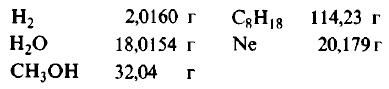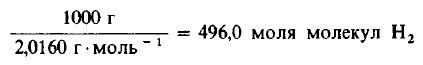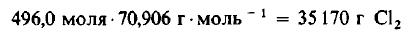«Nmol» redirects here. For the mathematical technique, see Method of lines.
| mole | |
|---|---|
| Unit system | SI |
| Unit of | amount of substance |
| Symbol | mol |
The mole, symbol mol, is the unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units (SI).[1][2][3] The quantity amount of substance is a measure of how many elementary entities of a given substance are in an object or sample. The mole is defined as containing exactly 6.02214076×1023 elementary entities. Depending on what the substance is, an elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an ion pair, or a subatomic particle such as an electron. For example, 10 moles of water (a chemical compound) and 10 moles of mercury (a chemical element), contain equal amounts of substance and the mercury contains exactly one atom for each molecule of the water, despite the two having different volumes and different masses.
The number of elementary entities in one mole is known as the Avogadro number, which is the approximate number of nucleons (protons or neutrons) in one gram of ordinary matter. The previous definition of a mole was the number of elementary entities equal to that of 12 grams of carbon-12, the most common isotope of carbon.
The mole is widely used in chemistry as a convenient way to express amounts of reactants and products of chemical reactions. For example, the chemical equation 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O can be interpreted to mean that for each 2 mol dihydrogen (H2) and 1 mol dioxygen (O2) that react, 2 mol of water (H2O) form. The concentration of a solution is commonly expressed by its molar concentration, defined as the amount of dissolved substance per unit volume of solution, for which the unit typically used is moles per litre (mol/L).
The term gram-molecule was formerly used for «mole of molecules», and gram-atom for «mole of atoms».[4] For example, 1 mole of MgBr2 is 1 gram-molecule of MgBr2 but 3 gram-atoms of MgBr2.[5][6]
Concepts[edit]
Nature of the particles[edit]
The mole corresponds to a given count of particles.[7] Usually the particles counted are chemically identical entities, individually distinct. For example, a solution may contain a certain number of dissolved molecules that are more or less independent of each other. However, in a solid the constituent particles are fixed and bound in a lattice arrangement, yet they may be separable without losing their chemical identity. Thus the solid is composed of a certain number of moles of such particles. In yet other cases, such as diamond, where the entire crystal is essentially a single molecule, the mole is still used to express the number of atoms bound together, rather than a count of molecules. Thus, common chemical conventions apply to the definition of the constituent particles of a substance, in other cases exact definitions may be specified.
The mass of a substance is equal to its relative atomic (or molecular) mass multiplied by the molar mass constant, which is almost exactly 1 g/mol.
Molar mass[edit]
The molar mass of a substance is the ratio of the mass of a sample of that substance to its amount of substance. The amount of substance is given as the number of moles in the sample.
For most practical purposes, the numerical value of the molar mass expressed with the unit gram per mole is the same as that of the mean mass of one molecule of the substance expressed with the unit dalton. For example, the molar mass of water is 18.015 g/mol.[8] Other methods include the use of the molar volume or the measurement of electric charge.[8]
The number of moles of a substance in a sample is obtained by dividing the mass of the sample by the molar mass of the compound. For example, 100 g of water is about 5.551 mol of water.[8]
The molar mass of a substance depends not only on its molecular formula, but also on the distribution of isotopes of each chemical element present in it. For example, the molar mass of calcium-40 is 39.96259098(22) g/mol, whereas the molar mass of calcium-42 is 41.95861801(27) g/mol, and of calcium with the normal isotopic mix is 40.078(4) g/mol.
Molar concentration[edit]
The molar concentration, also called molarity, of a solution of some substance is the number of moles per unit of volume of the final solution. In the SI its standard unit is mol/m3, although more practical units, such as mole per litre (mol/L) are used.
Molar fraction[edit]
The molar fraction or mole fraction of a substance in a mixture (such as a solution) is the number of moles of the compound in one sample of the mixture, divided by the total number of moles of all components. For example, if 20 g of NaCl is dissolved in 100 g of water, the amounts of the two substances in the solution will be (20 g)/(58.443 g/mol) = 0.34221 mol and (100 g)/(18.015 g/mol) = 5.5509 mol, respectively; and the molar fraction of NaCl will be 0.34221/(0.34221 + 5.5509) = 0.05807.
In a mixture of gases, the partial pressure of each component is proportional to its molar ratio.
History[edit]
Avogadro, who inspired the Avogadro constant
The history of the mole is intertwined with that of molecular mass, atomic mass units, and the Avogadro constant.
The first table of standard atomic weight was published by John Dalton (1766–1844) in 1805, based on a system in which the relative atomic mass of hydrogen was defined as 1. These relative atomic masses were based on the stoichiometric proportions of chemical reaction and compounds, a fact that greatly aided their acceptance: It was not necessary for a chemist to subscribe to atomic theory (an unproven hypothesis at the time) to make practical use of the tables. This would lead to some confusion between atomic masses (promoted by proponents of atomic theory) and equivalent weights (promoted by its opponents and which sometimes differed from relative atomic masses by an integer factor), which would last throughout much of the nineteenth century.
Jöns Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848) was instrumental in the determination of relative atomic masses to ever-increasing accuracy. He was also the first chemist to use oxygen as the standard to which other masses were referred. Oxygen is a useful standard, as, unlike hydrogen, it forms compounds with most other elements, especially metals. However, he chose to fix the atomic mass of oxygen as 100, which did not catch on.
Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (1816–56), Henri Victor Regnault (1810–78) and Stanislao Cannizzaro (1826–1910) expanded on Berzelius’ works, resolving many of the problems of unknown stoichiometry of compounds, and the use of atomic masses attracted a large consensus by the time of the Karlsruhe Congress (1860). The convention had reverted to defining the atomic mass of hydrogen as 1, although at the level of precision of measurements at that time – relative uncertainties of around 1% – this was numerically equivalent to the later standard of oxygen = 16. However the chemical convenience of having oxygen as the primary atomic mass standard became ever more evident with advances in analytical chemistry and the need for ever more accurate atomic mass determinations.
The name mole is an 1897 translation of the German unit Mol, coined by the chemist Wilhelm Ostwald in 1894 from the German word Molekül (molecule).[9][10][11] The related concept of equivalent mass had been in use at least a century earlier.[12]
Standardization[edit]
Developments in mass spectrometry led to the adoption of oxygen-16 as the standard substance, in lieu of natural oxygen.[citation needed]
The oxygen-16 definition was replaced with one based on carbon-12 during the 1960s. The mole was defined by International Bureau of Weights and Measures as «the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon-12.» Thus, by that definition, one mole of pure 12C had a mass of exactly 12 g.[4][7] The four different definitions were equivalent to within 1%.
| Scale basis | Scale basis relative to 12C = 12 |
Relative deviation from the 12C = 12 scale |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic mass of hydrogen = 1 | 1.00794(7) | −0.788% |
| Atomic mass of oxygen = 16 | 15.9994(3) | +0.00375% |
| Relative atomic mass of 16O = 16 | 15.9949146221(15) | +0.0318% |
Because a dalton, a unit commonly used to measure atomic mass, is exactly 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom, this definition of the mole entailed that the mass of one mole of a compound or element in grams was numerically equal to the average mass of one molecule or atom of the substance in daltons, and that the number of daltons in a gram was equal to the number of elementary entities in a mole. Because the mass of a nucleon (i.e. a proton or neutron) is approximately 1 dalton and the nucleons in an atom’s nucleus make up the overwhelming majority of its mass, this definition also entailed that the mass of one mole of a substance was roughly equivalent to the number of nucleons in one atom or molecule of that substance.
Since the definition of the gram was not mathematically tied to that of the dalton, the number of molecules per mole NA (the Avogadro constant) had to be determined experimentally. The experimental value adopted by CODATA in 2010 is NA = 6.02214129(27)×1023 mol−1.[13]
In 2011 the measurement was refined to 6.02214078(18)×1023 mol−1.[14]
The mole was made the seventh SI base unit in 1971 by the 14th CGPM.[15]
2019 redefinition of SI base units[edit]
In 2011, the 24th meeting of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) agreed to a plan for a possible revision of the SI base unit definitions at an undetermined date.
On 16 November 2018, after a meeting of scientists from more than 60 countries at the CGPM in Versailles, France, all SI base units were defined in terms of physical constants. This meant that each SI unit, including the mole, would not be defined in terms of any physical objects but rather they would be defined by physical constants that are, in their nature, exact.[2]
Such changes officially came into effect on 20 May 2019. Following such changes, «one mole» of a substance was redefined as containing «exactly 6.02214076×1023 elementary entities» of that substance.[16][17]
Criticism[edit]
Since its adoption into the International System of Units in 1971, numerous criticisms of the concept of the mole as a unit like the metre or the second have arisen:
- the number of molecules, etc. in a given amount of material is a fixed dimensionless quantity that can be expressed simply as a number, not requiring a distinct base unit;[7][18]
- The SI thermodynamic mole is irrelevant to analytical chemistry and could cause avoidable costs to advanced economies[19]
- The mole is not a true metric (i.e. measuring) unit, rather it is a parametric unit, and amount of substance is a parametric base quantity[20]
- the SI defines numbers of entities as quantities of dimension one, and thus ignores the ontological distinction between entities and units of continuous quantities[21]
In chemistry, it has been known since Proust’s law of definite proportions (1794) that knowledge of the mass of each of the components in a chemical system is not sufficient to define the system. Amount of substance can be described as mass divided by Proust’s «definite proportions», and contains information that is missing from the measurement of mass alone. As demonstrated by Dalton’s law of partial pressures (1803), a measurement of mass is not even necessary to measure the amount of substance (although in practice it is usual). There are many physical relationships between amount of substance and other physical quantities, the most notable one being the ideal gas law (where the relationship was first demonstrated in 1857). The term «mole» was first used in a textbook describing these colligative properties.[22]
Similar units[edit]
Like chemists, chemical engineers use the unit mole extensively, but different unit multiples may be more suitable for industrial use. For example, the SI unit for volume is the cubic metre, a much larger unit than the commonly used litre in the chemical laboratory. When amount of substance is also expressed in kmol (1000 mol) in industrial-scaled processes, the numerical value of molarity remains the same.
For convenience in avoiding conversions in the imperial (or US customary units), some engineers adopted the pound-mole (notation lb-mol or lbmol), which is defined as the number of entities in 12 lb of 12C. One lb-mol is equal to 453.59237 mol,[23] which value is the same as the number of grams in an international avoirdupois pound.
In the metric system, chemical engineers once used the kilogram-mole (notation kg-mol), which is defined as the number of entities in 12 kg of 12C, and often referred to the mole as the gram-mole (notation g-mol), when dealing with laboratory data.[23]
Late 20th-century chemical engineering practice came to use the kilomole (kmol), which is numerically identical to the kilogram-mole, but whose name and symbol adopt the SI convention for standard multiples of metric units – thus, kmol means 1000 mol. This is equivalent to the use of kg instead of g. The use of kmol is not only for «magnitude convenience» but also makes the equations used for modelling chemical engineering systems coherent. For example, the conversion of a flowrate of kg/s to kmol/s only requires the molecular mass without the factor 1000 unless the basic SI unit of mol/s were to be used.
Greenhouse and growth chamber lighting for plants is sometimes expressed in micromoles per square metre per second, where 1 mol photons = 6.02×1023 photons.[24] One mole of photons is sometimes referred to as an einstein.
Derived units and SI multiples[edit]
The only SI derived unit with a special name derived from the mole is the katal, defined as one mole per second of catalytic activity. Like other SI units, the mole can also be modified by adding a metric prefix that multiplies it by a power of 10:
| Submultiples | Multiples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | SI symbol | Name | Value | SI symbol | Name |
| 10−1 mol | dmol | decimole | 101 mol | damol | decamole |
| 10−2 mol | cmol | centimole | 102 mol | hmol | hectomole |
| 10−3 mol | mmol | millimole | 103 mol | kmol | kilomole |
| 10−6 mol | µmol | micromole | 106 mol | Mmol | megamole |
| 10−9 mol | nmol | nanomole | 109 mol | Gmol | gigamole |
| 10−12 mol | pmol | picomole | 1012 mol | Tmol | teramole |
| 10−15 mol | fmol | femtomole | 1015 mol | Pmol | petamole |
| 10−18 mol | amol | attomole | 1018 mol | Emol | examole |
| 10−21 mol | zmol | zeptomole | 1021 mol | Zmol | zettamole |
| 10−24 mol | ymol | yoctomole | 1024 mol | Ymol | yottamole |
| 10−27 mol | rmol | rontomole | 1027 mol | Rmol | ronnamole |
| 10−30 mol | qmol | quectomole | 1030 mol | Qmol | quettamole |
One fmol is exactly 602,214,076 molecules; attomole and smaller quantities cannot be exactly realized. The yoctomole, equal to around 0.6 of an individual molecule, did make appearances in scientific journals in the year the yocto- prefix was officially implemented.[25]
Mole Day[edit]
October 23, denoted 10/23 in the US, is recognized by some as Mole Day.[26] It is an informal holiday in honor of the unit among chemists. The date is derived from the Avogadro number, which is approximately 6.022×1023. It starts at 6:02 a.m. and ends at 6:02 p.m. Alternatively, some chemists celebrate June 2 (06/02), June 22 (6/22), or 6 February (06.02), a reference to the 6.02 or 6.022 part of the constant.[27][28][29]
See also[edit]
- Element-reactant-product table
- Faraday constant – Physical constant: Electric charge of one mole of electrons
- Mole fraction – Proportion of a constituent in a mixture
- Dalton (unit) – Standard unit of mass for atomic-scale chemical species
- Molecular mass – Mass of a given molecule in daltons
- Molar mass – Mass per amount of substance
References[edit]
- ^ IUPAC Gold Book. IUPAC – mole (M03980). International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1351/goldbook.M03980. S2CID 241546445.
- ^ a b «On the revision of the International System of Units – International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry». IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. 16 November 2018. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ BIPM (20 May 2019). «Mise en pratique for the definition of the mole in the SI». BIPM.org. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ a b International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (PDF) (8th ed.), pp. 114–15, ISBN 92-822-2213-6, archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-06-04, retrieved 2021-12-16
- ^ Wang, Yuxing; Bouquet, Frédéric; Sheikin, Ilya; Toulemonde, Pierre; Revaz, Bernard; Eisterer, Michael; Weber, Harald W.; Hinderer, Joerg; Junod, Alain; et al. (2003). «Specific heat of MgB2 after irradiation». Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 15 (6): 883–893. arXiv:cond-mat/0208169. Bibcode:2003JPCM…15..883W. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/15/6/315. S2CID 16981008.
- ^ Lortz, R.; Wang, Y.; Abe, S.; Meingast, C.; Paderno, Yu.; Filippov, V.; Junod, A.; et al. (2005). «Specific heat, magnetic susceptibility, resistivity and thermal expansion of the superconductor ZrB12«. Phys. Rev. B. 72 (2): 024547. arXiv:cond-mat/0502193. Bibcode:2005PhRvB..72b4547L. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.72.024547. S2CID 38571250.
- ^ a b c de Bièvre, Paul; Peiser, H. Steffen (1992). «‘Atomic Weight’ — The Name, Its History, Definition, and Units» (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 64 (10): 1535–43. doi:10.1351/pac199264101535.
- ^ a b c International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Realising the mole Archived 2008-08-29 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 25 September 2008.
- ^ Helm, Georg (1897). The Principles of Mathematical Chemistry: The Energetics of Chemical Phenomena. transl. by Livingston, J.; Morgan, R. New York: Wiley. p. 6.
- ^ Some sources place the date of first usage in English as 1902. Merriam–Webster proposes Archived 2011-11-02 at the Wayback Machine an etymology from Molekulärgewicht (molecular weight).
- ^ Ostwald, Wilhelm (1893). Hand- und Hilfsbuch zur Ausführung Physiko-Chemischer Messungen [Handbook and Auxiliary Book for Conducting Physico-Chemical Measurements]. Leipzig, Germany: Wilhelm Engelmann. p. 119. From p. 119: «Nennen wir allgemein das Gewicht in Grammen, welches dem Molekulargewicht eines gegebenen Stoffes numerisch gleich ist, ein Mol, so … « (If we call in general the weight in grams, which is numerically equal to the molecular weight of a given substance, a «mol», then … )
- ^ mole, n.8, Oxford English Dictionary, Draft Revision Dec. 2008
- ^ physics.nist.gov/ Archived 2015-06-29 at the Wayback Machine Fundamental Physical Constants: Avogadro Constant
- ^ Andreas, Birk; et al. (2011). «Determination of the Avogadro Constant by Counting the Atoms in a 28Si Crystal». Physical Review Letters. 106 (3): 30801. arXiv:1010.2317. Bibcode:2011PhRvL.106c0801A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.030801. PMID 21405263. S2CID 18291648.
- ^ «BIPM – Resolution 3 of the 14th CGPM». www.bipm.org. Archived from the original on 9 October 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
- ^ CIPM Report of 106th Meeting Archived 2018-01-27 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 7 April 2018
- ^ «Redefining the Mole». NIST. 2018-10-23. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- ^ Barański, Andrzej (2012). «The Atomic Mass Unit, the Avogadro Constant, and the Mole: A Way to Understanding». Journal of Chemical Education. 89 (1): 97–102. Bibcode:2012JChEd..89…97B. doi:10.1021/ed2001957.
- ^ Price, Gary (2010). «Failures of the global measurement system. Part 1: the case of chemistry». Accreditation and Quality Assurance. 15 (7): 421–427. doi:10.1007/s00769-010-0655-z. S2CID 95388009.
- ^ Johansson, Ingvar (2010). «Metrological thinking needs the notions of parametric quantities, units, and dimensions». Metrologia. 47 (3): 219–230. Bibcode:2010Metro..47..219J. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/47/3/012. S2CID 122242959.
- ^ Cooper, G.; Humphry, S. (2010). «The ontological distinction between units and entities». Synthese. 187 (2): 393–401. doi:10.1007/s11229-010-9832-1. S2CID 46532636.
- ^ The scientific foundations of analytical chemistry: Treated in an elementary manner. Macmillan and co., limited. 1900. OL 7204743M.
- ^ a b Himmelblau, David (1996). Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical Engineering (6 ed.). pp. 17–20. ISBN 978-0-13-305798-0.
- ^ «Lighting Radiation Conversion». Archived from the original on March 11, 2016. Retrieved March 10, 2016.
- ^ Chen, Da Yong; et al. (1991). «Low-cost, high-sensitivity laser-induced fluorescence detection for DNA sequencing by capillary gel electrophoresis». Journal of Chromatography. 559 (1–2): 237–246. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(91)80074-Q. PMID 1761625.
- ^ History of National Mole Day Foundation, Inc. Archived 2010-10-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Happy Mole Day! Archived 2014-07-29 at the Wayback Machine, Mary Bigelow. SciLinks blog, National Science Teachers Association. October 17, 2013.
- ^ What Is Mole Day? – Date and How to Celebrate. Archived 2014-07-30 at Wikiwix, Anne Marie Helmenstine. About.com.
- ^ The Perse School (Feb 7, 2013), The Perse School celebrates moles of the chemical variety, Cambridge Network, archived from the original on 2015-02-11, retrieved Feb 11, 2015,
As 6.02 corresponds to 6th February, the School has adopted the date as their ‘Mole Day’.
External links[edit]
- ChemTeam: The Origin of the Word ‘Mole’ at the Wayback Machine (archived December 22, 2007)
«Nmol» redirects here. For the mathematical technique, see Method of lines.
| mole | |
|---|---|
| Unit system | SI |
| Unit of | amount of substance |
| Symbol | mol |
The mole, symbol mol, is the unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units (SI).[1][2][3] The quantity amount of substance is a measure of how many elementary entities of a given substance are in an object or sample. The mole is defined as containing exactly 6.02214076×1023 elementary entities. Depending on what the substance is, an elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an ion pair, or a subatomic particle such as an electron. For example, 10 moles of water (a chemical compound) and 10 moles of mercury (a chemical element), contain equal amounts of substance and the mercury contains exactly one atom for each molecule of the water, despite the two having different volumes and different masses.
The number of elementary entities in one mole is known as the Avogadro number, which is the approximate number of nucleons (protons or neutrons) in one gram of ordinary matter. The previous definition of a mole was the number of elementary entities equal to that of 12 grams of carbon-12, the most common isotope of carbon.
The mole is widely used in chemistry as a convenient way to express amounts of reactants and products of chemical reactions. For example, the chemical equation 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O can be interpreted to mean that for each 2 mol dihydrogen (H2) and 1 mol dioxygen (O2) that react, 2 mol of water (H2O) form. The concentration of a solution is commonly expressed by its molar concentration, defined as the amount of dissolved substance per unit volume of solution, for which the unit typically used is moles per litre (mol/L).
The term gram-molecule was formerly used for «mole of molecules», and gram-atom for «mole of atoms».[4] For example, 1 mole of MgBr2 is 1 gram-molecule of MgBr2 but 3 gram-atoms of MgBr2.[5][6]
Concepts[edit]
Nature of the particles[edit]
The mole corresponds to a given count of particles.[7] Usually the particles counted are chemically identical entities, individually distinct. For example, a solution may contain a certain number of dissolved molecules that are more or less independent of each other. However, in a solid the constituent particles are fixed and bound in a lattice arrangement, yet they may be separable without losing their chemical identity. Thus the solid is composed of a certain number of moles of such particles. In yet other cases, such as diamond, where the entire crystal is essentially a single molecule, the mole is still used to express the number of atoms bound together, rather than a count of molecules. Thus, common chemical conventions apply to the definition of the constituent particles of a substance, in other cases exact definitions may be specified.
The mass of a substance is equal to its relative atomic (or molecular) mass multiplied by the molar mass constant, which is almost exactly 1 g/mol.
Molar mass[edit]
The molar mass of a substance is the ratio of the mass of a sample of that substance to its amount of substance. The amount of substance is given as the number of moles in the sample.
For most practical purposes, the numerical value of the molar mass expressed with the unit gram per mole is the same as that of the mean mass of one molecule of the substance expressed with the unit dalton. For example, the molar mass of water is 18.015 g/mol.[8] Other methods include the use of the molar volume or the measurement of electric charge.[8]
The number of moles of a substance in a sample is obtained by dividing the mass of the sample by the molar mass of the compound. For example, 100 g of water is about 5.551 mol of water.[8]
The molar mass of a substance depends not only on its molecular formula, but also on the distribution of isotopes of each chemical element present in it. For example, the molar mass of calcium-40 is 39.96259098(22) g/mol, whereas the molar mass of calcium-42 is 41.95861801(27) g/mol, and of calcium with the normal isotopic mix is 40.078(4) g/mol.
Molar concentration[edit]
The molar concentration, also called molarity, of a solution of some substance is the number of moles per unit of volume of the final solution. In the SI its standard unit is mol/m3, although more practical units, such as mole per litre (mol/L) are used.
Molar fraction[edit]
The molar fraction or mole fraction of a substance in a mixture (such as a solution) is the number of moles of the compound in one sample of the mixture, divided by the total number of moles of all components. For example, if 20 g of NaCl is dissolved in 100 g of water, the amounts of the two substances in the solution will be (20 g)/(58.443 g/mol) = 0.34221 mol and (100 g)/(18.015 g/mol) = 5.5509 mol, respectively; and the molar fraction of NaCl will be 0.34221/(0.34221 + 5.5509) = 0.05807.
In a mixture of gases, the partial pressure of each component is proportional to its molar ratio.
History[edit]
Avogadro, who inspired the Avogadro constant
The history of the mole is intertwined with that of molecular mass, atomic mass units, and the Avogadro constant.
The first table of standard atomic weight was published by John Dalton (1766–1844) in 1805, based on a system in which the relative atomic mass of hydrogen was defined as 1. These relative atomic masses were based on the stoichiometric proportions of chemical reaction and compounds, a fact that greatly aided their acceptance: It was not necessary for a chemist to subscribe to atomic theory (an unproven hypothesis at the time) to make practical use of the tables. This would lead to some confusion between atomic masses (promoted by proponents of atomic theory) and equivalent weights (promoted by its opponents and which sometimes differed from relative atomic masses by an integer factor), which would last throughout much of the nineteenth century.
Jöns Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848) was instrumental in the determination of relative atomic masses to ever-increasing accuracy. He was also the first chemist to use oxygen as the standard to which other masses were referred. Oxygen is a useful standard, as, unlike hydrogen, it forms compounds with most other elements, especially metals. However, he chose to fix the atomic mass of oxygen as 100, which did not catch on.
Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (1816–56), Henri Victor Regnault (1810–78) and Stanislao Cannizzaro (1826–1910) expanded on Berzelius’ works, resolving many of the problems of unknown stoichiometry of compounds, and the use of atomic masses attracted a large consensus by the time of the Karlsruhe Congress (1860). The convention had reverted to defining the atomic mass of hydrogen as 1, although at the level of precision of measurements at that time – relative uncertainties of around 1% – this was numerically equivalent to the later standard of oxygen = 16. However the chemical convenience of having oxygen as the primary atomic mass standard became ever more evident with advances in analytical chemistry and the need for ever more accurate atomic mass determinations.
The name mole is an 1897 translation of the German unit Mol, coined by the chemist Wilhelm Ostwald in 1894 from the German word Molekül (molecule).[9][10][11] The related concept of equivalent mass had been in use at least a century earlier.[12]
Standardization[edit]
Developments in mass spectrometry led to the adoption of oxygen-16 as the standard substance, in lieu of natural oxygen.[citation needed]
The oxygen-16 definition was replaced with one based on carbon-12 during the 1960s. The mole was defined by International Bureau of Weights and Measures as «the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon-12.» Thus, by that definition, one mole of pure 12C had a mass of exactly 12 g.[4][7] The four different definitions were equivalent to within 1%.
| Scale basis | Scale basis relative to 12C = 12 |
Relative deviation from the 12C = 12 scale |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic mass of hydrogen = 1 | 1.00794(7) | −0.788% |
| Atomic mass of oxygen = 16 | 15.9994(3) | +0.00375% |
| Relative atomic mass of 16O = 16 | 15.9949146221(15) | +0.0318% |
Because a dalton, a unit commonly used to measure atomic mass, is exactly 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom, this definition of the mole entailed that the mass of one mole of a compound or element in grams was numerically equal to the average mass of one molecule or atom of the substance in daltons, and that the number of daltons in a gram was equal to the number of elementary entities in a mole. Because the mass of a nucleon (i.e. a proton or neutron) is approximately 1 dalton and the nucleons in an atom’s nucleus make up the overwhelming majority of its mass, this definition also entailed that the mass of one mole of a substance was roughly equivalent to the number of nucleons in one atom or molecule of that substance.
Since the definition of the gram was not mathematically tied to that of the dalton, the number of molecules per mole NA (the Avogadro constant) had to be determined experimentally. The experimental value adopted by CODATA in 2010 is NA = 6.02214129(27)×1023 mol−1.[13]
In 2011 the measurement was refined to 6.02214078(18)×1023 mol−1.[14]
The mole was made the seventh SI base unit in 1971 by the 14th CGPM.[15]
2019 redefinition of SI base units[edit]
In 2011, the 24th meeting of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) agreed to a plan for a possible revision of the SI base unit definitions at an undetermined date.
On 16 November 2018, after a meeting of scientists from more than 60 countries at the CGPM in Versailles, France, all SI base units were defined in terms of physical constants. This meant that each SI unit, including the mole, would not be defined in terms of any physical objects but rather they would be defined by physical constants that are, in their nature, exact.[2]
Such changes officially came into effect on 20 May 2019. Following such changes, «one mole» of a substance was redefined as containing «exactly 6.02214076×1023 elementary entities» of that substance.[16][17]
Criticism[edit]
Since its adoption into the International System of Units in 1971, numerous criticisms of the concept of the mole as a unit like the metre or the second have arisen:
- the number of molecules, etc. in a given amount of material is a fixed dimensionless quantity that can be expressed simply as a number, not requiring a distinct base unit;[7][18]
- The SI thermodynamic mole is irrelevant to analytical chemistry and could cause avoidable costs to advanced economies[19]
- The mole is not a true metric (i.e. measuring) unit, rather it is a parametric unit, and amount of substance is a parametric base quantity[20]
- the SI defines numbers of entities as quantities of dimension one, and thus ignores the ontological distinction between entities and units of continuous quantities[21]
In chemistry, it has been known since Proust’s law of definite proportions (1794) that knowledge of the mass of each of the components in a chemical system is not sufficient to define the system. Amount of substance can be described as mass divided by Proust’s «definite proportions», and contains information that is missing from the measurement of mass alone. As demonstrated by Dalton’s law of partial pressures (1803), a measurement of mass is not even necessary to measure the amount of substance (although in practice it is usual). There are many physical relationships between amount of substance and other physical quantities, the most notable one being the ideal gas law (where the relationship was first demonstrated in 1857). The term «mole» was first used in a textbook describing these colligative properties.[22]
Similar units[edit]
Like chemists, chemical engineers use the unit mole extensively, but different unit multiples may be more suitable for industrial use. For example, the SI unit for volume is the cubic metre, a much larger unit than the commonly used litre in the chemical laboratory. When amount of substance is also expressed in kmol (1000 mol) in industrial-scaled processes, the numerical value of molarity remains the same.
For convenience in avoiding conversions in the imperial (or US customary units), some engineers adopted the pound-mole (notation lb-mol or lbmol), which is defined as the number of entities in 12 lb of 12C. One lb-mol is equal to 453.59237 mol,[23] which value is the same as the number of grams in an international avoirdupois pound.
In the metric system, chemical engineers once used the kilogram-mole (notation kg-mol), which is defined as the number of entities in 12 kg of 12C, and often referred to the mole as the gram-mole (notation g-mol), when dealing with laboratory data.[23]
Late 20th-century chemical engineering practice came to use the kilomole (kmol), which is numerically identical to the kilogram-mole, but whose name and symbol adopt the SI convention for standard multiples of metric units – thus, kmol means 1000 mol. This is equivalent to the use of kg instead of g. The use of kmol is not only for «magnitude convenience» but also makes the equations used for modelling chemical engineering systems coherent. For example, the conversion of a flowrate of kg/s to kmol/s only requires the molecular mass without the factor 1000 unless the basic SI unit of mol/s were to be used.
Greenhouse and growth chamber lighting for plants is sometimes expressed in micromoles per square metre per second, where 1 mol photons = 6.02×1023 photons.[24] One mole of photons is sometimes referred to as an einstein.
Derived units and SI multiples[edit]
The only SI derived unit with a special name derived from the mole is the katal, defined as one mole per second of catalytic activity. Like other SI units, the mole can also be modified by adding a metric prefix that multiplies it by a power of 10:
| Submultiples | Multiples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | SI symbol | Name | Value | SI symbol | Name |
| 10−1 mol | dmol | decimole | 101 mol | damol | decamole |
| 10−2 mol | cmol | centimole | 102 mol | hmol | hectomole |
| 10−3 mol | mmol | millimole | 103 mol | kmol | kilomole |
| 10−6 mol | µmol | micromole | 106 mol | Mmol | megamole |
| 10−9 mol | nmol | nanomole | 109 mol | Gmol | gigamole |
| 10−12 mol | pmol | picomole | 1012 mol | Tmol | teramole |
| 10−15 mol | fmol | femtomole | 1015 mol | Pmol | petamole |
| 10−18 mol | amol | attomole | 1018 mol | Emol | examole |
| 10−21 mol | zmol | zeptomole | 1021 mol | Zmol | zettamole |
| 10−24 mol | ymol | yoctomole | 1024 mol | Ymol | yottamole |
| 10−27 mol | rmol | rontomole | 1027 mol | Rmol | ronnamole |
| 10−30 mol | qmol | quectomole | 1030 mol | Qmol | quettamole |
One fmol is exactly 602,214,076 molecules; attomole and smaller quantities cannot be exactly realized. The yoctomole, equal to around 0.6 of an individual molecule, did make appearances in scientific journals in the year the yocto- prefix was officially implemented.[25]
Mole Day[edit]
October 23, denoted 10/23 in the US, is recognized by some as Mole Day.[26] It is an informal holiday in honor of the unit among chemists. The date is derived from the Avogadro number, which is approximately 6.022×1023. It starts at 6:02 a.m. and ends at 6:02 p.m. Alternatively, some chemists celebrate June 2 (06/02), June 22 (6/22), or 6 February (06.02), a reference to the 6.02 or 6.022 part of the constant.[27][28][29]
See also[edit]
- Element-reactant-product table
- Faraday constant – Physical constant: Electric charge of one mole of electrons
- Mole fraction – Proportion of a constituent in a mixture
- Dalton (unit) – Standard unit of mass for atomic-scale chemical species
- Molecular mass – Mass of a given molecule in daltons
- Molar mass – Mass per amount of substance
References[edit]
- ^ IUPAC Gold Book. IUPAC – mole (M03980). International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1351/goldbook.M03980. S2CID 241546445.
- ^ a b «On the revision of the International System of Units – International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry». IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. 16 November 2018. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ BIPM (20 May 2019). «Mise en pratique for the definition of the mole in the SI». BIPM.org. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ a b International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (PDF) (8th ed.), pp. 114–15, ISBN 92-822-2213-6, archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-06-04, retrieved 2021-12-16
- ^ Wang, Yuxing; Bouquet, Frédéric; Sheikin, Ilya; Toulemonde, Pierre; Revaz, Bernard; Eisterer, Michael; Weber, Harald W.; Hinderer, Joerg; Junod, Alain; et al. (2003). «Specific heat of MgB2 after irradiation». Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 15 (6): 883–893. arXiv:cond-mat/0208169. Bibcode:2003JPCM…15..883W. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/15/6/315. S2CID 16981008.
- ^ Lortz, R.; Wang, Y.; Abe, S.; Meingast, C.; Paderno, Yu.; Filippov, V.; Junod, A.; et al. (2005). «Specific heat, magnetic susceptibility, resistivity and thermal expansion of the superconductor ZrB12«. Phys. Rev. B. 72 (2): 024547. arXiv:cond-mat/0502193. Bibcode:2005PhRvB..72b4547L. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.72.024547. S2CID 38571250.
- ^ a b c de Bièvre, Paul; Peiser, H. Steffen (1992). «‘Atomic Weight’ — The Name, Its History, Definition, and Units» (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 64 (10): 1535–43. doi:10.1351/pac199264101535.
- ^ a b c International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Realising the mole Archived 2008-08-29 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 25 September 2008.
- ^ Helm, Georg (1897). The Principles of Mathematical Chemistry: The Energetics of Chemical Phenomena. transl. by Livingston, J.; Morgan, R. New York: Wiley. p. 6.
- ^ Some sources place the date of first usage in English as 1902. Merriam–Webster proposes Archived 2011-11-02 at the Wayback Machine an etymology from Molekulärgewicht (molecular weight).
- ^ Ostwald, Wilhelm (1893). Hand- und Hilfsbuch zur Ausführung Physiko-Chemischer Messungen [Handbook and Auxiliary Book for Conducting Physico-Chemical Measurements]. Leipzig, Germany: Wilhelm Engelmann. p. 119. From p. 119: «Nennen wir allgemein das Gewicht in Grammen, welches dem Molekulargewicht eines gegebenen Stoffes numerisch gleich ist, ein Mol, so … « (If we call in general the weight in grams, which is numerically equal to the molecular weight of a given substance, a «mol», then … )
- ^ mole, n.8, Oxford English Dictionary, Draft Revision Dec. 2008
- ^ physics.nist.gov/ Archived 2015-06-29 at the Wayback Machine Fundamental Physical Constants: Avogadro Constant
- ^ Andreas, Birk; et al. (2011). «Determination of the Avogadro Constant by Counting the Atoms in a 28Si Crystal». Physical Review Letters. 106 (3): 30801. arXiv:1010.2317. Bibcode:2011PhRvL.106c0801A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.030801. PMID 21405263. S2CID 18291648.
- ^ «BIPM – Resolution 3 of the 14th CGPM». www.bipm.org. Archived from the original on 9 October 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
- ^ CIPM Report of 106th Meeting Archived 2018-01-27 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 7 April 2018
- ^ «Redefining the Mole». NIST. 2018-10-23. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- ^ Barański, Andrzej (2012). «The Atomic Mass Unit, the Avogadro Constant, and the Mole: A Way to Understanding». Journal of Chemical Education. 89 (1): 97–102. Bibcode:2012JChEd..89…97B. doi:10.1021/ed2001957.
- ^ Price, Gary (2010). «Failures of the global measurement system. Part 1: the case of chemistry». Accreditation and Quality Assurance. 15 (7): 421–427. doi:10.1007/s00769-010-0655-z. S2CID 95388009.
- ^ Johansson, Ingvar (2010). «Metrological thinking needs the notions of parametric quantities, units, and dimensions». Metrologia. 47 (3): 219–230. Bibcode:2010Metro..47..219J. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/47/3/012. S2CID 122242959.
- ^ Cooper, G.; Humphry, S. (2010). «The ontological distinction between units and entities». Synthese. 187 (2): 393–401. doi:10.1007/s11229-010-9832-1. S2CID 46532636.
- ^ The scientific foundations of analytical chemistry: Treated in an elementary manner. Macmillan and co., limited. 1900. OL 7204743M.
- ^ a b Himmelblau, David (1996). Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical Engineering (6 ed.). pp. 17–20. ISBN 978-0-13-305798-0.
- ^ «Lighting Radiation Conversion». Archived from the original on March 11, 2016. Retrieved March 10, 2016.
- ^ Chen, Da Yong; et al. (1991). «Low-cost, high-sensitivity laser-induced fluorescence detection for DNA sequencing by capillary gel electrophoresis». Journal of Chromatography. 559 (1–2): 237–246. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(91)80074-Q. PMID 1761625.
- ^ History of National Mole Day Foundation, Inc. Archived 2010-10-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Happy Mole Day! Archived 2014-07-29 at the Wayback Machine, Mary Bigelow. SciLinks blog, National Science Teachers Association. October 17, 2013.
- ^ What Is Mole Day? – Date and How to Celebrate. Archived 2014-07-30 at Wikiwix, Anne Marie Helmenstine. About.com.
- ^ The Perse School (Feb 7, 2013), The Perse School celebrates moles of the chemical variety, Cambridge Network, archived from the original on 2015-02-11, retrieved Feb 11, 2015,
As 6.02 corresponds to 6th February, the School has adopted the date as their ‘Mole Day’.
External links[edit]
- ChemTeam: The Origin of the Word ‘Mole’ at the Wayback Machine (archived December 22, 2007)
В уроке 5 «Моль и молярная масса» из курса «Химия для чайников» рассмотрим моль как единицу измерения количества вещества; дадим определение числу Авогадро, а также научимся определять молярную массу и решать задачи на количество вещества. Базой для данного урока послужат основы химии, изложенные в прошлых уроках, так что если вы изучаете химию с нуля, то рекомендую их просмотреть хотя бы мельком.
Единица измерения количества вещества
До этого урока мы обсуждали лишь индивидуальные молекулы и атомы, а их массы мы выражали в атомных единицах массы. В реальной жизни с индивидуальными молекулами работать невозможно, потому что они ничтожно малы. Для этого химики взвешивают вещества ни в а.е.м., а в граммах.
Чтобы перейти от молекулярной шкалы измерения масс в лабораторную шкалу, используют единицу измерения количества вещества под названием моль. 1 моль содержит 6,022·1023 частиц (атомов или молекул) и является безразмерной величиной. Число 6,022·1023 носит название Число Авогадро, которое определяется как число частиц, содержащихся в 12 г атомов углерода 12C. Важно понимать, что 1 моль любого вещества содержит всегда одно и то же число частиц (6,022·1023).
Как уже было сказано, термин «моль» применяется не только к молекулам, но также и к атомам. Например, если вы говорите о моле гелия (He), то это означает, что вы имеет количество равное 6,022·1023 атомов. Точно так же, 1 моль воды (H2O) подразумевает количество равное 6,022·1023 молекул. Однако чаще всего моль применяют именно к молекулам.
Молярная масса вещества
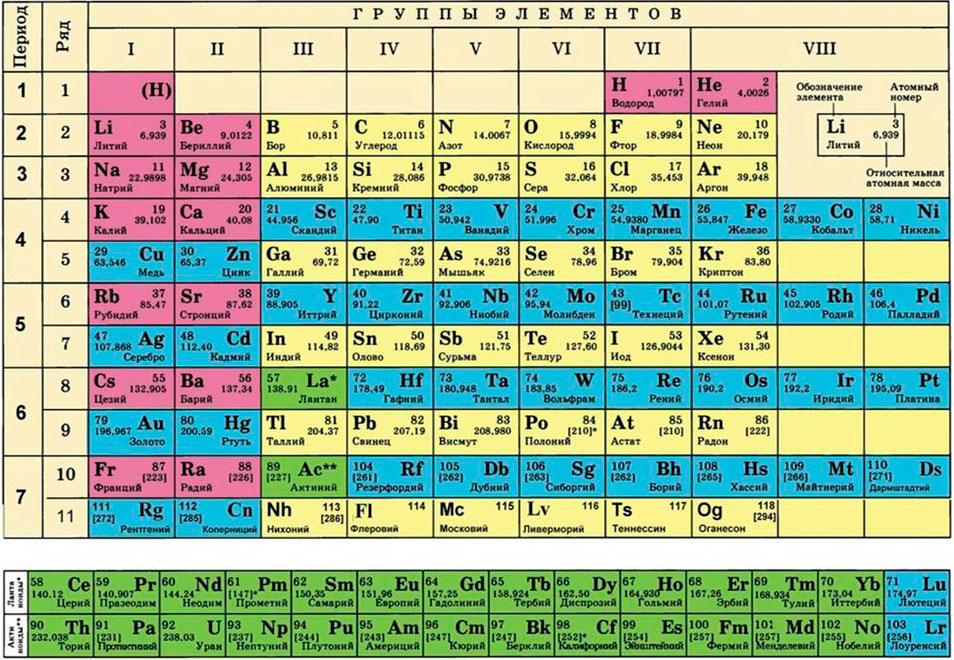
Молярная масса – это масса 1 моля вещества, выраженная в граммах. Молярную массу одного моля любого химического элемента без труда находят из таблицы Менделеева, так как молярная масса численно равна атомной массе, но размерности у них разные (молярная масса имеет размерность г/моль). Запишите и запомните формулы для вычисления молярной массы, количества вещества и числа молекул:
- Молярная масса формула M=m/n
- Количество вещества формула n=m/M
- Число молекул формула N =NA·n
где m — масса вещества, n — количество вещества (число молей), М — молярная масса, N — число молекул, NA — число Авогадро. Благодаря молярной массе вещества химики могут вести подсчет атомов и молекул в лаборатории просто путем их взвешивания. Этим и удобно использование понятия моль.
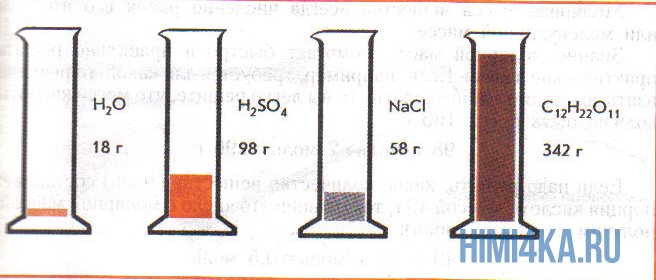
На рисунке изображены четыре колбы с различными веществами, но в каждой из них всего 1 моль вещества. Можете перепроверить, используя формулы выше.
Задачи на количество вещества
Пример 1. Сколько граммов Н2, Н2O, СН3ОН, октана (С8Н18) и газа неона (Ne) содержится в 1 моле?
Решение: Молекулярные массы (в атомных единицах массы) перечисленных веществ приведены в таблице Менделеева. 1 моль каждого из названных веществ имеет следующую массу:
Поскольку массы, указанные в решении примера 1, дают правильные относительные массы взвешиваемых молекул, указанная масса каждого из перечисленных веществ содержит одинаковое число молекул. Этим и удобно использование понятия моля. Нет даже необходимости знать, чему равно численное значение моля, хотя мы уже знаем, что оно составляет 6,022·1023; эта величина называется числом Авогадро и обозначается символом NA. Переход от индивидуальных молекул к молям означает увеличение шкалы измерения в 6,022·1023 раз. Число Авогадро представляет собой также множитель перевода атомных единиц массы в граммы: 1 г = 6,022·1023 а.е.м. Если мы понимаем под молекулярной массой массу моля вещества, то ее следует измерять в граммах на моль; если же мы действительно имеем в виду массу одной молекулы, то она численно совпадает
с молекулярной массой вещества, но выражается в атомных единицах массы на одну молекулу. Оба способа выражения молекулярной массы правильны.
Пример 2. Сколько молей составляют и сколько молекул содержат 8 г газообразного кислорода O2?
Решение: Выписываем из таблицы Менделеева атомную массу атома кислорода (O), которая равна 15,99 а.е.м, округляем до 16. Так как у нас молекула кислорода, состоящая из двух атомов O, то ее атомная масса равна 16×2=32 а.е.м. Хорошо, а теперь переводим ее в молярную массу: 32 а.е.м = 32 г/моль. Это означает, что 1 моль (6,022·1023 молекул) O2 имеет массу 32 грамма. Ну и в заключении по формулам выше находим количество вещества (моль) и число молекул, содержащихся в 8 граммах O2:
- n = m / M = 8г / 32г/моль = 0,25 моль
- N = NA × n = 6,022·1023 × 0,25 = 1,505·1023 молекул
Пример 3. 1 молекула Н2 реагирует с 1 молекулой Сl2, в результате чего образуются 2 молекулы газообразного хлористого водорода НСl. Какую массу газообразного хлора необходимо использовать, чтобы он полностью прореагировал с 1 килограммом (кг) газообразного водорода?
Решение: Молекулярные массы H2 и Cl2 равны 2,0160 и 70,906 г/моль соответственно. Следовательно, в 1000 г H2 содержится
Даже не выясняя, сколько молекул содержится в одном моле вещества, мы можем быть уверены, что 496 моля Cl2 содержат такое же число молекул, как и 496,0 моля, или 1000 г, H2. Сколько же граммов Cl2 содержится в 496 молях этого вещества? Поскольку молекулярная масса Cl2 равна 70,906 г/моль, то
Пример 4. Сколько молекул H2 и Cl2 принимает участие в реакции, описанной в примере 3?
Решение: В 496 молях любого вещества должно содержаться 496 моля × 6,022·1023 молекул/моль, что равно 2,99·1026 молекул.
Чтобы наглядно показать, сколь велико число Авогадро, приведем такой пример: 1 моль кокосовых орехов каждый диаметром 14 сантиметров (см) мог бы заполнить такой объем, какой занимает наша планета Земля. Использование молей в химических расчетах рассматривается в следующей главе, но представление об этом пришлось ввести уже здесь, поскольку нам необходимо знать, как осуществляется переход от молекулярной шкалы измерения масс к лабораторной шкале.
Надеюсь урок 5 «Моль и молярная масса» был познавательным и понятным. Если у вас возникли вопросы, пишите их в комментарии.
Моль — условное количество вещества
Добавлено: 3 октября 2021 в 12:58

Химия — наука, изучающая взаимодействие веществ на атомном и молекулярном уровнях. Эти процессы значительно отличаются от привычного нам макроуровня и поэтому требуют специфических подходов, в том числе к «подсчету» и «взвешиванию». Школьный курс химии включает понятия «моль» и «молярная масса». Они кажутся сложными, но если разобраться, то вы без труда поймете сущность этих понятий и научитесь ими пользоваться при решении задач.
Моль
Понятие «моль» попытаемся разобрать и, самое главное, понять на примере всем знакомой реакции взаимодействия кислорода и водорода. Когда одна молекула O2 соединяется с двумя молекулами H2, получается две молекулы H2O:
O2 + 2H2 = 2H2O
То есть, чтобы максимально полно провести химическую реакцию, мы должны взять на каждую молекулу кислорода две молекулы водорода. Итак, у нас есть 100 г кислорода. Сколько понадобится водорода для протекания процесса? И тут возникает первый вопрос: сколько молекул в 100 г кислорода? Наверное, миллиарды или даже миллиарды миллиардов? И сколько их в 100 г водорода? Уж точно в не в 2 раза меньше. Как вообще подсчитать молекулы, ведь они бывают совершенно разными, «тяжелыми» и «легкими». Этими вопросами задавались и люди, закладывавшие основу современной химической науки.
Был найден простой выход, который помогает легко и изящно решить проблему. Химики решили взять за единицу измерения не одну молекулу, а определенное их количество, причем очень большое. Таким образом эта единица измерения приводит микроуровень к макроуровню. Она называется «моль».
Моль — это количество вещества из 6,02214076⋅1023 атомов или молекул. Оно не имеет физического смысла и изначально было привязано к массе определенного количества (12 граммов) углерода-12, но позже переопределено, как и многие другие единицы системы СИ. В школьных расчетах количество структурных единиц в моле, которое также называется постоянной Авогадро, обычно округляют до 6,022⋅1023 и обозначают NA.
С этой величиной связано другое химическое понятие — «количество вещества», то есть количество структурных единиц в определенной его порции. Оно обозначается буквой ν (ню).
Примеры
В стакане содержится 2 моль воды. Сколько молекул воды находится в стакане?
N = ν⋅ NA =2 ⋅ 6,022⋅1023 = 12,044⋅1023 молекул воды.
Также можно решить обратную задачу. Сколько молей вещества составляют 24,088⋅1023 молекул воды?
ν⋅ = N / NA = 24,088⋅1023 / 6,022⋅1023 = 4 моля.
Моль и молярная масса: простое объяснение с примерами
Молярная масса
Итак, мы поняли, что моль — условное количество вещества, выбранное для удобства химиков. Это даже не миллиарды миллиардов, как мы предположили ранее, а миллиарды триллионов, что никак не облегчает задачу подсчета этих структурных единиц. Как же все-таки узнать, сколько атомов или молекул в 100 граммах того или иного вещества? Теперь хорошо бы связать количество вещества и его массу, ведь это не одно и то же. Нам поможет «молярная масса» — то есть масса 1 моль вещества или масса 6,022⋅1023 структурных единиц этого вещества.
Итак, молярная масса равна массе порции вещества m к количеству молекул ν в его порции:
М = m / ν.
Вооружившись этим знанием, мы можем переводить граммы в число молекул и наоборот. При этом следует учесть, что молярная масса численно идентична молекулярной массе (то есть массе молекулы), выраженной в атомных единицах массы, и относительной молекулярной массе.
Пример
Найдем массу 5 моль воды.
Чтобы решить эту задачу, обратимся к формуле молярной массы и выразим из нее массу:
m = М ⋅ ν
В этой формуле мы знаем количество вещества ν = 5 моль, а молярную массу сложной молекулы нужно определить, как сумму молярных масс составляющих ее химических элементов:
M (H2O) = 2 ⋅M (H) + M (O)
Моль и молярная масса: простое объяснение с примерами
Где взять молярные массы кислорода и водорода (в соединение входит два атома водорода, поэтому его молярную массу умножаем на 2)?
Для этого нам понадобится таблица Менделеева и значение «относительной атомной массы», которая, как мы уже знаем, идентична молекулярной. Это значение приведено для каждого химического элемента и для водорода равно 1,00797 (то есть близко к 1), для углерода — близко к 6, для кислорода — около 16. Подставим соответствующие значения в исходную формулу и получим:
M (H2O) = 2 ⋅M (H) + M (O) = 2 ⋅ 1 + 16 = 18 г/моль.
То есть масса 1 моль воды составляет 18 граммов. Теперь можем подсчитать массу 5 моль воды:
m = М ⋅ ν = 18 ⋅ 5 = 90 г.
Аналогичным образом мы можем подсчитать количество вещества, которое содержится в определенном образце заданной массы. Для примера возьмем оксид алюминия Al2O3 и узнаем, сколько моль в 400 граммах этого вещества. Для этого выразим количество вещества через молярную массу и подставим исходные данные:
ν = m / М = 400 / (2 ⋅ М (Al) + 3 ⋅ (O)) = 400 / (2 ⋅ 75 + 3 ⋅ 16) = 400 / (150 + 48) = 400 / 198 ≈ 2,02 моль.
Занимайтесь на курсах ЕГЭ и ОГЭ в паре TwoStu и получите максимум баллов на экзамене:

Эксперт по подготовке к ЕГЭ, ОГЭ и ВПР
Задать вопрос
Закончил Московский физико-технический институт (Физтех) по специальности прикладная физика и математика. Магистр физико-математических наук. Преподавательский стаж более 13 лет. Соучредитель курсов ЕГЭ и ОГЭ в паре TwoStu.
Читайте также:
Моль, молярная масса
В химических процессах участвуют мельчайшие частицы – молекулы, атомы, ионы, электроны. Число таких частиц даже в малой порции вещества очень велико. Поэтому, чтобы избежать математических операций с большими числами, для характеристики количества вещества, участвующего в химической реакции, используется специальная единица – моль.
Моль — это такое количество вещества, в котором содержится определенное число частиц (молекул, атомов, ионов), равное постоянной Авогадро
Постоянная Авогадро NA определяется как число атомов, содержащееся в 12 г изотопа 12С:
Таким образом, 1 моль любого вещества содержит 6,02 • 1023 частиц этого вещества.
1 моль кислорода содержит 6,02 • 1023 молекул O2.
1 моль серной кислоты содержит 6,02 • 1023 молекул H2SO4.
1 моль железа содержит 6,02 • 1023 атомов Fe.
1 моль серы содержит 6,02 • 1023 атомов S.
2 моль серы содержит 12,04 • 1023 атомов S.
0,5 моль серы содержит 3,01 • 1023 атомов S.
Исходя из этого, любое количество вещества можно выразить определенным числом молей ν (ню). Например, в образце вещества содержится 12,04 • 1023 молекул. Следовательно, количество вещества в этом образце составляет:
где N – число частиц данного вещества;
Nа – число частиц, которое содержит 1 моль вещества (постоянная Авогадро).
Молярная масса вещества (M) – масса, которую имеет 1 моль данного вещества.
Эта величина, равная отношению массы m вещества к количеству вещества ν, имеет размерность кг/моль или г/моль. Молярная масса, выраженная в г/моль, численно равна относительной относительной молекулярной массе Mr (для веществ атомного строения – относительной атомной массе Ar).
Например, молярная масса метана CH4 определяется следующим образом:
Мr(CH4) = Ar(C) + 4 Ar(H) = 12+4 =16
M(CH4)=16 г/моль, т.е. 16 г CH4 содержат 6,02 • 1023 молекул.
Молярную массу вещества можно вычислить, если известны его масса m и количество (число молей) ν, по формуле:
Соответственно, зная массу и молярную массу вещества, можно рассчитать число его молей:
или найти массу вещества по числу молей и молярной массе:
m = ν • M
Необходимо отметить, что значение молярной массы вещества определяется его качественным и количественным составом, т.е. зависит от Mr и Ar. Поэтому разные вещества при одинаковом количестве молей имеют различные массы m.
Пример №1. Вычислить массы метана CH4 и этана С2H6, взятых в количестве ν = 2 моль каждого.
Решение
Молярная масса метана M(CH4) равна 16 г/моль;
молярная масса этана M(С2Н6) = 2 • 12+6=30 г/моль.
Отсюда:
m(CH4) = 2 моль • 16 г/моль = 32 г;
m(С2Н6) = 2 моль • 30 г/моль = 60 г.
Таким образом, моль – это порция вещества, содержащая одно и то же число частиц, но имеющая разную массу для разных веществ, т.к. частицы вещества (атомы и молекулы) не одинаковы по массе.
n(CH4) = n(С2Н6), но m(CH4) < m(С2Н6)
Вычисление ν используется практически в каждой расчетной задаче.
Взаимосвязь:
Пример №2. Вычислите молярную массу сахара, взятого количеством вещества 2 моль и весом 684 г
Дано:
ν(сахара)=2 моль
m(сахара) =684 г
Найти: М=?
Решение:
М=m/ ν=684г/2моль=342г/моль
Ответ: М(сахара)=342г/моль
Пример №3. Вычислите массу (г) железа, взятого количеством вещества 0,5 моль?
Решение:
m = M · ν
M(Fe) = Ar(Fe) = 56 г/моль (Из периодической системы)
m (Fe) = 56 г/моль · 0,5 моль = 28 г
Ответ: m (Fe) =28 г
Пример №4. Вычислите массу (г) 12,04 · 1023 молекул оксида кальция CaО?
Дано:
N(CaO)= 12,04 * 1023 молекул
Решение:
m = M · ν,
ν= N/Na,
следовательно, формула для расчёта
m = M · (N/Na)
M(CaO) = Ar(Ca) + Ar(O) = 40 + 16 = 56 г/моль
m= 56 г/моль · (12,04 * 1023/6.02 · 1023 1/моль) = 112 г
Ответ: m=112г
Задания для закрепления
Задача 1. Вычислите массу воды (г), взятой количеством вещества 5 моль?
Задача 2. Вычислите массу 24,08 *1023 молекул серной кислоты H2SO4?
Задача 3. Определите число атомов в 56 г железа Fe?