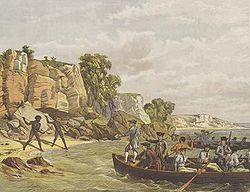Биография Джеймса Кука
27 Октября 1728 – 14 Февраля 1779 гг. (50 лет)
4.2
Средняя оценка: 4.2
Всего получено оценок: 272.
Джеймс Кук (1728–1779 гг.) — знаменитый мореплаватель, который нанёс на карту много мест, ранее неизвестных для своих современников. Служа в Королевских военно-морских силах Англии в ранге капитана, он был очень скрупулёзным, педантичным и аккуратным человеком, поэтому все карты, составленные им, были сделаны на совесть и служили морякам ещё несколько веков.
Опыт работы учителем географии — 35 лет.
Юные годы
Биография Джеймса Кука насыщена приключениями. Он родился 27 октября (7 ноября) 1728 г. в Мартоне. Позже семья переехала, и в возрасте 8 лет Джеймс поступил в школу в Грейт Айтоне. После того, как мальчик 5 лет отучился в школе, он стал работать на ферме, где его отец был управляющим. Когда Джеймсу исполнилось 18 лет, он нанялся юнгой на судно под названием «Геркулес», которое перевозило уголь.
Морская карьера
Наряду с работой, Джеймс много времени уделял обучению, изучая географию, навигацию, астрономию, математику. Читал большое количество литературы. Впоследствии все годы жизни он посвятил путешествиям.
В 1755 году его приняли на военный корабль в качестве матроса. В это время шла война с Францией, и молодой человек смог хорошо проявить себя. Он составил карту реки Святого Лаврентия, благодаря которой англичанам удалось успешно атаковать город Квебек. Таким образом он стал боцманом, а в 1757 году его назначили на пост капитана и доверили корабль «Солебей».
Первая экспедиция
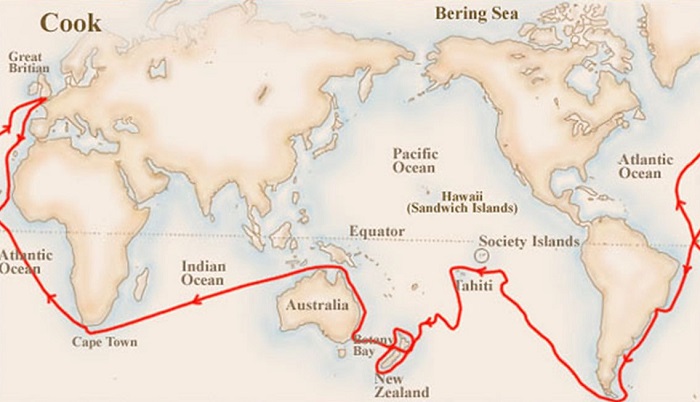
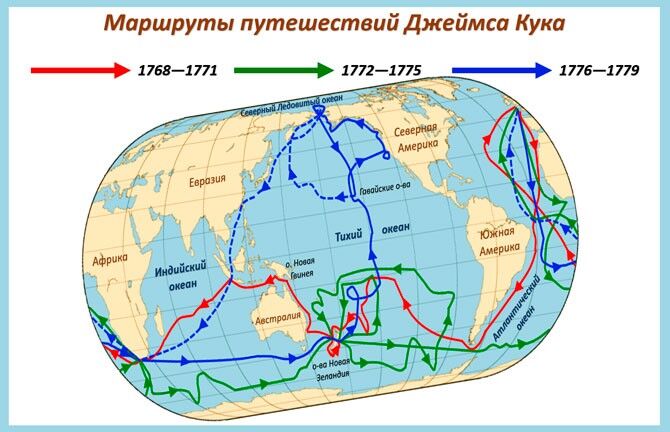
Так что открыл Джеймс Кук? Основной вклад в географию он сделал, проводя время в путешествиях. Цель первой экспедиции — исследовать прохождение Венеры через Солнце. Экспедиция длилась почти 3 года (с августа 1768 по июль 1771 года). Помимо астрономических наблюдений, Джеймсу необходимо было найти и установить берега восточного побережья Австралии.
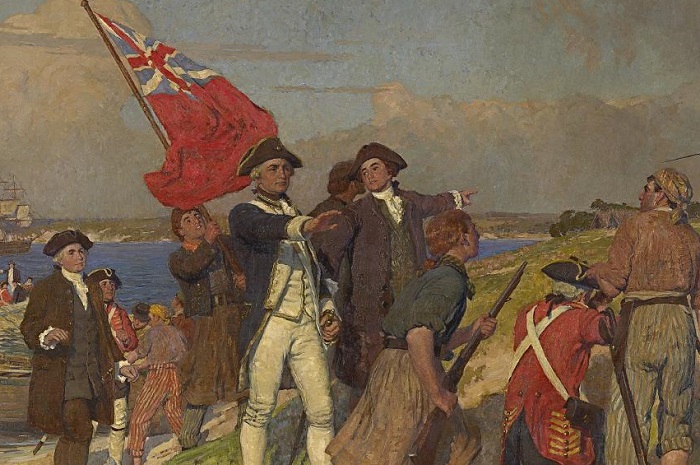
В 1769 году Кук достиг острова Таити. Там он и его команда должны были провести астрономическое исследование. Но всё необходимое оборудование украли туземцы. Осенью этого же года их корабль доплыл до Новой Зеландии. Вскоре выяснилось, что это не мыс Южного континента, как они считали ранее, а два острова. Благодаря этому открытию проход между ними начали называть проливом Кука. После этого путешественники прибыли к восточному побережью Австралии. В это время был открыт Большой Барьерный риф.
Второе и третье путешествия
Задачей второго плавания, которое также длилось почти 3 года, было исследование южных морей. Однако Кук вместе со своей командой не смог прорваться к материку сквозь льды. Он исследовал границы льдов и составил по ним подробные карты.
Последнее путешествие Кука длилось около 4 лет (с июля 1776 по октябрь 1780 года). Перед Джеймсом стояла задача найти Великий проход, который соединял два океана на севере. Но, выйдя в Берингов пролив, он не смог достичь цели, потому что опять помешали льды. Кук смог добраться лишь до 71-й параллели, где открыл остров Гавайи и остров Рождества.
Смерть
Джеймс Кук погиб от рук туземцев 14 февраля 1779 года. Его решение остановиться на острове Гавайи и подождать до лета, чтобы потом вновь двинуться в путь, оказалось фатальным.
Личная жизнь
В 1762 году Джеймс Кук женился на Элизабет Баттс. У них родилось 6 детей, жизнь которых была очень коротка. Первенец, названный в честь отца, прожил до 31 года, двое других — до 17 лет, ещё один ребёнок едва дожил до 4 лет, а ещё двое не перешагнули и годовалого возраста.
Интересные факты
Супруга Джеймса пережила его на 56 лет.
Помимо открытий, сделанных в путешествиях, Джеймс Кук создал карты берегов полуострова Лабрадор, которые использовались даже в начале XX века.
В честь мореплавателя назвали архипелаг, расположенный в Тихом океане.
Краткую биографию Джеймса Кука, а также его открытия изучают школьники 5 классов.
Другие варианты биографии
Более сжатая для доклада или сообщения в классе
Вариант 2
Тест по биографии
Доска почёта

Чтобы попасть сюда — пройдите тест.
-
Август Мандаринский
10/10
-
Али Исагаджиев
9/10
-
Мария Гринь
8/10
-
Абубакр Джураев
10/10
-
Ольга Оль
9/10
Оценка по биографии
4.2
Средняя оценка: 4.2
Всего получено оценок: 272.
А какая ваша оценка за эту биографию?
Джеймс Кук (годы жизни 1728 — 1779 гг.) — английский мореплаватель, краткая биография которого предложена в данной статье, стал известен благодаря открытию Тихоокеанских островов, Ньюфаундленда, первому описанию восточного побережья Австралии, Канады, Новой зеландии. Из географии мы знаем его как исследователя южных морей, картографа, первооткрывателя, исследователя западных берегов Северной Америки, Индийского, Атлантического и Тихого океанов.
Краткая биография английского мореплавателя
Родился 27 октября в Мартоне в 1728 г. В семье было пять детей. Когда мальчику было восемь лет, родители переехали в Грейт Айтон (Северный Йоркшир). С тринадцати лет он работал вместе с отцом на ферме.
В первое плаванье отправился, достигнув совершеннолетия (торговый корабль «Геркулес»). Судно принадлежало братьям Уокерам, Джеймс трудился под их началом до 1755 г. Летом этого же года он вошел в состав команды Королевского военно-морского флота, отказавшись от роли капитана на корабле Уокеров.
Служил на корабле «Игл» сначала матросом, но уже через месяц стал боцманом. Члены судна приняли участие в семилетней войне 1756 г.
Став мастером (по результатам экзамена), он попал на «Пемброк» (судно, которое обеспечило захват Квебека). Параллельно он занимался картографией. Последнее было отмечено адмиралтейством, а Кук переведен на корабль «Нортумберленд». Карты, составленные исследователем, были напечатаны в 1765 г.
Завершив исследование канадских вод в 1762 г., мореплаватель вернулся в Англию, где женился на Элизабет Баттс. С 1764 г. открыл Ньюфаундленд и полуостров Юкатан. Так, начав поприще с юнги, достиг звания капитана, заручившись поддержкой британского адмиралтейства.
Первая научная экспедиция 1768 г
Британское адмиралтейство переоборудовало судно «Индевор», во главе которого был поставлен Джеймс Кук. На борту присутствовали художники Бьюкен и Паркинсон.
Официальная задача – исследование хода Венеры через солнечный диск, для чего в составе команды входил астроном, а также член королевского общества Д. Банкс, чьи ботанические заметки о восточном береге Австралии были представлены впервые.
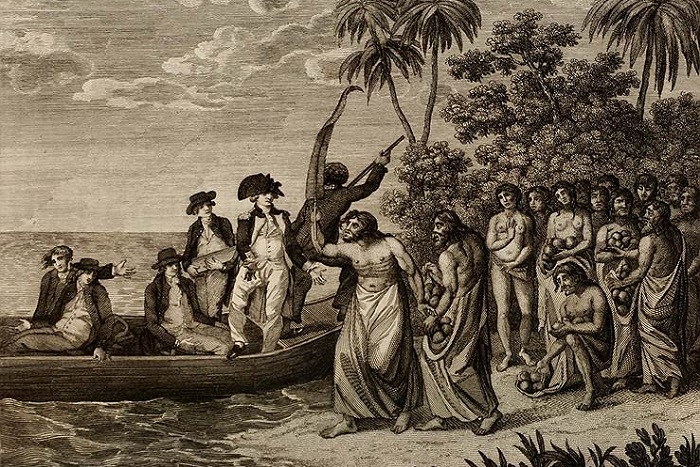
В апреле 1769 г. исследователь достиг Таити, где провел астрономические исследования. В ходе экспедиции Кук установил жесткую дисциплину на борту, целью которой было налаживание контактов с островитянами. Другие европейские страны не разделяли такое демократичное отношение к аборигенам.
Кук исследовал земли Новой Зеландии, открыл пролив Шарлотты. В 1770 г. был открыт восточный берег Австралии (ранее не изученный).
Следуя на север, был открыт Ботанический пролив. Экипаж вернулся в Британию в 1771 г. Потери среди экипажа были огромными, что связано с малярией, цингой, дизентерией.
Секретное задание капитана Кука
Исследование южных морей – основная идея экспедиции. Англия была одержима поиском Terra incognita. Южный континент не был найден в ходе данного исследования. Ранее Александр Далримпл приводил сведения о его существовании, однако убедительных данных получено не было.
Вторая научная экспедиция 1772 г
Тринадцатого июля Джеймс Кук отправился на поиски Южной земли, колонизация которой должна была открыть новые горизонты перед государством. Королевское общество рассматривало две кандидатуры: Кука и Банкса. Последний отказался от участия. Адмиралтейство назначило Джеймса начальником экспедиции, дав ему три недели отпуска после возвращения из первого плавания.
В плаванье были снаряжены корабли «Резолюшн» и «Эдвенчур» — первый возглавил Кук, второй Фюрно. Пунктом отправления послужил Плимут, откуда маршрут пролегал в Кейптаун, а затем на юг. Спустя полгода был пересечен Южный полярный круг.
В феврале судна сбились с курса, капитаны смогли воссоединиться только в июне. Плавание по Тихому океану сопровождалось изучением островов Новой Зеландии. Среди команды развилась цинга, в связи с чем, произвели посадку на Таити.
Затем посетили остров Хуахине, Тонгатапу и Эуа. Данные острова вошли в группу островов Дружбы. В 1774 г. были открыты острова Южная Георгия и Новая Каледония. Джемс Кук прибыл в Англию в 1775 г.
Третье кругосветное путешествие 1776 г
Двенадцатого июля «Резолюшн» покинул порт Плимута для исследования северо-западного пути. В экспедиции также участвовал корабль «Дискавери» под руководством Чарльза Клерка. Судна прибыли в Кейптаун, где были отремонтированы, после чего взяли курс на Новую Зеландию.
Летом 1777 г. исследователь высадился на Тасмании (для пополнения провианта). После чего двинулся в северном направлении. Это позволило открыть острова Рождества и Гавайские. Последние были названы Джеймсом Сендвичевыми (в честь Джона Монтегю).
В феврале 1778 г. двигаясь к берегам Северной Америки, судна получили повреждения во время шторма. Возникла необходимость ремонта. В октябре этого же года корабли достигли Алеутских остров, откуда направились к Гавайям.
Значение кругосветных экспедиций Джеймса Кука
В ходе путешествий были исследованы австралийские берега, открыт пролив между Австралией и Новой Гвинеей. Полученная информация была издана в виде руководств. Исследователь нанес на карту ранее не известные острова. В ходе плавания установлено, что неизведанного южного материка нет.
Джеймсу Куку принадлежит открытие Гавайских островов — место гибели мореплавателя в 1779 г.
Как умер Джеймс Кук
Что только не говорят о смерти английского мореплавателя, какие рассказы только не публикуют! Например, рассказывают, почему аборигены съели Кука. Что же на самом деле произошло?
Прибыв на Гаити в 1778 г., подходящее место для стоянки капитан Кук нашел только в 1779 г. Местные жители радушно приняли команду Кука, однако повторяющиеся эпизоды краж с корабля их ухудшили.
Исследователь предпринял попытку захватить местного вождя по имени Каланиопа. Островитяне окружили Кука и находящихся рядом с ним людей. В ходе схватки он был убит, а его тело захвачено.
Интересные факты
Вот несколько любопытных фактов:
-
Согласно записям судового журнала, аборигены не собирались нападать на членов экспедиции. Причиной послужило поведение Кука (последний попытался расправиться с их вождем на глазах тысячи туземцев). Тело удалось получить лишь на следующий день, а высказывание «съели Кука» носит иносказательный характер.
-
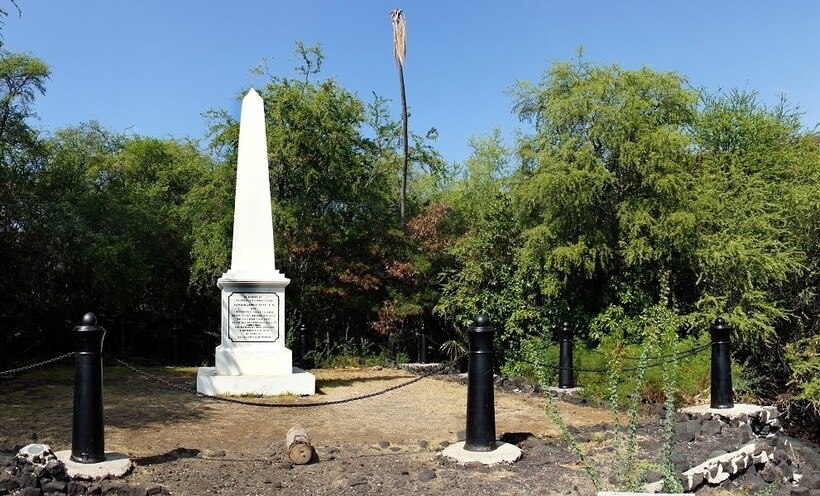
Кеалакекуа (бухта, где погиб Кук) является национальным достояниям, на ее территории воздвигнут обелиск в память об исследователе.
-
У Кука и его жены Элизабет родилось 6 детей. Жена пережила мужа на 56 лет и умерла в возрасте 93 лет в лондонском Ист-Энде.
-
Знаменита книга исследователя «Путешествие на Южный полюс и вокруг света», написанная в 1777 году.
Имя Джеймса Кука неизменно ассоциируется с путешествиями и географическими открытиями. За двадцать лет в море капитан внес большой вклад в картографию и освоение новых земель. В статье поговорим о трех кругосветных экспедициях Кука, его открытиях и узнаем, был ли он съеден аборигенами.
Биография Джеймса Кука
Джеймс Кук появился на свет 27 октября 1728 в пригороде Йоркшира, Англия. Окончив пять классов школы, Кук пошел работать на ферму вместе со своим отцом. По достижении совершеннолетия уходит юнгой на углевоз. С этого начинается история его любви к океану.
Следующие годы юноша работает на низших корабельных позициях, тратя все свободное время на учебу. Он увлекся навигацией и географией, а также их производными — астрономией и морскими экспедициями.
В 1755 г. Кук записывается в английский Королевский флот на позицию матроса и вскоре получает первое назначение. Тяжелая физическая работа приносит плоды — через месяц его повышают до боцмана.
ИНТЕРЕСНЫЙ ФАКТ. Перед поступлением во флот бывшие наниматели Кука предложили ему должность помощника капитана на их торговом корабле, но тот отказался и выбрал тяжелую работу матросом.
Через год началась война длиною в семь лет и будущий мореплаватель попал на передовую. Судно, на котором он работал, обеспечивало блокаду французских берегов, а чуть позднее — Бискайского залива.
В 1758 г. главной целью англичан было канадское побережье. Судно Кука отправили в Квебек. Перед ним стояла сложная стратегическая задача — проложить фарватер через часть реки Святого Лаврентия и обложить его буями для судов армии. Работать приходилось по ночам под постоянными обстрелами французов.
Молодой Кук справился. Британцы взяли Квебек. А Кука повысили до мастера и перевели на флагманское судно. Там он продолжил работу по изучению вод реки Святого Лаврентия и вернулся на английские земли лишь в 1762 г.
ЭТО ИНТЕРЕСНО. Несмотря на молодость Кука, карты его были настолько точны, что были опубликованы в Североамериканском морском картографическом учебнике для моряков 1765 г.
Опыт в картографии, полученный за войну, не прошел даром. Английское королевское общество избрало Кука на должность руководителя исследовательской кругосветной экспедицией.
Следующие 11 лет исследователь бороздил океаны. Он обогнул мир трижды. Созданные им карты использовались мореплавателями вплоть до XIX в. Капитан умер от рук гавайских туземцев 14 февраля 1779. Через неделю, 22 февраля, его останки похоронили в океане.
Экспедиции и географические открытия Кука
Всего Джеймс Кук совершил три кругосветных путешествия. Общая их продолжительность составила девять лет. Кто знает, сколько бы еще полезных миру открытий смог сделать отважный англичанин, если бы не трагический исход последней кругосветки.
Первая экспедиция Кука
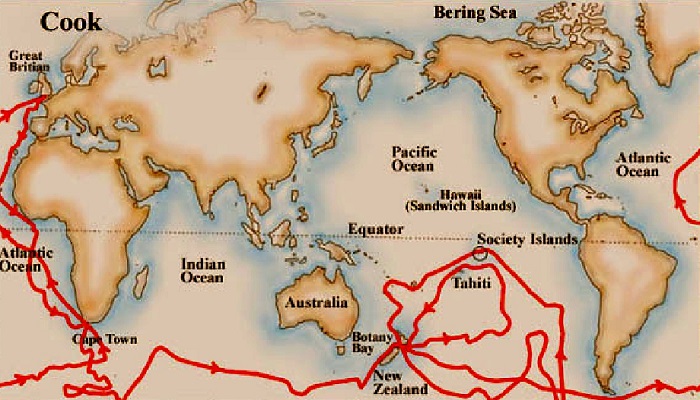
Первое кругосветное путешествие Джеймса Кука прошло в период с 1768 по 1771 гг. Целью вояжа стало наблюдение за путем Венеры по солнечному диску. Другая причина — поиск Южной земли. Третья — обследовать восточную часть Австралии.
Для справки
Южная земля, она же «неведомая земля», стала причиной многочисленных экспедиций. Фактически, ее никто не видел, но она была изображена на всех картах XV-XVI вв. Ученые умы того времени были уверены в ее существовании, полагая, что южная земля удерживает баланс планеты. По их мнению раз в северной части Земли так много суши, то она должна быть и в южной, чтобы предотвратить «переворот планеты». Европейцы соревновались в стремлении первыми открыть континент, чтобы начать его скорейшую колонизацию. XIV век — Магеллан был совсем недалеко от «неведомой Южной земли», открыв знаменитый пролив, однако так и не добрался до неё.
В составе первой экспедиции Джеймса Кука помимо самого капитана было два ботаника, астроном, два художника, врач и судовой персонал. Специально для путешествия Адмиралтейство переоборудовало угольное судно «Индевор». Корабль отличала малая осадка и 22 пушки на случай вооруженных конфликтов с аборигенами. Судно вышло из английского порта в августе 1768. Почти восемь месяцев занял путь до Таити. Там мореплаватели построили форт для наблюдения за небесными телами. На острове исследователи оставались до середины июля, попутно занимаясь ремонтом судна после длительного путешествия.
Следующей остановкой стала Новая Зеландия. Там их ждали негостеприимные туземцы, что привело к нескольким стычкам. В результате англичане быстро ретировались в поиске места для продолжительной остановки.
Найдя залив, которого не было на карте, Кук назвал его в честь Королевы Шарлотты. Там судно встало на ремонт, а путешественники обнаружили, что две части Новой Зеландии разделены проливом. Закончив с ремонтом, мореплаватели отправились к восточному побережью Австралии. Оттуда — на северо-запад. В пути команда открыла много новых растений, характерных для теплого австралийского климата.
Пройдя вдоль австралийских земель, судно отправилось в Индонезию, оттуда — в Кейптаун. За время нахождения в Индонезии на судно попали малярия и дизентерия, которые в закрытом пространстве переросли в страшную эпидемию. К моменту прибытия в Кейптаун более 20 членов экипажа погибли от болезней. В их числе был и астроном. Дальнейшее исследование было невозможным, поэтому в ЮАР Кук нанял матросов и судно вернулось в Британию в июле 1771 г.
Вторая экспедиция
К началу второго плавания вопрос об открытии Южной земли встал особо остро. Французы активно изучали те места и Англия не хотела, чтобы континент был потерян для британской колонизации.
Для экспедиции Англия снарядила два корабля по примеру соперников — французов. Те всегда отправляли в плавание 2-3 судна одновременно в целях безопасности. На суда «Adventure» и «Resolution» были назначены трое натуралистов, двое астрономов и художник. Капитанами стали Кук («Resolution») и Тобиас Фюрно («Adventure»). 13 июля 1772 г. мореплаватели вышли из Англии.
Путешественники провели несколько месяцев, исследуя прибрежную территорию Новой Зеландии и окрестных островов.
Из-за плохой погоды «Эдвенчур» и «Резолюшн» теряли друг друга дважды. В первый раз им удалось найтись. При второй потере на экипаж «Эдвенчура» напали новозеландцы. Восемь человек были убиты и съедены. После этого Фюрно решил вернуться в Англию.
Корабль Кука остался в Южном полушарии и продолжил изучение флоры и фауны островов Тонга, Фиджи, Пасхи и Таити. В сентябре 1774 г. была открыта Новая Каледония, в ноябре того же года — Южная Георгия.
В Англию первооткрыватели возвращаются в июле 1775 г.
ИНТЕРЕСНЫЙ ФАКТ. В ходе попыток найти неведомую землю команда наткнулась на многолетние льды там, где согласно картам, была Южная земля. Куку удалось доказать, что для колонизации земли сегодняшней Антарктиды непригодны, и мировое сообщество перестало отправлять туда экспедиции. Антарктиду открыли лишь в 1820 г.
Третье путешествие
Третий вояж был задуман для картографирования Северо-Западного прохода, который предположительно соединял Тихий и Атлантический океаны. Экспедиции многих стран пытались пройти через проход, но всегда неудачно — суда либо встречали многометровые слои льда и разворачивались либо погибали. В вояж вновь отправилось два судна — «Resolution» (капитан — Кук) и «Discovery» — Чарльз Клерк.
Путешественники покинули родину летом 1776 г. и отправилась в Кейптаун, оттуда через остров Кергелен и Тасманию, Тонгу и Таити.
В декабре 1777 г. Кук стал первооткрывателем острова Рождества. А всего спустя месяц на карте мореплавателей появилось новое название — Гавайи — остров, открытый Джеймсом Куком в январе 1778 года. Набравшись сил в южных широтах, суда отправились в северные воды. К октябрю 1778 г. суда прошли Берингов пролив, Северный полярный круг и Чукотское море. Натолкнувшись на бескрайние льды, экспедиция решила вернуться в теплые широты и продолжить путь весной. Так команда вернулась на Гавайи.
Отношения между местными жителями и англичанами начались с дружбы и интереса. Туземцы даже приняли Кука за одного из богов. Однако вскоре местные начали воровать все, что могли унести. Попытки вернуть украденное заканчивались вооруженными конфликтами между экипажем и туземцами. Поэтому Кук принял решение покинуть остров 4 февраля. Команде не удалось уплыть далеко из-за шторма, который сильно повредил одно из суден. 10 февраля экспедиция вернулась на Гавайи.
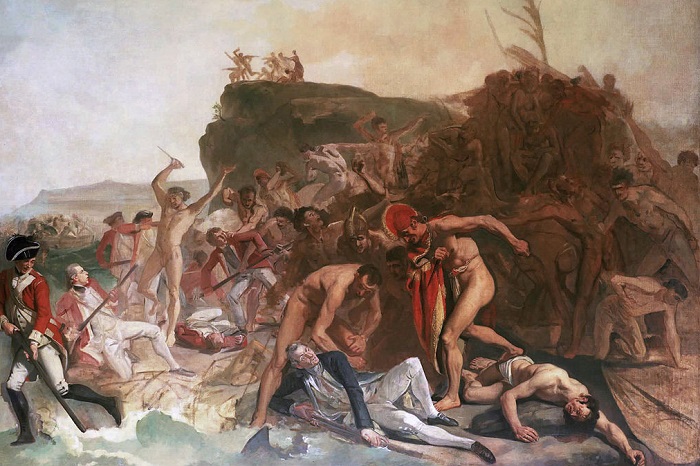
К тому времени местные стали проявлять откровенную враждебность. Кражи продолжались. Капитан решил применить шантаж для возвращения украденного и попытался взять в плен вождя местного племени. При подходе к кораблю англичан встретили несколько тысяч туземцев. Экипаж запаниковал, они пытались пройти к шлюпкам. В суматохе один из аборигенов ударил Кука копьем по голове. Когда тот упал, гавайцы набросились на него с ножами — все хотели поучаствовать в убийстве англичанина. После гибели Кука бразды правления вояжем перешли к капитану «Discovery» Клерку. В отместку за отказ гавайцами отдать тело Кука, англичане сожгли их поселения. Лишь после этого акта агрессии аборигены доставили на борт корзину с головой Кука и несколькими кусками мяса. После инцидента англичане покинули Гавайи и вернулись домой в октябре 1780 г.
Так съели ли туземцы Джеймса Кука?
Доподлинных свидетельств о том, что случилось с телом первооткрывателя, нет. Тем не менее, англичанам вернули лишь часть останков Кука — голову без нижней челюсти и 10 фунтов мяса (примерно 4,5 килограмма).
Занимательные факты о Джеймсе Куке
Семь фактов о Джеймсе Куке, о которых вы не знали:
-
По окончании Семилетней войны Кук женился на англичанке, у них родилось шестеро детей. Пятеро из них умерли в детстве.
-
Школа, в которой учился Кук, переделана в музей и функционирует до сих пор. В музее хранится самая большая коллекция, связанная с первооткрывателем.
-
Ошибочное мнение об открытии Австралии Джеймсом Куком появилось после композиции Владимира Высоцкого, где тот поет о том, как австралийские аборигены съели Кука. На самом деле Кук не открывал Австралию. За столетие до него там побывали испанцы и голландцы, изучившие западную часть материка. Сам Кук исследовал ее восточный берег.
-
Команда Кука была одной из первых, кому Адмиралтейство наказало «дружить» с туземцами и не вступать в конфликты. В то время европейцы взаимодействовали с туземцами лишь через насилие.
-
Капитан Клерк написал в своих дневниках, что туземцы не собирались нападать на англичан. Причиной конфликта стало их беспокойство за судьбу вождя. По мнению команды, в конфликте был виноват Кук и его вызывающее поведение.
-
Кук написал книгу «Три вояжа или капитан Джеймс Кук вокруг света».
-
Кук фактически не открыл ни одного нового континента, но его вклад в картографию был огромен — он нанес на карту десятки обнаруженных им островов и морских путей.
Память о Куке
На Гавайях, где Кук принял смерть от местных жителей, установлен памятник, изображающий капитана. На месте его убийства также установлен обелиск. Такой же обелиск можно увидеть в Кернеле, Австралия.
В память о капитане названы:
-
пролив в Новой Зеландии;
-
островная гряда в Тихом океане;
-
лунный кратер;
-
больница в Англии.
Джеймс Кук — биография
Джеймс Кук – военный моряк, исследователь, путешественник, картограф. Стоял во главе трех кругосветных экспедиций, выполнявших исследование Мирового океана.
Джеймс Кук не открыл ни одного нового континента, океана или морского пути, как другие путешественники в эпоху великих открытий. Однако это не помешало ему занять самое почетное место в ряду других исследователей и географов. Он был скрупулезным до дотошности, поэтому все составленные им карты характеризуются невероятной точностью и аккуратностью. Почти до XIX века все мореплаватели использовали только их. Кука считают личностью, которая достигла всего только благодаря самому себе.
Детство
Джеймс Кук родился в английской деревушке Мартон 27 октября 1728 года. По сохранившимся историческим сведениям, это произошло в семье шотландского батрака. На момент его рождения родители воспитывали четверых детей. В восьмилетнем возрасте мальчик с родителями переселяется в деревушку Грейт Айтон, и начинает посещать школу. В настоящее время там открыт его музей.
В школе Джеймс учился всего пять лет. Потом он начал свою трудовую биографию на ферме, где его папа был управляющим. Восемнадцатилетним юношей Кук поступил на судно «Геркулес» в качестве юнги. Так началась морская карьера будущего великого путешественника и картографа.
Путешествия
Корабли, на которых работал Кук, принадлежали Джону и Генри Уокерам. Когда выпадала свободная минута, Джеймс учил навигацию, географию, астрономию и математику, много читал. На протяжении двух лет он не работал на владельцев судна, побывал в восточной Англии и на Балтике. Потом братья Уокеры позвали его обратно, и предложили стать помощником капитана на судне «Френдшип». После трех лет работы на этой должности, его хотели поставить капитаном, но Кук ответил отказом.
Он решил поступить в Королевский ВМФ обычным матросом, и спустя восемь дней его распределили на судно под названием «Игл». Такое нестандартное решение до сих пор приводит в недоумение некоторых историков, они не понимают, зачем нужно было идти в матросы, если появилась перспектива стать капитаном. Но прошел всего месяц, и Джеймсу предложили боцманскую должность.
В 1756-м, во время Семилетней войны, корабль «Игл» стал участником блокады у берегов Франции. «Игл» победил в бою корабль «Герцог Аквитанский», но получил серьезные повреждения и отбыл в Англию для проведения ремонтных работ.
В 1757-м Кук выдержал экзамен на звание капитана, и получает в свое распоряжение судно «Солебей». Ему в этот день исполнилось 29 лет.
После взятия Квебека, Кук снова получил капитанскую должность, только теперь на корабле «Нортумберленд». Это можно было расценить, как профессиональный успех. Джеймс получил приказ от адмирала, и продолжил составлять карту реки Святого Лаврентия. Этим он занимался вплоть до 1762-го, а напечатали его труды спустя три года, в 1765-м.
Три кругосветных экспедиции
Кук возглавил три кругосветных путешествия, которые сыграли большую роль в представлении о строении мира.
Первая длилась на протяжении трех лет, по официальной версии, ее целью было исследование явления как Венера проходит сквозь Солнце. Но на самом деле Джеймс руководствовался секретными распоряжениями, которые приказывали путешественнику искать место расположения Южного материка.
В те годы сильные государства занимались завоеванием новых колоний, поэтому историки пришли к выводу, что под видом астрономических исследований Кук и его команда ищет новые земли. Экспедиция должна была выполнить еще одно задание – установить берега побережья Австралии с восточной стороны.
В итоге со своей основной задачей экспедиция справилась, однако эти сведения оказались ненужными, потому что содержали неточные показатели.
Материк они тоже не нашли. Открытие Южного материка состоялось в 1820-м, и удалось это русским морякам. Выяснилось, что Новая Зеландия состоит из двух отдельных островов, разделенных проливом(сейчас носит название пролив Кука). Джеймсу и его команде удалось исследовать восточный берег Австрии, и занести его на карту.
Какая конкретная цель ставилась перед Куком во второй экспедиции, неизвестно. Команда занималась исследованием южных морей, и это была настойчивая инициатива самого Джеймса, который не мог успокоиться, и продолжал искать Южный материк. Возможно, что эта инициатива исходила не только от него.
Третья экспедиция должна была найти Северо-Западный водный путь, но с этой задачей команда не справилась. Зато им удалось открыть остров Рождества и Гавайи.
Личная жизнь
В 1762 году Джеймс возвращается в Англию, и в том же году ведет под венец Элизабет Баттс. Личная жизнь известного путешественника сложилась нормально. Жена подарила ему шестерых детей. Первым родился мальчик, которого, как и отца, назвали Джеймсом. Он прожил дольше всех детей Кука. Умер в 31 год. Двое деток умерли еще до наступления семнадцатого дня рождения. Один скончался в четыре года, а двое умерли в младенчестве.
Эти смерти сильно повлияли на Элизабет, хотя она прожила достаточно долгую жизнь. Женщина умерла в 93 года, пережив любимого супруга на 56 лет. Она боготворила Джеймса, любую ситуацию измеряла по его моральному облику. Если ей что-то не нравилось в поведении других людей, она говорила, что господин Кук так никогда не поступал. Перед лицом смерти женщина хотела сжечь письма и бумаги Кука, потому что была твердо уверена, что это слишком личное, чтобы выставлять на всеобщее обозрение. Местом ее упокоения стал семейный склеп в Кембридже.
Смерть
16 января 1779-го года Джеймс Кук достиг берегов Гавайских островов. Жители окружили корабли, и Кук насчитал несколько тысяч туземцев, которые видели в нем Бога.
Вначале отношения экипажа и местных аборигенов складывались хорошо, но вскоре гавайцы стали воровать с суден все, что только можно. Моряки пытались противостоять этому явлению, вступали в драки с местными. С каждым разом противостояние накалялось.
Обстановка продолжала накаляться, и экипаж был вынужден уйти из залива. Однако начался шторм, и корабли получили серьезные повреждения. 10 февраля морякам пришлось вернуться , но к тому времени гавайцы видели в них врагов. Спустя три дня аборигены украли клещи, находившиеся на палубе. Вернуть их не удалось, началось серьезное столкновение.
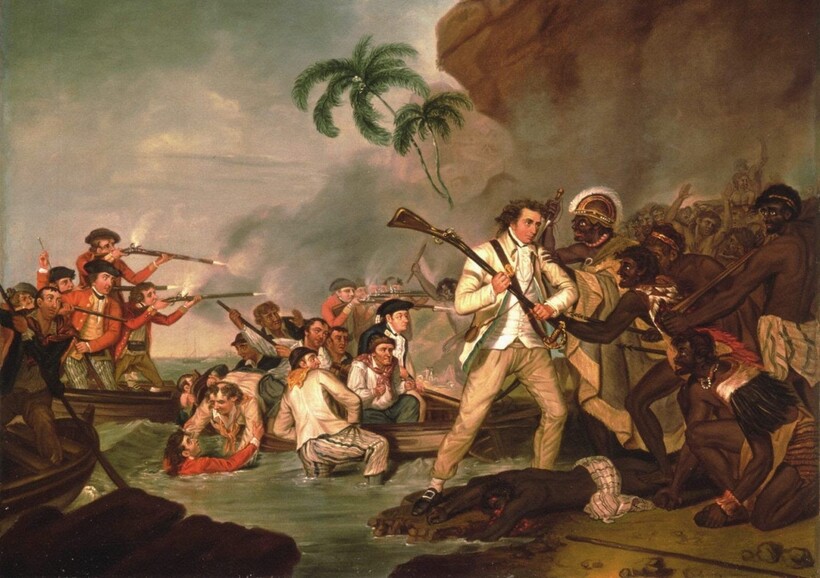
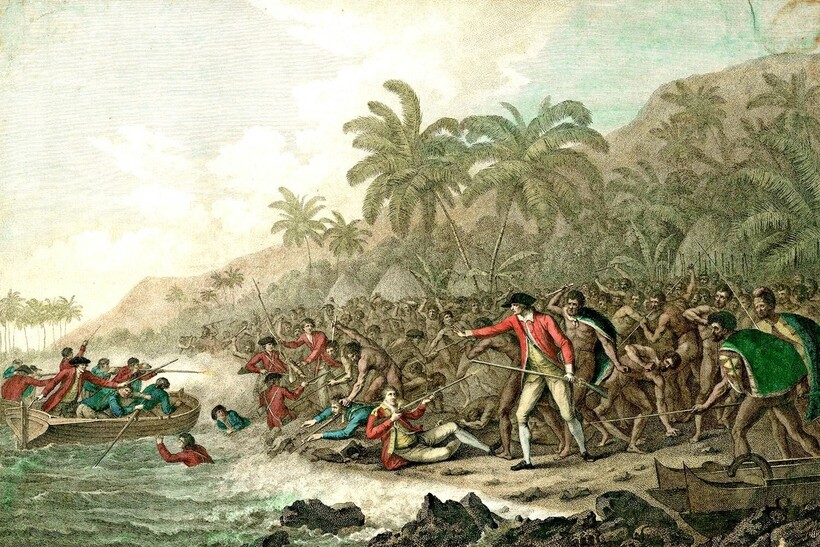
На следующий день моряки обнаружили пропажу баркаса. Кук предпринимал попытки его вернуть, взял вождя в заложники. Джеймс и его люди сопровождали вождя на судно, но тот заупрямился и не пошел. Неизвестно, кто распустил слух о том, что моряки убили кого-то из местных, который и стал причиной для очередной стычки. Кука и четверых матросов схватили гавайцы и съели 14 февраля 1779 года.
Память
В честь великого путешественника и картографа названо много объектов, ему поставили памятники в самых разных городах.
- Пролив, который делит Новую Зеландию и открытый Куком в 1769-м, носит его имя.
- Одному из тихоокеанских архипелагов тоже присвоили имя Джеймса Кука.
- Модуль космического корабля носит имя «Игл» — так называлось первое судно путешественника.
- 10 августа 1932 года в городке Крайстчерч открыли памятник Куку. Эту идею долго вынашивал филантроп и букмекер Мэтью Барнетт. Он стал организатором конкурсного проекта и спонсором для скульптора Уильяма Тезевея. Памятник передал городу безвозмездно.
- В 1935-м имя Джеймса Кука присвоено одному из лунных кратеров.
- В одной из песен Владимира Высоцкого есть упоминание о Джеймсе, и звучит риторический вопрос, зачем аборигены съели Кука.
Большую ценность представляют дневники, написанные лично капитаном. Ими вплотную занимаются исследователи. Биография Кука состоит из массы колоритных эпизодов, а самого путешественника возвели в ранг выдающихся первооткрывателей.
Ссылки
- Страница в Википедии
Для нас важна актуальность и достоверность информации. Если вы обнаружили ошибку или неточность, пожалуйста, сообщите нам. Выделите ошибку и нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Enter.
В этой статье вы найдете краткую биографию и историю путешествий английского мореплавателя и исследователя Мирового океана Джеймса Кука. Благодаря его открытиям были составлены точные карты, которыми моряки пользовались до середины XIX века. Читайте краткую биографию капитана Кука в этой статье.
- 63047
Мореплаватель Джеймс Кук – один из самых известных исследователей Мирового океана XVIII века. Он совершил 3 кругосветных морских путешествия, в ходе которых были составлены карты малоизвестных и редко посещаемых до него частей Ньюфаундленда и восточного побережья Канады, Австралии, Новой Зеландии, западного побережья Северной Америки, Тихого, Индийского и Атлантического океанов.
Карты Джеймса Кука были настолько точными, что все мореплаватели пользовались ими до середины XIX столетия. Все это благодаря его кропотливости и аккуратности в картографии.
Краткая биография
Джеймс Кук родился 27 октября 1728 года в английской деревушке Мартон. Его отец был простым батраком и кормильцем многодетной семьи.
В 1736 году семья переезжает в деревню Грейт Айтон, где Кук начинает посещать в местную школу. После пяти лет учёбы он начинает работать на ферме под началом своего отца, получившего к тому времени должность управляющего. В возрасте восемнадцати лет он нанимается юнгой на торговый бриг-угольщик «Геркулес». Так начинается морская жизнь Джеймса Кука.
Он стал ходить на каботажных судах, перевозивших уголь вдоль берегов Англии и Ирландии. Ему понравилась морская жизнь, он стал хорошим матросом, затем шкипером и вскоре завербовался на военный 60-пушечный корабль «Эгл».
Прилежный самоучка
Джеймс обратил на себя внимание офицеров, он был дисциплинирован, сообразителен и хорошо знал корабельное дело, и его назначили боцманом. В дальнейшем на исследовательских судах ему поручали выполнять разные гидрографические работы — измерять глубины разных рек и у побережий и составлять карты побережий и фарватера.
У Кука не было морского или военного образования. Он учился всему с ходу и очень быстро приобрел авторитет опытного морехода, умелого картографа, капитана.
Первая научная экспедиция
Когда английское правительство в 1768 году решило отправить научную экспедицию в Тихий океан, то выбор пал на знаменитого гидрографа Александра Далримпла. Но тот выставил такие требования, что Адмиралтейство отказалось от его услуг.
Среди предложенных кандидатур был опытный моряк Джеймс Кук. Он и возглавил парусное трехмачтовое судно «Индевор» для поисков новых земель. На тот момент ему исполнилось 40 лет. Первое путешествие Кука продлилось с 1768 по 1771 год.
Предстояло нелегкое путешествие по Тихому океану в сторону южных широт. Его команда состояла из 80 человек, на судно загрузили продовольствия на 18 месяцев пути. В качестве вооружения он взял с собой 20 артиллерийских пушек. С ним вместе отправлялись астрономы, ботаники, врачи.
Секретное задание
Ученые собирались наблюдать прохождение планеты Венера на фоне солнечного диска. Но у Кука было еще одно секретное задание — он должен был отыскать Южный материк (Terra Australis), который предположительно находился на другом краю Земли.
Дело в том, что в распоряжении английского Адмиралтейства имелись испанские карты XVII века, на которых были нанесены острова, расположенные в Южном полушарии. Эти земли следовало приобщить к британской короне. Капитану Джеймсу Куку и его команде было строго предписано уважительно относиться к аборигенам, никаких военных действий против них не производить.
Отплытие состоялось 26 августа 1768 года из Плимута. Курс был взят на архипелаг Таити, от него корабль «Индевор» стал двигаться дальше на юг, где вскоре Кук открыл Новую Зеландию. Там он оставался 6 месяцев и убедился, что этот остров разделен на две части. Затем ему удалось подойти к восточному побережью Австралии. На этом его первая экспедиция закончилась, требовалось возвращаться на родину.
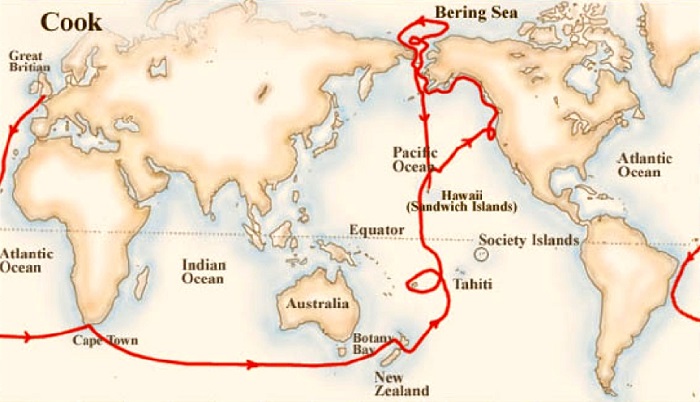
Вторая экспедиция Кука
Вторая экспедиция состоялась в 1772 году и завершилась в 1775 г. Теперь в распоряжение Джеймса Кука были переданы два корабля «Резольюшен» и «Эдвенчер». Отплыли, как и в прошлый раз, из Плимута и взяли направление на Кейптаун. После Кейптауна корабли повернули на юг.
17 января 1773 года впервые экспедиция пересекла Южный полярный круг, но корабли потеряли друг друга. Кук отправился в направлении Новой Зеландии, где они, как договаривались, и встретились. Взяв с собой нескольких островитян, которые согласились помочь в прокладывании маршрута, корабли поплыли далее на юг и снова потеряли друг друга из виду .
Во второй экспедиции Джеймс открыл острова Новая Каледония, Норфолк, Южные Сэндвичевы острова, но из- за льдов найти Южный материк ему не удалось. И он пришел к выводу, что его не существует.
Третье кругосветное путешествие
Третья кругосветная экспедиция Джеймса Кука состоялась в 1776 году и продолжалась почти 3 года – до 1779 года. Снова в его распоряжении оказались два корабля: «Резольюшен» и «Дискавери». На этот раз Кук искал новые земли в северо-западной части Тихого океана, думал найти проход вокруг Северной Америки.
В 1778 году он открыл Гавайские острова, дошел до Берингова пролива и, встретив льды, вернулся на Гавайи. Вечером 14 февраля 1779 года 50-летний капитан Джеймс Кук был убит жителями Гавайских островов в открытой стычке из-за кражи с его судна.
«Увидев, что Кук упал, гавайцы издали победоносный вопль. Тело его тут же втащили на берег, и окружавшая его толпа, жадно выхватывая кинжал друг у друга, принялась наносить ему множество ран, так как каждый хотел принять участие в его уничтожении».
Из дневника лейтенанта Кинга
|
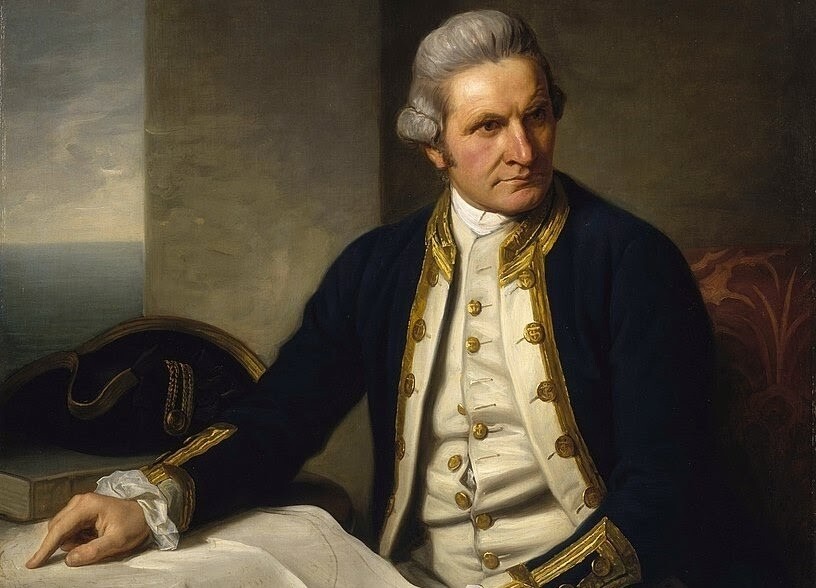
James Cook FRS |
|
|---|---|

Portrait by Sir Nathaniel Dance-Holland, c. 1775, National Maritime Museum |
|
| Born | 7 November [O.S. 27 October] 1728
Marton, North Riding of Yorkshire, England |
| Died | 14 February 1779 (aged 50)
Kealakekua Bay, Hawaiian Kingdom |
| Cause of death | Stab wound |
| Nationality | British |
| Education | Postgate School, Great Ayton |
| Occupation(s) | Explorer, navigator, cartographer |
| Spouse |
Elizabeth Batts (m. ) |
| Children | 6 |
| Military career | |
| Branch | Royal Navy |
| Service years | 1755–1779 |
| Rank | Captain (Post-captain) |
| Battles/wars |
|
| Signature | |
 |
James Cook FRS (7 November 1728[NB 1] – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and to New Zealand and Australia in particular. He made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand.
Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years’ War and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec, which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment for the direction of British overseas exploration, and it led to his commission in 1768 as commander of HMS Endeavour for the first of three Pacific voyages.
In these voyages, Cook sailed thousands of miles across largely uncharted areas of the globe. He mapped lands from New Zealand to Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean in greater detail and on a scale not previously charted by Western explorers. He surveyed and named features, and recorded islands and coastlines on European maps for the first time. He displayed a combination of seamanship, superior surveying and cartographic skills, physical courage, and an ability to lead men in adverse conditions.
Cook was attacked and killed in 1779 during his third exploratory voyage in the Pacific while attempting to kidnap the ruling chief of the island of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu, in order to reclaim a cutter taken from one of his ships after his crew took wood from a burial ground. Whilst there is controversy over Cook’s role as ‘an enabler of colonialism’[1] and the violence associated with his contacts with indigenous peoples, he left a legacy of scientific and geographical knowledge that influenced his successors well into the 20th century, and numerous memorials worldwide have been dedicated to him.
Early life and family
James Cook was born on 7 November 1728 (NS) in the village of Marton in the North Riding of Yorkshire and baptised on 14 November (N.S.) in the parish church of St Cuthbert, where his name can be seen in the church register.[2][3] He was the second of eight children of James Cook (1693–1779), a Scottish farm labourer from Ednam in Roxburghshire, and his locally born wife, Grace Pace (1702–1765), from Thornaby-on-Tees.[2][4][5] In 1736, his family moved to Airey Holme farm at Great Ayton, where his father’s employer, Thomas Skottowe, paid for him to attend the local school. In 1741, after five years’ schooling, he began work for his father, who had been promoted to farm manager. Despite not being formally educated he became capable in mathematics, astronomy and charting by the time of his Endeavour voyage.[6] For leisure, he would climb a nearby hill, Roseberry Topping, enjoying the opportunity for solitude.[7] Cooks’ Cottage, his parents’ last home, which he is likely to have visited, is now in Melbourne, Australia, having been moved from England and reassembled, brick by brick, in 1934.[8]
In 1745, when he was 16, Cook moved 20 miles (32 km) to the fishing village of Staithes, to be apprenticed as a shop boy to grocer and haberdasher William Sanderson.[2] Historians have speculated that this is where Cook first felt the lure of the sea while gazing out of the shop window.[5]
After 18 months, not proving suited for shop work, Cook travelled to the nearby port town of Whitby to be introduced to Sanderson’s friends John and Henry Walker.[8] The Walkers, who were Quakers, were prominent local ship-owners in the coal trade. Their house is now the Captain Cook Memorial Museum. Cook was taken on as a merchant navy apprentice in their small fleet of vessels, plying coal along the English coast. His first assignment was aboard the collier Freelove, and he spent several years on this and various other coasters, sailing between the Tyne and London. As part of his apprenticeship, Cook applied himself to the study of algebra, geometry, trigonometry, navigation and astronomy – all skills he would need one day to command his own ship.[5]
Elizabeth Cook, wife and for 56 years widow of James Cook, by William Henderson, 1830
His three-year apprenticeship completed, Cook began working on trading ships in the Baltic Sea. After passing his examinations in 1752, he soon progressed through the merchant navy ranks, starting with his promotion in that year to mate aboard the collier brig Friendship.[9] In 1755, within a month of being offered command of this vessel, he volunteered for service in the Royal Navy, when Britain was re-arming for what was to become the Seven Years’ War. Despite the need to start back at the bottom of the naval hierarchy, Cook realised his career would advance more quickly in military service and entered the Navy at Wapping on 17 June 1755.[10]
Cook married Elizabeth Batts, the daughter of Samuel Batts, keeper of the Bell Inn in Wapping[11] and one of his mentors, on 21 December 1762 at St Margaret’s Church, Barking, Essex.[12] The couple had six children: James (1763–1794), Nathaniel (1764–1780, lost aboard HMS Thunderer which foundered with all hands in a hurricane in the West Indies), Elizabeth (1767–1771), Joseph (1768–1768), George (1772–1772) and Hugh (1776–1793, who died of scarlet fever while a student at Christ’s College, Cambridge). When not at sea, Cook lived in the East End of London. He attended St Paul’s Church, Shadwell, where his son James was baptised. Cook has no direct descendants – all of his children died before having children of their own.[13]
Start of Royal Navy career
Cook’s first posting was with HMS Eagle, serving as able seaman and master’s mate under Captain Joseph Hamar for his first year aboard, and Captain Hugh Palliser thereafter.[14] In October and November 1755, he took part in Eagle’s capture of one French warship and the sinking of another, following which he was promoted to boatswain in addition to his other duties.[10] His first temporary command was in March 1756 when he was briefly master of Cruizer, a small cutter attached to Eagle while on patrol.[10][15]
In June 1757 Cook formally passed his master’s examinations at Trinity House, Deptford, qualifying him to navigate and handle a ship of the King’s fleet.[16] He then joined the frigate HMS Solebay as master under Captain Robert Craig.[17]
Newfoundland
During the Seven Years’ War, Cook served in North America as master aboard the fourth-rate Navy vessel HMS Pembroke.[18] With others in Pembroke‘s crew, he took part in the major amphibious assault that captured the Fortress of Louisbourg from the French in 1758, and in the siege of Quebec City in 1759. Throughout his service he demonstrated a talent for surveying and cartography and was responsible for mapping much of the entrance to the Saint Lawrence River during the siege, thus allowing General Wolfe to make his famous stealth attack during the 1759 Battle of the Plains of Abraham.[19]
Cook’s surveying ability was also put to use in mapping the jagged coast of Newfoundland in the 1760s, aboard HMS Grenville. He surveyed the northwest stretch in 1763 and 1764, the south coast between the Burin Peninsula and Cape Ray in 1765 and 1766, and the west coast in 1767. At this time, Cook employed local pilots to point out the «rocks and hidden dangers» along the south and west coasts. During the 1765 season, four pilots were engaged at a daily pay of 4 shillings each: John Beck for the coast west of «Great St Lawrence», Morgan Snook for Fortune Bay, John Dawson for Connaigre and Hermitage Bay, and John Peck for the «Bay of Despair».[20]
While in Newfoundland, Cook also conducted astronomical observations, in particular of the eclipse of the sun on 5 August 1766. By obtaining an accurate estimate of the time of the start and finish of the eclipse, and comparing these with the timings at a known position in England it was possible to calculate the longitude of the observation site in Newfoundland. This result was communicated to the Royal Society in 1767.[21]
His five seasons in Newfoundland produced the first large-scale and accurate maps of the island’s coasts and were the first scientific, large scale, hydrographic surveys to use precise triangulation to establish land outlines.[22] They also gave Cook his mastery of practical surveying, achieved under often adverse conditions, and brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and Royal Society at a crucial moment both in his career and in the direction of British overseas discovery. Cook’s maps were used into the 20th century, with copies being referenced by those sailing Newfoundland’s waters for 200 years.[23]
Following on from his exertions in Newfoundland, Cook wrote that he intended to go not only «farther than any man has been before me, but as far as I think it is possible for a man to go».[16]
First voyage (1768–1771)
On 25 May 1768,[24] the Admiralty commissioned Cook to command a scientific voyage to the Pacific Ocean. The purpose of the voyage was to observe and record the 1769 transit of Venus across the Sun which, when combined with observations from other places, would help to determine the distance of the Earth from the Sun.[25] Cook, at age 39, was promoted to lieutenant to grant him sufficient status to take the command.[26][27] For its part, the Royal Society agreed that Cook would receive a one hundred guinea gratuity in addition to his Naval pay.[28]
The expedition sailed aboard HMS Endeavour, departing England on 26 August 1768.[29] Cook and his crew rounded Cape Horn and continued westward across the Pacific, arriving at Tahiti on 13 April 1769, where the observations of the transit were made.[30] However, the result of the observations was not as conclusive or accurate as had been hoped. Once the observations were completed, Cook opened the sealed orders, which were additional instructions from the Admiralty for the second part of his voyage: to search the south Pacific for signs of the postulated rich southern continent of Terra Australis.[31]
Cook then sailed to New Zealand where he mapped the complete coastline, making only some minor errors. With the aid of Tupaia, a Tahitian priest who had joined the expedition, Cook was the first European to communicate with the Māori.[32] However, at least eight Māori were killed in violent encounters.[33] Cook then voyaged west, reaching the southeastern coast of Australia near today’s Point Hicks on 19 April 1770, and in doing so his expedition became the first recorded Europeans to have encountered its eastern coastline.[NB 2]
On 23 April, he made his first recorded direct observation of Aboriginal Australians at Brush Island near Bawley Point, noting in his journal: «… and were so near the Shore as to distinguish several people upon the Sea beach they appear’d to be of a very dark or black Colour but whether this was the real colour of their skins or the C[l]othes they might have on I know not.»[34]
Endeavour continued northwards along the coastline, keeping the land in sight with Cook charting and naming landmarks as he went. On 29 April, Cook and crew made their first landfall on the continent at a beach now known as Silver Beach on Botany Bay (Kamay Botany Bay National Park). Two Gweagal men of the Dharawal / Eora nation opposed their landing and in the confrontation one of them was shot and wounded.[35][36][37]
Cook and his crew stayed at Botany Bay for a week, collecting water, timber, fodder and botanical specimens and exploring the surrounding area. Cook sought to establish relations with the Indigenous population without success.[38][39] At first Cook named the inlet «Sting-Ray Harbour» after the many stingrays found there. This was later changed to «Botanist Bay» and finally Botany Bay after the unique specimens retrieved by the botanists Joseph Banks and Daniel Solander.[40] This first landing site was later to be promoted (particularly by Joseph Banks) as a suitable candidate for situating a settlement and British colonial outpost.[41]
After his departure from Botany Bay, he continued northwards. He stopped at Bustard Bay (now known as Seventeen Seventy) on 23 May 1770. On 24 May, Cook and Banks and others went ashore. Continuing north, on 11 June a mishap occurred when Endeavour ran aground on a shoal of the Great Barrier Reef, and then «nursed into a river mouth on 18 June 1770».[42] The ship was badly damaged, and his voyage was delayed almost seven weeks while repairs were carried out on the beach (near the docks of modern Cooktown, Queensland, at the mouth of the Endeavour River).[5] The crew’s encounters with the local Aboriginal people were mostly peaceful, although following a dispute over green turtles Cook ordered shots to be fired and one local was lightly wounded.[43]
The voyage then continued and at about midday on 22 August 1770, they reached the northernmost tip of the coast and, without leaving the ship, Cook named it York Cape (now Cape York).[44] Leaving the east coast, Cook turned west and nursed his battered ship through the dangerously shallow waters of Torres Strait. Searching for a vantage point, Cook saw a steep hill on a nearby island from the top of which he hoped to see «a passage into the Indian Seas». Cook named the island Possession Island, where he claimed the entire coastline that he had just explored as British territory.[45]
Return to England
Cook returned to England via Batavia (modern Jakarta, Indonesia), where many in his crew succumbed to malaria, and then the Cape of Good Hope, arriving at the island of Saint Helena on 30 April 1771.[46] The ship finally returned to England on 12 July 1771, anchoring in The Downs, with Cook going to Deal.[47]
Interlude
Cook’s journals were published upon his return, and he became something of a hero among the scientific community. Among the general public, however, the aristocratic botanist Joseph Banks was a greater hero.[5] Banks even attempted to take command of Cook’s second voyage but removed himself from the voyage before it began, and Johann Reinhold Forster and his son Georg Forster were taken on as scientists for the voyage. Cook’s son George was born five days before he left for his second voyage.[48]
Second voyage (1772–1775)
Portrait of James Cook by William Hodges, who accompanied Cook on his second voyage
Shortly after his return from the first voyage, Cook was promoted in August 1771 to the rank of commander.[49][50] In 1772, he was commissioned to lead another scientific expedition on behalf of the Royal Society, to search for the hypothetical Terra Australis. On his first voyage, Cook had demonstrated by circumnavigating New Zealand that it was not attached to a larger landmass to the south. Although he charted almost the entire eastern coastline of Australia, showing it to be continental in size, the Terra Australis was believed to lie further south. Despite this evidence to the contrary, Alexander Dalrymple and others of the Royal Society still believed that a massive southern continent should exist.[51]
Cook commanded HMS Resolution on this voyage, while Tobias Furneaux commanded its companion ship, HMS Adventure. Cook’s expedition circumnavigated the globe at an extreme southern latitude, becoming one of the first to cross the Antarctic Circle on 17 January 1773. In the Antarctic fog, Resolution and Adventure became separated. Furneaux made his way to New Zealand, where he lost some of his men during an encounter with Māori, and eventually sailed back to Britain, while Cook continued to explore the Antarctic, reaching 71°10’S on 31 January 1774.[16]
Illustration from the 1815 edition of Cook’s Voyages, depicting Cook watching a human sacrifice in Tahiti c. 1773
Cook almost encountered the mainland of Antarctica but turned towards Tahiti to resupply his ship. He then resumed his southward course in a second fruitless attempt to find the supposed continent. On this leg of the voyage, he brought a young Tahitian named Omai, who proved to be somewhat less knowledgeable about the Pacific than Tupaia had been on the first voyage. On his return voyage to New Zealand in 1774, Cook landed at the Friendly Islands, Easter Island, Norfolk Island, New Caledonia, and Vanuatu.
Before returning to England, Cook made a final sweep across the South Atlantic from Cape Horn and surveyed, mapped, and took possession for Britain of South Georgia, which had been explored by the English merchant Anthony de la Roché in 1675. Cook also discovered and named Clerke Rocks and the South Sandwich Islands («Sandwich Land»). He then turned north to South Africa and from there continued back to England. His reports upon his return home put to rest the popular myth of Terra Australis.[52]
Cook’s second voyage marked a successful employment of Larcum Kendall’s K1 copy of John Harrison’s H4 marine chronometer, which enabled Cook to calculate his longitudinal position with much greater accuracy. Cook’s log was full of praise for this time-piece which he used to make charts of the southern Pacific Ocean that were so remarkably accurate that copies of them were still in use in the mid-20th century.[53]
Upon his return, Cook was promoted to the rank of post-captain and given an honorary retirement from the Royal Navy, with a posting as an officer of the Greenwich Hospital. He reluctantly accepted, insisting that he be allowed to quit the post if an opportunity for active duty should arise.[54] His fame extended beyond the Admiralty; he was made a Fellow of the Royal Society and awarded the Copley Gold Medal for completing his second voyage without losing a man to scurvy.[55] Nathaniel Dance-Holland painted his portrait; he dined with James Boswell; he was described in the House of Lords as «the first navigator in Europe».[16] But he could not be kept away from the sea. A third voyage was planned, and Cook volunteered to find the Northwest Passage. He travelled to the Pacific and hoped to travel east to the Atlantic, while a simultaneous voyage travelled the opposite route.[56]
Third voyage (1776–1779)
Hawaii
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander Omai to Tahiti, or so the public was led to believe. The trip’s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent.[57] After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands.[58][59] After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the «Sandwich Islands» after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.[59]
North America
From the Sandwich Islands, Cook sailed north and then northeast to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He sighted the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming Cape Foulweather, after the bad weather which forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward.[60] He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook’s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove,[61] at the south end of Bligh Island. Relations between Cook’s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial but sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had been acceptable in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot «hosts» essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.[62]
After leaving Nootka Sound in search of the Northwest Passage, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska.[60] In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American northwest coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the west) and Spanish (from the south) exploratory probes of the northern limits of the Pacific.[16]
HMS Resolution and Discovery in Tahiti
By the second week of August 1778, Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed northeast up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice at a latitude of 70°44′ north. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then southeast down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands.[63] He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.[64]
Return to Hawaii
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay on Hawai’i Island, largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook’s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook’s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship.[5][64] Similarly, Cook’s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook’s (and to a limited extent, his crew’s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono.[65] Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook’s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.[64][66]
Death
Marker at the shoreline of Kealakekua Bay near the spot Captain Cook was slain
After a month’s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, Resolution‘s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay, including the theft of wood from a burial ground under Cook’s orders.[67] On 13 February 1779, an unknown group of Hawaiians stole one of Cook’s longboats. By then the Hawaiian people had become «insolent», even with threats to fire upon them.[68] Cook responded to the theft by attempting to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
The following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the king. Cook took the king (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu’s favourite wives, Kanekapolei, and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to the boats. They pleaded with the king not to go. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. At this point, the king began to understand that Cook was his enemy.[68] As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf.[69] He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana’ina) and then stabbed by one of the king’s attendants, Nuaa.[70][71] The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.[70][72]
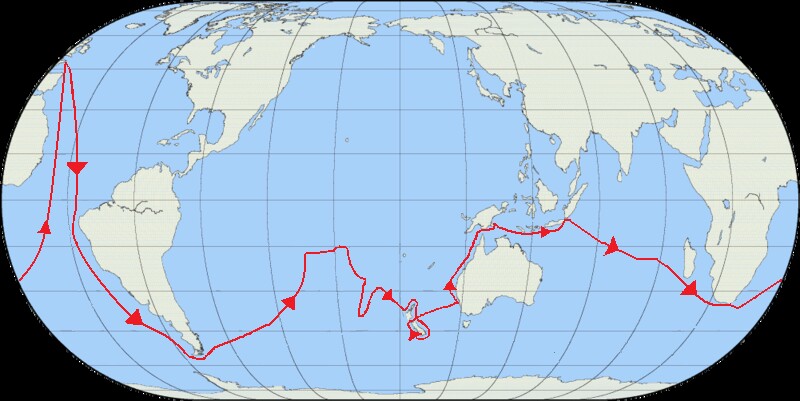
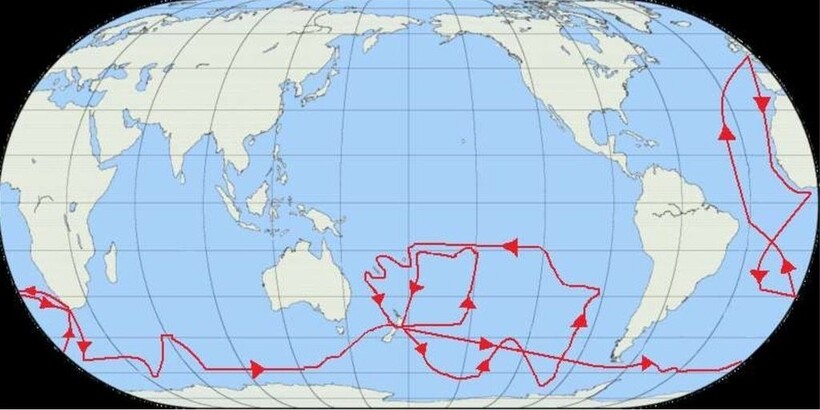
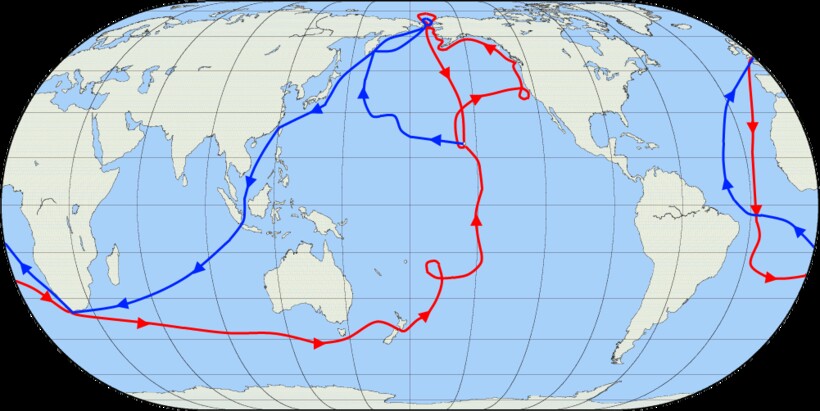
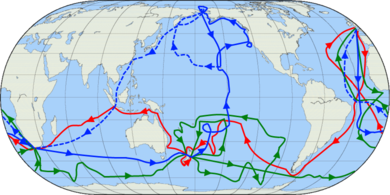
The routes of Captain James Cook’s voyages. The first voyage is shown in red, second voyage in green, and third voyage in blue. The route of Cook’s crew following his death is shown as a dashed blue line.
Aftermath
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled and baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook’s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.[73]
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait.[74] He died of tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook’s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery.[75] The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook’s account of the voyage.[76]
Legacy
Ethnographic collections
The Australian Museum acquired its «Cook Collection» in 1894 from the Government of New South Wales. At that time the collection consisted of 115 artefacts collected on Cook’s three voyages throughout the Pacific Ocean, during the period 1768–80, along with documents and memorabilia related to these voyages. Many of the ethnographic artefacts were collected at a time of first contact between Pacific Peoples and Europeans. In 1935 most of the documents and memorabilia were transferred to the Mitchell Library in the State Library of New South Wales. The provenance of the collection shows that the objects remained in the hands of Cook’s widow Elizabeth Cook, and her descendants, until 1886. In this year John Mackrell, the great-nephew of Isaac Smith, Elizabeth Cook’s cousin, organised the display of this collection at the request of the NSW Government at the Colonial and Indian Exhibition in London. In 1887 the London-based Agent-General for the New South Wales Government, Saul Samuel, bought John Mackrell’s items and also acquired items belonging to the other relatives Reverend Canon Frederick Bennett, Mrs Thomas Langton, H.M.C. Alexander, and William Adams. The collection remained with the Colonial Secretary of NSW until 1894, when it was transferred to the Australian Museum.[77]
Navigation and science
Cook’s 12 years sailing around the Pacific Ocean contributed much to Europeans’ knowledge of the area. Several islands, such as the Hawaiian group, were encountered for the first time by Europeans, and his more accurate navigational charting of large areas of the Pacific was a major achievement.[78] To create accurate maps, latitude and longitude must be accurately determined. Navigators had been able to work out latitude accurately for centuries by measuring the angle of the sun or a star above the horizon with an instrument such as a backstaff or quadrant. Longitude was more difficult to measure accurately because it requires precise knowledge of the time difference between points on the surface of the earth. The Earth turns a full 360 degrees relative to the sun each day. Thus longitude corresponds to time: 15 degrees every hour, or 1 degree every 4 minutes.[citation needed] Cook gathered accurate longitude measurements during his first voyage from his navigational skills, with the help of astronomer Charles Green, and by using the newly published Nautical Almanac tables, via the lunar distance method – measuring the angular distance from the moon to either the sun during daytime or one of eight bright stars during night-time to determine the time at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, and comparing that to his local time determined via the altitude of the sun, moon, or stars.
On his second voyage, Cook used the K1 chronometer made by Larcum Kendall, which was the shape of a large pocket watch, 5 inches (13 cm) in diameter. It was a copy of the H4 clock made by John Harrison, which proved to be the first to keep accurate time at sea when used on the ship Deptford‘s journey to Jamaica in 1761–62.[79] He succeeded in circumnavigating the world on his first voyage without losing a single man to scurvy, an unusual accomplishment at the time. He tested several preventive measures, most importantly the frequent replenishment of fresh food.[80] For presenting a paper on this aspect of the voyage to the Royal Society he was presented with the Copley Medal in 1776.[81][82] Cook became the first European to have extensive contact with various people of the Pacific. He correctly postulated a link among all the Pacific peoples, despite their being separated by great ocean stretches (see Malayo-Polynesian languages). Cook theorised that Polynesians originated from Asia, which scientist Bryan Sykes later verified.[83] In New Zealand the coming of Cook is often used to signify the onset of the colonisation[5][8]
which officially started more than 70 years after his crew became the second group of Europeans to visit that archipelago.
Cook carried several scientists on his voyages; they made significant observations and discoveries. Two botanists, Joseph Banks and the Swede Daniel Solander, sailed on the first voyage. The two collected over 3,000 plant species.[84] Banks subsequently strongly promoted British settlement of Australia,[85][86] leading to the establishment of New South Wales as a penal settlement in 1788. Artists also sailed on Cook’s first voyage. Sydney Parkinson was heavily involved in documenting the botanists’ findings, completing 264 drawings before his death near the end of the voyage. They were of immense scientific value to British botanists.[5][87] Cook’s second expedition included William Hodges, who produced notable landscape paintings of Tahiti, Easter Island, and other locations. Several officers who served under Cook went on to distinctive accomplishments. William Bligh, Cook’s sailing master, was given command of HMS Bounty in 1787 to sail to Tahiti and return with breadfruit. Bligh became known for the mutiny of his crew, which resulted in his being set adrift in 1789. He later became Governor of New South Wales, where he was the subject of another mutiny—the 1808 Rum Rebellion.[88] George Vancouver, one of Cook’s midshipmen, led a voyage of exploration to the Pacific Coast of North America from 1791 to 1794.[89] In honour of Vancouver’s former commander, his ship was named Discovery. George Dixon, who sailed under Cook on his third expedition, later commanded his own.[90] Henry Roberts, a lieutenant under Cook, spent many years after that voyage preparing the detailed charts that went into Cook’s posthumous atlas, published around 1784.
Cook’s contributions to knowledge gained international recognition during his lifetime. In 1779, while the American colonies were fighting Britain for their independence, Benjamin Franklin wrote to captains of colonial warships at sea, recommending that if they came into contact with Cook’s vessel, they were to «not consider her an enemy, nor suffer any plunder to be made of the effects contained in her, nor obstruct her immediate return to England by detaining her or sending her into any other part of Europe or to America; but that you treat the said Captain Cook and his people with all civility and kindness … as common friends to mankind.»[91]
Memorials
A U.S. coin, the 1928 Hawaii Sesquicentennial half-dollar, carries Cook’s image. Minted for the 150th anniversary of his discovery of the islands, its low mintage (10,008) has made this example of an early United States commemorative coin both scarce and expensive.[92] The site where he was killed in Hawaii was marked in 1874 by a white obelisk. This land, although in Hawaii, was deeded to the United Kingdom by Princess Likelike and her husband, Archibald Scott Cleghorn, to the British Consul to Hawaii, James Hay Wodehouse, in 1877.[93][94][failed verification] A nearby town is named Captain Cook, Hawaii; several Hawaiian businesses also carry his name. The Apollo 15 Command/Service Module Endeavour was named after Cook’s ship, HMS Endeavour,[95] as was the Space Shuttle Endeavour.[96] In addition, the first Crew Dragon capsule flown by SpaceX was named for Endeavour.[97] Another shuttle, Discovery, was named after Cook’s HMS Discovery.[98]
The first institution of higher education in North Queensland, Australia, was named after him, with James Cook University opening in Townsville in 1970.[99] Numerous institutions, landmarks and place names reflect the importance of Cook’s contributions, including the Cook Islands, Cook Strait, Cook Inlet and the Cook crater on the Moon.[100] Aoraki / Mount Cook, the highest summit in New Zealand, is named for him.[101] Another Mount Cook is on the border between the U.S. state of Alaska and the Canadian Yukon territory, and is designated Boundary Peak 182 as one of the official Boundary Peaks of the Hay–Herbert Treaty.[102] A larger-than-life statue of Cook upon a column stands in Hyde Park located in the centre of Sydney. A large aquatic monument is planned for Cook’s landing place at Botany Bay, Sydney.[103]
One of the earliest monuments to Cook in the United Kingdom is located at The Vache, erected in 1780 by Admiral Hugh Palliser, a contemporary of Cook and one-time owner of the estate.[104] A large obelisk was built in 1827 as a monument to Cook on Easby Moor overlooking his boyhood village of Great Ayton,[105] along with a smaller monument at the former location of Cook’s cottage.[106] There is also a monument to Cook in the church of St Andrew the Great, St Andrew’s Street, Cambridge, where his sons Hugh, a student at Christ’s College, and James were buried. Cook’s widow Elizabeth was also buried in the church and in her will left money for the memorial’s upkeep. The 250th anniversary of Cook’s birth was marked at the site of his birthplace in Marton by the opening of the Captain Cook Birthplace Museum, located within Stewart Park (1978). A granite vase just to the south of the museum marks the approximate spot where he was born.[107] Tributes also abound in post-industrial Middlesbrough, including a primary school,[108] shopping square[109] and the Bottle ‘O Notes, a public artwork by Claes Oldenburg, that was erected in the town’s Central Gardens in 1993. Also named after Cook is James Cook University Hospital, a major teaching hospital which opened in 2003 with a railway station serving it called James Cook opening in 2014.[110]
The Royal Research Ship RRS James Cook was built in 2006 to replace the RRS Charles Darwin in the UK’s Royal Research Fleet,[111] and Stepney Historical Trust placed a plaque on Free Trade Wharf in the Highway, Shadwell to commemorate his life in the East End of London. A statue erected in his honour can be viewed near Admiralty Arch on the south side of The Mall in London. In 2002, Cook was placed at number 12 in the BBC’s poll of the 100 Greatest Britons.[112]
In 1959, the Cooktown Re-enactment Association first performed a re-enactment of Cook’s 1770 landing at the site of modern Cooktown, Australia, and have continued the tradition each year, with the support and participation of many of the local Guugu Yimithirr people.[113]
Culture
Cook was a subject in many literary creations.
Letitia Elizabeth Landon, a popular poet known for her sentimental romantic poetry,[114] published a poetical illustration to a portrait of Captain Cook in 1837.[115]
In 1931, Kenneth Slessor’s poem «Five Visions of Captain Cook» was the «most dramatic break-through» in Australian poetry of the 20th century according to poet Douglas Stewart.[116]
The Australian slang phrase «Have a Captain Cook» means to have a look or conduct a brief inspection.[117]
Cook appears as a symbolic and generic figure in several Aboriginal myths, often from regions where Cook did not encounter Aboriginal people. Maddock states that Cook is usually portrayed as the bringer of Western colonialism to Australia and is presented as a villain who brings immense social change.[118]
Controversy
Statue of James Cook, Hyde Park, Sydney. The rear inscription reads: «Discovered this territory, 1770».
The period 2018 to 2021 marked the 250th anniversary of Cook’s first voyage of exploration. A number of countries, including Australia and New Zealand, arranged official events to commemorate the voyage[119][120] leading to widespread public debate about Cook’s legacy and the violence associated with his contacts with Indigenous peoples.[1][121] In the leadup to the commemorations, various memorials to Cook in Australia and New Zealand were vandalised and there were public calls for their removal or modification due to their alleged promotion of colonialist narratives.[122][123] On 1 July 2021, a statue of James Cook in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, was torn down following an earlier peaceful protest about the deaths of Indigenous residential school children in Canada.[124] There were also campaigns for the return of Indigenous artefacts taken during Cook’s voyages (see Gweagal shield).[125]
Alice Proctor argues that the controversies over public representations of Cook and the display of Indigenous artefacts from his voyages are part of a broader debate over the decolonisation of museums and public spaces and resistance to colonialist narratives.[126] While a number of commentators argue that Cook was an enabler of British colonialism in the Pacific,[1][127] Geoffrey Blainey, among others, notes that it was Banks who promoted Botany Bay as a site for colonisation after Cook’s death.[128] Robert Tombs defended Cook, arguing «He epitomized the Age of Enlightenment in which he lived» and in conducting his first voyage «was carrying out an enlightened mission, with instructions from the Royal Society to show ‘patience and forbearance’ towards native peoples».[129]
See also
- New Zealand places named by James Cook
- Australian places named by James Cook
- European and American voyages of scientific exploration
- Exploration of the Pacific
- List of places named after Captain James Cook
- List of sea captains
- Death of Cook (paintings)
References
Notes
- ^ Old Style date: 27 October
- ^ At this time, the International Date Line had yet to be established, so the dates in Cook’s journal are a day earlier than those accepted today.
Citations
- ^ a b c Daley, Paul (29 April 2020). «Commemorating Captain James Cook’s arrival, Australia should not omit his role in the suffering that followed». The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 16 March 2021.
- ^ a b c Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 25
- ^ Robson 2009, p. 2
- ^ Stamp 1978, p. 1
- ^ a b c d e f g h Collingridge 2003
- ^ Frost, Alan (19 October 2018). Mutiny, Mayhem, Mythology: Bounty’s Enigmatic Voyage. Sydney University Press. p. 255. ISBN 978-1-74332-587-2. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 15
- ^ a b c Horwitz 2003
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 11
- ^ a b c Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 27
- ^ «Famous 18th century people in Barking and Dagenham: James Cook and Dick Turpin» (PDF). London Borough of Barking and Dagenham. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 June 2012. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ Robson 2009, pp. 120–21
- ^ Stamp 1978, p. 138
- ^ Robson 2009, pp. 19–25
- ^ McLynn 2011, p. 21
- ^ a b c d e Williams, Glyn (17 February 2011). «Captain Cook: Explorer, Navigator and Pioneer». BBC. Archived from the original on 19 August 2011. Retrieved 5 September 2011.
- ^ Capper, Paul (1985–1996). «The Captain Cook Society: Cook’s Log». Life in the Royal Navy (1755–1767). Archived from the original on 21 July 2012. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Kemp & Dear 2005
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 19
- ^ Whiteley, William (1975). «James Cook in Newfoundland 1762–1767» (PDF). Newfoundland Historical Society Pamphlet Number 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2013. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
- ^ Cook, James; Bevis, J. (1 January 1767). «An Observation of an Eclipse of the Sun at the Island of New-Found-Land, August 5, 1766, by Mr. James Cook, with the Longitude of the Place of Observation Deduced from It». Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 57: 215–216. doi:10.1098/rstl.1767.0025.
- ^ Government of Canada (2012). «Captain James Cook R.N.» Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada. Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 32
- ^ Kippis, Andrew (1788). Narrative of the voyages round the world, performed by Captain James Cook; with an account of his life during the previous and intervening periods. Chapter 2. Archived from the original on 3 October 2018. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 95
- ^ Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 30
- ^ Beazley, Charles Raymond (1911). «Cook, James» . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 71.
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, p. cix
- ^ «The Sydney Morning Herald». National Library of Australia. 2 May 1931. p. 12. Retrieved 4 September 2012.
- ^ «BBC – History – Captain James Cook». Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ^ «Secret Instructions to Captain Cook, 30 June 1768» (PDF). National Archives of Australia. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 April 2020. Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ^ Salmond, Anne (1991). Two worlds : first meetings between Māori and Europeans, 1642–1772. Auckland, N.Z.: Viking. ISBN 0-670-83298-7. OCLC 26545658.
- ^ Beaglehole (1974). pp. 198-200, 202, 205-07
- ^ «Cook’s Journal: Daily Entries, 22 April 1770». Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Voices heard but not understood». Gujaga Foundation. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ^ «Cook’s Journal: Daily Entries, 29 April 1770». southseas.nla.gov.au. South Seas. Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- ^ Blainey (2020). pp. 141-43
- ^ FitzSimons, Peter (2019). James Cook : the story behind the man who mapped the world. Sydney, NSW. ISBN 978-0-7336-4127-5. OCLC 1109734011.
- ^ Blainey (2020). pp. 146-57
- ^ Beaglehole (1974). p. 230
- ^ Blainey (2020). p. 287
- ^ Robson 2004, p. 81
- ^ Blainey, Geoffrey (2020) pp 220-21
- ^ Cook, James (21 August 1770). «Cook’s Journal: Daily Entries». National Library of Australia. Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 28 August 2020.
- ^ Cook, James, Journal of the HMS Endeavour, 1768–1771, National Library of Australia, Manuscripts Collection, MS 1, 22 August 1770
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, p. 468
- ^ «The First Voyage (1768–1771)». The Captain Cook Society (CCS). Archived from the original on 3 April 2020. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
- ^ «Captain Cook: Obsession & Discovery. (Part 2 of 4) – Britain on DocuWatch – free streaming British history documentaries». 2011. Archived from the original on 7 April 2013. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 180
- ^ McLynn 2011, p. 167
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 182
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 263
- ^ «Captain James Cook: His voyages of exploration and the men that accompanied him». National Maritime Museum. Archived from the original on 21 April 2007. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- ^ Beaglehole 1974, p. 444
- ^ Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 79
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 268
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 327
- ^ Fish, Shirley (2011). The Manila-Acapulco Galleons : The Treasure Ships of the Pacific: With An Annotated List of the Transpacific Galleons 1565–1815. AuthorHouse. pp. 360–. ISBN 978-1-4567-7543-8. Archived from the original on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ a b Collingridge 2003, p. 380
- ^ a b Hayes 1999, pp. 42–43
- ^ «Resolution Cove». BC Geographical Names. Retrieved 6 March 2013.
- ^ Fisher 1979
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, pp. 615–23
- ^ a b c Obeyesekere 1992
- ^ Sahlins 1985
- ^ Obeyesekere 1997
- ^ Sparks, Jared (1847). Life of John Ledyard, American Traveller. C. C. Little and J. Brown. pp. 136–139. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- ^ a b Obeyesekere 1997, pp. 310–
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 410
- ^ a b Samwell, David; Townsend, Ebenezer (Jr); Gilbert, George; Hawaiian Historical Society; Ingraham, Joseph; Meares, John; Cartwright, Bruce (1791). Extracts from Voyages Made in the Years 1788 and 1789, from China to the Northwest Coast of America: With an Introductory Narrative of a Voyage Performed in 1786, from Bengal in the Ship «Nootka». Paradise of the Pacific Press. p. 76. Archived from the original on 18 May 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ Dibble, Sheldon (1843). History of the Sandwich Islands. Lahainaluna: Press of the Mission Seminary. p. 61.
- ^ «Muster for HMS Resolution during the third Pacific voyage, 1776–1780» (PDF). Captain Cook Society. 15 October 2012. p. 20. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 413
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 412
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 423
- ^ «Better Conceiv’d than Describ’d: the life and times of Captain James King (1750–84), Captain Cook’s Friend and Colleague. Steve Ragnall. 2013». The Captain Cook Society (CCS). Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ^ Thomsett, Sue. «Cook Collection, History of Acquisition». Electronic Museum Narrative. Australian Museum. Archived from the original on 18 February 2013. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ Cook, James; Clerke, Charles; Gore, John; King, James (1784). A voyage to the Pacific Ocean … – Google Books. Vol. 2. London: W. and A. Strahan. Archived from the original on 29 March 2014. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- ^ «Captain Cook – Cook’s Chronometer – English and Media Literacy, Documentaries». dl.nfsa.gov.au. 2011. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ Fernandez-Armesto 2006, p. 297
- ^ Stamp 1978, p. 105
- ^ Cook, Captain James (1767). «The Method Taken for Preserving the Health of the Crew of His Majesty’s Ship the Resolution during Her Late Voyage Round the World». Philosophical Transactions. 66: 402–06. doi:10.1098/rstl.1776.0023. S2CID 186212653. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ Sykes 2001
- ^ «The Endeavour Botanical Illustrations at the Natural History Museum». Natural History Museum. 2011. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Sir Joseph Banks». BBC. 2011. Archived from the original on 25 January 2012. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ Gilbert, L. A. Solander, Daniel (1733–1782). Australian Dictionary of Biography, National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. Archived from the original on 19 September 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «The Endeavour Botanical Illustrations at the Natural History Museum». Natural History Museum. 2011. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Biography: William Bligh | Royal Naval Museum at Portsmouth Historic Dockyard». royalnavalmuseum.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 9 December 2013. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ Phillips, Nan. Vancouver, George (1757–1798). Australian Dictionary of Biography. National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. Archived from the original on 15 August 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ Gough, Barry M. (1979). «Dixon, George». In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. IV (1771–1800) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ Franklin, Benjamin (1837). The works of Benjamin Franklin. Tappan, Whittemore, and Mason. pp. 123–24. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «Hawaii Sesquicentennial Half Dollar». coinsite.com. 2011. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ Gray, Chris (11 November 2000). «Captain Cook’s little corner of Hawaii under threat from new golf». The Independent. Archived from the original on 6 May 2018. Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ^ Coulter, John Wesley (June 1964). «Great Britain in Hawaii: The Captain Cook Monument». The Geographical Journal. London: The Royal Geographical Society. 130 (2): 256–261. doi:10.2307/1794586. JSTOR 1794586.
- ^ «Call Signs». NASA. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- ^ «Space Shuttle Endeavour». John F. Kennedy Space Center website. NASA. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- ^ «Astronauts name SpaceX spaceship ‘Endeavour’ after retired shuttle». 30 May 2020. Archived from the original on 3 June 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
- ^ «Space Shuttle Discovery». John F. Kennedy Space Center website. NASA. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- ^ «About James Cook University». James Cook University. 2011. Archived from the original on 20 December 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ «Planetary Names: Crater, craters: Cook on Moon». Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS/NASA. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Aoraki Mount Cook National Park & Mt Cook Village, New Zealand». Archived from the original on 1 October 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Map of Mount Cook, Yukon, Mountain – Canada Geographical Names Maps». Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Visentin, Lisa (28 April 2018). «Sydney to get new Captain Cook memorial as part of $50m revamp». The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- ^ «CCS – Cook Monument at the Vache, Chalfont St Giles – Access Restored». Archived from the original on 5 February 2012. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «Great Ayton – Captain Cook’s Monument». Archived from the original on 27 October 2011. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ^ «Captain Cook». The Sydney Morning Herald. NSW: National Library of Australia. 26 January 1935. p. 16. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ «The Captain Cook Birthplace Museum, Marton, Middlesbrough, UK». captcook-ne.co.uk. 2011. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Captain Cook Primary School». BBC. 2 December 2004. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Captain Cook Shopping Square». Captaincookshopping.com. Archived from the original on 28 March 2010. Retrieved 8 March 2010.
- ^ «Captain Cook and the Captain Cook Trail». Archived from the original on 6 September 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «RRS James Cook». Nautical Environment Research Council. 2011. Archived from the original on 3 July 2012. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ «BBC – Great Britons – Top 100». Internet Archive. Archived from the original on 4 December 2002. Retrieved 19 July 2017.
- ^ Kim, Sharnie; Stephen, Adam (19 June 2020). «Cooktown’s Indigenous people help commemorate 250 years since Captain Cook’s landing with re-enactment». ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 6 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ Jacolbe, Jessica (23 May 2019). «Life of Forgotten Poet Letitia Elizabeth Landon». Jstor Daily. Retrieved 9 October 2022.
- ^ Landon, Letitia Elizabeth (1837). «portrait». Fisher’s Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1838. Fisher, Son & Co.Landon, Letitia Elizabeth (1837). «poetical illustration». Fisher’s Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1838. Fisher, Son & Co. p. 23.
- ^ Herbert C. Jaffa, Kenneth Slessor: A Critical Study, Angus & Robertson, Sydney, 1977, p. 20.
- ^ Khoury, Matt (12 July 2017). «Australian slang: 33 phrases to help you talk like an Aussie». CNN. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Maddock, K. (1988). «Myth, History and a Sense of Oneself». In Beckett, J. R. (ed.). Past and Present: The Construction of Aboriginality. Canberra: Aboriginal Studies Press. pp. 11–30. ISBN 0-85575-190-8.
- ^ «250th anniversary of Captain Cook’s voyage to Australia». Australian Government, Office for the Arts. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ «Tuia Enounters 250». Archived from the original on 6 March 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ Roy, Eleanor Ainge (8 October 2019). «New Zealand wrestles with 250th anniversary of James Cook’s arrival». The Guardian. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ «Australia debates Captain Cook ‘discovery’ statue». BBC News. 23 August 2017. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ «Captain James Cook statue defaced in Gisborne». nzherald.co.nz. 13 June 2020. Archived from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 16 March 2021.
- ^ «Capt. James Cook statue recovered from Victoria Harbour; what’s next is undecided». Times Colonist. 3 July 2021. Archived from the original on 3 July 2021. Retrieved 4 July 2021.
- ^ «Shots Fired». ABC Radio National. 13 November 2020. Archived from the original on 7 March 2021. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ Proctor, Alice (2020) Chs 11, 21; pp 255-62 and passim
- ^ Proctor, Alice (2020). The Whole Picture: The colonial story of the art in our museums and why we need to talk about it. London: Cassell. p. 243. ISBN 9781-78840-1-555.
- ^ Blainey, Geoffrey (2020). Captain Cook’s Epic Voyage: the strange quest for a missing continent. Australia: Viking. p. 287. ISBN 978-1-76089-509-9.
- ^ Tombs, Robert (4 February 2021). «Captain Cook wasn’t a ‘genocidal’ villain. He was a true Enlightenment man». The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
Bibliography
- Beaglehole, J. C., ed. (1968). The Journals of Captain James Cook on His Voyages of Discovery. Vol. I: The Voyage of the Endeavour 1768–1771. Cambridge University Press. OCLC 223185477.
- Beaglehole, John Cawte (1974). The Life of Captain James Cook. A & C Black. ISBN 978-0-7136-1382-7.
- Collingridge, Vanessa (2003). Captain Cook: The Life, Death and Legacy of History’s Greatest Explorer. Ebury Press. ISBN 978-0-09-188898-5.
- Fernandez-Armesto, Felipe (2006). Pathfinders: A Global History of Exploration. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-06259-5.
- Fisher, Robin (1979). Captain James Cook and his times. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-7099-0050-4.
- Hayes, Derek (1999). Historical Atlas of the Pacific Northwest: Maps of exploration and Discovery. Sasquatch Books. ISBN 978-1-57061-215-2.
- Horwitz, Tony (October 2003). Blue Latitudes: Boldly Going Where Captain Cook Has Gone Before. Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-0-7475-6455-3.
- Hough, Richard (1994). Captain James Cook. Hodder and Stoughton. ISBN 978-0-340-82556-3.
- Kemp, Peter; Dear, I. C. B. (2005). The Oxford Companion to Ships and the Sea. OUP. ISBN 978-0-19-860616-1.
- Kippis, Andrew (1788). Narrative of the voyages round the world, performed by Captain James Cook; with an account of his life during the previous and intervening periods. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- McLynn, Frank (2011). Captain Cook: Master of the Seas. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-11421-8.
- Moorehead, Alan (1966). Fatal Impact: An Account of the Invasion of the South Pacific, 1767–1840. H Hamilton. ISBN 978-0-241-90757-3.
- Mundle, Rob (2013). Cook: from Sailor to Legend. ABC Books. ISBN 978-1-46070-061-7.
- Obeyesekere, Gananath (1992). The Apotheosis of Captain Cook: European Mythmaking in the Pacific. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691056807.
- Obeyesekere, Gananath (1997). The Apotheosis of Captain Cook: European Mythmaking in the Pacific (PDF). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-05752-1.
With new preface and afterword replying to criticism from Sahlins
- Rigby, Nigel; van der Merwe, Pieter (2002). Captain Cook in the Pacific. National Maritime Museum, London. ISBN 978-0-948065-43-9.
- Robson, John (2004). The Captain Cook Encyclopædia. Random House Australia. ISBN 978-0-7593-1011-7.
- Robson, John (2009). Captain Cook’s War and Peace: The Royal Navy Years 1755–1768. University of New South Wales Press. ISBN 978-1-74223-109-9.
- Sahlins, Marshall David (1985). Islands of history. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-73358-6.
- Sahlins, Marshall David (1995). How «Natives» Think: About Captain Cook, for example. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-73368-5.
- Sidney, John Baker (1981). The Australian Language: An Examination of the English Language and English Speech as Used in Australia, from Convict Days to the Present. Melbourne: Sun Books. ISBN 978-0-7251-0382-8.
- Stamp, Tom and Cordelia (1978). James Cook Maritime Scientist. Whitby: Caedmon of Whitby Press. ISBN 978-0-905355-04-7.
- Sykes, Bryan (2001). The Seven Daughters of Eve. Norton Publishing: New York City and London. ISBN 978-0-393-02018-2.
- Wagner, A. R. (1972). Historic Heraldry of Britain. London: Phillimore & Co Ltd. ISBN 978-0-85033-022-9.
- Wharton, W. J. L. (1893). Captain Cook’s Journal during his first voyage round the world made in H.M. Bark «Endeavour» 1768–71. Archived from the original on 22 March 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
Further reading
- Aughton, Peter (2002). Endeavour: The Story of Captain Cook’s First Great Epic Voyage. London: Cassell & Co. ISBN 978-0-304-36236-3.
- Beazley, Charles Raymond (1911). «Cook, James» . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). pp. 71–72.
- Edwards, Philip, ed. (2003). James Cook: The Journals. London: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-043647-1.
Prepared from the original manuscripts by J. C. Beaglehole 1955–67
- Forster, Georg, ed. (1986). A Voyage Round the World. Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3-05-000180-7.
Published first 1777 as: A Voyage round the World in His Britannic Majesty’s Sloop Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years, 1772, 3, 4, and 5
- Hawkesworth, John; Byron, John; Wallis, Samuel; Carteret, Philip; Cook, James; Banks, Joseph (1773), An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavour drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, esq, London Printed for W. Strahan and T. Cadell, Volume I, Volume II–III.
- Igler, David (2013). The Great Ocean: Pacific Worlds from Captain Cook to the Gold Rush. New York: Oxford U.P.[ISBN missing]
- Kippis, Andrew (1904). The Life and Voyages of Captain James Cook. George Newnes, London & Charles Scribner’s Sons, New York.
- Richardson, Brian. (2005) Longitude and Empire: How Captain Cook’s Voyages Changed the World (University of British Columbia Press.) ISBN 0-7748-1190-0.
- Sydney Daily Telegraph (1970) Captain Cook: His Artists – His Voyages The Sydney Daily Telegraph Portfolio of Original Works by Artists who sailed with Captain Cook. Australian Consolidated Press, Sydney
- Thomas, Nicholas The Extraordinary Voyages of Captain James Cook. Walker & Co., New York. ISBN 0-8027-1412-9 (2003)
- Uglow, Jenny, «Island Hopping» (review of Captain James Cook: The Journals, selected and edited by Philip Edwards, London, Folio Society, three volumes and a chart of the voyages, 1,309 pp.; and William Frame with Laura Walker, James Cook: The Voyages, McGill-Queen University Press, 224 pp.), The New York Review of Books, vol. LXVI, no. 2 (7 February 2019), pp. 18–20.
- Villiers, Alan (Summer 1956–57). «James Cook, Seaman». Quadrant. 1 (1): 7–16.[ISBN missing]
- Williams, Glyndwr, ed. (1997). Captain Cook’s Voyages: 1768–1779. London: The Folio Society.
- Withey, Lynne. Voyages of discovery: Captain Cook and the exploration of the Pacific (Univ of California Press, 1989).[ISBN missing]
External links
- Captain Cook Society
- Captain Cook historic plaque, Halifax
- «Explorer, navigator, coloniser: revisit Captain Cook’s legacy with the click of a mouse». The Conversation. 29 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- «Articles on Captain Cook». The Conversation. 2017–2020. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
Captain Cook., a poetical illustration by Letitia Elizabeth Landon in Fisher’s Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1838.
Biographical dictionaries
- «Cook, James (1728–1779)». Australian Dictionary of Biography (online ed.). National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. 1966. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- Williams, Glyndwr (1979). «Cook, James». In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. IV (1771–1800) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- Mackay, David. «Cook, James». Dictionary of New Zealand Biography. Ministry for Culture and Heritage.
Journals
- The Endeavour journal (1) and The Endeavour journal (2), as kept by James Cook – digitised and held by the National Library of Australia
- The South Seas Project: maps and online editions of the Journals of James Cook’s First Pacific Voyage, 1768–1771. Includes full text of journals kept by Cook, Joseph Banks and Sydney Parkinson, as well as the complete text of John Hawkesworth’s 1773 Account of Cook’s first voyage.
- Digitised copies of log books from James Cook’s voyages at the British Atmospheric Data Centre
- Works by James Cook at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about James Cook at Internet Archive
- Works by James Cook at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)
- Log book of Cook’s second voyage: high-resolution digitised version in Cambridge Digital Library
- Digitised Tapa cloth catalogue held at Auckland Libraries
Collections and museums
- The Library of the Royal Geographical Society of South Australia specialises in collecting works on Captain James Cook, his voyages and HMS Endeavour
- Cook’s Pacific Encounters: Cook-Forster Collection online Images and descriptions of more than 300 artefacts collected during the three Pacific voyages of James Cook.
- Images and descriptions of items associated with James Cook at the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa
- «Archival material relating to James Cook». UK National Archives.
- Captain Cook Birthplace Museum Marton
- Captain Cook Memorial Museum Whitby
- Cook’s manuscript maps Archived 1 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine of the south-east coast of Australia, held at the American Geographical Society Library at UW Milwaukee.
- Newspaper clippings about James Cook in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
|
James Cook FRS |
|
|---|---|

Portrait by Sir Nathaniel Dance-Holland, c. 1775, National Maritime Museum |
|
| Born | 7 November [O.S. 27 October] 1728
Marton, North Riding of Yorkshire, England |
| Died | 14 February 1779 (aged 50)
Kealakekua Bay, Hawaiian Kingdom |
| Cause of death | Stab wound |
| Nationality | British |
| Education | Postgate School, Great Ayton |
| Occupation(s) | Explorer, navigator, cartographer |
| Spouse |
Elizabeth Batts (m. ) |
| Children | 6 |
| Military career | |
| Branch | Royal Navy |
| Service years | 1755–1779 |
| Rank | Captain (Post-captain) |
| Battles/wars |
|
| Signature | |
 |
James Cook FRS (7 November 1728[NB 1] – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and to New Zealand and Australia in particular. He made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand.
Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years’ War and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec, which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment for the direction of British overseas exploration, and it led to his commission in 1768 as commander of HMS Endeavour for the first of three Pacific voyages.
In these voyages, Cook sailed thousands of miles across largely uncharted areas of the globe. He mapped lands from New Zealand to Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean in greater detail and on a scale not previously charted by Western explorers. He surveyed and named features, and recorded islands and coastlines on European maps for the first time. He displayed a combination of seamanship, superior surveying and cartographic skills, physical courage, and an ability to lead men in adverse conditions.
Cook was attacked and killed in 1779 during his third exploratory voyage in the Pacific while attempting to kidnap the ruling chief of the island of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu, in order to reclaim a cutter taken from one of his ships after his crew took wood from a burial ground. Whilst there is controversy over Cook’s role as ‘an enabler of colonialism’[1] and the violence associated with his contacts with indigenous peoples, he left a legacy of scientific and geographical knowledge that influenced his successors well into the 20th century, and numerous memorials worldwide have been dedicated to him.
Early life and family
James Cook was born on 7 November 1728 (NS) in the village of Marton in the North Riding of Yorkshire and baptised on 14 November (N.S.) in the parish church of St Cuthbert, where his name can be seen in the church register.[2][3] He was the second of eight children of James Cook (1693–1779), a Scottish farm labourer from Ednam in Roxburghshire, and his locally born wife, Grace Pace (1702–1765), from Thornaby-on-Tees.[2][4][5] In 1736, his family moved to Airey Holme farm at Great Ayton, where his father’s employer, Thomas Skottowe, paid for him to attend the local school. In 1741, after five years’ schooling, he began work for his father, who had been promoted to farm manager. Despite not being formally educated he became capable in mathematics, astronomy and charting by the time of his Endeavour voyage.[6] For leisure, he would climb a nearby hill, Roseberry Topping, enjoying the opportunity for solitude.[7] Cooks’ Cottage, his parents’ last home, which he is likely to have visited, is now in Melbourne, Australia, having been moved from England and reassembled, brick by brick, in 1934.[8]
In 1745, when he was 16, Cook moved 20 miles (32 km) to the fishing village of Staithes, to be apprenticed as a shop boy to grocer and haberdasher William Sanderson.[2] Historians have speculated that this is where Cook first felt the lure of the sea while gazing out of the shop window.[5]
After 18 months, not proving suited for shop work, Cook travelled to the nearby port town of Whitby to be introduced to Sanderson’s friends John and Henry Walker.[8] The Walkers, who were Quakers, were prominent local ship-owners in the coal trade. Their house is now the Captain Cook Memorial Museum. Cook was taken on as a merchant navy apprentice in their small fleet of vessels, plying coal along the English coast. His first assignment was aboard the collier Freelove, and he spent several years on this and various other coasters, sailing between the Tyne and London. As part of his apprenticeship, Cook applied himself to the study of algebra, geometry, trigonometry, navigation and astronomy – all skills he would need one day to command his own ship.[5]
Elizabeth Cook, wife and for 56 years widow of James Cook, by William Henderson, 1830
His three-year apprenticeship completed, Cook began working on trading ships in the Baltic Sea. After passing his examinations in 1752, he soon progressed through the merchant navy ranks, starting with his promotion in that year to mate aboard the collier brig Friendship.[9] In 1755, within a month of being offered command of this vessel, he volunteered for service in the Royal Navy, when Britain was re-arming for what was to become the Seven Years’ War. Despite the need to start back at the bottom of the naval hierarchy, Cook realised his career would advance more quickly in military service and entered the Navy at Wapping on 17 June 1755.[10]
Cook married Elizabeth Batts, the daughter of Samuel Batts, keeper of the Bell Inn in Wapping[11] and one of his mentors, on 21 December 1762 at St Margaret’s Church, Barking, Essex.[12] The couple had six children: James (1763–1794), Nathaniel (1764–1780, lost aboard HMS Thunderer which foundered with all hands in a hurricane in the West Indies), Elizabeth (1767–1771), Joseph (1768–1768), George (1772–1772) and Hugh (1776–1793, who died of scarlet fever while a student at Christ’s College, Cambridge). When not at sea, Cook lived in the East End of London. He attended St Paul’s Church, Shadwell, where his son James was baptised. Cook has no direct descendants – all of his children died before having children of their own.[13]
Start of Royal Navy career
Cook’s first posting was with HMS Eagle, serving as able seaman and master’s mate under Captain Joseph Hamar for his first year aboard, and Captain Hugh Palliser thereafter.[14] In October and November 1755, he took part in Eagle’s capture of one French warship and the sinking of another, following which he was promoted to boatswain in addition to his other duties.[10] His first temporary command was in March 1756 when he was briefly master of Cruizer, a small cutter attached to Eagle while on patrol.[10][15]
In June 1757 Cook formally passed his master’s examinations at Trinity House, Deptford, qualifying him to navigate and handle a ship of the King’s fleet.[16] He then joined the frigate HMS Solebay as master under Captain Robert Craig.[17]
Newfoundland
During the Seven Years’ War, Cook served in North America as master aboard the fourth-rate Navy vessel HMS Pembroke.[18] With others in Pembroke‘s crew, he took part in the major amphibious assault that captured the Fortress of Louisbourg from the French in 1758, and in the siege of Quebec City in 1759. Throughout his service he demonstrated a talent for surveying and cartography and was responsible for mapping much of the entrance to the Saint Lawrence River during the siege, thus allowing General Wolfe to make his famous stealth attack during the 1759 Battle of the Plains of Abraham.[19]
Cook’s surveying ability was also put to use in mapping the jagged coast of Newfoundland in the 1760s, aboard HMS Grenville. He surveyed the northwest stretch in 1763 and 1764, the south coast between the Burin Peninsula and Cape Ray in 1765 and 1766, and the west coast in 1767. At this time, Cook employed local pilots to point out the «rocks and hidden dangers» along the south and west coasts. During the 1765 season, four pilots were engaged at a daily pay of 4 shillings each: John Beck for the coast west of «Great St Lawrence», Morgan Snook for Fortune Bay, John Dawson for Connaigre and Hermitage Bay, and John Peck for the «Bay of Despair».[20]
While in Newfoundland, Cook also conducted astronomical observations, in particular of the eclipse of the sun on 5 August 1766. By obtaining an accurate estimate of the time of the start and finish of the eclipse, and comparing these with the timings at a known position in England it was possible to calculate the longitude of the observation site in Newfoundland. This result was communicated to the Royal Society in 1767.[21]
His five seasons in Newfoundland produced the first large-scale and accurate maps of the island’s coasts and were the first scientific, large scale, hydrographic surveys to use precise triangulation to establish land outlines.[22] They also gave Cook his mastery of practical surveying, achieved under often adverse conditions, and brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and Royal Society at a crucial moment both in his career and in the direction of British overseas discovery. Cook’s maps were used into the 20th century, with copies being referenced by those sailing Newfoundland’s waters for 200 years.[23]
Following on from his exertions in Newfoundland, Cook wrote that he intended to go not only «farther than any man has been before me, but as far as I think it is possible for a man to go».[16]
First voyage (1768–1771)
On 25 May 1768,[24] the Admiralty commissioned Cook to command a scientific voyage to the Pacific Ocean. The purpose of the voyage was to observe and record the 1769 transit of Venus across the Sun which, when combined with observations from other places, would help to determine the distance of the Earth from the Sun.[25] Cook, at age 39, was promoted to lieutenant to grant him sufficient status to take the command.[26][27] For its part, the Royal Society agreed that Cook would receive a one hundred guinea gratuity in addition to his Naval pay.[28]
The expedition sailed aboard HMS Endeavour, departing England on 26 August 1768.[29] Cook and his crew rounded Cape Horn and continued westward across the Pacific, arriving at Tahiti on 13 April 1769, where the observations of the transit were made.[30] However, the result of the observations was not as conclusive or accurate as had been hoped. Once the observations were completed, Cook opened the sealed orders, which were additional instructions from the Admiralty for the second part of his voyage: to search the south Pacific for signs of the postulated rich southern continent of Terra Australis.[31]
Cook then sailed to New Zealand where he mapped the complete coastline, making only some minor errors. With the aid of Tupaia, a Tahitian priest who had joined the expedition, Cook was the first European to communicate with the Māori.[32] However, at least eight Māori were killed in violent encounters.[33] Cook then voyaged west, reaching the southeastern coast of Australia near today’s Point Hicks on 19 April 1770, and in doing so his expedition became the first recorded Europeans to have encountered its eastern coastline.[NB 2]
On 23 April, he made his first recorded direct observation of Aboriginal Australians at Brush Island near Bawley Point, noting in his journal: «… and were so near the Shore as to distinguish several people upon the Sea beach they appear’d to be of a very dark or black Colour but whether this was the real colour of their skins or the C[l]othes they might have on I know not.»[34]
Endeavour continued northwards along the coastline, keeping the land in sight with Cook charting and naming landmarks as he went. On 29 April, Cook and crew made their first landfall on the continent at a beach now known as Silver Beach on Botany Bay (Kamay Botany Bay National Park). Two Gweagal men of the Dharawal / Eora nation opposed their landing and in the confrontation one of them was shot and wounded.[35][36][37]
Cook and his crew stayed at Botany Bay for a week, collecting water, timber, fodder and botanical specimens and exploring the surrounding area. Cook sought to establish relations with the Indigenous population without success.[38][39] At first Cook named the inlet «Sting-Ray Harbour» after the many stingrays found there. This was later changed to «Botanist Bay» and finally Botany Bay after the unique specimens retrieved by the botanists Joseph Banks and Daniel Solander.[40] This first landing site was later to be promoted (particularly by Joseph Banks) as a suitable candidate for situating a settlement and British colonial outpost.[41]
After his departure from Botany Bay, he continued northwards. He stopped at Bustard Bay (now known as Seventeen Seventy) on 23 May 1770. On 24 May, Cook and Banks and others went ashore. Continuing north, on 11 June a mishap occurred when Endeavour ran aground on a shoal of the Great Barrier Reef, and then «nursed into a river mouth on 18 June 1770».[42] The ship was badly damaged, and his voyage was delayed almost seven weeks while repairs were carried out on the beach (near the docks of modern Cooktown, Queensland, at the mouth of the Endeavour River).[5] The crew’s encounters with the local Aboriginal people were mostly peaceful, although following a dispute over green turtles Cook ordered shots to be fired and one local was lightly wounded.[43]
The voyage then continued and at about midday on 22 August 1770, they reached the northernmost tip of the coast and, without leaving the ship, Cook named it York Cape (now Cape York).[44] Leaving the east coast, Cook turned west and nursed his battered ship through the dangerously shallow waters of Torres Strait. Searching for a vantage point, Cook saw a steep hill on a nearby island from the top of which he hoped to see «a passage into the Indian Seas». Cook named the island Possession Island, where he claimed the entire coastline that he had just explored as British territory.[45]
Return to England
Cook returned to England via Batavia (modern Jakarta, Indonesia), where many in his crew succumbed to malaria, and then the Cape of Good Hope, arriving at the island of Saint Helena on 30 April 1771.[46] The ship finally returned to England on 12 July 1771, anchoring in The Downs, with Cook going to Deal.[47]
Interlude
Cook’s journals were published upon his return, and he became something of a hero among the scientific community. Among the general public, however, the aristocratic botanist Joseph Banks was a greater hero.[5] Banks even attempted to take command of Cook’s second voyage but removed himself from the voyage before it began, and Johann Reinhold Forster and his son Georg Forster were taken on as scientists for the voyage. Cook’s son George was born five days before he left for his second voyage.[48]
Second voyage (1772–1775)
Portrait of James Cook by William Hodges, who accompanied Cook on his second voyage
Shortly after his return from the first voyage, Cook was promoted in August 1771 to the rank of commander.[49][50] In 1772, he was commissioned to lead another scientific expedition on behalf of the Royal Society, to search for the hypothetical Terra Australis. On his first voyage, Cook had demonstrated by circumnavigating New Zealand that it was not attached to a larger landmass to the south. Although he charted almost the entire eastern coastline of Australia, showing it to be continental in size, the Terra Australis was believed to lie further south. Despite this evidence to the contrary, Alexander Dalrymple and others of the Royal Society still believed that a massive southern continent should exist.[51]
Cook commanded HMS Resolution on this voyage, while Tobias Furneaux commanded its companion ship, HMS Adventure. Cook’s expedition circumnavigated the globe at an extreme southern latitude, becoming one of the first to cross the Antarctic Circle on 17 January 1773. In the Antarctic fog, Resolution and Adventure became separated. Furneaux made his way to New Zealand, where he lost some of his men during an encounter with Māori, and eventually sailed back to Britain, while Cook continued to explore the Antarctic, reaching 71°10’S on 31 January 1774.[16]
Illustration from the 1815 edition of Cook’s Voyages, depicting Cook watching a human sacrifice in Tahiti c. 1773
Cook almost encountered the mainland of Antarctica but turned towards Tahiti to resupply his ship. He then resumed his southward course in a second fruitless attempt to find the supposed continent. On this leg of the voyage, he brought a young Tahitian named Omai, who proved to be somewhat less knowledgeable about the Pacific than Tupaia had been on the first voyage. On his return voyage to New Zealand in 1774, Cook landed at the Friendly Islands, Easter Island, Norfolk Island, New Caledonia, and Vanuatu.
Before returning to England, Cook made a final sweep across the South Atlantic from Cape Horn and surveyed, mapped, and took possession for Britain of South Georgia, which had been explored by the English merchant Anthony de la Roché in 1675. Cook also discovered and named Clerke Rocks and the South Sandwich Islands («Sandwich Land»). He then turned north to South Africa and from there continued back to England. His reports upon his return home put to rest the popular myth of Terra Australis.[52]
Cook’s second voyage marked a successful employment of Larcum Kendall’s K1 copy of John Harrison’s H4 marine chronometer, which enabled Cook to calculate his longitudinal position with much greater accuracy. Cook’s log was full of praise for this time-piece which he used to make charts of the southern Pacific Ocean that were so remarkably accurate that copies of them were still in use in the mid-20th century.[53]
Upon his return, Cook was promoted to the rank of post-captain and given an honorary retirement from the Royal Navy, with a posting as an officer of the Greenwich Hospital. He reluctantly accepted, insisting that he be allowed to quit the post if an opportunity for active duty should arise.[54] His fame extended beyond the Admiralty; he was made a Fellow of the Royal Society and awarded the Copley Gold Medal for completing his second voyage without losing a man to scurvy.[55] Nathaniel Dance-Holland painted his portrait; he dined with James Boswell; he was described in the House of Lords as «the first navigator in Europe».[16] But he could not be kept away from the sea. A third voyage was planned, and Cook volunteered to find the Northwest Passage. He travelled to the Pacific and hoped to travel east to the Atlantic, while a simultaneous voyage travelled the opposite route.[56]
Third voyage (1776–1779)
Hawaii
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander Omai to Tahiti, or so the public was led to believe. The trip’s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent.[57] After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands.[58][59] After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the «Sandwich Islands» after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.[59]
North America
From the Sandwich Islands, Cook sailed north and then northeast to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He sighted the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming Cape Foulweather, after the bad weather which forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward.[60] He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook’s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove,[61] at the south end of Bligh Island. Relations between Cook’s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial but sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had been acceptable in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot «hosts» essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.[62]
After leaving Nootka Sound in search of the Northwest Passage, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska.[60] In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American northwest coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the west) and Spanish (from the south) exploratory probes of the northern limits of the Pacific.[16]
HMS Resolution and Discovery in Tahiti
By the second week of August 1778, Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed northeast up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice at a latitude of 70°44′ north. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then southeast down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands.[63] He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.[64]
Return to Hawaii
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay on Hawai’i Island, largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook’s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook’s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship.[5][64] Similarly, Cook’s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook’s (and to a limited extent, his crew’s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono.[65] Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook’s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.[64][66]
Death
Marker at the shoreline of Kealakekua Bay near the spot Captain Cook was slain
After a month’s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, Resolution‘s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay, including the theft of wood from a burial ground under Cook’s orders.[67] On 13 February 1779, an unknown group of Hawaiians stole one of Cook’s longboats. By then the Hawaiian people had become «insolent», even with threats to fire upon them.[68] Cook responded to the theft by attempting to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
The following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the king. Cook took the king (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu’s favourite wives, Kanekapolei, and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to the boats. They pleaded with the king not to go. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. At this point, the king began to understand that Cook was his enemy.[68] As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf.[69] He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana’ina) and then stabbed by one of the king’s attendants, Nuaa.[70][71] The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.[70][72]
The routes of Captain James Cook’s voyages. The first voyage is shown in red, second voyage in green, and third voyage in blue. The route of Cook’s crew following his death is shown as a dashed blue line.
Aftermath
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled and baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook’s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.[73]
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait.[74] He died of tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook’s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery.[75] The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook’s account of the voyage.[76]
Legacy
Ethnographic collections
The Australian Museum acquired its «Cook Collection» in 1894 from the Government of New South Wales. At that time the collection consisted of 115 artefacts collected on Cook’s three voyages throughout the Pacific Ocean, during the period 1768–80, along with documents and memorabilia related to these voyages. Many of the ethnographic artefacts were collected at a time of first contact between Pacific Peoples and Europeans. In 1935 most of the documents and memorabilia were transferred to the Mitchell Library in the State Library of New South Wales. The provenance of the collection shows that the objects remained in the hands of Cook’s widow Elizabeth Cook, and her descendants, until 1886. In this year John Mackrell, the great-nephew of Isaac Smith, Elizabeth Cook’s cousin, organised the display of this collection at the request of the NSW Government at the Colonial and Indian Exhibition in London. In 1887 the London-based Agent-General for the New South Wales Government, Saul Samuel, bought John Mackrell’s items and also acquired items belonging to the other relatives Reverend Canon Frederick Bennett, Mrs Thomas Langton, H.M.C. Alexander, and William Adams. The collection remained with the Colonial Secretary of NSW until 1894, when it was transferred to the Australian Museum.[77]
Navigation and science
Cook’s 12 years sailing around the Pacific Ocean contributed much to Europeans’ knowledge of the area. Several islands, such as the Hawaiian group, were encountered for the first time by Europeans, and his more accurate navigational charting of large areas of the Pacific was a major achievement.[78] To create accurate maps, latitude and longitude must be accurately determined. Navigators had been able to work out latitude accurately for centuries by measuring the angle of the sun or a star above the horizon with an instrument such as a backstaff or quadrant. Longitude was more difficult to measure accurately because it requires precise knowledge of the time difference between points on the surface of the earth. The Earth turns a full 360 degrees relative to the sun each day. Thus longitude corresponds to time: 15 degrees every hour, or 1 degree every 4 minutes.[citation needed] Cook gathered accurate longitude measurements during his first voyage from his navigational skills, with the help of astronomer Charles Green, and by using the newly published Nautical Almanac tables, via the lunar distance method – measuring the angular distance from the moon to either the sun during daytime or one of eight bright stars during night-time to determine the time at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, and comparing that to his local time determined via the altitude of the sun, moon, or stars.
On his second voyage, Cook used the K1 chronometer made by Larcum Kendall, which was the shape of a large pocket watch, 5 inches (13 cm) in diameter. It was a copy of the H4 clock made by John Harrison, which proved to be the first to keep accurate time at sea when used on the ship Deptford‘s journey to Jamaica in 1761–62.[79] He succeeded in circumnavigating the world on his first voyage without losing a single man to scurvy, an unusual accomplishment at the time. He tested several preventive measures, most importantly the frequent replenishment of fresh food.[80] For presenting a paper on this aspect of the voyage to the Royal Society he was presented with the Copley Medal in 1776.[81][82] Cook became the first European to have extensive contact with various people of the Pacific. He correctly postulated a link among all the Pacific peoples, despite their being separated by great ocean stretches (see Malayo-Polynesian languages). Cook theorised that Polynesians originated from Asia, which scientist Bryan Sykes later verified.[83] In New Zealand the coming of Cook is often used to signify the onset of the colonisation[5][8]
which officially started more than 70 years after his crew became the second group of Europeans to visit that archipelago.
Cook carried several scientists on his voyages; they made significant observations and discoveries. Two botanists, Joseph Banks and the Swede Daniel Solander, sailed on the first voyage. The two collected over 3,000 plant species.[84] Banks subsequently strongly promoted British settlement of Australia,[85][86] leading to the establishment of New South Wales as a penal settlement in 1788. Artists also sailed on Cook’s first voyage. Sydney Parkinson was heavily involved in documenting the botanists’ findings, completing 264 drawings before his death near the end of the voyage. They were of immense scientific value to British botanists.[5][87] Cook’s second expedition included William Hodges, who produced notable landscape paintings of Tahiti, Easter Island, and other locations. Several officers who served under Cook went on to distinctive accomplishments. William Bligh, Cook’s sailing master, was given command of HMS Bounty in 1787 to sail to Tahiti and return with breadfruit. Bligh became known for the mutiny of his crew, which resulted in his being set adrift in 1789. He later became Governor of New South Wales, where he was the subject of another mutiny—the 1808 Rum Rebellion.[88] George Vancouver, one of Cook’s midshipmen, led a voyage of exploration to the Pacific Coast of North America from 1791 to 1794.[89] In honour of Vancouver’s former commander, his ship was named Discovery. George Dixon, who sailed under Cook on his third expedition, later commanded his own.[90] Henry Roberts, a lieutenant under Cook, spent many years after that voyage preparing the detailed charts that went into Cook’s posthumous atlas, published around 1784.
Cook’s contributions to knowledge gained international recognition during his lifetime. In 1779, while the American colonies were fighting Britain for their independence, Benjamin Franklin wrote to captains of colonial warships at sea, recommending that if they came into contact with Cook’s vessel, they were to «not consider her an enemy, nor suffer any plunder to be made of the effects contained in her, nor obstruct her immediate return to England by detaining her or sending her into any other part of Europe or to America; but that you treat the said Captain Cook and his people with all civility and kindness … as common friends to mankind.»[91]
Memorials
A U.S. coin, the 1928 Hawaii Sesquicentennial half-dollar, carries Cook’s image. Minted for the 150th anniversary of his discovery of the islands, its low mintage (10,008) has made this example of an early United States commemorative coin both scarce and expensive.[92] The site where he was killed in Hawaii was marked in 1874 by a white obelisk. This land, although in Hawaii, was deeded to the United Kingdom by Princess Likelike and her husband, Archibald Scott Cleghorn, to the British Consul to Hawaii, James Hay Wodehouse, in 1877.[93][94][failed verification] A nearby town is named Captain Cook, Hawaii; several Hawaiian businesses also carry his name. The Apollo 15 Command/Service Module Endeavour was named after Cook’s ship, HMS Endeavour,[95] as was the Space Shuttle Endeavour.[96] In addition, the first Crew Dragon capsule flown by SpaceX was named for Endeavour.[97] Another shuttle, Discovery, was named after Cook’s HMS Discovery.[98]
The first institution of higher education in North Queensland, Australia, was named after him, with James Cook University opening in Townsville in 1970.[99] Numerous institutions, landmarks and place names reflect the importance of Cook’s contributions, including the Cook Islands, Cook Strait, Cook Inlet and the Cook crater on the Moon.[100] Aoraki / Mount Cook, the highest summit in New Zealand, is named for him.[101] Another Mount Cook is on the border between the U.S. state of Alaska and the Canadian Yukon territory, and is designated Boundary Peak 182 as one of the official Boundary Peaks of the Hay–Herbert Treaty.[102] A larger-than-life statue of Cook upon a column stands in Hyde Park located in the centre of Sydney. A large aquatic monument is planned for Cook’s landing place at Botany Bay, Sydney.[103]
One of the earliest monuments to Cook in the United Kingdom is located at The Vache, erected in 1780 by Admiral Hugh Palliser, a contemporary of Cook and one-time owner of the estate.[104] A large obelisk was built in 1827 as a monument to Cook on Easby Moor overlooking his boyhood village of Great Ayton,[105] along with a smaller monument at the former location of Cook’s cottage.[106] There is also a monument to Cook in the church of St Andrew the Great, St Andrew’s Street, Cambridge, where his sons Hugh, a student at Christ’s College, and James were buried. Cook’s widow Elizabeth was also buried in the church and in her will left money for the memorial’s upkeep. The 250th anniversary of Cook’s birth was marked at the site of his birthplace in Marton by the opening of the Captain Cook Birthplace Museum, located within Stewart Park (1978). A granite vase just to the south of the museum marks the approximate spot where he was born.[107] Tributes also abound in post-industrial Middlesbrough, including a primary school,[108] shopping square[109] and the Bottle ‘O Notes, a public artwork by Claes Oldenburg, that was erected in the town’s Central Gardens in 1993. Also named after Cook is James Cook University Hospital, a major teaching hospital which opened in 2003 with a railway station serving it called James Cook opening in 2014.[110]
The Royal Research Ship RRS James Cook was built in 2006 to replace the RRS Charles Darwin in the UK’s Royal Research Fleet,[111] and Stepney Historical Trust placed a plaque on Free Trade Wharf in the Highway, Shadwell to commemorate his life in the East End of London. A statue erected in his honour can be viewed near Admiralty Arch on the south side of The Mall in London. In 2002, Cook was placed at number 12 in the BBC’s poll of the 100 Greatest Britons.[112]
In 1959, the Cooktown Re-enactment Association first performed a re-enactment of Cook’s 1770 landing at the site of modern Cooktown, Australia, and have continued the tradition each year, with the support and participation of many of the local Guugu Yimithirr people.[113]
Culture
Cook was a subject in many literary creations.
Letitia Elizabeth Landon, a popular poet known for her sentimental romantic poetry,[114] published a poetical illustration to a portrait of Captain Cook in 1837.[115]
In 1931, Kenneth Slessor’s poem «Five Visions of Captain Cook» was the «most dramatic break-through» in Australian poetry of the 20th century according to poet Douglas Stewart.[116]
The Australian slang phrase «Have a Captain Cook» means to have a look or conduct a brief inspection.[117]
Cook appears as a symbolic and generic figure in several Aboriginal myths, often from regions where Cook did not encounter Aboriginal people. Maddock states that Cook is usually portrayed as the bringer of Western colonialism to Australia and is presented as a villain who brings immense social change.[118]
Controversy
Statue of James Cook, Hyde Park, Sydney. The rear inscription reads: «Discovered this territory, 1770».
The period 2018 to 2021 marked the 250th anniversary of Cook’s first voyage of exploration. A number of countries, including Australia and New Zealand, arranged official events to commemorate the voyage[119][120] leading to widespread public debate about Cook’s legacy and the violence associated with his contacts with Indigenous peoples.[1][121] In the leadup to the commemorations, various memorials to Cook in Australia and New Zealand were vandalised and there were public calls for their removal or modification due to their alleged promotion of colonialist narratives.[122][123] On 1 July 2021, a statue of James Cook in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, was torn down following an earlier peaceful protest about the deaths of Indigenous residential school children in Canada.[124] There were also campaigns for the return of Indigenous artefacts taken during Cook’s voyages (see Gweagal shield).[125]
Alice Proctor argues that the controversies over public representations of Cook and the display of Indigenous artefacts from his voyages are part of a broader debate over the decolonisation of museums and public spaces and resistance to colonialist narratives.[126] While a number of commentators argue that Cook was an enabler of British colonialism in the Pacific,[1][127] Geoffrey Blainey, among others, notes that it was Banks who promoted Botany Bay as a site for colonisation after Cook’s death.[128] Robert Tombs defended Cook, arguing «He epitomized the Age of Enlightenment in which he lived» and in conducting his first voyage «was carrying out an enlightened mission, with instructions from the Royal Society to show ‘patience and forbearance’ towards native peoples».[129]
See also
- New Zealand places named by James Cook
- Australian places named by James Cook
- European and American voyages of scientific exploration
- Exploration of the Pacific
- List of places named after Captain James Cook
- List of sea captains
- Death of Cook (paintings)
References
Notes
- ^ Old Style date: 27 October
- ^ At this time, the International Date Line had yet to be established, so the dates in Cook’s journal are a day earlier than those accepted today.
Citations
- ^ a b c Daley, Paul (29 April 2020). «Commemorating Captain James Cook’s arrival, Australia should not omit his role in the suffering that followed». The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 16 March 2021.
- ^ a b c Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 25
- ^ Robson 2009, p. 2
- ^ Stamp 1978, p. 1
- ^ a b c d e f g h Collingridge 2003
- ^ Frost, Alan (19 October 2018). Mutiny, Mayhem, Mythology: Bounty’s Enigmatic Voyage. Sydney University Press. p. 255. ISBN 978-1-74332-587-2. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 15
- ^ a b c Horwitz 2003
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 11
- ^ a b c Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 27
- ^ «Famous 18th century people in Barking and Dagenham: James Cook and Dick Turpin» (PDF). London Borough of Barking and Dagenham. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 June 2012. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ Robson 2009, pp. 120–21
- ^ Stamp 1978, p. 138
- ^ Robson 2009, pp. 19–25
- ^ McLynn 2011, p. 21
- ^ a b c d e Williams, Glyn (17 February 2011). «Captain Cook: Explorer, Navigator and Pioneer». BBC. Archived from the original on 19 August 2011. Retrieved 5 September 2011.
- ^ Capper, Paul (1985–1996). «The Captain Cook Society: Cook’s Log». Life in the Royal Navy (1755–1767). Archived from the original on 21 July 2012. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Kemp & Dear 2005
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 19
- ^ Whiteley, William (1975). «James Cook in Newfoundland 1762–1767» (PDF). Newfoundland Historical Society Pamphlet Number 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2013. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
- ^ Cook, James; Bevis, J. (1 January 1767). «An Observation of an Eclipse of the Sun at the Island of New-Found-Land, August 5, 1766, by Mr. James Cook, with the Longitude of the Place of Observation Deduced from It». Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 57: 215–216. doi:10.1098/rstl.1767.0025.
- ^ Government of Canada (2012). «Captain James Cook R.N.» Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada. Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 32
- ^ Kippis, Andrew (1788). Narrative of the voyages round the world, performed by Captain James Cook; with an account of his life during the previous and intervening periods. Chapter 2. Archived from the original on 3 October 2018. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 95
- ^ Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 30
- ^ Beazley, Charles Raymond (1911). «Cook, James» . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 71.
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, p. cix
- ^ «The Sydney Morning Herald». National Library of Australia. 2 May 1931. p. 12. Retrieved 4 September 2012.
- ^ «BBC – History – Captain James Cook». Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ^ «Secret Instructions to Captain Cook, 30 June 1768» (PDF). National Archives of Australia. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 April 2020. Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ^ Salmond, Anne (1991). Two worlds : first meetings between Māori and Europeans, 1642–1772. Auckland, N.Z.: Viking. ISBN 0-670-83298-7. OCLC 26545658.
- ^ Beaglehole (1974). pp. 198-200, 202, 205-07
- ^ «Cook’s Journal: Daily Entries, 22 April 1770». Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Voices heard but not understood». Gujaga Foundation. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ^ «Cook’s Journal: Daily Entries, 29 April 1770». southseas.nla.gov.au. South Seas. Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- ^ Blainey (2020). pp. 141-43
- ^ FitzSimons, Peter (2019). James Cook : the story behind the man who mapped the world. Sydney, NSW. ISBN 978-0-7336-4127-5. OCLC 1109734011.
- ^ Blainey (2020). pp. 146-57
- ^ Beaglehole (1974). p. 230
- ^ Blainey (2020). p. 287
- ^ Robson 2004, p. 81
- ^ Blainey, Geoffrey (2020) pp 220-21
- ^ Cook, James (21 August 1770). «Cook’s Journal: Daily Entries». National Library of Australia. Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 28 August 2020.
- ^ Cook, James, Journal of the HMS Endeavour, 1768–1771, National Library of Australia, Manuscripts Collection, MS 1, 22 August 1770
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, p. 468
- ^ «The First Voyage (1768–1771)». The Captain Cook Society (CCS). Archived from the original on 3 April 2020. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
- ^ «Captain Cook: Obsession & Discovery. (Part 2 of 4) – Britain on DocuWatch – free streaming British history documentaries». 2011. Archived from the original on 7 April 2013. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 180
- ^ McLynn 2011, p. 167
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 182
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 263
- ^ «Captain James Cook: His voyages of exploration and the men that accompanied him». National Maritime Museum. Archived from the original on 21 April 2007. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- ^ Beaglehole 1974, p. 444
- ^ Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 79
- ^ Hough 1994, p. 268
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 327
- ^ Fish, Shirley (2011). The Manila-Acapulco Galleons : The Treasure Ships of the Pacific: With An Annotated List of the Transpacific Galleons 1565–1815. AuthorHouse. pp. 360–. ISBN 978-1-4567-7543-8. Archived from the original on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ a b Collingridge 2003, p. 380
- ^ a b Hayes 1999, pp. 42–43
- ^ «Resolution Cove». BC Geographical Names. Retrieved 6 March 2013.
- ^ Fisher 1979
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, pp. 615–23
- ^ a b c Obeyesekere 1992
- ^ Sahlins 1985
- ^ Obeyesekere 1997
- ^ Sparks, Jared (1847). Life of John Ledyard, American Traveller. C. C. Little and J. Brown. pp. 136–139. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- ^ a b Obeyesekere 1997, pp. 310–
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 410
- ^ a b Samwell, David; Townsend, Ebenezer (Jr); Gilbert, George; Hawaiian Historical Society; Ingraham, Joseph; Meares, John; Cartwright, Bruce (1791). Extracts from Voyages Made in the Years 1788 and 1789, from China to the Northwest Coast of America: With an Introductory Narrative of a Voyage Performed in 1786, from Bengal in the Ship «Nootka». Paradise of the Pacific Press. p. 76. Archived from the original on 18 May 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ Dibble, Sheldon (1843). History of the Sandwich Islands. Lahainaluna: Press of the Mission Seminary. p. 61.
- ^ «Muster for HMS Resolution during the third Pacific voyage, 1776–1780» (PDF). Captain Cook Society. 15 October 2012. p. 20. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 413
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 412
- ^ Collingridge 2003, p. 423
- ^ «Better Conceiv’d than Describ’d: the life and times of Captain James King (1750–84), Captain Cook’s Friend and Colleague. Steve Ragnall. 2013». The Captain Cook Society (CCS). Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ^ Thomsett, Sue. «Cook Collection, History of Acquisition». Electronic Museum Narrative. Australian Museum. Archived from the original on 18 February 2013. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ Cook, James; Clerke, Charles; Gore, John; King, James (1784). A voyage to the Pacific Ocean … – Google Books. Vol. 2. London: W. and A. Strahan. Archived from the original on 29 March 2014. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- ^ «Captain Cook – Cook’s Chronometer – English and Media Literacy, Documentaries». dl.nfsa.gov.au. 2011. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ Fernandez-Armesto 2006, p. 297
- ^ Stamp 1978, p. 105
- ^ Cook, Captain James (1767). «The Method Taken for Preserving the Health of the Crew of His Majesty’s Ship the Resolution during Her Late Voyage Round the World». Philosophical Transactions. 66: 402–06. doi:10.1098/rstl.1776.0023. S2CID 186212653. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ Sykes 2001
- ^ «The Endeavour Botanical Illustrations at the Natural History Museum». Natural History Museum. 2011. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Sir Joseph Banks». BBC. 2011. Archived from the original on 25 January 2012. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ Gilbert, L. A. Solander, Daniel (1733–1782). Australian Dictionary of Biography, National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. Archived from the original on 19 September 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «The Endeavour Botanical Illustrations at the Natural History Museum». Natural History Museum. 2011. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Biography: William Bligh | Royal Naval Museum at Portsmouth Historic Dockyard». royalnavalmuseum.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 9 December 2013. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ Phillips, Nan. Vancouver, George (1757–1798). Australian Dictionary of Biography. National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. Archived from the original on 15 August 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ Gough, Barry M. (1979). «Dixon, George». In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. IV (1771–1800) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ Franklin, Benjamin (1837). The works of Benjamin Franklin. Tappan, Whittemore, and Mason. pp. 123–24. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «Hawaii Sesquicentennial Half Dollar». coinsite.com. 2011. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ Gray, Chris (11 November 2000). «Captain Cook’s little corner of Hawaii under threat from new golf». The Independent. Archived from the original on 6 May 2018. Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ^ Coulter, John Wesley (June 1964). «Great Britain in Hawaii: The Captain Cook Monument». The Geographical Journal. London: The Royal Geographical Society. 130 (2): 256–261. doi:10.2307/1794586. JSTOR 1794586.
- ^ «Call Signs». NASA. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- ^ «Space Shuttle Endeavour». John F. Kennedy Space Center website. NASA. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- ^ «Astronauts name SpaceX spaceship ‘Endeavour’ after retired shuttle». 30 May 2020. Archived from the original on 3 June 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
- ^ «Space Shuttle Discovery». John F. Kennedy Space Center website. NASA. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- ^ «About James Cook University». James Cook University. 2011. Archived from the original on 20 December 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ «Planetary Names: Crater, craters: Cook on Moon». Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS/NASA. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Aoraki Mount Cook National Park & Mt Cook Village, New Zealand». Archived from the original on 1 October 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Map of Mount Cook, Yukon, Mountain – Canada Geographical Names Maps». Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Visentin, Lisa (28 April 2018). «Sydney to get new Captain Cook memorial as part of $50m revamp». The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- ^ «CCS – Cook Monument at the Vache, Chalfont St Giles – Access Restored». Archived from the original on 5 February 2012. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «Great Ayton – Captain Cook’s Monument». Archived from the original on 27 October 2011. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ^ «Captain Cook». The Sydney Morning Herald. NSW: National Library of Australia. 26 January 1935. p. 16. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ «The Captain Cook Birthplace Museum, Marton, Middlesbrough, UK». captcook-ne.co.uk. 2011. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Captain Cook Primary School». BBC. 2 December 2004. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ «Captain Cook Shopping Square». Captaincookshopping.com. Archived from the original on 28 March 2010. Retrieved 8 March 2010.
- ^ «Captain Cook and the Captain Cook Trail». Archived from the original on 6 September 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ «RRS James Cook». Nautical Environment Research Council. 2011. Archived from the original on 3 July 2012. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ «BBC – Great Britons – Top 100». Internet Archive. Archived from the original on 4 December 2002. Retrieved 19 July 2017.
- ^ Kim, Sharnie; Stephen, Adam (19 June 2020). «Cooktown’s Indigenous people help commemorate 250 years since Captain Cook’s landing with re-enactment». ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 6 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ Jacolbe, Jessica (23 May 2019). «Life of Forgotten Poet Letitia Elizabeth Landon». Jstor Daily. Retrieved 9 October 2022.
- ^ Landon, Letitia Elizabeth (1837). «portrait». Fisher’s Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1838. Fisher, Son & Co.Landon, Letitia Elizabeth (1837). «poetical illustration». Fisher’s Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1838. Fisher, Son & Co. p. 23.
- ^ Herbert C. Jaffa, Kenneth Slessor: A Critical Study, Angus & Robertson, Sydney, 1977, p. 20.
- ^ Khoury, Matt (12 July 2017). «Australian slang: 33 phrases to help you talk like an Aussie». CNN. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Maddock, K. (1988). «Myth, History and a Sense of Oneself». In Beckett, J. R. (ed.). Past and Present: The Construction of Aboriginality. Canberra: Aboriginal Studies Press. pp. 11–30. ISBN 0-85575-190-8.
- ^ «250th anniversary of Captain Cook’s voyage to Australia». Australian Government, Office for the Arts. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ «Tuia Enounters 250». Archived from the original on 6 March 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ Roy, Eleanor Ainge (8 October 2019). «New Zealand wrestles with 250th anniversary of James Cook’s arrival». The Guardian. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ «Australia debates Captain Cook ‘discovery’ statue». BBC News. 23 August 2017. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ «Captain James Cook statue defaced in Gisborne». nzherald.co.nz. 13 June 2020. Archived from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 16 March 2021.
- ^ «Capt. James Cook statue recovered from Victoria Harbour; what’s next is undecided». Times Colonist. 3 July 2021. Archived from the original on 3 July 2021. Retrieved 4 July 2021.
- ^ «Shots Fired». ABC Radio National. 13 November 2020. Archived from the original on 7 March 2021. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ Proctor, Alice (2020) Chs 11, 21; pp 255-62 and passim
- ^ Proctor, Alice (2020). The Whole Picture: The colonial story of the art in our museums and why we need to talk about it. London: Cassell. p. 243. ISBN 9781-78840-1-555.
- ^ Blainey, Geoffrey (2020). Captain Cook’s Epic Voyage: the strange quest for a missing continent. Australia: Viking. p. 287. ISBN 978-1-76089-509-9.
- ^ Tombs, Robert (4 February 2021). «Captain Cook wasn’t a ‘genocidal’ villain. He was a true Enlightenment man». The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
Bibliography
- Beaglehole, J. C., ed. (1968). The Journals of Captain James Cook on His Voyages of Discovery. Vol. I: The Voyage of the Endeavour 1768–1771. Cambridge University Press. OCLC 223185477.
- Beaglehole, John Cawte (1974). The Life of Captain James Cook. A & C Black. ISBN 978-0-7136-1382-7.
- Collingridge, Vanessa (2003). Captain Cook: The Life, Death and Legacy of History’s Greatest Explorer. Ebury Press. ISBN 978-0-09-188898-5.
- Fernandez-Armesto, Felipe (2006). Pathfinders: A Global History of Exploration. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-06259-5.
- Fisher, Robin (1979). Captain James Cook and his times. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-7099-0050-4.
- Hayes, Derek (1999). Historical Atlas of the Pacific Northwest: Maps of exploration and Discovery. Sasquatch Books. ISBN 978-1-57061-215-2.
- Horwitz, Tony (October 2003). Blue Latitudes: Boldly Going Where Captain Cook Has Gone Before. Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-0-7475-6455-3.
- Hough, Richard (1994). Captain James Cook. Hodder and Stoughton. ISBN 978-0-340-82556-3.
- Kemp, Peter; Dear, I. C. B. (2005). The Oxford Companion to Ships and the Sea. OUP. ISBN 978-0-19-860616-1.
- Kippis, Andrew (1788). Narrative of the voyages round the world, performed by Captain James Cook; with an account of his life during the previous and intervening periods. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- McLynn, Frank (2011). Captain Cook: Master of the Seas. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-11421-8.
- Moorehead, Alan (1966). Fatal Impact: An Account of the Invasion of the South Pacific, 1767–1840. H Hamilton. ISBN 978-0-241-90757-3.
- Mundle, Rob (2013). Cook: from Sailor to Legend. ABC Books. ISBN 978-1-46070-061-7.
- Obeyesekere, Gananath (1992). The Apotheosis of Captain Cook: European Mythmaking in the Pacific. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691056807.
- Obeyesekere, Gananath (1997). The Apotheosis of Captain Cook: European Mythmaking in the Pacific (PDF). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-05752-1.
With new preface and afterword replying to criticism from Sahlins
- Rigby, Nigel; van der Merwe, Pieter (2002). Captain Cook in the Pacific. National Maritime Museum, London. ISBN 978-0-948065-43-9.
- Robson, John (2004). The Captain Cook Encyclopædia. Random House Australia. ISBN 978-0-7593-1011-7.
- Robson, John (2009). Captain Cook’s War and Peace: The Royal Navy Years 1755–1768. University of New South Wales Press. ISBN 978-1-74223-109-9.
- Sahlins, Marshall David (1985). Islands of history. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-73358-6.
- Sahlins, Marshall David (1995). How «Natives» Think: About Captain Cook, for example. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-73368-5.
- Sidney, John Baker (1981). The Australian Language: An Examination of the English Language and English Speech as Used in Australia, from Convict Days to the Present. Melbourne: Sun Books. ISBN 978-0-7251-0382-8.
- Stamp, Tom and Cordelia (1978). James Cook Maritime Scientist. Whitby: Caedmon of Whitby Press. ISBN 978-0-905355-04-7.
- Sykes, Bryan (2001). The Seven Daughters of Eve. Norton Publishing: New York City and London. ISBN 978-0-393-02018-2.
- Wagner, A. R. (1972). Historic Heraldry of Britain. London: Phillimore & Co Ltd. ISBN 978-0-85033-022-9.
- Wharton, W. J. L. (1893). Captain Cook’s Journal during his first voyage round the world made in H.M. Bark «Endeavour» 1768–71. Archived from the original on 22 March 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
Further reading
- Aughton, Peter (2002). Endeavour: The Story of Captain Cook’s First Great Epic Voyage. London: Cassell & Co. ISBN 978-0-304-36236-3.
- Beazley, Charles Raymond (1911). «Cook, James» . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). pp. 71–72.
- Edwards, Philip, ed. (2003). James Cook: The Journals. London: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-043647-1.
Prepared from the original manuscripts by J. C. Beaglehole 1955–67
- Forster, Georg, ed. (1986). A Voyage Round the World. Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3-05-000180-7.
Published first 1777 as: A Voyage round the World in His Britannic Majesty’s Sloop Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years, 1772, 3, 4, and 5
- Hawkesworth, John; Byron, John; Wallis, Samuel; Carteret, Philip; Cook, James; Banks, Joseph (1773), An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavour drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, esq, London Printed for W. Strahan and T. Cadell, Volume I, Volume II–III.
- Igler, David (2013). The Great Ocean: Pacific Worlds from Captain Cook to the Gold Rush. New York: Oxford U.P.[ISBN missing]
- Kippis, Andrew (1904). The Life and Voyages of Captain James Cook. George Newnes, London & Charles Scribner’s Sons, New York.
- Richardson, Brian. (2005) Longitude and Empire: How Captain Cook’s Voyages Changed the World (University of British Columbia Press.) ISBN 0-7748-1190-0.
- Sydney Daily Telegraph (1970) Captain Cook: His Artists – His Voyages The Sydney Daily Telegraph Portfolio of Original Works by Artists who sailed with Captain Cook. Australian Consolidated Press, Sydney
- Thomas, Nicholas The Extraordinary Voyages of Captain James Cook. Walker & Co., New York. ISBN 0-8027-1412-9 (2003)
- Uglow, Jenny, «Island Hopping» (review of Captain James Cook: The Journals, selected and edited by Philip Edwards, London, Folio Society, three volumes and a chart of the voyages, 1,309 pp.; and William Frame with Laura Walker, James Cook: The Voyages, McGill-Queen University Press, 224 pp.), The New York Review of Books, vol. LXVI, no. 2 (7 February 2019), pp. 18–20.
- Villiers, Alan (Summer 1956–57). «James Cook, Seaman». Quadrant. 1 (1): 7–16.[ISBN missing]
- Williams, Glyndwr, ed. (1997). Captain Cook’s Voyages: 1768–1779. London: The Folio Society.
- Withey, Lynne. Voyages of discovery: Captain Cook and the exploration of the Pacific (Univ of California Press, 1989).[ISBN missing]
External links
- Captain Cook Society
- Captain Cook historic plaque, Halifax
- «Explorer, navigator, coloniser: revisit Captain Cook’s legacy with the click of a mouse». The Conversation. 29 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- «Articles on Captain Cook». The Conversation. 2017–2020. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
Captain Cook., a poetical illustration by Letitia Elizabeth Landon in Fisher’s Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1838.
Biographical dictionaries
- «Cook, James (1728–1779)». Australian Dictionary of Biography (online ed.). National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. 1966. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- Williams, Glyndwr (1979). «Cook, James». In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. IV (1771–1800) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- Mackay, David. «Cook, James». Dictionary of New Zealand Biography. Ministry for Culture and Heritage.
Journals
- The Endeavour journal (1) and The Endeavour journal (2), as kept by James Cook – digitised and held by the National Library of Australia
- The South Seas Project: maps and online editions of the Journals of James Cook’s First Pacific Voyage, 1768–1771. Includes full text of journals kept by Cook, Joseph Banks and Sydney Parkinson, as well as the complete text of John Hawkesworth’s 1773 Account of Cook’s first voyage.
- Digitised copies of log books from James Cook’s voyages at the British Atmospheric Data Centre
- Works by James Cook at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about James Cook at Internet Archive
- Works by James Cook at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)
- Log book of Cook’s second voyage: high-resolution digitised version in Cambridge Digital Library
- Digitised Tapa cloth catalogue held at Auckland Libraries
Collections and museums
- The Library of the Royal Geographical Society of South Australia specialises in collecting works on Captain James Cook, his voyages and HMS Endeavour
- Cook’s Pacific Encounters: Cook-Forster Collection online Images and descriptions of more than 300 artefacts collected during the three Pacific voyages of James Cook.
- Images and descriptions of items associated with James Cook at the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa
- «Archival material relating to James Cook». UK National Archives.
- Captain Cook Birthplace Museum Marton
- Captain Cook Memorial Museum Whitby
- Cook’s manuscript maps Archived 1 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine of the south-east coast of Australia, held at the American Geographical Society Library at UW Milwaukee.
- Newspaper clippings about James Cook in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
Джеймс Кук — великий английский исследователь, который пошел через три многолетние кругосветные экспедиции по изучению Мирового океана. В ходе путешествия сделал несколько значимых географических открытий. Его именем назван пролив в Новой Зеландии. Благодаря точности, с которой Кук наносил на карты расположение новых земель, они были актуальны среди мореплавателей до второй половины 19 века.
…
Оглавление:
- Что открыл Джеймс Кук
- Краткая биография
- Первая научная экспедиция
- Секретное задание капитана Кука
- Вторая научная экспедиция
- Третье кругосветное путешествие
- Значение кругосветных путешествий Джеймса Кука
- Как умер Джеймс Кук
- Интересные факты
Что открыл Джеймс Кук
Великий мореплаватель наиболее знаменит тем, что три раза совершил путешествие вокруг света. Он первый приблизился к Антарктиде, хоть немного не достиг ее, а также пересек Южный и Северный полярные круги.
Его значимые открытия:
- Большой Барьерный риф;
- острова Новой Зеландии, пролив между ними;
- Гавайи;
- Южные Сандвичевы острова.
Также он исследовал австралийское и североамериканское побережья. Вот как выглядит маршрут экспедиции Джеймса Кука на карте.
Краткая биография
Джеймс родился 27 октября 1728 года, его отец был бедным батраком. Когда ребенку исполняется 8 лет, семейство уезжает в деревню Грейт Айтон. Джеймса отдают на обучение в школу (которая сейчас превращена в музей) на пять лет, после чего он начинает работать с отцом на ферме (к тому времени он как раз получает должность управляющего).
Но недолго он принимал участие в сельской жизни. Когда Джеймсу исполняется 18 лет, он устраивается юнгой на корабль «Геркулес». Так и начинается его путь мореплавателя. В перерывах между работой на корабле юноша много читает, изучает географию, астрономию, математику.
Через несколько лет ему предлагают командование, но он резко меняет решение и становится простым матросом на другом корабле, где через месяц получает должность боцмана. Во время Семилетней войны Джеймс участвует в военных действиях и становится мастером. После службы в армии он приезжает домой и женится на Элизабет Баттс, с которой они заводят шестерых детей.
Первая научная экспедиция
Огромный опыт и успешная карьера кардинально изменили жизнь мореплавателя. Его попросили возглавить научную экспедицию, которая должна была исследовать прохождения Венеры через диск Солнца. Так он стал капитаном корабля «Индевор».
26 августа 1768 года началась экспедиция. Первой важной остановкой стал берег Таити, куда корабль прибыл спустя несколько месяцев. Отличительной чертой команды Кука было то, что он строго запретил конфликтовать с аборигенами. Нужно было поддерживать дружбу и не применять насилие, что для того времени было нонсенсом.
Благодаря такой политике, англичане смогли установить с местными доброжелательные отношения и успешно провести астрономические наблюдения. Результаты исследований помогли впоследствии рассчитать расстояние от Солнца до Земли.
Секретное задание капитана Кука
Несмотря на официальную цель миссии, у капитана было свое секретное задание – отправиться на поиски Южного материка (земли, которая располагалась на Южном полюсе), а также нанести на карту берега Австралии.
Завершив наблюдения, Джеймс отправился к Новой Зеландии, где обнаружил бухту, которую назвал заливом Королевы Шарлотты, а также пролив, впоследствии названный именем Кука. На этом участке пути ему помогал местный вождь Тупия, но избежать стычек с аборигенами все равно не удалось.
После корабль двинулся к Австралии. В апреле 1770 года Джеймс нашел залив, который назвал Ботаническим – из-за огромного количества новых растений. Вскоре кораблю потребовался ремонт, из-за чего команда оказалась на берегу между материком и Большим Барьерным рифом.
Пришлось двигаться медленно и осторожно, проходя вдоль берега, так как Кук не хотел отказываться от идеи исследовать побережье. Благодаря его настойчивости был обнаружен пролив между Новой Гвинеей и Австралией.
После этого корабль направился в Батавию, а затем в Кейптаун. Эта часть пути была сложной, так как люди стали умирать от малярии, дизентерии, которыми заразились в Индонезии. Когда корабль достиг Кейптауна, на нем осталось 12 человек из команды, которые могли выполнять свои обязанности. Всего умерло 22 человека. Чтобы продолжить свой путь, в команду пришлось нанимать еще людей. В Англию мореплаватель вернулся 12 июля 1771 года.
Вторая научная экспедиция
Уже спустя три недели после возвращения Куку пришлось готовиться к следующей экспедиции. Причина такой спешки была в конкуренции между Францией и Англией. Французы уже направили несколько кораблей в сторону Южного материка. Англичане не хотели отставать и отдавать им первенство в его открытии.
В этот раз в плавание пустились уже два корабля — «Резолюшн» под командованием Кука и «Эдвенчур», где капитаном был Тобиас Фюрно. 13 июля 1772 года путешественники отправились искать остров Обрезания, но не нашли его и поплыли на юг. Там корабли первыми попали за пределы Южного полярного круга. Но команда заболела цингой, и пришлось отправиться на Таити. Затем Кук побывал на нескольких островах, которые впоследствии назвал островами Дружбы из-за хороших отношений с местными жителями.
Но в Новой Зеландии англичане впервые увидели каннибализм. Позднее несколько членов команды второго корабля были съедены аборигенами. Экипаж прекращает экспедицию и возвращается на родину.
Кук решает продолжить путешествие и 21 декабря 1773 года снова пересекает полярный круг, достигнув самой южной точки за время всех своих путешествий. Затем исследователь открывает еще несколько территорий, среди которых Новая Каледония и Южная Георгия, а 30 июля 1775 года достигает берегов Англии.
Третье кругосветное путешествие
Целью третьего путешествия стало открытие прохода между Атлантическим и Тихим океанами. Туда также отправились два корабля: «Резолюшн», которым Кук уже управлял в прошлый раз, и «Дискавери», где капитаном был Чарльз Клерк.
12 июля 1776 года в экспедицию отправился «Резолюшн», а 1 августа – «Дискавери». Команда побывала в Кейптауне, Тасмании, Таити. Затем корабли пересекли экватор, открыли остров Рождества, Гавайские острова. Далее экспедиция двинулась к берегами Северной Америки.
Через Аляску корабли приплыли в Берингов пролив, а затем пересекли Северный полярный круг и оказались в Чукотском море. Дальше в северном направлении двигаться было нельзя, и Кук повернул к Алеутским островам, где познакомился с русскими промышленниками. Они дали ему перерисовать карту, которая была полнее, включала неизвестные английским исследователям острова.
Зимой 1779 года путешественники двигались вдоль побережья Гавайев, пытаясь найти место для ремонта. Там многочисленные стычки с местными жителями привели к гибели Джеймса Кука. Дома команда без своего начальника оказалась 7 октября 1780 года.
Значение кругосветных путешествий Джеймса Кука
Три экспедиции капитана имеют по-настоящему большое значение. Они помогли исследователям того времени больше понять о мире, открыть несколько неизвестных территорий, узнать о местах, где раньше никогда не бывали люди.
Первая экспедиция не нашла Южный материк, но сделала множество других больших открытий в Австралии, Новой Зеландии. Был обнаружен пролив Кука и несколько других, на карту нанесли часть побережья Австралии, а ботаники нашли новые растения.
Второе путешествие помогло открыть острова в Тихом океане. Кроме того, хотя исследователи не нашли Антарктиду, они поняли, что новых полезных для колонизации земель в этой части мира нет. Также во время этой поездки Кук подарил островитянам домашний скот – овец, свиней, кабанов. С помощью этих подарков он не только немного повысил уровень жизни аборигенов, но и способствовал уменьшению случаев каннибализма.
Третья трагическая экспедиция также была полезна научному сообществу. И хотя основной цели путешественники не достигли, они открыли Гавайи и несколько других больших островов.
Как умер Джеймс Кук
После Алеутских островов корабли снова прибыли на Гавайи, где местные жители приняли Кука за бога. Но дружелюбные отношения быстро начали портиться и переросли в вооруженные столкновения. Причинами стали кражи и стыки между англичанами и гавайцами.
С одного из кораблей был украден баркас. Чтобы вернуть его, Кук решил захватить в заложники местного вождя. Сначала тот последовал на корабль, но внезапно резко отказался идти дальше. Среди англичан и местных жителей, которые стояли у воды, началась паника. Во время столкновения моряков и островитян Кук был убит.
После этого начальником экспедиции стал Чарльз Клерк. Он пытался мирно забрать тело Кука у островитян, но ничего не вышло, поэтому пришлось провести специальную операцию. 22 февраля 1779 года его останки по морскому обычаю были преданы морю.
Интересные факты
Несколько занимательных фактов о жизни путешественника Джеймса Кука:
- Существует популярная теория, что гавайцы, которые убили Кука, съели его, но это лишь легенда.
- Карты, которые составил капитан, использовались еще почти два века, так как были очень точными.
- После смерти капитана команда истребила почти всех туземцев в порыве ярости.
- По характеру он был достаточно дипломатичным человеком, благодаря чему налаживал хорошие отношения со многими аборигенами.
- Один из лунных кратеров, а также вершина горы в Новой Зеландии названы именем Кука.
Капитан Кук – человек, посвятивший всю свою сознательную жизнь путешествиям и мореплаванию, добившийся успеха, благодаря своим знаниям, самоотверженности, смелости. Исследования Джеймса Кука значительно продвинули науку вперед, а люди получили наиболее полное на тот момент представление о том, как именно выглядит поверхность планеты.
Видео по теме: Капитан Кук – документальный фильм о мореплавателе
О походах русских путешественников в эпоху географических открытий можно почитать здесь.
Источники:
- https://shtorm777.ru/dzhejms-kuk-chto-otkryl-opisanie-ekspedicij-biografiya.html
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Кук,_Джеймс#Результаты_первой_экспедиции
- https://sitekid-ru.turbopages.org/sitekid.ru/s/planeta_zemlya/osvoenie_zemli/dzhejms_kuk.html
- http://мегафакты.рф/интересные-факты-о-куке