. Последний раз спектакль Иванова возобновляли в 1923 году, после чего он навсегда исчез со сцены Мариинского театра.
Другие интерпретации
Новый взгляд на балет Чайковского представили балетмейстер Александр Горский и художник Константин Коровин (1919, Большой театр). В их спектакле сцена представляла собой сервированный стол с огромным кофейным сервизом, из которого выходили танцоры. В финале Горский оставлял Клару в мистическом сне. Вместо Феи Драже и принца Коклюша Горский отдал Адажио маленьким героям — Кларе и принцу Щелкунчику. Эта идея оказалась настолько хороша, что прочно прижилась в России.
К.А. Коровин. Эскиз бутафории к балету «Щелкунчик» П.И. Чайковского. Китайский домик. 1919, Третьяковская галерея
Ещё дальше пошёл Василий Вайнонен 8. Он откорректировал сюжет Петипа, заставив детей в финале первого акта повзрослеть, и выявил в балете историю девочки, полюбившей уродливую куклу (он назвал её Машей, и это имя надолго прижилось в отечественных постановках). Вслед за Горским Вайнонен убрал Коклюша с Феей Драже. Общая тональность спектакля была светлой; это был идеальный детский спектакль с фантастическими фокусами, яркими куклами и ёлкой, сверкающей праздничными огнями. Трагические мотивы балетмейстер оставил без внимания. В финале Щелкунчик и Маша, как и положено в сказке, превращались в Принца и Принцессу. Этот спектакль стал своего рода эмблемой Мариинского театра.
Юрий Григорович 9, отталкиваясь от музыки Чайковского, в очередной раз переписал либретто, заимствовав лучшие идеи у Горского и Вайнонена. Григорович первым в России создал из «Щелкунчика» философскую притчу о недостижимости идеального счастья. В этом спектакле Маша, простившаяся во сне со своим детством, в финале просыпалась в своей комнате — снова девочка и снова среди игрушек. Эта история изумительно точно и гармонично легла на музыку Чайковского, выявив её драматический потенциал.
Между тем традиции пышного дореволюционного «Щелкунчика» продолжил великий реформатор балета Джордж Баланчин, создатель бессюжетных хореографических постановок, который оказал значительное влияние на развитие хореографической школы в США (1954, Нью-Йорк Сити балет). Когда-то, ещё будучи учеником балетного училища в Петербурге, он участвовал в том самом спектакле, который разочаровал Чайковского. Спустя многие годы он решил оттолкнуться от идей Иванова и поставить пышный дивертисмент, в котором сам сюжет убрал на второй план. У Баланчина дети, попав в кондитерский рай, остаются детьми и смотрят на происходящие чудеса со стороны. Адажио танцуют Фея Драже и Кавалер (так Баланчин обозвал принца Коклюша). Хотя в философские смыслы музыки Чайковского хореограф не углублялся, его версия стала самой популярной в США: на неё до сих пор ориентируются многие американские постановщики «Щелкунчика».
В 1973 году балет «Щелкунчик» соединился с искусством анимации (режиссёр мультфильма — Борис Степанцев). Зрителей поразила — и поражает до сих пор — фантазия его авторов: в начальном эпизоде вместе с Машей танцует метла, а в Вальсе цветов Принц и Маша взлетают в небеса, подобно героям Шагала. И пусть главная героиня вопреки Гофману, Дюма и Петипа превратилась в девочку-служанку, эта версия «Щелкунчика» стала в России не менее классической, чем балет Григоровича.
Из версий XXI века отметим постановку «Щелкунчика» художником Михаилом Шемякиным и хореографом Кириллом Симоновым 10. Идеолог спектакля Шемякин вольно обошёлся с сюжетом, зато подспудно воскресил дух Гофмана, поставив балет как злой гротеск про мышиное царство. В финале крысы съедают Машу и Щелкунчика, превратившихся в засахаренных куколок.
П. Чайковский. «Щелкунчик». Мариинский театр. Музыкальный руководитель и дирижер Валерий Гергиев, декорации, костюмы и постановка Михаила Шемякина, хореография Кирилла Симонова. Сцена из спектакля. Фото Н. Разиной
Память о том, что премьера «Щелкунчика» прошла в один вечер с премьерой «Иоланты», сподвигла режиссёра Сергея Женовача вновь соединить вместе эти два произведения. В 2015 году, поставив «Иоланту» в Большом театре, он предварил её сюитой из «Щелкунчика» и заставил слепую Иоланту вслушиваться в музыку балета и сопереживать ей.
Музыку из «Щелкунчика» мы можем слышать не только в оперных или концертных залах. Она звучит за кадром во многих фильмах («Один дома»), мультфильмах («Том и Джерри»), телесериалах («Друзья»).
Рождественский балет
Есть несколько музыкально-сценических произведений, которые воспринимаются во всём мире как рождественские или новогодние. В Германии такова опера «Гензель и Гретель» Энгельберта Хумпердинка (хотя её сюжет не имеет отношения к Рождеству), в Австрии — оперетта «Летучая мышь» Иоганна Штрауса, в США и России — балет «Щелкунчик».
«Щелкунчик», Большой театр, 2014
Американская традиция давать «Щелкунчика» к Рождеству обязана своим возникновением Баланчину. «Щелкунчик» в США — это синоним Рождества и зимних детских каникул. Любая, даже самая маленькая, балетная компания, каждая балетная школа показывает в декабре свой вариант балета. По смыслу многие из них восходят к пышной постановке Баланчина и мало отличаются друг от друга.
В советское время «Щелкунчик» по понятным причинам считался новогодним балетом. Многие культурные феномены, хоть сколько-нибудь связанные с праздником Рождества, в те годы привязывались к новогодней теме. Билеты на новогодние представления «Щелкунчика» в Большом, Мариинском, Михайловском театрах, в Музыкальном театре Станиславского и Немировича-Данченко раскупались задолго до Нового года.
После 1990-х, когда Рождество вновь стало официальным праздником, балет «Щелкунчик» мгновенно обрёл статус главного рождественского балета. И пусть его содержание выходит далеко за рамки религиозного праздника — «Щелкунчик» всегда дарит зрителям и слушателям самое настоящее рождественское чудо.
Примечания:
1 — горожан, обывателей
2 — 1811–1910; французский и российский солист балета, балетмейстер и педагог
3 — литературная основа большого музыкального сочинения
4- анонимная песня, написанная в 1792 году, очень популярная во времена Великой французской революции
5 — напиток, который готовится на основе орехов — миндального молока
6- избранные фрагменты, составившие короткий цикл
7 — театральное представление, состоящее из различных танцевальных номеров, в дополнение к основному представлению
8 — 1934 — Кировский театр, 1938 — Большой театр
9 — 1966, Большой театр
10 — 2001, Мариинский театр
“Мир детских сцен “Щелкунчика” с его своеобразной смесью
реально-бытового
и фантастического, простодушной игры и
острой иронии передан в музыке с удивительной чуткостью”.
Д. Житомирский.
От сказки до
балета.
Балет «Щелкунчик» П. И. Чайковского
по сюжету сказки Э. Гофмана.
Слайд 1
Здравствуйте,
ребята!
Сегодня
мы с вами отправляемся в сказочное новогоднее путешествие и
вместе окунемся в мир музыки П.И.Чайковского. Музыку Петра Ильича Чайковского
знают и любят во всем мире.
Чайковский – один из самых сказочных композиторов. Его музыкальное
наследие нельзя представить без трех его знаменитых балетов, музыку которых
любят люди всего земного шара. Все три балета – «Лебединое озеро», «Спящая
красавица» и «Щелкунчик» основаны на сказочных сюжетах, где переплетаются
реальные и сказочные персонажи, происходят волшебные превращения и всегда добро
побеждает зло.
Самое
волшебное и новогоднее произведение П.И. Чайковского, известное по всему миру –
балет «Щелкунчик». Это прекрасная музыка рассказывает про новогоднюю ночь и
события, которые происходят с героями сказки.
Слайд 2
В новогоднюю ночь
часто происходят чудеса.
Звучит музыкальная
тема «Феи Драже» П.И. Чайковского из балета «Щелкунчик».
Слышите? Как нежно и светло звучит музыка.
Тихо – тихо сядем
рядом, входит музыка в наш дом
В удивительном
наряде разноцветном, расписном.
То она метелью
кружит, то вдруг рыбкой проплывет,
То в волшебную
страну нас всех с собою уведет…
И сегодня сказочные звуки музыки всеми нами любимого композитора
П.И. Чайковского поведут нас в мир сказки.
-Вы любите сказки?
Наверное,
все мы любим сказки. Особенно, если события о которых они рассказывают,
происходят в новогоднюю ночь. Одну из таких новогодних сказок сочинил немецкий
писатель Эрнст Гофман «Щелкунчик и мышиный король».
А русский композитор Пётр Ильич Чайковский по этой сказке написал музыку и
получился прекрасный балет «Щелкунчик».
Слайд 3
Можете
назвать героев этой сказки? О чем эта сказка?
Сказка
о рождественском чуде, где оживает игрушечный Щелкунчик и побеждает в борьбе со
злой королевой. А Мари ему в этом помогает. Сказка заканчивается тем, что
Щелкунчик стал принцем, а Мари его принцессой.
П.И.
Чайковский тоже прочитал эту сказку, и она ему очень понравилась. И решил
написать музыкальный спектакль. Балет.
Знаете
ли вы, ребята, что такое балет?
Слайд
4
Балет — это театральное представление, в котором
действующие лица не говорят, а танцуют. Но только ли одни танцы составляют
балет? Нет, в балете, кроме танца, участвуют и другие виды искусства. В балете
объединены музыка, танец, драматическое и изобразительное
искусства, т.к. оформляются декорации, шьются костюмы.
Балет — искусство довольно молодое, ему
немногим более четырехсот лет. Родился балет в Северной Италии в эпоху
Возрождения.
А вы знаете, как называют танцовщиц балета?
Слайд 5
Посмотрите на иллюстрацию, какие необычные на них платья.
Кто знает, как они называются?
Слайд 6
А что у них на ногах, чешки?
Правильно, молодцы. На ногах у балерины
пуанты.
Ведь в балете танцуют на самых кончиках
пальцев, а для этого нужны специальные приспособления, уплотнения в обуви. Для
этого и изобрели пуанты.
Каждое движение в балете – это словно
рассказ о том, что человек мог бы сказать словами, но передает это движениями
танца, т.е. это театральное представление, в котором действующие лица не
говорят, а танцуют.
Перед путешествием в музыкальный театр, давайте вспомним,
как ведут себя в театре зрители?
Слайд 7
Представьте, что мы перенеслись в
театр Оперы и Балета. Большая сцена, красивые кресла, оркестровая яма, где
звучит «живая музыка» в исполнении оркестра, бархатный занавес — все располагает зрителя на
прекрасный отдых в мире прекрасного.
Устраивайтесь удобнее, я начинаю
рассказ.
Балет начинается с увертюры или,
по-другому, со вступления. Увертюра это инструментальная оркестровая пьеса,
исполняемая перед началом балета. Послушайте сейчас увертюру к балету и
после скажите, как звучит музыка. И выражает ли музыка увертюры новогоднее,
рождественское настроение?
Слушание:
увертюра из балета «Щелкунчик» П.И. Чайковского.
Как звучала
музыка? (Сказочно, таинственно, игриво, радостно, тихо, волшебно, танцевально).
Верно, музыка вводит нас в сказочное
настроение балета.
Открывается занавес. В
доме девочки Мари готовятся к Новогоднему празднику. В уютном доме все
готово. В дом к главной героине на праздник шествуют гости. Родители ведут с
собой своих детей. Наконец раздаются звуки марша, дети
радостно идут в комнату, где стоит праздничная, украшенная огнями и игрушками
елка.
Попытайтесь представить себя
действующими лицами балета: промаршируйте под его звуки.
(Учитель
играет на фортепиано мелодию «Марша» из балета «Щелкунчик»).
Представьте себе: нарядная елка,
много подарков, дети, весело и радостно марширующие под звуки «детского марша».
Вслушайтесь внимательно, и вы услышите легкие, грациозные шаги девочек, и
задорные шаги мальчиков. Музыка звучит волшебно, сказочно, как будто обещает
что-то необыкновенное.
Вернемся к нашему балету. Начинаются
танцы.
Танцы взрослых и детей прерывают приход старого
мастера игрушек. Он дарит детям заводные куклы. Куклы начинают танцевать.
Мастер еще подарил детям щипцы для колки орехов. Они сделаны в виде маленького
человечка – Щелкунчика.
Слайд
8
Щелкунчик особенно понравился Мари, хотя он очень
уродлив – с огромным ртом, в который вкладывали орехи, чтобы он их разгрызал.
Гости расходятся. Мари остаётся одна и готовится ко
сну. Часы показывают полночь. Вдруг происходит неожиданное: комната
наполняется мышами, с которыми пытаются сражаться детские игрушки – солдатики.
Кто-нибудь знает, что произойдёт дальше?
К удивлению и радости Мари, руководство игрушечным
войском берёт на себя тоже оживший Щелкунчик. Силы, конечно, не равны. Мышей
много, они сильные, неуязвимые. Ну что тут могут сделать солдатики с крохотными
сабельками да сломанный безжалостным братом Щелкунчик?
Как вы думаете, какой характер будет у музыки?
Будет ли меняться характер музыки в этой сцене?
Показ
видеофрагмента «Сражения»
Удалось
ли композитору и балетмейстеру создать образ сражения?
Щелкунчик вместе со своими оловянными солдатиками
храбро боролся с врагами, но силы были неравными, и Щелкунчика уже настигали
его противники. Тогда Мари бросила в предводителя мышей туфельку, и все его
войско в смятении разбежалось.
Щелкунчик же, победив своего заклятого врага,
превратился в прекрасного принца и вместе с Мари отправился в волшебную страну
сладостей и игрушек.
Слайд
9
Итак, путешествуем
дальше. Щелкунчик и Мари отправляются в чудесное путешествие в страну
сладостей, где их встречают ожившие сладости. Но сначала им придётся пройти
через зимний волшебный лес. Мы будем слушать сегодня один из самых красивых
отрывков балета «Щелкунчик», который называется «Вальс снежных хлопьев».
Его мелодия так красива, что её можно спеть!
Этот балет – не
просто сказочный, он – новогодний. И Пётр Ильич Чайковский для усиления
волшебного эффекта сочинил музыку, которую в балете поёт детский хор. Этот хор
расположен вместе с оркестром, ниже сцены, и его никто не видит. Зато все
слышат звук человеческих голосов, и это создаёт незабываемое впечатление.
Показ
видеофрагмента «Вальс снежных хлопьев»
Падают крупные
хлопья снега. Поднимается вихрь, и снежинки быстро кружатся. Постепенно метель
утихает, свет луны искрится на снегу.
Вы запомнили
название этой музыки?
Мари и Щелкунчик попадают в царство феи Драже.
А
теперь мы оказались перед вратами города Конфитюренбурга. Шумный весёлый город.
В волшебном царстве сладостей и игрушек к возвращению принца Щелкунчика и его
избранницы Мари готовится пышное празднество. Их радостно встречают фея Драже
со своей свитой и принцессы – сестры Щелкунчика. Мажордом
распоряжается о начале танцев.
Для
жителей Конфитюренбурга П.И. Чайковский сочинил свою музыку: Чай: китайский
танец, Шоколад: испанский танец, Кофе: арабский танец, Танец феи Драже, Трепак:
русский танец.
Вот, например, для
всеми нами любимого шоколада Чайковский сочинил «Испанский танец», потому, что
тогда считалось, что самый лучший на свете шоколад привозят к нам из Испании.
Представьте себе
людей одетых в красочные испанские наряды. Главную тему танца исполняют духовые
инструменты. Музыка словно переносит нас в знойную Испанию.
Показ
видеофрагмента «Испанский танец»
(дети щёлкают
пальцами в ритм музыки)
Какой характер музыки?
Испанский танец
(шоколад)- быстрый, задорный, слышны щелканья кастаньет. Бравурный, блестящий
танец в испанском стиле. Главная тема у солирующей трубы.
Звучание
какого испанского народного инструмента вы услышали? (кастаньеты)
Кофе: арабский танец
(видео)
Арабский танец
(кофе)- медленный, плавный, нежный. На монотонном, едва мерцающем фоне
вырисовывается нежная мелодия скрипок, слышен слегка играющий бубен.
Всех, кто попадает
в Конфитюренбург, угощают сладостями с чаем. А чай пришёл к нам из Китая.
Поэтому в балете есть «Китайский танец», который ещё называют «Танец
Чая». Прислушайтесь, как русский композитор передаёт в музыке восточный
колорит. Музыка звучит в высоком регистре, главную мелодию исполняют флейты.
Сама музыка острая, чёткая. Будто куклы, танцующие её, всё время подпрыгивают.
Показ видеофрагмента
«Китайский танец»
Какой характер музыки?
Китайский танец
(чай)- игривый, прыгающий, шуточный. Кажется, будто пляшут смешные фарфоровые
статуэтки.
Поскольку П. И.
Чайковский был воспитан на народной музыке, в своих сочинениях он использовал
народные темы. Балет «Щелкунчик» вобрал в себя движения народного танца «Трепак»
(это старинный русский танец в быстром темпе).
Трепак:
русский танец (видео)
Дети делятся на две группы: одни музыканты
(играют на детских музыкальных инструментах), другие танцоры (выполняют простые
танцевальные движения)
Живой,
ярко-темпераментный танец в русском народном стиле. К концу — убыстряется и
заканчивается настоящим вихрем плясового движения.
А
сейчас давайте послушаем «Танец феи Драже» (видео)
Что вы
можете сказать про эту музыку?
Этот
танец рисует нежный, грациозный образ сказочной феи сладостей. Музыка этого
танца звучит несколько необычно. Это происходит потому, что здесь звучит
инструмент, который редко используется в оркестре, он называется челеста.
Ее устройство напоминает маленькое пианино, только молоточки ударяют не по
струнам, а по металлическим пластинам, издающим звуки очень высокие, нежные,
как будто звучат колокольчики. В середине танца слышны переливы арфы,
напоминающие журчание ручейка.
Какой
характер? Танец феи Драже изящный, грациозный, искрящийся светом, волшебством.
Послушайте заключительный танец праздничного
представления и подумайте, как он может называться?
Вальс цветов
«Вальс цветов» очень
торжественный и праздничный, самый яркий из трех вальсов.
Во вступлении
к танцу слышатся звуки арфы. Они как бы одевают этот вальс в волшебный,
красочный наряд. Основную тему вальса вначале исполняют различные духовые
инструменты (валторны, кларнеты), а затем включается струнная смычковая группа.
Вальс звучит ярко, пышно, блестяще, радостно, взволнованно. «Вальс цветов»
выделяется своей поистине сказочной красотой. Зло побеждено, добро победило!
Итог урока. Рефлексия.
Вам
понравилась эта необыкновенная новогодняя история, чем?
Узнали ли вы что-то новое сегодня на уроке?
Что больше всего вам понравилось на уроке?
С каким
музыкальным жанром мы сегодня познакомились?
Что такое
балет?
Как называют
танцовщиц балета?
А танцоров?
Что на ногах
у балерин?
С какими
маршами мы сегодня познакомились?
Кто автор данных музыкальных произведений?
Вам
понравился балет П.И. Чайковского «Щелкунчик»?
Сегодня мы посмотрели фрагменты из
балета «Щелкунчик».
Петр Ильич Чайковский, как и в
других своих балетах, рассказал в нем о борьбе добра и зла. Нежное и преданное
чувство героини этого балета – Мари – побеждает злые силы и освобождает от
колдовства прекрасного юношу, которого колдун превратил в Щелкунчика.
К сожалению, наше пребывание в театре сегодня заканчивается, но у
нас будет возможность продолжить театральные встречи на следующих уроках.
Домашнее
задание:
По желанию можно нарисовать своего Щелкунчика, пусть
каждый проявит свою фантазию, выдумку.
Некоторые интересные факты, связанные с этим балетом:
Ø
впервые балет «Щелкунчик» был показан в Санкт-Петербурге в декабре
1892 года, на сцене Мариинского театра. Постановка этой волшебной сказки, рассказанной
на Рождество, стала традиционной в предновогодние дни. Этот спектакль нравится
всем без исключения, и его посещают с удовольствием и дети, и взрослые;
Ø
сохранились сведения, что на первом представлении балета в
Мариинском театре (декабрь 1892 года) публика была необычайно удивлена именно
силой звучания оркестра. В особенности привлек их внимание музыкальный
инструмент челеста;
Ø самый
большой Щелкунчик был сделан в Германии и имел высоту более 10 метров;
Ø согласно
немецкой легенде щелкунчики приносят удачу и оберегают дом. Поэтому
щелкунчики были популярны как рождественские подарки для детей.
На этом мы завершаем небольшое путешествие
в мир музыки Петра Ильича Чайковского. Его музыку знают и любят во всех странах
и на всех континентах. Бессмертная музыка Чайковского продолжает звучать,
занимая большое место в духовной жизни людей нашего времени.
Звук фонограммы заключительных
аккордов Па-де-де 2 акта из балета «Щелкунчик»
Дополнительный материал:
Содержание
сказки Гофмана «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король».
Эта сказка Эрнеста Теодора Амадея
Гофмана была опубликована в 1816 году. Ее главные герои — девочка по имени
Марихен (в разных редакциях девочку зовут Кларой или Мари) Штальбаум и странная
игрушка — щипцы для колки орехов в форме солдатика, тот самый легендарный
Щелкунчик, которого подарил Марихен ее крестный, сказочник Дроссельмейер.
Только он знал, что Щелкунчик – это не безобразная игрушка, а прекрасный принц,
которого заколдовала злая королева Мышильда.
В рождественскую ночь начинаются сказочные
превращения, благодаря которым Щелкунчик оживает и вступает в схватку с
мышами. В этой битве ему помогают тоже ожившие игрушки Марихен. И вот
счастливый финал – Щелкунчик убивает Мышиного короля, тем самым рассеивая злые
чары. И Марихен, полюбившая уродливую игрушку, видит перед собой
расколдованного принца. Он приглашает её в свою страну, где объявляет Марихен
своей принцессой.
Краткое содержание балета «Щелкунчик».
Основные события в балете разворачиваются накануне
большого и светлого праздника — Рождества.
В доме Штальбаума собрались гости и крестный Мари,
который пришел с кучей подарков для детей. Среди них заметно выделяется
кукла, предназначенная для колки орехов – Щелкунчик. Довольно неуклюжая
игрушка с широкой улыбкой сразу понравилась девочке Мари. Уже все дети ушли
спать, а она все не могла расстаться с Щелкунчиком.
Девочка так заигралась, что не заметила, как вокруг
все стало меняться. Елка стала огромных размеров и послышался странный шорох. В
комнате появилась армия мышей, а сам Щелкунчик внезапно ожил, превратившись в
прекрасного юношу. Он тут же собрал себе армию из солдатиков и отправился на
врага, но их силы были неравны. Мари, увидев это, решила помочь Щелкунчику и
кинула своим башмачком в Короля мышей. Враги испугались внезапной атаки и
разбежались.
Когда Мари очнулась, перед ней оказался ее крестный
– Дроссельмейер, представший в образе волшебника. Он рассказал об удивительном
сказочном мире, в который достаточно непросто попасть, преодолевая снежную
бурю. Но Мари вместе с Щелкунчиком отправляются в эту страну. Они
оказываются в чудесном городе Конфитюренбурге, где кругом много сладостей и
гостей, встречающих их. Фея Драже устраивает пышный бал в их честь и Мари
становится настоящей принцессой, после того, как Щелкунчик рассказал, как она
спасла его. Когда торжество заканчивается, волшебник помогает Мари вернуться
домой из своего чудесного путешествия.
Действие первое
01. Увертюра
02. Картина 1 сцена 1 — Украшение и зажигание елки
03. Картина 1 сцена 2 — Марш
04. Картина 1 сцена 3 — Детский галоп и выход родителей
05. Картина 1 сцена 4 — Выход Дроссельмейера
06. Картина 1 сцена 5 — Сценка и танец Гросфатер
07. Картина 1 сцена 6 — Отъезд гостей. Ночь
08. Картина 1 сцена 7 — Сражение
09. Картина 2 сцена 1 — Еловый лес зимой
10. Картина 2 сцена 2 — Вальс снежных хлопьев
Действие второе
01. Картина 3 сцена 1 — Дворец сластей Конфитюренбург
02. Картина 3 сцена 2 — Прибытие Мари и Щелкунчика
03. Картина 3 сцена 3 — Дивертисмент (а) Шоколад: испанский танец
04. Картина 3 сцена 3 — Дивертисмент (б) Кофе: арабский танец
05. Картина 3 сцена 3 — Дивертисмент (в) Чай: китайский танец
06. Картина 3 сцена 3 — Дивертисмент (г) Трепак: русский танец
07. Картина 3 сцена 3 — Дивертисмент (д) Танец пастушков
08. Картина 3 сцена 3 — Дивертисмент (е) Мамаша Гигонь и паяцы
09. Картина 3 сцена 4 — Вальс цветов
10. Картина 3 сцена 5 — Па-де-де — Танец Принца Оршада и Феи Драже
11. Картина 3 сцена 5 — Па-де-де — Вариация I: Тарантелла
12. Картина 3 сцена 5 — Па-де-де — Вариация II: Танец Феи Драже
13. Картина 3 сцена 5 — Па-де-де — Кода
14. Картина 3 сцена 6 — Финальный вальс
15. Апофеоз
Декабрь — время «Щелкунчика». Каждый год тысячи людей стремятся попасть на знаменитый балет, чтобы погрузиться в атмосферу праздника. Музыка Чайковского, мастерство артистов на сцене стали одной из самых красивых рождественских и новогодних традиций.
Кто придумал историю о Щелкунчике, как рождался балет, где посмотреть «Щелкунчика» на сцене и не только — рассказываем в нашем материале.
Как создавался великий балет
История балета началась со сказки.
В 1816 году немецкий писатель Эрнст Теодор Амадей Гофман написал сказочную повесть «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король». Произведение стало письменным изложением одной из сказок, которую Гофман сочинил в формате импровизации, общаясь с детьми своего близкого друга. Малыши Мари и Фриц так любили сказки старшего товарища, что в итоговой рукописи главные герои сказки получили их имена. Впрочем, есть вероятность, что в «Щелкунчике» писатель собрал сразу несколько на ходу придуманных сюжетов.
Сюжет сказки «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король»
В канун Рождества дети Мари и Фриц получают много подарков. Среди них — игрушка в виде маленького некрасивого человечка по имени Щелкунчик, умеющего разгрызать твёрдые орешки.
Вечером Мари подходит к шкафу с подарками и случайно видит настоящую битву: сражаются Мышиный король и его свита, выбравшиеся из-под пола, и армия игрушек, которую возглавляет Щелкунчик. Мари пытается помочь Щелкунчику, но чувствует сильную боль в руке и падает на пол. Утром девочка просыпается и рассказывает о ночной битве, но мать и доктор не верят Мари.
Крёстный Дроссельмейер приносит девочке отремонтированного Щелкунчика и рассказывает историю о нём: когда-то Щелкунчик был племянником Дроссельмейера, красивым и добрым юношей, но после проклятия королевы Мышильды превратился в маленького уродливого человечка. Чтобы вернуться в прежний облик, Щелкунчику нужно победить Мышиного короля и добиться любви Прекрасной Дамы. Ею становится Мари. Щелкунчик преподносит девочке трофеи поверженного Мышиного короля. Мари и Щелкунчик отправляются в волшебную страну, и Прекрасная Дама влюбляется в своего героя.
Родители Мари не верят воспоминаниям девочки и советуют поскорее забыть о странном сне, но девочка не может выбросить из головы воспоминания о Щелкунчике.
В финале сказки в доме появляется гость. Это племянник Дроссельмейера — красивый молодой человек. Он признаётся Мари, что перестал быть маленьким уродцем. Мари становится невестой бывшего Щелкунчика, на их свадьбе танцуют 2000 нарядных кукол.
Повесть «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король» была впервые опубликована в 1816 году в сборнике «Детские сказки» в Берлине. А спустя почти 30 лет, в 1844 году, появилось переложение сказки Гофмана — «История Щелкунчика».
П.-К. Гайсслер, иллюстрация к сказке о Щелкунчике, 1840 г.
В «Истории Щелкунчика» Александр Дюма-отец сохранил сюжетную линию, но в остальном французский вариант являл собой вольный перевод сказки с совершенно другой атмосферой и настроением. У Дюма-старшего акцент сместился на любовную линию: здесь искреннее светлое чувство оказывается всепобеждающим в борьбе со злым проклятием, и именно любовь помогает Щелкунчику из деревянного игрушечного уродца превратиться в настоящего человека.
«История Щелкунчика» послужила основой для создания великого балета Петра Ильича Чайковского.
Чайковский и «Щелкунчик»
Заказ на двухактный балет Чайковский получил в 1890 году от дирекции Императорских театров. Примерный сценарий постановки набросал балетмейстер Мариус Петипа — и в процессе работы этот сценарий неоднократно менялся. Премьера балета была запланирована на декабрь 1891 года, его хотели представить в один вечер с оперой, заказ на которую также был отдан Чайковскому.
Забегая вперёд, отметим: премьера балета состоялась 18 декабря 1892 года, на год позже запланированной даты. Балет «Щелкунчик» был представлен в один вечер с оперой П. И. Чайковского «Иоланта».
Изначально в либретто Мариуса Петипа был вложен несколько другой смысл, отличный от хорошо знакомого нам «Щелкунчика». Балетмейстер вдохновлялся Великой французской революцией, столетие которой отметили в 1889 году. Но в театр царской России конца XIX века революционная тематика не вписывалась, так что большинство идей Петипа так и остались идеями. Впрочем, мотив французской революционной песенки «Добрый путь, милый дю Молле!» Чайковский сохранил в итоговой партитуре.
Пётр Ильич Чайковский
Работа над «Щелкунчиком» давалась композитору нелегко. Настолько, что даже пришлось перенести премьеру на год. Чайковский, по его же собственному выражению, всё никак не мог «отделаться от балета». Композитор мучительно искал решение, пытаясь соединить сложную симфоническую музыку и довольно банальный сюжет, лишённый серьёзной драматургии.
С точки зрения музыки, результатом работы Петра Ильича Чайковского стало настоящее разнообразие мотивов и отсылок: помимо отголосков французских мелодий в балете исполняется арабский танец, основанный на грузинских колыбельных, звучит немецкий Grossvater Tanz — традиционная свадебная музыка (по одной версии, народная, по другой — написанная Карлом Готлибом Герингом).
В партитуре «Щелкунчика» композитор прибегает и к совершенно новым для русской музыки тех лет инструментам. Так «Танец феи Драже» Мариус Петипа описал как «звук падающих капель». Для музыкального сопровождения этого танца Чайковский выбрал французскую челесту. Ее сказочное звучание Пётр Ильич услышал в Париже во время премьеры «Бури» Эрнеста Шоссона. Клавишный металлофон издавал звуки совершенно божественные, чудные, лёгкие — и смог идеально, с точки зрения Чайковского, изобразить «звук падающих капель».
Нотный автограф П. И. Чайковского: набросок партитуры балета «Щелкунчик»
Фото из фондов Президентской библиотеки
Партитуру двухактного балета «Щелкунчик» Чайковский закончил в 1892 году. Постановка задумывалась в трёх картинах:
- первая — рождественский праздничный вечер в доме родителей Мари;
- вторая — сон Мари, в котором Щелкунчик сражается с крысиным войском и превращается в прекрасного принца;
- третья — волшебный город, в который попадают Мари и Щелкунчик.
Одна из главных загадок балета: как мыши превратились в крыс. В сказке Гофмана и последующем переложении Дюма-отца фигурирует именно мышиная свита. Но в своих черновых набросках Мариус Петипа пишет: «Появляются крысы с мышиным царём» — без других пояснений. Так в либретто появились крысы.
Премьера балета
Премьера «Щелкунчика» состоялась 18 декабря 1892 года на сцене Мариинского театра. Она вышла громкой.
«Трудно представить себе что-нибудь скучнее и бессмысленнее «Щелкунчика»
«Для танцовщиц в балете было весьма мало, для искусства — ровно ничего. Даже музыка оказалась довольно слабою»
«Невообразимая по безвкусию постановка»
Таковы были первые отзывы критиков о прошедшей премьере. Впрочем, и сам Чайковский признавался, что балет ему не нравится, постановка вышла аляповатой. Композитор даже вспоминал, что на премьере «ему было сложно смотреть на сцену».
Сцена из балета «Щелкунчик», Мариинский театр, 1892 г.
Были и положительные рецензии. И не от кого-нибудь, а от самого Александра Бенуа, одного из известнейших критиков конца XIX века. Он побывал на генеральной репетиции спектакля и отметил:
«Государь был в восхищении, призывал в ложу и наговорил массу сочувственных слов. Постановка… великолепна и в балете даже слишком великолепна — глаза устают от этой роскоши».
Даже получив тонны разгромной критики и, по сути, провалившись, «Щелкунчик», тем не менее, закрепился в репертуаре Мариинского театра больше чем на 30 лет.
«Щелкунчик» в России и в мире: на сцене и в кино
Среди известных вариаций балета П. И. Чайковского можно отметить:
-
1919 год — Большой театр, Москва, постановка Александра Горского
-
1923 год — Мариинский театр, Петербург, поставнока Фёдора Лопухова
-
1934 год — Мариинский театр, Петербург, постановка Василия Вайнонена, главные партии на премьере исполнили Галина Уланова и Константин Сергеев
-
1934 год — в Лондоне балет представил Николай Сергеев, эмигрировавший в Европу после Октябрьской революции
-
1954 год — воспитанник Мариинки Джордж Баланчин представил «Щелкунчика» в Нью-Йорке, балет показывают каждую зиму до сих пор
-
1966 год — в московском Большом театре состоялась премьера постановки Юрия Григоровича, которую многие специалисты называют практически идеальным решением партитуры Чайковского
-
1967 год — Рудольф Нуреев поставил балет Чайковского в Англии: сначала премьеру представили в Королевской шведской опере в Стокгольме, позже постановка нашла свой дом в Ковент-Гардене (Лондон), ещё через несколько лет Нуреев представил «Щелкунчика» в «Ла Скала» (Италия) и в Парижской опере
-
1976 год — премьера «Щелкунчика» Михаила Барышникова в Американском театре балета (Нью-Йорк), сам спектакль уже не идёт на сцене, но можно найти его видеоверсию
В 2001 году в Мариинском театре представили одну из самых необычных вариаций «Щелкунчика». Визуальный мир для балета создал художник Михаил Шемякин. Он разработал костюмы и декорации, тщательно продумал образы персонажей и даже диктовал хореографу характер пластики каждого героя. Эта красочная фантасмагория, насыщенная драматизмом музыки, причудливыми фантазиями автора, погружает зрителя в совсем другую атмосферу. На смену тихому семейному вечеру в канун Рождества приходит буйство эмоций и гротескных образов.
Сцена из балета «Щелкунчик», Мариинский театр. Фото: Мариинский театр
Знаменитую рождественскую сказку Гофмана не обошли вниманием и кинорежиссёры. Существует несколько версий «Щелкунчика» в кино. Среди самых известных:
-
«Щелкунчик и Крысиный Король», 2010 год, режиссёр Андрей Кончаловский;
-
«Щелкунчик», 1993 год, режиссёр Эмиль Ардолино — экранизации постановки балета Джорджа Баланчина (1954 год, Нью-Йорк);
-
«Щелкунчик и мышиный король», 2004 год, режиссёр Наталья Мальгина — мультфильм, главные роли в котором озвучил звёздный состав артистов: Георгий Тараторкин, Евгений Миронов, Марина Александрова, Ефим Шифрин, Юрий Гальцев и другие;
-
«Щелкунчик и четыре королевства», 2018 год, режиссёры Лассе Халльстрём, Джо Джонстон — голливудская версия в жанре фэнтези.
«Щелкунчик» в Петербурге
Каким бы сложным ни был уходящий 2022 год, театры продолжают верстать афиши и ждут любимых зрителей в своих залах. В конце года в этих залах традиционно прозвучит великая музыка Чайковского. У зрителей есть множество вариантов, где посмотреть «Щелкунчика» в Петербурге и подарить себе настоящий праздник в преддверии Нового года и Рождества.
-
Классическая постановка Василия Вайнонена в Мариинском театре
-
Балет Михаила Шемякина в Мариинском театре
-
Спектакль Театра балета имени Леонида Якобсона
-
Балет Начо Дуато в Михайловском театре
-
Спектакль Академии русского балета им. А. Я. Вагановой в БКЗ «Октябрьский»
-
Спектакль Театра русского балета им. Анны Павловой
-
«Щелкунчик, или рождественские сны и видения Мари Штальбаум» в Большом театре кукол
-
Рождественский спектакль в театре «Кукольный формат»
-
Спектакль Петербург-концерта на сцене Екатерининского собрания
-
«Щелкунчик и мышиный король» в Театре сказки
-
Спектакль Театра марионеток им. Е. С. Деммени
В преддверии новогодних праздников в самом центре Нью-Йорка появился рекламный билборд Spotify с изображением Петра Ильича Чайковского. По данным сервиса, композитор стал самым популярным российским музыкантом среди зарубежных пользователей. Для масштабной аудитории в 4,8 миллиона слушателей Spotify создал специальный плейлист «This is Tchaikovsky», в котором чаще всего слушают сказочные мелодии «Щелкунчика» и «Лебединого озера».
«…Если только у тебя есть глаза, ты всюду увидишь сверкающие цукатные рощи, прозрачные марципановые замки — словом, всякие чудеса и диковинки».
Такими словами заканчивается сказка Гофмана, по мотивам которой в конце XIX века был создан балет «Щелкунчик», ставший символом Нового года и Рождества по всему миру. VATNIKSTAN рассказывает о волшебстве и тайнах самого известного новогоднего спектакля, истории его создания и разнообразии постановок.
Сказка ложь, да в ней намёк!
В 1816 году немецкий писатель-романтик Эрнст Т. А. Гофман впервые опубликовал сказку «Щелкунчик и Мышиный король», действие которой происходит в рождественский вечер. Все гости веселятся, Мари и Фриц получают подарки от родителей и от крёстного волшебника Дроссельмейера, и в какой-то момент добираются до невзрачной игрушки, умеющей разгрызать орехи. Перед сном герои попадают в настоящую сказку, где ожившие куклы во главе со Щелкунчиком сражаются с войсками Мышиного короля. В конце любовь Мари и победа в битве рассеивают чары, и Щелкунчик превращается в племянника Дроссельмейера.
Но по мнению исследователей, вместе с волшебным сюжетом Гофман раскрывает особенности детской психики, когда настоящие и вымышленные события переплетаются между собой, а фантазия становится продолжением реальности.
Композиция выстраивается на сопоставлении картин настоящего и сказочного миров, когда день соединяется с ночными сновидениями и превращениями. Гофмановский психологизм отражается и в отделении детского сознания от взрослого приземлённого взгляда на жизнь.
По мотивам этой сказки Мариус Петипа написал либретто балета «Щелкунчик». Только он не знал немецкого языка, и поэтому использовал французский перевод. Александр Дюма-отец в предисловии к своему «Нюрнбергскому Щелкунчику» рассказывал, что однажды на празднике он был окружён и взят в плен детьми, которые в обмен на свободу требовали рассказать сказку. В тот вечер Дюма и пересказал гофмановскую историю.
Французский вариант сохранил последовательность событий и практически такое же название глав. Автор внёс лишь некоторые несущественные дополнения, например, перенёс действие в Нюрнберг, «славящийся своими игрушками, куклами и полишинелями», и включил в повествование гувернантку Трудхен. Впрочем, главными отличиями являются введение рассказчика с шутливыми комментариями, создание лёгкой праздничной атмосферы, а также отсутствие психологизма, остроты и мистицизма оригинала.
Либретто сказки или Французской революции?
Либретто Петипа ещё больше приближает сюжет к волшебной сказке, в которой реальность чётко отделена от вымысла. Первая половина балета связана с нашим миром, вторая происходит в царстве игрушек, куда герои попадают через сражение с Мышиным королём, рост ёлки и снежную бурю. Соединяет миры крёстный Дроссельмейер, который делает кукол и как настоящий волшебник превращает их в живых людей, что заметно подчёркнуто в либретто Петипа, по сравнению с оригиналом Гофмана.
Путешествие в чудесный мир Конфитюренбурга связано с таким интересным эпизодом, как рост ёлки, которого не было в оригинале Гофмана. В этот момент и происходит символическое перемещение в сказочное царство, в котором оказываются сын королевы игрушек Щелкунчик и принцесса Мари.
Однако, не всё было так сказочно… Изначально у Мариуса Петипа были намерения внести в сюжет мотивы… Французской революции! Известный русский балетмейстер Фёдор Лопухов первым обратил внимание на черновики, содержащие революционные отголоски:
II акт
Приют гармонии
В глубине фонтана
Танец карамели
Трубочки с кремом
Танец сквозь века
Паспье королевы
Толпа полишинелей
Карманьола
Две феи
Добрый путь, дорогой Дюмоле
В заметках присутствует танец народного восстания — карманьола, а также песенка антиправительственного содержания «Добрый путь, дорогой Дюмоле», намекающая на бегство Карла X в Англию. «Приют гармонии» же, по мнению Лопухова, может относиться к «празднику Верховного Существа», к размышлениям Робеспьера о гармонии природы и общества. Кроме того, в набросках балета Петипа встречаются и «костюмы времён Директории». Тем не менее в процессе работы над либретто автор отказался от такой задумки, убрав абсолютно все «революционные» мотивы. Почему это произошло? Повлияли на решение смерть дочери или болезнь самого Петипа? Или же идея не нашла поддержки в окружении? Мы можем только догадываться.
Первая постановка
Подготовка «Щелкунчика» началась после успешного спектакля «Спящая красавица», поставленного в 1890 году. Над новым балетом трудился тот же состав: либретто и хореография создавал Мариус Петипа, эскизы костюмов — Иван Всеволожский, а музыку заказали у Петра Чайковского. Композитор писал:
«Я всегда стремился как можно правдивее, искреннее выразить музыкой то, что имелось в тексте. Правдивость же и искренность не суть результат умствований, а непосредственный продукт внутреннего чувства».
Действительно, ведь музыкальное прочтение следовало за созданием программы балета, в которой был отражён не только сюжет, но и пожелания Петипа относительно музыкального размера, мелодии, длительности и прочего. Музыка должна точно передать идею постановки, образы героев и их переживания, атмосферу сказочного и реального миров.
Но работа над «Щелкунчиком» у Чайковского шла очень тяжело. Композитор переживал кризис. Так во время поездки в Америку на торжественное открытие Карнеги-холла весной 1891 года он узнал о смерти сестры Александры, а незадолго до этого из репертуара внезапно исключили «Пиковую даму», которой он очень дорожил…
«Сознание того, что дело не ладится, терзает и мучит меня до слёз, до болезни; … и я давно не чувствовал себя столь несчастным, как теперь. <…> Я тщательно напрягал все силы для работы, но ничего не выходило, кроме мерзости».
Несмотря на творческие муки, Чайковский создал великолепную партитуру. Летом 1892 года началась подготовка балетного спектакля, однако вскоре Петипа тяжело заболел и был вынужден передать постановку хореографии Льву Иванову, сумевшему собрать воедино музыку и пластику танца. Премьера, состоявшаяся в декабре того же года в Мариинском театре, пришлась публике по душе. Особенно эффектным получился вальс снежных хлопьев, в котором балетмейстер задействовал около 60 танцовщиц-снежинок!
Отзывы критиков оказались очень противоречивыми. В то время балет посчитали бессмысленной детской нелепицей, и только через года мнения изменились. Например, Сергей Худеков, автор известного четырёхтомника «История танцев», писал:
«Какое убожество фантазии! Какая нелепица в лицах! О смысле я уже и не говорю; он находится в безвестном отсутствии. Прелестная сказочка Гофмана искажена до неузнаваемости. Между всеми картинами нет никакого связующего звена. Каждая из них может быть поставлена самостоятельно или вынута из балета, без ущерба ходу действия. … Весь этот детский балет сделан чисто по-детски. Программа — это чисто детский лепет!.. Напрасно полагают, что можно роскошью постановки заменить убожество фантазии и мысли в этой программе…»
Советский «Щелкунчик»: от неудачи к мировой славе
Петербургская постановка Льва Иванова просуществовала до 1924 года, после чего хореография, к сожалению, была утрачена. Однако традиция «Щелкунчика» продолжилась в советское время. В 1919 году благодаря балетмейстеру Александру Горскому спектакль появился в Большом театре. В Северной столице в 1920‑е годы восстановлением балета занимался Фёдор Лопухов, представив в 1929 году совместно с Владимиром Дмитриевым новую постановку, отличную от классической программы.
Авторы создали передвижные декорации, цвета которых отражали музыкальные тональности. Хореография содержала акробатические элементы, а часть спектакля проходила под хлопки в ладоши или звуки метронома.
Также важно было обратить внимание зрителей на соотношение кукольного и человеческого — в конце представления все танцовщики срывали с себя маски, чтобы у публики не оставалось «никаких иллюзий». Постановка Лопухова шла совсем недолго, поскольку не была принята зрителями и не соответствовала революционному искусству того времени.
В 1934 году «Щелкунчик» вернулся на сцену Кировского театра в постановке Василия Вайнонена. В 1939 году этот спектакль был поставлен и в Москве. Отказавшись от экспериментов 1920‑х годов, балетмейстер обратился к классической программе с использованием современной балетной техники.
Кукольное больше не переплеталось с живым, не было психологизма гофмановского оригинала. Словом, «Щелкунчик» получился сказочным и светлым детским спектаклем, который до сих пор идёт в версии Вайнонена во многих театрах. Вместе с этим постановка стала новогодней традицией не только для зрителей, но и для юных танцовщиков — студентов балетных училищ, которые усердно готовятся к первым выходам на большую сцену.
Балет «Щелкунчик». Хореография Василия Вайнонена, постановка «Московский классический балет» под руководством Наталии Касаткиной и Владимира Василёва, 1993 год.
Выдающийся балетмейстер Юрий Григорович, напротив, наполнил балет таинственностью и более глубоким философским смыслом. Он размышлял, из чего исходить при постановке «Щелкунчика», опираться на музыку, сказку или его внутренние ощущения:
«Выбор мне сделать было нетрудно: я мечтал о воплощении „Щелкунчика“ именно Чайковского, я хотел выразить своё, личное понимание его гениальной музыки. Хотел найти ей пластический и театральный эквивалент, способный раскрыть не мои общие идеи, а моё субъективное её восприятие, её мир, мною пережитый и осмысленный через танец».
Фрагмент «Щелкунчика» в постановке Юрия Григоровича, запись 1967 года.
Премьера спектакля состоялась в 1966 году, и с тех пор вот уже на протяжении почти 55 лет на сцене Большого театра идёт легендарная постановка Григоровича! Балетмейстеру удалось передать трагические и волнующие ноты партитуры Чайковского. По выражению Григоровича, он «просто слушал музыку и шёл за ней», заставляя зрителей задуматься о мимолётности жизни или недосягаемости абсолютного счастья, ведь в конце спектакля невероятные приключения героев оказываются сном…
«Щелкунчик» в постановке Юрия Григоровича, в главных ролях Екатерина Максимова и Владимир Васильев.
Такой разный «Щелкунчик»
Всевозможные спектакли, кино, мультфильмы, сувениры и игрушки Щелкунчика создают праздничное настроение на протяжении долгих лет. Наверняка, многие из нас смотрели добрый советский мультфильм о Щелкунчике, созданный в 1973 году режиссёром Борисом Степанцевым. Хотя сюжет несколько отличается от литературного оригинала и либретто, именно благодаря детскому мультфильму мы впервые познакомились с этой волшебной историей.
Мультфильм «Щелкунчик», режиссёр Борис Степанцев, 1973 год.
Среди балетных постановок также существует огромное количество интерпретаций. Вот уже более 120 лет хореографы разных стран пытаются разгадать тайну либретто Петипа, передать скрытые смыслы и образы, создать новое прочтение классики. Редакции спектаклей поражают своим разнообразием! Некоторые постановщики занимались реконструкцией первого балета Льва Иванова или создавали классические спектакли с опорой на традиции. Другие стремились передать личные переживания, воспоминания о детстве, или же кардинальным образом изменить стилистику балета, перенести время и место действия, создать новых героев, обратиться к современной хореографии, акробатике или жанру мюзикла. Впрочем, некоторые версии слабо напоминают «Щелкунчика» …
Американская постановка, созданная Джорджем Баланчином в 1954 году для «Нью-Йорк Сити балет». Несмотря на то, что сам автор в молодости жил и танцевал в Петербурге, он не стал копировать хореографию, а создал новый красочный спектакль.
В 1991 году, вдохновившись комиксами Чарльза Бёрнса, хореограф Марк Моррис создал необычную постановку «Крепкого орешка». Смотрим Вальс снежных хлопьев и некоторые другие фрагменты балета.
«Щелкунчик» Мориса Бежара, созданный в 1998 году, рассказывает о детских воспоминаниях автора и важных моментах его жизни. Центральным в постановке становится образ умершей матери, который со временем становится всё более далёким и загадочным…
Чёрные снежные хлопья, крысы и мыши на кухне, странные превращения. Всё это в постановке Михаила Шемякина в Мариинском театре. По выражению хореографа, основной задачей было «вернуть сказке гофмановский дух с элементами гротескного юмора, странностями и перевоплощениями; соединить изобразительную часть с музыкальным драматизмом Чайковского».
Также предлагаем послушать интересные интерпретации музыки балета Чайковского. Гитара, джаз и рок-н-ролл в партитурах «Щелкунчика».
Читайте также историю жизни главных деятелей постановок Дягилева «Скромное обаяние „Русского балета“».
Поделиться
В 1890 году Чайковский получил заказ от дирекции Императорских театров на одноактную оперу и двухактный балет для постановки в один вечер. Для оперы композитор избрал сюжет полюбившейся ему драмы датского писателя X. Херца «Дочь короля Рене» («Иоланта»), а для балета — известную сказку Э. Т. А. Гофмана (1776—1822) «Щелкунчик и мышиный король» из сборника «Серапионовы братья» (1819—1821). Сказка была использована не в подлиннике, а во французском пересказе, сделанном А. Дюма-отцом под названием «История Щелкунчика». Чайковский, по свидетельству его брата Модеста, сам сначала «письменно изложил сюжет «Щелкунчика» со слов Всеволожского» и только затем приступил к совместной работе с хореографом Мариусом Петипа (1818—1910), сделавшим подробный план-заказ и балетмейстерскую экспозицию. Прославленный мастер, к тому времени служивший в России уже более сорока лет и поставивший множество спектаклей, давал Чайковскому самые подробные советы относительно характера музыки.
Работа композитора вынужденно прервалась весной 1891 года, когда Чайковский отправился в США на торжественное открытие Карнеги-холла. Даже на пароходе он сочинял, но, понимая, что к назначенному дирекцией сроку не успеет, еще из Парижа отправил Всеволожскому письмо с просьбой перенести премьеры «Иоланты» и «Щелкунчика» на следующий сезон. Только по возвращении из поездки работа пошла активнее. В течение января и февраля 1892 года Чайковский закончил и оркестровал балет. В марте в одном из симфонических концертов Русского музыкального общества была исполнена сюита из музыки к балету под управлением самого композитора. Успех был оглушительный: из шести номеров пять по требованию публики были повторены.
По сценарию и подробным указаниям тяжело заболевшего Петипа постановку «Щелкунчика» осуществил второй балетмейстер Мариинского театра Л. Иванов (1834—1901). Лев Иванович Иванов, окончивший в 1852 году Петербургское театральное училище, в это время заканчивал карьеру танцовщика и уже семь лет работал балетмейстером. Ему, помимо нескольких балетов, принадлежали постановки половецких плясок в «Князе Игоре» Бородина и танцев в опере-балете Римского-Корсакова «Млада». В. Красовская писала: «Танцевальное мышление Иванова не опиралось на музыку Чайковского, а жило по ее законам. <…> Иванов в отдельных элементах своей постановки как бы полностью растворяясь в музыке, из ее сокровенных глубин черпал всю спокойную, чистую, даже скромную пластику танца». «Нет в музыке «Щелкунчика» ни одного ритма, ни одного такта, который не перелился бы в танец», — отмечал А. Волынский. Именно в музыке находил балетмейстер источник хореографических решений. Особенно ярко проявилось это в новаторском симфонизированном танце снежных хлопьев.
Репетиции балета начались в конце сентября 1892 года. Премьера состоялась 6 (18) декабря. Критика была противоречивой — как положительной, так и резко отрицательной. Однако балет продержался в репертуаре Мариинского театра более тридцати лет. В 1923 году спектакль был восстановлен балетмейстером Ф. Лопуховым (1886—1973). В 1929 году он создал новую хореографическую версию спектакля. В первоначальном сценарии героиня балета именовалась Кларой, но в советские годы ее стали называть Машей (у Дюма — Мари). Позднее постановки балета на различных советских сценах осуществляли разные балетмейстеры.
Источник: Belcanto.ru
Балет «Щелкунчик»
Сюжет: 1 акт. Председатель с женой и приглашенными украшает елку. Все готово, время звать детей. Елка зажигается, как по волшебству. Дети входят и замирают, полные удивления и восторга. Начинается раздача подарков. Общее увлечение прерывается приездом советника Дроссельмайера. Дети председателя с нетерпением ждут подарков Дроссельмайера — их крестного. Последний заставляет внести две коробки: из одной он извлекает большой кочан капусты — для Клары, из другой — большой пирог — для Фрица. Увидев такие подарки, дети и их родители разочарованы. Дроссельмайер приказывает поставить подарки перед собой, заводит их, и из капусты появляется большая кукла, а из пирога — солдат. Еще из двух больших табакерок Дроссельмайера появляются черт и чертиха. Клара и Фриц в восторге, благодарят крестного и просят позволения унести игрушки. Родители запрещают — такими прекрасными игрушками не играют. Клара плачет, Фриц капризничает. В утешение советник достает из кармана еще подарок — Щелкунчика. Им играть можно.
Билеты на балет «Щелкунчик» в Большом театре на сайте Bolshoy-Teatr.com →
Клара сразу восхищена им и спрашивает советника о предназначении подарка. Он берет орех и раскалывает его Щелкунчиком. Фриц, заинтересовавшись, тоже хочет колоть им орехи. Родители указывают маленькой Кларе, что она должна поделиться с братом. Фриц колет им орехи — и у Щелкунчика ломаются зубы. Клара поднимает брошенную Фрицем игрушку, утешает и укладывает в кукольную колыбельку. Фриц с товарищами шумно дразнят девочку. Чтобы покончить с этим, председатель предлагает всем протанцевать «гроссфатер» («танец дедушек»). Гости благодарят председателя и его супругу и уезжают. Детям приказывают идти спать. Клара просит позволения взять с собой больного Щелкунчика, родители отказывают. Она в горе уходит, закутав потеплей своего любимца. Ночь. Клара в ночной рубашке еще раз возвращается взглянуть на своего дорогого больного. Ей страшно. Она подходит к кроватке Щелкунчика, от которого, как ей кажется, исходит таинственный свет. Бьет полночь. Клара смотрит на часы и с ужасом видит, что сова на них превратилась в Дроссельмайера, который смотрит на нее с насмешливой улыбкой. Она хочет бежать, но силы оставляют ее. В ночной тишине она слышит, как скребутся мыши и делает усилие, чтобы уйти, но мыши появляются со всех сторон. Тогда, в ужасе, она хочет забрать Щелкунчика и бежать, но это ей не удается. Все исчезает. Задняя дверь открывается, елка становится огромной. Часовой на часах окликает: «Кто идет?» Мыши не отвечают. Часовой стреляет, куклы перепуганы. Часовой будит зайчиков-барабанщиков. Происходит битва, мыши побеждают и пожирают пряничных солдатиков. Появляется мышиный царь, приветствуемый своими войсками. Щелкунчик вызывает свою старую гвардию, раздается призыв к оружию, снова разгорается битва. Чтобы защитить Щелкунчика, Клара бросает в Мышиного короля свой башмак и затем падает в обморок. Мыши исчезают. Щелкунчик превращается в благородного принца и бросается на помощь Кларе, которая приходит в себя. Еловый лес зимой. Начинает идти снег, поднимается вьюга, кружатся в танце снежинки-танцовщицы.
2 акт. Волшебный дворец Конфетенбурга. Самая фантастическая декорация. В глубине фонтаны из лимонада, миндального молока, оранжада и смородинового сиропа. Среди этих фонтанов на реке розовой воды виден павильон из леденцов с прозрачными колоннами, где находятся фея Драже и ее свита. При поднятии занавеса на сцене находятся всевозможные сладости и пирожные, серебристые солдатики стерегут дворец, посреди сцены стоит человечек в костюме из золотой парчи. Фея Драже со свитой сходят на сцену, все сласти преклоняются. На бушующей поверхности реки розовой воды появляются Клара и благородный принц в колеснице из раковины, в которую запряжены дельфины. Весь конфетный народ во главе с феей Драже приветствует жениха и невесту. Четыре крошечных, волшебно одетых принцессы Конфетенбурга бросаются на шею Щелкунчику — их брату. Щелкунчик растроган. Он представляет всем Клару как свою спасительницу. Происходит грандиозное празднество, во время которого Принц с феей Драже танцуют Па-де-де. Большая общая кода. Апофеоз.
Среди произведений позднего периода творческого пути Чайковского «Щелкунчик» занимает особое место: он не вписывается в сложившуюся в тот период традицию балетного жанра. Для Чайковского этот балет также является новаторским сочинением, ключевым для понимания позднего стиля композитора, его идейных устремлений, поисков смысла жизни, нравственных оценок. Темы детства и смерти, красоты нравственного подвига и предательства — вот основные образные сферы музыки Чайковского.
Традиционно в русском балетном театре «Щелкунчик» воспринимался как оптимистическая детская сказка, а философский подтекст был скрыт под пышностью и красотой сценического оформления, волшебств в сюжете. Именно поэтому балетмейстеры всего мира постоянно обращаются к этому балету Чайковского, находя в нем все новые и новые аспекты и в сюжете, и в музыкальной драматургии. Поистине неисчерпаемы глубинные слои музыки Чайковского. Содержательная многослойность сказки Гофмана и ее музыкальное воплощение в балете Чайковского было замечено лишь в ХХ веке.
Сюжетная композиция не соответствует сценическому членению балета, сделанному Петипа: реальные сцены (исходная ситуация) и ночные сцены (начало самой сказки) им никак не выделены, что рождает противоречие между структурой сказки, сюжетом и композицией сценического действия.
Музыкальная же композиция складывается отлично от программы и либретто Петипа. Внешне следуя сценарию Петипа, Чайковский осуществляет иное музыкальное членение балета. В общей композиции балета заложено противоречие между музыкальным и сценическим планами, однако между музыкальным и сюжетным возникает полное соответствие.
Религиозно-мифологические представления в сюжете «Щелкунчика» связаны с двумя ключевыми и кульминационными в драматургии мотивами — «роста елки» и зимы (зимнего леса), выражающими философский подтекст музыки балета. Рост елки — это вхождение на небо, движение в иной, небесный мир (по древнему верованию — царство мертвых); зима — символ застывания, замирания, остановки в развитии, т.е. смерти — перед Конфетенбургом — своего рода подготовка к неземному миру, путь в который проходит через лес.
На несколько смысловых сфер подразделяется и содержательная структура «Щелкунчика»: детские сцены, сцены со взрослыми, фантастические, романтические, религиозно-пантеистические сцены, сцены масок-марионеток. Каждой сфере соответствует особая манера, приемы письма, лексика, поэтому стиль балета в целом — многозначен и основывается на влиянии и претворении различных культурных слоев и традиций. Это: культура XVIII века (детские сцены, неоклассические аллюзии, маски дивертисмента; танец пастушков — в духе культа галантности,); французская культура (взрослые сцены, интонации маршей Французской революции и мотивов французских народных массовых танцев; цитирование песен «Добрый путь, дорогой Дюмоле», «Каде Руссель», «Жирофле-Жирофля»); немецкая культура в дважды опосредованном преломлении (ритуальный танец «Гроссфатер» как отсвет образов любимого Чайковским Шумана в изображении бюргерства и филистерства.
Балет сочинялся Чайковским в течение 1891-1892 года по заказу И.А.Всеволожского. Интересно, что сюжет известной сказки Гофмана (в переделке Дюма-сына) знаменитый балетмейстер М.Петипа разработал несколько ранее для ученического спектакля в Балетном училище императорских театров в Петербурге. Позже он разработал сценарий для Чайковского, создал балетмейстерский план будущего спектакля. Но ставил балет другой балетмейстер — Л.Иванов, ранее поставивший 2 акт «Лебединого озера», который живет до сих пор на сценах ведущих театров мира. Судьба «Щелкунчика» была очень противоречивой: успех у публики и страшная ругань критики — это начало. Позже поиски гармонии между музыкой Чайковского и сюжетом привели к множеству трактовок этой, казалось бы простой и ясной сказки. Поэтому «Щелкунчик» остается и на сегодняшний день одной из постоянно открываемых симфонических балетных партитур Чайковского.
П. Е. Вайдман
«ЩЕЛКУНЧИК», Ор. 71а, Сюита
Берлинский филармонический оркестр. Дирижер Герберт фон Караян. Запись 1967 года.