Как правильно пишется слово «квадрокоптер»
квадроко́птер
квадроко́птер, -а
Источник: Орфографический
академический ресурс «Академос» Института русского языка им. В.В. Виноградова РАН (словарная база
2020)
Делаем Карту слов лучше вместе
Привет! Меня зовут Лампобот, я компьютерная программа, которая помогает делать
Карту слов. Я отлично
умею считать, но пока плохо понимаю, как устроен ваш мир. Помоги мне разобраться!
Спасибо! Я стал чуточку лучше понимать мир эмоций.
Вопрос: баниться — это что-то нейтральное, положительное или отрицательное?
Ассоциации к слову «квадрокоптер»
Синонимы к слову «квадрокоптер»
Предложения со словом «квадрокоптер»
- Принцип управления такой «бабочкой-такси» похож на управление квадрокоптером.
- Тётя, едва вышла из машины, тут же запустила квадрокоптер, так и что с разведкой у нас всё было на уровне.
- Мы засекли при помощи квадрокоптера в полукилометре от базы какой-то странный лагерь, в котором то ли семь человек, то ли семь зомби.
- (все предложения)
Значение слова «квадрокоптер»
-
1. авиац. беспилотный летательный аппарат с четырьмя несущими винтами, вращающимися диагонально в противоположных направлениях (Викисловарь)
Все значения слова КВАДРОКОПТЕР
Отправить комментарий
Дополнительно
Квадрокоптер — беспилотный летательный аппарат с 4 пропеллерами, что обычно размещаются по краям коптера. Русское название «квадрокоптер» — калька с английского «quadcopter«, что переводиться как 4-роторный вертолет. Примеры квадрокоптеров: DJI Inspire 1, Phantom 2 Vision Plus.
Мультикоптер — общее название для беспилотных летательных аппаратов, у которых количество пропеллеров (несущих винтов) больше, чем 2. Образовано от слов «multi» (несколько) и «copter» (вертолет).
Гексакоптер — беспилотный летательный аппарат с 6 пропеллерами, что обычно размещаются по краям коптера. Название произошло от слов «hexa» («гекса«, с древнегреческого — «шесть«) и «copter«. Пример гексакоптеров: DJI Flame Wheel ARF KIT, DJI S900.
Октокоптер — беспилотный летательный аппарат с 8 пропеллерами, что обычно размещаются по краям коптера. Название произошло от слов «octo» («окто«, с латыни — «восемь«) и «copter». Примеры октокоптеров: DJI S1000, DJI S1000 .
Коптер — сокращение от слова «helicopter«, вертолет. Используется либо по прямому назначению, либо как обозначение беспилотного летательного аппарата с n-ым количеством несущих винтов.
Дрон — беспилотный летательный аппарат. Часто это название применяется для обозначения квадрокоптеров и других мультикоптеров, что является ошибкой, поскольку дроном называются беспилотники военного назначения, внешний вид которых существенно отличается от коптеров.
Ready-to-Fly — собирательное название для мульткоптеров, что не требуют сборки. Дословно это выражение можно перевести как «готовый к полету». Как правило, для первого полета таких мультикоптеров нужно лишь зарядить аккумуляторную батарею и, в некоторых случаях, откалибровать компас.
У компании DJI Innovations есть две серии таких квадрокоптеров (Inspire и Phantom).
Flying Platform (дословно «Летающая платформа») — собирательное название для мультикоптеров, в базовом комплекте с которыми идет лишь корпус с лучами, моторы, крепления и комплект проводов. Чтоб этот коптер взлетел, к нему нужно докупать дополнительные аксессуары.
Луч — вытянутая «рука» коптера что отходит от центральной платформы. Именно на лучах крепятся пропеллеры.
Карданная подвеска/(моторизованный) шарнир — крепление и одновременно стабилизатор для камеры, что крепиться к коптеру снизу.
Центральная платформа — основа коптера, его база. К ней крепятся все остальные части: лучи, крепление для камеры, передатчики и прочее.
FPV-камера — камера, что передает видео в режиме онлайн, но которая не предназначена для записи видео. Расшифровывается как «камера от первого лица» или «камера, что позволяет смотреть от первого лица».
Фонетический (звуко-буквенный) разбор слова «квадрокоптер» – транскрипция, слоги, ударение, разбор на гласные и согласные звуки. Число букв и звуков в слове.
квадроко́птер
квадрокоптер – слово из 4 слогов: ква-дро-ко-птер. Ударение падает на 3-й слог.
Транскрипция слова: [квадракопт’ир]
к — [к] — согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый(парный)
в — [в] — согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый(парный)
а — [а] — гласный, безударный
д — [д] — согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый(парный)
р — [р] — согласный, звонкий непарный, сонорный (всегда звонкий), твёрдый(парный)
о — [а] — гласный, безударный
к — [к] — согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый(парный)
о — [о] — гласный, ударный
п — [п] — согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый(парный)
т — [т’] — согласный, глухой парный, мягкий(парный)
е — [и] — гласный, безударный
р — [р] — согласный, звонкий непарный, сонорный (всегда звонкий), твёрдый(парный)
В слове 12 букв и 12 звуков.
Цветовая схема: квадрокоптер
Всего найдено: 15
Как правильно писать слово квадрокоптер или квадракоптер?
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Верное написание: квадрокоптер.
Подскажите, пожалуйста: как правильно написать “квадрофестиваль” или “квадро-фестиваль”? Имеется в виду фестиваль, на котором будут проводиться соревнования квадроциклистов. Спасибо)
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Следует писать слитно.
Нужны ли запятые в данном предложении: Подтверждать право управления необходимо и находясь за рулём квадроцикла.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Запятые не нужны. Не обособляется деепричастный оборот, если перед ним стоит усилительная частица и.
Подскажите, пожалуйста, нужна ли запятая перед _и:
Быстрый перекур, скупое «спасибо!» и снова в путь.
На удивление быстро вытягиваем квадроцикл и снова в путь.
Спасибо!
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
В обоих случаях перед и снова в путь лучше поставить тире.
Как правильно написать: квадрацикл или квадроцикл (речь идет о мототехнике)?
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильно: квадроцикл.
Здравствуйте!
Как правильно “тетралогия фильмов” или “квадрология фильмов”? И почему?
Заранее спасибо!
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Здесь используются греческие, а не латинские корни: монолог, диалог; дилогия, трилогия, тетралогия.
Подскажите, пожалуйста, как написать правильно слово квадрОцикл или квадрАцикл или?
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильно: квадроцикл.
Как называют “комплект” из четыре и пяти фильмов: из двух – дилогия, из трех – трилогия, из четырех – квадрология (?), из пяти – квантология, квантилогия, квинтология, кванталогия??? Или по-другому?
Подскажите, пожалуйста! Срочно, для газеты!
Спасибо!!!
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Вероятно, нужные слова – тетралогия, пенталогия.
Скажите, как правильно писать: квадрОцикл или квадрАцикл?
Спасибо.
Юлия.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
См. ответ на вопрос № 240491.
Будьте добры, подскажите, как пишется слово квадра/оцикл. Сейчас каждый пишет, как ему больше нравится.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильно: квадроцикл.
Здравствуйте! Ни в одном словаре не смогли найти слово “квадрацикл”. Или все-таки “квадрОцикл”? Как же писать правильно?
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильно: квадроцикл и квадрицикл.
Первый автомобиль, созданный Генри Фордом, назывался квадрицикл (от англ. bicycle “велосипед”; название связано с тем, что квадрицикл передвигался на четырех велосипедных колесах).
Современные мотовездеходы имеют название квадроцикл.
Здравствуйте! Как правильно: квадрацикл или квадроцикл?
Спасибо.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильно: квадроцикл и квадрицикл.
Первый автомобиль, созданный Генри Фордом, назывался квадрицикл (от англ. bicycle “велосипед”; название связано с тем, что квадрицикл передвигался на четырех велосипедных колесах).
Современные мотовездеходы имеют название квадроцикл.
Здравствуйте! Подскажите, пожалуйста, как правильно писать: квадрацикл или квадроцикл? Спасибо.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
См. в «Непростых словах».
Добрый день! Скажите, пожалуйста, как правильно пишется слово квадрАцикл или квадрОцикл? Это от слова квадра – четыре?
Спасибо.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
См. http://spravka.gramota.ru/hardwords.html?no=262&_sf=40 [«Непростые слова»].
Как правильно пишется слово “квадра/о/цикл”?
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильно: квадроцикл.
Первый автомобиль, созданный Генри Фордом, назывался квадрицикл (от англ. bicycle “велосипед”; название связано с тем, что квадрицикл передвигался на четырех велосипедных колесах). Современные мотовездеходы имеют название квадроцикл.
Еще одно родственное транспортное средство – квадрига. Это античная (древнегреческая, римская) колесница на двух колёсах, запряжённая четвёркой лошадей, расположенных в один ряд.
A quadcopter or quadrotor[1] is a type of helicopter with four rotors.[2]
Although quadrotor helicopters and convertiplanes have long been flown experimentally, the configuration remained a curiosity until the arrival of the modern UAV or drone. The small size and low inertia of drones allows use of a particularly simple flight control system, which has greatly increased the practicality of the small quadrotor in this application.
Design principles
Each rotor produces both lift and torque about its center of rotation, as well as drag opposite to the vehicle’s direction of flight.
Quadcopters generally have two rotors spinning clockwise (CW) and two counterclockwise (CCW). Flight control is provided by independent variation of the speed and hence lift and torque of each rotor. Pitch and roll are controlled by varying the net centre of thrust, with yaw controlled by varying the net torque.[3]
Unlike conventional helicopters, quadcopters do not usually have cyclic pitch control, in which the angle of the blades varies dynamically as they turn around the rotor hub. In the early days of flight, quadcopters (then referred to either as ‘quadrotors’ or simply as ‘helicopters’) were seen as a possible solution to some of the persistent problems in vertical flight. Torque-induced control issues (as well as efficiency issues originating from the tail rotor, which generates no useful lift) can be eliminated by counter-rotation, and the relatively short blades are much easier to construct. A number of manned designs appeared in the 1920s and 1930s. These vehicles were among the first successful heavier-than-air vertical take off and landing (VTOL) vehicles.[4] However, early prototypes suffered from poor performance,[4] and latter prototypes required too much pilot work load, due to poor stability augmentation[5] and limited control authority.
Torque
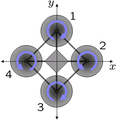
If all four rotors are spinning at the same angular velocity, with two rotating clockwise and two counterclockwise, the net torque about the yaw axis is zero, which means there is no need for a tail rotor as on conventional helicopters. Yaw is induced by mismatching the balance in aerodynamic torques (i.e., by offsetting the cumulative thrust commands between the counter-rotating blade pairs).[6][7]
-
Schematic of reaction torques on each motor of a quadcopter aircraft, due to spinning rotors. Rotors 1 and 3 spin in one direction, while rotors 2 and 4 spin in the opposite direction, yielding opposing torques for control.
-
A quadrotor hovers or adjusts its altitude by applying equal thrust to all four rotors.
-
A quadrotor adjusts its yaw by applying more thrust to rotors rotating in one direction.
-
A quadrotor adjusts its pitch or roll by applying more thrust to one rotor (or two adjacent rotors) and less thrust to the diametrically opposite rotor.
Vortex ring state
All quadcopters are subject to normal rotorcraft aerodynamics, including the vortex ring state.[citation needed]
Mechanical structure
The main mechanical components are a fuselage or frame, the four rotors (either fixed-pitch or variable-pitch), and motors. For best performance and simplest control algorithms, the motors and propellers are equidistant.[8]
Coaxial rotors
In order to allow more power and stability at reduced weight, a quadcopter, like any other multirotor can employ a coaxial rotor configuration. In this case, each arm has two motors running in opposite directions (one facing up and one facing down).[citation needed]
Operations
Autonomous flight
The quadcopter configuration is relatively simple to program for autonomous flight. This has allowed experiments with complex swarming behaviour based on basic sensing of the adjacent drones.[citation needed]
Endurance
The longest flight time achieved by a battery-powered quadcopter was 2 hours, 31 minutes and 30 seconds. The record was set by Ferdinand Kickinger of Germany in 2016.[9] In setting the record, Kickinger used low discharge-rate, high-capacity lithium-ion batteries and stripped the airframe of non-essential weight to reduce power draw and extend endurance.[10]
Alternative power sources like hydrogen fuel cells and hybrid gas-electric generators have been used to dramatically extend endurance because of the increased energy density of both hydrogen and gasoline, respectively.[11]
History
Pioneers
The first heavier-than-air aerodyne to take off vertically was a four-rotor helicopter designed by Louis Breguet. It was tested only in tethered flight and to an altitude of a few feet. In 1908 it was reported as having flown ‘several times’, although details are sparse.[12]
Etienne Oehmichen experimented with rotorcraft designs in the 1920s. Among the designs he tried, his helicopter No.2 had four rotors and eight propellers, all driven by a single engine. The Oehmichen No.2 used a steel-tube frame, with two-bladed rotors at the ends of the four arms. The angle of these blades could be varied by warping. Five of the propellers, spinning in the horizontal plane, stabilized the machine laterally. Another propeller was mounted at the nose for steering. The remaining pair of propellers functioned as its forward propulsion. The aircraft exhibited a considerable degree of stability and increase in control-accuracy for its time, and made over a thousand test flights during the middle 1920s. By 1923 it was able to remain airborne for several minutes at a time, and on April 14, 1924 it established the first-ever FAI distance record for helicopters of 360 m (390 yd). It demonstrated the ability to complete a circular course[13] and later, it completed the first 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) closed-circuit flight by a rotorcraft.
Dr. George de Bothezat and Ivan Jerome developed the de Bothezat helicopter, with six-bladed rotors at the end of an X-shaped structure. Two small propellers with variable pitch were used for thrust and yaw control. The vehicle used collective pitch control. Built by the US Air Service, it made its first flight in October 1922. About 100 flights were made by the end of 1923. The highest it ever reached was about 5 m (16 ft 5 in). Although demonstrating feasibility, it was underpowered, unresponsive, mechanically complex and susceptible to reliability problems. Pilot workload was too high during hover to attempt lateral motion.
Postwar era
The Convertawings Model A Quadrotor was intended to be the prototype for a line of much larger civil and military helicopters. The design featured two engines driving four rotors through a system of v belts. No tail rotor was needed and control was obtained by varying the thrust between rotors.[14] Flown many times from 1956, this helicopter proved the quadrotor design and it was also the first four-rotor helicopter to demonstrate successful forward flight. Due to a lack of orders for commercial or military versions however, the project was terminated. Convertawings proposed a Model E that would have a maximum weight of 42,000 lb (19 t) with a payload of 10,900 lb (4.9 t) over 300 miles and at up to 173 mph (278 km/h). The Hanson Elastic Articulated (EA) bearingless rotor grew out of work done in the early 1960s at Lockheed California by Thomas F. Hanson, who had previously worked at Convertawings on the quadrotor’s rotor design and control system.[15][16]
The Gloster Crop Sprayer project of 1960 was an early example of a quadcopter drone. To be powered by a 105 hp Potez 4E air-cooled flat four-cylinder engine, its 20 gal payload was discharged through a 22 ft spray boom. Two operators carried homing beacons at opposite ends of the spray run, so that the quadcopter would always home in on a beacon and not overshoot. However, despite the much simplified design and operational requirements compared to a piloted machine, the parent company board refused to develop it and it remained a paper project.[17]
The Curtiss-Wright VZ-7 of 1958 was a VTOL aircraft designed by Curtiss-Wright in competition for the US Army Transport and Research Command «flying jeep». The VZ-7 was controlled by changing the thrust of each of the four ducted fan rotors.
The Piasecki PA-97 was a proposal for a large hybrid aircraft in which four helicopter fuselages were combined with a lighter-than-air airship in the 1980s.
Current developments
The Bell Boeing Quad TiltRotor concept takes the fixed quadcopter concept further by combining it with the tilt rotor concept for a proposed C-130 sized military transport.
Airbus is developing a battery-powered quadcopter to act as an urban air taxi, at first with a pilot but potentially autonomous in the future.[18]
Drones
FPV «whoop» drones can be as light as 30 grams
In the first decades of the 2000s, the quadcopter layout has become popular for small-scale unmanned aerial vehicles or drones. The need for aircraft with greater maneuverability and hovering ability has led to a rise in quadcopter research. The four-rotor design allows quadcopters to be relatively simple in design yet highly reliable and maneuverable. Research is continuing to increase the abilities of quadcopters by making advances in multi-craft communication, environment exploration, and maneuverability. If these developing qualities can be combined, quadcopters would be capable of advanced autonomous missions that are currently not possible with other vehicles.[19]
While small toy remote-controlled quadcopters were produced in Japan already in the early 1990s, the first one with a camera to be produced in significant quantities (Draganflyer Stabilized Aerial Video System, retrospectively also Draganflyer I, by Canadian start-up Draganfly) was not designed until 1999.[20][21]
Around 2005 to 2010, advances in electronics allowed the production of cheap lightweight flight controllers, accelerometers (IMU), global positioning system and cameras. This resulted in the quadcopter configuration becoming popular for small unmanned aerial vehicles. With their small size and maneuverability, these quadcopters can be flown indoors as well as outdoors.[1][22]
For small drones, quadcopters are cheaper and more durable than conventional helicopters due to their mechanical simplicity.[23] Their smaller blades are also advantageous because they possess less kinetic energy, reducing their ability to cause damage. For small-scale quadcopters, this makes the vehicles safer for close interaction. It is also possible to fit quadcopters with guards that enclose the rotors, further reducing the potential for damage.[2] However, as size increases, fixed propeller quadcopters develop disadvantages relative to conventional helicopters. Increasing blade size increases their momentum. This means that changes in blade speed take longer, which negatively impacts control. Helicopters do not experience this problem as increasing the size of the rotor disk does not significantly impact the ability to control blade pitch.
Due to their ease of construction and control, quadcopters are popular as amateur model aircraft projects.[24][25]
Criminal activity
Throughout the 21st century, there have been reported cases of quadcopter drones being used for criminal activity. Due to the construction of the Mexico–United States border wall, some drug cartels have resorted to the use of quadcopters to smuggle drugs.[26] However, quadcopter drones do not necessarily only smuggle drugs across the border, but there are also cases where weapons and other prohibited items are smuggled into prisons around the world.[27]
Quadcopter drone crime is also occurring in Europe. In August 2021, a police officer in the Czech Republic seized a quadcopter that was transporting a sachet of methamphetamine.[28]
See also
- AeroVelo Atlas (2013) human-powered helicopter
- Modular design
References
- ^ a b Hoffmann, G.M.; Rajnarayan, D.G.; Waslander, S.L.; Dostal, D.; Jang, J.S.; Tomlin, C.J. (November 2004). «The Stanford Testbed of Autonomous Rotorcraft for Multi Agent Control (STARMAC)». In the Proceedings of the 23rd Digital Avionics System Conference. Salt Lake City, UT. pp. 12.E.4/1–10. doi:10.1109/DASC.2004.1390847. ISBN 0-7803-8539-X.
- ^ a b Hoffman, G.; Huang, H.; Waslander, S.L.; Tomlin, C.J. (20–23 August 2007). «Quadrotor Helicopter Flight Dynamics and Control: Theory and Experiment» (PDF). In the Conference of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. Hilton Head, South Carolina. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 August 2010.
- ^ Stafford, Jesse (Spring 2014). «How a Quadcopter works | Clay Allen». University of Alaska, Fairbanks. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ a b Leishman, J.G. (2000). Principles of Helicopter Aerodynamics. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521858601.
- ^ Anderson, S.B. (1997). «Historical Overview of V/STOL Aircraft Technology». NASA Technical Memorandum 81280.
- ^ «Quadrotor». Archived from the original on 27 December 2014. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Andrew Hobden. «Quadcopters: Yaw». hoverbear.org. Retrieved 3 April 2017.
- ^ Uriah (13 April 2010). «Wyvern Quadrotor Helicopter». Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Ferdinand Kickinger (30 April 2016), 151min30s FPV with Copter, archived from the original on 22 December 2021, retrieved 26 August 2018
- ^ SPK Drones. How Quadcopters Fly.
- ^ McNabb, Miriam (February 2018). US Manufacturer Harris Aerial Launches New Hybrid Gas Electric Drone. Dronelife
- ^ Young, Warren R. (1982). The Helicopters. The Epic of Flight. Chicago: Time-Life Books. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-8094-3350-6.
- ^ «A Successful French Helicopter» Flight 24 January 1924 p47
- ^ «1956 — 1564 — Flight Archive». flightglobal.com. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ «Patent US3261407 — Helicopter rotor system». google.com. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ Inan, Esin; Kiris, Ahmet (20 January 2007). The Seventh International Conference on Vibration Problems ICOVP 2005. ISBN 9781402054013. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ James, Derek N.; Gloster Aircraft Since 1917, Putnam, 1971, p.413.
- ^ «Airbus on track to fly its electric aerial taxi in 2018».
- ^ «Illumin — The Quadrotor’s Coming of Age». Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Darack, Ed. «A Brief History of Quadrotors». Air & Space Magazine.
- ^ «Our Story | Draganfly». draganfly.com. Archived from the original on 12 December 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ Büchi, Roland (2011). Fascination Quadrocopter. ISBN 978-3-8423-6731-9.
- ^ Pounds, P.; Mahony, R.; Corke, P. (December 2006). «Modelling and Control of a Quad-Rotor Robot» (PDF). In the Proceedings of the Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation. Auckland, New Zealand.
- ^ «How-To: Quadrocopter based on Arduino». MAKE. Archived from the original on 11 December 2011. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ «FrontPage — UAVP-NG — The Open Source Next Generation Multicopter». Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ «Drug smugglers turn to drones, advancing operations». DroneDJ. 21 December 2020. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ «Věznice | EAGLE.ONE». Eagle.One (in Czech). Retrieved 10 August 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Pokorný, Petr (10 August 2021). «Strážník v Doksech rukama chytil neregistrovaný dron, který přenášel pervitin». Českolipský deník (in Czech). Retrieved 10 August 2021.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Quadrotors.
- UPenn GRASP Laboratory Archived 2015-04-20 at the Wayback Machine
- ETH Zurich Research on Quadrotors
- FAA UAS Model Aircraft Operations safety guidelines
- TED Raffaello D’Andrea: The astounding athletic power of quadcopters
A quadcopter or quadrotor[1] is a type of helicopter with four rotors.[2]
Although quadrotor helicopters and convertiplanes have long been flown experimentally, the configuration remained a curiosity until the arrival of the modern UAV or drone. The small size and low inertia of drones allows use of a particularly simple flight control system, which has greatly increased the practicality of the small quadrotor in this application.
Design principles
Each rotor produces both lift and torque about its center of rotation, as well as drag opposite to the vehicle’s direction of flight.
Quadcopters generally have two rotors spinning clockwise (CW) and two counterclockwise (CCW). Flight control is provided by independent variation of the speed and hence lift and torque of each rotor. Pitch and roll are controlled by varying the net centre of thrust, with yaw controlled by varying the net torque.[3]
Unlike conventional helicopters, quadcopters do not usually have cyclic pitch control, in which the angle of the blades varies dynamically as they turn around the rotor hub. In the early days of flight, quadcopters (then referred to either as ‘quadrotors’ or simply as ‘helicopters’) were seen as a possible solution to some of the persistent problems in vertical flight. Torque-induced control issues (as well as efficiency issues originating from the tail rotor, which generates no useful lift) can be eliminated by counter-rotation, and the relatively short blades are much easier to construct. A number of manned designs appeared in the 1920s and 1930s. These vehicles were among the first successful heavier-than-air vertical take off and landing (VTOL) vehicles.[4] However, early prototypes suffered from poor performance,[4] and latter prototypes required too much pilot work load, due to poor stability augmentation[5] and limited control authority.
Torque
If all four rotors are spinning at the same angular velocity, with two rotating clockwise and two counterclockwise, the net torque about the yaw axis is zero, which means there is no need for a tail rotor as on conventional helicopters. Yaw is induced by mismatching the balance in aerodynamic torques (i.e., by offsetting the cumulative thrust commands between the counter-rotating blade pairs).[6][7]
-
Schematic of reaction torques on each motor of a quadcopter aircraft, due to spinning rotors. Rotors 1 and 3 spin in one direction, while rotors 2 and 4 spin in the opposite direction, yielding opposing torques for control.
-
A quadrotor hovers or adjusts its altitude by applying equal thrust to all four rotors.
-
A quadrotor adjusts its yaw by applying more thrust to rotors rotating in one direction.
-
A quadrotor adjusts its pitch or roll by applying more thrust to one rotor (or two adjacent rotors) and less thrust to the diametrically opposite rotor.
Vortex ring state
All quadcopters are subject to normal rotorcraft aerodynamics, including the vortex ring state.[citation needed]
Mechanical structure
The main mechanical components are a fuselage or frame, the four rotors (either fixed-pitch or variable-pitch), and motors. For best performance and simplest control algorithms, the motors and propellers are equidistant.[8]
Coaxial rotors
In order to allow more power and stability at reduced weight, a quadcopter, like any other multirotor can employ a coaxial rotor configuration. In this case, each arm has two motors running in opposite directions (one facing up and one facing down).[citation needed]
Operations
Autonomous flight
The quadcopter configuration is relatively simple to program for autonomous flight. This has allowed experiments with complex swarming behaviour based on basic sensing of the adjacent drones.[citation needed]
Endurance
The longest flight time achieved by a battery-powered quadcopter was 2 hours, 31 minutes and 30 seconds. The record was set by Ferdinand Kickinger of Germany in 2016.[9] In setting the record, Kickinger used low discharge-rate, high-capacity lithium-ion batteries and stripped the airframe of non-essential weight to reduce power draw and extend endurance.[10]
Alternative power sources like hydrogen fuel cells and hybrid gas-electric generators have been used to dramatically extend endurance because of the increased energy density of both hydrogen and gasoline, respectively.[11]
History
Pioneers
The first heavier-than-air aerodyne to take off vertically was a four-rotor helicopter designed by Louis Breguet. It was tested only in tethered flight and to an altitude of a few feet. In 1908 it was reported as having flown ‘several times’, although details are sparse.[12]
Etienne Oehmichen experimented with rotorcraft designs in the 1920s. Among the designs he tried, his helicopter No.2 had four rotors and eight propellers, all driven by a single engine. The Oehmichen No.2 used a steel-tube frame, with two-bladed rotors at the ends of the four arms. The angle of these blades could be varied by warping. Five of the propellers, spinning in the horizontal plane, stabilized the machine laterally. Another propeller was mounted at the nose for steering. The remaining pair of propellers functioned as its forward propulsion. The aircraft exhibited a considerable degree of stability and increase in control-accuracy for its time, and made over a thousand test flights during the middle 1920s. By 1923 it was able to remain airborne for several minutes at a time, and on April 14, 1924 it established the first-ever FAI distance record for helicopters of 360 m (390 yd). It demonstrated the ability to complete a circular course[13] and later, it completed the first 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) closed-circuit flight by a rotorcraft.
Dr. George de Bothezat and Ivan Jerome developed the de Bothezat helicopter, with six-bladed rotors at the end of an X-shaped structure. Two small propellers with variable pitch were used for thrust and yaw control. The vehicle used collective pitch control. Built by the US Air Service, it made its first flight in October 1922. About 100 flights were made by the end of 1923. The highest it ever reached was about 5 m (16 ft 5 in). Although demonstrating feasibility, it was underpowered, unresponsive, mechanically complex and susceptible to reliability problems. Pilot workload was too high during hover to attempt lateral motion.
Postwar era
The Convertawings Model A Quadrotor was intended to be the prototype for a line of much larger civil and military helicopters. The design featured two engines driving four rotors through a system of v belts. No tail rotor was needed and control was obtained by varying the thrust between rotors.[14] Flown many times from 1956, this helicopter proved the quadrotor design and it was also the first four-rotor helicopter to demonstrate successful forward flight. Due to a lack of orders for commercial or military versions however, the project was terminated. Convertawings proposed a Model E that would have a maximum weight of 42,000 lb (19 t) with a payload of 10,900 lb (4.9 t) over 300 miles and at up to 173 mph (278 km/h). The Hanson Elastic Articulated (EA) bearingless rotor grew out of work done in the early 1960s at Lockheed California by Thomas F. Hanson, who had previously worked at Convertawings on the quadrotor’s rotor design and control system.[15][16]
The Gloster Crop Sprayer project of 1960 was an early example of a quadcopter drone. To be powered by a 105 hp Potez 4E air-cooled flat four-cylinder engine, its 20 gal payload was discharged through a 22 ft spray boom. Two operators carried homing beacons at opposite ends of the spray run, so that the quadcopter would always home in on a beacon and not overshoot. However, despite the much simplified design and operational requirements compared to a piloted machine, the parent company board refused to develop it and it remained a paper project.[17]
The Curtiss-Wright VZ-7 of 1958 was a VTOL aircraft designed by Curtiss-Wright in competition for the US Army Transport and Research Command «flying jeep». The VZ-7 was controlled by changing the thrust of each of the four ducted fan rotors.
The Piasecki PA-97 was a proposal for a large hybrid aircraft in which four helicopter fuselages were combined with a lighter-than-air airship in the 1980s.
Current developments
The Bell Boeing Quad TiltRotor concept takes the fixed quadcopter concept further by combining it with the tilt rotor concept for a proposed C-130 sized military transport.
Airbus is developing a battery-powered quadcopter to act as an urban air taxi, at first with a pilot but potentially autonomous in the future.[18]
Drones
FPV «whoop» drones can be as light as 30 grams
In the first decades of the 2000s, the quadcopter layout has become popular for small-scale unmanned aerial vehicles or drones. The need for aircraft with greater maneuverability and hovering ability has led to a rise in quadcopter research. The four-rotor design allows quadcopters to be relatively simple in design yet highly reliable and maneuverable. Research is continuing to increase the abilities of quadcopters by making advances in multi-craft communication, environment exploration, and maneuverability. If these developing qualities can be combined, quadcopters would be capable of advanced autonomous missions that are currently not possible with other vehicles.[19]
While small toy remote-controlled quadcopters were produced in Japan already in the early 1990s, the first one with a camera to be produced in significant quantities (Draganflyer Stabilized Aerial Video System, retrospectively also Draganflyer I, by Canadian start-up Draganfly) was not designed until 1999.[20][21]
Around 2005 to 2010, advances in electronics allowed the production of cheap lightweight flight controllers, accelerometers (IMU), global positioning system and cameras. This resulted in the quadcopter configuration becoming popular for small unmanned aerial vehicles. With their small size and maneuverability, these quadcopters can be flown indoors as well as outdoors.[1][22]
For small drones, quadcopters are cheaper and more durable than conventional helicopters due to their mechanical simplicity.[23] Their smaller blades are also advantageous because they possess less kinetic energy, reducing their ability to cause damage. For small-scale quadcopters, this makes the vehicles safer for close interaction. It is also possible to fit quadcopters with guards that enclose the rotors, further reducing the potential for damage.[2] However, as size increases, fixed propeller quadcopters develop disadvantages relative to conventional helicopters. Increasing blade size increases their momentum. This means that changes in blade speed take longer, which negatively impacts control. Helicopters do not experience this problem as increasing the size of the rotor disk does not significantly impact the ability to control blade pitch.
Due to their ease of construction and control, quadcopters are popular as amateur model aircraft projects.[24][25]
Criminal activity
Throughout the 21st century, there have been reported cases of quadcopter drones being used for criminal activity. Due to the construction of the Mexico–United States border wall, some drug cartels have resorted to the use of quadcopters to smuggle drugs.[26] However, quadcopter drones do not necessarily only smuggle drugs across the border, but there are also cases where weapons and other prohibited items are smuggled into prisons around the world.[27]
Quadcopter drone crime is also occurring in Europe. In August 2021, a police officer in the Czech Republic seized a quadcopter that was transporting a sachet of methamphetamine.[28]
See also
- AeroVelo Atlas (2013) human-powered helicopter
- Modular design
References
- ^ a b Hoffmann, G.M.; Rajnarayan, D.G.; Waslander, S.L.; Dostal, D.; Jang, J.S.; Tomlin, C.J. (November 2004). «The Stanford Testbed of Autonomous Rotorcraft for Multi Agent Control (STARMAC)». In the Proceedings of the 23rd Digital Avionics System Conference. Salt Lake City, UT. pp. 12.E.4/1–10. doi:10.1109/DASC.2004.1390847. ISBN 0-7803-8539-X.
- ^ a b Hoffman, G.; Huang, H.; Waslander, S.L.; Tomlin, C.J. (20–23 August 2007). «Quadrotor Helicopter Flight Dynamics and Control: Theory and Experiment» (PDF). In the Conference of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. Hilton Head, South Carolina. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 August 2010.
- ^ Stafford, Jesse (Spring 2014). «How a Quadcopter works | Clay Allen». University of Alaska, Fairbanks. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ a b Leishman, J.G. (2000). Principles of Helicopter Aerodynamics. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521858601.
- ^ Anderson, S.B. (1997). «Historical Overview of V/STOL Aircraft Technology». NASA Technical Memorandum 81280.
- ^ «Quadrotor». Archived from the original on 27 December 2014. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Andrew Hobden. «Quadcopters: Yaw». hoverbear.org. Retrieved 3 April 2017.
- ^ Uriah (13 April 2010). «Wyvern Quadrotor Helicopter». Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Ferdinand Kickinger (30 April 2016), 151min30s FPV with Copter, archived from the original on 22 December 2021, retrieved 26 August 2018
- ^ SPK Drones. How Quadcopters Fly.
- ^ McNabb, Miriam (February 2018). US Manufacturer Harris Aerial Launches New Hybrid Gas Electric Drone. Dronelife
- ^ Young, Warren R. (1982). The Helicopters. The Epic of Flight. Chicago: Time-Life Books. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-8094-3350-6.
- ^ «A Successful French Helicopter» Flight 24 January 1924 p47
- ^ «1956 — 1564 — Flight Archive». flightglobal.com. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ «Patent US3261407 — Helicopter rotor system». google.com. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ Inan, Esin; Kiris, Ahmet (20 January 2007). The Seventh International Conference on Vibration Problems ICOVP 2005. ISBN 9781402054013. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ James, Derek N.; Gloster Aircraft Since 1917, Putnam, 1971, p.413.
- ^ «Airbus on track to fly its electric aerial taxi in 2018».
- ^ «Illumin — The Quadrotor’s Coming of Age». Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Darack, Ed. «A Brief History of Quadrotors». Air & Space Magazine.
- ^ «Our Story | Draganfly». draganfly.com. Archived from the original on 12 December 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ Büchi, Roland (2011). Fascination Quadrocopter. ISBN 978-3-8423-6731-9.
- ^ Pounds, P.; Mahony, R.; Corke, P. (December 2006). «Modelling and Control of a Quad-Rotor Robot» (PDF). In the Proceedings of the Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation. Auckland, New Zealand.
- ^ «How-To: Quadrocopter based on Arduino». MAKE. Archived from the original on 11 December 2011. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ «FrontPage — UAVP-NG — The Open Source Next Generation Multicopter». Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ «Drug smugglers turn to drones, advancing operations». DroneDJ. 21 December 2020. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ «Věznice | EAGLE.ONE». Eagle.One (in Czech). Retrieved 10 August 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Pokorný, Petr (10 August 2021). «Strážník v Doksech rukama chytil neregistrovaný dron, který přenášel pervitin». Českolipský deník (in Czech). Retrieved 10 August 2021.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Quadrotors.
- UPenn GRASP Laboratory Archived 2015-04-20 at the Wayback Machine
- ETH Zurich Research on Quadrotors
- FAA UAS Model Aircraft Operations safety guidelines
- TED Raffaello D’Andrea: The astounding athletic power of quadcopters
Разбор слова «квадрокоптер»: для переноса, на слоги, по составу
Объяснение правил деление (разбивки) слова «квадрокоптер» на слоги для переноса.
Онлайн словарь Soosle.ru поможет: фонетический и морфологический разобрать слово «квадрокоптер» по составу, правильно делить на слоги по провилам русского языка, выделить части слова, поставить ударение, укажет значение, синонимы, антонимы и сочетаемость к слову «квадрокоптер».
Содержимое:
- 1 Слоги в слове «квадрокоптер» деление на слоги
- 2 Как перенести слово «квадрокоптер»
- 3 Ударение в слове «квадрокоптер»
- 4 Фонетическая транскрипция слова «квадрокоптер»
- 5 Фонетический разбор слова «квадрокоптер» на буквы и звуки (Звуко-буквенный)
- 6 Предложения со словом «квадрокоптер»
- 7 Значение слова «квадрокоптер»
- 8 Как правильно пишется слово «квадрокоптер»
Слоги в слове «квадрокоптер» деление на слоги
Количество слогов: 4
По слогам: ква-дро-ко-птер
По правилам школьной программы слово «квадрокоптер» можно поделить на слоги разными способами. Допускается вариативность, то есть все варианты правильные. Например, такой:
квад-ро-коп-тер
По программе института слоги выделяются на основе восходящей звучности:
ква-дро-ко-птер
Ниже перечислены виды слогов и объяснено деление с учётом программы института и школ с углублённым изучением русского языка.
д примыкает к этому слогу, а не к предыдущему, так как не является сонорной (непарной звонкой согласной)
п примыкает к этому слогу, а не к предыдущему, так как не является сонорной (непарной звонкой согласной)
Как перенести слово «квадрокоптер»
ква—дрокоптер
квад—рокоптер
квадро—коптер
квадроко—птер
квадрокоп—тер
Ударение в слове «квадрокоптер»
квадроко́птер — ударение падает на 3-й слог
Фонетическая транскрипция слова «квадрокоптер»
[квадрак`опт’ир]
Фонетический разбор слова «квадрокоптер» на буквы и звуки (Звуко-буквенный)
| Буква | Звук | Характеристики звука | Цвет |
|---|---|---|---|
| к | [к] | согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый, шумный | к |
| в | [в] | согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый, шумный | в |
| а | [а] | гласный, безударный | а |
| д | [д] | согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый, шумный | д |
| р | [р] | согласный, звонкий непарный (сонорный), твёрдый | р |
| о | [а] | гласный, безударный | о |
| к | [к] | согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый, шумный | к |
| о | [`о] | гласный, ударный | о |
| п | [п] | согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый, шумный | п |
| т | [т’] | согласный, глухой парный, мягкий, шумный | т |
| е | [и] | гласный, безударный | е |
| р | [р] | согласный, звонкий непарный (сонорный), твёрдый | р |
Число букв и звуков:
На основе сделанного разбора делаем вывод, что в слове 12 букв и 12 звуков.
Буквы: 4 гласных буквы, 8 согласных букв.
Звуки: 4 гласных звука, 8 согласных звуков.
Предложения со словом «квадрокоптер»
Один из них запустил квадрокоптер с видеокамерой, которым часто пользовались для разведки.
Источник: И. Я. Негатин, Экспедитор, 2016.
И ещё там собирают и запускают квадрокоптеры!
Источник: Вольфганг Хекль, Новая жизнь старых вещей, 2013.
Значение слова «квадрокоптер»
1. авиац. беспилотный летательный аппарат с четырьмя несущими винтами, вращающимися диагонально в противоположных направлениях (Викисловарь)
Как правильно пишется слово «квадрокоптер»
Правописание слова «квадрокоптер»
Орфография слова «квадрокоптер»
Правильно слово пишется:
Нумерация букв в слове
Номера букв в слове «квадрокоптер» в прямом и обратном порядке:
Разбор слова «квадрокоптер»: для переноса, на слоги, по составу
Объяснение правил деление (разбивки) слова «квадрокоптер» на слоги для переноса.
Онлайн словарь Soosle.ru поможет: фонетический и морфологический разобрать слово «квадрокоптер» по составу, правильно делить на слоги по провилам русского языка, выделить части слова, поставить ударение, укажет значение, синонимы, антонимы и сочетаемость к слову «квадрокоптер».
Слоги в слове «квадрокоптер» деление на слоги
По правилам школьной программы слово «квадрокоптер» можно поделить на слоги разными способами. Допускается вариативность, то есть все варианты правильные. Например, такой:
квад-ро-коп-тер
По программе института слоги выделяются на основе восходящей звучности:
ква-дро-ко-птер
Ниже перечислены виды слогов и объяснено деление с учётом программы института и школ с углублённым изучением русского языка.
Как перенести слово «квадрокоптер»
Ударение в слове «квадрокоптер»
Фонетическая транскрипция слова «квадрокоптер»
Фонетический разбор слова «квадрокоптер» на буквы и звуки (Звуко-буквенный)
| Буква | Звук | Характеристики звука | Цвет |
|---|---|---|---|
| к | [ к ] | согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый, шумный | к |
| в | [ в ] | согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый, шумный | в |
| а | [ а ] | гласный, безударный | а |
| д | [ д ] | согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый, шумный | д |
| р | [ р ] | согласный, звонкий непарный (сонорный) , твёрдый | р |
| о | [ а ] | гласный, безударный | о |
| к | [ к ] | согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый, шумный | к |
| о | [ `о ] | гласный, ударный | о |
| п | [ п ] | согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый, шумный | п |
| т | [ т’ ] | согласный, глухой парный, мягкий, шумный | т |
| е | [ и ] | гласный, безударный | е |
| р | [ р ] | согласный, звонкий непарный (сонорный) , твёрдый | р |
Число букв и звуков:
На основе сделанного разбора делаем вывод, что в слове 12 букв и 12 звуков.
Буквы: 4 гласных буквы, 8 согласных букв.
Звуки: 4 гласных звука, 8 согласных звуков.
Фонетический разбор «квадрокоптер»
квадрокоптер — слово из 4 слогов: ква-дро-ко-птер. Ударение падает на 3-й слог.
Транскрипция слова: [квадракопт’ир]
к — [ к ] — согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый (парный)
в — [ в ] — согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый (парный)
а — [ а ] — гласный , безударный
д — [ д ] — согласный, звонкий парный, твёрдый (парный)
р — [ р ] — согласный, звонкий непарный, сонорный (всегда звонкий) , твёрдый (парный)
о — [ а ] — гласный , безударный
к — [ к ] — согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый (парный)
о — [ о ] — гласный , ударный
п — [ п ] — согласный, глухой парный, твёрдый (парный)
т — [ т’ ] — согласный, глухой парный, мягкий (парный)
е — [ и ] — гласный , безударный
р — [ р ] — согласный, звонкий непарный, сонорный (всегда звонкий) , твёрдый (парный)
В слове 12 букв и 12 звуков.
Цветовая схема: к в а д р о к о п т е р
Разбор сделан с помощью программы и не всегда может быть правильным. Представленный результат используйте исключительно для самопроверки.
Слова с буквой ё обязательно пишите через ё. Фонетические разборы слов «все» и «всё» будут разными!
Примеры других слов с разборами на буквы и звуки:
Рифма к слову квадроко́птер
Наиболее точные рифмы для «квадроко́птер»
- наш ё птан
- о бдал
- зат о птан
- о птик
- раст о птан
- заш ё птан
- т о птан
- приспос о бьте
- о птом
- ист о птан
- озл о бьте
- http://rifme.net/
- спод о бьтесь
- покор о бьте
- прот о птан
- упод о бьтесь
- о пта
- ст о птан
- угр о бьте
- ш ё птан
- син о птик
Менее строгие рифмы к слову квадрокоптер
- мотор о ллер
- комп о стер
- контр о ллер
- трансф о рмер
- п о ттер
- пр о пер
- кандиб о бер
- п о ртер
- р о кер
- т о стер
- Ассонансы
- п о кер
- п о стер
- д о кер
- бр о кер
- о тпер
- р о вер
- р о джер
- ч о ппер
- пул о вер
- газг о льдер
- дж о кер
- о рдер
- сп о йлер
- л о бстер
- о тмер
- р о ллер
- бр о йлер
- о вер
- к о лер
- т о ллер
- ш о кер
- п о хер
- п о зер
- ч о кер
- бульд о зер
- п о мер
- о пер
- в ё дер
- о бмер
- б о йлер
- б о мбер
- бл о гер
- с ё рфер
- б ё дер
- р ё бер
- н о мер
- д о пуск
- небоскр ё ба
- д о блесть
- х о бби
- шл ё пай
- озн о ба
- подс о бен
- зак о пан
- ок о па
- д о пил
- т о пчем
- к о пим
- п о прищ
- т о поль
- гардер о ба
- ут о пим
- ск о бка
- похл о пай
- работоспос о бность
- конкурентоспос о бность
- т о пай
- сугр о ба
- нед о бро
- неспос о бен
- захл о пнем
- о быск
- т о пим
- к о пан
- тр о пы
- о бщность
- п о был
- пор о бче
- в о пле
- л о пнем
- неуд о бен
- др о бен
- зл о ба
- хл о пать
- ш ё пот
- пр о бка
- о бнял
- д о был
- уд о бства
- о бувь
- кн о пка
- пос о бий
- гр о ба
- раз о бран
- т о плив
- уч ё ба
- нак о пим
- от о бран
- од о брен
- о блик
- кор о бка
- подр о бность
- авт о бус
- со о бществ
- все о бща
- поуд о бней
- пр о пасть
- т ё пел
- попр о буй
- н ё ба
- с о бран
- д о бро
- спос о бен
- о ба
- о пыт
- ос о ба
- под о бен
- с о бствен
- о бласть
- о бод
- о бух
- полуш ё пот
- о бжил
- о браз
- сн о ба
- несъед о бен
- трущ о ба
- хол о па
- в о бла
- http://rifme.net/
- р о ба
- правдопод о бий
- поспос о бствуй
- наскр ё бшей
- огл о бель
- с о боль
- о бще
- к о бра
- колд о бин
- шт о пор
- потор о пим
- беспод о бен
- похл ё бка
- т о пнем
- боеспос о бность
- л о бби
- дееспос о бен
- нат о пим
- чт о бы
- перепр о буй
- психотр о пный
- х о бот
- худ о ба
- сл о пай
- п о па
- гал о па
- об о бран
- платёжеспос о бней
- порастор о пней
- п о пка
- телеск о па
- испр о буй
- калейдоск о па
- надгр о бий
- обороноспос о бность
- с о пли
- с о пка
- р о пот
- прихл о пнем
- трудоспос о бен
- т о пкам
- о пись
- к о пен
- к о пны
- сир о па
- утр о ба
- р о пщем
- отхл ё бнут
- к о бальт
- богопод о бен
- ф о бий
- тор о пит
- севаст о поль
- подк о па
- о бок
- ам ё ба
- тр ё плам
- стыд о ба
- с о пел
- недот ё па
- т о би
- стетоск о па
- р о берт
- акр о поль
- о бе
- л о пай
- захл ё ба
- ж о пка
- черн о быль
- стробоск о па
- п о пой
- о би
- ск о пам
- периск о па
- о пий
- некр о поль
- хлебор о ба
- стр о па
- русоф о ба
- зад о брен
- п о пу
- автост о па
- р о блокс
- чащ о ба
- п о пик
- ст ё па
- сд о ба
- о пель
- эфи о па
- м о пса
- хип-х о па
- п о пе
- изот о па
- евр о па
- укр о пчик
- ст ё бел
- остол о па
- о па
- гороск о па
- обос о блен
- о бруч
- жизнеспос о бен
- потр ё пан
- неправдопод о бен
- отк о пан
- сгр ё бшей
- раск о пка
- загр о бен
- пот о па
- к о поть
- допот о пен
- посъед о бней
- о пус
- вк о пан
- поправдопод о бней
- ус о пша
- исподл о бья
- про о браз
- гл о бус
- гр ё бся
- препод о бен
- растр ё пан
- погр ё бшей
- в о бран
- микроск о па
- р о бость
- п о бран
Предложить свои рифмы
Введите слово. Бранные слова не учитываются.
Помогло? Сохраните и поделитесь ссылкой на сайт
Вы можете добавить сайт в закладки, чтобы пользоваться им при написании стихов в будущем (нажмите Ctrl+D). Или поделиться им в социальных сетях. Также советуем добавить в закладки быструю и упрощённую страницу поиска: помощник поэта.
Анаграммы/перестановки букв для слова квадрокоптер
- падек а тров
Популярные слова
Что искали другие
Если есть предложение, идея, благодарность или комментарий, пишите. Мы рады отзывам. Сообщения с объявлениями, ссылками или бранью удаляются роботом.
источники:
http://phoneticonline.ru/%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%B4%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80
http://rifme.net/r/%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%B4%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80/1