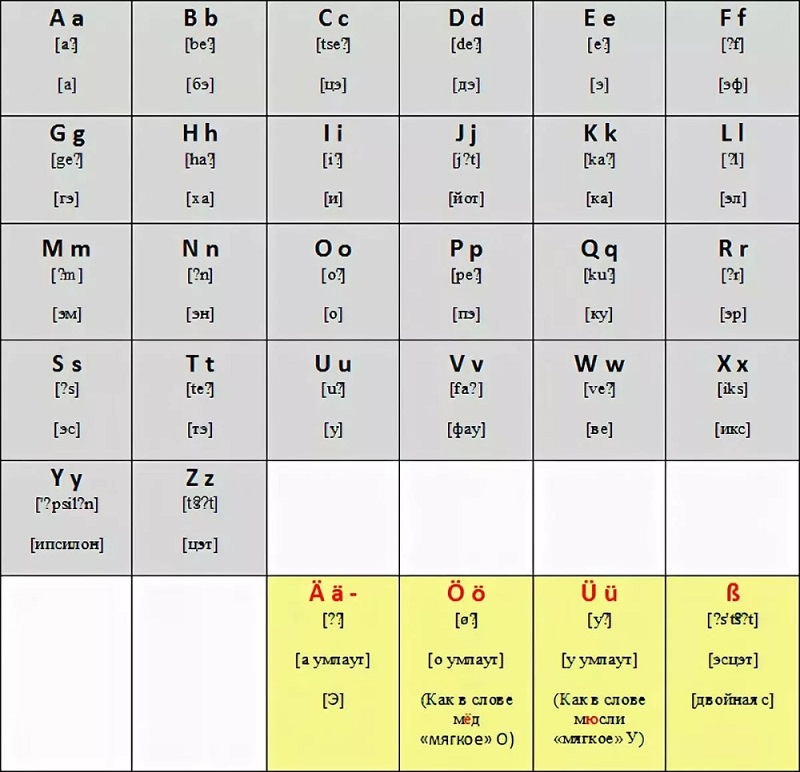
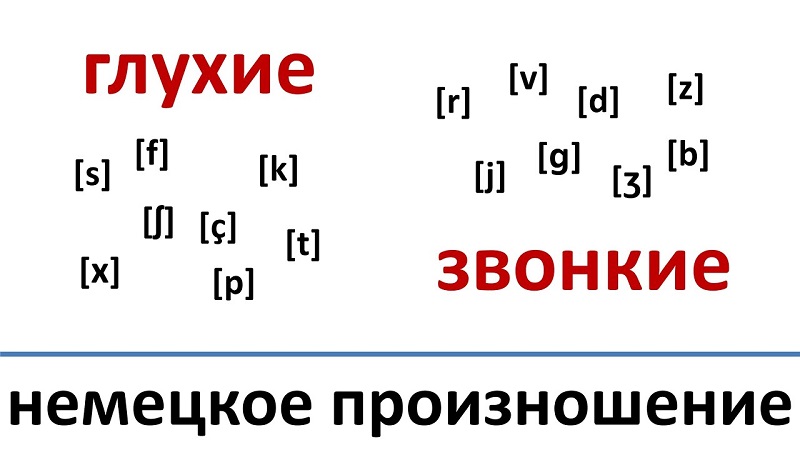
Любой язык начинается с алфавита, и немецкий — не исключение! Чтобы научиться читать по-немецки правильно, нужно сначала познакомиться со всеми немецкими буквами и звуками.
Немецкий алфавит — это алфавит на латинской основе, в его состав входит 26 букв:
A a [а], B b [бэ], C c [цэ], D d [дэ], E e [э], F f [эф], G g [гэ], H h [ха], I i [и], J j [йот], K k [ка], L l [эл], M m [эм], N n [эн], O o [о], P p [пэ], Q q [ку], R r [эр], S s [эс], T t [тэ], U u [у], V v [фау], W w [вэ], X x [икс], Y y [ипсилон], Z z [цэт].
Содержание
- Немецкий алфавит (прослушать)
- От звука к букве. Учимся читать на немецком языке
- Задания к уроку
Немецкий алфавит (прослушать)
Прослушать алфавит:
Также в немецком алфавите есть три умлаута (Ä, Ö, Ü).
Прослушать умлауты:
Умлауты (две точки над гласными) обозначают качественное изменения звуков u, o, a.
Правильное произнесение звуков в словах с умлаутами и без них очень важно, поскольку от этого зависит значение слова. Например, слово „schon“ произносится твердо, со звуком «о» и обозначает «уже», в то время как слово „schön“ имеет более мягкий звук, близкий к русскому «ё», и означает «приятный, милый». Будьте внимательны к значкам над гласными, чтобы избежать непонимания!
Чтобы говорить по-немецки правильно, обратите внимание на особенности произношения умлаутов немецкого языка:
В начале слова и после гласных умлаут «ä» читается как звук «э», после согласных: как «е. Чтобы правильно произнести умлаут «ö», положение языка должно быть как при «э», а губ – как при «о». Таким образом, выйдет звук, отдаленно похожий на русское «ё». Кстати, «ё» тоже можно назвать умлаутом, ведь это качественное изменение звука «е» в русском языке. Итак, чтобы произнести умлаут ü – положение языка должно быть как при «и», а губ – как при у. У вас получится звук, отчасти похожий на русское «ю».
Умлауты не так уж легко не только произносить, но и печатать. Если у вас нет немецкой раскладки, вы можете воспользоваться общепринятой заменой знаков:
ä – ae
ö – oe
ü – ue
Еще один необычный знак немецкого языка — это лигатура (т. е. соединение букв) «эсцет» (ß).
Чаще всего, «эсцет» приравнивают буквам «ss», однако помимо звука [s] обозначает долготу предыдущего звука, поэтому заменять «ß» на «s» не стоит — «ss» сигнализирует о краткости предыдущего звука, что важно помнить при изучении правил чтения.
Как и умлауты, «эсцет» не входит в состав алфавита и выносится за его пределы. Однако в словарях эти буквы подчиняются алфавитному порядку: Ää следует за Аа, Öö — за Оо, Üü — за Uu, ß — за «ss».
Правила чтения немецких слов довольно просты и подчиняются несложным правилам, а потому транскрипции в немецком языке нет — она появляется только у некоторых сложных слов, чаще всего пришедших в немецкий из других языков.
Ударение ставится перед ударным слогом, а долгий звук обозначается двоеточием.
От звука к букве. Учимся читать на немецком языке
В немецком языке один и тот же звук могут давать разные буквы. Приведенная ниже таблица поможет разобраться, какие буквы и буквосочетания читаются в немецком языке одинаково.
Помните! Открытым считается слог, который заканчивается на гласный: da. Закрытый слог заканчивается на согласный: das.
| Звук | Произношение | Буква | Положение в слове | Примеры |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [а] | [а]
|
а | в закрытом слоге | das |
|
[а:] |
[а:] |
ah
a aa |
в открытом слоге |
Nah, da, Saat |
| [s] | [с] | s
ß |
в конце слова и после долгих гласных | das, Naß |
| [z] | [з] | s | перед гласными и между ними | Saat |
|
[f] |
[ф] |
f | в начале, середине и конце слова | Faß |
| ff | в середине и конце слова | paff | ||
| v | в начале и середине слова | Vater | ||
| [v] | [в] | w | в начале и середине слова | was |
| [n] | [н]
|
n | в начале, середине и конце слова | nah, an |
| nn | в середине и конце слова после кратких звуков | wann | ||
| [d] | [д] | d | в начале и середине слова | das |
|
[t] |
[т] |
t | В начале, середине и конце слова | Tat |
| tt | В середине и конце слова | Satt | ||
| d | в конце слова | Sand | ||
| [ts] | [ц] | z | в начале, середине и конце слова | Zahn |
| tz | в середине и конце слова после кратких звуков | Satz | ||
| [b] | [б]
|
b | в начале и середине слова между гласными | Bahn |
|
[p] |
[п] |
p | в начале и середине слова | paß |
| pp | в середине и конце слова после кратких звуков | knapp | ||
| b | в конце слова и перед согласной | ab | ||
| [m] | [м] | m | в начале и середине слова | Mann |
| mm | в середине и конце слова после краткого звука | Damm | ||
| [g] | [г] | g | в начале и середине слова | Gast |
| [ŋ] | [н]
|
ng | в середине и конце слова после краткого звука | Sang |
| [ŋk] | [нк] | nk | в середине и конце слова после краткого звука | Bank |
|
[k] |
[к] |
k | в начале и середине слова | kann |
| ck | в середине и конце слова после краткого звука | Sack | ||
| g | в конце слова | Tag | ||
| [kv] | [кв] | qu | Quant | |
| [ks] | [кс]
|
x | Axt | |
| [i] | [и] | i | в закрытом слоге | Ist |
|
[i:] |
[и:] |
i |
в открытом слоге |
Ida, die, Ziehen, ihn |
| ie | ||||
| ieh | ||||
| ih | ||||
| [u] | [у] | u | в закрытом слоге | und |
| [u:] | [у:] | u |
в открытом слоге |
rufen |
| uh | Uhr | |||
| [ə] | [э] | e | в конечном слоге | Tasse |
|
[r] |
[р] | r | в начале слова или слога | Rat |
| rr | после согласного, кратких гласных и долгого [a:] | Paar, Brust | ||
| [r] | [а] | r | в конце слова | Vater, wir |
| [ɜ] | [э]
|
e
ä |
в закрытом слоге | Bett
März |
| [ɜː] | [э:] | ä
äh |
в открытом слоге | Käse, Bär,
Nähe, näht |
|
[e:] |
[е:] | e
ee eh |
в открытом слоге |
Rede, Weg, Tee, sehen |
| [ʃ] | [ш] | sch | в начале, середине и конце слова | Schuh |
| [ʃt] | [шт] | st | в начале слова | Strasse |
| [ʃp] | [шп] | sp | в начале слова | spät |
| [ai] | [ай]
|
ei
ai |
в начале, середине и конце слова | ein, mein,
Mai |
| [o:] | [о:] | o, oo
oh |
в открытом слоге | Brot, Boot,
Sohn |
| [o] | [о] | o | в закрытом слоге | oft |
| [x] | [х] | ch | после кратких звуков a, o, u | Fach, doch, Buch |
| [ç] | [хь] | ch | после кратких звуков | ich, recht, weich |
| g | в суффиксе -ig | ruhig | ||
| [j] | [й] | j | в начале слова перед гласными | ja |
| [ao] | [ау]
|
au | в начале, середине и конце слова | aus, Haus, Bau |
| [y:] | [ю:] | ü, üh, y | в открытом слоге | Üben, Kühe,
Tür, Physik |
| [y] | [ю] | ü | в закрытом слоге | Stück |
| [øː] | [ё:] | ö
öh |
в открытом слоге | Hören, Söhne, öl |
| [oe] | [ё] | ö | в закрытом слоге | zwölf |
| [tʃ ] | [ч] | tsch | в начале, середине и конце слова | Tscheche, Putsch |
| [u] | [у] | u | перед гласными в заимствованных словах | Union |
| [ʒ] | [ж] | j | перед гласными a, o, u во франц. заимствованиях | Journal, Jargon |
| g | перед гласными e, i во франц. заимствованиях | Ingenieur | ||
| [pf] | [пф] | pf | в начале, середине и конце слова | Pfad, Apfel, Kampf |
| [oi] | [ой] | eu
äu |
в начале, середине и конце слова | Euch, neun, neu, Räume |
Задания к уроку
Попробуйте применить знания на практике, выполняя следующие упражнения. Не бойтесь подглядывать в таблицу, со временем все звуки запомнятся, и необходимость в подсказках отпадет сама собой!
Упражнение 1. Прочитайте следующие слова:
Mein, liegen, Freunde, Tasche, Tag, jetzt, Jacke, spielen, stehen, wachsen, zusammen, Stunde, Träume, täglich, ruhig, schon, Bitte, Spaß, selten, ziemlich, oft, neun, Brot, die, Baum, Naß.
Прослушайте:
Ответы к Упражнению 1.
Mein [майн], liegen [‘ли: гэн], Freunde [;фройндэ], Tasche [‘ташэ], Tag [так], jetzt [ецт], Jacke [‘якэ], spielen [‘шпи: лен], stehen [‘штэ:ен], wachsen [‘ваксэн], zusammen [цу’замэн], Stunde [‘штундэ], Träume [‘троймэ], täglich [‘тэглихь], ruhig [‘ру: ихь], schon [шо: н], Bitte [‘битэ], Spaß [шпа: с], selten [‘зельтэн], ziemlich [‘цимлихь], oft [офт], neun [нойн], Brot [брот], die [ди:], Baum [баум], Naß [на: с].
На чтение 10 мин Просмотров 54.5к.
Содержание
- Буквы немецкого алфавита
- Онлайн карточки с немецким алфавитом
- Буквы образующие характерные буквосочетания
- Заключение
Основа каждого языка — его алфавит. Не исключением является и немецкий язык. Первое, что нужно выучить приступая к новому языку — это учить его алфавит и правила произношения, чтения и написание немецких букв и буквосочетаний. Чем мы, собственно, и займемся сейчас.
В немецком языке присутствуют 26 букв немецкого алфавита (официального) и еще четыре дополнительные буквы, которые в состав алфавита не включаются, но при этом часто встречаются и употребляются в самых разных словах.
А вы знали, что произношение начинает формироваться уже на этапе изучения алфавита? Чтобы не переучиваться потом, лучше сразу взять несколько уроков с преподавателем, а найти его можно в школе Deutsch Online. Записывайтесь и получайте первый урок-знакомство бесплатно!
Буквы немецкого алфавита
|
Буква немецкого алфавита |
Традиционная транскрипция |
Русский вариант произнесения |
Примеры слов с данной буквой |
| A a |
[a:] |
[а] |
amtlich – служебный, должностной |
| B b |
[bε:] |
[бэ] |
belgisch – бельгийский |
| C c |
[tsε:] |
[цэ] |
chronisch — хронический |
| D d |
[de:] |
[дэ] |
dauerhaft – длительный, продолжительный |
| E e |
[e:] |
[э] |
ehrlich – откровенный, честный |
| F f |
[εf] |
[эф] |
futuristisch — футуристический |
| G g |
[ge] |
[гэ] |
gänzlich – всецелый, совершенный |
| H h |
[ha:] |
[ха] (звук [х] похож на очень легкий выдох) |
häufig – частый, многочисленный |
| I i |
[i:] |
[и] |
innerlich — внутренний |
| J j |
[jot] |
[йот] |
jetzig – нынешний, теперешний |
| K k |
[ka:] |
[ка] |
kräftig – сильный, большой, крепкий |
| L l |
[εl] |
[эл] |
lächerlich – забавный, смехотворный |
| M m |
[εm] |
[эм] |
mißtrauisch — подозрительный |
| N n |
[εn] |
[эн] |
neutral – нейтральный |
| O o |
[o:] |
[о] |
orientalisch — восточный |
| P p |
[pe:] |
[пэ] |
polnisch — польский |
| Q q |
[ku:] |
[ку] |
quellend — пробивающийся (об источнике) |
| R r |
[εr] |
[эр] |
regnerisch — дождливый |
| S s |
[εs] |
[эс] |
smoken — собирать, присборивать |
| T t |
[te:] |
[тэ] |
tüchtig – умелый, дельный |
| U u |
[u:] |
[у] |
ursprünglich – исходный, изначальный |
| V v |
[fao] |
[фау] |
verträglich – переносимый, сносный |
| W w |
[ve:] |
[вэ] |
wahnsinnig – помешанный, безумный |
| X x |
[iks] |
[икс] |
Xenon-Scheinwerfer – ксеноновые фары |
| Y y |
[ypsilon] |
[ипсилон] |
dynamisch — динамичный |
| Z z |
[tsεt] |
[цэт[ |
zynisch — циничный |
| Дополнительные немецкие буквы к латинскому алфавиту, лежащему в основе немецкого языка: | |||
| Ä ä |
[ε] |
а-умлаут: [э] |
ärgerlich — досадный, раздражающий |
| Ö ö |
[ø] |
о-умлаут: как «ё» в слове «Лёня» |
örtlich — местный |
| Ü ü |
[y] |
у-умлаут: как «ю»в слове «Люся» |
überflüssig — излишний |
| ß |
[s] |
эсцет: как звук [с] |
das Geschoß – ярус, этаж |
Таким образом, в данной таблице были рассмотрены все существующие буквы немецкого алфавита, включая четыре дополнительные.
Далее, буквы могут образовывать в словах разные буквосочетания, которые подчиняются определенным правилам прочтения. Попробуем представить их также в виде наглядной таблицы.
Онлайн карточки с немецким алфавитом
Буквы образующие характерные буквосочетания
| Сочетание букв | Особенности звука | Транскр. | Русское прочтение |
Примеры слов |
|
ai |
сочетание двух гласных |
[ae] |
[ай] |
der Main [maen]– Майн (река) |
|
ah |
долгий гласный низкий звук |
[a:] |
[а:] |
der Hahn [ha:n] – кран; петух |
|
с |
перед e, ö, i, y, ü одна согласная буква дает звук-аффрикату |
[ts] |
[ц] |
das Cyklon [tsyklo:n] — циклон |
|
c |
в словах, заимствованных из других языков, чаще в начале слова |
[k] |
[к] |
die Couch [kaotʃ] — кушетка |
|
ch |
при постановке после гласных u, o, a; место образования звука значительно ниже в гортани, чем у русского [x] |
[x] |
[x] |
die Buche [bu:xә] — бук |
|
ch |
иногда в начале слова; сочетание двух согласных букв дает один взрывной глухой согласный звук |
[k] |
[к] |
das Chlor [klo:α] — хлор |
|
сh |
после ä, i, ö, e, y, ü, а также после m, r, l, n сочетание двух согласных букв дает один глухой щелевой согласный звук, похожий на звук [х] в слове «хитрый» |
[ç] |
[х] |
die Bücher [byçәα] – книгиdie Mönche [mønçә] — монахи |
|
ch |
в заимствованных словах |
[tʃ] |
[ч] |
die Couch [kaotʃ] – диван, кушетка |
|
chs |
в качестве неделимого сочетания букв в рамках одного слога |
[ks] |
[кс] |
der Lachs [laks] – сёмга, лосось |
|
сk |
сочетание двух согласных букв дает один глухой взрывной согласный звук |
[k] |
[к] |
der Zucker [tsukәα] — сахар |
|
е |
краткий гласный звук в закрытом слоге |
[ε] |
[э] |
hell [hεl] — светлый |
|
eh |
долгий гласный звук |
[e:] |
[э:] |
das Mehl [me:l] — мука |
|
ei |
дифтонг |
[ae] |
[ай] |
leise [laezә] — тихо |
|
ie |
дифтонг |
[i:] |
[и:] |
die Wiege [vi:gә] — колыбель |
|
eu |
дифтонг |
[oe] |
[ой] |
die Leute [loetә] — люди |
|
oh |
долгий гласный средний (подъем) |
[o:] |
[o:] |
der Lohn [lo:n] – зарплата |
|
oi, oy |
[oе] |
[ой] |
der Boykott [boekot] бойкот | |
|
j |
согласный звонкий щелевой звук |
[j] |
[й] |
jawohl [javo:l] – есть, так точно |
|
l |
сонорный звонкий согласный, представляющий собой что-то вроде перехода от русского мягкого [л`] к русскому твердому [л] в рамках одного звука |
[l] |
[л`]®[л] |
leer [le:α] — пустой |
|
ng |
это буквосочетание передает звонкий сонорный носовой звук, отсутствующий в русском языке |
[ŋ] |
носовой |
singen [ziŋәn] — петь |
|
nk |
это буквосочетание передает два звука: звонкий сонорный носовой звук, которого нет в русском + глухой аспирированный |
[ŋk] |
носовой |
sinken [ziŋkәn] – падать, погружаться, уменьшаться |
|
ph |
сочетание двух согласных букв дает один согласный щелевой звук |
[f] |
[ф] |
die Physik [fy:zik] физика |
|
qu |
сочетание согласной и гласной буквы дает сочетание двух согласных звуков |
[kv] |
[кв] |
der Quark [kvark] – творог |
|
rh |
сочетание в начале слова двух согласных букв дает один согласный звук |
[r] |
[р] |
der Rhytmus [rytmәs] – частота, ритм |
|
s |
щелевой звонкий согласный звук, если стоит впереди гласного или между двумя гласными |
[z] |
[з] |
der Käse [kε:sә] – сырsüchtig – охваченный какой-либо страстью |
|
sp, st |
s передает щелевой глухой согласный звук в начале слова/части сложносоставного слова, если за ним стоят p или t |
[ʃ] |
[ш] |
der Specht [ʃpәçt] – дятелdas Statut [ʃtatu:t] — устав |
|
sch |
три согласных буквы дают щелевой глухой согласный |
[ʃ] |
[ш] |
schon [ʃon] – уже |
|
s |
в прочих случаях, кроме трех перечисленных выше |
[s] |
[c] |
der Poster [postәα] – плакат, постер |
|
th |
две согласных буквы дают один смычный глухой согласный звук |
[t] |
[т] |
die Theorie [tεori:] – теория |
|
tsch |
четыре согласных буквы дают одну аффрикату |
[tʃ] |
[ч] |
der Deutsche [doetʃә] – немец |
|
uh |
сочетание гласной и согласной буквы дает долгий гласный звук |
[u:] |
[у:] |
der Uhu [u:hu] – филин |
|
ui |
сочетание букв |
[ui] |
[уи] |
die Ruine [rui:nә] – развалины, руины |
|
v |
в иностранных заимствованиях звонкий лабиально-дентальный согласный звук |
[v] |
[в] |
die Variante [variantә] — вариант |
|
v |
в прочих случаях лабиально-дентальный глухой согласный звук |
[f] |
[ф] |
die Vögel [fø:gәl] – птицы |
|
w |
звонкий лабиально-дентальный согласный звук |
[v] |
[в] |
wellig [vεliç] – волнистый |
|
х |
одна согласная буква дает аффрикату |
[ks] |
[кс] |
der Lurex [lu:rεks] – люрекс |
|
y |
типично немецкий звук, нечто среднее между ю и у, типа «ю» в слове «люк», может быть долгим и кратким |
[y] |
[ю-у] |
rhytmisch [rytmiʃ] – ритмическийpsychisch [psyçiʃ] — психический |
|
z |
одна согласная буква дает аффрикату |
[ts] |
[ц] |
die Zerbe [tsεαbә] – кедр |
|
äu |
[oe] |
[ой] |
die Säule [zoelә] – колонна | |
|
schtsch |
такого звука в немецком нет, это сочетание букв используется для передачи звука [щ] в иностранных словах |
[ʃtʃ] |
[щ] |
der Borschtsch [borʃtʃ] – борщ (суп) |
|
sh |
такого звука в немецком также нет, сочетание букв передает [ж] в иностранных словах |
[ʒ] |
[ж] |
Shukow [ʒukof] – Жуков (фамилия) |
|
ß = ss |
передает один щелевой согласный глухой звук; ß может либо заменяться на ss, либо пишется ß только после букв, передающих долгие гласные или дифтонги |
[s] |
[с] |
lassen [lasәn] — оставить, покинутьbeißen [baesәn] — кусать |
Из приведенной таблицы буквосочетаний и букв немецкого алфавита видно, что существуют отдельные звуки, которые передаются двумя, тремя и более буквами.
В то же время одна буква при прочтении может давать два звука (аффрикату), при этом некоторые буквы могут обозначать различные звуки в зависимости от их положения в слове и соседствующих букв.
Заключение
В заключение необходимо также отметить несколько общих, типичных для немецкого языка моментов:
- все немецкие сдвоенные согласные передают один звук и указывают при этом на краткость предшествующего гласного звука, например: rennen [rεnәn] – мчаться, нестись;
- все удвоенные немецкие гласные при прочтении являются одним долгим звуком, например: der Aal [а:l] – угорь;
- стоящая после гласных буква h никогда не читается, а лишь указывает на долготу предыдущего гласного; как едва заметный выдох она обычно слышна только в начале слога/слова, например: sehr [ze:r] – очень (не произносится), hier [hi:r] – здесь (произносится едва уловимо);
- для передачи русских букв я, ё, ю на письме используются буквосочетания немецких букв ja, jo, ju, наиболее близко передающие звучание этих не имеющих в немецком языке аналогов букв, например: Юра — Jura, Яша – Jascha;
- что касается буквы r, то в немецком языке присутствуют несколько вариантов ее прочтения: в начале слов — картавый язычковый [r], который произносится как долгий (в течение нескольких секунд) русский звук [х], но только с участием голоса; в начале слов возможен также раскатистый переднеязычный [r]; в середине слов [r] заметно тише, но вполне различим, а вот в конце буква r передает звук, совершенно не похожий на предыдущие два по своей сути, поскольку он является вокализованным [α], то есть более близким к гласному звуку. Для примера можно сравнить: der Rabe – ворон (громкий катящийся или раскатистый [r]), lehren — обучать, учить (приглушенный но вполне различимый катящийся или раскатистый [r]), der Zuschauer – зритель (вокализованный [α]);
- сочетание двух или нескольких согласных указывает на краткость предыдущего гласного даже в тех случаях, когда эти согласные обозначают один звук, например löschen [løʃәn] — гаснуть, затухать, стирать;
- гласные звуки, располагающиеся в начале корня или слова, всегда произносятся намного резче, с так называемым твердым приступом, например: der Alter [`altәα], что придает немецкой речи в целом более отрывистый и четкий характер по сравнению с нашей плавной родной речью;
- все немецкие согласные являются твердыми, все звонкие приглушаются и произносятся полузвонко, а на конце слов всегда полностью оглушаются, например: der Dieb [di:p] вор (согласный d – полузвонкий, а b на конце слова полностью приглушен);
- ударение в немецких словах преимущественно падает на первый слог (если в этих словах отсутствуют безударные приставки; если присутствуют – на второй), но с иностранными заимствованиями дело обстоит по-иному. К примеру, суффикс –tion всегда является ударным и читается [tsion], при этом ударение падает на о, а предшествующий i очень краток и является по сути как бы проскальзывающим, чем-то напоминая звук [j], однако приглушенный, практически без участия голоса. Например: die Kontribution [kontributio:n = kontributjo:n] – взнос, контрибуция.
Источник: http://online-teacher.ru/blog/буквы-немецкого-алфавита
- Русский алфавит
- Алфавиты и азбуки
- Немецкий алфавит
Немецкий алфавит
В современном немецком алфавите 26 букв. Также используются 3 умляута и 1 лигатура.
100%
Немецкий алфавит с названием букв на русском языке.
A aа B bбэ C cцэ D dдэ E eэ F fэф G gгэ H hха I iи J jйот K kка L lэль M mэм N nэн O oо P pпе Q qку R rэр S sэс T tте U uу V vфау W wве X xикс Y yипсилон Z zцэт Ä äэ Ö öмягкий о Ü üмягкий у ß ßэс
Скачать и распечатать алфавит
Картинка: png, 724×908 px, 48 Кб
Печатать Скачать
В немецком языке для изменения слов (морфологии) используются
3 умляута: Ää, Öö, Üü
1 лигатура: ß (эсцет).
Произношение: ä как русская э, ö как русская ё, ü как русская ю, ß как русская длинная с.
Лигатура образована сочетанием букв s+z, на письме часто используется запись ss (удвоенная s). Нет немецких слов, начинающихся с лигатуры. Долгое время лигатура имела строчное написание, с 2017 года официально получила заглавную запись.
Немецкий алфавит с нумерацией: буквы в прямом и обратном порядке с указанием позиции.
- A
1
26 - B
2
25 - C
3
24 - D
4
23 - E
5
22 - F
6
21 - G
7
20 - H
8
19 - I
9
18 - J
10
17 - K
11
16 - L
12
15 - M
13
14 - N
14
13 - O
15
12 - P
16
11 - Q
17
10 - R
18
9 - S
19
8 - T
20
7 - U
21
6 - V
22
5 - W
23
4 - X
24
3 - Y
25
2 - Z
26
1 - Ä
27 - Ö
28 - Ü
29 - ß
30
В немецком алфавите
6 букв, означающих гласные звуки: a, e, i, o, u, y;
20 букв, означающих согласные звуки: b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, l, m, n, p, q, r, s, t, v, w, x, z.
Умляуты образуют гласные звуки, лигатура — согласный.
Частотность немецких букв (про частотность букв подробно написано на главной странице сайта). В немецком языке
часто используемые буквы (более 6%): e, i, a;
редко используемые буквы (менее 1%): q, x, j, v + умляуты и лигатура.
| № | Буква | Транскрипция | Название | Звук | Частотность |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 — 26 | A a | [aː] | а | гласная | 6,01% |
| 2 — 25 | B b | [beː] | бэ | согласная | 2,15% |
| 3 — 24 | C c | [tseː] | цэ | согласная | 2,69% |
| 4 — 23 | D d | [deː] | дэ | согласная | 4,72% |
| 5 — 22 | E e | [eː] | э | гласная | 16,01% |
| 6 — 21 | F f | [ɛf] | эф | согласная | 1,83% |
| 7 — 20 | G g | [geː] | гэ | согласная | 3,06% |
| 8 — 19 | H h | [haː] | ха | согласная | 4,25% |
| 9 — 18 | I i | [iː] | и | гласная | 7,75% |
| 10 — 17 | J j | [jɔt] | йот | согласная | 0,30% |
| 11 — 16 | K k | [kaː] | ка | согласная | 1,54% |
| 12 — 15 | L l | [ɛl] | эль | согласная | 3,79% |
| 13 — 14 | M m | [ɛm] | эм | согласная | 2,80% |
| 14 — 13 | N n | [ɛn] | эн | согласная | 9,66% |
| 15 — 12 | O o | [oː] | о | гласная | 2,68% |
| 16 — 11 | P p | [peː] | пе | согласная | 1,05% |
| 17 — 10 | Q q | [kuː] | ку | согласная | 0,03% |
| 18 — 9 | R r | [ɛr] | эр | согласная | 7,74% |
| 19 — 8 | S s | [ɛs] | эс | согласная | 6,34% |
| 20 — 7 | T t | [teː] | те | согласная | 6,37% |
| 21 — 6 | U u | [uː] | у | гласная | 3,82% |
| 22 — 5 | V v | [faʊ] | фау | согласная | 0,92% |
| 23 — 4 | W w | [veː] | ве | согласная | 1,43% |
| 24 — 3 | X x | [iks] | икс | согласная | 0,05% |
| 25 — 2 | Y y | [‘ʏpsilɔn] | ипсилон | согласная | 0,11% |
| 26 — 1 | Z z | [t͡sɛt] | цэт | согласная | 1,24% |
| 27 | Ä ä | [ɛː] | э | гласная | 0,55% |
| 28 | Ö ö | [øː] | мягкий о | гласная | 0,27% |
| 29 | Ü ü | [yː] | мягкий у | гласная | 0,68% |
| 30 | ß ß | [ɛs’t͡sɛt] | эс | согласная | 0,17% |
Карта сайта
2015—2023 alphabetonline.ru — про алфавит от А до Я, от A до Z, от Альфы до Омеги
Содержание
- Зачем нужно знать алфавит немецкого языка?
- Становление алфавита и его специфические компоненты
- Буквы немецкого алфавита с произношением
- Немецкий алфавит смотреть видео
- Буквы образующие характерные буквосочетания
- Правила чтения и произношения
- Произношение немецких гласных
- Произношение немецких согласных
- Слова для тренировки произношения
- Важные моменты в произношении немецких букв
- Особенности ударения
- Сколько букв в немецком алфавите?
- Сколько гласных в немецком?
- Сколько согласных в немецком?
- Немецкий алфовит для детей
- Видео
- Плакаты
- История немецкой орфографии
- Средний возраст
- Ранний современный период
- 19 век и начало 20 века
- Реформа немецкой орфографии 1996 г.
- Немецкий телефонный алфавит
- Как запомнить алфавит
Зачем нужно знать алфавит немецкого языка?
Многие начинают изучать иностранные языки с алфавита, но мало кто понимает, для чего нужно знать алфавит. В такой ситуации всегда привожу простой пример:
если не знаешь, как объяснить написание (произношение) своего имени или фамилии, произнеси по буквам.
Вот для этого и нужно знать алфавит. А если вы собрались оформлять на немецком какие-либо документы, то тем более нужно уметь произнести свои персональные данные по буквам, чтобы служащий убедился, что при заполнении бланков нигде не допустил ошибку.
Но это просто, чтобы вы понимали, что в иностранном языке не бывает мелочей. Учиться всегда нужно ответственно
Становление алфавита и его специфические компоненты
Латинский алфавит, на котором базируется немецкий, изначально состоял из 21 буквы.
В первом варианте недоставало G, J, U, Y, W. Их роль делегировалась другим буквам, например, «C» использовалась для обозначения звуков [k] и [g], а «I» включала себя как звук [i], так и [j].
ФАКТ: Со временем развития языков и алфавита, стало понятно, что путаница среди народов, заимствовавших латынь, объясняется недостатком некоторых звуков. Поэтому постепенно количество букв увеличивалось.
Кроме этого, латинский алфавит включил в свой состав греческие буквы «Z» и «Y» для того, чтобы свободно записывать заимствованные слова.
Отдельным достижением группы германских языков стала буква «W», включенная в алфавит в XVI веке. Долгое время народам приходилось использовать сочетание двух «V» (диграф) для того, чтобы более точно передать нужный звук.
Несмотря на все корректировки, случившиеся в латинском алфавите, германские, романские, славянские и финно-угорские языки, которые перенимали латынь для своей письменности, всё равно вынуждены были вносить в неё дополнительные правки.
Такие как:
диграфы или буквенные сочетания для обозначения специфических звуков
«th» — в английском,
«sch» — в немецком или
«cz» — в польском, или например,
диакритические знаки, которые очень употребительны во французском языке (é, è, ê, î, û, ë, ç), они регулируют произношение звуков в зависимости от знака, записанного вместе с буквой
умляуты и лигатуры (ß)
Буквы немецкого алфавита с произношением
| Буква немецкого алфавита | Традиционная транскрипция | Русский вариант произнесения | Примеры слов с данной буквой |
| A a | [a:] | [а] | amtlich – служебный, должностной |
| B b | [bε:] | [бэ] | belgisch – бельгийский |
| C c | [tsε:] | [цэ] | chronisch — хронический |
| D d | [de:] | [дэ] | dauerhaft – длительный, продолжительный |
| E e | [e:] | [э] | ehrlich – откровенный, честный |
| F f | [εf] | [эф] | futuristisch — футуристический |
| G g | [ge] | [гэ] | gänzlich – всецелый, совершенный |
| H h | [ha:] | [ха]
(звук [х] похож на очень легкий выдох) |
häufig – частый, многочисленный |
| I i | [i:] | [и] | innerlich — внутренний |
| J j | [jot] | [йот] | jetzig – нынешний, теперешний |
| K k | [ka:] | [ка] | kräftig – сильный, большой, крепкий |
| L l | [εl] | [эл] | lächerlich – забавный, смехотворный |
| M m | [εm] | [эм] | mißtrauisch — подозрительный |
| N n | [εn] | [эн] | neutral – нейтральный |
| O o | [o:] | [о] | orientalisch — восточный |
| P p | [pe:] | [пэ] | polnisch — польский |
| Q q | [ku:] | [ку] | quellend — пробивающийся (об источнике) |
| R r | [εr] | [эр] | regnerisch — дождливый |
| S s | [εs] | [эс] | smoken — собирать, присборивать |
| T t | [te:] | [тэ] | tüchtig – умелый, дельный |
| U u | [u:] | [у] | ursprünglich – исходный, изначальный |
| V v | [fao] | [фау] | verträglich – переносимый, сносный |
| W w | [ve:] | [вэ] | wahnsinnig – помешанный, безумный |
| X x | [iks] | [икс] | Xenon-Scheinwerfer – ксеноновые фары |
| Y y | [ypsilon] | [ипсилон] | dynamisch — динамичный |
| Z z | [tsεt] | [цэт[ | zynisch — циничный |
| Дополнительные немецкие буквы к латинскому алфавиту, лежащему в основе немецкого языка: | |||
| Ä ä | [ε] | а-умлаут:
[э] |
ärgerlich — досадный, раздражающий |
| Ö ö | [ø] | о-умлаут:
как «ё» в слове «Лёня» |
örtlich — местный |
| Ü ü | [y] | у-умлаут:
как «ю»в слове «Люся» |
überflüssig — излишний |
| ß | [s] | эсцет:
как звук [с] |
das Geschoß – ярус, этаж |
Таким образом, в данной таблице были рассмотрены все существующие буквы немецкого алфавита, включая четыре дополнительные.
Далее, буквы могут образовывать в словах разные буквосочетания, которые подчиняются определенным правилам прочтения. Попробуем представить их также в виде наглядной таблицы.
Немецкий алфавит смотреть видео
Буквы образующие характерные буквосочетания
| Сочетание букв | Особенности звука | Транскр. | Русское прочтение |
Примеры слов |
| ai | сочетание двух гласных | [ae] | [ай] | der Main [maen]– Майн (река) |
| ah | долгий гласный низкий звук | [a:] | [а:] | der Hahn [ha:n] – кран; петух |
| с | перед e, ö, i, y, ü одна согласная буква дает звук-аффрикату | [ts] | [ц] | das Cyklon [tsyklo:n] — циклон |
| c | в словах, заимствованных из других языков, чаще в начале слова | [k] | [к] | die Couch [kaotʃ] — кушетка |
| ch | при постановке после гласных u, o, a; место образования звука значительно ниже в гортани, чем у русского [x] | [x] | [x] | die Buche [bu:xә] — бук |
| ch | иногда в начале слова; сочетание двух согласных букв дает один взрывной глухой согласный звук | [k] | [к] | das Chlor [klo:α] — хлор |
| сh | после ä, i, ö, e, y, ü, а также после m, r, l, n сочетание двух согласных букв дает один глухой щелевой согласный звук, похожий на звук [х] в слове «хитрый» | [ç] | [х] | die Bücher [byçәα] – книгиdie Mönche [mønçә] — монахи |
| ch | в заимствованных словах | [tʃ] | [ч] | die Couch [kaotʃ] – диван, кушетка |
| chs | в качестве неделимого сочетания букв в рамках одного слога | [ks] | [кс] | der Lachs [laks] – сёмга, лосось |
| сk | сочетание двух согласных букв дает один глухой взрывной согласный звук | [k] | [к] | der Zucker [tsukәα] — сахар |
| е | краткий гласный звук в закрытом слоге | [ε] | [э] | hell [hεl] — светлый |
| eh | долгий гласный звук | [e:] | [э:] | das Mehl [me:l] — мука |
| ei | дифтонг | [ae] | [ай] | leise [laezә] — тихо |
| ie | дифтонг | [i:] | [и:] | die Wiege [vi:gә] — колыбель |
| eu | дифтонг | [oe] | [ой] | die Leute [loetә] — люди |
| oh | долгий гласный средний (подъем) | [o:] | [o:] | der Lohn [lo:n] – зарплата |
| oi, oy | [oе] | [ой] | der Boykott [boekot] бойкот | |
| j | согласный звонкий щелевой звук | [j] | [й] | jawohl [javo:l] – есть, так точно |
| l | сонорный звонкий согласный, представляющий собой что-то вроде перехода от русского мягкого [л`] к русскому твердому [л] в рамках одного звука | [l] | [л`]®[л] | leer [le:α] — пустой |
| ng | это буквосочетание передает звонкий сонорный носовой звук, отсутствующий в русском языке | [ŋ] | носовой («в нос») [н] |
singen [ziŋәn] — петь |
| nk | это буквосочетание передает два звука: звонкий сонорный носовой звук, которого нет в русском + глухой аспирированный | [ŋk] | носовой + спирант [нк] |
sinken [ziŋkәn] – падать, погружаться, уменьшаться |
| ph | сочетание двух согласных букв дает один согласный щелевой звук | [f] | [ф] | die Physik [fy:zik] физика |
| qu | сочетание согласной и гласной буквы дает сочетание двух согласных звуков | [kv] | [кв] | der Quark [kvark] – творог |
| rh | сочетание в начале слова двух согласных букв дает один согласный звук | [r] | [р] | der Rhytmus [rytmәs] – частота, ритм |
| s | щелевой звонкий согласный звук, если стоит впереди гласного или между двумя гласными | [z] | [з] | der Käse [kε:sә] – сырsüchtig – охваченный какой-либо страстью |
| sp, st | s передает щелевой глухой согласный звук в начале слова/части сложносоставного слова, если за ним стоят p или t | [ʃ] | [ш] | der Specht [ʃpәçt] – дятелdas Statut [ʃtatu:t] — устав |
| sch | три согласных буквы дают щелевой глухой согласный | [ʃ] | [ш] | schon [ʃon] – уже |
| s | в прочих случаях, кроме трех перечисленных выше | [s] | [c] | der Poster [postәα] – плакат, постер |
| th | две согласных буквы дают один смычный глухой согласный звук | [t] | [т] | die Theorie [tεori:] – теория |
| tsch | четыре согласных буквы дают одну аффрикату | [tʃ] | [ч] | der Deutsche [doetʃә] – немец |
| uh | сочетание гласной и согласной буквы дает долгий гласный звук | [u:] | [у:] | der Uhu [u:hu] – филин |
| ui | сочетание букв | [ui] | [уи] | die Ruine [rui:nә] – развалины, руины |
| v | в иностранных заимствованиях звонкий лабиально-дентальный согласный звук | [v] | [в] | die Variante [variantә] — вариант |
| v | в прочих случаях лабиально-дентальный глухой согласный звук | [f] | [ф] | die Vögel [fø:gәl] – птицы |
| w | звонкий лабиально-дентальный согласный звук | [v] | [в] | wellig [vεliç] – волнистый |
| х | одна согласная буква дает аффрикату | [ks] | [кс] | der Lurex [lu:rεks] – люрекс |
| y | типично немецкий звук, нечто среднее между ю и у, типа «ю» в слове «люк», может быть долгим и кратким | [y] | [ю-у] | rhytmisch [rytmiʃ] – ритмическийpsychisch [psyçiʃ] — психический |
| z | одна согласная буква дает аффрикату | [ts] | [ц] | die Zerbe [tsεαbә] – кедр |
| äu | [oe] | [ой] | die Säule [zoelә] – колонна | |
| schtsch | такого звука в немецком нет, это сочетание букв используется для передачи звука [щ] в иностранных словах | [ʃtʃ] | [щ] | der Borschtsch [borʃtʃ] – борщ (суп) |
| sh | такого звука в немецком также нет, сочетание букв передает [ж] в иностранных словах | [ʒ] | [ж] | Shukow [ʒukof] – Жуков (фамилия) |
| ß = ss | передает один щелевой согласный глухой звук; ß может либо заменяться на ss, либо пишется ß только после букв, передающих долгие гласные или дифтонги | [s] | [с] | lassen [lasәn] — оставить, покинутьbeißen [baesәn] — кусать |
Из приведенной таблицы буквосочетаний и букв немецкого алфавита видно, что существуют отдельные звуки, которые передаются двумя, тремя и более буквами.
В то же время одна буква при прочтении может давать два звука (аффрикату), при этом некоторые буквы могут обозначать различные звуки в зависимости от их положения в слове и соседствующих букв.
Правила чтения и произношения
Понятно, что, как и в любом другом европейском языке, будь то английский, французский или, скажем, польский, у немцев есть строго определённые правила прочтения и произношения буквенных сочетаний и отдельных слогов, проще говоря, своя фонетика.
В немецком языке насчитывается свыше четырёх десятков звуков, из них 16 – гласных, три дифтонга, 22 согласных и три аффрикаты.
Произношение немецких гласных
У немцев существует чёткое разделение на гласные переднего и заднего рядов – по положению языка произносящего. Эти гласные могут быть как долгими, так и краткими, при этом восемь букв дают 16 звуков.
Слоги делятся на открытые и закрытые. Дифтонгом же именуют слитное произношение пары гласных в одном слоге (ei, ey, ai, ay – русское «ай» и т.д.).
- а, аа, ah – аналог долгого «а» в существительном «брат» или краткого «а» в существительном «такт»;
- ä, äh– аналог «э» в существительном «эра», открытый долгий;
- i, ie, ih– аналог «и» в существительном «синий», закрытый долгий.

А для более подробного ознакомления с особенностями произношения гласных настоящим настоятельно рекомендуется обратиться к справочной литературе и самоучителям.
Произношение немецких согласных
Из вышеприведённой таблицы видно, что ряд немецких согласных имеет одинаковое произношение с их прямыми аналогами в русском. Например,
- обозначающийся литерой h (именно в начале целого слова или отдельного слога) звук произносится на выдохе: Haus «хаус».

И здесь опять-таки следует помнить, что данный материал ни в коем случае не является и не может служить учебным пособием и что для уточнения правописания и произношения немецких согласных следует обратиться к соответствующим справочным пособиям.
Слова для тренировки произношения
- leute – люди;
- radieschen – редис;
- reise – путешествие;
- strand – пляж;
- volk – народ.
- wein – вино;
- zeit – время;
- zwieback – сухарик;
Важные моменты в произношении немецких букв
Следует понимать, что в немецком языке некоторые буквы имеют свои особенности произношения. Так, немецкая R, «эр», в начале слова будет грассирующим, «картавым», а может также быть переднеязычным, раскатистым – многое зависит от дикции произносящего; в середине слова она имеет уже тенденцию к исчезновению, но всё ещё различима на слух; в конце же слова она и вовсе «съезжает» на звук, очень близкий к гласной «а» – почти такой, как её произносят в английском.
Особенности ударения
В русском языке ударение «плавает», а у немцев оно фиксированное и попадает на первый слог слова, намного реже на его корень. При этом изменение формы слова никоим образом не влияет на место ударения.
Сколько букв в немецком алфавите?
На самом деле количество букв в немецком алфавите зависит от того, с какой стороны смотреть на вопрос. Помимо 26 стандартных букв (от A до Z), немецкий содержит также 4 особых: умлауты (Ü, Ä, Ö) и эсцет (ẞ). Строго категоризировать эти символы по историческим причинам оказалась трудно. Да и как не поспорить на эту тему, когда не все немецкоязычные страны используют полный набор особых знаков? Поэтому количество букв в немецком алфавите разное:
- 26 – общепринятый стандарт (без учёта особых букв);
- 27 – с учётом эсцет, без учёта умлаутов;
- 29 – с учётом умлаутов, без учета эсцет (актуально для Швейцарии и Лихтенштейна, где не используется ẞ);
- 30 – с учётом всех особых символов.
Сколько гласных в немецком?
Задавая вопрос «сколько гласных в…» мы, обычно, имеем в виду буквы. Но каждая буква может произноситься по-разному — например, долго или коротко, — и вот мы уже говорим о гласных звуках.
В немецком алфавите всего 8 гласных букв: A, E, I, O, U и умлауты Ä, Ö, Ü. Гласных звуков, образованных за счет произношения, значительно больше – 23. К ним также можно добавить 4 дифтонга (сочетания двух гласных звуков). Таким образом, гласных звуков в немецком – всего 27.
Сколько согласных в немецком?
Также, как и в случае с гласными, в немецком языке есть согласные буквы и согласные звуки. «Спаренные» согласные образуют не дифтонги, а фрикативы.
Всего в немецком языке 21 согласная буква и 23 согласных звука. С учётом 5 фрикативов согласных звуков в немецком становится 28.
ПоискSearchSearching is in progressСвежие записи
- Миндаль в сахаре: рецепт
- Глинтвейн (Glühwein): немецкий рецепт
- Немецкое печенье (Plätzchen)
- Как сделать повелительное наклонение более мягким?
- Wir: четвёртая форма повелительного наклонения
- Повелительное наклонение в немецком языке: таблица-шпаргалка
- Повелительное наклонение в немецком: sein, haben, werden
- Предложения в повелительном наклонении на немецком
- Повелительное наклонение в немецком: упражнения
- Повелительное наклонение (Imperativ) в немецком языке
- Времена года на немецком
- Запятая перед als и wie в немецком
- Wie или als в немецком
- Онлайн-тест «Wie или als»
- Дата в тетради, классная и домашняя работа на немецком языке
Немецкий алфовит для детей
Видео
Плакаты
История немецкой орфографии
Средний возраст
Самые старые известные немецкие тексты относятся к 8 веку. Они были написаны в основном в монастырях на различных местных диалектах древневерхненемецкого языка . В этих текстах буква z вместе с комбинациями, такими как tz , cz , zz , sz или zs, была выбрана для расшифровки звуков / ts / и / s (ː) / , что в конечном итоге является источником современных немецких букв z , tz и ß (старый sz — лигатура ). Однако после Каролингского Возрождения , во время правления династий Оттонов и Салиан в 10-м и 11-м веках, на немецком языке писали редко, а литературный язык был почти исключительно латинским .
Немец Ноткер — заметное исключение для своего периода: не только его немецкие композиции имеют высокую стилистическую ценность, но и его орфография также является первой, следовавшей строго согласованной системе.
Значительное производство немецких текстов возобновилось только во время правления династии Гогенштауфенов (в средние века ). Примерно в 1200 году, была тенденция к стандартизированному средневерхненемецкому языку и правописания в первый раз, на основе франконского — Швабском языке суда Гогенштауфенов. Однако этот язык использовался только в эпической поэзии и лирике миннесанга рыцарской культуры. Эти ранние тенденции стандартизации прекратились в период междуцарствия после смерти последнего короля Гогенштауфенов в 1254 году. Некоторые особенности современной немецкой орфографии все еще восходят к средневерхненемецкому: использование триграфа sch для / ʃ / и случайное использование v for / f /, потому что примерно в 12-м и 13-м веках прозвучало предокалическое / f / .
В последующих веках, единственный сорт , который показал отчетливую тенденцию быть использован в разных регионах был Средняя Нижненемецкая из Ганзы , на основе различного Любека и используются во многих областях северной Германии и в самом деле Северной Европе в целом.
Ранний современный период
К XVI веку на основе восточно-центральногерманских и австро-баварских сортов был разработан новый межрегиональный стандарт . На это повлияло несколько факторов:
- При династии Габсбургов в канцелярии была сильная тенденция к общему языку .
- Поскольку Восточная Центральная Германия была колонизирована только в период Высокого и Позднего Средневековья в ходе Ostsiedlung людьми из разных регионов Германии, разговорные разновидности были компромиссом разных диалектов.
- Восточная часть Центральной Германии была очень важной в культурном отношении, поскольку здесь находились университеты Эрфурта и Лейпцига и особенно с переводом Библии Лютера , который считался образцом для подражания.
- Изобретение книгопечатания привело к увеличению выпуска книг, и полиграфисты были заинтересованы в использовании общего языка для продажи своих книг на как можно более широкой территории.
Контрреформация середины 16 века вернула католицизм в Австрию и Баварию, что вызвало отказ от лютеранского языка. Вместо этого использовался особый южный межрегиональный язык, основанный на языке канцелярии Габсбургов.
В северной Германии лютеранский восточно-центральный немецкий язык заменил нижненемецкий письменный язык до середины 17 века. В начале 18 века лютеранский стандарт был также введен в южных штатах и странах, Австрии, Баварии и Швейцарии, из-за влияния северных немецких писателей, грамматиков, таких как Иоганн Кристоф Готчед, или обществ по культивированию языков, таких как Общество плодоносящих .
19 век и начало 20 века
Хотя к середине 18 века в целом была установлена одна норма, институциональной стандартизации не существовало. Только с введением обязательного образования в конце 18 — начале 19 века орфография была стандартизирована, хотя сначала независимо в каждом штате из-за политической раздробленности Германии. Только основание Германской империи в 1871 году позволило провести дальнейшую стандартизацию.
В 1876 году прусское правительство учредило Первую Орфографическую конференцию [ де ] для достижения стандартизации для всей Германской империи. Однако его результаты были отклонены, в частности, премьер-министром Пруссии Отто фон Бисмарком .
В 1880 году директор гимназии Конрад Дуден опубликовал Vollständiges Orthographisches Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache («Полный орфографический словарь немецкого языка»), известный просто как « Дуден ». В том же году Дуден был провозглашен авторитетом в Пруссии. Поскольку Пруссия была самым большим государством в Германской империи, ее правила также повлияли на правописание в других местах, например, в 1894 году, когда Швейцария признала Дюден.
В 1901 году министр внутренних дел Германской империи учредил Вторую орфографическую конференцию . Он объявил Duden авторитетным с некоторыми нововведениями. В 1902 году его результаты были одобрены правительствами Германской империи, Австрии и Швейцарии.
В 1944 году правительство нацистской Германии планировало реформу орфографии , но из-за Второй мировой войны она так и не была реализована.
После 1902 года правописание немецкого языка было фактически де-факто решено редакторами словарей Дудена. После Второй мировой войны этой традиции последовали два разных центра: Мангейм в Западной Германии и Лейпциг в Восточной Германии . К началу 1950-х годов несколько других издательств начали атаковать монополию Дудена на Западе, выпуская собственные словари, которые не всегда соответствовали «официальному» написанию, предписанному Дуденом. В ответ министры культуры федеральных земель Западной Германии официально объявили, что с ноября 1955 года написание Дудена является обязательным.
Редакторы Duden осторожно использовали свои возможности, потому что считали своей основной задачей документирование использования, а не создание правил. В то же время, однако, они оказались вынуждены проводить все более тонкие различия при выработке немецких правил орфографии, и каждый новый тираж вводил несколько исправленных орфографий.
Реформа немецкой орфографии 1996 г.
Основная статья: реформа немецкой орфографии 1996 г.
Орфография и пунктуация немецкого языка были изменены в 1996 году ( Reform der deutschen Rechtschreibung von 1996 ) с целью упростить немецкую орфографию и, таким образом, облегчить изучение языка без существенного изменения правил, знакомых пользователям языка. Правила нового правописания касаются соответствия между звуками и написанными буквами (включая правила написания заимствованных слов ), использования заглавных букв, соединенных и отдельных слов, написания с переносом, пунктуации и расстановки переносов в конце строки. Географические названия и фамилии были исключены из реформы.
Первоначально реформа была принята Германией, Австрией, Лихтенштейном и Швейцарией, а затем и Люксембургом.
Новая орфография обязательна только в школах. Решение Федерального конституционного суда Германии от 1998 года подтвердило, что не существует закона о правописании, которое люди используют в повседневной жизни, поэтому они могут использовать старое или новое правописание. Хотя реформа не пользуется большой популярностью в опросах общественного мнения, ее приняли все основные словари и большинство издательств.
Немецкий телефонный алфавит
Немецкий телефо́нный алфави́т (нем. Diktierregeln) — фонетический алфавит, появившийся в 1903 году и используемый для произнесения «по буквам» слов немецкого языка при разговоре по телефону или по любительской радиосвязи. Интересно отметить наличие отдельного кода для лигатуры ß и диграфа ch [4] .
- Sch — Schule.
- Ch — Charlotte.
В мореплавании используется немецкая версия. Тем не менее, в настоящее время в авиации и военном деле используется международная версия фонетического алфавита, а не немецкая.
Как запомнить алфавит
Если говорить откровенно, то прямой практической надобности в заучивании алфавита нет. Другое дело, что запомнив в развлекательной форме буквы, вы быстрее научитесь читать, потому что у вас в голове отложится гармония того, как буква выглядит, и как она произносится. Именно с этой целью мы предлагаем вам один из множества вариантов стишка-запоминалки.
ABCDE und F, wenn ich Teddybären treff,
GHIJK und L, schmuse ich mit Ihnen schnell.
MNOPQ und R, Teddybären lieb ich sehr,
STUVW und X, Teddybär schlaf ein ganz fix,
YZ mit mir in meinem Bett.
Вы можете составить для себе подобный стих сами, например, подряд написать слова на каждую букву и выучить уже текстом, или, возможно, вы придумаете песенку: многим ученикам алфавит легче дается под знакомую мелодию. А вот различные тонкости звучания дифтонгов и сочетаний согласных вы сможете выучить только в процессе чтения.
Источники:
- https://uesk.org/stati/chto-takoe-elektrodvigatel/
- http://TokIdet.ru/elektrooborudovanie/elektrodvigateli/princip-raboty.html
- https://inznan.ru/elektronika/kak-rabotaet-elektrodvigatel/
- https://amperof.ru/teoriya/princip-raboty-elektrodvigatelya.html
- https://uesk.org/stati/ustrojstvo-elektrodvigatelya/
- https://engineering-solutions.ru/motorcontrol/motor/
- https://eti.su/articles/elektricheskie-mashini/elektricheskie-mashini_1569.html
- https://uk-parkovaya.ru/smarthouse/equipment/beskollektornyj-dvigatel-postoannogo-toka-princip-raboty-ustrojstvo-vidy.html
- https://deutschpro.ru/novichkam/alfavit/nemetskij-alfavit-po-poryadku-dlya-detej.html
На чтение 7 мин. Просмотров 11.6k. Опубликовано 01.08.2020
Немецкий язык является, пожалуй, третьим по популярности для изучения его иностранцами после английского и французского. Ниже авторы публикуемого материала постарались дать самые общие представления о том, что такое современный немецкий язык и почему стоит задаться целью его изучить.
Сразу же оговоримся, данный материал ни в коей мере не является учебным пособием.
Содержание
- Немецкий алфавит
- Правила чтения и произношения
- Произношение немецких гласных
- Произношение немецких согласных
- Буквосочетания в гласных и согласных
- Произношение необычных символов
- Особенности ударения
- Слова для тренировки произношения
- Важные моменты в произношении немецких букв
- Почему стоит изучать немецкий язык
Немецкий алфавит
Алфавит на основе латиницы, состоящий из 26 пар букв, плюс к тому три также парных умляута или умлаута, кому как больше нравится (Ä ä – «а умлаут», Ö ö – «о умлаут», Ü ü – «у умлаут»), и, слава Богу, одна-единственная лигатура ß (то бишь эсцет, иначе «длинная» или сдвоенная S, она же «S острая») – главные «фишки» письменного языка (определённой части) населения вышеперечисленных стран.
Поговаривают, что вышеупомянутая эсцет досталась древним германцам от небезызвестных готов, а из-за постоянной путаницы ею вызываемой в 1996 году в самой Германии было принято решение заменить её на сдвоенную S, а в Швейцарии аналогичная замена имела место ещё в начале XX века. Причём такая замена оказалась, мягко говоря, не очень корректной: согласитесь, Masse и Maße то есть русские «масса» и «размеры» — это не совсем одно и то же, и даже совсем не одно и то же.
В итоге немцы, едва опомнившись, быстренько «включили заднюю» и решили всё-таки сохранить проблемную эсцет для дифтонгов и долгих гласных.
Итак, собственно современный немецкий алфавит:
| Немецкий алфавит | |||||
| A a – а | Ä ä – а умляут | B b – бэ | C c – цэ | D d – дэ | E e – э |
| F f – эф | G g – гэ | H h – ха | I i – и | J j – йот | K k – ка |
| L l – эль | M m – эм | N n – эн | O o – о | Ö ö – о умляут | P p – пэ |
| Q q –ку | R r – эр | S s –эс | ẞ ß – эсцет | T t – тэ | U u – у |
| Ü ü – у умляут | V v – фау | W w – вэ | X x – икс | Y y –ипсилон | Z z – цэт |
В настоящее время параллельно существует так называемый немецкий телефонный алфавит – фонетический, появившийся ещё в начале минувшего столетия для облегчения произнесения слов «по буквам», как это принято, например, в русском языке, во время сеансов любительской радиосвязи или просто при диктовке по телефону.
Правила чтения и произношения
Понятно, что, как и в любом другом европейском языке, будь то английский, французский или, скажем, польский, у немцев есть строго определённые правила прочтения и произношения буквенных сочетаний и отдельных слогов, проще говоря, своя фонетика.
В немецком языке насчитывается свыше четырёх десятков звуков, из них 16 – гласных, три дифтонга, 22 согласных и три аффрикаты.
Произношение немецких гласных
У немцев существует чёткое разделение на гласные переднего и заднего рядов – по положению языка произносящего. Эти гласные могут быть как долгими, так и краткими, при этом восемь букв дают 16 звуков.
Слоги делятся на открытые и закрытые. Дифтонгом же именуют слитное произношение пары гласных в одном слоге (ei, ey, ai, ay – русское «ай» и т.д.).
- а, аа, ah – аналог долгого «а» в существительном «брат» или краткого «а» в существительном «такт»;
- ä, äh– аналог «э» в существительном «эра», открытый долгий;
- i, ie, ih– аналог «и» в существительном «синий», закрытый долгий.
А для более подробного ознакомления с особенностями произношения гласных настоящим настоятельно рекомендуется обратиться к справочной литературе и самоучителям.
Произношение немецких согласных
Из вышеприведённой таблицы видно, что ряд немецких согласных имеет одинаковое произношение с их прямыми аналогами в русском. Например,
- обозначающийся литерой h (именно в начале целого слова или отдельного слога) звук произносится на выдохе: Haus «хаус».
И здесь опять-таки следует помнить, что данный материал ни в коем случае не является и не может служить учебным пособием и что для уточнения правописания и произношения немецких согласных следует обратиться к соответствующим справочным пособиям.
Буквосочетания в гласных и согласных
Немецкие буквенные сочетания из гласных:
- ei означает «ай»: Reich [Райх] – империя, государство,
- ie означает долгое «и»: Liebe [либэ] – любовь,
- eu означает «ой»: heute [хойтэ] – сегодня,
- äu означает «ой»: Häuser [хойзэр] – домa.
Наиболее часто встречающееся у немцев буквенное сочетание из согласных
- ch (после е, i, ö, ü и после l, m, n) звучит как мягкий хь в слове «химия»: welche вэльхе, richtig рихьтихь, manchmal манхьмаль.
- chsчитается и звучит как «кс»: например, Fuchs [фукс] – лиса,
- qu читается и звучит как «кв»: Quatsch [квач] — чепуха,
и так далее.
Произношение необычных символов
Под «необычными символами» здесь предлагается понимать немецкие умляуты (умлауты) и ту самую проблемную эсцет, «sz».
Так вот, для запоминания.
- Начать с эсцет: она произносится как сдвоенное S, также и пишется при замене на S.
- Произношение ä – а умляута уже обсуждалось выше.
- А ö – о умляут передаёт русский звук «э», например, mädchen – девочка.
- И, наконец, символ ü – у умляут передаёт «ю», müll – мусор.
Особенности ударения
В русском языке ударение «плавает», а у немцев оно фиксированное и попадает на первый слог слова, намного реже на его корень. При этом изменение формы слова никоим образом не влияет на место ударения.
Слова для тренировки произношения
- leute – люди;
- radieschen – редис;
- reise – путешествие;
- strand – пляж;
- volk – народ.
- wein – вино;
- zeit – время;
- zwieback – сухарик;
Важные моменты в произношении немецких букв
Следует понимать, что в немецком языке некоторые буквы имеют свои особенности произношения. Так, немецкая R, «эр», в начале слова будет грассирующим, «картавым», а может также быть переднеязычным, раскатистым – многое зависит от дикции произносящего; в середине слова она имеет уже тенденцию к исчезновению, но всё ещё различима на слух; в конце же слова она и вовсе «съезжает» на звук, очень близкий к гласной «а» – почти такой, как её произносят в английском.
Почему стоит изучать немецкий язык
Ответ на этот вопрос чрезвычайно прост и лежит на поверхности – этот язык один из самых распространённых и популярных в мире, помимо жителей Германии на различных диалектах немецкого говорит, всё или какая-то часть его, население Австрии, Лихтенштейна, Бельгии, Люксембурга, Швейцарии, а число потенциальных собеседников человека, говорящего по-немецки, приближается к 100 млн человек.
У нас в стране немецкий язык также не редкость – на нём в нашей стране могут свободно изъясняться почти 400 тысяч человек, проживающих, в частности, в Европейской части России, на территории бывшей автономии поволжских немцев, а также в Сибири.
В другой части света, в США носителями немецкого языка считаются более 2 млн человек, в Австралии его считают домашним ещё 79 тысяч, хотя в действительности немцев на пятом континенте существенно больше и так далее и тому подобное. Даже в далёкой Намибии он является одним из разговорных языков.
А ещё немецкий язык – один из языков официального делопроизводства ООН, ЕС и других международных организаций.
И вот ещё что, этот европейский язык – третий по распространённости во Всемирной Паутине после английского и русского.
Изучить язык великих Гёте, Шиллера и Канта стоит хотя бы уже потому, что его знание – это самый настоящий «золотой ключик» к личному приобщению к огромному пласту древней немецкой культуры, это самообразование, наконец, и дальнейшее саморазвитие.
С чего начинается изучение иностранного языка? Конечно, с алфавита. Немецкий язык – не исключение. Прежде чем начать разбирать грамматику и запоминать новую лексику, необходимо выучить немецкий алфавит с транскрипцией. Начнем!
Немецкий алфавит
Для составления немецкого алфавита за основу были взяты латинские символы. На сегодняшний день в немецком языке 26 букв. Также есть 3 умлаута (буквы с двумя точками) и 1 довольно необычный знак — ß — лигатура. Эти символы не включены в официальный алфавит, но, тем не менее, они часто встречаются в текстах. И очень важно замечать их, так как они меняют произношение и значение слова.
Отметим, что правила чтения немецких слов довольны просты. Но, все же, для начала необходимо посмотреть, какой звук дает каждая буква. Также, помимо изучения всех букв, необходимо будет запомнить правила ударения для правильного чтения немецких слов. К слову, на первые слоги обычно падает ударение, но также есть некоторые безударные приставки и исключения, о которых всегда нужно помнит.
Немецкий алфавит с транскрипцией в виде таблицы
| Немецкая буква | Транскрипция | Произношение | Пример |
| A a | [a] | а | das Alter — возраст |
| B b | [bε:] | бэ | brauchen — нуждаться |
| С с | [tseː] | цэ | der Character — характер |
| D d | [deː] | дэ | der Dill — укроп |
| E e | [eː] | э | ehrlich — честный, порядочный |
| F f | [ɛf] | эф | fein — тонкий |
| G g | [geː] | ге | die Gruppe — группа |
| H h | [haː] | ха | der Haushalt — домашнее хозяйство |
| I i | [iː] | и | die Idee — идея, мысль |
| J j | [jɔt] | йот | jagen – охотиться |
| K k | [kaː] | ка | der Kamm — расческа |
| L l | [ɛl] | эль | das Leben — жизнь |
| M m | [ɛm] | эм | das Messer — нож |
| N n | [ɛn] | эн | der Nachtisch — десерт |
| O o | [oː] | о | ordnen — приводить в порядок |
| P p | [peː] | пе | die Polizei — полиция |
| Q q | [kuː] | ку | der Quatsch — чушь, чепуха |
| R r | [ɛr] | эр | das Regal — полка, стеллаж |
| S s | [ɛs] | эс | sagen — сказать, говорить |
| T t | [teː] | те | trinken — пить |
| U u | [uː] | у | die Ursache — причина |
| V v | [faʊ] | фау | verkaufen — продавать |
| W w | [veː] | ве | die Wohnung — квартира |
| X x | [iks] | икс | die Xerocopie — ксерокопия |
| Y y | [‘ʏpsilɔn] | ипсилон | der Yoghurt — йогурт |
| Z z | [t͡sɛt] | цэт | die Zitrone — лимон |
Что же касается умлаутов и лигатуры, которые не вошли в официальный немецкий алфавит, они выглядят и произносятся так:
Ä ä — [ɛː] (в русском языке аналог — э). Ähnlich — похожий, подобный.
Ö ö — [øː] (аналога в русском языке этой букве нет). Наиболее приближенной считается буква ё, если при её произношении язык поднять вверх, к небу, и получится что-то среднее между о и ё. Das Öl — масло.
Ü ü — [yː] (Это мягкий звук [у]). Если проводить аналогию с русским языком, его можно приравнять к букве ю). Übrigens — впрочем, вообще.
ß- [ɛs’t͡sɛt]. (В русском языке этот звук схож с [эс]). Groß — большой, крупный.
Все перечисленные буквы дают 42 звука. После того как вы выучите весь немецкий алфавит с транскрипцией, необходимо будет также запомнить, как произносятся некоторые сочетания букв, а именно:
ch — звук х
sch — щ
shs — следует произносить как кс
ck — к
tsch — ч
qu — кв
sp или st в начале слова — произносится как шп или шт (соответственно)
суффикс — tion при чтении имеет что-то среднее между цион и цьон
Также необходимо обратить внимание, что буквы k, p, t произносятся с некоторым придыханием. Гласные буквы и звуки никогда не смягчаются (если это не умлауты).
Немецкий алфавит: песни для детей
Немецкий алфавит: история появления
В древние времена немецкие племена использовали руны для написания текстов. Однако уже в эпоху феодализма такого рода письменность становилась все больше не актуальной, ведь общаться на языке, основу которого составляли символы, отсутствующие в других народах, было практически невозможно. Это привело к тому, что немецкий язык постепенно начал меняться. В VIII веке в его алфавите появились знакомые нам латинские буквы. При этом, изначально он состоял из 21 символа: не было в нем букв j, w, u, g, w. Но звуков, которые дают эти буквы, не хватало для чтения некоторых заимствованных слов, которых все больше и больше появлялось в немецком языке. И, чтобы правильно проговаривать и записывать такие слова, указанные символы были все-таки официально добавлены в немецкий алфавит.
Основные правила и особенности немецкого языка формировались в эпоху Средневековья. А современному немецкому мы во многом обязаны Конраду Дудену. Ученый составил один из самых полных орфографических словарей, который вышел в 1880 году. В целом, немецкий алфавит от своего начала до современного вида прошел довольно долгий путь, поддавался некоторым изменениям и усовершенствованиям. В результате у нас есть 26 букв + 3 умлаута + 1 эсцет. Большинство букв в немецком языке имеют знакомые русские аналоги, поэтому их очень легко запомнить ученикам и студентам.
Заключение
В этой статье мы детально разобрали немецкий алфавит с транскрипцией, который просто необходим для изучения иностранного языка. Данный материал является первым шагом во всей системе обучения. Надеемся, что этот шаг был несложным и очень полезным для вас.
Не забудьте оценить наши старания. Комментарии приветствуются! По желанию подписывайтесь на нас в Яндекс.Дзен и в других социальных сетях!!!)))
Что нужно знать о немецком алфавите?
Немецкий алфавит (das deutsche Alphabet) состоит из 26 латинских букв. Кроме того, он состоит из:
Трех буквы с умлаутом: ä, ö, ü
буква ß (по-немецки Esszett, произносится «эсцет» по-русски)
Немецкий алфавит с транскрипцией:
A a [ a ]
Ä ä [ a-умлаут ]
(a- умлаут читается как немого долгое a, но на практике он больше звучит как “э”)
B b [бэ]
C c [цэ / ка / ш / ч]
D d [дэ]
E e [э]
F f [эфф]
G g [гэ]
H h [ха]
I i [и]
J j [йот]
K k [ка]
L l [эл]
M m [эм]
N n [эн]
O o [о]
Ö ö [ыу]
(о-умлаут — положение языка как при э, а губ — как при о)
P p [пэ]
Q q [ку]
R r [эр]
S s [эс, зэт, ш]
ß (эсцет)
T t [тэ]
U u [у]
Ü ü [у-умлаут]
V v [фау]
W w [вэ]
X x [икс]
Y y [ипсилон]
Z z [цэт]
Произношение: Длинные и короткие немецкие гласные.
На немецком языке всего 5 гласных, но гораздо больше звуков. Например, буква «а» может быть произнесена коротко или длинно.
Звук Произношение
[a] Stadt [Штадт]
[a:] Name/Zahl/Staat [Наме/Цаль/Штат]
[ɐ] der [дер]
[ɛ] sprechen [шпрехен]
[e:] reden/nehmen/Beet [реден/немен/Бет]
[ɪ] mit [мит]
[i:] Kilo/sie/ihr [Кило/зи/ир]
[ɔ] Tochter [Тохтер]
[o:] Ton/Sohn/Boot [Тон/Зон/Бот]
[ʊ] Mutter [Муттер]
[u:] suchen/ Stuhl [Зухен/ Штуль]
ЗАПОМНИ! Этот знак [:] означает, что гласный звук произносим как длинный.
Произношение: двойные гласные.
Дифтонги — это разные комбинации двух гласных. На немецком языке вы найдете следующие гласные:
Дифтонг Произношение
ei/ai Mai/ Brei [Май/ Брай]
au Frau [Фрау]
eu/äu Freund/ Leute/ Bäume [Фройнд/ Лойте/ Бойме]
Произношение: немецкие умлауты.
Так на практике произносятся немецкие умлауты:
Звук Произношение
œ können [кённен]
ɛ: Mädchen/zählen [Медхен/целен]
ø: Töne/Söhne [Тёне/Зёне]
ʏ fünf/sympatisch [фюнф/зимпатиш]
y: müde/Stühle/Typ [мюде/Штюле/Тип]
Scharfes s: когда применяется ß?
В немецком алфавите есть буква, которая имеет много названий на общем языке: Эсцет, Шарфес-С, Доппель-С,. Когда она используется? Даже у многих коренных немцев есть с этим проблемы, и правило согласно новой орфографии (после 1996 года) следующее:
Scharfes s используется, когда непосредственно перед буквой «ß» имеется гласная, произносится длинная или дифтонг (две гласные рядом друг с другом). Например: Maße, grüßen, Gruß, Straße [ на рус. Масе, грюсен, Грус, Штрас]
Немецкий телефонный алфавит: так пишется слово!
Чтобы избежать неточностей при написании слов по телефону, например, немецкий язык очень часто пишется с использованием имен. Каждой букве алфавита присваивается определенное имя, и стоит выучить эти имена, чтобы звонящий мог правильно записать свое имя или адрес.
Перед тем, как начать орфографию, вы должны сообщить, например, вызывающему абоненту: «Ich buchstabiere…» /»Я произношу по буквам…» /»Я произношу по буквам…»/ а потом произнести по буквам:
A wie Anton
B wie Berta
C wie Cäsar
D wie Dora
E wie Emil
F wie Friedrich
G wie Gustav
H wie Heinrich
I wie Ida
J wie Julius
K wie Kaufmann
L wie Ludwig
M wie Martha
N wie Nordpol
O wie Otto
P wie Paula
Q wie Quelle
R wie Richard
S wie Siegfried
T wie Theodor
U wie Ulrich
V wie Viktor
W wie Wilhelm
X wie Xanthippe
Y wie Ypsilon
Z wie Zeppelin
Ä wie Ärger
Ö wie Ökonom
Ü wie Übermut
Ch wie Charlotte
Sch wie Schule
ß wie Eszett
ИТОГ.
Немецкий алфавит состоит из 26 латинских букв. Кроме того, он состоит из: 3 буквы с умлаутом: ä, ö, ü буква ß (по-немецки Esszett, произносится «эсцет»)
В дополнение к немецкому алфавиту, вы должны читать немецкие звуки.
Чтобы избежать недоразумений при орфографии, стоит использовать немецкий телефонный алфавит.
German orthography is the orthography used in writing the German language, which is largely phonemic. However, it shows many instances of spellings that are historic or analogous to other spellings rather than phonemic. The pronunciation of almost every word can be derived from its spelling once the spelling rules are known, but the opposite is not generally the case.
Today, Standard High German orthography is regulated by the Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung (Council for German Orthography), composed of representatives from most German-speaking countries.
Alphabet[edit]
(Listen to a German speaker recite the alphabet in German)
The modern German alphabet consists of the twenty-six letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet plus four special letters.
Basic alphabet[edit]
| Capital | Lowercase | Name[1] | Name (IPA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | a | A | /aː/ |
| B | b | Be | /beː/ |
| C | c | Ce | /t͡seː/ |
| D | d | De | /deː/ |
| E | e | E | /eː/ |
| F | f | Ef | /ɛf/ |
| G | g | Ge | /ɡeː/ |
| H | h | Ha | /haː/ |
| I | i | I | /iː/ |
| J | j | Jott1, Je2 | /jɔt/1
/jeː/2 |
| K | k | Ka | /kaː/ |
| L | l | El | /ɛl/ |
| M | m | Em | /ɛm/ |
| N | n | En | /ɛn/ |
| O | o | O | /oː/ |
| P | p | Pe | /peː/ |
| Q | q | Qu1, Que2 | /kuː/1
/kveː/2 |
| R | r | Er | /ɛʁ/ |
| S | s | Es | /ɛs/ |
| T | t | Te | /teː/ |
| U | u | U | /uː/ |
| V | v | Vau | /faʊ̯/ |
| W | w | We | /veː/ |
| X | x | Ix | /ɪks/ |
| Y | y | Ypsilon | /ˈʏpsilɔn/1
/ʏˈpsiːlɔn/2 |
| Z | z | Zett | /t͡sɛt/ |
1in Germany
2in Austria
Special letters[edit]
German has four special letters; three are vowels accented with an umlaut sign (⟨ä, ö, ü⟩) and one is derived from a ligature of ⟨ſ⟩ (long s) and ⟨z⟩ (⟨ß⟩; called Eszett «ess-zed/zee» or scharfes S «sharp s»), all of which are officially considered distinct letters of the alphabet,[2] and have their own names separate from the letters they are based on.
(Listen to a German speaker naming these letters)
| Name (IPA) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ä | ä | /ɛː/ |
| Ö | ö | /øː/ |
| Ü | ü | /yː/ |
| ẞ | ß | Eszett: /ɛsˈt͡sɛt/ scharfes S: /ˈʃaʁfəs ɛs/ «sharp s» |
- Capital ẞ was declared an official letter of the German alphabet on 29 June 2017.[3] Previously represented as ⟨SS/SZ⟩.
- Historically, long s (ſ) was used as well, as in English and many other European languages.[4]
While the Council for German Orthography considers ⟨ä, ö, ü, ß⟩ distinct letters,[2] disagreement on how to categorize and count them has led to a dispute over the exact number of letters the German alphabet has, the number ranging between 26 (considering special letters as variants of ⟨a, o, u, s⟩) and 30 (counting all special letters separately).[5]
Use of special letters[edit]
Umlaut diacritic usage[edit]
The accented letters ⟨ä, ö, ü⟩ are used to indicate the presence of umlauts (fronting of back vowels). Before the introduction of the printing press, frontalization was indicated by placing an ⟨e⟩ after the back vowel to be modified, but German printers developed the space-saving typographical convention of replacing the full ⟨e⟩ with a small version placed above the vowel to be modified. In German Kurrent writing, the superscripted ⟨e⟩ was simplified to two vertical dashes (as the Kurrent ⟨e⟩ consists largely of two short vertical strokes), which have further been reduced to dots in both handwriting and German typesetting. Although the two dots of umlaut look like those in the diaeresis (trema), the two have different origins and functions.
When it is not possible to use the umlauts (for example, when using a restricted character set) the characters ⟨Ä, Ö, Ü, ä, ö, ü⟩ should be transcribed as ⟨Ae, Oe, Ue, ae, oe, ue⟩ respectively, following the earlier postvocalic-⟨e⟩ convention; simply using the base vowel (e.g. ⟨u⟩ instead of ⟨ü⟩) would be wrong and misleading. However, such transcription should be avoided if possible, especially with names. Names often exist in different variants, such as Müller and Mueller, and with such transcriptions in use one could not work out the correct spelling of the name.
Automatic back-transcribing is wrong not only for names. Consider, for example, das neue Buch («the new book»). This should never be changed to das neü Buch, as the second ⟨e⟩ is completely separate from the ⟨u⟩ and does not even belong in the same syllable; neue ([ˈnɔʏ.ə]) is neu (the root for «new») followed by ⟨e⟩, an inflection. The word ⟨neü⟩ does not exist in German.
Furthermore, in northern and western Germany, there are family names and place names in which ⟨e⟩ lengthens the preceding vowel (by acting as a Dehnungs-e), as in the former Dutch orthography, such as Straelen, which is pronounced with a long ⟨a⟩, not an ⟨ä⟩. Similar cases are Coesfeld and Bernkastel-Kues.
In proper names and ethnonyms, there may also appear a rare ⟨ë⟩ and ⟨ï⟩, which are not letters with an umlaut, but a diaeresis, used as in French and English to distinguish what could be a digraph, for example, ⟨ai⟩ in Karaïmen, ⟨eu⟩ in Alëuten, ⟨ie⟩ in Piëch, ⟨oe⟩ in von Loë and Hoëcker (although Hoëcker added the diaeresis himself), and ⟨ue⟩ in Niuë.[6] Occasionally, a diaeresis may be used in some well-known names, i.e.: Italiën[7] (usually written as Italien).
Swiss keyboards and typewriters do not allow easy input of uppercase letters with umlauts (nor ⟨ß⟩) because their positions are taken by the most frequent French diacritics. Uppercase umlauts were dropped because they are less common than lowercase ones (especially in Switzerland). Geographical names in particular are supposed to be written with ⟨a, o, u⟩ plus ⟨e⟩, except Österreich. The omission can cause some inconvenience, since the first letter of every noun is capitalized in German.
Unlike in Hungarian, the exact shape of the umlaut diacritics – especially when handwritten – is not important, because they are the only ones in the language (not counting the tittle on ⟨i⟩ and ⟨j⟩). They will be understood whether they look like dots (⟨¨⟩), acute accents (⟨ ˝ ⟩) or vertical bars (⟨‖⟩). A horizontal bar (macron, ⟨¯⟩), a breve (⟨˘⟩), a tiny ⟨N⟩ or ⟨e⟩, a tilde (⟨˜⟩), and such variations are often used in stylized writing (e.g. logos). However, the breve – or the ring (⟨°⟩) – was traditionally used in some scripts to distinguish a ⟨u⟩ from an ⟨n⟩. In rare cases, the ⟨n⟩ was underlined. The breved ⟨u⟩ was common in some Kurrent-derived handwritings; it was mandatory in Sütterlin.
Sharp s[edit]
German label «Delicacy / red cabbage.» Left cap is with old orthography, right with new.
Eszett or scharfes S (⟨ß⟩) represents the “s” sound. The German spelling reform of 1996 somewhat reduced usage of this letter in Germany and Austria. It is not used in Switzerland and Liechtenstein.
As ⟨ß⟩ derives from a ligature of lowercase letters, it is exclusively used in the middle or at the end of a word. The proper transcription when it cannot be used is ⟨ss⟩ (⟨sz⟩ and ⟨SZ⟩ in earlier times). This transcription can give rise to ambiguities, albeit rarely; one such case is in Maßen «in moderation» vs. in Massen «en masse». In all-caps, ⟨ß⟩ is replaced by ⟨SS⟩ or, optionally, by the uppercase ⟨ß⟩.[8] The uppercase ⟨ß⟩ was included in Unicode 5.1 as U+1E9E in 2008. Since 2010 its use is mandatory in official documentation in Germany when writing geographical names in all-caps.[9] The option of using the uppercase ⟨ẞ⟩ in all-caps was officially added to the German orthography in 2017.[10]
Although nowadays substituted correctly only by ⟨ss⟩, the letter actually originates from a distinct ligature: long s with (round) z (⟨ſz/ſʒ⟩). Some people therefore prefer to substitute ⟨ß⟩ by ⟨sz⟩, as it can avoid possible ambiguities (as in the above Maßen vs Massen example).
Incorrect use of the ⟨ß⟩ letter is a common type of spelling error even among native German writers. The spelling reform of 1996 changed the rules concerning ⟨ß⟩ and ⟨ss⟩ (no forced replacement of ⟨ss⟩ to ⟨ß⟩ at word’s end). This required a change of habits and is often disregarded: some people even incorrectly assumed that the ⟨ß⟩ had been abolished completely. However, if the vowel preceding the ⟨s⟩ is long, the correct spelling remains ⟨ß⟩ (as in Straße). If the vowel is short, it becomes ⟨ss⟩, e.g. Ich denke, dass… «I think that…». This follows the general rule in German that a long vowel is followed by a single consonant, while a short vowel is followed by a double consonant.
This change towards the so-called Heyse spelling, however, introduced a new sort of spelling error, as the long/short pronunciation differs regionally. It was already mostly abolished in the late 19th century (and finally with the first unified German spelling of 1901) in favor of the Adelung spelling. Besides the long/short pronunciation issue, which can be attributed to dialect speaking (for instance, in the northern parts of Germany Spaß is typically pronounced short, i.e. Spass, whereas particularly in Bavaria elongated may occur as in Geschoss which is pronounced Geschoß in certain regions), Heyse spelling also introduces reading ambiguities that do not occur with Adelung spelling such as Prozessorientierung (Adelung: Prozeßorientierung) vs. Prozessorarchitektur (Adelung: Prozessorarchitektur). It is therefore recommended to insert hyphens where required for reading assistance, i.e. Prozessor-Architektur vs. Prozess-Orientierung.
Long s[edit]
Wachstube and Wachſtube are distinguished in blackletter typesetting, though no longer in contemporary font styles.
In the Fraktur typeface and similar scripts, a long s (⟨ſ⟩) was used except in syllable endings (cf. Greek sigma) and sometimes it was historically used in antiqua fonts as well; but it went out of general use in the early 1940s along with the Fraktur typeface. An example where this convention would avoid ambiguity is Wachſtube (IPA: [ˈvax.ʃtuːbə]) «guardhouse», written ⟨Wachſtube/Wach-Stube⟩ and Wachstube (IPA: [ˈvaks.tuːbə]) «tube of wax», written ⟨Wachstube/Wachs-Tube⟩.
Sorting[edit]
There are three ways to deal with the umlauts in alphabetic sorting.
- Treat them like their base characters, as if the umlaut were not present (DIN 5007-1, section 6.1.1.4.1). This is the preferred method for dictionaries, where umlauted words (Füße «feet») should appear near their origin words (Fuß «foot»). In words which are the same except for one having an umlaut and one its base character (e.g. Müll vs. Mull), the word with the base character gets precedence.
- Decompose them (invisibly) to vowel plus ⟨e⟩ (DIN 5007-2, section 6.1.1.4.2). This is often preferred for personal and geographical names, wherein the characters are used unsystematically, as in German telephone directories (Müller, A.; Mueller, B.; Müller, C.).
- They are treated like extra letters either placed
- after their base letters (Austrian phone books have ⟨ä⟩ between ⟨az⟩ and ⟨b⟩ etc.) or
- at the end of the alphabet (as in Swedish or in extended ASCII).
Microsoft Windows in German versions offers the choice between the first two variants in its internationalisation settings.
A sort of combination of nos. 1 and 2 also exists, in use in a couple of lexica: The umlaut is sorted with the base character, but an ⟨ae, oe, ue⟩ in proper names is sorted with the umlaut if it is actually spoken that way (with the umlaut getting immediate precedence). A possible sequence of names then would be Mukovic; Muller; Müller; Mueller; Multmann in this order.
Eszett is sorted as though it were ⟨ss⟩. Occasionally it is treated as ⟨s⟩, but this is generally considered incorrect. Words distinguished only by ⟨ß⟩ vs. ⟨ss⟩ can only appear in the (presently used) Heyse writing and are even then rare and possibly dependent on local pronunciation, but if they appear, the word with ⟨ß⟩ gets precedence, and Geschoß (storey; South German pronunciation) would be sorted before Geschoss (projectile).
Accents in French loanwords are always ignored in collation.
In rare contexts (e.g. in older indices) ⟨sch⟩ (phonetic value equal to English ⟨sh⟩) and likewise ⟨st⟩ and ⟨ch⟩ are treated as single letters, but the vocalic digraphs ⟨ai, ei⟩ (historically ⟨ay, ey⟩), ⟨au, äu, eu⟩ and the historic ⟨ui, oi⟩ never are.
Personal names with special characters[edit]
German names containing umlauts (⟨ä, ö, ü⟩) and/or ⟨ß⟩ are spelled in the correct way in the non-machine-readable zone of the passport, but with ⟨AE, OE, UE⟩ and/or ⟨SS⟩ in the machine-readable zone, e.g. ⟨Müller⟩ becomes ⟨MUELLER⟩, ⟨Weiß⟩ becomes ⟨WEISS⟩, and ⟨Gößmann⟩ becomes ⟨GOESSMANN⟩. The transcription mentioned above is generally used for aircraft tickets et cetera, but sometimes (like in US visas) simple vowels are used (MULLER, GOSSMANN). As a result, passport, visa, and aircraft ticket may display different spellings of the same name. The three possible spelling variants of the same name (e.g. Müller/Mueller/Muller) in different documents sometimes lead to confusion, and the use of two different spellings within the same document may give persons unfamiliar with German orthography the impression that the document is a forgery.
Even before the introduction of the capital ⟨ẞ⟩, it was recommended to use the minuscule ⟨ß⟩ as a capital letter in family names in documents (e.g. HEINZ GROßE, today’s spelling: HEINZ GROẞE).
German naming law accepts umlauts and/or ⟨ß⟩ in family names as a reason for an official name change. Even a spelling change, e.g. from Müller to Mueller or from Weiß to Weiss is regarded as a name change.
Features of German spelling[edit]
Capitalization[edit]
A typical feature of German spelling is the general capitalization of nouns and of most nominalized words. In addition, capital letters are used: at the beginning of sentences (may be used after a colon, when the part of a sentence after the colon can be treated as a sentence); in the formal pronouns Sie ‘you’ and Ihr ‘your’ (optionally in other second-person pronouns in letters); in adjectives at the beginning of proper names (e. g. der Stille Ozean ‘the Pacific Ocean’); in adjectives with the suffix ‘-er’ from geographical names (e. g. Berliner); in adjectives with the suffix ‘-sch’ from proper names if written with the apostrophe before the suffix (e. g. Ohm’sches Gesetz ‘Ohm’s law’, also written ohmsches Gesetz).
Compound words[edit]
Compound words, including nouns, are written together, e.g. Haustür (Haus + Tür; «house door»), Tischlampe (Tisch + Lampe; «table lamp»), Kaltwasserhahn (Kalt + Wasser + Hahn; «cold water tap/faucet»). This can lead to long words: the longest word in regular use, Rechtsschutzversicherungsgesellschaften[11] («legal protection insurance companies»), consists of 39 letters.
Vowel length[edit]
Even though vowel length is phonemic in German, it is not consistently represented. However, there are different ways of identifying long vowels:
- A vowel in an open syllable (a free vowel) is long, for instance in ge-ben (‘to give’), sa-gen (‘to say’). The rule is unreliable in given names, cf. Oliver [ˈɔlivɐ].
- It is rare to see a bare i used to indicate a long vowel /iː/. Instead, the digraph ie is used, for instance in Liebe (‘love’), hier (‘here’). This use is a historical spelling based on the Middle High German diphthong /iə/ which was monophthongized in Early New High German. It has been generalized to words that etymologically never had that diphthong, for instance viel (‘much’), Friede (‘peace’) (Middle High German vil, vride). Occasionally – typically in word-final position – this digraph represents /iː.ə/ as in the plural noun Knie /kniː.ə/ (‘knees’) (cf. singular Knie /kniː/). In the words Viertel (viertel) /ˈfɪrtəl/ (‘quarter’), vierzehn /ˈfɪʁt͡seːn/ (‘fourteen’), vierzig /ˈfɪʁt͡sɪç/ (‘forty’), ie represents a short vowel, cf. vier /fiːɐ̯/ (‘four’). In Fraktur, where capital I and J are identical or near-identical
, the combinations Ie and Je are confusable; hence the combination Ie is not used at the start of a word, for example Igel (‘hedgehog’), Ire (‘Irishman’).
- A silent h indicates the vowel length in certain cases. That h derives from an old /x/ in some words, for instance sehen (‘to see’) zehn (‘ten’), but in other words it has no etymological justification, for instance gehen (‘to go’) or mahlen (‘to mill’). Occasionally a digraph can be redundantly followed by h, either due to analogy, such as sieht (‘sees’, from sehen) or etymology, such as Vieh (‘cattle’, MHG vihe), rauh (‘rough’, pre-1996 spelling, now written rau, MHG ruh).
- The letters a, e, o are doubled in a few words that have long vowels, for instance Saat (‘seed’), See (‘sea’/’lake’), Moor (‘moor’).
- A doubled consonant after a vowel indicates that the vowel is short, while a single consonant often indicates the vowel is long, e.g. Kamm (‘comb’) has a short vowel /kam/, while kam (‘came’) has a long vowel /kaːm/. Two consonants are not doubled: k, which is replaced by ck (until the spelling reform of 1996, however, ck was divided across a line break as k-k), and z, which is replaced by tz. In loanwords, kk (which may correspond with cc in the original spelling) and zz can occur.
- For different consonants and for sounds represented by more than one letter (ch and sch) after a vowel, no clear rule can be given, because they can appear after long vowels, yet are not redoubled if belonging to the same stem, e.g. Mond /moːnt/ ‘moon’, Hand /hant/ ‘hand’. On a stem boundary, reduplication usually takes place, e.g., nimm-t ‘takes’; however, in fixed, no longer productive derivatives, this too can be lost, e.g., Geschäft /ɡəˈʃɛft/ ‘business’ despite schaffen ‘to get something done’.
- ß indicates that the preceding vowel is long, e.g. Straße ‘street’ vs. a short vowel in Masse ‘mass’ or ‘host’/’lot’. In addition to that, texts written before the 1996 spelling reform also use ß at the ends of words and before consonants, e.g. naß ‘wet’ and mußte ‘had to’ (after the reform spelled nass and musste), so vowel length in these positions could not be detected by the ß, cf. Maß ‘measure’ and fußte ‘was based’ (after the reform still spelled Maß and fußte).
Double or triple consonants[edit]
Even though German does not have phonemic consonant length, there are many instances of doubled or even tripled consonants in the spelling. A single consonant following a checked vowel is doubled if another vowel follows, for instance immer ‘always’, lassen ‘let’. These consonants are analyzed as ambisyllabic because they constitute not only the syllable onset of the second syllable but also the syllable coda of the first syllable, which must not be empty because the syllable nucleus is a checked vowel.
By analogy, if a word has one form with a doubled consonant, all forms of that word are written with a doubled consonant, even if they do not fulfill the conditions for consonant doubling; for instance, rennen ‘to run’ → er rennt ‘he runs’; Küsse ‘kisses’ → Kuss ‘kiss’.
Doubled consonants can occur in composite words when the first part ends in the same consonant the second part starts with, e.g. in the word Schaffell (‘sheepskin’, composed of Schaf ‘sheep’ and Fell ‘skin, fur, pelt’).
Composite words can also have tripled letters. While this is usually a sign that the consonant is actually spoken long, it does not affect the pronunciation per se: the fff in Sauerstoffflasche (‘oxygen bottle’, composed of Sauerstoff ‘oxygen’ and Flasche ‘bottle’) is exactly as long as the ff in Schaffell. According to the spelling before 1996, the three consonants would be shortened before vowels, but retained before consonants and in hyphenation, so the word Schifffahrt (‘navigation, shipping’, composed of Schiff ‘ship’ and Fahrt ‘drive, trip, tour’) was then written Schiffahrt, whereas Sauerstoffflasche already had a triple fff. With the aforementioned change in ß spelling, even a new source of triple consonants sss, which in pre-1996 spelling could not occur as it was rendered ßs, was introduced, e. g. Mussspiel (‘compulsory round’ in certain card games, composed of muss ‘must’ and Spiel ‘game’).
Typical letters[edit]
- ei: This digraph represents the diphthong /aɪ̯/. The spelling goes back to the Middle High German pronunciation of that diphthong, which was [ei̯]. The spelling ai is found in only a very few native words (such as Saite ‘string’, Waise ‘orphan’) but is commonly used to Romanize /aɪ̯/ in foreign loans from languages such as Chinese.
- eu: This digraph represents the diphthong [ɔʏ̯], which goes back to the Middle High German monophthong [yː] represented by iu. When the sound is created by umlaut of au [aʊ̯] (from MHG [uː]), it is spelled äu.
- ß: This letter alternates with ss. For more information, see above.
- st, sp: At the beginning of a stressed syllable, these digraphs are pronounced [ʃt, ʃp]. In the Middle Ages, the sibilant that was inherited from Proto-Germanic /s/ was pronounced as an alveolo-palatal consonant [ɕ] or [ʑ] unlike the voiceless alveolar sibilant /s/ that had developed in the High German consonant shift. In the Late Middle Ages, certain instances of [ɕ] merged with /s/, but others developed into [ʃ]. The change to [ʃ] was represented in certain spellings such as Schnee ‘snow’, Kirsche ‘cherry’ (Middle High German snê, kirse). The digraphs st, sp, however, remained unaltered.
- v: The letter v occurs only in a few native words and then, it represents /f/. That goes back to the 12th and 13th century, when prevocalic /f/ was voiced to [v]. The voicing was lost again in the late Middle Ages, but the v still remains in certain words such as in Vogel (compare Scandinavian fugl or English fowl) ‘bird’ (hence, the letter v is sometimes called Vogel-vau), viel ‘much’. For further information, see Pronunciation of v in German.
- w: The letter w represents the sound /v/. In the 17th century, the former sound [w] became [v], but the spelling remained the same. An analogous sound change had happened in late-antique Latin.
- z: The letter z represents the sound /t͡s/. The sound, a product of the High German consonant shift, has been written with z since Old High German in the 8th century.
Foreign words[edit]
For technical terms, the foreign spelling is often retained such as ph /f/ or y /yː/ in the word Physik (physics) of Greek origin. For some common affixes however, like -graphie or Photo-, it is allowed to use -grafie or Foto- instead.[12] Both Photographie and Fotografie are correct, but the mixed variants Fotographie or Photografie are not.[12]
For other foreign words, both the foreign spelling and a revised German spelling are correct such as Delphin / Delfin[13] or Portemonnaie / Portmonee, though in the latter case the revised one does not usually occur.[14]
For some words for which the Germanized form was common even before the reform of 1996, the foreign version is no longer allowed. A notable example is the word Foto, with the meaning “photograph”, which may no longer be spelled as Photo.[15] Other examples are Telephon (telephone) which was already Germanized as Telefon some decades ago or Bureau (office) which got replaced by the Germanized version Büro even earlier.
Except for the common sequences sch (/ʃ/), ch ([x] or [ç]) and ck (/k/) the letter c appears only in loanwords or in proper nouns. In many loanwords, including most words of Latin origin, the letter c pronounced (/k/) has been replaced by k. Alternatively, German words which come from Latin words with c before e, i, y, ae, oe are usually pronounced with (/ts/) and spelled with z. However, certain older spellings occasionally remain, mostly for decorative reasons, such as Circus instead of Zirkus.
The letter q in German appears only in the sequence qu (/kv/) except for loanwords such as Coq au vin or Qigong (the latter is also written Chigong).
The letter x (Ix, /ɪks/) occurs almost exclusively in loanwords such as Xylofon (xylophone) and names, e.g. Alexander and Xanthippe. Native German words now pronounced with a /ks/ sound are usually written using chs or (c)ks, as with Fuchs (fox). Some exceptions occur such as Hexe (witch), Nixe (mermaid), Axt (axe) and Xanten.
The letter y (Ypsilon, /ˈʏpsilɔn/) occurs almost exclusively in loanwords, especially words of Greek origin, but some such words (such as Typ) have become so common that they are no longer perceived as foreign. It used to be more common in earlier centuries, and traces of this earlier usage persist in proper names. It is used either as an alternative letter for i, for instance in Mayer / Meyer (a common family name that occurs also in the spellings Maier / Meier), or especially in the Southwest, as a representation of [iː] that goes back to an old IJ (digraph), for instance in Schwyz or Schnyder (an Alemannic variant of the name Schneider).[citation needed] Another notable exception is Bayern («Bavaria») and derived words like bayrisch («Bavarian»); this actually used to be spelt with an i until the King of Bavaria introduced the y as a sign of his philhellenism (his son would become King of Greece later).
In loan words from the French language, spelling and accents are usually preserved. For instance, café in the sense of «coffeehouse» is always written Café in German; accentless Cafe would be considered erroneous, and the word cannot be written Kaffee, which means «coffee». (Café is normally pronounced /kaˈfeː/; Kaffee is mostly pronounced /ˈkafe/ in Germany but /kaˈfeː/ in Austria.) Thus, German typewriters and computer keyboards offer two dead keys: one for the acute and grave accents and one for circumflex. Other letters occur less often such as ç in loan words from French or Portuguese, and ñ in loan words from Spanish.
A number of loanwords from French are spelled in a partially adapted way: Quarantäne /kaʁanˈtɛːnə/ (quarantine), Kommuniqué /kɔmyniˈkeː, kɔmuniˈkeː/ (communiqué), Ouvertüre /u.vɛʁˈtyː.ʁə/ (overture) from French quarantaine, communiqué, ouverture. In Switzerland, where French is one of the official languages, people are less prone to use adapted and especially partially adapted spellings of loanwords from French and more often use original spellings, e. g. Communiqué.
In one curious instance, the word Ski (meaning as in English) is pronounced as if it were Schi all over the German-speaking areas (reflecting its pronunciation in its source language Norwegian), but only written that way in Austria.[16]
Grapheme-to-phoneme correspondences[edit]
This section lists German letters and letter combinations, and how to pronounce them transliterated into the International Phonetic Alphabet. This is the pronunciation of Standard German. Note that the pronunciation of standard German varies slightly from region to region. In fact, it is possible to tell where most German speakers come from by their accent in standard German (not to be confused with the different German dialects).
Foreign words are usually pronounced approximately as they are in the original language.
Consonants[edit]
Double consonants are pronounced as single consonants, except in compound words.
| Grapheme(s) | Phoneme(s) | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | otherwise | [b] or [b̥] | |
| syllable final | [p] | ||
| c | otherwise | [k] | Used in some loanwords and proper names. In many cases, the historically used letter c has been replaced by ⟨k⟩ or ⟨z⟩. |
| before ⟨ä, e, i(, ö)⟩ | [ts] | ||
| ch | after ⟨a, o, u⟩ | [x] | In Austro-Bavarian, especially in Austria, [ç] may always be substituted by [x]. Word-initial ⟨ch⟩ is used only in loanwords. In words of Ancient Greek origin, word-initial ⟨ch⟩ is pronounced [k] before ⟨a, o, l, r⟩ (with rare exceptions : Charisma, where both [k] and [ç] are possible); normally [ç] before ⟨e, i, y⟩ (but [k] in Southern Germany and Austria); [ç] before ⟨th⟩. In the word Orchester and in geographical names such as Chemnitz or Chur, ⟨ch⟩ is [k] (Chur is also sometimes pronounced with [x]). |
| after other vowels or consonants | [ç] | ||
| word-initially in words of Ancient Greek origin | [ç] or [k] | ||
| the suffix —chen | [ç] | ||
| In loanwords and foreign proper names | [tʃ], [ʃ] | ||
| chs | within a morpheme (e.g. Dachs [daks] «badger») | [ks] | |
| across a morpheme boundary (e.g. Dachs [daxs] «roof (gen.)») | [çs] or [xs] | ||
| ck | [k] | follows short vowels | |
| d | otherwise | [d] or [d̥] | |
| syllable final | [t] | ||
| dsch | [dʒ] or [tʃ] | used in loanwords and transliterations only. Words borrowed from English can alternatively retain the original ⟨j⟩ or ⟨g⟩. Many speakers pronounce ⟨dsch⟩ as [t͡ʃ] (= ⟨tsch⟩), because [dʒ] is not native to German. | |
| dt | [t] | Used in the word Stadt, in morpheme bounds (e. g. beredt, verwandt), and in some proper names. | |
| f | [f] | ||
| g | otherwise | [ɡ] or [ɡ̊] | [ʒ] before ⟨e, i⟩ in loanwords from French (as in Genie) |
| syllable final | [k] | ||
| when part of word-final -⟨ig⟩ | [ç] or [k] (Southern Germany) | ||
| h | before a vowel | [h] | |
| when lengthening a vowel | silent | ||
| j | [j] | [ʒ] in loanwords from French (as in Journalist [ʒʊʁnaˈlɪst], from French journaliste; note that -iste is Germanized to -ist, so the letter ⟨t⟩ remains pronounced) | |
| k | [k] | ||
| l | [l] | ||
| m | [m] | ||
| n | [n] | ||
| ng | usually | [ŋ] | |
| in compound words where the first element ends in ⟨n⟩ and the second element begins with ⟨g⟩ (-⟨n·g⟩-) | [nɡ] or [nɡ̊] | ||
| nk | [ŋk] | ||
| p | [p] | ||
| pf | [pf] | with some speakers [f] at the beginning of words (or at the beginning of compound words’ elements) | |
| ph | [f] | Used in words of Ancient Greek origin. | |
| qu | [kv] or [kw] (in a few regions) | ||
| r | [ʁ] before vowels, [ɐ] otherwise,
or [ɐ] after long vowels (except [aː]), [ʁ] otherwise |
[17] | |
| (Austro-Bavarian) | [r] or [ɾ] before vowels, [ɐ] otherwise | ||
| (Swiss Standard German) | [r] in all cases | ||
| rh | same as r | Used in words of Ancient Greek origin and in some proper names. | |
| s | before vowel (except after obstruents) | [z] or [z̥] | |
| before consonants, after obstruents, or when final | [s] | ||
| before ⟨p, t⟩ at the beginning of a word or syllable | [ʃ] | ||
| sch | otherwise | [ʃ] | |
| when part of the -chen diminutive of a word ending on ⟨s⟩, (e.g. Mäuschen «little mouse») | [sç] | ||
| ss | [s] | ||
| ß | [s] | ||
| t | [t] | Silent at the end of loanwords from French (although spelling may be otherwise Germanized: Debüt, Eklat, Kuvert, Porträt) | |
| th | [t] | Used in words of Ancient Greek origin and in some proper names. | |
| ti | otherwise | [ti] | Used in words of Latin origin. |
| in -⟨tion, tiär, tial, tiell⟩ | [tsɪ̯] | ||
| tsch | [tʃ] | ||
| tz | [ts] | follows short vowels | |
| tzsch | [tʃ] | Used in some proper names. | |
| v | otherwise | [f] | |
| in foreign borrowings not at the end of a word | [v] | ||
| w | [v] | ||
| x | [ks] | ||
| z | [ts] | ||
| zsch | [tʃ] | Used in some proper names. |
Vowels[edit]
| front | central | back | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | ||||||
| short | long | short | long | short | long | short | long |
| close | ([i] ⟨i⟩) | [iː] ⟨i, ie, ih, ieh⟩ | ([y] ⟨y⟩) | [yː] ⟨ü, üh, y⟩ | ([u] ⟨u⟩) | [uː] ⟨u, uh⟩ | |
| near-close | [ɪ] ⟨i⟩ | [ʏ] ⟨ ü, y⟩ | [ʊ] ⟨u⟩ | ||||
| close-mid | ([e] ⟨e⟩) | [eː] ⟨ä, äh, e, eh, ee⟩ | ([ø] ⟨ö⟩) | [øː] ⟨ö, öh⟩ | ([o] ⟨o⟩) | [oː] ⟨o, oh, oo⟩ | |
| mid | [ə] ⟨e⟩ | ||||||
| open-mid | [ɛ] ⟨ä, e⟩ | [ɛː] ⟨ä, äh⟩ | [œ] ⟨ö⟩ | [ɔ] ⟨o⟩ | |||
| near-open | [ɐ] -⟨er⟩ | ||||||
| open | [a] ⟨a⟩ | [aː] ⟨a, ah, aa⟩ |
Short vowels[edit]
Consonants are sometimes doubled in writing to indicate the preceding vowel is to be pronounced as a short vowel, mostly when the vowel is stressed. Most one-syllable words that end in a single consonant are pronounced with long vowels, but there are some exceptions such as an, das, es, in, mit, and von. The ⟨e⟩ in the ending —en is often silent, as in bitten «to ask, request». The ending —er is often pronounced [ɐ], but in some regions, people say [ʀ̩] or [r̩]. The ⟨e⟩ in the endings —el ([əl~l̩], e.g. Tunnel, Mörtel «mortar») and —em ([əm~m̩] in the dative case of adjectives, e.g. kleinem from klein «small») is pronounced short despite these endings have just a single consonant on the end, but this ⟨e⟩ is nearly always an unstressed syllable. The suffixes —in, —nis and the word endings —as, —is, —os, —us contain short unstressed vowels, but duplicate the final consonants in the plurals: Leserin «female reader» — Leserinnen «female readers», Kürbis «pumpkin» — Kürbisse «pumpkins».
- ⟨a⟩: [a] as in Wasser «water»
- ⟨ä⟩: [ɛ] as in Männer «men»
- ⟨e⟩: [ɛ] as in Bett «bed»; unstressed [ə] as in Ochse «ox»
- ⟨i⟩: [ɪ] as in Mittel «means»
- ⟨o⟩: [ɔ] as in kommen «to come»
- ⟨ö⟩: [œ] as in Göttin «goddess»
- ⟨u⟩: [ʊ] as in Mutter «mother»
- ⟨ü⟩: [ʏ] as in Müller «miller»
- ⟨y⟩: [ʏ] as in Dystrophie «dystrophy»
Long vowels[edit]
A vowel usually represents a long sound if the vowel in question occurs:
- as the final letter (except for ⟨e⟩)
- in any stressed open syllable as in Wagen «car»
- followed by a single consonant as in bot «offered»
- doubled as in Boot «boat»
- followed by an ⟨h⟩ as in Weh «pain»
Long vowels are generally pronounced with greater tenseness than short vowels.
The long vowels map as follows:
- ⟨a, ah, aa⟩: [aː]
- ⟨ä, äh⟩: [ɛː] or [eː]
- ⟨e, eh, ee⟩: [eː]
- ⟨i, ie, ih, ieh⟩: [iː]
- ⟨o, oh, oo⟩: [oː]
- ⟨ö, öh⟩: [øː]
- ⟨u, uh⟩: [uː]
- ⟨ü, üh⟩: [yː]
- ⟨y⟩: [yː]
Diphthongs[edit]
- ⟨au⟩: [aʊ]
- ⟨eu, äu⟩: [ɔʏ]
- ⟨ei, ai, ey, ay⟩: [aɪ]
Shortened long vowels
A pre-stress long vowel shortens:
- ⟨i⟩: [i]
- ⟨y⟩: [y]
- ⟨u⟩: [u]
- ⟨e⟩: [e]
- ⟨ö⟩: [ø]
- ⟨o⟩: [o]
Other vowels
- -⟨er⟩: /ər/, [ɐ]
- ⟨e⟩: [ə]
- ⟨ie⟩: [ɪ] (in the words: Viertel/viertel, vierzehn, vierzig)
Punctuation[edit]
The period (full stop) is used at the end of sentences, for abbreviations, and for ordinal numbers, such as der 1. for der erste (the first). The combination «abbreviation point+full stop at the end of a sentence» is simplified to a single point.
The comma is used between for enumerations (but the serial comma is not used), before adversative conjunctions, after vocative phrases, for clarifying words such as appositions, before and after infinitive and participle constructions, and between clauses in a sentence. A comma may link two independent clauses without a conjunction. The comma is not used before the direct speech; in this case, the colon is used. In some cases (e.g. infinitive phrases), using the comma is optional.
The exclamation mark and the question mark are used for exclamative and interrogative sentences. The exclamation mark may be used for addressing people in letters.
The semicolon is used for divisions of a sentence greater than that with the comma.
The colon is used before direct speech and quotes, after a generalizing word before enumerations (but not when the words das ist, das heißt, nämlich, zum Beispiel are inserted), before explanations and generalizations, and after words in questionnaires, timetables, etc. (e. g. Vater: Franz Müller).
The em dash is used for marking a sharp transition from one thought to another one, between remarks of a dialogue (as a quotation dash), between keywords in a review, between commands, for contrasting, for marking unexpected changes, for marking an unfinished direct speech, and sometimes instead of parentheses in parenthetical constructions.
The ellipsis is used for unfinished thoughts and incomplete citations.
The parenthesis are used for parenthetical information.
The square brackets are used instead of parentheses inside parentheses and for editor’s words inside quotations.
The quotation marks are written as »…« or „…“. They are used for direct speech, quotes, names of books, periodicals, films, etc., and for words in unusual meaning. Quotation inside a quotation is written in single quotation marks: ›…‹ or ‚…‘. If a quotation is followed by a period or a comma, it is placed outside the quotation marks.
The apostrophe is used for contracted forms (such as ’s for es) except forms with omitted final ⟨e⟩ (was sometimes used in this case in the past) and preposition+article contractions. It is also used for genitive of proper names ending in ⟨s, ß, x, z, ce⟩, but not if preceded by the definite article.
History of German orthography[edit]
Middle Ages[edit]
The oldest known German texts date back to the 8th century. They were written mainly in monasteries in different local dialects of Old High German. In these texts, ⟨z⟩ along with combinations such as ⟨tz, cz, zz, sz, zs⟩ was chosen to transcribe the sounds /ts/ and /s(ː)/, which is ultimately the origin of the modern German letters ⟨z, tz⟩ and ⟨ß⟩ (an old ⟨sz⟩ ligature). After the Carolingian Renaissance, however, during the reigns of the Ottonian and Salian dynasties in the 10th century and 11th century, German was rarely written, the literary language being almost exclusively Latin.
Notker the German is a notable exception in his period: not only are his German compositions of high stylistic value, but his orthography is also the first to follow a strictly coherent system.
Significant production of German texts only resumed during the reign of the Hohenstaufen dynasty (in the High Middle Ages). Around the year 1200, there was a tendency towards a standardized Middle High German language and spelling for the first time, based on the Franconian-Swabian language of the Hohenstaufen court. However, that language was used only in the epic poetry and minnesang lyric of the knight culture. These early tendencies of standardization ceased in the interregnum after the death of the last Hohenstaufen king in 1254. Certain features of today’s German orthography still date back to Middle High German: the use of the trigraph ⟨sch⟩ for /ʃ/ and the occasional use of ⟨v⟩ for /f/ because around the 12th and 13th century, the prevocalic /f/ was voiced.
In the following centuries, the only variety that showed a marked tendency to be used across regions was the Middle Low German of the Hanseatic League, based on the variety of Lübeck and used in many areas of northern Germany and indeed northern Europe in general.
Early modern period[edit]
By the 16th century, a new interregional standard developed on the basis of the East Central German and Austro-Bavarian varieties. This was influenced by several factors:
- Under the Habsburg dynasty, there was a strong tendency to a common language in the chancellery.
- Since Eastern Central Germany had been colonized only during the High and Late Middle Ages in the course of the Ostsiedlung by people from different regions of Germany, the varieties spoken were compromises of different dialects.
- Eastern Central Germany was culturally very important, being home to the universities of Erfurt and Leipzig and especially with the Luther Bible translation, which was considered exemplary.
- The invention of printing led to an increased production of books, and the printers were interested in using a common language to sell their books in an area as wide as possible.
Mid-16th century Counter-Reformation reintroduced Catholicism to Austria and Bavaria, prompting a rejection of the Lutheran language. Instead, a specific southern interregional language was used, based on the language of the Habsburg chancellery.
In northern Germany, the Lutheran East Central German replaced the Low German written language until the mid-17th century. In the early 18th century, the Lutheran standard was also introduced in the southern states and countries, Austria, Bavaria and Switzerland, due to the influence of northern German writers, grammarians such as Johann Christoph Gottsched or language cultivation societies such as the Fruitbearing Society.
19th century and early 20th century[edit]
(Becker, 1896)
(Falck-Lebahn, 1851)
(Smissen-Fraser, 1900)
(Schlomka, 1885)
Though, by the mid-18th century, one norm was generally established, there was no institutionalized standardization. Only with the introduction of compulsory education in late 18th and early 19th century was the spelling further standardized, though at first independently in each state because of the political fragmentation of Germany. Only the foundation of the German Empire in 1871 allowed for further standardization.
In 1876, the Prussian government instituted the First Orthographic Conference [de] to achieve a standardization for the entire German Empire. However, its results were rejected, notably by Prime Minister of Prussia Otto von Bismarck.
In 1880, Gymnasium director Konrad Duden published the Vollständiges Orthographisches Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache («Complete Orthographic Dictionary of the German Language»), known simply as the «Duden». In the same year, the Duden was declared to be authoritative in Prussia.[citation needed] Since Prussia was, by far, the largest state in the German Empire, its regulations also influenced spelling elsewhere, for instance, in 1894, when Switzerland recognized the Duden.[citation needed]
In 1901, the interior minister of the German Empire instituted the Second Orthographic Conference. It declared the Duden to be authoritative, with a few innovations. In 1902, its results were approved by the governments of the German Empire, Austria and Switzerland.
In 1944, the Nazi German government planned a reform of the orthography, but because of World War II, it was never implemented.
After 1902, German spelling was essentially decided de facto by the editors of the Duden dictionaries. After World War II, this tradition was followed with two different centers: Mannheim in West Germany and Leipzig in East Germany. By the early 1950s, a few other publishing houses had begun to attack the Duden monopoly in the West by putting out their own dictionaries, which did not always hold to the «official» spellings prescribed by Duden. In response, the Ministers of Culture of the federal states in West Germany officially declared the Duden spellings to be binding as of November 1955.
The Duden editors used their power cautiously because they considered their primary task to be the documentation of usage, not the creation of rules. At the same time, however, they found themselves forced to make finer and finer distinctions in the production of German spelling rules, and each new print run introduced a few reformed spellings.
German spelling reform of 1996[edit]
German spelling and punctuation was changed in 1996 (Reform der deutschen Rechtschreibung von 1996) with the intent to simplify German orthography, and thus to make the language easier to learn,[18] without substantially changing the rules familiar to users of the language. The rules of the new spelling concern correspondence between sounds and written letters (including rules for spelling loan words), capitalisation, joined and separate words, hyphenated spellings, punctuation, and hyphenation at the end of a line. Place names and family names were excluded from the reform.
The reform was adopted initially by Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein and Switzerland, and later by Luxembourg as well.
The new orthography is mandatory only in schools. A 1998 decision of the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany confirmed that there is no law on the spelling people use in daily life, so they can use the old or the new spelling.[19] While the reform is not very popular in opinion polls, it has been adopted by all major dictionaries and the majority of publishing houses.
See also[edit]
- Binnen-I, a convention for gender-neutral language in German
- German braille
- Non-English usage of quotation marks
- German phonology
- Antiqua-Fraktur dispute
- Spelling
- Punctuation
- English spelling
- Dutch orthography
- Otto Basler
References[edit]
- ^ DIN 5009:2022-06, section 4.2 „Buchstaben“ (letters), table 1
- ^ a b Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung 2018, p. 15, section 0 [Vorbemerkungen] (1): «Die Umlautbuchstaben ä, ö, ü»; p. 29, § 25 E2: «der Buchstabe ß»; et passim.
- ^ Official rules of German spelling updated, Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung, 29 June 2017, retrieved 29 June 2017.
- ^ Andrew West (2006): «The Rules for Long S».
- ^ «Das deutsche Alphabet – Wie viele Buchstaben hat das ABC?» (in German). www.buchstabieralphabet.org. Retrieved 2018-09-24.
- ^ Die Erde: Haack Kleiner Atlas; VEB Hermann Haack geographisch-kartographische Anstalt, Gotha, 1982; pages: 97, 100, 153, 278
- ^ Italien: Straßenatlas 1:300.000 mit Ortsregister; Kunth Verlag GmbH & Co. KG 2016/2017; München; page: III
- ^ Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung 2018, p. 29, § 25 E3
- ^ (in German) Empfehlungen und Hinweise für die Schreibweise geographischer Namen, 5. Ausgabe 2010 Archived 2011-07-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ (in German) Rechtschreibrat führt neuen Buchstaben ein, Die Zeit, 29 June 2017, retrieved 29 June 2017.
- ^ (according to the Guinness Book of Records)
- ^ a b canoo.net: Spelling for «Photographie/Fotografie» 2011-03-13
- ^ canoo.net: Spelling for «Delphin/Delfin» 2011-03-13
- ^ canoo.net: Spelling for «Portemonnaie/Portmonee» 2011-03-13
- ^ canoo.net: Spelling for «Foto» 2011-03-13
- ^ Wortherkunft, Sprachliches
Das Wort Ski wurde im 19. Jahrhundert vom norwegischen ski ‚Scheit (gespaltenes Holz); Schneeschuh‘ entlehnt, das seinerseits von dem gleichbedeutenden altnordischen skíð abstammt und mit dem deutschen Wort Scheit urverwandt ist.[1]
Als Pluralform sind laut Duden Ski und Skier bzw. Schi und Schier üblich.[2] Die Aussprache ist vornehmlich wie „Schi“ (wie auch original im Norwegischen), lokal bzw. dialektal kommt sie auch als „Schki“ (etwa in Graubünden oder im Wallis) vor.
- ^ Preu, Otto; Stötzer, Ursula (1985). Sprecherziehung für Studenten pädagogischer Berufe (4th ed.). Berlin: Verlag Volk und Wissen, Volkseigener Verlag. p. 104.
- ^ Upward, Chris (1997). «Spelling Reform in German» (PDF). Journal of the Simplified Spelling Society. J21: 22–24, 36. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-05.
- ^ Bundesverfassungsgericht, Urteil vom 14. Juli 1998, Az.: 1 BvR 1640/97 (in German), Federal Constitutional Court, 14 July 1998.
External links[edit]
- Regeln und Wörterverzeichnis. Aktualisierte Fassung des amtlichen Regelwerks entsprechend den Empfehlungen des Rats für deutsche Rechtschreibung 2016 (PDF) (in German), Mannheim: Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung, 2018, p. § 25 E3, retrieved 2019-05-07
German orthography is the orthography used in writing the German language, which is largely phonemic. However, it shows many instances of spellings that are historic or analogous to other spellings rather than phonemic. The pronunciation of almost every word can be derived from its spelling once the spelling rules are known, but the opposite is not generally the case.
Today, Standard High German orthography is regulated by the Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung (Council for German Orthography), composed of representatives from most German-speaking countries.
Alphabet[edit]
(Listen to a German speaker recite the alphabet in German)
The modern German alphabet consists of the twenty-six letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet plus four special letters.
Basic alphabet[edit]
| Capital | Lowercase | Name[1] | Name (IPA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | a | A | /aː/ |
| B | b | Be | /beː/ |
| C | c | Ce | /t͡seː/ |
| D | d | De | /deː/ |
| E | e | E | /eː/ |
| F | f | Ef | /ɛf/ |
| G | g | Ge | /ɡeː/ |
| H | h | Ha | /haː/ |
| I | i | I | /iː/ |
| J | j | Jott1, Je2 | /jɔt/1
/jeː/2 |
| K | k | Ka | /kaː/ |
| L | l | El | /ɛl/ |
| M | m | Em | /ɛm/ |
| N | n | En | /ɛn/ |
| O | o | O | /oː/ |
| P | p | Pe | /peː/ |
| Q | q | Qu1, Que2 | /kuː/1
/kveː/2 |
| R | r | Er | /ɛʁ/ |
| S | s | Es | /ɛs/ |
| T | t | Te | /teː/ |
| U | u | U | /uː/ |
| V | v | Vau | /faʊ̯/ |
| W | w | We | /veː/ |
| X | x | Ix | /ɪks/ |
| Y | y | Ypsilon | /ˈʏpsilɔn/1
/ʏˈpsiːlɔn/2 |
| Z | z | Zett | /t͡sɛt/ |
1in Germany
2in Austria
Special letters[edit]
German has four special letters; three are vowels accented with an umlaut sign (⟨ä, ö, ü⟩) and one is derived from a ligature of ⟨ſ⟩ (long s) and ⟨z⟩ (⟨ß⟩; called Eszett «ess-zed/zee» or scharfes S «sharp s»), all of which are officially considered distinct letters of the alphabet,[2] and have their own names separate from the letters they are based on.
(Listen to a German speaker naming these letters)
| Name (IPA) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ä | ä | /ɛː/ |
| Ö | ö | /øː/ |
| Ü | ü | /yː/ |
| ẞ | ß | Eszett: /ɛsˈt͡sɛt/ scharfes S: /ˈʃaʁfəs ɛs/ «sharp s» |
- Capital ẞ was declared an official letter of the German alphabet on 29 June 2017.[3] Previously represented as ⟨SS/SZ⟩.
- Historically, long s (ſ) was used as well, as in English and many other European languages.[4]
While the Council for German Orthography considers ⟨ä, ö, ü, ß⟩ distinct letters,[2] disagreement on how to categorize and count them has led to a dispute over the exact number of letters the German alphabet has, the number ranging between 26 (considering special letters as variants of ⟨a, o, u, s⟩) and 30 (counting all special letters separately).[5]
Use of special letters[edit]
Umlaut diacritic usage[edit]
The accented letters ⟨ä, ö, ü⟩ are used to indicate the presence of umlauts (fronting of back vowels). Before the introduction of the printing press, frontalization was indicated by placing an ⟨e⟩ after the back vowel to be modified, but German printers developed the space-saving typographical convention of replacing the full ⟨e⟩ with a small version placed above the vowel to be modified. In German Kurrent writing, the superscripted ⟨e⟩ was simplified to two vertical dashes (as the Kurrent ⟨e⟩ consists largely of two short vertical strokes), which have further been reduced to dots in both handwriting and German typesetting. Although the two dots of umlaut look like those in the diaeresis (trema), the two have different origins and functions.
When it is not possible to use the umlauts (for example, when using a restricted character set) the characters ⟨Ä, Ö, Ü, ä, ö, ü⟩ should be transcribed as ⟨Ae, Oe, Ue, ae, oe, ue⟩ respectively, following the earlier postvocalic-⟨e⟩ convention; simply using the base vowel (e.g. ⟨u⟩ instead of ⟨ü⟩) would be wrong and misleading. However, such transcription should be avoided if possible, especially with names. Names often exist in different variants, such as Müller and Mueller, and with such transcriptions in use one could not work out the correct spelling of the name.
Automatic back-transcribing is wrong not only for names. Consider, for example, das neue Buch («the new book»). This should never be changed to das neü Buch, as the second ⟨e⟩ is completely separate from the ⟨u⟩ and does not even belong in the same syllable; neue ([ˈnɔʏ.ə]) is neu (the root for «new») followed by ⟨e⟩, an inflection. The word ⟨neü⟩ does not exist in German.
Furthermore, in northern and western Germany, there are family names and place names in which ⟨e⟩ lengthens the preceding vowel (by acting as a Dehnungs-e), as in the former Dutch orthography, such as Straelen, which is pronounced with a long ⟨a⟩, not an ⟨ä⟩. Similar cases are Coesfeld and Bernkastel-Kues.
In proper names and ethnonyms, there may also appear a rare ⟨ë⟩ and ⟨ï⟩, which are not letters with an umlaut, but a diaeresis, used as in French and English to distinguish what could be a digraph, for example, ⟨ai⟩ in Karaïmen, ⟨eu⟩ in Alëuten, ⟨ie⟩ in Piëch, ⟨oe⟩ in von Loë and Hoëcker (although Hoëcker added the diaeresis himself), and ⟨ue⟩ in Niuë.[6] Occasionally, a diaeresis may be used in some well-known names, i.e.: Italiën[7] (usually written as Italien).
Swiss keyboards and typewriters do not allow easy input of uppercase letters with umlauts (nor ⟨ß⟩) because their positions are taken by the most frequent French diacritics. Uppercase umlauts were dropped because they are less common than lowercase ones (especially in Switzerland). Geographical names in particular are supposed to be written with ⟨a, o, u⟩ plus ⟨e⟩, except Österreich. The omission can cause some inconvenience, since the first letter of every noun is capitalized in German.
Unlike in Hungarian, the exact shape of the umlaut diacritics – especially when handwritten – is not important, because they are the only ones in the language (not counting the tittle on ⟨i⟩ and ⟨j⟩). They will be understood whether they look like dots (⟨¨⟩), acute accents (⟨ ˝ ⟩) or vertical bars (⟨‖⟩). A horizontal bar (macron, ⟨¯⟩), a breve (⟨˘⟩), a tiny ⟨N⟩ or ⟨e⟩, a tilde (⟨˜⟩), and such variations are often used in stylized writing (e.g. logos). However, the breve – or the ring (⟨°⟩) – was traditionally used in some scripts to distinguish a ⟨u⟩ from an ⟨n⟩. In rare cases, the ⟨n⟩ was underlined. The breved ⟨u⟩ was common in some Kurrent-derived handwritings; it was mandatory in Sütterlin.
Sharp s[edit]
German label «Delicacy / red cabbage.» Left cap is with old orthography, right with new.
Eszett or scharfes S (⟨ß⟩) represents the “s” sound. The German spelling reform of 1996 somewhat reduced usage of this letter in Germany and Austria. It is not used in Switzerland and Liechtenstein.
As ⟨ß⟩ derives from a ligature of lowercase letters, it is exclusively used in the middle or at the end of a word. The proper transcription when it cannot be used is ⟨ss⟩ (⟨sz⟩ and ⟨SZ⟩ in earlier times). This transcription can give rise to ambiguities, albeit rarely; one such case is in Maßen «in moderation» vs. in Massen «en masse». In all-caps, ⟨ß⟩ is replaced by ⟨SS⟩ or, optionally, by the uppercase ⟨ß⟩.[8] The uppercase ⟨ß⟩ was included in Unicode 5.1 as U+1E9E in 2008. Since 2010 its use is mandatory in official documentation in Germany when writing geographical names in all-caps.[9] The option of using the uppercase ⟨ẞ⟩ in all-caps was officially added to the German orthography in 2017.[10]
Although nowadays substituted correctly only by ⟨ss⟩, the letter actually originates from a distinct ligature: long s with (round) z (⟨ſz/ſʒ⟩). Some people therefore prefer to substitute ⟨ß⟩ by ⟨sz⟩, as it can avoid possible ambiguities (as in the above Maßen vs Massen example).
Incorrect use of the ⟨ß⟩ letter is a common type of spelling error even among native German writers. The spelling reform of 1996 changed the rules concerning ⟨ß⟩ and ⟨ss⟩ (no forced replacement of ⟨ss⟩ to ⟨ß⟩ at word’s end). This required a change of habits and is often disregarded: some people even incorrectly assumed that the ⟨ß⟩ had been abolished completely. However, if the vowel preceding the ⟨s⟩ is long, the correct spelling remains ⟨ß⟩ (as in Straße). If the vowel is short, it becomes ⟨ss⟩, e.g. Ich denke, dass… «I think that…». This follows the general rule in German that a long vowel is followed by a single consonant, while a short vowel is followed by a double consonant.
This change towards the so-called Heyse spelling, however, introduced a new sort of spelling error, as the long/short pronunciation differs regionally. It was already mostly abolished in the late 19th century (and finally with the first unified German spelling of 1901) in favor of the Adelung spelling. Besides the long/short pronunciation issue, which can be attributed to dialect speaking (for instance, in the northern parts of Germany Spaß is typically pronounced short, i.e. Spass, whereas particularly in Bavaria elongated may occur as in Geschoss which is pronounced Geschoß in certain regions), Heyse spelling also introduces reading ambiguities that do not occur with Adelung spelling such as Prozessorientierung (Adelung: Prozeßorientierung) vs. Prozessorarchitektur (Adelung: Prozessorarchitektur). It is therefore recommended to insert hyphens where required for reading assistance, i.e. Prozessor-Architektur vs. Prozess-Orientierung.
Long s[edit]
Wachstube and Wachſtube are distinguished in blackletter typesetting, though no longer in contemporary font styles.
In the Fraktur typeface and similar scripts, a long s (⟨ſ⟩) was used except in syllable endings (cf. Greek sigma) and sometimes it was historically used in antiqua fonts as well; but it went out of general use in the early 1940s along with the Fraktur typeface. An example where this convention would avoid ambiguity is Wachſtube (IPA: [ˈvax.ʃtuːbə]) «guardhouse», written ⟨Wachſtube/Wach-Stube⟩ and Wachstube (IPA: [ˈvaks.tuːbə]) «tube of wax», written ⟨Wachstube/Wachs-Tube⟩.
Sorting[edit]
There are three ways to deal with the umlauts in alphabetic sorting.
- Treat them like their base characters, as if the umlaut were not present (DIN 5007-1, section 6.1.1.4.1). This is the preferred method for dictionaries, where umlauted words (Füße «feet») should appear near their origin words (Fuß «foot»). In words which are the same except for one having an umlaut and one its base character (e.g. Müll vs. Mull), the word with the base character gets precedence.
- Decompose them (invisibly) to vowel plus ⟨e⟩ (DIN 5007-2, section 6.1.1.4.2). This is often preferred for personal and geographical names, wherein the characters are used unsystematically, as in German telephone directories (Müller, A.; Mueller, B.; Müller, C.).
- They are treated like extra letters either placed
- after their base letters (Austrian phone books have ⟨ä⟩ between ⟨az⟩ and ⟨b⟩ etc.) or
- at the end of the alphabet (as in Swedish or in extended ASCII).
Microsoft Windows in German versions offers the choice between the first two variants in its internationalisation settings.
A sort of combination of nos. 1 and 2 also exists, in use in a couple of lexica: The umlaut is sorted with the base character, but an ⟨ae, oe, ue⟩ in proper names is sorted with the umlaut if it is actually spoken that way (with the umlaut getting immediate precedence). A possible sequence of names then would be Mukovic; Muller; Müller; Mueller; Multmann in this order.
Eszett is sorted as though it were ⟨ss⟩. Occasionally it is treated as ⟨s⟩, but this is generally considered incorrect. Words distinguished only by ⟨ß⟩ vs. ⟨ss⟩ can only appear in the (presently used) Heyse writing and are even then rare and possibly dependent on local pronunciation, but if they appear, the word with ⟨ß⟩ gets precedence, and Geschoß (storey; South German pronunciation) would be sorted before Geschoss (projectile).
Accents in French loanwords are always ignored in collation.
In rare contexts (e.g. in older indices) ⟨sch⟩ (phonetic value equal to English ⟨sh⟩) and likewise ⟨st⟩ and ⟨ch⟩ are treated as single letters, but the vocalic digraphs ⟨ai, ei⟩ (historically ⟨ay, ey⟩), ⟨au, äu, eu⟩ and the historic ⟨ui, oi⟩ never are.
Personal names with special characters[edit]
German names containing umlauts (⟨ä, ö, ü⟩) and/or ⟨ß⟩ are spelled in the correct way in the non-machine-readable zone of the passport, but with ⟨AE, OE, UE⟩ and/or ⟨SS⟩ in the machine-readable zone, e.g. ⟨Müller⟩ becomes ⟨MUELLER⟩, ⟨Weiß⟩ becomes ⟨WEISS⟩, and ⟨Gößmann⟩ becomes ⟨GOESSMANN⟩. The transcription mentioned above is generally used for aircraft tickets et cetera, but sometimes (like in US visas) simple vowels are used (MULLER, GOSSMANN). As a result, passport, visa, and aircraft ticket may display different spellings of the same name. The three possible spelling variants of the same name (e.g. Müller/Mueller/Muller) in different documents sometimes lead to confusion, and the use of two different spellings within the same document may give persons unfamiliar with German orthography the impression that the document is a forgery.
Even before the introduction of the capital ⟨ẞ⟩, it was recommended to use the minuscule ⟨ß⟩ as a capital letter in family names in documents (e.g. HEINZ GROßE, today’s spelling: HEINZ GROẞE).
German naming law accepts umlauts and/or ⟨ß⟩ in family names as a reason for an official name change. Even a spelling change, e.g. from Müller to Mueller or from Weiß to Weiss is regarded as a name change.
Features of German spelling[edit]
Capitalization[edit]
A typical feature of German spelling is the general capitalization of nouns and of most nominalized words. In addition, capital letters are used: at the beginning of sentences (may be used after a colon, when the part of a sentence after the colon can be treated as a sentence); in the formal pronouns Sie ‘you’ and Ihr ‘your’ (optionally in other second-person pronouns in letters); in adjectives at the beginning of proper names (e. g. der Stille Ozean ‘the Pacific Ocean’); in adjectives with the suffix ‘-er’ from geographical names (e. g. Berliner); in adjectives with the suffix ‘-sch’ from proper names if written with the apostrophe before the suffix (e. g. Ohm’sches Gesetz ‘Ohm’s law’, also written ohmsches Gesetz).
Compound words[edit]
Compound words, including nouns, are written together, e.g. Haustür (Haus + Tür; «house door»), Tischlampe (Tisch + Lampe; «table lamp»), Kaltwasserhahn (Kalt + Wasser + Hahn; «cold water tap/faucet»). This can lead to long words: the longest word in regular use, Rechtsschutzversicherungsgesellschaften[11] («legal protection insurance companies»), consists of 39 letters.
Vowel length[edit]
Even though vowel length is phonemic in German, it is not consistently represented. However, there are different ways of identifying long vowels:
- A vowel in an open syllable (a free vowel) is long, for instance in ge-ben (‘to give’), sa-gen (‘to say’). The rule is unreliable in given names, cf. Oliver [ˈɔlivɐ].
- It is rare to see a bare i used to indicate a long vowel /iː/. Instead, the digraph ie is used, for instance in Liebe (‘love’), hier (‘here’). This use is a historical spelling based on the Middle High German diphthong /iə/ which was monophthongized in Early New High German. It has been generalized to words that etymologically never had that diphthong, for instance viel (‘much’), Friede (‘peace’) (Middle High German vil, vride). Occasionally – typically in word-final position – this digraph represents /iː.ə/ as in the plural noun Knie /kniː.ə/ (‘knees’) (cf. singular Knie /kniː/). In the words Viertel (viertel) /ˈfɪrtəl/ (‘quarter’), vierzehn /ˈfɪʁt͡seːn/ (‘fourteen’), vierzig /ˈfɪʁt͡sɪç/ (‘forty’), ie represents a short vowel, cf. vier /fiːɐ̯/ (‘four’). In Fraktur, where capital I and J are identical or near-identical
, the combinations Ie and Je are confusable; hence the combination Ie is not used at the start of a word, for example Igel (‘hedgehog’), Ire (‘Irishman’).
- A silent h indicates the vowel length in certain cases. That h derives from an old /x/ in some words, for instance sehen (‘to see’) zehn (‘ten’), but in other words it has no etymological justification, for instance gehen (‘to go’) or mahlen (‘to mill’). Occasionally a digraph can be redundantly followed by h, either due to analogy, such as sieht (‘sees’, from sehen) or etymology, such as Vieh (‘cattle’, MHG vihe), rauh (‘rough’, pre-1996 spelling, now written rau, MHG ruh).
- The letters a, e, o are doubled in a few words that have long vowels, for instance Saat (‘seed’), See (‘sea’/’lake’), Moor (‘moor’).
- A doubled consonant after a vowel indicates that the vowel is short, while a single consonant often indicates the vowel is long, e.g. Kamm (‘comb’) has a short vowel /kam/, while kam (‘came’) has a long vowel /kaːm/. Two consonants are not doubled: k, which is replaced by ck (until the spelling reform of 1996, however, ck was divided across a line break as k-k), and z, which is replaced by tz. In loanwords, kk (which may correspond with cc in the original spelling) and zz can occur.
- For different consonants and for sounds represented by more than one letter (ch and sch) after a vowel, no clear rule can be given, because they can appear after long vowels, yet are not redoubled if belonging to the same stem, e.g. Mond /moːnt/ ‘moon’, Hand /hant/ ‘hand’. On a stem boundary, reduplication usually takes place, e.g., nimm-t ‘takes’; however, in fixed, no longer productive derivatives, this too can be lost, e.g., Geschäft /ɡəˈʃɛft/ ‘business’ despite schaffen ‘to get something done’.
- ß indicates that the preceding vowel is long, e.g. Straße ‘street’ vs. a short vowel in Masse ‘mass’ or ‘host’/’lot’. In addition to that, texts written before the 1996 spelling reform also use ß at the ends of words and before consonants, e.g. naß ‘wet’ and mußte ‘had to’ (after the reform spelled nass and musste), so vowel length in these positions could not be detected by the ß, cf. Maß ‘measure’ and fußte ‘was based’ (after the reform still spelled Maß and fußte).
Double or triple consonants[edit]
Even though German does not have phonemic consonant length, there are many instances of doubled or even tripled consonants in the spelling. A single consonant following a checked vowel is doubled if another vowel follows, for instance immer ‘always’, lassen ‘let’. These consonants are analyzed as ambisyllabic because they constitute not only the syllable onset of the second syllable but also the syllable coda of the first syllable, which must not be empty because the syllable nucleus is a checked vowel.
By analogy, if a word has one form with a doubled consonant, all forms of that word are written with a doubled consonant, even if they do not fulfill the conditions for consonant doubling; for instance, rennen ‘to run’ → er rennt ‘he runs’; Küsse ‘kisses’ → Kuss ‘kiss’.
Doubled consonants can occur in composite words when the first part ends in the same consonant the second part starts with, e.g. in the word Schaffell (‘sheepskin’, composed of Schaf ‘sheep’ and Fell ‘skin, fur, pelt’).
Composite words can also have tripled letters. While this is usually a sign that the consonant is actually spoken long, it does not affect the pronunciation per se: the fff in Sauerstoffflasche (‘oxygen bottle’, composed of Sauerstoff ‘oxygen’ and Flasche ‘bottle’) is exactly as long as the ff in Schaffell. According to the spelling before 1996, the three consonants would be shortened before vowels, but retained before consonants and in hyphenation, so the word Schifffahrt (‘navigation, shipping’, composed of Schiff ‘ship’ and Fahrt ‘drive, trip, tour’) was then written Schiffahrt, whereas Sauerstoffflasche already had a triple fff. With the aforementioned change in ß spelling, even a new source of triple consonants sss, which in pre-1996 spelling could not occur as it was rendered ßs, was introduced, e. g. Mussspiel (‘compulsory round’ in certain card games, composed of muss ‘must’ and Spiel ‘game’).
Typical letters[edit]
- ei: This digraph represents the diphthong /aɪ̯/. The spelling goes back to the Middle High German pronunciation of that diphthong, which was [ei̯]. The spelling ai is found in only a very few native words (such as Saite ‘string’, Waise ‘orphan’) but is commonly used to Romanize /aɪ̯/ in foreign loans from languages such as Chinese.
- eu: This digraph represents the diphthong [ɔʏ̯], which goes back to the Middle High German monophthong [yː] represented by iu. When the sound is created by umlaut of au [aʊ̯] (from MHG [uː]), it is spelled äu.
- ß: This letter alternates with ss. For more information, see above.
- st, sp: At the beginning of a stressed syllable, these digraphs are pronounced [ʃt, ʃp]. In the Middle Ages, the sibilant that was inherited from Proto-Germanic /s/ was pronounced as an alveolo-palatal consonant [ɕ] or [ʑ] unlike the voiceless alveolar sibilant /s/ that had developed in the High German consonant shift. In the Late Middle Ages, certain instances of [ɕ] merged with /s/, but others developed into [ʃ]. The change to [ʃ] was represented in certain spellings such as Schnee ‘snow’, Kirsche ‘cherry’ (Middle High German snê, kirse). The digraphs st, sp, however, remained unaltered.
- v: The letter v occurs only in a few native words and then, it represents /f/. That goes back to the 12th and 13th century, when prevocalic /f/ was voiced to [v]. The voicing was lost again in the late Middle Ages, but the v still remains in certain words such as in Vogel (compare Scandinavian fugl or English fowl) ‘bird’ (hence, the letter v is sometimes called Vogel-vau), viel ‘much’. For further information, see Pronunciation of v in German.
- w: The letter w represents the sound /v/. In the 17th century, the former sound [w] became [v], but the spelling remained the same. An analogous sound change had happened in late-antique Latin.
- z: The letter z represents the sound /t͡s/. The sound, a product of the High German consonant shift, has been written with z since Old High German in the 8th century.
Foreign words[edit]
For technical terms, the foreign spelling is often retained such as ph /f/ or y /yː/ in the word Physik (physics) of Greek origin. For some common affixes however, like -graphie or Photo-, it is allowed to use -grafie or Foto- instead.[12] Both Photographie and Fotografie are correct, but the mixed variants Fotographie or Photografie are not.[12]
For other foreign words, both the foreign spelling and a revised German spelling are correct such as Delphin / Delfin[13] or Portemonnaie / Portmonee, though in the latter case the revised one does not usually occur.[14]
For some words for which the Germanized form was common even before the reform of 1996, the foreign version is no longer allowed. A notable example is the word Foto, with the meaning “photograph”, which may no longer be spelled as Photo.[15] Other examples are Telephon (telephone) which was already Germanized as Telefon some decades ago or Bureau (office) which got replaced by the Germanized version Büro even earlier.
Except for the common sequences sch (/ʃ/), ch ([x] or [ç]) and ck (/k/) the letter c appears only in loanwords or in proper nouns. In many loanwords, including most words of Latin origin, the letter c pronounced (/k/) has been replaced by k. Alternatively, German words which come from Latin words with c before e, i, y, ae, oe are usually pronounced with (/ts/) and spelled with z. However, certain older spellings occasionally remain, mostly for decorative reasons, such as Circus instead of Zirkus.
The letter q in German appears only in the sequence qu (/kv/) except for loanwords such as Coq au vin or Qigong (the latter is also written Chigong).
The letter x (Ix, /ɪks/) occurs almost exclusively in loanwords such as Xylofon (xylophone) and names, e.g. Alexander and Xanthippe. Native German words now pronounced with a /ks/ sound are usually written using chs or (c)ks, as with Fuchs (fox). Some exceptions occur such as Hexe (witch), Nixe (mermaid), Axt (axe) and Xanten.
The letter y (Ypsilon, /ˈʏpsilɔn/) occurs almost exclusively in loanwords, especially words of Greek origin, but some such words (such as Typ) have become so common that they are no longer perceived as foreign. It used to be more common in earlier centuries, and traces of this earlier usage persist in proper names. It is used either as an alternative letter for i, for instance in Mayer / Meyer (a common family name that occurs also in the spellings Maier / Meier), or especially in the Southwest, as a representation of [iː] that goes back to an old IJ (digraph), for instance in Schwyz or Schnyder (an Alemannic variant of the name Schneider).[citation needed] Another notable exception is Bayern («Bavaria») and derived words like bayrisch («Bavarian»); this actually used to be spelt with an i until the King of Bavaria introduced the y as a sign of his philhellenism (his son would become King of Greece later).
In loan words from the French language, spelling and accents are usually preserved. For instance, café in the sense of «coffeehouse» is always written Café in German; accentless Cafe would be considered erroneous, and the word cannot be written Kaffee, which means «coffee». (Café is normally pronounced /kaˈfeː/; Kaffee is mostly pronounced /ˈkafe/ in Germany but /kaˈfeː/ in Austria.) Thus, German typewriters and computer keyboards offer two dead keys: one for the acute and grave accents and one for circumflex. Other letters occur less often such as ç in loan words from French or Portuguese, and ñ in loan words from Spanish.
A number of loanwords from French are spelled in a partially adapted way: Quarantäne /kaʁanˈtɛːnə/ (quarantine), Kommuniqué /kɔmyniˈkeː, kɔmuniˈkeː/ (communiqué), Ouvertüre /u.vɛʁˈtyː.ʁə/ (overture) from French quarantaine, communiqué, ouverture. In Switzerland, where French is one of the official languages, people are less prone to use adapted and especially partially adapted spellings of loanwords from French and more often use original spellings, e. g. Communiqué.
In one curious instance, the word Ski (meaning as in English) is pronounced as if it were Schi all over the German-speaking areas (reflecting its pronunciation in its source language Norwegian), but only written that way in Austria.[16]
Grapheme-to-phoneme correspondences[edit]
This section lists German letters and letter combinations, and how to pronounce them transliterated into the International Phonetic Alphabet. This is the pronunciation of Standard German. Note that the pronunciation of standard German varies slightly from region to region. In fact, it is possible to tell where most German speakers come from by their accent in standard German (not to be confused with the different German dialects).
Foreign words are usually pronounced approximately as they are in the original language.
Consonants[edit]
Double consonants are pronounced as single consonants, except in compound words.
| Grapheme(s) | Phoneme(s) | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | otherwise | [b] or [b̥] | |
| syllable final | [p] | ||
| c | otherwise | [k] | Used in some loanwords and proper names. In many cases, the historically used letter c has been replaced by ⟨k⟩ or ⟨z⟩. |
| before ⟨ä, e, i(, ö)⟩ | [ts] | ||
| ch | after ⟨a, o, u⟩ | [x] | In Austro-Bavarian, especially in Austria, [ç] may always be substituted by [x]. Word-initial ⟨ch⟩ is used only in loanwords. In words of Ancient Greek origin, word-initial ⟨ch⟩ is pronounced [k] before ⟨a, o, l, r⟩ (with rare exceptions : Charisma, where both [k] and [ç] are possible); normally [ç] before ⟨e, i, y⟩ (but [k] in Southern Germany and Austria); [ç] before ⟨th⟩. In the word Orchester and in geographical names such as Chemnitz or Chur, ⟨ch⟩ is [k] (Chur is also sometimes pronounced with [x]). |
| after other vowels or consonants | [ç] | ||
| word-initially in words of Ancient Greek origin | [ç] or [k] | ||
| the suffix —chen | [ç] | ||
| In loanwords and foreign proper names | [tʃ], [ʃ] | ||
| chs | within a morpheme (e.g. Dachs [daks] «badger») | [ks] | |
| across a morpheme boundary (e.g. Dachs [daxs] «roof (gen.)») | [çs] or [xs] | ||
| ck | [k] | follows short vowels | |
| d | otherwise | [d] or [d̥] | |
| syllable final | [t] | ||
| dsch | [dʒ] or [tʃ] | used in loanwords and transliterations only. Words borrowed from English can alternatively retain the original ⟨j⟩ or ⟨g⟩. Many speakers pronounce ⟨dsch⟩ as [t͡ʃ] (= ⟨tsch⟩), because [dʒ] is not native to German. | |
| dt | [t] | Used in the word Stadt, in morpheme bounds (e. g. beredt, verwandt), and in some proper names. | |
| f | [f] | ||
| g | otherwise | [ɡ] or [ɡ̊] | [ʒ] before ⟨e, i⟩ in loanwords from French (as in Genie) |
| syllable final | [k] | ||
| when part of word-final -⟨ig⟩ | [ç] or [k] (Southern Germany) | ||
| h | before a vowel | [h] | |
| when lengthening a vowel | silent | ||
| j | [j] | [ʒ] in loanwords from French (as in Journalist [ʒʊʁnaˈlɪst], from French journaliste; note that -iste is Germanized to -ist, so the letter ⟨t⟩ remains pronounced) | |
| k | [k] | ||
| l | [l] | ||
| m | [m] | ||
| n | [n] | ||
| ng | usually | [ŋ] | |
| in compound words where the first element ends in ⟨n⟩ and the second element begins with ⟨g⟩ (-⟨n·g⟩-) | [nɡ] or [nɡ̊] | ||
| nk | [ŋk] | ||
| p | [p] | ||
| pf | [pf] | with some speakers [f] at the beginning of words (or at the beginning of compound words’ elements) | |
| ph | [f] | Used in words of Ancient Greek origin. | |
| qu | [kv] or [kw] (in a few regions) | ||
| r | [ʁ] before vowels, [ɐ] otherwise,
or [ɐ] after long vowels (except [aː]), [ʁ] otherwise |
[17] | |
| (Austro-Bavarian) | [r] or [ɾ] before vowels, [ɐ] otherwise | ||
| (Swiss Standard German) | [r] in all cases | ||
| rh | same as r | Used in words of Ancient Greek origin and in some proper names. | |
| s | before vowel (except after obstruents) | [z] or [z̥] | |
| before consonants, after obstruents, or when final | [s] | ||
| before ⟨p, t⟩ at the beginning of a word or syllable | [ʃ] | ||
| sch | otherwise | [ʃ] | |
| when part of the -chen diminutive of a word ending on ⟨s⟩, (e.g. Mäuschen «little mouse») | [sç] | ||
| ss | [s] | ||
| ß | [s] | ||
| t | [t] | Silent at the end of loanwords from French (although spelling may be otherwise Germanized: Debüt, Eklat, Kuvert, Porträt) | |
| th | [t] | Used in words of Ancient Greek origin and in some proper names. | |
| ti | otherwise | [ti] | Used in words of Latin origin. |
| in -⟨tion, tiär, tial, tiell⟩ | [tsɪ̯] | ||
| tsch | [tʃ] | ||
| tz | [ts] | follows short vowels | |
| tzsch | [tʃ] | Used in some proper names. | |
| v | otherwise | [f] | |
| in foreign borrowings not at the end of a word | [v] | ||
| w | [v] | ||
| x | [ks] | ||
| z | [ts] | ||
| zsch | [tʃ] | Used in some proper names. |
Vowels[edit]
| front | central | back | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | ||||||
| short | long | short | long | short | long | short | long |
| close | ([i] ⟨i⟩) | [iː] ⟨i, ie, ih, ieh⟩ | ([y] ⟨y⟩) | [yː] ⟨ü, üh, y⟩ | ([u] ⟨u⟩) | [uː] ⟨u, uh⟩ | |
| near-close | [ɪ] ⟨i⟩ | [ʏ] ⟨ ü, y⟩ | [ʊ] ⟨u⟩ | ||||
| close-mid | ([e] ⟨e⟩) | [eː] ⟨ä, äh, e, eh, ee⟩ | ([ø] ⟨ö⟩) | [øː] ⟨ö, öh⟩ | ([o] ⟨o⟩) | [oː] ⟨o, oh, oo⟩ | |
| mid | [ə] ⟨e⟩ | ||||||
| open-mid | [ɛ] ⟨ä, e⟩ | [ɛː] ⟨ä, äh⟩ | [œ] ⟨ö⟩ | [ɔ] ⟨o⟩ | |||
| near-open | [ɐ] -⟨er⟩ | ||||||
| open | [a] ⟨a⟩ | [aː] ⟨a, ah, aa⟩ |
Short vowels[edit]
Consonants are sometimes doubled in writing to indicate the preceding vowel is to be pronounced as a short vowel, mostly when the vowel is stressed. Most one-syllable words that end in a single consonant are pronounced with long vowels, but there are some exceptions such as an, das, es, in, mit, and von. The ⟨e⟩ in the ending —en is often silent, as in bitten «to ask, request». The ending —er is often pronounced [ɐ], but in some regions, people say [ʀ̩] or [r̩]. The ⟨e⟩ in the endings —el ([əl~l̩], e.g. Tunnel, Mörtel «mortar») and —em ([əm~m̩] in the dative case of adjectives, e.g. kleinem from klein «small») is pronounced short despite these endings have just a single consonant on the end, but this ⟨e⟩ is nearly always an unstressed syllable. The suffixes —in, —nis and the word endings —as, —is, —os, —us contain short unstressed vowels, but duplicate the final consonants in the plurals: Leserin «female reader» — Leserinnen «female readers», Kürbis «pumpkin» — Kürbisse «pumpkins».
- ⟨a⟩: [a] as in Wasser «water»
- ⟨ä⟩: [ɛ] as in Männer «men»
- ⟨e⟩: [ɛ] as in Bett «bed»; unstressed [ə] as in Ochse «ox»
- ⟨i⟩: [ɪ] as in Mittel «means»
- ⟨o⟩: [ɔ] as in kommen «to come»
- ⟨ö⟩: [œ] as in Göttin «goddess»
- ⟨u⟩: [ʊ] as in Mutter «mother»
- ⟨ü⟩: [ʏ] as in Müller «miller»
- ⟨y⟩: [ʏ] as in Dystrophie «dystrophy»
Long vowels[edit]
A vowel usually represents a long sound if the vowel in question occurs:
- as the final letter (except for ⟨e⟩)
- in any stressed open syllable as in Wagen «car»
- followed by a single consonant as in bot «offered»
- doubled as in Boot «boat»
- followed by an ⟨h⟩ as in Weh «pain»
Long vowels are generally pronounced with greater tenseness than short vowels.
The long vowels map as follows:
- ⟨a, ah, aa⟩: [aː]
- ⟨ä, äh⟩: [ɛː] or [eː]
- ⟨e, eh, ee⟩: [eː]
- ⟨i, ie, ih, ieh⟩: [iː]
- ⟨o, oh, oo⟩: [oː]
- ⟨ö, öh⟩: [øː]
- ⟨u, uh⟩: [uː]
- ⟨ü, üh⟩: [yː]
- ⟨y⟩: [yː]
Diphthongs[edit]
- ⟨au⟩: [aʊ]
- ⟨eu, äu⟩: [ɔʏ]
- ⟨ei, ai, ey, ay⟩: [aɪ]
Shortened long vowels
A pre-stress long vowel shortens:
- ⟨i⟩: [i]
- ⟨y⟩: [y]
- ⟨u⟩: [u]
- ⟨e⟩: [e]
- ⟨ö⟩: [ø]
- ⟨o⟩: [o]
Other vowels
- -⟨er⟩: /ər/, [ɐ]
- ⟨e⟩: [ə]
- ⟨ie⟩: [ɪ] (in the words: Viertel/viertel, vierzehn, vierzig)
Punctuation[edit]
The period (full stop) is used at the end of sentences, for abbreviations, and for ordinal numbers, such as der 1. for der erste (the first). The combination «abbreviation point+full stop at the end of a sentence» is simplified to a single point.
The comma is used between for enumerations (but the serial comma is not used), before adversative conjunctions, after vocative phrases, for clarifying words such as appositions, before and after infinitive and participle constructions, and between clauses in a sentence. A comma may link two independent clauses without a conjunction. The comma is not used before the direct speech; in this case, the colon is used. In some cases (e.g. infinitive phrases), using the comma is optional.
The exclamation mark and the question mark are used for exclamative and interrogative sentences. The exclamation mark may be used for addressing people in letters.
The semicolon is used for divisions of a sentence greater than that with the comma.
The colon is used before direct speech and quotes, after a generalizing word before enumerations (but not when the words das ist, das heißt, nämlich, zum Beispiel are inserted), before explanations and generalizations, and after words in questionnaires, timetables, etc. (e. g. Vater: Franz Müller).
The em dash is used for marking a sharp transition from one thought to another one, between remarks of a dialogue (as a quotation dash), between keywords in a review, between commands, for contrasting, for marking unexpected changes, for marking an unfinished direct speech, and sometimes instead of parentheses in parenthetical constructions.
The ellipsis is used for unfinished thoughts and incomplete citations.
The parenthesis are used for parenthetical information.
The square brackets are used instead of parentheses inside parentheses and for editor’s words inside quotations.
The quotation marks are written as »…« or „…“. They are used for direct speech, quotes, names of books, periodicals, films, etc., and for words in unusual meaning. Quotation inside a quotation is written in single quotation marks: ›…‹ or ‚…‘. If a quotation is followed by a period or a comma, it is placed outside the quotation marks.
The apostrophe is used for contracted forms (such as ’s for es) except forms with omitted final ⟨e⟩ (was sometimes used in this case in the past) and preposition+article contractions. It is also used for genitive of proper names ending in ⟨s, ß, x, z, ce⟩, but not if preceded by the definite article.
History of German orthography[edit]
Middle Ages[edit]
The oldest known German texts date back to the 8th century. They were written mainly in monasteries in different local dialects of Old High German. In these texts, ⟨z⟩ along with combinations such as ⟨tz, cz, zz, sz, zs⟩ was chosen to transcribe the sounds /ts/ and /s(ː)/, which is ultimately the origin of the modern German letters ⟨z, tz⟩ and ⟨ß⟩ (an old ⟨sz⟩ ligature). After the Carolingian Renaissance, however, during the reigns of the Ottonian and Salian dynasties in the 10th century and 11th century, German was rarely written, the literary language being almost exclusively Latin.
Notker the German is a notable exception in his period: not only are his German compositions of high stylistic value, but his orthography is also the first to follow a strictly coherent system.
Significant production of German texts only resumed during the reign of the Hohenstaufen dynasty (in the High Middle Ages). Around the year 1200, there was a tendency towards a standardized Middle High German language and spelling for the first time, based on the Franconian-Swabian language of the Hohenstaufen court. However, that language was used only in the epic poetry and minnesang lyric of the knight culture. These early tendencies of standardization ceased in the interregnum after the death of the last Hohenstaufen king in 1254. Certain features of today’s German orthography still date back to Middle High German: the use of the trigraph ⟨sch⟩ for /ʃ/ and the occasional use of ⟨v⟩ for /f/ because around the 12th and 13th century, the prevocalic /f/ was voiced.
In the following centuries, the only variety that showed a marked tendency to be used across regions was the Middle Low German of the Hanseatic League, based on the variety of Lübeck and used in many areas of northern Germany and indeed northern Europe in general.
Early modern period[edit]
By the 16th century, a new interregional standard developed on the basis of the East Central German and Austro-Bavarian varieties. This was influenced by several factors:
- Under the Habsburg dynasty, there was a strong tendency to a common language in the chancellery.
- Since Eastern Central Germany had been colonized only during the High and Late Middle Ages in the course of the Ostsiedlung by people from different regions of Germany, the varieties spoken were compromises of different dialects.
- Eastern Central Germany was culturally very important, being home to the universities of Erfurt and Leipzig and especially with the Luther Bible translation, which was considered exemplary.
- The invention of printing led to an increased production of books, and the printers were interested in using a common language to sell their books in an area as wide as possible.
Mid-16th century Counter-Reformation reintroduced Catholicism to Austria and Bavaria, prompting a rejection of the Lutheran language. Instead, a specific southern interregional language was used, based on the language of the Habsburg chancellery.
In northern Germany, the Lutheran East Central German replaced the Low German written language until the mid-17th century. In the early 18th century, the Lutheran standard was also introduced in the southern states and countries, Austria, Bavaria and Switzerland, due to the influence of northern German writers, grammarians such as Johann Christoph Gottsched or language cultivation societies such as the Fruitbearing Society.
19th century and early 20th century[edit]
(Becker, 1896)
(Falck-Lebahn, 1851)
(Smissen-Fraser, 1900)
(Schlomka, 1885)
Though, by the mid-18th century, one norm was generally established, there was no institutionalized standardization. Only with the introduction of compulsory education in late 18th and early 19th century was the spelling further standardized, though at first independently in each state because of the political fragmentation of Germany. Only the foundation of the German Empire in 1871 allowed for further standardization.
In 1876, the Prussian government instituted the First Orthographic Conference [de] to achieve a standardization for the entire German Empire. However, its results were rejected, notably by Prime Minister of Prussia Otto von Bismarck.
In 1880, Gymnasium director Konrad Duden published the Vollständiges Orthographisches Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache («Complete Orthographic Dictionary of the German Language»), known simply as the «Duden». In the same year, the Duden was declared to be authoritative in Prussia.[citation needed] Since Prussia was, by far, the largest state in the German Empire, its regulations also influenced spelling elsewhere, for instance, in 1894, when Switzerland recognized the Duden.[citation needed]
In 1901, the interior minister of the German Empire instituted the Second Orthographic Conference. It declared the Duden to be authoritative, with a few innovations. In 1902, its results were approved by the governments of the German Empire, Austria and Switzerland.
In 1944, the Nazi German government planned a reform of the orthography, but because of World War II, it was never implemented.
After 1902, German spelling was essentially decided de facto by the editors of the Duden dictionaries. After World War II, this tradition was followed with two different centers: Mannheim in West Germany and Leipzig in East Germany. By the early 1950s, a few other publishing houses had begun to attack the Duden monopoly in the West by putting out their own dictionaries, which did not always hold to the «official» spellings prescribed by Duden. In response, the Ministers of Culture of the federal states in West Germany officially declared the Duden spellings to be binding as of November 1955.
The Duden editors used their power cautiously because they considered their primary task to be the documentation of usage, not the creation of rules. At the same time, however, they found themselves forced to make finer and finer distinctions in the production of German spelling rules, and each new print run introduced a few reformed spellings.
German spelling reform of 1996[edit]
German spelling and punctuation was changed in 1996 (Reform der deutschen Rechtschreibung von 1996) with the intent to simplify German orthography, and thus to make the language easier to learn,[18] without substantially changing the rules familiar to users of the language. The rules of the new spelling concern correspondence between sounds and written letters (including rules for spelling loan words), capitalisation, joined and separate words, hyphenated spellings, punctuation, and hyphenation at the end of a line. Place names and family names were excluded from the reform.
The reform was adopted initially by Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein and Switzerland, and later by Luxembourg as well.
The new orthography is mandatory only in schools. A 1998 decision of the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany confirmed that there is no law on the spelling people use in daily life, so they can use the old or the new spelling.[19] While the reform is not very popular in opinion polls, it has been adopted by all major dictionaries and the majority of publishing houses.
See also[edit]
- Binnen-I, a convention for gender-neutral language in German
- German braille
- Non-English usage of quotation marks
- German phonology
- Antiqua-Fraktur dispute
- Spelling
- Punctuation
- English spelling
- Dutch orthography
- Otto Basler
References[edit]
- ^ DIN 5009:2022-06, section 4.2 „Buchstaben“ (letters), table 1
- ^ a b Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung 2018, p. 15, section 0 [Vorbemerkungen] (1): «Die Umlautbuchstaben ä, ö, ü»; p. 29, § 25 E2: «der Buchstabe ß»; et passim.
- ^ Official rules of German spelling updated, Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung, 29 June 2017, retrieved 29 June 2017.
- ^ Andrew West (2006): «The Rules for Long S».
- ^ «Das deutsche Alphabet – Wie viele Buchstaben hat das ABC?» (in German). www.buchstabieralphabet.org. Retrieved 2018-09-24.
- ^ Die Erde: Haack Kleiner Atlas; VEB Hermann Haack geographisch-kartographische Anstalt, Gotha, 1982; pages: 97, 100, 153, 278
- ^ Italien: Straßenatlas 1:300.000 mit Ortsregister; Kunth Verlag GmbH & Co. KG 2016/2017; München; page: III
- ^ Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung 2018, p. 29, § 25 E3
- ^ (in German) Empfehlungen und Hinweise für die Schreibweise geographischer Namen, 5. Ausgabe 2010 Archived 2011-07-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ (in German) Rechtschreibrat führt neuen Buchstaben ein, Die Zeit, 29 June 2017, retrieved 29 June 2017.
- ^ (according to the Guinness Book of Records)
- ^ a b canoo.net: Spelling for «Photographie/Fotografie» 2011-03-13
- ^ canoo.net: Spelling for «Delphin/Delfin» 2011-03-13
- ^ canoo.net: Spelling for «Portemonnaie/Portmonee» 2011-03-13
- ^ canoo.net: Spelling for «Foto» 2011-03-13
- ^ Wortherkunft, Sprachliches
Das Wort Ski wurde im 19. Jahrhundert vom norwegischen ski ‚Scheit (gespaltenes Holz); Schneeschuh‘ entlehnt, das seinerseits von dem gleichbedeutenden altnordischen skíð abstammt und mit dem deutschen Wort Scheit urverwandt ist.[1]
Als Pluralform sind laut Duden Ski und Skier bzw. Schi und Schier üblich.[2] Die Aussprache ist vornehmlich wie „Schi“ (wie auch original im Norwegischen), lokal bzw. dialektal kommt sie auch als „Schki“ (etwa in Graubünden oder im Wallis) vor.
- ^ Preu, Otto; Stötzer, Ursula (1985). Sprecherziehung für Studenten pädagogischer Berufe (4th ed.). Berlin: Verlag Volk und Wissen, Volkseigener Verlag. p. 104.
- ^ Upward, Chris (1997). «Spelling Reform in German» (PDF). Journal of the Simplified Spelling Society. J21: 22–24, 36. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-05.
- ^ Bundesverfassungsgericht, Urteil vom 14. Juli 1998, Az.: 1 BvR 1640/97 (in German), Federal Constitutional Court, 14 July 1998.
External links[edit]
- Regeln und Wörterverzeichnis. Aktualisierte Fassung des amtlichen Regelwerks entsprechend den Empfehlungen des Rats für deutsche Rechtschreibung 2016 (PDF) (in German), Mannheim: Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung, 2018, p. § 25 E3, retrieved 2019-05-07