«Covid» redirects here. Not to be confused with corvid.
| Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) |
|
|---|---|
| Other names | COVID, (the) coronavirus |
 |
|
|
Transmission and life-cycle of SARS-CoV-2 causing COVID-19 |
|
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, vomiting, loss of taste or smell; some cases asymptomatic[2][3] |
| Complications | Pneumonia, viral sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, kidney failure, cytokine release syndrome, respiratory failure, pulmonary fibrosis, paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, long COVID |
| Usual onset | 2–14 days (typically 5) from infection |
| Duration | 5 days to chronic |
| Causes | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) |
| Diagnostic method | rRT‑PCR testing, CT scan, Rapid antigen test |
| Prevention | Vaccination,[4] face coverings, quarantine, physical/social distancing, ventilation, hand washing[5] |
| Treatment | Symptomatic and supportive |
| Frequency | 664,338,243[6] confirmed cases |
| Deaths | 6,707,311[6] |
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.[7] The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever,[8] cough, headache,[9] fatigue, breathing difficulties, loss of smell, and loss of taste.[10][11][12] Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected do not develop noticeable symptoms.[13] Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction).[14] Older people are at a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some people continue to experience a range of effects (long COVID) for months after recovery, and damage to organs has been observed.[15] Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the long-term effects of the disease.[15]
COVID‑19 transmits when people breathe air contaminated by droplets and small airborne particles containing the virus. The risk of breathing these is highest when people are in close proximity, but they can be inhaled over longer distances, particularly indoors. Transmission can also occur if contaminated fluids are splashed or sprayed in the eyes, nose, or mouth, or, more rarely, via contaminated surfaces. People remain contagious for up to 20 days and can spread the virus even if they do not develop symptoms.[16][17]
Testing methods for COVID-19 to detect the virus’s nucleic acid include real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT‑PCR),[18][19] transcription-mediated amplification,[18][19][20] and reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT‑LAMP)[18][19] from a nasopharyngeal swab.[21]
Several COVID-19 vaccines have been approved and distributed in various countries, which have initiated mass vaccination campaigns. Other preventive measures include physical or social distancing, quarantining, ventilation of indoor spaces, use of face masks or coverings in public, covering coughs and sneezes, hand washing, and keeping unwashed hands away from the face. While work is underway to develop drugs that inhibit the virus, the primary treatment is symptomatic. Management involves the treatment of symptoms through supportive care, isolation, and experimental measures.
Nomenclature
During the initial outbreak in Wuhan, the virus and disease were commonly referred to as «coronavirus» and «Wuhan coronavirus»,[22][23][24] with the disease sometimes called «Wuhan pneumonia».[25][26] In the past, many diseases have been named after geographical locations, such as the Spanish flu,[27] Middle East respiratory syndrome, and Zika virus.[28] In January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended 2019-nCoV[29] and 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease[30] as interim names for the virus and disease per 2015 guidance and international guidelines against using geographical locations or groups of people in disease and virus names to prevent social stigma.[31][32][33] The official names COVID‑19 and SARS-CoV-2 were issued by the WHO on 11 February 2020 with COVID-19 being shorthand for «coronavirus disease 2019».[34][35] The WHO additionally uses «the COVID‑19 virus» and «the virus responsible for COVID‑19» in public communications.[34][36]
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of COVID-19 are variable depending on the type of variant contracted, ranging from mild symptoms to a potentially fatal illness.[37][38] Common symptoms include coughing, fever, loss of smell (anosmia) and taste (ageusia), with less common ones including headaches, nasal congestion and runny nose, muscle pain, sore throat, diarrhea, eye irritation,[39] and toes swelling or turning purple,[40] and in moderate to severe cases, breathing difficulties.[41] People with the COVID-19 infection may have different symptoms, and their symptoms may change over time. Three common clusters of symptoms have been identified: one respiratory symptom cluster with cough, sputum, shortness of breath, and fever; a musculoskeletal symptom cluster with muscle and joint pain, headache, and fatigue; and a cluster of digestive symptoms with abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.[41] In people without prior ear, nose, or throat disorders, loss of taste combined with loss of smell is associated with COVID-19 and is reported in as many as 88% of symptomatic cases.[42][43][44]
Of people who show symptoms, 81% develop only mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging) that require hospitalization, and 5% of patients develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, septic shock, or multiorgan dysfunction) requiring ICU admission.[45] At least a third of the people who are infected with the virus do not develop noticeable symptoms at any point in time.[46][47] These asymptomatic carriers tend not to get tested and can still spread the disease.[47][48][49][50] Other infected people will develop symptoms later (called «pre-symptomatic») or have very mild symptoms and can also spread the virus.[50]
As is common with infections, there is a delay between the moment a person first becomes infected and the appearance of the first symptoms. The median delay for COVID-19 is four to five days[51] possibly being infectious on 1-4 of those days.[52] Most symptomatic people experience symptoms within two to seven days after exposure, and almost all will experience at least one symptom within 12 days.[51][53]
Most people recover from the acute phase of the disease. However, some people—over half of a cohort of home-isolated young adults identified in June, 2021[54][55] continued to experience a range of effects, such as fatigue, for months even after recovery. This is the result of a condition called long COVID, which can be described as a range of persistent symptoms that continue for weeks and/or months at a time.[56] Long-term damage to organs has also been observed after the onset of COVID-19. Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the potential long-term effects of the disease.[57]
The Omicron variant became dominant in the U.S. in December 2021. Symptoms with the Omicron variant are less severe than they are with other variants.[58]
Cause
COVID‑19 is caused by infection with a strain of coronavirus known as ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2’ (SARS-CoV-2).[59]
Transmission
| Transmission of COVID-19 | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Mode of spread of COVID-19 |
 |
|
| Specialty | Infection prevention and control |
| Types | Respiratory droplet, airborne transmission, fomites |
| Prevention | Face coverings, quarantine, physical/social distancing, ventilation, hand washing, vaccination |
COVID-19 is mainly transmitted when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets/aerosols and small airborne particles containing the virus. Infected people exhale those particles as they breathe, talk, cough, sneeze, or sing.[60][61][62][63] Transmission is more likely the more physically close people are. However, infection can occur over longer distances, particularly indoors.[60][64]
Infectivity can begin four to five days before the onset of symptoms,[65] although contact tracing typically begins only two to three days before symptom onset.[66] Infected people can spread the disease even if they are pre-symptomatic or asymptomatic.[66] Most commonly, the peak viral load in upper respiratory tract samples occurs close to the time of symptom onset and declines after the first week after symptoms begin.[66] Current evidence suggests a duration of viral shedding and the period of infectiousness of up to ten days following symptom onset for people with mild to moderate COVID-19, and up to 20 days for persons with severe COVID-19, including immunocompromised people.[67][66]
Infectious particles range in size from aerosols that remain suspended in the air for long periods of time to larger droplets that remain airborne briefly or fall to the ground.[68][69][70][71] Additionally, COVID-19 research has redefined the traditional understanding of how respiratory viruses are transmitted.[71][72] The largest droplets of respiratory fluid do not travel far, but can be inhaled or land on mucous membranes on the eyes, nose, or mouth to infect.[70] Aerosols are highest in concentration when people are in close proximity, which leads to easier viral transmission when people are physically close,[70][71][72] but airborne transmission can occur at longer distances, mainly in locations that are poorly ventilated;[70] in those conditions small particles can remain suspended in the air for minutes to hours.[70]
The number of people generally infected by one infected person varies,[73] but it is estimated that the R0 («R nought» or «R zero») number is around 2.5.[74] The disease often spreads in clusters, where infections can be traced back to an index case or geographical location.[75] Often in these instances, superspreading events occur, where many people are infected by one person.[73]
Virology
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. It was first isolated from three people with pneumonia connected to the cluster of acute respiratory illness cases in Wuhan.[76] All structural features of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus particle occur in related coronaviruses in nature.[77]
Outside the human body, the virus is destroyed by household soap, which bursts its protective bubble.[78]
SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to the original SARS-CoV.[79] It is thought to have an animal (zoonotic) origin. Genetic analysis has revealed that the coronavirus genetically clusters with the genus Betacoronavirus, in subgenus Sarbecovirus (lineage B) together with two bat-derived strains. It is 96% identical at the whole genome level to other bat coronavirus samples (BatCov RaTG13).[80][81][82] The structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 include membrane glycoprotein (M), envelope protein (E), nucleocapsid protein (N), and the spike protein (S). The M protein of SARS-CoV-2 is about 98% similar to the M protein of bat SARS-CoV, maintains around 98% homology with pangolin SARS-CoV, and has 90% homology with the M protein of SARS-CoV; whereas, the similarity is only around 38% with the M protein of MERS-CoV.[83]
SARS-CoV-2 variants
The many thousands of SARS-CoV-2 variants are grouped into either clades or lineages.[84][85] The WHO, in collaboration with partners, expert networks, national authorities, institutions and researchers, have established nomenclature systems for naming and tracking SARS-CoV-2 genetic lineages by GISAID, Nextstrain and Pango. The expert group convened by the WHO recommended the labelling of variants using letters of the Greek alphabet, for example, Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Gamma, giving the justification that they «will be easier and more practical to discussed by non-scientific audiences.»[86] Nextstrain divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while GISAID divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR).[87] The Pango tool groups variants into lineages, with many circulating lineages being classed under the B.1 lineage.[85][88]
Several notable variants of SARS-CoV-2 emerged throughout 2020.[89][90] Cluster 5 emerged among minks and mink farmers in Denmark.[91] After strict quarantines and a mink euthanasia campaign, the cluster was assessed to no longer be circulating among humans in Denmark as of 1 February 2021.[92]
As of December 2021, there are five dominant variants of SARS-CoV-2 spreading among global populations: the Alpha variant (B.1.1.7, formerly called the UK variant), first found in London and Kent, the Beta variant (B.1.351, formerly called the South Africa variant), the Gamma variant (P.1, formerly called the Brazil variant), the Delta variant (B.1.617.2, formerly called the India variant),[93] and the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529), which had spread to 57 countries as of 7 December.[94][95]
Pathophysiology
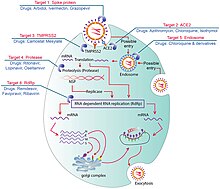
The SARS-CoV-2 virus can infect a wide range of cells and systems of the body. COVID‑19 is most known for affecting the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) and the lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs).[96] The lungs are the organs most affected by COVID‑19 because the virus accesses host cells via the receptor for the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is most abundant on the surface of type II alveolar cells of the lungs.[97] The virus uses a special surface glycoprotein called a «spike» to connect to the ACE2 receptor and enter the host cell.[98]
Respiratory tract
Following viral entry, COVID‑19 infects the ciliated epithelium of the nasopharynx and upper airways.[99]
Nervous system
One common symptom, loss of smell, results from infection of the support cells of the olfactory epithelium, with subsequent damage to the olfactory neurons.[100] The involvement of both the central and peripheral nervous system in COVID‑19 has been reported in many medical publications.[101] It is clear that many people with COVID-19 exhibit neurological or mental health issues. The virus is not detected in the central nervous system (CNS) of the majority of COVID-19 patients with neurological issues. However, SARS-CoV-2 has been detected at low levels in the brains of those who have died from COVID‑19, but these results need to be confirmed.[102] While virus has been detected in cerebrospinal fluid of autopsies, the exact mechanism by which it invades the CNS remains unclear and may first involve invasion of peripheral nerves given the low levels of ACE2 in the brain.[103][104][105] The virus may also enter the bloodstream from the lungs and cross the blood–brain barrier to gain access to the CNS, possibly within an infected white blood cell.[102]
Research conducted when Alpha was the dominant variant has suggested COVID-19 may cause brain damage. It is unknown if such damage is temporary or permanent, and whether Omicron has similar effects.[106][107] Observed individuals infected with COVID-19 (most with mild cases) experienced an additional 0.2% to 2% of brain tissue lost in regions of the brain connected to the sense of smell compared with uninfected individuals, and the overall effect on the brain was equivalent on average to at least one extra year of normal ageing; infected individuals also scored lower on several cognitive tests. All effects were more pronounced among older ages.[108]
Gastrointestinal tract
The virus also affects gastrointestinal organs as ACE2 is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelium[109] as well as endothelial cells and enterocytes of the small intestine.[110]
Cardiovascular system
The virus can cause acute myocardial injury and chronic damage to the cardiovascular system.[111][112] An acute cardiac injury was found in 12% of infected people admitted to the hospital in Wuhan, China,[113] and is more frequent in severe disease.[114] Rates of cardiovascular symptoms are high, owing to the systemic inflammatory response and immune system disorders during disease progression, but acute myocardial injuries may also be related to ACE2 receptors in the heart.[112] ACE2 receptors are highly expressed in the heart and are involved in heart function.[112][115]
A high incidence of thrombosis and venous thromboembolism occurs in people transferred to intensive care units with COVID‑19 infections, and may be related to poor prognosis.[116] Blood vessel dysfunction and clot formation (as suggested by high D-dimer levels caused by blood clots) may have a significant role in mortality, incidences[spelling?] of clots leading to pulmonary embolisms, and ischaemic events within the brain found as complications leading to death in people infected with COVID‑19.[117] Infection may initiate a chain of vasoconstrictive responses within the body, including pulmonary vasoconstriction – a possible mechanism in which oxygenation decreases during pneumonia.[117] Furthermore, damage of arterioles and capillaries was found in brain tissue samples of people who died from COVID‑19.[118][119]
COVID‑19 may also cause substantial structural changes to blood cells, sometimes persisting for months after hospital discharge.[120] A low level of blood lymphocytes may result from the virus acting through ACE2-related entry into lymphocytes.[121]
Other organs
Another common cause of death is complications related to the kidneys.[117] Early reports show that up to 30% of hospitalised patients both in China and in New York have experienced some injury to their kidneys, including some persons with no previous kidney problems.[122]
Autopsies of people who died of COVID‑19 have found diffuse alveolar damage, and lymphocyte-containing inflammatory infiltrates within the lung.[123]
Immunopathology
Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL‑2, IL‑7, IL‑6, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM‑CSF), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP‑10), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1), macrophage inflammatory protein 1‑alpha (MIP‑1‑alpha), and tumour necrosis factor (TNF‑α) indicative of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) suggest an underlying immunopathology.[113]
Interferon alpha plays a complex, Janus-faced role in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Although it promotes the elimination of virus-infected cells, it also upregulates the expression of ACE-2, thereby facilitating the SARS-Cov2 virus to enter cells and to replicate.[124][125] A competition of negative feedback loops (via protective effects of interferon alpha) and positive feedback loops (via upregulation of ACE-2) is assumed to determine the fate of patients suffering from COVID-19.[126]
Additionally, people with COVID‑19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) have classical serum biomarkers of CRS, including elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), D-dimer, and ferritin.[127]
Systemic inflammation results in vasodilation, allowing inflammatory lymphocytic and monocytic infiltration of the lung and the heart. In particular, pathogenic GM-CSF-secreting T cells were shown to correlate with the recruitment of inflammatory IL-6-secreting monocytes and severe lung pathology in people with COVID‑19.[128] Lymphocytic infiltrates have also been reported at autopsy.[123]
Viral and host factors
Virus proteins
Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the ACE2 receptors. It includes two subunits: S1 and S2. S1 determines the virus-host range and cellular tropism via the receptor-binding domain. S2 mediates the membrane fusion of the virus to its potential cell host via the H1 and HR2, which are heptad repeat regions. Studies have shown that S1 domain induced IgG and IgA antibody levels at a much higher capacity. It is the focus spike proteins expression that are involved in many effective COVID‑19 vaccines.[129]
The M protein is the viral protein responsible for the transmembrane transport of nutrients. It is the cause of the bud release and the formation of the viral envelope.[130] The N and E protein are accessory proteins that interfere with the host’s immune response.[130]
Host factors
Human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) is the host factor that SARS-CoV-2 virus targets causing COVID‑19. Theoretically, the usage of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) and ACE inhibitors upregulating ACE2 expression might increase morbidity with COVID‑19, though animal data suggest some potential protective effect of ARB; however no clinical studies have proven susceptibility or outcomes. Until further data is available, guidelines and recommendations for hypertensive patients remain.[131]
The effect of the virus on ACE2 cell surfaces leads to leukocytic infiltration, increased blood vessel permeability, alveolar wall permeability, as well as decreased secretion of lung surfactants. These effects cause the majority of the respiratory symptoms. However, the aggravation of local inflammation causes a cytokine storm eventually leading to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome.[132]
Among healthy adults not exposed to SARS-CoV-2, about 35% have CD4+ T cells that recognise the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (particularly the S2 subunit) and about 50% react to other proteins of the virus, suggesting cross-reactivity from previous common colds caused by other coronaviruses.[133]
It is unknown whether different persons use similar antibody genes in response to COVID‑19.[134]
Host cytokine response
The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the cytokine storm.[135] Levels of interleukin 1B, interferon-gamma, interferon-inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 were all associated with COVID‑19 disease severity. Treatment has been proposed to combat the cytokine storm as it remains to be one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in COVID‑19 disease.[136]
A cytokine storm is due to an acute hyperinflammatory response that is responsible for clinical illness in an array of diseases but in COVID‑19, it is related to worse prognosis and increased fatality. The storm causes acute respiratory distress syndrome, blood clotting events such as strokes, myocardial infarction, encephalitis, acute kidney injury, and vasculitis. The production of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and interferon-gamma, all crucial components of normal immune responses, inadvertently become the causes of a cytokine storm. The cells of the central nervous system, the microglia, neurons, and astrocytes, are also involved in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines affecting the nervous system, and effects of cytokine storms toward the CNS are not uncommon.[137]
Pregnancy response
There are many unknowns for pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic. Given that they are prone to have complications and severe disease infection with other types of coronaviruses, they have been identified as a vulnerable group and advised to take supplementary preventive measures.[138]
Physiological responses to pregnancy can include:
- Immunological: The immunological response to COVID-19, like other viruses, depends on a working immune system. It adapts during pregnancy to allow the development of the foetus whose genetic load is only partially shared with their mother, leading to a different immunological reaction to infections during the course of pregnancy.[138]
- Respiratory: Many factors can make pregnant women more vulnerable to hard respiratory infections. One of them is the total reduction of the lungs’ capacity and inability to clear secretions.[138]
- Coagulation: During pregnancy, there are higher levels of circulating coagulation factors, and the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection can be implicated. The thromboembolic events with associated mortality are a risk for pregnant women.[138]
However, from the evidence base, it is difficult to conclude whether pregnant women are at increased risk of grave consequences of this virus.[138]
In addition to the above, other clinical studies have proved that SARS-CoV-2 can affect the period of pregnancy in different ways. On the one hand, there is little evidence of its impact up to 12 weeks gestation. On the other hand, COVID-19 infection may cause increased rates of unfavourable outcomes in the course of the pregnancy. Some examples of these could be foetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and perinatal mortality, which refers to the foetal death past 22 or 28 completed weeks of pregnancy as well as the death among live-born children up to seven completed days of life.[138]
Unvaccinated women in later stages of pregnancy with COVID-19 are more likely than other patients to need very intensive care. Babies born to mothers with COVID-19 are more likely to have breathing problems. Pregnant women are strongly encouraged to get vaccinated.[139]
Diagnosis
COVID‑19 can provisionally be diagnosed on the basis of symptoms and confirmed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or other nucleic acid testing of infected secretions.[21][140] Along with laboratory testing, chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection.[141] Detection of a past infection is possible with serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the infection.[21]
Viral testing
The standard methods of testing for presence of SARS-CoV-2 are nucleic acid tests,[21][142] which detects the presence of viral RNA fragments.[143] As these tests detect RNA but not infectious virus, its «ability to determine duration of infectivity of patients is limited.»[144] The test is typically done on respiratory samples obtained by a nasopharyngeal swab; however, a nasal swab or sputum sample may also be used.[145][146] Results are generally available within hours.[21] The WHO has published several testing protocols for the disease.[147]
Several laboratories and companies have developed serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to infection. Several have been evaluated by Public Health England and approved for use in the UK.[148]
The University of Oxford’s CEBM has pointed to mounting evidence[149][150] that «a good proportion of ‘new’ mild cases and people re-testing positives after quarantine or discharge from hospital are not infectious, but are simply clearing harmless virus particles which their immune system has efficiently dealt with» and have called for «an international effort to standardize and periodically calibrate testing»[151] In September 2020, the UK government issued «guidance for procedures to be implemented in laboratories to provide assurance of positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA results during periods of low prevalence, when there is a reduction in the predictive value of positive test results».[152]
Imaging
A CT scan of a person with COVID-19 shows lesions (bright regions) in the lungs
CT scan of rapid progression stage of COVID-19
Chest X-ray showing COVID‑19 pneumonia
Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening.[141][153] Bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacities with a peripheral, asymmetric, and posterior distribution are common in early infection.[141][154] Subpleural dominance, crazy paving (lobular septal thickening with variable alveolar filling), and consolidation may appear as the disease progresses.[141][155] Characteristic imaging features on chest radiographs and computed tomography (CT) of people who are symptomatic include asymmetric peripheral ground-glass opacities without pleural effusions.[156]
Many groups have created COVID‑19 datasets that include imagery such as the Italian Radiological Society which has compiled an international online database of imaging findings for confirmed cases.[157] Due to overlap with other infections such as adenovirus, imaging without confirmation by rRT-PCR is of limited specificity in identifying COVID‑19.[156] A large study in China compared chest CT results to PCR and demonstrated that though imaging is less specific for the infection, it is faster and more sensitive.[140]
Coding
In late 2019, the WHO assigned emergency ICD-10 disease codes U07.1 for deaths from lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and U07.2 for deaths from clinically or epidemiologically diagnosed COVID‑19 without lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.[158]
Pathology
The main pathological findings at autopsy are:
- Macroscopy: pericarditis, lung consolidation and pulmonary oedema[123]
- Lung findings:
- minor serous exudation, minor fibrin exudation[123]
- pulmonary oedema, pneumocyte hyperplasia, large atypical pneumocytes, interstitial inflammation with lymphocytic infiltration and multinucleated giant cell formation[123]
- diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) with diffuse alveolar exudates. DAD is the cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and severe hypoxaemia.[123]
- organisation of exudates in alveolar cavities and pulmonary interstitial fibrosis[123]
- plasmocytosis in BAL[159]
- Blood and vessels: disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC);[160] leukoerythroblastic reaction,[161] endotheliitis,[162] hemophagocytosis[162]
- Heart: cardiac muscle cell necrosis[162]
- Liver: microvesicular steatosis[123]
- Nose: shedding of olfactory epithelium[100]
- Brain: infarction[162]
- Kidneys: acute tubular damage.[162]
- Spleen: white pulp depletion.[162]
Prevention
Without pandemic containment measures – such as social distancing, vaccination, and face masks – pathogens can spread exponentially.[163] This graphic shows how early adoption of containment measures tends to protect wider swaths of the population.
Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations,[164] washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.[165][166]
Those diagnosed with COVID‑19 or who believe they may be infected are advised by the CDC to stay home except to get medical care, call ahead before visiting a healthcare provider, wear a face mask before entering the healthcare provider’s office and when in any room or vehicle with another person, cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue, regularly wash hands with soap and water and avoid sharing personal household items.[167][168]
The first COVID‑19 vaccine was granted regulatory approval on 2 December 2020 by the UK medicines regulator MHRA.[169] It was evaluated for emergency use authorization (EUA) status by the US FDA, and in several other countries.[170] Initially, the US National Institutes of Health guidelines do not recommend any medication for prevention of COVID‑19, before or after exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, outside the setting of a clinical trial.[171][172] Without a vaccine, other prophylactic measures, or effective treatments, a key part of managing COVID‑19 is trying to decrease and delay the epidemic peak, known as «flattening the curve».[173] This is done by slowing the infection rate to decrease the risk of health services being overwhelmed, allowing for better treatment of active cases, and delaying additional cases until effective treatments or a vaccine become available.[173][174]
Vaccine
Different vaccine candidate types in development for SARS-CoV-2
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
Prior to the COVID‑19 pandemic, an established body of knowledge existed about the structure and function of coronaviruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This knowledge accelerated the development of various vaccine platforms during early 2020.[175] The initial focus of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was on preventing symptomatic, often severe illness.[176] In January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequence data was shared through GISAID, and by March 2020, the global pharmaceutical industry announced a major commitment to address COVID‑19.[177] In 2020, the first COVID‑19 vaccines were developed and made available to the public through emergency authorizations[178] and conditional approvals.[179][180] Initially, most COVID‑19 vaccines were two-dose vaccines, with the sole exception being the single-dose Janssen COVID-19 vaccine.[178] However, immunity from the vaccines has been found to wane over time, requiring people to get booster doses of the vaccine to maintain protection against COVID‑19.[178]
Face masks and respiratory hygiene
Masks with an exhalation valve. The valves are a weak point that can transmit the viruses outwards.
The WHO and the US CDC recommend individuals wear non-medical face coverings in public settings where there is an increased risk of transmission and where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain.[181][182] This recommendation is meant to reduce the spread of the disease by asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic individuals and is complementary to established preventive measures such as social distancing.[182][183] Face coverings limit the volume and travel distance of expiratory droplets dispersed when talking, breathing, and coughing.[182][183] A face covering without vents or holes will also filter out particles containing the virus from inhaled and exhaled air, reducing the chances of infection.[184] However, if the mask includes an exhalation valve, a wearer that is infected (and possibly asymptomatic) may transmit the virus through the valve. Many countries and local jurisdictions encourage or mandate the use of face masks or cloth face coverings by members of the public to limit the spread of the virus.[185]
Masks are also strongly recommended for those who may have been infected and those taking care of someone who may have the disease.[186] When not wearing a mask, the CDC recommends covering the mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing and recommends using the inside of the elbow if no tissue is available. Proper hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is encouraged. Healthcare professionals interacting directly with people who have COVID‑19 are advised to use respirators at least as protective as NIOSH-certified N95 or equivalent, in addition to other personal protective equipment.[187]
Indoor ventilation and avoiding crowded indoor spaces
The CDC recommends that crowded indoor spaces should be avoided.[188] When indoors, increasing the rate of air change, decreasing recirculation of air and increasing the use of outdoor air can reduce transmission.[188][189] The WHO recommends ventilation and air filtration in public spaces to help clear out infectious aerosols.[190][191][192]
Exhaled respiratory particles can build-up within enclosed spaces with inadequate ventilation. The risk of COVID‑19 infection increases especially in spaces where people engage in physical exertion or raise their voice (e.g., exercising, shouting, singing) as this increases exhalation of respiratory droplets. Prolonged exposure to these conditions, typically more than 15 minutes, leads to higher risk of infection.[188]
Displacement ventilation with large natural inlets can move stale air directly to the exhaust in laminar flow while significantly reducing the concentration of droplets and particles. Passive ventilation reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs but may lack controllability and heat recovery. Displacement ventilation can also be achieved mechanically with higher energy and maintenance costs. The use of large ducts and openings helps to prevent mixing in closed environments. Recirculation and mixing should be avoided because recirculation prevents dilution of harmful particles and redistributes possibly contaminated air, and mixing increases the concentration and range of infectious particles and keeps larger particles in the air.[193]
Hand-washing and hygiene
Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required.[194] The WHO also recommends that individuals wash hands often with soap and water for at least twenty seconds, especially after going to the toilet or when hands are visibly dirty, before eating and after blowing one’s nose.[195] When soap and water are not available, the CDC recommends using an alcohol-based hand sanitiser with at least 60% alcohol.[196] For areas where commercial hand sanitisers are not readily available, the WHO provides two formulations for local production. In these formulations, the antimicrobial activity arises from ethanol or isopropanol. Hydrogen peroxide is used to help eliminate bacterial spores in the alcohol; it is «not an active substance for hand antisepsis.» Glycerol is added as a humectant.[197]
Social distancing (also known as physical distancing) includes infection control actions intended to slow the spread of the disease by minimising close contact between individuals. Methods include quarantines; travel restrictions; and the closing of schools, workplaces, stadiums, theatres, or shopping centres. Individuals may apply social distancing methods by staying at home, limiting travel, avoiding crowded areas, using no-contact greetings, and physically distancing themselves from others.[198] Many governments are mandating or recommending social distancing in regions affected by the outbreak.[199]
Outbreaks have occurred in prisons due to crowding and an inability to enforce adequate social distancing.[200][201] In the United States, the prisoner population is ageing and many of them are at high risk for poor outcomes from COVID‑19 due to high rates of coexisting heart and lung disease, and poor access to high-quality healthcare.[200]
Surface cleaning
After being expelled from the body, coronaviruses can survive on surfaces for hours to days. If a person touches the dirty surface, they may deposit the virus at the eyes, nose, or mouth where it can enter the body and cause infection.[202] Evidence indicates that contact with infected surfaces is not the main driver of COVID‑19,[203][204][205] leading to recommendations for optimised disinfection procedures to avoid issues such as the increase of antimicrobial resistance through the use of inappropriate cleaning products and processes.[206][207] Deep cleaning and other surface sanitation has been criticised as hygiene theatre, giving a false sense of security against something primarily spread through the air.[208][209]
The amount of time that the virus can survive depends significantly on the type of surface, the temperature, and the humidity.[210] Coronaviruses die very quickly when exposed to the UV light in sunlight.[210] Like other enveloped viruses, SARS-CoV-2 survives longest when the temperature is at room temperature or lower, and when the relative humidity is low (<50%).[210]
On many surfaces, including glass, some types of plastic, stainless steel, and skin, the virus can remain infective for several days indoors at room temperature, or even about a week under ideal conditions.[210][211] On some surfaces, including cotton fabric and copper, the virus usually dies after a few hours.[210] The virus dies faster on porous surfaces than on non-porous surfaces due to capillary action within pores and faster aerosol droplet evaporation.[212][205][210] However, of the many surfaces tested, two with the longest survival times are N95 respirator masks and surgical masks, both of which are considered porous surfaces.[210]
The CDC says that in most situations, cleaning surfaces with soap or detergent, not disinfecting, is enough to reduce risk of transmission.[213][214] The CDC recommends that if a COVID‑19 case is suspected or confirmed at a facility such as an office or day care, all areas such as offices, bathrooms, common areas, shared electronic equipment like tablets, touch screens, keyboards, remote controls, and ATMs used by the ill persons should be disinfected.[215] Surfaces may be decontaminated with 62–71 per cent ethanol, 50–100 per cent isopropanol, 0.1 per cent sodium hypochlorite, 0.5 per cent hydrogen peroxide, 0.2–7.5 per cent povidone-iodine, or 50–200 ppm hypochlorous acid. Other solutions, such as benzalkonium chloride and chlorhexidine gluconate, are less effective. Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation may also be used,[190] although popular devices require 5–10 min exposure and may deteriorate some materials over time.[216] A datasheet comprising the authorised substances to disinfection in the food industry (including suspension or surface tested, kind of surface, use dilution, disinfectant and inocuylum volumes) can be seen in the supplementary material of.[206]
Self-isolation
Self-isolation at home has been recommended for those diagnosed with COVID‑19 and those who suspect they have been infected. Health agencies have issued detailed instructions for proper self-isolation.[217] Many governments have mandated or recommended self-quarantine for entire populations. The strongest self-quarantine instructions have been issued to those in high-risk groups.[218] Those who may have been exposed to someone with COVID‑19 and those who have recently travelled to a country or region with the widespread transmission have been advised to self-quarantine for 14 days from the time of last possible exposure.[219]
A 2021 Cochrane rapid review found that based upon low-certainty evidence, international travel-related control measures such as restricting cross-border travel may help to contain the spread of COVID‑19.[220] Additionally, symptom/exposure-based screening measures at borders may miss many positive cases.[220] While test-based border screening measures may be more effective, it could also miss many positive cases if only conducted upon arrival without follow-up. The review concluded that a minimum 10-day quarantine may be beneficial in preventing the spread of COVID‑19 and may be more effective if combined with an additional control measure like border screening.[220]
Treatment
An overview of COVID-19 therapeutics and drugs
Although several medications have been approved in different countries as of April 2022, not all countries have these medications. Patients with mild to moderate symptoms who are in the risk groups can take nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (marketed as Paxlovid) or remdesivir, either of which reduces the risk of serious illness or hospitalization.[221] In the US, the Biden Administration COVID-19 action plan includes the Test to Treat initiative, where people can go to a pharmacy, take a COVID test, and immediately receive free Paxlovid if they test positive.[222]
Highly effective vaccines have reduced mortality related to SARS-CoV-2; however, for those awaiting vaccination, as well as for the estimated millions of immunocompromised persons who are unlikely to respond robustly to vaccination, treatment remains important.[223] The cornerstone of management of COVID-19 has been supportive care, which includes treatment to relieve symptoms, fluid therapy, oxygen support and prone positioning as needed, and medications or devices to support other affected vital organs.[224][225][226]
Most cases of COVID-19 are mild. In these, supportive care includes medication such as paracetamol or NSAIDs to relieve symptoms (fever, body aches, cough), proper intake of fluids, rest, and nasal breathing.[227][228][229][230] Good personal hygiene and a healthy diet are also recommended.[231] As of April 2020 the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended that those who suspect they are carrying the virus isolate themselves at home and wear a face mask.[232]
As of November 2020 use of the glucocorticoid dexamethasone had been strongly recommended in those severe cases treated in hospital with low oxygen levels, to reduce the risk of death.[233][234][235] Noninvasive ventilation and, ultimately, admission to an intensive care unit for mechanical ventilation may be required to support breathing.[236] Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has been used to address respiratory failure, but its benefits are still under consideration.[237][238] Some of the cases of severe disease course are caused by systemic hyper-inflammation, the so-called cytokine storm.[239]
Prognosis and risk factors
The severity of COVID‑19 varies. The disease may take a mild course with few or no symptoms, resembling other common upper respiratory diseases such as the common cold. In 3–4% of cases (7.4% for those over age 65) symptoms are severe enough to cause hospitalisation.[240] Mild cases typically recover within two weeks, while those with severe or critical diseases may take three to six weeks to recover. Among those who have died, the time from symptom onset to death has ranged from two to eight weeks.[80] The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that the median time between the onset of symptoms and death was twelve days, with seven being hospitalised. However, people transferred to an ICU had a median time of ten days between hospitalisation and death.[241] Abnormal sodium levels during hospitalization with COVID-19 are associated with poor prognoses: high sodium with a greater risk of death, and low sodium with an increased chance of needing ventilator support.[242][243] Prolonged prothrombin time and elevated C-reactive protein levels on admission to the hospital are associated with severe course of COVID‑19 and with a transfer to ICU.[244][245]
Some early studies suggest 10% to 20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month.[246][247] A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems including fatigue and shortness of breath.[248] On 30 October 2020, WHO chief Tedros Adhanom warned that «to a significant number of people, the COVID virus poses a range of serious long-term effects.» He has described the vast spectrum of COVID‑19 symptoms that fluctuate over time as «really concerning». They range from fatigue, a cough and shortness of breath, to inflammation and injury of major organs – including the lungs and heart, and also neurological and psychologic effects. Symptoms often overlap and can affect any system in the body. Infected people have reported cyclical bouts of fatigue, headaches, months of complete exhaustion, mood swings, and other symptoms. Tedros therefore concluded that a strategy of achieving herd immunity by infection, rather than vaccination, is «morally unconscionable and unfeasible».[249]
In terms of hospital readmissions about 9% of 106,000 individuals had to return for hospital treatment within two months of discharge. The average to readmit was eight days since first hospital visit. There are several risk factors that have been identified as being a cause of multiple admissions to a hospital facility. Among these are advanced age (above 65 years of age) and presence of a chronic condition such as diabetes, COPD, heart failure or chronic kidney disease.[250][251]
According to scientific reviews smokers are more likely to require intensive care or die compared to non-smokers.[252][253] Acting on the same ACE2 pulmonary receptors affected by smoking, air pollution has been correlated with the disease.[253] Short term[254] and chronic[255] exposure to air pollution seems to enhance morbidity and mortality from COVID‑19.[256][257][258] Pre-existing heart and lung diseases[259] and also obesity, especially in conjunction with fatty liver disease, contributes to an increased health risk of COVID‑19.[253][260][261][262]
It is also assumed that those that are immunocompromised are at higher risk of getting severely sick from SARS-CoV-2.[263] One research study that looked into the COVID‑19 infections in hospitalised kidney transplant recipients found a mortality rate of 11%.[264]
Men with untreated hypogonadism were 2.4 times more likely than men with eugonadism to be hospitalized if they contracted COVID-19; Hypogonad men treated with testosterone were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than men who were not treated for hypogonadism.[265]
Genetic risk factors
Genetics plays an important role in the ability to fight off Covid.[266] For instance, those that do not produce detectable type I interferons or produce auto-antibodies against these may get much sicker from COVID‑19.[267][268] Genetic screening is able to detect interferon effector genes.[269] Some genetic variants are risk factors in specific populations. For instance, and allele of the DOCK2 gene (dedicator of cytokinesis 2 gene) is a common risk factor in Asian populations but much less common in Europe. The mutation leads to lower expression of DOCK2 especially in younger patients with severe Covid.[270] In fact, many other genes and genetic variants have been found that determine the outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infections.[271]
Children
While very young children have experienced lower rates of infection, older children have a rate of infection that is similar to the population as a whole.[272][273] Children are likely to have milder symptoms and are at lower risk of severe disease than adults.[274] The CDC reports that in the US roughly a third of hospitalised children were admitted to the ICU,[275] while a European multinational study of hospitalised children from June 2020, found that about 8% of children admitted to a hospital needed intensive care.[276] Four of the 582 children (0.7%) in the European study died, but the actual mortality rate may be «substantially lower» since milder cases that did not seek medical help were not included in the study.[277][278]
Complications
Complications may include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, septic shock, and death.[279][280][281][282] Cardiovascular complications may include heart failure, arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation), heart inflammation, and thrombosis, particularly venous thromboembolism.[283][284][285][286][287][288] Approximately 20–30% of people who present with COVID‑19 have elevated liver enzymes, reflecting liver injury.[289][172]
Neurologic manifestations include seizure, stroke, encephalitis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome (which includes loss of motor functions).[290][291] Following the infection, children may develop paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, which has symptoms similar to Kawasaki disease, which can be fatal.[292][293] In very rare cases, acute encephalopathy can occur, and it can be considered in those who have been diagnosed with COVID‑19 and have an altered mental status.[294]
In the case of pregnant women, it is important to note that, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, pregnant women are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill from COVID‑19.[295] This is because pregnant women with COVID‑19 appear to be more likely to develop respiratory and obstetric complications that can lead to miscarriage, premature delivery and intrauterine growth restriction.[295]
Fungal infections such as aspergillosis, candidiasis, cryptococcosis and mucormycosis have been recorded in patients recovering from COVID‑19.[296][297]
Longer-term effects
Some early studies suggest that 10–20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month.[298][247] A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems, including fatigue and shortness of breath.[299] About 5–10% of patients admitted to hospital progress to severe or critical disease, including pneumonia and acute respiratory failure.[300]
By a variety of mechanisms, the lungs are the organs most affected in COVID‑19.[301] In people requiring hospital admission, up to 98% of CT scans performed show lung abnormalities after 28 days of illness even if they had clinically improved.[302]
People with advanced age, severe disease, prolonged ICU stays, or who smoke are more likely to have long-lasting effects, including pulmonary fibrosis.[303] Overall, approximately one-third of those investigated after four weeks will have findings of pulmonary fibrosis or reduced lung function as measured by DLCO, even in asymptomatic people, but with the suggestion of continuing improvement with the passing of more time.[301] After severe disease, lung function can take anywhere from three months to a year or more to return to previous levels.[304]
The risks of cognitive deficit, dementia, psychotic disorders, and epilepsy or seizures persists at an increased level two years after infection.[305]
Immunity
The immune response by humans to SARS-CoV-2 virus occurs as a combination of the cell-mediated immunity and antibody production,[306] just as with most other infections.[307] B cells interact with T cells and begin dividing before selection into the plasma cell, partly on the basis of their affinity for antigen.[308] Since SARS-CoV-2 has been in the human population only since December 2019, it remains unknown if the immunity is long-lasting in people who recover from the disease.[309] The presence of neutralising antibodies in blood strongly correlates with protection from infection, but the level of neutralising antibody declines with time. Those with asymptomatic or mild disease had undetectable levels of neutralising antibody two months after infection. In another study, the level of neutralising antibodies fell four-fold one to four months after the onset of symptoms. However, the lack of antibodies in the blood does not mean antibodies will not be rapidly produced upon reexposure to SARS-CoV-2. Memory B cells specific for the spike and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 last for at least six months after the appearance of symptoms.[309]
As of August 2021, reinfection with COVID‑19 was possible but uncommon. The first case of reinfection was documented in August 2020.[310] A systematic review found 17 cases of confirmed reinfection in medical literature as of May 2021.[310] With the Omicron variant, as of 2022, reinfections have become common, albeit it is unclear how common.[311] COVID-19 reinfections are thought to likely be less severe than primary infections, especially if one was previously infected by the same variant.[311][additional citation(s) needed]
Mortality
Several measures are commonly used to quantify mortality.[312] These numbers vary by region and over time and are influenced by the volume of testing, healthcare system quality, treatment options, time since the initial outbreak, and population characteristics such as age, sex, and overall health.[313]
The mortality rate reflects the number of deaths within a specific demographic group divided by the population of that demographic group. Consequently, the mortality rate reflects the prevalence as well as the severity of the disease within a given population. Mortality rates are highly correlated to age, with relatively low rates for young people and relatively high rates among the elderly.[314][315][316] In fact, one relevant factor of mortality rates is the age structure of the countries’ populations. For example, the case fatality rate for COVID‑19 is lower in India than in the US since India’s younger population represents a larger percentage than in the US.[317]
Case fatality rate
The case fatality rate (CFR) reflects the number of deaths divided by the number of diagnosed cases within a given time interval. Based on Johns Hopkins University statistics, the global death-to-case ratio is 1.01% (6,707,311/664,338,243) as of 9 January 2023.[6] The number varies by region.[318][319]
-
Total confirmed cases over time
-
Total confirmed cases of COVID‑19 per million people[320]
-
Total deaths over time
-
Total confirmed deaths due to COVID‑19 per million people[321]
Infection fatality rate
A key metric in gauging the severity of COVID‑19 is the infection fatality rate (IFR), also referred to as the infection fatality ratio or infection fatality risk.[322][323][324] This metric is calculated by dividing the total number of deaths from the disease by the total number of infected individuals; hence, in contrast to the CFR, the IFR incorporates asymptomatic and undiagnosed infections as well as reported cases.[325]
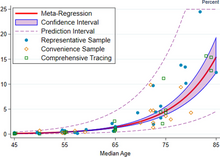
Estimates
The red line shows the estimate of infection fatality rate (IFR), in percentage terms, as a function of age. The shaded region depicts the 95% confidence interval for that estimate. Markers denotes specific observations used in the meta-analysis.[326]
The same relationship plotted on a log scale
A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy.[326] That study also found that most of these differences in IFR reflected corresponding differences in the age composition of the population and age-specific infection rates; in particular, the metaregression estimate of IFR is very low for children and younger adults (e.g., 0.002% at age 10 and 0.01% at age 25) but increases progressively to 0.4% at age 55, 1.4% at age 65, 4.6% at age 75, and 15% at age 85.[326] These results were also highlighted in a December 2020 report issued by the WHO.[327]
| Age group | IFR |
|---|---|
| 0–34 | 0.004% |
| 35–44 | 0.068% |
| 45–54 | 0.23% |
| 55–64 | 0.75% |
| 65–74 | 2.5% |
| 75–84 | 8.5% |
| 85 + | 28.3% |
An analysis of those IFR rates indicates that COVID‑19 is hazardous not only for the elderly but also for middle-aged adults, for whom the infection fatality rate of COVID-19 is two orders of magnitude greater than the annualised risk of a fatal automobile accident and far more dangerous than seasonal influenza.[326]
Earlier estimates of IFR
At an early stage of the pandemic, the World Health Organization reported estimates of IFR between 0.3% and 1%.[328][329] On 2 July, The WHO’s chief scientist reported that the average IFR estimate presented at a two-day WHO expert forum was about 0.6%.[330][331] In August, the WHO found that studies incorporating data from broad serology testing in Europe showed IFR estimates converging at approximately 0.5–1%.[332] Firm lower limits of IFRs have been established in a number of locations such as New York City and Bergamo in Italy since the IFR cannot be less than the population fatality rate. (After sufficient time however, people can get reinfected).[333] As of 10 July, in New York City, with a population of 8.4 million, 23,377 individuals (18,758 confirmed and 4,619 probable) have died with COVID‑19 (0.3% of the population).[334] Antibody testing in New York City suggested an IFR of ≈0.9%,[335] and ≈1.4%.[336] In Bergamo province, 0.6% of the population has died.[337] In September 2020, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported preliminary estimates of age-specific IFRs for public health planning purposes.[338]
Sex differences
| Percentage of infected people who are hospitalised | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.1 (0.07–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
0.9 (0.5–1.5) |
1.3 (0.7–2.1) |
2.6 (1.5–4.2) |
5.1 (2.9–8.3) |
7.8 (4.4–12.8) |
19.3 (10.9–31.6) |
2.6 (1.5–4.3) |
| Male | 0.2 (0.08–0.2) |
0.6 (0.3–0.9) |
1.2 (0.7–1.9) |
1.6 (0.9–2.6) |
3.2 (1.8–5.2) |
6.7 (3.7–10.9) |
11.0 (6.2–17.9) |
37.6 (21.1–61.3) |
3.3 (1.8–5.3) |
| Total | 0.1 (0.08–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
1.1 (0.6–1.7) |
1.4 (0.8–2.3) |
2.9 (1.6–4.7) |
5.8 (3.3–9.5) |
9.3 (5.2–15.1) |
26.2 (14.8–42.7) |
2.9 (1.7–4.8) |
| Percentage of hospitalised people who go to Intensive Care Unit | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 16.7 (14.3–19.3) |
8.7 (7.5–9.9) |
11.9 (10.9–13.0) |
16.6 (15.6–17.7) |
20.7 (19.8–21.6) |
23.1 (22.2–24.0) |
18.7 (18.0–19.5) |
4.2 (4.0–4.5) |
14.3 (13.9–14.7) |
| Male | 26.9 (23.1–31.1) |
14.0 (12.2–16.0) |
19.2 (17.6–20.9) |
26.9 (25.4–28.4) |
33.4 (32.0–34.8) |
37.3 (36.0–38.6) |
30.2 (29.1–31.3) |
6.8 (6.5–7.2) |
23.1 (22.6–23.6) |
| Total | 22.2 (19.1–25.7) |
11.6 (10.1–13.2) |
15.9 (14.5–17.3) |
22.2 (21.0–23.5) |
27.6 (26.5–28.7) |
30.8 (29.8–31.8) |
24.9 (24.1–25.8) |
5.6 (5.3–5.9) |
19.0 (18.7–19.44) |
| Percent of hospitalised people who die | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.5 (0.2–1.0) |
0.9 (0.5–1.3) |
1.5 (1.2–1.9) |
2.6 (2.3–3.0) |
5.2 (4.8–5.6) |
10.1 (9.5–10.6) |
16.7 (16.0–17.4) |
25.2 (24.4–26.0) |
14.4 (14.0–14.8) |
| Male | 0.7 (0.3–1.5) |
1.3 (0.8–1.9) |
2.2 (1.7–2.7) |
3.8 (3.3–4.4) |
7.6 (7.0–8.2) |
14.8 (14.1–15.6) |
24.6 (23.7–25.6) |
37.1 (36.1–38.2) |
21.2 (20.8–21.7) |
| Total | 0.6 (0.2–1.3) |
1.1 (0.7–1.6) |
1.9 (1.5–2.3) |
3.3 (2.9–3.8) |
6.5 (6.0–7.0) |
12.6 (12.0–13.2) |
21.0 (20.3–21.7) |
31.6 (30.9–32.4) |
18.1 (17.8–18.4) |
| Percent of infected people who die – infection fatality rate (IFR) | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.001 (<0.001–0.002) |
0.004 (0.002–0.007) |
0.01 (0.007–0.02) |
0.03 (0.02–0.06) |
0.1 (0.08–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
1.3 (0.7–2.1) |
4.9 (2.7–8.0) |
0.4 (0.2–0.6) |
| Male | 0.001 (<0.001–0.003) |
0.007 (0.003–0.01) |
0.03 (0.02–0.05) |
0.06 (0.03–0.1) |
0.2 (0.1–0.4) |
1.0 (0.6–1.6) |
2.7 (1.5–1.4) |
14.0 (7.9–22.7) |
0.7 (0.4–1.1) |
| Total | 0.001 (<0.001–0.002) |
0.005 (0.003–0.01) |
0.02 (0.01–0.03) |
0.05 (0.03–0.08) |
0.2 (0.1–0.3) |
0.7 (0.4–1.2) |
1.9 (1.1–3.2) |
8.3 (4.7–13.5) |
0.5 (0.3–0.9) |
| Numbers in parentheses are 95% credible intervals for the estimates. |
COVID‑19 case fatality rates are higher among men than women in most countries. However, in a few countries like India, Nepal, Vietnam, and Slovenia the fatality cases are higher in women than men.[317] Globally, men are more likely to be admitted to the ICU and more likely to die.[340][341] One meta-analysis found that globally, men were more likely to get COVID‑19 than women; there were approximately 55 men and 45 women per 100 infections (CI: 51.43–56.58).[342]
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported the death rate was 2.8% for men and 1.7% for women.[343] Later reviews in June 2020 indicated that there is no significant difference in susceptibility or in CFR between genders.[344][345] One review acknowledges the different mortality rates in Chinese men, suggesting that it may be attributable to lifestyle choices such as smoking and drinking alcohol rather than genetic factors.[346] Smoking, which in some countries like China is mainly a male activity, is a habit that contributes to increasing significantly the case fatality rates among men.[317] Sex-based immunological differences, lesser prevalence of smoking in women and men developing co-morbid conditions such as hypertension at a younger age than women could have contributed to the higher mortality in men.[347] In Europe as of February 2020, 57% of the infected people were men and 72% of those died with COVID‑19 were men.[348] As of April 2020, the US government is not tracking sex-related data of COVID‑19 infections.[349] Research has shown that viral illnesses like Ebola, HIV, influenza and SARS affect men and women differently.[349]
Ethnic differences
In the US, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred among African Americans and other minority groups.[350] Structural factors that prevent them from practising social distancing include their concentration in crowded substandard housing and in «essential» occupations such as retail grocery workers, public transit employees, health-care workers and custodial staff. Greater prevalence of lacking health insurance and care of underlying conditions such as diabetes,[351] hypertension, and heart disease also increase their risk of death.[352] Similar issues affect Native American and Latino communities.[350] On the one hand, in the Dominican Republic there is a clear example of both gender and ethnic inequality. In this Latin American territory, there is great inequality and precariousness that especially affects Dominican women, with greater emphasis on those of Haitian descent.[353] According to a US health policy non-profit, 34% of American Indian and Alaska Native People (AIAN) non-elderly adults are at risk of serious illness compared to 21% of white non-elderly adults.[354] The source attributes it to disproportionately high rates of many health conditions that may put them at higher risk as well as living conditions like lack of access to clean water.[355]
Leaders have called for efforts to research and address the disparities.[356] In the UK, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred in those of a Black, Asian, and other ethnic minority background.[357][358][359] More severe impacts upon patients including the relative incidence of the necessity of hospitalisation requirements, and vulnerability to the disease has been associated via DNA analysis to be expressed in genetic variants at chromosomal region 3, features that are associated with European Neanderthal heritage. That structure imposes greater risks that those affected will develop a more severe form of the disease.[360] The findings are from Professor Svante Pääbo and researchers he leads at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the Karolinska Institutet.[360] This admixture of modern human and Neanderthal genes is estimated to have occurred roughly between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago in Southern Europe.[360]
Comorbidities
Biological factors (immune response) and the general behaviour (habits) can strongly determine the consequences of COVID‑19.[317] Most of those who die of COVID‑19 have pre-existing (underlying) conditions, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus,[351] and cardiovascular disease.[361] According to March data from the United States, 89% of those hospitalised had preexisting conditions.[362] The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that out of 8.8% of deaths where medical charts were available, 96.1% of people had at least one comorbidity with the average person having 3.4 diseases.[241] According to this report the most common comorbidities are hypertension (66% of deaths), type 2 diabetes (29.8% of deaths), ischaemic heart disease (27.6% of deaths), atrial fibrillation (23.1% of deaths) and chronic renal failure (20.2% of deaths).
Most critical respiratory comorbidities according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are: moderate or severe asthma, pre-existing COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis.[363] Evidence stemming from meta-analysis of several smaller research papers also suggests that smoking can be associated with worse outcomes.[364][365] When someone with existing respiratory problems is infected with COVID‑19, they might be at greater risk for severe symptoms.[366] COVID‑19 also poses a greater risk to people who misuse opioids and amphetamines, insofar as their drug use may have caused lung damage.[367]
In August 2020, the CDC issued a caution that tuberculosis (TB) infections could increase the risk of severe illness or death. The WHO recommended that people with respiratory symptoms be screened for both diseases, as testing positive for COVID‑19 could not rule out co-infections. Some projections have estimated that reduced TB detection due to the pandemic could result in 6.3 million additional TB cases and 1.4 million TB-related deaths by 2025.[368]
History
The virus is thought to be of natural animal origin, most likely through spillover infection.[77][369][370] A joint-study conducted in early 2021 by the People’s Republic of China and the World Health Organization indicated that the virus descended from a coronavirus that infects wild bats, and likely spread to humans through an intermediary wildlife host.[371] There are several theories about where the index case originated and investigations into the origin of the pandemic are ongoing.[372] According to articles published in July 2022 in Science, virus transmission into humans occurred through two spillover events in November 2019 and was likely due to live wildlife trade on the Huanan wet market in the city of Wuhan (Hubei, China).[373][374][375] Doubts about the conclusions have mostly centred on the precise site of spillover.[376] Earlier phylogenetics estimated that SARS-CoV-2 arose in October or November 2019.[377][378][379] A phylogenetic algorithm analysis suggested that the virus may have been circulating in Guangdong before Wuhan.[380] U.S intelligence agencies and other scientists have found that the virus may have been unintentionally leaked from a laboratory such as the Wuhan Institute of Virology, but that it was not developed as a biological weapon and is unlikely to have been genetically engineered.[381][382][383][384]
The first confirmed human infections were in Wuhan. A study of the first 41 cases of confirmed COVID‑19, published in January 2020 in The Lancet, reported the earliest date of onset of symptoms as 1 December 2019.[385][386][387] Official publications from the WHO reported the earliest onset of symptoms as 8 December 2019.[388] Human-to-human transmission was confirmed by the WHO and Chinese authorities by 20 January 2020.[389][390] According to official Chinese sources, these were mostly linked to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, which also sold live animals.[391] In May 2020, George Gao, the director of the CDC, said animal samples collected from the seafood market had tested negative for the virus, indicating that the market was the site of an early superspreading event, but that it was not the site of the initial outbreak.[392] Traces of the virus have been found in wastewater samples that were collected in Milan and Turin, Italy, on 18 December 2019.[393]
By December 2019, the spread of infection was almost entirely driven by human-to-human transmission.[343][394] The number of COVID-19 cases in Hubei gradually increased, reaching sixty by 20 December,[395] and at least 266 by 31 December.[396] On 24 December, Wuhan Central Hospital sent a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) sample from an unresolved clinical case to sequencing company Vision Medicals. On 27 and 28 December, Vision Medicals informed the Wuhan Central Hospital and the Chinese CDC of the results of the test, showing a new coronavirus.[397] A pneumonia cluster of unknown cause was observed on 26 December and treated by the doctor Zhang Jixian in Hubei Provincial Hospital, who informed the Wuhan Jianghan CDC on 27 December.[398] On 30 December, a test report addressed to Wuhan Central Hospital, from company CapitalBio Medlab, stated an erroneous positive result for SARS, causing a group of doctors at Wuhan Central Hospital to alert their colleagues and relevant hospital authorities of the result. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission issued a notice to various medical institutions on «the treatment of pneumonia of unknown cause» that same evening.[399] Eight of these doctors, including Li Wenliang (punished on 3 January),[400] were later admonished by the police for spreading false rumours and another, Ai Fen, was reprimanded by her superiors for raising the alarm.[401]
The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission made the first public announcement of a pneumonia outbreak of unknown cause on 31 December, confirming 27 cases[402][403][404] – enough to trigger an investigation.[405]
During the early stages of the outbreak, the number of cases doubled approximately every seven and a half days.[406] In early and mid-January 2020, the virus spread to other Chinese provinces, helped by the Chinese New Year migration and Wuhan being a transport hub and major rail interchange.[80] On 20 January, China reported nearly 140 new cases in one day, including two people in Beijing and one in Shenzhen.[407] Later official data shows 6,174 people had already developed symptoms by then,[343] and more may have been infected.[408] A report in The Lancet on 24 January indicated human transmission, strongly recommended personal protective equipment for health workers, and said testing for the virus was essential due to its «pandemic potential».[113][409] On 30 January, the WHO declared COVID-19 a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.[408] By this time, the outbreak spread by a factor of 100 to 200 times.[410]
Italy had its first confirmed cases on 31 January 2020, two tourists from China.[411] Italy overtook China as the country with the most deaths on 19 March 2020.[412] By 26 March the United States had overtaken China and Italy with the highest number of confirmed cases in the world.[413] Research on coronavirus genomes indicates the majority of COVID-19 cases in New York came from European travellers, rather than directly from China or any other Asian country.[414] Retesting of prior samples found a person in France who had the virus on 27 December 2019,[415][416] and a person in the United States who died from the disease on 6 February 2020.[417]
RT-PCR testing of untreated wastewater samples from Brazil and Italy have suggested detection of SARS-CoV-2 as early as November and December 2019, respectively, but the methods of such sewage studies have not been optimised, many have not been peer-reviewed, details are often missing, and there is a risk of false positives due to contamination or if only one gene target is detected.[418] A September 2020 review journal article said, «The possibility that the COVID‑19 infection had already spread to Europe at the end of last year is now indicated by abundant, even if partially circumstantial, evidence,» including pneumonia case numbers and radiology in France and Italy in November and December.[419]
As of 1 October 2021, Reuters reported that it had estimated the worldwide total number of deaths due to COVID‑19 to have exceeded five million.[420]
Misinformation
After the initial outbreak of COVID‑19, misinformation and disinformation regarding the origin, scale, prevention, treatment, and other aspects of the disease rapidly spread online.[421][422][423]
In September 2020, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published preliminary estimates of the risk of death by age groups in the United States, but those estimates were widely misreported and misunderstood.[424][425]
Other species
Humans appear to be capable of spreading the virus to some other animals, a type of disease transmission referred to as zooanthroponosis.
Some pets, especially cats and ferrets, can catch this virus from infected humans.[426][427] Symptoms in cats include respiratory (such as a cough) and digestive symptoms.[426] Cats can spread the virus to other cats, and may be able to spread the virus to humans, but cat-to-human transmission of SARS-CoV-2 has not been proven.[426][428] Compared to cats, dogs are less susceptible to this infection.[428] Behaviours which increase the risk of transmission include kissing, licking, and petting the animal.[428]
The virus does not appear to be able to infect pigs, ducks, or chickens at all.[426] Mice, rats, and rabbits, if they can be infected at all, are unlikely to be involved in spreading the virus.[428]
Tigers and lions in zoos have become infected as a result of contact with infected humans.[428] As expected, monkeys and great ape species such as orangutans can also be infected with the COVID‑19 virus.[428]
Minks, which are in the same family as ferrets, have been infected.[428] Minks may be asymptomatic, and can also spread the virus to humans.[428] Multiple countries have identified infected animals in mink farms.[429] Denmark, a major producer of mink pelts, ordered the slaughter of all minks over fears of viral mutations,[429] following an outbreak referred to as Cluster 5. A vaccine for mink and other animals is being researched.[429]
Research
International research on vaccines and medicines in COVID‑19 is underway by government organisations, academic groups, and industry researchers.[430][431] The CDC has classified it to require a BSL3 grade laboratory.[432] There has been a great deal of COVID‑19 research, involving accelerated research processes and publishing shortcuts to meet the global demand.[433]
As of December 2020, hundreds of clinical trials have been undertaken, with research happening on every continent except Antarctica.[434] As of November 2020, more than 200 possible treatments have been studied in humans.[435]
Transmission and prevention research
Modelling research has been conducted with several objectives, including predictions of the dynamics of transmission,[436] diagnosis and prognosis of infection,[437] estimation of the impact of interventions,[438][439] or allocation of resources.[440] Modelling studies are mostly based on compartmental models in epidemiology,[441] estimating the number of infected people over time under given conditions. Several other types of models have been developed and used during the COVID‑19 including computational fluid dynamics models to study the flow physics of COVID‑19,[442] retrofits of crowd movement models to study occupant exposure,[443] mobility-data based models to investigate transmission,[444] or the use of macroeconomic models to assess the economic impact of the pandemic.[445] Further, conceptual frameworks from crisis management research have been applied to better understand the effects of COVID‑19 on organisations worldwide.[446][447]
Seven possible drug targets in viral replication process and drugs
Repurposed antiviral drugs make up most of the research into COVID‑19 treatments.[448][449] Other candidates in trials include vasodilators, corticosteroids, immune therapies, lipoic acid, bevacizumab, and recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.[449]
In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) initiated the Solidarity trial to assess the treatment effects of some promising drugs: an experimental drug called remdesivir; anti-malarial drugs chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine; two anti-HIV drugs, lopinavir/ritonavir; and interferon-beta.[450][451] More than 300 active clinical trials are underway as of April 2020.[172]
Research on the antimalarial drugs hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine showed that they were ineffective at best,[452][453] and that they may reduce the antiviral activity of remdesivir.[454] By May 2020, France, Italy, and Belgium had banned the use of hydroxychloroquine as a COVID‑19 treatment.[455]
In June, initial results from the randomised RECOVERY Trial in the United Kingdom showed that dexamethasone reduced mortality by one third for people who are critically ill on ventilators and one fifth for those receiving supplemental oxygen.[456] Because this is a well-tested and widely available treatment, it was welcomed by the WHO, which is in the process of updating treatment guidelines to include dexamethasone and other steroids.[457][458] Based on those preliminary results, dexamethasone treatment has been recommended by the NIH for patients with COVID‑19 who are mechanically ventilated or who require supplemental oxygen but not in patients with COVID‑19 who do not require supplemental oxygen.[459]
In September 2020, the WHO released updated guidance on using corticosteroids for COVID‑19.[460][461] The WHO recommends systemic corticosteroids rather than no systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of people with severe and critical COVID‑19 (strong recommendation, based on moderate certainty evidence).[460] The WHO suggests not to use corticosteroids in the treatment of people with non-severe COVID‑19 (conditional recommendation, based on low certainty evidence).[460] The updated guidance was based on a meta-analysis of clinical trials of critically ill COVID‑19 patients.[462][463]
In September 2020, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) endorsed the use of dexamethasone in adults and adolescents from twelve years of age and weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who require supplemental oxygen therapy.[464][465] Dexamethasone can be taken by mouth or given as an injection or infusion (drip) into a vein.[464]
In November 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an emergency use authorization for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19.[466] Bamlanivimab is authorised for people with positive results of direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing who are twelve years of age and older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb), and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19 or hospitalisation.[466] This includes those who are 65 years of age or older, or who have chronic medical conditions.[466]
In February 2021, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID‑19 in people twelve years of age or older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who test positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19. The authorised use includes treatment for those who are 65 years of age or older or who have certain chronic medical conditions.[467]
In April 2021, the FDA revoked the emergency use authorization (EUA) that allowed for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab, when administered alone, to be used for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19 in adults and certain paediatric patients.[468]
Cytokine storm
Various therapeutic strategies for targeting cytokine storm
A cytokine storm can be a complication in the later stages of severe COVID‑19. A cytokine storm is a potentially deadly immune reaction where a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are released too quickly. A cytokine storm can lead to ARDS and multiple organ failure.[469] Data collected from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, China indicates that patients who had more severe responses to COVID‑19 had greater amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in their system than patients who had milder responses. These high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines indicate presence of a cytokine storm.[470]
Tocilizumab has been included in treatment guidelines by China’s National Health Commission after a small study was completed.[471][472] It is undergoing a Phase II non-randomised trial at the national level in Italy after showing positive results in people with severe disease.[473][474] Combined with a serum ferritin blood test to identify a cytokine storm (also called cytokine storm syndrome, not to be confused with cytokine release syndrome), it is meant to counter such developments, which are thought to be the cause of death in some affected people.[475] The interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist was approved by the FDA to undergo a Phase III clinical trial assessing its effectiveness on COVID‑19 based on retrospective case studies for the treatment of steroid-refractory cytokine release syndrome induced by a different cause, CAR T cell therapy, in 2017.[476] There is no randomised, controlled evidence that tocilizumab is an efficacious treatment for CRS. Prophylactic tocilizumab has been shown to increase serum IL-6 levels by saturating the IL-6R, driving IL-6 across the blood–brain barrier, and exacerbating neurotoxicity while having no effect on the incidence of CRS.[477]
Lenzilumab, an anti-GM-CSF monoclonal antibody, is protective in murine models for CAR T cell-induced CRS and neurotoxicity and is a viable therapeutic option due to the observed increase of pathogenic GM-CSF secreting T cells in hospitalised patients with COVID‑19.[478]
Passive antibodies
Transferring purified and concentrated antibodies produced by the immune systems of those who have recovered from COVID‑19 to people who need them is being investigated as a non-vaccine method of passive immunisation.[479][480] Viral neutralisation is the anticipated mechanism of action by which passive antibody therapy can mediate defence against SARS-CoV-2. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is the primary target for neutralising antibodies.[481] As of 8 August 2020, eight neutralising antibodies targeting the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 have entered clinical studies.[482] It has been proposed that selection of broad-neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV might be useful for treating not only COVID‑19 but also future SARS-related CoV infections.[481] Other mechanisms, however, such as antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity or phagocytosis, may be possible.[479] Other forms of passive antibody therapy, for example, using manufactured monoclonal antibodies, are in development.[479]
The use of passive antibodies to treat people with active COVID‑19 is also being studied. This involves the production of convalescent serum, which consists of the liquid portion of the blood from people who recovered from the infection and contains antibodies specific to this virus, which is then administered to active patients.[479] This strategy was tried for SARS with inconclusive results.[479] An updated Cochrane review in May 2021 found high certainty evidence that, for the treatment of people with moderate to severe COVID‑19, convalescent plasma did not reduce mortality or bring about symptom improvement.[480] There continues to be uncertainty about the safety of convalescent plasma administration to people with COVID‑19 and differing outcomes measured in different studies limits their use in determining efficacy.[480]
Bioethics
Since the outbreak of the COVID‑19 pandemic, scholars have explored the bioethics, normative economics, and political theories of healthcare policies related to the public health crisis.[483] Academics have pointed to the moral distress of healthcare workers, ethics of distributing scarce healthcare resources such as ventilators,[484] and the global justice of vaccine diplomacies.[citation needed] The socio-economic inequalities between genders,[485] races,[486] groups with disabilities,[487] communities,[488] regions, countries,[489] and continents have also drawn attention in academia and the general public.
Effects on other diseases
The use of social distancing and the wearing of surgical masks and similar precautions against COVID‑19 may have caused a drop in the spread of the common cold and the flu.[490][491]
See also
- Coronavirus diseases, a group of closely related syndromes
- Disease X, a WHO term
- Law of declining virulence – Disproved hypothesis of epidemiologist Theobald Smith
- Theory of virulence – Theory by biologist Paul W. Ewald
References
- ^ «Covid-19». Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ «Symptoms of Coronavirus». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 13 May 2020. Archived from the original on 17 June 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- ^ «Q&A on coronaviruses (COVID-19)». World Health Organization (WHO). 17 April 2020. Archived from the original on 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 vaccines». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ Talic S, Shah S, Wild H, Gasevic D, Maharaj A, Ademi Z, et al. (November 2021). «Effectiveness of public health measures in reducing the incidence of covid-19, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and covid-19 mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 375: e068302. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068302. ISSN 1756-1833. PMC 9423125. PMID 34789505. S2CID 244271780.
- ^ a b c «COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU)». ArcGIS. Johns Hopkins University. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ Page J, Hinshaw D, McKay B (26 February 2021). «In Hunt for Covid-19 Origin, Patient Zero Points to Second Wuhan Market – The man with the first confirmed infection of the new coronavirus told the WHO team that his parents had shopped there». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ Islam MA (April 2021). «Prevalence and characteristics of fever in adult and paediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 17515 patients». PLOS ONE. 16 (4): e0249788. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1649788I. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0249788. PMC 8023501. PMID 33822812.
- ^ Islam MA (November 2020). «Prevalence of Headache in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 14,275 Patients». Frontiers in Neurology. 11: 562634. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.562634. PMC 7728918. PMID 33329305.
- ^ Saniasiaya J, Islam MA (April 2021). «Prevalence of Olfactory Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Meta-analysis of 27,492 Patients». The Laryngoscope. 131 (4): 865–878. doi:10.1002/lary.29286. ISSN 0023-852X. PMC 7753439. PMID 33219539.
- ^ Saniasiaya J, Islam MA (November 2020). «Prevalence and Characteristics of Taste Disorders in Cases of COVID-19: A Meta-analysis of 29,349 Patients». Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 165 (1): 33–42. doi:10.1177/0194599820981018. PMID 33320033. S2CID 229174644.
- ^ Agyeman AA, Chin KL, Landersdorfer CB, Liew D, Ofori-Asenso R (August 2020). «Smell and Taste Dysfunction in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis». Mayo Clin. Proc. 95 (8): 1621–1631. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.05.030. PMC 7275152. PMID 32753137.
- ^ Oran DP, Topol EJ (January 2021). «The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic: A Systematic Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (5): M20-6976. doi:10.7326/M20-6976. PMC 7839426. PMID 33481642.
- ^ «Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 6 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ a b CDC (11 February 2020). «Post-COVID Conditions». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ «Clinical Questions about COVID-19: Questions and Answers». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 17 November 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b c «Overview of Testing for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ a b c «Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ Gorzalski AJ, Tian H, Laverdure C, Morzunov S, Verma SC, VanHooser S, Pandori MW (August 2020). «High-Throughput Transcription-mediated amplification on the Hologic Panther is a highly sensitive method of detection for SARS-CoV-2». Journal of Clinical Virology. 129: 104501. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104501. PMC 7286273. PMID 32619959.
- ^ a b c d e Li C, Zhao C, Bao J, Tang B, Wang Y, Gu B (November 2020). «Laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)». Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 510: 35–46. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.045. PMC 7329657. PMID 32621814.
- ^ «2nd U.S. Case Of Wuhan Coronavirus Confirmed». NPR. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (2 February 2020). «Wuhan Coronavirus Looks Increasingly Like a Pandemic, Experts Say». The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Griffiths J. «Wuhan coronavirus deaths spike again as outbreak shows no signs of slowing». CNN. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Jiang S, Xia S, Ying T, Lu L (May 2020). «A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome». Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 17 (5): 554. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0372-4. PMC 7091741. PMID 32024976.
- ^ Chan JF, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KK, Chu H, Yang J, et al. (February 2020). «A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster». Lancet. 395 (10223): 514–523. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. PMC 7159286. PMID 31986261.
- ^ Shablovsky S (September 2017). «The legacy of the Spanish flu». Science. 357 (6357): 1245. Bibcode:2017Sci…357.1245S. doi:10.1126/science.aao4093. ISSN 0036-8075. S2CID 44116811.
- ^ «Stop the coronavirus stigma now». Nature. 580 (7802): 165. 7 April 2020. Bibcode:2020Natur.580..165.. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01009-0. PMID 32265571. S2CID 214809950. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 1» (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). 21 January 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 10» (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). 30 January 2020.
- ^ «Novel coronavirus named ‘Covid-19’: WHO». Today. Singapore. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ «The coronavirus spreads racism against – and among – ethnic Chinese». The Economist. 17 February 2020. Archived from the original on 17 February 2020. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- ^ World Health Organization Best Practices for the Naming of New Human Infectious Diseases (PDF) (Report). World Health Organization (WHO). May 2015. hdl:10665/163636.
- ^ a b «Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 22» (PDF). WHO. 11 February 2020.
- ^ Gover AR, Harper SB, Langton L (July 2020). «Anti-Asian Hate Crime During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Exploring the Reproduction of Inequality». American Journal of Criminal Justice. 45 (4): 647–667. doi:10.1007/s12103-020-09545-1. PMC 7364747. PMID 32837171.
- ^ «Symptoms of Coronavirus». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 22 February 2021. Archived from the original on 4 March 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
- ^ Grant MC, Geoghegan L, Arbyn M, Mohammed Z, McGuinness L, Clarke EL, Wade RG (23 June 2020). «The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries». PLOS ONE. 15 (6): e0234765. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1534765G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0234765. PMC 7310678. PMID 32574165. S2CID 220046286.
- ^ Pardhan S, Vaughan M, Zhang J, Smith L, Chichger H (1 November 2020). «Sore eyes as the most significant ocular symptom experienced by people with COVID-19: a comparison between pre-COVID-19 and during COVID-19 states». BMJ Open Ophthalmology. 5 (1): e000632. doi:10.1136/bmjophth-2020-000632. PMC 7705420. PMID 34192153.
- ^ «COVID toes, rashes: How the coronavirus can affect your skin». www.aad.org. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ a b «Clinical characteristics of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ Paderno A, Mattavelli D, Rampinelli V, Grammatica A, Raffetti E, Tomasoni M, et al. (December 2020). «Olfactory and Gustatory Outcomes in COVID-19: A Prospective Evaluation in Nonhospitalized Subjects». Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 163 (6): 1144–1149. doi:10.1177/0194599820939538. PMC 7331108. PMID 32600175.
- ^ Chabot AB, Huntwork MP (September 2021). «Turmeric as a Possible Treatment for COVID-19-Induced Anosmia and Ageusia». Cureus. 13 (9): e17829. doi:10.7759/cureus.17829. PMC 8502749. PMID 34660038.
- ^ Niazkar HR, Zibaee B, Nasimi A, Bahri N (July 2020). «The neurological manifestations of COVID-19: a review article». Neurological Sciences. 41 (7): 1667–1671. doi:10.1007/s10072-020-04486-3. PMC 7262683. PMID 32483687.
- ^ «Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 6 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Oran DP, Topol EJ (May 2021). «The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic : A Systematic Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (5): 655–662. doi:10.7326/M20-6976. PMC 7839426. PMID 33481642.
- «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- Nogrady B (November 2020). «What the data say about asymptomatic COVID infections». Nature. 587 (7835): 534–535. Bibcode:2020Natur.587..534N. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03141-3. PMID 33214725.
- ^ a b Gao Z, Xu Y, Sun C, Wang X, Guo Y, Qiu S, Ma K (February 2021). «A systematic review of asymptomatic infections with COVID-19». Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi. 54 (1): 12–16. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.05.001. PMC 7227597. PMID 32425996.
- ^ Oran DP, Topol EJ (September 2020). «Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection : A Narrative Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 173 (5): 362–367. doi:10.7326/M20-3012. PMC 7281624. PMID 32491919.
- ^ Lai CC, Liu YH, Wang CY, Wang YH, Hsueh SC, Yen MY, et al. (June 2020). «Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Facts and myths». Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi. 53 (3): 404–412. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012. PMC 7128959. PMID 32173241.
- ^ a b Furukawa NW, Brooks JT, Sobel J (July 2020). «Evidence Supporting Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 While Presymptomatic or Asymptomatic». Emerging Infectious Diseases. 26 (7). doi:10.3201/eid2607.201595. PMC 7323549. PMID 32364890.
- ^ a b Gandhi RT, Lynch JB, Del Rio C (October 2020). «Mild or Moderate Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (18): 1757–1766. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009249. PMID 32329974.
- ^ Byrne AW, McEvoy D, Collins AB, Hunt K, Casey M, Barber A, et al. (August 2020). «Inferred duration of infectious period of SARS-CoV-2: rapid scoping review and analysis of available evidence for asymptomatic and symptomatic COVID-19 cases». BMJ Open. 10 (8): e039856. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039856. PMC 7409948. PMID 32759252.
- ^ Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC (August 2020). «Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review». JAMA. 324 (8): 782–793. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12839. PMID 32648899. S2CID 220465311.
- ^ «Half of young adults with COVID-19 had persistent symptoms after 6 months». medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 10 July 2021.
- ^ Blomberg B, Mohn KG, Brokstad KA, Zhou F, Linchausen DW, Hansen BA, et al. (September 2021). «Long COVID in a prospective cohort of home-isolated patients». Nature Medicine. 27 (9): 1607–1613. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01433-3. PMC 8440190. PMID 34163090. S2CID 235625772.
- ^ CDC (1 September 2022). «Post-COVID Conditions». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «COVID-19 and Your Health». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 23 January 2021.
- ^ CDC (29 March 2022). «Omicron Variant: What You Need to Know». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 15 June 2022.
- ^ Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL (March 2021). «Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 19 (3): 141–154. doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7. PMC 7537588. PMID 33024307.
- ^ a b Wang CC, Prather KA, Sznitman J, Jimenez JL, Lakdawala SS, Tufekci Z, Marr LC (August 2021). «Airborne transmission of respiratory viruses». Science. 373 (6558). Bibcode:2021Sci…373…..W. doi:10.1126/science.abd9149. PMC 8721651. PMID 34446582.
- ^ Greenhalgh T, Jimenez JL, Prather KA, Tufekci Z, Fisman D, Schooley R (May 2021). «Ten scientific reasons in support of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2». Lancet. 397 (10285): 1603–1605. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00869-2. PMC 8049599. PMID 33865497.
- ^ Bourouiba L (13 July 2021). «Fluid Dynamics of Respiratory Infectious Diseases». Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 23 (1): 547–577. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-111820-025044. hdl:1721.1/131115. PMID 34255991. S2CID 235823756. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ Stadnytskyi, Valentyn; Bax, Christina E.; Bax, Adriaan; Anfinrud, Philip (2 June 2020). «The airborne lifetime of small speech droplets and their potential importance in SARS-CoV-2 transmission». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (22): 11875–11877. doi:10.1073/pnas.2006874117. PMC 7275719. PMID 32404416.
- ^ Miller SL, Nazaroff WW, Jimenez JL, Boerstra A, Buonanno G, Dancer SJ, et al. (March 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by inhalation of respiratory aerosol in the Skagit Valley Chorale superspreading event». Indoor Air. 31 (2): 314–323. doi:10.1111/ina.12751. PMC 7537089. PMID 32979298.
- ^ He, Xi; Lau, Eric H. Y.; Wu, Peng; Deng, Xilong; Wang, Jian; Hao, Xinxin; Lau, Yiu Chung; Wong, Jessica Y.; Guan, Yujuan; Tan, Xinghua; Mo, Xiaoneng; Chen, Yanqing; Liao, Baolin; Chen, Weilie; Hu, Fengyu; Zhang, Qing; Zhong, Mingqiu; Wu, Yanrong; Zhao, Lingzhai; Zhang, Fuchun; Cowling, Benjamin J.; Li, Fang; Leung, Gabriel M. (September 2020). «Author Correction: Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19». Nature Medicine. 26 (9): 1491–1493. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1016-z. PMC 7413015. PMID 32770170. S2CID 221050261.
- ^ a b c d Communicable Diseases Network Australia. «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): CDNA National Guidelines for Public Health Units». 5.1. Communicable Diseases Network Australia/Australian Government Department of Health.
- ^ «Clinical Questions about COVID-19: Questions and Answers». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 4 March 2021.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 May 2021. Retrieved 8 May 2021.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): How is it transmitted?». World Health Organization. 30 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d e • «COVID-19: epidemiology, virology and clinical features». GOV.UK. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
• Communicable Diseases Network Australia. «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) — CDNA Guidelines for Public Health Units». Version 4.4. Australian Government Department of Health. Retrieved 17 May 2021.{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)
• Public Health Agency of Canada (3 November 2020). «COVID-19: Main modes of transmission». aem. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
• «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
• Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE (January 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Viral, Host, and Environmental Factors». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (1): 69–79. doi:10.7326/M20-5008. ISSN 0003-4819. PMC 7505025. PMID 32941052. - ^ a b c Tang JW, Marr LC, Li Y, Dancer SJ (April 2021). «Covid-19 has redefined airborne transmission». BMJ. 373: n913. doi:10.1136/bmj.n913. PMID 33853842.
- ^ a b Morawska L, Allen J, Bahnfleth W, Bluyssen PM, Boerstra A, Buonanno G, et al. (May 2021). «A paradigm shift to combat indoor respiratory infection» (PDF). Science. 372 (6543): 689–691. Bibcode:2021Sci…372..689M. doi:10.1126/science.abg2025. PMID 33986171. S2CID 234487289.
- ^ a b Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE (January 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Viral, Host, and Environmental Factors». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (1): 69–79. doi:10.7326/M20-5008. ISSN 0003-4819. PMC 7505025. PMID 32941052.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Healthcare Workers». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 29 March 2022.
- ^ Liu T, Gong D, Xiao J, Hu J, He G, Rong Z, Ma W (October 2020). «Cluster infections play important roles in the rapid evolution of COVID-19 transmission: A systematic review». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 99: 374–380. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.073. PMC 7405860. PMID 32768702.
- ^ «Outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): increased transmission beyond China – fourth update» (PDF). European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 14 February 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- ^ a b Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF (April 2020). «The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Medicine. 26 (4): 450–452. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9. PMC 7095063. PMID 32284615.
- ^ Gibbens S (18 March 2020). «Why soap is preferable to bleach in the fight against coronavirus». National Geographic. Archived from the original on 2 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ^ Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. (February 2020). «A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (8): 727–733. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. PMC 7092803. PMID 31978945.
- ^ a b c Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) (PDF) (Report). World Health Organization (WHO). February 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 February 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ «Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Rathore JS, Ghosh C (August 2020). «Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), a newly emerged pathogen: an overview». Pathogens and Disease. 78 (6). doi:10.1093/femspd/ftaa042. OCLC 823140442. PMC 7499575. PMID 32840560.
- ^ Thomas S (October 2020). «The Structure of the Membrane Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Resembles the Sugar Transporter SemiSWEET». Pathogens & Immunity. 5 (1): 342–363. doi:10.20411/pai.v5i1.377. PMC 7608487. PMID 33154981.
- ^ Koyama T, Platt D, Parida L (July 2020). «Variant analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes». Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 98 (7): 495–504. doi:10.2471/BLT.20.253591. PMC 7375210. PMID 32742035.
We detected in total 65776 variants with 5775 distinct variants.
- ^ a b Rambaut A, Holmes EC, O’Toole Á, Hill V, McCrone JT, Ruis C, et al. (November 2020). «A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology». Nature Microbiology. 5 (11): 1403–1407. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0770-5. PMC 7610519. PMID 32669681.
- ^ «Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants». World Health Organization. 1 July 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2021.
- ^ Alm E, Broberg EK, Connor T, Hodcroft EB, Komissarov AB, Maurer-Stroh S, et al. (August 2020). «Geographical and temporal distribution of SARS-CoV-2 clades in the WHO European Region, January to June 2020». Euro Surveillance. 25 (32). doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.32.2001410. PMC 7427299. PMID 32794443.
- ^ «PANGO lineages». cov-lineages.org. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ Lauring AS, Hodcroft EB (February 2021). «Genetic Variants of SARS-CoV-2-What Do They Mean?». JAMA. 325 (6): 529–531. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.27124. PMID 33404586. S2CID 230783233.
- ^ Abdool Karim SS, de Oliveira T (May 2021). «New SARS-CoV-2 Variants – Clinical, Public Health, and Vaccine Implications». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 384 (19): 1866–1868. doi:10.1056/nejmc2100362. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 8008749. PMID 33761203.
- ^ Mallapaty S (November 2020). «COVID mink analysis shows mutations are not dangerous – yet». Nature. 587 (7834): 340–341. Bibcode:2020Natur.587..340M. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03218-z. PMID 33188367. S2CID 226947606.
- ^ Larsen HD, Fonager J, Lomholt FK, Dalby T, Benedetti G, Kristensen B, et al. (February 2021). «Preliminary report of an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 in mink and mink farmers associated with community spread, Denmark, June to November 2020». Euro Surveillance. 26 (5): 2100009. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.5.210009. PMC 7863232. PMID 33541485.
As at 1 February 2021, we assess that the cluster 5 variant is no longer circulating among humans in Denmark.
- ^ «New COVID-19 Variants». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 28 June 2021 [First published 11 February 2020]. Retrieved 15 July 2021.
- ^ «COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update Edition 69». World Health Organization (WHO). 7 December 2021.
- ^ «Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Harrison AG, Lin T, Wang P (December 2020). «Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis». Trends in Immunology. 41 (12): 1100–1115. doi:10.1016/j.it.2020.10.004. PMC 7556779. PMID 33132005.
- ^ Verdecchia P, Cavallini C, Spanevello A, Angeli F (June 2020). «The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection». European Journal of Internal Medicine. 76: 14–20. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037. PMC 7167588. PMID 32336612.
- ^ Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V (April 2020). «Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses». Nature Microbiology. 5 (4): 562–569. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y. PMC 7095430. PMID 32094589.
- ^ Marik PE, Iglesias J, Varon J, Kory P (January 2021). «A scoping review of the pathophysiology of COVID-19». International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology. 35: 20587384211048026. doi:10.1177/20587384211048026. PMC 8477699. PMID 34569339.
- ^ a b Meunier N, Briand L, Jacquin-Piques A, Brondel L, Pénicaud L (June 2020). «COVID 19-Induced Smell and Taste Impairments: Putative Impact on Physiology». Frontiers in Physiology. 11: 625110. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.625110. PMC 7870487. PMID 33574768.
- ^ Guerrero JI, Barragán LA, Martínez JD, Montoya JP, Peña A, Sobrino FE, et al. (June 2021). «Central and peripheral nervous system involvement by COVID-19: a systematic review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, neuropathology, neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and cerebrospinal fluid findings». BMC Infectious Diseases. 21 (1): 515. doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06185-6. PMC 8170436. PMID 34078305.
- ^ a b Pezzini A, Padovani A (November 2020). «Lifting the mask on neurological manifestations of COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Neurology. 16 (11): 636–644. doi:10.1038/s41582-020-0398-3. PMC 7444680. PMID 32839585.
- ^ Li YC, Bai WZ, Hashikawa T (June 2020). «The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 552–555. doi:10.1002/jmv.25728. PMC 7228394. PMID 32104915.
- ^ Baig AM, Khaleeq A, Ali U, Syeda H (April 2020). «Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms». ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (7): 995–998. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00122. PMC 7094171. PMID 32167747.
- ^ Yavarpour-Bali H, Ghasemi-Kasman M (September 2020). «Update on neurological manifestations of COVID-19». Life Sciences. 257: 118063. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118063. PMC 7346808. PMID 32652139.
- ^ Covid can shrink brain and damage its tissue, finds research The Guardian
- ^ Scans reveal how Covid may change the brain BBC
- ^ «Even mild Covid is linked to brain damage months after illness, scans show». NBC News.
- ^ Gu J, Han B, Wang J (May 2020). «COVID-19: Gastrointestinal Manifestations and Potential Fecal-Oral Transmission». Gastroenterology. 158 (6): 1518–1519. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054. PMC 7130192. PMID 32142785.
- ^ Mönkemüller K, Fry L, Rickes S (May 2020). «COVID-19, coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 and the small bowel». Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas. 112 (5): 383–388. doi:10.17235/reed.2020.7137/2020. PMID 32343593. S2CID 216645754.
- ^ Almamlouk R, Kashour T, Obeidat S, Bois MC, Maleszewski JJ, Omrani OA, et al. (August 2022). «COVID-19-Associated cardiac pathology at the postmortem evaluation: a collaborative systematic review». Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 28 (8): 1066–1075. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.03.021. PMC 8941843. PMID 35339672.
- ^ a b c Zheng YY, Ma YT, Zhang JY, Xie X (May 2020). «COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system». Nature Reviews. Cardiology. 17 (5): 259–260. doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5. PMC 7095524. PMID 32139904.
- ^ a b c Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. (February 2020). «Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China». Lancet. 395 (10223): 497–506. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. PMC 7159299. PMID 31986264.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Myocardial infarction and other coronary artery disease issues». UpToDate. Retrieved 28 September 2020.
- ^ Turner AJ, Hiscox JA, Hooper NM (June 2004). «ACE2: from vasopeptidase to SARS virus receptor». Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 25 (6): 291–4. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2004.04.001. PMC 7119032. PMID 15165741.
- ^ Abou-Ismail MY, Diamond A, Kapoor S, Arafah Y, Nayak L (October 2020). «The hypercoagulable state in COVID-19: Incidence, pathophysiology, and management». Thrombosis Research. Elsevier BV. 194: 101–115. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.06.029. PMC 7305763. PMID 32788101.
- ^ a b c Wadman M (April 2020). «How does coronavirus kill? Clinicians trace a ferocious rampage through the body, from brain to toes». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abc3208.
- ^ «NIH study uncovers blood vessel damage and inflammation in COVID-19 patients’ brains but no infection». National Institutes of Health (NIH). 30 December 2020. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ^ Lee MH, Perl DP, Nair G, Li W, Maric D, Murray H, et al. (February 2021). «Microvascular Injury in the Brains of Patients with Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 384 (5): 481–483. doi:10.1056/nejmc2033369. PMC 7787217. PMID 33378608.
- ^ Kubánková M, Hohberger B, Hoffmanns J, Fürst J, Herrmann M, Guck J, Kräter M (July 2021). «Physical phenotype of blood cells is altered in COVID-19». Biophysical Journal. 120 (14): 2838–2847. Bibcode:2021BpJ…120.2838K. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2021.05.025. PMC 8169220. PMID 34087216.
- ^ Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Sehgal K, Nair N, Mahajan S, Sehrawat TS, et al. (July 2020). «Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19». Nature Medicine. 26 (7): 1017–1032. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3. PMID 32651579. S2CID 220462000.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Kidney Damage Caused by COVID-19». Johns Hopkins Medicine. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Eketunde AO, Mellacheruvu SP, Oreoluwa P (July 2020). «A Review of Postmortem Findings in Patients With COVID-19». Cureus. Cureus, Inc. 12 (7): e9438. doi:10.7759/cureus.9438. PMC 7451084. PMID 32864262. S2CID 221352704.
- ^ Ziegler, CGK; Allon, SJ; Nyquist, SK; Mbano, IM; Miao, VN; Tzouanas, CN; Cao, Y; Yousif, AS; Bals, J; Hauser, BM; Feldman, J; Muus, C; Wadsworth MH, 2nd; Kazer, SW; Hughes, TK; Doran, B; Gatter, GJ; Vukovic, M; Taliaferro, F; Mead, BE; Guo, Z; Wang, JP; Gras, D; Plaisant, M; Ansari, M; Angelidis, I; Adler, H; Sucre, JMS; Taylor, CJ; Lin, B; Waghray, A; Mitsialis, V; Dwyer, DF; Buchheit, KM; Boyce, JA; Barrett, NA; Laidlaw, TM; Carroll, SL; Colonna, L; Tkachev, V; Peterson, CW; Yu, A; Zheng, HB; Gideon, HP; Winchell, CG; Lin, PL; Bingle, CD; Snapper, SB; Kropski, JA; Theis, FJ; Schiller, HB; Zaragosi, LE; Barbry, P; Leslie, A; Kiem, HP; Flynn, JL; Fortune, SM; Berger, B; Finberg, RW; Kean, LS; Garber, M; Schmidt, AG; Lingwood, D; Shalek, AK; Ordovas-Montanes, J; HCA Lung Biological Network. Electronic address, lung-network@humancellatlas.org.; HCA Lung Biological, Network. (28 May 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues». Cell. 181 (5): 1016–1035.e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035. PMC 7252096. PMID 32413319.
- ^ Sajuthi, SP; DeFord, P; Li, Y; Jackson, ND; Montgomery, MT; Everman, JL; Rios, CL; Pruesse, E; Nolin, JD; Plender, EG; Wechsler, ME; Mak, ACY; Eng, C; Salazar, S; Medina, V; Wohlford, EM; Huntsman, S; Nickerson, DA; Germer, S; Zody, MC; Abecasis, G; Kang, HM; Rice, KM; Kumar, R; Oh, S; Rodriguez-Santana, J; Burchard, EG; Seibold, MA (12 October 2020). «Type 2 and interferon inflammation regulate SARS-CoV-2 entry factor expression in the airway epithelium». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5139. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5139S. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18781-2. PMC 7550582. PMID 33046696.
- ^
- ^ Zhang C, Wu Z, Li JW, Zhao H, Wang GQ (May 2020). «Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (5): 105954. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954. PMC 7118634. PMID 32234467.
- ^ Gómez-Rial J, Rivero-Calle I, Salas A, Martinón-Torres F (2020). «Role of Monocytes/Macrophages in Covid-19 Pathogenesis: Implications for Therapy». Infection and Drug Resistance. 13: 2485–2493. doi:10.2147/IDR.S258639. PMC 7383015. PMID 32801787.
- ^ Dai L, Gao GF (February 2021). «Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Immunology. 21 (2): 73–82. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00480-0. ISSN 1474-1733. PMC 7747004. PMID 33340022.
- ^ a b Boopathi S, Poma AB, Kolandaivel P (April 2020). «Novel 2019 coronavirus structure, mechanism of action, antiviral drug promises and rule out against its treatment». Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 39 (9): 3409–3418. doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1758788. PMC 7196923. PMID 32306836.
- ^ Kai H, Kai M (July 2020). «Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors-lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19». Hypertension Research. 43 (7): 648–654. doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8. PMC 7184165. PMID 32341442.
- ^ Chen HX, Chen ZH, Shen HH (October 2020). «[Structure of SARS-CoV-2 and treatment of COVID-19]». Sheng Li Xue Bao. 72 (5): 617–630. PMID 33106832.
- ^ Jeyanathan M, Afkhami S, Smaill F, Miller MS, Lichty BD, Xing Z (4 September 2020). «Immunological considerations for COVID-19 vaccine strategies». Nature Reviews Immunology. 20 (10): 615–632. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00434-6. ISSN 1474-1741. PMC 7472682. PMID 32887954.
- ^ Zhang Q, Ju B, Ge J, Chan JF, Cheng L, Wang R, et al. (July 2021). «Potent and protective IGHV3-53/3-66 public antibodies and their shared escape mutant on the spike of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Communications. 12 (1): 4210. Bibcode:2021NatCo..12.4210Z. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24514-w. PMC 8270942. PMID 34244522. S2CID 235786394.
- ^ Soy M, Keser G, Atagündüz P, Tabak F, Atagündüz I, Kayhan S (July 2020). «Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment». Clinical Rheumatology. 39 (7): 2085–2094. doi:10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5. PMC 7260446. PMID 32474885.
- ^ Quirch M, Lee J, Rehman S (August 2020). «Hazards of the Cytokine Storm and Cytokine-Targeted Therapy in Patients With COVID-19: Review». Journal of Medical Internet Research. 22 (8): e20193. doi:10.2196/20193. PMC 7428145. PMID 32707537.
- ^ Bhaskar S, Sinha A, Banach M, Mittoo S, Weissert R, Kass JS, et al. (2020). «Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper». Frontiers in Immunology. 11: 1648. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648. PMC 7365905. PMID 32754159.
- ^ a b c d e f Wastnedge EA, Reynolds RM, van Boeckel SR, Stock SJ, Denison FC, Maybin JA, Critchley HO (January 2021). «Pregnancy and COVID-19». Physiological Reviews. 101 (1): 303–318. doi:10.1152/physrev.00024.2020. PMC 7686875. PMID 32969772.
- ^ Campbell D (10 October 2021). «One in six most critically ill NHS Covid patients are unvaccinated pregnant women». The Guardian. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, Zhan C, Chen C, Lv W, et al. (August 2020). «Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases». Radiology. 296 (2): E32–E40. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200642. PMC 7233399. PMID 32101510.
- ^ a b c d Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, Gholamrezanezhad A (July 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findings in 919 Patients». AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 215 (1): 87–93. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.23034. PMID 32174129.
- ^ «2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Summary». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: Laboratory testing for 2019-nCoV in humans». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Bullard J, Dust K, Funk D, Strong JE, Alexander D, Garnett L, et al. (December 2020). «Predicting Infectious Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 From Diagnostic Samples». Clinical Infectious Diseases. 71 (10): 2663–2666. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa638. PMC 7314198. PMID 32442256.
- ^ «Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens from Persons for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 4 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ «Real-Time RT-PCR Panel for Detection 2019-nCoV». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 29 January 2020. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ «Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ «NHS staff will be first to get new coronavirus antibody test, medical chief promises». The Independent. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Heneghan C, Jefferson T (1 September 2020). «Virological characterization of COVID-19 patients that test re-positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR». CEBM. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ Lu J, Peng J, Xiong Q, Liu Z, Lin H, Tan X, et al. (September 2020). «Clinical, immunological and virological characterization of COVID-19 patients that test re-positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR». EBioMedicine. 59: 102960. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102960. PMC 7444471. PMID 32853988.
- ^ Spencer E, Jefferson T, Brassey J, Heneghan C (11 September 2020). «When is Covid, Covid?». The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ «SARS-CoV-2 RNA testing: assurance of positive results during periods of low prevalence». GOV.UK. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ «ACR Recommendations for the use of Chest Radiography and Computed Tomography (CT) for Suspected COVID-19 Infection». American College of Radiology. 22 March 2020. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020.
- ^ Pormohammad A, Ghorbani S, Khatami A, Razizadeh MH, Alborzi E, Zarei M, et al. (October 2020). «Comparison of influenza type A and B with COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical, laboratory and radiographic findings». Reviews in Medical Virology. 31 (3): e2179. doi:10.1002/rmv.2179. PMC 7646051. PMID 33035373. S2CID 222255245.
- ^ Lee EY, Ng MY, Khong PL (April 2020). «COVID-19 pneumonia: what has CT taught us?». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (4): 384–385. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30134-1. PMC 7128449. PMID 32105641.
- ^ a b Li Y, Xia L (June 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of Chest CT in Diagnosis and Management». AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 214 (6): 1280–1286. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.22954. PMID 32130038. S2CID 212416282.
- ^ «COVID-19 Database». Società Italiana di Radiologia Medica e Interventistica (in Italian). Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ «ICD-10 Version:2019». World Health Organization (WHO). 2019. Archived from the original on 31 March 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
U07.2 – COVID-19, virus not identified – COVID-19 NOS – Use this code when COVID-19 is diagnosed clinically or epidemiologically but laboratory testing is inconclusive or not available. Use additional code, if desired, to identify pneumonia or other manifestations
- ^ Giani M, Seminati D, Lucchini A, Foti G, Pagni F (May 2020). «Exuberant Plasmocytosis in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Specimen of the First Patient Requiring Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for SARS-CoV-2 in Europe». Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 15 (5): e65–e66. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.03.008. PMC 7118681. PMID 32194247.
- ^ Lillicrap D (April 2020). «Disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with 2019-nCoV pneumonia». Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 18 (4): 786–787. doi:10.1111/jth.14781. PMC 7166410. PMID 32212240.
- ^ Mitra A, Dwyre DM, Schivo M, Thompson GR, Cohen SH, Ku N, Graff JP (August 2020). «Leukoerythroblastic reaction in a patient with COVID-19 infection». American Journal of Hematology. 95 (8): 999–1000. doi:10.1002/ajh.25793. PMC 7228283. PMID 32212392.
- ^ a b c d e f Satturwar S, Fowkes M, Farver C, Wilson AM, Eccher A, Girolami I, et al. (May 2021). «Postmortem Findings Associated With SARS-CoV-2: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis». The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 45 (5): 587–603. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000001650. PMC 8132567. PMID 33481385. S2CID 231679276.
- ^ Maier BF, Brockmann D (May 2020). «Effective containment explains subexponential growth in recent confirmed COVID-19 cases in China». Science. 368 (6492): 742–746. arXiv:2002.07572. Bibcode:2020Sci…368..742M. doi:10.1126/science.abb4557. PMC 7164388. PMID 32269067. («… initial exponential growth expected for an unconstrained outbreak.»)
- ^ «Viral Load Exposure Factors». ReallyCorrect.com.
- ^ «Recommendation Regarding the Use of Cloth Face Coverings, Especially in Areas of Significant Community-Based Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 28 June 2020.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 and Potential Airborne Transmission». COVID-19 Published Science and Research. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5 April 2020). «What to Do if You Are Sick». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) – Prevention & Treatment». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 March 2020. Archived from the original on 11 March 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ «UK medicines regulator gives approval for first UK COVID-19 vaccine». Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, Government of the UK. 2 December 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ Mueller B (2 December 2020). «U.K. Approves Pfizer Coronavirus Vaccine, a First in the West». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines». nih.gov. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ a b c Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB (May 2020). «Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review». JAMA. 323 (18): 1824–1836. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019. PMID 32282022.
- ^ a b Anderson RM, Heesterbeek H, Klinkenberg D, Hollingsworth TD (March 2020). «How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?». Lancet. 395 (10228): 931–934. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5. PMC 7158572. PMID 32164834.
A key issue for epidemiologists is helping policy makers decide the main objectives of mitigation – e.g. minimising morbidity and associated mortality, avoiding an epidemic peak that overwhelms health-care services, keeping the effects on the economy within manageable levels, and flattening the epidemic curve to wait for vaccine development and manufacture on scale and antiviral drug therapies.
- ^ Wiles S (14 March 2020). «After ‘Flatten the Curve’, we must now ‘Stop the Spread’. Here’s what that means». The Spinoff. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Li YD, Chi WY, Su JH, Ferrall L, Hung CF, Wu TC (December 2020). «Coronavirus vaccine development: from SARS and MERS to COVID-19». Journal of Biomedical Science. 27 (1): 104. doi:10.1186/s12929-020-00695-2. PMC 7749790. PMID 33341119.
- ^ Subbarao K (July 2021). «The success of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and challenges ahead». Cell Host & Microbe. 29 (7): 1111–1123. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.016. PMC 8279572. PMID 34265245.
- ^ Padilla TB (24 February 2021). «No one is safe unless everyone is safe». BusinessWorld. Archived from the original on 23 February 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ a b c Rogers K (11 May 2022). «COVID-19 vaccine». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 12 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- ^ «Swissmedic grants authorisation for the first COVID-19 vaccine in Switzerland» (Press release). Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products (Swissmedic). 18 December 2020. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ «EMA recommends first COVID-19 vaccine for authorisation in the EU». European Medicines Agency (EMA) (Press release). 21 December 2020. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2020.
- ^ «Wear masks in public says WHO, in update of COVID-19 advice». Reuters. 5 June 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ a b c «Recommendation Regarding the Use of Cloth Face Coverings, Especially in Areas of Significant Community-Based Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ a b «Using face masks in the community – Technical Report» (PDF). ECDC. 8 April 2020.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: Community Use of Cloth Masks to Control the Spread of SARS-CoV-2». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 November 2020.
- ^ Greenhalgh T, Schmid MB, Czypionka T, Bassler D, Gruer L (April 2020). «Face masks for the public during the covid-19 crisis». BMJ. 369: m1435. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1435. PMID 32273267. S2CID 215516381.
- ^ «Caring for Someone Sick at Home». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ «Using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 June 2020. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- ^ a b c CDC (11 February 2020). «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ^ «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 7 September 2020. Retrieved 14 October 2020.
- ^ a b National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD) (9 July 2020). «COVID-19 Employer Information for Office Buildings». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 9 July 2020.
- ^ WHO’s Science in 5 on COVID-19 — Ventilation — 30 October 2020. World Health Organization (WHO). 30 October 2020. Archived from the original on 25 October 2022. Retrieved 8 December 2022 – via YouTube.
- ^ Somsen GA, van Rijn C, Kooij S, Bem RA, Bonn D (July 2020). «Small droplet aerosols in poorly ventilated spaces and SARS-CoV-2 transmission». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. Elsesier. 8 (7): 658–659. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30245-9. PMC 7255254. PMID 32473123.
- ^ Lipinski T, Ahmad D, Serey N, Jouhara H (1 November 2020). «Review of ventilation strategies to reduce the risk of disease transmission in high occupancy buildings». International Journal of Thermofluids. 7–8: 100045. doi:10.1016/j.ijft.2020.100045. ISSN 2666-2027. S2CID 221642242.
- ^ «Social distancing: what you need to do – Coronavirus (COVID-19)». nhs.uk. 2 June 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ «Advice for the public on COVID-19 – World Health Organization». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 and Your Health». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
To prevent the spread of germs, including COVID-19, CDC recommends washing hands with soap and water whenever possible because it reduces the amount of many types of germs and chemicals on hands. But if soap and water are not readily available, using a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol can help you avoid getting sick and spreading germs to others.
- ^ «WHO-recommended handrub formulations». WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: First Global Patient Safety Challenge Clean Care Is Safer Care. World Health Organization (WHO). 19 March 2009. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ Nussbaumer-Streit B, Mayr V, Dobrescu AI, Chapman A, Persad E, Klerings I, et al. (September 2020). «Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: a rapid review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (9): CD013574. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013574.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 8133397. PMID 33959956.
- ^ Qian M, Jiang J (May 2020). «COVID-19 and social distancing». Zeitschrift für Gesundheitswissenschaften = Journal of Public Health. 30 (1): 259–261. doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01321-z. PMC 7247774. PMID 32837835.
- ^ a b Hawks L, Woolhandler S, McCormick D (August 2020). «COVID-19 in Prisons and Jails in the United States». JAMA Internal Medicine. 180 (8): 1041–1042. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1856. PMID 32343355.
- ^ Waldstein D (6 May 2020). «To Fight Virus in Prisons, C.D.C. Suggests More Screenings». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 7 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ «How COVID-19 Spreads». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 18 September 2020. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- ^ Goldman E (August 2020). «Exaggerated risk of transmission of COVID-19 by fomites». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (8): 892–893. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30561-2. PMC 7333993. PMID 32628907.
- ^ Weixel N (5 April 2021). «CDC says risk of COVID-19 transmission on surfaces 1 in 10,000». The Hill. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ a b «Science Brief: SARS-CoV-2 and Surface (Fomite) Transmission for Indoor Community Environments». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 April 2021. Archived from the original on 5 April 2021.
- ^ a b Pedreira A, Taşkın Y, García MR (January 2021). «A Critical Review of Disinfection Processes to Control SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in the Food Industry». Foods. 10 (2): 283. doi:10.3390/foods10020283. PMC 7911259. PMID 33572531. S2CID 231900820.
- ^ Rezasoltani S, Yadegar A, Hatami B, Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Zali MR (2020). «Antimicrobial Resistance as a Hidden Menace Lurking Behind the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Global Impacts of Too Much Hygiene on AMR». Frontiers in Microbiology. 11: 590683. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.590683. PMC 7769770. PMID 33384670.
- ^ Thompson D (8 February 2021). «Hygiene Theater Is Still a Huge Waste of Time». The Atlantic. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ Thompson D (27 July 2020). «Hygiene Theater Is a Huge Waste of Time». The Atlantic. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g Bueckert M, Gupta R, Gupta A, Garg M, Mazumder A (November 2020). «Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronaviruses on Dry Surfaces: Potential for Indirect Transmission». Materials. 13 (22): 5211. Bibcode:2020Mate…13.5211B. doi:10.3390/ma13225211. PMC 7698891. PMID 33218120.
- ^ Bhardwaj R, Agrawal A (November 2020). «How coronavirus survives for days on surfaces». Physics of Fluids. 32 (11): 111706. Bibcode:2020PhFl…32k1706B. doi:10.1063/5.0033306. PMC 7713872. PMID 33281435.
- ^ Chatterjee S, Murallidharan JS, Agrawal A, Bhardwaj R (February 2021). «Why coronavirus survives longer on impermeable than porous surfaces». Physics of Fluids. 33 (2): 021701. Bibcode:2021PhFl…33b1701C. doi:10.1063/5.0037924. PMC 7978145. PMID 33746485.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ^ Anthes E (8 April 2021). «Has the Era of Overzealous Cleaning Finally Come to an End?». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ^ «Interim Recommendations for US Community Facilities with Suspected/Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ «Yes, UV phone sanitizers work. That doesn’t mean you need one». The Washington Post. 16 February 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ Patiño-Lugo DF, Vélez M, Velásquez Salazar P, Vera-Giraldo CY, Vélez V, Marín IC, et al. (June 2020). «Non-pharmaceutical interventions for containment, mitigation and suppression of COVID-19 infection». Colombia Medica. 51 (2): e4266. doi:10.25100/cm.v51i2.4266. PMC 7518730. PMID 33012884.
- ^ «COVID-19 Informational Resources for High-Risk Groups | Keeping Education ACTIVE | Partnership to Fight Chronic Disease». fightchronicdisease.org. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ «Quarantine and Isolation». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 29 July 2021. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ a b c Burns J, Movsisyan A, Stratil JM, Biallas RL, Coenen M, Emmert-Fees KM, et al. (Cochrane Public Health Group) (March 2021). «International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (3): CD013717. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMC 8406796. PMID 33763851. S2CID 232356197.
- ^ «COVID Treatment Guidelines: Clinical Management Summary». NIH Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. 8 April 2022. Archived from the original on 5 November 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Wise, Jeff (17 April 2022). «What Happened to Paxlovid, the COVID Wonder Drug?». Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 19 April 2022. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Tao K, Tzou PL, Nouhin J, Bonilla H, Jagannathan P, Shafer RW (July 2021). «SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Therapy». Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 34 (4): e0010921. doi:10.1128/CMR.00109-21. PMC 8404831. PMID 34319150. S2CID 236472654.
- ^ Fisher D, Heymann D (February 2020). «Q&A: The novel coronavirus outbreak causing COVID-19». BMC Medicine. 18 (1): 57. doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01533-w. PMC 7047369. PMID 32106852.
- ^ Liu K, Fang YY, Deng Y, Liu W, Wang MF, Ma JP, et al. (May 2020). «Clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus cases in tertiary hospitals in Hubei Province». Chinese Medical Journal. 133 (9): 1025–1031. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000744. PMC 7147277. PMID 32044814.
- ^ Wang T, Du Z, Zhu F, Cao Z, An Y, Gao Y, Jiang B (March 2020). «Comorbidities and multi-organ injuries in the treatment of COVID-19». Lancet. Elsevier BV. 395 (10228): e52. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30558-4. PMC 7270177. PMID 32171074.
- ^ Wang Y, Wang Y, Chen Y, Qin Q (March 2020). «Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 568–576. doi:10.1002/jmv.25748. PMC 7228347. PMID 32134116.
- ^ «Coronavirus». WebMD. Archived from the original on 1 February 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ Martel J, Ko YF, Young JD, Ojcius DM (May 2020). «Could nasal breathing help to mitigate the severity of COVID-19». Microbes and Infection. 22 (4–5): 168–171. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.002. PMC 7200356. PMID 32387333.
- ^ «Coronavirus recovery: breathing exercises». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2020.
- ^ Wang L, Wang Y, Ye D, Liu Q (March 2020). «Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (6): 105948. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105948. PMC 7156162. PMID 32201353.
- ^ U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5 April 2020). «What to Do if You Are Sick». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ «Update to living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 371: m4475. November 2020. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4475. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 33214213. S2CID 227059995.
- ^ «Q&A: Dexamethasone and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- ^ «Home». National COVID-19 Clinical Evidence Taskforce. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- ^ Motseki, Thabiso Patrick (7 June 2022). «COVID-19 Vaccination Guidelines». www.nih.gov. National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- ^ Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. (April 2020). «Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 382 (18): 1708–1720. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2002032. PMC 7092819. PMID 32109013.
- ^ Henry BM (April 2020). «COVID-19, ECMO, and lymphopenia: a word of caution». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. Elsevier BV. 8 (4): e24. doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30119-3. PMC 7118650. PMID 32178774.
- ^ Kim JS, Lee JY, Yang JW, Lee KH, Effenberger M, Szpirt W, et al. (2021). «Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19». Theranostics. 11 (1): 316–329. doi:10.7150/thno.49713. PMC 7681075. PMID 33391477.
- ^ Doshi P (October 2020). «Will covid-19 vaccines save lives? Current trials aren’t designed to tell us». BMJ. 371: m4037. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4037. PMID 33087398. S2CID 224817161.
- ^ a b Palmieri L, Andrianou X, Barbariol P, Bella A, Bellino S, Benelli E, et al. (22 July 2020). Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 patients dying in Italy Report based on available data on July 22nd, 2020 (PDF) (Report). Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
- ^ Tzoulis P, Waung JA, Bagkeris E, Hussein Z, Biddanda A, Cousins J, et al. (May 2021). «Dysnatremia is a Predictor for Morbidity and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19». The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 106 (6): 1637–1648. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab107. PMC 7928894. PMID 33624101.
- ^ Tzoulis P, Grossman AB, Baldeweg SE, Bouloux P, Kaltsas G (September 2021). «MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Dysnatraemia in COVID-19: prevalence, prognostic impact, pathophysiology, and management». European Journal of Endocrinology. 185 (4): R103–R111. doi:10.1530/EJE-21-0281. PMC 8428074. PMID 34370712.
- ^ Baranovskii DS, Klabukov ID, Krasilnikova OA, Nikogosov DA, Polekhina NV, Baranovskaia DR, et al. (December 1975). «Letter: Acid secretion by gastric mucous membrane». The American Journal of Physiology. 229 (6): 21–25. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1853510. PMC 7738209. PMID 33210948. S2CID 227065216.
- ^ Christensen B, Favaloro EJ, Lippi G, Van Cott EM (October 2020). «Hematology Laboratory Abnormalities in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 46 (7): 845–849. doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715458. PMC 7645834. PMID 32877961.
- ^ «Living with Covid19». NIHR Themed Reviews. National Institute for Health Research. 15 October 2020. doi:10.3310/themedreview_41169.
- ^ a b «How long does COVID-19 last?». UK COVID Symptom Study. 6 June 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ «Summary of COVID-19 Long Term Health Effects: Emerging evidence and Ongoing Investigation» (PDF). University of Washington. 1 September 2020. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ «Long-term symptoms of COVID-19 ‘really concerning’, says WHO chief». UN News. 30 October 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2021.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) – Prognosis». BMJ. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ Lavery AM, Preston LE, Ko JY, Chevinsky JR, DeSisto CL, Pennington AF, et al. (November 2020). «Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Discharged and Experiencing Same-Hospital Readmission – United States, March–August 2020». MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (45): 1695–1699. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6945e2. PMC 7660660. PMID 33180754.
- ^ Vardavas CI, Nikitara K (March 2020). «COVID-19 and smoking: A systematic review of the evidence». Tobacco Induced Diseases. 18: 20. doi:10.18332/tid/119324. PMC 7083240. PMID 32206052.
- ^ a b c Engin AB, Engin ED, Engin A (August 2020). «Two important controversial risk factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Obesity and smoking». Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 78: 103411. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2020.103411. PMC 7227557. PMID 32422280.
- ^ Setti L, Passarini F, De Gennaro G, Barbieri P, Licen S, Perrone MG, et al. (September 2020). «Potential role of particulate matter in the spreading of COVID-19 in Northern Italy: first observational study based on initial epidemic diffusion». BMJ Open. 10 (9): e039338. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039338. PMC 7517216. PMID 32973066.
- ^ Wu X, Nethery RC, Sabath MB, Braun D, Dominici F (November 2020). «Air pollution and COVID-19 mortality in the United States: Strengths and limitations of an ecological regression analysis». Science Advances. 6 (45): eabd4049. Bibcode:2020SciA….6.4049W. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abd4049. PMC 7673673. PMID 33148655.
- ^ Pansini R, Fornacca D (June 2021). «Early Spread of COVID-19 in the Air-Polluted Regions of Eight Severely Affected Countries». Atmosphere. 12 (6): 795. Bibcode:2021Atmos..12..795P. doi:10.3390/atmos12060795.
- ^ Comunian S, Dongo D, Milani C, Palestini P (June 2020). «Air Pollution and Covid-19: The Role of Particulate Matter in the Spread and Increase of Covid-19’s Morbidity and Mortality». International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 17 (12): 4487. doi:10.3390/ijerph17124487. PMC 7345938. PMID 32580440.
- ^ Domingo JL, Marquès M, Rovira J (September 2020). «Influence of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on COVID-19 pandemic. A review». Environmental Research. 188: 109861. Bibcode:2020ER….188j9861D. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109861. PMC 7309850. PMID 32718835.
- ^ «COVID-19: Who’s at higher risk of serious symptoms?». Mayo Clinic.
- ^ Tamara A, Tahapary DL (July 2020). «Obesity as a predictor for a poor prognosis of COVID-19: A systematic review». Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome. 14 (4): 655–659. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.020. PMC 7217103. PMID 32438328.
- ^ Petrakis D, Margină D, Tsarouhas K, Tekos F, Stan M, Nikitovic D, et al. (July 2020). «Obesity – A risk factor for increased COVID-19, severity and lethality (Review)». Molecular Medicine Reports. 22 (1): 9–19. doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11127. PMC 7248467. PMID 32377709.
- ^ Roca-Fernández A, Dennis A, Nicholls R, McGonigle J, Kelly M, Banerjee R, et al. (29 March 2021). «Hepatic Steatosis, Rather Than Underlying Obesity, Increases the Risk of Infection and Hospitalization for COVID-19». Frontiers in Medicine. 8: 636637. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.636637. ISSN 2296-858X. PMC 8039134. PMID 33855033.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020.
- ^ Devresse A, Belkhir L, Vo B, Ghaye B, Scohy A, Kabamba B, et al. (November 2020). «COVID-19 Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Single-Center Case Series of 22 Cases From Belgium». Kidney Medicine. 2 (4): 459–466. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2020.06.001. PMC 7295531. PMID 32775986.
- ^ Dhindsa S, Champion C, Deol E, Lui M, Campbell R, Newman J, et al. (September 2022). «Association of Male Hypogonadism With Risk of Hospitalization for COVID-19». JAMA Network Open. 5 (9): e2229747. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.29747. PMC 9440397. PMID 36053534.
- ^ Shelton JF, Shastri AJ, Ye C, Weldon CH, Filshtein-Sonmez T, Coker D, et al. (June 2021). «Trans-ancestry analysis reveals genetic and nongenetic associations with COVID-19 susceptibility and severity». Nature Genetics. 53 (6): 801–808. doi:10.1038/s41588-021-00854-7. PMID 33888907. S2CID 233372385.
- ^ Wallis C. «One in Seven Dire COVID Cases May Result from a Faulty Immune Response». Scientific American.
- ^ Bastard P, Rosen LB, Zhang Q, Michailidis E, Hoffmann HH, Zhang Y, et al. (October 2020). «Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19». Science. 370 (6515): eabd4585. doi:10.1126/science.abd4585. PMC 7857397. PMID 32972996. S2CID 221914095.
- ^ Fusco DN, Brisac C, John SP, Huang YW, Chin CR, Xie T, et al. (June 2013). «A genetic screen identifies interferon-α effector genes required to suppress hepatitis C virus replication». Gastroenterology. 144 (7): 1438–49, 1449.e1-9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.026. PMC 3665646. PMID 23462180.
- ^ Namkoong H, Edahiro R, Takano T, Nishihara H, Shirai Y, Sonehara K, et al. (September 2022). «DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19». Nature. 609 (7928): 754–760. Bibcode:2022Natur.609..754N. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05163-5. PMC 9492544. PMID 35940203.
- ^ Kousathanas A, Pairo-Castineira E, Rawlik K, Stuckey A, Odhams CA, Walker S, et al. (July 2022). «Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19». Nature. 607 (7917): 97–103. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04576-6. PMC 9259496. PMID 35255492.
- ^ «COVID-19 in children and the role of school settings in transmission – first update». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 23 December 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ «Estimated Disease Burden of COVID-19». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ Reardon S (2 September 2021). «Why don’t kids tend to get as sick from Covid-19?». Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-090121-1. S2CID 239653475. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ «Information for Pediatric Healthcare Providers». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ Götzinger F, Santiago-García B, Noguera-Julián A, Lanaspa M, Lancella L, Calò Carducci FI, et al. (September 2020). «COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: a multinational, multicentre cohort study». The Lancet. Child & Adolescent Health. 4 (9): 653–661. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30177-2. PMC 7316447. PMID 32593339.
- ^ Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M (April 2020). «Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. 8 (4): e21. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30311-1. PMC 7118626. PMID 32171062.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ Hui DS, I Azhar E, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, et al. (February 2020). «The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health – The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 91: 264–266. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. PMC 7128332. PMID 31953166.
- ^ Murthy S, Gomersall CD, Fowler RA (April 2020). «Care for Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19». JAMA. 323 (15): 1499–1500. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.3633. PMID 32159735.
- ^ Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R (2020). «Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19)». StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 32150360. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Heymann DL, Shindo N, et al. (WHO Scientific and Technical Advisory Group for Infectious Hazards) (February 2020). «COVID-19: what is next for public health?». Lancet. 395 (10224): 542–545. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30374-3. PMC 7138015. PMID 32061313.
- ^ Romiti GF, Corica B, Lip GY, Proietti M (June 2021). «Prevalence and Impact of Atrial Fibrillation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis». Journal of Clinical Medicine. 10 (11): 2490. doi:10.3390/jcm10112490. PMC 8200114. PMID 34199857.
- ^ Wen W, Zhang H, Zhou M, Cheng Y, Ye L, Chen J, et al. (November 2020). «Arrhythmia in patients with severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a meta-analysis». European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 24 (21): 11395–11401. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202011_23632. PMID 33215461. S2CID 227077132.
- ^ Long B, Brady WJ, Koyfman A, Gottlieb M (July 2020). «Cardiovascular complications in COVID-19». The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 38 (7): 1504–1507. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.04.048. PMC 7165109. PMID 32317203.
- ^ Puntmann VO, Carerj ML, Wieters I, Fahim M, Arendt C, Hoffmann J, et al. (November 2020). «Outcomes of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients Recently Recovered From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». JAMA Cardiology. 5 (11): 1265–1273. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3557. PMC 7385689. PMID 32730619.
- ^ Lindner D, Fitzek A, Bräuninger H, Aleshcheva G, Edler C, Meissner K, et al. (November 2020). «Association of Cardiac Infection With SARS-CoV-2 in Confirmed COVID-19 Autopsy Cases». JAMA Cardiology. 5 (11): 1281–1285. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3551. PMC 7385672. PMID 32730555.
- ^ Siripanthong B, Nazarian S, Muser D, Deo R, Santangeli P, Khanji MY, et al. (September 2020). «Recognizing COVID-19-related myocarditis: The possible pathophysiology and proposed guideline for diagnosis and management». Heart Rhythm. 17 (9): 1463–1471. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.001. PMC 7199677. PMID 32387246.
- ^ Xu L, Liu J, Lu M, Yang D, Zheng X (May 2020). «Liver injury during highly pathogenic human coronavirus infections». Liver International. 40 (5): 998–1004. doi:10.1111/liv.14435. PMC 7228361. PMID 32170806.
- ^ Carod-Artal FJ (May 2020). «Neurological complications of coronavirus and COVID-19». Revista de Neurología. 70 (9): 311–322. doi:10.33588/rn.7009.2020179. PMID 32329044. S2CID 226200547.
- ^ Toscano G, Palmerini F, Ravaglia S, Ruiz L, Invernizzi P, Cuzzoni MG, et al. (June 2020). «Guillain-Barré Syndrome Associated with SARS-CoV-2». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (26): 2574–2576. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2009191. PMC 7182017. PMID 32302082.
- ^ «Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents temporally related to COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ HAN Archive – 00432. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (Report). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ Poyiadji N, Shahin G, Noujaim D, Stone M, Patel S, Griffith B (August 2020). «COVID-19-associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Imaging Features». Radiology. 296 (2): E119–E120. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020201187. PMC 7233386. PMID 32228363.
- ^ a b Córdoba-Vives S, Peñaranda G (April 2020). «COVID-19 y Embarazo». Medical Journal of Costa Rica (in Spanish): 629. Archived from the original on 18 June 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ Das S, Dhar S (July 2021). «Mucormycosis Following COVID-19 Infections: an Insight». The Indian Journal of Surgery. 84 (3): 585–586. doi:10.1007/s12262-021-03028-1. PMC 8270771. PMID 34276145. S2CID 235782159.
- ^ Baruah C, Devi P, Deka B, Sharma DK (June 2021). «Mucormycosis and Aspergillosis have been Linked to Covid-19-Related Fungal Infections in India». Advancements in Case Studies. 3 (1). doi:10.31031/AICS.2021.03.000555. ISSN 2639-0531. S2CID 244678882 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ «Living with Covid19». NIHR Themed Review. National Institute for Health Research. 15 October 2020. doi:10.3310/themedreview_41169. S2CID 241034526.
- ^ «Summary of COVID-19 Long Term Health Effects: Emerging evidence and Ongoing Investigation» (PDF). University of Washington. 1 September 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. (February 2020). «Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China». Lancet. 395 (10223): 497–506. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. PMC 7159299. PMID 31986264.
- ^ a b Torres-Castro R, Vasconcello-Castillo L, Alsina-Restoy X, Solis-Navarro L, Burgos F, Puppo H, Vilaró J (November 2020). «Respiratory function in patients post-infection by COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Pulmonology. Elsevier BV. 27 (4): 328–337. doi:10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.10.013. PMC 7687368. PMID 33262076. S2CID 227162748.
- ^ Shaw B, Daskareh M, Gholamrezanezhad A (January 2021). «The lingering manifestations of COVID-19 during and after convalescence: update on long-term pulmonary consequences of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)». La Radiologia Medica. 126 (1): 40–46. doi:10.1007/s11547-020-01295-8. PMC 7529085. PMID 33006087.
- ^ Zhao YM, Shang YM, Song WB, Li QQ, Xie H, Xu QF, et al. (August 2020). «Follow-up study of the pulmonary function and related physiological characteristics of COVID-19 survivors three months after recovery». EClinicalMedicine. 25: 100463. doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.11.003. PMC 7654356. PMID 32838236.
- ^ «COVID-19 Lung Damage». Johns Hopkins Medicine. 28 February 2022. Retrieved 21 May 2022.
- ^ Taquet M, Sillett R, Zhu L, Mendel J, Camplisson I, Dercon Q, Harrison PJ (17 August 2022). «Neurological and psychiatric risk trajectories after SARS-CoV-2 infection: an analysis of 2-year retrospective cohort studies including 1 284 437 patients». The Lancet Psychiatry. 9 (10): 815–827. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(22)00260-7. ISSN 2215-0366. PMC 9385200. PMID 35987197. S2CID 251626731.
- ^ «Immune responses and correlates of protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 18 May 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- ^ Vabret N, Britton GJ, Gruber C, Hegde S, Kim J, Kuksin M, et al. (June 2020). «Immunology of COVID-19: Current State of the Science». Immunity. 52 (6): 910–941. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.002. PMC 7200337. PMID 32505227.
- ^ Wang Z, Muecksch F, Schaefer-Babajew D, Finkin S, Viant C, Gaebler C, et al. (July 2021). «Naturally enhanced neutralizing breadth against SARS-CoV-2 one year after infection». Nature. 595 (7867): 426–431. Bibcode:2021Natur.595..426W. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03696-9. PMC 8277577. PMID 34126625.
- ^ a b Cohen JI, Burbelo PD (December 2020). «Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Vaccines». Clinical Infectious Diseases. 73 (11): e4223–e4228. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1866. PMC 7799323. PMID 33338197. S2CID 229323810.
- ^ a b Wang J, Kaperak C, Sato T, Sakuraba A (August 2021). «COVID-19 reinfection: a rapid systematic review of case reports and case series». Journal of Investigative Medicine. 69 (6): 1253–1255. doi:10.1136/jim-2021-001853. ISSN 1081-5589. PMID 34006572. S2CID 234773697.
- ^ a b «How soon after catching COVID-19 can you get it again?». ABC News. 2 May 2022. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (May 2012). «Lesson 3: Measures of Risk Section 3: Mortality Frequency Measures». Principles of Epidemiology in Public Health Practice (Third ed.). U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). No. SS1978. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Ritchie H, Roser M (25 March 2020). Chivers T (ed.). «What do we know about the risk of dying from COVID-19?». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Castagnoli R, Votto M, Licari A, Brambilla I, Bruno R, Perlini S, et al. (September 2020). «Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review». JAMA Pediatrics. 174 (9): 882–889. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1467. PMID 32320004.
- ^ Lu X, Zhang L, Du H, Zhang J, Li YY, Qu J, et al. (April 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 382 (17): 1663–1665. doi:10.1056/nejmc2005073. PMC 7121177. PMID 32187458.
- ^ Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, Tong S (June 2020). «Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China». Pediatrics. 145 (6): e20200702. doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0702. PMID 32179660. S2CID 219118986.
- ^ a b c d Dehingia N (2021). «Sex differences in COVID-19 case fatality: do we know enough?». The Lancet. Global Health. 9 (1): e14–e15. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30464-2. PMC 7834645. PMID 33160453.
- ^ Lazzerini M, Putoto G (May 2020). «COVID-19 in Italy: momentous decisions and many uncertainties». The Lancet. Global Health. 8 (5): e641–e642. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30110-8. PMC 7104294. PMID 32199072.
- ^ Ritchie H, Ortiz-Ospina E, Beltekian D, Mathieu E, Hasell J, MacDonald B, et al. (5 March 2020). «What do we know about the risk of dying from COVID-19?». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ «Total confirmed cases of COVID-19 per million people». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2022.[needs update]
- ^ «Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million people». Our World in Data.
- ^ Mallapaty S (June 2020). «How deadly is the coronavirus? Scientists are close to an answer». Nature. 582 (7813): 467–468. Bibcode:2020Natur.582..467M. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01738-2. PMID 32546810. S2CID 219726496.
- ^ Alwan NA, Burgess RA, Ashworth S, Beale R, Bhadelia N, Bogaert D, et al. (October 2020). «Scientific consensus on the COVID-19 pandemic: we need to act now». Lancet. 396 (10260): e71–e72. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32153-X. PMC 7557300. PMID 33069277.
- ^ Meyerowitz-Katz G, Merone L (December 2020). «A systematic review and meta-analysis of published research data on COVID-19 infection fatality rates». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 101: 138–148. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.1464. PMC 7524446. PMID 33007452.
- ^ Zhang D, Hu M, Ji Q (October 2020). «Financial markets under the global pandemic of COVID-19». Finance Research Letters. 36: 101528. Bibcode:2020CSFX….500043D. doi:10.1016/j.csfx.2020.100043. PMC 7402242. PMID 32837360.
- ^ a b c d e Levin AT, Hanage WP, Owusu-Boaitey N, Cochran KB, Walsh SP, Meyerowitz-Katz G (December 2020). «Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications». European Journal of Epidemiology. 35 (12): 1123–1138. doi:10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1. PMC 7721859. PMID 33289900.
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- ^ World Health Organization (22 December 2020). «Background paper on Covid-19 disease and vaccines: prepared by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on immunization working group on COVID-19 vaccines». World Health Organization. hdl:10665/338095.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 30» (PDF). 19 February 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 31» (PDF). 20 February 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (4 July 2020). «The Pandemic’s Big Mystery: How Deadly Is the Coronavirus? – Even with more than 500,000 dead worldwide, scientists are struggling to learn how often the virus kills. Here’s why». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ «Global Research and Innovation Forum on COVID-19: Virtual Press Conference» (PDF). World Health Organization. 2 July 2020.
- ^ «Estimating mortality from COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 21 September 2020.
- ^ Shaffer C (23 October 2021). «Covid-19 still rife in Iran». New Scientist. 252 (3357): 10–11. Bibcode:2021NewSc.252…10S. doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(21)01865-0. ISSN 0262-4079. PMC 8536311. PMID 34720322.
- ^ «COVID-19: Data». City of New York.
- ^ Wilson L (May 2020). «SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, Infection Fatality Rate (IFR) Implied by the Serology, Antibody, Testing in New York City». SSRN 3590771.
- ^ Yang W, Kandula S, Huynh M, Greene SK, Van Wye G, Li W, et al. (February 2021). «Estimating the infection-fatality risk of SARS-CoV-2 in New York City during the spring 2020 pandemic wave: a model-based analysis». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 21 (2): 203–212. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30769-6. PMC 7572090. PMID 33091374.
- ^ Modi C (21 April 2020). «How deadly is COVID-19? Data Science offers answers from Italy mortality data». Medium. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 September 2020. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^ Salje H, Tran Kiem C, Lefrancq N, Courtejoie N, Bosetti P, Paireau J, et al. (July 2020). «Estimating the burden of SARS-CoV-2 in France». Science. 369 (6500): 208–211. Bibcode:2020Sci…369..208S. doi:10.1126/science.abc3517. PMC 7223792. PMID 32404476.
- ^ McIntosh K (April 2021). «Covid 19 Clinical Features». UpToDate. Retrieved 12 May 2021.
- ^ Peckham H, de Gruijter NM, Raine C, Radziszewska A, Ciurtin C, Wedderburn LR, et al. (December 2020). «Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 6317. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.6317P. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6. PMC 7726563. PMID 33298944.
- ^ Abate BB, Kassie AM, Kassaw MW, Aragie TG, Masresha SA (October 2020). «Sex difference in coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ Open. 10 (10): e040129. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040129. PMC 7539579. PMID 33028563.
- ^ a b c The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team (February 2020). «The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) – China, 2020». China CDC Weekly. 2 (8): 113–122. doi:10.46234/ccdcw2020.032. PMC 839292. PMID 34594836.
- ^ Hu Y, Sun J, Dai Z, Deng H, Li X, Huang Q, et al. (June 2020). «Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis». Journal of Clinical Virology. 127: 104371. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371. PMC 7195434. PMID 32315817.
- ^ Fu L, Wang B, Yuan T, Chen X, Ao Y, Fitzpatrick T, et al. (June 2020). «Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis». The Journal of Infection. 80 (6): 656–665. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.041. PMC 7151416. PMID 32283155.
- ^ Yuki K, Fujiogi M, Koutsogiannaki S (June 2020). «COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review». Clinical Immunology. 215: 108427. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427. PMC 7169933. PMID 32325252. S2CID 216028003.
- ^ Rabin RC (20 March 2020). «In Italy, Coronavirus Takes a Higher Toll on Men». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 weekly surveillance report». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b Gupta AH (3 April 2020). «Does Covid-19 Hit Women and Men Differently? U.S. Isn’t Keeping Track». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b Dorn AV, Cooney RE, Sabin ML (April 2020). «COVID-19 exacerbating inequalities in the US». Lancet. 395 (10232): 1243–1244. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30893-X. PMC 7162639. PMID 32305087.
- ^ a b Shauly-Aharonov, Michal; Shafrir, Asher; Paltiel, Ora; Calderon-Margalit, Ronit; Safadi, Rifaat; Bicher, Roee; Barenholz-Goultschin, Orit; Stokar, Joshua (22 July 2021). «Both high and low pre-infection glucose levels associated with increased risk for severe COVID-19: New insights from a population-based study». PLOS ONE. 16 (7): e0254847. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1654847S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0254847. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 8297851. PMID 34293038.
- ^ Adams ML, Katz DL, Grandpre J (August 2020). «Population-Based Estimates of Chronic Conditions Affecting Risk for Complications from Coronavirus Disease, United States». Emerging Infectious Diseases. 26 (8): 1831–1833. doi:10.3201/eid2608.200679. PMC 7392427. PMID 32324118.
- ^ Batthyány K (13 October 2020). «Coronavirus y Desigualdades preexistentes: Género y Cuidados». CLACSO (Consejo Latinoamericano de Ciencias Sociales). Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ «COVID-19 Presents Significant Risks for American Indian and Alaska Native People». 14 May 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 Presents Significant Risks for American Indian and Alaska Native People». 14 May 2020.
- ^ Laurencin CT, McClinton A (June 2020). «The COVID-19 Pandemic: a Call to Action to Identify and Address Racial and Ethnic Disparities». Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities. 7 (3): 398–402. doi:10.1007/s40615-020-00756-0. PMC 7166096. PMID 32306369.
- ^ «How coronavirus deaths in the UK compare by race and ethnicity». The Independent. 9 June 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ «Emerging findings on the impact of COVID-19 on black and minority ethnic people». The Health Foundation. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ Butcher B, Massey J (9 June 2020). «Why are more BAME people dying from coronavirus?». BBC News. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ a b c «The ancient Neanderthal hand in severe COVID-19». ScienceDaily. 30 September 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- ^ «WHO Director-General’s statement on the advice of the IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus». World Health Organization (WHO).
- ^ Garg S, Kim L, Whitaker M, O’Halloran A, Cummings C, Holstein R, et al. (April 2020). «Hospitalization Rates and Characteristics of Patients Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019 – COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1–30, 2020». MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (15): 458–464. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3. PMC 7755063. PMID 32298251.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ Zhao Q, Meng M, Kumar R, Wu Y, Huang J, Lian N, et al. (October 2020). «The impact of COPD and smoking history on the severity of COVID-19: A systemic review and meta-analysis». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (10): 1915–1921. doi:10.1002/jmv.25889. PMC 7262275. PMID 32293753.
- ^ «Smoking and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ DeRobertis J (3 May 2020). «People who use drugs are more vulnerable to coronavirus. Here’s what clinics are doing to help». The Advocate (Louisiana). Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020.
- ^ Frutos R, Gavotte L, Devaux CA (November 2021). «Understanding the origin of COVID-19 requires to change the paradigm on zoonotic emergence from the spillover to the circulation model». Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 95: 104812. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104812. PMC 7969828. PMID 33744401.
- ^ Holmes EC, Goldstein SA, Rasmussen AL, Robertson DL, Crits-Christoph A, Wertheim JO, et al. (September 2021). «The origins of SARS-CoV-2: A critical review». Cell. 184 (19): 4848–4856. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.017. PMC 8373617. PMID 34480864.
- ^ «WHO-convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part». World Health Organization. 30 March 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ^ Duarte F (24 February 2020). «As the cases of coronavirus increase in China and around the world, the hunt is on to identify «patient zero»«. BBC News. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ Pekar JE, Magee P, Parker E, Moshiri N, Izhikevich K, Havens JL, et al. (26 July 2022). «The molecular epidemiology of multiple zoonotic origins of SARS-CoV-2». Science. 377 (6609): 960–966. Bibcode:2022Sci…377..960P. doi:10.1126/science.abp8337. PMC 9348752. PMID 35881005.
- ^ Gill V (26 July 2022). «Covid origin studies say evidence points to Wuhan market».
- ^ Worobey M, Levy JI, Serrano LM, Crits-Christoph A, Pekar JE, Goldstein SA, et al. (July 2022). «The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan was the early epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic». Science. 377 (6609): 951–959. Bibcode:2022Sci…377..951W. doi:10.1126/science.abp8715. PMC 9348750. PMID 35881010. S2CID 251067542.
- ^ «Debate deepens over Wuhan wet market’s role in kickstarting the pandemic». National Geographic. 27 July 2022.
- ^ Li X, Zai J, Zhao Q, Nie Q, Li Y, Foley BT, Chaillon A (June 2020). «Evolutionary history, potential intermediate animal host, and cross-species analyses of SARS-CoV-2». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 602–611. doi:10.1002/jmv.25731. PMC 7228310. PMID 32104911.
- ^ Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF (April 2020). «The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Medicine. 26 (4): 450–452. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9. PMC 7095063. PMID 32284615.
- ^ van Dorp L, Acman M, Richard D, Shaw LP, Ford CE, Ormond L, et al. (September 2020). «Emergence of genomic diversity and recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2». Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 83: 104351. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104351. PMC 7199730. PMID 32387564.
- ^ Grose TK (13 May 2020). «Did the Coronavirus Originate Outside of Wuhan?». U.S. News & World Report.
- ^ Wolf ZB (25 May 2021). «Analysis: Why scientists are suddenly more interested in the lab-leak theory of Covid’s origin». CNN. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ Maxmen A (September 2021). «US COVID origins report: researchers pleased with scientific approach». Nature. 597 (7875): 159–160. Bibcode:2021Natur.597..159M. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-02366-0. PMID 34465917. S2CID 237373547.
- ^ Paun C, Zeller S, Reader R, Leonard B, Scullion G (4 November 2022). «Cross-examining the lab-leak theorists». Politico. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ Hosenball M, Zengerle P (30 October 2021). «U.S. spy agencies say origins of COVID-19 may never be known». Reuters. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ Wu YC, Chen CS, Chan YJ (March 2020). «The outbreak of COVID-19: An overview». Journal of the Chinese Medical Association. 83 (3): 217–220. doi:10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000270. PMC 7153464. PMID 32134861.
- ^ Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF (February 2020). «A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern». Lancet. 395 (10223): 470–473. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9. PMC 7135038. PMID 31986257.
- ^ Cohen J (January 2020). «Wuhan seafood market may not be source of novel virus spreading globally». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abb0611.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus – China». World Health Organization (WHO). 12 January 2020. Archived from the original on 14 January 2020.
- ^ Kessler G (17 April 2020). «Trump’s false claim that the WHO said the coronavirus was ‘not communicable’«. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Kuo L (21 January 2020). «China confirms human-to-human transmission of coronavirus». The Guardian. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ Epidemiology Working Group For Ncip Epidemic Response; Chinese Center for Disease Control Prevention (February 2020). «[The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China]». Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi (in Chinese). 41 (2): 145–151. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003. PMID 32064853. S2CID 211133882.
- ^ Areddy JT (26 May 2020). «China Rules Out Animal Market and Lab as Coronavirus Origin». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ Kelland K (19 June 2020). «Italy sewage study suggests COVID-19 was there in December 2019». Reuters. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ Heymann DL, Shindo N (February 2020). «COVID-19: what is next for public health?». Lancet. 395 (10224): 542–545. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3. PMC 7138015. PMID 32061313.
- ^ Bryner J (14 March 2020). «1st known case of coronavirus traced back to November in China». livescience.com. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ Canadian Politics (8 April 2020). «The birth of a pandemic: How COVID-19 went from Wuhan to Toronto | National Post». National Post. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ 高昱 (26 February 2020). «独家 | 新冠病毒基因测序溯源:警报是何时拉响的» [Exclusive | Tracing the New Coronavirus gene sequencing: when did the alarm sound]. Caixin (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 27 February 2020. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- ^ 路子康. «最早上报疫情的她,怎样发现这种不一样的肺炎». 中国网新闻 (in Chinese (China)). 北京. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ «Undiagnosed pneumonia – China (HU): RFI». ProMED Mail. ProMED. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ «‘Hero who told the truth’: Chinese rage over coronavirus death of whistleblower doctor». The Guardian. 7 February 2020.
- ^ Kuo L (11 March 2020). «Coronavirus: Wuhan doctor speaks out against authorities». The Guardian. London.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ^ «武汉现不明原因肺炎 官方确认属实:已经做好隔离». Xinhua Net 新華網. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ 武汉市卫健委关于当前我市肺炎疫情的情况通报. WJW.Wuhan.gov.cn (in Chinese). Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 9 January 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ «Mystery pneumonia virus probed in China». BBC News. 3 January 2020. Archived from the original on 5 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. (March 2020). «Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (13): 1199–1207. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316. PMC 7121484. PMID 31995857.
- ^ «China confirms sharp rise in cases of SARS-like virus across the country». 20 January 2020. Archived from the original on 20 January 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- ^ a b «Flattery and foot dragging: China’s influence over the WHO under scrutiny». The Globe and Mail. 25 April 2020.
- ^ Horton R (18 March 2020). «Scientists have been sounding the alarm on coronavirus for months. Why did Britain fail to act?». The Guardian. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ «China delayed releasing coronavirus info, frustrating WHO». Associated Press. 2 June 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Primi due casi in Italia» [Coronavirus: First two cases in Italy]. Corriere della sera (in Italian). 31 January 2020. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Number of COVID-19 deaths in Italy surpasses China as total reaches 3,405». Sky News. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (26 March 2020). «The U.S. Now Leads the World in Confirmed Coronavirus Cases». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ «Studies Show N.Y. Outbreak Originated in Europe». The New York Times. 8 April 2020. Archived from the original on 8 April 2020.
- ^ Irish J (4 May 2020). Lough RM, Graff P (eds.). «After retesting samples, French hospital discovers COVID-19 case from December». Reuters. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ Deslandes A, Berti V, Tandjaoui-Lambotte Y, Alloui C, Carbonnelle E, Zahar JR, et al. (June 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 was already spreading in France in late December 2019». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (6): 106006. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106006. PMC 7196402. PMID 32371096.
- ^ «2 died with coronavirus weeks before 1st U.S. virus death». PBS NewsHour. 22 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ Michael-Kordatou I, Karaolia P, Fatta-Kassinos D (October 2020). «Sewage analysis as a tool for the COVID-19 pandemic response and management: the urgent need for optimised protocols for SARS-CoV-2 detection and quantification». Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 8 (5): 104306. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2020.104306. PMC 7384408. PMID 32834990.
- ^ Platto S, Xue T, Carafoli E (September 2020). «COVID19: an announced pandemic». Cell Death & Disease. 11 (9): 799. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02995-9. PMC 7513903. PMID 32973152.
- ^ Kavya B, Abraham R (3 October 2021). Shumaker L, Wardell J (eds.). «Global COVID-19 deaths hit 5 million as Delta variant sweeps the world». Reuters.com. Reuters.
- ^ «China coronavirus: Misinformation spreads online about origin and scale». BBC News. 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 4 February 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ Taylor J (31 January 2020). «Bat soup, dodgy cures and ‘diseasology’: the spread of coronavirus misinformation». The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
- ^ «Here’s A Running List Of Disinformation Spreading About The Coronavirus». Buzzfeed News. Archived from the original on 6 February 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ «Misleading claim circulates online about infection fatality ratio of Covid-19 in the US». Fact Check. 8 October 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ a b c d Kampf G, Brüggemann Y, Kaba HE, Steinmann J, Pfaender S, Scheithauer S, Steinmann E (December 2020). «Potential sources, modes of transmission and effectiveness of prevention measures against SARS-CoV-2». The Journal of Hospital Infection. 106 (4): 678–697. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2020.09.022. PMC 7500278. PMID 32956786.
- ^ Shi J, Wen Z, Zhong G, Yang H, Wang C, Huang B, et al. (May 2020). «Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS-coronavirus 2». Science. 368 (6494): 1016–1020. doi:10.1126/science.abb7015. PMC 7164390. PMID 32269068.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Salajegheh Tazerji S, Magalhães Duarte P, Rahimi P, Shahabinejad F, Dhakal S, Singh Malik Y, et al. (September 2020). «Transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to animals: an updated review». Journal of Translational Medicine. 18 (1): 358. doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02534-2. PMC 7503431. PMID 32957995.
- ^ a b c Gorman J (22 January 2021). «The Coronavirus Kills Mink, So They Too May Get a Vaccine». The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ Dhama K, Sharun K, Tiwari R, Dadar M, Malik YS, Singh KP, Chaicumpa W (June 2020). «COVID-19, an emerging coronavirus infection: advances and prospects in designing and developing vaccines, immunotherapeutics, and therapeutics». Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 16 (6): 1232–1238. doi:10.1080/21645515.2020.1735227. PMC 7103671. PMID 32186952.
- ^ Zhang L, Liu Y (May 2020). «Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: A systematic review». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (5): 479–490. doi:10.1002/jmv.25707. PMC 7166986. PMID 32052466.
- ^ «Interim Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines for Handling and Processing Specimens Associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Lab Biosafety Guidelines. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Aristovnik A, Ravšelj D, Umek L (November 2020). «A Bibliometric Analysis of COVID-19 across Science and Social Science Research Landscape». Sustainability. 12 (21): 9132. doi:10.3390/su12219132.
- ^ Kupferschmidt K (3 December 2020). «First-of-its-kind African trial tests common drugs to prevent severe COVID-19». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abf9987. Retrieved 8 March 2022.
- ^ Reardon S (November 2020). «For COVID Drugs, Months of Frantic Development Lead to Few Outright Successes». Scientific American. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ^ Kucharski AJ, Russell TW, Diamond C, Liu Y, Edmunds J, Funk S, Eggo RM (May 2020). «Early dynamics of transmission and control of COVID-19: a mathematical modelling study». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (5): 553–558. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30144-4. PMC 7158569. PMID 32171059.
- ^ «Update to living systematic review on prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of covid-19». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 372: n236. 3 February 2021. doi:10.1136/bmj.n236. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 33536183. S2CID 231775762.
- ^ Giordano G, Blanchini F, Bruno R, Colaneri P, Di Filippo A, Di Matteo A, Colaneri M (June 2020). «Modelling the COVID-19 epidemic and implementation of population-wide interventions in Italy». Nature Medicine. 26 (6): 855–860. arXiv:2003.09861. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0883-7. PMC 7175834. PMID 32322102.
- ^ Prem K, Liu Y, Russell TW, Kucharski AJ, Eggo RM, Davies N, et al. (May 2020). «The effect of control strategies to reduce social mixing on outcomes of the COVID-19 epidemic in Wuhan, China: a modelling study». The Lancet. Public Health. 5 (5): e261–e270. doi:10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30073-6. PMC 7158905. PMID 32220655.
- ^ Emanuel EJ, Persad G, Upshur R, Thome B, Parker M, Glickman A, et al. (May 2020). «Fair Allocation of Scarce Medical Resources in the Time of Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (21): 2049–2055. doi:10.1056/NEJMsb2005114. PMID 32202722.
- ^ Kermack WO, McKendrick AG (1927). «A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character. 115 (772): 700–721. Bibcode:1927RSPSA.115..700K. doi:10.1098/rspa.1927.0118.
- ^ Mittal R, Ni R, Seo JH (2020). «The flow physics of COVID-19». Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 894: –2. arXiv:2004.09354. Bibcode:2020JFM…894F…2M. doi:10.1017/jfm.2020.330.
- ^ Ronchi E, Lovreglio R (October 2020). «EXPOSED: An occupant exposure model for confined spaces to retrofit crowd models during a pandemic». Safety Science. 130: 104834. arXiv:2005.04007. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104834. PMC 7373681. PMID 32834509.
- ^ Badr HS, Du H, Marshall M, Dong E, Squire MM, Gardner LM (November 2020). «Association between mobility patterns and COVID-19 transmission in the USA: a mathematical modelling study». The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 20 (11): 1247–1254. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30553-3. PMC 7329287. PMID 32621869.
- ^ McKibbin W, Roshen F (2020). «The global macroeconomic impacts of COVID-19: Seven scenarios» (PDF). CAMA Working Paper. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3547729. S2CID 216307705.
- ^ Bundy J, Pfarrer MD, Short CE, Coombs WT (July 2017). «Crises and crisis management: Integration, interpretation, and research development». Journal of Management. 43 (6): 1661–92. doi:10.1177/0149206316680030. S2CID 152223772.
- ^ Kraus S, Clauss T, Breier M, Gast J, Zardini A, Tiberius V (2020). «The economics of COVID-19: initial empirical evidence on how family firms in five European countries cope with the corona crisis». International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research. 26 (5): 1067–1092. doi:10.1108/IJEBR-04-2020-0214. ISSN 1355-2554. S2CID 219144929.
- ^ «COVID-19 treatment and vaccine tracker» (PDF). Milken Institute. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ a b Koch S, Pong W (13 March 2020). «First up for COVID-19: nearly 30 clinical readouts before end of April». BioCentury Inc. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Kupferschmidt K, Cohen J (March 2020). «WHO launches global megatrial of the four most promising coronavirus treatments». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abb8497.
- ^ «UN health chief announces global ‘solidarity trial’ to jumpstart search for COVID-19 treatment». UN News. 18 March 2020. Archived from the original on 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- ^ «Citing safety concerns, the W.H.O. paused tests of a drug Trump said he had taken». The New York Times. 26 May 2020. Archived from the original on 26 May 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Hydroxychloroquine does not benefit adults hospitalized with COVID-19». National Institutes of Health (NIH) (Press release). 9 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Warns of Newly Discovered Potential Drug Interaction That May Reduce Effectiveness of a COVID-19 Treatment Authorized for Emergency Use». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 June 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ^ «France bans use of hydroxychloroquine, drug touted by Trump, in coronavirus patients». CBS News. 27 May 2020.
- ^ Boseley S (16 June 202). «Recovery trial for Covid-19 treatments: what we know so far». The Guardian. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «WHO welcomes preliminary results about dexamethasone use in treating critically ill COVID-19 patients». World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). 16 June 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «Q&A: Dexamethasone and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ «Corticosteroids». COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (2020). Corticosteroids for COVID-19: living guidance, 2 September 2020 (Report). hdl:10665/334125. WHO/2019-nCoV/Corticosteroids/2020.1.
- ^ «WHO updates clinical care guidance with corticosteroid recommendations». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Sterne JA, Murthy S, Diaz JV, Slutsky AS, Villar J, Angus DC, et al. (The WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group) (October 2020). «Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis». JAMA. 324 (13): 1330–1341. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17023. PMC 7489434. PMID 32876694. S2CID 221467783.
- ^ Prescott HC, Rice TW (October 2020). «Corticosteroids in COVID-19 ARDS: Evidence and Hope During the Pandemic». JAMA. 324 (13): 1292–1295. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.16747. PMID 32876693. S2CID 221468015.
- ^ a b «EMA endorses use of dexamethasone in COVID-19 patients on oxygen or mechanical ventilation». European Medicines Agency (EMA) (Press release). 18 September 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2020. Text was copied from this source which is European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ Dexamethasone in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 (PDF) (Report). European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2020.
- ^ a b c
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 9 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 10 February 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Revokes Emergency Use Authorization for Monoclonal Antibody Bamlanivimab». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 16 April 2021. Retrieved 16 April 2021.
- ^ Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S (April 2020). «Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19». Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis. 10 (2): 102–108. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001. PMC 7104082. PMID 32282863.
- ^ Zhao Z, Wei Y, Tao C (January 2021). «An enlightening role for cytokine storm in coronavirus infection». Clinical Immunology. 222: 108615. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108615. PMC 7583583. PMID 33203513.
- ^ Liu R, Miller J (3 March 2020). «China approves use of Roche drug in battle against coronavirus complications». Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Xu X, Han M, Li T, Sun W, Wang D, Fu B, et al. (May 2020). «Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (20): 10970–10975. Bibcode:2020PNAS..11710970X. doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117. PMC 7245089. PMID 32350134.
- ^ Ovadia D, Agenzia Z. «COVID-19 – Italy launches an independent trial on tocilizumab». Univadis from Medscape. Aptus Health. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ «Tocilizumab in COVID-19 Pneumonia (TOCIVID-19) (TOCIVID-19)». clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Various sources:
- «How doctors can potentially significantly reduce the number of deaths from Covid-19». Vox. 12 March 2020. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- Ruan Q, Yang K, Wang W, Jiang L, Song J (May 2020). «Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China». Intensive Care Medicine. 46 (5): 846–848. doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x. PMC 7080116. PMID 32125452.
- Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ (March 2020). «COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression». Lancet. 395 (10229): 1033–1034. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. PMC 7270045. PMID 32192578.
- ^ Slater H (26 March 2020). «FDA Approves Phase III Clinical Trial of Tocilizumab for COVID-19 Pneumonia». cancernetwork.com. Cancer Network. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Locke FL, Neelapu SS, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, et al. (2017). «Preliminary Results of Prophylactic Tocilizumab after Axicabtageneciloleucel (axi-cel; KTE-C19) Treatment for Patients with Refractory, Aggressive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)». Blood. 130 (Supplement 1): 1547. doi:10.1182/blood.V130.Suppl_1.1547.1547. S2CID 155698207.
- ^ Sterner RM, Sakemura R, Cox MJ, Yang N, Khadka RH, Forsman CL, et al. (February 2019). «GM-CSF inhibition reduces cytokine release syndrome and neuroinflammation but enhances CAR T cell function in xenografts». Blood. 133 (7): 697–709. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-10-881722. PMC 6376281. PMID 30463995.
- ^ a b c d e Casadevall A, Pirofski LA (April 2020). «The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19». The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 130 (4): 1545–1548. doi:10.1172/JCI138003. PMC 7108922. PMID 32167489.
- ^ a b c Piechotta V, Iannizzi C, Chai KL, Valk SJ, Kimber C, Dorando E, et al. (May 2021). «Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (5): CD013600. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4. PMC 8135693. PMID 34013969.
- ^ a b Ho M (April 2020). «Perspectives on the development of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2». Antibody Therapeutics. 3 (2): 109–114. doi:10.1093/abt/tbaa009. PMC 7291920. PMID 32566896.
- ^ Yang L, Liu W, Yu X, Wu M, Reichert JM, Ho M (July 2020). «COVID-19 antibody therapeutics tracker: a global online database of antibody therapeutics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19». Antibody Therapeutics. 3 (3): 205–212. doi:10.1093/abt/tbaa020. PMC 7454247. PMID 33215063.
- ^ Maccaro A, Piaggio D, Pagliara S, Pecchia L (June 2021). «The role of ethics in science: a systematic literature review from the first wave of COVID-19». Health and Technology. 11 (5): 1063–1071. doi:10.1007/s12553-021-00570-6. ISSN 2190-7188. PMC 8175060. PMID 34104626.
- ^ McGuire AL, Aulisio MP, Davis FD, Erwin C, Harter TD, Jagsi R, et al. (July 2020). «Ethical Challenges Arising in the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview from the Association of Bioethics Program Directors (ABPD) Task Force». The American Journal of Bioethics. 20 (7): 15–27. doi:10.1080/15265161.2020.1764138. PMID 32511078. S2CID 219552665.
- ^ Wenham C, Smith J, Morgan R (March 2020). «COVID-19: the gendered impacts of the outbreak». Lancet. 395 (10227): 846–848. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30526-2. PMC 7124625. PMID 32151325.
- ^ Tolchin B, Hull SC, Kraschel K (October 2020). «Triage and justice in an unjust pandemic: ethical allocation of scarce medical resources in the setting of racial and socioeconomic disparities». Journal of Medical Ethics. 47 (3): 200–202. doi:10.1136/medethics-2020-106457. PMID 33067315. S2CID 223558059.
- ^ Sabatello M, Burke TB, McDonald KE, Appelbaum PS (October 2020). «Disability, Ethics, and Health Care in the COVID-19 Pandemic». American Journal of Public Health. 110 (10): 1523–1527. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2020.305837. PMC 7483109. PMID 32816541.
- ^ Chin T, Kahn R, Li R, Chen JT, Krieger N, Buckee CO, et al. (September 2020). «US-county level variation in intersecting individual, household and community characteristics relevant to COVID-19 and planning an equitable response: a cross-sectional analysis». BMJ Open. 10 (9): e039886. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039886. PMC 7467554. PMID 32873684.
- ^ Elgar FJ, Stefaniak A, Wohl MJ (October 2020). «The trouble with trust: Time-series analysis of social capital, income inequality, and COVID-19 deaths in 84 countries». Social Science & Medicine. 263: 113365. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113365. PMC 7492158. PMID 32981770.
- ^ Uttley H (2 March 2021). «Pandemic sends demand for cold and flu remedies to record low». The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ^ «2020–2021 Flu Season Summary». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 25 October 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
Further reading
- Erola Pairo-Castineira; Sara Clohisey; Lucija Klarić; et al. (11 December 2020). «Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in Covid-19». Nature. doi:10.1038/S41586-020-03065-Y. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 33307546. Wikidata Q104287299. Scholia Q104287299.
- «Progress report on the coronavirus pandemic». Nature. 584 (7821): 325. 1 August 2020. doi:10.1038/D41586-020-02414-1. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 32814893. Wikidata Q98568681.
- COVID-19 infection prevention and control measures for primary care, including general practitioner practices, dental clinics and pharmacy settings: first update. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) (Report). October 2020.
External links
Health agencies
- Coronavirus disease (COVID‑19) Facts by the World Health Organization (WHO)
- Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Coronavirus (COVID‑19) by the UK National Health Service (NHS)
Directories
- Coronavirus Resource Center at the Center for Inquiry
- COVID-19 at Curlie
- COVID‑19 Resource Directory on OpenMD
- COVID‑19 Information on FireMountain.net Archived 13 January 2022 at the Wayback Machine
Medical journals
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‑19) by JAMA
- BMJ’s Coronavirus (covid‑19) Hub by the BMJ
- Novel Coronavirus Information Center by Elsevier
- COVID‑19 Resource Centre by The Lancet
- Coronavirus (COVID‑19) Research Highlights by Springer Nature
- Coronavirus (Covid‑19) by The New England Journal of Medicine
- Covid‑19: Novel Coronavirus Archived 24 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine by Wiley Publishing
Treatment guidelines
- «JHMI Clinical Recommendations for Available Pharmacologic Therapies for COVID-19» (PDF). Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- «Bouncing Back From COVID-19: Your Guide to Restoring Movement» (PDF). Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- «Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19». Infectious Diseases Society of America.
- «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines» (PDF). National Institutes of Health.
- World Health Organization (2022). Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline, 14 January 2022 (Report). hdl:10665/351006. WHO/2019-nCoV/therapeutics/2022.1.
- NHS England and NHS Improvement. National Guidance for post-COVID syndrome assessment clinics (Report).
«Covid» redirects here. Not to be confused with corvid.
| Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) |
|
|---|---|
| Other names | COVID, (the) coronavirus |
 |
|
|
Transmission and life-cycle of SARS-CoV-2 causing COVID-19 |
|
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, vomiting, loss of taste or smell; some cases asymptomatic[2][3] |
| Complications | Pneumonia, viral sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, kidney failure, cytokine release syndrome, respiratory failure, pulmonary fibrosis, paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, long COVID |
| Usual onset | 2–14 days (typically 5) from infection |
| Duration | 5 days to chronic |
| Causes | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) |
| Diagnostic method | rRT‑PCR testing, CT scan, Rapid antigen test |
| Prevention | Vaccination,[4] face coverings, quarantine, physical/social distancing, ventilation, hand washing[5] |
| Treatment | Symptomatic and supportive |
| Frequency | 664,338,243[6] confirmed cases |
| Deaths | 6,707,311[6] |
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.[7] The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever,[8] cough, headache,[9] fatigue, breathing difficulties, loss of smell, and loss of taste.[10][11][12] Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected do not develop noticeable symptoms.[13] Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction).[14] Older people are at a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some people continue to experience a range of effects (long COVID) for months after recovery, and damage to organs has been observed.[15] Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the long-term effects of the disease.[15]
COVID‑19 transmits when people breathe air contaminated by droplets and small airborne particles containing the virus. The risk of breathing these is highest when people are in close proximity, but they can be inhaled over longer distances, particularly indoors. Transmission can also occur if contaminated fluids are splashed or sprayed in the eyes, nose, or mouth, or, more rarely, via contaminated surfaces. People remain contagious for up to 20 days and can spread the virus even if they do not develop symptoms.[16][17]
Testing methods for COVID-19 to detect the virus’s nucleic acid include real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT‑PCR),[18][19] transcription-mediated amplification,[18][19][20] and reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT‑LAMP)[18][19] from a nasopharyngeal swab.[21]
Several COVID-19 vaccines have been approved and distributed in various countries, which have initiated mass vaccination campaigns. Other preventive measures include physical or social distancing, quarantining, ventilation of indoor spaces, use of face masks or coverings in public, covering coughs and sneezes, hand washing, and keeping unwashed hands away from the face. While work is underway to develop drugs that inhibit the virus, the primary treatment is symptomatic. Management involves the treatment of symptoms through supportive care, isolation, and experimental measures.
Nomenclature
During the initial outbreak in Wuhan, the virus and disease were commonly referred to as «coronavirus» and «Wuhan coronavirus»,[22][23][24] with the disease sometimes called «Wuhan pneumonia».[25][26] In the past, many diseases have been named after geographical locations, such as the Spanish flu,[27] Middle East respiratory syndrome, and Zika virus.[28] In January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended 2019-nCoV[29] and 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease[30] as interim names for the virus and disease per 2015 guidance and international guidelines against using geographical locations or groups of people in disease and virus names to prevent social stigma.[31][32][33] The official names COVID‑19 and SARS-CoV-2 were issued by the WHO on 11 February 2020 with COVID-19 being shorthand for «coronavirus disease 2019».[34][35] The WHO additionally uses «the COVID‑19 virus» and «the virus responsible for COVID‑19» in public communications.[34][36]
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of COVID-19 are variable depending on the type of variant contracted, ranging from mild symptoms to a potentially fatal illness.[37][38] Common symptoms include coughing, fever, loss of smell (anosmia) and taste (ageusia), with less common ones including headaches, nasal congestion and runny nose, muscle pain, sore throat, diarrhea, eye irritation,[39] and toes swelling or turning purple,[40] and in moderate to severe cases, breathing difficulties.[41] People with the COVID-19 infection may have different symptoms, and their symptoms may change over time. Three common clusters of symptoms have been identified: one respiratory symptom cluster with cough, sputum, shortness of breath, and fever; a musculoskeletal symptom cluster with muscle and joint pain, headache, and fatigue; and a cluster of digestive symptoms with abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.[41] In people without prior ear, nose, or throat disorders, loss of taste combined with loss of smell is associated with COVID-19 and is reported in as many as 88% of symptomatic cases.[42][43][44]
Of people who show symptoms, 81% develop only mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging) that require hospitalization, and 5% of patients develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, septic shock, or multiorgan dysfunction) requiring ICU admission.[45] At least a third of the people who are infected with the virus do not develop noticeable symptoms at any point in time.[46][47] These asymptomatic carriers tend not to get tested and can still spread the disease.[47][48][49][50] Other infected people will develop symptoms later (called «pre-symptomatic») or have very mild symptoms and can also spread the virus.[50]
As is common with infections, there is a delay between the moment a person first becomes infected and the appearance of the first symptoms. The median delay for COVID-19 is four to five days[51] possibly being infectious on 1-4 of those days.[52] Most symptomatic people experience symptoms within two to seven days after exposure, and almost all will experience at least one symptom within 12 days.[51][53]
Most people recover from the acute phase of the disease. However, some people—over half of a cohort of home-isolated young adults identified in June, 2021[54][55] continued to experience a range of effects, such as fatigue, for months even after recovery. This is the result of a condition called long COVID, which can be described as a range of persistent symptoms that continue for weeks and/or months at a time.[56] Long-term damage to organs has also been observed after the onset of COVID-19. Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the potential long-term effects of the disease.[57]
The Omicron variant became dominant in the U.S. in December 2021. Symptoms with the Omicron variant are less severe than they are with other variants.[58]
Cause
COVID‑19 is caused by infection with a strain of coronavirus known as ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2’ (SARS-CoV-2).[59]
Transmission
| Transmission of COVID-19 | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Mode of spread of COVID-19 |
 |
|
| Specialty | Infection prevention and control |
| Types | Respiratory droplet, airborne transmission, fomites |
| Prevention | Face coverings, quarantine, physical/social distancing, ventilation, hand washing, vaccination |
COVID-19 is mainly transmitted when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets/aerosols and small airborne particles containing the virus. Infected people exhale those particles as they breathe, talk, cough, sneeze, or sing.[60][61][62][63] Transmission is more likely the more physically close people are. However, infection can occur over longer distances, particularly indoors.[60][64]
Infectivity can begin four to five days before the onset of symptoms,[65] although contact tracing typically begins only two to three days before symptom onset.[66] Infected people can spread the disease even if they are pre-symptomatic or asymptomatic.[66] Most commonly, the peak viral load in upper respiratory tract samples occurs close to the time of symptom onset and declines after the first week after symptoms begin.[66] Current evidence suggests a duration of viral shedding and the period of infectiousness of up to ten days following symptom onset for people with mild to moderate COVID-19, and up to 20 days for persons with severe COVID-19, including immunocompromised people.[67][66]
Infectious particles range in size from aerosols that remain suspended in the air for long periods of time to larger droplets that remain airborne briefly or fall to the ground.[68][69][70][71] Additionally, COVID-19 research has redefined the traditional understanding of how respiratory viruses are transmitted.[71][72] The largest droplets of respiratory fluid do not travel far, but can be inhaled or land on mucous membranes on the eyes, nose, or mouth to infect.[70] Aerosols are highest in concentration when people are in close proximity, which leads to easier viral transmission when people are physically close,[70][71][72] but airborne transmission can occur at longer distances, mainly in locations that are poorly ventilated;[70] in those conditions small particles can remain suspended in the air for minutes to hours.[70]
The number of people generally infected by one infected person varies,[73] but it is estimated that the R0 («R nought» or «R zero») number is around 2.5.[74] The disease often spreads in clusters, where infections can be traced back to an index case or geographical location.[75] Often in these instances, superspreading events occur, where many people are infected by one person.[73]
Virology
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. It was first isolated from three people with pneumonia connected to the cluster of acute respiratory illness cases in Wuhan.[76] All structural features of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus particle occur in related coronaviruses in nature.[77]
Outside the human body, the virus is destroyed by household soap, which bursts its protective bubble.[78]
SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to the original SARS-CoV.[79] It is thought to have an animal (zoonotic) origin. Genetic analysis has revealed that the coronavirus genetically clusters with the genus Betacoronavirus, in subgenus Sarbecovirus (lineage B) together with two bat-derived strains. It is 96% identical at the whole genome level to other bat coronavirus samples (BatCov RaTG13).[80][81][82] The structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 include membrane glycoprotein (M), envelope protein (E), nucleocapsid protein (N), and the spike protein (S). The M protein of SARS-CoV-2 is about 98% similar to the M protein of bat SARS-CoV, maintains around 98% homology with pangolin SARS-CoV, and has 90% homology with the M protein of SARS-CoV; whereas, the similarity is only around 38% with the M protein of MERS-CoV.[83]
SARS-CoV-2 variants
The many thousands of SARS-CoV-2 variants are grouped into either clades or lineages.[84][85] The WHO, in collaboration with partners, expert networks, national authorities, institutions and researchers, have established nomenclature systems for naming and tracking SARS-CoV-2 genetic lineages by GISAID, Nextstrain and Pango. The expert group convened by the WHO recommended the labelling of variants using letters of the Greek alphabet, for example, Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Gamma, giving the justification that they «will be easier and more practical to discussed by non-scientific audiences.»[86] Nextstrain divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while GISAID divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR).[87] The Pango tool groups variants into lineages, with many circulating lineages being classed under the B.1 lineage.[85][88]
Several notable variants of SARS-CoV-2 emerged throughout 2020.[89][90] Cluster 5 emerged among minks and mink farmers in Denmark.[91] After strict quarantines and a mink euthanasia campaign, the cluster was assessed to no longer be circulating among humans in Denmark as of 1 February 2021.[92]
As of December 2021, there are five dominant variants of SARS-CoV-2 spreading among global populations: the Alpha variant (B.1.1.7, formerly called the UK variant), first found in London and Kent, the Beta variant (B.1.351, formerly called the South Africa variant), the Gamma variant (P.1, formerly called the Brazil variant), the Delta variant (B.1.617.2, formerly called the India variant),[93] and the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529), which had spread to 57 countries as of 7 December.[94][95]
Pathophysiology
The SARS-CoV-2 virus can infect a wide range of cells and systems of the body. COVID‑19 is most known for affecting the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) and the lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs).[96] The lungs are the organs most affected by COVID‑19 because the virus accesses host cells via the receptor for the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is most abundant on the surface of type II alveolar cells of the lungs.[97] The virus uses a special surface glycoprotein called a «spike» to connect to the ACE2 receptor and enter the host cell.[98]
Respiratory tract
Following viral entry, COVID‑19 infects the ciliated epithelium of the nasopharynx and upper airways.[99]
Nervous system
One common symptom, loss of smell, results from infection of the support cells of the olfactory epithelium, with subsequent damage to the olfactory neurons.[100] The involvement of both the central and peripheral nervous system in COVID‑19 has been reported in many medical publications.[101] It is clear that many people with COVID-19 exhibit neurological or mental health issues. The virus is not detected in the central nervous system (CNS) of the majority of COVID-19 patients with neurological issues. However, SARS-CoV-2 has been detected at low levels in the brains of those who have died from COVID‑19, but these results need to be confirmed.[102] While virus has been detected in cerebrospinal fluid of autopsies, the exact mechanism by which it invades the CNS remains unclear and may first involve invasion of peripheral nerves given the low levels of ACE2 in the brain.[103][104][105] The virus may also enter the bloodstream from the lungs and cross the blood–brain barrier to gain access to the CNS, possibly within an infected white blood cell.[102]
Research conducted when Alpha was the dominant variant has suggested COVID-19 may cause brain damage. It is unknown if such damage is temporary or permanent, and whether Omicron has similar effects.[106][107] Observed individuals infected with COVID-19 (most with mild cases) experienced an additional 0.2% to 2% of brain tissue lost in regions of the brain connected to the sense of smell compared with uninfected individuals, and the overall effect on the brain was equivalent on average to at least one extra year of normal ageing; infected individuals also scored lower on several cognitive tests. All effects were more pronounced among older ages.[108]
Gastrointestinal tract
The virus also affects gastrointestinal organs as ACE2 is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelium[109] as well as endothelial cells and enterocytes of the small intestine.[110]
Cardiovascular system
The virus can cause acute myocardial injury and chronic damage to the cardiovascular system.[111][112] An acute cardiac injury was found in 12% of infected people admitted to the hospital in Wuhan, China,[113] and is more frequent in severe disease.[114] Rates of cardiovascular symptoms are high, owing to the systemic inflammatory response and immune system disorders during disease progression, but acute myocardial injuries may also be related to ACE2 receptors in the heart.[112] ACE2 receptors are highly expressed in the heart and are involved in heart function.[112][115]
A high incidence of thrombosis and venous thromboembolism occurs in people transferred to intensive care units with COVID‑19 infections, and may be related to poor prognosis.[116] Blood vessel dysfunction and clot formation (as suggested by high D-dimer levels caused by blood clots) may have a significant role in mortality, incidences[spelling?] of clots leading to pulmonary embolisms, and ischaemic events within the brain found as complications leading to death in people infected with COVID‑19.[117] Infection may initiate a chain of vasoconstrictive responses within the body, including pulmonary vasoconstriction – a possible mechanism in which oxygenation decreases during pneumonia.[117] Furthermore, damage of arterioles and capillaries was found in brain tissue samples of people who died from COVID‑19.[118][119]
COVID‑19 may also cause substantial structural changes to blood cells, sometimes persisting for months after hospital discharge.[120] A low level of blood lymphocytes may result from the virus acting through ACE2-related entry into lymphocytes.[121]
Other organs
Another common cause of death is complications related to the kidneys.[117] Early reports show that up to 30% of hospitalised patients both in China and in New York have experienced some injury to their kidneys, including some persons with no previous kidney problems.[122]
Autopsies of people who died of COVID‑19 have found diffuse alveolar damage, and lymphocyte-containing inflammatory infiltrates within the lung.[123]
Immunopathology
Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL‑2, IL‑7, IL‑6, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM‑CSF), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP‑10), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1), macrophage inflammatory protein 1‑alpha (MIP‑1‑alpha), and tumour necrosis factor (TNF‑α) indicative of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) suggest an underlying immunopathology.[113]
Interferon alpha plays a complex, Janus-faced role in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Although it promotes the elimination of virus-infected cells, it also upregulates the expression of ACE-2, thereby facilitating the SARS-Cov2 virus to enter cells and to replicate.[124][125] A competition of negative feedback loops (via protective effects of interferon alpha) and positive feedback loops (via upregulation of ACE-2) is assumed to determine the fate of patients suffering from COVID-19.[126]
Additionally, people with COVID‑19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) have classical serum biomarkers of CRS, including elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), D-dimer, and ferritin.[127]
Systemic inflammation results in vasodilation, allowing inflammatory lymphocytic and monocytic infiltration of the lung and the heart. In particular, pathogenic GM-CSF-secreting T cells were shown to correlate with the recruitment of inflammatory IL-6-secreting monocytes and severe lung pathology in people with COVID‑19.[128] Lymphocytic infiltrates have also been reported at autopsy.[123]
Viral and host factors
Virus proteins
Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the ACE2 receptors. It includes two subunits: S1 and S2. S1 determines the virus-host range and cellular tropism via the receptor-binding domain. S2 mediates the membrane fusion of the virus to its potential cell host via the H1 and HR2, which are heptad repeat regions. Studies have shown that S1 domain induced IgG and IgA antibody levels at a much higher capacity. It is the focus spike proteins expression that are involved in many effective COVID‑19 vaccines.[129]
The M protein is the viral protein responsible for the transmembrane transport of nutrients. It is the cause of the bud release and the formation of the viral envelope.[130] The N and E protein are accessory proteins that interfere with the host’s immune response.[130]
Host factors
Human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) is the host factor that SARS-CoV-2 virus targets causing COVID‑19. Theoretically, the usage of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) and ACE inhibitors upregulating ACE2 expression might increase morbidity with COVID‑19, though animal data suggest some potential protective effect of ARB; however no clinical studies have proven susceptibility or outcomes. Until further data is available, guidelines and recommendations for hypertensive patients remain.[131]
The effect of the virus on ACE2 cell surfaces leads to leukocytic infiltration, increased blood vessel permeability, alveolar wall permeability, as well as decreased secretion of lung surfactants. These effects cause the majority of the respiratory symptoms. However, the aggravation of local inflammation causes a cytokine storm eventually leading to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome.[132]
Among healthy adults not exposed to SARS-CoV-2, about 35% have CD4+ T cells that recognise the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (particularly the S2 subunit) and about 50% react to other proteins of the virus, suggesting cross-reactivity from previous common colds caused by other coronaviruses.[133]
It is unknown whether different persons use similar antibody genes in response to COVID‑19.[134]
Host cytokine response
The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the cytokine storm.[135] Levels of interleukin 1B, interferon-gamma, interferon-inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 were all associated with COVID‑19 disease severity. Treatment has been proposed to combat the cytokine storm as it remains to be one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in COVID‑19 disease.[136]
A cytokine storm is due to an acute hyperinflammatory response that is responsible for clinical illness in an array of diseases but in COVID‑19, it is related to worse prognosis and increased fatality. The storm causes acute respiratory distress syndrome, blood clotting events such as strokes, myocardial infarction, encephalitis, acute kidney injury, and vasculitis. The production of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and interferon-gamma, all crucial components of normal immune responses, inadvertently become the causes of a cytokine storm. The cells of the central nervous system, the microglia, neurons, and astrocytes, are also involved in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines affecting the nervous system, and effects of cytokine storms toward the CNS are not uncommon.[137]
Pregnancy response
There are many unknowns for pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic. Given that they are prone to have complications and severe disease infection with other types of coronaviruses, they have been identified as a vulnerable group and advised to take supplementary preventive measures.[138]
Physiological responses to pregnancy can include:
- Immunological: The immunological response to COVID-19, like other viruses, depends on a working immune system. It adapts during pregnancy to allow the development of the foetus whose genetic load is only partially shared with their mother, leading to a different immunological reaction to infections during the course of pregnancy.[138]
- Respiratory: Many factors can make pregnant women more vulnerable to hard respiratory infections. One of them is the total reduction of the lungs’ capacity and inability to clear secretions.[138]
- Coagulation: During pregnancy, there are higher levels of circulating coagulation factors, and the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection can be implicated. The thromboembolic events with associated mortality are a risk for pregnant women.[138]
However, from the evidence base, it is difficult to conclude whether pregnant women are at increased risk of grave consequences of this virus.[138]
In addition to the above, other clinical studies have proved that SARS-CoV-2 can affect the period of pregnancy in different ways. On the one hand, there is little evidence of its impact up to 12 weeks gestation. On the other hand, COVID-19 infection may cause increased rates of unfavourable outcomes in the course of the pregnancy. Some examples of these could be foetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and perinatal mortality, which refers to the foetal death past 22 or 28 completed weeks of pregnancy as well as the death among live-born children up to seven completed days of life.[138]
Unvaccinated women in later stages of pregnancy with COVID-19 are more likely than other patients to need very intensive care. Babies born to mothers with COVID-19 are more likely to have breathing problems. Pregnant women are strongly encouraged to get vaccinated.[139]
Diagnosis
COVID‑19 can provisionally be diagnosed on the basis of symptoms and confirmed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or other nucleic acid testing of infected secretions.[21][140] Along with laboratory testing, chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection.[141] Detection of a past infection is possible with serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the infection.[21]
Viral testing
The standard methods of testing for presence of SARS-CoV-2 are nucleic acid tests,[21][142] which detects the presence of viral RNA fragments.[143] As these tests detect RNA but not infectious virus, its «ability to determine duration of infectivity of patients is limited.»[144] The test is typically done on respiratory samples obtained by a nasopharyngeal swab; however, a nasal swab or sputum sample may also be used.[145][146] Results are generally available within hours.[21] The WHO has published several testing protocols for the disease.[147]
Several laboratories and companies have developed serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to infection. Several have been evaluated by Public Health England and approved for use in the UK.[148]
The University of Oxford’s CEBM has pointed to mounting evidence[149][150] that «a good proportion of ‘new’ mild cases and people re-testing positives after quarantine or discharge from hospital are not infectious, but are simply clearing harmless virus particles which their immune system has efficiently dealt with» and have called for «an international effort to standardize and periodically calibrate testing»[151] In September 2020, the UK government issued «guidance for procedures to be implemented in laboratories to provide assurance of positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA results during periods of low prevalence, when there is a reduction in the predictive value of positive test results».[152]
Imaging
A CT scan of a person with COVID-19 shows lesions (bright regions) in the lungs
CT scan of rapid progression stage of COVID-19
Chest X-ray showing COVID‑19 pneumonia
Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening.[141][153] Bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacities with a peripheral, asymmetric, and posterior distribution are common in early infection.[141][154] Subpleural dominance, crazy paving (lobular septal thickening with variable alveolar filling), and consolidation may appear as the disease progresses.[141][155] Characteristic imaging features on chest radiographs and computed tomography (CT) of people who are symptomatic include asymmetric peripheral ground-glass opacities without pleural effusions.[156]
Many groups have created COVID‑19 datasets that include imagery such as the Italian Radiological Society which has compiled an international online database of imaging findings for confirmed cases.[157] Due to overlap with other infections such as adenovirus, imaging without confirmation by rRT-PCR is of limited specificity in identifying COVID‑19.[156] A large study in China compared chest CT results to PCR and demonstrated that though imaging is less specific for the infection, it is faster and more sensitive.[140]
Coding
In late 2019, the WHO assigned emergency ICD-10 disease codes U07.1 for deaths from lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and U07.2 for deaths from clinically or epidemiologically diagnosed COVID‑19 without lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.[158]
Pathology
The main pathological findings at autopsy are:
- Macroscopy: pericarditis, lung consolidation and pulmonary oedema[123]
- Lung findings:
- minor serous exudation, minor fibrin exudation[123]
- pulmonary oedema, pneumocyte hyperplasia, large atypical pneumocytes, interstitial inflammation with lymphocytic infiltration and multinucleated giant cell formation[123]
- diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) with diffuse alveolar exudates. DAD is the cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and severe hypoxaemia.[123]
- organisation of exudates in alveolar cavities and pulmonary interstitial fibrosis[123]
- plasmocytosis in BAL[159]
- Blood and vessels: disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC);[160] leukoerythroblastic reaction,[161] endotheliitis,[162] hemophagocytosis[162]
- Heart: cardiac muscle cell necrosis[162]
- Liver: microvesicular steatosis[123]
- Nose: shedding of olfactory epithelium[100]
- Brain: infarction[162]
- Kidneys: acute tubular damage.[162]
- Spleen: white pulp depletion.[162]
Prevention
Without pandemic containment measures – such as social distancing, vaccination, and face masks – pathogens can spread exponentially.[163] This graphic shows how early adoption of containment measures tends to protect wider swaths of the population.
Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations,[164] washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.[165][166]
Those diagnosed with COVID‑19 or who believe they may be infected are advised by the CDC to stay home except to get medical care, call ahead before visiting a healthcare provider, wear a face mask before entering the healthcare provider’s office and when in any room or vehicle with another person, cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue, regularly wash hands with soap and water and avoid sharing personal household items.[167][168]
The first COVID‑19 vaccine was granted regulatory approval on 2 December 2020 by the UK medicines regulator MHRA.[169] It was evaluated for emergency use authorization (EUA) status by the US FDA, and in several other countries.[170] Initially, the US National Institutes of Health guidelines do not recommend any medication for prevention of COVID‑19, before or after exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, outside the setting of a clinical trial.[171][172] Without a vaccine, other prophylactic measures, or effective treatments, a key part of managing COVID‑19 is trying to decrease and delay the epidemic peak, known as «flattening the curve».[173] This is done by slowing the infection rate to decrease the risk of health services being overwhelmed, allowing for better treatment of active cases, and delaying additional cases until effective treatments or a vaccine become available.[173][174]
Vaccine
Different vaccine candidate types in development for SARS-CoV-2
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
Prior to the COVID‑19 pandemic, an established body of knowledge existed about the structure and function of coronaviruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This knowledge accelerated the development of various vaccine platforms during early 2020.[175] The initial focus of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was on preventing symptomatic, often severe illness.[176] In January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequence data was shared through GISAID, and by March 2020, the global pharmaceutical industry announced a major commitment to address COVID‑19.[177] In 2020, the first COVID‑19 vaccines were developed and made available to the public through emergency authorizations[178] and conditional approvals.[179][180] Initially, most COVID‑19 vaccines were two-dose vaccines, with the sole exception being the single-dose Janssen COVID-19 vaccine.[178] However, immunity from the vaccines has been found to wane over time, requiring people to get booster doses of the vaccine to maintain protection against COVID‑19.[178]
Face masks and respiratory hygiene
Masks with an exhalation valve. The valves are a weak point that can transmit the viruses outwards.
The WHO and the US CDC recommend individuals wear non-medical face coverings in public settings where there is an increased risk of transmission and where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain.[181][182] This recommendation is meant to reduce the spread of the disease by asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic individuals and is complementary to established preventive measures such as social distancing.[182][183] Face coverings limit the volume and travel distance of expiratory droplets dispersed when talking, breathing, and coughing.[182][183] A face covering without vents or holes will also filter out particles containing the virus from inhaled and exhaled air, reducing the chances of infection.[184] However, if the mask includes an exhalation valve, a wearer that is infected (and possibly asymptomatic) may transmit the virus through the valve. Many countries and local jurisdictions encourage or mandate the use of face masks or cloth face coverings by members of the public to limit the spread of the virus.[185]
Masks are also strongly recommended for those who may have been infected and those taking care of someone who may have the disease.[186] When not wearing a mask, the CDC recommends covering the mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing and recommends using the inside of the elbow if no tissue is available. Proper hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is encouraged. Healthcare professionals interacting directly with people who have COVID‑19 are advised to use respirators at least as protective as NIOSH-certified N95 or equivalent, in addition to other personal protective equipment.[187]
Indoor ventilation and avoiding crowded indoor spaces
The CDC recommends that crowded indoor spaces should be avoided.[188] When indoors, increasing the rate of air change, decreasing recirculation of air and increasing the use of outdoor air can reduce transmission.[188][189] The WHO recommends ventilation and air filtration in public spaces to help clear out infectious aerosols.[190][191][192]
Exhaled respiratory particles can build-up within enclosed spaces with inadequate ventilation. The risk of COVID‑19 infection increases especially in spaces where people engage in physical exertion or raise their voice (e.g., exercising, shouting, singing) as this increases exhalation of respiratory droplets. Prolonged exposure to these conditions, typically more than 15 minutes, leads to higher risk of infection.[188]
Displacement ventilation with large natural inlets can move stale air directly to the exhaust in laminar flow while significantly reducing the concentration of droplets and particles. Passive ventilation reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs but may lack controllability and heat recovery. Displacement ventilation can also be achieved mechanically with higher energy and maintenance costs. The use of large ducts and openings helps to prevent mixing in closed environments. Recirculation and mixing should be avoided because recirculation prevents dilution of harmful particles and redistributes possibly contaminated air, and mixing increases the concentration and range of infectious particles and keeps larger particles in the air.[193]
Hand-washing and hygiene
Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required.[194] The WHO also recommends that individuals wash hands often with soap and water for at least twenty seconds, especially after going to the toilet or when hands are visibly dirty, before eating and after blowing one’s nose.[195] When soap and water are not available, the CDC recommends using an alcohol-based hand sanitiser with at least 60% alcohol.[196] For areas where commercial hand sanitisers are not readily available, the WHO provides two formulations for local production. In these formulations, the antimicrobial activity arises from ethanol or isopropanol. Hydrogen peroxide is used to help eliminate bacterial spores in the alcohol; it is «not an active substance for hand antisepsis.» Glycerol is added as a humectant.[197]
Social distancing (also known as physical distancing) includes infection control actions intended to slow the spread of the disease by minimising close contact between individuals. Methods include quarantines; travel restrictions; and the closing of schools, workplaces, stadiums, theatres, or shopping centres. Individuals may apply social distancing methods by staying at home, limiting travel, avoiding crowded areas, using no-contact greetings, and physically distancing themselves from others.[198] Many governments are mandating or recommending social distancing in regions affected by the outbreak.[199]
Outbreaks have occurred in prisons due to crowding and an inability to enforce adequate social distancing.[200][201] In the United States, the prisoner population is ageing and many of them are at high risk for poor outcomes from COVID‑19 due to high rates of coexisting heart and lung disease, and poor access to high-quality healthcare.[200]
Surface cleaning
After being expelled from the body, coronaviruses can survive on surfaces for hours to days. If a person touches the dirty surface, they may deposit the virus at the eyes, nose, or mouth where it can enter the body and cause infection.[202] Evidence indicates that contact with infected surfaces is not the main driver of COVID‑19,[203][204][205] leading to recommendations for optimised disinfection procedures to avoid issues such as the increase of antimicrobial resistance through the use of inappropriate cleaning products and processes.[206][207] Deep cleaning and other surface sanitation has been criticised as hygiene theatre, giving a false sense of security against something primarily spread through the air.[208][209]
The amount of time that the virus can survive depends significantly on the type of surface, the temperature, and the humidity.[210] Coronaviruses die very quickly when exposed to the UV light in sunlight.[210] Like other enveloped viruses, SARS-CoV-2 survives longest when the temperature is at room temperature or lower, and when the relative humidity is low (<50%).[210]
On many surfaces, including glass, some types of plastic, stainless steel, and skin, the virus can remain infective for several days indoors at room temperature, or even about a week under ideal conditions.[210][211] On some surfaces, including cotton fabric and copper, the virus usually dies after a few hours.[210] The virus dies faster on porous surfaces than on non-porous surfaces due to capillary action within pores and faster aerosol droplet evaporation.[212][205][210] However, of the many surfaces tested, two with the longest survival times are N95 respirator masks and surgical masks, both of which are considered porous surfaces.[210]
The CDC says that in most situations, cleaning surfaces with soap or detergent, not disinfecting, is enough to reduce risk of transmission.[213][214] The CDC recommends that if a COVID‑19 case is suspected or confirmed at a facility such as an office or day care, all areas such as offices, bathrooms, common areas, shared electronic equipment like tablets, touch screens, keyboards, remote controls, and ATMs used by the ill persons should be disinfected.[215] Surfaces may be decontaminated with 62–71 per cent ethanol, 50–100 per cent isopropanol, 0.1 per cent sodium hypochlorite, 0.5 per cent hydrogen peroxide, 0.2–7.5 per cent povidone-iodine, or 50–200 ppm hypochlorous acid. Other solutions, such as benzalkonium chloride and chlorhexidine gluconate, are less effective. Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation may also be used,[190] although popular devices require 5–10 min exposure and may deteriorate some materials over time.[216] A datasheet comprising the authorised substances to disinfection in the food industry (including suspension or surface tested, kind of surface, use dilution, disinfectant and inocuylum volumes) can be seen in the supplementary material of.[206]
Self-isolation
Self-isolation at home has been recommended for those diagnosed with COVID‑19 and those who suspect they have been infected. Health agencies have issued detailed instructions for proper self-isolation.[217] Many governments have mandated or recommended self-quarantine for entire populations. The strongest self-quarantine instructions have been issued to those in high-risk groups.[218] Those who may have been exposed to someone with COVID‑19 and those who have recently travelled to a country or region with the widespread transmission have been advised to self-quarantine for 14 days from the time of last possible exposure.[219]
A 2021 Cochrane rapid review found that based upon low-certainty evidence, international travel-related control measures such as restricting cross-border travel may help to contain the spread of COVID‑19.[220] Additionally, symptom/exposure-based screening measures at borders may miss many positive cases.[220] While test-based border screening measures may be more effective, it could also miss many positive cases if only conducted upon arrival without follow-up. The review concluded that a minimum 10-day quarantine may be beneficial in preventing the spread of COVID‑19 and may be more effective if combined with an additional control measure like border screening.[220]
Treatment
An overview of COVID-19 therapeutics and drugs
Although several medications have been approved in different countries as of April 2022, not all countries have these medications. Patients with mild to moderate symptoms who are in the risk groups can take nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (marketed as Paxlovid) or remdesivir, either of which reduces the risk of serious illness or hospitalization.[221] In the US, the Biden Administration COVID-19 action plan includes the Test to Treat initiative, where people can go to a pharmacy, take a COVID test, and immediately receive free Paxlovid if they test positive.[222]
Highly effective vaccines have reduced mortality related to SARS-CoV-2; however, for those awaiting vaccination, as well as for the estimated millions of immunocompromised persons who are unlikely to respond robustly to vaccination, treatment remains important.[223] The cornerstone of management of COVID-19 has been supportive care, which includes treatment to relieve symptoms, fluid therapy, oxygen support and prone positioning as needed, and medications or devices to support other affected vital organs.[224][225][226]
Most cases of COVID-19 are mild. In these, supportive care includes medication such as paracetamol or NSAIDs to relieve symptoms (fever, body aches, cough), proper intake of fluids, rest, and nasal breathing.[227][228][229][230] Good personal hygiene and a healthy diet are also recommended.[231] As of April 2020 the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended that those who suspect they are carrying the virus isolate themselves at home and wear a face mask.[232]
As of November 2020 use of the glucocorticoid dexamethasone had been strongly recommended in those severe cases treated in hospital with low oxygen levels, to reduce the risk of death.[233][234][235] Noninvasive ventilation and, ultimately, admission to an intensive care unit for mechanical ventilation may be required to support breathing.[236] Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has been used to address respiratory failure, but its benefits are still under consideration.[237][238] Some of the cases of severe disease course are caused by systemic hyper-inflammation, the so-called cytokine storm.[239]
Prognosis and risk factors
The severity of COVID‑19 varies. The disease may take a mild course with few or no symptoms, resembling other common upper respiratory diseases such as the common cold. In 3–4% of cases (7.4% for those over age 65) symptoms are severe enough to cause hospitalisation.[240] Mild cases typically recover within two weeks, while those with severe or critical diseases may take three to six weeks to recover. Among those who have died, the time from symptom onset to death has ranged from two to eight weeks.[80] The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that the median time between the onset of symptoms and death was twelve days, with seven being hospitalised. However, people transferred to an ICU had a median time of ten days between hospitalisation and death.[241] Abnormal sodium levels during hospitalization with COVID-19 are associated with poor prognoses: high sodium with a greater risk of death, and low sodium with an increased chance of needing ventilator support.[242][243] Prolonged prothrombin time and elevated C-reactive protein levels on admission to the hospital are associated with severe course of COVID‑19 and with a transfer to ICU.[244][245]
Some early studies suggest 10% to 20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month.[246][247] A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems including fatigue and shortness of breath.[248] On 30 October 2020, WHO chief Tedros Adhanom warned that «to a significant number of people, the COVID virus poses a range of serious long-term effects.» He has described the vast spectrum of COVID‑19 symptoms that fluctuate over time as «really concerning». They range from fatigue, a cough and shortness of breath, to inflammation and injury of major organs – including the lungs and heart, and also neurological and psychologic effects. Symptoms often overlap and can affect any system in the body. Infected people have reported cyclical bouts of fatigue, headaches, months of complete exhaustion, mood swings, and other symptoms. Tedros therefore concluded that a strategy of achieving herd immunity by infection, rather than vaccination, is «morally unconscionable and unfeasible».[249]
In terms of hospital readmissions about 9% of 106,000 individuals had to return for hospital treatment within two months of discharge. The average to readmit was eight days since first hospital visit. There are several risk factors that have been identified as being a cause of multiple admissions to a hospital facility. Among these are advanced age (above 65 years of age) and presence of a chronic condition such as diabetes, COPD, heart failure or chronic kidney disease.[250][251]
According to scientific reviews smokers are more likely to require intensive care or die compared to non-smokers.[252][253] Acting on the same ACE2 pulmonary receptors affected by smoking, air pollution has been correlated with the disease.[253] Short term[254] and chronic[255] exposure to air pollution seems to enhance morbidity and mortality from COVID‑19.[256][257][258] Pre-existing heart and lung diseases[259] and also obesity, especially in conjunction with fatty liver disease, contributes to an increased health risk of COVID‑19.[253][260][261][262]
It is also assumed that those that are immunocompromised are at higher risk of getting severely sick from SARS-CoV-2.[263] One research study that looked into the COVID‑19 infections in hospitalised kidney transplant recipients found a mortality rate of 11%.[264]
Men with untreated hypogonadism were 2.4 times more likely than men with eugonadism to be hospitalized if they contracted COVID-19; Hypogonad men treated with testosterone were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than men who were not treated for hypogonadism.[265]
Genetic risk factors
Genetics plays an important role in the ability to fight off Covid.[266] For instance, those that do not produce detectable type I interferons or produce auto-antibodies against these may get much sicker from COVID‑19.[267][268] Genetic screening is able to detect interferon effector genes.[269] Some genetic variants are risk factors in specific populations. For instance, and allele of the DOCK2 gene (dedicator of cytokinesis 2 gene) is a common risk factor in Asian populations but much less common in Europe. The mutation leads to lower expression of DOCK2 especially in younger patients with severe Covid.[270] In fact, many other genes and genetic variants have been found that determine the outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infections.[271]
Children
While very young children have experienced lower rates of infection, older children have a rate of infection that is similar to the population as a whole.[272][273] Children are likely to have milder symptoms and are at lower risk of severe disease than adults.[274] The CDC reports that in the US roughly a third of hospitalised children were admitted to the ICU,[275] while a European multinational study of hospitalised children from June 2020, found that about 8% of children admitted to a hospital needed intensive care.[276] Four of the 582 children (0.7%) in the European study died, but the actual mortality rate may be «substantially lower» since milder cases that did not seek medical help were not included in the study.[277][278]
Complications
Complications may include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, septic shock, and death.[279][280][281][282] Cardiovascular complications may include heart failure, arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation), heart inflammation, and thrombosis, particularly venous thromboembolism.[283][284][285][286][287][288] Approximately 20–30% of people who present with COVID‑19 have elevated liver enzymes, reflecting liver injury.[289][172]
Neurologic manifestations include seizure, stroke, encephalitis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome (which includes loss of motor functions).[290][291] Following the infection, children may develop paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, which has symptoms similar to Kawasaki disease, which can be fatal.[292][293] In very rare cases, acute encephalopathy can occur, and it can be considered in those who have been diagnosed with COVID‑19 and have an altered mental status.[294]
In the case of pregnant women, it is important to note that, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, pregnant women are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill from COVID‑19.[295] This is because pregnant women with COVID‑19 appear to be more likely to develop respiratory and obstetric complications that can lead to miscarriage, premature delivery and intrauterine growth restriction.[295]
Fungal infections such as aspergillosis, candidiasis, cryptococcosis and mucormycosis have been recorded in patients recovering from COVID‑19.[296][297]
Longer-term effects
Some early studies suggest that 10–20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month.[298][247] A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems, including fatigue and shortness of breath.[299] About 5–10% of patients admitted to hospital progress to severe or critical disease, including pneumonia and acute respiratory failure.[300]
By a variety of mechanisms, the lungs are the organs most affected in COVID‑19.[301] In people requiring hospital admission, up to 98% of CT scans performed show lung abnormalities after 28 days of illness even if they had clinically improved.[302]
People with advanced age, severe disease, prolonged ICU stays, or who smoke are more likely to have long-lasting effects, including pulmonary fibrosis.[303] Overall, approximately one-third of those investigated after four weeks will have findings of pulmonary fibrosis or reduced lung function as measured by DLCO, even in asymptomatic people, but with the suggestion of continuing improvement with the passing of more time.[301] After severe disease, lung function can take anywhere from three months to a year or more to return to previous levels.[304]
The risks of cognitive deficit, dementia, psychotic disorders, and epilepsy or seizures persists at an increased level two years after infection.[305]
Immunity
The immune response by humans to SARS-CoV-2 virus occurs as a combination of the cell-mediated immunity and antibody production,[306] just as with most other infections.[307] B cells interact with T cells and begin dividing before selection into the plasma cell, partly on the basis of their affinity for antigen.[308] Since SARS-CoV-2 has been in the human population only since December 2019, it remains unknown if the immunity is long-lasting in people who recover from the disease.[309] The presence of neutralising antibodies in blood strongly correlates with protection from infection, but the level of neutralising antibody declines with time. Those with asymptomatic or mild disease had undetectable levels of neutralising antibody two months after infection. In another study, the level of neutralising antibodies fell four-fold one to four months after the onset of symptoms. However, the lack of antibodies in the blood does not mean antibodies will not be rapidly produced upon reexposure to SARS-CoV-2. Memory B cells specific for the spike and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 last for at least six months after the appearance of symptoms.[309]
As of August 2021, reinfection with COVID‑19 was possible but uncommon. The first case of reinfection was documented in August 2020.[310] A systematic review found 17 cases of confirmed reinfection in medical literature as of May 2021.[310] With the Omicron variant, as of 2022, reinfections have become common, albeit it is unclear how common.[311] COVID-19 reinfections are thought to likely be less severe than primary infections, especially if one was previously infected by the same variant.[311][additional citation(s) needed]
Mortality
Several measures are commonly used to quantify mortality.[312] These numbers vary by region and over time and are influenced by the volume of testing, healthcare system quality, treatment options, time since the initial outbreak, and population characteristics such as age, sex, and overall health.[313]
The mortality rate reflects the number of deaths within a specific demographic group divided by the population of that demographic group. Consequently, the mortality rate reflects the prevalence as well as the severity of the disease within a given population. Mortality rates are highly correlated to age, with relatively low rates for young people and relatively high rates among the elderly.[314][315][316] In fact, one relevant factor of mortality rates is the age structure of the countries’ populations. For example, the case fatality rate for COVID‑19 is lower in India than in the US since India’s younger population represents a larger percentage than in the US.[317]
Case fatality rate
The case fatality rate (CFR) reflects the number of deaths divided by the number of diagnosed cases within a given time interval. Based on Johns Hopkins University statistics, the global death-to-case ratio is 1.01% (6,707,311/664,338,243) as of 9 January 2023.[6] The number varies by region.[318][319]
-
Total confirmed cases over time
-
Total confirmed cases of COVID‑19 per million people[320]
-
Total deaths over time
-
Total confirmed deaths due to COVID‑19 per million people[321]
Infection fatality rate
A key metric in gauging the severity of COVID‑19 is the infection fatality rate (IFR), also referred to as the infection fatality ratio or infection fatality risk.[322][323][324] This metric is calculated by dividing the total number of deaths from the disease by the total number of infected individuals; hence, in contrast to the CFR, the IFR incorporates asymptomatic and undiagnosed infections as well as reported cases.[325]
Estimates
The red line shows the estimate of infection fatality rate (IFR), in percentage terms, as a function of age. The shaded region depicts the 95% confidence interval for that estimate. Markers denotes specific observations used in the meta-analysis.[326]
The same relationship plotted on a log scale
A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy.[326] That study also found that most of these differences in IFR reflected corresponding differences in the age composition of the population and age-specific infection rates; in particular, the metaregression estimate of IFR is very low for children and younger adults (e.g., 0.002% at age 10 and 0.01% at age 25) but increases progressively to 0.4% at age 55, 1.4% at age 65, 4.6% at age 75, and 15% at age 85.[326] These results were also highlighted in a December 2020 report issued by the WHO.[327]
| Age group | IFR |
|---|---|
| 0–34 | 0.004% |
| 35–44 | 0.068% |
| 45–54 | 0.23% |
| 55–64 | 0.75% |
| 65–74 | 2.5% |
| 75–84 | 8.5% |
| 85 + | 28.3% |
An analysis of those IFR rates indicates that COVID‑19 is hazardous not only for the elderly but also for middle-aged adults, for whom the infection fatality rate of COVID-19 is two orders of magnitude greater than the annualised risk of a fatal automobile accident and far more dangerous than seasonal influenza.[326]
Earlier estimates of IFR
At an early stage of the pandemic, the World Health Organization reported estimates of IFR between 0.3% and 1%.[328][329] On 2 July, The WHO’s chief scientist reported that the average IFR estimate presented at a two-day WHO expert forum was about 0.6%.[330][331] In August, the WHO found that studies incorporating data from broad serology testing in Europe showed IFR estimates converging at approximately 0.5–1%.[332] Firm lower limits of IFRs have been established in a number of locations such as New York City and Bergamo in Italy since the IFR cannot be less than the population fatality rate. (After sufficient time however, people can get reinfected).[333] As of 10 July, in New York City, with a population of 8.4 million, 23,377 individuals (18,758 confirmed and 4,619 probable) have died with COVID‑19 (0.3% of the population).[334] Antibody testing in New York City suggested an IFR of ≈0.9%,[335] and ≈1.4%.[336] In Bergamo province, 0.6% of the population has died.[337] In September 2020, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported preliminary estimates of age-specific IFRs for public health planning purposes.[338]
Sex differences
| Percentage of infected people who are hospitalised | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.1 (0.07–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
0.9 (0.5–1.5) |
1.3 (0.7–2.1) |
2.6 (1.5–4.2) |
5.1 (2.9–8.3) |
7.8 (4.4–12.8) |
19.3 (10.9–31.6) |
2.6 (1.5–4.3) |
| Male | 0.2 (0.08–0.2) |
0.6 (0.3–0.9) |
1.2 (0.7–1.9) |
1.6 (0.9–2.6) |
3.2 (1.8–5.2) |
6.7 (3.7–10.9) |
11.0 (6.2–17.9) |
37.6 (21.1–61.3) |
3.3 (1.8–5.3) |
| Total | 0.1 (0.08–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
1.1 (0.6–1.7) |
1.4 (0.8–2.3) |
2.9 (1.6–4.7) |
5.8 (3.3–9.5) |
9.3 (5.2–15.1) |
26.2 (14.8–42.7) |
2.9 (1.7–4.8) |
| Percentage of hospitalised people who go to Intensive Care Unit | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 16.7 (14.3–19.3) |
8.7 (7.5–9.9) |
11.9 (10.9–13.0) |
16.6 (15.6–17.7) |
20.7 (19.8–21.6) |
23.1 (22.2–24.0) |
18.7 (18.0–19.5) |
4.2 (4.0–4.5) |
14.3 (13.9–14.7) |
| Male | 26.9 (23.1–31.1) |
14.0 (12.2–16.0) |
19.2 (17.6–20.9) |
26.9 (25.4–28.4) |
33.4 (32.0–34.8) |
37.3 (36.0–38.6) |
30.2 (29.1–31.3) |
6.8 (6.5–7.2) |
23.1 (22.6–23.6) |
| Total | 22.2 (19.1–25.7) |
11.6 (10.1–13.2) |
15.9 (14.5–17.3) |
22.2 (21.0–23.5) |
27.6 (26.5–28.7) |
30.8 (29.8–31.8) |
24.9 (24.1–25.8) |
5.6 (5.3–5.9) |
19.0 (18.7–19.44) |
| Percent of hospitalised people who die | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.5 (0.2–1.0) |
0.9 (0.5–1.3) |
1.5 (1.2–1.9) |
2.6 (2.3–3.0) |
5.2 (4.8–5.6) |
10.1 (9.5–10.6) |
16.7 (16.0–17.4) |
25.2 (24.4–26.0) |
14.4 (14.0–14.8) |
| Male | 0.7 (0.3–1.5) |
1.3 (0.8–1.9) |
2.2 (1.7–2.7) |
3.8 (3.3–4.4) |
7.6 (7.0–8.2) |
14.8 (14.1–15.6) |
24.6 (23.7–25.6) |
37.1 (36.1–38.2) |
21.2 (20.8–21.7) |
| Total | 0.6 (0.2–1.3) |
1.1 (0.7–1.6) |
1.9 (1.5–2.3) |
3.3 (2.9–3.8) |
6.5 (6.0–7.0) |
12.6 (12.0–13.2) |
21.0 (20.3–21.7) |
31.6 (30.9–32.4) |
18.1 (17.8–18.4) |
| Percent of infected people who die – infection fatality rate (IFR) | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.001 (<0.001–0.002) |
0.004 (0.002–0.007) |
0.01 (0.007–0.02) |
0.03 (0.02–0.06) |
0.1 (0.08–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
1.3 (0.7–2.1) |
4.9 (2.7–8.0) |
0.4 (0.2–0.6) |
| Male | 0.001 (<0.001–0.003) |
0.007 (0.003–0.01) |
0.03 (0.02–0.05) |
0.06 (0.03–0.1) |
0.2 (0.1–0.4) |
1.0 (0.6–1.6) |
2.7 (1.5–1.4) |
14.0 (7.9–22.7) |
0.7 (0.4–1.1) |
| Total | 0.001 (<0.001–0.002) |
0.005 (0.003–0.01) |
0.02 (0.01–0.03) |
0.05 (0.03–0.08) |
0.2 (0.1–0.3) |
0.7 (0.4–1.2) |
1.9 (1.1–3.2) |
8.3 (4.7–13.5) |
0.5 (0.3–0.9) |
| Numbers in parentheses are 95% credible intervals for the estimates. |
COVID‑19 case fatality rates are higher among men than women in most countries. However, in a few countries like India, Nepal, Vietnam, and Slovenia the fatality cases are higher in women than men.[317] Globally, men are more likely to be admitted to the ICU and more likely to die.[340][341] One meta-analysis found that globally, men were more likely to get COVID‑19 than women; there were approximately 55 men and 45 women per 100 infections (CI: 51.43–56.58).[342]
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported the death rate was 2.8% for men and 1.7% for women.[343] Later reviews in June 2020 indicated that there is no significant difference in susceptibility or in CFR between genders.[344][345] One review acknowledges the different mortality rates in Chinese men, suggesting that it may be attributable to lifestyle choices such as smoking and drinking alcohol rather than genetic factors.[346] Smoking, which in some countries like China is mainly a male activity, is a habit that contributes to increasing significantly the case fatality rates among men.[317] Sex-based immunological differences, lesser prevalence of smoking in women and men developing co-morbid conditions such as hypertension at a younger age than women could have contributed to the higher mortality in men.[347] In Europe as of February 2020, 57% of the infected people were men and 72% of those died with COVID‑19 were men.[348] As of April 2020, the US government is not tracking sex-related data of COVID‑19 infections.[349] Research has shown that viral illnesses like Ebola, HIV, influenza and SARS affect men and women differently.[349]
Ethnic differences
In the US, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred among African Americans and other minority groups.[350] Structural factors that prevent them from practising social distancing include their concentration in crowded substandard housing and in «essential» occupations such as retail grocery workers, public transit employees, health-care workers and custodial staff. Greater prevalence of lacking health insurance and care of underlying conditions such as diabetes,[351] hypertension, and heart disease also increase their risk of death.[352] Similar issues affect Native American and Latino communities.[350] On the one hand, in the Dominican Republic there is a clear example of both gender and ethnic inequality. In this Latin American territory, there is great inequality and precariousness that especially affects Dominican women, with greater emphasis on those of Haitian descent.[353] According to a US health policy non-profit, 34% of American Indian and Alaska Native People (AIAN) non-elderly adults are at risk of serious illness compared to 21% of white non-elderly adults.[354] The source attributes it to disproportionately high rates of many health conditions that may put them at higher risk as well as living conditions like lack of access to clean water.[355]
Leaders have called for efforts to research and address the disparities.[356] In the UK, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred in those of a Black, Asian, and other ethnic minority background.[357][358][359] More severe impacts upon patients including the relative incidence of the necessity of hospitalisation requirements, and vulnerability to the disease has been associated via DNA analysis to be expressed in genetic variants at chromosomal region 3, features that are associated with European Neanderthal heritage. That structure imposes greater risks that those affected will develop a more severe form of the disease.[360] The findings are from Professor Svante Pääbo and researchers he leads at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the Karolinska Institutet.[360] This admixture of modern human and Neanderthal genes is estimated to have occurred roughly between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago in Southern Europe.[360]
Comorbidities
Biological factors (immune response) and the general behaviour (habits) can strongly determine the consequences of COVID‑19.[317] Most of those who die of COVID‑19 have pre-existing (underlying) conditions, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus,[351] and cardiovascular disease.[361] According to March data from the United States, 89% of those hospitalised had preexisting conditions.[362] The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that out of 8.8% of deaths where medical charts were available, 96.1% of people had at least one comorbidity with the average person having 3.4 diseases.[241] According to this report the most common comorbidities are hypertension (66% of deaths), type 2 diabetes (29.8% of deaths), ischaemic heart disease (27.6% of deaths), atrial fibrillation (23.1% of deaths) and chronic renal failure (20.2% of deaths).
Most critical respiratory comorbidities according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are: moderate or severe asthma, pre-existing COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis.[363] Evidence stemming from meta-analysis of several smaller research papers also suggests that smoking can be associated with worse outcomes.[364][365] When someone with existing respiratory problems is infected with COVID‑19, they might be at greater risk for severe symptoms.[366] COVID‑19 also poses a greater risk to people who misuse opioids and amphetamines, insofar as their drug use may have caused lung damage.[367]
In August 2020, the CDC issued a caution that tuberculosis (TB) infections could increase the risk of severe illness or death. The WHO recommended that people with respiratory symptoms be screened for both diseases, as testing positive for COVID‑19 could not rule out co-infections. Some projections have estimated that reduced TB detection due to the pandemic could result in 6.3 million additional TB cases and 1.4 million TB-related deaths by 2025.[368]
History
The virus is thought to be of natural animal origin, most likely through spillover infection.[77][369][370] A joint-study conducted in early 2021 by the People’s Republic of China and the World Health Organization indicated that the virus descended from a coronavirus that infects wild bats, and likely spread to humans through an intermediary wildlife host.[371] There are several theories about where the index case originated and investigations into the origin of the pandemic are ongoing.[372] According to articles published in July 2022 in Science, virus transmission into humans occurred through two spillover events in November 2019 and was likely due to live wildlife trade on the Huanan wet market in the city of Wuhan (Hubei, China).[373][374][375] Doubts about the conclusions have mostly centred on the precise site of spillover.[376] Earlier phylogenetics estimated that SARS-CoV-2 arose in October or November 2019.[377][378][379] A phylogenetic algorithm analysis suggested that the virus may have been circulating in Guangdong before Wuhan.[380] U.S intelligence agencies and other scientists have found that the virus may have been unintentionally leaked from a laboratory such as the Wuhan Institute of Virology, but that it was not developed as a biological weapon and is unlikely to have been genetically engineered.[381][382][383][384]
The first confirmed human infections were in Wuhan. A study of the first 41 cases of confirmed COVID‑19, published in January 2020 in The Lancet, reported the earliest date of onset of symptoms as 1 December 2019.[385][386][387] Official publications from the WHO reported the earliest onset of symptoms as 8 December 2019.[388] Human-to-human transmission was confirmed by the WHO and Chinese authorities by 20 January 2020.[389][390] According to official Chinese sources, these were mostly linked to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, which also sold live animals.[391] In May 2020, George Gao, the director of the CDC, said animal samples collected from the seafood market had tested negative for the virus, indicating that the market was the site of an early superspreading event, but that it was not the site of the initial outbreak.[392] Traces of the virus have been found in wastewater samples that were collected in Milan and Turin, Italy, on 18 December 2019.[393]
By December 2019, the spread of infection was almost entirely driven by human-to-human transmission.[343][394] The number of COVID-19 cases in Hubei gradually increased, reaching sixty by 20 December,[395] and at least 266 by 31 December.[396] On 24 December, Wuhan Central Hospital sent a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) sample from an unresolved clinical case to sequencing company Vision Medicals. On 27 and 28 December, Vision Medicals informed the Wuhan Central Hospital and the Chinese CDC of the results of the test, showing a new coronavirus.[397] A pneumonia cluster of unknown cause was observed on 26 December and treated by the doctor Zhang Jixian in Hubei Provincial Hospital, who informed the Wuhan Jianghan CDC on 27 December.[398] On 30 December, a test report addressed to Wuhan Central Hospital, from company CapitalBio Medlab, stated an erroneous positive result for SARS, causing a group of doctors at Wuhan Central Hospital to alert their colleagues and relevant hospital authorities of the result. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission issued a notice to various medical institutions on «the treatment of pneumonia of unknown cause» that same evening.[399] Eight of these doctors, including Li Wenliang (punished on 3 January),[400] were later admonished by the police for spreading false rumours and another, Ai Fen, was reprimanded by her superiors for raising the alarm.[401]
The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission made the first public announcement of a pneumonia outbreak of unknown cause on 31 December, confirming 27 cases[402][403][404] – enough to trigger an investigation.[405]
During the early stages of the outbreak, the number of cases doubled approximately every seven and a half days.[406] In early and mid-January 2020, the virus spread to other Chinese provinces, helped by the Chinese New Year migration and Wuhan being a transport hub and major rail interchange.[80] On 20 January, China reported nearly 140 new cases in one day, including two people in Beijing and one in Shenzhen.[407] Later official data shows 6,174 people had already developed symptoms by then,[343] and more may have been infected.[408] A report in The Lancet on 24 January indicated human transmission, strongly recommended personal protective equipment for health workers, and said testing for the virus was essential due to its «pandemic potential».[113][409] On 30 January, the WHO declared COVID-19 a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.[408] By this time, the outbreak spread by a factor of 100 to 200 times.[410]
Italy had its first confirmed cases on 31 January 2020, two tourists from China.[411] Italy overtook China as the country with the most deaths on 19 March 2020.[412] By 26 March the United States had overtaken China and Italy with the highest number of confirmed cases in the world.[413] Research on coronavirus genomes indicates the majority of COVID-19 cases in New York came from European travellers, rather than directly from China or any other Asian country.[414] Retesting of prior samples found a person in France who had the virus on 27 December 2019,[415][416] and a person in the United States who died from the disease on 6 February 2020.[417]
RT-PCR testing of untreated wastewater samples from Brazil and Italy have suggested detection of SARS-CoV-2 as early as November and December 2019, respectively, but the methods of such sewage studies have not been optimised, many have not been peer-reviewed, details are often missing, and there is a risk of false positives due to contamination or if only one gene target is detected.[418] A September 2020 review journal article said, «The possibility that the COVID‑19 infection had already spread to Europe at the end of last year is now indicated by abundant, even if partially circumstantial, evidence,» including pneumonia case numbers and radiology in France and Italy in November and December.[419]
As of 1 October 2021, Reuters reported that it had estimated the worldwide total number of deaths due to COVID‑19 to have exceeded five million.[420]
Misinformation
After the initial outbreak of COVID‑19, misinformation and disinformation regarding the origin, scale, prevention, treatment, and other aspects of the disease rapidly spread online.[421][422][423]
In September 2020, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published preliminary estimates of the risk of death by age groups in the United States, but those estimates were widely misreported and misunderstood.[424][425]
Other species
Humans appear to be capable of spreading the virus to some other animals, a type of disease transmission referred to as zooanthroponosis.
Some pets, especially cats and ferrets, can catch this virus from infected humans.[426][427] Symptoms in cats include respiratory (such as a cough) and digestive symptoms.[426] Cats can spread the virus to other cats, and may be able to spread the virus to humans, but cat-to-human transmission of SARS-CoV-2 has not been proven.[426][428] Compared to cats, dogs are less susceptible to this infection.[428] Behaviours which increase the risk of transmission include kissing, licking, and petting the animal.[428]
The virus does not appear to be able to infect pigs, ducks, or chickens at all.[426] Mice, rats, and rabbits, if they can be infected at all, are unlikely to be involved in spreading the virus.[428]
Tigers and lions in zoos have become infected as a result of contact with infected humans.[428] As expected, monkeys and great ape species such as orangutans can also be infected with the COVID‑19 virus.[428]
Minks, which are in the same family as ferrets, have been infected.[428] Minks may be asymptomatic, and can also spread the virus to humans.[428] Multiple countries have identified infected animals in mink farms.[429] Denmark, a major producer of mink pelts, ordered the slaughter of all minks over fears of viral mutations,[429] following an outbreak referred to as Cluster 5. A vaccine for mink and other animals is being researched.[429]
Research
International research on vaccines and medicines in COVID‑19 is underway by government organisations, academic groups, and industry researchers.[430][431] The CDC has classified it to require a BSL3 grade laboratory.[432] There has been a great deal of COVID‑19 research, involving accelerated research processes and publishing shortcuts to meet the global demand.[433]
As of December 2020, hundreds of clinical trials have been undertaken, with research happening on every continent except Antarctica.[434] As of November 2020, more than 200 possible treatments have been studied in humans.[435]
Transmission and prevention research
Modelling research has been conducted with several objectives, including predictions of the dynamics of transmission,[436] diagnosis and prognosis of infection,[437] estimation of the impact of interventions,[438][439] or allocation of resources.[440] Modelling studies are mostly based on compartmental models in epidemiology,[441] estimating the number of infected people over time under given conditions. Several other types of models have been developed and used during the COVID‑19 including computational fluid dynamics models to study the flow physics of COVID‑19,[442] retrofits of crowd movement models to study occupant exposure,[443] mobility-data based models to investigate transmission,[444] or the use of macroeconomic models to assess the economic impact of the pandemic.[445] Further, conceptual frameworks from crisis management research have been applied to better understand the effects of COVID‑19 on organisations worldwide.[446][447]
Seven possible drug targets in viral replication process and drugs
Repurposed antiviral drugs make up most of the research into COVID‑19 treatments.[448][449] Other candidates in trials include vasodilators, corticosteroids, immune therapies, lipoic acid, bevacizumab, and recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.[449]
In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) initiated the Solidarity trial to assess the treatment effects of some promising drugs: an experimental drug called remdesivir; anti-malarial drugs chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine; two anti-HIV drugs, lopinavir/ritonavir; and interferon-beta.[450][451] More than 300 active clinical trials are underway as of April 2020.[172]
Research on the antimalarial drugs hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine showed that they were ineffective at best,[452][453] and that they may reduce the antiviral activity of remdesivir.[454] By May 2020, France, Italy, and Belgium had banned the use of hydroxychloroquine as a COVID‑19 treatment.[455]
In June, initial results from the randomised RECOVERY Trial in the United Kingdom showed that dexamethasone reduced mortality by one third for people who are critically ill on ventilators and one fifth for those receiving supplemental oxygen.[456] Because this is a well-tested and widely available treatment, it was welcomed by the WHO, which is in the process of updating treatment guidelines to include dexamethasone and other steroids.[457][458] Based on those preliminary results, dexamethasone treatment has been recommended by the NIH for patients with COVID‑19 who are mechanically ventilated or who require supplemental oxygen but not in patients with COVID‑19 who do not require supplemental oxygen.[459]
In September 2020, the WHO released updated guidance on using corticosteroids for COVID‑19.[460][461] The WHO recommends systemic corticosteroids rather than no systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of people with severe and critical COVID‑19 (strong recommendation, based on moderate certainty evidence).[460] The WHO suggests not to use corticosteroids in the treatment of people with non-severe COVID‑19 (conditional recommendation, based on low certainty evidence).[460] The updated guidance was based on a meta-analysis of clinical trials of critically ill COVID‑19 patients.[462][463]
In September 2020, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) endorsed the use of dexamethasone in adults and adolescents from twelve years of age and weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who require supplemental oxygen therapy.[464][465] Dexamethasone can be taken by mouth or given as an injection or infusion (drip) into a vein.[464]
In November 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an emergency use authorization for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19.[466] Bamlanivimab is authorised for people with positive results of direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing who are twelve years of age and older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb), and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19 or hospitalisation.[466] This includes those who are 65 years of age or older, or who have chronic medical conditions.[466]
In February 2021, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID‑19 in people twelve years of age or older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who test positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19. The authorised use includes treatment for those who are 65 years of age or older or who have certain chronic medical conditions.[467]
In April 2021, the FDA revoked the emergency use authorization (EUA) that allowed for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab, when administered alone, to be used for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19 in adults and certain paediatric patients.[468]
Cytokine storm
Various therapeutic strategies for targeting cytokine storm
A cytokine storm can be a complication in the later stages of severe COVID‑19. A cytokine storm is a potentially deadly immune reaction where a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are released too quickly. A cytokine storm can lead to ARDS and multiple organ failure.[469] Data collected from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, China indicates that patients who had more severe responses to COVID‑19 had greater amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in their system than patients who had milder responses. These high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines indicate presence of a cytokine storm.[470]
Tocilizumab has been included in treatment guidelines by China’s National Health Commission after a small study was completed.[471][472] It is undergoing a Phase II non-randomised trial at the national level in Italy after showing positive results in people with severe disease.[473][474] Combined with a serum ferritin blood test to identify a cytokine storm (also called cytokine storm syndrome, not to be confused with cytokine release syndrome), it is meant to counter such developments, which are thought to be the cause of death in some affected people.[475] The interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist was approved by the FDA to undergo a Phase III clinical trial assessing its effectiveness on COVID‑19 based on retrospective case studies for the treatment of steroid-refractory cytokine release syndrome induced by a different cause, CAR T cell therapy, in 2017.[476] There is no randomised, controlled evidence that tocilizumab is an efficacious treatment for CRS. Prophylactic tocilizumab has been shown to increase serum IL-6 levels by saturating the IL-6R, driving IL-6 across the blood–brain barrier, and exacerbating neurotoxicity while having no effect on the incidence of CRS.[477]
Lenzilumab, an anti-GM-CSF monoclonal antibody, is protective in murine models for CAR T cell-induced CRS and neurotoxicity and is a viable therapeutic option due to the observed increase of pathogenic GM-CSF secreting T cells in hospitalised patients with COVID‑19.[478]
Passive antibodies
Transferring purified and concentrated antibodies produced by the immune systems of those who have recovered from COVID‑19 to people who need them is being investigated as a non-vaccine method of passive immunisation.[479][480] Viral neutralisation is the anticipated mechanism of action by which passive antibody therapy can mediate defence against SARS-CoV-2. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is the primary target for neutralising antibodies.[481] As of 8 August 2020, eight neutralising antibodies targeting the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 have entered clinical studies.[482] It has been proposed that selection of broad-neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV might be useful for treating not only COVID‑19 but also future SARS-related CoV infections.[481] Other mechanisms, however, such as antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity or phagocytosis, may be possible.[479] Other forms of passive antibody therapy, for example, using manufactured monoclonal antibodies, are in development.[479]
The use of passive antibodies to treat people with active COVID‑19 is also being studied. This involves the production of convalescent serum, which consists of the liquid portion of the blood from people who recovered from the infection and contains antibodies specific to this virus, which is then administered to active patients.[479] This strategy was tried for SARS with inconclusive results.[479] An updated Cochrane review in May 2021 found high certainty evidence that, for the treatment of people with moderate to severe COVID‑19, convalescent plasma did not reduce mortality or bring about symptom improvement.[480] There continues to be uncertainty about the safety of convalescent plasma administration to people with COVID‑19 and differing outcomes measured in different studies limits their use in determining efficacy.[480]
Bioethics
Since the outbreak of the COVID‑19 pandemic, scholars have explored the bioethics, normative economics, and political theories of healthcare policies related to the public health crisis.[483] Academics have pointed to the moral distress of healthcare workers, ethics of distributing scarce healthcare resources such as ventilators,[484] and the global justice of vaccine diplomacies.[citation needed] The socio-economic inequalities between genders,[485] races,[486] groups with disabilities,[487] communities,[488] regions, countries,[489] and continents have also drawn attention in academia and the general public.
Effects on other diseases
The use of social distancing and the wearing of surgical masks and similar precautions against COVID‑19 may have caused a drop in the spread of the common cold and the flu.[490][491]
See also
- Coronavirus diseases, a group of closely related syndromes
- Disease X, a WHO term
- Law of declining virulence – Disproved hypothesis of epidemiologist Theobald Smith
- Theory of virulence – Theory by biologist Paul W. Ewald
References
- ^ «Covid-19». Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ «Symptoms of Coronavirus». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 13 May 2020. Archived from the original on 17 June 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- ^ «Q&A on coronaviruses (COVID-19)». World Health Organization (WHO). 17 April 2020. Archived from the original on 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 vaccines». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ Talic S, Shah S, Wild H, Gasevic D, Maharaj A, Ademi Z, et al. (November 2021). «Effectiveness of public health measures in reducing the incidence of covid-19, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and covid-19 mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 375: e068302. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068302. ISSN 1756-1833. PMC 9423125. PMID 34789505. S2CID 244271780.
- ^ a b c «COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU)». ArcGIS. Johns Hopkins University. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ Page J, Hinshaw D, McKay B (26 February 2021). «In Hunt for Covid-19 Origin, Patient Zero Points to Second Wuhan Market – The man with the first confirmed infection of the new coronavirus told the WHO team that his parents had shopped there». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ Islam MA (April 2021). «Prevalence and characteristics of fever in adult and paediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 17515 patients». PLOS ONE. 16 (4): e0249788. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1649788I. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0249788. PMC 8023501. PMID 33822812.
- ^ Islam MA (November 2020). «Prevalence of Headache in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 14,275 Patients». Frontiers in Neurology. 11: 562634. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.562634. PMC 7728918. PMID 33329305.
- ^ Saniasiaya J, Islam MA (April 2021). «Prevalence of Olfactory Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Meta-analysis of 27,492 Patients». The Laryngoscope. 131 (4): 865–878. doi:10.1002/lary.29286. ISSN 0023-852X. PMC 7753439. PMID 33219539.
- ^ Saniasiaya J, Islam MA (November 2020). «Prevalence and Characteristics of Taste Disorders in Cases of COVID-19: A Meta-analysis of 29,349 Patients». Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 165 (1): 33–42. doi:10.1177/0194599820981018. PMID 33320033. S2CID 229174644.
- ^ Agyeman AA, Chin KL, Landersdorfer CB, Liew D, Ofori-Asenso R (August 2020). «Smell and Taste Dysfunction in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis». Mayo Clin. Proc. 95 (8): 1621–1631. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.05.030. PMC 7275152. PMID 32753137.
- ^ Oran DP, Topol EJ (January 2021). «The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic: A Systematic Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (5): M20-6976. doi:10.7326/M20-6976. PMC 7839426. PMID 33481642.
- ^ «Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 6 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ a b CDC (11 February 2020). «Post-COVID Conditions». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ «Clinical Questions about COVID-19: Questions and Answers». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 17 November 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b c «Overview of Testing for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ a b c «Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ Gorzalski AJ, Tian H, Laverdure C, Morzunov S, Verma SC, VanHooser S, Pandori MW (August 2020). «High-Throughput Transcription-mediated amplification on the Hologic Panther is a highly sensitive method of detection for SARS-CoV-2». Journal of Clinical Virology. 129: 104501. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104501. PMC 7286273. PMID 32619959.
- ^ a b c d e Li C, Zhao C, Bao J, Tang B, Wang Y, Gu B (November 2020). «Laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)». Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 510: 35–46. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.045. PMC 7329657. PMID 32621814.
- ^ «2nd U.S. Case Of Wuhan Coronavirus Confirmed». NPR. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (2 February 2020). «Wuhan Coronavirus Looks Increasingly Like a Pandemic, Experts Say». The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Griffiths J. «Wuhan coronavirus deaths spike again as outbreak shows no signs of slowing». CNN. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Jiang S, Xia S, Ying T, Lu L (May 2020). «A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome». Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 17 (5): 554. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0372-4. PMC 7091741. PMID 32024976.
- ^ Chan JF, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KK, Chu H, Yang J, et al. (February 2020). «A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster». Lancet. 395 (10223): 514–523. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. PMC 7159286. PMID 31986261.
- ^ Shablovsky S (September 2017). «The legacy of the Spanish flu». Science. 357 (6357): 1245. Bibcode:2017Sci…357.1245S. doi:10.1126/science.aao4093. ISSN 0036-8075. S2CID 44116811.
- ^ «Stop the coronavirus stigma now». Nature. 580 (7802): 165. 7 April 2020. Bibcode:2020Natur.580..165.. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01009-0. PMID 32265571. S2CID 214809950. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 1» (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). 21 January 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 10» (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). 30 January 2020.
- ^ «Novel coronavirus named ‘Covid-19’: WHO». Today. Singapore. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ «The coronavirus spreads racism against – and among – ethnic Chinese». The Economist. 17 February 2020. Archived from the original on 17 February 2020. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- ^ World Health Organization Best Practices for the Naming of New Human Infectious Diseases (PDF) (Report). World Health Organization (WHO). May 2015. hdl:10665/163636.
- ^ a b «Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 22» (PDF). WHO. 11 February 2020.
- ^ Gover AR, Harper SB, Langton L (July 2020). «Anti-Asian Hate Crime During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Exploring the Reproduction of Inequality». American Journal of Criminal Justice. 45 (4): 647–667. doi:10.1007/s12103-020-09545-1. PMC 7364747. PMID 32837171.
- ^ «Symptoms of Coronavirus». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 22 February 2021. Archived from the original on 4 March 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
- ^ Grant MC, Geoghegan L, Arbyn M, Mohammed Z, McGuinness L, Clarke EL, Wade RG (23 June 2020). «The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries». PLOS ONE. 15 (6): e0234765. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1534765G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0234765. PMC 7310678. PMID 32574165. S2CID 220046286.
- ^ Pardhan S, Vaughan M, Zhang J, Smith L, Chichger H (1 November 2020). «Sore eyes as the most significant ocular symptom experienced by people with COVID-19: a comparison between pre-COVID-19 and during COVID-19 states». BMJ Open Ophthalmology. 5 (1): e000632. doi:10.1136/bmjophth-2020-000632. PMC 7705420. PMID 34192153.
- ^ «COVID toes, rashes: How the coronavirus can affect your skin». www.aad.org. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ a b «Clinical characteristics of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ Paderno A, Mattavelli D, Rampinelli V, Grammatica A, Raffetti E, Tomasoni M, et al. (December 2020). «Olfactory and Gustatory Outcomes in COVID-19: A Prospective Evaluation in Nonhospitalized Subjects». Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 163 (6): 1144–1149. doi:10.1177/0194599820939538. PMC 7331108. PMID 32600175.
- ^ Chabot AB, Huntwork MP (September 2021). «Turmeric as a Possible Treatment for COVID-19-Induced Anosmia and Ageusia». Cureus. 13 (9): e17829. doi:10.7759/cureus.17829. PMC 8502749. PMID 34660038.
- ^ Niazkar HR, Zibaee B, Nasimi A, Bahri N (July 2020). «The neurological manifestations of COVID-19: a review article». Neurological Sciences. 41 (7): 1667–1671. doi:10.1007/s10072-020-04486-3. PMC 7262683. PMID 32483687.
- ^ «Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 6 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Oran DP, Topol EJ (May 2021). «The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic : A Systematic Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (5): 655–662. doi:10.7326/M20-6976. PMC 7839426. PMID 33481642.
- «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- Nogrady B (November 2020). «What the data say about asymptomatic COVID infections». Nature. 587 (7835): 534–535. Bibcode:2020Natur.587..534N. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03141-3. PMID 33214725.
- ^ a b Gao Z, Xu Y, Sun C, Wang X, Guo Y, Qiu S, Ma K (February 2021). «A systematic review of asymptomatic infections with COVID-19». Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi. 54 (1): 12–16. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.05.001. PMC 7227597. PMID 32425996.
- ^ Oran DP, Topol EJ (September 2020). «Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection : A Narrative Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 173 (5): 362–367. doi:10.7326/M20-3012. PMC 7281624. PMID 32491919.
- ^ Lai CC, Liu YH, Wang CY, Wang YH, Hsueh SC, Yen MY, et al. (June 2020). «Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Facts and myths». Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi. 53 (3): 404–412. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012. PMC 7128959. PMID 32173241.
- ^ a b Furukawa NW, Brooks JT, Sobel J (July 2020). «Evidence Supporting Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 While Presymptomatic or Asymptomatic». Emerging Infectious Diseases. 26 (7). doi:10.3201/eid2607.201595. PMC 7323549. PMID 32364890.
- ^ a b Gandhi RT, Lynch JB, Del Rio C (October 2020). «Mild or Moderate Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (18): 1757–1766. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009249. PMID 32329974.
- ^ Byrne AW, McEvoy D, Collins AB, Hunt K, Casey M, Barber A, et al. (August 2020). «Inferred duration of infectious period of SARS-CoV-2: rapid scoping review and analysis of available evidence for asymptomatic and symptomatic COVID-19 cases». BMJ Open. 10 (8): e039856. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039856. PMC 7409948. PMID 32759252.
- ^ Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC (August 2020). «Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review». JAMA. 324 (8): 782–793. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12839. PMID 32648899. S2CID 220465311.
- ^ «Half of young adults with COVID-19 had persistent symptoms after 6 months». medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 10 July 2021.
- ^ Blomberg B, Mohn KG, Brokstad KA, Zhou F, Linchausen DW, Hansen BA, et al. (September 2021). «Long COVID in a prospective cohort of home-isolated patients». Nature Medicine. 27 (9): 1607–1613. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01433-3. PMC 8440190. PMID 34163090. S2CID 235625772.
- ^ CDC (1 September 2022). «Post-COVID Conditions». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «COVID-19 and Your Health». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 23 January 2021.
- ^ CDC (29 March 2022). «Omicron Variant: What You Need to Know». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 15 June 2022.
- ^ Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL (March 2021). «Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 19 (3): 141–154. doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7. PMC 7537588. PMID 33024307.
- ^ a b Wang CC, Prather KA, Sznitman J, Jimenez JL, Lakdawala SS, Tufekci Z, Marr LC (August 2021). «Airborne transmission of respiratory viruses». Science. 373 (6558). Bibcode:2021Sci…373…..W. doi:10.1126/science.abd9149. PMC 8721651. PMID 34446582.
- ^ Greenhalgh T, Jimenez JL, Prather KA, Tufekci Z, Fisman D, Schooley R (May 2021). «Ten scientific reasons in support of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2». Lancet. 397 (10285): 1603–1605. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00869-2. PMC 8049599. PMID 33865497.
- ^ Bourouiba L (13 July 2021). «Fluid Dynamics of Respiratory Infectious Diseases». Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 23 (1): 547–577. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-111820-025044. hdl:1721.1/131115. PMID 34255991. S2CID 235823756. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ Stadnytskyi, Valentyn; Bax, Christina E.; Bax, Adriaan; Anfinrud, Philip (2 June 2020). «The airborne lifetime of small speech droplets and their potential importance in SARS-CoV-2 transmission». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (22): 11875–11877. doi:10.1073/pnas.2006874117. PMC 7275719. PMID 32404416.
- ^ Miller SL, Nazaroff WW, Jimenez JL, Boerstra A, Buonanno G, Dancer SJ, et al. (March 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by inhalation of respiratory aerosol in the Skagit Valley Chorale superspreading event». Indoor Air. 31 (2): 314–323. doi:10.1111/ina.12751. PMC 7537089. PMID 32979298.
- ^ He, Xi; Lau, Eric H. Y.; Wu, Peng; Deng, Xilong; Wang, Jian; Hao, Xinxin; Lau, Yiu Chung; Wong, Jessica Y.; Guan, Yujuan; Tan, Xinghua; Mo, Xiaoneng; Chen, Yanqing; Liao, Baolin; Chen, Weilie; Hu, Fengyu; Zhang, Qing; Zhong, Mingqiu; Wu, Yanrong; Zhao, Lingzhai; Zhang, Fuchun; Cowling, Benjamin J.; Li, Fang; Leung, Gabriel M. (September 2020). «Author Correction: Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19». Nature Medicine. 26 (9): 1491–1493. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1016-z. PMC 7413015. PMID 32770170. S2CID 221050261.
- ^ a b c d Communicable Diseases Network Australia. «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): CDNA National Guidelines for Public Health Units». 5.1. Communicable Diseases Network Australia/Australian Government Department of Health.
- ^ «Clinical Questions about COVID-19: Questions and Answers». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 4 March 2021.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 May 2021. Retrieved 8 May 2021.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): How is it transmitted?». World Health Organization. 30 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d e • «COVID-19: epidemiology, virology and clinical features». GOV.UK. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
• Communicable Diseases Network Australia. «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) — CDNA Guidelines for Public Health Units». Version 4.4. Australian Government Department of Health. Retrieved 17 May 2021.{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)
• Public Health Agency of Canada (3 November 2020). «COVID-19: Main modes of transmission». aem. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
• «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
• Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE (January 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Viral, Host, and Environmental Factors». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (1): 69–79. doi:10.7326/M20-5008. ISSN 0003-4819. PMC 7505025. PMID 32941052. - ^ a b c Tang JW, Marr LC, Li Y, Dancer SJ (April 2021). «Covid-19 has redefined airborne transmission». BMJ. 373: n913. doi:10.1136/bmj.n913. PMID 33853842.
- ^ a b Morawska L, Allen J, Bahnfleth W, Bluyssen PM, Boerstra A, Buonanno G, et al. (May 2021). «A paradigm shift to combat indoor respiratory infection» (PDF). Science. 372 (6543): 689–691. Bibcode:2021Sci…372..689M. doi:10.1126/science.abg2025. PMID 33986171. S2CID 234487289.
- ^ a b Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE (January 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Viral, Host, and Environmental Factors». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (1): 69–79. doi:10.7326/M20-5008. ISSN 0003-4819. PMC 7505025. PMID 32941052.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Healthcare Workers». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 29 March 2022.
- ^ Liu T, Gong D, Xiao J, Hu J, He G, Rong Z, Ma W (October 2020). «Cluster infections play important roles in the rapid evolution of COVID-19 transmission: A systematic review». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 99: 374–380. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.073. PMC 7405860. PMID 32768702.
- ^ «Outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): increased transmission beyond China – fourth update» (PDF). European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 14 February 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- ^ a b Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF (April 2020). «The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Medicine. 26 (4): 450–452. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9. PMC 7095063. PMID 32284615.
- ^ Gibbens S (18 March 2020). «Why soap is preferable to bleach in the fight against coronavirus». National Geographic. Archived from the original on 2 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ^ Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. (February 2020). «A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (8): 727–733. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. PMC 7092803. PMID 31978945.
- ^ a b c Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) (PDF) (Report). World Health Organization (WHO). February 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 February 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ «Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Rathore JS, Ghosh C (August 2020). «Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), a newly emerged pathogen: an overview». Pathogens and Disease. 78 (6). doi:10.1093/femspd/ftaa042. OCLC 823140442. PMC 7499575. PMID 32840560.
- ^ Thomas S (October 2020). «The Structure of the Membrane Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Resembles the Sugar Transporter SemiSWEET». Pathogens & Immunity. 5 (1): 342–363. doi:10.20411/pai.v5i1.377. PMC 7608487. PMID 33154981.
- ^ Koyama T, Platt D, Parida L (July 2020). «Variant analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes». Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 98 (7): 495–504. doi:10.2471/BLT.20.253591. PMC 7375210. PMID 32742035.
We detected in total 65776 variants with 5775 distinct variants.
- ^ a b Rambaut A, Holmes EC, O’Toole Á, Hill V, McCrone JT, Ruis C, et al. (November 2020). «A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology». Nature Microbiology. 5 (11): 1403–1407. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0770-5. PMC 7610519. PMID 32669681.
- ^ «Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants». World Health Organization. 1 July 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2021.
- ^ Alm E, Broberg EK, Connor T, Hodcroft EB, Komissarov AB, Maurer-Stroh S, et al. (August 2020). «Geographical and temporal distribution of SARS-CoV-2 clades in the WHO European Region, January to June 2020». Euro Surveillance. 25 (32). doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.32.2001410. PMC 7427299. PMID 32794443.
- ^ «PANGO lineages». cov-lineages.org. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ Lauring AS, Hodcroft EB (February 2021). «Genetic Variants of SARS-CoV-2-What Do They Mean?». JAMA. 325 (6): 529–531. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.27124. PMID 33404586. S2CID 230783233.
- ^ Abdool Karim SS, de Oliveira T (May 2021). «New SARS-CoV-2 Variants – Clinical, Public Health, and Vaccine Implications». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 384 (19): 1866–1868. doi:10.1056/nejmc2100362. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 8008749. PMID 33761203.
- ^ Mallapaty S (November 2020). «COVID mink analysis shows mutations are not dangerous – yet». Nature. 587 (7834): 340–341. Bibcode:2020Natur.587..340M. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03218-z. PMID 33188367. S2CID 226947606.
- ^ Larsen HD, Fonager J, Lomholt FK, Dalby T, Benedetti G, Kristensen B, et al. (February 2021). «Preliminary report of an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 in mink and mink farmers associated with community spread, Denmark, June to November 2020». Euro Surveillance. 26 (5): 2100009. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.5.210009. PMC 7863232. PMID 33541485.
As at 1 February 2021, we assess that the cluster 5 variant is no longer circulating among humans in Denmark.
- ^ «New COVID-19 Variants». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 28 June 2021 [First published 11 February 2020]. Retrieved 15 July 2021.
- ^ «COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update Edition 69». World Health Organization (WHO). 7 December 2021.
- ^ «Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Harrison AG, Lin T, Wang P (December 2020). «Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis». Trends in Immunology. 41 (12): 1100–1115. doi:10.1016/j.it.2020.10.004. PMC 7556779. PMID 33132005.
- ^ Verdecchia P, Cavallini C, Spanevello A, Angeli F (June 2020). «The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection». European Journal of Internal Medicine. 76: 14–20. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037. PMC 7167588. PMID 32336612.
- ^ Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V (April 2020). «Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses». Nature Microbiology. 5 (4): 562–569. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y. PMC 7095430. PMID 32094589.
- ^ Marik PE, Iglesias J, Varon J, Kory P (January 2021). «A scoping review of the pathophysiology of COVID-19». International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology. 35: 20587384211048026. doi:10.1177/20587384211048026. PMC 8477699. PMID 34569339.
- ^ a b Meunier N, Briand L, Jacquin-Piques A, Brondel L, Pénicaud L (June 2020). «COVID 19-Induced Smell and Taste Impairments: Putative Impact on Physiology». Frontiers in Physiology. 11: 625110. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.625110. PMC 7870487. PMID 33574768.
- ^ Guerrero JI, Barragán LA, Martínez JD, Montoya JP, Peña A, Sobrino FE, et al. (June 2021). «Central and peripheral nervous system involvement by COVID-19: a systematic review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, neuropathology, neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and cerebrospinal fluid findings». BMC Infectious Diseases. 21 (1): 515. doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06185-6. PMC 8170436. PMID 34078305.
- ^ a b Pezzini A, Padovani A (November 2020). «Lifting the mask on neurological manifestations of COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Neurology. 16 (11): 636–644. doi:10.1038/s41582-020-0398-3. PMC 7444680. PMID 32839585.
- ^ Li YC, Bai WZ, Hashikawa T (June 2020). «The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 552–555. doi:10.1002/jmv.25728. PMC 7228394. PMID 32104915.
- ^ Baig AM, Khaleeq A, Ali U, Syeda H (April 2020). «Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms». ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (7): 995–998. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00122. PMC 7094171. PMID 32167747.
- ^ Yavarpour-Bali H, Ghasemi-Kasman M (September 2020). «Update on neurological manifestations of COVID-19». Life Sciences. 257: 118063. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118063. PMC 7346808. PMID 32652139.
- ^ Covid can shrink brain and damage its tissue, finds research The Guardian
- ^ Scans reveal how Covid may change the brain BBC
- ^ «Even mild Covid is linked to brain damage months after illness, scans show». NBC News.
- ^ Gu J, Han B, Wang J (May 2020). «COVID-19: Gastrointestinal Manifestations and Potential Fecal-Oral Transmission». Gastroenterology. 158 (6): 1518–1519. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054. PMC 7130192. PMID 32142785.
- ^ Mönkemüller K, Fry L, Rickes S (May 2020). «COVID-19, coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 and the small bowel». Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas. 112 (5): 383–388. doi:10.17235/reed.2020.7137/2020. PMID 32343593. S2CID 216645754.
- ^ Almamlouk R, Kashour T, Obeidat S, Bois MC, Maleszewski JJ, Omrani OA, et al. (August 2022). «COVID-19-Associated cardiac pathology at the postmortem evaluation: a collaborative systematic review». Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 28 (8): 1066–1075. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.03.021. PMC 8941843. PMID 35339672.
- ^ a b c Zheng YY, Ma YT, Zhang JY, Xie X (May 2020). «COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system». Nature Reviews. Cardiology. 17 (5): 259–260. doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5. PMC 7095524. PMID 32139904.
- ^ a b c Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. (February 2020). «Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China». Lancet. 395 (10223): 497–506. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. PMC 7159299. PMID 31986264.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Myocardial infarction and other coronary artery disease issues». UpToDate. Retrieved 28 September 2020.
- ^ Turner AJ, Hiscox JA, Hooper NM (June 2004). «ACE2: from vasopeptidase to SARS virus receptor». Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 25 (6): 291–4. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2004.04.001. PMC 7119032. PMID 15165741.
- ^ Abou-Ismail MY, Diamond A, Kapoor S, Arafah Y, Nayak L (October 2020). «The hypercoagulable state in COVID-19: Incidence, pathophysiology, and management». Thrombosis Research. Elsevier BV. 194: 101–115. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.06.029. PMC 7305763. PMID 32788101.
- ^ a b c Wadman M (April 2020). «How does coronavirus kill? Clinicians trace a ferocious rampage through the body, from brain to toes». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abc3208.
- ^ «NIH study uncovers blood vessel damage and inflammation in COVID-19 patients’ brains but no infection». National Institutes of Health (NIH). 30 December 2020. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ^ Lee MH, Perl DP, Nair G, Li W, Maric D, Murray H, et al. (February 2021). «Microvascular Injury in the Brains of Patients with Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 384 (5): 481–483. doi:10.1056/nejmc2033369. PMC 7787217. PMID 33378608.
- ^ Kubánková M, Hohberger B, Hoffmanns J, Fürst J, Herrmann M, Guck J, Kräter M (July 2021). «Physical phenotype of blood cells is altered in COVID-19». Biophysical Journal. 120 (14): 2838–2847. Bibcode:2021BpJ…120.2838K. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2021.05.025. PMC 8169220. PMID 34087216.
- ^ Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Sehgal K, Nair N, Mahajan S, Sehrawat TS, et al. (July 2020). «Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19». Nature Medicine. 26 (7): 1017–1032. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3. PMID 32651579. S2CID 220462000.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Kidney Damage Caused by COVID-19». Johns Hopkins Medicine. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Eketunde AO, Mellacheruvu SP, Oreoluwa P (July 2020). «A Review of Postmortem Findings in Patients With COVID-19». Cureus. Cureus, Inc. 12 (7): e9438. doi:10.7759/cureus.9438. PMC 7451084. PMID 32864262. S2CID 221352704.
- ^ Ziegler, CGK; Allon, SJ; Nyquist, SK; Mbano, IM; Miao, VN; Tzouanas, CN; Cao, Y; Yousif, AS; Bals, J; Hauser, BM; Feldman, J; Muus, C; Wadsworth MH, 2nd; Kazer, SW; Hughes, TK; Doran, B; Gatter, GJ; Vukovic, M; Taliaferro, F; Mead, BE; Guo, Z; Wang, JP; Gras, D; Plaisant, M; Ansari, M; Angelidis, I; Adler, H; Sucre, JMS; Taylor, CJ; Lin, B; Waghray, A; Mitsialis, V; Dwyer, DF; Buchheit, KM; Boyce, JA; Barrett, NA; Laidlaw, TM; Carroll, SL; Colonna, L; Tkachev, V; Peterson, CW; Yu, A; Zheng, HB; Gideon, HP; Winchell, CG; Lin, PL; Bingle, CD; Snapper, SB; Kropski, JA; Theis, FJ; Schiller, HB; Zaragosi, LE; Barbry, P; Leslie, A; Kiem, HP; Flynn, JL; Fortune, SM; Berger, B; Finberg, RW; Kean, LS; Garber, M; Schmidt, AG; Lingwood, D; Shalek, AK; Ordovas-Montanes, J; HCA Lung Biological Network. Electronic address, lung-network@humancellatlas.org.; HCA Lung Biological, Network. (28 May 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues». Cell. 181 (5): 1016–1035.e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035. PMC 7252096. PMID 32413319.
- ^ Sajuthi, SP; DeFord, P; Li, Y; Jackson, ND; Montgomery, MT; Everman, JL; Rios, CL; Pruesse, E; Nolin, JD; Plender, EG; Wechsler, ME; Mak, ACY; Eng, C; Salazar, S; Medina, V; Wohlford, EM; Huntsman, S; Nickerson, DA; Germer, S; Zody, MC; Abecasis, G; Kang, HM; Rice, KM; Kumar, R; Oh, S; Rodriguez-Santana, J; Burchard, EG; Seibold, MA (12 October 2020). «Type 2 and interferon inflammation regulate SARS-CoV-2 entry factor expression in the airway epithelium». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5139. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5139S. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18781-2. PMC 7550582. PMID 33046696.
- ^
- ^ Zhang C, Wu Z, Li JW, Zhao H, Wang GQ (May 2020). «Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (5): 105954. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954. PMC 7118634. PMID 32234467.
- ^ Gómez-Rial J, Rivero-Calle I, Salas A, Martinón-Torres F (2020). «Role of Monocytes/Macrophages in Covid-19 Pathogenesis: Implications for Therapy». Infection and Drug Resistance. 13: 2485–2493. doi:10.2147/IDR.S258639. PMC 7383015. PMID 32801787.
- ^ Dai L, Gao GF (February 2021). «Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Immunology. 21 (2): 73–82. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00480-0. ISSN 1474-1733. PMC 7747004. PMID 33340022.
- ^ a b Boopathi S, Poma AB, Kolandaivel P (April 2020). «Novel 2019 coronavirus structure, mechanism of action, antiviral drug promises and rule out against its treatment». Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 39 (9): 3409–3418. doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1758788. PMC 7196923. PMID 32306836.
- ^ Kai H, Kai M (July 2020). «Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors-lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19». Hypertension Research. 43 (7): 648–654. doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8. PMC 7184165. PMID 32341442.
- ^ Chen HX, Chen ZH, Shen HH (October 2020). «[Structure of SARS-CoV-2 and treatment of COVID-19]». Sheng Li Xue Bao. 72 (5): 617–630. PMID 33106832.
- ^ Jeyanathan M, Afkhami S, Smaill F, Miller MS, Lichty BD, Xing Z (4 September 2020). «Immunological considerations for COVID-19 vaccine strategies». Nature Reviews Immunology. 20 (10): 615–632. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00434-6. ISSN 1474-1741. PMC 7472682. PMID 32887954.
- ^ Zhang Q, Ju B, Ge J, Chan JF, Cheng L, Wang R, et al. (July 2021). «Potent and protective IGHV3-53/3-66 public antibodies and their shared escape mutant on the spike of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Communications. 12 (1): 4210. Bibcode:2021NatCo..12.4210Z. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24514-w. PMC 8270942. PMID 34244522. S2CID 235786394.
- ^ Soy M, Keser G, Atagündüz P, Tabak F, Atagündüz I, Kayhan S (July 2020). «Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment». Clinical Rheumatology. 39 (7): 2085–2094. doi:10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5. PMC 7260446. PMID 32474885.
- ^ Quirch M, Lee J, Rehman S (August 2020). «Hazards of the Cytokine Storm and Cytokine-Targeted Therapy in Patients With COVID-19: Review». Journal of Medical Internet Research. 22 (8): e20193. doi:10.2196/20193. PMC 7428145. PMID 32707537.
- ^ Bhaskar S, Sinha A, Banach M, Mittoo S, Weissert R, Kass JS, et al. (2020). «Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper». Frontiers in Immunology. 11: 1648. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648. PMC 7365905. PMID 32754159.
- ^ a b c d e f Wastnedge EA, Reynolds RM, van Boeckel SR, Stock SJ, Denison FC, Maybin JA, Critchley HO (January 2021). «Pregnancy and COVID-19». Physiological Reviews. 101 (1): 303–318. doi:10.1152/physrev.00024.2020. PMC 7686875. PMID 32969772.
- ^ Campbell D (10 October 2021). «One in six most critically ill NHS Covid patients are unvaccinated pregnant women». The Guardian. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, Zhan C, Chen C, Lv W, et al. (August 2020). «Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases». Radiology. 296 (2): E32–E40. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200642. PMC 7233399. PMID 32101510.
- ^ a b c d Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, Gholamrezanezhad A (July 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findings in 919 Patients». AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 215 (1): 87–93. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.23034. PMID 32174129.
- ^ «2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Summary». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: Laboratory testing for 2019-nCoV in humans». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Bullard J, Dust K, Funk D, Strong JE, Alexander D, Garnett L, et al. (December 2020). «Predicting Infectious Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 From Diagnostic Samples». Clinical Infectious Diseases. 71 (10): 2663–2666. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa638. PMC 7314198. PMID 32442256.
- ^ «Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens from Persons for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 4 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ «Real-Time RT-PCR Panel for Detection 2019-nCoV». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 29 January 2020. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ «Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ «NHS staff will be first to get new coronavirus antibody test, medical chief promises». The Independent. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Heneghan C, Jefferson T (1 September 2020). «Virological characterization of COVID-19 patients that test re-positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR». CEBM. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ Lu J, Peng J, Xiong Q, Liu Z, Lin H, Tan X, et al. (September 2020). «Clinical, immunological and virological characterization of COVID-19 patients that test re-positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR». EBioMedicine. 59: 102960. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102960. PMC 7444471. PMID 32853988.
- ^ Spencer E, Jefferson T, Brassey J, Heneghan C (11 September 2020). «When is Covid, Covid?». The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ «SARS-CoV-2 RNA testing: assurance of positive results during periods of low prevalence». GOV.UK. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ «ACR Recommendations for the use of Chest Radiography and Computed Tomography (CT) for Suspected COVID-19 Infection». American College of Radiology. 22 March 2020. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020.
- ^ Pormohammad A, Ghorbani S, Khatami A, Razizadeh MH, Alborzi E, Zarei M, et al. (October 2020). «Comparison of influenza type A and B with COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical, laboratory and radiographic findings». Reviews in Medical Virology. 31 (3): e2179. doi:10.1002/rmv.2179. PMC 7646051. PMID 33035373. S2CID 222255245.
- ^ Lee EY, Ng MY, Khong PL (April 2020). «COVID-19 pneumonia: what has CT taught us?». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (4): 384–385. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30134-1. PMC 7128449. PMID 32105641.
- ^ a b Li Y, Xia L (June 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of Chest CT in Diagnosis and Management». AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 214 (6): 1280–1286. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.22954. PMID 32130038. S2CID 212416282.
- ^ «COVID-19 Database». Società Italiana di Radiologia Medica e Interventistica (in Italian). Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ «ICD-10 Version:2019». World Health Organization (WHO). 2019. Archived from the original on 31 March 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
U07.2 – COVID-19, virus not identified – COVID-19 NOS – Use this code when COVID-19 is diagnosed clinically or epidemiologically but laboratory testing is inconclusive or not available. Use additional code, if desired, to identify pneumonia or other manifestations
- ^ Giani M, Seminati D, Lucchini A, Foti G, Pagni F (May 2020). «Exuberant Plasmocytosis in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Specimen of the First Patient Requiring Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for SARS-CoV-2 in Europe». Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 15 (5): e65–e66. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.03.008. PMC 7118681. PMID 32194247.
- ^ Lillicrap D (April 2020). «Disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with 2019-nCoV pneumonia». Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 18 (4): 786–787. doi:10.1111/jth.14781. PMC 7166410. PMID 32212240.
- ^ Mitra A, Dwyre DM, Schivo M, Thompson GR, Cohen SH, Ku N, Graff JP (August 2020). «Leukoerythroblastic reaction in a patient with COVID-19 infection». American Journal of Hematology. 95 (8): 999–1000. doi:10.1002/ajh.25793. PMC 7228283. PMID 32212392.
- ^ a b c d e f Satturwar S, Fowkes M, Farver C, Wilson AM, Eccher A, Girolami I, et al. (May 2021). «Postmortem Findings Associated With SARS-CoV-2: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis». The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 45 (5): 587–603. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000001650. PMC 8132567. PMID 33481385. S2CID 231679276.
- ^ Maier BF, Brockmann D (May 2020). «Effective containment explains subexponential growth in recent confirmed COVID-19 cases in China». Science. 368 (6492): 742–746. arXiv:2002.07572. Bibcode:2020Sci…368..742M. doi:10.1126/science.abb4557. PMC 7164388. PMID 32269067. («… initial exponential growth expected for an unconstrained outbreak.»)
- ^ «Viral Load Exposure Factors». ReallyCorrect.com.
- ^ «Recommendation Regarding the Use of Cloth Face Coverings, Especially in Areas of Significant Community-Based Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 28 June 2020.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 and Potential Airborne Transmission». COVID-19 Published Science and Research. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5 April 2020). «What to Do if You Are Sick». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) – Prevention & Treatment». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 March 2020. Archived from the original on 11 March 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ «UK medicines regulator gives approval for first UK COVID-19 vaccine». Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, Government of the UK. 2 December 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ Mueller B (2 December 2020). «U.K. Approves Pfizer Coronavirus Vaccine, a First in the West». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines». nih.gov. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ a b c Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB (May 2020). «Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review». JAMA. 323 (18): 1824–1836. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019. PMID 32282022.
- ^ a b Anderson RM, Heesterbeek H, Klinkenberg D, Hollingsworth TD (March 2020). «How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?». Lancet. 395 (10228): 931–934. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5. PMC 7158572. PMID 32164834.
A key issue for epidemiologists is helping policy makers decide the main objectives of mitigation – e.g. minimising morbidity and associated mortality, avoiding an epidemic peak that overwhelms health-care services, keeping the effects on the economy within manageable levels, and flattening the epidemic curve to wait for vaccine development and manufacture on scale and antiviral drug therapies.
- ^ Wiles S (14 March 2020). «After ‘Flatten the Curve’, we must now ‘Stop the Spread’. Here’s what that means». The Spinoff. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Li YD, Chi WY, Su JH, Ferrall L, Hung CF, Wu TC (December 2020). «Coronavirus vaccine development: from SARS and MERS to COVID-19». Journal of Biomedical Science. 27 (1): 104. doi:10.1186/s12929-020-00695-2. PMC 7749790. PMID 33341119.
- ^ Subbarao K (July 2021). «The success of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and challenges ahead». Cell Host & Microbe. 29 (7): 1111–1123. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.016. PMC 8279572. PMID 34265245.
- ^ Padilla TB (24 February 2021). «No one is safe unless everyone is safe». BusinessWorld. Archived from the original on 23 February 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ a b c Rogers K (11 May 2022). «COVID-19 vaccine». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 12 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- ^ «Swissmedic grants authorisation for the first COVID-19 vaccine in Switzerland» (Press release). Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products (Swissmedic). 18 December 2020. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ «EMA recommends first COVID-19 vaccine for authorisation in the EU». European Medicines Agency (EMA) (Press release). 21 December 2020. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2020.
- ^ «Wear masks in public says WHO, in update of COVID-19 advice». Reuters. 5 June 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ a b c «Recommendation Regarding the Use of Cloth Face Coverings, Especially in Areas of Significant Community-Based Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ a b «Using face masks in the community – Technical Report» (PDF). ECDC. 8 April 2020.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: Community Use of Cloth Masks to Control the Spread of SARS-CoV-2». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 November 2020.
- ^ Greenhalgh T, Schmid MB, Czypionka T, Bassler D, Gruer L (April 2020). «Face masks for the public during the covid-19 crisis». BMJ. 369: m1435. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1435. PMID 32273267. S2CID 215516381.
- ^ «Caring for Someone Sick at Home». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ «Using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 June 2020. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- ^ a b c CDC (11 February 2020). «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ^ «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 7 September 2020. Retrieved 14 October 2020.
- ^ a b National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD) (9 July 2020). «COVID-19 Employer Information for Office Buildings». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 9 July 2020.
- ^ WHO’s Science in 5 on COVID-19 — Ventilation — 30 October 2020. World Health Organization (WHO). 30 October 2020. Archived from the original on 25 October 2022. Retrieved 8 December 2022 – via YouTube.
- ^ Somsen GA, van Rijn C, Kooij S, Bem RA, Bonn D (July 2020). «Small droplet aerosols in poorly ventilated spaces and SARS-CoV-2 transmission». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. Elsesier. 8 (7): 658–659. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30245-9. PMC 7255254. PMID 32473123.
- ^ Lipinski T, Ahmad D, Serey N, Jouhara H (1 November 2020). «Review of ventilation strategies to reduce the risk of disease transmission in high occupancy buildings». International Journal of Thermofluids. 7–8: 100045. doi:10.1016/j.ijft.2020.100045. ISSN 2666-2027. S2CID 221642242.
- ^ «Social distancing: what you need to do – Coronavirus (COVID-19)». nhs.uk. 2 June 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ «Advice for the public on COVID-19 – World Health Organization». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 and Your Health». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
To prevent the spread of germs, including COVID-19, CDC recommends washing hands with soap and water whenever possible because it reduces the amount of many types of germs and chemicals on hands. But if soap and water are not readily available, using a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol can help you avoid getting sick and spreading germs to others.
- ^ «WHO-recommended handrub formulations». WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: First Global Patient Safety Challenge Clean Care Is Safer Care. World Health Organization (WHO). 19 March 2009. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ Nussbaumer-Streit B, Mayr V, Dobrescu AI, Chapman A, Persad E, Klerings I, et al. (September 2020). «Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: a rapid review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (9): CD013574. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013574.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 8133397. PMID 33959956.
- ^ Qian M, Jiang J (May 2020). «COVID-19 and social distancing». Zeitschrift für Gesundheitswissenschaften = Journal of Public Health. 30 (1): 259–261. doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01321-z. PMC 7247774. PMID 32837835.
- ^ a b Hawks L, Woolhandler S, McCormick D (August 2020). «COVID-19 in Prisons and Jails in the United States». JAMA Internal Medicine. 180 (8): 1041–1042. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1856. PMID 32343355.
- ^ Waldstein D (6 May 2020). «To Fight Virus in Prisons, C.D.C. Suggests More Screenings». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 7 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ «How COVID-19 Spreads». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 18 September 2020. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- ^ Goldman E (August 2020). «Exaggerated risk of transmission of COVID-19 by fomites». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (8): 892–893. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30561-2. PMC 7333993. PMID 32628907.
- ^ Weixel N (5 April 2021). «CDC says risk of COVID-19 transmission on surfaces 1 in 10,000». The Hill. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ a b «Science Brief: SARS-CoV-2 and Surface (Fomite) Transmission for Indoor Community Environments». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 April 2021. Archived from the original on 5 April 2021.
- ^ a b Pedreira A, Taşkın Y, García MR (January 2021). «A Critical Review of Disinfection Processes to Control SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in the Food Industry». Foods. 10 (2): 283. doi:10.3390/foods10020283. PMC 7911259. PMID 33572531. S2CID 231900820.
- ^ Rezasoltani S, Yadegar A, Hatami B, Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Zali MR (2020). «Antimicrobial Resistance as a Hidden Menace Lurking Behind the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Global Impacts of Too Much Hygiene on AMR». Frontiers in Microbiology. 11: 590683. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.590683. PMC 7769770. PMID 33384670.
- ^ Thompson D (8 February 2021). «Hygiene Theater Is Still a Huge Waste of Time». The Atlantic. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ Thompson D (27 July 2020). «Hygiene Theater Is a Huge Waste of Time». The Atlantic. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g Bueckert M, Gupta R, Gupta A, Garg M, Mazumder A (November 2020). «Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronaviruses on Dry Surfaces: Potential for Indirect Transmission». Materials. 13 (22): 5211. Bibcode:2020Mate…13.5211B. doi:10.3390/ma13225211. PMC 7698891. PMID 33218120.
- ^ Bhardwaj R, Agrawal A (November 2020). «How coronavirus survives for days on surfaces». Physics of Fluids. 32 (11): 111706. Bibcode:2020PhFl…32k1706B. doi:10.1063/5.0033306. PMC 7713872. PMID 33281435.
- ^ Chatterjee S, Murallidharan JS, Agrawal A, Bhardwaj R (February 2021). «Why coronavirus survives longer on impermeable than porous surfaces». Physics of Fluids. 33 (2): 021701. Bibcode:2021PhFl…33b1701C. doi:10.1063/5.0037924. PMC 7978145. PMID 33746485.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ^ Anthes E (8 April 2021). «Has the Era of Overzealous Cleaning Finally Come to an End?». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ^ «Interim Recommendations for US Community Facilities with Suspected/Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ «Yes, UV phone sanitizers work. That doesn’t mean you need one». The Washington Post. 16 February 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ Patiño-Lugo DF, Vélez M, Velásquez Salazar P, Vera-Giraldo CY, Vélez V, Marín IC, et al. (June 2020). «Non-pharmaceutical interventions for containment, mitigation and suppression of COVID-19 infection». Colombia Medica. 51 (2): e4266. doi:10.25100/cm.v51i2.4266. PMC 7518730. PMID 33012884.
- ^ «COVID-19 Informational Resources for High-Risk Groups | Keeping Education ACTIVE | Partnership to Fight Chronic Disease». fightchronicdisease.org. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ «Quarantine and Isolation». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 29 July 2021. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ a b c Burns J, Movsisyan A, Stratil JM, Biallas RL, Coenen M, Emmert-Fees KM, et al. (Cochrane Public Health Group) (March 2021). «International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (3): CD013717. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMC 8406796. PMID 33763851. S2CID 232356197.
- ^ «COVID Treatment Guidelines: Clinical Management Summary». NIH Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. 8 April 2022. Archived from the original on 5 November 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Wise, Jeff (17 April 2022). «What Happened to Paxlovid, the COVID Wonder Drug?». Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 19 April 2022. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Tao K, Tzou PL, Nouhin J, Bonilla H, Jagannathan P, Shafer RW (July 2021). «SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Therapy». Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 34 (4): e0010921. doi:10.1128/CMR.00109-21. PMC 8404831. PMID 34319150. S2CID 236472654.
- ^ Fisher D, Heymann D (February 2020). «Q&A: The novel coronavirus outbreak causing COVID-19». BMC Medicine. 18 (1): 57. doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01533-w. PMC 7047369. PMID 32106852.
- ^ Liu K, Fang YY, Deng Y, Liu W, Wang MF, Ma JP, et al. (May 2020). «Clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus cases in tertiary hospitals in Hubei Province». Chinese Medical Journal. 133 (9): 1025–1031. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000744. PMC 7147277. PMID 32044814.
- ^ Wang T, Du Z, Zhu F, Cao Z, An Y, Gao Y, Jiang B (March 2020). «Comorbidities and multi-organ injuries in the treatment of COVID-19». Lancet. Elsevier BV. 395 (10228): e52. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30558-4. PMC 7270177. PMID 32171074.
- ^ Wang Y, Wang Y, Chen Y, Qin Q (March 2020). «Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 568–576. doi:10.1002/jmv.25748. PMC 7228347. PMID 32134116.
- ^ «Coronavirus». WebMD. Archived from the original on 1 February 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ Martel J, Ko YF, Young JD, Ojcius DM (May 2020). «Could nasal breathing help to mitigate the severity of COVID-19». Microbes and Infection. 22 (4–5): 168–171. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.002. PMC 7200356. PMID 32387333.
- ^ «Coronavirus recovery: breathing exercises». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2020.
- ^ Wang L, Wang Y, Ye D, Liu Q (March 2020). «Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (6): 105948. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105948. PMC 7156162. PMID 32201353.
- ^ U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5 April 2020). «What to Do if You Are Sick». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ «Update to living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 371: m4475. November 2020. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4475. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 33214213. S2CID 227059995.
- ^ «Q&A: Dexamethasone and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- ^ «Home». National COVID-19 Clinical Evidence Taskforce. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- ^ Motseki, Thabiso Patrick (7 June 2022). «COVID-19 Vaccination Guidelines». www.nih.gov. National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- ^ Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. (April 2020). «Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 382 (18): 1708–1720. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2002032. PMC 7092819. PMID 32109013.
- ^ Henry BM (April 2020). «COVID-19, ECMO, and lymphopenia: a word of caution». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. Elsevier BV. 8 (4): e24. doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30119-3. PMC 7118650. PMID 32178774.
- ^ Kim JS, Lee JY, Yang JW, Lee KH, Effenberger M, Szpirt W, et al. (2021). «Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19». Theranostics. 11 (1): 316–329. doi:10.7150/thno.49713. PMC 7681075. PMID 33391477.
- ^ Doshi P (October 2020). «Will covid-19 vaccines save lives? Current trials aren’t designed to tell us». BMJ. 371: m4037. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4037. PMID 33087398. S2CID 224817161.
- ^ a b Palmieri L, Andrianou X, Barbariol P, Bella A, Bellino S, Benelli E, et al. (22 July 2020). Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 patients dying in Italy Report based on available data on July 22nd, 2020 (PDF) (Report). Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
- ^ Tzoulis P, Waung JA, Bagkeris E, Hussein Z, Biddanda A, Cousins J, et al. (May 2021). «Dysnatremia is a Predictor for Morbidity and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19». The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 106 (6): 1637–1648. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab107. PMC 7928894. PMID 33624101.
- ^ Tzoulis P, Grossman AB, Baldeweg SE, Bouloux P, Kaltsas G (September 2021). «MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Dysnatraemia in COVID-19: prevalence, prognostic impact, pathophysiology, and management». European Journal of Endocrinology. 185 (4): R103–R111. doi:10.1530/EJE-21-0281. PMC 8428074. PMID 34370712.
- ^ Baranovskii DS, Klabukov ID, Krasilnikova OA, Nikogosov DA, Polekhina NV, Baranovskaia DR, et al. (December 1975). «Letter: Acid secretion by gastric mucous membrane». The American Journal of Physiology. 229 (6): 21–25. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1853510. PMC 7738209. PMID 33210948. S2CID 227065216.
- ^ Christensen B, Favaloro EJ, Lippi G, Van Cott EM (October 2020). «Hematology Laboratory Abnormalities in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 46 (7): 845–849. doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715458. PMC 7645834. PMID 32877961.
- ^ «Living with Covid19». NIHR Themed Reviews. National Institute for Health Research. 15 October 2020. doi:10.3310/themedreview_41169.
- ^ a b «How long does COVID-19 last?». UK COVID Symptom Study. 6 June 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ «Summary of COVID-19 Long Term Health Effects: Emerging evidence and Ongoing Investigation» (PDF). University of Washington. 1 September 2020. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ «Long-term symptoms of COVID-19 ‘really concerning’, says WHO chief». UN News. 30 October 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2021.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) – Prognosis». BMJ. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ Lavery AM, Preston LE, Ko JY, Chevinsky JR, DeSisto CL, Pennington AF, et al. (November 2020). «Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Discharged and Experiencing Same-Hospital Readmission – United States, March–August 2020». MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (45): 1695–1699. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6945e2. PMC 7660660. PMID 33180754.
- ^ Vardavas CI, Nikitara K (March 2020). «COVID-19 and smoking: A systematic review of the evidence». Tobacco Induced Diseases. 18: 20. doi:10.18332/tid/119324. PMC 7083240. PMID 32206052.
- ^ a b c Engin AB, Engin ED, Engin A (August 2020). «Two important controversial risk factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Obesity and smoking». Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 78: 103411. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2020.103411. PMC 7227557. PMID 32422280.
- ^ Setti L, Passarini F, De Gennaro G, Barbieri P, Licen S, Perrone MG, et al. (September 2020). «Potential role of particulate matter in the spreading of COVID-19 in Northern Italy: first observational study based on initial epidemic diffusion». BMJ Open. 10 (9): e039338. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039338. PMC 7517216. PMID 32973066.
- ^ Wu X, Nethery RC, Sabath MB, Braun D, Dominici F (November 2020). «Air pollution and COVID-19 mortality in the United States: Strengths and limitations of an ecological regression analysis». Science Advances. 6 (45): eabd4049. Bibcode:2020SciA….6.4049W. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abd4049. PMC 7673673. PMID 33148655.
- ^ Pansini R, Fornacca D (June 2021). «Early Spread of COVID-19 in the Air-Polluted Regions of Eight Severely Affected Countries». Atmosphere. 12 (6): 795. Bibcode:2021Atmos..12..795P. doi:10.3390/atmos12060795.
- ^ Comunian S, Dongo D, Milani C, Palestini P (June 2020). «Air Pollution and Covid-19: The Role of Particulate Matter in the Spread and Increase of Covid-19’s Morbidity and Mortality». International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 17 (12): 4487. doi:10.3390/ijerph17124487. PMC 7345938. PMID 32580440.
- ^ Domingo JL, Marquès M, Rovira J (September 2020). «Influence of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on COVID-19 pandemic. A review». Environmental Research. 188: 109861. Bibcode:2020ER….188j9861D. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109861. PMC 7309850. PMID 32718835.
- ^ «COVID-19: Who’s at higher risk of serious symptoms?». Mayo Clinic.
- ^ Tamara A, Tahapary DL (July 2020). «Obesity as a predictor for a poor prognosis of COVID-19: A systematic review». Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome. 14 (4): 655–659. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.020. PMC 7217103. PMID 32438328.
- ^ Petrakis D, Margină D, Tsarouhas K, Tekos F, Stan M, Nikitovic D, et al. (July 2020). «Obesity – A risk factor for increased COVID-19, severity and lethality (Review)». Molecular Medicine Reports. 22 (1): 9–19. doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11127. PMC 7248467. PMID 32377709.
- ^ Roca-Fernández A, Dennis A, Nicholls R, McGonigle J, Kelly M, Banerjee R, et al. (29 March 2021). «Hepatic Steatosis, Rather Than Underlying Obesity, Increases the Risk of Infection and Hospitalization for COVID-19». Frontiers in Medicine. 8: 636637. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.636637. ISSN 2296-858X. PMC 8039134. PMID 33855033.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020.
- ^ Devresse A, Belkhir L, Vo B, Ghaye B, Scohy A, Kabamba B, et al. (November 2020). «COVID-19 Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Single-Center Case Series of 22 Cases From Belgium». Kidney Medicine. 2 (4): 459–466. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2020.06.001. PMC 7295531. PMID 32775986.
- ^ Dhindsa S, Champion C, Deol E, Lui M, Campbell R, Newman J, et al. (September 2022). «Association of Male Hypogonadism With Risk of Hospitalization for COVID-19». JAMA Network Open. 5 (9): e2229747. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.29747. PMC 9440397. PMID 36053534.
- ^ Shelton JF, Shastri AJ, Ye C, Weldon CH, Filshtein-Sonmez T, Coker D, et al. (June 2021). «Trans-ancestry analysis reveals genetic and nongenetic associations with COVID-19 susceptibility and severity». Nature Genetics. 53 (6): 801–808. doi:10.1038/s41588-021-00854-7. PMID 33888907. S2CID 233372385.
- ^ Wallis C. «One in Seven Dire COVID Cases May Result from a Faulty Immune Response». Scientific American.
- ^ Bastard P, Rosen LB, Zhang Q, Michailidis E, Hoffmann HH, Zhang Y, et al. (October 2020). «Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19». Science. 370 (6515): eabd4585. doi:10.1126/science.abd4585. PMC 7857397. PMID 32972996. S2CID 221914095.
- ^ Fusco DN, Brisac C, John SP, Huang YW, Chin CR, Xie T, et al. (June 2013). «A genetic screen identifies interferon-α effector genes required to suppress hepatitis C virus replication». Gastroenterology. 144 (7): 1438–49, 1449.e1-9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.026. PMC 3665646. PMID 23462180.
- ^ Namkoong H, Edahiro R, Takano T, Nishihara H, Shirai Y, Sonehara K, et al. (September 2022). «DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19». Nature. 609 (7928): 754–760. Bibcode:2022Natur.609..754N. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05163-5. PMC 9492544. PMID 35940203.
- ^ Kousathanas A, Pairo-Castineira E, Rawlik K, Stuckey A, Odhams CA, Walker S, et al. (July 2022). «Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19». Nature. 607 (7917): 97–103. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04576-6. PMC 9259496. PMID 35255492.
- ^ «COVID-19 in children and the role of school settings in transmission – first update». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 23 December 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ «Estimated Disease Burden of COVID-19». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ Reardon S (2 September 2021). «Why don’t kids tend to get as sick from Covid-19?». Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-090121-1. S2CID 239653475. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ «Information for Pediatric Healthcare Providers». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ Götzinger F, Santiago-García B, Noguera-Julián A, Lanaspa M, Lancella L, Calò Carducci FI, et al. (September 2020). «COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: a multinational, multicentre cohort study». The Lancet. Child & Adolescent Health. 4 (9): 653–661. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30177-2. PMC 7316447. PMID 32593339.
- ^ Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M (April 2020). «Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. 8 (4): e21. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30311-1. PMC 7118626. PMID 32171062.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ Hui DS, I Azhar E, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, et al. (February 2020). «The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health – The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 91: 264–266. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. PMC 7128332. PMID 31953166.
- ^ Murthy S, Gomersall CD, Fowler RA (April 2020). «Care for Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19». JAMA. 323 (15): 1499–1500. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.3633. PMID 32159735.
- ^ Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R (2020). «Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19)». StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 32150360. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Heymann DL, Shindo N, et al. (WHO Scientific and Technical Advisory Group for Infectious Hazards) (February 2020). «COVID-19: what is next for public health?». Lancet. 395 (10224): 542–545. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30374-3. PMC 7138015. PMID 32061313.
- ^ Romiti GF, Corica B, Lip GY, Proietti M (June 2021). «Prevalence and Impact of Atrial Fibrillation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis». Journal of Clinical Medicine. 10 (11): 2490. doi:10.3390/jcm10112490. PMC 8200114. PMID 34199857.
- ^ Wen W, Zhang H, Zhou M, Cheng Y, Ye L, Chen J, et al. (November 2020). «Arrhythmia in patients with severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a meta-analysis». European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 24 (21): 11395–11401. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202011_23632. PMID 33215461. S2CID 227077132.
- ^ Long B, Brady WJ, Koyfman A, Gottlieb M (July 2020). «Cardiovascular complications in COVID-19». The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 38 (7): 1504–1507. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.04.048. PMC 7165109. PMID 32317203.
- ^ Puntmann VO, Carerj ML, Wieters I, Fahim M, Arendt C, Hoffmann J, et al. (November 2020). «Outcomes of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients Recently Recovered From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». JAMA Cardiology. 5 (11): 1265–1273. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3557. PMC 7385689. PMID 32730619.
- ^ Lindner D, Fitzek A, Bräuninger H, Aleshcheva G, Edler C, Meissner K, et al. (November 2020). «Association of Cardiac Infection With SARS-CoV-2 in Confirmed COVID-19 Autopsy Cases». JAMA Cardiology. 5 (11): 1281–1285. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3551. PMC 7385672. PMID 32730555.
- ^ Siripanthong B, Nazarian S, Muser D, Deo R, Santangeli P, Khanji MY, et al. (September 2020). «Recognizing COVID-19-related myocarditis: The possible pathophysiology and proposed guideline for diagnosis and management». Heart Rhythm. 17 (9): 1463–1471. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.001. PMC 7199677. PMID 32387246.
- ^ Xu L, Liu J, Lu M, Yang D, Zheng X (May 2020). «Liver injury during highly pathogenic human coronavirus infections». Liver International. 40 (5): 998–1004. doi:10.1111/liv.14435. PMC 7228361. PMID 32170806.
- ^ Carod-Artal FJ (May 2020). «Neurological complications of coronavirus and COVID-19». Revista de Neurología. 70 (9): 311–322. doi:10.33588/rn.7009.2020179. PMID 32329044. S2CID 226200547.
- ^ Toscano G, Palmerini F, Ravaglia S, Ruiz L, Invernizzi P, Cuzzoni MG, et al. (June 2020). «Guillain-Barré Syndrome Associated with SARS-CoV-2». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (26): 2574–2576. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2009191. PMC 7182017. PMID 32302082.
- ^ «Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents temporally related to COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ HAN Archive – 00432. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (Report). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ Poyiadji N, Shahin G, Noujaim D, Stone M, Patel S, Griffith B (August 2020). «COVID-19-associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Imaging Features». Radiology. 296 (2): E119–E120. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020201187. PMC 7233386. PMID 32228363.
- ^ a b Córdoba-Vives S, Peñaranda G (April 2020). «COVID-19 y Embarazo». Medical Journal of Costa Rica (in Spanish): 629. Archived from the original on 18 June 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ Das S, Dhar S (July 2021). «Mucormycosis Following COVID-19 Infections: an Insight». The Indian Journal of Surgery. 84 (3): 585–586. doi:10.1007/s12262-021-03028-1. PMC 8270771. PMID 34276145. S2CID 235782159.
- ^ Baruah C, Devi P, Deka B, Sharma DK (June 2021). «Mucormycosis and Aspergillosis have been Linked to Covid-19-Related Fungal Infections in India». Advancements in Case Studies. 3 (1). doi:10.31031/AICS.2021.03.000555. ISSN 2639-0531. S2CID 244678882 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ «Living with Covid19». NIHR Themed Review. National Institute for Health Research. 15 October 2020. doi:10.3310/themedreview_41169. S2CID 241034526.
- ^ «Summary of COVID-19 Long Term Health Effects: Emerging evidence and Ongoing Investigation» (PDF). University of Washington. 1 September 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. (February 2020). «Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China». Lancet. 395 (10223): 497–506. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. PMC 7159299. PMID 31986264.
- ^ a b Torres-Castro R, Vasconcello-Castillo L, Alsina-Restoy X, Solis-Navarro L, Burgos F, Puppo H, Vilaró J (November 2020). «Respiratory function in patients post-infection by COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Pulmonology. Elsevier BV. 27 (4): 328–337. doi:10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.10.013. PMC 7687368. PMID 33262076. S2CID 227162748.
- ^ Shaw B, Daskareh M, Gholamrezanezhad A (January 2021). «The lingering manifestations of COVID-19 during and after convalescence: update on long-term pulmonary consequences of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)». La Radiologia Medica. 126 (1): 40–46. doi:10.1007/s11547-020-01295-8. PMC 7529085. PMID 33006087.
- ^ Zhao YM, Shang YM, Song WB, Li QQ, Xie H, Xu QF, et al. (August 2020). «Follow-up study of the pulmonary function and related physiological characteristics of COVID-19 survivors three months after recovery». EClinicalMedicine. 25: 100463. doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.11.003. PMC 7654356. PMID 32838236.
- ^ «COVID-19 Lung Damage». Johns Hopkins Medicine. 28 February 2022. Retrieved 21 May 2022.
- ^ Taquet M, Sillett R, Zhu L, Mendel J, Camplisson I, Dercon Q, Harrison PJ (17 August 2022). «Neurological and psychiatric risk trajectories after SARS-CoV-2 infection: an analysis of 2-year retrospective cohort studies including 1 284 437 patients». The Lancet Psychiatry. 9 (10): 815–827. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(22)00260-7. ISSN 2215-0366. PMC 9385200. PMID 35987197. S2CID 251626731.
- ^ «Immune responses and correlates of protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 18 May 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- ^ Vabret N, Britton GJ, Gruber C, Hegde S, Kim J, Kuksin M, et al. (June 2020). «Immunology of COVID-19: Current State of the Science». Immunity. 52 (6): 910–941. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.002. PMC 7200337. PMID 32505227.
- ^ Wang Z, Muecksch F, Schaefer-Babajew D, Finkin S, Viant C, Gaebler C, et al. (July 2021). «Naturally enhanced neutralizing breadth against SARS-CoV-2 one year after infection». Nature. 595 (7867): 426–431. Bibcode:2021Natur.595..426W. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03696-9. PMC 8277577. PMID 34126625.
- ^ a b Cohen JI, Burbelo PD (December 2020). «Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Vaccines». Clinical Infectious Diseases. 73 (11): e4223–e4228. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1866. PMC 7799323. PMID 33338197. S2CID 229323810.
- ^ a b Wang J, Kaperak C, Sato T, Sakuraba A (August 2021). «COVID-19 reinfection: a rapid systematic review of case reports and case series». Journal of Investigative Medicine. 69 (6): 1253–1255. doi:10.1136/jim-2021-001853. ISSN 1081-5589. PMID 34006572. S2CID 234773697.
- ^ a b «How soon after catching COVID-19 can you get it again?». ABC News. 2 May 2022. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (May 2012). «Lesson 3: Measures of Risk Section 3: Mortality Frequency Measures». Principles of Epidemiology in Public Health Practice (Third ed.). U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). No. SS1978. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Ritchie H, Roser M (25 March 2020). Chivers T (ed.). «What do we know about the risk of dying from COVID-19?». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Castagnoli R, Votto M, Licari A, Brambilla I, Bruno R, Perlini S, et al. (September 2020). «Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review». JAMA Pediatrics. 174 (9): 882–889. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1467. PMID 32320004.
- ^ Lu X, Zhang L, Du H, Zhang J, Li YY, Qu J, et al. (April 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 382 (17): 1663–1665. doi:10.1056/nejmc2005073. PMC 7121177. PMID 32187458.
- ^ Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, Tong S (June 2020). «Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China». Pediatrics. 145 (6): e20200702. doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0702. PMID 32179660. S2CID 219118986.
- ^ a b c d Dehingia N (2021). «Sex differences in COVID-19 case fatality: do we know enough?». The Lancet. Global Health. 9 (1): e14–e15. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30464-2. PMC 7834645. PMID 33160453.
- ^ Lazzerini M, Putoto G (May 2020). «COVID-19 in Italy: momentous decisions and many uncertainties». The Lancet. Global Health. 8 (5): e641–e642. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30110-8. PMC 7104294. PMID 32199072.
- ^ Ritchie H, Ortiz-Ospina E, Beltekian D, Mathieu E, Hasell J, MacDonald B, et al. (5 March 2020). «What do we know about the risk of dying from COVID-19?». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ «Total confirmed cases of COVID-19 per million people». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2022.[needs update]
- ^ «Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million people». Our World in Data.
- ^ Mallapaty S (June 2020). «How deadly is the coronavirus? Scientists are close to an answer». Nature. 582 (7813): 467–468. Bibcode:2020Natur.582..467M. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01738-2. PMID 32546810. S2CID 219726496.
- ^ Alwan NA, Burgess RA, Ashworth S, Beale R, Bhadelia N, Bogaert D, et al. (October 2020). «Scientific consensus on the COVID-19 pandemic: we need to act now». Lancet. 396 (10260): e71–e72. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32153-X. PMC 7557300. PMID 33069277.
- ^ Meyerowitz-Katz G, Merone L (December 2020). «A systematic review and meta-analysis of published research data on COVID-19 infection fatality rates». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 101: 138–148. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.1464. PMC 7524446. PMID 33007452.
- ^ Zhang D, Hu M, Ji Q (October 2020). «Financial markets under the global pandemic of COVID-19». Finance Research Letters. 36: 101528. Bibcode:2020CSFX….500043D. doi:10.1016/j.csfx.2020.100043. PMC 7402242. PMID 32837360.
- ^ a b c d e Levin AT, Hanage WP, Owusu-Boaitey N, Cochran KB, Walsh SP, Meyerowitz-Katz G (December 2020). «Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications». European Journal of Epidemiology. 35 (12): 1123–1138. doi:10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1. PMC 7721859. PMID 33289900.
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- ^ World Health Organization (22 December 2020). «Background paper on Covid-19 disease and vaccines: prepared by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on immunization working group on COVID-19 vaccines». World Health Organization. hdl:10665/338095.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 30» (PDF). 19 February 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 31» (PDF). 20 February 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (4 July 2020). «The Pandemic’s Big Mystery: How Deadly Is the Coronavirus? – Even with more than 500,000 dead worldwide, scientists are struggling to learn how often the virus kills. Here’s why». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ «Global Research and Innovation Forum on COVID-19: Virtual Press Conference» (PDF). World Health Organization. 2 July 2020.
- ^ «Estimating mortality from COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 21 September 2020.
- ^ Shaffer C (23 October 2021). «Covid-19 still rife in Iran». New Scientist. 252 (3357): 10–11. Bibcode:2021NewSc.252…10S. doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(21)01865-0. ISSN 0262-4079. PMC 8536311. PMID 34720322.
- ^ «COVID-19: Data». City of New York.
- ^ Wilson L (May 2020). «SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, Infection Fatality Rate (IFR) Implied by the Serology, Antibody, Testing in New York City». SSRN 3590771.
- ^ Yang W, Kandula S, Huynh M, Greene SK, Van Wye G, Li W, et al. (February 2021). «Estimating the infection-fatality risk of SARS-CoV-2 in New York City during the spring 2020 pandemic wave: a model-based analysis». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 21 (2): 203–212. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30769-6. PMC 7572090. PMID 33091374.
- ^ Modi C (21 April 2020). «How deadly is COVID-19? Data Science offers answers from Italy mortality data». Medium. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 September 2020. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^ Salje H, Tran Kiem C, Lefrancq N, Courtejoie N, Bosetti P, Paireau J, et al. (July 2020). «Estimating the burden of SARS-CoV-2 in France». Science. 369 (6500): 208–211. Bibcode:2020Sci…369..208S. doi:10.1126/science.abc3517. PMC 7223792. PMID 32404476.
- ^ McIntosh K (April 2021). «Covid 19 Clinical Features». UpToDate. Retrieved 12 May 2021.
- ^ Peckham H, de Gruijter NM, Raine C, Radziszewska A, Ciurtin C, Wedderburn LR, et al. (December 2020). «Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 6317. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.6317P. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6. PMC 7726563. PMID 33298944.
- ^ Abate BB, Kassie AM, Kassaw MW, Aragie TG, Masresha SA (October 2020). «Sex difference in coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ Open. 10 (10): e040129. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040129. PMC 7539579. PMID 33028563.
- ^ a b c The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team (February 2020). «The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) – China, 2020». China CDC Weekly. 2 (8): 113–122. doi:10.46234/ccdcw2020.032. PMC 839292. PMID 34594836.
- ^ Hu Y, Sun J, Dai Z, Deng H, Li X, Huang Q, et al. (June 2020). «Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis». Journal of Clinical Virology. 127: 104371. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371. PMC 7195434. PMID 32315817.
- ^ Fu L, Wang B, Yuan T, Chen X, Ao Y, Fitzpatrick T, et al. (June 2020). «Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis». The Journal of Infection. 80 (6): 656–665. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.041. PMC 7151416. PMID 32283155.
- ^ Yuki K, Fujiogi M, Koutsogiannaki S (June 2020). «COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review». Clinical Immunology. 215: 108427. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427. PMC 7169933. PMID 32325252. S2CID 216028003.
- ^ Rabin RC (20 March 2020). «In Italy, Coronavirus Takes a Higher Toll on Men». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 weekly surveillance report». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b Gupta AH (3 April 2020). «Does Covid-19 Hit Women and Men Differently? U.S. Isn’t Keeping Track». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b Dorn AV, Cooney RE, Sabin ML (April 2020). «COVID-19 exacerbating inequalities in the US». Lancet. 395 (10232): 1243–1244. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30893-X. PMC 7162639. PMID 32305087.
- ^ a b Shauly-Aharonov, Michal; Shafrir, Asher; Paltiel, Ora; Calderon-Margalit, Ronit; Safadi, Rifaat; Bicher, Roee; Barenholz-Goultschin, Orit; Stokar, Joshua (22 July 2021). «Both high and low pre-infection glucose levels associated with increased risk for severe COVID-19: New insights from a population-based study». PLOS ONE. 16 (7): e0254847. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1654847S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0254847. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 8297851. PMID 34293038.
- ^ Adams ML, Katz DL, Grandpre J (August 2020). «Population-Based Estimates of Chronic Conditions Affecting Risk for Complications from Coronavirus Disease, United States». Emerging Infectious Diseases. 26 (8): 1831–1833. doi:10.3201/eid2608.200679. PMC 7392427. PMID 32324118.
- ^ Batthyány K (13 October 2020). «Coronavirus y Desigualdades preexistentes: Género y Cuidados». CLACSO (Consejo Latinoamericano de Ciencias Sociales). Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ «COVID-19 Presents Significant Risks for American Indian and Alaska Native People». 14 May 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 Presents Significant Risks for American Indian and Alaska Native People». 14 May 2020.
- ^ Laurencin CT, McClinton A (June 2020). «The COVID-19 Pandemic: a Call to Action to Identify and Address Racial and Ethnic Disparities». Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities. 7 (3): 398–402. doi:10.1007/s40615-020-00756-0. PMC 7166096. PMID 32306369.
- ^ «How coronavirus deaths in the UK compare by race and ethnicity». The Independent. 9 June 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ «Emerging findings on the impact of COVID-19 on black and minority ethnic people». The Health Foundation. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ Butcher B, Massey J (9 June 2020). «Why are more BAME people dying from coronavirus?». BBC News. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ a b c «The ancient Neanderthal hand in severe COVID-19». ScienceDaily. 30 September 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- ^ «WHO Director-General’s statement on the advice of the IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus». World Health Organization (WHO).
- ^ Garg S, Kim L, Whitaker M, O’Halloran A, Cummings C, Holstein R, et al. (April 2020). «Hospitalization Rates and Characteristics of Patients Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019 – COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1–30, 2020». MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (15): 458–464. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3. PMC 7755063. PMID 32298251.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ Zhao Q, Meng M, Kumar R, Wu Y, Huang J, Lian N, et al. (October 2020). «The impact of COPD and smoking history on the severity of COVID-19: A systemic review and meta-analysis». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (10): 1915–1921. doi:10.1002/jmv.25889. PMC 7262275. PMID 32293753.
- ^ «Smoking and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ DeRobertis J (3 May 2020). «People who use drugs are more vulnerable to coronavirus. Here’s what clinics are doing to help». The Advocate (Louisiana). Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020.
- ^ Frutos R, Gavotte L, Devaux CA (November 2021). «Understanding the origin of COVID-19 requires to change the paradigm on zoonotic emergence from the spillover to the circulation model». Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 95: 104812. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104812. PMC 7969828. PMID 33744401.
- ^ Holmes EC, Goldstein SA, Rasmussen AL, Robertson DL, Crits-Christoph A, Wertheim JO, et al. (September 2021). «The origins of SARS-CoV-2: A critical review». Cell. 184 (19): 4848–4856. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.017. PMC 8373617. PMID 34480864.
- ^ «WHO-convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part». World Health Organization. 30 March 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ^ Duarte F (24 February 2020). «As the cases of coronavirus increase in China and around the world, the hunt is on to identify «patient zero»«. BBC News. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ Pekar JE, Magee P, Parker E, Moshiri N, Izhikevich K, Havens JL, et al. (26 July 2022). «The molecular epidemiology of multiple zoonotic origins of SARS-CoV-2». Science. 377 (6609): 960–966. Bibcode:2022Sci…377..960P. doi:10.1126/science.abp8337. PMC 9348752. PMID 35881005.
- ^ Gill V (26 July 2022). «Covid origin studies say evidence points to Wuhan market».
- ^ Worobey M, Levy JI, Serrano LM, Crits-Christoph A, Pekar JE, Goldstein SA, et al. (July 2022). «The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan was the early epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic». Science. 377 (6609): 951–959. Bibcode:2022Sci…377..951W. doi:10.1126/science.abp8715. PMC 9348750. PMID 35881010. S2CID 251067542.
- ^ «Debate deepens over Wuhan wet market’s role in kickstarting the pandemic». National Geographic. 27 July 2022.
- ^ Li X, Zai J, Zhao Q, Nie Q, Li Y, Foley BT, Chaillon A (June 2020). «Evolutionary history, potential intermediate animal host, and cross-species analyses of SARS-CoV-2». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 602–611. doi:10.1002/jmv.25731. PMC 7228310. PMID 32104911.
- ^ Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF (April 2020). «The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Medicine. 26 (4): 450–452. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9. PMC 7095063. PMID 32284615.
- ^ van Dorp L, Acman M, Richard D, Shaw LP, Ford CE, Ormond L, et al. (September 2020). «Emergence of genomic diversity and recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2». Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 83: 104351. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104351. PMC 7199730. PMID 32387564.
- ^ Grose TK (13 May 2020). «Did the Coronavirus Originate Outside of Wuhan?». U.S. News & World Report.
- ^ Wolf ZB (25 May 2021). «Analysis: Why scientists are suddenly more interested in the lab-leak theory of Covid’s origin». CNN. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ Maxmen A (September 2021). «US COVID origins report: researchers pleased with scientific approach». Nature. 597 (7875): 159–160. Bibcode:2021Natur.597..159M. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-02366-0. PMID 34465917. S2CID 237373547.
- ^ Paun C, Zeller S, Reader R, Leonard B, Scullion G (4 November 2022). «Cross-examining the lab-leak theorists». Politico. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ Hosenball M, Zengerle P (30 October 2021). «U.S. spy agencies say origins of COVID-19 may never be known». Reuters. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ Wu YC, Chen CS, Chan YJ (March 2020). «The outbreak of COVID-19: An overview». Journal of the Chinese Medical Association. 83 (3): 217–220. doi:10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000270. PMC 7153464. PMID 32134861.
- ^ Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF (February 2020). «A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern». Lancet. 395 (10223): 470–473. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9. PMC 7135038. PMID 31986257.
- ^ Cohen J (January 2020). «Wuhan seafood market may not be source of novel virus spreading globally». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abb0611.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus – China». World Health Organization (WHO). 12 January 2020. Archived from the original on 14 January 2020.
- ^ Kessler G (17 April 2020). «Trump’s false claim that the WHO said the coronavirus was ‘not communicable’«. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Kuo L (21 January 2020). «China confirms human-to-human transmission of coronavirus». The Guardian. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ Epidemiology Working Group For Ncip Epidemic Response; Chinese Center for Disease Control Prevention (February 2020). «[The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China]». Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi (in Chinese). 41 (2): 145–151. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003. PMID 32064853. S2CID 211133882.
- ^ Areddy JT (26 May 2020). «China Rules Out Animal Market and Lab as Coronavirus Origin». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ Kelland K (19 June 2020). «Italy sewage study suggests COVID-19 was there in December 2019». Reuters. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ Heymann DL, Shindo N (February 2020). «COVID-19: what is next for public health?». Lancet. 395 (10224): 542–545. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3. PMC 7138015. PMID 32061313.
- ^ Bryner J (14 March 2020). «1st known case of coronavirus traced back to November in China». livescience.com. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ Canadian Politics (8 April 2020). «The birth of a pandemic: How COVID-19 went from Wuhan to Toronto | National Post». National Post. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ 高昱 (26 February 2020). «独家 | 新冠病毒基因测序溯源:警报是何时拉响的» [Exclusive | Tracing the New Coronavirus gene sequencing: when did the alarm sound]. Caixin (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 27 February 2020. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- ^ 路子康. «最早上报疫情的她,怎样发现这种不一样的肺炎». 中国网新闻 (in Chinese (China)). 北京. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ «Undiagnosed pneumonia – China (HU): RFI». ProMED Mail. ProMED. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ «‘Hero who told the truth’: Chinese rage over coronavirus death of whistleblower doctor». The Guardian. 7 February 2020.
- ^ Kuo L (11 March 2020). «Coronavirus: Wuhan doctor speaks out against authorities». The Guardian. London.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ^ «武汉现不明原因肺炎 官方确认属实:已经做好隔离». Xinhua Net 新華網. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ 武汉市卫健委关于当前我市肺炎疫情的情况通报. WJW.Wuhan.gov.cn (in Chinese). Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 9 January 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ «Mystery pneumonia virus probed in China». BBC News. 3 January 2020. Archived from the original on 5 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. (March 2020). «Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (13): 1199–1207. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316. PMC 7121484. PMID 31995857.
- ^ «China confirms sharp rise in cases of SARS-like virus across the country». 20 January 2020. Archived from the original on 20 January 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- ^ a b «Flattery and foot dragging: China’s influence over the WHO under scrutiny». The Globe and Mail. 25 April 2020.
- ^ Horton R (18 March 2020). «Scientists have been sounding the alarm on coronavirus for months. Why did Britain fail to act?». The Guardian. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ «China delayed releasing coronavirus info, frustrating WHO». Associated Press. 2 June 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Primi due casi in Italia» [Coronavirus: First two cases in Italy]. Corriere della sera (in Italian). 31 January 2020. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Number of COVID-19 deaths in Italy surpasses China as total reaches 3,405». Sky News. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (26 March 2020). «The U.S. Now Leads the World in Confirmed Coronavirus Cases». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ «Studies Show N.Y. Outbreak Originated in Europe». The New York Times. 8 April 2020. Archived from the original on 8 April 2020.
- ^ Irish J (4 May 2020). Lough RM, Graff P (eds.). «After retesting samples, French hospital discovers COVID-19 case from December». Reuters. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ Deslandes A, Berti V, Tandjaoui-Lambotte Y, Alloui C, Carbonnelle E, Zahar JR, et al. (June 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 was already spreading in France in late December 2019». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (6): 106006. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106006. PMC 7196402. PMID 32371096.
- ^ «2 died with coronavirus weeks before 1st U.S. virus death». PBS NewsHour. 22 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ Michael-Kordatou I, Karaolia P, Fatta-Kassinos D (October 2020). «Sewage analysis as a tool for the COVID-19 pandemic response and management: the urgent need for optimised protocols for SARS-CoV-2 detection and quantification». Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 8 (5): 104306. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2020.104306. PMC 7384408. PMID 32834990.
- ^ Platto S, Xue T, Carafoli E (September 2020). «COVID19: an announced pandemic». Cell Death & Disease. 11 (9): 799. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02995-9. PMC 7513903. PMID 32973152.
- ^ Kavya B, Abraham R (3 October 2021). Shumaker L, Wardell J (eds.). «Global COVID-19 deaths hit 5 million as Delta variant sweeps the world». Reuters.com. Reuters.
- ^ «China coronavirus: Misinformation spreads online about origin and scale». BBC News. 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 4 February 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ Taylor J (31 January 2020). «Bat soup, dodgy cures and ‘diseasology’: the spread of coronavirus misinformation». The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
- ^ «Here’s A Running List Of Disinformation Spreading About The Coronavirus». Buzzfeed News. Archived from the original on 6 February 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ «Misleading claim circulates online about infection fatality ratio of Covid-19 in the US». Fact Check. 8 October 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ a b c d Kampf G, Brüggemann Y, Kaba HE, Steinmann J, Pfaender S, Scheithauer S, Steinmann E (December 2020). «Potential sources, modes of transmission and effectiveness of prevention measures against SARS-CoV-2». The Journal of Hospital Infection. 106 (4): 678–697. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2020.09.022. PMC 7500278. PMID 32956786.
- ^ Shi J, Wen Z, Zhong G, Yang H, Wang C, Huang B, et al. (May 2020). «Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS-coronavirus 2». Science. 368 (6494): 1016–1020. doi:10.1126/science.abb7015. PMC 7164390. PMID 32269068.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Salajegheh Tazerji S, Magalhães Duarte P, Rahimi P, Shahabinejad F, Dhakal S, Singh Malik Y, et al. (September 2020). «Transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to animals: an updated review». Journal of Translational Medicine. 18 (1): 358. doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02534-2. PMC 7503431. PMID 32957995.
- ^ a b c Gorman J (22 January 2021). «The Coronavirus Kills Mink, So They Too May Get a Vaccine». The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ Dhama K, Sharun K, Tiwari R, Dadar M, Malik YS, Singh KP, Chaicumpa W (June 2020). «COVID-19, an emerging coronavirus infection: advances and prospects in designing and developing vaccines, immunotherapeutics, and therapeutics». Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 16 (6): 1232–1238. doi:10.1080/21645515.2020.1735227. PMC 7103671. PMID 32186952.
- ^ Zhang L, Liu Y (May 2020). «Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: A systematic review». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (5): 479–490. doi:10.1002/jmv.25707. PMC 7166986. PMID 32052466.
- ^ «Interim Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines for Handling and Processing Specimens Associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Lab Biosafety Guidelines. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Aristovnik A, Ravšelj D, Umek L (November 2020). «A Bibliometric Analysis of COVID-19 across Science and Social Science Research Landscape». Sustainability. 12 (21): 9132. doi:10.3390/su12219132.
- ^ Kupferschmidt K (3 December 2020). «First-of-its-kind African trial tests common drugs to prevent severe COVID-19». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abf9987. Retrieved 8 March 2022.
- ^ Reardon S (November 2020). «For COVID Drugs, Months of Frantic Development Lead to Few Outright Successes». Scientific American. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ^ Kucharski AJ, Russell TW, Diamond C, Liu Y, Edmunds J, Funk S, Eggo RM (May 2020). «Early dynamics of transmission and control of COVID-19: a mathematical modelling study». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (5): 553–558. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30144-4. PMC 7158569. PMID 32171059.
- ^ «Update to living systematic review on prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of covid-19». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 372: n236. 3 February 2021. doi:10.1136/bmj.n236. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 33536183. S2CID 231775762.
- ^ Giordano G, Blanchini F, Bruno R, Colaneri P, Di Filippo A, Di Matteo A, Colaneri M (June 2020). «Modelling the COVID-19 epidemic and implementation of population-wide interventions in Italy». Nature Medicine. 26 (6): 855–860. arXiv:2003.09861. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0883-7. PMC 7175834. PMID 32322102.
- ^ Prem K, Liu Y, Russell TW, Kucharski AJ, Eggo RM, Davies N, et al. (May 2020). «The effect of control strategies to reduce social mixing on outcomes of the COVID-19 epidemic in Wuhan, China: a modelling study». The Lancet. Public Health. 5 (5): e261–e270. doi:10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30073-6. PMC 7158905. PMID 32220655.
- ^ Emanuel EJ, Persad G, Upshur R, Thome B, Parker M, Glickman A, et al. (May 2020). «Fair Allocation of Scarce Medical Resources in the Time of Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (21): 2049–2055. doi:10.1056/NEJMsb2005114. PMID 32202722.
- ^ Kermack WO, McKendrick AG (1927). «A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character. 115 (772): 700–721. Bibcode:1927RSPSA.115..700K. doi:10.1098/rspa.1927.0118.
- ^ Mittal R, Ni R, Seo JH (2020). «The flow physics of COVID-19». Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 894: –2. arXiv:2004.09354. Bibcode:2020JFM…894F…2M. doi:10.1017/jfm.2020.330.
- ^ Ronchi E, Lovreglio R (October 2020). «EXPOSED: An occupant exposure model for confined spaces to retrofit crowd models during a pandemic». Safety Science. 130: 104834. arXiv:2005.04007. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104834. PMC 7373681. PMID 32834509.
- ^ Badr HS, Du H, Marshall M, Dong E, Squire MM, Gardner LM (November 2020). «Association between mobility patterns and COVID-19 transmission in the USA: a mathematical modelling study». The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 20 (11): 1247–1254. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30553-3. PMC 7329287. PMID 32621869.
- ^ McKibbin W, Roshen F (2020). «The global macroeconomic impacts of COVID-19: Seven scenarios» (PDF). CAMA Working Paper. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3547729. S2CID 216307705.
- ^ Bundy J, Pfarrer MD, Short CE, Coombs WT (July 2017). «Crises and crisis management: Integration, interpretation, and research development». Journal of Management. 43 (6): 1661–92. doi:10.1177/0149206316680030. S2CID 152223772.
- ^ Kraus S, Clauss T, Breier M, Gast J, Zardini A, Tiberius V (2020). «The economics of COVID-19: initial empirical evidence on how family firms in five European countries cope with the corona crisis». International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research. 26 (5): 1067–1092. doi:10.1108/IJEBR-04-2020-0214. ISSN 1355-2554. S2CID 219144929.
- ^ «COVID-19 treatment and vaccine tracker» (PDF). Milken Institute. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ a b Koch S, Pong W (13 March 2020). «First up for COVID-19: nearly 30 clinical readouts before end of April». BioCentury Inc. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Kupferschmidt K, Cohen J (March 2020). «WHO launches global megatrial of the four most promising coronavirus treatments». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abb8497.
- ^ «UN health chief announces global ‘solidarity trial’ to jumpstart search for COVID-19 treatment». UN News. 18 March 2020. Archived from the original on 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- ^ «Citing safety concerns, the W.H.O. paused tests of a drug Trump said he had taken». The New York Times. 26 May 2020. Archived from the original on 26 May 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Hydroxychloroquine does not benefit adults hospitalized with COVID-19». National Institutes of Health (NIH) (Press release). 9 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Warns of Newly Discovered Potential Drug Interaction That May Reduce Effectiveness of a COVID-19 Treatment Authorized for Emergency Use». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 June 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ^ «France bans use of hydroxychloroquine, drug touted by Trump, in coronavirus patients». CBS News. 27 May 2020.
- ^ Boseley S (16 June 202). «Recovery trial for Covid-19 treatments: what we know so far». The Guardian. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «WHO welcomes preliminary results about dexamethasone use in treating critically ill COVID-19 patients». World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). 16 June 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «Q&A: Dexamethasone and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ «Corticosteroids». COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (2020). Corticosteroids for COVID-19: living guidance, 2 September 2020 (Report). hdl:10665/334125. WHO/2019-nCoV/Corticosteroids/2020.1.
- ^ «WHO updates clinical care guidance with corticosteroid recommendations». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Sterne JA, Murthy S, Diaz JV, Slutsky AS, Villar J, Angus DC, et al. (The WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group) (October 2020). «Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis». JAMA. 324 (13): 1330–1341. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17023. PMC 7489434. PMID 32876694. S2CID 221467783.
- ^ Prescott HC, Rice TW (October 2020). «Corticosteroids in COVID-19 ARDS: Evidence and Hope During the Pandemic». JAMA. 324 (13): 1292–1295. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.16747. PMID 32876693. S2CID 221468015.
- ^ a b «EMA endorses use of dexamethasone in COVID-19 patients on oxygen or mechanical ventilation». European Medicines Agency (EMA) (Press release). 18 September 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2020. Text was copied from this source which is European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ Dexamethasone in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 (PDF) (Report). European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2020.
- ^ a b c
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 9 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 10 February 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Revokes Emergency Use Authorization for Monoclonal Antibody Bamlanivimab». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 16 April 2021. Retrieved 16 April 2021.
- ^ Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S (April 2020). «Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19». Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis. 10 (2): 102–108. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001. PMC 7104082. PMID 32282863.
- ^ Zhao Z, Wei Y, Tao C (January 2021). «An enlightening role for cytokine storm in coronavirus infection». Clinical Immunology. 222: 108615. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108615. PMC 7583583. PMID 33203513.
- ^ Liu R, Miller J (3 March 2020). «China approves use of Roche drug in battle against coronavirus complications». Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Xu X, Han M, Li T, Sun W, Wang D, Fu B, et al. (May 2020). «Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (20): 10970–10975. Bibcode:2020PNAS..11710970X. doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117. PMC 7245089. PMID 32350134.
- ^ Ovadia D, Agenzia Z. «COVID-19 – Italy launches an independent trial on tocilizumab». Univadis from Medscape. Aptus Health. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ «Tocilizumab in COVID-19 Pneumonia (TOCIVID-19) (TOCIVID-19)». clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Various sources:
- «How doctors can potentially significantly reduce the number of deaths from Covid-19». Vox. 12 March 2020. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- Ruan Q, Yang K, Wang W, Jiang L, Song J (May 2020). «Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China». Intensive Care Medicine. 46 (5): 846–848. doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x. PMC 7080116. PMID 32125452.
- Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ (March 2020). «COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression». Lancet. 395 (10229): 1033–1034. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. PMC 7270045. PMID 32192578.
- ^ Slater H (26 March 2020). «FDA Approves Phase III Clinical Trial of Tocilizumab for COVID-19 Pneumonia». cancernetwork.com. Cancer Network. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Locke FL, Neelapu SS, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, et al. (2017). «Preliminary Results of Prophylactic Tocilizumab after Axicabtageneciloleucel (axi-cel; KTE-C19) Treatment for Patients with Refractory, Aggressive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)». Blood. 130 (Supplement 1): 1547. doi:10.1182/blood.V130.Suppl_1.1547.1547. S2CID 155698207.
- ^ Sterner RM, Sakemura R, Cox MJ, Yang N, Khadka RH, Forsman CL, et al. (February 2019). «GM-CSF inhibition reduces cytokine release syndrome and neuroinflammation but enhances CAR T cell function in xenografts». Blood. 133 (7): 697–709. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-10-881722. PMC 6376281. PMID 30463995.
- ^ a b c d e Casadevall A, Pirofski LA (April 2020). «The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19». The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 130 (4): 1545–1548. doi:10.1172/JCI138003. PMC 7108922. PMID 32167489.
- ^ a b c Piechotta V, Iannizzi C, Chai KL, Valk SJ, Kimber C, Dorando E, et al. (May 2021). «Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (5): CD013600. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4. PMC 8135693. PMID 34013969.
- ^ a b Ho M (April 2020). «Perspectives on the development of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2». Antibody Therapeutics. 3 (2): 109–114. doi:10.1093/abt/tbaa009. PMC 7291920. PMID 32566896.
- ^ Yang L, Liu W, Yu X, Wu M, Reichert JM, Ho M (July 2020). «COVID-19 antibody therapeutics tracker: a global online database of antibody therapeutics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19». Antibody Therapeutics. 3 (3): 205–212. doi:10.1093/abt/tbaa020. PMC 7454247. PMID 33215063.
- ^ Maccaro A, Piaggio D, Pagliara S, Pecchia L (June 2021). «The role of ethics in science: a systematic literature review from the first wave of COVID-19». Health and Technology. 11 (5): 1063–1071. doi:10.1007/s12553-021-00570-6. ISSN 2190-7188. PMC 8175060. PMID 34104626.
- ^ McGuire AL, Aulisio MP, Davis FD, Erwin C, Harter TD, Jagsi R, et al. (July 2020). «Ethical Challenges Arising in the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview from the Association of Bioethics Program Directors (ABPD) Task Force». The American Journal of Bioethics. 20 (7): 15–27. doi:10.1080/15265161.2020.1764138. PMID 32511078. S2CID 219552665.
- ^ Wenham C, Smith J, Morgan R (March 2020). «COVID-19: the gendered impacts of the outbreak». Lancet. 395 (10227): 846–848. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30526-2. PMC 7124625. PMID 32151325.
- ^ Tolchin B, Hull SC, Kraschel K (October 2020). «Triage and justice in an unjust pandemic: ethical allocation of scarce medical resources in the setting of racial and socioeconomic disparities». Journal of Medical Ethics. 47 (3): 200–202. doi:10.1136/medethics-2020-106457. PMID 33067315. S2CID 223558059.
- ^ Sabatello M, Burke TB, McDonald KE, Appelbaum PS (October 2020). «Disability, Ethics, and Health Care in the COVID-19 Pandemic». American Journal of Public Health. 110 (10): 1523–1527. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2020.305837. PMC 7483109. PMID 32816541.
- ^ Chin T, Kahn R, Li R, Chen JT, Krieger N, Buckee CO, et al. (September 2020). «US-county level variation in intersecting individual, household and community characteristics relevant to COVID-19 and planning an equitable response: a cross-sectional analysis». BMJ Open. 10 (9): e039886. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039886. PMC 7467554. PMID 32873684.
- ^ Elgar FJ, Stefaniak A, Wohl MJ (October 2020). «The trouble with trust: Time-series analysis of social capital, income inequality, and COVID-19 deaths in 84 countries». Social Science & Medicine. 263: 113365. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113365. PMC 7492158. PMID 32981770.
- ^ Uttley H (2 March 2021). «Pandemic sends demand for cold and flu remedies to record low». The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ^ «2020–2021 Flu Season Summary». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 25 October 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
Further reading
- Erola Pairo-Castineira; Sara Clohisey; Lucija Klarić; et al. (11 December 2020). «Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in Covid-19». Nature. doi:10.1038/S41586-020-03065-Y. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 33307546. Wikidata Q104287299. Scholia Q104287299.
- «Progress report on the coronavirus pandemic». Nature. 584 (7821): 325. 1 August 2020. doi:10.1038/D41586-020-02414-1. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 32814893. Wikidata Q98568681.
- COVID-19 infection prevention and control measures for primary care, including general practitioner practices, dental clinics and pharmacy settings: first update. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) (Report). October 2020.
External links
Health agencies
- Coronavirus disease (COVID‑19) Facts by the World Health Organization (WHO)
- Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Coronavirus (COVID‑19) by the UK National Health Service (NHS)
Directories
- Coronavirus Resource Center at the Center for Inquiry
- COVID-19 at Curlie
- COVID‑19 Resource Directory on OpenMD
- COVID‑19 Information on FireMountain.net Archived 13 January 2022 at the Wayback Machine
Medical journals
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‑19) by JAMA
- BMJ’s Coronavirus (covid‑19) Hub by the BMJ
- Novel Coronavirus Information Center by Elsevier
- COVID‑19 Resource Centre by The Lancet
- Coronavirus (COVID‑19) Research Highlights by Springer Nature
- Coronavirus (Covid‑19) by The New England Journal of Medicine
- Covid‑19: Novel Coronavirus Archived 24 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine by Wiley Publishing
Treatment guidelines
- «JHMI Clinical Recommendations for Available Pharmacologic Therapies for COVID-19» (PDF). Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- «Bouncing Back From COVID-19: Your Guide to Restoring Movement» (PDF). Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- «Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19». Infectious Diseases Society of America.
- «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines» (PDF). National Institutes of Health.
- World Health Organization (2022). Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline, 14 January 2022 (Report). hdl:10665/351006. WHO/2019-nCoV/therapeutics/2022.1.
- NHS England and NHS Improvement. National Guidance for post-COVID syndrome assessment clinics (Report).
«Covid» redirects here. Not to be confused with corvid.
| Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) |
|
|---|---|
| Other names | COVID, (the) coronavirus |
 |
|
|
Transmission and life-cycle of SARS-CoV-2 causing COVID-19 |
|
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, vomiting, loss of taste or smell; some cases asymptomatic[2][3] |
| Complications | Pneumonia, viral sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, kidney failure, cytokine release syndrome, respiratory failure, pulmonary fibrosis, paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, long COVID |
| Usual onset | 2–14 days (typically 5) from infection |
| Duration | 5 days to chronic |
| Causes | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) |
| Diagnostic method | rRT‑PCR testing, CT scan, Rapid antigen test |
| Prevention | Vaccination,[4] face coverings, quarantine, physical/social distancing, ventilation, hand washing[5] |
| Treatment | Symptomatic and supportive |
| Frequency | 664,338,243[6] confirmed cases |
| Deaths | 6,707,311[6] |
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.[7] The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever,[8] cough, headache,[9] fatigue, breathing difficulties, loss of smell, and loss of taste.[10][11][12] Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected do not develop noticeable symptoms.[13] Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction).[14] Older people are at a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some people continue to experience a range of effects (long COVID) for months after recovery, and damage to organs has been observed.[15] Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the long-term effects of the disease.[15]
COVID‑19 transmits when people breathe air contaminated by droplets and small airborne particles containing the virus. The risk of breathing these is highest when people are in close proximity, but they can be inhaled over longer distances, particularly indoors. Transmission can also occur if contaminated fluids are splashed or sprayed in the eyes, nose, or mouth, or, more rarely, via contaminated surfaces. People remain contagious for up to 20 days and can spread the virus even if they do not develop symptoms.[16][17]
Testing methods for COVID-19 to detect the virus’s nucleic acid include real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT‑PCR),[18][19] transcription-mediated amplification,[18][19][20] and reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT‑LAMP)[18][19] from a nasopharyngeal swab.[21]
Several COVID-19 vaccines have been approved and distributed in various countries, which have initiated mass vaccination campaigns. Other preventive measures include physical or social distancing, quarantining, ventilation of indoor spaces, use of face masks or coverings in public, covering coughs and sneezes, hand washing, and keeping unwashed hands away from the face. While work is underway to develop drugs that inhibit the virus, the primary treatment is symptomatic. Management involves the treatment of symptoms through supportive care, isolation, and experimental measures.
Nomenclature
During the initial outbreak in Wuhan, the virus and disease were commonly referred to as «coronavirus» and «Wuhan coronavirus»,[22][23][24] with the disease sometimes called «Wuhan pneumonia».[25][26] In the past, many diseases have been named after geographical locations, such as the Spanish flu,[27] Middle East respiratory syndrome, and Zika virus.[28] In January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended 2019-nCoV[29] and 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease[30] as interim names for the virus and disease per 2015 guidance and international guidelines against using geographical locations or groups of people in disease and virus names to prevent social stigma.[31][32][33] The official names COVID‑19 and SARS-CoV-2 were issued by the WHO on 11 February 2020 with COVID-19 being shorthand for «coronavirus disease 2019».[34][35] The WHO additionally uses «the COVID‑19 virus» and «the virus responsible for COVID‑19» in public communications.[34][36]
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of COVID-19 are variable depending on the type of variant contracted, ranging from mild symptoms to a potentially fatal illness.[37][38] Common symptoms include coughing, fever, loss of smell (anosmia) and taste (ageusia), with less common ones including headaches, nasal congestion and runny nose, muscle pain, sore throat, diarrhea, eye irritation,[39] and toes swelling or turning purple,[40] and in moderate to severe cases, breathing difficulties.[41] People with the COVID-19 infection may have different symptoms, and their symptoms may change over time. Three common clusters of symptoms have been identified: one respiratory symptom cluster with cough, sputum, shortness of breath, and fever; a musculoskeletal symptom cluster with muscle and joint pain, headache, and fatigue; and a cluster of digestive symptoms with abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.[41] In people without prior ear, nose, or throat disorders, loss of taste combined with loss of smell is associated with COVID-19 and is reported in as many as 88% of symptomatic cases.[42][43][44]
Of people who show symptoms, 81% develop only mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging) that require hospitalization, and 5% of patients develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, septic shock, or multiorgan dysfunction) requiring ICU admission.[45] At least a third of the people who are infected with the virus do not develop noticeable symptoms at any point in time.[46][47] These asymptomatic carriers tend not to get tested and can still spread the disease.[47][48][49][50] Other infected people will develop symptoms later (called «pre-symptomatic») or have very mild symptoms and can also spread the virus.[50]
As is common with infections, there is a delay between the moment a person first becomes infected and the appearance of the first symptoms. The median delay for COVID-19 is four to five days[51] possibly being infectious on 1-4 of those days.[52] Most symptomatic people experience symptoms within two to seven days after exposure, and almost all will experience at least one symptom within 12 days.[51][53]
Most people recover from the acute phase of the disease. However, some people—over half of a cohort of home-isolated young adults identified in June, 2021[54][55] continued to experience a range of effects, such as fatigue, for months even after recovery. This is the result of a condition called long COVID, which can be described as a range of persistent symptoms that continue for weeks and/or months at a time.[56] Long-term damage to organs has also been observed after the onset of COVID-19. Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the potential long-term effects of the disease.[57]
The Omicron variant became dominant in the U.S. in December 2021. Symptoms with the Omicron variant are less severe than they are with other variants.[58]
Cause
COVID‑19 is caused by infection with a strain of coronavirus known as ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2’ (SARS-CoV-2).[59]
Transmission
| Transmission of COVID-19 | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Mode of spread of COVID-19 |
 |
|
| Specialty | Infection prevention and control |
| Types | Respiratory droplet, airborne transmission, fomites |
| Prevention | Face coverings, quarantine, physical/social distancing, ventilation, hand washing, vaccination |
COVID-19 is mainly transmitted when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets/aerosols and small airborne particles containing the virus. Infected people exhale those particles as they breathe, talk, cough, sneeze, or sing.[60][61][62][63] Transmission is more likely the more physically close people are. However, infection can occur over longer distances, particularly indoors.[60][64]
Infectivity can begin four to five days before the onset of symptoms,[65] although contact tracing typically begins only two to three days before symptom onset.[66] Infected people can spread the disease even if they are pre-symptomatic or asymptomatic.[66] Most commonly, the peak viral load in upper respiratory tract samples occurs close to the time of symptom onset and declines after the first week after symptoms begin.[66] Current evidence suggests a duration of viral shedding and the period of infectiousness of up to ten days following symptom onset for people with mild to moderate COVID-19, and up to 20 days for persons with severe COVID-19, including immunocompromised people.[67][66]
Infectious particles range in size from aerosols that remain suspended in the air for long periods of time to larger droplets that remain airborne briefly or fall to the ground.[68][69][70][71] Additionally, COVID-19 research has redefined the traditional understanding of how respiratory viruses are transmitted.[71][72] The largest droplets of respiratory fluid do not travel far, but can be inhaled or land on mucous membranes on the eyes, nose, or mouth to infect.[70] Aerosols are highest in concentration when people are in close proximity, which leads to easier viral transmission when people are physically close,[70][71][72] but airborne transmission can occur at longer distances, mainly in locations that are poorly ventilated;[70] in those conditions small particles can remain suspended in the air for minutes to hours.[70]
The number of people generally infected by one infected person varies,[73] but it is estimated that the R0 («R nought» or «R zero») number is around 2.5.[74] The disease often spreads in clusters, where infections can be traced back to an index case or geographical location.[75] Often in these instances, superspreading events occur, where many people are infected by one person.[73]
Virology
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. It was first isolated from three people with pneumonia connected to the cluster of acute respiratory illness cases in Wuhan.[76] All structural features of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus particle occur in related coronaviruses in nature.[77]
Outside the human body, the virus is destroyed by household soap, which bursts its protective bubble.[78]
SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to the original SARS-CoV.[79] It is thought to have an animal (zoonotic) origin. Genetic analysis has revealed that the coronavirus genetically clusters with the genus Betacoronavirus, in subgenus Sarbecovirus (lineage B) together with two bat-derived strains. It is 96% identical at the whole genome level to other bat coronavirus samples (BatCov RaTG13).[80][81][82] The structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 include membrane glycoprotein (M), envelope protein (E), nucleocapsid protein (N), and the spike protein (S). The M protein of SARS-CoV-2 is about 98% similar to the M protein of bat SARS-CoV, maintains around 98% homology with pangolin SARS-CoV, and has 90% homology with the M protein of SARS-CoV; whereas, the similarity is only around 38% with the M protein of MERS-CoV.[83]
SARS-CoV-2 variants
The many thousands of SARS-CoV-2 variants are grouped into either clades or lineages.[84][85] The WHO, in collaboration with partners, expert networks, national authorities, institutions and researchers, have established nomenclature systems for naming and tracking SARS-CoV-2 genetic lineages by GISAID, Nextstrain and Pango. The expert group convened by the WHO recommended the labelling of variants using letters of the Greek alphabet, for example, Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Gamma, giving the justification that they «will be easier and more practical to discussed by non-scientific audiences.»[86] Nextstrain divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while GISAID divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR).[87] The Pango tool groups variants into lineages, with many circulating lineages being classed under the B.1 lineage.[85][88]
Several notable variants of SARS-CoV-2 emerged throughout 2020.[89][90] Cluster 5 emerged among minks and mink farmers in Denmark.[91] After strict quarantines and a mink euthanasia campaign, the cluster was assessed to no longer be circulating among humans in Denmark as of 1 February 2021.[92]
As of December 2021, there are five dominant variants of SARS-CoV-2 spreading among global populations: the Alpha variant (B.1.1.7, formerly called the UK variant), first found in London and Kent, the Beta variant (B.1.351, formerly called the South Africa variant), the Gamma variant (P.1, formerly called the Brazil variant), the Delta variant (B.1.617.2, formerly called the India variant),[93] and the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529), which had spread to 57 countries as of 7 December.[94][95]
Pathophysiology
The SARS-CoV-2 virus can infect a wide range of cells and systems of the body. COVID‑19 is most known for affecting the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) and the lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs).[96] The lungs are the organs most affected by COVID‑19 because the virus accesses host cells via the receptor for the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is most abundant on the surface of type II alveolar cells of the lungs.[97] The virus uses a special surface glycoprotein called a «spike» to connect to the ACE2 receptor and enter the host cell.[98]
Respiratory tract
Following viral entry, COVID‑19 infects the ciliated epithelium of the nasopharynx and upper airways.[99]
Nervous system
One common symptom, loss of smell, results from infection of the support cells of the olfactory epithelium, with subsequent damage to the olfactory neurons.[100] The involvement of both the central and peripheral nervous system in COVID‑19 has been reported in many medical publications.[101] It is clear that many people with COVID-19 exhibit neurological or mental health issues. The virus is not detected in the central nervous system (CNS) of the majority of COVID-19 patients with neurological issues. However, SARS-CoV-2 has been detected at low levels in the brains of those who have died from COVID‑19, but these results need to be confirmed.[102] While virus has been detected in cerebrospinal fluid of autopsies, the exact mechanism by which it invades the CNS remains unclear and may first involve invasion of peripheral nerves given the low levels of ACE2 in the brain.[103][104][105] The virus may also enter the bloodstream from the lungs and cross the blood–brain barrier to gain access to the CNS, possibly within an infected white blood cell.[102]
Research conducted when Alpha was the dominant variant has suggested COVID-19 may cause brain damage. It is unknown if such damage is temporary or permanent, and whether Omicron has similar effects.[106][107] Observed individuals infected with COVID-19 (most with mild cases) experienced an additional 0.2% to 2% of brain tissue lost in regions of the brain connected to the sense of smell compared with uninfected individuals, and the overall effect on the brain was equivalent on average to at least one extra year of normal ageing; infected individuals also scored lower on several cognitive tests. All effects were more pronounced among older ages.[108]
Gastrointestinal tract
The virus also affects gastrointestinal organs as ACE2 is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelium[109] as well as endothelial cells and enterocytes of the small intestine.[110]
Cardiovascular system
The virus can cause acute myocardial injury and chronic damage to the cardiovascular system.[111][112] An acute cardiac injury was found in 12% of infected people admitted to the hospital in Wuhan, China,[113] and is more frequent in severe disease.[114] Rates of cardiovascular symptoms are high, owing to the systemic inflammatory response and immune system disorders during disease progression, but acute myocardial injuries may also be related to ACE2 receptors in the heart.[112] ACE2 receptors are highly expressed in the heart and are involved in heart function.[112][115]
A high incidence of thrombosis and venous thromboembolism occurs in people transferred to intensive care units with COVID‑19 infections, and may be related to poor prognosis.[116] Blood vessel dysfunction and clot formation (as suggested by high D-dimer levels caused by blood clots) may have a significant role in mortality, incidences[spelling?] of clots leading to pulmonary embolisms, and ischaemic events within the brain found as complications leading to death in people infected with COVID‑19.[117] Infection may initiate a chain of vasoconstrictive responses within the body, including pulmonary vasoconstriction – a possible mechanism in which oxygenation decreases during pneumonia.[117] Furthermore, damage of arterioles and capillaries was found in brain tissue samples of people who died from COVID‑19.[118][119]
COVID‑19 may also cause substantial structural changes to blood cells, sometimes persisting for months after hospital discharge.[120] A low level of blood lymphocytes may result from the virus acting through ACE2-related entry into lymphocytes.[121]
Other organs
Another common cause of death is complications related to the kidneys.[117] Early reports show that up to 30% of hospitalised patients both in China and in New York have experienced some injury to their kidneys, including some persons with no previous kidney problems.[122]
Autopsies of people who died of COVID‑19 have found diffuse alveolar damage, and lymphocyte-containing inflammatory infiltrates within the lung.[123]
Immunopathology
Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL‑2, IL‑7, IL‑6, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM‑CSF), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP‑10), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1), macrophage inflammatory protein 1‑alpha (MIP‑1‑alpha), and tumour necrosis factor (TNF‑α) indicative of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) suggest an underlying immunopathology.[113]
Interferon alpha plays a complex, Janus-faced role in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Although it promotes the elimination of virus-infected cells, it also upregulates the expression of ACE-2, thereby facilitating the SARS-Cov2 virus to enter cells and to replicate.[124][125] A competition of negative feedback loops (via protective effects of interferon alpha) and positive feedback loops (via upregulation of ACE-2) is assumed to determine the fate of patients suffering from COVID-19.[126]
Additionally, people with COVID‑19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) have classical serum biomarkers of CRS, including elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), D-dimer, and ferritin.[127]
Systemic inflammation results in vasodilation, allowing inflammatory lymphocytic and monocytic infiltration of the lung and the heart. In particular, pathogenic GM-CSF-secreting T cells were shown to correlate with the recruitment of inflammatory IL-6-secreting monocytes and severe lung pathology in people with COVID‑19.[128] Lymphocytic infiltrates have also been reported at autopsy.[123]
Viral and host factors
Virus proteins
Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the ACE2 receptors. It includes two subunits: S1 and S2. S1 determines the virus-host range and cellular tropism via the receptor-binding domain. S2 mediates the membrane fusion of the virus to its potential cell host via the H1 and HR2, which are heptad repeat regions. Studies have shown that S1 domain induced IgG and IgA antibody levels at a much higher capacity. It is the focus spike proteins expression that are involved in many effective COVID‑19 vaccines.[129]
The M protein is the viral protein responsible for the transmembrane transport of nutrients. It is the cause of the bud release and the formation of the viral envelope.[130] The N and E protein are accessory proteins that interfere with the host’s immune response.[130]
Host factors
Human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) is the host factor that SARS-CoV-2 virus targets causing COVID‑19. Theoretically, the usage of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) and ACE inhibitors upregulating ACE2 expression might increase morbidity with COVID‑19, though animal data suggest some potential protective effect of ARB; however no clinical studies have proven susceptibility or outcomes. Until further data is available, guidelines and recommendations for hypertensive patients remain.[131]
The effect of the virus on ACE2 cell surfaces leads to leukocytic infiltration, increased blood vessel permeability, alveolar wall permeability, as well as decreased secretion of lung surfactants. These effects cause the majority of the respiratory symptoms. However, the aggravation of local inflammation causes a cytokine storm eventually leading to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome.[132]
Among healthy adults not exposed to SARS-CoV-2, about 35% have CD4+ T cells that recognise the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (particularly the S2 subunit) and about 50% react to other proteins of the virus, suggesting cross-reactivity from previous common colds caused by other coronaviruses.[133]
It is unknown whether different persons use similar antibody genes in response to COVID‑19.[134]
Host cytokine response
The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the cytokine storm.[135] Levels of interleukin 1B, interferon-gamma, interferon-inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 were all associated with COVID‑19 disease severity. Treatment has been proposed to combat the cytokine storm as it remains to be one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in COVID‑19 disease.[136]
A cytokine storm is due to an acute hyperinflammatory response that is responsible for clinical illness in an array of diseases but in COVID‑19, it is related to worse prognosis and increased fatality. The storm causes acute respiratory distress syndrome, blood clotting events such as strokes, myocardial infarction, encephalitis, acute kidney injury, and vasculitis. The production of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and interferon-gamma, all crucial components of normal immune responses, inadvertently become the causes of a cytokine storm. The cells of the central nervous system, the microglia, neurons, and astrocytes, are also involved in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines affecting the nervous system, and effects of cytokine storms toward the CNS are not uncommon.[137]
Pregnancy response
There are many unknowns for pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic. Given that they are prone to have complications and severe disease infection with other types of coronaviruses, they have been identified as a vulnerable group and advised to take supplementary preventive measures.[138]
Physiological responses to pregnancy can include:
- Immunological: The immunological response to COVID-19, like other viruses, depends on a working immune system. It adapts during pregnancy to allow the development of the foetus whose genetic load is only partially shared with their mother, leading to a different immunological reaction to infections during the course of pregnancy.[138]
- Respiratory: Many factors can make pregnant women more vulnerable to hard respiratory infections. One of them is the total reduction of the lungs’ capacity and inability to clear secretions.[138]
- Coagulation: During pregnancy, there are higher levels of circulating coagulation factors, and the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection can be implicated. The thromboembolic events with associated mortality are a risk for pregnant women.[138]
However, from the evidence base, it is difficult to conclude whether pregnant women are at increased risk of grave consequences of this virus.[138]
In addition to the above, other clinical studies have proved that SARS-CoV-2 can affect the period of pregnancy in different ways. On the one hand, there is little evidence of its impact up to 12 weeks gestation. On the other hand, COVID-19 infection may cause increased rates of unfavourable outcomes in the course of the pregnancy. Some examples of these could be foetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and perinatal mortality, which refers to the foetal death past 22 or 28 completed weeks of pregnancy as well as the death among live-born children up to seven completed days of life.[138]
Unvaccinated women in later stages of pregnancy with COVID-19 are more likely than other patients to need very intensive care. Babies born to mothers with COVID-19 are more likely to have breathing problems. Pregnant women are strongly encouraged to get vaccinated.[139]
Diagnosis
COVID‑19 can provisionally be diagnosed on the basis of symptoms and confirmed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or other nucleic acid testing of infected secretions.[21][140] Along with laboratory testing, chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection.[141] Detection of a past infection is possible with serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the infection.[21]
Viral testing
The standard methods of testing for presence of SARS-CoV-2 are nucleic acid tests,[21][142] which detects the presence of viral RNA fragments.[143] As these tests detect RNA but not infectious virus, its «ability to determine duration of infectivity of patients is limited.»[144] The test is typically done on respiratory samples obtained by a nasopharyngeal swab; however, a nasal swab or sputum sample may also be used.[145][146] Results are generally available within hours.[21] The WHO has published several testing protocols for the disease.[147]
Several laboratories and companies have developed serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to infection. Several have been evaluated by Public Health England and approved for use in the UK.[148]
The University of Oxford’s CEBM has pointed to mounting evidence[149][150] that «a good proportion of ‘new’ mild cases and people re-testing positives after quarantine or discharge from hospital are not infectious, but are simply clearing harmless virus particles which their immune system has efficiently dealt with» and have called for «an international effort to standardize and periodically calibrate testing»[151] In September 2020, the UK government issued «guidance for procedures to be implemented in laboratories to provide assurance of positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA results during periods of low prevalence, when there is a reduction in the predictive value of positive test results».[152]
Imaging
A CT scan of a person with COVID-19 shows lesions (bright regions) in the lungs
CT scan of rapid progression stage of COVID-19
Chest X-ray showing COVID‑19 pneumonia
Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening.[141][153] Bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacities with a peripheral, asymmetric, and posterior distribution are common in early infection.[141][154] Subpleural dominance, crazy paving (lobular septal thickening with variable alveolar filling), and consolidation may appear as the disease progresses.[141][155] Characteristic imaging features on chest radiographs and computed tomography (CT) of people who are symptomatic include asymmetric peripheral ground-glass opacities without pleural effusions.[156]
Many groups have created COVID‑19 datasets that include imagery such as the Italian Radiological Society which has compiled an international online database of imaging findings for confirmed cases.[157] Due to overlap with other infections such as adenovirus, imaging without confirmation by rRT-PCR is of limited specificity in identifying COVID‑19.[156] A large study in China compared chest CT results to PCR and demonstrated that though imaging is less specific for the infection, it is faster and more sensitive.[140]
Coding
In late 2019, the WHO assigned emergency ICD-10 disease codes U07.1 for deaths from lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and U07.2 for deaths from clinically or epidemiologically diagnosed COVID‑19 without lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.[158]
Pathology
The main pathological findings at autopsy are:
- Macroscopy: pericarditis, lung consolidation and pulmonary oedema[123]
- Lung findings:
- minor serous exudation, minor fibrin exudation[123]
- pulmonary oedema, pneumocyte hyperplasia, large atypical pneumocytes, interstitial inflammation with lymphocytic infiltration and multinucleated giant cell formation[123]
- diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) with diffuse alveolar exudates. DAD is the cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and severe hypoxaemia.[123]
- organisation of exudates in alveolar cavities and pulmonary interstitial fibrosis[123]
- plasmocytosis in BAL[159]
- Blood and vessels: disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC);[160] leukoerythroblastic reaction,[161] endotheliitis,[162] hemophagocytosis[162]
- Heart: cardiac muscle cell necrosis[162]
- Liver: microvesicular steatosis[123]
- Nose: shedding of olfactory epithelium[100]
- Brain: infarction[162]
- Kidneys: acute tubular damage.[162]
- Spleen: white pulp depletion.[162]
Prevention
Without pandemic containment measures – such as social distancing, vaccination, and face masks – pathogens can spread exponentially.[163] This graphic shows how early adoption of containment measures tends to protect wider swaths of the population.
Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations,[164] washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.[165][166]
Those diagnosed with COVID‑19 or who believe they may be infected are advised by the CDC to stay home except to get medical care, call ahead before visiting a healthcare provider, wear a face mask before entering the healthcare provider’s office and when in any room or vehicle with another person, cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue, regularly wash hands with soap and water and avoid sharing personal household items.[167][168]
The first COVID‑19 vaccine was granted regulatory approval on 2 December 2020 by the UK medicines regulator MHRA.[169] It was evaluated for emergency use authorization (EUA) status by the US FDA, and in several other countries.[170] Initially, the US National Institutes of Health guidelines do not recommend any medication for prevention of COVID‑19, before or after exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, outside the setting of a clinical trial.[171][172] Without a vaccine, other prophylactic measures, or effective treatments, a key part of managing COVID‑19 is trying to decrease and delay the epidemic peak, known as «flattening the curve».[173] This is done by slowing the infection rate to decrease the risk of health services being overwhelmed, allowing for better treatment of active cases, and delaying additional cases until effective treatments or a vaccine become available.[173][174]
Vaccine
Different vaccine candidate types in development for SARS-CoV-2
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
Prior to the COVID‑19 pandemic, an established body of knowledge existed about the structure and function of coronaviruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This knowledge accelerated the development of various vaccine platforms during early 2020.[175] The initial focus of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was on preventing symptomatic, often severe illness.[176] In January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequence data was shared through GISAID, and by March 2020, the global pharmaceutical industry announced a major commitment to address COVID‑19.[177] In 2020, the first COVID‑19 vaccines were developed and made available to the public through emergency authorizations[178] and conditional approvals.[179][180] Initially, most COVID‑19 vaccines were two-dose vaccines, with the sole exception being the single-dose Janssen COVID-19 vaccine.[178] However, immunity from the vaccines has been found to wane over time, requiring people to get booster doses of the vaccine to maintain protection against COVID‑19.[178]
Face masks and respiratory hygiene
Masks with an exhalation valve. The valves are a weak point that can transmit the viruses outwards.
The WHO and the US CDC recommend individuals wear non-medical face coverings in public settings where there is an increased risk of transmission and where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain.[181][182] This recommendation is meant to reduce the spread of the disease by asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic individuals and is complementary to established preventive measures such as social distancing.[182][183] Face coverings limit the volume and travel distance of expiratory droplets dispersed when talking, breathing, and coughing.[182][183] A face covering without vents or holes will also filter out particles containing the virus from inhaled and exhaled air, reducing the chances of infection.[184] However, if the mask includes an exhalation valve, a wearer that is infected (and possibly asymptomatic) may transmit the virus through the valve. Many countries and local jurisdictions encourage or mandate the use of face masks or cloth face coverings by members of the public to limit the spread of the virus.[185]
Masks are also strongly recommended for those who may have been infected and those taking care of someone who may have the disease.[186] When not wearing a mask, the CDC recommends covering the mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing and recommends using the inside of the elbow if no tissue is available. Proper hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is encouraged. Healthcare professionals interacting directly with people who have COVID‑19 are advised to use respirators at least as protective as NIOSH-certified N95 or equivalent, in addition to other personal protective equipment.[187]
Indoor ventilation and avoiding crowded indoor spaces
The CDC recommends that crowded indoor spaces should be avoided.[188] When indoors, increasing the rate of air change, decreasing recirculation of air and increasing the use of outdoor air can reduce transmission.[188][189] The WHO recommends ventilation and air filtration in public spaces to help clear out infectious aerosols.[190][191][192]
Exhaled respiratory particles can build-up within enclosed spaces with inadequate ventilation. The risk of COVID‑19 infection increases especially in spaces where people engage in physical exertion or raise their voice (e.g., exercising, shouting, singing) as this increases exhalation of respiratory droplets. Prolonged exposure to these conditions, typically more than 15 minutes, leads to higher risk of infection.[188]
Displacement ventilation with large natural inlets can move stale air directly to the exhaust in laminar flow while significantly reducing the concentration of droplets and particles. Passive ventilation reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs but may lack controllability and heat recovery. Displacement ventilation can also be achieved mechanically with higher energy and maintenance costs. The use of large ducts and openings helps to prevent mixing in closed environments. Recirculation and mixing should be avoided because recirculation prevents dilution of harmful particles and redistributes possibly contaminated air, and mixing increases the concentration and range of infectious particles and keeps larger particles in the air.[193]
Hand-washing and hygiene
Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required.[194] The WHO also recommends that individuals wash hands often with soap and water for at least twenty seconds, especially after going to the toilet or when hands are visibly dirty, before eating and after blowing one’s nose.[195] When soap and water are not available, the CDC recommends using an alcohol-based hand sanitiser with at least 60% alcohol.[196] For areas where commercial hand sanitisers are not readily available, the WHO provides two formulations for local production. In these formulations, the antimicrobial activity arises from ethanol or isopropanol. Hydrogen peroxide is used to help eliminate bacterial spores in the alcohol; it is «not an active substance for hand antisepsis.» Glycerol is added as a humectant.[197]
Social distancing (also known as physical distancing) includes infection control actions intended to slow the spread of the disease by minimising close contact between individuals. Methods include quarantines; travel restrictions; and the closing of schools, workplaces, stadiums, theatres, or shopping centres. Individuals may apply social distancing methods by staying at home, limiting travel, avoiding crowded areas, using no-contact greetings, and physically distancing themselves from others.[198] Many governments are mandating or recommending social distancing in regions affected by the outbreak.[199]
Outbreaks have occurred in prisons due to crowding and an inability to enforce adequate social distancing.[200][201] In the United States, the prisoner population is ageing and many of them are at high risk for poor outcomes from COVID‑19 due to high rates of coexisting heart and lung disease, and poor access to high-quality healthcare.[200]
Surface cleaning
After being expelled from the body, coronaviruses can survive on surfaces for hours to days. If a person touches the dirty surface, they may deposit the virus at the eyes, nose, or mouth where it can enter the body and cause infection.[202] Evidence indicates that contact with infected surfaces is not the main driver of COVID‑19,[203][204][205] leading to recommendations for optimised disinfection procedures to avoid issues such as the increase of antimicrobial resistance through the use of inappropriate cleaning products and processes.[206][207] Deep cleaning and other surface sanitation has been criticised as hygiene theatre, giving a false sense of security against something primarily spread through the air.[208][209]
The amount of time that the virus can survive depends significantly on the type of surface, the temperature, and the humidity.[210] Coronaviruses die very quickly when exposed to the UV light in sunlight.[210] Like other enveloped viruses, SARS-CoV-2 survives longest when the temperature is at room temperature or lower, and when the relative humidity is low (<50%).[210]
On many surfaces, including glass, some types of plastic, stainless steel, and skin, the virus can remain infective for several days indoors at room temperature, or even about a week under ideal conditions.[210][211] On some surfaces, including cotton fabric and copper, the virus usually dies after a few hours.[210] The virus dies faster on porous surfaces than on non-porous surfaces due to capillary action within pores and faster aerosol droplet evaporation.[212][205][210] However, of the many surfaces tested, two with the longest survival times are N95 respirator masks and surgical masks, both of which are considered porous surfaces.[210]
The CDC says that in most situations, cleaning surfaces with soap or detergent, not disinfecting, is enough to reduce risk of transmission.[213][214] The CDC recommends that if a COVID‑19 case is suspected or confirmed at a facility such as an office or day care, all areas such as offices, bathrooms, common areas, shared electronic equipment like tablets, touch screens, keyboards, remote controls, and ATMs used by the ill persons should be disinfected.[215] Surfaces may be decontaminated with 62–71 per cent ethanol, 50–100 per cent isopropanol, 0.1 per cent sodium hypochlorite, 0.5 per cent hydrogen peroxide, 0.2–7.5 per cent povidone-iodine, or 50–200 ppm hypochlorous acid. Other solutions, such as benzalkonium chloride and chlorhexidine gluconate, are less effective. Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation may also be used,[190] although popular devices require 5–10 min exposure and may deteriorate some materials over time.[216] A datasheet comprising the authorised substances to disinfection in the food industry (including suspension or surface tested, kind of surface, use dilution, disinfectant and inocuylum volumes) can be seen in the supplementary material of.[206]
Self-isolation
Self-isolation at home has been recommended for those diagnosed with COVID‑19 and those who suspect they have been infected. Health agencies have issued detailed instructions for proper self-isolation.[217] Many governments have mandated or recommended self-quarantine for entire populations. The strongest self-quarantine instructions have been issued to those in high-risk groups.[218] Those who may have been exposed to someone with COVID‑19 and those who have recently travelled to a country or region with the widespread transmission have been advised to self-quarantine for 14 days from the time of last possible exposure.[219]
A 2021 Cochrane rapid review found that based upon low-certainty evidence, international travel-related control measures such as restricting cross-border travel may help to contain the spread of COVID‑19.[220] Additionally, symptom/exposure-based screening measures at borders may miss many positive cases.[220] While test-based border screening measures may be more effective, it could also miss many positive cases if only conducted upon arrival without follow-up. The review concluded that a minimum 10-day quarantine may be beneficial in preventing the spread of COVID‑19 and may be more effective if combined with an additional control measure like border screening.[220]
Treatment
An overview of COVID-19 therapeutics and drugs
Although several medications have been approved in different countries as of April 2022, not all countries have these medications. Patients with mild to moderate symptoms who are in the risk groups can take nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (marketed as Paxlovid) or remdesivir, either of which reduces the risk of serious illness or hospitalization.[221] In the US, the Biden Administration COVID-19 action plan includes the Test to Treat initiative, where people can go to a pharmacy, take a COVID test, and immediately receive free Paxlovid if they test positive.[222]
Highly effective vaccines have reduced mortality related to SARS-CoV-2; however, for those awaiting vaccination, as well as for the estimated millions of immunocompromised persons who are unlikely to respond robustly to vaccination, treatment remains important.[223] The cornerstone of management of COVID-19 has been supportive care, which includes treatment to relieve symptoms, fluid therapy, oxygen support and prone positioning as needed, and medications or devices to support other affected vital organs.[224][225][226]
Most cases of COVID-19 are mild. In these, supportive care includes medication such as paracetamol or NSAIDs to relieve symptoms (fever, body aches, cough), proper intake of fluids, rest, and nasal breathing.[227][228][229][230] Good personal hygiene and a healthy diet are also recommended.[231] As of April 2020 the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended that those who suspect they are carrying the virus isolate themselves at home and wear a face mask.[232]
As of November 2020 use of the glucocorticoid dexamethasone had been strongly recommended in those severe cases treated in hospital with low oxygen levels, to reduce the risk of death.[233][234][235] Noninvasive ventilation and, ultimately, admission to an intensive care unit for mechanical ventilation may be required to support breathing.[236] Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has been used to address respiratory failure, but its benefits are still under consideration.[237][238] Some of the cases of severe disease course are caused by systemic hyper-inflammation, the so-called cytokine storm.[239]
Prognosis and risk factors
The severity of COVID‑19 varies. The disease may take a mild course with few or no symptoms, resembling other common upper respiratory diseases such as the common cold. In 3–4% of cases (7.4% for those over age 65) symptoms are severe enough to cause hospitalisation.[240] Mild cases typically recover within two weeks, while those with severe or critical diseases may take three to six weeks to recover. Among those who have died, the time from symptom onset to death has ranged from two to eight weeks.[80] The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that the median time between the onset of symptoms and death was twelve days, with seven being hospitalised. However, people transferred to an ICU had a median time of ten days between hospitalisation and death.[241] Abnormal sodium levels during hospitalization with COVID-19 are associated with poor prognoses: high sodium with a greater risk of death, and low sodium with an increased chance of needing ventilator support.[242][243] Prolonged prothrombin time and elevated C-reactive protein levels on admission to the hospital are associated with severe course of COVID‑19 and with a transfer to ICU.[244][245]
Some early studies suggest 10% to 20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month.[246][247] A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems including fatigue and shortness of breath.[248] On 30 October 2020, WHO chief Tedros Adhanom warned that «to a significant number of people, the COVID virus poses a range of serious long-term effects.» He has described the vast spectrum of COVID‑19 symptoms that fluctuate over time as «really concerning». They range from fatigue, a cough and shortness of breath, to inflammation and injury of major organs – including the lungs and heart, and also neurological and psychologic effects. Symptoms often overlap and can affect any system in the body. Infected people have reported cyclical bouts of fatigue, headaches, months of complete exhaustion, mood swings, and other symptoms. Tedros therefore concluded that a strategy of achieving herd immunity by infection, rather than vaccination, is «morally unconscionable and unfeasible».[249]
In terms of hospital readmissions about 9% of 106,000 individuals had to return for hospital treatment within two months of discharge. The average to readmit was eight days since first hospital visit. There are several risk factors that have been identified as being a cause of multiple admissions to a hospital facility. Among these are advanced age (above 65 years of age) and presence of a chronic condition such as diabetes, COPD, heart failure or chronic kidney disease.[250][251]
According to scientific reviews smokers are more likely to require intensive care or die compared to non-smokers.[252][253] Acting on the same ACE2 pulmonary receptors affected by smoking, air pollution has been correlated with the disease.[253] Short term[254] and chronic[255] exposure to air pollution seems to enhance morbidity and mortality from COVID‑19.[256][257][258] Pre-existing heart and lung diseases[259] and also obesity, especially in conjunction with fatty liver disease, contributes to an increased health risk of COVID‑19.[253][260][261][262]
It is also assumed that those that are immunocompromised are at higher risk of getting severely sick from SARS-CoV-2.[263] One research study that looked into the COVID‑19 infections in hospitalised kidney transplant recipients found a mortality rate of 11%.[264]
Men with untreated hypogonadism were 2.4 times more likely than men with eugonadism to be hospitalized if they contracted COVID-19; Hypogonad men treated with testosterone were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than men who were not treated for hypogonadism.[265]
Genetic risk factors
Genetics plays an important role in the ability to fight off Covid.[266] For instance, those that do not produce detectable type I interferons or produce auto-antibodies against these may get much sicker from COVID‑19.[267][268] Genetic screening is able to detect interferon effector genes.[269] Some genetic variants are risk factors in specific populations. For instance, and allele of the DOCK2 gene (dedicator of cytokinesis 2 gene) is a common risk factor in Asian populations but much less common in Europe. The mutation leads to lower expression of DOCK2 especially in younger patients with severe Covid.[270] In fact, many other genes and genetic variants have been found that determine the outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infections.[271]
Children
While very young children have experienced lower rates of infection, older children have a rate of infection that is similar to the population as a whole.[272][273] Children are likely to have milder symptoms and are at lower risk of severe disease than adults.[274] The CDC reports that in the US roughly a third of hospitalised children were admitted to the ICU,[275] while a European multinational study of hospitalised children from June 2020, found that about 8% of children admitted to a hospital needed intensive care.[276] Four of the 582 children (0.7%) in the European study died, but the actual mortality rate may be «substantially lower» since milder cases that did not seek medical help were not included in the study.[277][278]
Complications
Complications may include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, septic shock, and death.[279][280][281][282] Cardiovascular complications may include heart failure, arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation), heart inflammation, and thrombosis, particularly venous thromboembolism.[283][284][285][286][287][288] Approximately 20–30% of people who present with COVID‑19 have elevated liver enzymes, reflecting liver injury.[289][172]
Neurologic manifestations include seizure, stroke, encephalitis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome (which includes loss of motor functions).[290][291] Following the infection, children may develop paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, which has symptoms similar to Kawasaki disease, which can be fatal.[292][293] In very rare cases, acute encephalopathy can occur, and it can be considered in those who have been diagnosed with COVID‑19 and have an altered mental status.[294]
In the case of pregnant women, it is important to note that, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, pregnant women are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill from COVID‑19.[295] This is because pregnant women with COVID‑19 appear to be more likely to develop respiratory and obstetric complications that can lead to miscarriage, premature delivery and intrauterine growth restriction.[295]
Fungal infections such as aspergillosis, candidiasis, cryptococcosis and mucormycosis have been recorded in patients recovering from COVID‑19.[296][297]
Longer-term effects
Some early studies suggest that 10–20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month.[298][247] A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems, including fatigue and shortness of breath.[299] About 5–10% of patients admitted to hospital progress to severe or critical disease, including pneumonia and acute respiratory failure.[300]
By a variety of mechanisms, the lungs are the organs most affected in COVID‑19.[301] In people requiring hospital admission, up to 98% of CT scans performed show lung abnormalities after 28 days of illness even if they had clinically improved.[302]
People with advanced age, severe disease, prolonged ICU stays, or who smoke are more likely to have long-lasting effects, including pulmonary fibrosis.[303] Overall, approximately one-third of those investigated after four weeks will have findings of pulmonary fibrosis or reduced lung function as measured by DLCO, even in asymptomatic people, but with the suggestion of continuing improvement with the passing of more time.[301] After severe disease, lung function can take anywhere from three months to a year or more to return to previous levels.[304]
The risks of cognitive deficit, dementia, psychotic disorders, and epilepsy or seizures persists at an increased level two years after infection.[305]
Immunity
The immune response by humans to SARS-CoV-2 virus occurs as a combination of the cell-mediated immunity and antibody production,[306] just as with most other infections.[307] B cells interact with T cells and begin dividing before selection into the plasma cell, partly on the basis of their affinity for antigen.[308] Since SARS-CoV-2 has been in the human population only since December 2019, it remains unknown if the immunity is long-lasting in people who recover from the disease.[309] The presence of neutralising antibodies in blood strongly correlates with protection from infection, but the level of neutralising antibody declines with time. Those with asymptomatic or mild disease had undetectable levels of neutralising antibody two months after infection. In another study, the level of neutralising antibodies fell four-fold one to four months after the onset of symptoms. However, the lack of antibodies in the blood does not mean antibodies will not be rapidly produced upon reexposure to SARS-CoV-2. Memory B cells specific for the spike and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 last for at least six months after the appearance of symptoms.[309]
As of August 2021, reinfection with COVID‑19 was possible but uncommon. The first case of reinfection was documented in August 2020.[310] A systematic review found 17 cases of confirmed reinfection in medical literature as of May 2021.[310] With the Omicron variant, as of 2022, reinfections have become common, albeit it is unclear how common.[311] COVID-19 reinfections are thought to likely be less severe than primary infections, especially if one was previously infected by the same variant.[311][additional citation(s) needed]
Mortality
Several measures are commonly used to quantify mortality.[312] These numbers vary by region and over time and are influenced by the volume of testing, healthcare system quality, treatment options, time since the initial outbreak, and population characteristics such as age, sex, and overall health.[313]
The mortality rate reflects the number of deaths within a specific demographic group divided by the population of that demographic group. Consequently, the mortality rate reflects the prevalence as well as the severity of the disease within a given population. Mortality rates are highly correlated to age, with relatively low rates for young people and relatively high rates among the elderly.[314][315][316] In fact, one relevant factor of mortality rates is the age structure of the countries’ populations. For example, the case fatality rate for COVID‑19 is lower in India than in the US since India’s younger population represents a larger percentage than in the US.[317]
Case fatality rate
The case fatality rate (CFR) reflects the number of deaths divided by the number of diagnosed cases within a given time interval. Based on Johns Hopkins University statistics, the global death-to-case ratio is 1.01% (6,707,311/664,338,243) as of 9 January 2023.[6] The number varies by region.[318][319]
-
Total confirmed cases over time
-
Total confirmed cases of COVID‑19 per million people[320]
-
Total deaths over time
-
Total confirmed deaths due to COVID‑19 per million people[321]
Infection fatality rate
A key metric in gauging the severity of COVID‑19 is the infection fatality rate (IFR), also referred to as the infection fatality ratio or infection fatality risk.[322][323][324] This metric is calculated by dividing the total number of deaths from the disease by the total number of infected individuals; hence, in contrast to the CFR, the IFR incorporates asymptomatic and undiagnosed infections as well as reported cases.[325]
Estimates
The red line shows the estimate of infection fatality rate (IFR), in percentage terms, as a function of age. The shaded region depicts the 95% confidence interval for that estimate. Markers denotes specific observations used in the meta-analysis.[326]
The same relationship plotted on a log scale
A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy.[326] That study also found that most of these differences in IFR reflected corresponding differences in the age composition of the population and age-specific infection rates; in particular, the metaregression estimate of IFR is very low for children and younger adults (e.g., 0.002% at age 10 and 0.01% at age 25) but increases progressively to 0.4% at age 55, 1.4% at age 65, 4.6% at age 75, and 15% at age 85.[326] These results were also highlighted in a December 2020 report issued by the WHO.[327]
| Age group | IFR |
|---|---|
| 0–34 | 0.004% |
| 35–44 | 0.068% |
| 45–54 | 0.23% |
| 55–64 | 0.75% |
| 65–74 | 2.5% |
| 75–84 | 8.5% |
| 85 + | 28.3% |
An analysis of those IFR rates indicates that COVID‑19 is hazardous not only for the elderly but also for middle-aged adults, for whom the infection fatality rate of COVID-19 is two orders of magnitude greater than the annualised risk of a fatal automobile accident and far more dangerous than seasonal influenza.[326]
Earlier estimates of IFR
At an early stage of the pandemic, the World Health Organization reported estimates of IFR between 0.3% and 1%.[328][329] On 2 July, The WHO’s chief scientist reported that the average IFR estimate presented at a two-day WHO expert forum was about 0.6%.[330][331] In August, the WHO found that studies incorporating data from broad serology testing in Europe showed IFR estimates converging at approximately 0.5–1%.[332] Firm lower limits of IFRs have been established in a number of locations such as New York City and Bergamo in Italy since the IFR cannot be less than the population fatality rate. (After sufficient time however, people can get reinfected).[333] As of 10 July, in New York City, with a population of 8.4 million, 23,377 individuals (18,758 confirmed and 4,619 probable) have died with COVID‑19 (0.3% of the population).[334] Antibody testing in New York City suggested an IFR of ≈0.9%,[335] and ≈1.4%.[336] In Bergamo province, 0.6% of the population has died.[337] In September 2020, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported preliminary estimates of age-specific IFRs for public health planning purposes.[338]
Sex differences
| Percentage of infected people who are hospitalised | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.1 (0.07–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
0.9 (0.5–1.5) |
1.3 (0.7–2.1) |
2.6 (1.5–4.2) |
5.1 (2.9–8.3) |
7.8 (4.4–12.8) |
19.3 (10.9–31.6) |
2.6 (1.5–4.3) |
| Male | 0.2 (0.08–0.2) |
0.6 (0.3–0.9) |
1.2 (0.7–1.9) |
1.6 (0.9–2.6) |
3.2 (1.8–5.2) |
6.7 (3.7–10.9) |
11.0 (6.2–17.9) |
37.6 (21.1–61.3) |
3.3 (1.8–5.3) |
| Total | 0.1 (0.08–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
1.1 (0.6–1.7) |
1.4 (0.8–2.3) |
2.9 (1.6–4.7) |
5.8 (3.3–9.5) |
9.3 (5.2–15.1) |
26.2 (14.8–42.7) |
2.9 (1.7–4.8) |
| Percentage of hospitalised people who go to Intensive Care Unit | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 16.7 (14.3–19.3) |
8.7 (7.5–9.9) |
11.9 (10.9–13.0) |
16.6 (15.6–17.7) |
20.7 (19.8–21.6) |
23.1 (22.2–24.0) |
18.7 (18.0–19.5) |
4.2 (4.0–4.5) |
14.3 (13.9–14.7) |
| Male | 26.9 (23.1–31.1) |
14.0 (12.2–16.0) |
19.2 (17.6–20.9) |
26.9 (25.4–28.4) |
33.4 (32.0–34.8) |
37.3 (36.0–38.6) |
30.2 (29.1–31.3) |
6.8 (6.5–7.2) |
23.1 (22.6–23.6) |
| Total | 22.2 (19.1–25.7) |
11.6 (10.1–13.2) |
15.9 (14.5–17.3) |
22.2 (21.0–23.5) |
27.6 (26.5–28.7) |
30.8 (29.8–31.8) |
24.9 (24.1–25.8) |
5.6 (5.3–5.9) |
19.0 (18.7–19.44) |
| Percent of hospitalised people who die | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.5 (0.2–1.0) |
0.9 (0.5–1.3) |
1.5 (1.2–1.9) |
2.6 (2.3–3.0) |
5.2 (4.8–5.6) |
10.1 (9.5–10.6) |
16.7 (16.0–17.4) |
25.2 (24.4–26.0) |
14.4 (14.0–14.8) |
| Male | 0.7 (0.3–1.5) |
1.3 (0.8–1.9) |
2.2 (1.7–2.7) |
3.8 (3.3–4.4) |
7.6 (7.0–8.2) |
14.8 (14.1–15.6) |
24.6 (23.7–25.6) |
37.1 (36.1–38.2) |
21.2 (20.8–21.7) |
| Total | 0.6 (0.2–1.3) |
1.1 (0.7–1.6) |
1.9 (1.5–2.3) |
3.3 (2.9–3.8) |
6.5 (6.0–7.0) |
12.6 (12.0–13.2) |
21.0 (20.3–21.7) |
31.6 (30.9–32.4) |
18.1 (17.8–18.4) |
| Percent of infected people who die – infection fatality rate (IFR) | |||||||||
| 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | 70–79 | 80+ | Total | |
| Female | 0.001 (<0.001–0.002) |
0.004 (0.002–0.007) |
0.01 (0.007–0.02) |
0.03 (0.02–0.06) |
0.1 (0.08–0.2) |
0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
1.3 (0.7–2.1) |
4.9 (2.7–8.0) |
0.4 (0.2–0.6) |
| Male | 0.001 (<0.001–0.003) |
0.007 (0.003–0.01) |
0.03 (0.02–0.05) |
0.06 (0.03–0.1) |
0.2 (0.1–0.4) |
1.0 (0.6–1.6) |
2.7 (1.5–1.4) |
14.0 (7.9–22.7) |
0.7 (0.4–1.1) |
| Total | 0.001 (<0.001–0.002) |
0.005 (0.003–0.01) |
0.02 (0.01–0.03) |
0.05 (0.03–0.08) |
0.2 (0.1–0.3) |
0.7 (0.4–1.2) |
1.9 (1.1–3.2) |
8.3 (4.7–13.5) |
0.5 (0.3–0.9) |
| Numbers in parentheses are 95% credible intervals for the estimates. |
COVID‑19 case fatality rates are higher among men than women in most countries. However, in a few countries like India, Nepal, Vietnam, and Slovenia the fatality cases are higher in women than men.[317] Globally, men are more likely to be admitted to the ICU and more likely to die.[340][341] One meta-analysis found that globally, men were more likely to get COVID‑19 than women; there were approximately 55 men and 45 women per 100 infections (CI: 51.43–56.58).[342]
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported the death rate was 2.8% for men and 1.7% for women.[343] Later reviews in June 2020 indicated that there is no significant difference in susceptibility or in CFR between genders.[344][345] One review acknowledges the different mortality rates in Chinese men, suggesting that it may be attributable to lifestyle choices such as smoking and drinking alcohol rather than genetic factors.[346] Smoking, which in some countries like China is mainly a male activity, is a habit that contributes to increasing significantly the case fatality rates among men.[317] Sex-based immunological differences, lesser prevalence of smoking in women and men developing co-morbid conditions such as hypertension at a younger age than women could have contributed to the higher mortality in men.[347] In Europe as of February 2020, 57% of the infected people were men and 72% of those died with COVID‑19 were men.[348] As of April 2020, the US government is not tracking sex-related data of COVID‑19 infections.[349] Research has shown that viral illnesses like Ebola, HIV, influenza and SARS affect men and women differently.[349]
Ethnic differences
In the US, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred among African Americans and other minority groups.[350] Structural factors that prevent them from practising social distancing include their concentration in crowded substandard housing and in «essential» occupations such as retail grocery workers, public transit employees, health-care workers and custodial staff. Greater prevalence of lacking health insurance and care of underlying conditions such as diabetes,[351] hypertension, and heart disease also increase their risk of death.[352] Similar issues affect Native American and Latino communities.[350] On the one hand, in the Dominican Republic there is a clear example of both gender and ethnic inequality. In this Latin American territory, there is great inequality and precariousness that especially affects Dominican women, with greater emphasis on those of Haitian descent.[353] According to a US health policy non-profit, 34% of American Indian and Alaska Native People (AIAN) non-elderly adults are at risk of serious illness compared to 21% of white non-elderly adults.[354] The source attributes it to disproportionately high rates of many health conditions that may put them at higher risk as well as living conditions like lack of access to clean water.[355]
Leaders have called for efforts to research and address the disparities.[356] In the UK, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred in those of a Black, Asian, and other ethnic minority background.[357][358][359] More severe impacts upon patients including the relative incidence of the necessity of hospitalisation requirements, and vulnerability to the disease has been associated via DNA analysis to be expressed in genetic variants at chromosomal region 3, features that are associated with European Neanderthal heritage. That structure imposes greater risks that those affected will develop a more severe form of the disease.[360] The findings are from Professor Svante Pääbo and researchers he leads at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the Karolinska Institutet.[360] This admixture of modern human and Neanderthal genes is estimated to have occurred roughly between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago in Southern Europe.[360]
Comorbidities
Biological factors (immune response) and the general behaviour (habits) can strongly determine the consequences of COVID‑19.[317] Most of those who die of COVID‑19 have pre-existing (underlying) conditions, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus,[351] and cardiovascular disease.[361] According to March data from the United States, 89% of those hospitalised had preexisting conditions.[362] The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that out of 8.8% of deaths where medical charts were available, 96.1% of people had at least one comorbidity with the average person having 3.4 diseases.[241] According to this report the most common comorbidities are hypertension (66% of deaths), type 2 diabetes (29.8% of deaths), ischaemic heart disease (27.6% of deaths), atrial fibrillation (23.1% of deaths) and chronic renal failure (20.2% of deaths).
Most critical respiratory comorbidities according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are: moderate or severe asthma, pre-existing COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis.[363] Evidence stemming from meta-analysis of several smaller research papers also suggests that smoking can be associated with worse outcomes.[364][365] When someone with existing respiratory problems is infected with COVID‑19, they might be at greater risk for severe symptoms.[366] COVID‑19 also poses a greater risk to people who misuse opioids and amphetamines, insofar as their drug use may have caused lung damage.[367]
In August 2020, the CDC issued a caution that tuberculosis (TB) infections could increase the risk of severe illness or death. The WHO recommended that people with respiratory symptoms be screened for both diseases, as testing positive for COVID‑19 could not rule out co-infections. Some projections have estimated that reduced TB detection due to the pandemic could result in 6.3 million additional TB cases and 1.4 million TB-related deaths by 2025.[368]
History
The virus is thought to be of natural animal origin, most likely through spillover infection.[77][369][370] A joint-study conducted in early 2021 by the People’s Republic of China and the World Health Organization indicated that the virus descended from a coronavirus that infects wild bats, and likely spread to humans through an intermediary wildlife host.[371] There are several theories about where the index case originated and investigations into the origin of the pandemic are ongoing.[372] According to articles published in July 2022 in Science, virus transmission into humans occurred through two spillover events in November 2019 and was likely due to live wildlife trade on the Huanan wet market in the city of Wuhan (Hubei, China).[373][374][375] Doubts about the conclusions have mostly centred on the precise site of spillover.[376] Earlier phylogenetics estimated that SARS-CoV-2 arose in October or November 2019.[377][378][379] A phylogenetic algorithm analysis suggested that the virus may have been circulating in Guangdong before Wuhan.[380] U.S intelligence agencies and other scientists have found that the virus may have been unintentionally leaked from a laboratory such as the Wuhan Institute of Virology, but that it was not developed as a biological weapon and is unlikely to have been genetically engineered.[381][382][383][384]
The first confirmed human infections were in Wuhan. A study of the first 41 cases of confirmed COVID‑19, published in January 2020 in The Lancet, reported the earliest date of onset of symptoms as 1 December 2019.[385][386][387] Official publications from the WHO reported the earliest onset of symptoms as 8 December 2019.[388] Human-to-human transmission was confirmed by the WHO and Chinese authorities by 20 January 2020.[389][390] According to official Chinese sources, these were mostly linked to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, which also sold live animals.[391] In May 2020, George Gao, the director of the CDC, said animal samples collected from the seafood market had tested negative for the virus, indicating that the market was the site of an early superspreading event, but that it was not the site of the initial outbreak.[392] Traces of the virus have been found in wastewater samples that were collected in Milan and Turin, Italy, on 18 December 2019.[393]
By December 2019, the spread of infection was almost entirely driven by human-to-human transmission.[343][394] The number of COVID-19 cases in Hubei gradually increased, reaching sixty by 20 December,[395] and at least 266 by 31 December.[396] On 24 December, Wuhan Central Hospital sent a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) sample from an unresolved clinical case to sequencing company Vision Medicals. On 27 and 28 December, Vision Medicals informed the Wuhan Central Hospital and the Chinese CDC of the results of the test, showing a new coronavirus.[397] A pneumonia cluster of unknown cause was observed on 26 December and treated by the doctor Zhang Jixian in Hubei Provincial Hospital, who informed the Wuhan Jianghan CDC on 27 December.[398] On 30 December, a test report addressed to Wuhan Central Hospital, from company CapitalBio Medlab, stated an erroneous positive result for SARS, causing a group of doctors at Wuhan Central Hospital to alert their colleagues and relevant hospital authorities of the result. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission issued a notice to various medical institutions on «the treatment of pneumonia of unknown cause» that same evening.[399] Eight of these doctors, including Li Wenliang (punished on 3 January),[400] were later admonished by the police for spreading false rumours and another, Ai Fen, was reprimanded by her superiors for raising the alarm.[401]
The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission made the first public announcement of a pneumonia outbreak of unknown cause on 31 December, confirming 27 cases[402][403][404] – enough to trigger an investigation.[405]
During the early stages of the outbreak, the number of cases doubled approximately every seven and a half days.[406] In early and mid-January 2020, the virus spread to other Chinese provinces, helped by the Chinese New Year migration and Wuhan being a transport hub and major rail interchange.[80] On 20 January, China reported nearly 140 new cases in one day, including two people in Beijing and one in Shenzhen.[407] Later official data shows 6,174 people had already developed symptoms by then,[343] and more may have been infected.[408] A report in The Lancet on 24 January indicated human transmission, strongly recommended personal protective equipment for health workers, and said testing for the virus was essential due to its «pandemic potential».[113][409] On 30 January, the WHO declared COVID-19 a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.[408] By this time, the outbreak spread by a factor of 100 to 200 times.[410]
Italy had its first confirmed cases on 31 January 2020, two tourists from China.[411] Italy overtook China as the country with the most deaths on 19 March 2020.[412] By 26 March the United States had overtaken China and Italy with the highest number of confirmed cases in the world.[413] Research on coronavirus genomes indicates the majority of COVID-19 cases in New York came from European travellers, rather than directly from China or any other Asian country.[414] Retesting of prior samples found a person in France who had the virus on 27 December 2019,[415][416] and a person in the United States who died from the disease on 6 February 2020.[417]
RT-PCR testing of untreated wastewater samples from Brazil and Italy have suggested detection of SARS-CoV-2 as early as November and December 2019, respectively, but the methods of such sewage studies have not been optimised, many have not been peer-reviewed, details are often missing, and there is a risk of false positives due to contamination or if only one gene target is detected.[418] A September 2020 review journal article said, «The possibility that the COVID‑19 infection had already spread to Europe at the end of last year is now indicated by abundant, even if partially circumstantial, evidence,» including pneumonia case numbers and radiology in France and Italy in November and December.[419]
As of 1 October 2021, Reuters reported that it had estimated the worldwide total number of deaths due to COVID‑19 to have exceeded five million.[420]
Misinformation
After the initial outbreak of COVID‑19, misinformation and disinformation regarding the origin, scale, prevention, treatment, and other aspects of the disease rapidly spread online.[421][422][423]
In September 2020, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published preliminary estimates of the risk of death by age groups in the United States, but those estimates were widely misreported and misunderstood.[424][425]
Other species
Humans appear to be capable of spreading the virus to some other animals, a type of disease transmission referred to as zooanthroponosis.
Some pets, especially cats and ferrets, can catch this virus from infected humans.[426][427] Symptoms in cats include respiratory (such as a cough) and digestive symptoms.[426] Cats can spread the virus to other cats, and may be able to spread the virus to humans, but cat-to-human transmission of SARS-CoV-2 has not been proven.[426][428] Compared to cats, dogs are less susceptible to this infection.[428] Behaviours which increase the risk of transmission include kissing, licking, and petting the animal.[428]
The virus does not appear to be able to infect pigs, ducks, or chickens at all.[426] Mice, rats, and rabbits, if they can be infected at all, are unlikely to be involved in spreading the virus.[428]
Tigers and lions in zoos have become infected as a result of contact with infected humans.[428] As expected, monkeys and great ape species such as orangutans can also be infected with the COVID‑19 virus.[428]
Minks, which are in the same family as ferrets, have been infected.[428] Minks may be asymptomatic, and can also spread the virus to humans.[428] Multiple countries have identified infected animals in mink farms.[429] Denmark, a major producer of mink pelts, ordered the slaughter of all minks over fears of viral mutations,[429] following an outbreak referred to as Cluster 5. A vaccine for mink and other animals is being researched.[429]
Research
International research on vaccines and medicines in COVID‑19 is underway by government organisations, academic groups, and industry researchers.[430][431] The CDC has classified it to require a BSL3 grade laboratory.[432] There has been a great deal of COVID‑19 research, involving accelerated research processes and publishing shortcuts to meet the global demand.[433]
As of December 2020, hundreds of clinical trials have been undertaken, with research happening on every continent except Antarctica.[434] As of November 2020, more than 200 possible treatments have been studied in humans.[435]
Transmission and prevention research
Modelling research has been conducted with several objectives, including predictions of the dynamics of transmission,[436] diagnosis and prognosis of infection,[437] estimation of the impact of interventions,[438][439] or allocation of resources.[440] Modelling studies are mostly based on compartmental models in epidemiology,[441] estimating the number of infected people over time under given conditions. Several other types of models have been developed and used during the COVID‑19 including computational fluid dynamics models to study the flow physics of COVID‑19,[442] retrofits of crowd movement models to study occupant exposure,[443] mobility-data based models to investigate transmission,[444] or the use of macroeconomic models to assess the economic impact of the pandemic.[445] Further, conceptual frameworks from crisis management research have been applied to better understand the effects of COVID‑19 on organisations worldwide.[446][447]
Seven possible drug targets in viral replication process and drugs
Repurposed antiviral drugs make up most of the research into COVID‑19 treatments.[448][449] Other candidates in trials include vasodilators, corticosteroids, immune therapies, lipoic acid, bevacizumab, and recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.[449]
In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) initiated the Solidarity trial to assess the treatment effects of some promising drugs: an experimental drug called remdesivir; anti-malarial drugs chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine; two anti-HIV drugs, lopinavir/ritonavir; and interferon-beta.[450][451] More than 300 active clinical trials are underway as of April 2020.[172]
Research on the antimalarial drugs hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine showed that they were ineffective at best,[452][453] and that they may reduce the antiviral activity of remdesivir.[454] By May 2020, France, Italy, and Belgium had banned the use of hydroxychloroquine as a COVID‑19 treatment.[455]
In June, initial results from the randomised RECOVERY Trial in the United Kingdom showed that dexamethasone reduced mortality by one third for people who are critically ill on ventilators and one fifth for those receiving supplemental oxygen.[456] Because this is a well-tested and widely available treatment, it was welcomed by the WHO, which is in the process of updating treatment guidelines to include dexamethasone and other steroids.[457][458] Based on those preliminary results, dexamethasone treatment has been recommended by the NIH for patients with COVID‑19 who are mechanically ventilated or who require supplemental oxygen but not in patients with COVID‑19 who do not require supplemental oxygen.[459]
In September 2020, the WHO released updated guidance on using corticosteroids for COVID‑19.[460][461] The WHO recommends systemic corticosteroids rather than no systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of people with severe and critical COVID‑19 (strong recommendation, based on moderate certainty evidence).[460] The WHO suggests not to use corticosteroids in the treatment of people with non-severe COVID‑19 (conditional recommendation, based on low certainty evidence).[460] The updated guidance was based on a meta-analysis of clinical trials of critically ill COVID‑19 patients.[462][463]
In September 2020, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) endorsed the use of dexamethasone in adults and adolescents from twelve years of age and weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who require supplemental oxygen therapy.[464][465] Dexamethasone can be taken by mouth or given as an injection or infusion (drip) into a vein.[464]
In November 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an emergency use authorization for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19.[466] Bamlanivimab is authorised for people with positive results of direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing who are twelve years of age and older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb), and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19 or hospitalisation.[466] This includes those who are 65 years of age or older, or who have chronic medical conditions.[466]
In February 2021, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID‑19 in people twelve years of age or older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who test positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19. The authorised use includes treatment for those who are 65 years of age or older or who have certain chronic medical conditions.[467]
In April 2021, the FDA revoked the emergency use authorization (EUA) that allowed for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab, when administered alone, to be used for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19 in adults and certain paediatric patients.[468]
Cytokine storm
Various therapeutic strategies for targeting cytokine storm
A cytokine storm can be a complication in the later stages of severe COVID‑19. A cytokine storm is a potentially deadly immune reaction where a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are released too quickly. A cytokine storm can lead to ARDS and multiple organ failure.[469] Data collected from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, China indicates that patients who had more severe responses to COVID‑19 had greater amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in their system than patients who had milder responses. These high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines indicate presence of a cytokine storm.[470]
Tocilizumab has been included in treatment guidelines by China’s National Health Commission after a small study was completed.[471][472] It is undergoing a Phase II non-randomised trial at the national level in Italy after showing positive results in people with severe disease.[473][474] Combined with a serum ferritin blood test to identify a cytokine storm (also called cytokine storm syndrome, not to be confused with cytokine release syndrome), it is meant to counter such developments, which are thought to be the cause of death in some affected people.[475] The interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist was approved by the FDA to undergo a Phase III clinical trial assessing its effectiveness on COVID‑19 based on retrospective case studies for the treatment of steroid-refractory cytokine release syndrome induced by a different cause, CAR T cell therapy, in 2017.[476] There is no randomised, controlled evidence that tocilizumab is an efficacious treatment for CRS. Prophylactic tocilizumab has been shown to increase serum IL-6 levels by saturating the IL-6R, driving IL-6 across the blood–brain barrier, and exacerbating neurotoxicity while having no effect on the incidence of CRS.[477]
Lenzilumab, an anti-GM-CSF monoclonal antibody, is protective in murine models for CAR T cell-induced CRS and neurotoxicity and is a viable therapeutic option due to the observed increase of pathogenic GM-CSF secreting T cells in hospitalised patients with COVID‑19.[478]
Passive antibodies
Transferring purified and concentrated antibodies produced by the immune systems of those who have recovered from COVID‑19 to people who need them is being investigated as a non-vaccine method of passive immunisation.[479][480] Viral neutralisation is the anticipated mechanism of action by which passive antibody therapy can mediate defence against SARS-CoV-2. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is the primary target for neutralising antibodies.[481] As of 8 August 2020, eight neutralising antibodies targeting the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 have entered clinical studies.[482] It has been proposed that selection of broad-neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV might be useful for treating not only COVID‑19 but also future SARS-related CoV infections.[481] Other mechanisms, however, such as antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity or phagocytosis, may be possible.[479] Other forms of passive antibody therapy, for example, using manufactured monoclonal antibodies, are in development.[479]
The use of passive antibodies to treat people with active COVID‑19 is also being studied. This involves the production of convalescent serum, which consists of the liquid portion of the blood from people who recovered from the infection and contains antibodies specific to this virus, which is then administered to active patients.[479] This strategy was tried for SARS with inconclusive results.[479] An updated Cochrane review in May 2021 found high certainty evidence that, for the treatment of people with moderate to severe COVID‑19, convalescent plasma did not reduce mortality or bring about symptom improvement.[480] There continues to be uncertainty about the safety of convalescent plasma administration to people with COVID‑19 and differing outcomes measured in different studies limits their use in determining efficacy.[480]
Bioethics
Since the outbreak of the COVID‑19 pandemic, scholars have explored the bioethics, normative economics, and political theories of healthcare policies related to the public health crisis.[483] Academics have pointed to the moral distress of healthcare workers, ethics of distributing scarce healthcare resources such as ventilators,[484] and the global justice of vaccine diplomacies.[citation needed] The socio-economic inequalities between genders,[485] races,[486] groups with disabilities,[487] communities,[488] regions, countries,[489] and continents have also drawn attention in academia and the general public.
Effects on other diseases
The use of social distancing and the wearing of surgical masks and similar precautions against COVID‑19 may have caused a drop in the spread of the common cold and the flu.[490][491]
See also
- Coronavirus diseases, a group of closely related syndromes
- Disease X, a WHO term
- Law of declining virulence – Disproved hypothesis of epidemiologist Theobald Smith
- Theory of virulence – Theory by biologist Paul W. Ewald
References
- ^ «Covid-19». Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ «Symptoms of Coronavirus». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 13 May 2020. Archived from the original on 17 June 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- ^ «Q&A on coronaviruses (COVID-19)». World Health Organization (WHO). 17 April 2020. Archived from the original on 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 vaccines». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ Talic S, Shah S, Wild H, Gasevic D, Maharaj A, Ademi Z, et al. (November 2021). «Effectiveness of public health measures in reducing the incidence of covid-19, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and covid-19 mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 375: e068302. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068302. ISSN 1756-1833. PMC 9423125. PMID 34789505. S2CID 244271780.
- ^ a b c «COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU)». ArcGIS. Johns Hopkins University. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ Page J, Hinshaw D, McKay B (26 February 2021). «In Hunt for Covid-19 Origin, Patient Zero Points to Second Wuhan Market – The man with the first confirmed infection of the new coronavirus told the WHO team that his parents had shopped there». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ Islam MA (April 2021). «Prevalence and characteristics of fever in adult and paediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 17515 patients». PLOS ONE. 16 (4): e0249788. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1649788I. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0249788. PMC 8023501. PMID 33822812.
- ^ Islam MA (November 2020). «Prevalence of Headache in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 14,275 Patients». Frontiers in Neurology. 11: 562634. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.562634. PMC 7728918. PMID 33329305.
- ^ Saniasiaya J, Islam MA (April 2021). «Prevalence of Olfactory Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Meta-analysis of 27,492 Patients». The Laryngoscope. 131 (4): 865–878. doi:10.1002/lary.29286. ISSN 0023-852X. PMC 7753439. PMID 33219539.
- ^ Saniasiaya J, Islam MA (November 2020). «Prevalence and Characteristics of Taste Disorders in Cases of COVID-19: A Meta-analysis of 29,349 Patients». Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 165 (1): 33–42. doi:10.1177/0194599820981018. PMID 33320033. S2CID 229174644.
- ^ Agyeman AA, Chin KL, Landersdorfer CB, Liew D, Ofori-Asenso R (August 2020). «Smell and Taste Dysfunction in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis». Mayo Clin. Proc. 95 (8): 1621–1631. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.05.030. PMC 7275152. PMID 32753137.
- ^ Oran DP, Topol EJ (January 2021). «The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic: A Systematic Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (5): M20-6976. doi:10.7326/M20-6976. PMC 7839426. PMID 33481642.
- ^ «Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 6 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ a b CDC (11 February 2020). «Post-COVID Conditions». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ «Clinical Questions about COVID-19: Questions and Answers». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 17 November 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b c «Overview of Testing for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ a b c «Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ Gorzalski AJ, Tian H, Laverdure C, Morzunov S, Verma SC, VanHooser S, Pandori MW (August 2020). «High-Throughput Transcription-mediated amplification on the Hologic Panther is a highly sensitive method of detection for SARS-CoV-2». Journal of Clinical Virology. 129: 104501. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104501. PMC 7286273. PMID 32619959.
- ^ a b c d e Li C, Zhao C, Bao J, Tang B, Wang Y, Gu B (November 2020). «Laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)». Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 510: 35–46. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.045. PMC 7329657. PMID 32621814.
- ^ «2nd U.S. Case Of Wuhan Coronavirus Confirmed». NPR. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (2 February 2020). «Wuhan Coronavirus Looks Increasingly Like a Pandemic, Experts Say». The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Griffiths J. «Wuhan coronavirus deaths spike again as outbreak shows no signs of slowing». CNN. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Jiang S, Xia S, Ying T, Lu L (May 2020). «A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome». Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 17 (5): 554. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0372-4. PMC 7091741. PMID 32024976.
- ^ Chan JF, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KK, Chu H, Yang J, et al. (February 2020). «A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster». Lancet. 395 (10223): 514–523. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. PMC 7159286. PMID 31986261.
- ^ Shablovsky S (September 2017). «The legacy of the Spanish flu». Science. 357 (6357): 1245. Bibcode:2017Sci…357.1245S. doi:10.1126/science.aao4093. ISSN 0036-8075. S2CID 44116811.
- ^ «Stop the coronavirus stigma now». Nature. 580 (7802): 165. 7 April 2020. Bibcode:2020Natur.580..165.. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01009-0. PMID 32265571. S2CID 214809950. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 1» (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). 21 January 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 10» (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). 30 January 2020.
- ^ «Novel coronavirus named ‘Covid-19’: WHO». Today. Singapore. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ «The coronavirus spreads racism against – and among – ethnic Chinese». The Economist. 17 February 2020. Archived from the original on 17 February 2020. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- ^ World Health Organization Best Practices for the Naming of New Human Infectious Diseases (PDF) (Report). World Health Organization (WHO). May 2015. hdl:10665/163636.
- ^ a b «Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 22» (PDF). WHO. 11 February 2020.
- ^ Gover AR, Harper SB, Langton L (July 2020). «Anti-Asian Hate Crime During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Exploring the Reproduction of Inequality». American Journal of Criminal Justice. 45 (4): 647–667. doi:10.1007/s12103-020-09545-1. PMC 7364747. PMID 32837171.
- ^ «Symptoms of Coronavirus». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 22 February 2021. Archived from the original on 4 March 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
- ^ Grant MC, Geoghegan L, Arbyn M, Mohammed Z, McGuinness L, Clarke EL, Wade RG (23 June 2020). «The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries». PLOS ONE. 15 (6): e0234765. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1534765G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0234765. PMC 7310678. PMID 32574165. S2CID 220046286.
- ^ Pardhan S, Vaughan M, Zhang J, Smith L, Chichger H (1 November 2020). «Sore eyes as the most significant ocular symptom experienced by people with COVID-19: a comparison between pre-COVID-19 and during COVID-19 states». BMJ Open Ophthalmology. 5 (1): e000632. doi:10.1136/bmjophth-2020-000632. PMC 7705420. PMID 34192153.
- ^ «COVID toes, rashes: How the coronavirus can affect your skin». www.aad.org. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ a b «Clinical characteristics of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ Paderno A, Mattavelli D, Rampinelli V, Grammatica A, Raffetti E, Tomasoni M, et al. (December 2020). «Olfactory and Gustatory Outcomes in COVID-19: A Prospective Evaluation in Nonhospitalized Subjects». Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 163 (6): 1144–1149. doi:10.1177/0194599820939538. PMC 7331108. PMID 32600175.
- ^ Chabot AB, Huntwork MP (September 2021). «Turmeric as a Possible Treatment for COVID-19-Induced Anosmia and Ageusia». Cureus. 13 (9): e17829. doi:10.7759/cureus.17829. PMC 8502749. PMID 34660038.
- ^ Niazkar HR, Zibaee B, Nasimi A, Bahri N (July 2020). «The neurological manifestations of COVID-19: a review article». Neurological Sciences. 41 (7): 1667–1671. doi:10.1007/s10072-020-04486-3. PMC 7262683. PMID 32483687.
- ^ «Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 6 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Oran DP, Topol EJ (May 2021). «The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic : A Systematic Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (5): 655–662. doi:10.7326/M20-6976. PMC 7839426. PMID 33481642.
- «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- Nogrady B (November 2020). «What the data say about asymptomatic COVID infections». Nature. 587 (7835): 534–535. Bibcode:2020Natur.587..534N. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03141-3. PMID 33214725.
- ^ a b Gao Z, Xu Y, Sun C, Wang X, Guo Y, Qiu S, Ma K (February 2021). «A systematic review of asymptomatic infections with COVID-19». Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi. 54 (1): 12–16. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.05.001. PMC 7227597. PMID 32425996.
- ^ Oran DP, Topol EJ (September 2020). «Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection : A Narrative Review». Annals of Internal Medicine. 173 (5): 362–367. doi:10.7326/M20-3012. PMC 7281624. PMID 32491919.
- ^ Lai CC, Liu YH, Wang CY, Wang YH, Hsueh SC, Yen MY, et al. (June 2020). «Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Facts and myths». Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi. 53 (3): 404–412. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012. PMC 7128959. PMID 32173241.
- ^ a b Furukawa NW, Brooks JT, Sobel J (July 2020). «Evidence Supporting Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 While Presymptomatic or Asymptomatic». Emerging Infectious Diseases. 26 (7). doi:10.3201/eid2607.201595. PMC 7323549. PMID 32364890.
- ^ a b Gandhi RT, Lynch JB, Del Rio C (October 2020). «Mild or Moderate Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (18): 1757–1766. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009249. PMID 32329974.
- ^ Byrne AW, McEvoy D, Collins AB, Hunt K, Casey M, Barber A, et al. (August 2020). «Inferred duration of infectious period of SARS-CoV-2: rapid scoping review and analysis of available evidence for asymptomatic and symptomatic COVID-19 cases». BMJ Open. 10 (8): e039856. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039856. PMC 7409948. PMID 32759252.
- ^ Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC (August 2020). «Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review». JAMA. 324 (8): 782–793. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12839. PMID 32648899. S2CID 220465311.
- ^ «Half of young adults with COVID-19 had persistent symptoms after 6 months». medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 10 July 2021.
- ^ Blomberg B, Mohn KG, Brokstad KA, Zhou F, Linchausen DW, Hansen BA, et al. (September 2021). «Long COVID in a prospective cohort of home-isolated patients». Nature Medicine. 27 (9): 1607–1613. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01433-3. PMC 8440190. PMID 34163090. S2CID 235625772.
- ^ CDC (1 September 2022). «Post-COVID Conditions». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «COVID-19 and Your Health». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 23 January 2021.
- ^ CDC (29 March 2022). «Omicron Variant: What You Need to Know». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 15 June 2022.
- ^ Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL (March 2021). «Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 19 (3): 141–154. doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7. PMC 7537588. PMID 33024307.
- ^ a b Wang CC, Prather KA, Sznitman J, Jimenez JL, Lakdawala SS, Tufekci Z, Marr LC (August 2021). «Airborne transmission of respiratory viruses». Science. 373 (6558). Bibcode:2021Sci…373…..W. doi:10.1126/science.abd9149. PMC 8721651. PMID 34446582.
- ^ Greenhalgh T, Jimenez JL, Prather KA, Tufekci Z, Fisman D, Schooley R (May 2021). «Ten scientific reasons in support of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2». Lancet. 397 (10285): 1603–1605. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00869-2. PMC 8049599. PMID 33865497.
- ^ Bourouiba L (13 July 2021). «Fluid Dynamics of Respiratory Infectious Diseases». Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 23 (1): 547–577. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-111820-025044. hdl:1721.1/131115. PMID 34255991. S2CID 235823756. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ Stadnytskyi, Valentyn; Bax, Christina E.; Bax, Adriaan; Anfinrud, Philip (2 June 2020). «The airborne lifetime of small speech droplets and their potential importance in SARS-CoV-2 transmission». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (22): 11875–11877. doi:10.1073/pnas.2006874117. PMC 7275719. PMID 32404416.
- ^ Miller SL, Nazaroff WW, Jimenez JL, Boerstra A, Buonanno G, Dancer SJ, et al. (March 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by inhalation of respiratory aerosol in the Skagit Valley Chorale superspreading event». Indoor Air. 31 (2): 314–323. doi:10.1111/ina.12751. PMC 7537089. PMID 32979298.
- ^ He, Xi; Lau, Eric H. Y.; Wu, Peng; Deng, Xilong; Wang, Jian; Hao, Xinxin; Lau, Yiu Chung; Wong, Jessica Y.; Guan, Yujuan; Tan, Xinghua; Mo, Xiaoneng; Chen, Yanqing; Liao, Baolin; Chen, Weilie; Hu, Fengyu; Zhang, Qing; Zhong, Mingqiu; Wu, Yanrong; Zhao, Lingzhai; Zhang, Fuchun; Cowling, Benjamin J.; Li, Fang; Leung, Gabriel M. (September 2020). «Author Correction: Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19». Nature Medicine. 26 (9): 1491–1493. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1016-z. PMC 7413015. PMID 32770170. S2CID 221050261.
- ^ a b c d Communicable Diseases Network Australia. «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): CDNA National Guidelines for Public Health Units». 5.1. Communicable Diseases Network Australia/Australian Government Department of Health.
- ^ «Clinical Questions about COVID-19: Questions and Answers». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 4 March 2021.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 May 2021. Retrieved 8 May 2021.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): How is it transmitted?». World Health Organization. 30 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d e • «COVID-19: epidemiology, virology and clinical features». GOV.UK. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
• Communicable Diseases Network Australia. «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) — CDNA Guidelines for Public Health Units». Version 4.4. Australian Government Department of Health. Retrieved 17 May 2021.{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)
• Public Health Agency of Canada (3 November 2020). «COVID-19: Main modes of transmission». aem. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
• «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
• Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE (January 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Viral, Host, and Environmental Factors». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (1): 69–79. doi:10.7326/M20-5008. ISSN 0003-4819. PMC 7505025. PMID 32941052. - ^ a b c Tang JW, Marr LC, Li Y, Dancer SJ (April 2021). «Covid-19 has redefined airborne transmission». BMJ. 373: n913. doi:10.1136/bmj.n913. PMID 33853842.
- ^ a b Morawska L, Allen J, Bahnfleth W, Bluyssen PM, Boerstra A, Buonanno G, et al. (May 2021). «A paradigm shift to combat indoor respiratory infection» (PDF). Science. 372 (6543): 689–691. Bibcode:2021Sci…372..689M. doi:10.1126/science.abg2025. PMID 33986171. S2CID 234487289.
- ^ a b Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE (January 2021). «Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Viral, Host, and Environmental Factors». Annals of Internal Medicine. 174 (1): 69–79. doi:10.7326/M20-5008. ISSN 0003-4819. PMC 7505025. PMID 32941052.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Healthcare Workers». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 29 March 2022.
- ^ Liu T, Gong D, Xiao J, Hu J, He G, Rong Z, Ma W (October 2020). «Cluster infections play important roles in the rapid evolution of COVID-19 transmission: A systematic review». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 99: 374–380. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.073. PMC 7405860. PMID 32768702.
- ^ «Outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): increased transmission beyond China – fourth update» (PDF). European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 14 February 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- ^ a b Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF (April 2020). «The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Medicine. 26 (4): 450–452. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9. PMC 7095063. PMID 32284615.
- ^ Gibbens S (18 March 2020). «Why soap is preferable to bleach in the fight against coronavirus». National Geographic. Archived from the original on 2 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ^ Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. (February 2020). «A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (8): 727–733. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. PMC 7092803. PMID 31978945.
- ^ a b c Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) (PDF) (Report). World Health Organization (WHO). February 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 February 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ «Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Rathore JS, Ghosh C (August 2020). «Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), a newly emerged pathogen: an overview». Pathogens and Disease. 78 (6). doi:10.1093/femspd/ftaa042. OCLC 823140442. PMC 7499575. PMID 32840560.
- ^ Thomas S (October 2020). «The Structure of the Membrane Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Resembles the Sugar Transporter SemiSWEET». Pathogens & Immunity. 5 (1): 342–363. doi:10.20411/pai.v5i1.377. PMC 7608487. PMID 33154981.
- ^ Koyama T, Platt D, Parida L (July 2020). «Variant analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes». Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 98 (7): 495–504. doi:10.2471/BLT.20.253591. PMC 7375210. PMID 32742035.
We detected in total 65776 variants with 5775 distinct variants.
- ^ a b Rambaut A, Holmes EC, O’Toole Á, Hill V, McCrone JT, Ruis C, et al. (November 2020). «A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology». Nature Microbiology. 5 (11): 1403–1407. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0770-5. PMC 7610519. PMID 32669681.
- ^ «Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants». World Health Organization. 1 July 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2021.
- ^ Alm E, Broberg EK, Connor T, Hodcroft EB, Komissarov AB, Maurer-Stroh S, et al. (August 2020). «Geographical and temporal distribution of SARS-CoV-2 clades in the WHO European Region, January to June 2020». Euro Surveillance. 25 (32). doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.32.2001410. PMC 7427299. PMID 32794443.
- ^ «PANGO lineages». cov-lineages.org. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ Lauring AS, Hodcroft EB (February 2021). «Genetic Variants of SARS-CoV-2-What Do They Mean?». JAMA. 325 (6): 529–531. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.27124. PMID 33404586. S2CID 230783233.
- ^ Abdool Karim SS, de Oliveira T (May 2021). «New SARS-CoV-2 Variants – Clinical, Public Health, and Vaccine Implications». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 384 (19): 1866–1868. doi:10.1056/nejmc2100362. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 8008749. PMID 33761203.
- ^ Mallapaty S (November 2020). «COVID mink analysis shows mutations are not dangerous – yet». Nature. 587 (7834): 340–341. Bibcode:2020Natur.587..340M. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03218-z. PMID 33188367. S2CID 226947606.
- ^ Larsen HD, Fonager J, Lomholt FK, Dalby T, Benedetti G, Kristensen B, et al. (February 2021). «Preliminary report of an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 in mink and mink farmers associated with community spread, Denmark, June to November 2020». Euro Surveillance. 26 (5): 2100009. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.5.210009. PMC 7863232. PMID 33541485.
As at 1 February 2021, we assess that the cluster 5 variant is no longer circulating among humans in Denmark.
- ^ «New COVID-19 Variants». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 28 June 2021 [First published 11 February 2020]. Retrieved 15 July 2021.
- ^ «COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update Edition 69». World Health Organization (WHO). 7 December 2021.
- ^ «Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Harrison AG, Lin T, Wang P (December 2020). «Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis». Trends in Immunology. 41 (12): 1100–1115. doi:10.1016/j.it.2020.10.004. PMC 7556779. PMID 33132005.
- ^ Verdecchia P, Cavallini C, Spanevello A, Angeli F (June 2020). «The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection». European Journal of Internal Medicine. 76: 14–20. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037. PMC 7167588. PMID 32336612.
- ^ Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V (April 2020). «Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses». Nature Microbiology. 5 (4): 562–569. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y. PMC 7095430. PMID 32094589.
- ^ Marik PE, Iglesias J, Varon J, Kory P (January 2021). «A scoping review of the pathophysiology of COVID-19». International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology. 35: 20587384211048026. doi:10.1177/20587384211048026. PMC 8477699. PMID 34569339.
- ^ a b Meunier N, Briand L, Jacquin-Piques A, Brondel L, Pénicaud L (June 2020). «COVID 19-Induced Smell and Taste Impairments: Putative Impact on Physiology». Frontiers in Physiology. 11: 625110. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.625110. PMC 7870487. PMID 33574768.
- ^ Guerrero JI, Barragán LA, Martínez JD, Montoya JP, Peña A, Sobrino FE, et al. (June 2021). «Central and peripheral nervous system involvement by COVID-19: a systematic review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, neuropathology, neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and cerebrospinal fluid findings». BMC Infectious Diseases. 21 (1): 515. doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06185-6. PMC 8170436. PMID 34078305.
- ^ a b Pezzini A, Padovani A (November 2020). «Lifting the mask on neurological manifestations of COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Neurology. 16 (11): 636–644. doi:10.1038/s41582-020-0398-3. PMC 7444680. PMID 32839585.
- ^ Li YC, Bai WZ, Hashikawa T (June 2020). «The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 552–555. doi:10.1002/jmv.25728. PMC 7228394. PMID 32104915.
- ^ Baig AM, Khaleeq A, Ali U, Syeda H (April 2020). «Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms». ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (7): 995–998. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00122. PMC 7094171. PMID 32167747.
- ^ Yavarpour-Bali H, Ghasemi-Kasman M (September 2020). «Update on neurological manifestations of COVID-19». Life Sciences. 257: 118063. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118063. PMC 7346808. PMID 32652139.
- ^ Covid can shrink brain and damage its tissue, finds research The Guardian
- ^ Scans reveal how Covid may change the brain BBC
- ^ «Even mild Covid is linked to brain damage months after illness, scans show». NBC News.
- ^ Gu J, Han B, Wang J (May 2020). «COVID-19: Gastrointestinal Manifestations and Potential Fecal-Oral Transmission». Gastroenterology. 158 (6): 1518–1519. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054. PMC 7130192. PMID 32142785.
- ^ Mönkemüller K, Fry L, Rickes S (May 2020). «COVID-19, coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 and the small bowel». Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas. 112 (5): 383–388. doi:10.17235/reed.2020.7137/2020. PMID 32343593. S2CID 216645754.
- ^ Almamlouk R, Kashour T, Obeidat S, Bois MC, Maleszewski JJ, Omrani OA, et al. (August 2022). «COVID-19-Associated cardiac pathology at the postmortem evaluation: a collaborative systematic review». Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 28 (8): 1066–1075. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.03.021. PMC 8941843. PMID 35339672.
- ^ a b c Zheng YY, Ma YT, Zhang JY, Xie X (May 2020). «COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system». Nature Reviews. Cardiology. 17 (5): 259–260. doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5. PMC 7095524. PMID 32139904.
- ^ a b c Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. (February 2020). «Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China». Lancet. 395 (10223): 497–506. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. PMC 7159299. PMID 31986264.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Myocardial infarction and other coronary artery disease issues». UpToDate. Retrieved 28 September 2020.
- ^ Turner AJ, Hiscox JA, Hooper NM (June 2004). «ACE2: from vasopeptidase to SARS virus receptor». Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 25 (6): 291–4. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2004.04.001. PMC 7119032. PMID 15165741.
- ^ Abou-Ismail MY, Diamond A, Kapoor S, Arafah Y, Nayak L (October 2020). «The hypercoagulable state in COVID-19: Incidence, pathophysiology, and management». Thrombosis Research. Elsevier BV. 194: 101–115. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.06.029. PMC 7305763. PMID 32788101.
- ^ a b c Wadman M (April 2020). «How does coronavirus kill? Clinicians trace a ferocious rampage through the body, from brain to toes». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abc3208.
- ^ «NIH study uncovers blood vessel damage and inflammation in COVID-19 patients’ brains but no infection». National Institutes of Health (NIH). 30 December 2020. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ^ Lee MH, Perl DP, Nair G, Li W, Maric D, Murray H, et al. (February 2021). «Microvascular Injury in the Brains of Patients with Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 384 (5): 481–483. doi:10.1056/nejmc2033369. PMC 7787217. PMID 33378608.
- ^ Kubánková M, Hohberger B, Hoffmanns J, Fürst J, Herrmann M, Guck J, Kräter M (July 2021). «Physical phenotype of blood cells is altered in COVID-19». Biophysical Journal. 120 (14): 2838–2847. Bibcode:2021BpJ…120.2838K. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2021.05.025. PMC 8169220. PMID 34087216.
- ^ Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Sehgal K, Nair N, Mahajan S, Sehrawat TS, et al. (July 2020). «Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19». Nature Medicine. 26 (7): 1017–1032. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3. PMID 32651579. S2CID 220462000.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Kidney Damage Caused by COVID-19». Johns Hopkins Medicine. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Eketunde AO, Mellacheruvu SP, Oreoluwa P (July 2020). «A Review of Postmortem Findings in Patients With COVID-19». Cureus. Cureus, Inc. 12 (7): e9438. doi:10.7759/cureus.9438. PMC 7451084. PMID 32864262. S2CID 221352704.
- ^ Ziegler, CGK; Allon, SJ; Nyquist, SK; Mbano, IM; Miao, VN; Tzouanas, CN; Cao, Y; Yousif, AS; Bals, J; Hauser, BM; Feldman, J; Muus, C; Wadsworth MH, 2nd; Kazer, SW; Hughes, TK; Doran, B; Gatter, GJ; Vukovic, M; Taliaferro, F; Mead, BE; Guo, Z; Wang, JP; Gras, D; Plaisant, M; Ansari, M; Angelidis, I; Adler, H; Sucre, JMS; Taylor, CJ; Lin, B; Waghray, A; Mitsialis, V; Dwyer, DF; Buchheit, KM; Boyce, JA; Barrett, NA; Laidlaw, TM; Carroll, SL; Colonna, L; Tkachev, V; Peterson, CW; Yu, A; Zheng, HB; Gideon, HP; Winchell, CG; Lin, PL; Bingle, CD; Snapper, SB; Kropski, JA; Theis, FJ; Schiller, HB; Zaragosi, LE; Barbry, P; Leslie, A; Kiem, HP; Flynn, JL; Fortune, SM; Berger, B; Finberg, RW; Kean, LS; Garber, M; Schmidt, AG; Lingwood, D; Shalek, AK; Ordovas-Montanes, J; HCA Lung Biological Network. Electronic address, lung-network@humancellatlas.org.; HCA Lung Biological, Network. (28 May 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues». Cell. 181 (5): 1016–1035.e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035. PMC 7252096. PMID 32413319.
- ^ Sajuthi, SP; DeFord, P; Li, Y; Jackson, ND; Montgomery, MT; Everman, JL; Rios, CL; Pruesse, E; Nolin, JD; Plender, EG; Wechsler, ME; Mak, ACY; Eng, C; Salazar, S; Medina, V; Wohlford, EM; Huntsman, S; Nickerson, DA; Germer, S; Zody, MC; Abecasis, G; Kang, HM; Rice, KM; Kumar, R; Oh, S; Rodriguez-Santana, J; Burchard, EG; Seibold, MA (12 October 2020). «Type 2 and interferon inflammation regulate SARS-CoV-2 entry factor expression in the airway epithelium». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5139. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5139S. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18781-2. PMC 7550582. PMID 33046696.
- ^
- ^ Zhang C, Wu Z, Li JW, Zhao H, Wang GQ (May 2020). «Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (5): 105954. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954. PMC 7118634. PMID 32234467.
- ^ Gómez-Rial J, Rivero-Calle I, Salas A, Martinón-Torres F (2020). «Role of Monocytes/Macrophages in Covid-19 Pathogenesis: Implications for Therapy». Infection and Drug Resistance. 13: 2485–2493. doi:10.2147/IDR.S258639. PMC 7383015. PMID 32801787.
- ^ Dai L, Gao GF (February 2021). «Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19». Nature Reviews. Immunology. 21 (2): 73–82. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00480-0. ISSN 1474-1733. PMC 7747004. PMID 33340022.
- ^ a b Boopathi S, Poma AB, Kolandaivel P (April 2020). «Novel 2019 coronavirus structure, mechanism of action, antiviral drug promises and rule out against its treatment». Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 39 (9): 3409–3418. doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1758788. PMC 7196923. PMID 32306836.
- ^ Kai H, Kai M (July 2020). «Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors-lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19». Hypertension Research. 43 (7): 648–654. doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8. PMC 7184165. PMID 32341442.
- ^ Chen HX, Chen ZH, Shen HH (October 2020). «[Structure of SARS-CoV-2 and treatment of COVID-19]». Sheng Li Xue Bao. 72 (5): 617–630. PMID 33106832.
- ^ Jeyanathan M, Afkhami S, Smaill F, Miller MS, Lichty BD, Xing Z (4 September 2020). «Immunological considerations for COVID-19 vaccine strategies». Nature Reviews Immunology. 20 (10): 615–632. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00434-6. ISSN 1474-1741. PMC 7472682. PMID 32887954.
- ^ Zhang Q, Ju B, Ge J, Chan JF, Cheng L, Wang R, et al. (July 2021). «Potent and protective IGHV3-53/3-66 public antibodies and their shared escape mutant on the spike of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Communications. 12 (1): 4210. Bibcode:2021NatCo..12.4210Z. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24514-w. PMC 8270942. PMID 34244522. S2CID 235786394.
- ^ Soy M, Keser G, Atagündüz P, Tabak F, Atagündüz I, Kayhan S (July 2020). «Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment». Clinical Rheumatology. 39 (7): 2085–2094. doi:10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5. PMC 7260446. PMID 32474885.
- ^ Quirch M, Lee J, Rehman S (August 2020). «Hazards of the Cytokine Storm and Cytokine-Targeted Therapy in Patients With COVID-19: Review». Journal of Medical Internet Research. 22 (8): e20193. doi:10.2196/20193. PMC 7428145. PMID 32707537.
- ^ Bhaskar S, Sinha A, Banach M, Mittoo S, Weissert R, Kass JS, et al. (2020). «Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper». Frontiers in Immunology. 11: 1648. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648. PMC 7365905. PMID 32754159.
- ^ a b c d e f Wastnedge EA, Reynolds RM, van Boeckel SR, Stock SJ, Denison FC, Maybin JA, Critchley HO (January 2021). «Pregnancy and COVID-19». Physiological Reviews. 101 (1): 303–318. doi:10.1152/physrev.00024.2020. PMC 7686875. PMID 32969772.
- ^ Campbell D (10 October 2021). «One in six most critically ill NHS Covid patients are unvaccinated pregnant women». The Guardian. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, Zhan C, Chen C, Lv W, et al. (August 2020). «Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases». Radiology. 296 (2): E32–E40. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200642. PMC 7233399. PMID 32101510.
- ^ a b c d Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, Gholamrezanezhad A (July 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findings in 919 Patients». AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 215 (1): 87–93. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.23034. PMID 32174129.
- ^ «2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Summary». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: Laboratory testing for 2019-nCoV in humans». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Bullard J, Dust K, Funk D, Strong JE, Alexander D, Garnett L, et al. (December 2020). «Predicting Infectious Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 From Diagnostic Samples». Clinical Infectious Diseases. 71 (10): 2663–2666. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa638. PMC 7314198. PMID 32442256.
- ^ «Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens from Persons for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 4 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ «Real-Time RT-PCR Panel for Detection 2019-nCoV». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 29 January 2020. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ «Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ «NHS staff will be first to get new coronavirus antibody test, medical chief promises». The Independent. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Heneghan C, Jefferson T (1 September 2020). «Virological characterization of COVID-19 patients that test re-positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR». CEBM. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ Lu J, Peng J, Xiong Q, Liu Z, Lin H, Tan X, et al. (September 2020). «Clinical, immunological and virological characterization of COVID-19 patients that test re-positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR». EBioMedicine. 59: 102960. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102960. PMC 7444471. PMID 32853988.
- ^ Spencer E, Jefferson T, Brassey J, Heneghan C (11 September 2020). «When is Covid, Covid?». The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ «SARS-CoV-2 RNA testing: assurance of positive results during periods of low prevalence». GOV.UK. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ «ACR Recommendations for the use of Chest Radiography and Computed Tomography (CT) for Suspected COVID-19 Infection». American College of Radiology. 22 March 2020. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020.
- ^ Pormohammad A, Ghorbani S, Khatami A, Razizadeh MH, Alborzi E, Zarei M, et al. (October 2020). «Comparison of influenza type A and B with COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical, laboratory and radiographic findings». Reviews in Medical Virology. 31 (3): e2179. doi:10.1002/rmv.2179. PMC 7646051. PMID 33035373. S2CID 222255245.
- ^ Lee EY, Ng MY, Khong PL (April 2020). «COVID-19 pneumonia: what has CT taught us?». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (4): 384–385. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30134-1. PMC 7128449. PMID 32105641.
- ^ a b Li Y, Xia L (June 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of Chest CT in Diagnosis and Management». AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 214 (6): 1280–1286. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.22954. PMID 32130038. S2CID 212416282.
- ^ «COVID-19 Database». Società Italiana di Radiologia Medica e Interventistica (in Italian). Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ «ICD-10 Version:2019». World Health Organization (WHO). 2019. Archived from the original on 31 March 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
U07.2 – COVID-19, virus not identified – COVID-19 NOS – Use this code when COVID-19 is diagnosed clinically or epidemiologically but laboratory testing is inconclusive or not available. Use additional code, if desired, to identify pneumonia or other manifestations
- ^ Giani M, Seminati D, Lucchini A, Foti G, Pagni F (May 2020). «Exuberant Plasmocytosis in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Specimen of the First Patient Requiring Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for SARS-CoV-2 in Europe». Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 15 (5): e65–e66. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.03.008. PMC 7118681. PMID 32194247.
- ^ Lillicrap D (April 2020). «Disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with 2019-nCoV pneumonia». Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 18 (4): 786–787. doi:10.1111/jth.14781. PMC 7166410. PMID 32212240.
- ^ Mitra A, Dwyre DM, Schivo M, Thompson GR, Cohen SH, Ku N, Graff JP (August 2020). «Leukoerythroblastic reaction in a patient with COVID-19 infection». American Journal of Hematology. 95 (8): 999–1000. doi:10.1002/ajh.25793. PMC 7228283. PMID 32212392.
- ^ a b c d e f Satturwar S, Fowkes M, Farver C, Wilson AM, Eccher A, Girolami I, et al. (May 2021). «Postmortem Findings Associated With SARS-CoV-2: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis». The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 45 (5): 587–603. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000001650. PMC 8132567. PMID 33481385. S2CID 231679276.
- ^ Maier BF, Brockmann D (May 2020). «Effective containment explains subexponential growth in recent confirmed COVID-19 cases in China». Science. 368 (6492): 742–746. arXiv:2002.07572. Bibcode:2020Sci…368..742M. doi:10.1126/science.abb4557. PMC 7164388. PMID 32269067. («… initial exponential growth expected for an unconstrained outbreak.»)
- ^ «Viral Load Exposure Factors». ReallyCorrect.com.
- ^ «Recommendation Regarding the Use of Cloth Face Coverings, Especially in Areas of Significant Community-Based Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 28 June 2020.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 and Potential Airborne Transmission». COVID-19 Published Science and Research. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5 April 2020). «What to Do if You Are Sick». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) – Prevention & Treatment». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 March 2020. Archived from the original on 11 March 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ «UK medicines regulator gives approval for first UK COVID-19 vaccine». Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, Government of the UK. 2 December 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ Mueller B (2 December 2020). «U.K. Approves Pfizer Coronavirus Vaccine, a First in the West». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines». nih.gov. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ a b c Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB (May 2020). «Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review». JAMA. 323 (18): 1824–1836. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019. PMID 32282022.
- ^ a b Anderson RM, Heesterbeek H, Klinkenberg D, Hollingsworth TD (March 2020). «How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?». Lancet. 395 (10228): 931–934. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5. PMC 7158572. PMID 32164834.
A key issue for epidemiologists is helping policy makers decide the main objectives of mitigation – e.g. minimising morbidity and associated mortality, avoiding an epidemic peak that overwhelms health-care services, keeping the effects on the economy within manageable levels, and flattening the epidemic curve to wait for vaccine development and manufacture on scale and antiviral drug therapies.
- ^ Wiles S (14 March 2020). «After ‘Flatten the Curve’, we must now ‘Stop the Spread’. Here’s what that means». The Spinoff. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Li YD, Chi WY, Su JH, Ferrall L, Hung CF, Wu TC (December 2020). «Coronavirus vaccine development: from SARS and MERS to COVID-19». Journal of Biomedical Science. 27 (1): 104. doi:10.1186/s12929-020-00695-2. PMC 7749790. PMID 33341119.
- ^ Subbarao K (July 2021). «The success of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and challenges ahead». Cell Host & Microbe. 29 (7): 1111–1123. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.016. PMC 8279572. PMID 34265245.
- ^ Padilla TB (24 February 2021). «No one is safe unless everyone is safe». BusinessWorld. Archived from the original on 23 February 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ a b c Rogers K (11 May 2022). «COVID-19 vaccine». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 12 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- ^ «Swissmedic grants authorisation for the first COVID-19 vaccine in Switzerland» (Press release). Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products (Swissmedic). 18 December 2020. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ «EMA recommends first COVID-19 vaccine for authorisation in the EU». European Medicines Agency (EMA) (Press release). 21 December 2020. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2020.
- ^ «Wear masks in public says WHO, in update of COVID-19 advice». Reuters. 5 June 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ a b c «Recommendation Regarding the Use of Cloth Face Coverings, Especially in Areas of Significant Community-Based Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ a b «Using face masks in the community – Technical Report» (PDF). ECDC. 8 April 2020.
- ^ «Scientific Brief: Community Use of Cloth Masks to Control the Spread of SARS-CoV-2». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 November 2020.
- ^ Greenhalgh T, Schmid MB, Czypionka T, Bassler D, Gruer L (April 2020). «Face masks for the public during the covid-19 crisis». BMJ. 369: m1435. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1435. PMID 32273267. S2CID 215516381.
- ^ «Caring for Someone Sick at Home». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ «Using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 June 2020. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- ^ a b c CDC (11 February 2020). «Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ^ «Transmission of COVID-19». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 7 September 2020. Retrieved 14 October 2020.
- ^ a b National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD) (9 July 2020). «COVID-19 Employer Information for Office Buildings». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 9 July 2020.
- ^ WHO’s Science in 5 on COVID-19 — Ventilation — 30 October 2020. World Health Organization (WHO). 30 October 2020. Archived from the original on 25 October 2022. Retrieved 8 December 2022 – via YouTube.
- ^ Somsen GA, van Rijn C, Kooij S, Bem RA, Bonn D (July 2020). «Small droplet aerosols in poorly ventilated spaces and SARS-CoV-2 transmission». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. Elsesier. 8 (7): 658–659. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30245-9. PMC 7255254. PMID 32473123.
- ^ Lipinski T, Ahmad D, Serey N, Jouhara H (1 November 2020). «Review of ventilation strategies to reduce the risk of disease transmission in high occupancy buildings». International Journal of Thermofluids. 7–8: 100045. doi:10.1016/j.ijft.2020.100045. ISSN 2666-2027. S2CID 221642242.
- ^ «Social distancing: what you need to do – Coronavirus (COVID-19)». nhs.uk. 2 June 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ «Advice for the public on COVID-19 – World Health Organization». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 and Your Health». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
To prevent the spread of germs, including COVID-19, CDC recommends washing hands with soap and water whenever possible because it reduces the amount of many types of germs and chemicals on hands. But if soap and water are not readily available, using a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol can help you avoid getting sick and spreading germs to others.
- ^ «WHO-recommended handrub formulations». WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: First Global Patient Safety Challenge Clean Care Is Safer Care. World Health Organization (WHO). 19 March 2009. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ Nussbaumer-Streit B, Mayr V, Dobrescu AI, Chapman A, Persad E, Klerings I, et al. (September 2020). «Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: a rapid review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (9): CD013574. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013574.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 8133397. PMID 33959956.
- ^ Qian M, Jiang J (May 2020). «COVID-19 and social distancing». Zeitschrift für Gesundheitswissenschaften = Journal of Public Health. 30 (1): 259–261. doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01321-z. PMC 7247774. PMID 32837835.
- ^ a b Hawks L, Woolhandler S, McCormick D (August 2020). «COVID-19 in Prisons and Jails in the United States». JAMA Internal Medicine. 180 (8): 1041–1042. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1856. PMID 32343355.
- ^ Waldstein D (6 May 2020). «To Fight Virus in Prisons, C.D.C. Suggests More Screenings». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 7 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ «How COVID-19 Spreads». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 18 September 2020. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- ^ Goldman E (August 2020). «Exaggerated risk of transmission of COVID-19 by fomites». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (8): 892–893. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30561-2. PMC 7333993. PMID 32628907.
- ^ Weixel N (5 April 2021). «CDC says risk of COVID-19 transmission on surfaces 1 in 10,000». The Hill. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ a b «Science Brief: SARS-CoV-2 and Surface (Fomite) Transmission for Indoor Community Environments». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 April 2021. Archived from the original on 5 April 2021.
- ^ a b Pedreira A, Taşkın Y, García MR (January 2021). «A Critical Review of Disinfection Processes to Control SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in the Food Industry». Foods. 10 (2): 283. doi:10.3390/foods10020283. PMC 7911259. PMID 33572531. S2CID 231900820.
- ^ Rezasoltani S, Yadegar A, Hatami B, Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Zali MR (2020). «Antimicrobial Resistance as a Hidden Menace Lurking Behind the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Global Impacts of Too Much Hygiene on AMR». Frontiers in Microbiology. 11: 590683. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.590683. PMC 7769770. PMID 33384670.
- ^ Thompson D (8 February 2021). «Hygiene Theater Is Still a Huge Waste of Time». The Atlantic. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ Thompson D (27 July 2020). «Hygiene Theater Is a Huge Waste of Time». The Atlantic. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g Bueckert M, Gupta R, Gupta A, Garg M, Mazumder A (November 2020). «Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronaviruses on Dry Surfaces: Potential for Indirect Transmission». Materials. 13 (22): 5211. Bibcode:2020Mate…13.5211B. doi:10.3390/ma13225211. PMC 7698891. PMID 33218120.
- ^ Bhardwaj R, Agrawal A (November 2020). «How coronavirus survives for days on surfaces». Physics of Fluids. 32 (11): 111706. Bibcode:2020PhFl…32k1706B. doi:10.1063/5.0033306. PMC 7713872. PMID 33281435.
- ^ Chatterjee S, Murallidharan JS, Agrawal A, Bhardwaj R (February 2021). «Why coronavirus survives longer on impermeable than porous surfaces». Physics of Fluids. 33 (2): 021701. Bibcode:2021PhFl…33b1701C. doi:10.1063/5.0037924. PMC 7978145. PMID 33746485.
- ^ CDC (11 February 2020). «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ^ Anthes E (8 April 2021). «Has the Era of Overzealous Cleaning Finally Come to an End?». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ^ «Interim Recommendations for US Community Facilities with Suspected/Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ «Yes, UV phone sanitizers work. That doesn’t mean you need one». The Washington Post. 16 February 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ Patiño-Lugo DF, Vélez M, Velásquez Salazar P, Vera-Giraldo CY, Vélez V, Marín IC, et al. (June 2020). «Non-pharmaceutical interventions for containment, mitigation and suppression of COVID-19 infection». Colombia Medica. 51 (2): e4266. doi:10.25100/cm.v51i2.4266. PMC 7518730. PMID 33012884.
- ^ «COVID-19 Informational Resources for High-Risk Groups | Keeping Education ACTIVE | Partnership to Fight Chronic Disease». fightchronicdisease.org. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ «Quarantine and Isolation». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 29 July 2021. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ a b c Burns J, Movsisyan A, Stratil JM, Biallas RL, Coenen M, Emmert-Fees KM, et al. (Cochrane Public Health Group) (March 2021). «International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (3): CD013717. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMC 8406796. PMID 33763851. S2CID 232356197.
- ^ «COVID Treatment Guidelines: Clinical Management Summary». NIH Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. 8 April 2022. Archived from the original on 5 November 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Wise, Jeff (17 April 2022). «What Happened to Paxlovid, the COVID Wonder Drug?». Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 19 April 2022. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Tao K, Tzou PL, Nouhin J, Bonilla H, Jagannathan P, Shafer RW (July 2021). «SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Therapy». Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 34 (4): e0010921. doi:10.1128/CMR.00109-21. PMC 8404831. PMID 34319150. S2CID 236472654.
- ^ Fisher D, Heymann D (February 2020). «Q&A: The novel coronavirus outbreak causing COVID-19». BMC Medicine. 18 (1): 57. doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01533-w. PMC 7047369. PMID 32106852.
- ^ Liu K, Fang YY, Deng Y, Liu W, Wang MF, Ma JP, et al. (May 2020). «Clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus cases in tertiary hospitals in Hubei Province». Chinese Medical Journal. 133 (9): 1025–1031. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000744. PMC 7147277. PMID 32044814.
- ^ Wang T, Du Z, Zhu F, Cao Z, An Y, Gao Y, Jiang B (March 2020). «Comorbidities and multi-organ injuries in the treatment of COVID-19». Lancet. Elsevier BV. 395 (10228): e52. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30558-4. PMC 7270177. PMID 32171074.
- ^ Wang Y, Wang Y, Chen Y, Qin Q (March 2020). «Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 568–576. doi:10.1002/jmv.25748. PMC 7228347. PMID 32134116.
- ^ «Coronavirus». WebMD. Archived from the original on 1 February 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ Martel J, Ko YF, Young JD, Ojcius DM (May 2020). «Could nasal breathing help to mitigate the severity of COVID-19». Microbes and Infection. 22 (4–5): 168–171. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.002. PMC 7200356. PMID 32387333.
- ^ «Coronavirus recovery: breathing exercises». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2020.
- ^ Wang L, Wang Y, Ye D, Liu Q (March 2020). «Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (6): 105948. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105948. PMC 7156162. PMID 32201353.
- ^ U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5 April 2020). «What to Do if You Are Sick». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ «Update to living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 371: m4475. November 2020. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4475. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 33214213. S2CID 227059995.
- ^ «Q&A: Dexamethasone and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- ^ «Home». National COVID-19 Clinical Evidence Taskforce. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- ^ Motseki, Thabiso Patrick (7 June 2022). «COVID-19 Vaccination Guidelines». www.nih.gov. National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- ^ Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. (April 2020). «Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 382 (18): 1708–1720. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2002032. PMC 7092819. PMID 32109013.
- ^ Henry BM (April 2020). «COVID-19, ECMO, and lymphopenia: a word of caution». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. Elsevier BV. 8 (4): e24. doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30119-3. PMC 7118650. PMID 32178774.
- ^ Kim JS, Lee JY, Yang JW, Lee KH, Effenberger M, Szpirt W, et al. (2021). «Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19». Theranostics. 11 (1): 316–329. doi:10.7150/thno.49713. PMC 7681075. PMID 33391477.
- ^ Doshi P (October 2020). «Will covid-19 vaccines save lives? Current trials aren’t designed to tell us». BMJ. 371: m4037. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4037. PMID 33087398. S2CID 224817161.
- ^ a b Palmieri L, Andrianou X, Barbariol P, Bella A, Bellino S, Benelli E, et al. (22 July 2020). Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 patients dying in Italy Report based on available data on July 22nd, 2020 (PDF) (Report). Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
- ^ Tzoulis P, Waung JA, Bagkeris E, Hussein Z, Biddanda A, Cousins J, et al. (May 2021). «Dysnatremia is a Predictor for Morbidity and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19». The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 106 (6): 1637–1648. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab107. PMC 7928894. PMID 33624101.
- ^ Tzoulis P, Grossman AB, Baldeweg SE, Bouloux P, Kaltsas G (September 2021). «MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Dysnatraemia in COVID-19: prevalence, prognostic impact, pathophysiology, and management». European Journal of Endocrinology. 185 (4): R103–R111. doi:10.1530/EJE-21-0281. PMC 8428074. PMID 34370712.
- ^ Baranovskii DS, Klabukov ID, Krasilnikova OA, Nikogosov DA, Polekhina NV, Baranovskaia DR, et al. (December 1975). «Letter: Acid secretion by gastric mucous membrane». The American Journal of Physiology. 229 (6): 21–25. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1853510. PMC 7738209. PMID 33210948. S2CID 227065216.
- ^ Christensen B, Favaloro EJ, Lippi G, Van Cott EM (October 2020). «Hematology Laboratory Abnormalities in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 46 (7): 845–849. doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715458. PMC 7645834. PMID 32877961.
- ^ «Living with Covid19». NIHR Themed Reviews. National Institute for Health Research. 15 October 2020. doi:10.3310/themedreview_41169.
- ^ a b «How long does COVID-19 last?». UK COVID Symptom Study. 6 June 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ «Summary of COVID-19 Long Term Health Effects: Emerging evidence and Ongoing Investigation» (PDF). University of Washington. 1 September 2020. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ «Long-term symptoms of COVID-19 ‘really concerning’, says WHO chief». UN News. 30 October 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2021.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) – Prognosis». BMJ. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ Lavery AM, Preston LE, Ko JY, Chevinsky JR, DeSisto CL, Pennington AF, et al. (November 2020). «Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Discharged and Experiencing Same-Hospital Readmission – United States, March–August 2020». MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (45): 1695–1699. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6945e2. PMC 7660660. PMID 33180754.
- ^ Vardavas CI, Nikitara K (March 2020). «COVID-19 and smoking: A systematic review of the evidence». Tobacco Induced Diseases. 18: 20. doi:10.18332/tid/119324. PMC 7083240. PMID 32206052.
- ^ a b c Engin AB, Engin ED, Engin A (August 2020). «Two important controversial risk factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Obesity and smoking». Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 78: 103411. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2020.103411. PMC 7227557. PMID 32422280.
- ^ Setti L, Passarini F, De Gennaro G, Barbieri P, Licen S, Perrone MG, et al. (September 2020). «Potential role of particulate matter in the spreading of COVID-19 in Northern Italy: first observational study based on initial epidemic diffusion». BMJ Open. 10 (9): e039338. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039338. PMC 7517216. PMID 32973066.
- ^ Wu X, Nethery RC, Sabath MB, Braun D, Dominici F (November 2020). «Air pollution and COVID-19 mortality in the United States: Strengths and limitations of an ecological regression analysis». Science Advances. 6 (45): eabd4049. Bibcode:2020SciA….6.4049W. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abd4049. PMC 7673673. PMID 33148655.
- ^ Pansini R, Fornacca D (June 2021). «Early Spread of COVID-19 in the Air-Polluted Regions of Eight Severely Affected Countries». Atmosphere. 12 (6): 795. Bibcode:2021Atmos..12..795P. doi:10.3390/atmos12060795.
- ^ Comunian S, Dongo D, Milani C, Palestini P (June 2020). «Air Pollution and Covid-19: The Role of Particulate Matter in the Spread and Increase of Covid-19’s Morbidity and Mortality». International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 17 (12): 4487. doi:10.3390/ijerph17124487. PMC 7345938. PMID 32580440.
- ^ Domingo JL, Marquès M, Rovira J (September 2020). «Influence of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on COVID-19 pandemic. A review». Environmental Research. 188: 109861. Bibcode:2020ER….188j9861D. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109861. PMC 7309850. PMID 32718835.
- ^ «COVID-19: Who’s at higher risk of serious symptoms?». Mayo Clinic.
- ^ Tamara A, Tahapary DL (July 2020). «Obesity as a predictor for a poor prognosis of COVID-19: A systematic review». Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome. 14 (4): 655–659. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.020. PMC 7217103. PMID 32438328.
- ^ Petrakis D, Margină D, Tsarouhas K, Tekos F, Stan M, Nikitovic D, et al. (July 2020). «Obesity – A risk factor for increased COVID-19, severity and lethality (Review)». Molecular Medicine Reports. 22 (1): 9–19. doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11127. PMC 7248467. PMID 32377709.
- ^ Roca-Fernández A, Dennis A, Nicholls R, McGonigle J, Kelly M, Banerjee R, et al. (29 March 2021). «Hepatic Steatosis, Rather Than Underlying Obesity, Increases the Risk of Infection and Hospitalization for COVID-19». Frontiers in Medicine. 8: 636637. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.636637. ISSN 2296-858X. PMC 8039134. PMID 33855033.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020.
- ^ Devresse A, Belkhir L, Vo B, Ghaye B, Scohy A, Kabamba B, et al. (November 2020). «COVID-19 Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Single-Center Case Series of 22 Cases From Belgium». Kidney Medicine. 2 (4): 459–466. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2020.06.001. PMC 7295531. PMID 32775986.
- ^ Dhindsa S, Champion C, Deol E, Lui M, Campbell R, Newman J, et al. (September 2022). «Association of Male Hypogonadism With Risk of Hospitalization for COVID-19». JAMA Network Open. 5 (9): e2229747. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.29747. PMC 9440397. PMID 36053534.
- ^ Shelton JF, Shastri AJ, Ye C, Weldon CH, Filshtein-Sonmez T, Coker D, et al. (June 2021). «Trans-ancestry analysis reveals genetic and nongenetic associations with COVID-19 susceptibility and severity». Nature Genetics. 53 (6): 801–808. doi:10.1038/s41588-021-00854-7. PMID 33888907. S2CID 233372385.
- ^ Wallis C. «One in Seven Dire COVID Cases May Result from a Faulty Immune Response». Scientific American.
- ^ Bastard P, Rosen LB, Zhang Q, Michailidis E, Hoffmann HH, Zhang Y, et al. (October 2020). «Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19». Science. 370 (6515): eabd4585. doi:10.1126/science.abd4585. PMC 7857397. PMID 32972996. S2CID 221914095.
- ^ Fusco DN, Brisac C, John SP, Huang YW, Chin CR, Xie T, et al. (June 2013). «A genetic screen identifies interferon-α effector genes required to suppress hepatitis C virus replication». Gastroenterology. 144 (7): 1438–49, 1449.e1-9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.026. PMC 3665646. PMID 23462180.
- ^ Namkoong H, Edahiro R, Takano T, Nishihara H, Shirai Y, Sonehara K, et al. (September 2022). «DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19». Nature. 609 (7928): 754–760. Bibcode:2022Natur.609..754N. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05163-5. PMC 9492544. PMID 35940203.
- ^ Kousathanas A, Pairo-Castineira E, Rawlik K, Stuckey A, Odhams CA, Walker S, et al. (July 2022). «Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19». Nature. 607 (7917): 97–103. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04576-6. PMC 9259496. PMID 35255492.
- ^ «COVID-19 in children and the role of school settings in transmission – first update». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 23 December 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ «Estimated Disease Burden of COVID-19». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ Reardon S (2 September 2021). «Why don’t kids tend to get as sick from Covid-19?». Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-090121-1. S2CID 239653475. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ «Information for Pediatric Healthcare Providers». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ Götzinger F, Santiago-García B, Noguera-Julián A, Lanaspa M, Lancella L, Calò Carducci FI, et al. (September 2020). «COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: a multinational, multicentre cohort study». The Lancet. Child & Adolescent Health. 4 (9): 653–661. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30177-2. PMC 7316447. PMID 32593339.
- ^ Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M (April 2020). «Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?». The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. 8 (4): e21. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30311-1. PMC 7118626. PMID 32171062.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ Hui DS, I Azhar E, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, et al. (February 2020). «The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health – The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 91: 264–266. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. PMC 7128332. PMID 31953166.
- ^ Murthy S, Gomersall CD, Fowler RA (April 2020). «Care for Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19». JAMA. 323 (15): 1499–1500. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.3633. PMID 32159735.
- ^ Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R (2020). «Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19)». StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 32150360. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Heymann DL, Shindo N, et al. (WHO Scientific and Technical Advisory Group for Infectious Hazards) (February 2020). «COVID-19: what is next for public health?». Lancet. 395 (10224): 542–545. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30374-3. PMC 7138015. PMID 32061313.
- ^ Romiti GF, Corica B, Lip GY, Proietti M (June 2021). «Prevalence and Impact of Atrial Fibrillation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis». Journal of Clinical Medicine. 10 (11): 2490. doi:10.3390/jcm10112490. PMC 8200114. PMID 34199857.
- ^ Wen W, Zhang H, Zhou M, Cheng Y, Ye L, Chen J, et al. (November 2020). «Arrhythmia in patients with severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a meta-analysis». European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 24 (21): 11395–11401. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202011_23632. PMID 33215461. S2CID 227077132.
- ^ Long B, Brady WJ, Koyfman A, Gottlieb M (July 2020). «Cardiovascular complications in COVID-19». The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 38 (7): 1504–1507. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.04.048. PMC 7165109. PMID 32317203.
- ^ Puntmann VO, Carerj ML, Wieters I, Fahim M, Arendt C, Hoffmann J, et al. (November 2020). «Outcomes of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients Recently Recovered From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». JAMA Cardiology. 5 (11): 1265–1273. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3557. PMC 7385689. PMID 32730619.
- ^ Lindner D, Fitzek A, Bräuninger H, Aleshcheva G, Edler C, Meissner K, et al. (November 2020). «Association of Cardiac Infection With SARS-CoV-2 in Confirmed COVID-19 Autopsy Cases». JAMA Cardiology. 5 (11): 1281–1285. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3551. PMC 7385672. PMID 32730555.
- ^ Siripanthong B, Nazarian S, Muser D, Deo R, Santangeli P, Khanji MY, et al. (September 2020). «Recognizing COVID-19-related myocarditis: The possible pathophysiology and proposed guideline for diagnosis and management». Heart Rhythm. 17 (9): 1463–1471. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.001. PMC 7199677. PMID 32387246.
- ^ Xu L, Liu J, Lu M, Yang D, Zheng X (May 2020). «Liver injury during highly pathogenic human coronavirus infections». Liver International. 40 (5): 998–1004. doi:10.1111/liv.14435. PMC 7228361. PMID 32170806.
- ^ Carod-Artal FJ (May 2020). «Neurological complications of coronavirus and COVID-19». Revista de Neurología. 70 (9): 311–322. doi:10.33588/rn.7009.2020179. PMID 32329044. S2CID 226200547.
- ^ Toscano G, Palmerini F, Ravaglia S, Ruiz L, Invernizzi P, Cuzzoni MG, et al. (June 2020). «Guillain-Barré Syndrome Associated with SARS-CoV-2». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (26): 2574–2576. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2009191. PMC 7182017. PMID 32302082.
- ^ «Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents temporally related to COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ HAN Archive – 00432. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (Report). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ Poyiadji N, Shahin G, Noujaim D, Stone M, Patel S, Griffith B (August 2020). «COVID-19-associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Imaging Features». Radiology. 296 (2): E119–E120. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020201187. PMC 7233386. PMID 32228363.
- ^ a b Córdoba-Vives S, Peñaranda G (April 2020). «COVID-19 y Embarazo». Medical Journal of Costa Rica (in Spanish): 629. Archived from the original on 18 June 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ Das S, Dhar S (July 2021). «Mucormycosis Following COVID-19 Infections: an Insight». The Indian Journal of Surgery. 84 (3): 585–586. doi:10.1007/s12262-021-03028-1. PMC 8270771. PMID 34276145. S2CID 235782159.
- ^ Baruah C, Devi P, Deka B, Sharma DK (June 2021). «Mucormycosis and Aspergillosis have been Linked to Covid-19-Related Fungal Infections in India». Advancements in Case Studies. 3 (1). doi:10.31031/AICS.2021.03.000555. ISSN 2639-0531. S2CID 244678882 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ «Living with Covid19». NIHR Themed Review. National Institute for Health Research. 15 October 2020. doi:10.3310/themedreview_41169. S2CID 241034526.
- ^ «Summary of COVID-19 Long Term Health Effects: Emerging evidence and Ongoing Investigation» (PDF). University of Washington. 1 September 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. (February 2020). «Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China». Lancet. 395 (10223): 497–506. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. PMC 7159299. PMID 31986264.
- ^ a b Torres-Castro R, Vasconcello-Castillo L, Alsina-Restoy X, Solis-Navarro L, Burgos F, Puppo H, Vilaró J (November 2020). «Respiratory function in patients post-infection by COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Pulmonology. Elsevier BV. 27 (4): 328–337. doi:10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.10.013. PMC 7687368. PMID 33262076. S2CID 227162748.
- ^ Shaw B, Daskareh M, Gholamrezanezhad A (January 2021). «The lingering manifestations of COVID-19 during and after convalescence: update on long-term pulmonary consequences of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)». La Radiologia Medica. 126 (1): 40–46. doi:10.1007/s11547-020-01295-8. PMC 7529085. PMID 33006087.
- ^ Zhao YM, Shang YM, Song WB, Li QQ, Xie H, Xu QF, et al. (August 2020). «Follow-up study of the pulmonary function and related physiological characteristics of COVID-19 survivors three months after recovery». EClinicalMedicine. 25: 100463. doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.11.003. PMC 7654356. PMID 32838236.
- ^ «COVID-19 Lung Damage». Johns Hopkins Medicine. 28 February 2022. Retrieved 21 May 2022.
- ^ Taquet M, Sillett R, Zhu L, Mendel J, Camplisson I, Dercon Q, Harrison PJ (17 August 2022). «Neurological and psychiatric risk trajectories after SARS-CoV-2 infection: an analysis of 2-year retrospective cohort studies including 1 284 437 patients». The Lancet Psychiatry. 9 (10): 815–827. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(22)00260-7. ISSN 2215-0366. PMC 9385200. PMID 35987197. S2CID 251626731.
- ^ «Immune responses and correlates of protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2». European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 18 May 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- ^ Vabret N, Britton GJ, Gruber C, Hegde S, Kim J, Kuksin M, et al. (June 2020). «Immunology of COVID-19: Current State of the Science». Immunity. 52 (6): 910–941. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.002. PMC 7200337. PMID 32505227.
- ^ Wang Z, Muecksch F, Schaefer-Babajew D, Finkin S, Viant C, Gaebler C, et al. (July 2021). «Naturally enhanced neutralizing breadth against SARS-CoV-2 one year after infection». Nature. 595 (7867): 426–431. Bibcode:2021Natur.595..426W. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03696-9. PMC 8277577. PMID 34126625.
- ^ a b Cohen JI, Burbelo PD (December 2020). «Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Vaccines». Clinical Infectious Diseases. 73 (11): e4223–e4228. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1866. PMC 7799323. PMID 33338197. S2CID 229323810.
- ^ a b Wang J, Kaperak C, Sato T, Sakuraba A (August 2021). «COVID-19 reinfection: a rapid systematic review of case reports and case series». Journal of Investigative Medicine. 69 (6): 1253–1255. doi:10.1136/jim-2021-001853. ISSN 1081-5589. PMID 34006572. S2CID 234773697.
- ^ a b «How soon after catching COVID-19 can you get it again?». ABC News. 2 May 2022. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (May 2012). «Lesson 3: Measures of Risk Section 3: Mortality Frequency Measures». Principles of Epidemiology in Public Health Practice (Third ed.). U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). No. SS1978. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Ritchie H, Roser M (25 March 2020). Chivers T (ed.). «What do we know about the risk of dying from COVID-19?». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Castagnoli R, Votto M, Licari A, Brambilla I, Bruno R, Perlini S, et al. (September 2020). «Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review». JAMA Pediatrics. 174 (9): 882–889. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1467. PMID 32320004.
- ^ Lu X, Zhang L, Du H, Zhang J, Li YY, Qu J, et al. (April 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children». The New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 382 (17): 1663–1665. doi:10.1056/nejmc2005073. PMC 7121177. PMID 32187458.
- ^ Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, Tong S (June 2020). «Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China». Pediatrics. 145 (6): e20200702. doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0702. PMID 32179660. S2CID 219118986.
- ^ a b c d Dehingia N (2021). «Sex differences in COVID-19 case fatality: do we know enough?». The Lancet. Global Health. 9 (1): e14–e15. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30464-2. PMC 7834645. PMID 33160453.
- ^ Lazzerini M, Putoto G (May 2020). «COVID-19 in Italy: momentous decisions and many uncertainties». The Lancet. Global Health. 8 (5): e641–e642. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30110-8. PMC 7104294. PMID 32199072.
- ^ Ritchie H, Ortiz-Ospina E, Beltekian D, Mathieu E, Hasell J, MacDonald B, et al. (5 March 2020). «What do we know about the risk of dying from COVID-19?». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ «Total confirmed cases of COVID-19 per million people». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2022.[needs update]
- ^ «Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million people». Our World in Data.
- ^ Mallapaty S (June 2020). «How deadly is the coronavirus? Scientists are close to an answer». Nature. 582 (7813): 467–468. Bibcode:2020Natur.582..467M. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01738-2. PMID 32546810. S2CID 219726496.
- ^ Alwan NA, Burgess RA, Ashworth S, Beale R, Bhadelia N, Bogaert D, et al. (October 2020). «Scientific consensus on the COVID-19 pandemic: we need to act now». Lancet. 396 (10260): e71–e72. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32153-X. PMC 7557300. PMID 33069277.
- ^ Meyerowitz-Katz G, Merone L (December 2020). «A systematic review and meta-analysis of published research data on COVID-19 infection fatality rates». International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 101: 138–148. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.1464. PMC 7524446. PMID 33007452.
- ^ Zhang D, Hu M, Ji Q (October 2020). «Financial markets under the global pandemic of COVID-19». Finance Research Letters. 36: 101528. Bibcode:2020CSFX….500043D. doi:10.1016/j.csfx.2020.100043. PMC 7402242. PMID 32837360.
- ^ a b c d e Levin AT, Hanage WP, Owusu-Boaitey N, Cochran KB, Walsh SP, Meyerowitz-Katz G (December 2020). «Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications». European Journal of Epidemiology. 35 (12): 1123–1138. doi:10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1. PMC 7721859. PMID 33289900.
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- ^ World Health Organization (22 December 2020). «Background paper on Covid-19 disease and vaccines: prepared by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on immunization working group on COVID-19 vaccines». World Health Organization. hdl:10665/338095.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 30» (PDF). 19 February 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 31» (PDF). 20 February 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (4 July 2020). «The Pandemic’s Big Mystery: How Deadly Is the Coronavirus? – Even with more than 500,000 dead worldwide, scientists are struggling to learn how often the virus kills. Here’s why». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ «Global Research and Innovation Forum on COVID-19: Virtual Press Conference» (PDF). World Health Organization. 2 July 2020.
- ^ «Estimating mortality from COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 21 September 2020.
- ^ Shaffer C (23 October 2021). «Covid-19 still rife in Iran». New Scientist. 252 (3357): 10–11. Bibcode:2021NewSc.252…10S. doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(21)01865-0. ISSN 0262-4079. PMC 8536311. PMID 34720322.
- ^ «COVID-19: Data». City of New York.
- ^ Wilson L (May 2020). «SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, Infection Fatality Rate (IFR) Implied by the Serology, Antibody, Testing in New York City». SSRN 3590771.
- ^ Yang W, Kandula S, Huynh M, Greene SK, Van Wye G, Li W, et al. (February 2021). «Estimating the infection-fatality risk of SARS-CoV-2 in New York City during the spring 2020 pandemic wave: a model-based analysis». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 21 (2): 203–212. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30769-6. PMC 7572090. PMID 33091374.
- ^ Modi C (21 April 2020). «How deadly is COVID-19? Data Science offers answers from Italy mortality data». Medium. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 September 2020. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^ Salje H, Tran Kiem C, Lefrancq N, Courtejoie N, Bosetti P, Paireau J, et al. (July 2020). «Estimating the burden of SARS-CoV-2 in France». Science. 369 (6500): 208–211. Bibcode:2020Sci…369..208S. doi:10.1126/science.abc3517. PMC 7223792. PMID 32404476.
- ^ McIntosh K (April 2021). «Covid 19 Clinical Features». UpToDate. Retrieved 12 May 2021.
- ^ Peckham H, de Gruijter NM, Raine C, Radziszewska A, Ciurtin C, Wedderburn LR, et al. (December 2020). «Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 6317. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.6317P. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6. PMC 7726563. PMID 33298944.
- ^ Abate BB, Kassie AM, Kassaw MW, Aragie TG, Masresha SA (October 2020). «Sex difference in coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ Open. 10 (10): e040129. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040129. PMC 7539579. PMID 33028563.
- ^ a b c The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team (February 2020). «The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) – China, 2020». China CDC Weekly. 2 (8): 113–122. doi:10.46234/ccdcw2020.032. PMC 839292. PMID 34594836.
- ^ Hu Y, Sun J, Dai Z, Deng H, Li X, Huang Q, et al. (June 2020). «Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis». Journal of Clinical Virology. 127: 104371. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371. PMC 7195434. PMID 32315817.
- ^ Fu L, Wang B, Yuan T, Chen X, Ao Y, Fitzpatrick T, et al. (June 2020). «Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis». The Journal of Infection. 80 (6): 656–665. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.041. PMC 7151416. PMID 32283155.
- ^ Yuki K, Fujiogi M, Koutsogiannaki S (June 2020). «COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review». Clinical Immunology. 215: 108427. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427. PMC 7169933. PMID 32325252. S2CID 216028003.
- ^ Rabin RC (20 March 2020). «In Italy, Coronavirus Takes a Higher Toll on Men». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 weekly surveillance report». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b Gupta AH (3 April 2020). «Does Covid-19 Hit Women and Men Differently? U.S. Isn’t Keeping Track». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b Dorn AV, Cooney RE, Sabin ML (April 2020). «COVID-19 exacerbating inequalities in the US». Lancet. 395 (10232): 1243–1244. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30893-X. PMC 7162639. PMID 32305087.
- ^ a b Shauly-Aharonov, Michal; Shafrir, Asher; Paltiel, Ora; Calderon-Margalit, Ronit; Safadi, Rifaat; Bicher, Roee; Barenholz-Goultschin, Orit; Stokar, Joshua (22 July 2021). «Both high and low pre-infection glucose levels associated with increased risk for severe COVID-19: New insights from a population-based study». PLOS ONE. 16 (7): e0254847. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1654847S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0254847. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 8297851. PMID 34293038.
- ^ Adams ML, Katz DL, Grandpre J (August 2020). «Population-Based Estimates of Chronic Conditions Affecting Risk for Complications from Coronavirus Disease, United States». Emerging Infectious Diseases. 26 (8): 1831–1833. doi:10.3201/eid2608.200679. PMC 7392427. PMID 32324118.
- ^ Batthyány K (13 October 2020). «Coronavirus y Desigualdades preexistentes: Género y Cuidados». CLACSO (Consejo Latinoamericano de Ciencias Sociales). Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ «COVID-19 Presents Significant Risks for American Indian and Alaska Native People». 14 May 2020.
- ^ «COVID-19 Presents Significant Risks for American Indian and Alaska Native People». 14 May 2020.
- ^ Laurencin CT, McClinton A (June 2020). «The COVID-19 Pandemic: a Call to Action to Identify and Address Racial and Ethnic Disparities». Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities. 7 (3): 398–402. doi:10.1007/s40615-020-00756-0. PMC 7166096. PMID 32306369.
- ^ «How coronavirus deaths in the UK compare by race and ethnicity». The Independent. 9 June 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ «Emerging findings on the impact of COVID-19 on black and minority ethnic people». The Health Foundation. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ Butcher B, Massey J (9 June 2020). «Why are more BAME people dying from coronavirus?». BBC News. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ a b c «The ancient Neanderthal hand in severe COVID-19». ScienceDaily. 30 September 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- ^ «WHO Director-General’s statement on the advice of the IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus». World Health Organization (WHO).
- ^ Garg S, Kim L, Whitaker M, O’Halloran A, Cummings C, Holstein R, et al. (April 2020). «Hospitalization Rates and Characteristics of Patients Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019 – COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1–30, 2020». MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (15): 458–464. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3. PMC 7755063. PMID 32298251.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ Zhao Q, Meng M, Kumar R, Wu Y, Huang J, Lian N, et al. (October 2020). «The impact of COPD and smoking history on the severity of COVID-19: A systemic review and meta-analysis». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (10): 1915–1921. doi:10.1002/jmv.25889. PMC 7262275. PMID 32293753.
- ^ «Smoking and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ DeRobertis J (3 May 2020). «People who use drugs are more vulnerable to coronavirus. Here’s what clinics are doing to help». The Advocate (Louisiana). Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020.
- ^ Frutos R, Gavotte L, Devaux CA (November 2021). «Understanding the origin of COVID-19 requires to change the paradigm on zoonotic emergence from the spillover to the circulation model». Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 95: 104812. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104812. PMC 7969828. PMID 33744401.
- ^ Holmes EC, Goldstein SA, Rasmussen AL, Robertson DL, Crits-Christoph A, Wertheim JO, et al. (September 2021). «The origins of SARS-CoV-2: A critical review». Cell. 184 (19): 4848–4856. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.017. PMC 8373617. PMID 34480864.
- ^ «WHO-convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part». World Health Organization. 30 March 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ^ Duarte F (24 February 2020). «As the cases of coronavirus increase in China and around the world, the hunt is on to identify «patient zero»«. BBC News. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ Pekar JE, Magee P, Parker E, Moshiri N, Izhikevich K, Havens JL, et al. (26 July 2022). «The molecular epidemiology of multiple zoonotic origins of SARS-CoV-2». Science. 377 (6609): 960–966. Bibcode:2022Sci…377..960P. doi:10.1126/science.abp8337. PMC 9348752. PMID 35881005.
- ^ Gill V (26 July 2022). «Covid origin studies say evidence points to Wuhan market».
- ^ Worobey M, Levy JI, Serrano LM, Crits-Christoph A, Pekar JE, Goldstein SA, et al. (July 2022). «The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan was the early epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic». Science. 377 (6609): 951–959. Bibcode:2022Sci…377..951W. doi:10.1126/science.abp8715. PMC 9348750. PMID 35881010. S2CID 251067542.
- ^ «Debate deepens over Wuhan wet market’s role in kickstarting the pandemic». National Geographic. 27 July 2022.
- ^ Li X, Zai J, Zhao Q, Nie Q, Li Y, Foley BT, Chaillon A (June 2020). «Evolutionary history, potential intermediate animal host, and cross-species analyses of SARS-CoV-2». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (6): 602–611. doi:10.1002/jmv.25731. PMC 7228310. PMID 32104911.
- ^ Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF (April 2020). «The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2». Nature Medicine. 26 (4): 450–452. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9. PMC 7095063. PMID 32284615.
- ^ van Dorp L, Acman M, Richard D, Shaw LP, Ford CE, Ormond L, et al. (September 2020). «Emergence of genomic diversity and recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2». Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 83: 104351. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104351. PMC 7199730. PMID 32387564.
- ^ Grose TK (13 May 2020). «Did the Coronavirus Originate Outside of Wuhan?». U.S. News & World Report.
- ^ Wolf ZB (25 May 2021). «Analysis: Why scientists are suddenly more interested in the lab-leak theory of Covid’s origin». CNN. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ Maxmen A (September 2021). «US COVID origins report: researchers pleased with scientific approach». Nature. 597 (7875): 159–160. Bibcode:2021Natur.597..159M. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-02366-0. PMID 34465917. S2CID 237373547.
- ^ Paun C, Zeller S, Reader R, Leonard B, Scullion G (4 November 2022). «Cross-examining the lab-leak theorists». Politico. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ Hosenball M, Zengerle P (30 October 2021). «U.S. spy agencies say origins of COVID-19 may never be known». Reuters. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ Wu YC, Chen CS, Chan YJ (March 2020). «The outbreak of COVID-19: An overview». Journal of the Chinese Medical Association. 83 (3): 217–220. doi:10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000270. PMC 7153464. PMID 32134861.
- ^ Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF (February 2020). «A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern». Lancet. 395 (10223): 470–473. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9. PMC 7135038. PMID 31986257.
- ^ Cohen J (January 2020). «Wuhan seafood market may not be source of novel virus spreading globally». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abb0611.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus – China». World Health Organization (WHO). 12 January 2020. Archived from the original on 14 January 2020.
- ^ Kessler G (17 April 2020). «Trump’s false claim that the WHO said the coronavirus was ‘not communicable’«. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Kuo L (21 January 2020). «China confirms human-to-human transmission of coronavirus». The Guardian. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ Epidemiology Working Group For Ncip Epidemic Response; Chinese Center for Disease Control Prevention (February 2020). «[The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China]». Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi (in Chinese). 41 (2): 145–151. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003. PMID 32064853. S2CID 211133882.
- ^ Areddy JT (26 May 2020). «China Rules Out Animal Market and Lab as Coronavirus Origin». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ Kelland K (19 June 2020). «Italy sewage study suggests COVID-19 was there in December 2019». Reuters. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ Heymann DL, Shindo N (February 2020). «COVID-19: what is next for public health?». Lancet. 395 (10224): 542–545. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3. PMC 7138015. PMID 32061313.
- ^ Bryner J (14 March 2020). «1st known case of coronavirus traced back to November in China». livescience.com. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ Canadian Politics (8 April 2020). «The birth of a pandemic: How COVID-19 went from Wuhan to Toronto | National Post». National Post. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ 高昱 (26 February 2020). «独家 | 新冠病毒基因测序溯源:警报是何时拉响的» [Exclusive | Tracing the New Coronavirus gene sequencing: when did the alarm sound]. Caixin (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 27 February 2020. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- ^ 路子康. «最早上报疫情的她,怎样发现这种不一样的肺炎». 中国网新闻 (in Chinese (China)). 北京. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ «Undiagnosed pneumonia – China (HU): RFI». ProMED Mail. ProMED. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ «‘Hero who told the truth’: Chinese rage over coronavirus death of whistleblower doctor». The Guardian. 7 February 2020.
- ^ Kuo L (11 March 2020). «Coronavirus: Wuhan doctor speaks out against authorities». The Guardian. London.
- ^ «Novel Coronavirus». World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ^ «武汉现不明原因肺炎 官方确认属实:已经做好隔离». Xinhua Net 新華網. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ 武汉市卫健委关于当前我市肺炎疫情的情况通报. WJW.Wuhan.gov.cn (in Chinese). Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 9 January 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ «Mystery pneumonia virus probed in China». BBC News. 3 January 2020. Archived from the original on 5 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. (March 2020). «Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (13): 1199–1207. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316. PMC 7121484. PMID 31995857.
- ^ «China confirms sharp rise in cases of SARS-like virus across the country». 20 January 2020. Archived from the original on 20 January 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- ^ a b «Flattery and foot dragging: China’s influence over the WHO under scrutiny». The Globe and Mail. 25 April 2020.
- ^ Horton R (18 March 2020). «Scientists have been sounding the alarm on coronavirus for months. Why did Britain fail to act?». The Guardian. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ «China delayed releasing coronavirus info, frustrating WHO». Associated Press. 2 June 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Primi due casi in Italia» [Coronavirus: First two cases in Italy]. Corriere della sera (in Italian). 31 January 2020. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus: Number of COVID-19 deaths in Italy surpasses China as total reaches 3,405». Sky News. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ McNeil Jr DG (26 March 2020). «The U.S. Now Leads the World in Confirmed Coronavirus Cases». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ «Studies Show N.Y. Outbreak Originated in Europe». The New York Times. 8 April 2020. Archived from the original on 8 April 2020.
- ^ Irish J (4 May 2020). Lough RM, Graff P (eds.). «After retesting samples, French hospital discovers COVID-19 case from December». Reuters. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ Deslandes A, Berti V, Tandjaoui-Lambotte Y, Alloui C, Carbonnelle E, Zahar JR, et al. (June 2020). «SARS-CoV-2 was already spreading in France in late December 2019». International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 55 (6): 106006. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106006. PMC 7196402. PMID 32371096.
- ^ «2 died with coronavirus weeks before 1st U.S. virus death». PBS NewsHour. 22 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ Michael-Kordatou I, Karaolia P, Fatta-Kassinos D (October 2020). «Sewage analysis as a tool for the COVID-19 pandemic response and management: the urgent need for optimised protocols for SARS-CoV-2 detection and quantification». Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 8 (5): 104306. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2020.104306. PMC 7384408. PMID 32834990.
- ^ Platto S, Xue T, Carafoli E (September 2020). «COVID19: an announced pandemic». Cell Death & Disease. 11 (9): 799. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02995-9. PMC 7513903. PMID 32973152.
- ^ Kavya B, Abraham R (3 October 2021). Shumaker L, Wardell J (eds.). «Global COVID-19 deaths hit 5 million as Delta variant sweeps the world». Reuters.com. Reuters.
- ^ «China coronavirus: Misinformation spreads online about origin and scale». BBC News. 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 4 February 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ Taylor J (31 January 2020). «Bat soup, dodgy cures and ‘diseasology’: the spread of coronavirus misinformation». The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
- ^ «Here’s A Running List Of Disinformation Spreading About The Coronavirus». Buzzfeed News. Archived from the original on 6 February 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ «Misleading claim circulates online about infection fatality ratio of Covid-19 in the US». Fact Check. 8 October 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ a b c d Kampf G, Brüggemann Y, Kaba HE, Steinmann J, Pfaender S, Scheithauer S, Steinmann E (December 2020). «Potential sources, modes of transmission and effectiveness of prevention measures against SARS-CoV-2». The Journal of Hospital Infection. 106 (4): 678–697. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2020.09.022. PMC 7500278. PMID 32956786.
- ^ Shi J, Wen Z, Zhong G, Yang H, Wang C, Huang B, et al. (May 2020). «Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS-coronavirus 2». Science. 368 (6494): 1016–1020. doi:10.1126/science.abb7015. PMC 7164390. PMID 32269068.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Salajegheh Tazerji S, Magalhães Duarte P, Rahimi P, Shahabinejad F, Dhakal S, Singh Malik Y, et al. (September 2020). «Transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to animals: an updated review». Journal of Translational Medicine. 18 (1): 358. doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02534-2. PMC 7503431. PMID 32957995.
- ^ a b c Gorman J (22 January 2021). «The Coronavirus Kills Mink, So They Too May Get a Vaccine». The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ Dhama K, Sharun K, Tiwari R, Dadar M, Malik YS, Singh KP, Chaicumpa W (June 2020). «COVID-19, an emerging coronavirus infection: advances and prospects in designing and developing vaccines, immunotherapeutics, and therapeutics». Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 16 (6): 1232–1238. doi:10.1080/21645515.2020.1735227. PMC 7103671. PMID 32186952.
- ^ Zhang L, Liu Y (May 2020). «Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: A systematic review». Journal of Medical Virology. 92 (5): 479–490. doi:10.1002/jmv.25707. PMC 7166986. PMID 32052466.
- ^ «Interim Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines for Handling and Processing Specimens Associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)». Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Lab Biosafety Guidelines. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Aristovnik A, Ravšelj D, Umek L (November 2020). «A Bibliometric Analysis of COVID-19 across Science and Social Science Research Landscape». Sustainability. 12 (21): 9132. doi:10.3390/su12219132.
- ^ Kupferschmidt K (3 December 2020). «First-of-its-kind African trial tests common drugs to prevent severe COVID-19». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abf9987. Retrieved 8 March 2022.
- ^ Reardon S (November 2020). «For COVID Drugs, Months of Frantic Development Lead to Few Outright Successes». Scientific American. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ^ Kucharski AJ, Russell TW, Diamond C, Liu Y, Edmunds J, Funk S, Eggo RM (May 2020). «Early dynamics of transmission and control of COVID-19: a mathematical modelling study». The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 20 (5): 553–558. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30144-4. PMC 7158569. PMID 32171059.
- ^ «Update to living systematic review on prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of covid-19». BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 372: n236. 3 February 2021. doi:10.1136/bmj.n236. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 33536183. S2CID 231775762.
- ^ Giordano G, Blanchini F, Bruno R, Colaneri P, Di Filippo A, Di Matteo A, Colaneri M (June 2020). «Modelling the COVID-19 epidemic and implementation of population-wide interventions in Italy». Nature Medicine. 26 (6): 855–860. arXiv:2003.09861. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0883-7. PMC 7175834. PMID 32322102.
- ^ Prem K, Liu Y, Russell TW, Kucharski AJ, Eggo RM, Davies N, et al. (May 2020). «The effect of control strategies to reduce social mixing on outcomes of the COVID-19 epidemic in Wuhan, China: a modelling study». The Lancet. Public Health. 5 (5): e261–e270. doi:10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30073-6. PMC 7158905. PMID 32220655.
- ^ Emanuel EJ, Persad G, Upshur R, Thome B, Parker M, Glickman A, et al. (May 2020). «Fair Allocation of Scarce Medical Resources in the Time of Covid-19». The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (21): 2049–2055. doi:10.1056/NEJMsb2005114. PMID 32202722.
- ^ Kermack WO, McKendrick AG (1927). «A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character. 115 (772): 700–721. Bibcode:1927RSPSA.115..700K. doi:10.1098/rspa.1927.0118.
- ^ Mittal R, Ni R, Seo JH (2020). «The flow physics of COVID-19». Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 894: –2. arXiv:2004.09354. Bibcode:2020JFM…894F…2M. doi:10.1017/jfm.2020.330.
- ^ Ronchi E, Lovreglio R (October 2020). «EXPOSED: An occupant exposure model for confined spaces to retrofit crowd models during a pandemic». Safety Science. 130: 104834. arXiv:2005.04007. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104834. PMC 7373681. PMID 32834509.
- ^ Badr HS, Du H, Marshall M, Dong E, Squire MM, Gardner LM (November 2020). «Association between mobility patterns and COVID-19 transmission in the USA: a mathematical modelling study». The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 20 (11): 1247–1254. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30553-3. PMC 7329287. PMID 32621869.
- ^ McKibbin W, Roshen F (2020). «The global macroeconomic impacts of COVID-19: Seven scenarios» (PDF). CAMA Working Paper. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3547729. S2CID 216307705.
- ^ Bundy J, Pfarrer MD, Short CE, Coombs WT (July 2017). «Crises and crisis management: Integration, interpretation, and research development». Journal of Management. 43 (6): 1661–92. doi:10.1177/0149206316680030. S2CID 152223772.
- ^ Kraus S, Clauss T, Breier M, Gast J, Zardini A, Tiberius V (2020). «The economics of COVID-19: initial empirical evidence on how family firms in five European countries cope with the corona crisis». International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research. 26 (5): 1067–1092. doi:10.1108/IJEBR-04-2020-0214. ISSN 1355-2554. S2CID 219144929.
- ^ «COVID-19 treatment and vaccine tracker» (PDF). Milken Institute. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ a b Koch S, Pong W (13 March 2020). «First up for COVID-19: nearly 30 clinical readouts before end of April». BioCentury Inc. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Kupferschmidt K, Cohen J (March 2020). «WHO launches global megatrial of the four most promising coronavirus treatments». Science. doi:10.1126/science.abb8497.
- ^ «UN health chief announces global ‘solidarity trial’ to jumpstart search for COVID-19 treatment». UN News. 18 March 2020. Archived from the original on 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- ^ «Citing safety concerns, the W.H.O. paused tests of a drug Trump said he had taken». The New York Times. 26 May 2020. Archived from the original on 26 May 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Hydroxychloroquine does not benefit adults hospitalized with COVID-19». National Institutes of Health (NIH) (Press release). 9 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Warns of Newly Discovered Potential Drug Interaction That May Reduce Effectiveness of a COVID-19 Treatment Authorized for Emergency Use». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 June 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ^ «France bans use of hydroxychloroquine, drug touted by Trump, in coronavirus patients». CBS News. 27 May 2020.
- ^ Boseley S (16 June 202). «Recovery trial for Covid-19 treatments: what we know so far». The Guardian. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «WHO welcomes preliminary results about dexamethasone use in treating critically ill COVID-19 patients». World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). 16 June 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «Q&A: Dexamethasone and COVID-19». World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ «Corticosteroids». COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (2020). Corticosteroids for COVID-19: living guidance, 2 September 2020 (Report). hdl:10665/334125. WHO/2019-nCoV/Corticosteroids/2020.1.
- ^ «WHO updates clinical care guidance with corticosteroid recommendations». World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Sterne JA, Murthy S, Diaz JV, Slutsky AS, Villar J, Angus DC, et al. (The WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group) (October 2020). «Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis». JAMA. 324 (13): 1330–1341. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17023. PMC 7489434. PMID 32876694. S2CID 221467783.
- ^ Prescott HC, Rice TW (October 2020). «Corticosteroids in COVID-19 ARDS: Evidence and Hope During the Pandemic». JAMA. 324 (13): 1292–1295. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.16747. PMID 32876693. S2CID 221468015.
- ^ a b «EMA endorses use of dexamethasone in COVID-19 patients on oxygen or mechanical ventilation». European Medicines Agency (EMA) (Press release). 18 September 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2020. Text was copied from this source which is European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ Dexamethasone in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 (PDF) (Report). European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2020.
- ^ a b c
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 9 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 10 February 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Revokes Emergency Use Authorization for Monoclonal Antibody Bamlanivimab». U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 16 April 2021. Retrieved 16 April 2021.
- ^ Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S (April 2020). «Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19». Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis. 10 (2): 102–108. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001. PMC 7104082. PMID 32282863.
- ^ Zhao Z, Wei Y, Tao C (January 2021). «An enlightening role for cytokine storm in coronavirus infection». Clinical Immunology. 222: 108615. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108615. PMC 7583583. PMID 33203513.
- ^ Liu R, Miller J (3 March 2020). «China approves use of Roche drug in battle against coronavirus complications». Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Xu X, Han M, Li T, Sun W, Wang D, Fu B, et al. (May 2020). «Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (20): 10970–10975. Bibcode:2020PNAS..11710970X. doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117. PMC 7245089. PMID 32350134.
- ^ Ovadia D, Agenzia Z. «COVID-19 – Italy launches an independent trial on tocilizumab». Univadis from Medscape. Aptus Health. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ «Tocilizumab in COVID-19 Pneumonia (TOCIVID-19) (TOCIVID-19)». clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Various sources:
- «How doctors can potentially significantly reduce the number of deaths from Covid-19». Vox. 12 March 2020. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- Ruan Q, Yang K, Wang W, Jiang L, Song J (May 2020). «Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China». Intensive Care Medicine. 46 (5): 846–848. doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x. PMC 7080116. PMID 32125452.
- Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ (March 2020). «COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression». Lancet. 395 (10229): 1033–1034. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. PMC 7270045. PMID 32192578.
- ^ Slater H (26 March 2020). «FDA Approves Phase III Clinical Trial of Tocilizumab for COVID-19 Pneumonia». cancernetwork.com. Cancer Network. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Locke FL, Neelapu SS, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, et al. (2017). «Preliminary Results of Prophylactic Tocilizumab after Axicabtageneciloleucel (axi-cel; KTE-C19) Treatment for Patients with Refractory, Aggressive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)». Blood. 130 (Supplement 1): 1547. doi:10.1182/blood.V130.Suppl_1.1547.1547. S2CID 155698207.
- ^ Sterner RM, Sakemura R, Cox MJ, Yang N, Khadka RH, Forsman CL, et al. (February 2019). «GM-CSF inhibition reduces cytokine release syndrome and neuroinflammation but enhances CAR T cell function in xenografts». Blood. 133 (7): 697–709. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-10-881722. PMC 6376281. PMID 30463995.
- ^ a b c d e Casadevall A, Pirofski LA (April 2020). «The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19». The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 130 (4): 1545–1548. doi:10.1172/JCI138003. PMC 7108922. PMID 32167489.
- ^ a b c Piechotta V, Iannizzi C, Chai KL, Valk SJ, Kimber C, Dorando E, et al. (May 2021). «Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (5): CD013600. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4. PMC 8135693. PMID 34013969.
- ^ a b Ho M (April 2020). «Perspectives on the development of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2». Antibody Therapeutics. 3 (2): 109–114. doi:10.1093/abt/tbaa009. PMC 7291920. PMID 32566896.
- ^ Yang L, Liu W, Yu X, Wu M, Reichert JM, Ho M (July 2020). «COVID-19 antibody therapeutics tracker: a global online database of antibody therapeutics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19». Antibody Therapeutics. 3 (3): 205–212. doi:10.1093/abt/tbaa020. PMC 7454247. PMID 33215063.
- ^ Maccaro A, Piaggio D, Pagliara S, Pecchia L (June 2021). «The role of ethics in science: a systematic literature review from the first wave of COVID-19». Health and Technology. 11 (5): 1063–1071. doi:10.1007/s12553-021-00570-6. ISSN 2190-7188. PMC 8175060. PMID 34104626.
- ^ McGuire AL, Aulisio MP, Davis FD, Erwin C, Harter TD, Jagsi R, et al. (July 2020). «Ethical Challenges Arising in the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview from the Association of Bioethics Program Directors (ABPD) Task Force». The American Journal of Bioethics. 20 (7): 15–27. doi:10.1080/15265161.2020.1764138. PMID 32511078. S2CID 219552665.
- ^ Wenham C, Smith J, Morgan R (March 2020). «COVID-19: the gendered impacts of the outbreak». Lancet. 395 (10227): 846–848. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30526-2. PMC 7124625. PMID 32151325.
- ^ Tolchin B, Hull SC, Kraschel K (October 2020). «Triage and justice in an unjust pandemic: ethical allocation of scarce medical resources in the setting of racial and socioeconomic disparities». Journal of Medical Ethics. 47 (3): 200–202. doi:10.1136/medethics-2020-106457. PMID 33067315. S2CID 223558059.
- ^ Sabatello M, Burke TB, McDonald KE, Appelbaum PS (October 2020). «Disability, Ethics, and Health Care in the COVID-19 Pandemic». American Journal of Public Health. 110 (10): 1523–1527. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2020.305837. PMC 7483109. PMID 32816541.
- ^ Chin T, Kahn R, Li R, Chen JT, Krieger N, Buckee CO, et al. (September 2020). «US-county level variation in intersecting individual, household and community characteristics relevant to COVID-19 and planning an equitable response: a cross-sectional analysis». BMJ Open. 10 (9): e039886. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039886. PMC 7467554. PMID 32873684.
- ^ Elgar FJ, Stefaniak A, Wohl MJ (October 2020). «The trouble with trust: Time-series analysis of social capital, income inequality, and COVID-19 deaths in 84 countries». Social Science & Medicine. 263: 113365. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113365. PMC 7492158. PMID 32981770.
- ^ Uttley H (2 March 2021). «Pandemic sends demand for cold and flu remedies to record low». The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ^ «2020–2021 Flu Season Summary». U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 25 October 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
Further reading
- Erola Pairo-Castineira; Sara Clohisey; Lucija Klarić; et al. (11 December 2020). «Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in Covid-19». Nature. doi:10.1038/S41586-020-03065-Y. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 33307546. Wikidata Q104287299. Scholia Q104287299.
- «Progress report on the coronavirus pandemic». Nature. 584 (7821): 325. 1 August 2020. doi:10.1038/D41586-020-02414-1. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 32814893. Wikidata Q98568681.
- COVID-19 infection prevention and control measures for primary care, including general practitioner practices, dental clinics and pharmacy settings: first update. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) (Report). October 2020.
External links
Health agencies
- Coronavirus disease (COVID‑19) Facts by the World Health Organization (WHO)
- Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Coronavirus (COVID‑19) by the UK National Health Service (NHS)
Directories
- Coronavirus Resource Center at the Center for Inquiry
- COVID-19 at Curlie
- COVID‑19 Resource Directory on OpenMD
- COVID‑19 Information on FireMountain.net Archived 13 January 2022 at the Wayback Machine
Medical journals
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‑19) by JAMA
- BMJ’s Coronavirus (covid‑19) Hub by the BMJ
- Novel Coronavirus Information Center by Elsevier
- COVID‑19 Resource Centre by The Lancet
- Coronavirus (COVID‑19) Research Highlights by Springer Nature
- Coronavirus (Covid‑19) by The New England Journal of Medicine
- Covid‑19: Novel Coronavirus Archived 24 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine by Wiley Publishing
Treatment guidelines
- «JHMI Clinical Recommendations for Available Pharmacologic Therapies for COVID-19» (PDF). Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- «Bouncing Back From COVID-19: Your Guide to Restoring Movement» (PDF). Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- «Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19». Infectious Diseases Society of America.
- «Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines» (PDF). National Institutes of Health.
- World Health Organization (2022). Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline, 14 January 2022 (Report). hdl:10665/351006. WHO/2019-nCoV/therapeutics/2022.1.
- NHS England and NHS Improvement. National Guidance for post-COVID syndrome assessment clinics (Report).
Название коронавируса официально внесли в оксфордский словарь английского языка. COVID-19 получил определение как вызванное коронавирусом острое респираторное заболевание, особенно опасное для пожилых и людей с сопутствующими заболеваниями. Лингвисты в беседе с сайтом «Невские новости» рассказали, русифицировалось ли новое слово и можно ли его склонять.
Лексикографы помимо COVID-19 внесли и неологизмы, такие, как «самоизоляция», «социальная дистанция» и аббревиатура WFH (work from home — «работа из дома»).
Илья Мищенко, переводчик, лингвист Топонимической комиссии Санкт-Петербурга, сообщил, что на данный момент стоит придерживаться латинского написания болезни. Если использовать аббревиатуру на русском языке, то она изменится, так как ее будет необходимо перевести.
Эксперт сомневается, что болезнь можно будет называть «ковидом».
Сергей Кузнецов, советский и российский лингвист-русист, специалист в области семантики, морфологии, теории и практики лексикографии, основатель и глава Центра коммуникативных компетенций Центра экспертиз СПбГУ, наоборот же считает, что слово уже прошло стадию русификации, и писать его кириллицей допустимо. Речь идет именно об аббревиатуре — КОВИД-19.
Портал «Текст.ру» считает, что COVID-19 правильнее писать латиницей.
Аббревиатура COVID-19 расшифровывается как CoronaVirus Disease 2019, что в переводе с английского на русский означает «коронавирусное заболевание 2019 года».
Этим термином официально назвали вирус, обнаруженный в китайском городе Ухань 31 декабря 2019 года и вызвавший самую опасную эпидемию XXI века. К концу мая 2020 года количество жертв COVID-19 в мире превысило 370 тысяч человек, большую часть из которых составляют преклонные старики. В большинстве языков аббревиатура COVID произносится как «ковид», и от неё уже успели понаделать модных слов, таких как COVIDiot, например.
- serega
- 2017-02-28 19:55:05
- 1-4
- Английский язык
- 5+3 б
девятнадцать по-английски как написать?
- Следить
- Отметить нарушение!
Отправить
Войти чтобы добавить комментарий
Ответы и объяснения
- snowzilla
- Мегамозг
- 2017-02-28 19:55:05
19 на английском языке пишется вот так: nineteen.
Ответ: 19 по-английски — nineteen
- 0 комментариев
- Отметить нарушение!
- Спасибо 0
Отправить
Войти чтобы добавить комментарий
Знаешь ответ? Добавь его сюда!
Правило
Слово «ковид» пишут с буквой «д» на конце. Написание этого слова важно запомнить, так как его невозможно проверить.
Русский вариант повторяет аббревиатуру COVID, которую можно расшифровать как COronaVIrus Disease. Полное название практически не употребляется, а вот аббревиатура часто используется в разговорной речи для определения вирусной инфекции.
Значение слова
«Ковид» — коронавирусная инфекция, которая провоцирует заболевания легких и может быть причиной пневмонии.
Примеры употребления слова в предложениях
- Диагностировать Ковид-19 можно только путем проведения специального тестирования.
- Распространение Ковид-19 было признано пандемией, что вызвало закрытие стран на карантин.
- Пока нет точных сведений, какой процент людей способен переносить инфекцию Ковид-19 бессимптомно.
|
На разных ТВ-каналах дикторы, похоже, не могут договориться и произносят COVID-19 кто с ударением на первый, а кто — на второй слог. То же самое наблюдалось и до сих пор наблюдается с произношением африканского вируса Эбола, а также итальянского города Бергамо. Скорее всего, ответ на этот вопрос про кОвид/ковИд мы получим чуть позже, когда одна из форм закрепится как наиболее употребимая и словари начнут её давать в качестве нормы. система выбрала этот ответ лучшим COVID-19 (название нового коронавируса) — это Произносят название в разных странах по-разному. Где-то перечисляют буквы в соответствии с правилами английского языка, а американцы чаще просто говорят: «ковид найнтин». Прослушать варианты произнесения названия различными людьми из США, Великобритании, Испании и других стран можно здесь. Рождённый в С С С Р более года назад Моя младшая сестра как-то в разговоре заметила, что с ударением на И говорят обыватели: ковИд. А практически все знакомые медицинские работники или люди, каким-то боком к врачеванию относящиеся — все говорят: кОвид. Наверное, не просто так. Наверное, им так на всяких учёбах-конференциях произносят название этого вируса поганого. Алекс98 более года назад В период распространения новой коронавирусной инфекции никто особенно не вдается в подробности произношения названия COVID-19. А вопрос довольно-таки интересный. Насколько мне известно, в большинстве случаев разные люди произносят по-разному. В большинстве случаев, ударение ставится на вторую гласную букву (английскую «I»). Из телевизионных новостных источников информации ударение такое же. Считаю правильным говорить именно: «КовИд» с ударением на «И». Хотя я бы предпочел проще называть — коронавирус, хоть Ковид это и сокращенно и быстрее говорится, лично мне это слово как-то не нравится, не по душе. линза более года назад Думаю, что произнесение данной аббревиатуры «COVID-19», так же, как и других служебных аббревиатур, может делиться на разговорный, общепринятый вариант, так и на специфический, профессиональный. Привожу примеры:
Так и в случае с этим проклятым Ковидом, лучше бы никогда не знать и не произносить это слово. Медики говорят кОвид, учителя говорят ковИд, а простые люди, вообще называют «наказанием за грехи», и «чёртовой заразой»… Так что поверьте, в данное время, в отношении пандемии во всём мире, не так важны ударения в слове, которым назвали вирусную беду. Joel Miller более года назад SARS-CoV-2 — РНК-вирус, из-за которого сейчас эпидемия идет. При чем это — международное название вируса. Есть еще синоним — 2019-nCoV. Болезнь, которую вызывает этот вирус — COVID-19, сокращенно от COronaVIrusDisease-2019. В простонародье, да и в медицинских кругах болезнь просто называют «Ковид», или «Корона», в официальных источниках — новая коронавирусная инфекция — сокращенно НКВИ. Пучеглазик 2 года назад Многие интересуются, как правильно произносится название «Ковид-19» («Covid-19»). Немногие знают, что оно означает не название вируса (коронавируса), а название болезни, которую вызывает эта вирусная инфекция. Covid-19 означает «атипичная инфекционная пневмония», а число «19» означает год, когда она была обнаружена. Касательно ударения в этом слове нет особого правила, поэтому можно произносить как «кОвид», так и «ковИд», значения не имеет. Точно в цель более года назад COVID-19 — это болезнь, которую вызывает коронавирусная инфекция, простым словом. Сама аббревиатура произошла от COrona Virus Dease 2019 — COVID-19. Так как слово относительное новое, то определенных правил произношения еще не сформировалось. Кто-то произносит его как ковИд (ударение на «И») а кто-то как кОвид (ударение на букву «О»). Оба варианта правильные. владсандрович более года назад В этом страшно живучем вирусе, который уже явно многих испугал собой и надоел думаю уж точно практически всем, ударение люди из области медицины, делают на первый слог то есть его название COVID-19, правильно произносить как кОвид-19. alexm12 2 года назад Правильно COVID-19 произносится как «Си О Ви Ай Ди Найнтин» или «Цэ О Вэ И Дэ девятнадцать». Если вам эту аббревиатуру хочется произносить, как ввели м моду американцы, одним словом, то говорите «ковид». Павел Ппп более года назад Правильно писать «короновирус» или «КОВИБ». КОроноВИрусная Болезнь. Знаете ответ? |
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать грубую лексику.
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать разговорную лексику.
Потеря обоняния может быть симптомом COVID-19.
Losing your sense of smell can be a symptom of COVID-19.
Это вызвано предотвращением распространения коронавируса COVID-19.
This is caused by preventing the spread of the coronavirus COVID-19.
Сегодня мы живём в эпоху COVID-19.
Today, we live in the time of COVID-19.
COVID-19 станет тяжёлым испытанием для систем здравоохранения.
COVID-19 is going to be a huge burden on health systems.
COVID-19 также выявил некоторые реальные недостатки мировых поставок медицинских услуг.
COVID-19 has also revealed some real weaknesses in our global health supply chains.
За это время примерно 1250 человек будут инфицированы COVID-19.
In that time, roughly 1,250 people will be confirmed infected with COVID-19.
Риск молодого здорового человека умереть от COVID-19 составляет около пяти тысячных процента.
The risk of a young healthy person dying of COVID-19 is around five thousandths of a percent.
Ясно, что пандемия COVID-19 является глобальным кризисом.
It is clear that the COVID-19 pandemic is a global crisis.
Однако COVID-19 разрушает надежды на достижение этой цели.
However, COVID-19 is set to dash hopes of achieving this goal.
Вместо этого в целях остановки распространения COVID-19 правительство агрессивно продвигает социальное дистанцирование в крупных городах.
Instead, the government has been aggressive in promoting social distancing in major cities to stop the spread of COVID-19.
Все собранные пробы будут проверены на наличие гриппа и COVID-19.
All samples collected will be tested for the presence of influenza and COVID-19.
Пока нет данных относительно взаимосвязи между инфекцией COVID-19 и родами.
There are no data yet concerning the implications of COVID-19 infections for labour.
О микроскопических поражениях и патофизиологии COVID-19 имеется мало данных.
Few data are available about microscopic lesions and the pathophysiology of COVID-19.
Более 1700 врачей были инфицированы COVID-19, шесть из них скончались.
Over 1,700 doctors have been infected with COVID-19, six of them have died.
COVID-19 высветил всю нашу предвзятость и открыл необъективность наших инфраструктур.
COVID-19 has shone a light on inequity and revealed our prejudiced infrastructures.
Меньше одного процента людей этой группы наверное попадут в больницу после инфицирования COVID-19.
Fewer than one percent of people in that age-group need to be taken to hospital after becoming infected with COVID-19.
Новый коронавирус под названием COVID-19 сотрясает весь мир, словно мощное землетрясение.
The novel coronavirus known as COVID-19 is shaking up the world like a massive earthquake.
Заслуги комплексной системы здравоохранения страны в основном заключаются в сдерживании распространения COVID-19.
The country’s comprehensive health system is mainly credited for containing the spread of COVID-19.
Результатов: 1052. Точных совпадений: 1046. Затраченное время: 204 мс
Documents
Корпоративные решения
Спряжение
Синонимы
Корректор
Справка и о нас
Индекс слова: 1-300, 301-600, 601-900
Индекс выражения: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Индекс фразы: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Translingual[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From COVID and the year 2019. The format was established by the World Health Organization (WHO) and is to be used for the names of future outbreaks.[1][2][3]
Alternative forms[edit]
- Covid-19
Proper noun[edit]
COVID-19
- (pathology) A disease caused by a coronavirus discovered in 2019, in a zoonotic pandemic starting in Wuhan, Hubei, China.
- (virology, metonymically) Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2; the virus which causes the disease.
Synonyms[edit]
- (virus): SARS-CoV-2
- (virus): 2019-nCoV
Coordinate terms[edit]
(disease):
- MERS
- SARS
(virus):
- MERS-CoV
- SARS-CoV
Descendants[edit]
- → Samoan: KOVITI-19
- → Thai: โควิด-19
See also[edit]
- ACE2
- TMPRSS2
References[edit]
- ^ NBC News, «Coronavirus gets official name from WHO: COVID-19», Erika Edwards, 11 February 2020
- ^ BBC News, «Coronavirus officially named Covid-19, says WHO», 11 February 2020
- ^ Agence France Presse, «Novel coronavirus named ‘Covid-19’: UN health agency», AFP News Agency, 11 February 2020
English[edit]
Alternative forms[edit]
- Covid-19
Etymology[edit]
Abbreviation of coronavirus disease + 19 from 2019, the year the virus was discovered. Coined by the World Health Organization on February 11, 2020. Intended to avoid stigma by not referring to a place, animal, career, or group of people.
Pronunciation[edit]
- (General American) IPA(key): /ˈkoʊ.vɪd naɪnˈtin/, /ˈkʌ.vɪd naɪnˈtin/
- (Received Pronunciation) IPA(key): /ˈkəʊ.vɪd naɪnˈtiːn/, /ˈkɒ.vɪd naɪnˈtiːn/
-
Audio (Southern England) (file)
Proper noun[edit]
COVID-19
- (medicine) COVID-19 (disease)
-
diagnosed with COVID-19
- Synonyms: coronavirus disease 2019, 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease, Wuhan pneumonia, Wuhan flu
- Hypernym: COVID
- Coordinate terms: pneumonia, acute respiratory disease, severe acute respiratory syndrome, Middle East respiratory syndrome
-
2020 January 11, “Coronavirus”, in World Health Organization[1]:
-
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by a newly discovered coronavirus.
-
-
2021 February 12, “Coronavirus (COVID-19) update”, in U.S. Food & Drug Administration[2]:
-
This week, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for a a monoclonal antibody combination for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients
-
-
2021 July 23, “COVID-positive man boards Indonesia flight disguised as wife”, in Aljazeera[3]:
-
Indonesia reported a record daily number of 1,566 COVID-19 deaths on Friday, taking total fatalities to 80,598, data from the country’s COVID-19 task force showed.
-
-
- (virology, metonymically) SARS-CoV-2 (virus that causes the COVID-19 disease)
- Synonyms: China virus, Chinese virus, Wuhan coronavirus, Wuhan flu, Wuhan virus, kung flu
- Hypernyms: virus, coronavirus
- Coordinate terms: influenza, MERS-related coronavirus, SARS-related coronavirus
-
2020 January 11, “Coronavirus”, in World Health Organization[4]:
-
Most people infected with the COVID-19 virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment.
-
-
2021 February 5, “Redoubling public health measures needed due to COVID-19 virus variants”, in World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe[5]:
-
As we enter the first months of 2021, increasing numbers of reports of variants of the COVID-19 virus mark a new development in the pandemic.
-
Derived terms[edit]
- COVID toes
[edit]
- Miss Rona
Translations[edit]
disease
- Apache:
- Western Apache: Cowid ńgóstʼáítsʼádah, cowid ńgóstʼáítsʼádah, nantʼaʼ chʼah kah naghaa
- Arabic: كوفيد-19، كوڤيد-١٩ (kōvid-19)
- Burmese: ကိုဗစ်-၁၉ (kuibac-19)
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: 新冠肺炎 (zh) (xīnguān fèiyán); (literal) 2019冠狀病毒病 (zh) (2019 Guānzhuàng Bìngdú Bìng), 新型冠状病毒肺炎 (xīnxíng guānzhuàng bìngdú fèiyán)
- Dhivehi: ކޮވިޑް-19 (koviḍ-19)
- Dutch: Covid-19 m, corona (nl) m (informal)
- Esperanto: KOVIM-19
- Finnish: COVID-19 (fi)
- French: Covid-19 (fr) m or f, COVID-19 (fr) m or f
- Georgian: კოვიდ-19 (ḳovid-19), კორონავირუსი (ḳoronavirusi)
- German: COVID-19 (de)
- Hebrew: קובי»ד-19 (kovi»d-19)
- Hindi: कोविड-१९ m (koviḍ-19), कोविड-19 m (koviḍ-19)
- Japanese: 新型肺炎 (Shingata haien), 新型コロナウイルス感染症 (Shingata koronauirusu kansenshō)
- Kannada: ಕೋವಿಡ್ ೧೯ (kōviḍ 19)
- Khmer: កូវីដ-១៩ (kouviit dɑp pram buən)
- Korean: 신형코로나비루스감염증 (sinhyeongkoronabiruseugamyeomjeung), 신종 코로나 감염증 (sinjong korona gamyeomjeung), 코로나19 (korona19), 악성비루스 (akseongbiruseu)
- Maori: KOWHEORI-19
- Navajo: Dikos Ntsaaígíí-19
- Northwestern Ojibwa: biiwaabik-wiiwakwaan aakoziwin
- Polish: COVID-19 (pl) m
- Samoan: KOVITI-19
- Serbo-Croatian: Ковид-19 (Kovid-19)
- Russian: Ковид-19 (Kovid-19)
- Spanish: covid-19 m or f
- Portuguese: Covid-19 f, corona (pt) m (informal)
- Thai: โควิด-19 (koo-wìt-sìp-gâao)
- Vietnamese: COVID-19 (vi), Cô Vy (informal)
- Welsh: COVID-19 m, y Gofid Mawr m (informal)
- Yiddish: קאָװיד־19 (kovid-19)
French[edit]
Proper noun[edit]
COVID-19 m or f
- Alternative letter-case form of Covid-19
-
2020, M. Underner, J. Perriot, G. Peiffer, N. Jaafari, “COVID-19 et modifications du comportement tabagique [COVID-19 and changes in smoking]”, in Revue des Maladies Respiratoires, DOI:10.1016/j.rmr.2020.08.004:
-
La COVID-19, apparue en Chine en décembre 2019, est due à un nouveau coronavirus, le coronavirus 2019, à l’origine de la pandémie actuelle.
- COVID-19, which appeared in China in December 2019, is a novel coronavirus, the 2019 coronavirus, which is the origin of the current pandemic.
-
-
2021 February 15, “Données sur la COVID-19 au Québec [Data on COVID-19 in Quebec]”, in Québec[6]:
-
Au Québec, pour le moment, la propagation du coronavirus (COVID‑19) est sous contrôle, mais les présentes semaines sont critiques.
- In Quebec, for the moment, the transmission of coronavirus (COVID‑19) is under control, but the next weeks are critical.
-
-
Italian[edit]
Proper noun[edit]
COVID-19 f
- Alternative letter-case form of Covid-19
Portuguese[edit]
Proper noun[edit]
COVID-19 m or f
- Alternative letter-case form of Covid-19
Tagalog[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Borrowed from English COVID-19.
Noun[edit]
COVID-19
- COVID-19
Vietnamese[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- (Hà Nội) IPA(key): [ko˧˧ vit̚˧˦ mɨəj˨˩ t͡ɕin˧˦], [ko˧˧ vit̚˧˨ʔ mɨəj˨˩ t͡ɕin˧˦]
- (Huế) IPA(key): [kow˧˧ vit̚˦˧˥ mɨj˦˩ t͡ɕin˦˧˥], [kow˧˧ vit̚˨˩ʔ mɨj˦˩ t͡ɕin˦˧˥]
- (Hồ Chí Minh City) IPA(key): [kow˧˧ vɨt̚˦˥ mɨj˨˩ cɨn˦˥], [kow˧˧ vɨt̚˨˩˨ mɨj˨˩ cɨn˦˥] ~ [kow˧˧ jɨt̚˦˥ mɨj˨˩ cɨn˦˥], [kow˧˧ jɨt̚˨˩˨ mɨj˨˩ cɨn˦˥]
- Phonetic: cô vít mười chín, cô vịt mười chín
Proper noun[edit]
COVID-19
- COVID-19
Synonyms[edit]
- (COVID-19): Cô Vy (colloquial)
Эта статья об инфекционном заболевании; о пандемии, вызванной заболеванием, см. Пандемия COVID-19.
Запрос «ковид» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения.
COVID-19 (аббр. от англ. COronaVIrus Disease 2019 — [2], рус. кови́д[см. «Терминология»]), ранее коронави́русная инфе́кция 2019-nCoV[3] — потенциально тяжёлая[⇨] острая респираторная инфекция, вызываемая коронавирусом SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV)[4]. Представляет собой опасное заболевание[5], которое может протекать как в форме острой респираторной вирусной инфекции лёгкого течения[6][7], так и в тяжёлой форме[8]. К наиболее распространённым симптомам заболевания относятся повышенная температура тела, утомляемость и сухой кашель[9]. Вирус способен поражать различные органы через прямое инфицирование или посредством иммунного ответа организма[10]. Наиболее частым осложнением заболевания является вирусная пневмония, способная приводить к острому респираторному дистресс-синдрому и последующей острой дыхательной недостаточности, при которых чаще всего необходимы кислородная терапия и респираторная поддержка[11]. В число осложнений входят полиорганная недостаточность, септический шок и венозная тромбоэмболия[12].
Распространяется вирус воздушно-капельным путём через вдыхание распылённых в воздухе при кашле, чихании или разговоре[13] капель с вирусом, а также через попадание вируса на поверхности с последующим занесением в глаза, нос или рот. Основным средством предотвращения распространения инфекции являются маски, однако они должны применяться вместе с комплексом других мер профилактики, включая соблюдение безопасной дистанции и избегание пребывания в замкнутых пространствах с большим количеством людей[14]. К числу эффективных мер профилактики относятся частое мытьё рук и соблюдение правил респираторной гигиены[9].
Вакцинация является безопасным и эффективным способом снижения рисков: смерти от заболевания, тяжёлого течения, симптоматических случаев и возникновения самой инфекции[15][16]. Вакцины являются важнейшим новым средством борьбы с заболеванием, но прохождение вакцинации не означает, что можно пренебрегать стандартными мерами профилактики[17], поскольку вакцинация в первую очередь направлена на защиту от заболевания, а не от инфекции[18]. После вакцинации обычно могут появиться кратковременные лёгкие побочные эффекты, среди которых головные боли, боли в мышцах, озноб и повышение температуры[19].
У большинства заразившихся инфекция протекает в лёгкой форме или бессимптомно[20]. Примерно в 80 % какое-либо специфическое лечение не требуется, а выздоровление происходит само по себе[6][9]. Примерно в 15 % случаев заболевание протекает в тяжёлой форме с необходимостью применения кислородной терапии, ещё в 5 % состояние больных критическое[21]. Ранние данные показывают, что омикрон-штамм вызывает менее тяжёлую инфекцию, нежели предыдущие варианты[22]. В редких случаях поражение вирусом детей и подростков, предположительно, может приводить к развитию воспалительного синдрома[23]. Также возможны долгосрочные последствия, называемые постковидным синдромом[24].
Тяжёлые формы болезни с большей вероятностью могут развиться у пожилых людей и у людей с определёнными сопутствующими заболеваниями, включающими астму, диабет и сердечные заболевания[25]. Высокая смертность от заболевания может объясняться тем, что оно может поражать разные органы, включая лёгкие, сердце, почки и печень, по этой же причине может оказаться неэффективным лечение[26]. В тяжёлых или критических случаях Всемирная организация здравоохранения (ВОЗ) рекомендует применять кортикостероиды и барицитиниб (ингибитор янус-киназ)[27]. В тяжёлых случаях также применяются средства для поддержания функций жизненно важных органов[28].
Симптомы
Симптомы COVID-19
Наиболее распространёнными симптомами являются[29]:
- лихорадка,
- сухой кашель,
- усталость,
- потеря вкуса или обоняния.
Менее часто встречаются ломота в теле, боль в горле, диарея, конъюнктивит, головная боль, кожная сыпь или изменение цвета пальцев рук или ног[30].
Потеря обоняния является высоко специфичным симптомом и может наблюдаться без сопутствующих лихорадки или кашля[31]. Медианная продолжительность потери обоняния или вкуса составляет примерно 8 дней[32]. Потеря обоняния, по предварительным оценкам, происходит у 80 % заразившихся коронавирусом[33][неавторитетный источник?].
Согласно ВОЗ опасными симптомами, при которых необходима медицинская помощь, являются[30]:
- одышка или затруднённое дыхание,
- боли в груди или ощущение её сдавливания,
- потеря возможности двигаться или разговаривать.
Эпидемиология
![Сглаживание кривой заболеваемости за счёт замедления скорости распространения инфекции, позволяющее медицинским учреждениям справляться с возникающей нагрузкой[34][35]](https://wiki2.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6e/20200406_Flatten_the_curve_animated_GIF_-_International_version.gif/im324-640px-20200406_Flatten_the_curve_animated_GIF_-_International_version.gif)
Сглаживание кривой заболеваемости за счёт замедления скорости распространения инфекции, позволяющее медицинским учреждениям справляться с возникающей нагрузкой[34][35]
31 декабря 2019 года Всемирная организация здравоохранения была проинформирована об обнаружении случаев пневмонии, вызванной неизвестным возбудителем, 3 января китайские службы сообщили ВОЗ о 44 случаях пневмонии в городе Ухань провинции Хубэй[36]. Патоген оказался новым коронавирусом (ныне известным как SARS-CoV-2, ранее — под временным названием 2019-nCoV[3]), который ранее не обнаруживался среди человеческой популяции[37]. 30 января 2020 года в связи со вспышкой эпидемии ВОЗ объявила чрезвычайную ситуацию международного значения в области здравоохранения[37], а 28 февраля 2020 года ВОЗ повысила оценку рисков на глобальном уровне с высоких на очень высокие[38]. 11 марта 2020 года эпидемия была признана пандемией[4]. Пандемия опасна тем, что одновременное заболевание инфекцией множества людей может привести к перегруженности системы здравоохранения с повышенным количеством госпитализаций и летальных исходов[39]. Системы здравоохранения могут оказаться не готовы к необычайно большому количеству тяжелобольных пациентов[40]. Наиболее важной ответной мерой по отношению к инфекции являются не лечебные мероприятия, а снижение скорости её распространения[⇨][39], чтобы растянуть её во времени и снизить, таким образом, нагрузку на системы здравоохранения[40]. Эпидемия закончится, как только среди населения выработается достаточный коллективный иммунитет[40]. Тем не менее, вероятен сценарий, по которому вирус займёт своё место среди других ОРВИ и будет сосуществовать с людьми ещё долгое время[41].
Заболеванию подвержены люди всех возрастов, медианный же возраст людей с инфекцией SARS-CoV-2 составляет 50 лет. Тяжёлые формы заболевания чаще бывают у пожилых людей возрастом за 60 лет с сопутствующими заболеваниями. Большинство молодых людей и детей переносят заболевание в лёгкой форме, в том числе в виде лёгкой пневмонии, или асимптоматически[41].
В китайском отчёте с информацией по 72 314 случаям заболевания в 81 % случаев заболевание проходило в лёгкой форме, в 14 % — в тяжёлой и в 5 % состояние пациентов было критическим[41].
Причины заболевания и его развитие
Вирусология
Коронавирусное заболевание COVID-19 вызывается ранее неизвестным бетакоронавирусом SARS-CoV-2, который был обнаружен в образцах жидкости, взятой из лёгких в группе пациентов с пневмонией в китайском городе Ухань в декабре 2019 года. SARS-CoV-2 относится к подроду Sarbecovirus и является седьмым по счёту известным коронавирусом, способным заражать человека[37].
SARS-CoV-2 является РНК-содержащим вирусом с оболочкой. На основании исследований выдвинута гипотеза, что вирус является результатом рекомбинации коронавируса летучих мышей с другим, пока ещё не известным, коронавирусом. Предполагается, что человеку вирус передался от панголина[43][37]. Функциональные сайты белка пепломера вируса SARS-CoV-2 практически идентичны таковому у вируса, обнаруженного у панголинов[44]. Полный геном вируса расшифрован, находится в открытом доступе и доступен в том числе через базу GenBank[37].
По мере своей эволюции у вируса происходят генетические мутации и формируются линии генетических поколений, вместе составляющие дерево генетических поколений. Некоторые мутации могут сказываться на скорости распространения вируса, на тяжести вызываемого им заболевания или на эффективности тех или иных методов лечения[45]. Вирусы с такими мутациями называют «вариантами» вируса[45] или штаммами[46]. При этом не все варианты являются штаммами, новые штаммы появляются, если у варианта вируса изменяются физические свойства[46].
В соответствии с классификацией, предложенной ВОЗ, вызывающие опасения варианты коронавируса SARS-CoV-2 именуют буквами греческого алфавита[47]. По состоянию на ноябрь 2021 года выделяют штаммы: Альфа, Бета, Дельта, Гамма и Омикрон.
Передача инфекции
Вирус передаётся воздушно-капельным путём через вдыхание мелких капель, распылённых в воздухе при кашле, чихании или разговоре[13]. Капли с вирусом могут попадать на поверхности и предметы, а затем инфицировать прикоснувшегося к ним человека через последующие прикосновения к глазам, носу или рту[9]. Вирус может оставаться жизнеспособным в течение нескольких часов, попадая на поверхности предметов. На стальных поверхностях и на пластике он может сохраняться до 2—3 дней[48]. Исследование с сильным распылением показало, что вирус мог бы находиться в воздухе до нескольких часов, однако ВОЗ уточняет, что в естественных и медицинских условиях распыление происходит иным способом, а о передаче вируса по воздуху пока не сообщалось[49]. Хотя жизнеспособный вирус может содержаться в выделяемых фекалиях, нет каких-либо доказательств возможности заражения фекально-оральным путём[50]. Есть также сообщения о том, что вирус обнаруживался в крови и слюне[37].
Заразными являются асимптоматические, пресимптоматические и симптоматические инфицированные. Наиболее заразным считается период незадолго до развития симптомов и на ранней стадии заболевания[51]. На долю пресимптоматических инфицированных может приходиться более половины всех случаев передачи инфекции[52]. Что касается асимптоматических инфицированных, пока непонятно, насколько значимая роль принадлежит передаче инфекции в данном случае[51]. Однако массовая вакцинация способствует уменьшению доли симптоматических случаев, в результате чего роль асимптоматических инфекций в передаче может возрасти[52].
Есть сообщения о передаче инфекции от человека домашним кошкам, тиграм и львам. Экспериментально выяснено, что вирус может легко передаваться между домашними кошками. Возможность передачи от кошек к человеку требует дальнейших исследований[53].
Предположительно вирус эффективнее передаётся в сухих и холодных условиях, а также в тропических с высокой абсолютной влажностью. Пока есть лишь косвенные свидетельства в пользу зимней сезонности в северном полушарии[54]. Однако анализ корреляционных связей между метеорологическими параметрами и скоростью распространения инфекции в китайских городах не выявил взаимосвязи скорости распространения с температурой окружающей среды[55].
Патогенез
После попадания в дыхательные пути основными мишенями вируса становятся эпителиальные клетки дыхательных путей, альвеолярные эпителиальные клетки и эндотелиальные клетки сосудов[56]. Вирус попадает в клетку присоединением белка пепломера к рецептору — ангиотензинпревращающему ферменту 2 (АПФ2) клетки[57]. Этим же путём происходило проникновение в случае вируса SARS-CoV, однако структурный 3D-анализ пепломера на поверхности вируса в случае SARS-CoV-2 предполагает возможно более сильное взаимодействие с рецептором[44]. Входу в клетку также способствует предварительная преактивация пепломера фурином, которая отсутствовала у вируса SARS-CoV[58]. После присоединения к рецептору вирус SARS-CoV-2 использует рецепторы клетки и эндосомы для проникновения. Помогает проникновению трансмембранная сериновая протеаза 2 (TMPRSS2)[57].
После попадания вируса в нос в течение нескольких дней происходит локальная репликация вируса и его распространение по сообщающимся дыхательным путям, на этом этапе инфекция протекает бессимптомно с ограниченным иммунным ответом, но человек является заразным, а вирус обнаруживается анализом мазка из носа. Далее происходит распространение инфекции на остальные части верхних дыхательных путей, в результате чего могут возникнуть симптомы лихорадки, недомогания и сухого кашля. На этом этапе инфицированные клетки высвобождают CXCL10 (англ.) (рус., интерфероны бета и гамма, а иммунного ответа может хватить для предотвращения дальнейшего распространения инфекции, что происходит у большинства заболевших[59]. Адекватный клеточный иммунный ответ (через CD4+ и CD8+ T-клетки) ассоциируется с более лёгким течением заболевания[60]. У примерно пятой части заболевших инфекция распространяется на нижние дыхательные пути с развитием более тяжёлых симптомов[59]. При этом по сравнению с другими вирусами альвеолярные макрофаги, играющие значимую роль на ранних стадиях инфекций, не вырабатывают интерфероны в ответ на воздействие вируса, механизм чего пока неизвестен[61]. Воспаление и повышение свёртываемости крови являются естественными защитными механизмами организма, однако в тяжёлых случаях они могут усугублять заболевание[62][63].
Наибольшую значимость для исхода заболевания играет течение инфекции в лёгких. Из-за поражения альвеол вирусом возникает местная воспалительная реакция с выбросом большого количества цитокинов, среди которых IL-6, IL-1, фактор некроза опухоли α и интерферон гамма[63]. Активная репликация вируса в лёгких, помимо респираторных симптомов, приводит к лихорадке, болям в мышцах и головной боли. Повышенные уровни провоспалительных цитокинов коррелируют с тяжёлым течением пневмонии и усилением эффекта матового стекла в лёгких[64]. Сам же эффект матового стекла возникает из-за частичного заполнения альвеол жидкостью, клеточным детритом, гиалиновыми мембранами и воспалительными клетками[65][66], в результате чего из-за смещения воздуха в альвеолах наблюдается помутнение в лёгких, но бронхи и сосуды при этом остаются различимыми[67].
Помимо нарушений работы дыхательной системы у больных могут наблюдаться неврологические, сердечно-сосудистые, кишечные нарушения, а также нарушения работы почек. Однако в данных направлениях о патогенезе пока мало что известно[10].
Тяжёлые случаи COVID-19 также связывают с коагулопатией. Вирус инфицирует и поражает эндотелиальные клетки, выстилающие сосуды лёгких, в результате чего нарушается нормальное функционирование сосудов и поддержание их тонуса, а в дальнейшем изменения приводят к повышению свёртываемости крови и образованию тромбов[68]. В одном исследовании обнаружена взаимосвязь между тромбообразованием и наличием протромботических аутоантител у пациентов, что схоже с антифосфолипидным синдромом, при этом данные аутоантитела приводят к повышенной активности нейтрофилов[69]. Тромбоцитопения является следствием захвата тромбоцитов в микротромбах, при этом на образование тромбов расходуются факторы свёртывания крови, на дефицит которых указывает удлинённое протромбиновое время[63]. D-димер образуется в результате расщепления фибрина плазмином, а повышенное количество D-димера может указывать на избыток полимеризованного фибрина внутри сосудов и во внесосудистом пространстве[63]. Повышенные уровни D-димера, фибриногена и продуктов деградации фибрина[en] со значительно пониженным уровнем антитромбина служат индикаторами плохого прогноза у пациентов с COVID-19[70].
Высокий уровень вирусовыделения в глотке наблюдается в первую неделю с появления симптомов, достигая наибольшего уровня на 4-й день, что предполагает активную репликацию вируса в верхних дыхательных путях. Продолжительность вирусовыделения после исчезновения симптомов заболевания оценивается в 8—20 дней[37]. Однако обнаружение РНК вируса после выздоровления не означает наличия жизнеспособного вируса[71].
Иммунитет
См. также: § Серологические тесты
Наибольшее количество антител против SARS-CoV-2 вырабатывается через две—три недели после заражения, после чего их количество начинает снижаться. Гуморальный иммунный ответ проявляется выработкой антител IgA, IgM и IgG, обнаруживаемых в плазме крови и слюне. При этом в тяжёлых случаях инфекции по сравнению с лёгкими наблюдаются более высокие титры антител IgA и IgG. В течение 3—5 месяцев после инфекции уровни IgM и IgA снижаются[72]. В одном исследовании титры нейтрализующих антител IgG сохранялись длительное время с небольшим снижением спустя 6 месяцев после заболевания[73]. Роль клеточного иммунитета пока выясняется[72]. Среди людей пассивная иммунизация антителами показывала ограниченный эффект, что предполагает возможную значимую роль T-клеток в контроле инфекционного процесса[73]. Выделение РНК вируса снижается с наступлением выздоровления и может продолжаться некоторое время — от дней до недель, однако это не означает наличие жизнеспособного вируса[74].
В исследовании с участием 12 541 медицинских работников постинфекционный иммунитет значительно снижал риск реинфекции в течение 6 месяцев после перенесённой инфекции, при этом среди переболевших, у которых наблюдались антитела IgG к спайковому белку, не было симптоматических инфекций, а подтверждённых асимптоматических инфекций было всего две. Однако по исследованию невозможно судить о том, обеспечивалась ли защита гуморальным иммунитетом или же иммунитетом клеточным[75]. О случаях реинфекции появляются сообщения повсеместно[76]. Согласно систематическому обзору от августа 2021 года по итогам примерно года с начала пандемии реинфекции возникали примерно у 3 человек на 1000 ранее выздоровевших пациентов[77].
Хотя SARS-CoV-2 обладает способностью обхода врождённого иммунитета, предполагается, что большое количество лёгких и асимптоматических случаев объясняется работой адаптивного иммунитета[78] вследствие ранее перенесённых инфекций, вызванных циркулирующими среди населения коронавирусами простуды[79]. У 40 %—60 % не переболевших COVID-19 лиц обнаруживаются кросс-реактивные CD4+ T-клетки, которые могут обеспечивать частичный иммунитет от COVID-19[78]. Обнаруживаются и кросс-реактивные к SARS-CoV-2 антитела, которые способны распознавать вирус SARS-CoV-2. Возможно, что наличие кросс-реактивного иммунитета влияет на тяжесть переносимой инфекции и на её распределение по возрастам. Дети обычно чаще болеют коронавирусными инфекциями, что гипотетически может давать им некоторую защиту от COVID-19[80]. Альтернативно большое количество асимптоматических случаев может оказаться следствием отложенного иммунного ответа интерферонами типа I, поскольку, несмотря на активную репликацию вируса, наблюдается низкая выработка интерферонов I типа и провоспалительных цитокинов и хемокинов, что в случае заболевания приводит к задержке в появлении симптомов[81].
Также есть сведения, что примерно через 6 месяцев после первоначального заражения защита от повторного составляла примерно 80 % без существенной разницы в показателях повторного заражения между мужчинами и женщинами. Но для лиц в возрасте 65 лет и старше эта защита уменьшается до 47 %. В другом исследовании на протяжении 9 месяцев брали анализы у более чем 9500 человек из примерно 3500 случайно выбранных домохозяйств в Ухане, в результате около 40 % инфицированных вырабатывали нейтрализующие антитела, которые можно было обнаружить за весь период исследования[82].
Клиническая картина
Для инфекции, вызываемой вирусом SARS-CoV-2, инкубационный период составляет 1—14 дней[43], может протекать бессимптомно, в лёгкой форме и в тяжёлой форме, с риском смерти[83], но полная клиническая картина пока ещё не ясна[84]. Симптомы развиваются в среднем на 5—6 день с момента заражения[43]. Есть единичные сообщения о случаях длительного инкубационного периода, однако они могут оказаться результатом возможного повторного воздействия вируса, в остальных же исследованиях инкубационный период не превышает 10,6 дней[85]. Пациенты с лёгкими симптомами обычно выздоравливают в течение недели[86]. В среднем длительность симптомов не превышает 20 дней[85].
В общем случае по степени тяжести заболевание может быть[87]:
- лёгкого и среднего течения, включая лёгкую пневмонию;
- тяжёлым, с одышкой и гипоксией;
- критическим, с дыхательной недостаточностью, шоком или нарушением работы органов.
| Состояние | День |
|---|---|
| Госпитализация | 7 (4—8) |
| Одышка | 8 (5—13) |
| Острый респираторный дистресс-синдром |
9 (8—14) |
| Механическая вентиляция лёгких |
10,5 (7—14) |
| Перевод в отделение реанимации |
10,5 |
По данным одного исследования, у всех пациентов, поступивших в больницу, обнаруживается пневмония с инфильтратами на рентгеновском снимке[89]. Особенностью болезни, выявляемой через компьютерную томографию, являются двусторонние изменения по типу «матового стекла», затрагивающие в основном нижние отделы лёгких и реже средний отдел правого лёгкого[90]. В другом исследовании отклонения от нормы на снимках обнаруживаются у 75 % больных[91]. При этом пневмония может обнаруживаться и в асимптоматических случаях инфекции[92]. У трети пациентов развивается острый респираторный дистресс-синдром[93]. При остром респираторном дистресс-синдроме могут обнаруживаться также тахикардия, тахипноэ или цианоз, сопровождающий гипоксию[37].
Также на фоне инфекции возможны дыхательная недостаточность, сепсис и септический (инфекционно-токсический) шок[7].
У беременных некоторые симптомы заболевания могут быть схожи с симптомами адаптации организма к беременности или с побочными явлениями, возникающими из-за беременности. Такие симптомы могут включать лихорадку, одышку и усталость[37].
Заболеванию подвержены дети всех возрастов, по сравнению со взрослыми у детей заболевание обычно протекает в менее тяжёлой форме[94], однако со схожими проявлениями, включая пневмонию[95]. Осложнения среди детей также встречаются реже и в более лёгкой форме[37]. Согласно анализу 2143 случаев заболевания среди детей, тяжёлые и критические случаи наблюдаются лишь в 5,9 % случаев, а более уязвимыми для инфекции являются маленькие дети[94]. Также у детей чаще, чем у взрослых, может встречаться одновременное заражение другими вирусами[37]. Есть сообщения о кластерах детей с многосистемным воспалительным синдромом, предположительно, связанным с COVID-19. Болезнь проявляется схоже с синдромом Кавасаки и с инфекционно-токсическим шоком[23].
Осложнения
У большинства COVID-19 протекает в лёгкой или средней форме, но в некоторых случаях COVID-19 вызывает сильные воспалительные процессы, называемые цитокиновым штормом, который может привести к смертельной пневмонии и острому респираторному дистресс-синдрому. При этом профили цитокинового шторма могут различаться у разных пациентов[96]. Обычно COVID-19 сопровождается синдромом высвобождения цитокинов, при котором наблюдается повышенный уровень интерлейкина-6 (IL-6), коррелирующего с дыхательной недостаточностью, острым респираторным дистресс-синдромом и осложнениями[97]. Повышенные уровни провоспалительных цитокинов могут также свидетельствовать о развитии вторичного гемофагоцитарного лимфогистиоцитоза (англ.) (рус.[98].
Воспалительные процессы могут затронуть сердечно-сосудистую систему, приводя к аритмиям и миокардиту. Острая сердечная недостаточность встречается в основном среди тяжело или критически больных пациентов. Инфекция может оказывать долгосрочное воздействие на состояние здоровья сердечно-сосудистой системы. В случае пациентов с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями в истории болезней может потребоваться строгий контроль их состояния[98].
Возможные осложнения COVID-19[98]:
- острый респираторный дистресс-синдром, от 15 % до 33 %;
- острая дыхательная недостаточность, 8 %;
- острая сердечная недостаточность, от 7 % до 20 %;
- вторичная инфекция, от 6 % до 10 %;
- острая почечная недостаточность, от 14 % до 53 %;
- септический шок, от 4 % до 8 %;
- кардиомиопатии, у 33 % критических;
- диссеминированное внутрисосудистое свёртывание, у 71 % погибших;
- осложнения беременности, не исключаются.
Редкие осложнения включают мукормикоз[99] и энцефалит[100]. Энцефалит встречается лишь примерно у 0,215 % госпитализированных пациентов, однако среди пациентов с тяжёлым течением болезни его частота увеличивается до 6,7 %[100].
Гипервоспалительный синдром, связанный с COVID-19
При COVID-19 определялись повышенные уровни некоторых цитокинов. Однако часто эти уровни были в десятки раз ниже, чем при ОРДС, вызванным другими причинами. Это относится также и к уровню провоспалительного цитокина IL-6, являющегося одним из основных маркеров наличия цитокинового шторма. Широкое признание термина «цитокиновый шторм» и его ведущей роли в патогенезе COVID-19 мотивировало использование иммуномодулирующих методов лечения, таких как кортикостероиды в высоких дозировках и ингибиторы IL-6, как в условиях клинических испытаний, так и непосредственно для лечения тяжёлых форм COVID-19. Применение этих средств во многом было следствием синонимичного употребления термина «синдром высвобождения цитокинов» по отношению к термину «цитокиновый шторм». По этой причине в тяжёлых случаях COVID-19 применялись средства против синдрома высвобождения цитокинов, однако в случае COVID-19 уровень IL-6, ключевого медиатора для синдрома высвобождения цитокинов, на порядки ниже, чем в тяжёлых случаях COVID-19[101]. Между тем, применение блокатора IL-6 может снизить на одну неделю ответ организма в виде повышения уровня C-реактивного белка и повышения температуры тела, что повышает риск инфекции и одновременно может замаскировать традиционные клинические признаки[102]. В целом использование цитокиновых блокаторов вне рандомизированных испытаний пока является неоправданным[103].
В последующем синдром цитокинового шторма в тяжёлых случаях COVID-19 получил название гипервоспалительного синдрома, связанного с COVID-19. В одном из исследований для данного синдрома уже выдвинуты критерии диагностики, в том числе в сравнении с другими синдромами цитокинового шторма. Определение критериев диагностики является важным, поскольку позволяет определить пациентов, которым могут помочь терапии, направленные на лечение цитокинового шторма. При этом синдром цитокиного шторма в случае COVID-19 является достаточно уникальным, поскольку уровни ферритинов и IL-6 хоть и повышены, но меньше по сравнению с другими синдромами цитокинового шторма, а лёгкие поражаются в первую очередь в рамках ОРДС с предрасположенностью к свёртыванию крови. Одним из возможных подходов для раннего диагностирования цитокинового шторма среди пациентов с COVID-19 является выявление фебрильных пациентов с гиперферритинемией[104]. Однако из-за низкого уровня цитокинов по сравнению с другими синдромами цитокинового шторма, но схожими уровнями некоторых нецитокиновых биомаркеров, системное воспаление явно отличается от других синдромов цитокинового шторма и рассматривание воспалительного процесса как результата цитокинового шторма может оказаться неверным. Возможно, следует рассмотреть другие вероятные модели возникновения дисфункции внутренних органов[103].
В качестве объяснения цитокинового шторма предложена версия отложенного иммунного ответа интерферонами I типа. Коронавирусы обладают механизмами подавления ответа интерферонами I типа, что ассоциируется с тяжёлой степенью заболевания. Данная способность позволяет им обходить врождённый иммунитет в течение первых 10 дней заболевания. В результате накопленная вирусная нагрузка приводит к гипервоспалению и цитокиновому шторму. Исследования крови пациентов с COVID-19 показали, что высокая виремия ассоциируется с повышенными ответом интерферонами I типа и выработкой цитокинов, совместно влияющих на тяжесть заболевания. Подавление работы генов, стимулируемых интерфероном, одновременно с повышенным уровнем активации NF-κB приводит к цитокиновому шторму и гипервоспалению, обнаруживаемых у критически больных пациентов[78].
Профилактика
Ведутся разработки вакцин, по состоянию на начало сентября 2020 года были опубликованы данные о четырёх вакцинах-кандидатах, одна из которых разработана в России. Три вакцины являются аденовирус-векторными, одна — мРНК-вакцина. Однако перед началом массовой вакцинации все вакцины должны показать свою безопасность и эффективность в широкомасштабных клинических испытаниях[105][⇨].
Индивидуальная профилактика
Всемирная организация здравоохранения (ВОЗ) дала общие рекомендации по снижению риска заражения SARS-CoV-2[106]:

Применение медицинских масок среди населения
- регулярно мыть руки с мылом или спиртосодержащим средством;
- при кашле или чихании прикрывать нос и рот согнутым локтем или одноразовой салфеткой с последующим обязательным мытьём рук;
- соблюдать дистанцию в 1 метр по отношению к другим людям в общественных местах, особенно, если у них наблюдаются респираторные симптомы или повышенная температура;
- по возможности не трогать руками нос, рот и глаза;
- при наличии лихорадки, кашля и затруднённого дыхания обратиться в медицинское учреждение за помощью.
Хотя при благоприятных условиях вирус может днями оставаться жизнеспособным на различных поверхностях, он уничтожается менее, чем за минуту, обычными дезинфицирующими средствами, такими как гипохлорит натрия и перекись водорода[107].
Употребление алкоголя не способствует уничтожению вируса, не обеспечивает дезинфекции полости рта и глотки, однако оказывает разрушительное воздействие на иммунную систему организма. Употребление алкоголя ослабляет её и снижает защитные способности организма против инфекционных заболеваний. Также употребление алкоголя является фактором риска развития острого респираторного дистресс-синдрома[108]. Курение может повышать шансы на инфицирование, поскольку подношение сигареты ко рту повышает шансы на занесение вируса в рот человека через руки[109].
Рекомендации для заболевших
Медицинские маски обычному населению рекомендуются в случае наличия респираторных симптомов[37] или в случае ухода за больным, у которого может быть COVID-19[110]. Исследования гриппа и гриппоподобных заболеваний показывают, что ношение масок больными может предотвратить заражение других людей и контаминацию окружающих вещей и поверхностей. При наличии симптомов, схожих с COVID-19, ВОЗ рекомендует больным ношение масок с соблюдением инструкций по их правильному использованию и утилизации, самоизоляцию, консультирование у медицинских работников при плохом самочувствии, мытьё рук и соблюдение дистанции по отношению к другим людям[111]. Заболевшим рекомендуется носить медицинскую или хирургические маски[112].
ВОЗ рекомендует использовать пульсоксиметры для контроля насыщения крови кислородом и определения необходимости обращения за медицинской помощью[113], согласно временным рекомендациям Минздрава РФ от 08.04.2020 кислородотерапия показана при значении SpO2 менее 93 %[114].
Рекомендации для здоровых
Метаанализ и систематический обзор применения масок во время пандемии показал, что они очень эффективны в предотвращении распространения инфекции SARS-CoV-2 при широком применении среди населения. Маски могут предотвратить вдыхание крупных или мелких капель с вирусом. Исследования также показывают, что маски способны фильтровать субмикронные частицы пыли[115]. Рекомендации же по ношению масок в разных странах могут отличаться друг от друга[37][111], многие страны рекомендуют применение тканевых масок или других средств для защиты лица[116]. Рекомендации ВОЗ в общем случае сводятся к ношению масок здоровыми людьми в регионах с массовым распространением инфекции или при невозможности обеспечения социального дистанцирования. В условиях массового распространения инфекции с некоторыми оговорками рекомендуется надевать маски в общественных местах, например, в магазинах, на рабочих местах, в местах проведения массовых мероприятий и в учреждениях закрытого типа, в том числе в школах[116]. Маски полагается менять через каждые 2—3 часа ношения, одноразовые маски не предназначены для повторного использования или обработки, многоразовые же необходимо обрабатывать перед повторным использованием[117].
ВОЗ не рекомендует полагаться на стратегию ношения резиновых перчаток в общественных местах как меру снижения распространения инфекции SARS-CoV-2, эффективным является мытьё рук[118]. Человек может контаминировать нос или глаза прикосновением рук как без перчаток, так и в них[118] Перчатки рекомендуется использовать при уходе за больными или при уборке[118][119]. При этом выяснилось, что длительное применение перчаток может приводить к дерматиту[120].
Избежать заражения можно, соблюдая дистанцию при нахождении рядом с больными людьми и избегая контакта с ними[86], а также воздерживаясь от рукопожатий[106]. ВОЗ всем рекомендует соблюдение дистанции по крайней мере в 1 метр с другими людьми, особенно, если у них есть симптомы респираторного заболевания[111]. В России по состоянию на 17 ноября 2020 года контактировавшим положен домашний карантин на 14 дней, выйти из которого можно по истечении этого срока без необходимости проведения лабораторного тестирования, если не появились симптомы, схожие с COVID-19[121].
Рекомендации для медицинских работников
Медицинским работникам ВОЗ рекомендует использовать маски при уходе за больными, а респираторы — при выполнении процедур, во время которых может произойти распыление в воздухе жидкостей[86]. ВОЗ отмечает, что медицинские маски должны быть зарезервированы для медицинских работников, у населения они могут создать ложное ощущение безопасности и привести к пренебрежению другими мерами профилактики, в то время как медицинским работникам маски необходимы[111]. Для предотвращения распространения внутрибольничной инфекции, в том числе среди медицинского персонала, важно, чтобы медицинские работники соблюдали меры предосторожности[122].
Базовые принципы в рекомендациях ВОЗ включают в себя[123]:
- соблюдение гигиены рук и респираторной гигиены;
- стандартные меры предосторожности, включая ношение пациентами масок, медицинскими работниками — средств индивидуальной защиты, слежение за чистотой и отходами;
- дополнительные меры предосторожности, включая адекватную вентиляцию помещений, ношение медицинских масок, перчаток и приспособлений для защиты глаз, ограничение контактов пациентов, по возможности помещение их в палаты с отрицательным давлением;
- соблюдение мер предосторожности при выполнении процедур, при которых может произойти распыление в воздухе контаминированных жидкостей;
- отношение ко всем лабораторным образцам как к потенциально заразным.
В медицинских учреждениях также рекомендуется чистить и проводить дезинфекцию столов, стульев, стен, компьютерной техники и других поверхностей. Эффективными против SARS-CoV-2 являются этиловый спирт (70—90 %), основанные на хлоре продукты (например, гипохлорит), перекись водорода (более 0,5 %)[124].
Эффективность средств персональной защиты
По данным на июнь 2020 года анализ применения масок, лицевых щитков и соблюдения дистанции между людьми, опубликованный в Lancet, достоверно (среднее качество доказательств) показал, что значительно снижает вероятность заражения соблюдение дистанции между людьми в 1 метр и более, таким образом, дистанцирование уменьшает распространение инфекции. С гораздо меньшим уровнем достоверности (низкое качество доказательств) снижает вероятность заразиться ношение масок и защиты глаз. Специалисты, выполнившие метаанализ, рекомендуют соблюдать дистанцию с другими людьми больше одного метра, а в людных местах, где дистанцию соблюсти невозможно, предлагают использовать маски для лица или респираторы и защиту глаз (лицевые щитки или очки)[125]. При этом исследование, в ходе которого визуализировалось распространение капель от больного человека, показало, что лицевые щитки сами по себе не могут заменить маски, так как капли с вирусными частицами могут свободно распространяться в разных направлениях вокруг щитка[126].
Меры общественной профилактики
На время пандемии наиболее эффективной мерой предотвращения распространения инфекции является контролирование её источников, включая раннюю диагностику, своевременное оповещение о случаях заражения, изоляцию больных, а также периодическое оповещение населения об обстановке и поддержание порядка[127]. Многие страны принимают меры социального дистанцирования, включая ограничение перемещений между городами, закрытие школ и университетов, переход на удалённую работу и помещение заболевших в карантин. Подобные меры могут помочь замедлить скорость распространения инфекции[128]. Массовые мероприятия могут сводиться к минимуму или откладываться[39]. Согласно моделирующим исследованиям во время пандемии COVID-19 карантин играет важную роль в замедлении распространения инфекции и снижении смертности, но больший эффект достигается введением карантина вместе с другими мерами профилактики или контроля[129].
В силу того, что сезонные коронавирусы лучше распространяются в зимние месяцы в странах с выраженной сменой сезонов, в таких странах зимой имеет смысл усиление мер по снижению распространения инфекции[130].
Вакцинопрофилактика COVID-19
Вакцинация против COVID-19 предназначена для формирования приобретённого иммунитета против вируса SARS-CoV-2 путём тренировки собственной иммунной системы. Из-за возможного тяжёлого течения заболевания необходима безопасная и эффективная вакцина, которая поможет защитить людей, что особенно важно для медицинских работников и людей, входящих в группы риска[131]. Во всём мире регулирующие органы находятся под сильным давлением не только систем здравоохранения, но также под политическим и экономически давлением, направленном на широкомасштабное применение вакцин вне клинических испытаний. Разрешение применения вакцин-кандидатов в рамках чрезвычайной ситуации в долгосрочной перспективе может привести к преждевременному завершению исследований, в ходе которых могут выявиться случаи связанного с вакцинацией усиленного течения заболевания или другие побочные эффекты[132]. В целом согласно данным систематического обзора большинство вакцин является безопасными и эффективными, рекомендуется вакцинация в два этапа (двумя дозами). Однако дополнительные исследования необходимы для оценки вакцин в долгосрочной перспективе и для выяснения влияния таких параметров как возраст и дозировка[133].
По данным Всемирной организации здравоохранения по состоянию на 17 декабря 2020 года в доклинической разработке было 166 вакцин-кандидатов, 56 вакцин-кандидатов проходили клинические испытания[134]. Из числа отечественных вакцин в России зарегистрированы Гам-Ковид-Вак (Спутник V), Эпиваккорона и КовиВак[135].
Не содержащие живого вируса вакцины не могут вызвать заболевание, но поскольку вакцины тренируют иммунную систему, могут возникать такие симптомы как лихорадка, что является нормальной реакцией организма и свидетельствует о возникновении иммунной реакции[136]. Защита от инфекции в случае двухкомпонентных вакцин обычно формируется в течение двух недель после полной вакцинации, в случае однокомпонентных — в течение нескольких недель[137], что означает, что в этот период организм всё ещё уязвим для инфекции SARS-CoV-2[136]. Вакцина также может оказаться полезной после уже перенесённого COVID-19, поскольку реинфекции возможны, а заболевание ассоциируется с риском тяжёлого течения[136].
Вакцинация, хотя и не устраняет полностью риск заболеть, снижает этот риск по сравнению с непривитыми группами населения. Однако в большей степени она защищает от риска развития тяжёлого заболевания, госпитализации и смерти, являясь важным средством среди ответных мер пандемии. Вакцинация также уменьшает вероятность заражения других людей от вакцинированного человека[138].
Альтернативные вакцины в профилактике
Исследуется также возможность применения противопневмококковых вакцин для предотвращения сопутствующих COVID-19 бактериальных инфекций[139][140].
Согласно исследованиям на животных и людях вакцина БЦЖ обладает иммуномодулирующими свойствами, однако пока они не изучены, а их характеристики неизвестны. В отсутствие доказательств возможной защиты от COVID-19 ВОЗ не рекомендует применение вакцины БЦЖ для предотвращения COVID-19, рекомендации к применению сводятся лишь для профилактики туберкулёза среди новорождённых в странах с повышенным риском заболеваемости[141]. Существует исследование, связывающее снижение тяжести течения COVID-19 с вакцинацией прививкой MMR[142][143][144], при этом исследование проведено на небольшой выборке всего в 80 человек, и его выводы требуют дальнейшего изучения[143]. В целом пока нет доказательств, что вакцина против какой-либо другой инфекции может защитить от COVID-19[145].
Диагностика
Всемирная организация здравоохранения предоставила рекомендации по диагностированию заболевания у людей с подозрением на инфекцию SARS-CoV-2[146].
В России вирус SARS-CoV-2 предлагается диагностировать согласно временному алгоритму, опубликованному Министерством здравоохранения РФ[7], также в России уже разработаны средства для лабораторной диагностики коронавируса[147].
Лабораторная диагностика
Полимеразная цепная реакция
![Тестовый комплект Центров по контролю и профилактике заболеваний США для лабораторного определения коронавируса SARS-CoV-2[148]](https://wiki2.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/02/CDC_2019-nCoV_Laboratory_Test_Kit.jpg/im244-295px-CDC_2019-nCoV_Laboratory_Test_Kit.jpg)
Диагностировать вирус возможно при помощи полимеразной цепной реакции с обратной транскрипцией в реальном времени. В случае подозрения на инфекцию, но отрицательного результата теста, может быть произведено повторное взятие образцов для анализа из разных участков дыхательных путей[37]. В одном исследовании с выборкой в 5700 пациентов в 3,2 % случаев положительным был результат второго тестирования, результат первого — отрицательным[149].
Серологические тесты
В отличие от ПЦР, тесты на антитела не определяют наличие активного вируса в организме, но определяют наличие иммунитета к нему, то есть наличие IgM- и IgG-антител в крови[150]. Если обнаруживаются одновременно антитела IgG и IgM, то это означает, что инфекция была в течение нескольких предшествующих недель, если же обнаруживаются лишь IgG, то инфекция была ранее. При этом тесты не показывают, выздоровел ли человек[151]. Таким образом, тесты могут использоваться для определения тех, кто был инфицирован[150].
Рентгенологическое обследование
При подозрении на пневмонию рентгеновский снимок может показать инфильтраты в обоих лёгких, реже — лишь в одном. Если есть признаки пневмонии, но рентгеновский снимок ничего не показал, более точная картина может быть получена с помощью компьютерной томографии[37]. Согласно временным рекомендациям Минздрава РФ от 26.10.2020 лучевое обследование показано при умеренном, тяжёлом и крайне тяжёлом течении острой респираторной инфекции, а в случае лёгкого заболевания — по конкретным показания, например, при наличии факторов риска[152]. Увеличение количества затемнений (на снимках — белого цвета) и приближение к картине «белого лёгкого» означает приближение вероятного летального исхода[153].
У детей картина схожа со случаями у взрослых, однако вирусная пневмония обычно протекает в лёгкой форме, поэтому отклонения от нормы могут быть не замечены на рентгеновских снимках, а диагноз может оказаться неверный[95].
Диагностические показатели и биомаркеры
Поскольку COVID-19 проявляется в широком спектре клинических форм с разными степенями тяжести, одной из задач диагностики является также своевременное определение пациентов, у которых заболевание с большей вероятностью может прогрессировать в тяжёлую форму. Для этих целей требуется определение соответствующих биомаркеров[154]. Сильным предиктором смертности при госпитализации является уровень сатурации (SaO2) ниже 90 %, своевременное выявление гипоксии и госпитализация могут помочь в снижении смертности[155]. В зависимости от тяжести течения заболевания проводится соответствующий рутинный анализ крови для ведения пациента и своевременного реагирования на изменения его состояния[156]. Увеличенное протромбиновое время и повышенный уровень С-реактивного белка при госпитализации были ассоциированы с тяжёлым течением COVID-19 и переводом в отделение интенсивной терапии[157][158].
В одном из небольших исследований показано, что у большинства больных уровень прокальцитонина (англ.) (рус. в крови был в норме, однако он был повышенным у 3-х из 4 больных, у которых была обнаружена вторичная бактериальная инфекция[159]. Согласно метаанализу от 23 сентября 2020 года примерно у 3 из 4 тяжело или критически больных пациентов прокальцитонин не повышен, однако повышенные уровни прокальцитонина связаны с повышенным риском осложнений, прокальцитонин может указывать на риск повреждений внутренних органов. При этом уровень прокальцитонина обычно в норме при первичном обследовании. В текущих руководствах по лечению COVID-19 пока не утверждена стратегия по назначению антибиотиков согласно уровню прокальцитонина, для определения возможности выявления вторичных бактериальных инфекций на основе прокальцитонина требуются дополнительные исследования[160]. Отрицательный же тест на прокальцитонин может указывать на вероятное отсутствие бактериальной вторичной инфекции[161].
Эозинопения также часто встречается среди пациентов, но не зависит от степени тяжести болезни. Эозинопения может служить маркером COVID-19 у больных с подозрением на инфекцию SARS-CoV-2, если присутствуют соответствующие симптомы и аномалии в рентгеновских исследованиях[162].
У критически больных пациентов наблюдается повышенное содержание маркеров воспалительных процессов в плазме крови[74]. В небольшом исследовании отмечено, что у пациентов, попадающих в отделение интенсивной терапии, в крови выше уровни IL-2, IL-7, IL-10, GCSF (англ.) (рус., IP-10 (англ.) (рус., MCP1, MIP1A и фактора некроза опухоли (ФНО-α)[159].
Лимфопения (англ.) (рус. (см. Лейкоцитарная формула) среди пациентов COVID-19 является наиболее частой и встречается примерно в 83 % случаев[74]. В случаях с летальным исходом лимфопения становилась более тяжёлой со временем, вплоть до смерти[163]. Помимо лимфопении, с тяжёлым течением заболевания также могут быть связаны нейтрофилия, повышенный уровень аланинаминотрансферазы и аспартатаминотрансферазы в сыворотке крови, повышенный уровень лактатдегидрогеназы, высокий уровень C-реактивного белка и высокий уровень ферритинов[74].
Степень тяжести заболевания при отсутствии сепсиса определяется исходя из степени насыщения артериальной крови кислородом и частоты дыхания[164]. На тяжёлую степень заболевания также может указывать обнаружение РНК вируса в крови пациента[74]. На сепсис может указывать уровень лактата в крови от 2 ммоль/л[156]. С летальными исходами ассоциируются повышенный уровень D-димера и лимфопения[74].
Дифференциальный диагноз
По симптомам COVID-19 невозможно отличить от других острых респираторных инфекций, в частности, от простуды и других ОРВИ[37]. Пневмония при COVID-19 также не может быть клинически отличимой от пневмоний, вызванных другими патогенами[156]. Ключевым фактором диагностики является история путешествий или контактов больного[37][156]. В случаях группового заболевания пневмонией, особенно у военнослужащих, могут быть заподозрены аденовирусная или микоплазменная инфекции[37].
Другие инфекции могут быть исключены тестами на конкретных возбудителей: бактериальная пневмония может быть исключена положительным посевом крови или мокроты либо молекулярным тестированием, другие вирусные инфекции — через полимеразную цепную реакцию с обратной траскрипцией[37]. Диагностировать грипп могут помочь также экспресс-тесты, однако их отрицательный результат не исключает грипп[156]. Положительный же диагноз на другой патоген не исключает одновременного заражения вирусом SARS-CoV-2 (коинфекции)[165]. В исследовании с выборкой 5700 человек коинфекция SARS-CoV-2 и другим респираторным вирусом обнаруживалась у 2,1 % человек[149].
Лечение
![Порядок надевания средств индивидуальной защиты[166]](https://wiki2.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b5/DonningCDC2020.jpg/im244-301px-DonningCDC2020.jpg)
![Коронавирусный стационар при Сеченовском университете[167]](https://wiki2.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6f/%D0%A1%D0%BE%D1%82%D1%80%D1%83%D0%B4%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA_%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%80%D1%83%D1%81%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE_%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B0_%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8_%D0%A1%D0%B5%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BC_%D1%83%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%B5%D1%80%D1%81%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%82%D0%B5_%D1%80%D1%8F%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%BC_%D1%81_%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%B4._%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%83%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BC.jpg/im244-320px-thumbnail.jpg)
Антибиотики против вирусов бесполезны и не применяются в лечении. Однако они могут быть назначены в случае обнаружения бактериальной вторичной инфекции[25]. В основном пациенты получают симптоматическую и поддерживающую терапию[168]. Основной задачей лечения больных с острой дыхательной недостаточностью является поддержание достаточного уровня оксигенации организма, поскольку недостаток кислорода может привести к необратимым нарушениям в работе жизненно важных органов и летальному исходу[11]. В тяжёлых случаях лечение направлено на поддержание жизненно важных функций организма.
Если лечение в стационаре по каким-либо причинам невозможно, в лёгких случаях без тревожных признаков и при отсутствии хронических болезней допустим уход за больным в домашних условиях. Однако при наличии одышки, кровохарканья, повышенного выделения мокроты, признаков гастроэнтерита или изменениях психического состояния показана госпитализация[37].
ВОЗ также предупреждает, что курение, применение народных средств, в том числе на основе трав, и самолечение, включая антибиотики, никак не помогут бороться с инфекцией, но могут нанести вред здоровью[9].
По состоянию на июль 2022 года существуют доказательства высокой (отмечены «H«) или средней степени достоверности по положительному влиянию на следующие события [169][170]:
- Уменьшение смертности: системные кортикостероиды (+/- ингибиторы ИЛ-6), ингибиторы янус-киназыH
- Риск ИВЛ: ингибиторы ИЛ-6 (+/- системные кортикостероиды)H
- Риск госпитализации: молнупиравир, нирматрелвир/ритонавир
- Продолжительность госпитализации: ингибиторы янус-киназы и витамин D ( имеют прямые доказательства эффективности), а также системные кортикостероиды + ингибиторы ИЛ-6
- Срок клинического выздоровления: молнупиравир
- Срок ИВЛ: игибиторы янус-киназ.
Также имеются доказательства низкого качества о возможной эффективности по тем или иным событиям следующих препаратов (групп препаратов): средства от вирусных гепатитов, азитромицин, цефепим, доксициклин, солевые растворы, фавипиравир, антикоагулянты в терапевтических дозах (возможно, уменьшают риск тромбоза, но при этом могут повышать риск кровотечений), ремдесивир и ингибиторы протеинкиназы (при этом эта группа средств имеет доказанный вред в виде негативного профиля безопасности). [169]
Поддерживающее лечение
Пациентам со случаями средней тяжести заболевания и с тяжёлыми случаями требуется поддерживающее лечение и кислородная терапия[54]. Всемирная организация здравоохранения рекомендует всем странам обеспечить доступность устройств для измерения уровня кислорода в крови и медицинских устройств кислородной терапии[171]. Острый респираторный дистресс-синдром предполагает механическую вентиляцию лёгких. В более тяжёлых случаях применяется экстракорпоральная мембранная оксигенация, которая является сложным и комплексным методом поддержки пациентов при острой гипоксической дыхательной недостаточности. Этот метод применяется и при тяжёлых формах сердечной недостаточности, которая также может возникнуть на фоне инфекции SARS-CoV-2[172]. Пациенты, выжившие после критического состояния, острого респираторного дистресс-синдрома или экстракорпоральной мембранной оксигенации, обычно проходят длительный этап реабилитации и могут провести больше времени в стационаре[173].
Всемирная организация здравоохранения опубликовала руководство по ведению тяжелобольных в случае подозрения на новый коронавирус[174]. В Кокрановском сотрудничестве также была подготовлена специальная тематическая подборка доказательной базы в соответствии с рекомендациями ВОЗ. Подборка включает в себя информацию по жидкостной реанимации и применению вазопрессоров, по механической вентиляции лёгких и её отмене, по лечению гипоксии, по фармакологическому лечению и по питанию в отделениях реанимации[175].
Экстракорпоральная мембранная оксигенация
При экстракорпоральной мембранной оксигенации (ЭКМО) венозная кровь перенаправляется в специальный аппарат с мембранами, по сути представляющими собой искусственные лёгкие. Кровь насыщается кислородом и из неё удаляется углекислый газ, а затем она снова возвращается в другую вену или артерию. По текущим данным данный метод помогает снизить летальность среди пациентов с острым респираторным дистресс-синдромом[176].
Однако сам по себе метод является ресурсоёмким и дорогостоящим способом поддержания жизни, а в числе осложнений возможны больничные инфекции. Хотя он может помочь при дыхательной или сердечной недостаточности, он не поможет в случае множественного отказа органов или септического шока. Поскольку на текущий момент неизвестны соотношения разных причин смерти, сложно оценить возможную пользу в целом от применения ЭКМО при COVID-19[176]. Согласно когортному исследованию Организации экстракорпорального жизнеобеспечения среди пациентов с COVID-19 на 90-й день с начала терапии внутрибольничная смертность составила 38 %. В наиболее большом рандимизированном исследовании применения ЭКМО при остром повреждении лёгких смертность на 60-й день составляла 35 % против 46 % в контрольной группе. Предварительные данные указывают на потенциальную пользу применения ЭКМО в случаях COVID-19[173].
В условиях эпидемии применение ЭКМО ограничено, как и в случае пандемии. В странах с малыми ресурсами в таких случаях больше жизней может быть спасено применением устройств для измерения уровня кислорода в крови и терапией кислородом[176].
Лечение кортикостероидами
SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV и SARS-CoV-2 приводят к большому выбросу цитокинов[159], вызывая сильный иммунный ответ[177]. Иммунный ответ является одной из причин возникновения острого повреждения лёгких и острого респираторного дистресс-синдрома[177]. В начале пандемии Китаем применялись кортикостероиды, однако ВОЗ не рекомендовала их использование вне РКИ из-за отсутствия доказательств возможной эффективности[177], китайская же команда медиков апеллировала, утверждая, что малые дозы помогают снизить смертность[178]. Согласно предварительным результатам исследования RECOVERY, проведённого в Великобритании, дексаметазон помогает на треть снизить смертность пациентов, находящихся на искусственной вентиляции лёгких, и на пятую часть — среди пациентов, которым требуется кислородная терапия[179]. Метаанализ и систематический обзор лечения COVID-19 различными препаратами показывает, что глюкокортикостероиды, вероятно, всё же снижают смертность и риск необходимости механической вентиляции лёгких среди пациентов в сравнении с обычным уходом за больным[180]. Однако 1707 пациентов в исследовании не подошли для рандомизации, а данные о причинах отказа отсутствуют, поэтому есть некоторая неопределённость по части пациентов с сопутствующими заболеваниями[181].
Экспериментальное лечение
См. также: § Экспериментальные терапии и направления исследований
Хотя на практике применяются нелицензированные препараты и экспериментальные терапии, например, с применением противовирусных средств, подобное лечение должно проходить в рамках этически обоснованных клинических исследований[37]. Исследования серий случаев могут быть предвзятыми, что может создать ложное ощущение безопасности и эффективности экспериментальных терапий[102]. Критически важным является применение средств, обоснованных как научными исследованиями, так и этически[182][183]. ВОЗ подготовила протокол для проведения рандомизированных контролируемых исследований[171]. Проводимые исследования должны быть высококачественными, низкое качество исследований приводит к пустой трате ресурсов и по определению не является этичным[184]. Применение же средств с недоказанной эффективностью может нанести вред пациентам, находящимся в критическом состоянии[183]. Например, хлорохин, гидроксихлорохин, азитромицин, а также лопинавир и ритонавир ассоциируются с потенциальным повышением риска смерти из-за проблем с сердцем[185][37].
Назначения терапий должны основываться не на гипотезах, а на клинических исследованиях, подтверждающих эффективность. Гипотезы же могут являться основанием для проведения спланированного клинического испытания[40]. ВОЗ считает этически допустимым индивидуальное применение экспериментальных терапий вне клинических исследований в связи с экстренной ситуацией, если пациент был проинформирован и дал своё согласие. Подобные терапии должны проходить под наблюдением, а результаты должны быть задокументированы и предоставлены научному и медицинскому сообществу[186].
Неэффективные лекарства
В метаанализе The LIVING Project проведён обзор исследований терапий по различным критериям, в числе которых снижение смертности от всех причин на 20 %, снижение риска серьёзных осложнений на 20 % и снижение риска механической вентиляции лёгких на 20 %. Согласно метаанализу есть доказательства неэффективности гидроксихлорохина и комбинации лопинавира и ритонавира в снижении смертности от всех причин и снижения риска серьёзных осложнений. Комбинация лопинавира и ритонавира также неэффективна по части снижения риска необходимости механической вентиляции лёгких. Нет доказательств эффективности или неэффективности по сравнению со стандартным уходом для следующих средств: интерферон β-1a и колхицин[187].
Лопинавир/Ритонавир
Не имеет преимуществ перед стандартным лечением (поддерживающей терапией) ни в монотерапии, ни в сочетании с умифеновиром или интерферонами, при этом значительно повышает риск побочных эффектов[188][189].
Гидроксихлорохин
По опыту лечения малярии и системной красной волчанки хлорохина и гидроксихлорохина, оба препарата относительно хорошо переносятся пациентами, однако обладают серьёзными побочными эффектами в менее 10 % случаев, среди которых пролонгация QT (англ.) (рус., гипогликемия, психоневрологические побочные эффекты и ретинопатия[57]. Ранние результаты лечения этими препаратами показали обнадёживающие результаты, в свете чего их использование получило одобрение Дональда Трампа[190], впоследствии же метаанализ и систематический обзор исследований применения гидроксихлорохина показал, что он не снижает смертность среди госпитализированных пациентов. Однако в комбинации с азитромицином он, наоборот, увеличивает смертность[191]. Применение аминохинолинов в лечении COVID-19 бесперспективно, если только не появятся новые высококачественные исследования с иными результатами[190]. Когортное исследование пациентов с ревматическими нарушениями, принимавших гидроксихлорохин, не обнаружило какого-либо профилактического эффекта[192]. Аналогичные результаты показало рандомизированное исследование профилактики после возможного заражения, при этом в группе гидроксихлорохина чаще наблюдались побочные эффекты[193].
Азитромицин
По результатам семи исследований с участием 8822 пациентов было выявлено, что азитромицин не влияет на смертность, риск и продолжительность ИВЛ и продолжительность госпитализации. Поэтому лечение азитромицином COVID-19 не оправдано из-за недостаточной эффективности и высокого риска формирования антибиотикорезистентности[194].
Реконвалесцентная плазма
Иммунная система производит антитела, которые помогают в борьбе с вирусом. Реконвалесцентная плазма содержит антитела и может использоваться в целях пассивной иммунизации других людей путём переливания, имеется успешный опыт использования подобной практики в лечении некоторых вирусных заболеваний[195]. Кокрейновский мета-анализ по реконвалесцентной плазме утверждает на основании восьми РКИ, оценивающих эффективность и безопасность плазмы выздоравливающих, что с высокой степенью достоверности реконвалесцентная плазма не влияет или практически не влияет ни на смертность в течение 28 дней, ни на клиническое улучшение больных COVID-19 средней или тяжёлой степени тяжести[196].
Центры по контролю и профилактике заболеваний США рекомендуют не использовать реконвалесцентную плазму с низкими титрами антител, плазму с высокими титрами рекомендуется не использовать у госпитализированных больных без нарушений в работе иммунной системы (за исключением применения в рамках клинических испытаний среди пациентов, которым не требуется механическая вентиляция лёгких). Для каких-либо рекомендаций за или против применения среди негоспитализированных пациентов или среди больных с нарушениями работы иммунной системы пока недостаточно данных[197].
Постковидный синдром
Иногда в результате перенесённого заболевания возникают долговременные осложнения, получившие название постковидный синдром[198][199][200]. Точного определения постковидного синдрома нет[24]. Согласно статистике Великобритании примерно у каждого пятого больного с подтверждённым диагнозом симптомы длились 5 недель или дольше, а у каждого 10-го — 12 недель и дольше[201]. Обычно постковидный синдром определяется как симптомы длительностью более 2 месяцев[24]. Симптомы могут включать в себя[202][203]:
- усталость;
- одышку;
- боли или ощущение сдавливания в груди;
- проблемы с памятью и концентрацией внимания;
- проблемы со сном;
- учащённое сердцебиение;
- головокружение;
- ощущения покалывания;
- боли в суставах;
- депрессия и тревожность;
- звон или болевые ощущения в ушах;
- боли в животе, диарея, потеря аппетита;
- высокая температура тела, кашель, головные боли, боль в горле, изменения обоняния или вкуса;
- сыпь;
- потерю волос.
Мультисистемный воспалительный синдром, связанный с COVID-19
Самостоятельная реабилитация
После перенесённой тяжёлой формы COVID-19 некоторым может потребоваться реабилитация на дому. Реабилитационные мероприятия могут включать в себя методы купирования одышки, выполнение повседневных действий, определённые физические упражнения, восстановление проблем, связанных с голосом или с приёмом пищи, преодоление трудностей, связанных с памятью или мышлением и решение проблем, связанных со стрессом. Врач при выписке может назначить индивидуальные рекомендации по реабилитации, а помощь может оказываться семьёй или друзьями[204].
При некоторых состояниях во время реабилитации может потребоваться обращение к врачу. Согласно ВОЗ, обращение к врачу требуется если[204]:
- одышка не снижается, несмотря на использование методов контроля дыхания в состоянии покоя;
- сильная одышка возникает при выполнении минимальной физической активности даже в положениях, предполагающих облегчение одышки;
- нет видимого улучшения умственных процессов и снижения усталости, в результате чего затрудняется повседневная деятельность или не получается вернуться к служебных обязанностям;
- возникают симптомы тошноты, головокружения, сильной одышки, ощущения липкой кожи, повышенного потоотделения, ощущения сдавливания в груди или если усиливаются боли.
Прогноз
| Страна | Летальность |
|---|---|
| Италия | 11,7 % |
| Испания | 8,7 % |
| Великобритания | 7,1 % |
| Иран | 6,5 % |
| Китай | 2,3 %[Прим. к табл. 1] |
| США | 1,7 % |
| Германия | 1 % |
| Австралия | 0,4 % |
|
Летальность и тяжесть заболевания связаны с возрастом пациентов и наличием сопутствующих заболеваний[205]. Основной причиной летальных исходов является дыхательная недостаточность, развивающаяся на фоне острого респираторного дистресс-синдрома[37]. Также выздоровлению могут препятствовать шок и острая почечная недостаточность[206].
Согласно анализу 44 672 подтверждённых случаев в Китае (из общего числа в 72 314 случаев по данным с 31 декабря 2019 года по 11 февраля 2020 года), летальность составляла 2,3 %. Среди погибших было больше пожилых людей возрастом от 60 лет и людей с хроническими болезнями. Среди критически больных летальность составляла 49 %[37][207]. Итоговая летальность среди пациентов без сопутствующих заболеваний в Китае была намного ниже и составляла 0,9 %[71].
Уровень летальности может отличаться между странами, в некоторых странах уровень летальности оказался выше, чем в Китае. В целом по миру по состоянию на 8 апреля он оценивался примерно в 5,85 %[37]. Летальность среди госпитализированных варьируется от 4 % до 11 %[107]. На различия между странами могут влиять различные факторы[37]. Например, высокая летальность в Италии в начале пандемии частично объясняется большим количеством пожилого населения в стране[208].
В сравнении с тяжёлым острым респираторным синдромом и ближневосточным респираторным синдромом летальность у COVID-19 намного ниже. Однако заболевание COVID-19 легче распространяется и уже отняло намного больше жизней[37].
Факторы риска
В число факторов, способствующих большей вероятности протекания болезни в тяжёлой форме, входят:
- пожилой возраст[206];
- мужской пол[209];
- диабет[25];
- ожирение[206];
- курение в анамнезе[206];
- хронические заболевания лёгких[71] (ХОБЛ)[206];
- сердечные заболевания[25] (ишемическая болезнь)[206];
- гипертония[71][206];
- хронические заболевания почек[206][71];
- хронические заболевания печени[206];
- злокачественные новообразования[206];
- ВИЧ-инфекция[210]
Астма, судя по всему, не является фактором риска для COVID-19[211][212], по данным же Центров по контролю и профилактике заболеваний США факторами риска могут оказаться астма средней тяжести и тяжёлая форма[213].
Беременность является фактором риска в случае тяжёлого течения заболевания — чаще требуется интенсивная терапия, при отсутствии же тяжёлого течения заболевание проходит легче, чем у небеременных. При этом важно учитывать, что беременные женщины и новорождённые младенцы могут с большей вероятностью нуждаться в специализированной помощи вне зависимости от COVID-19[214].
Согласно систематическому обзору желудочно-кишечных проявлений наличие симптомов гастроэнтерита повышает риск развития тяжёлого или критического состояния, а также острого респираторного дистресс-синдрома[215].
Из сердечных заболеваний риск смерти повышают коронарная недостаточность, сердечная недостаточность и аритмии[216].
Курение является фактором риска для многих инфекционных и неинфекционных заболеваний, в том числе для респираторных[217]. Исследования показывают, что у курильщиков более высокий риск развития тяжёлой формы COVID-19 и летального исхода[218]. Возможно, что повышенный риск развития тяжёлого заболевания у мужчин также связан с тем, что мужчины чаще курят, нежели женщины[206]. Шансы на прогрессирование до тяжёлой формы заболевания увеличиваются у людей с более длительной историей курения. Возможно, это связано с тем, что длительное курение может привести к развитию хронической обструктивной болезни лёгких (ХОБЛ). Сама по себе ХОБЛ значительно увеличивает риск развития тяжёлой формы[219].
Учёные также выявили, что примерно у 10 % больных с угрожающей жизни формой заболевания обнаруживаются антитела к интерферону, в 95 % случаев среди мужчин. Эксперименты подтвердили, что эти антитела блокируют работу интерферона I типа. Ещё у 3,5 % человек обнаруживаются мутации 13 различных генов, которые играют критическую роль в защите от вирусов гриппа. В обоих случаях нарушения связаны с выработкой и работой набора из 17 белков из группы интерферонов I типа, защищающих клетки и организм в целом от вирусов[220].
Экспериментальные терапии и направления исследований
В целях определения эффективных терапий ВОЗ запустила международное исследование Solidarity, которое будет изучать эффективность применения различных терапий по сравнению с обычным поддерживающим лечением[221]. Результаты исследования с участием более 30 стран были опубликованы в виде препринта и проходят этап рецензирования[222].
Противовирусные средства
Разработка противовирусных средств предполагает прерывание репликации вируса на каком-либо из этапов его жизненного цикла, при этом не уничтожая сами клетки человеческого тела. Вирусы быстро размножаются, часто мутируют и легко адаптируются, развивая в конечном итоге нечувствительность к лекарствам и вакцинам. По этой причине разработка противовирусных средств очень затруднена[223]. Ведутся клинические испытания различных противовирусных средств[224].
Согласно систематическому обзору от января 2022 года некоторые антивирусные средства могут улучшать клинические исходы у пациентов, однако ни одно не показало эффективности по части снижения смертности[225].
Иммуномодуляторы
Средства против синдрома высвобождения цитокинов
Тоцилизумаб и сарилумаб являются иммуносупрессорами, ингибируют интерлейкин-6, применяются при ревматологических нарушениях и в лечении цитокинового шторма. В случае COVID-19 испытываются на возможность снижения вызываемого вирусом цитокинового шторма и уменьшения риска осложнений. Однако решение о применении иммуносупрессоров является сложным и предполагает принятие взвешенного решения с учётом преимуществ противовоспалительного действия и негативного эффекта от вмешательства в работу иммунной системы. Против цитокинового шторма испытываются и другие препараты[37]. Предварительные выводы в небольшом ретроспективном обзоре лечения 21 пациента тоцилизумабом предполагали быстрое улучшение состояния тяжело и критически больных пациентов[226]. Рандомизированное слепое испытание тоцилизумаба среди больных с гипервоспалительными состояниями показало отсутствие эффективности как в снижении смертности, так и в предотвращении интубации, однако некоторые отличия по сравнению с группой плацебо были[227]. Другие два рандомизированных исследования показали возможное снижение рисков необходимости вентиляции лёгких и смерти по ходу течения заболевания, но на конечной выживаемости тоцилизумаб не сказался[228][229]. Данные исследования RECOVERY показали, что введение тоцилизумаба в дополнение к терапии дексаметазоном госпитализированным пациентам на кислороде дополнительно снижает риск смерти на 14 %, а продолжительность пребывания пациентов в больнице — на 5 полных дней[230].
Интерфероны
В начале пандемии проводились исследования с систематическим использование интерферонов, более поздние же исследования не смогли продемонстрировать эффективности интерферонов, а некоторые исследования предположили возможный вред при применении в тяжёлых случаях заболевания. Проводимые на раннем этапе пандемии исследования по применению интерферона альфа небольшие и не позволяют делать какие-либо выводы о возможности его применения. Интерфероны альфа и бета не рекомендуются к применению, за исключением контролируемых испытаний[231].
Другие иммунотерапии
Моноклональные антитела
Моноклональные антитела представляют собой потенциальный способ пассивной иммунизации, они могут связываться с шиповидными белками вируса, нейтрализуя его и препятствуя его вхождению в клетки организма[232][233]. В то время как вакцины являются лучшим средством профилактики, моноклональные антитела могут оказаться полезными для определённых уязвимых групп населения, например, в случаях, когда пациенты входят в группы риска и не были вакцинированы, или если они заболели в период после вакцинации, когда иммунитет ещё не успел сформироваться. Недостатком моноклональных антител является то, что они могут дать лишь временную защиту и затратны в производстве[233].
Среди групп риска в лёгких и среднетяжёлых случаях, когда высок риск госпитализации, ВОЗ рекомендует применение моноклональных антител. В 2021 году рекомендовался казиривимаб/имдевимаб, в 2022 году к рекомендациям добавился альтернативный препарат — сотровимаб[27].
Средства от гиперкоагуляции
COVID-19 может вызывать различные нарушения, связанные с тромбоэмболией. Антикоагулянты используются в лечении и предотвращении подобных нарушений[234]. При коагулопатиях, связанных с COVID-19, часто применяют терапию антикоагулянами, чаще всего используется гепарин, при этом нередко сообщается о гепарином-индуцированной тромбоцитопении[235]. Поскольку интенсивная терапия антикоагулянтами может приводить к кровотечениям, риск тромботических нарушений сам по себе не является оправданием для использования данного вида терапии. Существующие руководства опираются в основном на экспертные мнения и могут значительно отличаться друг от друга, в том числе по профилактике или лечению, однако в одном эксперты сходятся — в необходимости качественных рандомизированных испытаний для определения подходящей дозировки в случаях COVID-19[236]. Ретроспективный анализ 2773 пациентов с COVID-19 показал значительное снижение внутрибольничной смертности среди больных, которым требовалась механическая вентиляция лёгких, если им назначалась терапия антикоагулянтами[62]. Рандомизированное исследование REMAP-CAP было досрочно прекращено и показало обратные результаты для пациентов с тяжёлым состоянием, которым требовалась интенсивная терапия: лечение антикоагулянтами не влияло на исходы, но приводило к кровотечениям[237].
Некоторые руководства предлагают использовать антикоагулянты для профилактики тромбообразования среди пациентов с COVID-19, однако по состоянию на начало октября было недостаточно доказательств для определения соотношения возможных рисков и пользы среди госпитализированных пациентов[234].
Сравнение COVID-19 с гриппом

Вирусы гриппа и COVID-19 распространяются мелкими каплями, возникающими при кашле, чиханье или разговоре, после чего капли могут попасть в нос или рот находящихся поблизости людей или могут попасть в лёгкие на вдохе, при оседании на предметах вирус может быть занесён также контактным путём при последующем прикосновении к носу, рту или глазам[238]. В случае гриппа важную роль играет распространение болезни среди детей, а COVID-19 заражает, прежде всего, взрослых, от которых уже заражаются дети, как показывают предварительные данные обследования китайских домохозяйств[239][240]. Заболевания различаются по контагиозности, при сезонном гриппе от одного больного заражаются примерно 1,3 человека (индекс репродукции R = 1,28), при COVID-19 больной распространяет заболевание на 2—2,5 человека[241].
Симптомы у заболеваний схожие, но при COVID-19 может возникать потеря обоняния или вкуса, при гриппе же потеря обоняния или вкуса обычно не происходит. Проблемы с дыханием могут быть при обоих заболеваниях, но при гриппе они менее вероятны и ассоциируются с пневмонией. При COVID-19 возможен пониженный уровень кислорода даже при бессимптомном течении заболевания[238].
Оба заболевания могут протекать как в лёгкой, так и в тяжёлой форме, иногда приводя к смертельным исходам[242]. При обоих заболеваниях возможны различные осложнения, начиная от пневмонии и дыхательной недостаточности и заканчивая полиорганной недостаточностью и сепсисом, но в случае COVID-19 могут образовываться сгустки в венах и артериях лёгких, сердца, ног и мозга, а у детей есть риск возникновения мультисистемного воспалительного синдрома. В случаях обоих заболеваний в группах риска находятся пожилые люди и люди с сопутствующими заболеваниями, но при гриппе в группу риска также входят дети[238]. Помимо поражения лёгких при COVID-19 выше риск дисфункции других органов, среди которых по значимости выделяются почки, возможны также длительные последствия и заболевания, требующие постоянного лечения[243][244]. В случаях COVID-19 риск госпитализации и смерти выше, чем при гриппе, особенно у людей, входящих в группы риска[238], а также выше затраты на систему здравоохранения[243].
В обоих случаях лечение направлено на облегчение симптомов, а в тяжёлых случаях может потребоваться госпитализация и поддерживающее лечение, например, механическая вентиляция лёгких[242]. COVID-19 нередко пытаются сравнивать с гриппом, однако накапливающиеся научные данные показывают, что COVID-19 опаснее гриппа для госпитализированных пациентов[244].
Терминология
11 февраля 2020 года Всемирная организация по здравоохранению дала заболеванию официальное название — COVID-19[245]. Заболеваниям, вызываемым вирусами, названия даются в целях обеспечения возможности обсуждения распространения, способов передачи, профилактики, тяжести заболевания и методов лечения[246]. COVID-19 — сокращённо от «COronaVIrus Disease» — «заболевание, вызванное коронавирусом». В этом названии «СО» означает «корона» (corona), «VI» — «вирус» (virus), «D» — «болезнь» (disease), а «19» — год, в котором было выявлено впервые заболевание (сообщено в ВОЗ 31 декабря 2019 года[247]).
Вирус же, вызывающий заболевание, называется по-другому — SARS-CoV-2. Такое название дано, поскольку вирус генетически схож с вирусом SARS-CoV, который в 2003 году был ответственен за вспышку тяжёлого острого респираторного синдрома в Китае. Однако часто используются формулировки «вирус COVID-19», «коронавирусная инфекция COVID-19» или «вирус, вызывающий COVID-19». Тем не менее название заболевания не является названием вируса и не предназначено для замещения названия SARS-CoV-2, данного Международным комитетом по таксономии[246].
В русском языке также употребляется название «ковид»[248]. Оно стало популярным во второй волне пандемии, частично вытеснив использовавшееся неспециалистами во время первой волны слово «коронавирус» для обозначения заболевания[1]. Впоследствии слово «ковид» привело к словообразованию с появлением таких слов, как «ковидный», «ковидник», «ковидиот»[249] и «ковидарий»[1]. Лингвист Максим Кронгауз отмечает, что несмотря на отсутствие слова в словарях общего назначения, его можно использовать, руководствуясь узусом, то есть словоупотреблением[1].
Дезинформация
После первоначальной вспышки COVID-19 мистификации и дезинформация относительно происхождения, масштабов, профилактики, лечения и других аспектов заболевания быстро распространились в интернете[250][251][252]. Дезинформация может стоить человеческих жизней. Отсутствие достаточного уровня доверия и достоверной информации может негативно сказаться на диагностике, а кампании по иммунизации населения могут не достигнуть поставленных целей, и вирус продолжит циркулировать[253]. Также во время пандемии появилась проблема ковид-диссидентства. Ковид-диссидентами называют людей, которые не верят в существование вируса или сильно преуменьшают значимость проблемы. Такие люди могут не носить маски, не соблюдать дистанцию или предписания правительства, а при заболевании не сразу обращаться к врачам. Известны случаи, когда такие люди впоследствии лежали в реанимации или были при смерти, но уже ничего не могли изменить[254].
Решающее значение в борьбе с инфодемией, дезинформацией и слухами играет распространение точной и надёжной информации через платформы социальных медиа[255]. В совместном заявлении ВОЗ, ООН, ЮНИСЕФ и другие организации призвали страны-члены ООН разработать и реализовать планы по противодействию распространения инфодемии путём своевременного распространения точной информации, основанной на научных данных и доказательствах, среди всех сообществ, особенно среди людей, входящих в группы риска, а также путём борьбы с дезинформацией, проявляя при этом уважение к свободе выражения мнений[253].
См. также
- Исследование RECOVERY
- Тяжёлый острый респираторный синдром
- Ближневосточный респираторный синдром
- Острая респираторная вирусная инфекция
- Обновляющийся каталог рекомендаций eCOVID-19
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Максим Кронгауз. Входит или не входит: стало ли слово «ковид» частью языка?. nplus1.ru. Дата обращения: 21 января 2021. Архивировано 16 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Медицинская реабилитация детей, перенесших COVID19 в режиме дистанционного дневного стационара с использованием цифровых технологий. Временное методическое руководство № 71 (pdf). Департамент здравоохранения города Москвы (2000). Дата обращения: 27 ноября 2021. Архивировано 2 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) (англ.). WHO/Europe. WHO (9 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 9 марта 2020. Архивировано 18 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) - Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment | BMJ Best Practice (англ.). BMJ Best Practices. Дата обращения: 19 ноября 2021. Архивировано 19 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ Коронавирусная инфекция 2019-nCoV внесена в перечень опасных заболеваний // Минздрав России. — 2020. — 2 февраля. — Дата обращения: 28.11.2021.
- ↑ 1 2 David L. Heymann, Nahoko Shindo. COVID-19: what is next for public health? (англ.) // The Lancet. — Elsevier, 2020. — 13 February. — ISSN 1474-547X 0140-6736, 1474-547X. — doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Профилактика, диагностика и лечение новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19). Временные методические рекомендации. Минздрав России (3 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 5 мая 2022. Архивировано 25 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infection is suspected: interim guidance, 28 January 2020 (англ.). WHO (28 января 2020). Дата обращения: 28 ноября 2021. Архивировано 25 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 Вопросы и ответы о COVID-19. ВОЗ. Дата обращения: 1 марта 2020. Архивировано 25 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Wim Trypsteen, Jolien Van Cleemput, Willem van Snippenberg, Sarah Gerlo, Linos Vandekerckhove. On the whereabouts of SARS-CoV-2 in the human body: A systematic review (англ.) // PLOS Pathogens. — 2020. — 30 October (vol. 16, iss. 10). — P. e1009037. — ISSN 1553-7374. — doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009037. Архивировано 4 мая 2022 года.
- ↑ 1 2 С. Н. Авдеев. Практические рекомендации по кислородотерапии и респираторной поддержке пациентов с COVID-19 на дореанимационном этапе : [рус.] / С. Н. Авдеев, Н. А. Царева, З. М. Мержоева … [] // Пульмонология. — 2020. — Т. 30, № 2 (2 июня). — С. 151—163. — ISSN 2541-9617.
- ↑ Коронавирусная болезнь 2019 (COVID-19) - Симптомы, диагностика и лечение. BMJ Best Practices (21 декабря 2020). Дата обращения: 17 января 2021. Архивировано 19 января 2021 года. (требуется подписка)
- ↑ 1 2 Вопросы и ответы о COVID-19. ВОЗ. Дата обращения: 10 августа 2020. Архивировано 25 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Часто задаваемые вопросы об использовании масок для профилактики COVID-19. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (1 декабря 2020). Дата обращения: 19 июня 2021. Архивировано 19 июня 2021 года.
- ↑ Qiao Liu, Chenyuan Qin, Min Liu, Jue Liu. Effectiveness and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in real-world studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Infectious Diseases of Poverty. — 2021. — 14 November (vol. 10, iss. 1). — P. 132. — ISSN 2049-9957. — doi:10.1186/s40249-021-00915-3. — PMID 34776011. Архивировано 30 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ Qiao Liu, Chenyuan Qin, Min Liu, Jue Liu. Effectiveness and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in real-world studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Infectious Diseases of Poverty. — 2021. — 14 November (vol. 10, iss. 1). — P. 132. — ISSN 2049-9957. — doi:10.1186/s40249-021-00915-3. Архивировано 30 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ Поиск вакцины против COVID-19. ВОЗ. Дата обращения: 19 июня 2021. Архивировано 19 марта 2021 года.
- ↑ Harald Brüssow, Sophie Zuber. Can a combination of vaccination and face mask wearing contain the COVID-19 pandemic? (англ.) // Microbial Biotechnology. — 2021. — 28 December. — ISSN 1751-7915. — doi:10.1111/1751-7915.13997. Архивировано 2 февраля 2022 года.
- ↑ Hisham Ahmed Mushtaq, Anwar Khedr, Thoyaja Koritala, Brian N. Bartlett, Nitesh K. Jain. A review of adverse effects of COVID-19 vaccines (англ.) // Le Infezioni in Medicina. — 2022. — 1 March (vol. 30, iss. 1). — P. 1–10. — ISSN 2532-8689. — doi:10.53854/liim-3001-1. — PMID 35350266.
- ↑ Глыбочко П.В., Фомин В.В., Авдеев С.Н. и др. Клиническая характеристика 1007 больных тяжелой SARS-CoV-2 пневмонией, нуждавшихся в респираторной поддержке // Клиническая фармакология и терапия : научный журнал. — М.: ООО «Фармапресс», 2020. — 17 мая (т. 29, № 2). — С. 21—29. — ISSN 0869-5490. — doi:10.32756/0869-5490-2020-2-21-29. Архивировано 5 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 46 (англ.). WHO (6 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 7 марта 2020. Архивировано 20 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ COVID-19: Questions and answers (англ.). UpToDate (январь 2022). Дата обращения: 18 февраля 2022. Архивировано 18 февраля 2022 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents temporally related to COVID-19 (англ.). WHO. Дата обращения: 18 мая 2020. Архивировано 15 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Petter Brodin. Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity (англ.) // Nature Medicine. — 2021. — January (vol. 27, iss. 1). — P. 28–33. — ISSN 1546-170X. — doi:10.1038/s41591-020-01202-8. Архивировано 17 января 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Рекомендации ВОЗ для населения в связи c распространением нового коронавируса (2019-nCoV): мифы и ложные представления.
- ↑ Mudatsir Mudatsir, Jonny Karunia Fajar, Laksmi Wulandari, Gatot Soegiarto, Muhammad Ilmawan. Predictors of COVID-19 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // F1000Research. — 2021. — 6 January (vol. 9). — P. 1107. — ISSN 2046-1402. — doi:10.12688/f1000research.26186.2. — PMID 33163160. Архивировано 29 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 WHO recommends two new drugs to treat COVID-19 (англ.). WHO recommends two new drugs to treat COVID-19. World Health Organization (14 января 2022). Дата обращения: 16 января 2022. Архивировано 16 января 2022 года.
- ↑ Prevention, Treatment of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) (англ.). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (29 января 2020). Дата обращения: 29 января 2020. Архивировано 15 декабря 2019 года.
- ↑ Health topics : Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) (англ.). World Health Organization. Дата обращения: 12 декабря 2021. Архивировано 12 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Coronavirus (англ.). Всемирная организация здравоохранения. Дата обращения: 9 декабря 2020. Архивировано 9 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Janine Makaronidis, Jessica Mok, Nyaladzi Balogun, Cormac G. Magee, Rumana Z. Omar. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in people with an acute loss in their sense of smell and/or taste in a community-based population in London, UK: An observational cohort study (англ.) // PLOS Medicine. — 2020. — 1 October (vol. 17, iss. 10). — P. e1003358. — ISSN 1549-1676. — doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003358. Архивировано 4 мая 2022 года.
- ↑ Mark W. Tenforde. Symptom Duration and Risk Factors for Delayed Return to Usual Health Among Outpatients with COVID-19 in a Multistate Health Care Systems Network — United States, March–June 2020 (англ.) // MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. — 2020. — 31 July (vol. 69). — ISSN 1545-861X 0149-2195, 1545-861X. — doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6930e1. Архивировано 4 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Стефани Сазерленд Как COVID-19 поражает органы чувств // В мире науки, 2021, № 4, с. 58 — 61
- ↑ Roy M. Anderson, Hans Heesterbeek, Don Klinkenberg, T. Déirdre Hollingsworth. How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic? (англ.) // Lancet (London, England). — 2020. — 21 March (vol. 395, iss. 10228). — P. 931—934. — ISSN 1474-547X. — doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5. Архивировано 15 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Beating Coronavirus: Flatten the Curve, Raise the Line — COVID-19: What You Need to Know (CME Eligible) (англ.). Coursera (апрель 2020). Дата обращения: 25 апреля 2020. Архивировано 22 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ Pneumonia of unknown cause – China. World Health Organization (5 января 2020). Дата обращения: 18 апреля 2020. Архивировано 18 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Nicholas J. Beeching, Tom E. Fletcher, Robert Fowler. COVID-19. BMJ Best Practices. BMJ Publishing Group (17 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 22 февраля 2020. Архивировано 22 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 39 (англ.). WHO (28 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 29 февраля 2020. Архивировано 29 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Summary (англ.). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (18 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 21 марта 2020. Архивировано 21 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 О.Ю. Реброва, В.В. Власов, С.Е. Бащинский, В.А. Аксёнов. TWIMC: Комментарий ОСДМ о коронавирусной инфекции. OСДМ (22 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 22 марта 2020. Архивировано 22 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Ben Hu, Hua Guo, Peng Zhou, Zheng-Li Shi. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 (англ.) // Nature Reviews Microbiology. — 2020-10-06. — 6 October. — P. 1–14. — ISSN 1740-1534. — doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7. Архивировано 31 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ New Images of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 Now Available. NIAID Now. U. S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (13 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 4 марта 2020. Архивировано 22 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) (англ.). WHO (24 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 4 марта 2020. Архивировано 29 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Xiaolu Tang, Changcheng Wu, Xiang Li, Yuhe Song, Xinmin Yao. On the origin and continuing evolution of SARS-CoV-2 (англ.) // National Science Review. — 2020. — 3 March. — doi:10.1093/nsr/nwaa036. Архивировано 23 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 CDC. Basics of COVID-19 (англ.). COVID-19 and Your Health. U. S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (11 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 25 ноября 2021. Архивировано 25 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Davide Zella, Marta Giovanetti, Francesca Benedetti, Francesco Unali, Silvia Spoto. The variants question: What is the problem? (англ.) // Journal of Medical Virology. — 2021. — Vol. 93, iss. 12. — P. 6479–6485. — ISSN 1096-9071. — doi:10.1002/jmv.27196. Архивировано 27 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ Diana Duong. Alpha, Beta, Delta, Gamma: What’s important to know about SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern? (англ.) // CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association Journal. — 2021. — 12 July (vol. 193, iss. 27). — P. E1059–E1060. — ISSN 0820-3946. — doi:10.1503/cmaj.1095949. Архивировано 21 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ New coronavirus stable for hours on surfaces (англ.). National Institutes of Health (NIH). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (17 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 21 марта 2020. Архивировано 23 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Modes of transmission of virus causing COVID-19: implications for IPC precaution recommendations. World Health Organization (29 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 3 апреля 2020. Архивировано 3 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Yong Zhang, Cao Chen, Yang Song, Shuangli Zhu, Dongyan Wang. Excretion of SARS-CoV-2 through faecal specimens (англ.) // Emerging Microbes & Infections. — 2020. — 1 January (vol. 9, iss. 1). — P. 2501–2508. — doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1844551. — PMID 33161824. Архивировано 3 марта 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): How is it transmitted? (англ.). World Health Organization. Дата обращения: 20 декабря 2020. Архивировано 20 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Pratha Sah, Meagan C. Fitzpatrick, Charlotte F. Zimmer, Elaheh Abdollahi, Lyndon Juden-Kelly. Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. — 2021. — 24 August (vol. 118, iss. 34). — ISSN 1091-6490 0027-8424, 1091-6490. — doi:10.1073/pnas.2109229118. — PMID 34376550. Архивировано 12 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ Peter J. Halfmann, Masato Hatta, Shiho Chiba, Tadashi Maemura, Shufang Fan. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Domestic Cats (англ.) // New England Journal of Medicine. — 2020. — 13 May. — ISSN 0028-4793. — doi:10.1056/NEJMc2013400.
- ↑ 1 2 Disease background of COVID-19 (англ.). European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Дата обращения: 20 марта 2020. Архивировано 16 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Ye Yao, Jinhua Pan, Zhixi Liu, Xia Meng, Weidong Wang. No Association of COVID-19 transmission with temperature or UV radiation in Chinese cities (англ.) // The European Respiratory Journal. — 2020-04-08. — 8 April. — ISSN 1399-3003. — doi:10.1183/13993003.00517-2020.
- ↑ Andrew G. Harrison, Tao Lin, Penghua Wang. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis (англ.) // Trends in Immunology. — 2020. — 1 December (vol. 41, iss. 12). — P. 1100–1115. — ISSN 1471-4981 1471-4906, 1471-4981. — doi:10.1016/j.it.2020.10.004.
- ↑ 1 2 3 James M. Sanders, Marguerite L. Monogue, Tomasz Z. Jodlowski, James B. Cutrell. Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 13 April. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019. Архивировано 21 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ Jian Shang, Yushun Wan, Chuming Luo, Gang Ye, Qibin Geng. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 (англ.) // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. — National Academy of Sciences, 2020. — 6 May. — ISSN 1091-6490 0027-8424, 1091-6490. — doi:10.1073/pnas.2003138117. Архивировано 10 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Anant Parasher. COVID-19: Current understanding of its pathophysiology, clinical presentation and treatment (англ.) // Postgraduate Medical Journal. — 2020-09-25. — 25 September. — ISSN 1469-0756 0032-5473, 1469-0756. — doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138577. Архивировано 31 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Amy H. Attaway, Rachel G. Scheraga, Adarsh Bhimraj, Michelle Biehl, Umur Hatipoğlu. Severe covid-19 pneumonia: pathogenesis and clinical management (англ.) // BMJ. — 2021-03-10. — 10 March (vol. 372). — P. n436. — ISSN 1756-1833. — doi:10.1136/bmj.n436. — PMID 33692022. Архивировано 1 сентября 2021 года.
- ↑ Louise Dalskov, Michelle Møhlenberg, Jacob Thyrsted, Julia Blay-Cadanet, Ebbe Toftgaard Poulsen. SARS-CoV-2 evades immune detection in alveolar macrophages // EMBO reports. — 2020-10-28. — С. e51252. — ISSN 1469-3178. — doi:10.15252/embr.202051252. Архивировано 20 января 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Toshiaki Iba, Jerrold H. Levy, Jean Marie Connors, Theodore E. Warkentin, Jecko Thachil. The unique characteristics of COVID-19 coagulopathy (англ.) // Critical Care. — 2020. — 18 June (vol. 24, iss. 1). — P. 360. — ISSN 1364-8535. — doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03077-0.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Jerzy Windyga. COVID-19 и нарушения гемостаза. empendium.com (12 августа 2020). Дата обращения: 28 декабря 2020. Архивировано 28 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Muge Cevik, Krutika Kuppalli, Jason Kindrachuk, Malik Peiris. Virology, transmission, and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 (англ.) // BMJ. — 2020. — 23 October (vol. 371). — ISSN 1756-1833. — doi:10.1136/bmj.m3862. Архивировано 31 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Mario G. Santamarina, Dominique Boisier, Roberto Contreras, Martiniano Baque, Mariano Volpacchio. COVID-19: a hypothesis regarding the ventilation-perfusion mismatch (англ.) // Critical Care. — 2020-07-06. — 6 July (vol. 24, iss. 1). — P. 395. — ISSN 1364-8535. — doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03125-9.
- ↑ И. Е. Тюрин, А. Д. Струтынская. Визуализация изменений в легких при коронавирусной инфекции (обзор литературы и собственные данные) (англ.) // Пульмонология : журн. — 2020. — 18 November (vol. 30, no. 5). — P. 658—670. — ISSN 2541-9617. — doi:10.18093/0869-0189-2020-30-5-658-670. Архивировано 1 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Tamer F. Ali, Mohamed A. Tawab, Mona A. ElHariri. CT chest of COVID-19 patients: what should a radiologist know? (англ.) // Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. — 2020-07-07. — 7 July (vol. 51, iss. 1). — P. 120. — ISSN 2090-4762. — doi:10.1186/s43055-020-00245-8. Архивировано 12 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Toshiaki Iba, Jean Marie Connors, Jerrold H. Levy. The coagulopathy, endotheliopathy, and vasculitis of COVID-19 (англ.) // Inflammation Research. — 2020-09-12. — 12 September. — P. 1–9. — ISSN 1023-3830. — doi:10.1007/s00011-020-01401-6. Архивировано 1 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Yu Zuo, Shanea K. Estes, Ramadan A. Ali, Alex A. Gandhi, Srilakshmi Yalavarthi. Prothrombotic autoantibodies in serum from patients hospitalized with COVID-19 (англ.) // Science Translational Medicine. — 2020. — 18 November (vol. 12, iss. 570). — ISSN 1946-6242. — doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abd3876. — PMID 33139519. Архивировано 14 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Marya AlSamman, Amy Caggiula, Sangrag Ganguli, Monika Misak, Ali Pourmand. Non-respiratory presentations of COVID-19, a clinical review (англ.) // The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. — 2020. — November (vol. 38, iss. 11). — P. 2444–2454. — ISSN 0735-6757. — doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.09.054. — PMID 33039218. Архивировано 30 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 CDC. Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) (англ.). U. S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (11 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 25 апреля 2020. Архивировано 25 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Jorge Carrillo, Nuria Izquierdo-Useros, Carlos Ávila-Nieto, Edwards Pradenas, Bonaventura Clotet. Humoral immune responses and neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2; implications in pathogenesis and protective immunity (англ.) // Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. — 2020. — 17 November. — ISSN 1090-2104. — doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.108. — PMID 33187644. Архивировано 22 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Jennifer M. Dan, Jose Mateus, Yu Kato, Kathryn M. Hastie, Esther Dawen Yu. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection (англ.) // Science. — 2021. — 6 January. — ISSN 1095-9203 0036-8075, 1095-9203. — doi:10.1126/science.abf4063. Архивировано 10 января 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 CDC. Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) (англ.). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). U. S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (11 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 31 марта 2020. Архивировано 2 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Sheila F. Lumley, Denise O’Donnell, Nicole E. Stoesser, Philippa C. Matthews, Alison Howarth. Antibody Status and Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Care Workers (англ.) // New England Journal of Medicine. — 2020. — 23 December. — ISSN 0028-4793. — doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034545.
- ↑ Lancelot Mark Pinto, Viral Nanda, Ayesha Sunavala, Camilla Rodriques. Reinfection in COVID-19: A scoping review (англ.) // Medical Journal, Armed Forces India. — 2021. — July (vol. 77). — P. S257–S263. — ISSN 0377-1237. — doi:10.1016/j.mjafi.2021.02.010. — PMID 34334891.
- ↑ Sahar Sotoodeh Ghorbani, Niloufar Taherpour, Sahar Bayat, Hadis Ghajari, Parisa Mohseni. Epidemiologic characteristics of cases with reinfection, recurrence, and hospital readmission due to COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Journal of Medical Virology. — 2022. — January (vol. 94, iss. 1). — P. 44–53. — ISSN 1096-9071. — doi:10.1002/jmv.27281. — PMID 34411311. Архивировано 30 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Margarida Sa Ribero, Nolwenn Jouvenet, Marlène Dreux, Sébastien Nisole. Interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and the type I interferon response (англ.) // PLoS Pathogens. — 2020. — 29 July (vol. 16, iss. 7). — ISSN 1553-7366. — doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008737. — PMID 32726355. Архивировано 2 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ Marc Lipsitch, Yonatan H. Grad, Alessandro Sette, Shane Crotty. Cross-reactive memory T cells and herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2 (англ.) // Nature Reviews Immunology. — 2020. — November (vol. 20, iss. 11). — P. 709–713. — ISSN 1474-1741. — doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00460-4. Архивировано 7 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Kevin W. Ng, Nikhil Faulkner, Georgina H. Cornish, Annachiara Rosa, Ruth Harvey. Preexisting and de novo humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in humans (англ.) // Science. — 2020. — 11 December (vol. 370, iss. 6522). — P. 1339–1343. — ISSN 1095-9203 0036-8075, 1095-9203. — doi:10.1126/science.abe1107. Архивировано 7 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Evasion of Type I Interferon by SARS-CoV-2 (англ.) // Cell Reports. — 2020-10-06. — Vol. 33, iss. 1. — P. 108234. — ISSN 2211-1247. — doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108234. Архивировано 18 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Nature. COVID research updates: Older people are at higher risk of getting COVID twice (англ.). Nature Portfolio (19 марта 2021). Дата обращения: 23 марта 2021. Архивировано 3 января 2022 года.
- ↑ Symptoms // 2019 Novel Coronavirus, Wuhan, China. — Centers For Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- ↑ Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Summary. — Centers For Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 2020. — 16 February. — Дата обращения: 18.02.2020. (Общая информация о COVID-19 по данным Центров по контролю и профилактике заболеваний США.)
- ↑ 1 2 Malahat Khalili, Mohammad Karamouzian, Naser Nasiri, Sara Javadi, Ali Mirzazadeh. Epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Epidemiology & Infection. — 2020/ed. — Vol. 148. — ISSN 1469-4409 0950-2688, 1469-4409. — doi:10.1017/S0950268820001430.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Sasmita Poudel Adhikari, Sha Meng, Yu-Ju Wu, Yu-Ping Mao, Rui-Xue Ye. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review (англ.) // Infectious Diseases of Poverty. — 2020. — 17 March (vol. 9, iss. 1). — P. 29. — ISSN 2049-9957. — doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00646-x.
- ↑ CDC. Healthcare Workers (англ.). U. S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (11 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 19 января 2021. Архивировано 19 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Claudio Ronco, Paolo Navalesi, Jean Louis Vincent. Coronavirus epidemic: preparing for extracorporeal organ support in intensive care (англ.) // The Lancet. — Elsevier, 2020. — 6 February. — ISSN 2213-2619 2213-2600, 2213-2619. — doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30060-6. Архивировано 18 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Carlos del Rio, Preeti N. Malani. 2019 Novel Coronavirus—Important Information for Clinicians (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020-02-05. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1490. Архивировано 9 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ Sana Salehi, Aidin Abedi, Sudheer Balakrishnan, Ali Gholamrezanezhad. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findings in 919 Patients (англ.) // American Journal of Roentgenology. — 2020. — 14 March. — P. 1—7. — ISSN 0361-803X. — doi:10.2214/AJR.20.23034. Архивировано 9 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): increased transmission beyond China – fourth update. ECDC (14 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 15 февраля 2020. Архивировано из оригинала 15 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ Heshui Shi, Xiaoyu Han, Nanchuan Jiang, Yukun Cao, Osamah Alwalid. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study (англ.) // The Lancet Infectious Diseases. — Elsevier, 2020. — 24 February. — ISSN 1474-4457 1473-3099, 1474-4457. — doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30086-4.
- ↑ Alfonso J. Rodriguez-Morales, Jaime A. Cardona-Ospina, Estefanía Gutiérrez-Ocampo, Rhuvi Villamizar-Peña, Yeimer Holguin-Rivera. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease. — 2020. — 13 March. — P. 101623. — ISSN 1873-0442. — doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623. Архивировано 28 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Yuanyuan Dong, Xi Mo, Yabin Hu, Xin Qi, Fang Jiang. Epidemiological Characteristics of 2143 Pediatric Patients With 2019 Coronavirus Disease in China (англ.) // Pediatrics (англ.) (рус.. — American Academy of Pediatrics (англ.) (рус., 2020. — 16 March. — ISSN 1098-4275. — doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0702. — PMID 32179660. Архивировано 17 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Wei Xia, Jianbo Shao, Yu Guo, Xuehua Peng, Zhen Li. Clinical and CT features in pediatric patients with COVID-19 infection: Different points from adults (англ.) // Pediatric Pulmonology. — 2020. — 5 March. — ISSN 1099-0496. — doi:10.1002/ppul.24718. Архивировано 20 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Marveh Rahmati, Mohammad Amin Moosavi. Cytokine-targeted therapy in severely ill COVID-19 patients: Options and cautions (англ.) // Eurasian Journal Of Medicine And Oncology. — 2020. — Vol. 4, iss. 2. — P. 179—181. — doi:10.14744/ejmo.2020.72142/. Архивировано 20 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ John B. Moore, Carl H. June. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19 (англ.) // Science. — 2020. — 1 May (vol. 368, iss. 6490). — P. 473—474. — ISSN 1095-9203 0036-8075, 1095-9203. — doi:10.1126/science.abb8925. — PMID 32303591. Архивировано 12 августа 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Nicholas J. Beeching, Tom E. Fletcher, Robert Fowler. Complications : [арх. 18.04.2020] // Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). — BMJ Best Practice. — Дата обращения: 18.04.2020.
- ↑ John, Teny M.; Jacob, Ceena N.; Kontoyiannis, Dimitrios P. (15 April 2021). “When Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus and Severe COVID-19 Converge: The Perfect Storm for Mucormycosis”. Journal of Fungi. 7 (4). DOI:10.3390/jof7040298. ISSN 2309-608X. Архивировано из оригинала 2021-05-15. Дата обращения 9 May 2021.
- ↑ 1 2 Isabel Siow, Keng Siang Lee, John J. Y. Zhang, Seyed Ehsan Saffari, Adeline Ng. Encephalitis as a neurological complication of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of incidence, outcomes, and predictors (англ.) // European Journal of Neurology. — 2021. — 13 May. — ISSN 1468-1331. — doi:10.1111/ene.14913. — PMID 33982853. Архивировано 22 августа 2021 года.
- ↑ Pratik Sinha, Michael A. Matthay, Carolyn S. Calfee. Is a “Cytokine Storm” Relevant to COVID-19? (англ.) // JAMA Internal Medicine. — 2020. — 1 September (vol. 180, iss. 9). — P. 1152. — ISSN 2168-6106. — doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3313. — PMID 32602883. Архивировано 20 октября 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Timothy A. C. Snow, Mervyn Singer, Nishkantha Arulkumaran. Immunomodulators in COVID-19: Two Sides to Every Coin (англ.) // American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. — 2020. — 14 September (vol. 202, iss. 10). — P. 1460–1462. — ISSN 1073-449X. — doi:10.1164/rccm.202008-3148LE. Архивировано 17 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Daniel E. Leisman, Lukas Ronner, Rachel Pinotti, Matthew D. Taylor, Pratik Sinha. Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes (англ.) // The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. — 2020. — 16 October. — ISSN 2213-2619 2213-2600, 2213-2619. — doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30404-5.
- ↑ Randy Q. Cron, Grant S. Schulert, Rachel S. Tattersall. Defining the scourge of COVID-19 hyperinflammatory syndrome (англ.) // The Lancet Rheumatology. — 2020. — 29 сентября. — ISSN 2665-9913. — doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30335-0.
- ↑ Naor Bar-Zeev, Tom Inglesby. COVID-19 vaccines: early success and remaining challenges (англ.) // The Lancet. — 2020. — 4 September. — ISSN 1474-547X 0140-6736, 1474-547X. — doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31867-5.
- ↑ 1 2 Рекомендации ВОЗ для населения. ВОЗ. Дата обращения: 14 февраля 2020. Архивировано 18 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Tanu Singhal. A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) (англ.) // The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. — 2020. — 1 April (vol. 87, iss. 4). — P. 281—286. — ISSN 0973-7693. — doi:10.1007/s12098-020-03263-6.
- ↑ Алкоголь и COVID-19: что нужно знать. Всемирная организация здравоохранения. Дата обращения: 18 апреля 2020. Архивировано 4 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ Часто задаваемые вопросы об употреблении табака и COVID-19. Центр СМИ : Вопросы и ответы. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (27 мая 2020). Дата обращения: 20 ноября 2021. Архивировано 20 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ В каких случаях и как следует носить маску. Всемирная организация здравоохранения. Дата обращения: 20 марта 2020. Архивировано 29 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Advice on the use of masks in the community, during home care and in healthcare settings in the context of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak (англ.). World Health Organization (6 апреля 2020). Дата обращения: 7 апреля 2020. Архивировано 28 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Рекомендации ВОЗ для населения. ВОЗ (7 октября 2020). Дата обращения: 30 января 2021. Архивировано 30 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Home care for patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 and management of their contacts (англ.). www.who.int. Дата обращения: 9 января 2021. Архивировано 11 января 2021 года.
- ↑ ВРЕМЕННЫЕ МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЕ РЕКОМЕНДАЦИИ — ПРОФИЛАКТИКА, ДИАГНОСТИКА И ЛЕЧЕНИЕ НОВОЙ КОРОНАВИРУСНОЙ ИНФЕКЦИИ (COVID-19). Дата обращения: 9 января 2021. Архивировано 12 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Yanni Li, Mingming Liang, Liang Gao, Mubashir Ayaz Ahmed, John Patrick Uy. Face masks to prevent transmission of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // American Journal of Infection Control. — 2020-12-19. — 19 December. — ISSN 1527-3296. — doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2020.12.007. — PMID 33347937. Архивировано 3 марта 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Применение масок в контексте COVID-19. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (5 июня 2020). — Временные рекомендации. Дата обращения: 30 июля 2020. Архивировано 14 июля 2020 года.
- ↑ Вопросы и ответы : В каких случаях следует носить маску?. Официальная информация о коронавирусе в России. Стопкоронавирус.рф. Дата обращения: 10 февраля 2021. Архивировано 11 января 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Rational use of personal protective equipment for COVID-19 and considerations during severe shortages (англ.). World Health Organization (23 декабря 2020). Дата обращения: 25 марта 2021. Архивировано 25 марта 2021 года.
- ↑ COVID-19 and Your Health (англ.). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. U.S. CDC (11 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 30 января 2021. Архивировано 30 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Jasmine Anedda, Caterina Ferreli, Franco Rongioletti, Laura Atzori. Changing gears: Medical gloves in the era of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (англ.) // Clinics in Dermatology. — 2020. — December (vol. 38, iss. 6). — P. 734–736. — ISSN 0738-081X. — doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.08.003. — PMID 33341206. Архивировано 9 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Роспотребнадзор: для выписки пациента с COVID-19 к труду достаточно одного отрицательного теста методом ПЦР. ГАРАНТ.РУ (16 ноября 2020). Дата обращения: 5 февраля 2021. Архивировано 5 февраля 2021 года.
- ↑ Srinivas Murthy, Charles D. Gomersall, Robert A. Fowler. Care for Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 11 March. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.3633. Архивировано 18 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Nicholas J. Beeching, Tom E. Fletcher, Robert Fowler. Approach : [арх. 18.04.2020] // Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). — BMJ Best Practice. — Дата обращения: 18.04.2020.
- ↑ Subject in Focus: Cleaning and Disinfection of Environmental Surfaces (англ.). World Health Organization (14 мая 2020). Дата обращения: 16 мая 2020. Архивировано 16 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ Chu, Derek K. Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 : a systematic review and meta-analysis : [англ.] / Derek K. Chu, Elie A. Akl // The Lancet. — 2020. — Vol. S0140-6736, no. 20 (1 June). — P. 31142–31149. — ISSN 1474-547X 0140-6736, 1474-547X. — doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31142-9. — PMID 32497510.
- ↑ Face Shields, Masks with Valves Ineffective Against COVID-19 Spread (англ.). AIP Publishing LLC (1 сентября 2020). Дата обращения: 2 ноября 2020. Архивировано 1 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Pengfei Sun, Xiaosheng Lu, Chao Xu, Wenjuan Sun, Bo Pan. Understanding of COVID-19 based on current evidence (англ.) // Journal of Medical Virology. — 2020. — 25 February. — ISSN 1096-9071. — doi:10.1002/jmv.25722. Архивировано 29 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ Nicholas J. Beeching, Tom E. Fletcher, Robert Fowler. Prevention : [арх. 18.04.2020] // Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). — BMJ Best Practice. — Дата обращения: 18.04.2020.
- ↑ Barbara Nussbaumer-Streit, Verena Mayr, Andreea Iulia Dobrescu, Andrea Chapman, Emma Persad. Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: a rapid review (англ.) // Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. — 2020. — 8 April (vol. 4). — P. CD013574. — ISSN 1469-493X. — doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013574. — PMID 32267544. Архивировано 2 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ G. L. Nichols, E. L. Gillingham, H. L. Macintyre, S. Vardoulakis, S. Hajat. Coronavirus seasonality, respiratory infections and weather (англ.) // BMC infectious diseases. — 2021. — 26 October (vol. 21, iss. 1). — P. 1101. — ISSN 1471-2334. — doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06785-2. — PMID 34702177. Архивировано 2 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ COVID-19 vaccines: key facts (англ.). Human regulatory. European Medicines Agency. Дата обращения: 18 декабря 2020. Архивировано 18 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Jerome Amir Singh, Ross E. G. Upshur. The granting of emergency use designation to COVID-19 candidate vaccines: implications for COVID-19 vaccine trials (англ.) // The Lancet Infectious Diseases. — 2020-12-08. — 8 December. — ISSN 1474-4457 1473-3099, 1474-4457. — doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30923-3.
- ↑ Kai Xing, Xiao-Yan Tu, Miao Liu, Zhang-Wu Liang, Jiang-Nan Chen. Efficacy and safety of COVID-19 vaccines: a systematic review // Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi = Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics. — 2021-03. — Т. 23, вып. 3. — С. 221–228. — ISSN 1008-8830. Архивировано 3 июня 2021 года.
- ↑ Draft landscape of COVID-19 candidate vaccines (англ.). Всемирная организация здравоохранения (17 декабря 2020). Дата обращения: 18 декабря 2020. Архивировано 18 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Чем различаются три российские вакцины от COVID-19. стопкоронавирус.рф (27 февраля 2021). Дата обращения: 5 мая 2022. Архивировано 25 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Facts about COVID-19 Vaccines (англ.). U. S. CDC (27 января 2021). Дата обращения: 28 января 2021.
- ↑ Ответы на вопросы по поводу вакцинации и путешествий этим летом. www.euro.who.int. ВОЗ (30 июня 2021). Дата обращения: 31 июля 2021. Архивировано 13 июля 2021 года.
- ↑ Vaccine efficacy, effectiveness and protection (англ.). www.who.int. World Health Organization (14 июля 2021). Дата обращения: 15 сентября 2021. Архивировано 15 сентября 2021 года.
- ↑ Root‐Bernstein Robert. Age and Location in Severity of COVID‐19 Pathology: Do Lactoferrin and Pneumococcal Vaccination Explain Low Infant Mortality and Regional Differences? (англ.) // BioEssays. — 2020. — 31 August (vol. 42, no. 11). — P. 2000076. — ISSN 0265-9247. — doi:10.1002/bies.202000076. [исправить]
- ↑ Noale M. et al. (EPICOVID19 Working Group). The Association between Influenza and Pneumococcal Vaccinations and SARS-Cov-2 Infection: Data from the EPICOVID19 Web-Based Survey (англ.) // Vaccines. — 2020. — Vol. 8, no. 3. — P. 471. — ISSN 2076-393X. — doi:10.3390/vaccines8030471. [исправить]
- ↑ Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination and COVID-19 (англ.). World Health Organization (12 апреля 2020). Дата обращения: 4 мая 2020. Архивировано 4 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ MMR Vaccination: A Potential Strategy to Reduce Severity and Mortality of COVID-19 Illness — The American Journal of Medicine. Дата обращения: 21 ноября 2020. Архивировано 2 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Analysis of Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR) Titers of Recovered COVID-19 Patients | mBio. Дата обращения: 21 ноября 2020. Архивировано 24 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ MMR vaccine could protect against COVID-19. Дата обращения: 21 ноября 2020. Архивировано 21 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Vaccines (англ.). Newsroom. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (28 октября 2020). Дата обращения: 18 декабря 2020. Архивировано 18 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases (англ.). World Heath Organization (17 января 2020). Дата обращения: 9 февраля 2020. Архивировано 17 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Роспотребнадзор разработал средства для лабораторной диагностики нового коронавируса. Роспотребнадзор (21 января 2020). Дата обращения: 19 февраля 2020. Архивировано 10 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ CDC CDC Tests for 2019-nCoV (англ.). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 12 февраля 2020. Архивировано 14 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Safiya Richardson, Jamie S. Hirsch, Mangala Narasimhan, James M. Crawford, Thomas McGinn. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020-04-22. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775. Архивировано 27 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Jennifer Abbasi. The Promise and Peril of Antibody Testing for COVID-19 (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 17 April. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6170. Архивировано 20 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ What we know about theCOVID-19 immune response (англ.). World Health Organization (2 августа 2020). Дата обращения: 9 января 2021. Архивировано 19 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Авторский коллектив. Профилактика, диагностика и лечение новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19). Минздрав РФ (26 октября 2020). Дата обращения: 17 января 2021. Архивировано 7 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Супотницкий М. В. Новый коронавирус SARS-CoV-2 в аспекте глобальной эпидемиологии коронавирусных инфекций : [рус.] // Вестник войск РХБ защиты : журн.. — 2020. — Т. 4, № 1 (10 марта). — С. 32—65. — ISSN 2587-5728. — doi:10.35825/2587-5728-2020-4-1-32-65.
- ↑ John E. L. Wong, Yee Sin Leo, Chorh Chuan Tan. COVID-19 in Singapore—Current Experience: Critical Global Issues That Require Attention and Action (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 20 February. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2467. Архивировано 21 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ Fernando Mejía, Carlos Medina, Enrique Cornejo, Enrique Morello, Sergio Vásquez. Oxygen saturation as a predictor of mortality in hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 in a public hospital in Lima, Peru (англ.) // PLOS ONE. — 2020. — 28 December (vol. 15, iss. 12). — P. e0244171. — ISSN 1932-6203. — doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0244171. Архивировано 4 мая 2022 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 Coronavirus: novel coronavirus (COVID-19) infection (англ.). Elsevier (12 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 21 марта 2020. Архивировано 21 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ D. S. Baranovskii, I. D. Klabukov, O. A. Krasilnikova, D. A. Nikogosov, N. V. Polekhina. Prolonged prothrombin time as an early prognostic indicator of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with COVID-19 related pneumonia // Current Medical Research and Opinion. — 2020-11-19. — С. 1. — ISSN 1473-4877. — doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1853510. Архивировано 18 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Bianca Christensen, Emmanuel J. Favaloro, Giuseppe Lippi, Elizabeth M. Van Cott. Hematology Laboratory Abnormalities in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) // Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. — 2020-10. — Т. 46, вып. 7. — С. 845–849. — ISSN 1098-9064. — doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715458. Архивировано 4 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Chaolin Huang, Yeming Wang, Xingwang Li, Lili Ren, Jianping Zhao. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China (англ.) // The Lancet. — Elsevier, 2020-01-24. — 24 January. — ISSN 1474-547X. — doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. — PMID 31986264. Архивировано 12 июля 2020 года.
- ↑ Natale Vazzana, Francesco Dipaola, Silvia Ognibene. Procalcitonin and secondary bacterial infections in COVID-19: association with disease severity and outcomes (англ.) // Acta Clinica Belgica. — 2020. — 23 September. — P. 1–5. — ISSN 1784-3286. — doi:10.1080/17843286.2020.1824749.
- ↑ Pedro Garrido, Pitter Cueto, Conxita Rovira, Elisabet Garcia, Ana Parra. Clinical value of procalcitonin in critically ill patients infected by SARS-CoV-2 (англ.) // The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. — 2020. — 7 November. — ISSN 1532-8171 0735-6757, 1532-8171. — doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.11.011.
- ↑ Jin-jin Zhang, Xiang Dong, Yi-Yuan Cao, Ya-dong Yuan, Yi-bin Yang. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected by SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China (англ.) // Allergy. — 2020. — 19 February. — ISSN 1398-9995. — doi:10.1111/all.14238. Архивировано 22 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ Dawei Wang, Bo Hu, Chang Hu, Fangfang Zhu, Xing Liu. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 7 February. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585. Архивировано 1 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Zhangkai J. Cheng, Jing Shan. 2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know (англ.) // Infection. — 2020-02-18. — 18 February. — ISSN 1439-0973. — doi:10.1007/s15010-020-01401-y. Архивировано 17 декабря 2021 года.
- ↑ David Kim, James Quinn, Benjamin Pinsky, Nigam H. Shah, Ian Brown. Rates of Co-infection Between SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Pathogens (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 15 April. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6266. Архивировано 28 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Sequence for putting on personal protective equipment (PPE). CDC. Дата обращения: 18 марта 2020. Архивировано 5 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ При Сеченовском университете открылся стационар для приема пациентов с COVID-19. Сайт Москвы. Официальный сайт Мэра Москвы (6 апреля 2020). Дата обращения: 19 июня 2020. Архивировано 26 июня 2020 года.
- ↑ Главное о китайском коронавирусе. Есть ли опасность массового заражения жителей России Архивная копия от 25 января 2020 на Wayback Machine. Телеканал 360°, 22 января 2020.
- ↑ 1 2 Reed AC Siemieniuk, Jessica J. Bartoszko, Dena Zeraatkar, Elena Kum, Anila Qasim. Drug treatments for covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis (англ.) // BMJ. — 2020-07-30. — Vol. 370. — P. m2980. — ISSN 1756-1833. — doi:10.1136/bmj.m2980.
- ↑ Arnav Agarwal, Bram Rochwerg, François Lamontagne, Reed AC Siemieniuk, Thomas Agoritsas. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19 (англ.) // BMJ. — 2020-09-04. — Vol. 370. — P. m3379. — ISSN 1756-1833. — doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379.
- ↑ 1 2 Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 41. World Health Organization (1 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 8 марта 2020. Архивировано 14 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Claudio Ronco, Paolo Navalesi, Jean Louis Vincent. Coronavirus epidemic: preparing for extracorporeal organ support in intensive care (англ.) // The Lanset Respiratory Medicine. — 2020. — 6 February. — doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30060-6. Архивировано 2 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Ryan P. Barbaro, Graeme MacLaren, Philip S. Boonstra, Theodore J. Iwashyna, Arthur S. Slutsky. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support in COVID-19: an international cohort study of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization registry (англ.) // The Lancet. — 2020. — 25 September. — ISSN 1474-547X 0140-6736, 1474-547X. — doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32008-0.
- ↑ Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected (англ.). World Health Organization. Дата обращения: 17 февраля 2020. Архивировано 31 января 2020 года.
- ↑ Michael Brown, Harald Herkner, Toby Lasserson, Liz Bickerdike, Robin Featherstone, Monaz Mehta. Coronavirus (COVID-19): evidence relevant to critical care. Cochrane Special Collections. Кокрейновская библиотека (11 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 17 февраля 2020. Архивировано 10 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Graeme MacLaren, Dale Fisher, Daniel Brodie. Preparing for the Most Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: The Potential Role of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 19 February. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2342. Архивировано 23 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Clark D Russell, Jonathan E Millar, J Kenneth Baillie. Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury : [англ.] // The Lancet. — Elsevier, 2020. — 6 February.
- ↑ Lianhan Shang, Jianping Zhao, Yi Hu, Ronghui Du, Bin Cao. On the use of corticosteroids for 2019-nCoV pneumonia (англ.) // The Lancet. — Elsevier, 2020. — 11 February (vol. 0, iss. 0). — ISSN 1474-547X 0140-6736, 1474-547X. — doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30361-5.
- ↑ Вопросы и ответы: дексаметазон и COVID-19. Центр СМИ. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (25 июня 2020). Дата обращения: 12 сентября 2020. Архивировано 12 сентября 2020 года.
- ↑ Reed AC Siemieniuk, Jessica J. Bartoszko, Long Ge, Dena Zeraatkar, Ariel Izcovich. Drug treatments for covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis (англ.) // BMJ. — 2020. — 30 July (vol. 370). — ISSN 1756-1833. — doi:10.1136/bmj.m2980. Архивировано 11 сентября 2020 года.
- ↑ Michael A. Matthay, B. Taylor Thompson. Dexamethasone in hospitalised patients with COVID-19: addressing uncertainties (англ.) // The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. — 2020. — 29 October. — ISSN 2213-2619 2213-2600, 2213-2619. — doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30503-8.
- ↑ Anthony S. Fauci, H. Clifford Lane, Robert R. Redfield. Covid-19 — Navigating the Uncharted (англ.) // New England Journal of Medicine. — 2020-02-28. — 28 February. — ISSN 0028-4793. — doi:10.1056/NEJMe2002387. Архивировано 5 января 2022 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Yonghong Xiao, Mili Estee Torok. Taking the right measures to control COVID-19 (англ.) // The Lancet Infectious Diseases. — Elsevier, 2020. — 5 March. — ISSN 1474-4457 1473-3099, 1474-4457. — doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30152-3.
- ↑ Elizabeth B. Pathak. Convalescent plasma is ineffective for covid-19 (англ.) // BMJ. — 2020. — 22 October (vol. 371). — ISSN 1756-1833. — doi:10.1136/bmj.m4072. Архивировано 24 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Andre C. Kalil. Treating COVID-19—Off-Label Drug Use, Compassionate Use, and Randomized Clinical Trials During Pandemics (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 24 March. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4742. Архивировано 4 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Off-label use of medicines for COVID-19 (англ.). World Health Organization (31 марта 2020). — Scientific brief. Дата обращения: 2 апреля 2020. Архивировано 2 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ Sophie Juul, Emil Eik Nielsen, Joshua Feinberg, Faiza Siddiqui, Caroline Kamp Jørgensen. Interventions for treatment of COVID-19: Second edition of a living systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses (The LIVING Project) (англ.) // PLOS ONE. — 2021-11-03. — Vol. 16, iss. 3. — P. e0248132. — ISSN 1932-6203. — doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0248132. Архивировано 4 мая 2022 года.
- ↑ Ahmed Wadaa-Allah, Marwa S. Emhamed, Mohammed A. Sadeq, Nesrine Ben Hadj Dahman, Irfan Ullah. Efficacy of the current investigational drugs for the treatment of COVID-19: a scoping review // Annals of Medicine. — Т. 53, вып. 1. — С. 318–334. — ISSN 0785-3890. — doi:10.1080/07853890.2021.1875500. Архивировано 4 мая 2022 года.
- ↑ Tejas K. Patel, Parvati B. Patel, Manish Barvaliya, Manoj Kumar Saurabh, Hira Lal Bhalla. Efficacy and safety of lopinavir-ritonavir in COVID-19: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials // Journal of Infection and Public Health. — 2021-6. — Т. 14, вып. 6. — С. 740–748. — ISSN 1876-0341. — doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2021.03.015. Архивировано 17 октября 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 The Lancet Infectious Diseases. Curing COVID-19 (англ.) // The Lancet Infectious Diseases. — 2020. — 10 September. — ISSN 1474-4457 1473-3099, 1474-4457. — doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30706-4.
- ↑ Thibault Fiolet, Anthony Guihur, Mathieu Rebeaud, Matthieu Mulot, Nathan Peiffer-Smadja. Effect of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin on the mortality of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Clinical Microbiology and Infection. — 2020. — 26 August. — ISSN 1198-743X. — doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.022. Архивировано 21 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Chris A. Gentry, Mary Beth Humphrey, Sharanjeet K. Thind, Sage C. Hendrickson, George Kurdgelashvili. Long-term hydroxychloroquine use in patients with rheumatic conditions and development of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective cohort study (англ.) // The Lancet Rheumatology. — 2020-09-21. — 21 September. — ISSN 2665-9913. — doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30305-2.
- ↑ David R. Boulware, Matthew F. Pullen, Ananta S. Bangdiwala, Katelyn A. Pastick, Sarah M. Lofgren. A Randomized Trial of Hydroxychloroquine as Postexposure Prophylaxis for Covid-19 (англ.) // New England Journal of Medicine. — 2020. — 6 August (vol. 383, iss. 6). — P. 517–525. — ISSN 0028-4793. — doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2016638.
- ↑ Ahmed M. Kamel, Mona S. A. Monem, Nour A. Sharaf, Nada Magdy, Samar F. Farid. Efficacy and safety of azithromycin in Covid-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (англ.) // Reviews in Medical Virology. — Vol. n/a, iss. n/a. — P. e2258. — ISSN 1099-1654. — doi:10.1002/rmv.2258. Архивировано 4 июня 2021 года.
- ↑ Vanessa Piechotta, Claire Iannizzi, Khai Li Chai, Sarah J. Valk, Catherine Kimber. Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review (англ.) // The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. — 2021. — 20 May (vol. 5). — P. CD013600. — ISSN 1469-493X. — doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4. — PMID 34013969. Архивировано 7 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ What are the effects of convalescent plasma for people with moderate to severe COVID‐19?. Сochrane Library.
- ↑ Convalescent Plasma and Immune Globulins (англ.). COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. CDC (21 апреля 2021). Дата обращения: 9 августа 2021. Архивировано 27 июня 2021 года.
- ↑ В МКБ-10 включен постковидный синдром Архивная копия от 4 ноября 2021 на Wayback Machine // 14.12.2020 г. МУИР.
- ↑ Emergency use ICD codes for COVID-19 disease outbreak (англ.). www.who.int. Дата обращения: 20 декабря 2020. Архивировано 20 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Архивированная копия. Дата обращения: 20 декабря 2020. Архивировано 3 марта 2021 года.
- ↑ Priya Venkatesan. NICE guideline on long COVID (англ.) // The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. — 2021-01-13. — 13 January. — ISSN 2213-2619 2213-2600, 2213-2619. — doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00031-X.
- ↑ Long-term effects of coronavirus (long COVID) (англ.). Health A to Z. U. K. National Health Service (7 января 2021). Дата обращения: 13 января 2021. Архивировано 12 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Sandra Lopez-Leon, Talia Wegman-Ostrosky, Carol Perelman, Rosalinda Sepulveda, Paulina A. Rebolledo. More than 50 long-term effects of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Scientific Reports. — 2021. — 9 August (vol. 11, iss. 1). — P. 16144. — ISSN 2045-2322. — doi:10.1038/s41598-021-95565-8. — PMID 33532785. Архивировано 17 ноября 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Рекомендации для поддержки самостоятельной реабилитации после болезни, вызванной COVID-19. Европейское региональное бюро ВОЗ. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (2020). Дата обращения: 5 февраля 2021. Архивировано 26 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Morteza Abdullatif Khafaie, Fakher Rahim. Cross-Country Comparison of Case Fatality Rates of COVID-19/SARS-COV-2 (англ.) // Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives. — 2020. — April (vol. 11, iss. 2). — P. 74—80. — ISSN 2210-9099. — doi:10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.2.03. — PMID 32257772. Архивировано 14 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Xinyang Li, Xianrui Zhong, Yongbo Wang, Xiantao Zeng, Ting Luo. Clinical determinants of the severity of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // PLOS ONE. — 2021. — 5 March (vol. 16, iss. 5). — P. e0250602. — ISSN 1932-6203. — doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0250602. — PMID 33939733. Архивировано 3 мая 2022 года.
- ↑ The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team. Vital Surveillances: The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) (англ.) // China CDC Weekly. — China, 2020. — February (vol. 2, iss. 8). — P. 113—122. Архивировано 19 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ Graziano Onder, Giovanni Rezza, Silvio Brusaferro. Case-Fatality Rate and Characteristics of Patients Dying in Relation to COVID-19 in Italy (англ.) // JAMA. — 2020. — 23 March. — doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4683. Архивировано 11 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Adam Booth, Angus Bruno Reed, Sonia Ponzo, Arrash Yassaee, Mert Aral. Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis // PloS One. — 2021. — Т. 16, вып. 3. — С. e0247461. — ISSN 1932-6203. — doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247461. Архивировано 5 марта 2021 года.
- ↑ Paddy Ssentongo, Emily S. Heilbrunn, Anna E. Ssentongo, Shailesh Advani, Vernon M. Chinchilli. Epidemiology and outcomes of COVID-19 in HIV-infected individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // Scientific Reports. — 2021-03-18. — Vol. 11, iss. 1. — ISSN 2045-2322. — doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85359-3. Архивировано 29 марта 2021 года.
- ↑ Andrew W. Lindsley, Justin T. Schwartz, Marc E. Rothenberg. Eosinophil responses during COVID-19 infections and coronavirus vaccination (англ.) // The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. — 2020. — July (vol. 146, iss. 1). — P. 1–7. — ISSN 1097-6825. — doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.021. — PMID 32344056. Архивировано 15 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Yuanyuan Wang, Jingjing Chen, Wei Chen, Ling Liu, Mei Dong. Does Asthma Increase the Mortality of Patients with COVID-19?: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (англ.) // International Archives of Allergy and Immunology. — 2020. — 22 September. — P. 1–7. — ISSN 1423-0097 1018-2438, 1423-0097. — doi:10.1159/000510953. — PMID 32358994. Архивировано 22 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ CDC. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) (англ.). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. U. S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (11 февраля 2020). Дата обращения: 7 декабря 2020. Архивировано 6 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Новое исследование помогает лучше понять последствия COVID-19 для беременных женщин и их младенцев. Пресс-релизы. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (1 сентября 2020). Дата обращения: 21 декабря 2020. Архивировано 3 ноября 2020 года.
- ↑ Ren Mao, Yun Qiu, Jin-Shen He, Jin-Yu Tan, Xue-Hua Li. Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis (англ.) // The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. — Elsevier, 2020. — 12 May. — ISSN 2468-1156 2468-1253, 2468-1156. — doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30126-6.
- ↑ Mandeep R. Mehra, Sapan S. Desai, SreyRam Kuy, Timothy D. Henry, Amit N. Patel. Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19 (англ.) // New England Journal of Medicine. — 2020. — 1 May. — ISSN 0028-4793. — doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007621. Архивировано 7 января 2022 года.
- ↑ Заявление ВОЗ: Табакокурение и COVID-19 . Центр СМИ. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (11 мая 2020). — Информационный бюллетень. Дата обращения: 17 августа 2020. Архивировано 17 августа 2020 года.
- ↑ Smoking and COVID-19 (англ.). Scientific Brief. World Health Organization (30 июня 2020). Дата обращения: 25 августа 2020. Архивировано 23 августа 2020 года.
- ↑ Askin Gülsen, Burcu Arpinar Yigitbas, Berat Uslu, Daniel Drömann, Oguz Kilinc. The Effect of Smoking on COVID-19 Symptom Severity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (англ.) // Pulmonary Medicine. — 2020. — 8 September (vol. 2020). — ISSN 2090-1836. — doi:10.1155/2020/7590207. — PMID 32963831. Архивировано 2 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ Scientists discover genetic and immunologic underpinnings of some cases of severe COVID-19 (англ.). National Institutes of Health (NIH). U. S. National Institutes of Health (24 сентября 2020). Дата обращения: 16 октября 2020. Архивировано 16 октября 2020 года.
- ↑ “Solidarity” clinical trial for COVID-19 treatments (англ.). World Health Organization. Дата обращения: 26 апреля 2020. Архивировано 26 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Solidarity Therapeutics Trial produces conclusive evidence on the effectiveness of repurposed drugs for COVID-19 in record time (англ.). Всемирная организация здравоохранения (15 октября 2020). Дата обращения: 17 октября 2020. Архивировано 16 октября 2020 года.
- ↑ Coronavirus Resource Center. Harvard Health. Harvard Health Publishing (20 марта 2020). Дата обращения: 22 марта 2020. Архивировано 11 января 2022 года.
- ↑ Feng He, Yu Deng, Weina Li. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): What we know? (англ.) // Journal of Medical Virology. — 2020. — 14 March. — ISSN 1096-9071. — doi:10.1002/jmv.25766. Архивировано 21 марта 2020 года.
- ↑ Charan Thej Reddy Vegivinti, Kirk W. Evanson, Hannah Lyons, Izzet Akosman, Averi Barrett. Efficacy of antiviral therapies for COVID-19: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials (англ.) // BMC Infectious Diseases. — 2022-01-31. — 31 January (vol. 22, iss. 1). — P. 107. — ISSN 1471-2334. — doi:10.1186/s12879-022-07068-0. — PMID 35100985. Архивировано 9 февраля 2022 года.
- ↑ Xiaoling Xu, Mingfeng Han, Tiantian Li, Wei Sun, Dongsheng Wang. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab (англ.) // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. — National Academy of Sciences, 2020. — 29 April. — ISSN 1091-6490 0027-8424, 1091-6490. — doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117. Архивировано 1 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ John H. Stone, Matthew J. Frigault, Naomi J. Serling-Boyd, Ana D. Fernandes, Liam Harvey. Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 (англ.) // New England Journal of Medicine. — 2020. — 21 October. — ISSN 0028-4793. — doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028836. Архивировано 29 августа 2021 года.
- ↑ Olivier Hermine, Xavier Mariette, Pierre-Louis Tharaux, Matthieu Resche-Rigon, Raphaël Porcher. Effect of Tocilizumab vs Usual Care in Adults Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Moderate or Severe Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial (англ.) // JAMA internal medicine. — 2020. — 20 October. — ISSN 2168-6114. — doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820. — PMID 33080017. Архивировано 31 октября 2020 года.
- ↑ Carlos Salama, Jian Han, Linda Yau, William G. Reiss, Benjamin Kramer. Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia (англ.) // New England Journal of Medicine. — 2020-12-17. — 17 December. — ISSN 0028-4793. — doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2030340.
- ↑ Groundbreaking COVID-19 treatments to be fast-tracked through clinical trials (англ.). GOV.UK. Дата обращения: 15 февраля 2021. Архивировано 15 февраля 2021 года.
- ↑ Interferons (англ.). COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. U. S. National Institutes of Health (16 декабря 2021). Дата обращения: 9 февраля 2022. Архивировано 9 февраля 2022 года.
- ↑ Juan P. Jaworski. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 treatment and prevention (англ.) // Biomedical Journal. — 2020. — 25 November. — ISSN 2319-4170. — doi:10.1016/j.bj.2020.11.011. Архивировано 10 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Peter C. Taylor, Andrew C. Adams, Matthew M. Hufford, Inmaculada de la Torre, Kevin Winthrop. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19 (англ.) // Nature Reviews Immunology. — 2021. — June (vol. 21, iss. 6). — P. 382–393. — ISSN 1474-1741. — doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00542-x. Архивировано 8 октября 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Flumignan RLG, Tinôco JD, Pascoal PIF, Areias LL, Cossi MS, Fernandes MICD, Costa IKF, Souza L, Matar CF, Tendal B, Trevisani VFM, Atallah ÁN, Nakano LCU. Prophylactic anticoagulants for people hospitalised with COVID‐19 (англ.) // Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. — 2020. — 2 October (iss. 10, no. CD013739). — ISSN 1469-493X. — doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013739. Архивировано 2 мая 2021 года.
- ↑ Hidesaku Asakura, Haruhiko Ogawa. COVID-19-associated coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation (англ.) // International Journal of Hematology. — 2020. — 7 November. — P. 1–13. — ISSN 0925-5710. — doi:10.1007/s12185-020-03029-y. — PMID 33161508. Архивировано 30 декабря 2020 года.
- ↑ Tobias Tritschler, Marie-Eve Mathieu, Leslie Skeith, Marc Rodger, Saskia Middeldorp. Anticoagulant interventions in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A scoping review of randomized controlled trials and call for international collaboration (англ.) // Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. — 2020. — Vol. 18, iss. 11. — P. 2958–2967. — ISSN 1538-7836. — doi:10.1111/jth.15094. Архивировано 14 августа 2021 года.
- ↑ The Lancet Haematology. COVID-19 and thrombosis: a continuing story (англ.) // The Lancet Haematology. — 2021. — 1 February (vol. 8, iss. 2). — P. e95. — ISSN 2352-3026. — doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00002-8.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Marianna Sockrider, Shazia Jamil, Lekshmi Santhosh, W. Graham Carlos. COVID-19 Infection versus Influenza (Flu) and Other Respiratory Illnesses (англ.) // American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. — 2020. — 15 November (vol. 202, iss. 10). — P. P27–P28. — ISSN 1535-4970. — doi:10.1164/rccm.2020C16. — PMID 33021812. Архивировано 7 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Вопросы и ответы: сходства и различия возбудителей COVID‑19 и гриппа. Всемирная организация здравоохранения. Дата обращения: 21 марта 2020. Архивировано 26 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Q&A: Similarities and differences – COVID-19 and influenza (англ.). World Health Organization. Дата обращения: 26 апреля 2020. Архивировано 26 апреля 2020 года.
- ↑ Kara Rogers. What Is the Difference Between Influenza and COVID-19? (англ.). Encyclopedia Britannica. Дата обращения: 20 августа 2021. Архивировано 20 августа 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Coronavirus Disease 2019 vs. the Flu (англ.). John Hopkins Medicine. Дата обращения: 21 марта 2020. Архивировано 4 мая 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Yan Xie, Benjamin Bowe, Geetha Maddukuri, Ziyad Al-Aly. Comparative evaluation of clinical manifestations and risk of death in patients admitted to hospital with covid-19 and seasonal influenza: cohort study (англ.) // BMJ. — 2020. — 15 December (vol. 371). — ISSN 1756-1833. — doi:10.1136/bmj.m4677. Архивировано 11 января 2021 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Алексей Водовозов. COVID vs грипп: оценка рисков у госпитализированных пациентов. XX2ВЕК (23 декабря 2020). Дата обращения: 11 января 2021. Архивировано 12 января 2021 года.
- ↑ Китайской коронавирусной пневмонии присвоили название COVID-19 Архивная копия от 2 мая 2021 на Wayback Machine // Статья от 11.02.2020 г. «ТАСС».
- ↑ 1 2 Наименование заболевания, вызванного коронавирусом (COVID-19), и вирусного возбудителя. Всемирная организация здравоохранения. Дата обращения: 7 марта 2020. Архивировано 24 июня 2020 года.
- ↑ Супотницкий М. В. Новый коронавирус SARS-CoV-2 в аспекте глобальной эпидемиологии коронавирусных инфекций Архивная копия от 4 февраля 2021 на Wayback Machine / Научная статья, 27 НЦ МО РФ, doi 10.35825/2587-5728-2020-4-1-32-65 // Журнал «Вестник войск РХБ защиты». 2020 г. Том 4. № 1. С. 52-53 (прим. 35, 36). ISSN 2587-5728.
- ↑ КОВИ́Д1 // Словарь русского языка коронавирусной эпохи. — СПб : Институт лингвистических исследований РАН, 2021. — С. 82—85. — 550 с. — ISBN 978-5-6044839-0-9.
- ↑ Пандемия COVID-19 и её влияние на развитие современной этимологии. ФБУЗ «Центр гигиенического образования населения» Роспотребнадзора. Роспотребнадзор. Дата обращения: 21 января 2021. Архивировано 21 января 2021 года.
- ↑ China coronavirus: Misinformation spreads online about origin and scale, BBC News Online (30 января 2020). Архивировано 4 февраля 2020 года. Дата обращения: 25 июля 2020.
- ↑ Taylor, Josh. Bat soup, dodgy cures and ’diseasology’: the spread of coronavirus misinformation (31 января 2020). Архивировано 2 февраля 2020 года. Дата обращения: 25 июля 2020.
- ↑ Here’s A Running List Of Disinformation Spreading About The Coronavirus. Buzzfeed News. Дата обращения: 8 февраля 2020. Архивировано 6 февраля 2020 года.
- ↑ 1 2 WHO, UN, UNICEF, UNDP, UNESCO, UNAIDS, ITU, UN Global Pulse, and IFRC. Managing the COVID-19 infodemic: Promoting healthy behaviours and mitigating the harm from misinformation and disinformation (англ.). World Health Organization (23 сентября 2020). Дата обращения: 2 августа 2021. Архивировано 2 августа 2021 года.
- ↑ Ольга Просвирова. Анатомия »ковид-диссидентства». Почему на фоне пандемии так легко поверить в заговор (рус.), BBC News Русская служба (26 декабря 2020). Архивировано 27 декабря 2020 года. Дата обращения: 21 января 2021.
- ↑ Shu-Feng Tsao, Helen Chen, Therese Tisseverasinghe, Yang Yang, Lianghua Li. What social media told us in the time of COVID-19: a scoping review (англ.) // The Lancet Digital Health. — 2021-03-01. — 1 March (vol. 3, iss. 3). — P. e175–e194. — ISSN 2589-7500. — doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30315-0. — PMID 33518503. Архивировано 2 августа 2021 года.
Ссылки
- Коронавирус. — Всемирная организация здравоохранения. — Дата обращения: 18.02.2020. (Общая информация о коронавирусах от ВОЗ.)
- Рекомендации ВОЗ для населения в связи c распространением нового коронавируса (2019-nCoV): мифы и ложные представления. — Всемирная организация здравоохранения. — Дата обращения: 08.02.2020.
- Санитарно-эпидемиологические правила СП 3.1.3597-20 «Профилактика новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19)» // Утверждены постановлением Главного государственного санитарного врача РФ от 22.05.2020 г. № 15, зарегистрировано в Минюсте РФ 26.05.2020 г.
- Коронавирус COVID–19. — Правительство Российской Федерации. (Официальный интернет-ресурс для информирования населения по вопросам коронавируса (COVID-19).)
- Информация о новой коронавирусной инфекции. — Министерство здравоохранения Российской Федерации.
|
D
|
Эта страница в последний раз была отредактирована 7 января 2023 в 16:52.
Как только страница обновилась в Википедии она обновляется в Вики 2.
Обычно почти сразу, изредка в течении часа.
Объявлены официальные наименования вируса, вызывающего заболевание COVID‑19 (ранее известный как «новый коронавирус 2019 г.»), и соответствующего заболевания. Официальные наименования:
Заболевание
коронавирусная инфекция
(COVID-19)
Вирус
коронавирус тяжелого острого респираторного синдрома‑2
(SARS-CoV-2)
Почему заболевание и вирус по-разному называются?
Нередко наименования вирусов и вызываемых ими заболеваний не совпадают. Например, вирус ВИЧ вызывает СПИД. Людям часто бывает известно наименование заболевания, например, «корь», а не соответствующего вируса (rubeola).
Присвоение названий вирусам и заболеваниям происходит различным образом и для различных целей.
Наименования вирусов основаны на их генетической структуре, что упрощает разработку диагностических тестов, вакцин и лекарственных препаратов. Эту работу проводят вирусологи и другие представители научной общественности, поэтому наименования вирусам присваивает Международный комитет по таксономии вирусов (ICTV).
Наименования заболеваний требуются для того, чтобы давать характеристику различным аспектам профилактики, распространения, передачи, тяжести течения, а также лечения заболеваний. Задачей ВОЗ является обеспечение готовности и реагирования на заболевания человека, в связи с чем ВОЗ указывает официальные наименования заболеваний в Международной классификации болезней (МКБ).
Одиннадцатого февраля 2020 г. Международный комитет по таксономии вирусов присвоил новому вирусу наименование SARS-CoV-2 (коронавирус тяжелого острого респираторного синдрома‑2). Данное название выбрано по причине того, что этот вирус имеет генетическое родство с возбудителем вспышки ТОРС в 2003 г. Это разные вирусы, хотя они и связаны генетически.
Согласно рекомендациям, разработанным ранее совместно со Всемирной организацией по охране здоровья животных (МЭБ), а также Продовольственной и сельскохозяйственной организацией Объединенных Наций (ФАО), 11 февраля 2020 г. ВОЗ объявила о присвоении данному заболеванию названия «COVID‑19».
- Выступление Генерального директора ВОЗ на пресс-брифинге 11 февраля 2020 г.
- Доклад ВОЗ о текущем положении дел, 11 февраля 2020 г. – на английском языке
Работа по присвоению названий вирусу и заболеванию проходила на фоне тесного сотрудничества ВОЗ и Международного комитета по таксономии вирусов.
Каким наименованием этого вируса пользуется ВОЗ?
С точки зрения информирования о рисках использование наименования «ТОРС» может повлечь за собой неоправданные последствия в смысле создания тревожных настроений в некоторых группах населения, в особенности, в Азии, регионе, больше всего пострадавшем от вспышки ТОРС в 2003 г.
По этой и другим причинам ВОЗ приняла решение в публичной сфере называть вирус «вирусом, вызывающим COVID‑19» или «коронавирусной инфекцией COVID‑19». Ни одно из этих наименований не заменяет официального названия вируса, присвоенного Международным комитетом по таксономии вирусов.
Во избежание несогласованности за исключением необходимых случаев в материалы, опубликованные до момента присвоения вирусу официального названия, изменений вноситься не будет.
Дополнительная информация:
- Как присваивают названия инфекционным болезням? – на английском языке
- Подробнее о коронавирусной инфекции COVID-2019
- Пресс брифинги ВОЗ по COVID-2019 – на английском языке
- Международная классификация болезней – на английском языке
- Международный комитет по таксономии вирусов – на английском языке

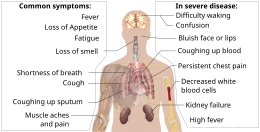

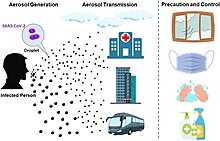





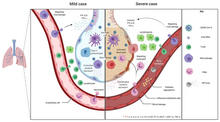

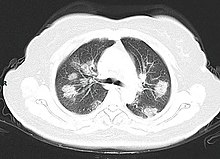


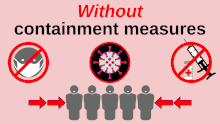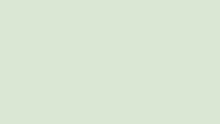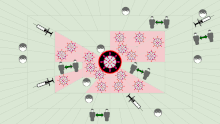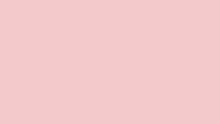





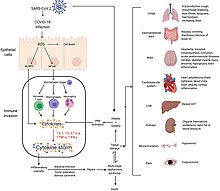


![Total confirmed cases of COVID‑19 per million people[320]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/75/World_map_of_total_confirmed_COVID-19_cases_per_million_people.svg/255px-World_map_of_total_confirmed_COVID-19_cases_per_million_people.svg.png)

![Total confirmed deaths due to COVID‑19 per million people[321]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3a/World_map_of_total_confirmed_COVID-19_deaths_per_million_people_by_country.svg/255px-World_map_of_total_confirmed_COVID-19_deaths_per_million_people_by_country.svg.png)