For the leavening agent of which baking soda is a common ingredient, see Baking powder.
|
||
|
||

Crystal structure |
||
|
||
| Names | ||
|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
sodium hydrogencarbonate |
||
| Other names
Baking soda, bicarb (laboratory slang), bicarbonate of soda, nahcolite, natrium hydrogen carbonate, natron |
||
| Identifiers | ||
|
CAS Number |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
|
|
Beilstein Reference |
4153970 | |
| ChEBI |
|
|
| ChEMBL |
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
|
| DrugBank |
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.122 |
|
| EC Number |
|
|
| E number | E500(ii) (acidity regulators, …) | |
|
IUPHAR/BPS |
|
|
| KEGG |
|
|
| MeSH | Sodium+bicarbonate | |
|
PubChem CID |
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
|
| UNII |
|
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
|
|
InChI
|
||
|
SMILES
|
||
| Properties | ||
|
Chemical formula |
NaHCO 3 |
|
| Molar mass | 84.0066 g mol−1 | |
| Appearance | White crystals | |
| Odor | Odorless | |
| Density |
|
|
| Melting point | (Decomposes to sodium carbonate starting at 50 °C[1][6]) | |
|
Solubility in water |
|
|
| Solubility | 0.02 wt% acetone, 2.13 wt% methanol @22 °C.[4] insoluble in ethanol | |
| log P | −0.82 | |
| Acidity (pKa) |
|
|
|
Refractive index (nD) |
nα = 1.377 nβ = 1.501 nγ = 1.583 | |
| Structure | ||
|
Crystal structure |
Monoclinic | |
| Thermochemistry | ||
|
Heat capacity (C) |
87.6 J/mol K[7] | |
|
Std molar |
101.7 J/mol K[7] | |
|
Std enthalpy of |
−950.8 kJ/mol[7] | |
|
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵) |
−851.0 kJ/mol[7] | |
| Pharmacology | ||
|
ATC code |
B05CB04 (WHO) B05XA02 (WHO), QG04BQ01 (WHO) | |
|
Routes of |
Intravenous, oral | |
| Hazards | ||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | ||
|
Main hazards |
Causes serious eye irritation | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
2 0 1 |
|
| Flash point | Incombustible | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | ||
|
LD50 (median dose) |
4220 mg/kg (rat, oral)[8] | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | |
| Related compounds | ||
|
Other anions |
Sodium carbonate | |
|
Other cations |
|
|
|
Related compounds |
|
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references |
Cupcakes baked with baking soda as a raising agent
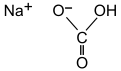
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate[9]), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cation (Na+) and a bicarbonate anion (HCO3−). Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline, but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). The natural mineral form is nahcolite. It is a component of the mineral natron and is found dissolved in many mineral springs.[10]
Nomenclature[edit]
Because it has long been known and widely used, the salt has many different names such as baking soda, bread soda, cooking soda, and bicarbonate of soda and can often be found near baking powder in stores. The term baking soda is more common in the United States, while bicarbonate of soda is more common in Australia, United Kingdom and Ireland.[11] and in many northern/central European countries it is called Natron. Abbreviated colloquial forms such as sodium bicarb, bicarb soda, bicarbonate, and bicarb are common.[12]
The word saleratus, from Latin sal æratus (meaning «aerated salt»), was widely used in the 19th century for both sodium bicarbonate and potassium bicarbonate.[13]
Its E number food additive code is E500.[14]
The prefix bi in bicarbonate comes from an outdated naming system predating molecular knowledge in reference to the two molar equivalents of carbon dioxide (known as carbonic acid in the ancient chemistry language) that potassium hydrocarbonate/bicarbonate releases upon decomposition to (di)potassium carbonate and to potassium oxide (potash).[15] The modern chemical formulas of these compounds now express their precise chemical compositions which were unknown when the name bi-carbonate of potash was coined (see also: bicarbonate).
Uses[edit]
Cooking[edit]
Leavening[edit]
In cooking, baking soda is primarily used in baking as a leavening agent. When it reacts with acid, carbon dioxide is released, which causes expansion of the batter and forms the characteristic texture and grain in cakes, quick breads, soda bread, and other baked and fried foods. The acid–base reaction can be generically represented as follows:[16]
- NaHCO3 + H+ → Na+ + CO2 + H2O
Acidic materials that induce this reaction include hydrogen phosphates, cream of tartar, lemon juice, yogurt, buttermilk, cocoa, and vinegar. Baking soda may be used together with sourdough, which is acidic, making a lighter product with a less acidic taste.[17]
Heat can also by itself cause sodium bicarbonate to act as a raising agent in baking because of thermal decomposition, releasing carbon dioxide at temperatures above 80 °C (180 °F), as follows:[18]
- 2 NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
When used this way on its own, without the presence of an acidic component (whether in the batter or by the use of a baking powder containing acid), only half the available CO2 is released (one CO2 molecule is formed for every two equivalents of NaHCO3). Additionally, in the absence of acid, thermal decomposition of sodium bicarbonate also produces sodium carbonate, which is strongly alkaline and gives the baked product a bitter, «soapy» taste and a yellow color. Since the reaction occurs slowly at room temperature, mixtures (cake batter, etc.) can be allowed to stand without rising until they are heated in the oven.[citation needed]
Baking powder[edit]
Baking powder, also sold for cooking, contains around 30% of bicarbonate, and various acidic ingredients which are activated by the addition of water, without the need for additional acids in the cooking medium.[19][20][21] Many forms of baking powder contain sodium bicarbonate combined with calcium acid phosphate, sodium aluminium phosphate, or cream of tartar.[22] Baking soda is alkaline; the acid used in baking powder avoids a metallic taste when the chemical change during baking creates sodium carbonate.[23]
Pyrotechnics[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is one of the main components of the common «black snake» firework. The effect is caused by the thermal decomposition, which produces carbon dioxide gas to produce a long snake-like ash as a combustion product of the other main component, sucrose.[24] Sodium bicarbonate is also used to delay combustion reactions by releasing CO2 and H2O when heated, both of which are flame retardants.
Mild disinfectant[edit]
It has weak disinfectant properties,[25][26] and it may be an effective fungicide against some organisms.[27] Because baking soda will absorb musty smells, it has become a reliable method for used book sellers when making books less malodorous.[28]
Fire extinguisher[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate can be used to extinguish small grease or electrical fires by being thrown over the fire, as heating of sodium bicarbonate releases carbon dioxide.[29] However, it should not be applied to fires in deep fryers; the sudden release of gas may cause the grease to splatter.[29] Sodium bicarbonate is used in BC dry chemical fire extinguishers as an alternative to the more corrosive monoammonium phosphate in ABC extinguishers. The alkaline nature of sodium bicarbonate makes it the only dry chemical agent, besides Purple-K, that was used in large-scale fire suppression systems installed in commercial kitchens. Because it can act as an alkali, the agent has a mild saponification effect on hot grease, which forms a smothering, soapy foam.[citation needed]
Neutralization of acids[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate reacts spontaneously with acids, releasing CO2 gas as a reaction product. It is commonly used to neutralize unwanted acid solutions or acid spills in chemical laboratories.[30] It is not appropriate to use sodium bicarbonate to neutralize base[31] even though it is amphoteric, reacting with both acids and bases.[citation needed]
Agriculture[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate when applied on leaves, can prevent the growth of fungi; however, it does not kill the fungus. Excessive amount of sodium bicarbonate can cause discolouration of fruits (two percent solution) and chlorosis (one percent solution).[32]
Medical uses and health[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate mixed with water can be used as an antacid to treat acid indigestion and heartburn.[33] Its reaction with stomach acid produces salt, water, and carbon dioxide:
- NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2(g)
A mixture of sodium bicarbonate and polyethylene glycol such as PegLyte,[34] dissolved in water and taken orally, is an effective gastrointestinal lavage preparation and laxative prior to gastrointestinal surgery, gastroscopy, etc.[citation needed]
Intravenous sodium bicarbonate in an aqueous solution is sometimes used for cases of acidosis, or when insufficient sodium or bicarbonate ions are in the blood.[35] In cases of respiratory acidosis, the infused bicarbonate ion drives the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer of plasma to the left, and thus raises the pH. For this reason, sodium bicarbonate is used in medically supervised cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Infusion of bicarbonate is indicated only when the blood pH is markedly low (< 7.1–7.0).[36]
HCO3− is used for treatment of hyperkalemia, as it will drive K+ back into cells during periods of acidosis.[37] Since sodium bicarbonate can cause alkalosis, it is sometimes used to treat aspirin overdoses. Aspirin requires an acidic environment for proper absorption, and a basic environment will diminish aspirin absorption in cases of overdose.[38] Sodium bicarbonate has also been used in the treatment of tricyclic antidepressant overdose.[39] It can also be applied topically as a paste, with three parts baking soda to one part water, to relieve some kinds of insect bites and stings (as well as accompanying swelling).[40]
Some alternative practitioners, such as Tullio Simoncini, have promoted baking soda as a cancer cure, which the American Cancer Society has warned against due to both its unproven effectiveness and potential danger in use.[41] Edzard Ernst has called the promotion of sodium bicarbonate as a cancer cure «one of the more sickening alternative cancer scams I have seen for a long time».[42]
Sodium bicarbonate can be added to local anesthetics, to speed up the onset of their effects and make their injection less painful.[43] It is also a component of Moffett’s solution, used in nasal surgery.[citation needed]
It has been proposed that acidic diets weaken bones.[44] One systematic meta-analysis of the research shows no such effect.[45] Another also finds that there is no evidence that alkaline diets improve bone health, but suggests that there «may be some value» to alkaline diets for other reasons.[46]
Antacid (such as baking soda) solutions have been prepared and used by protesters to alleviate the effects of exposure to tear gas during protests.[failed verification][47]
Similarly to its use in baking, sodium bicarbonate is used together with a mild acid such as tartaric acid as the excipient in effervescent tablets: when such a tablet is dropped in a glass of water, the carbonate leaves the reaction medium as carbon dioxide gas (HCO3− + H+ → H2O + CO2↑ or, more precisely, HCO3− + H3O+ → 2 H2O + CO2↑). This makes the tablet disintegrate, leaving the medication suspended and/or dissolved in the water together with the resulting salt (in this example, sodium tartrate).[48]
Personal hygiene[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is also used as an ingredient in some mouthwashes. It has anticaries and abrasive properties.[49] It works as a mechanical cleanser on the teeth and gums, neutralizes the production of acid in the mouth, and also acts as an antiseptic to help prevent infections.[50][51] Sodium bicarbonate in combination with other ingredients can be used to make a dry or wet deodorant.[52][53] Sodium bicarbonate may be used as a buffering agent, combined with table salt, when creating a solution for nasal irrigation.[54]
It is used in eye hygiene to treat blepharitis. This is done by addition of a teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate to cool water that was recently boiled, followed by gentle scrubbing of the eyelash base with a cotton swab dipped in the solution.[55][56]
Veterinary uses[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is used as a cattle feed supplement, in particular as a buffering agent for the rumen.[57]
Cleaning agent[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is used in a process for removing paint and corrosion called sodablasting. As a blasting medium, sodium bicarbonate is used to remove surface contamination from softer and less resilient substrates such as aluminium, copper or timber which could be damaged by silica sand abrasive media.[58]
A manufacturer recommends a paste made from baking soda with minimal water as a gentle scouring powder,[29] and is useful in removing surface rust, as the rust forms a water-soluble compound when in a concentrated alkaline solution;[59] cold water should be used, as hot-water solutions can corrode steel.[60] Sodium bicarbonate attacks the thin protective oxide layer that forms on aluminium, making it unsuitable for cleaning this metal.[61] A solution in warm water will remove the tarnish from silver when the silver is in contact with a piece of aluminium foil.[61][62] Baking soda is commonly added to washing machines as a replacement for water softener and to remove odors from clothes. It is also almost as effective in removing heavy tea and coffee stains from cups as Sodium hydroxide, when diluted with warm water.
During the Manhattan Project to develop the nuclear bomb in the early 1940s, the chemical toxicity of uranium was an issue. Uranium oxides were found to stick very well to cotton cloth, and did not wash out with soap or laundry detergent. However, the uranium would wash out with a 2% solution of sodium bicarbonate. Clothing can become contaminated with toxic dust of depleted uranium (DU), which is very dense, hence used for counterweights in a civilian context, and in armour-piercing projectiles. DU is not removed by normal laundering; washing with about 6 ounces (170 g) of baking soda in 2 gallons (7.5 L) of water will help to wash it out.[63]
Odor control[edit]
It is often claimed that baking soda is an effective odor remover,[64][better source needed] and it is often recommended that an open box be kept in the refrigerator to absorb odor.[65] This idea was promoted by the leading U.S. brand of baking soda, Arm & Hammer, in an advertising campaign starting in 1972.[66] Though this campaign is considered a classic of marketing, leading within a year to more than half of American refrigerators containing a box of baking soda,[67][68] there is little evidence that it is in fact effective in this application.[69][70]
Hydrogen gas production[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate can be used as a catalyst in gas production. Its performance for this application is «good», however not usually used.[citation needed] Hydrogen gas is produced via electrolysis of water, process in which electric current is applied through a volume of water, which causes the hydrogen atoms to separate from the oxygen atoms. This demonstration is usually done in high school chemistry classes to show electrolysis.
Chemistry[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is an amphoteric compound. Aqueous solutions are mildly alkaline due to the formation of carbonic acid and hydroxide ion:
- HCO−
3 + H2O → H
2CO
3 + OH−
Sodium bicarbonate can often be used as a safer alternative to sodium hydroxide, and as such can be used as a wash to remove any acidic impurities from a «crude» liquid, producing a purer sample. Reaction of sodium bicarbonate and an acid produces a salt and carbonic acid, which readily decomposes to carbon dioxide and water:
- NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O+CO2
- H2CO3 → H2O + CO2(g)
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with acetic acid (found in vinegar), producing sodium acetate, water, and carbon dioxide:
- NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2(g)
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with bases such as sodium hydroxide to form carbonates:
- NaHCO3 + NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
Thermal decomposition[edit]
At temperatures from 80–100 °C (176–212 °F), sodium bicarbonate gradually decomposes into sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide. The conversion is faster at 200 °C (392 °F):[71]
- 2 NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
Most bicarbonates undergo this dehydration reaction. Further heating converts the carbonate into the oxide (above 850 °C/1,560 °F):[71]
- Na2CO3 → Na2O + CO2
These conversions are relevant to the use of NaHCO3 as a fire-suppression agent («BC powder») in some dry-powder fire extinguishers.[citation needed]
Stability and shelf life[edit]
If kept cool (room temperature) and dry (an airtight container is recommended to keep out moist air), sodium bicarbonate can be kept without a significant amount of decomposition for at least two or three years.[72][73][74][75]
History[edit]
The word natron has been in use in many languages throughout modern times (in the forms of anatron, natrum and natron) and originated (like Spanish, French and English natron as well as ‘sodium’) via Arabic naṭrūn (or anatrūn; cf. the Lower Egyptian “Natrontal” Wadi El Natrun, where a mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate for the dehydration of mummies was used [76]) from Greek nítron (νίτρον) (Herodotus; Attic lítron (λίτρον)), which can be traced back to ancient Egyptian ntr. The Greek nítron (soda, saltpeter) was also used in Latin (sal) nitrum and in German Salniter (the source of Nitrogen, Nitrat etc.).[77][78]
In 1791, French chemist Nicolas Leblanc produced sodium carbonate, also known as soda ash. The pharmacist Valentin Rose the Younger is credited with the discovery of sodium bicarbonate in 1801 in Berlin. In 1846, two American bakers, John Dwight and Austin Church, established the first factory in the United States to produce baking soda from sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide.[79]
Saleratus, potassium or sodium bicarbonate, is mentioned in the novel Captains Courageous by Rudyard Kipling as being used extensively in the 1800s in commercial fishing to prevent freshly caught fish from spoiling.[80]
In 1919, US Senator Lee Overman declared that bicarbonate of soda could cure the Spanish flu. In the midst of the debate on 26 January 1919, he interrupted the discussion to announce the discovery of a cure. «I want to say, for the benefit of those who are making this investigation,» he reported, «that I was told by a judge of a superior court in the mountain country of North Carolina they have discovered a remedy for this disease.» The purported cure implied a critique of modern science and an appreciation for the simple wisdom of simple people. «They say that common baking soda will cure the disease,» he continued, «that they have cured it with it, that they have no deaths up there at all; they use common baking soda, which cures the disease.»[81]
Production[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is produced industrially from sodium carbonate:[82]
- Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O → 2 NaHCO3
It is produced on the scale of about 100,000 tonnes/year (as of 2001)[dubious – discuss][83] with a worldwide production capacity of 2.4 million tonnes per year (as of 2002).[84] Commercial quantities of baking soda are also produced by a similar method: soda ash, mined in the form of the ore trona, is dissolved in water and treated with carbon dioxide. Sodium bicarbonate precipitates as a solid from this solution.[citation needed]
Regarding the Solvay process, sodium bicarbonate is an intermediate in the reaction of sodium chloride, ammonia, and carbon dioxide. The product however shows low purity (75pc).[citation needed]
- NaCl + CO2 + NH3 + H2O → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
Although of no practical value, NaHCO3 may be obtained by the reaction of carbon dioxide with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide:[citation needed]
- CO2 + NaOH → NaHCO3
Mining[edit]
Naturally occurring deposits of nahcolite (NaHCO3) are found in the Eocene-age (55.8–33.9 Mya) Green River Formation, Piceance Basin in Colorado. Nahcolite was deposited as beds during periods of high evaporation in the basin. It is commercially mined using common underground mining techniques such as bore, drum, and longwall mining in a fashion very similar to coal mining.[citation needed]
It is also produced by solution mining, pumping heated water through nahcolite beds and crystalizing the dissolved nahcolite through a cooling crystallization process.
In popular culture[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate, as «bicarbonate of soda», was a frequent source of punch lines for Groucho Marx in Marx Brothers movies. In Duck Soup, Marx plays the leader of a nation at war. In one scene, he receives a message from the battlefield that his general is reporting a gas attack, and Groucho tells his aide: «Tell him to take a teaspoonful of bicarbonate of soda and a half a glass of water.»[85] In A Night at the Opera, Groucho’s character addresses the opening night crowd at an opera by saying of the lead tenor: «Signor Lassparri comes from a very famous family. His mother was a well-known bass singer. His father was the first man to stuff spaghetti with bicarbonate of soda, thus causing and curing indigestion at the same time.»[86]
In the Joseph L. Mankewicz classic All About Eve, the Max Fabian character (Gregory Ratoff) has an extended scene with Margo Channing (Bette Davis) in which, suffering from heartburn, he requests and then drinks bicarbonate of soda, eliciting a prominent burp. Channing promises to always keep a box of bicarb with Max’s name on it.
See also[edit]
- Carbonic acid
- List of ineffective cancer treatments
- List of minerals
- Natron
- Natrona (disambiguation)
- Trona
References[edit]
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 4.90
- ^ a b c Haynes, p. 5.194
- ^ a b c «Sodium Bicarbonate» (PDF). United Nations Environment Programme. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 May 2011.
- ^ Ellingboe JL, Runnels JH (1966). «Solubilities of Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Bicarbonate in Acetone-Water and Methanol-Water Mixtures». J. Chem. Eng. Data. 11 (3): 323–324. doi:10.1021/je60030a009.
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 7.23
- ^ Pasquali I, Bettini R, Giordano F (2007). «Thermal behaviour of diclofenac, diclofenac sodium and sodium bicarbonate compositions». Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. 90 (3): 903–907. doi:10.1007/s10973-006-8182-1. S2CID 95695262.
- ^ a b c d Haynes, p. 5.19
- ^ Chambers M. «Sodium bicarbonate [USP:JAN]». ChemIDplus. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations 2005 (PDF), IUPAC, p. 137, archived (PDF) from the original on 18 May 2017
- ^ «Mineral Springs – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics».
- ^ «What’s the difference between bicarbonate of soda, baking soda and baking powder?». ThatsLife! Pacific Network.
- ^ PubChem. «Sodium bicarbonate». pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ «Definition of SALERATUS». www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ «Approved additives and E numbers». Food Standards Agency. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ^ Wollaston, WH (January 1814). «I. A Synoptic scale of chemical equivalents». Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 104: 1–22. doi:10.1098/rstl.1814.0001. S2CID 96774986.
- ^ Bent AJ, ed. (1997). The Technology of Cake Making (6 ed.). Springer. p. 102. ISBN 9780751403497. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ^ Cascio J. «Sourdough» (PDF). University of Alaska Fairbanks Cooperative Extension Service. FNH-00061. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2017.
- ^ «The Many Practical Uses of Baking Soda in the Kitchen». About.com Food. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ Czernohorsky JH, Hooker R. «The Chemistry of Baking» (PDF). New Zealand Institute of Chemistry. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 November 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ «Baking Soda and Baking Powder». FineCooking.com. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ «Baking Soda FAQs». Arm & Hammer Multi-Brand. Church & Dwight Company. What is the difference baking soda and baking powder?. Archived from the original on 27 June 2017. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ «Glossary Ingredients». Cooking.com. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate». BRP Adhikary. 11 July 2016. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ «Sugar snake». MEL Science. MEL Science 2015–2019. Archived from the original on 6 October 2019. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ^ Malik YS, Goyal SM (May 2006). «Virucidal efficacy of sodium bicarbonate on a food contact surface against feline calicivirus, a norovirus surrogate». International Journal of Food Microbiology. 109 (1–2): 160–3. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.08.033. PMID 16540196.
- ^ Rutala WA, Barbee SL, Aguiar NC, Sobsey MD, Weber DJ (January 2000). «Antimicrobial activity of home disinfectants and natural products against potential human pathogens». Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 21 (1): 33–8. doi:10.1086/501694. PMID 10656352. S2CID 34461187.
- ^ Zamani M, Sharifi Tehrani A, Ali Abadi AA (2007). «Evaluation of antifungal activity of carbonate and bicarbonate salts alone or in combination with biocontrol agents in control of citrus green mold». Communications in Agricultural and Applied Biological Sciences. 72 (4): 773–7. PMID 18396809.
- ^ Altman G (22 May 2006). «Book Repair for BookThinkers: How To Remove Odors From Books». The BookThinker (69).
- ^ a b c «Arm & Hammer Baking Soda – Basics – The Magic of Arm & Hammer Baking Soda». armandhammer.com. Archived from the original on 31 August 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2009.
- ^ «Prepare for Emergencies from Uncontrolled Hazards». American Chemical Society.
- ^ Hurum D. «Laboratory Safety» (PDF). Civil Engineering. Northwestern University.
- ^ «Horticulture myths». University of Vermont Extension Department of Plant and Soil Science. Archived from the original on 7 August 2019. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate». Jackson Siegelbaum Gastroenterology. 1998. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- ^ «PegLyte». Pendo Phama.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate Intravenous Infusion» (PDF). Consumer Medicine Information. Better Health Channel. 13 July 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 August 2008.
- ^ «Respiratory Acidosis: Treatment & Medication». emedicine. 26 March 2020.
- ^ Dart RC (2004). Medical Toxicology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 910–. ISBN 978-0-7817-2845-4.
- ^ Cloth Diapers. Donald C. Cooper PhD. pp. 46–.
- ^ [old info]Knudsen K, Abrahamsson J (April 1997). «Epinephrine and sodium bicarbonate independently and additively increase survival in experimental amitriptyline poisoning». Critical Care Medicine. 25 (4): 669–74. doi:10.1097/00003246-199704000-00019. PMID 9142034.
- ^ «Insect bites and stings: First aid». Mayo Clinic. 15 January 2008.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate». American Cancer Society. 28 November 2008. Archived from the original on 19 February 2013. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Ernst E (3 February 2017). «This must be the most sickening cancer scam I have seen for a while».
- ^ Edgcombe H, Hocking G, Radcliffe J (2005). «Anaesthesia UK : Local Anaesthetic Pharmacology». John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK.
- ^ Fox D (15 December 2001). «Hard cheese». New Scientist. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ Fenton, T. R.; Tough, S. C.; Lyon, A. W.; Eliasziw, M.; Hanley, D. A. (2011). «Causal assessment of dietary acid load and bone disease: A systematic review & meta-analysis applying Hill’s epidemiologic criteria for causality». Nutrition Journal. 10: 41. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-10-41. PMC 3114717. PMID 21529374.
- ^ Schwalfenberg, Gerry K. (2012). «The Alkaline Diet: Is There Evidence That an Alkaline pH Diet Benefits Health?». Journal of Environmental and Public Health. 2012: 1–7. doi:10.1155/2012/727630. PMC 3195546. PMID 22013455.
- ^ «Medical information from Prague 2000». Archived from the original on 18 October 2014.
- ^ Shirsand, S. B.; Suresh, Sarasija; Jodhana, L. S.; Swamy, P. V. (2010). «Formulation Design and Optimization of Fast Disintegrating Lorazepam Tablets by Effervescent Method». Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 72 (4): 431–436. doi:10.4103/0250-474X.73911. ISSN 0250-474X. PMC 3013557. PMID 21218052.
- ^ Storehagen S, Ose N, Midha S. «Dentifrices and mouthwashes ingredients and their use» (PDF). Institutt for klinisk odontologi. Universitetet i Oslo.
- ^ US 4132770A, Barth J, «Oral Product», issued 1979
- ^ Iqbal K, Asmat M, Jawed S, Mushtaque A, Mohsin F, Hanif S, et al. (July 2011). «Role of different ingredients of tooth pastes and mouthwashes in oral health» (PDF). Journal of Pakistan Dental Association. 20 (3): 163–70.
- ^ Lamb JH (1946). «Sodium Bicarbonate: An Excellent Deodorant». The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 7 (3): 131–133. doi:10.1038/jid.1946.13.
- ^ «Bicarb soda: natural body deodorant». sustainableecho.com. 10 March 2009.
- ^ Metson RB (2005). The Harvard Medical School Guide to Healing Your Sinues. McGraw Hill. p. 68. ISBN 9780071444699.
- ^ «Blepharitis : Information for patients leaflet» (PDF). Ouh.nhs.uk. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ «Blepharitis. Treatment and Causes. Eyelid inflammation | Patient». Patient. Archived from the original on 5 December 2015. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ Paton LJ, Beauchemin KA, Veira DM, von Keyserlingk MA (2006). «Use of sodium bicarbonate, offered free choice or blended into the ration, to reduce the risk of ruminal acidosis in cattle». Canadian Journal of Animal Science. 86 (3): 429–437. doi:10.4141/A06-014.
- ^ «Blast Away Grime With Baking Soda». Popular Mechanics. 5 August 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ Housecroft CE, Sharpe AG (2008). «Chapter 22: d-block metal chemistry: the first row elements». Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd Edition. Pearson. p. 716. ISBN 978-0-13-175553-6.
- ^ «Science Lab.com». MSDS- Sodium carbonate. sciencelab.com. Archived from the original on 5 September 2012.
- ^ a b «Finishing Techniques in Metalwork». Philadelphia Museum of Art.
- ^ «Put a Shine on It». scifun.chem.wisc.edu. Archived from the original on 31 July 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ Orcutt JA. «Depleted Uranium and Health: Facts and Helpful Suggestions». Pharmacology and Toxicology of Uranium Compounds. McGraw-Hill. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013. Retrieved 21 March 2012.
- ^ Raymond J (10 June 2016). «Kitchen Odor Eliminating Candles, Products, and Tricks». cravedujour.com. Archived from the original on 7 August 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^
Vicki Lansky, Martha Campbell, Baking Soda: Over 500 Fabulous, Fun, and Frugal Uses You’ve Probably Never Thought Of, 2009, ISBN 1931863733, p. 28 - ^ «A trusted solution for more than 170 years. Pure and simple.», Arm & Hammer «About Us» page
- ^ Keith Sawyer, Group Genius: The Creative Power of Collaboration, 2017, ISBN 0465093582, «keep food tasting fresh»
- ^ Clayton M. Christensen, Scott Cook, Taddy Hall, Marketing Malpractice: The Cause and the Cure, Harvard Business Review, December 2005, [1]
- ^ «Myth #100: An Open Box of Baking Soda in the Fridge absorbs Odors», Bruce Weinstein, Mark Scarbrough, Lobsters Scream When You Boil Them; And 100 Other Myths About Food and Cooking, 2011, ISBN 1439195382, p. 312
- ^ «Baking Soda as Odor Absorber | Cook’s Illustrated». Cooksillustrated.com. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ a b «Decomposition of Carbonates». General Chemistry Online. Archived from the original on 2 October 1999. Retrieved 16 March 2010.
- ^ PubChem. «Sodium bicarbonate». pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 16 May 2021.
- ^ «Sodium bicarbonate (S300) batch numbering and shelf life statement – Solvay Chemicals, Inc» (PDF). 31 January 2019.
- ^ «Re: Shelf Life – Sodium Bicarbonate (all grades) – Tronox Alkali Corporation» (PDF). 1 April 2015.
- ^ «Does Baking Soda Go Bad? How to Know If It’s Still Good». The Spruce Eats. Retrieved 16 May 2021.
- ^ Renate Gerner: Instruments and substances used in mummification. In: Renate Gerner, Rosemarie Drenkhahn (ed.): Mumie und Computer. A multidisciplinary research project in Hanover. Special exhibition of the Kestner Museum Hanover from September 26, 1991 to January 19, 1992. Kestner Museum, Hanover 1991, ISBN 3-924029-17-2, p. 28 f.
- ^ Franz Dornseiff: «The Greek words in German.» Walter de Gruyter & Co, Berlin 1950, p. 44.
- ^ Friedrich Kluge, Alfred Götze (Philologist): Etymological Dictionary of the German Language. 20th edition, ed. by Walther Mitzka, De Gruyter, Berlin / New York 1967; Reprint (“21st unchanged edition”) ibid 1975, ISBN 3-11-005709-3, p. 504.
- ^ «Company History». Church & Dwight Co. Archived from the original on 16 October 2011.
- ^ Kipling R (1897). Captains Courageous. p. 25.
- ^ Bristow, Nancy K. (2012), American Pandemic: The Lost Worlds of the 1918 Influenza Epidemic, Oxford University Press, p. 178, ISBN 978-0199811342
- ^ Thieme C (2000). «Sodium Carbonates». Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a24_299. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Holleman AF, Wiberg E (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Page 45, section 3.6.2.1 of «Process Best Practices Reference Document (BREF) for Soda Ash,» report produced by the European Soda Ash Producer’s Association Archived 3 October 2006 at the Wayback Machine, March 2004.
- ^ «Duck Soup (1933)». IMDb. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «A Night at the Opera (1935)». IMDb. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
Bibliography[edit]
- Haynes WM, ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-1439855119.
External links[edit]
- International Chemical Safety Card 1044
For the leavening agent of which baking soda is a common ingredient, see Baking powder.

|
||
|
||

Crystal structure |
||
|
||
| Names | ||
|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
sodium hydrogencarbonate |
||
| Other names
Baking soda, bicarb (laboratory slang), bicarbonate of soda, nahcolite, natrium hydrogen carbonate, natron |
||
| Identifiers | ||
|
CAS Number |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
|
|
Beilstein Reference |
4153970 | |
| ChEBI |
|
|
| ChEMBL |
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
|
| DrugBank |
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.122 |
|
| EC Number |
|
|
| E number | E500(ii) (acidity regulators, …) | |
|
IUPHAR/BPS |
|
|
| KEGG |
|
|
| MeSH | Sodium+bicarbonate | |
|
PubChem CID |
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
|
| UNII |
|
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
|
|
InChI
|
||
|
SMILES
|
||
| Properties | ||
|
Chemical formula |
NaHCO 3 |
|
| Molar mass | 84.0066 g mol−1 | |
| Appearance | White crystals | |
| Odor | Odorless | |
| Density |
|
|
| Melting point | (Decomposes to sodium carbonate starting at 50 °C[1][6]) | |
|
Solubility in water |
|
|
| Solubility | 0.02 wt% acetone, 2.13 wt% methanol @22 °C.[4] insoluble in ethanol | |
| log P | −0.82 | |
| Acidity (pKa) |
|
|
|
Refractive index (nD) |
nα = 1.377 nβ = 1.501 nγ = 1.583 | |
| Structure | ||
|
Crystal structure |
Monoclinic | |
| Thermochemistry | ||
|
Heat capacity (C) |
87.6 J/mol K[7] | |
|
Std molar |
101.7 J/mol K[7] | |
|
Std enthalpy of |
−950.8 kJ/mol[7] | |
|
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵) |
−851.0 kJ/mol[7] | |
| Pharmacology | ||
|
ATC code |
B05CB04 (WHO) B05XA02 (WHO), QG04BQ01 (WHO) | |
|
Routes of |
Intravenous, oral | |
| Hazards | ||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | ||
|
Main hazards |
Causes serious eye irritation | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
2 0 1 |
|
| Flash point | Incombustible | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | ||
|
LD50 (median dose) |
4220 mg/kg (rat, oral)[8] | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | |
| Related compounds | ||
|
Other anions |
Sodium carbonate | |
|
Other cations |
|
|
|
Related compounds |
|
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references |
Cupcakes baked with baking soda as a raising agent
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate[9]), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cation (Na+) and a bicarbonate anion (HCO3−). Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline, but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). The natural mineral form is nahcolite. It is a component of the mineral natron and is found dissolved in many mineral springs.[10]
Nomenclature[edit]
Because it has long been known and widely used, the salt has many different names such as baking soda, bread soda, cooking soda, and bicarbonate of soda and can often be found near baking powder in stores. The term baking soda is more common in the United States, while bicarbonate of soda is more common in Australia, United Kingdom and Ireland.[11] and in many northern/central European countries it is called Natron. Abbreviated colloquial forms such as sodium bicarb, bicarb soda, bicarbonate, and bicarb are common.[12]
The word saleratus, from Latin sal æratus (meaning «aerated salt»), was widely used in the 19th century for both sodium bicarbonate and potassium bicarbonate.[13]
Its E number food additive code is E500.[14]
The prefix bi in bicarbonate comes from an outdated naming system predating molecular knowledge in reference to the two molar equivalents of carbon dioxide (known as carbonic acid in the ancient chemistry language) that potassium hydrocarbonate/bicarbonate releases upon decomposition to (di)potassium carbonate and to potassium oxide (potash).[15] The modern chemical formulas of these compounds now express their precise chemical compositions which were unknown when the name bi-carbonate of potash was coined (see also: bicarbonate).
Uses[edit]
Cooking[edit]
Leavening[edit]
In cooking, baking soda is primarily used in baking as a leavening agent. When it reacts with acid, carbon dioxide is released, which causes expansion of the batter and forms the characteristic texture and grain in cakes, quick breads, soda bread, and other baked and fried foods. The acid–base reaction can be generically represented as follows:[16]
- NaHCO3 + H+ → Na+ + CO2 + H2O
Acidic materials that induce this reaction include hydrogen phosphates, cream of tartar, lemon juice, yogurt, buttermilk, cocoa, and vinegar. Baking soda may be used together with sourdough, which is acidic, making a lighter product with a less acidic taste.[17]
Heat can also by itself cause sodium bicarbonate to act as a raising agent in baking because of thermal decomposition, releasing carbon dioxide at temperatures above 80 °C (180 °F), as follows:[18]
- 2 NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
When used this way on its own, without the presence of an acidic component (whether in the batter or by the use of a baking powder containing acid), only half the available CO2 is released (one CO2 molecule is formed for every two equivalents of NaHCO3). Additionally, in the absence of acid, thermal decomposition of sodium bicarbonate also produces sodium carbonate, which is strongly alkaline and gives the baked product a bitter, «soapy» taste and a yellow color. Since the reaction occurs slowly at room temperature, mixtures (cake batter, etc.) can be allowed to stand without rising until they are heated in the oven.[citation needed]
Baking powder[edit]
Baking powder, also sold for cooking, contains around 30% of bicarbonate, and various acidic ingredients which are activated by the addition of water, without the need for additional acids in the cooking medium.[19][20][21] Many forms of baking powder contain sodium bicarbonate combined with calcium acid phosphate, sodium aluminium phosphate, or cream of tartar.[22] Baking soda is alkaline; the acid used in baking powder avoids a metallic taste when the chemical change during baking creates sodium carbonate.[23]
Pyrotechnics[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is one of the main components of the common «black snake» firework. The effect is caused by the thermal decomposition, which produces carbon dioxide gas to produce a long snake-like ash as a combustion product of the other main component, sucrose.[24] Sodium bicarbonate is also used to delay combustion reactions by releasing CO2 and H2O when heated, both of which are flame retardants.
Mild disinfectant[edit]
It has weak disinfectant properties,[25][26] and it may be an effective fungicide against some organisms.[27] Because baking soda will absorb musty smells, it has become a reliable method for used book sellers when making books less malodorous.[28]
Fire extinguisher[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate can be used to extinguish small grease or electrical fires by being thrown over the fire, as heating of sodium bicarbonate releases carbon dioxide.[29] However, it should not be applied to fires in deep fryers; the sudden release of gas may cause the grease to splatter.[29] Sodium bicarbonate is used in BC dry chemical fire extinguishers as an alternative to the more corrosive monoammonium phosphate in ABC extinguishers. The alkaline nature of sodium bicarbonate makes it the only dry chemical agent, besides Purple-K, that was used in large-scale fire suppression systems installed in commercial kitchens. Because it can act as an alkali, the agent has a mild saponification effect on hot grease, which forms a smothering, soapy foam.[citation needed]
Neutralization of acids[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate reacts spontaneously with acids, releasing CO2 gas as a reaction product. It is commonly used to neutralize unwanted acid solutions or acid spills in chemical laboratories.[30] It is not appropriate to use sodium bicarbonate to neutralize base[31] even though it is amphoteric, reacting with both acids and bases.[citation needed]
Agriculture[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate when applied on leaves, can prevent the growth of fungi; however, it does not kill the fungus. Excessive amount of sodium bicarbonate can cause discolouration of fruits (two percent solution) and chlorosis (one percent solution).[32]
Medical uses and health[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate mixed with water can be used as an antacid to treat acid indigestion and heartburn.[33] Its reaction with stomach acid produces salt, water, and carbon dioxide:
- NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2(g)
A mixture of sodium bicarbonate and polyethylene glycol such as PegLyte,[34] dissolved in water and taken orally, is an effective gastrointestinal lavage preparation and laxative prior to gastrointestinal surgery, gastroscopy, etc.[citation needed]
Intravenous sodium bicarbonate in an aqueous solution is sometimes used for cases of acidosis, or when insufficient sodium or bicarbonate ions are in the blood.[35] In cases of respiratory acidosis, the infused bicarbonate ion drives the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer of plasma to the left, and thus raises the pH. For this reason, sodium bicarbonate is used in medically supervised cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Infusion of bicarbonate is indicated only when the blood pH is markedly low (< 7.1–7.0).[36]
HCO3− is used for treatment of hyperkalemia, as it will drive K+ back into cells during periods of acidosis.[37] Since sodium bicarbonate can cause alkalosis, it is sometimes used to treat aspirin overdoses. Aspirin requires an acidic environment for proper absorption, and a basic environment will diminish aspirin absorption in cases of overdose.[38] Sodium bicarbonate has also been used in the treatment of tricyclic antidepressant overdose.[39] It can also be applied topically as a paste, with three parts baking soda to one part water, to relieve some kinds of insect bites and stings (as well as accompanying swelling).[40]
Some alternative practitioners, such as Tullio Simoncini, have promoted baking soda as a cancer cure, which the American Cancer Society has warned against due to both its unproven effectiveness and potential danger in use.[41] Edzard Ernst has called the promotion of sodium bicarbonate as a cancer cure «one of the more sickening alternative cancer scams I have seen for a long time».[42]
Sodium bicarbonate can be added to local anesthetics, to speed up the onset of their effects and make their injection less painful.[43] It is also a component of Moffett’s solution, used in nasal surgery.[citation needed]
It has been proposed that acidic diets weaken bones.[44] One systematic meta-analysis of the research shows no such effect.[45] Another also finds that there is no evidence that alkaline diets improve bone health, but suggests that there «may be some value» to alkaline diets for other reasons.[46]
Antacid (such as baking soda) solutions have been prepared and used by protesters to alleviate the effects of exposure to tear gas during protests.[failed verification][47]
Similarly to its use in baking, sodium bicarbonate is used together with a mild acid such as tartaric acid as the excipient in effervescent tablets: when such a tablet is dropped in a glass of water, the carbonate leaves the reaction medium as carbon dioxide gas (HCO3− + H+ → H2O + CO2↑ or, more precisely, HCO3− + H3O+ → 2 H2O + CO2↑). This makes the tablet disintegrate, leaving the medication suspended and/or dissolved in the water together with the resulting salt (in this example, sodium tartrate).[48]
Personal hygiene[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is also used as an ingredient in some mouthwashes. It has anticaries and abrasive properties.[49] It works as a mechanical cleanser on the teeth and gums, neutralizes the production of acid in the mouth, and also acts as an antiseptic to help prevent infections.[50][51] Sodium bicarbonate in combination with other ingredients can be used to make a dry or wet deodorant.[52][53] Sodium bicarbonate may be used as a buffering agent, combined with table salt, when creating a solution for nasal irrigation.[54]
It is used in eye hygiene to treat blepharitis. This is done by addition of a teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate to cool water that was recently boiled, followed by gentle scrubbing of the eyelash base with a cotton swab dipped in the solution.[55][56]
Veterinary uses[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is used as a cattle feed supplement, in particular as a buffering agent for the rumen.[57]
Cleaning agent[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is used in a process for removing paint and corrosion called sodablasting. As a blasting medium, sodium bicarbonate is used to remove surface contamination from softer and less resilient substrates such as aluminium, copper or timber which could be damaged by silica sand abrasive media.[58]
A manufacturer recommends a paste made from baking soda with minimal water as a gentle scouring powder,[29] and is useful in removing surface rust, as the rust forms a water-soluble compound when in a concentrated alkaline solution;[59] cold water should be used, as hot-water solutions can corrode steel.[60] Sodium bicarbonate attacks the thin protective oxide layer that forms on aluminium, making it unsuitable for cleaning this metal.[61] A solution in warm water will remove the tarnish from silver when the silver is in contact with a piece of aluminium foil.[61][62] Baking soda is commonly added to washing machines as a replacement for water softener and to remove odors from clothes. It is also almost as effective in removing heavy tea and coffee stains from cups as Sodium hydroxide, when diluted with warm water.
During the Manhattan Project to develop the nuclear bomb in the early 1940s, the chemical toxicity of uranium was an issue. Uranium oxides were found to stick very well to cotton cloth, and did not wash out with soap or laundry detergent. However, the uranium would wash out with a 2% solution of sodium bicarbonate. Clothing can become contaminated with toxic dust of depleted uranium (DU), which is very dense, hence used for counterweights in a civilian context, and in armour-piercing projectiles. DU is not removed by normal laundering; washing with about 6 ounces (170 g) of baking soda in 2 gallons (7.5 L) of water will help to wash it out.[63]
Odor control[edit]
It is often claimed that baking soda is an effective odor remover,[64][better source needed] and it is often recommended that an open box be kept in the refrigerator to absorb odor.[65] This idea was promoted by the leading U.S. brand of baking soda, Arm & Hammer, in an advertising campaign starting in 1972.[66] Though this campaign is considered a classic of marketing, leading within a year to more than half of American refrigerators containing a box of baking soda,[67][68] there is little evidence that it is in fact effective in this application.[69][70]
Hydrogen gas production[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate can be used as a catalyst in gas production. Its performance for this application is «good», however not usually used.[citation needed] Hydrogen gas is produced via electrolysis of water, process in which electric current is applied through a volume of water, which causes the hydrogen atoms to separate from the oxygen atoms. This demonstration is usually done in high school chemistry classes to show electrolysis.
Chemistry[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is an amphoteric compound. Aqueous solutions are mildly alkaline due to the formation of carbonic acid and hydroxide ion:
- HCO−
3 + H2O → H
2CO
3 + OH−
Sodium bicarbonate can often be used as a safer alternative to sodium hydroxide, and as such can be used as a wash to remove any acidic impurities from a «crude» liquid, producing a purer sample. Reaction of sodium bicarbonate and an acid produces a salt and carbonic acid, which readily decomposes to carbon dioxide and water:
- NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O+CO2
- H2CO3 → H2O + CO2(g)
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with acetic acid (found in vinegar), producing sodium acetate, water, and carbon dioxide:
- NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2(g)
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with bases such as sodium hydroxide to form carbonates:
- NaHCO3 + NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
Thermal decomposition[edit]
At temperatures from 80–100 °C (176–212 °F), sodium bicarbonate gradually decomposes into sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide. The conversion is faster at 200 °C (392 °F):[71]
- 2 NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
Most bicarbonates undergo this dehydration reaction. Further heating converts the carbonate into the oxide (above 850 °C/1,560 °F):[71]
- Na2CO3 → Na2O + CO2
These conversions are relevant to the use of NaHCO3 as a fire-suppression agent («BC powder») in some dry-powder fire extinguishers.[citation needed]
Stability and shelf life[edit]
If kept cool (room temperature) and dry (an airtight container is recommended to keep out moist air), sodium bicarbonate can be kept without a significant amount of decomposition for at least two or three years.[72][73][74][75]
History[edit]
The word natron has been in use in many languages throughout modern times (in the forms of anatron, natrum and natron) and originated (like Spanish, French and English natron as well as ‘sodium’) via Arabic naṭrūn (or anatrūn; cf. the Lower Egyptian “Natrontal” Wadi El Natrun, where a mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate for the dehydration of mummies was used [76]) from Greek nítron (νίτρον) (Herodotus; Attic lítron (λίτρον)), which can be traced back to ancient Egyptian ntr. The Greek nítron (soda, saltpeter) was also used in Latin (sal) nitrum and in German Salniter (the source of Nitrogen, Nitrat etc.).[77][78]
In 1791, French chemist Nicolas Leblanc produced sodium carbonate, also known as soda ash. The pharmacist Valentin Rose the Younger is credited with the discovery of sodium bicarbonate in 1801 in Berlin. In 1846, two American bakers, John Dwight and Austin Church, established the first factory in the United States to produce baking soda from sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide.[79]
Saleratus, potassium or sodium bicarbonate, is mentioned in the novel Captains Courageous by Rudyard Kipling as being used extensively in the 1800s in commercial fishing to prevent freshly caught fish from spoiling.[80]
In 1919, US Senator Lee Overman declared that bicarbonate of soda could cure the Spanish flu. In the midst of the debate on 26 January 1919, he interrupted the discussion to announce the discovery of a cure. «I want to say, for the benefit of those who are making this investigation,» he reported, «that I was told by a judge of a superior court in the mountain country of North Carolina they have discovered a remedy for this disease.» The purported cure implied a critique of modern science and an appreciation for the simple wisdom of simple people. «They say that common baking soda will cure the disease,» he continued, «that they have cured it with it, that they have no deaths up there at all; they use common baking soda, which cures the disease.»[81]
Production[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate is produced industrially from sodium carbonate:[82]
- Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O → 2 NaHCO3
It is produced on the scale of about 100,000 tonnes/year (as of 2001)[dubious – discuss][83] with a worldwide production capacity of 2.4 million tonnes per year (as of 2002).[84] Commercial quantities of baking soda are also produced by a similar method: soda ash, mined in the form of the ore trona, is dissolved in water and treated with carbon dioxide. Sodium bicarbonate precipitates as a solid from this solution.[citation needed]
Regarding the Solvay process, sodium bicarbonate is an intermediate in the reaction of sodium chloride, ammonia, and carbon dioxide. The product however shows low purity (75pc).[citation needed]
- NaCl + CO2 + NH3 + H2O → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
Although of no practical value, NaHCO3 may be obtained by the reaction of carbon dioxide with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide:[citation needed]
- CO2 + NaOH → NaHCO3
Mining[edit]
Naturally occurring deposits of nahcolite (NaHCO3) are found in the Eocene-age (55.8–33.9 Mya) Green River Formation, Piceance Basin in Colorado. Nahcolite was deposited as beds during periods of high evaporation in the basin. It is commercially mined using common underground mining techniques such as bore, drum, and longwall mining in a fashion very similar to coal mining.[citation needed]
It is also produced by solution mining, pumping heated water through nahcolite beds and crystalizing the dissolved nahcolite through a cooling crystallization process.
In popular culture[edit]
Sodium bicarbonate, as «bicarbonate of soda», was a frequent source of punch lines for Groucho Marx in Marx Brothers movies. In Duck Soup, Marx plays the leader of a nation at war. In one scene, he receives a message from the battlefield that his general is reporting a gas attack, and Groucho tells his aide: «Tell him to take a teaspoonful of bicarbonate of soda and a half a glass of water.»[85] In A Night at the Opera, Groucho’s character addresses the opening night crowd at an opera by saying of the lead tenor: «Signor Lassparri comes from a very famous family. His mother was a well-known bass singer. His father was the first man to stuff spaghetti with bicarbonate of soda, thus causing and curing indigestion at the same time.»[86]
In the Joseph L. Mankewicz classic All About Eve, the Max Fabian character (Gregory Ratoff) has an extended scene with Margo Channing (Bette Davis) in which, suffering from heartburn, he requests and then drinks bicarbonate of soda, eliciting a prominent burp. Channing promises to always keep a box of bicarb with Max’s name on it.
See also[edit]
- Carbonic acid
- List of ineffective cancer treatments
- List of minerals
- Natron
- Natrona (disambiguation)
- Trona
References[edit]
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 4.90
- ^ a b c Haynes, p. 5.194
- ^ a b c «Sodium Bicarbonate» (PDF). United Nations Environment Programme. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 May 2011.
- ^ Ellingboe JL, Runnels JH (1966). «Solubilities of Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Bicarbonate in Acetone-Water and Methanol-Water Mixtures». J. Chem. Eng. Data. 11 (3): 323–324. doi:10.1021/je60030a009.
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 7.23
- ^ Pasquali I, Bettini R, Giordano F (2007). «Thermal behaviour of diclofenac, diclofenac sodium and sodium bicarbonate compositions». Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. 90 (3): 903–907. doi:10.1007/s10973-006-8182-1. S2CID 95695262.
- ^ a b c d Haynes, p. 5.19
- ^ Chambers M. «Sodium bicarbonate [USP:JAN]». ChemIDplus. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations 2005 (PDF), IUPAC, p. 137, archived (PDF) from the original on 18 May 2017
- ^ «Mineral Springs – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics».
- ^ «What’s the difference between bicarbonate of soda, baking soda and baking powder?». ThatsLife! Pacific Network.
- ^ PubChem. «Sodium bicarbonate». pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ «Definition of SALERATUS». www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ «Approved additives and E numbers». Food Standards Agency. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ^ Wollaston, WH (January 1814). «I. A Synoptic scale of chemical equivalents». Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 104: 1–22. doi:10.1098/rstl.1814.0001. S2CID 96774986.
- ^ Bent AJ, ed. (1997). The Technology of Cake Making (6 ed.). Springer. p. 102. ISBN 9780751403497. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ^ Cascio J. «Sourdough» (PDF). University of Alaska Fairbanks Cooperative Extension Service. FNH-00061. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2017.
- ^ «The Many Practical Uses of Baking Soda in the Kitchen». About.com Food. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ Czernohorsky JH, Hooker R. «The Chemistry of Baking» (PDF). New Zealand Institute of Chemistry. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 November 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ «Baking Soda and Baking Powder». FineCooking.com. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ «Baking Soda FAQs». Arm & Hammer Multi-Brand. Church & Dwight Company. What is the difference baking soda and baking powder?. Archived from the original on 27 June 2017. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ «Glossary Ingredients». Cooking.com. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate». BRP Adhikary. 11 July 2016. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ «Sugar snake». MEL Science. MEL Science 2015–2019. Archived from the original on 6 October 2019. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ^ Malik YS, Goyal SM (May 2006). «Virucidal efficacy of sodium bicarbonate on a food contact surface against feline calicivirus, a norovirus surrogate». International Journal of Food Microbiology. 109 (1–2): 160–3. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.08.033. PMID 16540196.
- ^ Rutala WA, Barbee SL, Aguiar NC, Sobsey MD, Weber DJ (January 2000). «Antimicrobial activity of home disinfectants and natural products against potential human pathogens». Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 21 (1): 33–8. doi:10.1086/501694. PMID 10656352. S2CID 34461187.
- ^ Zamani M, Sharifi Tehrani A, Ali Abadi AA (2007). «Evaluation of antifungal activity of carbonate and bicarbonate salts alone or in combination with biocontrol agents in control of citrus green mold». Communications in Agricultural and Applied Biological Sciences. 72 (4): 773–7. PMID 18396809.
- ^ Altman G (22 May 2006). «Book Repair for BookThinkers: How To Remove Odors From Books». The BookThinker (69).
- ^ a b c «Arm & Hammer Baking Soda – Basics – The Magic of Arm & Hammer Baking Soda». armandhammer.com. Archived from the original on 31 August 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2009.
- ^ «Prepare for Emergencies from Uncontrolled Hazards». American Chemical Society.
- ^ Hurum D. «Laboratory Safety» (PDF). Civil Engineering. Northwestern University.
- ^ «Horticulture myths». University of Vermont Extension Department of Plant and Soil Science. Archived from the original on 7 August 2019. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate». Jackson Siegelbaum Gastroenterology. 1998. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- ^ «PegLyte». Pendo Phama.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate Intravenous Infusion» (PDF). Consumer Medicine Information. Better Health Channel. 13 July 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 August 2008.
- ^ «Respiratory Acidosis: Treatment & Medication». emedicine. 26 March 2020.
- ^ Dart RC (2004). Medical Toxicology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 910–. ISBN 978-0-7817-2845-4.
- ^ Cloth Diapers. Donald C. Cooper PhD. pp. 46–.
- ^ [old info]Knudsen K, Abrahamsson J (April 1997). «Epinephrine and sodium bicarbonate independently and additively increase survival in experimental amitriptyline poisoning». Critical Care Medicine. 25 (4): 669–74. doi:10.1097/00003246-199704000-00019. PMID 9142034.
- ^ «Insect bites and stings: First aid». Mayo Clinic. 15 January 2008.
- ^ «Sodium Bicarbonate». American Cancer Society. 28 November 2008. Archived from the original on 19 February 2013. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Ernst E (3 February 2017). «This must be the most sickening cancer scam I have seen for a while».
- ^ Edgcombe H, Hocking G, Radcliffe J (2005). «Anaesthesia UK : Local Anaesthetic Pharmacology». John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK.
- ^ Fox D (15 December 2001). «Hard cheese». New Scientist. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ Fenton, T. R.; Tough, S. C.; Lyon, A. W.; Eliasziw, M.; Hanley, D. A. (2011). «Causal assessment of dietary acid load and bone disease: A systematic review & meta-analysis applying Hill’s epidemiologic criteria for causality». Nutrition Journal. 10: 41. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-10-41. PMC 3114717. PMID 21529374.
- ^ Schwalfenberg, Gerry K. (2012). «The Alkaline Diet: Is There Evidence That an Alkaline pH Diet Benefits Health?». Journal of Environmental and Public Health. 2012: 1–7. doi:10.1155/2012/727630. PMC 3195546. PMID 22013455.
- ^ «Medical information from Prague 2000». Archived from the original on 18 October 2014.
- ^ Shirsand, S. B.; Suresh, Sarasija; Jodhana, L. S.; Swamy, P. V. (2010). «Formulation Design and Optimization of Fast Disintegrating Lorazepam Tablets by Effervescent Method». Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 72 (4): 431–436. doi:10.4103/0250-474X.73911. ISSN 0250-474X. PMC 3013557. PMID 21218052.
- ^ Storehagen S, Ose N, Midha S. «Dentifrices and mouthwashes ingredients and their use» (PDF). Institutt for klinisk odontologi. Universitetet i Oslo.
- ^ US 4132770A, Barth J, «Oral Product», issued 1979
- ^ Iqbal K, Asmat M, Jawed S, Mushtaque A, Mohsin F, Hanif S, et al. (July 2011). «Role of different ingredients of tooth pastes and mouthwashes in oral health» (PDF). Journal of Pakistan Dental Association. 20 (3): 163–70.
- ^ Lamb JH (1946). «Sodium Bicarbonate: An Excellent Deodorant». The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 7 (3): 131–133. doi:10.1038/jid.1946.13.
- ^ «Bicarb soda: natural body deodorant». sustainableecho.com. 10 March 2009.
- ^ Metson RB (2005). The Harvard Medical School Guide to Healing Your Sinues. McGraw Hill. p. 68. ISBN 9780071444699.
- ^ «Blepharitis : Information for patients leaflet» (PDF). Ouh.nhs.uk. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ «Blepharitis. Treatment and Causes. Eyelid inflammation | Patient». Patient. Archived from the original on 5 December 2015. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ Paton LJ, Beauchemin KA, Veira DM, von Keyserlingk MA (2006). «Use of sodium bicarbonate, offered free choice or blended into the ration, to reduce the risk of ruminal acidosis in cattle». Canadian Journal of Animal Science. 86 (3): 429–437. doi:10.4141/A06-014.
- ^ «Blast Away Grime With Baking Soda». Popular Mechanics. 5 August 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ Housecroft CE, Sharpe AG (2008). «Chapter 22: d-block metal chemistry: the first row elements». Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd Edition. Pearson. p. 716. ISBN 978-0-13-175553-6.
- ^ «Science Lab.com». MSDS- Sodium carbonate. sciencelab.com. Archived from the original on 5 September 2012.
- ^ a b «Finishing Techniques in Metalwork». Philadelphia Museum of Art.
- ^ «Put a Shine on It». scifun.chem.wisc.edu. Archived from the original on 31 July 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ Orcutt JA. «Depleted Uranium and Health: Facts and Helpful Suggestions». Pharmacology and Toxicology of Uranium Compounds. McGraw-Hill. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013. Retrieved 21 March 2012.
- ^ Raymond J (10 June 2016). «Kitchen Odor Eliminating Candles, Products, and Tricks». cravedujour.com. Archived from the original on 7 August 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^
Vicki Lansky, Martha Campbell, Baking Soda: Over 500 Fabulous, Fun, and Frugal Uses You’ve Probably Never Thought Of, 2009, ISBN 1931863733, p. 28 - ^ «A trusted solution for more than 170 years. Pure and simple.», Arm & Hammer «About Us» page
- ^ Keith Sawyer, Group Genius: The Creative Power of Collaboration, 2017, ISBN 0465093582, «keep food tasting fresh»
- ^ Clayton M. Christensen, Scott Cook, Taddy Hall, Marketing Malpractice: The Cause and the Cure, Harvard Business Review, December 2005, [1]
- ^ «Myth #100: An Open Box of Baking Soda in the Fridge absorbs Odors», Bruce Weinstein, Mark Scarbrough, Lobsters Scream When You Boil Them; And 100 Other Myths About Food and Cooking, 2011, ISBN 1439195382, p. 312
- ^ «Baking Soda as Odor Absorber | Cook’s Illustrated». Cooksillustrated.com. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ a b «Decomposition of Carbonates». General Chemistry Online. Archived from the original on 2 October 1999. Retrieved 16 March 2010.
- ^ PubChem. «Sodium bicarbonate». pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 16 May 2021.
- ^ «Sodium bicarbonate (S300) batch numbering and shelf life statement – Solvay Chemicals, Inc» (PDF). 31 January 2019.
- ^ «Re: Shelf Life – Sodium Bicarbonate (all grades) – Tronox Alkali Corporation» (PDF). 1 April 2015.
- ^ «Does Baking Soda Go Bad? How to Know If It’s Still Good». The Spruce Eats. Retrieved 16 May 2021.
- ^ Renate Gerner: Instruments and substances used in mummification. In: Renate Gerner, Rosemarie Drenkhahn (ed.): Mumie und Computer. A multidisciplinary research project in Hanover. Special exhibition of the Kestner Museum Hanover from September 26, 1991 to January 19, 1992. Kestner Museum, Hanover 1991, ISBN 3-924029-17-2, p. 28 f.
- ^ Franz Dornseiff: «The Greek words in German.» Walter de Gruyter & Co, Berlin 1950, p. 44.
- ^ Friedrich Kluge, Alfred Götze (Philologist): Etymological Dictionary of the German Language. 20th edition, ed. by Walther Mitzka, De Gruyter, Berlin / New York 1967; Reprint (“21st unchanged edition”) ibid 1975, ISBN 3-11-005709-3, p. 504.
- ^ «Company History». Church & Dwight Co. Archived from the original on 16 October 2011.
- ^ Kipling R (1897). Captains Courageous. p. 25.
- ^ Bristow, Nancy K. (2012), American Pandemic: The Lost Worlds of the 1918 Influenza Epidemic, Oxford University Press, p. 178, ISBN 978-0199811342
- ^ Thieme C (2000). «Sodium Carbonates». Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a24_299. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Holleman AF, Wiberg E (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Page 45, section 3.6.2.1 of «Process Best Practices Reference Document (BREF) for Soda Ash,» report produced by the European Soda Ash Producer’s Association Archived 3 October 2006 at the Wayback Machine, March 2004.
- ^ «Duck Soup (1933)». IMDb. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «A Night at the Opera (1935)». IMDb. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
Bibliography[edit]
- Haynes WM, ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-1439855119.
External links[edit]
- International Chemical Safety Card 1044
Гидрокарбонат натрия NaHCO3 (другие названия: питьевая сода, пищевая сода, бикарбонат натрия, натрий двууглекислый) — кристаллическая соль, однако чаще всего она встречается в виде порошка тонкого помола белого цвета.
Химическая формула
Содержание
- 1 Безопасность
- 2 Химические свойства
- 2.1 Реакция с кислотами
- 3 Термическое разложение
- 4 Применение
- 4.1 Кулинария
- 4.2 Медицина
- 4.3 Пожаротушение
- 5 Производство
- 6 Хранение
- 7 См. также
- 8 Примечания
- 9 Ссылки
Безопасность
Двууглекилый натрий не токсичен, пожаро- и взрывобезопасен.
Представляет собой мелкокристаллический порошок, который при попадании на слизистые оболочки вызывает раздражение. При постоянной работе в атмосфере, загрязненной пылью двууглекислого натрия, может возникнуть раздражение дыхательных путей.[1]
Химические свойства
Гидрокарбонат натрия — кислая натриевая соль угольной кислоты.
Молекулярная масса (по международным атомным массам 1971 г.) — 84,00.[1]
Реакция с кислотами
Гидрокарбонат натрия реагирует с кислотами, с образованием соли и угольной кислоты, которая тут же распадается на углекислый газ и воду:
- NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2CO3
- H2CO3 → H2O + CO2↑
в кулинарии чаще встречается такая реакция с уксусной кислотой, с образованием ацетата натрия:
- NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2↑
Термическое разложение
При температуре 60 °C гидрокарбонат натрия распадается на карбонат натрия, углекислый газ и воду (процесс разложения наиболее эффективен при 200 °C):
- 2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2↑
При дальнейшем нагревании до 1000 °C (например при тушении пожара порошковыми системами) полученный карбонат натрия распадается на углекислый газ и оксид натрия:
- Na2CO3 → Na2O + CO2
Применение
Гидрокарбонат натрия
Двууглекислый натрий (бикарбонат), применяется в химической, пищевой, легкой, медицинской, фармацевтической промышленности, цветной металлургии, поставляется в розничную торговлю.
Зарегистрирован в качестве пищевой добавки E500.
Применение:
- в химической промышленности — для производства красителей, пенопластов и других органических продуктов, фтористых реактивов, товаров бытовой химии, наполнителей в огнетушителях, для отделения двуокиси углерода, сероводорода из газовых смесей (газ поглощается в растворе гидрокарбоната при повышенном давлении и пониженной температуре, раствор восстанавливается при подогреве и пониженном давлении).
- в легкой промышленности — в производстве подошвенных резин и искусственных кож, кожевенном производстве (дубление и нейтрализация кож), текстильной промышленности (отделка шелковых и хлопчатобумажных тканей).
- в пищевой промышленности — хлебопечении, производстве кондитерских изделий, приготовлении напитков.
Кулинария
Основное применение питьевой соды — кулинария, где она применяется, преимущественно, в качестве основного или дополнительного разрыхлителя при выпечке (так как при нагревании выделяет углекислый газ), самостоятельно или в составе комплексных разрыхлителей (например, пекарского порошка, в смести с карбонатом аммония), например, в бисквитном и песочном тесте.
Медицина
Раствор питьевой соды используется в качестве слабого антисептика для полосканий, а также как традиционное кислотонейтрализующее средство от изжоги и болей в желудке (современная медицина не рекомендует применять из-за побочных эффектов, в том числе, из-за «кислотного рикошета») или для устранения ацидоза и т. п.
Пожаротушение
Гидрокарбонат натрия входит в состав порошка, применяемого в порошковых системах пожаротушения, утилизируя тепло и оттесняя кислород от очага горения выделяемым углекислым газом.
Производство
В РФ производят соду по ГОСТ 2156-76 «Натрий двууглекислый. Технические условия».[2]
Хранение
Хранить в закрытых упаковках, не допуская попадания влаги.
Гарантийный срок хранения натрия двууглекислого — 12 месяцев со дня изготовления.
Срок годности не ограничен.
См. также
- Карбонат натрия
- Пищевые добавки
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 ГОСТ 2156-76 «Натрий двууглекислый. Технические условия».[1]
Ссылки
- http://www.infrahim.ru/pfm/187.html
- http://www.uk-him.ru/rus/catalogue/3/43
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
| Гидрокарбонат натрия | |
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Систематическое наименование |
гидрокарбонат натрия |
| Традиционные названия | пищевая (питьевая) сода, сода двууглекислая, двууглекислый натрий, бикарбонат натрия, кислый углекислый натрий |
| Хим. формула | CHNaO₃ |
| Рац. формула | NaHCO3 |
| Состояние | твёрдое |
| Молярная масса | 84,0066 г/моль |
| Плотность | 2,159 г/см³ |
| Т. разл. | 60—200 °C |
| Растворимость в воде | 9,59 г/100 мл |
| ГОСТ | ГОСТ 2156-76 ГОСТ 4201-79 ГОСТ 32802-2014 |
| Рег. номер CAS | 144-55-8 |
| PubChem | 516892 |
| Рег. номер EINECS | 205-633-8 |
| SMILES |
[Na+].OC([O-])=O |
| InChI |
1S/CH2O3.Na/c2-1(3)4;/h(H2,2,3,4);/q;+1/p-1 UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Рег. номер EC | 205-633-8 |
| Кодекс Алиментариус | E500(ii) |
| RTECS | VZ0950000 |
| ChEBI | 32139 |
| ChemSpider | 8609 |
| ЛД50 | 4220 мг/кг |
| Приводятся данные для стандартных условий (25 °C, 100 кПа), если не указано иного. |
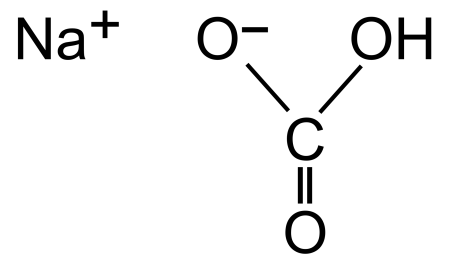
Гидрокарбонат натрия (лат. Natrii hydrocarbonas), другие названия: бикарбонат натрия, чайная сада, питьевая или пищевая сода, двууглекислый натрий — неорганическое соединение, натриевая кислая соль угольной кислоты с химической формулой NaHCO3.
В обычном виде — мелкокристаллический порошок белого цвета.
Используется в промышленности, пищевой промышленности, в кулинарии, в медицине как нейтрализатор химических ожогов кожи и слизистых оболочек концентрированными кислотами и для снижения кислотности желудочного сока. Также применяется в буферных растворах.
Содержание
- 1 Химические свойства
- 1.1 Реакция с кислотами
- 2 Термическое разложение
- 3 Получение
- 4 Применение
- 4.1 В химической промышленности
- 4.2 В кулинарии
- 4.3 В медицине
- 4.3.1 Противопоказания к применению в медицинских целях
- 4.4 Пожаротушение
- 4.5 В быту
- 4.6 В транспорте
- 5 Производство
- 6 Хранение
- 7 Безопасность
Химические свойства
Гидрокарбонат натрия — кислая натриевая соль угольной кислоты. Проявляет все свойства соли сильного основания и слабой кислоты. В водных растворах имеет слабощелочную реакцию. В широком диапазоне концентраций в водном растворе pH раствора изменяется незначительно, на этом основано применение раствора вещества в качестве буферного раствора.
Реакция с кислотами
Гидрокарбонат натрия реагирует с кислотами с образованием соответствующей кислоте соли, например, хлорида натрия, сульфата натрия и угольной кислоты, которая в процессе реакции распадается на углекислый газ и воду, при этом углекислый газ выделяется из раствора в виде пузырьков:
- NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2CO3
- H2CO3 → H2O + CO2↑
- 2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2↑
В быту обычно применяется реакция «гашения соды» уксусной кислотой, с образованием ацетата натрия или гашение лимонной кислотой с образование цитрата натрия, реакция с уксусной кислотой:
- NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2↑
Термическое разложение
При температуре выше 60 °C гидрокарбонат натрия начинает распадаться на карбонат натрия, углекислый газ и воду (процесс разложения наиболее эффективен при 200 °C, при более высоких температурах карбонат натрия начинает распадаться на оксид натрия и углекислый газ):
- 2NaHCO3 →60−200∘C Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2↑
При этом процессе выделения воды в виде водяного пара и углекислого газa масса исходного продукта уменьшается примерно на 37 %.
Получение
В промышленности гидрокарбонат натрия получают аммиачно-хлоридным способом. В концентрированный раствор хлорида натрия, насыщенный аммиаком, под давлением пропускают углекислый газ. В процессе синтеза происходят две реакции:
- NH3 + CO2 + H2O → NH4HCO3
- NH4HCO3 + NaCl → NaHCO3↓ + NH4Cl
В холодной воде гидрокарбонат натрия мало растворим, и его отделяют от охлаждённого раствора фильтрованием, а из полученного после фильтрования раствора хлорида аммония снова получают аммиак, возвращаемый в производство вновь:
- 2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → 2NH3↑ + CaCl2 + 2H2O
Применение
Двууглекислый натрий (бикарбонат) применяется в химической, пищевой, лёгкой, медицинской, фармацевтической промышленности, цветной металлургии, в быту. Зарегистрирован в качестве пищевой добавки E500 (ii), входит в состав пищевой добавки E500.
В химической промышленности
Применяется для производства красителей, пенопластов и других органических продуктов, фторорганических соединений, продуктов бытовой химии, наполнителей в огнетушителях, Реагент для отделения диоксида углерода, сероводорода из газовых смесей, например, отходящих газов топливосжигающих установок. В этом процессе углекислый газ поглощается раствором гидрокарбоната натрия при повышенном давлении и пониженной температуре, далее поглощённый углекислый газ выделяется из раствора при подогреве и снижении давления;
В лёгкой промышленности — в производстве резины для подошв обуви и в производстве искусственных кож, кожевенном производстве при дублении и нейтрализации кожи после кислого дубления, текстильной промышленности при отделке шёлковых и хлопчатобумажных тканей;
В пищевой промышленности — в хлебопечении, производстве кондитерских изделий, приготовлении газированных напитков.
В кулинарии
Основное применение пищевой соды в пищевой промышленности и в быту — кулинария, где применяется, преимущественно, в качестве основного или дополнительного разрыхлителя в составе кислого и пресного теста. При добавлении питьевой соды в кислое тесто происходит реакция с молочной кислотой, продуцированной при заквашивании дрожжевыми микроорганизмами, при этой реакции выделяется углекислый газ, вспучивающий тесто.
При добавлении в пресное тесто углекислый газ выделяется при выпечке из-за термического разложения.
При применении соды в чистом виде важно соблюсти правильную дозировку, так как она оставляет в продукте карбонат натрия, дающий определённый привкус. Порядок замешивания для теста: соду — в муку, кислые компоненты (уксус, кефир и пр.) — в жидкость.
В медицине
Традиционно раствор питьевой соды используется для дезинфекции зубов и дёсен при зубных болях и полости рта и горла, при сильном кашле, ангине, фарингите, а также как общепринятое средство от изжоги и болей в желудке.
Применяется при заболеваниях, сопровождающиеся выраженным ацидозом (при диабете, инфекциях и др), для борьбы с ацидозом при хирургических вмешательствах (назначается 3-5 г. внутрь).
Применяется в качестве антиаритмического средства.
Как антацидное средство (как и все другие щелочи) применяется при язвенной болезни желудка, и двенадцатиперстной кишки, при повышенной кислотности желудочного сока.
Имеются так же данные о применении препарата (в виде капельных и внутривенных вливаний) при гипертонической болезни, симптоматической почечной гипертонии, и хронической почечной недостаточности. Эффект связан с увеличением выделения ионов натрия и хлора и возрастанием осмотического диуреза.
В виде свечей применяется против укачивания при морской и воздушной болезнях
Применяется в качестве отхаркивающего средства, т.к. повышая щелочные резервы крови, сдвигает в щелочную сторону реакцию бронхиальной слизи, делая мокроту менее вязкой.
При ринитах, конъюнктивитах, стоматитах, ларингитах и т.п. применяют для полосканий, промываний, ингаляций 0,5 — 2% р-ры гидрокарбоната натрия.
Применяется внутривенно с целью быстрого устранения метаболического ацидоза во время реанимационных мероприятий, заболеваниях почек.
Нужно иметь ввиду, что в результате применения может возникнуть т.н. кислотный рикошет (при реакции содой с соляной кислотой происходит выделение CO2, который оказывает раздражающее действие на стенку желудка, усиливая выделение гастрина).
В альтернативной медицине питьевая сода иногда заявляется как «лекарство» от рака, однако, никакой экспериментально подтверждённой эффективности применения такого «лечения» не существует.
Противопоказания к применению в медицинских целях
Индивидуальная гиперчувствительность; состояния, сопровождающиеся развитием алкалоза; гипокальциемия, при приеме внутрь усиливает алкалоз и повышает риск развития тетанических судорог, гипохлоремия — снижение концентрации в крови ионов Cl—, в том числе вызванная рвотой, или снижением всасывания в желудочно-кишечном тракте, может привести к тяжёлому алкалозу.
Является источником натрия, тем самым увеличивая объём циркулирующей крови, усугубляя отёки и повышая артериальное давление. Применение при сниженной скорости клубочковой фильтрации может привести к метаболическому алкалозу.
Пожаротушение
Гидрокарбонат натрия вместе с карбонатом аммония используется в качестве наполнителя в огнетушителях с сухим наполнением и в стационарных системах сухого пожаротушения. Это применение обусловлено тем, что от воздействия высокой температуры в очаге горения вещество выделяет углекислый газ, атмосфера которого затрудняет доступ кислорода воздуха в очаг горения.
В быту
Применяется как безопасное для здоровья средство для чистки поверхностей столовой и кухонной посуды, поверхностей кухонных столов, иных поверхностей, соприкасающихся с пищей, путем протирки их с помощью влажной тряпки с сухим порошком питьевой соды.
В транспорте
Применяется для нейтрализации следов электролита — серной кислоты на поверхности пластмассовых корпусов свинцовых аккумуляторов насыщенным водным раствором питьевой соды.
Производство
В Российской Федерации двууглекислый натрий выпускается в соответствии с требованиями и техническими условиями, выпускается на предприятиях АО «Башкирская содовая компания» в г. Стерлитамак, Республика Башкортостан, а также на Крымском содовом заводе в г. Красноперекопск, Крымский полуостров.
Хранение
Гидрокарбонат натрия хранят в закрытых упаковках, в сухом месте вдали от источников огня. Гарантийный срок хранения натрия двууглекислого — 12 месяцев со дня изготовления. Срок годности не ограничен.
Безопасность
Вещество нетоксично, пожаро- и взрывобезопасно.
Имеет солоноватый, мыльный вкус. При попадании пыли вещества на слизистые оболочки глаз и носа вызывает лёгкое раздражение. При частой работе в атмосфере, загрязнённой пылью двууглекислого натрия, может возникнуть раздражение верхних дыхательных путей. Предельно допустимая концентрация пыли бикарбоната натрия в воздухе производственных помещений 5 мг/м3.
- ГОСТ 2156-76. Натрий двууглекислый. Технические условия (с Изменениями № 1, 2, 3, 4).
- ГОСТ 32802-2014. Добавки пищевые. Натрия карбонаты E500. Общие технические условия.
На чтение 5 мин. Просмотров 5.5k. Опубликовано 10.11.2018
Обновлено 07.04.2020
Словом «сода» называют несколько сложных химических веществ. Пищевая, питьевая, гидрокарбонат натрия, химическая формула NaHCO3, кислая натриевая соль угольной кислоты. Кальцинированная, бельевая, карбонат натрия, химическая формула Na2CO3, натриевая соль угольной кислоты.
Каустическая, гидроксид натрия, химическая формула NaOH. Есть еще некоторые технические виды соды – кристаллогидраты, содержащие карбонат натрия, и различные марки каустика. Вышеперечисленные соединения имеют различные свойства и химические формулы. Но все они хорошо растворяются в воде, а их растворы имеют более или менее выраженную щелочную реакцию. Рассмотрим их подробнее.
Содержание
- Формула пищевой соды
- Растворяется ли пищевая сода в воде?
- Кальцинированная сода и ее кристаллогидраты
- Каустик и его технические марки
Формула пищевой соды
Гидрокарбонат натрия – химическое название белого кристаллического порошка белого цвета со средним размером кристаллов 0,05 — 0,20 мм. Синонимы, часто встречающиеся в научно-популярной литературе и в быту, — пищевая сода, чайная, питьевая, натрий двууглекислый, бикарбонат натрия.
Двууглекислый натрий (бикарбонат) – широко востребованное вещество в разных сферах жизни. Он применяется в химической промышленности и медицине, в легкой, пищевой отраслях, в металлургии. В пищевой промышленности сода включена в состав добавки E500.
Формула питьевой соды в химии NaHCO3 говорит о том, что это кислая натриевая соль угольной кислоты. Ее химические свойства как у соли сильного основания и слабой кислоты.
Гидрокарбонат натрия активно вступает в реакцию с кислотами. В результате образуется соль соответствующей кислоты, угольная кислота, которая в свою очередь распадается на углекислый газ и воду. Сильное образование пузырьков — это углекислый газ, высвобождающийся в процессе реакции.
Вот как происходит реакция с соляной кислотой:
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2CO3
H2CO3 → H2O + CO2↑.
Реакция соды пищевой с уксусной кислотой:
NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2↑
В результате взаимодействия соды NaHCO3 с уксусной кислотой CH3COOH образуются: CH3COONa – ацетат натрия, вода H2O и углекислый газ CO2.
Многими, наверное, замечено, что если залить пищевую соду кипятком, она так же начинает гаситься, что выражается в обильном образовании пузырьков. Это происходит реакция термического разложения.
Гидракарбонат натрия термически малоустойчив. При нагревании порошок соды пищевой разлагается с образованием карбоната натрия (соды кальцинированной) и выделением диоксида углерода, а также воды в газовую фазу.
2NaHCO3↔ Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
Аналогично разлагаются и водные растворы бикарбоната натрия.
Растворяется ли пищевая сода в воде?
Есть 2 важные момента в растворении натрия гидрокарбоната в воде. Если мы растворяем соду притемпературе до 50 °С, происходит реакция гидролиза соли. Это обратимое взаимодействие соли с водой. Приводит к образованию слабого электролита.
А если растворяем соду в горячей воде, то уже образуется карбонат натрия, и в этом случае, водный раствор имеет сильнощелочную реакцию. Отсюда вывод: растворимость гидрокарбоната натрия в воде невелика, но при повышении температуры и она повышается.
При взаимодействии с водой двууглекислый натрий распадается на гидроксид натрия NaOH , который придает щелочность воде, угольную кислоту H2CO3, которая, в свою очередь, сразу же распадается на воду и углекислый газ H2O + CO2.
Химическая формула растворения соды в воде:
NaHCO3 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 (H2O + CO2) + NaOH
Водный раствор соды пищевой на растительные и животные ткани практически не действует.
Кальцинированная сода и ее кристаллогидраты
Карбонат натрия, или соду кальцинированную, натриевая соль угольной кислоты, не следует путать с содой пищевой. Химическая формула соды кальцинированной Na2CO3. Еще ее называют содой бельевой, потому что применяют в изготовлении моющих и чистящих средств бытовой химии. Добывается из природных кристаллогидратов путем термического разложения. Кальцинированная сода, безводный карбонат натрия, представляет собой бесцветный порошок.
Различные кристаллогидраты кальцинированной соды имеют свои названия:
- Натрит, натрон – декагидрат карбоната натрия. Химическая формула: Na2CO3 • 10H2O
- Термонатрит – моногидрат карбоната натрия. Химическая формула: Na2CO3 • H2O
Эти кристаллогидраты еще называют кристаллической содой, технической содой.
Каустик и его технические марки
Каустическая сода, гидроксид натрия, химическая формула: NaOH. Ее еще называют едким натром, каустиком, едкой щелочью. Сильное основание, молекулы полностью диссоциируют в воде. Даже на воздухе то вещество начинает активно впитывать воду и «расплывается».
Опасная едкая щелочь может оставлять на коже сильные ожоги. Поэтому при работе с каустической содой необходимо соблюдать технику безопасности.
Применяется в быту, в химической, целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности, для производства мыла и био-дизельного топлива.
В России производится несколько видов технической соды – натра едкого:
- РД — раствор диафрагменный, бесцветная или окрашенная жидкость с массовой долей NaOH 44,0 % — 46,0 %;
- РХ — раствор химический с массовой долей NaOH 45,5 %, допускается небольшой осадок;
- РР — раствор ртутный, прозрачная жидкость с массовой долей NaOH 42,0 %;
- ТД — твердый диафрагменный, плавленая масса белого цвета с массовой долей NaOH 94,0 %;
- ТР — твёрдый ртутный, чешуированная масса белого цвета, с массовой долей NaOH 98,5 %.
Как видите, сода соде рознь. Принимать внутрь можно только пищевую, остальные виды — технические. Особенно осторожно необходимо обращаться с каустической содой. Это едкое агрессивное вещество оставляет долго незаживающие ожоги на коже. Поэтому, работать с растворами каустика нужно в защитной одежде, маске и резиновых перчатках.
С точки зрения химии содой называют целый класс соединений — натриевых
— кальцинированную соду (карбонат натрия Na2CO3);
— кристаллогидраты карбоната натрия (Na2CO3•10H2O, Na2CO3•7H2O, Na2CO3•H2O);
— пищевую соду (натрий углекислый кислый NaHCO3, который также называют бикарбонатом или гидрокарбонатом натрия).
Все натриевые соли угольной кислоты представляют собой бесцветные кристаллы, которые, будучи размолотыми в мелкий порошок, становятся белыми; без запаха, хорошо растворяющиеся в воде.
Водный раствор имеет щелочную реакцию. При этом раствор NaHCO3 сохраняет стабильный рН в большом диапазоне концентраций, поэтому на его основе изготавливают стандарт-титр «Натрий углекислый кислый» 0,1 H.
При нагревании свыше 60 °С гидрокарбонат натрия разлагается с выделением углекислого газа. На этом свойстве основано применение пищевой соды в кулинарии в качестве разрыхлителя, а также в порошковых огнетушителях и противопожарных системах (выделяющийся СО2 не поддерживает горение и блокирует доступ кислорода к огню).
Производство
Соду добывают из минералов нахколита, натрита, термонатрита, троны. Также она содержится в золе некоторых растений. Само название химического реактива, «сода», возникло из-за того, что первоначально ее добывали из золы Salsola soda (Солянки содоносной).
Большую часть мирового объема соды производят искусственным путем.
Применение калицинированной соды и кристаллогидратов карбоната натрия:

— изготовление керамики; изделий из высококачественных марок стекла (хрустальных, из электровакуумного, оптического стекла); особых видов стекла (пеностекло, «жидкое стекло»);
— в процессах производства цветных и черных металлов — например, чугуна, алюминия, вольфрама; для обезжиривания металлов;
— для очистки нефтепродуктов;
— в изготовлении целлюлозы;
— в кожевенном производстве (дубление кож);
— для смягчения воды в промышленных установках;
— в мыловарении;
— для нейтрализации кислых сред;
— в газоочистке;
— в быту — для чистки и мытья посуды, обезжиривания, смягчения воды, нейтрализации кислоты.
Применение натрия углекислого кислого:
— в пищевой промышленности и домашней кулинарии как регулятор 
— в системах пожаротушения;
— при производстве красителей, органических продуктов, в т.ч. пенопластов, искусственной резины и кожи, фтористых хим. реактивов; для выделения H2S и СО2 из газовых смесей, товаров бытовой химии;
— в медицине, фармацевтике, быту для лечения изжоги, ожогов, укусов пчел и ос, в качестве антисептика;
— для обработки хлопковых и шелковых тканей; дубления кож;
— в качестве поглотителя запахов, чистящего средства, средства для удаления накипи.
Магазин химических реактивов и лабораторного оборудования Prime Chemicals Group предлагает купить кальцинированную соду и другие химреактивы по хорошим ценам, с самовывозом со склада в Мытищах или с доставкой по Москве и Московской области. Широкий выбор и отличный сервис делают сотрудничество с нами удобным.















