| Mercedes-Benz G-Class | |
|---|---|

Mercedes-Benz G 500 (W463), second generation |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer |
|
| Also called |
|
| Production | 1979–present |
| Assembly |
|
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Military off-roader Off-road vehicle Luxury SUV Pickup truck |
| Related |
|
The Mercedes-Benz G-Class, sometimes colloquially called the G-Wagen[3] (as an abbreviation of Geländewagen) is a four-wheel drive automobile manufactured by Magna Steyr (formerly Steyr-Daimler-Puch) in Austria and sold by Mercedes-Benz. Originally developed as a military off-roader, later more luxurious models were added to the line. In certain markets, it has been sold under the Puch name as Puch G until 2000.
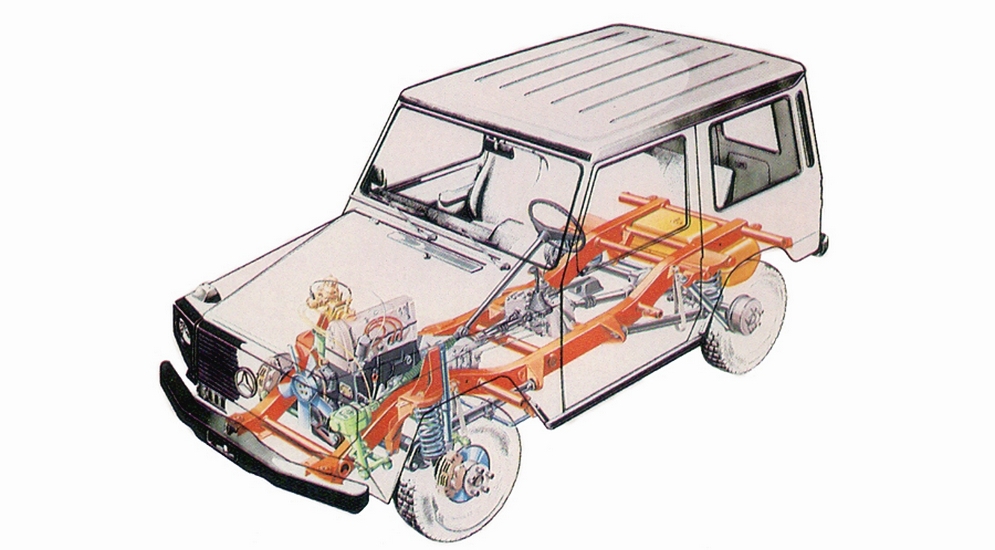
The G-Wagen is characterised by its boxy styling and body-on-frame construction. It uses three fully locking differentials, one of the few passenger car vehicles to have such a feature.
Despite the introduction of an intended replacement, the unibody SUV Mercedes-Benz GL-Class in 2006, the G-Class is still in production and is one of the longest-produced vehicles in Daimler’s history, with a span of 43 years. Only the Unimog surpasses it.[4] In 2018, Mercedes-Benz launched a technically new second generation, still with only minor design changes.
The 400,000th unit was built on 4 December 2020.[5]
History[edit]
Very early, carburetted grey market Mercedes-Benz 230 G Cabriolet
The G-class was developed as a military vehicle from a suggestion by the Shah of Iran (at the time a significant Mercedes shareholder) to Mercedes[6] and was later offered as a civilian vehicle in 1979. In this military role the vehicle was sometimes referred to as the «Wolf». The Peugeot P4 was a variant made under licence in France with a Peugeot engine. The first military in the world to use it was the Argentine Army (Ejército Argentino) beginning in 1981 with the military model 461, at least one of these was captured in the Falklands and subsequently served with the Royal Air Force.[7]
The development of the G-Class started in 1972 with a cooperative agreement between Daimler-Benz and Steyr-Daimler-Puch in Graz, Austria. Mercedes-Benz engineers in Stuttgart were in charge of design and testing, while the team in Graz developed the production plans. The first wooden model was presented to Daimler-Benz management in 1973, with the first drivable prototype beginning various testing including German coalfields, the Sahara Desert, and the Arctic Circle in 1974. Construction commenced on a new production facility in Graz, where the new cross-country vehicle would be assembled nearly entirely by hand in 1975, with production of the «G Model» beginning in Graz in 1979. In 1980, the Vatican took delivery of a specially made G-Wagen outfitted with a clear thermoplastic top which served as the Popemobile. The “Papa G” later took up permanent residence at the Mercedes-Benz Museum in Stuttgart, Germany.[citation needed]
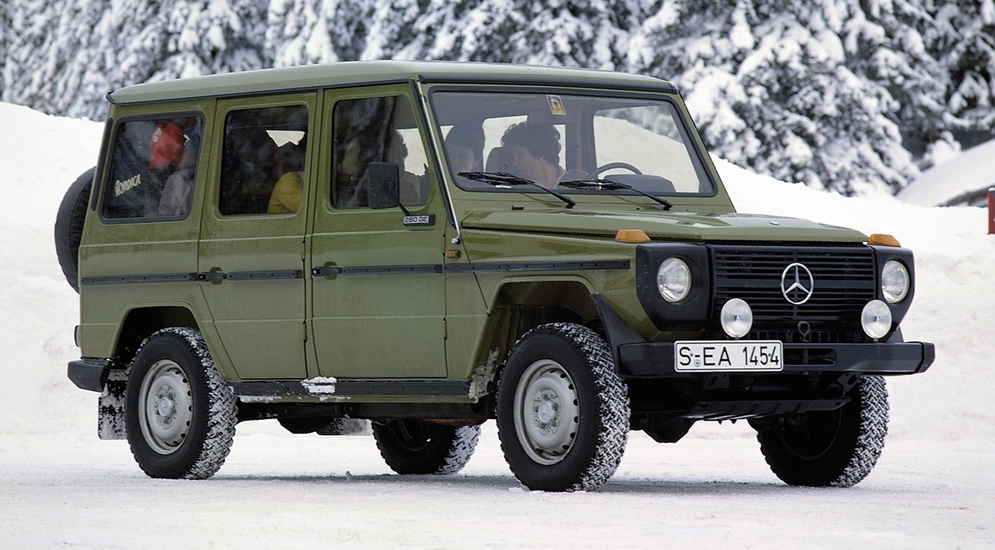
The first major refinements were introduced in 1981, including an automatic transmission, air conditioning, an auxiliary fuel tank, protective headlamp grilles and a cable winch. Fuel injection became available in 1982, when the 230 GE was introduced in Turin,[8] along with more comfortable and supportive front seats, auxiliary heating, wider tires and fender flares. For 1985, differential locks, central door locking and a tachometer became standard and by 1986 over 50,000 G Models had been produced.[citation needed]
The G-Wagen was facelifted in 1990. In 1989, for the 10th anniversary of the G Model, a new model variant with permanent 4-wheel drive, a wood-trimmed interior and optional Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) debuted at the Frankfurt International Motor Show. Production began the following April. For 1992, production began on a new sub-series for professional users. The civilian model began to offer cruise control, a stainless-steel spare-tire cover, running boards and Burl Walnut wood interior trim. In the same year, the 100,000th G Model was built in Graz and in 1994, the model line was officially renamed the G-Class. Ventilated front disc brakes and a driver’s air bag became standard. In 1996 the automatic transmission became an electronically controlled 5-speed unit and headlamp washers, cruise control, and a front passenger’s air bag were added. In 1998, the range-topping G 500 with a 296 hp V8 was introduced for series production.[citation needed]
For 1999 a limited run of V8 powered «G 500 Classic» special editions marked the model’s 20th anniversary. A multifunction steering wheel was added to all models. Later in the year, the new G 55 AMG debuted as the most powerful G-Class yet, with 354 hp. The U.S. market launch of the G-Class took place in 2001. New alloy wheels, a chrome grille and body-colour bumpers plus a more luxurious cabin were introduced. New dynamic control systems included the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), Brake Assist, and the 4 wheel Electronic Traction System (4 ETS). The G 55 AMG was upgraded in 2004 with a supercharged V8 engine developing 476 hp.[citation needed]
In 2006, a documentary filmmaker was the first foreigner to reach Siberia, the world’s coldest region, with a passenger vehicle in winter, driving a stock G 500 nearly 19,000 km without a single breakdown, in temperatures as frigid as −63˚F/-53 °C.[citation needed]
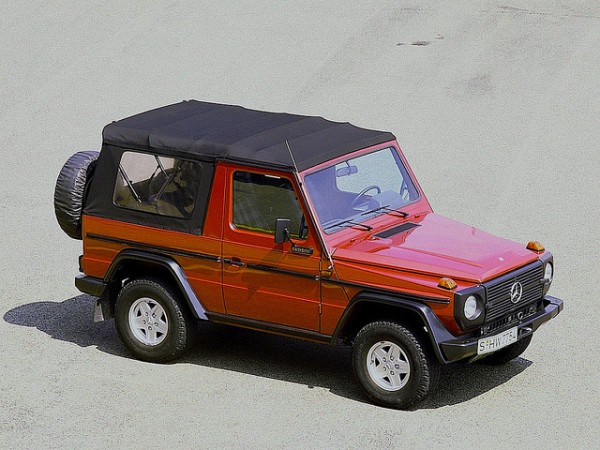
W460 (1979–1992)[edit]
| W460 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door SWB convertible 2-door cab chassis (pickup truck) 3-door SWB station wagon 3-door SWB panel van 3-door LWB station wagon 3-door LWB panel van 5-door LWB station wagon |
| Layout | Front engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Mercedes-Benz W460 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.0L M 102.964 E20 I4 2.3L M 115.973 I4 2.6L M 115 2.6 Brabus I4 2.8L M 110.994 I6 2.4L OM 616 I4 diesel 2.5L OM 602 I5 diesel 3.0L OM 617 I5 diesel |
| Transmission | 4-speed manual 5-speed manual 4-speed 720.1 (W4A 018) automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) (2-door) 2,850 mm (112.2 in) (4-door) |
| Curb weight | 3,913.21 lb (1,775 kg)[9] |
The W460 was introduced at a press event held at the off-road proving ground in Toulon, France, and went on sale in September 1979 with three engine choices and five body variants. Over the next decade, the engine and transmission choices were expanded or updated along with more and more optional extra cost creature comforts (air conditioning, automatic transmission, power windows, etc.).
The G-Wagen gained its global fame in 1980 when Mercedes-Benz built a Popemobile based on 230 G cabriolet during the first visit of Pope John Paul II in Germany.
Mercedes-Benz never officially exported the G-Wagen to the United States because it was considered more of a utilitarian vehicle and didn’t fit the American perception of what Mercedes-Benz was. During the 1980s, the grey import specialists brought the W460 to the United States and modified them to meet the US regulations. In 1988, the new federal law, Motor Vehicle Safety Compliance Act, closed the loopholes and tightened up the regulations for grey imports, making it more difficult and more expensive for the registered importers to federalise the W460 in a very small number. The other issue was severely underpowered engines in the 230 GE, 280 GE, and 300 GD models might not have appealed to the American market as was the case with the Mercedes-Benz 380 SEL in the early 1980s.
The 200 GE was built specifically for Italian markets and other markets where a heavy tax penalty was incurred for engines larger than 2 litres. The 300 GD was the most popular model while the 280 GE was the most powerful. Despite the availability of turbocharged diesel engines in other Mercedes-Benz vehicles, one was never fitted to the W460.
The rarest W460 variants were the 230 GE 2.6 Brabus (1989–?), the 280 GE AMG, and the 560 GE (1993).[citation needed] Brabus increased the engine displacement of the 2.3-litre four-cylinder inline engine to 2.6 litres, increasing the power to 114 kW (155 PS; 153 bhp). AMG modified the 2.8-litre six-cylinder inline petrol engine for more power, 134 kW (182 PS; 180 bhp). Only two units of the 560 GE were built in 1993 as part of a feasibility study that resulted in a limited series of the W463 500 GE for 1993–1994 and the W463 G 500 from 1998 on.[10]
Derivations[edit]
G-Wagen W462 ELBO (1988–?)[edit]
This version was assembled from Complete Knock Down (CKD) by ELBO, formerly a Steyr-Daimler-Puch branch division, in Thessaloniki, Greece for the Greek Army. Additionally, the CKD was also assembled at Mercedes-Benz’s Aksaray plant in Turkey. The engine options were a 2.3-litre four-cylinder inline petrol and later a 2.9-litre five-cylinder inline diesel.
Peugeot P4 VLTT (1981–1988)[edit]
The W460 was assembled in France under licence by Peugeot for the French Army with Peugeot engine and transmission from the 504 and 604 respectively as well as its own seats and wiring system. The front differential gear lock was omitted because Peugeot used its own axles. They are easily identified by rectangular headlamps.
Puch G (1979–2000)[edit]
An agreement between Daimler-Benz AG and Steyr-Daimler-Puch stipulated that G-Wagens sold in Austria, Switzerland, Yugoslavia (and its successor states: Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Serbia, and Slovenia), Mongolia, and Eastern European COMECON countries were called Puch G and elsewhere as Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen/G-Class. The reason for the different branding was due to Puch’s reputation for its all-terrain vehicles, the Haflinger and Pinzgauer. Since the agreement expired in 2000, consumers could order a retrofit kit from Magna’s Puch Competence Centre to replace the Mercedes-Benz brands with Puch emblems.[11]
For Pope John Paul II’s visit to Austria in 1983, Puch emblems was used on the Papamobile instead.
Engines[edit]
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm-urban, 90 km/h, 120 km/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| 200 GE (Italy only) | 1986-1991 | I4 (M 102.964 E20) | 1,997 cc (121.9 cu in) | 87 kW (118 PS; 117 bhp) at 5,200 rpm | 178 N⋅m (131 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 18 seconds | 140 km/h (87 mph) | 16.0 L/100 km (14.7 mpg‑US) — — |
| 230 G | 1979–1982 | I4 (M 115.973) | 2,307 cc (140.8 cu in) | 67 kW (91 PS; 90 bhp) at 5,000 rpm | 167 N⋅m (123 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 26 seconds | 128 km/h (80 mph) | 19.8 L/100 km (11.9 mpg‑US) 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US) 19.8 L/100 km (11.9 mpg‑US) |
| 230 GE | 1972–1990 | I4 (M 115.973 E23) | 2,299 cc (140.3 cu in) | 93 kW (126 PS; 125 bhp) at 5,100 rpm | 192 N⋅m (142 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 17 seconds | 152 km/h (94 mph) | 17.2 L/100 km (13.7 mpg‑US) 12.2 L/100 km (19.3 mpg‑US) 16.2 L/100 km (14.5 mpg‑US) |
| 230 GE 2.6 Brabus | 1989–1990 | I4 (M 115.973 2.6 Brabus) | 2,587 cc (157.9 cu in) | 114 kW (155 PS; 153 bhp) at 5,500 rpm | 260 N⋅m (192 lb⋅ft) at 3,300 rpm | 14.7 seconds | 158 km/h (98 mph) | 17.2 L/100 km (13.7 mpg‑US) 12.2 L/100 km (19.3 mpg‑US) 16.2 L/100 km (14.5 mpg‑US) |
| 280 GE | 1979–1990 | I6 (M 110.994) | 2,746 cc (167.6 cu in) | 116 kW (158 PS; 156 bhp) at 5,250 rpm | 226 N⋅m (167 lb⋅ft) at 4,250 rpm | 14 seconds | 165 km/h (103 mph) | 22.4 L/100 km (10.5 mpg‑US) 14.0 L/100 km (16.8 mpg‑US) 18.8 L/100 km (12.5 mpg‑US) |
| 280 GE AMG | 1979–1990 | I6 (M 110.994) | 2,746 cc (167.6 cu in) | 134 kW (182 PS; 180 bhp) at 5,250 rpm | 226 N⋅m (167 lb⋅ft) at 4,250 rpm | 14 seconds | 165 km/h (103 mph) | 22.4 L/100 km (10.5 mpg‑US) 14.0 L/100 km (16.8 mpg‑US) 18.8 L/100 km (12.5 mpg‑US) |
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| 240 GD | 1979–1988 | I4 (OM 616.936, OM 616.938, OM 616.941) | 2,399 cc (146.4 cu in) | 53 kW (72 PS; 71 bhp) at 4,400 rpm | 137 N⋅m (101 lb⋅ft) at 2,400 rpm | 32 seconds | 115 km/h (71 mph) | 14.4 L/100 km (16.3 mpg‑US) 12.0 L/100 km (19.6 mpg‑US) — |
| 250 GD | 1988–1991 | I5 (OM 602.930) | 2,497 cc (152.4 cu in) | 63 kW (86 PS; 84 bhp) at 5,150 rpm | 154 N⋅m (114 lb⋅ft) at 2,200–2,800 rpm | 27 seconds | 127 km/h (79 mph) | 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) 10.0 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) — |
| 300 GD | 1979–1991 | I5 (OM 617.931, OM 617.932) | 2,998 cc (182.9 cu in) | 65 kW (88 PS; 87 bhp) at 4,400 rpm | 172 N⋅m (127 lb⋅ft) at 2,400 rpm | 27 seconds | 127 km/h (79 mph) | 14.6 L/100 km (16.1 mpg‑US) 11.7 L/100 km (20.1 mpg‑US) 18.8 L/100 km (12.5 mpg‑US) |
W461 (1992–2022)[edit]
| W461 | |
|---|---|

Mercedes G-Class G 280 CDI EDITION.30 PUR |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1992–2022 (military variant)[12] Civilian variant produced until 2014 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door SWB convertible 2-door cab chassis (pickup truck) 3-door SWB panel van 3-door LWB panel van 5-door LWB station wagon |
| Layout | Front engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Mercedes-Benz W461 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.3L M 102 E 23 I4 2.5L OM 602.930 I5 diesel 2.7L OM 612 DE 27 LA I5 turbodiesel 2.9L OM 602 D 29 I5 diesel 2.9L OM 602 DE 29 LA I5 turbodiesel 3.0L OM 642 DE 30 LA red. V6 turbodiesel |
| Transmission | 4-speed 720.1 (W4A 018) automatic 5-speed manual 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) (2-door) 2,850 mm (112.2 in) (4-door) |
| Curb weight | 4,728.92 lb (2,145 kg)[13] |
After the new W463 was introduced in 1989 with an extensively updated chassis and a revised front end, the production of the W460 ended in 1991 and was replaced by the W461. The W461 has essentially the same chassis as the W460 but with the powertrain of the W463 and the body of the W460. While the W463 is aimed at consumers who seek more creature comforts and better driving dynamics, the W461 is built specifically for military, public authorities, and non-governmental organisations.[14] That included the 24-Volt electrical system for the W461.
During the 1990s, the W461 was offered with a 2.3-litre four inline petrol engine and a 2.9-litre five inline diesel engine from 1992 to 2001. From 2001 to 2014, the W461 model for military and public authorities was offered with a 2.7-litre five inline turbodiesel engine and later with a 3.0-litre V6 turbodiesel engine. They were called G 270 CDI Worker (2001–2006) and G 280 CDI Worker (2007–2009) respectively.
On 1 October 2021, Mercedes-Benz announced a new variation of W461 called W464.
Civilian Editions[edit]
Over the years, Mercedes-Benz had introduced the civilian version of the W461, built in limited numbers and for a limited period of time. They targeted primarily the consumers who wanted the «stripped down» version and did not need the creature comforts. The engine choice was often limited to one type, namely a diesel engine, per series. Those editions were named as PUR or Professional.
EDITION.30 PUR[edit]
In 2009, Mercedes-Benz, celebrating the 30-year anniversary of the G-Class, introduced the G 280 CDI EDITION.30 PUR as a five-door long wheelbase station wagon. The consumers could order theirs with «Off-Road Package 1» or «Off-Road Package 2». The passenger compartment had four seats upholstered in hard-wearing fabric or vinyl, rubber floor coverings, spray-protected/water-resistant controls, drainage apertures in the footwells, and a wood floor in the load compartment with load lashing lugs and rails. The dashboard received a new instrument cluster from the W463 and dual air bags and the climate control remained manually operated as did the window winders and locks. The exterior received flexible wheel arch flaring, protective grilles for headlamps, taillamps, front turn signal indicators, a walk-on hood/bonnet for easy access to the optional roof rack, a towing lug attached to the front bumper and two-section barn doors at the rear.
PROFESSIONAL[edit]
The success of the limited series «EDITION.30 PUR» led to the G 280 CDI Professional in 2009 and its successor, the G 300 CDI Professional, in 2010. Initially the 280 CDI Professional was limited to a five-door long wheelbase station wagon design before the body variants were expanded to five different body variations: a three-door long wheelbase panel van (Kastenwagen in German), a five-door long wheelbase station wagon, a two-door cabriolet and a two or four-door cab chassis truck (Pritschenwagen in German) for the G 300 CDI Professional.[15] The production of the civilian variant continued until 2014. However, the military variant continues to this day.[14]
G 300 CDI Professional (W461), Front View
G 300 CDI Professional (W461), Rear View
G 300 CDI Professional Pritschenwagen (W461), Front View
G 300 CDI Professional Pritschenwagen (W461), Rear View
USMC Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV)
Puch G (1990-2001)
Engines[edit]
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm-urban, extra urban, combined) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| 230 GE G 230 |
1992–2001 | I4 (M 102 E 23) | 2,298 cc (140.2 cu in) | 92 kW (125 PS; 123 bhp) at 5,100 rpm | 188 N⋅m (139 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 19–20 seconds | 144–147 km/h (89–91 mph) | 17.2 L/100 km (13.7 mpg‑US) 12.2 L/100 km (19.3 mpg‑US) 16.2 L/100 km (14.5 mpg‑US) |
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| 250 GD «Wolf» (Bundeswehr) |
1990–1991 | I5 (OM 602.930) | 2,497 cc (152.4 cu in) | 68 kW (92 PS; 91 bhp) at 4,600 rpm | 154 N⋅m (114 lb⋅ft) at 2,200–2,800 rpm | 27 seconds | 127 km/h (79 mph) | 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) 10.0 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) — |
| G 270 CDI Worker (Military) | 2001–2006 | I5 (OM 612 DE 27 LA) | 2,685 cc (163.8 cu in) | 115 kW (156 PS; 154 bhp) at 3,800 rpm | 400 N⋅m (295 lb⋅ft) at 1,800–2,400 rpm | — | — | — |
| G 280 CDI Worker (Military) | 2007–2014 | V6 turbo (OM 642 DE 30 LA red.) | 2,987 cc (182.3 cu in) | 135 kW (184 PS; 181 bhp) at 3,800 rpm | 400 N⋅m (295 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,600 rpm | — | 120 km/h (75 mph) | — |
| G 280 CDI EDITION.30PUR | 2009 | 13 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | 14.1 L/100 km (16.7 mpg‑US) 9.8 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 11.4 L/100 km (20.6 mpg‑US)* |
||||
| G 280 CDI Professional | 2009 | 18 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | |||||
| G 300 CDI Professional | 2010–2014 | |||||||
| 290 GD G 290 DIESEL |
1992–1997 | I5 (OM 602 D 29) | 2,874 cc (175.4 cu in) | 70 kW (95 PS; 94 bhp) at 4,000 rpm | 192 N⋅m (142 lb⋅ft) at 2,300 rpm | 25–27 seconds | 135–138 km/h (84–86 mph) | 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US) 9.8 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 12.6 L/100 km (18.7 mpg‑US) |
| 290 GD T G 290 TURBODIESEL |
1998–2001 | I5 (OM 602 DE 29 LA) | 2,874 cc (175.4 cu in) | 89 kW (121 PS; 119 bhp) at 3,800 rpm | 280 N⋅m (207 lb⋅ft) at 1,900–2,300 rpm | 17.2 seconds | 137 km/h (85 mph) | 12.0 L/100 km (19.6 mpg‑US) 10.0 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 10.9 L/100 km (21.6 mpg‑US) |
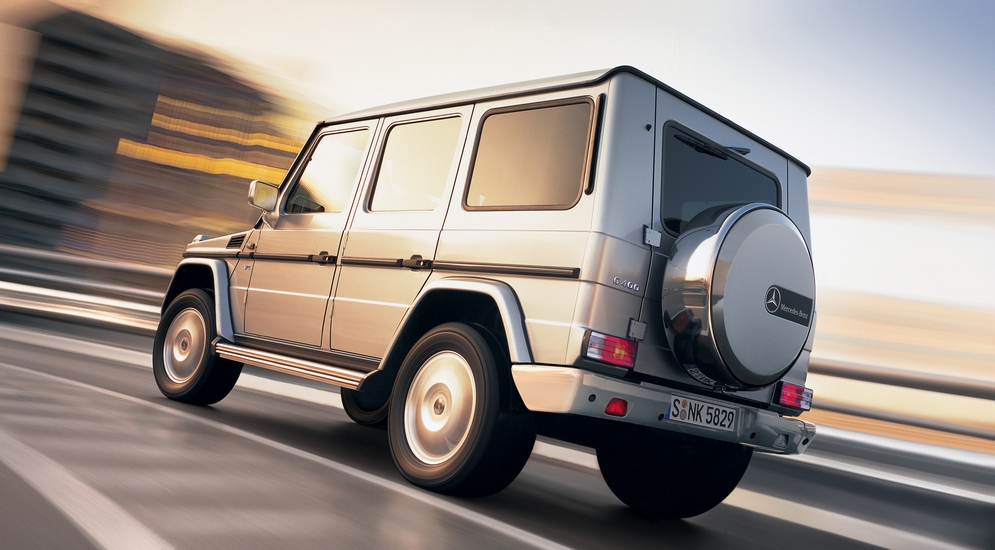
G-Class W463, first generation (1990–2018)[edit]
| W463 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1990–2018 |
| Model years | 1991–2018 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door SWB 2-door SWB convertible 5-door LWB station wagon |
| Layout | Front engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Mercedes-Benz W463 |
| Related | KSU Gazal-1 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.0L M 102.965 E 20 KAT I4 2.3L M 102.989 E 23 KAT I4 3.0L M 103.987 E 30 KAT I6 3.2L M 104.996 E 32 I6 3.2L M 112.945 E 32 V6 3.6L M 104.992 E 36 I6 4.0L M 176 DE 40 AL twin-turbo V8 5.0L M 117.965 E 50 V8 5.0L M 113.965 E 50 V8 5.4L M 113 E 55 V8 5.4L M 113 E 55 ML supercharged V8 5.5L M 273 KE 55 V8 5.5L M 157 DE 55 twin-turbo V8 6.0L M 117.965 E 50 bored to 6.0 litres[16] V8 6.0L M 279 E 60 AL twin-turbo V12 6.3L M 137 E 63 V12 2.5L OM 602.931 D 25 I5 Diesel 2.7L OM 612.965 DE 27 LA turbo I5 Diesel 3.0L OM 603.931 D 30 I6 Diesel 3.0L OM 606.964 D 30 LA turbo I6 Diesel 3.0L OM 642 DE 30 LA V6 turbo Diesel 3.5L OM 603.972 D 35 A turbo I6 Diesel 4.0 OM 628.962 DE 40 LA biturbo V8 Diesel |
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) (2-door) 2,850 mm (112.2 in) (4-door) |
| Length | Pre-2003: 4,661 mm (183.5 in) 2004–09: 4,714 mm (185.6 in) (LWB) 2010–18: 4,686 mm (184.5 in) |
| Width | Pre-2003: 1,760 mm (69.3 in) 2004–09: 1,811 mm (71.3 in) 2004–09 AMG: 1,864 mm (73.4 in) 2010–18: 1,824 mm (71.8 in) 2010–18 AMG: 1,857 mm (73.1 in) |
| Height | Pre-2003: 1,836 mm (72.3 in) 2004–09: 1,976 mm (77.8 in) 2010–18: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) |
| Kerb weight | 2,580 kg (5,690 lb) (G 55 AMG) |
For 1990, the W460 was extensively revised, and a new chassis number, W463, was assigned. The W463 moved the G-Class from spartan and utilitarian to a luxury model on par with the Mercedes-Benz S-Class and the luxurious Range Rover. Thus, no three-door panel vans in short and long wheelbase lengths or barn doors in the rear were offered for the W463: those features are exclusive to the W461. The W461 continued in production as military and utilitarian vehicles for the government agencies and non-government organisations.[14]
The exterior was revised to smoothen out the front end and the front fenders/wings were vertically flattened out at the front underneath headlamps. The fender flares and front end (cooling grille and headlamp bezels) were painted in body colour. The headlamps have square and slightly recessed bezels whilst the grille is narrower to give space for the front numberplate attached to the top of the bumper. The front bumpers are form-fitted and have integrated fog lamps while the rear bumpers have the integrated red rear fog lamp and white reversing lamp. The fuel filler is now covered by a panel. The side running boards were given a standard fitment. The external rear view mirrors have a new housing that pivots on anchors attached to the front doors. New revised tail lamps without white reversing lamps were fitted in the rear.
The interior was significantly updated with wood trim and leather upholstery for the first time. The centre console is smoother and better integrated with the dashboard and the lower part of the dashboard is covered with rubber pads for better knee protection in the event of a frontal collision. The electric differential lock switches are placed prominently in the middle of the dashboard with other electric switches and the instrument cluster has a smoother and more curved housing that meets the dashboard fluidly. The gauges are integrated into one panel rather than a few separate gauges attached to the instrument cluster. The climate control panel was revised to include the temperature and fan speed dials and the door panels are fully trimmed with ruffled leather paneling and soft paddings. The seats are more plush and have several defined cushions along with lumbar support.
The new features included ABS and full-time four-wheel-drive with electrically locking differentials. The engines were carried over from the W460/W461, including the 200 GE, 230 GE, and 300 GE models for petrol engines along with the 250 GD and 300 GD for diesel engines. In 1994, the Geländewagen was renamed as the G-Class when model names were revised to reflect the new corporate nomenclature.
When Mercedes-Benz didn’t consider selling the G-Class in the United States, a small registered importer based in New Mexico, Europa International, Inc., began the expensive process of certifying and modifying the G-Class for the US market and started selling them in 1993. When the new G 500 was introduced in 1998, Europa International sought and received the «small-volume manufacturer status», allowing the company to be the exclusive importer and distributor of the G 500 in the United States. The sales success of the G 500 was attributed to Europa International’s clever marketing toward high-end luxury clientele and led Mercedes-Benz to the decision of purchasing the distribution rights and including the G-Class in its official US model ranges.[17]
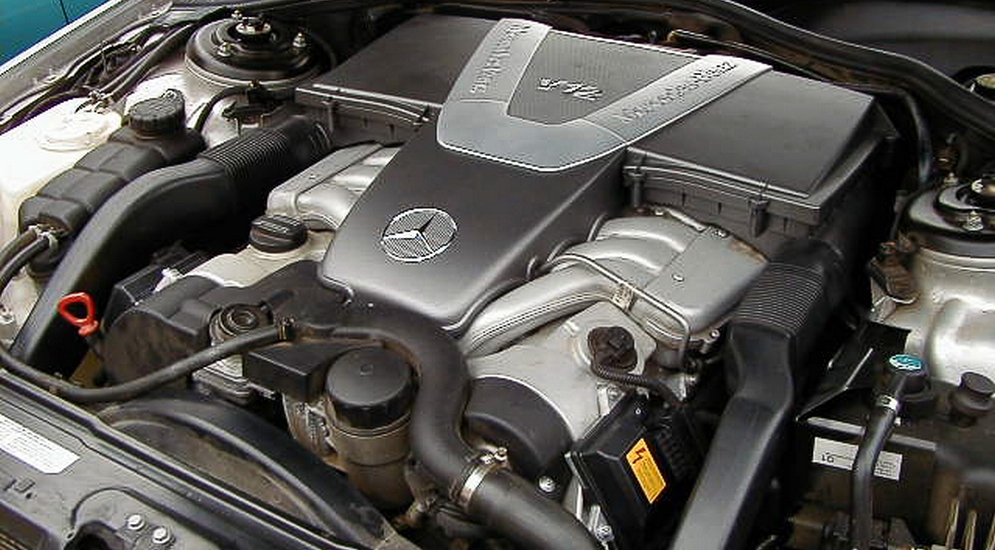
The first generation W463 had the widest range of engines ever fitted to a Mercedes-Benz vehicle during its entire 28-year model run: from four to twelve cylinders; and from natural aspiration to supercharger, turbo, and twin turbo. Towards the end of the first-generation model run the W463 had the highest number of paint colour options at 22, including the bright and intense colours of the Crazy Color Edition.
Models[edit]
The W463 had the highest number of body variations and derivations of any post-war Mercedes-Benz:
- two-door cabriolet
- three-door station wagon with short wheelbase
- four-door pickup truck with six wheels (Mercedes-AMG G 63 6×6)
- four-door cabriolet with extended wheelbase (Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet)
- five-door station wagon with long wheelbase
- five-door station wagon with extended wheelbase (custom built by AMG)
- five-door station wagon with long wheelbase and widened track (Mercedes-Benz G 500 4×4²)
Special models and special editions[edit]
500 GE (1993–1994)[edit]
A significant model was the 500 GE with the first-ever V8 engine for the G-Class. It was produced in a limited number from 1993 to 1994 and as a 5-door, long wheelbase station wagon only. The V8 engine wasn’t reintroduced until 1998 when the G 500 entered into a regular production.
G 500 Classic Special-Edition (1999)[edit]
G 500 Classic Special-Edition Press-Information Brochure 16. March 1999.
G 500 Classic Special-Edition Cabrio
In 1999, the factory presented the luxuriously equipped G 500 Classic Special-Edition model is unveiled to mark the 20th anniversary of the Mercedes-Benz G-Class. All Classic Special-Edition models were equipped with the 500 V8 engine, all of them received a special Almandinschwarz-Metallic (182) paintwork, which in certain lighting conditions looks black or dark aubergine purple. This limited series design inherited everything from the original classic G-Class, but benefited from the technical developments of the new generation released in 2000. Thus, it remained true to the expression of the Classic, yet technically modern. Among other things, all Classic Special-Edition G-Class receive unique 18″ alloy wheels painted in body color inside, with exterior elements painted in vehicle color, Classic inscription strip on the side of the vehicle, stainless steel and painted spare wheel cover, new instrument cluster, equipped with Becker navigation and Hi-Fy with a multi-functional steering wheel appearing for the first time, ultrasonic reversing assist, front and rear seat heating, anti-theft alarm system, illuminated thresholds. The interior is made of black and aubergine purple nappa leather that harmonizes incredibly well with the exterior color, with black suede carpets embroidered with classic lettering and fine burr walnut interior elements. A total of 500 Classic Special-Editions of all versions were produced. 6 RHD and 494 LHD are the most long wheelbase, less short wheelbase and only 12 Cabrios. The G 500 Classic Special-Edition Cabrio is the rarest G-Class Cabrio model ever produced until the end of production of the G-Class Cabrio in 2014.
Grand Edition (2006)[edit]
The 500 units of the G 500 and G 55 AMG Grand Edition were built and shipped to the United States when Mercedes-Benz decided to end the sales of G-Class in the United States for 2006 before rescinding its decision. The exterior had an exclusive Allanite Grey Magno metallic paint finish and brushed aluminium trim stripes with «Grand Edition» lettering. The interior had matte-silk wood trim on the dashboard and centre console, designo exclusive leather upholstery, and door sills with illuminated «Grand Edition» lettering.
G 500 Guard (2009–2018)[edit]
An armoured version of the long wheelbase G 500 five-door station wagon with bullet resistance level FB6 or FB7.[18]
G-Class LIMITED.30 (2009)[edit]
The LIMITED.30 model is a special edition, celebrating the 30-year anniversary of the G-model (1979–2009). This edition includes designo platinum black paint finish, specially designed light-alloy wheels and EDITION30 lettering on the wings. The interior has designo leather in the colour «chablis» and designo trim in anthracite poplar wood.[19]
G 55 AMG KOMPRESSOR «Edition 79» (2009)[edit]
Like the LIMITED.30 special edition, the «Edition 79» is exclusive to the Middle East market, celebrating the sales launch in 1979. This edition includes designo magno alanite grey paint finish, a crash bar at the front, carbon fibre side trim stripes, 19-inch AMG wheels with titanium finish, chrome protection grilles for the front turn signal indicators, designo leather upholstery in black/sand colour, a carbon fibre dashboard and centre console trims and an edition logo, e.g. «1 out of 79», placed in front of the gear selector. The vehicle was unveiled in 2009 at the Dubai International Motor Show.[20]
BA3 Final Edition and Edition Selection (2011)[edit]
The BA3 Final Edition was launched in 2011 to mark the final production run of the three-door, short wheelbase station wagon. The single model variation was G 350 CDI BlueTEC. This farewell special is distinguished by body-coloured AMG flared wheel arches with 5-twin-spoke light-alloy wheels, carbon optics stripes, an AMG radiator grille, 18-inch alloys, extra chrome trims inside and outside, black leather interior offset by walnut burr veneers and ambient lighting.
At the same time, Mercedes-Benz offered the «Edition Select» special for the five-door model, G 500. Edition Selection applies the same special edition treatment to the G 500/G 550 even though the five-door long wheelbase station wagon would continue for several more years.[21]
G 55 AMG long «mastermind» Limited (2012)[edit]
As a brand awareness collaboration for the Fashion Week, Mercedes-Benz Japan and mastermind JAPAN built five units for the Japanese market. Externally, the chrome trims and wheels were done in black paint finish, and two stickers were affixed to the side panels at the rear. The mastermind JAPAN skull and bone badges were affixed to the headrests and spare wheel cover. The interior was done in black leather trim with the roof liner finished in light grey Alcantara.[22]
G 550 Night Edition (2013–2015)[edit]
Exclusive to the Japanese market, 100 units of the G 550 Night Edition were produced with a black paint finish, AMG badges on the front fenders/wings and five twin-spoke, aluminium wheels finished in titanium grey. Two choices of interior colours were offered: porcelain white (60 units) and classic red (40 units). The dashboard and centre console were trimmed with designo piano lacquer black wood. The roof liner was Alcantara in anthracite colour. The sales price was ¥13,900,000 JPY.[23]
G-Class Cabriolet «Final Edition 200» (2013–2014)[edit]
To commemorate the production end of the two-door cabriolet, Mercedes-Benz introduced the «Final Edition 200» with the G 500 being the only model variation. All of the 200 units had been sold out prior to its premiere at 2013 Frankfurt Auto Show. Externally, the soft top and tonneau cover are beige in colour, the grille is chrome-coloured, and the 5-spoke light-alloy wheels are painted in titanium grey. The B-pillars are fitted with «Final Edition 200» badges. The interior received designo leather seats and door panels coloured in ecru with black trim, satin-finished light brown poplar wood trim, and an AMG performance steering wheel.[24]
G 500 4×4²[edit]
Rear quarter view of G 500 4×4²
Continuing with the G 63 AMG 6×6 formula, Mercedes-Benz introduced the G 500 4×4², using the body of the long wheelbase 5-door station wagon on a shortened chassis from the G 63 AMG 6×6. The G500 4×4², along with the G 500/G 550, received a new 4.0-litre biturbo V8 (M176), producing 310 kW (416 hp). The exterior is the same as the Mercedes-AMG G 63 and G 65 despite the G 500 4×4² not being a Mercedes-AMG edition.[25]
Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet (2017)[edit]
Following the success of the G 63 AMG 6×6 and G 500 4×4², Mercedes-Benz introduced the first SUV under the sub-brand name Mercedes-Maybach at the Geneva Motor Show in March 2017.[26] G 650 Landaulet used the extended chassis with the portal axles and raised suspension system from the G 500 4×4². The rear end of the G 650 Landaulet was built from the rear part of the W463 cabriolet with a folding fabric roof covering the rear half of the body behind the B-pillar. The rear passenger doors with no wheel-opening cut-out were from the G 55 with extended wheelbase (2001). The front end is from the Mercedes-AMG G 65 with more chrome trims. The light alloy wheels and extendable side running boards are chrome plated. The powertrain is from the G 65 with the 463 kW (621 hp) biturbo V12.
The interior is finished in ultimate luxury as found in Mercedes-Maybach GLS-Class and S-Class. Like the original Maybach 62 Landaulet, a division wall is installed behind the driver and front passenger. The second row seats are moved further back from the rear passenger doors and are the same rear seats as used in the Mercedes-Maybach S-Class. A second control panel and centre console is installed behind the division wall toward the rear. The dashboard above the second set is one set of the two front passenger’s dashboards with a glove box and hold two large LED monitors.
The sales price was €749,700, and the production was limited to 99 units.[27]
Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet
The rear view of the Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet
AMG models[edit]
500 GE 6.0 AMG (1993-1995)[edit]
For the first time, an AMG version of the G-Class was offered in 1993 with the 500 GE 6.0 AMG. The M 117.965 E 50 engine was bored from 5.0 to 6.0 litres, producing 243 kW (326 hp) and 525 N⋅m (387 lb⋅ft). The increased output did not make the 500 GE 6.0 AMG much faster with a time of 10.9 seconds for 0–100 km/h (62 mph). Only thirteen units were built in long wheel base form and only one unit with a short wheel base.[28][29][16]
G 36 AMG (1994–1997)[edit]
After AMG entered into co-operation with Mercedes-Benz in 1993, the G 36 AMG was introduced and fitted with the M104.992, the same engine as found in the C 36 AMG and E 36 AMG.
G 43 AMG (1997–1998)[edit]
A total of 38 units of the G43 AMG were produced between 1997 and 1998, all of the as special orders under country code «293 Company Vehicle», mostly for VIPs and probably secret services. 6 of them bore 463.233 chassis numbers, as though they were G320 LWBs that had their V6 engine replaced with a type M113.982 V8 engine. Bizarrely, the remaining 32 units were coded 463.241, meaning that they were meaning to be G500 LWB that had the M113.982 AMG 4.3-litre engine fitted in lieu of the M113.962 standard 5-litre engine.
G 63 AMG V12 (2002)[edit]
The G 63 AMG V12 was a very limited production run with only five units built in 2002. It was the first G-Class with a V12 engine before Mercedes-AMG officially introduced the more powerful G 65 AMG. The engine produced 326 kW (437 hp) and propelled the G 63 AMG to 100 km/h (62 mph) in 6.5 seconds.[30]
G 55 AMG (2002–2003) and G 55 AMG Kompressor (2004–2012)[edit]
Citing the sales success of the G 500 in the United States and the absorption of AMG into DaimlerChrysler AG, Mercedes-Benz began to expand the AMG versions to several models, including the G-Class. To coincide with the official launch of the G-Class in the United States, Mercedes-Benz introduced the 55 AMG along with the G 500 in 2001 for the 2002 model year. The G 55 AMG visually did not differ from the G 500 other than side exhaust pipes, wider tyres, AMG five-spoke wheels, chrome tip at bottom of front bumper, and AMG lettering in the rear. The G 55 AMG became the favourite of celebrities and the wealthy.
For the 2005 model year, AMG revised the G 55 AMG by adding a supercharger to the 5.4-litre V8 engine, increasing the output to 350 kW (469 hp). To differentiate the G 55 AMG KOMPRESSOR from the G 500 visually, AMG changed the radiator grille to three thick fins, added the embossed metal KOMPRESSOR lettering underneath the V8 badge on the front fenders/wings, and introduced new light-alloy wheels in titanium grey and three new metallic paint colours (Calcite White, Periclase Green, and Teallite Blue). The 0–100 km/h (62 mph) acceleration was reduced from 7.4 to 5.6 seconds. Yet, the top speed remained at 210 km/h (130 mph). The engine was upgraded again for 2006 (2007MY in USA) to 368 kW (493 hp) then again to 373 kW (500 hp) for 2008 (2009MY in USA).
G 63 AMG (2012–2018)[edit]
The supercharged 5.4-litre V8 was replaced by the new 5.5-litre biturbo V8 for 2012 (2013MY in USA) for better fuel consumption and lower emissions. AMG made some more changes to the exterior to give the G 63 AMG a more «brawly» appearance: single horizontal fin with twin chrome edges in the middle of the radiator grille with a more prominent three-pointed star ornament in the middle, a new light-alloy wheel design, three enlarged airflow inlets on both sides and in the middle of the front bumper, vertical chrome stripes to cover the small bumper guards and exterior rear-view mirrors from the GL-Class and ML-Class. The mechanical upgrade was an AMG sports exhaust system with high-gloss chrome inserts, larger AMG high performance brakes with six-piston fixed calipers at the front from the ML 63 AMG and revised suspension and damper settings for more dynamic handling characteristics. The new E-SELECT gear selector from the Mercedes-Benz SLS replaced the standard gear selector.
For 2016, the name was changed to Mercedes-AMG G 63.
G 65 AMG (2012–2018)[edit]
The G 63 AMG V12, built in 2012, demonstrated the feasibility of installing a V12 engine in the G-Class. The new G 65 AMG was introduced at the same time as the G 63 AMG, making the G 65 AMG the third passenger SUV to have a V12 engine with Lamborghini LM002 (built from 1986 to 1993) being the first one. G 65 AMG was equipped as the G 63 AMG other than minor cosmetic differences with V12 BITURBO badges on the front fenders/wings, floor mats and seat backs.
Like the G 63, the name was changed to Mercedes-AMG G 65 for 2016.
G 63 AMG 6×6 (2013–2015)[edit]
To mark the thirtieth anniversary of G-Wagen production, Mercedes-Benz introduced the new stretched version with six-wheel-drive system and portal axles.[31][32] The G 63 AMG 6×6 was derived from a model developed specifically for the Australian Army in 2007. Despite the heavy weight and large dimensions, the G 63 AMG 6×6 could accelerate to 100 km/h (62 mph) in six seconds and reach a top speed of 160 km/h (99 mph).
The consumer reception of the G 63 AMG 6×6 was stronger than anticipated, and Mercedes-Benz sold slightly more than 100 units, with the last customer delivery taking place in May 2015.[33]
Mercedes-Benz G 63 AMG 6×6
Rear quarter view of the Mercedes-Benz G 63 6×6
Mercedes-Benz G 63 6×6 dashboard
Mercedes-Benz G 63 6×6 tyre pressure regulation switches
Brabus G 63 700 AMG 6×6
Concept cars[edit]
Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen Light Armoured Patrol Vehicle 6.X CONCEPT (2010)[edit]
It is an armoured patrol vehicle developed with EADS, based on LAPV 5.4. It included a diesel engine, 1.3 tonnes of cargo capacity, a monocoque full steel body, compact 2,850 mm (112.2 in) wheelbase, modular armour plate and mine deflector plate underneath the floor, adjustable variable lift front and rear coil-over air shock absorbers with a maximum of 450 mm (17.7 in) of ground clearance and hydraulic brakes with four ventilated discs. EADS provided the communication technology: vehicle data recorder system, integrated communication system for UHF or VHF bands, integrated mobile command, control and information system, and jamming system. The vehicle was unveiled in EUROSATORY 2010.[34]
Ener-G-Force (2012)[edit]
Mercedes-Benz Ener-G Force
The rear view of the Mercedes-Benz Ener-G Force
The Ener-G-Force was a concept vehicle in response to the Los Angeles Design Challenge 2012 for a future police car. The vehicle was unveiled at the 2012 LA Auto Show. The concept vehicle was hydrogen-powered with fuel cells generating the electricity to the electric motors inside the wheel hubs. A roof rack contained the water tanks with a hydrogen converter, and the body included a three-panel greenhouse, 20-inch wheels and side skirts illuminating the charge and operation status of energy packs.[35][36]
Marketing[edit]
The W463 was positioned in the marketplace as a luxury passenger vehicle to compete with the likes of Range Rover. After Mercedes-Benz launched the G-Class in the United States with the G 500 and G 55 AMG models, the G-Class became very popular with celebrities, film stars, and the wealthy. The G-Class has appeared in numerous films, television series, and music videos ever since.[37]
As part of Mercedes-Benz’s attempt to demonstrate the off-road capability of the G-Class SUV, seven G-Class vehicles took a journey from Halls Creek in Western Australia to Wiluna. However, shock absorbers on six of the vehicles (5 civilian G 350s and 1 military model) were broken during their trip on the corrugations of the Canning Stock Route on day 7. Mercedes-Benz Australia later arranged for the replacement shock absorbers to land in Perth, before transferring to a light plane destined for a remote Aboriginal settlement close to Well 33, about 1000 km from Wiluna. The parts would be delivered by the sole surviving vehicle, a G-Professional.[38][39]
End of production debacle and revised decisions[edit]
Mercedes-Benz announced that 2005 would be the final year of the G-Class to be sold in the United States, citing the new GL-Class as its successor. The 500 units of G 500 and G 55 AMG Grand Edition were built and shipped to the United States. However, an unexpected order placed by the U.S. Marine Corps for 157 Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV) based on the G-Class, replacing its ageing, slow, and cumbersome Desert Patrol Vehicles, caused Mercedes-Benz to rescind its decision and to continue offering the G-Class in the United States.
This Grand Edition also led to the rumours of the end of production of the W463 in 2006. A few factors contributed to the rumours: the increasing difficulties in meeting the newer and stricter safety and emission regulations, especially the new EU regulations on pedestrian protection; Mercedes-Benz had introduced new GL-Class as an intended successor; and military contracts fulfilled. An outcry among enthusiasts who admired the G-Class for its tremendous off-road potential along with its reputation and cachet showed that a market still existed for such a vehicle. On 11 November 2005, Dieter Zetsche, DaimlerChrysler Board of Management member and head of the Mercedes Car Group, announced that G-Class production would continue. At the Paris Motor Show in September 2006, Mercedes-Benz reiterated that the G-Class would continue to be manufactured through 2015 due to the strong worldwide demand by both civilian and military buyers.[40] Daimler AG extended the manufacturing contract with Magna Steyr to continue producing the W463 until 2017.
In late 2017, the end of production of the first generation W463 was announced with the heavily reengineered and updated successor to be introduced in 2018 for the 2019 model year.[41]
Updates (1990–2018)[edit]
1994 update[edit]
The update was minor with the model designation revised to reflect the new nomenclature system and with an enlarged six-cylinder inline petrol engine for the G 320, replacing the G 300. The Italy-only 200 GE/G 200 and 230 GE/G 230 were dropped, marking the end for the G-Class with the four-cylinder inline engine until G 350 was reintroduced for Chinese market in 2020. After the 200 GE/G 200, 230 GE/G 230, and 300 GE/G 300 were dropped in 1994, manual transmission was dropped from the W463 for good. The steering wheel received the driver’s side airbag.
1997 update[edit]
The W463 received its mechanical update in 1997. The update included a new power-assisted folding mechanism for its convertible. The engine range was revised with six-cylinder engines shifting from inline to V-form for both petrol and diesel versions. The G 500 was reintroduced with a new V8 petrol engine. The W463 received dual airbags for the driver and the front passenger.
2002 update[edit]
The external rear-view mirrors were revised with integrated turn signal repeaters and power-assisted mirror control, eliminating the separate turn signal indicators attached to the body. The front and rear turn signal indicators received a clear lens. The newly-revised headlamps for both American and international markets were also given clear glass lenses. The interior was updated with more creature comforts and better control switches. In 2002, Mercedes-Benz officially launched the G-Class in the United States for the first time since its inception in 1979 with the G 500 and G 55 AMG.
2005 update[edit]
Mercedes-Benz announced the new G55 AMG Kompressor model with a more powerful, supercharged 5.4L V8 engine (code 113.993, or M113K), replacing the naturally aspirated 5.0L V8 engine (113.982, or M113). The G 500 was renamed as G 550 for certain markets (not USA until 2009).
2006 update[edit]
This minor update revised the engine range with a new 3.2-litre V6 diesel engine in the G 320 CDI, replacing both the G 270 CDI and G 400 CDI. The G 500 and G 55 AMG Kompressor continued unchanged. The G 320 with the petrol engine was dropped, marking the suspension of six-cylinder petrol engines until 2018. The G 55 AMG Kompressor remained as a five-door station wagon while the G 320 CDI and G 500 were offered in three body styles: two-door cabriolet and station wagons with three-door short and five-door long wheelbases.
2007 update[edit]
Mercedes-Benz showcased a heavily revised 2007 model at the Paris Motor Show in September 2006 with emphasis on an updated interior, engine range, and new safety equipment.[42]
For 2007, the G-Class received its first high-intensity discharge headlamps, reversing camera, and tire pressure monitoring system (the latter two are federally mandated safety equipment for the United States). 2007 G500’s in the USA start to phase out the 722.6 5spd transmission, and instead start coming with the new 722.9 7spd transmission. The G55(K)’s still have the 722.6 5spd transmission. The G 500 could be fitted with the sports side exhaust pipes from the G 55 AMG for extra cost. The power output for the G 55 AMG was increased from 350 kW (469 hp) to 368 kW (493 hp).
The interior received a new instrument cluster with four chrome-trimmed round gauges from the C-Class and a new four-spoke multi-function steering wheel with options of full leather cover or combination of leather and wood. The centre console was updated with new control switches for the vehicle’s functions and a new climate control panel along with new COMAND APS infotainment and navigation system. In conjunction with the reversing camera, COMAND APS displays the rear view and graph representation of distance and width, assisting the driver during reversing maneuvers. The new ARTICO upholstery colour, cognac, was added to black and grey interior colour options.
2008 update[edit]
The 2008 update included a new radiator grille with three thicker horizontal fins, replacing the previous seven, thinner fins. The COMAND APS infotainment and navigation system was revised with many new or extended functions such as the LINGUATRONIC voice control system, a 12-speaker Harman Kardon Logic 7 surround sound stereo system, TV tuner and a special off-road menu for the G 320 CDI and G 500 model. Heated and ventilated front seats were also offered.
Last year for the G500 in the USA.
2009 update[edit]
The 2009 G550 replaces the 2008 G500, and gets a new 5.5-litre V8 petrol engine with 285 kW (382 hp) [mated to the 722.9 7spd transmission], replacing the 5.0-litre 218 kW (292 hp) that was in the 2008 G500. The new engine will improve the acceleration for the new G550.
For the 30th anniversary of production, Mercedes-Benz offered two special anniversary editions. One was the G 500/G 550 with a more opulent interior and exclusive designo leather upholstery along with special decals. Another one was a new utility model, the G 280 CDI Edition 30 PUR, consisting of the W461 chassis with a 3.0-litre V6 turbodiesel engine (OM 642 DE LA red.) and the W463 four-wheel-drive system.
2011 update[edit]
Last year for the G55(K) [with 722.6 5spd transmission], in the USA.
2012 update[edit]
G 63 AMG with revised front end
After its last major update in 2007, the interior received a completely redesigned instrument panel and centre console adapted from the ML-Class. The COMAND APS touchscreen and control panel were moved up toward the top of the dashboard for easier viewing and operation. The COMAND APS was updated with the MBrace2 telematics system. Additional safety features included DISTRONIC adaptive cruise control, blind-spot monitoring, revised PARKTRONIC reverse sensors and rear-view camera and revised ATS4 stability control for improved trailer stabilising functionality.
Externally, the G-Class received the same horizontal bars of LED daytime running lamps underneath the headlamps and the new external side rear-view mirrors as the GL-Class and ML-Class models. The AMG version received a new front bumper with three large air intakes.
The 5.4-litre supercharged V8 [with 722.6 5spd transmission] in the 2011 G55(K) will be replaced by a new 5.5-litre biturbo V8 [with 722.9 7spd transmission] for increased performance on the upcoming 2013 G63. Topping out the G-Class model range was a new G 65 AMG with a 6-litre biturbo V12 petrol engine. Two models were carried over unchanged: the G 350 CDI BlueTEC and G 500/G 550.[43]
2016 update[edit]
For the 2016 model year, the outgoing M273 5.5-litre naturally aspirated V8 fitted to the G 500/G 550 was replaced by the new M176 4.0-litre biturbo V8 for increased horsepower and torque.[44]
Technical data[edit]
Engine (1990–2018)[edit]
Notes: (m) and (a) denote «manual» and «automatic» transmissions where applicable. Fuel consumption marked with * denotes the older EEC regulation of «urban, 90 km/h, and 120 km/h» (U/90/120). Top speed with ** denotes the «electronically limited».
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm combined) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| 200 GE (Italy) |
1990–1994 | I4 (M 102.965 E 20 KAT) | 1,996 cc (121.8 cu in) | 87 kW (117 hp) at 5,200 rpm | 172 N⋅m (127 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 20.8 seconds | 144 km/h (89 mph) | 15.6 L/100 km (15.1 mpg‑US)* 11.1 L/100 km (21.2 mpg‑US)* 15.7 L/100 km (15.0 mpg‑US)* |
| 230 GE G 230 |
1990–1995 | I4 (M 102.989 E 23 KAT) | 2,298 cc (140.2 cu in) | 93 kW (125 hp) at 5,000 rpm | 190 N⋅m (140 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 17.7 seconds (m) | 145 km/h (90 mph) (m) | 16.4 L/100 km (14.3 mpg‑US)* (m) 12.7 L/100 km (18.5 mpg‑US)* 17.3 L/100 km (13.6 mpg‑US)* |
| 18.4 seconds (a) | 144 km/h (89 mph) (a) | 15.1 L/100 km (15.6 mpg‑US)* (a) 13.1 L/100 km (18.0 mpg‑US)* 18.0 L/100 km (13.1 mpg‑US)* |
||||||
| 300 GE G 300 |
1990–1994 | I6 (M 103.987 E 30 KAT) | 2,962 cc (180.8 cu in) | 125 kW (168 hp) at 5,700 rpm | 190 N⋅m (140 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 13.5 seconds (m) | 164 km/h (102 mph) (m) | 18.7 L/100 km (12.6 mpg‑US)* (m) 13.4 L/100 km (17.6 mpg‑US)* 17.7 L/100 km (13.3 mpg‑US)* |
| 14 seconds (a) | 162 km/h (101 mph) (a) | 18.2 L/100 km (12.9 mpg‑US)* (a) 14.2 L/100 km (16.6 mpg‑US)* 19.2 L/100 km (12.3 mpg‑US)* |
||||||
| G 320 | 1994–1998 | I6 (M 104.996 E 32) | 3,199 cc (195.2 cu in) | 155 kW (208 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 300 N⋅m (221 lb⋅ft) at 3,750 rpm | 12.1 seconds | 175 km/h (109 mph) | 16.6 L/100 km (14.2 mpg‑US)* 14.0 L/100 km (16.8 mpg‑US)* 18.4 L/100 km (12.8 mpg‑US)* |
| 1997–2006 | V6 (M 112.945 E 32) | 3,199 cc (195.2 cu in) | 160 kW (215 hp) at 5,600 rpm | 300 N⋅m (221 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,800 rpm | 10.9 seconds | 175 km/h (109 mph) | 15.5 L/100 km (15.2 mpg‑US) | |
| G 36 AMG | 1994–1995 | I6 (M 104.992 E 36) | 3,606 cc (220.1 cu in) | 206 kW (276 hp) at 5,750 rpm | 385 N⋅m (284 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 9.6 seconds | 190 km/h (118 mph) | — |
| 500 GE | 1993–1994 | V8 (M 117.965 E 50) | 4,973 cc (303.5 cu in) | 177 kW (237 hp) at 5,200 rpm | 365 N⋅m (269 lb⋅ft) at 3,750 rpm | 11.4 seconds | 180 km/h (112 mph) | — 16.1 L/100 km (14.6 mpg‑US)* 21.8 L/100 km (10.8 mpg‑US)* |
| 500 GE 6.0 AMG[16] | 1993 | V8 (M 117.965 E 50) | 5,953 cc (363.3 cu in) | 243 kW (326 hp) at 5,250 rpm | 525 N⋅m (387 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 10.9 seconds | 195 km/h (121 mph) | — |
| G 500 G 550 (USA, 2005–2018) |
1998–2008 | V8 (M 113.965 E 50) | 4,966 cc (303.0 cu in) | 218 kW (292 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 456 N⋅m (336 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,000 rpm | 9.7–10.2 seconds | 190 km/h (118 mph) | 16.7 L/100 km (14.1 mpg‑US) |
| 2008–2015 | V8 (M 273 KE 55) | 5,461 cc (333.3 cu in) | 285 kW (382 hp) at 6,000 rpm | 530 N⋅m (391 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,800 rpm | 5.9–6.1 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 14.9 L/100 km (15.8 mpg‑US) | |
| 2015–2018 | V8 biturbo (M 176 DE 40 AL) | 3,982 cc (243.0 cu in) | 310 kW (416 hp) at 5,250–5,500 rpm | 610 N⋅m (450 lb⋅ft) at 2,250–4,750 rpm | 5.9 seconds | 12.3 L/100 km (19.1 mpg‑US) | ||
| G 500 4×4² | 2015–2018 | 7.4 seconds | 13.8 L/100 km (17.0 mpg‑US) | |||||
| G 55 AMG | 2001–2003 | V8 (M 113 E 55) | 5,439 cc (331.9 cu in) | 260 kW (349 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 525 N⋅m (387 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,000 rpm | 7.4 seconds | 209 km/h (130 mph) | 15.9 L/100 km (14.8 mpg‑US) |
| 2004–2006 | V8 supercharged (M 113 E 55 ML) | 350 kW (469 hp) at 6,100 rpm | 700 N⋅m (516 lb⋅ft) at 2,650–4,500 rpm | 5.6 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 16.3 L/100 km (14.4 mpg‑US) | ||
| 2006–2008 | 368 kW (493 hp) at 6,100 rpm | 700 N⋅m (516 lb⋅ft) at 2,750–4,000 rpm | 5.5 seconds | 15.9 L/100 km (14.8 mpg‑US) | ||||
| 2008–2012 | 373 kW (500 hp) at 6,100 rpm | |||||||
| G 63 AMG (V8) | 2012–2015 | V8 biturbo (M 157 DE 55 AL) | 5,461 cc (333.3 cu in) | 400 kW (536 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 800 N⋅m (590 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–5,000 rpm | 5.4 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph)** | 13.8 L/100 km (17.0 mpg‑US) |
| Mercedes-AMG G 63 |
2015–2018 | 420 kW (563 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 800 N⋅m (590 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–5,000 rpm | |||||
| G 63 AMG (V12) | 2002–2003 | V12 (M 137 E 63) | 6,258 cc (381.9 cu in) | 326 kW (437 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 620 N⋅m (457 lb⋅ft) at 4,400 rpm | 6.5 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | — |
| G 63 AMG 6×6 | 2013–2015 | V8 biturbo (M 157 DE 55 AL red.) | 5,461 cc (333.3 cu in) | 400 kW (536 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 760 N⋅m (561 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–5,000 rpm | 7.9 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | — — 15.6 L/100 km (15.1 mpg‑US) |
| G 65 AMG | 2012–2015 | V12 biturbo (M 279 E 60 AL) | 5,980 cc (365 cu in) | 450 kW (603 hp) at 4,300–5,600 rpm | 1,000 N⋅m (738 lb⋅ft) at 2,300–4,300 rpm | 5.3 seconds | 230 km/h (143 mph) | 17.0 L/100 km (13.8 mpg‑US) |
| Mercedes-AMG G 65 |
2015–2018 | 463 kW (621 hp) at 4,800–5,400 rpm | ||||||
| Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet | 2017-2018 | 6.0 seconds | 180 km/h (112 mph) | — | ||||
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| 250 GD | 1990–1992 | I5 (OM 602.931 D 25) | 2,497 cc (152.4 cu in) | 69 kW (93 hp) at 4,600 rpm | 158 N⋅m (117 lb⋅ft) at 2,600–3,100 rpm | 28.1 seconds | 132 km/h (82 mph) | 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US)* 10.5 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US)* 15.2 L/100 km (15.5 mpg‑US)* |
| G 270 CDI | 2002–2006 | I5 turbo (OM 612.965 DE 27 LA) | 2,685 cc (163.8 cu in) | 115 kW (154 hp) at 4,200 rpm | 400 N⋅m (295 lb⋅ft) at 1,800–2,600 rpm | 13.2–13.7 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) 9.6 L/100 km (25 mpg‑US) 10.9 L/100 km (21.6 mpg‑US) |
| 300 GD G 300 D |
1990–1994 | I6 (OM 603.931 D 30) | 2,996 cc (182.8 cu in) | 83 kW (111 hp) at 4,600 rpm | 191 N⋅m (141 lb⋅ft) at 2,700–2,900 rpm | 22.2 seconds (m) | 141 km/h (88 mph) (m) | 14.7 L/100 km (16.0 mpg‑US)* (m) 10.9 L/100 km (21.6 mpg‑US)* 16.0 L/100 km (14.7 mpg‑US)* |
| 23.3–23.6 seconds (a) | 138–141 km/h (86–88 mph) (a) | 12.5 L/100 km (18.8 mpg‑US)* (a) 10.8 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US)* 15.9 L/100 km (14.8 mpg‑US)* |
||||||
| G 300 D TURBODIESEL | 1996–2001 | I6 turbo (OM 606.964 D 30 LA) | 2,996 cc (182.8 cu in) | 130 kW (174 hp) at 4,400 rpm | 330 N⋅m (243 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–3,600 rpm | 14.2 seconds (m) | 164 km/h (102 mph) | 14.6 L/100 km (16.1 mpg‑US) 10.6 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US) 12.1 L/100 km (19.4 mpg‑US) |
| G 320 CDI | 2006–2009 | V6 turbo (OM 642 DE 30 LA) | 2,987 cc (182.3 cu in) | 165 kW (221 hp) at 3,800 rpm | 540 N⋅m (398 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,400 rpm | 8.8–9.1 seconds | 177 km/h (110 mph) | 13.4 L/100 km (17.6 mpg‑US) 9.7 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 11.0 L/100 km (21.4 mpg‑US) |
| 350 GD T G 350 TURBODIESEL |
1992–1996 | I6 turbo (OM 603.972 D 35 A) | 3,449 cc (210.5 cu in) | 100 kW (134 hp) at 4,000 rpm | 305 N⋅m (225 lb⋅ft) at 1,800 rpm | 16 seconds | 150 km/h (93 mph) | 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US) 11.8 L/100 km (19.9 mpg‑US) 16.9 L/100 km (13.9 mpg‑US) |
| G 350 CDI | 2009-2010 | V6 turbo (OM 642 DE 30 LA) | 2,987 cc (182.3 cu in) | 165 kW (221 hp) at 3,800 rpm | 540 N⋅m (398 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,400 rpm | 8.8–9.1 seconds | 177 km/h (110 mph) | 16.1 L/100 km (14.6 mpg‑US) 11.0 L/100 km (21.4 mpg‑US) 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) |
| G 350 CDI BlueTEC | 2010-2015 | 155 kW (208 hp) at 3,400 rpm | 175 km/h (109 mph) | 13.6 L/100 km (17.3 mpg‑US) 9.8 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 11.2 L/100 km (21.0 mpg‑US) |
||||
| G 350 d | 2015–2018 | V6 turbo (OM 642 LS DE 30 LA) | 180 kW (241 hp) at 3,600 rpm | 600 N⋅m (443 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,400 rpm | 8.8 seconds | 192 km/h (119 mph) | 11.1 L/100 km (21.2 mpg‑US) 9.1 L/100 km (26 mpg‑US) 9.9 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) |
|
| G 350 d Professional | 2016-2018 | 160 km/h (99 mph) | ||||||
| G 400 CDI | 2001-2006 | V8 biturbo (OM 628.962 DE 40 LA) | 3,996 cc (243.9 cu in) | 184 kW (247 hp) at 4,000 rpm | 560 N⋅m (413 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–2,600 rpm | 9.9–10.3 seconds | 182 km/h (113 mph) | 16.1 L/100 km (14.6 mpg‑US) 11.0 L/100 km (21.4 mpg‑US) 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) |
G-Class W463, second generation (2018–present)[edit]
| Mercedes-Benz G-Class (W463) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 2018–present |
| Model years | 2019–present |
| Assembly | Austria: Graz (Magna Steyr) |
| Designer | Balázs Filczer[45] |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size luxury SUV |
| Body style | 5-door SUV |
| Layout | F4 (4MATIC) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 9G-Tronic, AMG SpeedShift TCT (9-speed automatic) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,890 mm (113.8 in) |
| Length | 4,725–4,817 mm (186.0–189.6 in) |
| Width | 1,931 mm (76.0 in) |
| Height | 1,969 mm (77.5 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,354–2,485 kg (5,190–5,478 lb) |
The second generation G-Class (W463) was launched on 14 January 2018 at the North American International Auto Show in Detroit.[46]
In contrast to its predecessor, the new G-Class has grown 121 millimeters in width and 53 millimeters in length. The ground clearance has increased by 6 millimeters.[47] The increase in width is for more driving stability, sturdier side impact protection, and more seating comfort. The increased length, especially in the front end, is due to the new 2019 EU pedestrian impact safety regulations: the previous generation did not have enough open space between the car’s front end and the rigid components beneath for the crumple zone as to mitigate the injury to a pedestrian’s body.
A major change was with the steering system which was switched from a recirculating ball system to variable-ratio rack-and-pinion with adaptive electric power assistance. The new steering system allows safety and convenience equipment such as active lane-keeping assist, Pre-Safe collision avoidance systems and self-parking capability. The rack-and-pinion steering system does not work with solid front suspension so a change was made to use independent front suspension.
The extensive, ground-up redesign allowed engineers to incorporate more lightweight materials such as high-strength and ultra-high-strength steels and aluminums. In addition, the redesign led to an improved manufacturing process which increased structural rigidity. The gap between the doors and body shell is much narrower than the previous generation. Despite the increased dimensions, the weight has been reduced by about 170 kilograms.
The second generation W463 is similar visually to the first generation, and the chassis code, W463, is still retained rather than W464 as some media outlets erroneously reported. However, only three parts from the previous generation were carried over to the new generation: the headlamp washers, the push-button door handles and the spare wheel cover bolted to the rear tailgate.[48]
The new G 500 (renamed to G 550 for 2020 onwards) is powered by the 4.0-liter M176 V8 twin-turbo engine, producing 416 hp and 450 lb⋅ft of torque. It is mated to a nine-speed automatic 9G-Tronic transmission with torque-converter.[49][50]
For the new diesel variant, the G 350d was initially released for the 2019 model year, powered by the 2.9-liter OM656 inline-6 turbocharged diesel engine, producing 282 hp and 443 lb⋅ft of torque.[51] The G 400d was later introduced for the 2020 model year onwards. The G 400d features the same OM656 engine as the G 350d, but output has been increased to 326 hp and 516 lb⋅ft of torque.[52] Both models are still produced by Mercedes-Benz, however certain markets only sell one of the two.[53]
The redesign also allowed newer safety and collision avoidance equipment from the W222 S-Class to be fitted to the G-Class for the first time. In addition, the updated interior has a new instrument cluster and infotainment system from other Mercedes-Benz models (A-Class (W177) and E-Class (W213)), air vents, steering column-mounted gear selector, multimedia system and control panel on the tunnel console, a higher level of luxury trimming and 64-color ambient lighting. A Burmester surround sound system and a larger dual 12-inch LCD display with smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay and Android Auto) were offered as optional equipment. One design element carried over to the new generation was the front passenger’s grab bar on the dashboard.[54]
The new G 550 and AMG G 63 have gone on sale in the United States with a starting price of $125,495 and $144,695 respectively. The 2019 G-Class for the US market has the widest range of exterior colors available, totaling 24, of any Mercedes-Benz passenger vehicle.[50]
In September 2020, the G 350 was introduced for the Chinese market to circumvent the heavy taxation on larger engine displacement.[55] It is powered by the 2.0-liter M264 turbocharged inline-4, producing 255 hp and 273 lb-ft of torque.The G 350 is the first G-Class with a four-cylinder inline engine since the previous model, the G 230, was dropped in 1995.
AMG models[edit]
AMG G 63[edit]
Alongside the new G 550, Mercedes-AMG unveiled the new G 63 in March 2018 at the Geneva International Motor Show. The model is powered by the V8 twin-turbo M177 engine, producing 577 hp and 627 lb⋅ft of torque, an increase of 14 hp and 66 lb⋅ft over the previous generation G 63 AMG. Mercedes-AMG claims a 0-60 mph time of 4.4 seconds and a top speed of 149 mph with the optional Driver’s Package. The G 63 now defaults to a rear-biased 40:60 torque split versus the 50:50 split of its predecessor.[56][57][58]
In addition to the performance increases over the standard G 550 with the AMG model, the G 63 also features AMG-developed suspension, larger red brake calipers and perforated brake discs, AMG-specific transmission modes, radiator grille, flared wheel arches, striking side pipes on the exhaust system, and wider wheels up to 22-inches in diameter. The model features distinct front and rear fascias and body styling, as well as an AMG-specific interior with a standard AMG Performance steering wheel with flattened bottom.[56]
-
AMG G 63
-
AMG G 63 rear
-
AMG G 63 (Japan) interior
AMG G 63 Edition 1[edit]
To commemorate the launch of the second-generation G-63, Mercedes-AMG released the Edition 1 special edition at market launch. The special model features Designo Night Black Magno paint with contrasting matte Graphite Grey sports stripes along the vehicle sides, a decorative red stripe on the exterior mirrors, and Night Package featuring gloss black trim and accents. The Edition 1 also features matte black 22-inch forged wheels with red-painted rim flanges and a cross-spoke design, as well as red accents throughout the interior.[56]
-
AMG G 63 Edition 1 at the Geneva Motor Show 2018
-
AMG G 63 Edition 1 rear
AMG G 63 Trail Package[edit]
The optional AMG Trail Package can be specified for the G 63 model only, offering greater off-road capability and styling. The package adds softer settings for the adaptive dampers to enhance off-road driving and maneuverability. 20-inch wheels with five sets of twin spokes and all-terrain tires are part of the package. A black skid plate and mud flaps behind the rear wheels are fitted to the body.[59]
AMG G 63 4×4²[edit]
Following the previous generation’s G 63 AMG 6×6 and G 500/G 550 4×4², Mercedes-Benz-AMG introduced the new G 63 4×4² for the second generation iteration in June of 2022 via YouTube.[60] The AMG G 63 4×4² features the same M177 V8 twin-turbo as the standard AMG G 63 but with output increased to 585 hp from 577 hp, and raised portal axles like the previous generation G 500/G 550 4×4², except now with independent front axles.[61][62] The model went on sale Fall 2022 for the 2023 model year at a price of $350,050 USD.[63]
Compared to the standard AMG G 63, the AMG G 63 4×4² features a raised height, larger carbon-fiber fenders, 22-inch wheels with 37-inch Pirelli 325/55R22 all-terrain tires, LED light bar, roof rack with carbon-fiber windscreen, carbon-fiber spare tire cover, and rugged styling. With this increase in height, the model offers a ground clearance 4.3 inches over stock at 13.8 inches, wading depth 8.2 inches over stock at 35.8 inches, and 41.3° approach and 36.8° departure angles.[64]
Additionally, compared to the previous generation G 500/G 550 4×4², the wheelbase is increased by 0.9 inch to 113.1 inches, height is increased by 0.8 inch to 88.8 inches, width is increased by 5.4 inches to 82.5 inches, and length is increased by 3.9 inches to 181.1 inches, or 194.5 inches when accounting for the spare tire carrier. Weight is decreased by 379 lbs to 6,315 lbs. Mercedes-Benz claims an estimated 5.0 0-60 mph time.[63]
Special models[edit]
Mercedes-Benz G 550 manufaktur Program (W463) front view
Mercedes-Benz G 550 manufaktur Program (W463) rear view
G manufaktur (Individualisation Programme)[edit]
Mercedes-Benz has introduced the bespoke/individualisation programme exclusive for the G-Class: G manufaktur. Similar to the Mercedes-Benz designo programme, buyers can specify different colour and material options. For the exterior, buyers can choose from 26 exclusive G manufaktur paint colours, and the Black Accents covers for the fender flares, roof, front and rear bumpers, external rear-view mirrors, rub stripes, spare wheel cover ring, wheels, side exhaust pipe tips, etc in gloss black paint. For the interior, 64 different seat colour combinations and three patterns can be specified. The dashboard and steering wheel cover can be ordered with a two-toned colour combination. On the passenger grab bar, the G manufaktur brand is etched on the stainless steel trim.[65]
Stronger Than Time[edit]
To celebrate the 40th anniversary of the G-Class and the 20th anniversary of the G 55 AMG, Mercedes-Benz introduced the Stronger Than Time edition for the G 400 d, G 500, and Mercedes-AMG G 63. For the G 400 d and G 500, the edition is fitted with the AMG Line exterior package, black 20-inch AMG wheels, and stainless steel trim for the running boards, spare wheel cover, and door sills. The puddle lamps display the G-Class logo and Stronger Than Time on the ground. The driver’s assistance package, LED headlamps, Burmester surround stereo system, and sunroof are added as standard equipment. The G 63 has a dark chrome grille and matte chrome covering the running boards, exhaust outlets, mirror caps, portions of the front and rear bumper, skid plate, and sections of the spare wheel cover. The 22-inch matte black AMG wheels are fitted to the G 63.
Three interior designs can be chosen: black Nappa leather with gold stitching and open-pore black ash wood trim; a mix of Macchiato Beige and Yacht Blue leather with light brown sen wood trim; and Macchiato Beige and Lounge Red with piano black lacquer. The Nappa leather trim covers the roof grab handles and the instrument cluster cover. The two-tone black and Titanium Grey Pearl Nappa leather with carbon fiber trim is exclusive to the G 63 model.
Professional Line[edit]
With the success of Worker, Pur, and Professional variants in the previous W461 generation, Mercedes-Benz introduced the new Professional Line Exterior at the IAA Mobility 2021 in Munich.[66] Professional Line Exterior is an exterior accessory options that the owners can customise their G-Class vehicles. The options include climbing ladder, roof rack, simpler spare wheel holder, black trims, headlamp protection grill shield, and like. Unlike the previous Worker, Pur, and Professional variants, Professional Line Exterior isn’t a stripped-down utilitian version of G-Class and based on W461 chassis.[67]
-
W 463 Professional Line rear
Concept cars[edit]
Mercedes-Benz Concept EQG front view at the IAA 2021
Mercedes-Benz Concept EQG rear view at the IAA 2021
Concept EQG[edit]
On 5 September 2021, Mercedes-Benz previewed Concept EQG, the G-Class concept car with pure electric drive, at IAA Mobility 2021 in Munich.[68] Externally, Concept EQG carries the styling of the second generation G-Class, with updated elements to distinguish the electric variant, such as a square tire cover, extensive additional LED lighting including a LED Black Panel grille, updated front and rear fascias, new 22-inch wheels, and special roof rack. While Mercedes-Benz has not revealed the technical data yet, Concept EQG has four electric motors that are placed closer to the wheels and that can operate independently; the battery packs are 108 kWH. Additionally, a two-speed gearbox allows the gear reductions for the off-road travel.[68][69] The model names are EQG 560 4MATIC and EQG 580 4MATIC.[70][71] The production version is confirmed for 2024.[72][73]
Technical data[edit]
Engines (2018–present)[edit]
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm combined) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| G 350 (China) | 09/2020–present | I4 turbocharger (M264 E20 DEH LA) | 1,991 cc (121.5 cu in) | 190 kW (258 PS; 255 hp) | 370 N⋅m (273 lb⋅ft) | 8.1 seconds | 190 km/h (118 mph) | 10.7 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US) |
| G 500 G 550 (US and certain markets) |
05/2018–present | V8 twin-turbo (M176 DE40 LA) | 3,982 cc (243.0 cu in) | 310 kW (421 PS; 416 hp) at 5,250–5,500 rpm | 610 N⋅m (450 lb⋅ft) at 2,250–4,750 rpm |
5.9 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 11.5–12.1 L/100 km (20.5–19.4 mpg‑US) |
| Mercedes-AMG G 63 | 06/2018–present | V8 twin-turbo (M 177 DE 40 AL) | 3,982 cc (243.0 cu in) | 430 kW (585 PS; 577 hp) at 6,000 rpm | 850 N⋅m (627 lb⋅ft) at 2,500–3,500 rpm | 4.5 seconds | 220 km/h (137 mph) / 240 km/h (149 mph)* | 11.5–12.1 L/100 km (20.5–19.4 mpg‑US) |
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| G 350 d | 01/2019–present | Inline 6 turbo (OM 656 D 29 R SCR) | 2,925 cc (178.5 cu in) | 210 kW (286 PS; 282 hp) at 3,400 rpm | 600 N⋅m (443 lb⋅ft) at 1,200–3,200 rpm | 7.4 seconds | 199 km/h (124 mph) | 9.6–9.8 L/100 km (25–24 mpg‑US) |
| G 400 d | 07/2019–present | Inline 6 turbo (OM 656 D 29 R SCR) | 2,925 cc (178.5 cu in) | 243 kW (330 PS; 326 hp) at 3,400 rpm | 700 N⋅m (516 lb⋅ft) at 1,200–3,200 rpm | 6.4 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 9.6 L/100 km (25 mpg‑US) |
*With optional extra cost AMG Driver’s Package
Transmission (2018–present)[edit]
| Model | Years | Types |
|---|---|---|
| G 350 | 2020–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
| G 500 / G 550 | 2018–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
| Mercedes-AMG G 63 | 2018–present | 9-speed automatic AMG SPEEDSHIFT TCT 9G |
| G 350 d | 2019–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
| G 400 d | 2019–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
Safety[edit]
Gallery[edit]
Mercedes-Benz G 500
Mercedes-AMG G 63 Edition 1
Mercedes-AMG G 63 Edition 1 rear
Military operators[edit]
Map of military Mercedes-Benz G-Class operators
Albania
- Since the 2010s, the Albanian Army has been using G-Class vehicles.
Algeria
- Since the 2010s, the Algerian Army, Gendarmerie Nationale and the Algerian police have been using several models of G-Class vehicles 4×4 6×6 G 500. Most of those vehicles are manufactured in Bouchekif factory Tiaret, owned by the Algerian army.[1] First G-Class wagons released in 2015.[citation needed]
Argentina
- Since the 1980s, the Argentine Army has used the MB-230G (short and long chassis) for different purposes. 900 remain in service.[75]
Australia
- In October 2007, Mercedes-Benz became the preferred tenderer for the Australian Defence Force to replace the fleet of Land Rover Perentie in Project Land 121 Overlander.[76] Mercedes-Benz was the sole tenderer with neither Toyota for the Land Cruiser or Land Rover for the Defender submitting a proposal. In October 2008, an initial contract for 1200 vehicles was signed.[77] 2,268 vehicles were purchased with ten variants including 6×6.[78][79] Australia is the first military customer to receive 6×6 vehicles and these are the first six-wheel military vehicles built by Mercedes-Benz since 1941.[80]
Austria
- The Austrian Army has been a long time user of various Puch G models.
Belgium
- The Belgian Police or «Gendarmerie-Rijkswacht» has been a long time user of first G 500 models.
Bulgaria
- The Bulgarian Army operates 600+ vehicles in various configurations, most of them armed.
Cambodia
- Royal Gendarmerie of Cambodia purchased 30 armored Mercedes-Benz G-Class from RMA Cambodia.
Cameroon
- 60 «Wolf» in service with the Cameroon Armed Forces.[81]
Canada
- A total of 1,159 vehicles have been ordered by the Canadian Army beginning in late 2003.[82] An armoured kit can be fitted (or removed) in 8 hours by three soldiers. Their light armour has been criticised for leading to loss of life in Afghanistan, however it is considerably better than the Iltis predecessor.[83]
- Delivery of these vehicles to Reserve units has also begun. They will be deployed in armoured reconnaissance units. It is in the final stages of fully replacing the Iltis in most units as the armoured reconnaissance vehicle in use LFCA. Other units will replace the Iltis with a militarized Chevrolet Silverado known as the MILCOTS (or colloquially as the «Milverado».) For the most exposed missions in Afghanistan 75 RG-31 Nyalas built by BAE Land Systems OMC, South Africa were used.[84]
Croatia
- Croatia bought 300 to 320 vehicles for needs of Croatian army and for operations in Afghanistan additional 30 RG-31 vehicles were delivered. Croatia uses mix of 4×4 vehicles in peacekeeping operations and the G-Class is a very popular choice within the Croatian Army. G-Class is supplemented by Land Rover Wolf and Iveco LMV.
Denmark
- The Danish military bought the 240 GD (/24, /28 and /34 variants) to supersede the M151A1, the Volkswagen 181 («Jagdwagen») and the Land Rover 88.[85] First deliveries of the 240 GD were in 1985 and later the 290 GD (/24 and /28 variants) were also introduced. More than 1,300 have been put in service. A few 300 GE’s have also been used — mainly by the Danish army EOD-services.[86] Currently the Danes are taking delivery of over 2,000 270CDIs in several variants, starting in 2003.[87]
East Timor
- used by units of Army of the Timor Leste Defence Force.[citation needed]
Egypt
- The Egyptian Army uses the G 320 (4 × 4) armoured personnel carrier has been designed as a private venture by the Kader Factory for Developed Industries and is based on the chassis of the commercial German Mercedes-Benz MB 320G (4 × 4) light vehicle. This vehicle is based on the long-wheelbase version of the German Mercedes-Benz G 320 4 × 4 with the chassis frame being modified by a heavy-duty suspension which has been designed to withstand the additional weight imposed by the armour package.[88]
Estonia
- The Estonian Defence Forces have a small number of various G-Class vehicles, which were purchased to replace the outdated UAZ and Volkswagen Iltis vehicles.
Finland
- The Finnish Army uses the Geländewagen mostly as armored vehicles and ambulances, but other versions are also in service.
France
- The French Army has the Peugeot P4 which is a derivative from the G-Class equipped with Peugeot engine and equipment.
A Wolf of the German Army
Germany
- The German Armed Forces uses the G-Class under the name «Wolf». Over 12,000 vehicles have been delivered in over 50 versions, ranging from ambulance vehicles to armored vehicles used by the German special forces. In the 1970s the cheaper Volkswagen Iltis was preferred; now the Iltis is replaced by the «Wolf» and the armoured variant LAPV Enok.
A Greek Army vehicle in Military Police colours
Greece
- The Greek Army as well as Air Force, Navy and Police have several versions (462) of the Geländewagen, manufactured by ELBO the Hellenic Vehicles Industry.[2]
Hungary
- The Hungarian Ground Forces have 233 of G-270 CDI BA 10, which is mounted with UMF light-machine gun platform, and 5 of G-280 CDI BA6 C+R SSA FB6. More will be purchased between 2010 and 2013.
Indonesia
- Paspampres (Indonesian Presidential Security forces) are using G 270 CDI for their fleet with SIRINA lights, Gunner Roof Mount, Bullbar, Black Grill, Roof and Rear View Mirror Handles. New model of G 300 CDI in 2010 acquired not less than 30 units for presidential and vice-presidential escort purposes. The Paspampres uses black G 300 CDI with the Military Police in white and ensigns with Indonesian MP insignia.
Iraq
- The Kurdish Peshmerga has 60 «Wolf» including 20 lightly armored type to help fight off the ISIL forces.[89]
Ireland
- The Irish Army used a number of G-Wagens as ambulances.
Kosovo
- The KSF use more than 200.
Latvia
- The Latvian Land Forces and Latvian National Guards use different modifications of Geländewagen, including armored.
Lebanon
- The Lebanese Army operates 20 G-wagon donated by Royal Dutch Army as ambulances
Lithuania
- The Lithuanian Armed Forces operates approximately 200 formerly Dutch GD vehicles since delivery in 2016.[90] On December 17, 2021, the National Defence Volunteer Force will receive 125 ex-Dutch GDs for patrolling the land border with Belarus.[91]
Luxembourg
- The Military of Luxembourg uses the 300D variant of the Geländewagen.
Norwegian military MB240GD
Malaysia
- Locally built by DEFTECH since 2001, the G-Wagon is used along with Land Rover Defender as light transport of Malaysian Army.[92] It uses the GD280 chassis.[93]
Mexico
- The Mexican naval defense secretary (SEMAR) announced in 2008, a contract to purchase large numbers of Mercedes-Benz military vehicles for the Mexican Marine corps. As of May 16, 2009 The SEMAR has received 20 of the 84 G-Class vehicles in order.[94][95]
Mongolia
- The Ministry of Defense of Mongolia operates 10 G-class vehicles (Wolf) donated by the German Government in 2010.[96]
Netherlands
- The Royal Netherlands Army uses various versions of the Mercedes-Benz G-Class, mostly 461 290GD manual gearbox, 290GD TD manual gearbox models and a 280cdi V6 model with automatic gearbox. The Dutch police and Koninklijke Marechaussee also use the G-Class. Most of the police versions are armored 463 models.
North Korea
- The Korean People’s Army appears to have acquired G-class vehicles, some of which were seen on the Workers’ Party of Korea 65th anniversary military parade.[97] At the funeral of Kim Jong-il his hearse was flanked by G-Class vehicles.[98]
Norway
- The Norwegian Army bought 240 GD to replace Volvo and Land Rover 4×4 vehicles in the mid-1980s, and 300 GD to use as ambulances. The 300GD is also used to transport the launch control station and optical sensors for the NASAMS Air-defense system. During the 90’s 290 GD’s where bought, and in the first half of the 00’s a small number of armoured 270 CDI’s were put into service. Today the Defence Forces operates a total of 3000 vehicles. The escort company of the Norwegian Royal Guard employs a black G 500 AMG with police lights on the roof.
Poland
- 96 GD 290 and 25 MB290GD WD in service with Wojska Lądowe. 13 GD 290 in service with the Żandarmeria Wojskowa.[99]
Portugal
- The Portuguese Marine Corps uses the G-class for light transport along with Toyota Landcruiser and Land Rover Defender 90.[100]
Russia
- Police, state security units, military and governmental agencies are using the G-Class. Mostly civilian versions in black. Security escort vehicles for both the President and Prime Minister are black G 500 and G 55 AMG.
Serbia
- The Serbian Military currently uses Puch 300GD model. They also uses the following models in 300GD33, 300GD6 and 300GD10 variants, for transport of VIP persons in 300GD3-LUX and 300GD6-LUX and Special Forces Brigade is use modified version designed for access to combat zone.
Singapore
- The Singapore Army bought the 270 and 290 versions as secondary military transport. It is used in soft-top truck configuration and is known as a 1.5-tonner or simply «MB» to its users. And also some were used also for patrolling in a «jeep» form. The Army also deploys the extremely short-wheelbase, soft-top version for its Colonels, Battalion COs, Brigade and Division Commanders as personal field transports.
Slovenia
- The Military of Slovenia uses Mercedes-Benz G-Class vehicles mainly for transport.
Slovakia
- The Armed Forces of Slovak republic uses Mercedes-Benz G-280 CDI in 5th Special Forces Regiment.
Sweden
- The Swedish Army uses MB 290/T (1994), MB 290GD (2000) and MB 270 CDI (2005). The GW is to be the main light terrain vehicle in the Swedish armed forces in the future. In 2011 a framework agreement was signed between FMV and Daimler AG. An initial contract for 105 300 CDI was signed.[101][102]
Switzerland
- The Swiss Armed Forces uses the 230 with soft top as the primary general purpose carrier, and a hardtop version as mobile radio access point. It is in service since 1985 and gradually replaced Willys Jeeps, Steyr-Puch Haflinger light transports and Pinzgauer medium transports in the liaison and transport role. All versions in Swiss Army use are unarmed. From 2014, the Steyr Daimler Puch 230 GE is going to be gradually replaced by the Mercedes-Benz G 300 CDI 4×4 hardtop version, starting with a first series of 3,200 vehicles.
United Kingdom
- An Argentine Army G-Class captured by the British Army during the Falklands War was subsequently used by No. 18 Squadron RAF in West Germany for several years.[103] The British Commanders’-in-Chief Mission to the Soviet Forces in Germany (BRIXMIS) also used a number.[104]
Ukraine
- Police, state security units, military and governmental agencies are using the G-Class. Mostly civilian versions in black. Security escort vehicles for both the President and Prime Minister are black G 500 and G 55 AMG.
United States
-
The USMC Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV) is a modified version of the Mercedes-Benz Geländewagen 290. It replaces the modified M-151A21⁄4 ton truck jeep used by the Marines as an FAV in the 1990s. The U.S. Marine Corps acquired 157 of the IFAVs distributed as follows:
- (I) Marine Expeditionary Force (MEF) Camp Pendleton, CA (33);
- (II) MEF Camp Lejeune, NC (25);
- (III) MEF on Okinawa, Japan (27);
- (IV) 17 Force Recon, Afghanistan (22);
- (V) 3 Force Recon Bn, Iraq (23);
- (VI) 1st Provisional DMZ Police Company, Korea (15); and
- (VII) various miscellaneous (12)
In the late 1990s the USMC acquired the G-Class model as the Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV), which was essentially a ’97 to ’01 DaimlerChrysler model 290 GDT, a diesel-power 2-door with a pick-up bed.[105] This was compact and light enough to be transported inside a Sikorsky CH-53 Sea Stallion Helicopter.[105]
Bodystyles[edit]
| Code | Bodywork | Wheelbase | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Convertible with fixed windshield | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | Only civilian types: 460 and 463 |
| 2 | Van | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 3 | Station Wagon | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | All types except Professional and Greenline military types |
| 4 | Van | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | Only 460/461/Professional/Worker and military types |
| 5 | Pickup | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | Only 460/461 types and G 63 6×6 (W463) |
| 6 | Station Wagon | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | All types |
| 7 | Convertible with folding windshield | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | Only military types |
| 8 | Code unused | N/A | N/A |
| 9 | Chassis Cab | 3,120 mm (122.8 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 9,1 | Chassis Cab | 3,400 mm (133.9 in) | Only 460/461/Professional and military types |
| 10 | Convertible with folding windshield | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | Only military types |
| 11 | Chassis Double Cab | 3,120 mm (122.8 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 11,1 | Chassis Double Cab | 3,400 mm (133.9 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 11,2 | Chassis Double Cab 6×6 | 3,400 mm (133.9 in) | Only Greenline military types |
US sales figures[106]
- 2018: 3,970
- 2017: 4,188
- 2016: 3,950
- 2015: 3,616
- 2014: 3,090
- 2013: 2,494
- 2012: 1,330
- 2011: 1,191
- 2010: 919
- 2009: 662
- 2008: 931
- 2007: 1,152
- 2006: 587
- 2005: 1,334
- 2004: 1,491
- 2003: 1,980
- 2002: 3,114
- 2001: 674
Motorsport[edit]
In 1983 a specially modified 280 GE won the Paris–Dakar Rally driven by Jacky Ickx and Claude Brasseur.[107]
In Popular Culture[edit]
A 1990 G-Class appears in the action film The Bourne Supremacy. It is involved in the film’s last chase and is eventually destroyed in a crash with a concrete post.[108]
See also[edit]
- Force Trax — a very similar Indian SUV
- Force Gurkha — SUV based on G-Class chassis
- Beijing BJ80 — similar Chinese SUV
References[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b «Algerian factory unveils new locally assembled truck for Algerian military». Db-defenceweb.co.za. Archived from the original on 2015-10-09. Retrieved 2015-03-16.
- ^ a b «Cross country 1/4 ton military jeeps». ELBO. Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ O’Kane, Sean (5 September 2021). «Mercedes-Benz Reveals an Electric G-Wagen Concept for the Future». The Verge. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class to be produced till 2020». MSN Arabia. Archived from the original on 21 May 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ Padeanu, Adrian (4 December 2020). «Mercedes G-Class Reaches Production Milestone: 400,000th SUV Assembled». Motor1.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen, Austria». Archived from the original on 2016-12-27. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ «Oh Lord won’t you buy me a Mercedes Benz». 15 September 2016.
- ^ Büschi, Hans-Ulrich, ed. (5 March 1987). Automobil Revue 1987 (in German and French). Vol. 82. Berne, Switzerland: Hallwag AG. p. 382. ISBN 3-444-00458-3.
- ^ «1979 Mercedes-Benz G-class (W460) 230 G (90 Hp) 4WD». auto-data.net. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- ^ «560 GE (W460)». W463.de. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ «Accessories». Puch. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ Westbrook, Justin T. (18 May 2018). «The Outgoing Mercedes G-Class Is Still In Production Because Icons Never Die». Jalopnik.
- ^ «1992 Mercedes-Benz G-class (W463) 350 GD Turbo (136 Hp) 4MATIC Automatic». auto-data.net. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Sorokanich, Bob (15 May 2018). «You Can Still Buy a Brand-New Old-Style G-Wagen, Sort of». Road & Track.
- ^ Raudonikis, Matt (8 December 2016). «Mercedes-Benz W461 G300 CDI Cab-Chassis: First-Drive». Which Car.
- ^ a b c «AMG Motoren». Nast Sonderfahrzeug (in German). Retrieved 12 August 2020.
- ^ O’Neill, Chris (August 2018). «Here’s How the Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen Got Around the 25-Year Import Rule». Auto Trader.
- ^ Deppe, Philip (23 June 2011). «Mercedes-Benz Guard safety philosophy: Licenced to protect». Mercedes-Benz Passion. Archived from the original on 2012-05-18.
- ^ «The magazine 4WheelFun crowns the G-Class as «2009 superstar»: Best in class: the G-Class». Archived from the original on 2016-01-07. Retrieved 2012-12-06.
- ^ Abuelsamid, Sam (15 December 2009). «Mercedes-Benz SLS goes from zero to gold in seconds for Dubai show». Autoblog.
- ^ Joseph, Noah (5 May 2011). «Mercedes-Benz gears up for the demise of the G-Class with BA3 Final Edition and Edition Select». Autoblog.
- ^ Homma, Masaaki (9 January 2012). «mastermind JAPAN x Mercedes-Benz G-550». Freshness.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G550 «Night Edition» Japan Exclusive». Hype Beast. April 2016.
- ^ Davis, Jim (3 September 2013). «Mercedes G-Class Cabriolet Final Edition». eMercedes-Benz.
- ^ Sellmeyer, Des (21 February 2015). «Exclusive: Mercedes-Benz G500 4×4² Review». GT Spirit.
- ^ «The new Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet, Strictly Limited: an open-air luxury both on and off road». Mercedes-Benz. Retrieved 18 February 2020.
- ^ Knecht, Jochen (6 March 2017). «Brutalo-Teilcabrio feiert Genf-Premiere». Auto Motor und Sport (in German).
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz 500 GE 6.0». Brabus. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Felshart, Luca (24 April 2019). «Mercedes-Benz 500 GE 6.0 AMG von BRABUS Classic». Mercedes Fans.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz M137 V12 engine». motor-car.net. Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- ^ «The Automotive Declaration of Independence». Mercedes-Benz. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- ^ Gorzelany, Jim (6 March 2013). «A Six-Wheeled Mercedes G-Class Could Be The Ultimate Road Warrior». Forbes.
- ^ Anderson, Brad (17 February 2015). «Mercedes-Benz G63 AMG 6×6 Sold Out». GT Spirit.
- ^ Joseph, Noah (6 July 2010). «Mercedes-Benz G-Wagon LAPV 6.X Concept ready to blitz the front».
- ^ Ross, Jeffrey (16 November 2012). «Mercedes-Benz Ener-G-Force concept is a G-Class for the future». Autoblog.
- ^ Harley, Michael (29 November 2012). «Mercedes-Benz Ener-G-Force Concept is mean, clean and green». Autoblog.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class Search Result». Internet Movie Car Database. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Korzeniewski, Jeremy (8 August 2011). «Australian Outback cripples fleet of Mercedes G-Wagens during PR event».
- ^ Beissmann, Tim (5 August 2011). «Mercedes-Benz G-Class broken by the Australian Outback». Car Advice.
- ^ «Mercedes To Continue Producing G-Class». eMercedes-Benz. 11 November 2005. Archived from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ «Mercedes bids current G-Class adieu with three special editions». NY Daily News. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- ^ Meiners, Jens (6 May 2010). «Mercedes to show face-lifted G-Class ute at upcoming Paris auto show (AutoWeek Magazine)». Autoweek.com. Archived from the original on 8 September 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ Ramsey, Jonathon (11 April 2012). «Mercedes introduces 2013 G-Class, including 612-HP G65 AMG». Autoblog.
- ^ Meiners, Jens (20 October 2015). «2016 Mercedes-Benz G550». Car and Driver.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class Design 2018». group-media.mercedes-benz.com. Retrieved 2022-07-28.
- ^ Luchian, Elena (14 January 2018). «Live from Detroit — Master G is back! This is the 2019 Mercedes-Benz G-Class». MercedesBlog.
- ^ Schäfer, Patrick (15 January 2018). «Die Mercedes G-Klasse bleibt ein klassischer Geländewagen». SpringerProfessional (in German).
- ^ Pollard, Tim (23 August 2018). «Mercedes-Benz G-class review: we test the year’s hardest, gnarliest 4×4». CAR Magazine. Archived from the original on 24 August 2018.
- ^ «The new Mercedes-Benz G-Class». MBUSA Newsroom. 2018-05-07. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ a b «The next-generation G-Class». Mercedes-Benz USA. 13 May 2019. Archived from the original on 10 May 2019.
- ^ «The new Mercedes-Benz G 350 d.» www.mercedes-benz.com. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «2022 Mercedes-Benz G400d First Drive: Is This Diesel G Great?». MotorTrend. 2022-05-09. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «Mercedes G-Class G400d review: ‘the best version of the best off-roader’ Reviews 2022». Top Gear. 2021-09-22. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «Future Models 2019 Mercedes-Benz G-Class». Mercedes-Benz USA. 9 February 2019. Archived from the original on 9 February 2019.
- ^ «Mercedes G350 Revealed in China, 4-Cylinder G-Class Costs $209,000».
- ^ a b c «The new 2019 Mercedes-AMG G63». MBUSA Newsroom. 2018-02-13. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ Ewing, Steven. «2019 Mercedes-AMG G63 brings 577 hp to Geneva». CNET. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «2019 Mercedes-AMG G63 Driven: The Speedier G-wagen». Car and Driver. 2018-02-13. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ Bruce, Chris (14 June 2019). «Mercedes Celebrates G-Class Anniversary With Exclusive Puddle Lamps». Motor1.
- ^ G-Class Private Lounge – Walkaround | Mercedes-AMG G 63 4×4², retrieved 2022-12-12
- ^ «2023 Mercedes-AMG G63 4×4 Squared First Look: Portal to the Past». MotorTrend. 2022-06-14. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ Perkins, Chris (2022-06-14). «The 2023 Mercedes-AMG G63 4×4 Squared is a 585-HP Factory Monster Truck». Road & Track. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ a b «2022 Mercedes-AMG 4×4² First Drive: Same Lunacy, Back for Round 2». MotorTrend. 2022-10-21. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «2023 Mercedes-AMG G63 4×4 Squared First Look Review: The Uber-Overlander». CarBuzz. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «G manufaktur». Mercedes-Benz. Retrieved 5 July 2020.
- ^ Jordan, Markus (2 September 2021). «Neue G-Klasse Professional steht auf der IAA Mobility 2021 #MBIAA21». MB Passion.
- ^ Tsui, Chris (7 September 2021). «New Mercedes G-Wagen Off-Road Trim Finally Starts to Unlock the Truck’s Potential». The Drive.
- ^ a b Smith, Christopher (5 September 2021). «Mercedes Concept EQG Debuts In Munich With Electric G-Class Style». Motor1.
- ^ Page, Felix (16 August 2021). «Mercedes primes luxury EQG electric G-Class 4×4». Autocar.
- ^ Oliva, Jacob (1 April 2021). «Mercedes EQG Trademarks Remind Us Electric G-Class Is Coming». Motor1.
- ^ Hong, Matthew (17 August 2021). «Mercedes-Benz EQG – fully electric G-Class to get true 4×4 capabilities, EQG 580 4Matic with 523 PS, 855 Nm?». Paul Tan.
- ^ Padeanu, Adrian (16 August 2021). «Mercedes EQG Could Keep Ladder Frame, Add Big Battery For Electric G-Class». Motor 1.
- ^ Lye, Gerard (6 September 2021). «Mercedes-Benz Concept EQG debuts – previews an all-electric G-Class; 4 electric motors, 2-speed gearbox». Paul Tan.
- ^ «Official Mercedes-Benz G-Class 2019 safety rating». EuroNCAP. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- ^ «ORBAT del Ejército Argentino». Archived from the original on 2019-04-26. Retrieved 2019-04-26.
- ^ Minister for Defence Brendan Nelson (5 October 2007). «New defence contracts deliver a boost for Brisbane» (Press release). Department of Defence. Archived from the original on 31 October 2007.
{{cite press release}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Ridgway, Steve (13 November 2008). «$350m wagon deal» (PDF). Army: The Soldiers’ Newspaper (1202 ed.). Canberra, Australia: Department of Defence. ISSN 0729-5685. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ «G Wagon». Australian Army. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ «G-wagon booklet» (PDF). Australian Army. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ Duff, Craig (13 September 2012). «Cars Guide: Merc G-wagons for military». The Daily Telegraph. pp. 21–22 (90–91). Retrieved 16 September 2012.
- ^ «France donates military equipment to Cameroon». defenceWeb. 2016-12-12. Retrieved 2021-10-06.
- ^ Armoured Vehicles – Mercedes G-Wagon – Blast Resistant Vehicles – Nyala APV – IED – MND Gordon O’Connor – Afghan Mission – Procurement Priorities – CASR – Canadian American Strategic Review Archived April 21, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Mercedes G-Wagon – Kandahar – Afghanistan – Gumbad IED – Media Response – Canadian Forces – CASR – Canadian American Strategic Review Archived May 4, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Canadian Army — Equipment Archived June 20, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Danish army Mercedes 240 GD/24». Armyvehicles.dk. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Danish army Mercedes 300 GE/28». Armyvehicles.dk. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Danish army Mercedes G270CDI/28». Armyvehicles.dk. Archived from the original on 2011-02-11. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Kader G 320 armoured personnel carrier (Egypt) – Jane’s Armour and Artillery». Articles.janes.com. 2007-10-04. Archived from the original on 2012-05-03. Retrieved 2012-04-12.
- ^ «Germany and the Kurds: Supplying Arms as Part of Evolving German Foreign Policy?». sldinfo.com. 3 September 2014. Archived from the original on 2014-09-08. Retrieved 2014-09-03.
- ^ Tomkins, Richard (18 August 2016). «Lithuania receives surplus vehicles from the Netherlands». United Press International. Archived from the original on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- ^ «Lithuania Acquires Dutch Geländewagens for Belarus Border». 20 December 2021.
- ^ «Ahmad Zahid: 84 G-WAGON Masih Beroperasi» (in Malay). KL Security Review. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-04.
- ^ «Archived copy». www.deftech.com.my. Archived from the original on 13 November 2011. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ «Secretaria de Marina – Armada de México». Semar.gob.mx. Archived from the original on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ «Recibe Semar vehículos para incrementar capacidad operativa :: El Informador». Informador.com.mx. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ Батлан хамгаалах салбарт 140 мянган еврогийн vнэ бvхий 10 машин бэлэглэлээ. «Olloo.mn — Єдєр бvр дэлхий даяар». Archived from the original on 2012-07-06. Retrieved 2012-07-18.
- ^ [1] Archived October 1, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Kim Jong-il’s Funeral Held in N. Korea (PHOTOS)». Ibtimes.com. 2011-12-28. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2012-04-12.
- ^ «Zestawienie pojazdów użytkowych Wojska Polskiego – Militarypedia (note: it does provide its own sources)» (in Polish). Militarypedia.corran.pl. Archived from the original on 2011-08-22. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Archived copy». Archived from the original on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2011-12-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Henrik Svensk. «Personterrängbil 5 -MB 290/T Geländewagen». SoldF.com. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ Henrik Svensk. «Personterrängbil 5 Geländewagen». Soldf.com. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ Carr, Clare (15 September 2016). «Oh Lord won’t you buy me a Mercedes Benz». RAF Museum. Archived from the original on 19 January 2018. Retrieved 18 January 2018.
- ^ «Later Years | BRIXMIS».
- ^ a b U.S. Marine Corps’ G-Wagen Archived 2016-11-24 at the Wayback Machine Truck Trend
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class US car sales figures». 8 November 2015. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class History». Edmunds. Archived from the original on 3 July 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ «1990 Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse [W463]». imcdb.org. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
Bibliography[edit]
General[edit]
- Arthur, Gordon (2021). Australian G-Wagons [sic]: Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse 4×4 und 6×6 Geländewagen der Australischen Streitkräfte [Australian G-Wagons [sic]: Mercedes-Benz G-Class 4×4 and 6×6 off-road vehicles of the Australian Defence Force]. International Special No. 8010 (in English and German). Erlangen, Germany: Tankograd Publishing. OCLC 1268193713.
- Barrett, Frank (1998). Illustrated Buyer’s Guide Mercedes-Benz. Motorbooks International Illustrated Buyer’s Guide series (2nd ed.). Osceola, WI, USA: MBI Publishing. ISBN 0-7603-0451-3.
- Bolsinger, Markus; Lengert, Axel; Peters, Wolfgang (2013). Legend – The G Class: from 1979 to today. Bielefeld, Germany: Delius Klasing. ISBN 9783768836241.
- Breuninger, Martin (1993). Das G-Buch: Alles über den Geländewagen von Mercedes-Benz [The G Book: Everything about the Geländewagen from Mercedes-Benz] (in German). Radolfzell, Germany: Tufa. ASIN B002UNICHS.
- ———————— (1995). Das G-Reisebuch – mit dem Geländewagen von Mercedes-Benz unterwegs [The G Travel Book: On the move with the Geländewagen from Mercedes-Benz] (in German). Radolfzell, Germany: Tufa. ASIN B002UNICIM.
- ———————— (2004). The Legend Keeps on Driving: 25 Years of Mercedes-Benz G-Class. Radolfzell, Germany: Tufa. ISBN 0962554154.
- Clarke, R.M., ed. (1999). Mercedes G-Wagen 1981–1994. Road Test Portfolio Series. Cobham, Surrey, UK: Brooklands Books. ISBN 1855203081.
- ——————, ed. (2006). Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen Gold Portfolio 1981–2005. Road Test Portfolio Series. Cobham, Surrey, UK: Brooklands Books. ISBN 1855206994.
- Füngeling, Michael (2001). Das große Mercedes-G-Buch Baureihen 460, 461, 463 [The Big Mercedes G Book 460, 461, 463 series]. Ein Off-road-Sachbuch series (in German) (2nd, expanded ed.). Ottobrunn: AC Verlag. ISBN 3930193248.
- García Loperena, Gastón Javier (2018). Mercedes-Benz G en el Ejército Argentino (in Spanish). Buenos Aires, Argentina: 1884 Círculo Militar. ISBN 9789874112156.
- Giesen, Norbert (2021). Mercedes G-Modell. Bewegte Zeiten series (in German). Bielefeld, Germany: Delius Klasing. ISBN 978366712230-8.
- Greene, Nik (2020). Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen: All models including AMG specials, 1979 to 2006. Essential Buyer’s Guide series. Dorchester, Dorset, UK: Veloce Publishing. ISBN 9781787115149.
- Hack, Joachim (2019). Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse: seit 40 Jahren nicht zu stoppen [Mercedes-Benz G-Class: unstoppable for 40 years] (in German) (1. Auflage ed.). Stuttgart. ISBN 9783613041721.
- Kittler, Eberhard (2005). Deutsche Autos [German Cars] (in German). Vol. Offroader und SUV — seit [since] 1945. Stuttgart: Motorbuch Verlag. ISBN 361302490X.
- Long, Brian (2016). Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen: 1979 to 2015. Mercedes-Benz series. Dorchester, Dorset, UK: Veloce Publishing. ISBN 9781845847777.
- Sand, Jörg (2011). Das Neue Große Mercedes G-Klasse-Buch [The New Big Mercedes G Class Book] (in German) (updated and revised ed.). Königswinter, Germany: Heel Verlag. ISBN 9783868524710.
- ————— (2015). Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse: Baureihe W 460 / W461; alle Modelle von 1979 bis 2000 [Mercedes-Benz G-Class: W 460 / W461 series; all models from 1979 to 2000]. Praxisratgeber Klassikerkauf series (in German). Königswinter, Germany: Heel Verlag. ISBN 9783958430259.
- ————— (2022). The Mercedes-Benz G-Class: The Complete History of an Off-Road Classic. Atglen, PA, USA: Schiffer Publishing. ISBN 9780764362637.
- Seper, Hans (2009). 100 Jahre Steyr 1864–1964 [100 Years of Steyr 1864–1964] (in German) (3rd (facsimile) ed.). Gnas, Austria: Weishaupt Verlag. ISBN 9783705902909.
- Sippel, Kai (2007). Das G-Modell als Einsatzfahrzeug. Mercedes-Benz/Puch – Geländewagen im Behördendienst [The G Model as Emergency Vehicle: Mercedes-Benz/Puch Geländewagen in Public Service] (in German). Kai Sippel. ISBN 9783000218422.
- Skarics, Rudolf (editor-in-chief) (1999). 100 Years of Steyr-Daimler-Puch Graz 1899–1999. Graz, Austria: Steyr-Daimler-Puch. ISBN 3950110712.
- Stroh, Gari M. (2008). Overland: A Mercedes-Benz Journey Through the Americas. West Palm Beach, FL, USA: StarGroup International. ISBN 9781884886911.
- Storz, Alexander Franc (2013). Mercedes G-Modell – seit 1979. Schrader-Typen-Chronik series (in German) (revised ed.). Stuttgart: Motorbuch Verlag. ISBN 9783613035829.
- Taylor, James (1994). Mercedes-Benz since 1945: A Collector’s Guide. Vol. 4: The 1980s. Croydon, UK: Motor Racing Publications. pp. 89–96. ISBN 0947981772.
Workshop manuals[edit]
- Russek, Peter (2006). Mercedes-Benz G-Models / Puch G / 240 GD, 300 GD, 230 G, 230 GE, 280 GE, 250 GD. Pocket Mechanic Vehicle Manual. Caversham, Reading, Berkshire, UK: Peter Russek Publications. ISBN 1898780773.
- Sand, Jörg (2008). Das Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse Schrauberhandbuch: reparieren und optimieren leicht gemacht [The Mercedes-Benz G Class Gearheads’ Handbook: repairing and optimizing made easy] (in German). Königswinter, Germany: Heel. ISBN 9783898807180.
- Mercedes-Benz G / Puch G / 240 GD, 300 GD bis 1989; 300 GD ab 1990; 230 G, 230 GE bis 1984; 230 GE ab 1985; 280 GE, 250 GD ab 1988. Reparaturanleitung, Band 1201. (in German) (3rd ed.). Zug, Switzerland: Verlag Bucheli. 2011. ISBN 9783716819203.
- Mercedes-Benz Technical Companion. Cambridge, MA, USA: Bentley Publishers. 1998. ISBN 9780837610337.
External links[edit]
- Official website
Press kit:
- The new generation Mercedes-Benz G-Class: Forever young
- Mercedes-Benz G 63 AMG 6×6: Taking the desert by storm
| Mercedes-Benz G-Class | |
|---|---|

Mercedes-Benz G 500 (W463), second generation |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer |
|
| Also called |
|
| Production | 1979–present |
| Assembly |
|
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Military off-roader Off-road vehicle Luxury SUV Pickup truck |
| Related |
|
The Mercedes-Benz G-Class, sometimes colloquially called the G-Wagen[3] (as an abbreviation of Geländewagen) is a four-wheel drive automobile manufactured by Magna Steyr (formerly Steyr-Daimler-Puch) in Austria and sold by Mercedes-Benz. Originally developed as a military off-roader, later more luxurious models were added to the line. In certain markets, it has been sold under the Puch name as Puch G until 2000.
The G-Wagen is characterised by its boxy styling and body-on-frame construction. It uses three fully locking differentials, one of the few passenger car vehicles to have such a feature.
Despite the introduction of an intended replacement, the unibody SUV Mercedes-Benz GL-Class in 2006, the G-Class is still in production and is one of the longest-produced vehicles in Daimler’s history, with a span of 43 years. Only the Unimog surpasses it.[4] In 2018, Mercedes-Benz launched a technically new second generation, still with only minor design changes.
The 400,000th unit was built on 4 December 2020.[5]
History[edit]
Very early, carburetted grey market Mercedes-Benz 230 G Cabriolet
The G-class was developed as a military vehicle from a suggestion by the Shah of Iran (at the time a significant Mercedes shareholder) to Mercedes[6] and was later offered as a civilian vehicle in 1979. In this military role the vehicle was sometimes referred to as the «Wolf». The Peugeot P4 was a variant made under licence in France with a Peugeot engine. The first military in the world to use it was the Argentine Army (Ejército Argentino) beginning in 1981 with the military model 461, at least one of these was captured in the Falklands and subsequently served with the Royal Air Force.[7]
The development of the G-Class started in 1972 with a cooperative agreement between Daimler-Benz and Steyr-Daimler-Puch in Graz, Austria. Mercedes-Benz engineers in Stuttgart were in charge of design and testing, while the team in Graz developed the production plans. The first wooden model was presented to Daimler-Benz management in 1973, with the first drivable prototype beginning various testing including German coalfields, the Sahara Desert, and the Arctic Circle in 1974. Construction commenced on a new production facility in Graz, where the new cross-country vehicle would be assembled nearly entirely by hand in 1975, with production of the «G Model» beginning in Graz in 1979. In 1980, the Vatican took delivery of a specially made G-Wagen outfitted with a clear thermoplastic top which served as the Popemobile. The “Papa G” later took up permanent residence at the Mercedes-Benz Museum in Stuttgart, Germany.[citation needed]
The first major refinements were introduced in 1981, including an automatic transmission, air conditioning, an auxiliary fuel tank, protective headlamp grilles and a cable winch. Fuel injection became available in 1982, when the 230 GE was introduced in Turin,[8] along with more comfortable and supportive front seats, auxiliary heating, wider tires and fender flares. For 1985, differential locks, central door locking and a tachometer became standard and by 1986 over 50,000 G Models had been produced.[citation needed]
The G-Wagen was facelifted in 1990. In 1989, for the 10th anniversary of the G Model, a new model variant with permanent 4-wheel drive, a wood-trimmed interior and optional Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) debuted at the Frankfurt International Motor Show. Production began the following April. For 1992, production began on a new sub-series for professional users. The civilian model began to offer cruise control, a stainless-steel spare-tire cover, running boards and Burl Walnut wood interior trim. In the same year, the 100,000th G Model was built in Graz and in 1994, the model line was officially renamed the G-Class. Ventilated front disc brakes and a driver’s air bag became standard. In 1996 the automatic transmission became an electronically controlled 5-speed unit and headlamp washers, cruise control, and a front passenger’s air bag were added. In 1998, the range-topping G 500 with a 296 hp V8 was introduced for series production.[citation needed]
For 1999 a limited run of V8 powered «G 500 Classic» special editions marked the model’s 20th anniversary. A multifunction steering wheel was added to all models. Later in the year, the new G 55 AMG debuted as the most powerful G-Class yet, with 354 hp. The U.S. market launch of the G-Class took place in 2001. New alloy wheels, a chrome grille and body-colour bumpers plus a more luxurious cabin were introduced. New dynamic control systems included the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), Brake Assist, and the 4 wheel Electronic Traction System (4 ETS). The G 55 AMG was upgraded in 2004 with a supercharged V8 engine developing 476 hp.[citation needed]
In 2006, a documentary filmmaker was the first foreigner to reach Siberia, the world’s coldest region, with a passenger vehicle in winter, driving a stock G 500 nearly 19,000 km without a single breakdown, in temperatures as frigid as −63˚F/-53 °C.[citation needed]
W460 (1979–1992)[edit]
| W460 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door SWB convertible 2-door cab chassis (pickup truck) 3-door SWB station wagon 3-door SWB panel van 3-door LWB station wagon 3-door LWB panel van 5-door LWB station wagon |
| Layout | Front engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Mercedes-Benz W460 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.0L M 102.964 E20 I4 2.3L M 115.973 I4 2.6L M 115 2.6 Brabus I4 2.8L M 110.994 I6 2.4L OM 616 I4 diesel 2.5L OM 602 I5 diesel 3.0L OM 617 I5 diesel |
| Transmission | 4-speed manual 5-speed manual 4-speed 720.1 (W4A 018) automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) (2-door) 2,850 mm (112.2 in) (4-door) |
| Curb weight | 3,913.21 lb (1,775 kg)[9] |
The W460 was introduced at a press event held at the off-road proving ground in Toulon, France, and went on sale in September 1979 with three engine choices and five body variants. Over the next decade, the engine and transmission choices were expanded or updated along with more and more optional extra cost creature comforts (air conditioning, automatic transmission, power windows, etc.).
The G-Wagen gained its global fame in 1980 when Mercedes-Benz built a Popemobile based on 230 G cabriolet during the first visit of Pope John Paul II in Germany.
Mercedes-Benz never officially exported the G-Wagen to the United States because it was considered more of a utilitarian vehicle and didn’t fit the American perception of what Mercedes-Benz was. During the 1980s, the grey import specialists brought the W460 to the United States and modified them to meet the US regulations. In 1988, the new federal law, Motor Vehicle Safety Compliance Act, closed the loopholes and tightened up the regulations for grey imports, making it more difficult and more expensive for the registered importers to federalise the W460 in a very small number. The other issue was severely underpowered engines in the 230 GE, 280 GE, and 300 GD models might not have appealed to the American market as was the case with the Mercedes-Benz 380 SEL in the early 1980s.
The 200 GE was built specifically for Italian markets and other markets where a heavy tax penalty was incurred for engines larger than 2 litres. The 300 GD was the most popular model while the 280 GE was the most powerful. Despite the availability of turbocharged diesel engines in other Mercedes-Benz vehicles, one was never fitted to the W460.
The rarest W460 variants were the 230 GE 2.6 Brabus (1989–?), the 280 GE AMG, and the 560 GE (1993).[citation needed] Brabus increased the engine displacement of the 2.3-litre four-cylinder inline engine to 2.6 litres, increasing the power to 114 kW (155 PS; 153 bhp). AMG modified the 2.8-litre six-cylinder inline petrol engine for more power, 134 kW (182 PS; 180 bhp). Only two units of the 560 GE were built in 1993 as part of a feasibility study that resulted in a limited series of the W463 500 GE for 1993–1994 and the W463 G 500 from 1998 on.[10]
Derivations[edit]
G-Wagen W462 ELBO (1988–?)[edit]
This version was assembled from Complete Knock Down (CKD) by ELBO, formerly a Steyr-Daimler-Puch branch division, in Thessaloniki, Greece for the Greek Army. Additionally, the CKD was also assembled at Mercedes-Benz’s Aksaray plant in Turkey. The engine options were a 2.3-litre four-cylinder inline petrol and later a 2.9-litre five-cylinder inline diesel.
Peugeot P4 VLTT (1981–1988)[edit]
The W460 was assembled in France under licence by Peugeot for the French Army with Peugeot engine and transmission from the 504 and 604 respectively as well as its own seats and wiring system. The front differential gear lock was omitted because Peugeot used its own axles. They are easily identified by rectangular headlamps.
Puch G (1979–2000)[edit]
An agreement between Daimler-Benz AG and Steyr-Daimler-Puch stipulated that G-Wagens sold in Austria, Switzerland, Yugoslavia (and its successor states: Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Serbia, and Slovenia), Mongolia, and Eastern European COMECON countries were called Puch G and elsewhere as Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen/G-Class. The reason for the different branding was due to Puch’s reputation for its all-terrain vehicles, the Haflinger and Pinzgauer. Since the agreement expired in 2000, consumers could order a retrofit kit from Magna’s Puch Competence Centre to replace the Mercedes-Benz brands with Puch emblems.[11]
For Pope John Paul II’s visit to Austria in 1983, Puch emblems was used on the Papamobile instead.
Engines[edit]
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm-urban, 90 km/h, 120 km/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| 200 GE (Italy only) | 1986-1991 | I4 (M 102.964 E20) | 1,997 cc (121.9 cu in) | 87 kW (118 PS; 117 bhp) at 5,200 rpm | 178 N⋅m (131 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 18 seconds | 140 km/h (87 mph) | 16.0 L/100 km (14.7 mpg‑US) — — |
| 230 G | 1979–1982 | I4 (M 115.973) | 2,307 cc (140.8 cu in) | 67 kW (91 PS; 90 bhp) at 5,000 rpm | 167 N⋅m (123 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 26 seconds | 128 km/h (80 mph) | 19.8 L/100 km (11.9 mpg‑US) 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US) 19.8 L/100 km (11.9 mpg‑US) |
| 230 GE | 1972–1990 | I4 (M 115.973 E23) | 2,299 cc (140.3 cu in) | 93 kW (126 PS; 125 bhp) at 5,100 rpm | 192 N⋅m (142 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 17 seconds | 152 km/h (94 mph) | 17.2 L/100 km (13.7 mpg‑US) 12.2 L/100 km (19.3 mpg‑US) 16.2 L/100 km (14.5 mpg‑US) |
| 230 GE 2.6 Brabus | 1989–1990 | I4 (M 115.973 2.6 Brabus) | 2,587 cc (157.9 cu in) | 114 kW (155 PS; 153 bhp) at 5,500 rpm | 260 N⋅m (192 lb⋅ft) at 3,300 rpm | 14.7 seconds | 158 km/h (98 mph) | 17.2 L/100 km (13.7 mpg‑US) 12.2 L/100 km (19.3 mpg‑US) 16.2 L/100 km (14.5 mpg‑US) |
| 280 GE | 1979–1990 | I6 (M 110.994) | 2,746 cc (167.6 cu in) | 116 kW (158 PS; 156 bhp) at 5,250 rpm | 226 N⋅m (167 lb⋅ft) at 4,250 rpm | 14 seconds | 165 km/h (103 mph) | 22.4 L/100 km (10.5 mpg‑US) 14.0 L/100 km (16.8 mpg‑US) 18.8 L/100 km (12.5 mpg‑US) |
| 280 GE AMG | 1979–1990 | I6 (M 110.994) | 2,746 cc (167.6 cu in) | 134 kW (182 PS; 180 bhp) at 5,250 rpm | 226 N⋅m (167 lb⋅ft) at 4,250 rpm | 14 seconds | 165 km/h (103 mph) | 22.4 L/100 km (10.5 mpg‑US) 14.0 L/100 km (16.8 mpg‑US) 18.8 L/100 km (12.5 mpg‑US) |
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| 240 GD | 1979–1988 | I4 (OM 616.936, OM 616.938, OM 616.941) | 2,399 cc (146.4 cu in) | 53 kW (72 PS; 71 bhp) at 4,400 rpm | 137 N⋅m (101 lb⋅ft) at 2,400 rpm | 32 seconds | 115 km/h (71 mph) | 14.4 L/100 km (16.3 mpg‑US) 12.0 L/100 km (19.6 mpg‑US) — |
| 250 GD | 1988–1991 | I5 (OM 602.930) | 2,497 cc (152.4 cu in) | 63 kW (86 PS; 84 bhp) at 5,150 rpm | 154 N⋅m (114 lb⋅ft) at 2,200–2,800 rpm | 27 seconds | 127 km/h (79 mph) | 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) 10.0 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) — |
| 300 GD | 1979–1991 | I5 (OM 617.931, OM 617.932) | 2,998 cc (182.9 cu in) | 65 kW (88 PS; 87 bhp) at 4,400 rpm | 172 N⋅m (127 lb⋅ft) at 2,400 rpm | 27 seconds | 127 km/h (79 mph) | 14.6 L/100 km (16.1 mpg‑US) 11.7 L/100 km (20.1 mpg‑US) 18.8 L/100 km (12.5 mpg‑US) |
W461 (1992–2022)[edit]
| W461 | |
|---|---|

Mercedes G-Class G 280 CDI EDITION.30 PUR |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1992–2022 (military variant)[12] Civilian variant produced until 2014 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door SWB convertible 2-door cab chassis (pickup truck) 3-door SWB panel van 3-door LWB panel van 5-door LWB station wagon |
| Layout | Front engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Mercedes-Benz W461 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.3L M 102 E 23 I4 2.5L OM 602.930 I5 diesel 2.7L OM 612 DE 27 LA I5 turbodiesel 2.9L OM 602 D 29 I5 diesel 2.9L OM 602 DE 29 LA I5 turbodiesel 3.0L OM 642 DE 30 LA red. V6 turbodiesel |
| Transmission | 4-speed 720.1 (W4A 018) automatic 5-speed manual 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) (2-door) 2,850 mm (112.2 in) (4-door) |
| Curb weight | 4,728.92 lb (2,145 kg)[13] |
After the new W463 was introduced in 1989 with an extensively updated chassis and a revised front end, the production of the W460 ended in 1991 and was replaced by the W461. The W461 has essentially the same chassis as the W460 but with the powertrain of the W463 and the body of the W460. While the W463 is aimed at consumers who seek more creature comforts and better driving dynamics, the W461 is built specifically for military, public authorities, and non-governmental organisations.[14] That included the 24-Volt electrical system for the W461.
During the 1990s, the W461 was offered with a 2.3-litre four inline petrol engine and a 2.9-litre five inline diesel engine from 1992 to 2001. From 2001 to 2014, the W461 model for military and public authorities was offered with a 2.7-litre five inline turbodiesel engine and later with a 3.0-litre V6 turbodiesel engine. They were called G 270 CDI Worker (2001–2006) and G 280 CDI Worker (2007–2009) respectively.
On 1 October 2021, Mercedes-Benz announced a new variation of W461 called W464.
Civilian Editions[edit]
Over the years, Mercedes-Benz had introduced the civilian version of the W461, built in limited numbers and for a limited period of time. They targeted primarily the consumers who wanted the «stripped down» version and did not need the creature comforts. The engine choice was often limited to one type, namely a diesel engine, per series. Those editions were named as PUR or Professional.
EDITION.30 PUR[edit]
In 2009, Mercedes-Benz, celebrating the 30-year anniversary of the G-Class, introduced the G 280 CDI EDITION.30 PUR as a five-door long wheelbase station wagon. The consumers could order theirs with «Off-Road Package 1» or «Off-Road Package 2». The passenger compartment had four seats upholstered in hard-wearing fabric or vinyl, rubber floor coverings, spray-protected/water-resistant controls, drainage apertures in the footwells, and a wood floor in the load compartment with load lashing lugs and rails. The dashboard received a new instrument cluster from the W463 and dual air bags and the climate control remained manually operated as did the window winders and locks. The exterior received flexible wheel arch flaring, protective grilles for headlamps, taillamps, front turn signal indicators, a walk-on hood/bonnet for easy access to the optional roof rack, a towing lug attached to the front bumper and two-section barn doors at the rear.
PROFESSIONAL[edit]
The success of the limited series «EDITION.30 PUR» led to the G 280 CDI Professional in 2009 and its successor, the G 300 CDI Professional, in 2010. Initially the 280 CDI Professional was limited to a five-door long wheelbase station wagon design before the body variants were expanded to five different body variations: a three-door long wheelbase panel van (Kastenwagen in German), a five-door long wheelbase station wagon, a two-door cabriolet and a two or four-door cab chassis truck (Pritschenwagen in German) for the G 300 CDI Professional.[15] The production of the civilian variant continued until 2014. However, the military variant continues to this day.[14]
G 300 CDI Professional (W461), Front View
G 300 CDI Professional (W461), Rear View
G 300 CDI Professional Pritschenwagen (W461), Front View
G 300 CDI Professional Pritschenwagen (W461), Rear View
USMC Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV)
Puch G (1990-2001)
Engines[edit]
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm-urban, extra urban, combined) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| 230 GE G 230 |
1992–2001 | I4 (M 102 E 23) | 2,298 cc (140.2 cu in) | 92 kW (125 PS; 123 bhp) at 5,100 rpm | 188 N⋅m (139 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 19–20 seconds | 144–147 km/h (89–91 mph) | 17.2 L/100 km (13.7 mpg‑US) 12.2 L/100 km (19.3 mpg‑US) 16.2 L/100 km (14.5 mpg‑US) |
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| 250 GD «Wolf» (Bundeswehr) |
1990–1991 | I5 (OM 602.930) | 2,497 cc (152.4 cu in) | 68 kW (92 PS; 91 bhp) at 4,600 rpm | 154 N⋅m (114 lb⋅ft) at 2,200–2,800 rpm | 27 seconds | 127 km/h (79 mph) | 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) 10.0 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) — |
| G 270 CDI Worker (Military) | 2001–2006 | I5 (OM 612 DE 27 LA) | 2,685 cc (163.8 cu in) | 115 kW (156 PS; 154 bhp) at 3,800 rpm | 400 N⋅m (295 lb⋅ft) at 1,800–2,400 rpm | — | — | — |
| G 280 CDI Worker (Military) | 2007–2014 | V6 turbo (OM 642 DE 30 LA red.) | 2,987 cc (182.3 cu in) | 135 kW (184 PS; 181 bhp) at 3,800 rpm | 400 N⋅m (295 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,600 rpm | — | 120 km/h (75 mph) | — |
| G 280 CDI EDITION.30PUR | 2009 | 13 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | 14.1 L/100 km (16.7 mpg‑US) 9.8 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 11.4 L/100 km (20.6 mpg‑US)* |
||||
| G 280 CDI Professional | 2009 | 18 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | |||||
| G 300 CDI Professional | 2010–2014 | |||||||
| 290 GD G 290 DIESEL |
1992–1997 | I5 (OM 602 D 29) | 2,874 cc (175.4 cu in) | 70 kW (95 PS; 94 bhp) at 4,000 rpm | 192 N⋅m (142 lb⋅ft) at 2,300 rpm | 25–27 seconds | 135–138 km/h (84–86 mph) | 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US) 9.8 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 12.6 L/100 km (18.7 mpg‑US) |
| 290 GD T G 290 TURBODIESEL |
1998–2001 | I5 (OM 602 DE 29 LA) | 2,874 cc (175.4 cu in) | 89 kW (121 PS; 119 bhp) at 3,800 rpm | 280 N⋅m (207 lb⋅ft) at 1,900–2,300 rpm | 17.2 seconds | 137 km/h (85 mph) | 12.0 L/100 km (19.6 mpg‑US) 10.0 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 10.9 L/100 km (21.6 mpg‑US) |
G-Class W463, first generation (1990–2018)[edit]
| W463 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1990–2018 |
| Model years | 1991–2018 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door SWB 2-door SWB convertible 5-door LWB station wagon |
| Layout | Front engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Mercedes-Benz W463 |
| Related | KSU Gazal-1 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.0L M 102.965 E 20 KAT I4 2.3L M 102.989 E 23 KAT I4 3.0L M 103.987 E 30 KAT I6 3.2L M 104.996 E 32 I6 3.2L M 112.945 E 32 V6 3.6L M 104.992 E 36 I6 4.0L M 176 DE 40 AL twin-turbo V8 5.0L M 117.965 E 50 V8 5.0L M 113.965 E 50 V8 5.4L M 113 E 55 V8 5.4L M 113 E 55 ML supercharged V8 5.5L M 273 KE 55 V8 5.5L M 157 DE 55 twin-turbo V8 6.0L M 117.965 E 50 bored to 6.0 litres[16] V8 6.0L M 279 E 60 AL twin-turbo V12 6.3L M 137 E 63 V12 2.5L OM 602.931 D 25 I5 Diesel 2.7L OM 612.965 DE 27 LA turbo I5 Diesel 3.0L OM 603.931 D 30 I6 Diesel 3.0L OM 606.964 D 30 LA turbo I6 Diesel 3.0L OM 642 DE 30 LA V6 turbo Diesel 3.5L OM 603.972 D 35 A turbo I6 Diesel 4.0 OM 628.962 DE 40 LA biturbo V8 Diesel |
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) (2-door) 2,850 mm (112.2 in) (4-door) |
| Length | Pre-2003: 4,661 mm (183.5 in) 2004–09: 4,714 mm (185.6 in) (LWB) 2010–18: 4,686 mm (184.5 in) |
| Width | Pre-2003: 1,760 mm (69.3 in) 2004–09: 1,811 mm (71.3 in) 2004–09 AMG: 1,864 mm (73.4 in) 2010–18: 1,824 mm (71.8 in) 2010–18 AMG: 1,857 mm (73.1 in) |
| Height | Pre-2003: 1,836 mm (72.3 in) 2004–09: 1,976 mm (77.8 in) 2010–18: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) |
| Kerb weight | 2,580 kg (5,690 lb) (G 55 AMG) |
For 1990, the W460 was extensively revised, and a new chassis number, W463, was assigned. The W463 moved the G-Class from spartan and utilitarian to a luxury model on par with the Mercedes-Benz S-Class and the luxurious Range Rover. Thus, no three-door panel vans in short and long wheelbase lengths or barn doors in the rear were offered for the W463: those features are exclusive to the W461. The W461 continued in production as military and utilitarian vehicles for the government agencies and non-government organisations.[14]
The exterior was revised to smoothen out the front end and the front fenders/wings were vertically flattened out at the front underneath headlamps. The fender flares and front end (cooling grille and headlamp bezels) were painted in body colour. The headlamps have square and slightly recessed bezels whilst the grille is narrower to give space for the front numberplate attached to the top of the bumper. The front bumpers are form-fitted and have integrated fog lamps while the rear bumpers have the integrated red rear fog lamp and white reversing lamp. The fuel filler is now covered by a panel. The side running boards were given a standard fitment. The external rear view mirrors have a new housing that pivots on anchors attached to the front doors. New revised tail lamps without white reversing lamps were fitted in the rear.
The interior was significantly updated with wood trim and leather upholstery for the first time. The centre console is smoother and better integrated with the dashboard and the lower part of the dashboard is covered with rubber pads for better knee protection in the event of a frontal collision. The electric differential lock switches are placed prominently in the middle of the dashboard with other electric switches and the instrument cluster has a smoother and more curved housing that meets the dashboard fluidly. The gauges are integrated into one panel rather than a few separate gauges attached to the instrument cluster. The climate control panel was revised to include the temperature and fan speed dials and the door panels are fully trimmed with ruffled leather paneling and soft paddings. The seats are more plush and have several defined cushions along with lumbar support.
The new features included ABS and full-time four-wheel-drive with electrically locking differentials. The engines were carried over from the W460/W461, including the 200 GE, 230 GE, and 300 GE models for petrol engines along with the 250 GD and 300 GD for diesel engines. In 1994, the Geländewagen was renamed as the G-Class when model names were revised to reflect the new corporate nomenclature.
When Mercedes-Benz didn’t consider selling the G-Class in the United States, a small registered importer based in New Mexico, Europa International, Inc., began the expensive process of certifying and modifying the G-Class for the US market and started selling them in 1993. When the new G 500 was introduced in 1998, Europa International sought and received the «small-volume manufacturer status», allowing the company to be the exclusive importer and distributor of the G 500 in the United States. The sales success of the G 500 was attributed to Europa International’s clever marketing toward high-end luxury clientele and led Mercedes-Benz to the decision of purchasing the distribution rights and including the G-Class in its official US model ranges.[17]
The first generation W463 had the widest range of engines ever fitted to a Mercedes-Benz vehicle during its entire 28-year model run: from four to twelve cylinders; and from natural aspiration to supercharger, turbo, and twin turbo. Towards the end of the first-generation model run the W463 had the highest number of paint colour options at 22, including the bright and intense colours of the Crazy Color Edition.
Models[edit]
The W463 had the highest number of body variations and derivations of any post-war Mercedes-Benz:
- two-door cabriolet
- three-door station wagon with short wheelbase
- four-door pickup truck with six wheels (Mercedes-AMG G 63 6×6)
- four-door cabriolet with extended wheelbase (Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet)
- five-door station wagon with long wheelbase
- five-door station wagon with extended wheelbase (custom built by AMG)
- five-door station wagon with long wheelbase and widened track (Mercedes-Benz G 500 4×4²)
Special models and special editions[edit]
500 GE (1993–1994)[edit]
A significant model was the 500 GE with the first-ever V8 engine for the G-Class. It was produced in a limited number from 1993 to 1994 and as a 5-door, long wheelbase station wagon only. The V8 engine wasn’t reintroduced until 1998 when the G 500 entered into a regular production.
G 500 Classic Special-Edition (1999)[edit]
G 500 Classic Special-Edition Press-Information Brochure 16. March 1999.
G 500 Classic Special-Edition Cabrio
In 1999, the factory presented the luxuriously equipped G 500 Classic Special-Edition model is unveiled to mark the 20th anniversary of the Mercedes-Benz G-Class. All Classic Special-Edition models were equipped with the 500 V8 engine, all of them received a special Almandinschwarz-Metallic (182) paintwork, which in certain lighting conditions looks black or dark aubergine purple. This limited series design inherited everything from the original classic G-Class, but benefited from the technical developments of the new generation released in 2000. Thus, it remained true to the expression of the Classic, yet technically modern. Among other things, all Classic Special-Edition G-Class receive unique 18″ alloy wheels painted in body color inside, with exterior elements painted in vehicle color, Classic inscription strip on the side of the vehicle, stainless steel and painted spare wheel cover, new instrument cluster, equipped with Becker navigation and Hi-Fy with a multi-functional steering wheel appearing for the first time, ultrasonic reversing assist, front and rear seat heating, anti-theft alarm system, illuminated thresholds. The interior is made of black and aubergine purple nappa leather that harmonizes incredibly well with the exterior color, with black suede carpets embroidered with classic lettering and fine burr walnut interior elements. A total of 500 Classic Special-Editions of all versions were produced. 6 RHD and 494 LHD are the most long wheelbase, less short wheelbase and only 12 Cabrios. The G 500 Classic Special-Edition Cabrio is the rarest G-Class Cabrio model ever produced until the end of production of the G-Class Cabrio in 2014.
Grand Edition (2006)[edit]
The 500 units of the G 500 and G 55 AMG Grand Edition were built and shipped to the United States when Mercedes-Benz decided to end the sales of G-Class in the United States for 2006 before rescinding its decision. The exterior had an exclusive Allanite Grey Magno metallic paint finish and brushed aluminium trim stripes with «Grand Edition» lettering. The interior had matte-silk wood trim on the dashboard and centre console, designo exclusive leather upholstery, and door sills with illuminated «Grand Edition» lettering.
G 500 Guard (2009–2018)[edit]
An armoured version of the long wheelbase G 500 five-door station wagon with bullet resistance level FB6 or FB7.[18]
G-Class LIMITED.30 (2009)[edit]
The LIMITED.30 model is a special edition, celebrating the 30-year anniversary of the G-model (1979–2009). This edition includes designo platinum black paint finish, specially designed light-alloy wheels and EDITION30 lettering on the wings. The interior has designo leather in the colour «chablis» and designo trim in anthracite poplar wood.[19]
G 55 AMG KOMPRESSOR «Edition 79» (2009)[edit]
Like the LIMITED.30 special edition, the «Edition 79» is exclusive to the Middle East market, celebrating the sales launch in 1979. This edition includes designo magno alanite grey paint finish, a crash bar at the front, carbon fibre side trim stripes, 19-inch AMG wheels with titanium finish, chrome protection grilles for the front turn signal indicators, designo leather upholstery in black/sand colour, a carbon fibre dashboard and centre console trims and an edition logo, e.g. «1 out of 79», placed in front of the gear selector. The vehicle was unveiled in 2009 at the Dubai International Motor Show.[20]
BA3 Final Edition and Edition Selection (2011)[edit]
The BA3 Final Edition was launched in 2011 to mark the final production run of the three-door, short wheelbase station wagon. The single model variation was G 350 CDI BlueTEC. This farewell special is distinguished by body-coloured AMG flared wheel arches with 5-twin-spoke light-alloy wheels, carbon optics stripes, an AMG radiator grille, 18-inch alloys, extra chrome trims inside and outside, black leather interior offset by walnut burr veneers and ambient lighting.
At the same time, Mercedes-Benz offered the «Edition Select» special for the five-door model, G 500. Edition Selection applies the same special edition treatment to the G 500/G 550 even though the five-door long wheelbase station wagon would continue for several more years.[21]
G 55 AMG long «mastermind» Limited (2012)[edit]
As a brand awareness collaboration for the Fashion Week, Mercedes-Benz Japan and mastermind JAPAN built five units for the Japanese market. Externally, the chrome trims and wheels were done in black paint finish, and two stickers were affixed to the side panels at the rear. The mastermind JAPAN skull and bone badges were affixed to the headrests and spare wheel cover. The interior was done in black leather trim with the roof liner finished in light grey Alcantara.[22]
G 550 Night Edition (2013–2015)[edit]
Exclusive to the Japanese market, 100 units of the G 550 Night Edition were produced with a black paint finish, AMG badges on the front fenders/wings and five twin-spoke, aluminium wheels finished in titanium grey. Two choices of interior colours were offered: porcelain white (60 units) and classic red (40 units). The dashboard and centre console were trimmed with designo piano lacquer black wood. The roof liner was Alcantara in anthracite colour. The sales price was ¥13,900,000 JPY.[23]
G-Class Cabriolet «Final Edition 200» (2013–2014)[edit]
To commemorate the production end of the two-door cabriolet, Mercedes-Benz introduced the «Final Edition 200» with the G 500 being the only model variation. All of the 200 units had been sold out prior to its premiere at 2013 Frankfurt Auto Show. Externally, the soft top and tonneau cover are beige in colour, the grille is chrome-coloured, and the 5-spoke light-alloy wheels are painted in titanium grey. The B-pillars are fitted with «Final Edition 200» badges. The interior received designo leather seats and door panels coloured in ecru with black trim, satin-finished light brown poplar wood trim, and an AMG performance steering wheel.[24]
G 500 4×4²[edit]
Rear quarter view of G 500 4×4²
Continuing with the G 63 AMG 6×6 formula, Mercedes-Benz introduced the G 500 4×4², using the body of the long wheelbase 5-door station wagon on a shortened chassis from the G 63 AMG 6×6. The G500 4×4², along with the G 500/G 550, received a new 4.0-litre biturbo V8 (M176), producing 310 kW (416 hp). The exterior is the same as the Mercedes-AMG G 63 and G 65 despite the G 500 4×4² not being a Mercedes-AMG edition.[25]
Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet (2017)[edit]
Following the success of the G 63 AMG 6×6 and G 500 4×4², Mercedes-Benz introduced the first SUV under the sub-brand name Mercedes-Maybach at the Geneva Motor Show in March 2017.[26] G 650 Landaulet used the extended chassis with the portal axles and raised suspension system from the G 500 4×4². The rear end of the G 650 Landaulet was built from the rear part of the W463 cabriolet with a folding fabric roof covering the rear half of the body behind the B-pillar. The rear passenger doors with no wheel-opening cut-out were from the G 55 with extended wheelbase (2001). The front end is from the Mercedes-AMG G 65 with more chrome trims. The light alloy wheels and extendable side running boards are chrome plated. The powertrain is from the G 65 with the 463 kW (621 hp) biturbo V12.
The interior is finished in ultimate luxury as found in Mercedes-Maybach GLS-Class and S-Class. Like the original Maybach 62 Landaulet, a division wall is installed behind the driver and front passenger. The second row seats are moved further back from the rear passenger doors and are the same rear seats as used in the Mercedes-Maybach S-Class. A second control panel and centre console is installed behind the division wall toward the rear. The dashboard above the second set is one set of the two front passenger’s dashboards with a glove box and hold two large LED monitors.
The sales price was €749,700, and the production was limited to 99 units.[27]
Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet
The rear view of the Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet
AMG models[edit]
500 GE 6.0 AMG (1993-1995)[edit]
For the first time, an AMG version of the G-Class was offered in 1993 with the 500 GE 6.0 AMG. The M 117.965 E 50 engine was bored from 5.0 to 6.0 litres, producing 243 kW (326 hp) and 525 N⋅m (387 lb⋅ft). The increased output did not make the 500 GE 6.0 AMG much faster with a time of 10.9 seconds for 0–100 km/h (62 mph). Only thirteen units were built in long wheel base form and only one unit with a short wheel base.[28][29][16]
G 36 AMG (1994–1997)[edit]
After AMG entered into co-operation with Mercedes-Benz in 1993, the G 36 AMG was introduced and fitted with the M104.992, the same engine as found in the C 36 AMG and E 36 AMG.
G 43 AMG (1997–1998)[edit]
A total of 38 units of the G43 AMG were produced between 1997 and 1998, all of the as special orders under country code «293 Company Vehicle», mostly for VIPs and probably secret services. 6 of them bore 463.233 chassis numbers, as though they were G320 LWBs that had their V6 engine replaced with a type M113.982 V8 engine. Bizarrely, the remaining 32 units were coded 463.241, meaning that they were meaning to be G500 LWB that had the M113.982 AMG 4.3-litre engine fitted in lieu of the M113.962 standard 5-litre engine.
G 63 AMG V12 (2002)[edit]
The G 63 AMG V12 was a very limited production run with only five units built in 2002. It was the first G-Class with a V12 engine before Mercedes-AMG officially introduced the more powerful G 65 AMG. The engine produced 326 kW (437 hp) and propelled the G 63 AMG to 100 km/h (62 mph) in 6.5 seconds.[30]
G 55 AMG (2002–2003) and G 55 AMG Kompressor (2004–2012)[edit]
Citing the sales success of the G 500 in the United States and the absorption of AMG into DaimlerChrysler AG, Mercedes-Benz began to expand the AMG versions to several models, including the G-Class. To coincide with the official launch of the G-Class in the United States, Mercedes-Benz introduced the 55 AMG along with the G 500 in 2001 for the 2002 model year. The G 55 AMG visually did not differ from the G 500 other than side exhaust pipes, wider tyres, AMG five-spoke wheels, chrome tip at bottom of front bumper, and AMG lettering in the rear. The G 55 AMG became the favourite of celebrities and the wealthy.
For the 2005 model year, AMG revised the G 55 AMG by adding a supercharger to the 5.4-litre V8 engine, increasing the output to 350 kW (469 hp). To differentiate the G 55 AMG KOMPRESSOR from the G 500 visually, AMG changed the radiator grille to three thick fins, added the embossed metal KOMPRESSOR lettering underneath the V8 badge on the front fenders/wings, and introduced new light-alloy wheels in titanium grey and three new metallic paint colours (Calcite White, Periclase Green, and Teallite Blue). The 0–100 km/h (62 mph) acceleration was reduced from 7.4 to 5.6 seconds. Yet, the top speed remained at 210 km/h (130 mph). The engine was upgraded again for 2006 (2007MY in USA) to 368 kW (493 hp) then again to 373 kW (500 hp) for 2008 (2009MY in USA).
G 63 AMG (2012–2018)[edit]
The supercharged 5.4-litre V8 was replaced by the new 5.5-litre biturbo V8 for 2012 (2013MY in USA) for better fuel consumption and lower emissions. AMG made some more changes to the exterior to give the G 63 AMG a more «brawly» appearance: single horizontal fin with twin chrome edges in the middle of the radiator grille with a more prominent three-pointed star ornament in the middle, a new light-alloy wheel design, three enlarged airflow inlets on both sides and in the middle of the front bumper, vertical chrome stripes to cover the small bumper guards and exterior rear-view mirrors from the GL-Class and ML-Class. The mechanical upgrade was an AMG sports exhaust system with high-gloss chrome inserts, larger AMG high performance brakes with six-piston fixed calipers at the front from the ML 63 AMG and revised suspension and damper settings for more dynamic handling characteristics. The new E-SELECT gear selector from the Mercedes-Benz SLS replaced the standard gear selector.
For 2016, the name was changed to Mercedes-AMG G 63.
G 65 AMG (2012–2018)[edit]
The G 63 AMG V12, built in 2012, demonstrated the feasibility of installing a V12 engine in the G-Class. The new G 65 AMG was introduced at the same time as the G 63 AMG, making the G 65 AMG the third passenger SUV to have a V12 engine with Lamborghini LM002 (built from 1986 to 1993) being the first one. G 65 AMG was equipped as the G 63 AMG other than minor cosmetic differences with V12 BITURBO badges on the front fenders/wings, floor mats and seat backs.
Like the G 63, the name was changed to Mercedes-AMG G 65 for 2016.
G 63 AMG 6×6 (2013–2015)[edit]
To mark the thirtieth anniversary of G-Wagen production, Mercedes-Benz introduced the new stretched version with six-wheel-drive system and portal axles.[31][32] The G 63 AMG 6×6 was derived from a model developed specifically for the Australian Army in 2007. Despite the heavy weight and large dimensions, the G 63 AMG 6×6 could accelerate to 100 km/h (62 mph) in six seconds and reach a top speed of 160 km/h (99 mph).
The consumer reception of the G 63 AMG 6×6 was stronger than anticipated, and Mercedes-Benz sold slightly more than 100 units, with the last customer delivery taking place in May 2015.[33]
Mercedes-Benz G 63 AMG 6×6
Rear quarter view of the Mercedes-Benz G 63 6×6
Mercedes-Benz G 63 6×6 dashboard
Mercedes-Benz G 63 6×6 tyre pressure regulation switches
Brabus G 63 700 AMG 6×6
Concept cars[edit]
Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen Light Armoured Patrol Vehicle 6.X CONCEPT (2010)[edit]
It is an armoured patrol vehicle developed with EADS, based on LAPV 5.4. It included a diesel engine, 1.3 tonnes of cargo capacity, a monocoque full steel body, compact 2,850 mm (112.2 in) wheelbase, modular armour plate and mine deflector plate underneath the floor, adjustable variable lift front and rear coil-over air shock absorbers with a maximum of 450 mm (17.7 in) of ground clearance and hydraulic brakes with four ventilated discs. EADS provided the communication technology: vehicle data recorder system, integrated communication system for UHF or VHF bands, integrated mobile command, control and information system, and jamming system. The vehicle was unveiled in EUROSATORY 2010.[34]
Ener-G-Force (2012)[edit]
Mercedes-Benz Ener-G Force
The rear view of the Mercedes-Benz Ener-G Force
The Ener-G-Force was a concept vehicle in response to the Los Angeles Design Challenge 2012 for a future police car. The vehicle was unveiled at the 2012 LA Auto Show. The concept vehicle was hydrogen-powered with fuel cells generating the electricity to the electric motors inside the wheel hubs. A roof rack contained the water tanks with a hydrogen converter, and the body included a three-panel greenhouse, 20-inch wheels and side skirts illuminating the charge and operation status of energy packs.[35][36]
Marketing[edit]
The W463 was positioned in the marketplace as a luxury passenger vehicle to compete with the likes of Range Rover. After Mercedes-Benz launched the G-Class in the United States with the G 500 and G 55 AMG models, the G-Class became very popular with celebrities, film stars, and the wealthy. The G-Class has appeared in numerous films, television series, and music videos ever since.[37]
As part of Mercedes-Benz’s attempt to demonstrate the off-road capability of the G-Class SUV, seven G-Class vehicles took a journey from Halls Creek in Western Australia to Wiluna. However, shock absorbers on six of the vehicles (5 civilian G 350s and 1 military model) were broken during their trip on the corrugations of the Canning Stock Route on day 7. Mercedes-Benz Australia later arranged for the replacement shock absorbers to land in Perth, before transferring to a light plane destined for a remote Aboriginal settlement close to Well 33, about 1000 km from Wiluna. The parts would be delivered by the sole surviving vehicle, a G-Professional.[38][39]
End of production debacle and revised decisions[edit]
Mercedes-Benz announced that 2005 would be the final year of the G-Class to be sold in the United States, citing the new GL-Class as its successor. The 500 units of G 500 and G 55 AMG Grand Edition were built and shipped to the United States. However, an unexpected order placed by the U.S. Marine Corps for 157 Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV) based on the G-Class, replacing its ageing, slow, and cumbersome Desert Patrol Vehicles, caused Mercedes-Benz to rescind its decision and to continue offering the G-Class in the United States.
This Grand Edition also led to the rumours of the end of production of the W463 in 2006. A few factors contributed to the rumours: the increasing difficulties in meeting the newer and stricter safety and emission regulations, especially the new EU regulations on pedestrian protection; Mercedes-Benz had introduced new GL-Class as an intended successor; and military contracts fulfilled. An outcry among enthusiasts who admired the G-Class for its tremendous off-road potential along with its reputation and cachet showed that a market still existed for such a vehicle. On 11 November 2005, Dieter Zetsche, DaimlerChrysler Board of Management member and head of the Mercedes Car Group, announced that G-Class production would continue. At the Paris Motor Show in September 2006, Mercedes-Benz reiterated that the G-Class would continue to be manufactured through 2015 due to the strong worldwide demand by both civilian and military buyers.[40] Daimler AG extended the manufacturing contract with Magna Steyr to continue producing the W463 until 2017.
In late 2017, the end of production of the first generation W463 was announced with the heavily reengineered and updated successor to be introduced in 2018 for the 2019 model year.[41]
Updates (1990–2018)[edit]
1994 update[edit]
The update was minor with the model designation revised to reflect the new nomenclature system and with an enlarged six-cylinder inline petrol engine for the G 320, replacing the G 300. The Italy-only 200 GE/G 200 and 230 GE/G 230 were dropped, marking the end for the G-Class with the four-cylinder inline engine until G 350 was reintroduced for Chinese market in 2020. After the 200 GE/G 200, 230 GE/G 230, and 300 GE/G 300 were dropped in 1994, manual transmission was dropped from the W463 for good. The steering wheel received the driver’s side airbag.
1997 update[edit]
The W463 received its mechanical update in 1997. The update included a new power-assisted folding mechanism for its convertible. The engine range was revised with six-cylinder engines shifting from inline to V-form for both petrol and diesel versions. The G 500 was reintroduced with a new V8 petrol engine. The W463 received dual airbags for the driver and the front passenger.
2002 update[edit]
The external rear-view mirrors were revised with integrated turn signal repeaters and power-assisted mirror control, eliminating the separate turn signal indicators attached to the body. The front and rear turn signal indicators received a clear lens. The newly-revised headlamps for both American and international markets were also given clear glass lenses. The interior was updated with more creature comforts and better control switches. In 2002, Mercedes-Benz officially launched the G-Class in the United States for the first time since its inception in 1979 with the G 500 and G 55 AMG.
2005 update[edit]
Mercedes-Benz announced the new G55 AMG Kompressor model with a more powerful, supercharged 5.4L V8 engine (code 113.993, or M113K), replacing the naturally aspirated 5.0L V8 engine (113.982, or M113). The G 500 was renamed as G 550 for certain markets (not USA until 2009).
2006 update[edit]
This minor update revised the engine range with a new 3.2-litre V6 diesel engine in the G 320 CDI, replacing both the G 270 CDI and G 400 CDI. The G 500 and G 55 AMG Kompressor continued unchanged. The G 320 with the petrol engine was dropped, marking the suspension of six-cylinder petrol engines until 2018. The G 55 AMG Kompressor remained as a five-door station wagon while the G 320 CDI and G 500 were offered in three body styles: two-door cabriolet and station wagons with three-door short and five-door long wheelbases.
2007 update[edit]
Mercedes-Benz showcased a heavily revised 2007 model at the Paris Motor Show in September 2006 with emphasis on an updated interior, engine range, and new safety equipment.[42]
For 2007, the G-Class received its first high-intensity discharge headlamps, reversing camera, and tire pressure monitoring system (the latter two are federally mandated safety equipment for the United States). 2007 G500’s in the USA start to phase out the 722.6 5spd transmission, and instead start coming with the new 722.9 7spd transmission. The G55(K)’s still have the 722.6 5spd transmission. The G 500 could be fitted with the sports side exhaust pipes from the G 55 AMG for extra cost. The power output for the G 55 AMG was increased from 350 kW (469 hp) to 368 kW (493 hp).
The interior received a new instrument cluster with four chrome-trimmed round gauges from the C-Class and a new four-spoke multi-function steering wheel with options of full leather cover or combination of leather and wood. The centre console was updated with new control switches for the vehicle’s functions and a new climate control panel along with new COMAND APS infotainment and navigation system. In conjunction with the reversing camera, COMAND APS displays the rear view and graph representation of distance and width, assisting the driver during reversing maneuvers. The new ARTICO upholstery colour, cognac, was added to black and grey interior colour options.
2008 update[edit]
The 2008 update included a new radiator grille with three thicker horizontal fins, replacing the previous seven, thinner fins. The COMAND APS infotainment and navigation system was revised with many new or extended functions such as the LINGUATRONIC voice control system, a 12-speaker Harman Kardon Logic 7 surround sound stereo system, TV tuner and a special off-road menu for the G 320 CDI and G 500 model. Heated and ventilated front seats were also offered.
Last year for the G500 in the USA.
2009 update[edit]
The 2009 G550 replaces the 2008 G500, and gets a new 5.5-litre V8 petrol engine with 285 kW (382 hp) [mated to the 722.9 7spd transmission], replacing the 5.0-litre 218 kW (292 hp) that was in the 2008 G500. The new engine will improve the acceleration for the new G550.
For the 30th anniversary of production, Mercedes-Benz offered two special anniversary editions. One was the G 500/G 550 with a more opulent interior and exclusive designo leather upholstery along with special decals. Another one was a new utility model, the G 280 CDI Edition 30 PUR, consisting of the W461 chassis with a 3.0-litre V6 turbodiesel engine (OM 642 DE LA red.) and the W463 four-wheel-drive system.
2011 update[edit]
Last year for the G55(K) [with 722.6 5spd transmission], in the USA.
2012 update[edit]
G 63 AMG with revised front end
After its last major update in 2007, the interior received a completely redesigned instrument panel and centre console adapted from the ML-Class. The COMAND APS touchscreen and control panel were moved up toward the top of the dashboard for easier viewing and operation. The COMAND APS was updated with the MBrace2 telematics system. Additional safety features included DISTRONIC adaptive cruise control, blind-spot monitoring, revised PARKTRONIC reverse sensors and rear-view camera and revised ATS4 stability control for improved trailer stabilising functionality.
Externally, the G-Class received the same horizontal bars of LED daytime running lamps underneath the headlamps and the new external side rear-view mirrors as the GL-Class and ML-Class models. The AMG version received a new front bumper with three large air intakes.
The 5.4-litre supercharged V8 [with 722.6 5spd transmission] in the 2011 G55(K) will be replaced by a new 5.5-litre biturbo V8 [with 722.9 7spd transmission] for increased performance on the upcoming 2013 G63. Topping out the G-Class model range was a new G 65 AMG with a 6-litre biturbo V12 petrol engine. Two models were carried over unchanged: the G 350 CDI BlueTEC and G 500/G 550.[43]
2016 update[edit]
For the 2016 model year, the outgoing M273 5.5-litre naturally aspirated V8 fitted to the G 500/G 550 was replaced by the new M176 4.0-litre biturbo V8 for increased horsepower and torque.[44]
Technical data[edit]
Engine (1990–2018)[edit]
Notes: (m) and (a) denote «manual» and «automatic» transmissions where applicable. Fuel consumption marked with * denotes the older EEC regulation of «urban, 90 km/h, and 120 km/h» (U/90/120). Top speed with ** denotes the «electronically limited».
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm combined) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| 200 GE (Italy) |
1990–1994 | I4 (M 102.965 E 20 KAT) | 1,996 cc (121.8 cu in) | 87 kW (117 hp) at 5,200 rpm | 172 N⋅m (127 lb⋅ft) at 3,500 rpm | 20.8 seconds | 144 km/h (89 mph) | 15.6 L/100 km (15.1 mpg‑US)* 11.1 L/100 km (21.2 mpg‑US)* 15.7 L/100 km (15.0 mpg‑US)* |
| 230 GE G 230 |
1990–1995 | I4 (M 102.989 E 23 KAT) | 2,298 cc (140.2 cu in) | 93 kW (125 hp) at 5,000 rpm | 190 N⋅m (140 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 17.7 seconds (m) | 145 km/h (90 mph) (m) | 16.4 L/100 km (14.3 mpg‑US)* (m) 12.7 L/100 km (18.5 mpg‑US)* 17.3 L/100 km (13.6 mpg‑US)* |
| 18.4 seconds (a) | 144 km/h (89 mph) (a) | 15.1 L/100 km (15.6 mpg‑US)* (a) 13.1 L/100 km (18.0 mpg‑US)* 18.0 L/100 km (13.1 mpg‑US)* |
||||||
| 300 GE G 300 |
1990–1994 | I6 (M 103.987 E 30 KAT) | 2,962 cc (180.8 cu in) | 125 kW (168 hp) at 5,700 rpm | 190 N⋅m (140 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 13.5 seconds (m) | 164 km/h (102 mph) (m) | 18.7 L/100 km (12.6 mpg‑US)* (m) 13.4 L/100 km (17.6 mpg‑US)* 17.7 L/100 km (13.3 mpg‑US)* |
| 14 seconds (a) | 162 km/h (101 mph) (a) | 18.2 L/100 km (12.9 mpg‑US)* (a) 14.2 L/100 km (16.6 mpg‑US)* 19.2 L/100 km (12.3 mpg‑US)* |
||||||
| G 320 | 1994–1998 | I6 (M 104.996 E 32) | 3,199 cc (195.2 cu in) | 155 kW (208 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 300 N⋅m (221 lb⋅ft) at 3,750 rpm | 12.1 seconds | 175 km/h (109 mph) | 16.6 L/100 km (14.2 mpg‑US)* 14.0 L/100 km (16.8 mpg‑US)* 18.4 L/100 km (12.8 mpg‑US)* |
| 1997–2006 | V6 (M 112.945 E 32) | 3,199 cc (195.2 cu in) | 160 kW (215 hp) at 5,600 rpm | 300 N⋅m (221 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,800 rpm | 10.9 seconds | 175 km/h (109 mph) | 15.5 L/100 km (15.2 mpg‑US) | |
| G 36 AMG | 1994–1995 | I6 (M 104.992 E 36) | 3,606 cc (220.1 cu in) | 206 kW (276 hp) at 5,750 rpm | 385 N⋅m (284 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 9.6 seconds | 190 km/h (118 mph) | — |
| 500 GE | 1993–1994 | V8 (M 117.965 E 50) | 4,973 cc (303.5 cu in) | 177 kW (237 hp) at 5,200 rpm | 365 N⋅m (269 lb⋅ft) at 3,750 rpm | 11.4 seconds | 180 km/h (112 mph) | — 16.1 L/100 km (14.6 mpg‑US)* 21.8 L/100 km (10.8 mpg‑US)* |
| 500 GE 6.0 AMG[16] | 1993 | V8 (M 117.965 E 50) | 5,953 cc (363.3 cu in) | 243 kW (326 hp) at 5,250 rpm | 525 N⋅m (387 lb⋅ft) at 4,000 rpm | 10.9 seconds | 195 km/h (121 mph) | — |
| G 500 G 550 (USA, 2005–2018) |
1998–2008 | V8 (M 113.965 E 50) | 4,966 cc (303.0 cu in) | 218 kW (292 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 456 N⋅m (336 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,000 rpm | 9.7–10.2 seconds | 190 km/h (118 mph) | 16.7 L/100 km (14.1 mpg‑US) |
| 2008–2015 | V8 (M 273 KE 55) | 5,461 cc (333.3 cu in) | 285 kW (382 hp) at 6,000 rpm | 530 N⋅m (391 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,800 rpm | 5.9–6.1 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 14.9 L/100 km (15.8 mpg‑US) | |
| 2015–2018 | V8 biturbo (M 176 DE 40 AL) | 3,982 cc (243.0 cu in) | 310 kW (416 hp) at 5,250–5,500 rpm | 610 N⋅m (450 lb⋅ft) at 2,250–4,750 rpm | 5.9 seconds | 12.3 L/100 km (19.1 mpg‑US) | ||
| G 500 4×4² | 2015–2018 | 7.4 seconds | 13.8 L/100 km (17.0 mpg‑US) | |||||
| G 55 AMG | 2001–2003 | V8 (M 113 E 55) | 5,439 cc (331.9 cu in) | 260 kW (349 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 525 N⋅m (387 lb⋅ft) at 2,800–4,000 rpm | 7.4 seconds | 209 km/h (130 mph) | 15.9 L/100 km (14.8 mpg‑US) |
| 2004–2006 | V8 supercharged (M 113 E 55 ML) | 350 kW (469 hp) at 6,100 rpm | 700 N⋅m (516 lb⋅ft) at 2,650–4,500 rpm | 5.6 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 16.3 L/100 km (14.4 mpg‑US) | ||
| 2006–2008 | 368 kW (493 hp) at 6,100 rpm | 700 N⋅m (516 lb⋅ft) at 2,750–4,000 rpm | 5.5 seconds | 15.9 L/100 km (14.8 mpg‑US) | ||||
| 2008–2012 | 373 kW (500 hp) at 6,100 rpm | |||||||
| G 63 AMG (V8) | 2012–2015 | V8 biturbo (M 157 DE 55 AL) | 5,461 cc (333.3 cu in) | 400 kW (536 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 800 N⋅m (590 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–5,000 rpm | 5.4 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph)** | 13.8 L/100 km (17.0 mpg‑US) |
| Mercedes-AMG G 63 |
2015–2018 | 420 kW (563 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 800 N⋅m (590 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–5,000 rpm | |||||
| G 63 AMG (V12) | 2002–2003 | V12 (M 137 E 63) | 6,258 cc (381.9 cu in) | 326 kW (437 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 620 N⋅m (457 lb⋅ft) at 4,400 rpm | 6.5 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | — |
| G 63 AMG 6×6 | 2013–2015 | V8 biturbo (M 157 DE 55 AL red.) | 5,461 cc (333.3 cu in) | 400 kW (536 hp) at 5,500 rpm | 760 N⋅m (561 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–5,000 rpm | 7.9 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | — — 15.6 L/100 km (15.1 mpg‑US) |
| G 65 AMG | 2012–2015 | V12 biturbo (M 279 E 60 AL) | 5,980 cc (365 cu in) | 450 kW (603 hp) at 4,300–5,600 rpm | 1,000 N⋅m (738 lb⋅ft) at 2,300–4,300 rpm | 5.3 seconds | 230 km/h (143 mph) | 17.0 L/100 km (13.8 mpg‑US) |
| Mercedes-AMG G 65 |
2015–2018 | 463 kW (621 hp) at 4,800–5,400 rpm | ||||||
| Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet | 2017-2018 | 6.0 seconds | 180 km/h (112 mph) | — | ||||
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| 250 GD | 1990–1992 | I5 (OM 602.931 D 25) | 2,497 cc (152.4 cu in) | 69 kW (93 hp) at 4,600 rpm | 158 N⋅m (117 lb⋅ft) at 2,600–3,100 rpm | 28.1 seconds | 132 km/h (82 mph) | 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US)* 10.5 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US)* 15.2 L/100 km (15.5 mpg‑US)* |
| G 270 CDI | 2002–2006 | I5 turbo (OM 612.965 DE 27 LA) | 2,685 cc (163.8 cu in) | 115 kW (154 hp) at 4,200 rpm | 400 N⋅m (295 lb⋅ft) at 1,800–2,600 rpm | 13.2–13.7 seconds | 160 km/h (99 mph) | 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) 9.6 L/100 km (25 mpg‑US) 10.9 L/100 km (21.6 mpg‑US) |
| 300 GD G 300 D |
1990–1994 | I6 (OM 603.931 D 30) | 2,996 cc (182.8 cu in) | 83 kW (111 hp) at 4,600 rpm | 191 N⋅m (141 lb⋅ft) at 2,700–2,900 rpm | 22.2 seconds (m) | 141 km/h (88 mph) (m) | 14.7 L/100 km (16.0 mpg‑US)* (m) 10.9 L/100 km (21.6 mpg‑US)* 16.0 L/100 km (14.7 mpg‑US)* |
| 23.3–23.6 seconds (a) | 138–141 km/h (86–88 mph) (a) | 12.5 L/100 km (18.8 mpg‑US)* (a) 10.8 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US)* 15.9 L/100 km (14.8 mpg‑US)* |
||||||
| G 300 D TURBODIESEL | 1996–2001 | I6 turbo (OM 606.964 D 30 LA) | 2,996 cc (182.8 cu in) | 130 kW (174 hp) at 4,400 rpm | 330 N⋅m (243 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–3,600 rpm | 14.2 seconds (m) | 164 km/h (102 mph) | 14.6 L/100 km (16.1 mpg‑US) 10.6 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US) 12.1 L/100 km (19.4 mpg‑US) |
| G 320 CDI | 2006–2009 | V6 turbo (OM 642 DE 30 LA) | 2,987 cc (182.3 cu in) | 165 kW (221 hp) at 3,800 rpm | 540 N⋅m (398 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,400 rpm | 8.8–9.1 seconds | 177 km/h (110 mph) | 13.4 L/100 km (17.6 mpg‑US) 9.7 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 11.0 L/100 km (21.4 mpg‑US) |
| 350 GD T G 350 TURBODIESEL |
1992–1996 | I6 turbo (OM 603.972 D 35 A) | 3,449 cc (210.5 cu in) | 100 kW (134 hp) at 4,000 rpm | 305 N⋅m (225 lb⋅ft) at 1,800 rpm | 16 seconds | 150 km/h (93 mph) | 13.5 L/100 km (17.4 mpg‑US) 11.8 L/100 km (19.9 mpg‑US) 16.9 L/100 km (13.9 mpg‑US) |
| G 350 CDI | 2009-2010 | V6 turbo (OM 642 DE 30 LA) | 2,987 cc (182.3 cu in) | 165 kW (221 hp) at 3,800 rpm | 540 N⋅m (398 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,400 rpm | 8.8–9.1 seconds | 177 km/h (110 mph) | 16.1 L/100 km (14.6 mpg‑US) 11.0 L/100 km (21.4 mpg‑US) 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) |
| G 350 CDI BlueTEC | 2010-2015 | 155 kW (208 hp) at 3,400 rpm | 175 km/h (109 mph) | 13.6 L/100 km (17.3 mpg‑US) 9.8 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) 11.2 L/100 km (21.0 mpg‑US) |
||||
| G 350 d | 2015–2018 | V6 turbo (OM 642 LS DE 30 LA) | 180 kW (241 hp) at 3,600 rpm | 600 N⋅m (443 lb⋅ft) at 1,600–2,400 rpm | 8.8 seconds | 192 km/h (119 mph) | 11.1 L/100 km (21.2 mpg‑US) 9.1 L/100 km (26 mpg‑US) 9.9 L/100 km (24 mpg‑US) |
|
| G 350 d Professional | 2016-2018 | 160 km/h (99 mph) | ||||||
| G 400 CDI | 2001-2006 | V8 biturbo (OM 628.962 DE 40 LA) | 3,996 cc (243.9 cu in) | 184 kW (247 hp) at 4,000 rpm | 560 N⋅m (413 lb⋅ft) at 1,700–2,600 rpm | 9.9–10.3 seconds | 182 km/h (113 mph) | 16.1 L/100 km (14.6 mpg‑US) 11.0 L/100 km (21.4 mpg‑US) 12.8 L/100 km (18.4 mpg‑US) |
G-Class W463, second generation (2018–present)[edit]
| Mercedes-Benz G-Class (W463) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 2018–present |
| Model years | 2019–present |
| Assembly | Austria: Graz (Magna Steyr) |
| Designer | Balázs Filczer[45] |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size luxury SUV |
| Body style | 5-door SUV |
| Layout | F4 (4MATIC) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 9G-Tronic, AMG SpeedShift TCT (9-speed automatic) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,890 mm (113.8 in) |
| Length | 4,725–4,817 mm (186.0–189.6 in) |
| Width | 1,931 mm (76.0 in) |
| Height | 1,969 mm (77.5 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,354–2,485 kg (5,190–5,478 lb) |
The second generation G-Class (W463) was launched on 14 January 2018 at the North American International Auto Show in Detroit.[46]
In contrast to its predecessor, the new G-Class has grown 121 millimeters in width and 53 millimeters in length. The ground clearance has increased by 6 millimeters.[47] The increase in width is for more driving stability, sturdier side impact protection, and more seating comfort. The increased length, especially in the front end, is due to the new 2019 EU pedestrian impact safety regulations: the previous generation did not have enough open space between the car’s front end and the rigid components beneath for the crumple zone as to mitigate the injury to a pedestrian’s body.
A major change was with the steering system which was switched from a recirculating ball system to variable-ratio rack-and-pinion with adaptive electric power assistance. The new steering system allows safety and convenience equipment such as active lane-keeping assist, Pre-Safe collision avoidance systems and self-parking capability. The rack-and-pinion steering system does not work with solid front suspension so a change was made to use independent front suspension.
The extensive, ground-up redesign allowed engineers to incorporate more lightweight materials such as high-strength and ultra-high-strength steels and aluminums. In addition, the redesign led to an improved manufacturing process which increased structural rigidity. The gap between the doors and body shell is much narrower than the previous generation. Despite the increased dimensions, the weight has been reduced by about 170 kilograms.
The second generation W463 is similar visually to the first generation, and the chassis code, W463, is still retained rather than W464 as some media outlets erroneously reported. However, only three parts from the previous generation were carried over to the new generation: the headlamp washers, the push-button door handles and the spare wheel cover bolted to the rear tailgate.[48]
The new G 500 (renamed to G 550 for 2020 onwards) is powered by the 4.0-liter M176 V8 twin-turbo engine, producing 416 hp and 450 lb⋅ft of torque. It is mated to a nine-speed automatic 9G-Tronic transmission with torque-converter.[49][50]
For the new diesel variant, the G 350d was initially released for the 2019 model year, powered by the 2.9-liter OM656 inline-6 turbocharged diesel engine, producing 282 hp and 443 lb⋅ft of torque.[51] The G 400d was later introduced for the 2020 model year onwards. The G 400d features the same OM656 engine as the G 350d, but output has been increased to 326 hp and 516 lb⋅ft of torque.[52] Both models are still produced by Mercedes-Benz, however certain markets only sell one of the two.[53]
The redesign also allowed newer safety and collision avoidance equipment from the W222 S-Class to be fitted to the G-Class for the first time. In addition, the updated interior has a new instrument cluster and infotainment system from other Mercedes-Benz models (A-Class (W177) and E-Class (W213)), air vents, steering column-mounted gear selector, multimedia system and control panel on the tunnel console, a higher level of luxury trimming and 64-color ambient lighting. A Burmester surround sound system and a larger dual 12-inch LCD display with smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay and Android Auto) were offered as optional equipment. One design element carried over to the new generation was the front passenger’s grab bar on the dashboard.[54]
The new G 550 and AMG G 63 have gone on sale in the United States with a starting price of $125,495 and $144,695 respectively. The 2019 G-Class for the US market has the widest range of exterior colors available, totaling 24, of any Mercedes-Benz passenger vehicle.[50]
In September 2020, the G 350 was introduced for the Chinese market to circumvent the heavy taxation on larger engine displacement.[55] It is powered by the 2.0-liter M264 turbocharged inline-4, producing 255 hp and 273 lb-ft of torque.The G 350 is the first G-Class with a four-cylinder inline engine since the previous model, the G 230, was dropped in 1995.
AMG models[edit]
AMG G 63[edit]
Alongside the new G 550, Mercedes-AMG unveiled the new G 63 in March 2018 at the Geneva International Motor Show. The model is powered by the V8 twin-turbo M177 engine, producing 577 hp and 627 lb⋅ft of torque, an increase of 14 hp and 66 lb⋅ft over the previous generation G 63 AMG. Mercedes-AMG claims a 0-60 mph time of 4.4 seconds and a top speed of 149 mph with the optional Driver’s Package. The G 63 now defaults to a rear-biased 40:60 torque split versus the 50:50 split of its predecessor.[56][57][58]
In addition to the performance increases over the standard G 550 with the AMG model, the G 63 also features AMG-developed suspension, larger red brake calipers and perforated brake discs, AMG-specific transmission modes, radiator grille, flared wheel arches, striking side pipes on the exhaust system, and wider wheels up to 22-inches in diameter. The model features distinct front and rear fascias and body styling, as well as an AMG-specific interior with a standard AMG Performance steering wheel with flattened bottom.[56]
-
AMG G 63
-
AMG G 63 rear
-
AMG G 63 (Japan) interior
AMG G 63 Edition 1[edit]
To commemorate the launch of the second-generation G-63, Mercedes-AMG released the Edition 1 special edition at market launch. The special model features Designo Night Black Magno paint with contrasting matte Graphite Grey sports stripes along the vehicle sides, a decorative red stripe on the exterior mirrors, and Night Package featuring gloss black trim and accents. The Edition 1 also features matte black 22-inch forged wheels with red-painted rim flanges and a cross-spoke design, as well as red accents throughout the interior.[56]
-
AMG G 63 Edition 1 at the Geneva Motor Show 2018
-
AMG G 63 Edition 1 rear
AMG G 63 Trail Package[edit]
The optional AMG Trail Package can be specified for the G 63 model only, offering greater off-road capability and styling. The package adds softer settings for the adaptive dampers to enhance off-road driving and maneuverability. 20-inch wheels with five sets of twin spokes and all-terrain tires are part of the package. A black skid plate and mud flaps behind the rear wheels are fitted to the body.[59]
AMG G 63 4×4²[edit]
Following the previous generation’s G 63 AMG 6×6 and G 500/G 550 4×4², Mercedes-Benz-AMG introduced the new G 63 4×4² for the second generation iteration in June of 2022 via YouTube.[60] The AMG G 63 4×4² features the same M177 V8 twin-turbo as the standard AMG G 63 but with output increased to 585 hp from 577 hp, and raised portal axles like the previous generation G 500/G 550 4×4², except now with independent front axles.[61][62] The model went on sale Fall 2022 for the 2023 model year at a price of $350,050 USD.[63]
Compared to the standard AMG G 63, the AMG G 63 4×4² features a raised height, larger carbon-fiber fenders, 22-inch wheels with 37-inch Pirelli 325/55R22 all-terrain tires, LED light bar, roof rack with carbon-fiber windscreen, carbon-fiber spare tire cover, and rugged styling. With this increase in height, the model offers a ground clearance 4.3 inches over stock at 13.8 inches, wading depth 8.2 inches over stock at 35.8 inches, and 41.3° approach and 36.8° departure angles.[64]
Additionally, compared to the previous generation G 500/G 550 4×4², the wheelbase is increased by 0.9 inch to 113.1 inches, height is increased by 0.8 inch to 88.8 inches, width is increased by 5.4 inches to 82.5 inches, and length is increased by 3.9 inches to 181.1 inches, or 194.5 inches when accounting for the spare tire carrier. Weight is decreased by 379 lbs to 6,315 lbs. Mercedes-Benz claims an estimated 5.0 0-60 mph time.[63]
Special models[edit]
Mercedes-Benz G 550 manufaktur Program (W463) front view
Mercedes-Benz G 550 manufaktur Program (W463) rear view
G manufaktur (Individualisation Programme)[edit]
Mercedes-Benz has introduced the bespoke/individualisation programme exclusive for the G-Class: G manufaktur. Similar to the Mercedes-Benz designo programme, buyers can specify different colour and material options. For the exterior, buyers can choose from 26 exclusive G manufaktur paint colours, and the Black Accents covers for the fender flares, roof, front and rear bumpers, external rear-view mirrors, rub stripes, spare wheel cover ring, wheels, side exhaust pipe tips, etc in gloss black paint. For the interior, 64 different seat colour combinations and three patterns can be specified. The dashboard and steering wheel cover can be ordered with a two-toned colour combination. On the passenger grab bar, the G manufaktur brand is etched on the stainless steel trim.[65]
Stronger Than Time[edit]
To celebrate the 40th anniversary of the G-Class and the 20th anniversary of the G 55 AMG, Mercedes-Benz introduced the Stronger Than Time edition for the G 400 d, G 500, and Mercedes-AMG G 63. For the G 400 d and G 500, the edition is fitted with the AMG Line exterior package, black 20-inch AMG wheels, and stainless steel trim for the running boards, spare wheel cover, and door sills. The puddle lamps display the G-Class logo and Stronger Than Time on the ground. The driver’s assistance package, LED headlamps, Burmester surround stereo system, and sunroof are added as standard equipment. The G 63 has a dark chrome grille and matte chrome covering the running boards, exhaust outlets, mirror caps, portions of the front and rear bumper, skid plate, and sections of the spare wheel cover. The 22-inch matte black AMG wheels are fitted to the G 63.
Three interior designs can be chosen: black Nappa leather with gold stitching and open-pore black ash wood trim; a mix of Macchiato Beige and Yacht Blue leather with light brown sen wood trim; and Macchiato Beige and Lounge Red with piano black lacquer. The Nappa leather trim covers the roof grab handles and the instrument cluster cover. The two-tone black and Titanium Grey Pearl Nappa leather with carbon fiber trim is exclusive to the G 63 model.
Professional Line[edit]
With the success of Worker, Pur, and Professional variants in the previous W461 generation, Mercedes-Benz introduced the new Professional Line Exterior at the IAA Mobility 2021 in Munich.[66] Professional Line Exterior is an exterior accessory options that the owners can customise their G-Class vehicles. The options include climbing ladder, roof rack, simpler spare wheel holder, black trims, headlamp protection grill shield, and like. Unlike the previous Worker, Pur, and Professional variants, Professional Line Exterior isn’t a stripped-down utilitian version of G-Class and based on W461 chassis.[67]
-
W 463 Professional Line rear
Concept cars[edit]
Mercedes-Benz Concept EQG front view at the IAA 2021
Mercedes-Benz Concept EQG rear view at the IAA 2021
Concept EQG[edit]
On 5 September 2021, Mercedes-Benz previewed Concept EQG, the G-Class concept car with pure electric drive, at IAA Mobility 2021 in Munich.[68] Externally, Concept EQG carries the styling of the second generation G-Class, with updated elements to distinguish the electric variant, such as a square tire cover, extensive additional LED lighting including a LED Black Panel grille, updated front and rear fascias, new 22-inch wheels, and special roof rack. While Mercedes-Benz has not revealed the technical data yet, Concept EQG has four electric motors that are placed closer to the wheels and that can operate independently; the battery packs are 108 kWH. Additionally, a two-speed gearbox allows the gear reductions for the off-road travel.[68][69] The model names are EQG 560 4MATIC and EQG 580 4MATIC.[70][71] The production version is confirmed for 2024.[72][73]
Technical data[edit]
Engines (2018–present)[edit]
| Model | Years | Configuration | Displacement | Power | Torque | 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) | Top speed | Fuel consumption/efficiency (EU-norm combined) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol engines | ||||||||
| G 350 (China) | 09/2020–present | I4 turbocharger (M264 E20 DEH LA) | 1,991 cc (121.5 cu in) | 190 kW (258 PS; 255 hp) | 370 N⋅m (273 lb⋅ft) | 8.1 seconds | 190 km/h (118 mph) | 10.7 L/100 km (22 mpg‑US) |
| G 500 G 550 (US and certain markets) |
05/2018–present | V8 twin-turbo (M176 DE40 LA) | 3,982 cc (243.0 cu in) | 310 kW (421 PS; 416 hp) at 5,250–5,500 rpm | 610 N⋅m (450 lb⋅ft) at 2,250–4,750 rpm |
5.9 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 11.5–12.1 L/100 km (20.5–19.4 mpg‑US) |
| Mercedes-AMG G 63 | 06/2018–present | V8 twin-turbo (M 177 DE 40 AL) | 3,982 cc (243.0 cu in) | 430 kW (585 PS; 577 hp) at 6,000 rpm | 850 N⋅m (627 lb⋅ft) at 2,500–3,500 rpm | 4.5 seconds | 220 km/h (137 mph) / 240 km/h (149 mph)* | 11.5–12.1 L/100 km (20.5–19.4 mpg‑US) |
| Diesel engines | ||||||||
| G 350 d | 01/2019–present | Inline 6 turbo (OM 656 D 29 R SCR) | 2,925 cc (178.5 cu in) | 210 kW (286 PS; 282 hp) at 3,400 rpm | 600 N⋅m (443 lb⋅ft) at 1,200–3,200 rpm | 7.4 seconds | 199 km/h (124 mph) | 9.6–9.8 L/100 km (25–24 mpg‑US) |
| G 400 d | 07/2019–present | Inline 6 turbo (OM 656 D 29 R SCR) | 2,925 cc (178.5 cu in) | 243 kW (330 PS; 326 hp) at 3,400 rpm | 700 N⋅m (516 lb⋅ft) at 1,200–3,200 rpm | 6.4 seconds | 210 km/h (130 mph) | 9.6 L/100 km (25 mpg‑US) |
*With optional extra cost AMG Driver’s Package
Transmission (2018–present)[edit]
| Model | Years | Types |
|---|---|---|
| G 350 | 2020–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
| G 500 / G 550 | 2018–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
| Mercedes-AMG G 63 | 2018–present | 9-speed automatic AMG SPEEDSHIFT TCT 9G |
| G 350 d | 2019–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
| G 400 d | 2019–present | 9-speed automatic 9G-TRONIC |
Safety[edit]
Gallery[edit]
Mercedes-Benz G 500
Mercedes-AMG G 63 Edition 1
Mercedes-AMG G 63 Edition 1 rear
Military operators[edit]
Map of military Mercedes-Benz G-Class operators
Albania
- Since the 2010s, the Albanian Army has been using G-Class vehicles.
Algeria
- Since the 2010s, the Algerian Army, Gendarmerie Nationale and the Algerian police have been using several models of G-Class vehicles 4×4 6×6 G 500. Most of those vehicles are manufactured in Bouchekif factory Tiaret, owned by the Algerian army.[1] First G-Class wagons released in 2015.[citation needed]
Argentina
- Since the 1980s, the Argentine Army has used the MB-230G (short and long chassis) for different purposes. 900 remain in service.[75]
Australia
- In October 2007, Mercedes-Benz became the preferred tenderer for the Australian Defence Force to replace the fleet of Land Rover Perentie in Project Land 121 Overlander.[76] Mercedes-Benz was the sole tenderer with neither Toyota for the Land Cruiser or Land Rover for the Defender submitting a proposal. In October 2008, an initial contract for 1200 vehicles was signed.[77] 2,268 vehicles were purchased with ten variants including 6×6.[78][79] Australia is the first military customer to receive 6×6 vehicles and these are the first six-wheel military vehicles built by Mercedes-Benz since 1941.[80]
Austria
- The Austrian Army has been a long time user of various Puch G models.
Belgium
- The Belgian Police or «Gendarmerie-Rijkswacht» has been a long time user of first G 500 models.
Bulgaria
- The Bulgarian Army operates 600+ vehicles in various configurations, most of them armed.
Cambodia
- Royal Gendarmerie of Cambodia purchased 30 armored Mercedes-Benz G-Class from RMA Cambodia.
Cameroon
- 60 «Wolf» in service with the Cameroon Armed Forces.[81]
Canada
- A total of 1,159 vehicles have been ordered by the Canadian Army beginning in late 2003.[82] An armoured kit can be fitted (or removed) in 8 hours by three soldiers. Their light armour has been criticised for leading to loss of life in Afghanistan, however it is considerably better than the Iltis predecessor.[83]
- Delivery of these vehicles to Reserve units has also begun. They will be deployed in armoured reconnaissance units. It is in the final stages of fully replacing the Iltis in most units as the armoured reconnaissance vehicle in use LFCA. Other units will replace the Iltis with a militarized Chevrolet Silverado known as the MILCOTS (or colloquially as the «Milverado».) For the most exposed missions in Afghanistan 75 RG-31 Nyalas built by BAE Land Systems OMC, South Africa were used.[84]
Croatia
- Croatia bought 300 to 320 vehicles for needs of Croatian army and for operations in Afghanistan additional 30 RG-31 vehicles were delivered. Croatia uses mix of 4×4 vehicles in peacekeeping operations and the G-Class is a very popular choice within the Croatian Army. G-Class is supplemented by Land Rover Wolf and Iveco LMV.
Denmark
- The Danish military bought the 240 GD (/24, /28 and /34 variants) to supersede the M151A1, the Volkswagen 181 («Jagdwagen») and the Land Rover 88.[85] First deliveries of the 240 GD were in 1985 and later the 290 GD (/24 and /28 variants) were also introduced. More than 1,300 have been put in service. A few 300 GE’s have also been used — mainly by the Danish army EOD-services.[86] Currently the Danes are taking delivery of over 2,000 270CDIs in several variants, starting in 2003.[87]
East Timor
- used by units of Army of the Timor Leste Defence Force.[citation needed]
Egypt
- The Egyptian Army uses the G 320 (4 × 4) armoured personnel carrier has been designed as a private venture by the Kader Factory for Developed Industries and is based on the chassis of the commercial German Mercedes-Benz MB 320G (4 × 4) light vehicle. This vehicle is based on the long-wheelbase version of the German Mercedes-Benz G 320 4 × 4 with the chassis frame being modified by a heavy-duty suspension which has been designed to withstand the additional weight imposed by the armour package.[88]
Estonia
- The Estonian Defence Forces have a small number of various G-Class vehicles, which were purchased to replace the outdated UAZ and Volkswagen Iltis vehicles.
Finland
- The Finnish Army uses the Geländewagen mostly as armored vehicles and ambulances, but other versions are also in service.
France
- The French Army has the Peugeot P4 which is a derivative from the G-Class equipped with Peugeot engine and equipment.
A Wolf of the German Army
Germany
- The German Armed Forces uses the G-Class under the name «Wolf». Over 12,000 vehicles have been delivered in over 50 versions, ranging from ambulance vehicles to armored vehicles used by the German special forces. In the 1970s the cheaper Volkswagen Iltis was preferred; now the Iltis is replaced by the «Wolf» and the armoured variant LAPV Enok.
A Greek Army vehicle in Military Police colours
Greece
- The Greek Army as well as Air Force, Navy and Police have several versions (462) of the Geländewagen, manufactured by ELBO the Hellenic Vehicles Industry.[2]
Hungary
- The Hungarian Ground Forces have 233 of G-270 CDI BA 10, which is mounted with UMF light-machine gun platform, and 5 of G-280 CDI BA6 C+R SSA FB6. More will be purchased between 2010 and 2013.
Indonesia
- Paspampres (Indonesian Presidential Security forces) are using G 270 CDI for their fleet with SIRINA lights, Gunner Roof Mount, Bullbar, Black Grill, Roof and Rear View Mirror Handles. New model of G 300 CDI in 2010 acquired not less than 30 units for presidential and vice-presidential escort purposes. The Paspampres uses black G 300 CDI with the Military Police in white and ensigns with Indonesian MP insignia.
Iraq
- The Kurdish Peshmerga has 60 «Wolf» including 20 lightly armored type to help fight off the ISIL forces.[89]
Ireland
- The Irish Army used a number of G-Wagens as ambulances.
Kosovo
- The KSF use more than 200.
Latvia
- The Latvian Land Forces and Latvian National Guards use different modifications of Geländewagen, including armored.
Lebanon
- The Lebanese Army operates 20 G-wagon donated by Royal Dutch Army as ambulances
Lithuania
- The Lithuanian Armed Forces operates approximately 200 formerly Dutch GD vehicles since delivery in 2016.[90] On December 17, 2021, the National Defence Volunteer Force will receive 125 ex-Dutch GDs for patrolling the land border with Belarus.[91]
Luxembourg
- The Military of Luxembourg uses the 300D variant of the Geländewagen.
Norwegian military MB240GD
Malaysia
- Locally built by DEFTECH since 2001, the G-Wagon is used along with Land Rover Defender as light transport of Malaysian Army.[92] It uses the GD280 chassis.[93]
Mexico
- The Mexican naval defense secretary (SEMAR) announced in 2008, a contract to purchase large numbers of Mercedes-Benz military vehicles for the Mexican Marine corps. As of May 16, 2009 The SEMAR has received 20 of the 84 G-Class vehicles in order.[94][95]
Mongolia
- The Ministry of Defense of Mongolia operates 10 G-class vehicles (Wolf) donated by the German Government in 2010.[96]
Netherlands
- The Royal Netherlands Army uses various versions of the Mercedes-Benz G-Class, mostly 461 290GD manual gearbox, 290GD TD manual gearbox models and a 280cdi V6 model with automatic gearbox. The Dutch police and Koninklijke Marechaussee also use the G-Class. Most of the police versions are armored 463 models.
North Korea
- The Korean People’s Army appears to have acquired G-class vehicles, some of which were seen on the Workers’ Party of Korea 65th anniversary military parade.[97] At the funeral of Kim Jong-il his hearse was flanked by G-Class vehicles.[98]
Norway
- The Norwegian Army bought 240 GD to replace Volvo and Land Rover 4×4 vehicles in the mid-1980s, and 300 GD to use as ambulances. The 300GD is also used to transport the launch control station and optical sensors for the NASAMS Air-defense system. During the 90’s 290 GD’s where bought, and in the first half of the 00’s a small number of armoured 270 CDI’s were put into service. Today the Defence Forces operates a total of 3000 vehicles. The escort company of the Norwegian Royal Guard employs a black G 500 AMG with police lights on the roof.
Poland
- 96 GD 290 and 25 MB290GD WD in service with Wojska Lądowe. 13 GD 290 in service with the Żandarmeria Wojskowa.[99]
Portugal
- The Portuguese Marine Corps uses the G-class for light transport along with Toyota Landcruiser and Land Rover Defender 90.[100]
Russia
- Police, state security units, military and governmental agencies are using the G-Class. Mostly civilian versions in black. Security escort vehicles for both the President and Prime Minister are black G 500 and G 55 AMG.
Serbia
- The Serbian Military currently uses Puch 300GD model. They also uses the following models in 300GD33, 300GD6 and 300GD10 variants, for transport of VIP persons in 300GD3-LUX and 300GD6-LUX and Special Forces Brigade is use modified version designed for access to combat zone.
Singapore
- The Singapore Army bought the 270 and 290 versions as secondary military transport. It is used in soft-top truck configuration and is known as a 1.5-tonner or simply «MB» to its users. And also some were used also for patrolling in a «jeep» form. The Army also deploys the extremely short-wheelbase, soft-top version for its Colonels, Battalion COs, Brigade and Division Commanders as personal field transports.
Slovenia
- The Military of Slovenia uses Mercedes-Benz G-Class vehicles mainly for transport.
Slovakia
- The Armed Forces of Slovak republic uses Mercedes-Benz G-280 CDI in 5th Special Forces Regiment.
Sweden
- The Swedish Army uses MB 290/T (1994), MB 290GD (2000) and MB 270 CDI (2005). The GW is to be the main light terrain vehicle in the Swedish armed forces in the future. In 2011 a framework agreement was signed between FMV and Daimler AG. An initial contract for 105 300 CDI was signed.[101][102]
Switzerland
- The Swiss Armed Forces uses the 230 with soft top as the primary general purpose carrier, and a hardtop version as mobile radio access point. It is in service since 1985 and gradually replaced Willys Jeeps, Steyr-Puch Haflinger light transports and Pinzgauer medium transports in the liaison and transport role. All versions in Swiss Army use are unarmed. From 2014, the Steyr Daimler Puch 230 GE is going to be gradually replaced by the Mercedes-Benz G 300 CDI 4×4 hardtop version, starting with a first series of 3,200 vehicles.
United Kingdom
- An Argentine Army G-Class captured by the British Army during the Falklands War was subsequently used by No. 18 Squadron RAF in West Germany for several years.[103] The British Commanders’-in-Chief Mission to the Soviet Forces in Germany (BRIXMIS) also used a number.[104]
Ukraine
- Police, state security units, military and governmental agencies are using the G-Class. Mostly civilian versions in black. Security escort vehicles for both the President and Prime Minister are black G 500 and G 55 AMG.
United States
-
The USMC Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV) is a modified version of the Mercedes-Benz Geländewagen 290. It replaces the modified M-151A21⁄4 ton truck jeep used by the Marines as an FAV in the 1990s. The U.S. Marine Corps acquired 157 of the IFAVs distributed as follows:
- (I) Marine Expeditionary Force (MEF) Camp Pendleton, CA (33);
- (II) MEF Camp Lejeune, NC (25);
- (III) MEF on Okinawa, Japan (27);
- (IV) 17 Force Recon, Afghanistan (22);
- (V) 3 Force Recon Bn, Iraq (23);
- (VI) 1st Provisional DMZ Police Company, Korea (15); and
- (VII) various miscellaneous (12)
In the late 1990s the USMC acquired the G-Class model as the Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV), which was essentially a ’97 to ’01 DaimlerChrysler model 290 GDT, a diesel-power 2-door with a pick-up bed.[105] This was compact and light enough to be transported inside a Sikorsky CH-53 Sea Stallion Helicopter.[105]
Bodystyles[edit]
| Code | Bodywork | Wheelbase | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Convertible with fixed windshield | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | Only civilian types: 460 and 463 |
| 2 | Van | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 3 | Station Wagon | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | All types except Professional and Greenline military types |
| 4 | Van | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | Only 460/461/Professional/Worker and military types |
| 5 | Pickup | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | Only 460/461 types and G 63 6×6 (W463) |
| 6 | Station Wagon | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | All types |
| 7 | Convertible with folding windshield | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) | Only military types |
| 8 | Code unused | N/A | N/A |
| 9 | Chassis Cab | 3,120 mm (122.8 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 9,1 | Chassis Cab | 3,400 mm (133.9 in) | Only 460/461/Professional and military types |
| 10 | Convertible with folding windshield | 2,850 mm (112.2 in) | Only military types |
| 11 | Chassis Double Cab | 3,120 mm (122.8 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 11,1 | Chassis Double Cab | 3,400 mm (133.9 in) | Only 460/461 and military types |
| 11,2 | Chassis Double Cab 6×6 | 3,400 mm (133.9 in) | Only Greenline military types |
US sales figures[106]
- 2018: 3,970
- 2017: 4,188
- 2016: 3,950
- 2015: 3,616
- 2014: 3,090
- 2013: 2,494
- 2012: 1,330
- 2011: 1,191
- 2010: 919
- 2009: 662
- 2008: 931
- 2007: 1,152
- 2006: 587
- 2005: 1,334
- 2004: 1,491
- 2003: 1,980
- 2002: 3,114
- 2001: 674
Motorsport[edit]
In 1983 a specially modified 280 GE won the Paris–Dakar Rally driven by Jacky Ickx and Claude Brasseur.[107]
In Popular Culture[edit]
A 1990 G-Class appears in the action film The Bourne Supremacy. It is involved in the film’s last chase and is eventually destroyed in a crash with a concrete post.[108]
See also[edit]
- Force Trax — a very similar Indian SUV
- Force Gurkha — SUV based on G-Class chassis
- Beijing BJ80 — similar Chinese SUV
References[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b «Algerian factory unveils new locally assembled truck for Algerian military». Db-defenceweb.co.za. Archived from the original on 2015-10-09. Retrieved 2015-03-16.
- ^ a b «Cross country 1/4 ton military jeeps». ELBO. Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ O’Kane, Sean (5 September 2021). «Mercedes-Benz Reveals an Electric G-Wagen Concept for the Future». The Verge. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class to be produced till 2020». MSN Arabia. Archived from the original on 21 May 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ Padeanu, Adrian (4 December 2020). «Mercedes G-Class Reaches Production Milestone: 400,000th SUV Assembled». Motor1.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen, Austria». Archived from the original on 2016-12-27. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ «Oh Lord won’t you buy me a Mercedes Benz». 15 September 2016.
- ^ Büschi, Hans-Ulrich, ed. (5 March 1987). Automobil Revue 1987 (in German and French). Vol. 82. Berne, Switzerland: Hallwag AG. p. 382. ISBN 3-444-00458-3.
- ^ «1979 Mercedes-Benz G-class (W460) 230 G (90 Hp) 4WD». auto-data.net. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- ^ «560 GE (W460)». W463.de. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ «Accessories». Puch. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ Westbrook, Justin T. (18 May 2018). «The Outgoing Mercedes G-Class Is Still In Production Because Icons Never Die». Jalopnik.
- ^ «1992 Mercedes-Benz G-class (W463) 350 GD Turbo (136 Hp) 4MATIC Automatic». auto-data.net. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Sorokanich, Bob (15 May 2018). «You Can Still Buy a Brand-New Old-Style G-Wagen, Sort of». Road & Track.
- ^ Raudonikis, Matt (8 December 2016). «Mercedes-Benz W461 G300 CDI Cab-Chassis: First-Drive». Which Car.
- ^ a b c «AMG Motoren». Nast Sonderfahrzeug (in German). Retrieved 12 August 2020.
- ^ O’Neill, Chris (August 2018). «Here’s How the Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen Got Around the 25-Year Import Rule». Auto Trader.
- ^ Deppe, Philip (23 June 2011). «Mercedes-Benz Guard safety philosophy: Licenced to protect». Mercedes-Benz Passion. Archived from the original on 2012-05-18.
- ^ «The magazine 4WheelFun crowns the G-Class as «2009 superstar»: Best in class: the G-Class». Archived from the original on 2016-01-07. Retrieved 2012-12-06.
- ^ Abuelsamid, Sam (15 December 2009). «Mercedes-Benz SLS goes from zero to gold in seconds for Dubai show». Autoblog.
- ^ Joseph, Noah (5 May 2011). «Mercedes-Benz gears up for the demise of the G-Class with BA3 Final Edition and Edition Select». Autoblog.
- ^ Homma, Masaaki (9 January 2012). «mastermind JAPAN x Mercedes-Benz G-550». Freshness.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G550 «Night Edition» Japan Exclusive». Hype Beast. April 2016.
- ^ Davis, Jim (3 September 2013). «Mercedes G-Class Cabriolet Final Edition». eMercedes-Benz.
- ^ Sellmeyer, Des (21 February 2015). «Exclusive: Mercedes-Benz G500 4×4² Review». GT Spirit.
- ^ «The new Mercedes-Maybach G 650 Landaulet, Strictly Limited: an open-air luxury both on and off road». Mercedes-Benz. Retrieved 18 February 2020.
- ^ Knecht, Jochen (6 March 2017). «Brutalo-Teilcabrio feiert Genf-Premiere». Auto Motor und Sport (in German).
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz 500 GE 6.0». Brabus. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Felshart, Luca (24 April 2019). «Mercedes-Benz 500 GE 6.0 AMG von BRABUS Classic». Mercedes Fans.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz M137 V12 engine». motor-car.net. Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- ^ «The Automotive Declaration of Independence». Mercedes-Benz. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- ^ Gorzelany, Jim (6 March 2013). «A Six-Wheeled Mercedes G-Class Could Be The Ultimate Road Warrior». Forbes.
- ^ Anderson, Brad (17 February 2015). «Mercedes-Benz G63 AMG 6×6 Sold Out». GT Spirit.
- ^ Joseph, Noah (6 July 2010). «Mercedes-Benz G-Wagon LAPV 6.X Concept ready to blitz the front».
- ^ Ross, Jeffrey (16 November 2012). «Mercedes-Benz Ener-G-Force concept is a G-Class for the future». Autoblog.
- ^ Harley, Michael (29 November 2012). «Mercedes-Benz Ener-G-Force Concept is mean, clean and green». Autoblog.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class Search Result». Internet Movie Car Database. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Korzeniewski, Jeremy (8 August 2011). «Australian Outback cripples fleet of Mercedes G-Wagens during PR event».
- ^ Beissmann, Tim (5 August 2011). «Mercedes-Benz G-Class broken by the Australian Outback». Car Advice.
- ^ «Mercedes To Continue Producing G-Class». eMercedes-Benz. 11 November 2005. Archived from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ «Mercedes bids current G-Class adieu with three special editions». NY Daily News. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- ^ Meiners, Jens (6 May 2010). «Mercedes to show face-lifted G-Class ute at upcoming Paris auto show (AutoWeek Magazine)». Autoweek.com. Archived from the original on 8 September 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ Ramsey, Jonathon (11 April 2012). «Mercedes introduces 2013 G-Class, including 612-HP G65 AMG». Autoblog.
- ^ Meiners, Jens (20 October 2015). «2016 Mercedes-Benz G550». Car and Driver.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class Design 2018». group-media.mercedes-benz.com. Retrieved 2022-07-28.
- ^ Luchian, Elena (14 January 2018). «Live from Detroit — Master G is back! This is the 2019 Mercedes-Benz G-Class». MercedesBlog.
- ^ Schäfer, Patrick (15 January 2018). «Die Mercedes G-Klasse bleibt ein klassischer Geländewagen». SpringerProfessional (in German).
- ^ Pollard, Tim (23 August 2018). «Mercedes-Benz G-class review: we test the year’s hardest, gnarliest 4×4». CAR Magazine. Archived from the original on 24 August 2018.
- ^ «The new Mercedes-Benz G-Class». MBUSA Newsroom. 2018-05-07. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ a b «The next-generation G-Class». Mercedes-Benz USA. 13 May 2019. Archived from the original on 10 May 2019.
- ^ «The new Mercedes-Benz G 350 d.» www.mercedes-benz.com. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «2022 Mercedes-Benz G400d First Drive: Is This Diesel G Great?». MotorTrend. 2022-05-09. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «Mercedes G-Class G400d review: ‘the best version of the best off-roader’ Reviews 2022». Top Gear. 2021-09-22. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «Future Models 2019 Mercedes-Benz G-Class». Mercedes-Benz USA. 9 February 2019. Archived from the original on 9 February 2019.
- ^ «Mercedes G350 Revealed in China, 4-Cylinder G-Class Costs $209,000».
- ^ a b c «The new 2019 Mercedes-AMG G63». MBUSA Newsroom. 2018-02-13. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ Ewing, Steven. «2019 Mercedes-AMG G63 brings 577 hp to Geneva». CNET. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «2019 Mercedes-AMG G63 Driven: The Speedier G-wagen». Car and Driver. 2018-02-13. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ Bruce, Chris (14 June 2019). «Mercedes Celebrates G-Class Anniversary With Exclusive Puddle Lamps». Motor1.
- ^ G-Class Private Lounge – Walkaround | Mercedes-AMG G 63 4×4², retrieved 2022-12-12
- ^ «2023 Mercedes-AMG G63 4×4 Squared First Look: Portal to the Past». MotorTrend. 2022-06-14. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ Perkins, Chris (2022-06-14). «The 2023 Mercedes-AMG G63 4×4 Squared is a 585-HP Factory Monster Truck». Road & Track. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ a b «2022 Mercedes-AMG 4×4² First Drive: Same Lunacy, Back for Round 2». MotorTrend. 2022-10-21. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «2023 Mercedes-AMG G63 4×4 Squared First Look Review: The Uber-Overlander». CarBuzz. Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ^ «G manufaktur». Mercedes-Benz. Retrieved 5 July 2020.
- ^ Jordan, Markus (2 September 2021). «Neue G-Klasse Professional steht auf der IAA Mobility 2021 #MBIAA21». MB Passion.
- ^ Tsui, Chris (7 September 2021). «New Mercedes G-Wagen Off-Road Trim Finally Starts to Unlock the Truck’s Potential». The Drive.
- ^ a b Smith, Christopher (5 September 2021). «Mercedes Concept EQG Debuts In Munich With Electric G-Class Style». Motor1.
- ^ Page, Felix (16 August 2021). «Mercedes primes luxury EQG electric G-Class 4×4». Autocar.
- ^ Oliva, Jacob (1 April 2021). «Mercedes EQG Trademarks Remind Us Electric G-Class Is Coming». Motor1.
- ^ Hong, Matthew (17 August 2021). «Mercedes-Benz EQG – fully electric G-Class to get true 4×4 capabilities, EQG 580 4Matic with 523 PS, 855 Nm?». Paul Tan.
- ^ Padeanu, Adrian (16 August 2021). «Mercedes EQG Could Keep Ladder Frame, Add Big Battery For Electric G-Class». Motor 1.
- ^ Lye, Gerard (6 September 2021). «Mercedes-Benz Concept EQG debuts – previews an all-electric G-Class; 4 electric motors, 2-speed gearbox». Paul Tan.
- ^ «Official Mercedes-Benz G-Class 2019 safety rating». EuroNCAP. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- ^ «ORBAT del Ejército Argentino». Archived from the original on 2019-04-26. Retrieved 2019-04-26.
- ^ Minister for Defence Brendan Nelson (5 October 2007). «New defence contracts deliver a boost for Brisbane» (Press release). Department of Defence. Archived from the original on 31 October 2007.
{{cite press release}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Ridgway, Steve (13 November 2008). «$350m wagon deal» (PDF). Army: The Soldiers’ Newspaper (1202 ed.). Canberra, Australia: Department of Defence. ISSN 0729-5685. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ «G Wagon». Australian Army. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ «G-wagon booklet» (PDF). Australian Army. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ Duff, Craig (13 September 2012). «Cars Guide: Merc G-wagons for military». The Daily Telegraph. pp. 21–22 (90–91). Retrieved 16 September 2012.
- ^ «France donates military equipment to Cameroon». defenceWeb. 2016-12-12. Retrieved 2021-10-06.
- ^ Armoured Vehicles – Mercedes G-Wagon – Blast Resistant Vehicles – Nyala APV – IED – MND Gordon O’Connor – Afghan Mission – Procurement Priorities – CASR – Canadian American Strategic Review Archived April 21, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Mercedes G-Wagon – Kandahar – Afghanistan – Gumbad IED – Media Response – Canadian Forces – CASR – Canadian American Strategic Review Archived May 4, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Canadian Army — Equipment Archived June 20, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Danish army Mercedes 240 GD/24». Armyvehicles.dk. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Danish army Mercedes 300 GE/28». Armyvehicles.dk. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Danish army Mercedes G270CDI/28». Armyvehicles.dk. Archived from the original on 2011-02-11. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Kader G 320 armoured personnel carrier (Egypt) – Jane’s Armour and Artillery». Articles.janes.com. 2007-10-04. Archived from the original on 2012-05-03. Retrieved 2012-04-12.
- ^ «Germany and the Kurds: Supplying Arms as Part of Evolving German Foreign Policy?». sldinfo.com. 3 September 2014. Archived from the original on 2014-09-08. Retrieved 2014-09-03.
- ^ Tomkins, Richard (18 August 2016). «Lithuania receives surplus vehicles from the Netherlands». United Press International. Archived from the original on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- ^ «Lithuania Acquires Dutch Geländewagens for Belarus Border». 20 December 2021.
- ^ «Ahmad Zahid: 84 G-WAGON Masih Beroperasi» (in Malay). KL Security Review. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-04.
- ^ «Archived copy». www.deftech.com.my. Archived from the original on 13 November 2011. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ «Secretaria de Marina – Armada de México». Semar.gob.mx. Archived from the original on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ «Recibe Semar vehículos para incrementar capacidad operativa :: El Informador». Informador.com.mx. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ Батлан хамгаалах салбарт 140 мянган еврогийн vнэ бvхий 10 машин бэлэглэлээ. «Olloo.mn — Єдєр бvр дэлхий даяар». Archived from the original on 2012-07-06. Retrieved 2012-07-18.
- ^ [1] Archived October 1, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Kim Jong-il’s Funeral Held in N. Korea (PHOTOS)». Ibtimes.com. 2011-12-28. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2012-04-12.
- ^ «Zestawienie pojazdów użytkowych Wojska Polskiego – Militarypedia (note: it does provide its own sources)» (in Polish). Militarypedia.corran.pl. Archived from the original on 2011-08-22. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ «Archived copy». Archived from the original on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2011-12-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Henrik Svensk. «Personterrängbil 5 -MB 290/T Geländewagen». SoldF.com. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ Henrik Svensk. «Personterrängbil 5 Geländewagen». Soldf.com. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ Carr, Clare (15 September 2016). «Oh Lord won’t you buy me a Mercedes Benz». RAF Museum. Archived from the original on 19 January 2018. Retrieved 18 January 2018.
- ^ «Later Years | BRIXMIS».
- ^ a b U.S. Marine Corps’ G-Wagen Archived 2016-11-24 at the Wayback Machine Truck Trend
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class US car sales figures». 8 November 2015. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ^ «Mercedes-Benz G-Class History». Edmunds. Archived from the original on 3 July 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ «1990 Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse [W463]». imcdb.org. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
Bibliography[edit]
General[edit]
- Arthur, Gordon (2021). Australian G-Wagons [sic]: Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse 4×4 und 6×6 Geländewagen der Australischen Streitkräfte [Australian G-Wagons [sic]: Mercedes-Benz G-Class 4×4 and 6×6 off-road vehicles of the Australian Defence Force]. International Special No. 8010 (in English and German). Erlangen, Germany: Tankograd Publishing. OCLC 1268193713.
- Barrett, Frank (1998). Illustrated Buyer’s Guide Mercedes-Benz. Motorbooks International Illustrated Buyer’s Guide series (2nd ed.). Osceola, WI, USA: MBI Publishing. ISBN 0-7603-0451-3.
- Bolsinger, Markus; Lengert, Axel; Peters, Wolfgang (2013). Legend – The G Class: from 1979 to today. Bielefeld, Germany: Delius Klasing. ISBN 9783768836241.
- Breuninger, Martin (1993). Das G-Buch: Alles über den Geländewagen von Mercedes-Benz [The G Book: Everything about the Geländewagen from Mercedes-Benz] (in German). Radolfzell, Germany: Tufa. ASIN B002UNICHS.
- ———————— (1995). Das G-Reisebuch – mit dem Geländewagen von Mercedes-Benz unterwegs [The G Travel Book: On the move with the Geländewagen from Mercedes-Benz] (in German). Radolfzell, Germany: Tufa. ASIN B002UNICIM.
- ———————— (2004). The Legend Keeps on Driving: 25 Years of Mercedes-Benz G-Class. Radolfzell, Germany: Tufa. ISBN 0962554154.
- Clarke, R.M., ed. (1999). Mercedes G-Wagen 1981–1994. Road Test Portfolio Series. Cobham, Surrey, UK: Brooklands Books. ISBN 1855203081.
- ——————, ed. (2006). Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen Gold Portfolio 1981–2005. Road Test Portfolio Series. Cobham, Surrey, UK: Brooklands Books. ISBN 1855206994.
- Füngeling, Michael (2001). Das große Mercedes-G-Buch Baureihen 460, 461, 463 [The Big Mercedes G Book 460, 461, 463 series]. Ein Off-road-Sachbuch series (in German) (2nd, expanded ed.). Ottobrunn: AC Verlag. ISBN 3930193248.
- García Loperena, Gastón Javier (2018). Mercedes-Benz G en el Ejército Argentino (in Spanish). Buenos Aires, Argentina: 1884 Círculo Militar. ISBN 9789874112156.
- Giesen, Norbert (2021). Mercedes G-Modell. Bewegte Zeiten series (in German). Bielefeld, Germany: Delius Klasing. ISBN 978366712230-8.
- Greene, Nik (2020). Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen: All models including AMG specials, 1979 to 2006. Essential Buyer’s Guide series. Dorchester, Dorset, UK: Veloce Publishing. ISBN 9781787115149.
- Hack, Joachim (2019). Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse: seit 40 Jahren nicht zu stoppen [Mercedes-Benz G-Class: unstoppable for 40 years] (in German) (1. Auflage ed.). Stuttgart. ISBN 9783613041721.
- Kittler, Eberhard (2005). Deutsche Autos [German Cars] (in German). Vol. Offroader und SUV — seit [since] 1945. Stuttgart: Motorbuch Verlag. ISBN 361302490X.
- Long, Brian (2016). Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen: 1979 to 2015. Mercedes-Benz series. Dorchester, Dorset, UK: Veloce Publishing. ISBN 9781845847777.
- Sand, Jörg (2011). Das Neue Große Mercedes G-Klasse-Buch [The New Big Mercedes G Class Book] (in German) (updated and revised ed.). Königswinter, Germany: Heel Verlag. ISBN 9783868524710.
- ————— (2015). Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse: Baureihe W 460 / W461; alle Modelle von 1979 bis 2000 [Mercedes-Benz G-Class: W 460 / W461 series; all models from 1979 to 2000]. Praxisratgeber Klassikerkauf series (in German). Königswinter, Germany: Heel Verlag. ISBN 9783958430259.
- ————— (2022). The Mercedes-Benz G-Class: The Complete History of an Off-Road Classic. Atglen, PA, USA: Schiffer Publishing. ISBN 9780764362637.
- Seper, Hans (2009). 100 Jahre Steyr 1864–1964 [100 Years of Steyr 1864–1964] (in German) (3rd (facsimile) ed.). Gnas, Austria: Weishaupt Verlag. ISBN 9783705902909.
- Sippel, Kai (2007). Das G-Modell als Einsatzfahrzeug. Mercedes-Benz/Puch – Geländewagen im Behördendienst [The G Model as Emergency Vehicle: Mercedes-Benz/Puch Geländewagen in Public Service] (in German). Kai Sippel. ISBN 9783000218422.
- Skarics, Rudolf (editor-in-chief) (1999). 100 Years of Steyr-Daimler-Puch Graz 1899–1999. Graz, Austria: Steyr-Daimler-Puch. ISBN 3950110712.
- Stroh, Gari M. (2008). Overland: A Mercedes-Benz Journey Through the Americas. West Palm Beach, FL, USA: StarGroup International. ISBN 9781884886911.
- Storz, Alexander Franc (2013). Mercedes G-Modell – seit 1979. Schrader-Typen-Chronik series (in German) (revised ed.). Stuttgart: Motorbuch Verlag. ISBN 9783613035829.
- Taylor, James (1994). Mercedes-Benz since 1945: A Collector’s Guide. Vol. 4: The 1980s. Croydon, UK: Motor Racing Publications. pp. 89–96. ISBN 0947981772.
Workshop manuals[edit]
- Russek, Peter (2006). Mercedes-Benz G-Models / Puch G / 240 GD, 300 GD, 230 G, 230 GE, 280 GE, 250 GD. Pocket Mechanic Vehicle Manual. Caversham, Reading, Berkshire, UK: Peter Russek Publications. ISBN 1898780773.
- Sand, Jörg (2008). Das Mercedes-Benz G-Klasse Schrauberhandbuch: reparieren und optimieren leicht gemacht [The Mercedes-Benz G Class Gearheads’ Handbook: repairing and optimizing made easy] (in German). Königswinter, Germany: Heel. ISBN 9783898807180.
- Mercedes-Benz G / Puch G / 240 GD, 300 GD bis 1989; 300 GD ab 1990; 230 G, 230 GE bis 1984; 230 GE ab 1985; 280 GE, 250 GD ab 1988. Reparaturanleitung, Band 1201. (in German) (3rd ed.). Zug, Switzerland: Verlag Bucheli. 2011. ISBN 9783716819203.
- Mercedes-Benz Technical Companion. Cambridge, MA, USA: Bentley Publishers. 1998. ISBN 9780837610337.
External links[edit]
- Official website
Press kit:
- The new generation Mercedes-Benz G-Class: Forever young
- Mercedes-Benz G 63 AMG 6×6: Taking the desert by storm
В России G-Class знают в основном как любимый транспорт бандитов и вообще всех, чья жизнь определенно удалась – шикарный, быстрый, брутальный и неприлично дорогой. Кое-кто вспомнит о старых утилитарных версиях «Гелика» для немецкой армии. На самом деле воплощений у этого коробчатого автомобиля за без малого 40 лет на конвейере намного больше. И появлением своим в Европе он обязан не чему иному, как исламской революции в Иране.
Иранский проект
История создания машины, в общем-то, вполне обычна для сурового внедорожника – авто понадобилось военным. Но в отличие от прижимистых европейских военных, иранский шах Мохаммед Реза Пехлеви пожелал для своей армии машину в должной степени уникальную и к тому же особо надежную. Это позволило запустить в серию проект, который компании Mercedes и Puch – поставщика разнообразной полноприводной техники, готовили с 1972 года для конкурса на армейский внедорожник ФРГ.
Конкурс этот партнеры с треском проиграли – его выиграл Фольксваген с моделью Iltis. Будущий Гелендваген не прошел в первую очередь потому, что был дороже и к тому же еще не производился серийно. Но потенциал конструкции оказался достаточно высоким, да и машина была разработана универсальной – она подходила не только военным заказчикам, но и гражданским.
Mercedes-Benz 280 GE LWB (W460) ‘1979–90
У творца будущего «Гелика» есть вполне конкретное имя. И как ни странно, оно роднит Gelandewagen и Татру. Ведь создал машину Эрих Ледвинка, сын Ганса Ледвинки, который стал автором многочисленных чешских машин. Он тоже был специалистом по автомобилям повышенной проходимости. Кстати, хребтовые рамы и качающиеся полуоси на современных армейских внедорожниках марки «Tatra» – это его наследие, как и двигатели воздушного охлаждения.
Его сын продолжил традиции: конструкторский коллектив под руководством Эриха к 70-м годам был автором почти десятка полноприводных шасси, и именно ему поручили создать машину для этого ответственного проекта. К счастью, от хребтовой рамы Ледвинка он отказался, хотя она была частью фирменного стиля конструирования Puch на тот момент. В остальном машина была умеренно-передовой. Передние дисковые тормоза, подвеска пружинная, без рессор, блокировки переднего и заднего дифференциала и вариант с полностью закрытым кузовом отличали машину от большинства армейских внедорожников того времени.
Как бы то ни было, в результате целевого финансирования и планов на покупку 20 тысяч этих машин армией Ирана к 1978 году производство было запущено, для чего построили новый завод в австрийском Граце. Но тут случилась Исламская революция, и опальный шах бежал в Каир. Пришедшие на его смену фундаменталисты ни о каком Гелендвагене знать не хотели. Проект подвис в воздухе, потому что в армии Бундесвера его тоже не ждали.
Первой армией, закупившей внедорожник, оказалась аргентинская, затем норвежская. И лишь потом на машину обратили внимание пограничники ФРГ и полицейские службы. Следом подтянулись и многочисленные гражданские службы, и частные покупатели. Лишь спустя годы армия ФРГ сменила гнев на милость, и со временем этот внедорожник под многими марками стал непременным атрибутом почти всех европейских военных.
Доисторический «Гелик»
Первый кузов носил имя W460 и, собственно, с него началась история непрерывного апгрейда на протяжении 35 лет. Для начала покупателям предложили пять вариантов кузовов: короткобазный кабриолет, длиннобазные трех- и пятидверки, а также фургон. Военные заказчики могли выбрать еще длиннобазные открытые версии для особых нужд.
Двигателей предлагалось всего четыре: два бензиновых и два дизельных. Карбюраторный мотор на 230G мощностью 90 л. с. и 150-сильный мотор с впрыском на 280G серии М 110 дополняли дизели серии OM 616 мощностью 72 л. с. на 240GD и OM 603 на более мощном 300 GD о 88 лошадях. Да, как видите, изначально Гелендваген имел довольно скромную энерговооруженность. Зато для любого кузова можно было заказать кондиционер, ведь машину готовили для жарких стран.
Усовершенствования начались сразу после начала выпуска. Оказалось, что покупателей интересуют в первую очередь мощные моторы и длиннобазные закрытые кузова, что стало сюрпризом. С появлением коробки-«автомата» оказалось, что это вполне востребованная опция для внедорожника такого класса. Итог гонки за мощность и комфорт вы можете видеть сейчас. А тогда у машины было не так уж много конкурентов – разве что Range Rover.
К 1982 году автомобиль получил лебедку, АКПП и новый мотор с впрыском серии М 102 для модели 230GE. А к 1983 году стандартной коробкой для бензинового Гелендвагена стал именно «автомат», «механика» же перешла в разряд опций. В 1987 году появился новый дизель для модели 250GD, мощностью 84 л. с.
Общее число изменений техники исчислялось десятками – только топливный бак модифицировали два раза, причем предлагалась версия со стандартным и увеличенным объемом. Менялась и внешность, и интерьер, машина успела пережить три фейслифтинга и пару обновлений салона. Именно тогда появились характерные расширители арок для более широкой резины, и предназначались они для машин с широкими «песчаными» покрышками.
Ранний «Гелик»
История машины, которую большая часть из читателей знают как «Гелик», началась в 1989 году с появлением кузова W463. Внешность машины изменилась не очень значительно, но внутри она действительно преобразилась.
Mercedes-Benz 500 GE (W463) ‘1993
На этот раз машиной занималось конструкторское бюро самого Мерседеса, и авто в этом кузове были предназначены только для гражданского рынка. Для военных оставили кузов 460, а с 1991 года еще более упрощенную версию W461. И ничто не мешало создавать все более дорогие и шикарные версии гражданской модели. Отдельно отмечу, что никакой унификации между сериями больше не было, различались даже сами кузова и рамы. Военный и «мирный» – это два разных Гелендвагена.
Mercedes-Benz 290 (W461) 1992–97
Изначально W463 предлагалась тоже с четырьмя моторами. На 230GE и 300GE уже стоял новый агрегат серии М103. Дизельные версии 250 GD и 300GD также получили новое «сердце» серии OM603. С 1991 года появился и более мощный турбодизель на модели 350GD, а более слабые дизели на W463 больше не предлагались.
В 1993 году Mercedes провел переименование моделей, теперь Гелендваген назывался G-класс и относился к легковым машинам. Наименование моделей выглядело примерно так: G350TD, где первая буква обозначала принадлежность к классу, а далее шел моторный индекс. Тогда же появился первый G500 c мотором V8 серии М 117, на тот момент уже несколько устаревшим 16-клапанником (по два на цилиндр), но вполне подходящим для внедорожника. Мощность нового мотора составила 241 л. с., что являлось своеобразным рекордом в этом классе машин.
В 1994 году на G320 появился первый многоклапанный мотор с легковых машин серии М 104. В 1996 году на автомобиле впервые применили электронно-управляемую пятиступенчатую АКПП серии 722.6. – первой модификацией с такой коробкой стал как раз G350TD, но вскоре ее получили и все остальные версии. Что же до бензиновых двигателей, то М104 довольно скоро заменили на самые современные моторы М 112 для модели G320 к 1997 году.
Под капотом Mercedes-Benz G 36 AMG (W463) ‘1994–97
Промежуточный «Гелик»
В 1997 году произошло еще одно знаменательное событие, выпустили второй по счету G500, на этот раз с мотором М 113, как на новейшем на тот момент W220, мощностью уже 296 л. с. Максимальная скорость «кирпича» перевалила за 200 км/ч, что можно считать своеобразной победой грубой мощи над разумом. Ускорились работы по модернизации салона, и к 2000 году машина получила, наконец, обновленный салон в «легковом» стиле, с системой Comand. А подушки безопасности, дисковые вентилируемые тормоза спереди, центральный замок и прочее уже были в базовой комплектации.
В том же 2000-м появилась и новая топовая дизельная версия G400 мощностью 250 л. с. Как я уже писал в обзорах, крайне неудачная из-за проблем с топливной аппаратурой. Гонка мощностей продолжилась и на бензиновых версиях. На этот раз G55 AMG имел мощность уже 354 л. с.
Под капотом Mercedes-Benz S 320 CDI (W220) ‘1998–2002
На 2001 год приходится очередное обновление салона. На этот раз его перетрясли очень основательно. Появились многофункциональный руль, климат-контроль, система Comand 2.0. Линейку дизельных моторов дополнили турбодизелем 2.7 на модели G270 CDI – с электронным впрыском.
2002 год отметился заменой системы тормозов. Новый блок АБС включал в себя систему ESP уже для базовой комплектации, систему 4-ETS, которая позволяла обходиться без включения блокировок на легком бездорожье, и конечно же, модным Brake Assist, на случай, если вы боитесь нажимать как следует на педаль тормоза.
Поздний «Гелик»
«Ползущий апгрейд» немного приостановился в связи с выходом на рынки США, но продолжилась «гонка вооружений». В 2002 вышла G 63 AMG с V12 мотором серии М 137 мощностью 444 л. с. Но уже в 2004 году новая версия G55 AMG получила уже компрессорный мотор мощностью 476 л. с., более дешевой серии М 113, который последовательно форсировали до мощности сначала в 500 л. с. в 2006 году, а затем и до 507 л. с. в 2008-м. Снова моторы V12 появились на Гелендвагене в 2012 году с выходом серии G65 AMG с мотором М 275 мощностью 612 л. с., а вместо G55 выпустили G63, с двигателем серии М 157 мощностью 544 л. с.
Mercedes-Benz M275 и Mercedes-Benz M137
Мощнее пока ничего не придумали, хотя тюнинговые версии бывают заметно мощнее. Но очевидно, что покупателям не очень нужны серийные тысячесильные внедорожники с динамикой спорткара. Это чисто имиджевая модель, которая пользуется заслуженной популярностью, но основной спрос приходится на дизельные модификации средней мощности.
Следующий серьезный рестайлинг модели произошел в 2012 году: серьезно обновились почти все системы, и в очередной раз заменили салон. Опознать его можно по «айпадику» на самом видном месте и уменьшевшейся брутальности. Внутри изменения кузова не столь заметны, но машину «вписали» в новые нормы безопасности по фронтальному и боковому ударам. А заодно – полностью заменили электрику. На данный момент это последнее серьезное обновление. Если, конечно не считать выпуск монстров AMG 6×6 и 4×4.
На фоне этого великолепия с серией W463 тихие изменения «служебной» W461 «потерялись». Она давно не числится в каталогах компании, ее предлагают только на заказ – как в армию, так и в «гражданские» компании, которым нужен неприхотливый внедорожник. Там тоже обновились основные агрегаты – самая популярная версия получила современный дизель OM642 на 183 л. с. При этом салон, кузов и электрика пока остаются такими же, как примерно пятнадцать лет назад.
Немного о том, что это за машина
Не стоит воспринимать Гелендваген как шикарный и супер комфортный автомобиль. Престиж и комфорт вообще не всегда идут рука об руку, и наш сегодняшний герой как нельзя лучше иллюстрирует этот принцип. В основе этой машины старый военный «грузовик», и за все годы избавиться от этого наследия не удалось.
Более того, M-класс появился именно потому, что что-то сделать с классической конструкцией G-класса попросту нереально. Ход у машин жесткий, и чем мощнее моторы, тем жестче машина на ходу. Кажется даже, что на низкопрофильной резине обычный «Гелик» пожестче иных седанов от AMG – душу может вытрясти легко и непринужденно.
Правда, при этом вы будете улыбаться, поскольку ощущение энергоемкости и прочности сочетается с довольно интересной управляемостью. Пока подвески машины исправны, она умудряется неплохо ехать по асфальту. Правда, только по ровному и не выше 130-140 км/ч, но все же и это достижение. Да и в поворотах он способен удивить – здоровенная и высокая машина аккуратно прописывает кривую без запредельных кренов, а руль наливается приятной тяжестью. Но оговорка насчет исправности подвесок тут неспроста: небольшой износ, не та резина и… от благородства манер остается немного.
С комфортом подвесок разобрались. С салоном ситуация та же. Если внимательно присмотреться, то даже в последних версиях за всей роскошью можно рассмотреть типичный «военный уазик». Тонкие рамки дверей с вечными сквозняками, табуретки вместо кресел, мелкие и не очень огрехи сборки. Почему так?
Потому что доля ручного труда тут больше, чем у современных машин, да и многие нюансы конструкции нельзя замазать даже самыми толстыми слоями кожи. Что же касается исполнения салона на машинах до 2000 года или даже до 2008-2012-го, то счесть это салоном шикарной легковушки не сможет даже человек, который прилетел в наш бренный мир на машине времени из семидесятых. Салоны совсем старых авто вообще скроены крайне строго и лишь слегка облагорожены деревянными вставками и кожей.
Mercedes-Benz (W463) ‘2008–12
В начале века что-то поменялось, и дизайнеры отказались от старых линий, сделав что-то странное, но с явным намеком на то, что машина-то легковая. Убрали старомодные рычажки климатики, предложив модный автоматический климат-контроль, поставили нормальную мультимедийную систему, да и дверные обивки стали меньше походить на жестяную болванку, которую обтянули кожей. Причем явно только для того, чтобы водитель не обжег руку о раскаленную солнцем дверь. Но все равно салон мрачноват и выделяется грубостью форм. Если вы хотите благородства линий, то поищите себе лучше старый добрый W126, он поражает воображение и сейчас.
Mercedes-Benz S-Klasse (W126)
А если вы искали удобный «всепролазный» Мерседес, то это к GL-классу. Более комфортный автомобиль найти на вторичном (да и на первичном тоже) рынке весьма затруднительно. А Гелендваген – это про харизму. Чего-чего, а харизмы ему не занимать, даже в 37-летнем возрасте.
Читайте также:
История
Появлением в своем модельном ряду внедорожного кубика G-Class Mercedes-Benz обязан сотрудничеству с австрийской компанией Steyr-Daimler-Puch. Именно специалисты этой компании еще в 1972 году начали разработку автомобиля, который бы сочетал в себе такие качества как высокая проходимость, так комфорт и максимальная безопасность. Первая, выполненная из дерева копия будущей модели была произведена в Граце (Австрия) в 1973 году. Одобрив дизайн новинки, инженеры обеих компаний приступили к разработке технических компонентов автомобиля. В 1974 году была произведена первая экспериментальная партия среднеразмерных внедорожников, испытывали которую не только на немецкой земле, но и в Сахаре и за Полярным кругом.
Серийное производство модели, которой дали название Gel?ndewagen или G-Wagen, что в переводе с немецкого означает «внедорожник» стартовало в 1979 году.
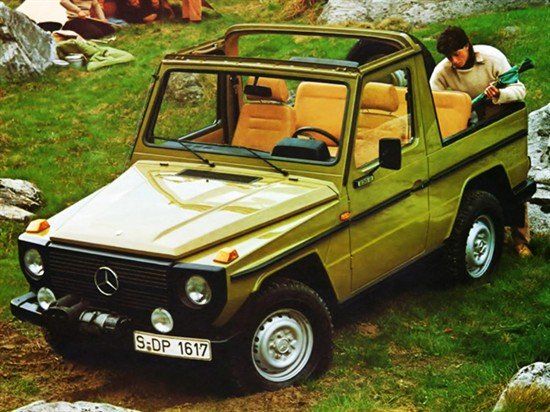

Модель сразу же обрела широкую популярность среди любителей внедорожных приключений и соревнований. Слава о G-Wagen достигла и Ватикана, и в 1980 году компания получила заказ на изготовление специального автомобиля на основе этого внедорожника для Папы Римского.
Первое поколение G-Wagen (W460) имело две версии – со стандартной (2400 мм) и удлиненной (2850 мм) колесной базой. Производился внедорожник в трех кузовных модификациях – кабриолет, двух- и четырехдверный универсал.
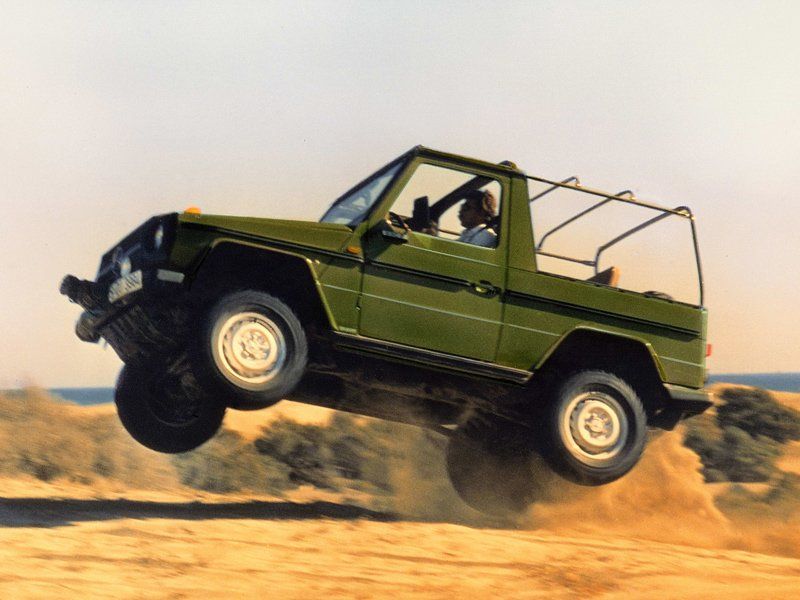

Оснащался автомобиль тремя бензиновыми (объемом 2.0, 2.3 и 2.8 литра) и тремя дизельными (объемом 2.4, 2.5 и 3.0 литра) моторами, которые агрегатировались с 4-х или 5-ступенчатой механической, а также 4-ступенчатой автоматической трансмиссиями.
Автомобиль часто использовали для своих нужд вооруженные силы разных стран, он также служил в качестве спецтехники.
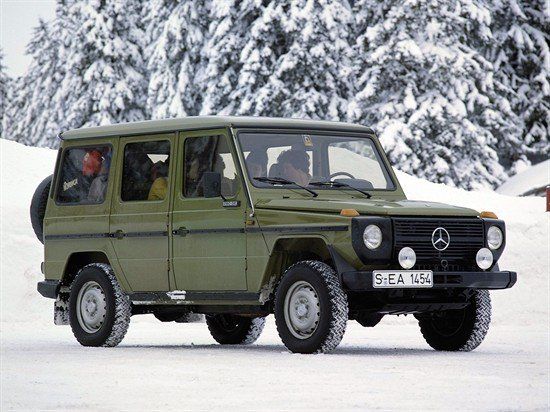

Первое время автомобиль продавался только на европейском рынке, причем приоритетными странами для сбыта был государства Восточной Европы, Австрия и Швейцария. В США эта модель завозилась в качестве «серого» импорта.
Второе поколение (W463) этого внедорожника появилось в продаже в 1990-м году и с тех пор пережило целый ряд модернизаций и рестайлингов.
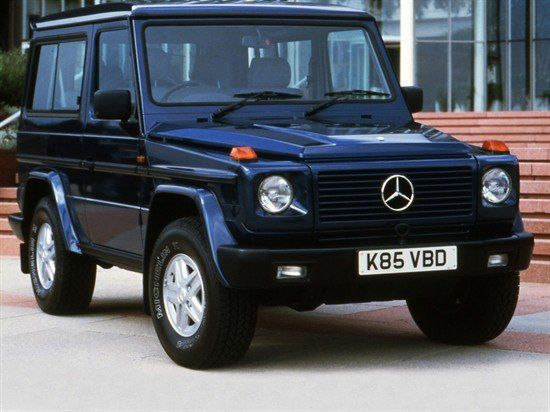

Начиная с 1994 года, автомобиль продавался под привычным названием Mercedes-Benz G-Class. Наряду с гражданскими версиями, началось производство специальных модификаций «кубика» от AMG — G55 AMG.
Первый рестайлинг имел место в 1997 году, когда помимо обновления экстерьера и интерьера машина получила новые двигатели. В этом же году компания возродила производство G-Class в кузове кабриолет.
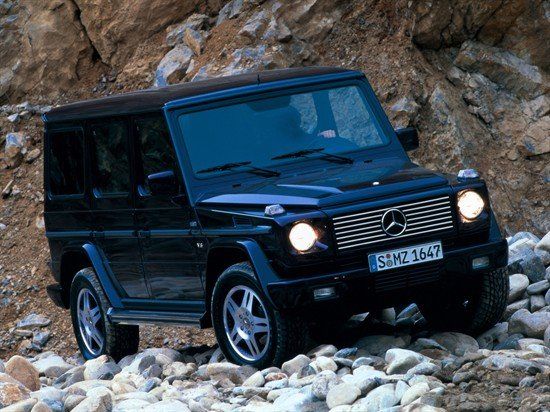

Дважды, в 2005 и 2006 годах, чтобы подогреть интерес к своему внедорожному детищу, компания распространяла информацию о возможном прекращении производства «кубика», выпуская вслед за этим лимитированные «финальные» серии. А в 2007 году на Парижском автосалоне Mercedes-Benz представил обновленный G-Class.
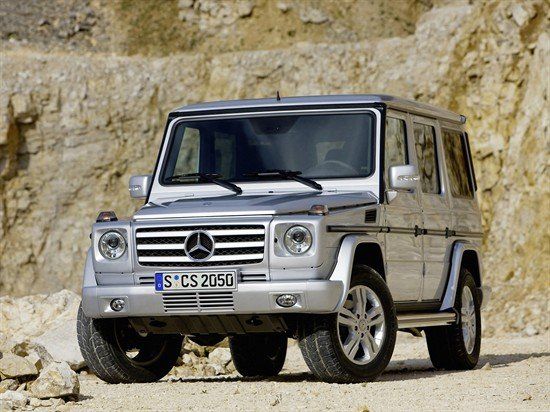

И даже после этого в компании не раз поговаривали о прекращении производства этой модели, анонсируя, что на смену «кубику» придет более прогрессивная в технологическом плане модель GL-Class. Однако этого не случилось, и G-Class, последнее обновление внешности которого состоялось летом 2012 года, до сих пор продается на мировых рынках.
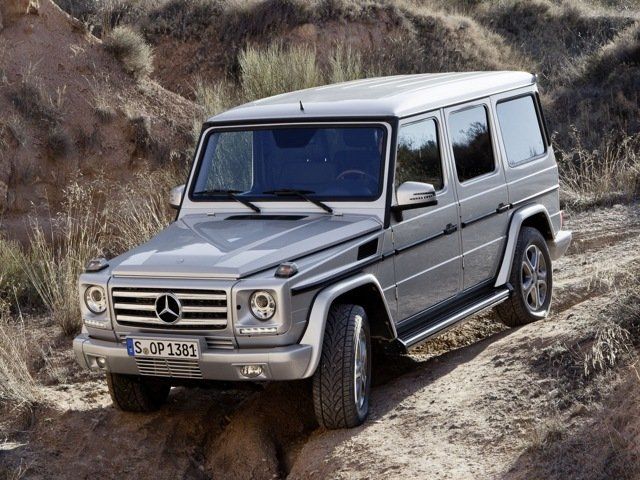

Экстерьер
Сохранив «кубический» дизайн кузова автомобиля, после планового фейслифта 2012 года модель в стандартной версии обзавелась только светодиодными дневными ходовыми огнями, расположенными под квадратными корпусами фар головного света, такими же повторителями указателей поворота, вмонтированными в корпуса боковых зеркал.
В специальной версии G 63 AMG изменения «внешности» более ощутимые: помимо перечисленных выше новинок, модель получила новую решетку радиатора с двойным «лезвием», делящим ее пополам по горизонтали и новый бампер с прямоугольной секцией центрального воздухозаборника и большими квадратными боковыми нишами. В остальном экстерьер модели остался неизменным.
Так, на передней части выделяются крупные круглые фары головного света, заключенные в квадратные корпуса, прямоугольный капот с возвышением в центральной части.
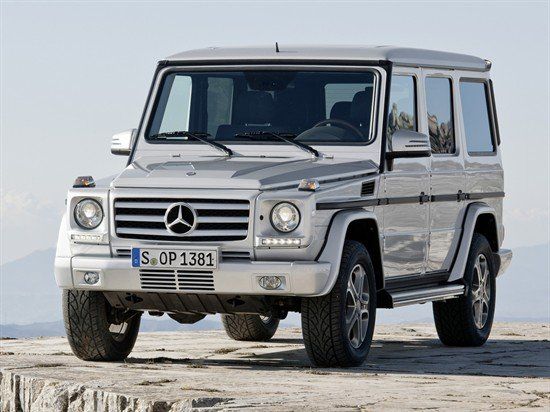

Квадратные указатели поворота установлены сверху на передних крыльях. Передние стойки модели установлены практически вертикально, а крыша, боковые и задняя багажная дверь выполнены без единой плавной линии. Передние и задние колесные арки также квадратной формы с небольшим вылетом. По бокам кузова проходит жесткий пластиковый молдинг. Единственные не имеющие острых углов детали кормы G-Class – это крепящийся к задней двери круглый бокс для запасного колеса и задние фонари овальной формы.
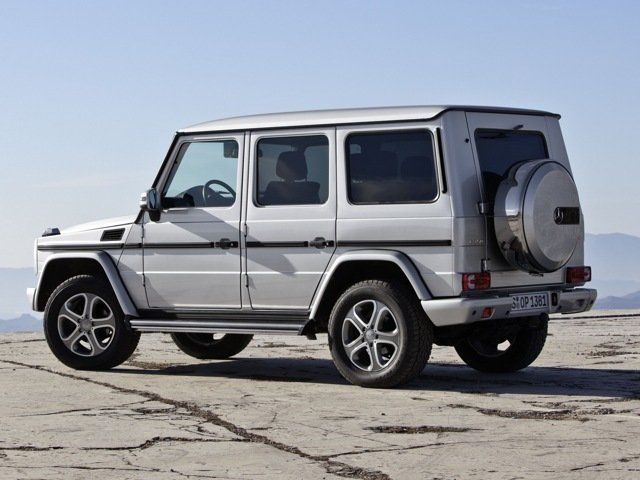

Модель по-прежнему выпускается в двух кузовных модификациях – универсал и кабриолет. Колесная база составляет 2850 мм. Длина кузова – 4662 мм, ширина – 1760 мм, высота – 1951 мм.
Интерьер
А вот в салоне обновленной модели округлостей гораздо больше. Это и новый четырехспицевый руль с шестиугольной ступицей, и крупные колодцы приборов на пережившей редизайн панели, и такие же по форме органы управления климатической системой. Преобразилась U-образная центральная консоль, над которой располагается монитор мультимедийной системы COMAND APS, и расположенный под ним блок клавиш, которыми эта система управляется.
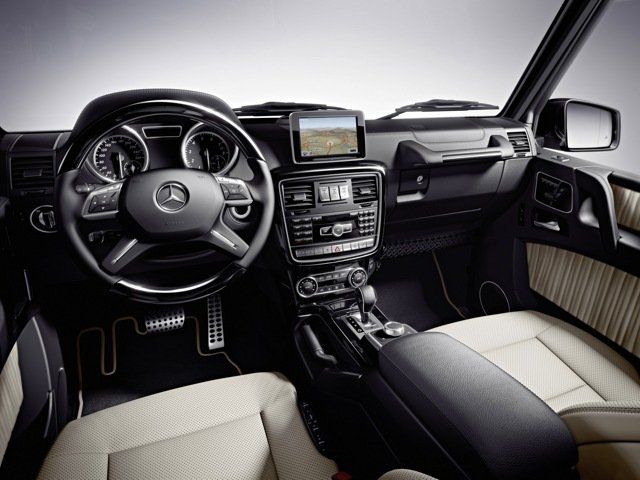

Особое место, между центральными воздуховодами, занимают клавиши переключения трех блокирующихся дифференциалов. В центральный туннель со стороны водителя интегрирован рычаг стояночного тормоза, а на самом туннеле расположен укороченный селектор КПП и джойстик, при помощи которого можно выбирать режимы КПП. Позади него находится массивный подлокотник, под которым – контейнер для мелочевки. Над крышкой перчаточного ящика привычно располагается рукоять, за которую удобно держаться при посадке в автомобиль.
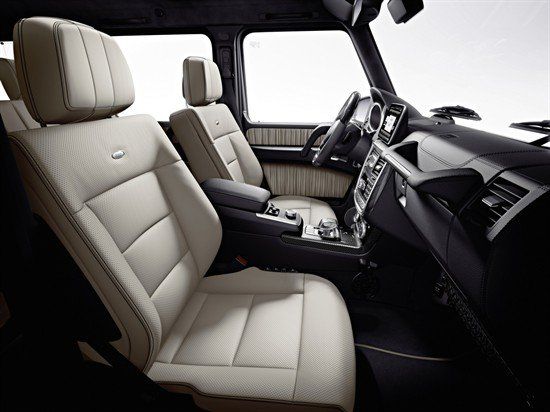

Передние и задние кресла модели обладают широким рифлеными сиденьями и спинками (у передних есть небольшая боковая поддержка). В передних подголовниках размещаются дополнительные экраны мультимедийной системы.
Технические характеристики
В стандартной версии G-Class оснащается одним бензиновым (объем 5.5 литра, мощность 388 л.с.) и дизельным (объем 3.0, мощность 210 л.с.) двигателями. Версии AMG, G 63 AMG и G 65 AMG оборудуются бензиновыми моторами объемом 5.5 (мощность 544 л.с.) и 6.0 (мощность 612 л.с.) литра. В паре с двигателями, устанавливаемыми на стандартные версии внедорожника, работает 7-ступенчатая автоматическая трансмиссия G-TRONIC PLUS, а моторы серии AMG агрегатируются с 7-скоростной АКПП AMG SPEEDSHIFT PLUS 7G-TRONIC. Привод автомобиля – полный.
В России новый Мерседес Гелендваген предлагается только с бензиновым 388-сильным мотором объемом 5,5 литра, который комплектуются исключительно 7-ступенчатой автоматической коробкой передач 7G-Tronic. Стоимость автомобиля составляет 5 150 000 рублей.
Максимальная скорость Mercedes-Benz G500 составляет 210 км/ч, а разгон с 0 до 100 км/ч занимает 6,1 секунды. Средний расход топлива — 16 литров на 100 км пути.
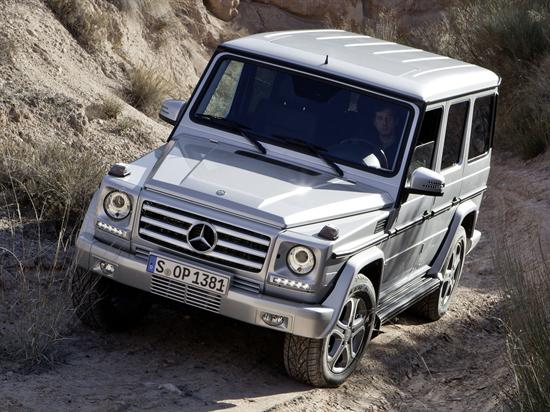
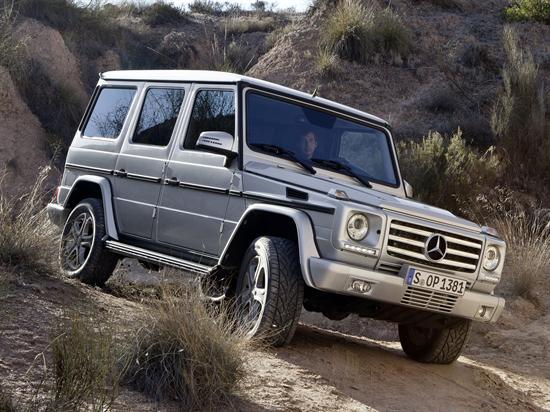
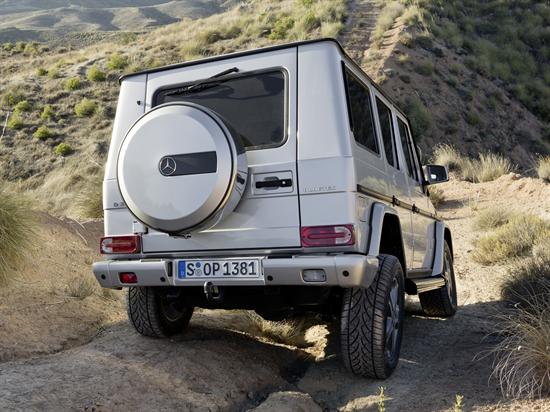



Подробнее
Gelandewagen (Гелендваген) – что это за автомобиль?
Очень часто по телевидению или радио можно услышать слово «Гелик». Вспомните хотя бы известный сериал «Физрук», где герой Дмитрия Нагиева ездит на Гелике. Ну, а на Yotube можно найти популярный клип «Гелик Вани».
Гелик — это сокращенное название Гелендвагена, то есть модели Mercedes-Benz G-класса. Гелендваген дословно с немецкого переводится, как «внедорожник». Также эту модель часто называют просто «Кубик» из-за ее характерной формы кузова.
Есть даже определенное сходство между российскими УАЗ-451 или более продвинутым УАЗ-Хантер, о котором мы ранее рассказывали на Vodi.su, и Мерседес-Бенц G-класса. Правда, это сходство только внешнее, так как Гелик значительно превосходит УАЗ по всем характеристикам:
- уровень комфорта;
- технические характеристики;
- ну и, конечно же, цена.
Хотя обе машины разрабатывались вначале для нужд армии, и лишь потом стали доступны более широкому кругу автолюбителей.
История создания
Прежде всего нужно сказать, что Гелендваген лишь продается под торговой маркой Мерседес-Бенц. На самом же деле его производят в Австрии на заводах компании Magna Steyr. Данная компания, в свою очередь, принадлежит канадской корпорации Magna International — одному из ведущих мировых производителей запчастей практически для всех марок авто.
Magna Steyr — это крупнейший в мире производитель автомобилей, который не имеет собственного бренда.
Помимо Гелендвагенов здесь выпускают:
- Mercedes-Benz E-класса;
- BMW X3;
- Saab 9-3 Convertible;
- Jeep Grand Cherokee;
- некоторые из моделей Крайслер, например Chrysler Voyager.
В год компания производит примерно 200-250 тысяч автомобилей.
Гелендваген в гражданской версии впервые сошел с конвейера в 1979 году, и с тех пор его характерная форма кузова абсолютно не претерпела изменений, что нельзя сказать об экстерьере и технических характеристиках.
Самый первый Гелик — это Mercedes-Benz W460. Его взяли на вооружение различные силовые структуры и армия. Он выпускался в двух модификациях: на 3 или 5 дверей. Рассчитан на 4-5 человек. Бронированная версия поставлялась специально в норвежские вооруженные силы.
Технические характеристики:
- полный привод;
- длина колесной базы варьировалась в пределах 2400-2850 миллиметров;
- широкий выбор различных версий силового агрегата — бензин, дизель, турбодизель объемом от двух до трех литров.
Самый мощный двигатель — 280 GE M110, имел объем 2,8 литра, развивал мощность в 156 л.с., работал на бензине. Позже появилась модификация Mercedes-Benz W461 с трехлитровым турбодизелем мощностью 184 л.с. Эта модель (G 280/300 CDI Professional) выпускалась вплоть до 2013 года, правда, в лимитированной серии.
Geländewagen в автосалонах России
Если у вас появится желание гордо именовать себя «владельцем Гелика», чтобы все оборачивались, когда вы едете, то одного хотения, к сожалению, мало. Нужно иметь еще как минимум 6 700 000 рублей. Именно столько стоит самый дешевый новый Geländewagen G-350 d.
Цены на представленные в автомобильных салонах внедорожники Мерседес G-класса на начало 2017 года следующие:
- G 350 d — 6,7 миллиона рублей;
- G 500 — 8 380 000 рублей;
- G 500 4×4 — 19 миллионов 240 тысяч;
- Mercedes-AMG G 63 — 11,6 млн. рублей.
Ну, а за самый дорогой экземпляр спецсерии AMG — Mercedes-AMG G 65 — придется выложить целых 21 миллион 50 тысяч рублей. Действительно, только очень обеспеченные люди могут позволить себе это удовольствие. Правда, читая новости о стритрейсерах на Гелендвагенах, создается впечатление, что в Москве таких обеспеченных людей довольно много.
Все представленные автомобили оснащены полным приводом 4Matic. На них устанавливают исключительно автоматические коробки передач:
- АКП 7G-TRONIC PLUS — с ее помощью водитель может легко переключаться, например, с седьмой передачи на пятую;
- АКП AMG SPEEDSHIFT PLUS 7G-TRONIC — для комфортного управления здесь установлено три режима переключения передач: Контролируемая эффективность, Спорт, Ручной режим.
Можно выбирать как бензиновые, так и дизельные двигатели. На G 500 и AMG G 63 устанавливают 8-клапанный бензиновый двигатель объемом 4 литра (421 л.с.) и 5,5 л. (571 л.с.). Для модели AMG G 65 разработан супермощный 12-клапанный агрегат на 6 литров, который развивает мощность в 630 л.с. при 4300-5600 об/мин. А скорость ограничена на показателе 230 км/час.
Дизельный движок для самого дешевого Гелендвагена G 350 d имеет объем 3 литра, при этом его мощность равняется 180 кВт при 3600 об/мин, то есть примерно 244 л.с. (как перевести Киловатты в л.с. мы уже рассказывали на Vodi.su). Как видим, даже самая доступная модель отличается прекрасными характеристиками.
Загрузка…
Mercedes Gelandewagen, задуманный как утилитарный внедорожник, перевозчик солдат, за 36 лет своей славной истории превратился в настоящий Rolls-Royce среди вездеходов. А его простой функциональный дизайн, который когда-то обвиняли в некой рабоче-крестьянской примитивности, теперь называют не иначе как классическим.
Датой рождения автомобиля официально провозглашено 10 февраля 1979 года. В этот день впервые был представлен публике новый автомобиль и запущен конвейер производства. Но 1979 год — это лишь условная дата, символ. История Mercedes-Benz G-class началась значительно раньше…
«Гелендваген» — живая легенда мира внедорожников. Этот автомобиль есть и в гараже Папы римского и в автопарке президента России. Но, мало кто знает, что история Gelandewagen (в переводе с немецкого «автомобиль для бездорожья»), началась еще в 1926 году, когда был создан экспериментальный Mercedes-Benz G1, оснащенный вторым задним мостом, призванным улучшить проходимость автомобиля.
Прототип G1 и последующие за ним модификации G2 и G3 в серию не пошли: производство внедорожников Mercedes-Benz началось лишь в 1934 году, когда была организована мелкосерийная сборка модели G4. Этот шестиметровый трехосный автомобиль, оснащавшийся двигателями от спортивных моделей Mercedes-Benz 500К и 540К (но без компрессора), использовался верхушкой Третьего рейха.
За три года было собрано всего 57 экземпляров Mercedes-Benz G4, после чего компания запустила в серию новый вариант внедорожника — армейскую модель G5.
Этот внешне непримечательный автомобиль с малогабаритным кузовом и слабеньким мотором имел одну уникальную особенность: систему поворота колес задней оси. То есть G5 был не только полноприводным, но и полноуправляемым, что обеспечивало ему фантастическую маневренность.
Последняя модель выпускалась с 1937 по 1941 год и разошлась в количестве 378 экземпляров, однако в известности она значительно уступала гиганту Mercedes-Benz G4.
Новейшая история Gelandewagen берет начало в 1972 году, когда австрийская компания Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG в рамках совместного проекта с Mercedes-Benz, приступила к работе над внедорожником под кодовым названием Н2. Согласно техзаданию, спущенному отделом маркетинга Mercedes-Benz в конструкторское бюро Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG, это должен был быть универсальный автомобиль, одинаково пригодный как для военных нужд, так и для использования частными владельцами.
Австрийцы сработали оперативно: полноразмерный макет внедорожника, изготовленный по старинке из дерева, был готов к весне 1973 года, а через год уже начались ходовые испытания прототипа будущего Gelandewagen.
Впрочем, неизвестно, как сложилась бы дальнейшая судьба этой модели, если бы ровно 40 лет тому назад, в 1975 году, не произошло знаковое событие, придавшее новый толчок работе над проектом.
Именно тогда Daimler-Benz договорился со Steyr-Daimler-Puch (Австрия) о совместном производстве внедорожников. Выбор места и партнера был не случаен. Во-первых, изначально планировали выпускать машину сравнительно мелкой серией – около 10 тысяч в год. Загружать производственные площади в Германии ради такого количества не было никакого смысла. Во-вторых, Steyr к тому моменту мог похвастаться большим опытом проектирования и производства полноприводной техники. С его конвейеров уже сходили машины вагонной компоновки – Pinzgauer и Haflinger, созданные коллективом инженеров под руководством Эриха Ледвинки – сына легендарного инженера Ганса Ледвинки, долгое время работавшего на Tatra.
Ничего удивительного, что проектирование будущего совместного внедорожника было поручено именно Ледвинке. Первый прототип H2 (т. е. Haflinger 2) с бензиновым мотором и коробкой передач от легкового Mercedes-Benz был готов в рекордные сроки. Поскольку машину проектировали прежде всего как армейскую, кузов был подчеркнуто упрощенной формы, с плоскими панелями и откидным лобовым стеклом для открытой модели. Отличить опытный H2 от будущего серийного Geländewagen можно было лишь по упрощенной передней части. Знаменитая радиаторная решетка с утопленными круглыми фарами появится только в 1976 году на прототипе Expedition.
Прототип 1975 года.
Сама конструкция H2, особенно если сравнивать с другими творениями Эриха Лендвинки, выглядела весьма консервативно. Обычная лестничная рама, рычажно-пружинная зависимая подвеска всех колес, дисковые тормоза спереди, барабанные сзади. Естественно, с усилителем. При этом будущая звезда офф-роуда могла похвастаться постоянным полным приводом с блокировками центрального и заднего дифференциалов. И никаких хребтовых рам, как на внедорожниках Steyr, управляемых задних колес и полностью независимой подвески, как на довоенном Mercedes-Benz G5.
Уже в 1974 году прототипы принялись наматывать километры по самым суровым местам: на горном полигоне Steyr-Daimler-Puch – трассе Schöckl недалеко от Граца, в угольном карьере, в Скандинавии за Полярным кругом, в песчаных и каменистых пустынях Северной Африки, на Аравийском полуострове, а также на бездорожье Аргентины.
Прототип «Expedition» 1976 года.
Однако с запуском в серию никто не торопился. Серьезным стимулом для проекта стал крупный заказ на 20 тысяч автомобилей для армии Ирана. Уже в феврале 1977 года Daimler-Benz AG совместно со Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG создают совместное предприятие GFG (Geländefahrzeug-Gesellschaft). Производство было решено наладить на заводе в Граце, принадлежащем Steyr-Daimler-Puch.
По условиям договора в ФРГ делали двигатель, трансмиссию, мосты, рулевое управление и крупные детали кузова. За штампованные детали меньшего размера, а также раздаточную коробку отвечали австрийцы. Любопытными были условия раздела рынков сбыта. Большая часть выпущенных вездеходов должна была носить звезду Mercedes-Benz на радиаторной решетке, и лишь 10% от общего выпуска продавалось под маркой Puch. По условиям соглашения их реализация допускалась только в Австрии, Швейцарии, а также в странах Восточной Европы.
О гелендвагене часто говорят, что он был создан по заказу Бундесвера — отсюда его солидность, выносливость и безотказность. Однако правда состояла в том, что рынком сбыта первоначально являлся гражданский сектор, а не военный. В семидесятых годах Бундесвер, правда, планировал закупку новых полноприводных автомобилей, но заключил договорённость с правительствами Франции и Италии, касающуюся общего развития под рабочим названием «Европейский Джип». Согласно спецификациям, транспортное средство должно было быть плавающим, а Geländewagen не оправдывал ожиданий немецких военных. Однако этот проект закрылся в 1976 году и Бундесвер объявил тендер на поставку 8800 единиц вседорожников, упустив требование плавучести. Daimler-Benz выставил на конкурс прототип своего вездехода, но по некоторым обстоятельствам армия выбрала Volkswagen VW 183, более известный как Iltis.
Выбор Бундесвера был обусловлен, в первую очередь, сроками поставки — Volkswagen объявил, что первые автомобили передаст до конца 1978 года, — а также ценой. Daimler-Benz потерпел поражение. В 1976 году Geländewagen был ещё прототипом, в который предстояло внести много поправок и усовершенствований. Кроме того, выбор был обусловлен и политическими мотивами — в предыдущем тендере Бундесвер уже заключил договор о поставке Unimog, и отказ в то время государственному Volkswagen означал бы предоставление полного преимущества Daimler-Benz.
Не подлежит сомнению факт, что заинтересованность автомобилем со стороны армии разбудило амбиции менеджеров Daimler. Анализ гражданского рынка был не слишком оптимистичен и окупаемость продукции мог гарантировать лишь крупный заказ какой-либо страны для своей армии. Когда в 1976 году Geländewagen участвовал в тендере Бундесвера, решение о его будущем было уже решено — аналитики констатировали, что продукция будет рентабельной.
Уже в 1978 году был готов предсерийный образец с мягким быстросъемным верхом, который теперь назывался Geländewagen (т. е. автомобиль для пересеченной местности). Однако новое иранское правительство, пришедшее к власти в 1979 году после знаменитой исламской революции, столь важный заказ аннулировало. Германская армия, на которую партнеры возлагали большие надежды, к новой машине интереса не проявила. К счастью, положение несколько выправилось за счет пограничников ФРГ, а также армий Аргентины и Норвегии.
Что же позволило Geländewagen преодолеть все встретившиеся трудности? В значительной степени можно сказать, что случай.
В семидесятых годах одним из основных заказчиков Daimler была иранская королевская семья. Амбициозный шах Reza Pahlawi хотел сделать из своей страны третью после США и СССР военную державу. Обладая громадными доходами от экспорта нефти, он мог себе это позволить. Одной из идей, сопутствующих осуществлению мечты, была идея покупки 20 000 полноприводных автомобилей для иранской армии. В 1975 году такой заказ получил именно Mercedes.
Это было как ветер в паруса после полного штиля. В феврале 1977 года Daimler-Benz AG совместно со Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG образовали союз с названием GFG (Geländefahrzeug-Gesellschaft), в котором обе фирмы внесли по половине взносов. Новая компания была призвана к разработке, внедрению и дальнейшему улучшению конструкции Geländewagen, а также продвижению продаж модели. Двигатель, коробка передач, мосты должен был производить Daimler, а раздаточную коробку Steyr-Daimler-Puch. Всё остальное могли поставлять другие фирмы. Продукцию планировали производить на предприятии в Граце, принадлежащем на 100% Steyr-Daimler-Puch.
Одним из условий между партнёрами было разделение рынка. На отечественном рынке Steyr в Австрии, Швейцарии, а также странах тогдашнего «восточного блока», в том числе Польше, Geländewagen продавали под маркой PUCH. В остальных странах автомобиль продавали под маркой Mercedes-Benz. Соответственно в первом случае на решётке радиатора красовалась эмблема «PUCH», а на остальных — «Mercedes».
Закладка камней под построение монтажного павильона Geländewagen в Граце.
11 марта 1977 канцлер Австрии Bruno Kreisky лично заложил камни под построение нового павильона предприятий Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG в Graz-Thondorf, площадь которого превышала 40 000 квадратных метров. Союз GFG взял полный контроль над проектом в конце 1978 года — но несколько месяцев спустя шах Reza Pahlawi ввёл военное положение в Иране. В середине января исламская революция вынудила бежать его из страны. Стало ясно, что заказ на 20 000 автомобилей пропал вместе с ним, но маховик производства уже было не остановить.
Монтажная линия Geländewagen в январе 1979 года.
Удачная премьера
Хотя у менеджеров Mercedes-Benz и не было слишком много поводов к радости, премьера Geländewagen увенчалась успехом. Журналисты высказывались о новом автомобиле если не восторженно, то позитивно.
Конвейер Mercedes-Benz G-class заработал в павильоне №12 завода Граца 1 февраля 1979 года, а первые презентации автомобиля с кузовом W460 публике последовали с 5 по 10 февраля 1979 года. Также для прессы близ Марселя в южной части Франции в Le Castellet были продемонстрированы четыре модели в двух вариантах — короткобазном и длиннобазном, а также пять вариантов кузова. Две из них — 230G и 280G были оснащены бензиновыми двигателями, а две других — 240GD и 300GD — дизельными. Все автомобили были оборудованы четырёхступенчатой механической коробкой переключения передач и подключаемым передним приводом. В зависимости от предпочтений, покупатель мог выбрать накрытый брезентом короткобазный кабриолет, либо короткобазную или длиннобазную закрытую версии. Для военных была предоставлена возможность заказа длиннобазной модели как трёхдверного, так и пятидверного вариантов, покрытых брезентом. Палитра цветов была ограничена пятью оттенками: белый кремовый (Crèmeweiß), жёлтая пшеница (Weizengelb), бежевый (Coloradobeige), красный (Karminrot), а также зелёный (Agavengrün).
Но больше всего выделяло Mercedes G-class среди остальных моделей — подключение переднего привода без необходимости остановки. То же самое касалось системы блокировки дифференциалов. На премьере было объявлено, что в ближайшем будущем G-class будет доступен с четырёхступенчатой автоматической коробкой передач. В дальнейшем время покажет, что начало серийного выпуска даст лишь небольшую передышку менеджерам и инженерам, участвующим в проекте «Geländewagen».
В течение непродолжительного времени после дебюта Mercedes G-class рынок выставил автомобилю собственную оценку. А она уже была не так полна энтузиазма, как первые отзывы от приглашённых во Францию журналистов.
Никто не оспаривал уникальных вседорожных свойств Geländewagen, комфортно себя чувствующего как на трассе, так и на пересечённой местности. Рано было оценивать выносливость конструкции, но применяемые решения в виде стальной рамы с закреплённым на ней кузовом, мостов и раздаточной коробки, казалось бы, гарантировали безотказность. Кроме того, конструкторы автомобиля раскрыли, что на протяжении пяти лет прототипы Mercedes G-class подвергались убийственным испытаниям, проходившим на полигоне Steyr-Daimler-Puch, трассе Schöckl недалеко от Граца, в ущелье карьера между Kolonią и Aachen, в Скандинавии за Полярным Кругом, песчаных и каменистых пустынях Северной Африки, на Аравийском полуострове, а также на бездорожье Аргентины.
Тревожные звонки раздавались по поводу качества отдельного оборудования. Руководство проекта было в курсе ряда систематически проявляющихся неполадок, но проблема лежала преимущественно на стороне поставщиков деталей, не способных поставить заказанные части в соответствии со спецификацией качества Mercedes-Benz.
Рынок вывел основные принципы позиционирования Mercedes-Benz G-Class. Geländewagen не должен был быть простым надёжным транспортным средством и удобным полноприводным автомобилем. Задание, которое было поручено конструкторам, было усложнено: необходимо было построить автомобиль с возможностями, не встречавшимися прежде. С одной стороны он должен был характеризоваться безотказностью и выносливостью в разных географических условиях — оправдать ожидания лесных служб, отраслей земледелия, энергетики, военных; с другой — должен быть удобным, хорошо оснащённым и главное — безопасным транспортным средством. Самое интересное в том, что такой автомобиль удалось построить с тем отличием, что удовлетворить сразу две противоположные группы покупателей было сложно.
В 1979 году производственная мощность Граца составляла 10 000 вседорожных автомобилей в год, при этом в первые три года с завода должны были выехать 1 000, 5 500 и 6 000 автомобилей соответственно. Эти цифры оказались заниженными, потому что в первом году была выпущена 2 801 штука, а в последующих соответственно 7 533 и 6 950 штук. Перевыполнение производственных планов обеспечили заказы немецких служб — пограничных войск и местной полиции. Проигранный бундесверовский тендер был вполне компенсирован. Интересной подробностью является то, что несколько проданных в Аргентину экземпляров вернулось в Европу в виде английских трофеев после окончания Фолклендской войны в 1982 году.
Вскоре была обнаружена серьёзная стратегическая ошибка. Вместо короткобазной модели с открытым кузовом, на которую ставило руководство Daimler, наибольшей популярностью пользовался длиннобазный закрытый W460. Чтобы справиться с потоком заказов, потребовалось быстрое изменение приоритетов — корректировка бизнес-планов и заказов запасных частей у поставщиков. Досадными последствиями ошибки стали десятки уже сделанных, но не проданных кабриолетов.
Ошибки планирования, возникшие из-за невыявленных потребностей и ожиданий рынка, касались также внутренностей транспортного средства, дополнительного оборудования, а также двигателя. В последующем станет ясно, что ошибка тянется от специалистов, которым параметры удобств водителя и пассажиров показались более важными, нежели мощность двигателя. Из числа четырёх типов двигателей, представленных на рынок Mercedes-Benz G-class, большим тиражом выпускались слабые девяностосильные безиновые двигатели объёмом 2,3 л., а также дизельные модели объёмом 2,4 л. Покупателиже искали «Мерседесы» с бензиновым двигателем 2,8 л. (150 л.с.), а также трёхлитровые дизельные модели мощностью 88 л.с.
В рекламных буклетах 1979 года в названии модели с двигателем 2,8 л. указывалась буква «E», указывающая на электронный впрыск. Правда, такие до конца 1981 г. почти не поставлялись из-за нехватки запасных частей. Вообще, «Мерседес» в то время страдал от недостатка двигателей M110. Фактически их распространение началось лишь со второй половины 80-х годов, когда модель 280 GE поступила в массовую продажу.
Внесение несущественных изменений во внешний вид и оборудование автомобиля стало регулярной особенностью, которая сопровождает G-class и до наших дней. Если в 1979 году военные сетовали на слишком низкую мощность двигателей, то частные клиенты жаловались на слишком спартанский внутренний вид, нехватку АКПП, кондиционера, а также небольшую гамму расцветок кузова. Именно эти замечания клиентов повлекли, после короткой передышки, возникшей из-за запуска в серию новой продукции, продолжение работы конструкторов. Первые изменения в G-class произошли во второй половине 1981 года. Теперь можно было заказать автомобиль с АКПП, механической лебёдкой, увеличенным на 16 литров топливным баком. В длиннобазной версии предлагались боковые скамьи в багажник. Весной 1982 года Geländewagen получил руль от модели W123, а бензиновые версии G230 и G280 дождались установки электронного впрыска, что повлекло за собой как снятие ограничений на продажи 280 GE, так и начало производства модели 230 GE. Двигатель M102, использовавшийся в моделях E 230 в серии W123 и W124 заменил карбюраторный двигатель M115, устанавливаемый на модели 230 G с 1979 года. Однако производство последнего окончено не было; он был изъят из предложений для Германии, Австрии и Швейцарии, однако для остальных стран поставлялся до середины 1986 года.
В ответ на пожелания потенциальных покупателей в 1983 году были произведены новые улучшения G-класса. Прежде всего, это коснулось расширения гаммы цветов — теперь к выбору предлагалось 4 дополнительных цвета «металлик». Кроме того, механическая КПП перешла в разряд опций. Осенью 1983 года были добавлены новая подсветка переключателей, а клавиши, включающие вентиляторы, заменены поворотной ручкой. Третий фейс-лифтинг произошёл в сентябре 1985 года.
Стандартом стала установка механических блокировок дифференциалов на обе оси и усиленный передний бампер, оборудованный системой для буксировки автомобиля. Внутри появилась новая обивка сидений, заднего дивана, потолка и дверей. По-новому расположились указатели на приборной панели. В качестве опции появился центральный замок, а также резиновые расширители, скрывающие установку при необходимости нестандартных шин.
В сентябре 1987 года модель 240 GD была заменена на 250 GD с механической коробкой передач, а остальные модели были подвергнуты уже четвёртому по счёту фейс-лифтингу. Наиболее существенным изменением стала установка стального бензобака, ёмкость которого была увеличена с 70 до 81,5 литров. Теперь можно было заказать G-class с электрическими стеклоподъёмниками и даже выдвижной антенной.
Изначально бизнес-план проекта «Geländewagen» предполагал, что автомобиль будет производиться в течение 10-ти лет. В июле 1986 года был построен 50-титысячный автомобиль, а в следующем году встал вопрос, что делать дальше. В течение восьми лет, с одной стороны, конструкция автомобиля была доработана, с другой — было очевидно, что необходимы дальнейшие усовершенствования и инвестиции. Если десятью годами ранее идея автомобиля, на равных востребованного военными и семьями с детьми, имела хоть какое-нибудь обоснование, то теперь она казалась напрочь лишённой смысла. Люди, использующие автомобиль ежедневно, нуждались в более комфортных сиденьях, кондиционировании салона, более солидной панели приборов и стереосистеме. Быстро растущий сегмент гражданских покупателей ждал значительных изменений в комфорте, который уже был доступен в других легковых автомобилях.
В этих условиях последовало новое решение о модернизации G-класса, а именно о создании новой модели, ориентированной исключительно на гражданских лиц. Линия с индексом W463 была призвана предложить комфорт наравне с другими легковыми моделями, используя уже готовые решения. Как и в случае с W460, проект W463 был покрыт тайной. На этот раз работы были поручены отделу легковых автомобилей Штутгарта.
Новый G-class был представлен во время выставки IAA во Франкфурте в сентябре 1989 года. Автомобиль произвёл фурор. Снаружи от отличался только некоторыми деталями — пластиковой решёткой радиатора, боковыми зеркалами, новым передним бампером со встроенными противотуманными фарами, задним бампером с ПТФ, увеличенными задними фарами, перемещённой на левую сторону выхлопной трубой и размещённым справа топливным баком. Весьма революционные изменения произошли с интерьером. Это был полностью другой автомобиль — перепроектированная панель приборов и центральная консоль, кондиционер, кожаный салон, элегантные сиденья, аудиосистема и наконец, электрическая крыша. Существенно расширен диапазон дополнительных опций. Новая модель была также оснащена подушкой безопасности и ABS, являющимся стандартом для легковых автомобилей.
При проектировании оказалось, что для корректной работы ABS необходимо было изменение типа привода — теперь W463 характеризуют постоянный привод на четыре колеса с блокировкой центрального межосевого дифференциала. Конструктивные изменения коснулись также рамы и мостов. Подобно серии W460, G-class серии W463 был оснащён блокировками дифференциалов с той разницей, что включались они теперь кнопкой на центральной консоли.
В момент начала продаж W463 заинтересованный покупатель имел выбор из четырёх моделей — двух бензиновых: 230 GE (126 л.с.) и 300 GE (177 л.с.) и двух дизельных : 250 GD(94 л.с.) и 300 GD (113 л.с.). Все они были оборудованы четырёхступенчатой АКПП, хотя опционально можно было заказать и ручную коробку переключения передач.
Уже в первые месяцы продаж Mercedes G-class использовал решения, сохранившиеся до наших дней. Желание менеджеров Daimler угодить сразу двум разным в ожиданиях и потребностях группам клиентов вылилось в несколько лет работ, но в конце концов нашло счастливый финал.
Следствием яркой рекламной кампании новой серии W463 явился упадок продаж W460. Перед премьерой W463 в моделях W460 было произведено ещё несколько изменений. Это пластиковый бак объёмом 96 литров, заменивший предыдущий металлический, а также на 8 лошадиных сил более мощный двигатель 300 GD. По случаю празднования десятилетия G-class была выпущена ограниченная партия модели 230 GE «Classic» в 300 штук, выделявшаяся тёмно-синим цветом «металлик» и рядом хромированных деталей. Однако было ясно, что после ввода в серию W463 будущее модели W460 изменится. Так и случилось.
Игрушечная модель 230 GE Classic
В 1991 году была объявлена модернизация старой линейки G-class с индексом W460 и она была замещена на W461. Когда в следующем году был показан преемник, оказалось, что «модернизация» заключается в значительной степени в лишении автомобиля всех новшеств, которыми была наделена серия W460 — в расчёте на спрос со стороны гражданских лиц. Сиденья оказались прорезиненными, палитра доступных оттенков была сокращена, внутреннее убранство получило аскетичный вид в противовес комфорту и эстетике.
С этой минуты Mercedes G-class начал развивать серии в разных направлениях, учитывая потребности целевых групп покупателей. Модели серии W461 стали типичными «рабочими лошадками», востребованными различными государственными службами и вооружёнными силами, тогда как серия W463 стала эволюционировать в направлении класса полноприводных автомобилей «люкс».
Построенный в неполные три года Mercedes W463 не был свободен от проблем с качеством деталей, получаемых от поставщиков. Когда в апреле 1990 года — через полгода после премьеры — новый автомобиль попал в конечном итоге в автосалоны и получил многотысячные заказы— покупатели были вынуждены долгие месяцы ждать, в то время как сотни транспортных средств стояли на заводской площадке в Граце, ожидая замены дефектных компонентов.
Несмотря на временные трудности, касающиеся старта продаж моделей W463, начало 90-х годов вошло в историю продаж G-класса. В 1990 году были произведены 12 103 единицы G-class, а в следующем — 11 540 единиц. Эти результаты были обусловлены не только огромной заинтересованностью клиентов моделями W463, но и большими параллельными поставками для войск. В конце 80-х годов были подписаны серьёзные контракты в том числе с Бундесвером, заказавшим 12 000 автомобилей разных типов, а также швейцарской армией, закупившей 4 000 единиц автомобилей. Кроме того, в Граце производились комплекты CKD, предназначенные для выпуска в греческом предприятии ELBO в Салониках так называемой серии W462 для потребностей греческой армии и полиции.
Линейка W462
Неудивительно, что на выпуск первых 50 000 единиц Mercedes-Benz G-class потребовалось 8 лет, тогда как построение вторых 50 000 с 1987 по 1992 года — уже только 5. Зато выпуск третьих символических 50 000 занял уже почти 10 лет.
Подобно W460 в восьмидесятых годах, серия W463 требовала постоянной модернизации в девяностых. Не проходило и года, как то один, то другой компонент заменяли на более современный и предлагали различные дополнительные опции. Премьеры новых моделей характеризовались демонстрацией всё более совершенных технологий и более мощных двигателей.
Уже в мае 1992 года был выпущен Mercedes-Benz 350 GD с турбированным двигателем мощностью 136 л.с.и четырёхступенчатой коробкой переключения передач. Он заменил все прежние дизельные модели, выпускавшиеся с 1990 года.
1993 год принёс изменение названий в модификациях серии W463. Теперь буква «G», указывающая на класс автомобиля, была переставлена перед цифровым обозначением. Модель 300GE стали называть G 300, а турбированная модификация 350 GD получила обозначение G 350 TD.
Однако, прежде чем был введён новый принцип именования моделей, на рынок была выпущена лимитированная серия количеством 500 единиц 500 GE с двигателем V8 и мощностью 241 л.с., который уже устанавливали ранее на легковой «Мерседес» 450 SE. Автомобиль был оснащён АКПП и катализатором, интерьер характеризовали кожаные сиденья с подогревом, отделка «под дерево» центральной консоли, электрическая крыша. Довершала впечатление специальная окраска кузова «Amethyst blue», а также пороги из нержавеющей стали. Интересной подробностью является то, что модель 500 GE была оснащена только двумя блокировками дифференциалов (межосевой и задней).
В 1994 году была выпущена модель G 320, заменившая выпускаемую с 1990 года G 300, по-прежнему предлагаемую за пределами Германии. Автомобиль был оснащён шестицилиндровым бензиновым двигателем мощностью 210 л.с., устанавливаемый до этого на автомобили E- и S-класса, а также четырёхступенчатой АКПП.
Автомобиль 500 GE
Предлагаемая с 1992 года модель G 350 TD в 1996 году была заменена на G 300 TD (177 л.с.), в которой была впервые установлена пятиступенчатая АКПП с электронным управлением.
В 1997 году рядная «шестёрка», устанавливаемая на модели G 320, была заменена на более современный V6, который поставляли с пятиступенчатой АКПП, опробованной ранее на G 300 TD.
Автомобиль G 300 TD Cabrio
Непрерывное усовершенствование Mercedes-Benz G-class и применение новых технологических решений требовалось для удержания объёма продаж на постоянном уровне, обеспечивающем окупаемость продукции. Если первую половину девяностых можно было назвать «золотыми годами» G-класса, то вторую половину характеризовало падение интереса. В 1997 году выпуск достиг тревожной отметки в 3 791 штук. Стратегия установки новых двигателей и небольших изменений внешнего вида уже не была эффективной. Требовался новый подход к развитию G-class.
Через три года после окончания продаж ограниченной серии 500GE, в 1998 году была продемонстрирована новая «пятисотка». На этот раз модель была обозначена индексом G 500, а установленный двигатель имел мощность 296 л.с., т.е. на 55 лошадиных сил больше предшественника. G 500 стал первым «Мерседесом» G-класса, перешагнув порог скорости в 200 км/ч. На этой модели впервые были применены электрорегулируемые сиденья, а также белые указатели поворота. В 1999 году наступил двадцатый юбилей Mercedes-Benz G-class и к этой дате был приурочен выпуск ограниченной серии G 500 Classic, показанной на выставке во Франкфурте.
В 2000 году модель G 300 TD была заменена на новую — G 400 CDI, с которой «гелендваген» вступил в 21-летний возраст. Четырёхлитровый дизель имел мощность 250 л.с. и работал на современной технологии Common Rail, которая заключается в непосредственном впрыске топлива, обеспечивающем не только лучшие технические характеристики, но и низкий уровень шума, выхлопов, а также низкое потребление топлива. В салоне появилась система COMAND, управляющая аудио- и видеоустройствами, а также GPS-навигацией.
Система COMAND 2.0
Новое тысячелетие не могло быть открыто иначе, чем презентацией новой модели. На этот раз это была G 270 CDI, которая в 2001 году дополнила линейку G-class с двигателями Common Rail. Однако ещё не все рыночные ниши были заняты.
Трудно поверить, но свыше двадцати лет Mercedes-Benz G-class официально не продавался на территории Северной Америки. Никто бы не обратил на это внимание, если бы в 2002 году G-class не был ввезён в автосалоны США и Канады. Причина кроется в том, что раньше «гелендваген» не отвечал требованиям американского рынка, поэтому для клиентов из США поставляли M-класс. Неофициально поговаривали, что премьера G-class за
Атлантикой была связана с тендерами на многозадачный автомобиль, объявленными одновременно американской и канадской армиями. Американские морские войска уже в 2000 году получили 100 адаптированных для их нужд Mercedes G-class, а в октябре 2003 года было объявлено, что Daimler оказался победителем тендера на поставку свыше восьмисот автомобилей G 270 CDI для канадской армии. Не секрет, что рост продаж продукции в 2002-2003 годах был вызван именно началом продаж в Соединённых Штатах, благодаря проданным свыше 6 500 единицам автомобилей.
Вояка G 270 CDI
Другим оружием «Мерседеса» оказалась марка AMG, в 1999 году поглощённая Daimler. В 1998 году была продемонстрирована модель G 55 AMG — самый быстрый, надёжный и роскошно обустроенный автомобиль G-класса в истории. Его сердцем являлся уже использованный в других моделях AMG двигатель V8 мощностью 354 л.с., благодаря которому автомобиль разгонялся до 100 км/ч за 7,4 секунды и с ограничением максимальной скорости в 209 км/ч. Трудно представить, но G55 AMG сохранил все решения, в том числе полный привод, характеризующие серию W463. Были доступны закрытые модели с длинным и коротким вариантами кузова, а также кабриолет, оборудованный электрогидравлической системой открытия и закрытия крыши. Весной 2004 года на автосалоне в Женеве состоялась премьера G 55 AMG с компрессором мощностью 476 л.с. с разгоном до 100 км/ч за 5,6 сек. Таким образом, G-class занял не очень большой, но зато имиджевый сегмент роскошных спортивных автомобилей.
G 55 AMG Kompressor
В 2004 году казалось, что двадцать пятый юбилей подведёт очередную черту. Многие задавали вопрос: как долго можно производить эту модель автомобиля? На новый юбилей была выпущена партия «Classic 25″. Через пять лет, когда «гелендваген» вступит в 31-й год жизни, этот вопрос будет по-прежнему актуален.
Характерные угловатые черты G-класса остаются неизменными, как и сама конструкция автомобиля, заключающаяся в простом креплении кузова к массивной раме, пружинах, блокировках дифференциалов и наличием раздаточной коробки. Отличает G-класс 2009 года от его родоначальника несоизмеримый комфорт, поколения новых двигателей и АКПП, системы безопасности вроде ESP и 4ETS.
В 2001 году (и в 2014 — прим. авт.) была официально исключена из каталогов «Мерседеса» серия W461. На самом деле её производство никогда не прекращалось — она оставалась доступной для больших правительственных заказов. За 30 лет она не встречала конкурентов в тендерах на поставку автомобилей для вооружённых сил. И если «Мерседес» где-то и проигрывал, то поводом к отказу являлась скорее цена, так как безотказность и выносливость автомобиля никто никогда не оспаривал.
Серия W461 Professional
Самым известным бронированным Mercedes-Benz G-class стал «папамобиль», изготовленный в 1980 году для Папы римского Иоанна Павла II: в задней части кузова этой машины был установлен купол из пулестойкого стекла. Ну а в России эта модель удостоилась чести стать приближенной к «престолу», пополнив президентский автопарк.
http://gelandewagen.mercedes-ru.ru/mercedes-gelandewagen-history/ — По материалам журналов «Club4x4″ и «Гелендваген».
http://www.g-class.ru/index.asp?zz=m62864297
А вот вам еще истории некоторых автомобильных брендов: вот вам немного про историю Чероки, а вот Великолепный Добл — возможно, мы и сейчас катались бы на бесшумных паровых автомобилях. Можно еще вспомнить про Историю Вольво (Volvo). Вот еще Майбах (Maybach): человек — машина. Приведу еще одну автомобильную историю: История «месье Мерседеса» или например Крах инженера Такера : история создания автомобиля «завтрашнего дня». Почитайте еще кому интересна История компании BMW
Оригинал статьи находится на сайте ИнфоГлаз.рф Ссылка на статью, с которой сделана эта копия — http://infoglaz.ru/?p=77597
Всего пару лет назад знаменитый «Гелендваген» отметил уже 38-годовщину своего производства – эта модель выпускается еще с 1979.
Таким сроком на конвейере никого не удивишь – многие удачные машины японских производителей также выпускаются достаточно долго. Но в Мерседес Гелендваген главное другое – на протяжении всех лет дизайн внедорожника остается практически неизменным.
Да, в него вносятся определенные улучшения и дополнения, да и по убранству рестайлинговая модель 2015 года сильно выделяется от предыдущего поколения – но общая концепция остается постоянной, и для непосвященного человека отличить 463-ий кузов от предыдущего будет практически неразрешимой задачей.
Так вот, несмотря на несколько устаревшую, по мнению критиков, внешность и неказистый дизайн, в Mercedes-Benz не планируют пока снимать G-класс с производства или вносить в конструкцию какие-то радикальные изменения.
Лучшее тому свидетельство – обновление модели, произошедшее в 2015 году. Ни внешне, ни в техническом плане Гелик не получил каких-то серьезных изменений – все основные доработки коснулись интерьера и линейки более мощных и экономичных силовых агрегатов. На фото представлена версия G63 AMG.
Содержание
- Новый Mercedes-Benz G-класс – найти 5 отличий
- Экстерьер
- Интерьер
- Технические характеристики
- Комплектации и цены
- G350 d
- G500
- G500 4×4
- AMG
- G65
- Видео
Новый Mercedes-Benz G-класс – найти 5 отличий
Экстерьер
Как говорилось выше, в облике рестайлингового Мерседес Гелендваген нет ничего нового. Все тот же угловатый кузов брутального вида, установленный на мощную раму лестничного типа – наследие армейского прошлого внедорожника. Рама, состоящая из U-образных профилей и лонжеронов, имеет дополнительный слой полимерной защиты, надежно предохраняющей металл от преждевременной коррозии и повышающей ее жесткость.
Главное отличие кузова Гелика – измененная форма переднего бампера, с расположенными по углам воздухозаборникам и новые зеркала заднего вида. В нижней части кузова спереди установлена защита днища скругленной формы.
Еще одно отличие – новая оптика. Внедорожник получил LED дневные ходовые огни, интегрированные в задний бампер светодиодные противотуманные фары, а также поворотники с подсветкой ближнего пространства. Противотуманки, устанавливающиеся в передний бампер, теперь имеют опцию «бокового света».
От своего предшественника Mercedes G-класс 2015 года также можно отличить по расширенным колесным аркам, что теперь устанавливаются даже в базовую комплектацию, и дискам диаметром 18 д. Для более дорогих версий предлагаются колеса размером от 19 до 21 д.
Интерьер
Но если отличий во внешности обновленного Гелика не так уж много, то стоит заглянуть в салон. Приложив определенное усилие для открытия двери, – а инженеры остались верны концепции «брутального внедорожника для настоящего мужчины», и она открывается не так и легко – можно увидеть, что ничего общего с предыдущими поколениями здесь нет.
Если снаружи Мерседес Гелендваген производит впечатление утилитарного вездехода, то внутри царит атмосфера роскоши и комфорта, уступающая разве что Bentley Bentayga.
В отделке интерьера широко используются натуральная кожа, дерево, качественные ткани, полированный металл и карбон. Передние комфортабельные сиденья имеют функцию пневматической регулировки подпоров и электрическую регулировку по высоте и наклону с запоминанием положения.
Сзади также установлены три полноценных кресла, но ввиду особенностей конструкции там не так много места, как кажется. Все сиденья имеют электроподогрев уже в штатной комплектации, но их форма далека от идеальной – отсутствие боковой поддержки, низкие подголовники и плоские подушки не дадут расслабиться в длительном путешествии. В этом плане Mercedes G-класса уступает современным кроссоверам, таким как Рендж Ровер Велар.
Приборная панель классического типа, с двумя шахтами и четырехспицевым мультирулем. Расположенными на руле клавишами можно не только управлять приборами и регулировать работу мультимедийной системы, но и принимать входящие вызовы, управлять бортовым компьютером и многое другое.
На центральной консоли несколько архаичной формы расположены дефлекторы обдува и клавиши управления бортовыми системами. Над ней устанавливается выносной дисплей новейшей мультимедийной системы COMAND Online с диагональю 7.0 дюймов с дополнительным контролером на подлокотнике. Она включает в себя проигрыватель CD/DVD с разъемами USB, беспроводной интерфейс, жесткий диск размером 80 Гб, возможность подключения телефона и интернет-браузер.
Система объемного звука от Harmon/Kardon и подсветка салона Ambient Lighting устанавливаются уже в стандартной версии Гелика, как и двухзонный климат-контроль THERMATIC.
Технические характеристики
Основное отличие обновленного Мерседес Гелендваген – новые бензиновые и дизельные моторы.
- G350. На эту версию устанавливается 6-цилиндровый V-образный турбомотор OM642 объемом 3.0 литра. Он способен развивать мощность в 245 л. с. и достигать крутящего момента в 600 Нм, а максимальная скорость составляет 192 км/ч, разгон – 8,8 с.
- G500 оснащается атмосферным бензиновым мотором M176 V8, имеющим объем 4.0 л. Мощность равна 422 л. с., а крутящий момент достигает 530 Нм. Максимальная скорость – 210 км/ч, ускорение – 5,9 с.
- У версии G63 AMG с битурбированным двигателем M157 DE55LA при объеме в 5.5 л удалось выжать мощность в 571 л.с. и достичь момента в 760 Нм. С этим мотором внедорожник способен развить скорость в 210 км/ч.
- Самой заряженной версией является G65 AMG. Мощность 6-литрового битурбированного агрегата M279 KE60LA V12 увеличена до 630 л. с., а вращающий момент равен феноменальным 1000 Нм. Предел скорости ограничен 230 км/ч, разгон – 5,3 с.
При том что все без исключения моторы стали мощнее как минимум на 7-10%, инженерам удалось добиться топливной экономичности. Для примера – с новым мотором расход топлива у G500 составляет 12.4 л/100 км против 17.6 л у прежней версии.
Гелик оснащается двумя вариантами 7-ступенчатых автоматических трансмиссий:
- Модели G350 и G500 комплектуются 7G-TRONIC PLUS.
- Для топовых версий G63 AMG и G65 AMG предлагается более производительная коробка AMG SPEEDSHIFT PLUS 7G-TRONIC. Ее главная особенность – три режима работы, один из которых позволяет переключать передачи вручную посредством подрулевых лепестков.
Обе трансмиссии оснащаются пониженной передачей и блокировкой дифференциалов, позволяющими внедорожнику уверенно чувствовать себя на любой местности.
Комплектации и цены
Цена на Mercedes-Benz G-класс зависит от комплектаций – они различаются между собой силовым агрегатом, трансмиссией и рядом опций.
G350 d
Базовой является G350 d с 3-литровым турбодизелем и 7G-TRONIC PLUS – она обойдется покупателю в цену от 6.7 млн рублей.
G500
Более мощная версия G500 с такой же трансмиссией и бензиновым 4-литровым мотором будет стоить уже от 8.38 млн р. Для этих двух моделей предлагается дополнительный пакет опций Life Style стоимостью порядка 1 млн р., включающий в себя колесные диски диаметром 19 дюймов, подогрев руля, тонировку стекол, противоугонную систему, комфортабельные передние кресла, пакет парковки с мониторингом слепых зон, люк в крыше и хром-пакет.
G500 4×4
Отдельно стоит отметить комплектацию G500 4×4. Это внедорожная версия Гелика G500, оснащенная измененной лифтованной подвеской.
Клиренс автомобиля увеличен до 450 мм, устанавливаются три механические блокировки дифференциалов, расширенные арки, полная металлическая защита днища, регулируемые амортизаторы и огромные колеса диаметром 22 дюйма. Цена экстремального внедорожника составляет 19.24 млн р. Снят с продажи.
AMG
Заряженные версии AMG обойдутся на порядок дороже. Комплектация G63 с битурбированным 5.5-литровым бензиновым двигателем и производительной трансмиссией AMG 7G-TRONIC стоит 11.6 млн р. Сюда также входят 20-дюймовые диски, выхлопная система и обвес из нержавеющей стали, улучшенная отделка салона, более мощные тормоза и модернизированная подвеска с пружинами и амортизаторами спирального типа.
G65
Самой дорогой является комплектация G65 – она обойдется в 21 млн р. За эти деньги покупатель получает хром-пакет, включающий в себя накладки на кузов, бампера и патрубки выхлопной системы, декоративную отделку алюминием с фирменными шильдиками, уникальный кожаный салон со вставками из карбона и натурального дерева, ряд опций, потолок из алькантары и многое другое.