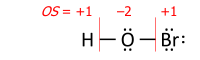Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
В химии термины «окисление» и «восстановление» означает реакции, при которых атом или группа атомов теряют или, соответственно, приобретают электроны. Степень окисления — это приписываемая одному либо нескольким атомам численная величина, характеризующая количество перераспределяемых электронов и показывающая, каким образом эти электроны распределяются между атомами при реакции. Определение этой величины может быть как простой, так и довольно сложной процедурой, в зависимости от атомов и состоящих из них молекул. Более того, атомы некоторых элементов могут обладать несколькими степенями окисления. К счастью, для определения степени окисления существуют несложные однозначные правила, для уверенного пользования которыми достаточно знания основ химии и алгебры.
-
1
Определите, является ли рассматриваемое вещество элементарным. Степень окисления атомов вне химического соединения равна нулю. Это правило справедливо как для веществ, образованных из отдельных свободных атомов, так и для таких, которые состоят из двух, либо многоатомных молекул одного элемента.
- Например, Al(s) и Cl2 имеют степень окисления 0, поскольку оба находятся в химически несвязанном элементарном состоянии.
- Обратите внимание, что аллотропная форма серы S8, или октасера, несмотря на свое нетипичное строение, также характеризуется нулевой степенью окисления.
-
2
Определите, состоит ли рассматриваемое вещество из ионов. Степень окисления ионов равняется их заряду. Это справедливо как для свободных ионов, так и для тех, которые входят в состав химических соединений.
- Например, степень окисления иона Cl— равняется -1.
- Степень окисления иона Cl в составе химического соединения NaCl также равна -1. Поскольку ион Na, по определению, имеет заряд +1, мы заключаем, что заряд иона Cl -1, и таким образом степень его окисления равна -1.
-
3
Учтите, что ионы металлов могут иметь несколько степеней окисления. Атомы многих металлических элементов могут ионизироваться на разные величины. Например, заряд ионов такого металла как железо (Fe) равняется +2, либо +3.[1]
Заряд ионов металла (и их степень окисления) можно определить по зарядам ионов других элементов, с которыми данный металл входит в состав химического соединения; в тексте этот заряд обозначается римскими цифрами: так, железо (III) имеет степень окисления +3.- В качестве примера рассмотрим соединение, содержащее ион алюминия. Общий заряд соединения AlCl3 равен нулю. Поскольку нам известно, что ионы Cl— имеют заряд -1, и в соединении содержится 3 таких иона, для общей нейтральности рассматриваемого вещества ион Al должен иметь заряд +3. Таким образом, в данном случае степень окисления алюминия равна +3.
-
4
Степень окисления кислорода равна -2 (за некоторыми исключениями). Почти во всех случаях атомы кислорода имеют степень окисления -2. Есть несколько исключений из этого правила:
- Если кислород находится в элементарном состоянии (O2), его степень окисления равна 0, как и в случае других элементарных веществ.
- Если кислород входит в состав перекиси, его степень окисления равна -1. Перекиси — это группа соединений, содержащих простую кислород-кислородную связь (то есть анион перекиси O2-2). К примеру, в составе молекулы H2O2 (перекись водорода) кислород имеет заряд и степень окисления -1.
- В соединении с фтором кислород обладает степенью окисления +2, читайте правило для фтора ниже.
-
5
Водород характеризуется степенью окисления +1, за некоторыми исключениями. Как и для кислорода, здесь также существуют исключения. Как правило, степень окисления водорода равна +1 (если он не находится в элементарном состоянии H2). Однако в соединениях, называемых гидридами, степень окисления водорода составляет -1.
- Например, в H2O степень окисления водорода равна +1, поскольку атом кислорода имеет заряд -2, и для общей нейтральности необходимы два заряда +1. Тем не менее, в составе гидрида натрия степень окисления водорода уже -1, так как ион Na несет заряд +1, и для общей электронейтральности заряд атома водорода (а тем самым и его степень окисления) должен равняться -1.
-
6
Фтор всегда имеет степень окисления -1. Как уже было отмечено, степень окисления некоторых элементов (ионы металлов, атомы кислорода в перекисях и так далее) может меняться в зависимости от ряда факторов. Степень окисления фтора, однако, неизменно составляет -1. Это объясняется тем, что данный элемент имеет наибольшую электроотрицательность — иначе говоря, атомы фтора наименее охотно расстаются с собственными электронами и наиболее активно притягивают чужие электроны. Таким образом, их заряд остается неизменным.
-
7
Сумма степеней окисления в соединении равна его заряду. Степени окисления всех атомов, входящих в химическое соединение, в сумме должны давать заряд этого соединения. Например, если соединение нейтрально, сумма степеней окисления всех его атомов должна равняться нулю; если соединение является многоатомным ионом с зарядом -1, сумма степеней окисления равна -1, и так далее.
- Это хороший метод проверки — если сумма степеней окисления не равна общему заряду соединения, значит вы где-то ошиблись.
Реклама
-
1
Найдите атомы, не имеющие строгих правил относительно степени окисления. По отношению к некоторым элементам нет твердо установленных правил нахождения степени окисления. Если атом не подпадает ни под одно правило из перечисленных выше, и вы не знаете его заряда (например, атом входит в состав комплекса, и его заряд не указан), вы можете установить степень окисления такого атома методом исключения. Вначале определите заряд всех остальных атомов соединения, а затем из известного общего заряда соединения вычислите степень окисления данного атома.
- Например, в соединении Na2SO4 неизвестен заряд атома серы (S) — мы лишь знаем, что он не нулевой, поскольку сера находится не в элементарном состоянии. Это соединение служит хорошим примером для иллюстрации алгебраического метода определения степени окисления.
-
2
Найдите степени окисления остальных элементов, входящих в соединение. С помощью описанных выше правил определите степени окисления остальных атомов соединения. Не забывайте об исключениях из правил в случае атомов O, H и так далее.
- Для Na2SO4, пользуясь нашими правилами, мы находим, что заряд (а значит и степень окисления) иона Na равен +1, а для каждого из атомов кислорода он составляет -2.
-
3
Умножьте количество атомов на их степень окисления. Теперь, когда нам известны степени окисления всех атомов за исключением одного, необходимо учесть, что атомов некоторых элементов может быть несколько. Умножьте число атомов каждого элемента (оно указано в химической формуле соединения в виде подстрочного числа, следующего за символом элемента) на его степень окисления.
- В Na2SO4 мы имеем 2 атома Na и 4 атома O. Таким образом, умножая 2 × +1, получаем степень окисления всех атомов Na (2), а умножая 4 × -2 — степень окисления атомов O (-8).
-
4
Сложите предыдущие результаты. Суммируя результаты умножения, получаем степень окисления соединения без учета вклада искомого атома.
- В нашем примере для Na2SO4 мы складываем 2 и -8 и получаем -6.
-
5
Найдите неизвестную степень окисления из заряда соединения. Теперь у вас есть все данные для простого расчета искомой степени окисления. Запишите уравнение, в левой части которого будет сумма числа, полученного на предыдущем шаге вычислений, и неизвестной степени окисления, а в правой — общий заряд соединения. Иными словами, (Сумма известных степеней окисления) + (искомая степень окисления) = (заряд соединения).
- В нашем случае Na2SO4 решение выглядит следующим образом:
- (Сумма известных степеней окисления) + (искомая степень окисления) = (заряд соединения)
- -6 + S = 0
- S = 0 + 6
- S = 6. В Na2SO4 сера имеет степень окисления 6.
Реклама
- В нашем случае Na2SO4 решение выглядит следующим образом:
Советы
- В соединениях сумма всех степеней окисления должна равняться заряду. Например, если соединение представляет собой двухатомный ион, сумма степеней окисления атомов должна быть равна общему ионному заряду.
- Очень полезно уметь пользоваться периодической таблицей Менделеева и знать, где в ней располагаются металлические и неметаллические элементы.
- Степень окисления атомов в элементарном виде всегда равна нулю. Степень окисления единичного иона равна его заряду. Элементы группы 1A таблицы Менделеева, такие как водород, литий, натрий, в элементарном виде имеют степень окисления +1; степень окисления металлов группы 2A, таких как магний и кальций, в элементарном виде равна +2. Кислород и водород, в зависимости от вида химической связи, могут иметь 2 различных значения степени окисления.
Реклама
Что вам понадобится
- Периодическая таблица элементов
- Доступ в интернет или справочники по химии
- Лист бумаги, ручка или карандаш
- Калькулятор
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 640 197 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
Темы кодификатора ЕГЭ: Электроотрицательность. Степень окисления и валентность химических элементов.
Когда атомы взаимодействуют и образуют химическую связь, электроны между ними в большинстве случаев распределяются неравномерно, поскольку свойства атомов различаются. Более электроотрицательный атом сильнее притягивает к себе электронную плотность. Атом, который притянул к себе электронную плотность, приобретает частичный отрицательный заряд δ—, его «партнер» — частичный положительный заряд δ+. Если разность электроотрицательностей атомов, образующих связь, не превышает 1,7, мы называем связь ковалентной полярной. Если разность электроотрицательностей, образующих химическую связь, превышает 1,7, то такую связь мы называем ионной.
Степень окисления – это вспомогательный условный заряд атома элемента в соединении, вычисленный из предположения, что все соединения состоят из ионов (все полярные связи – ионные).
Что значит «условный заряд»? Мы просто-напросто договариваемся, что немного упростим ситуацию: будем считать любые полярные связи полностью ионными, и будем считать, что электрон полностью уходит или приходит от одного атома к другому, даже если на самом деле это не так. А уходит условно электрон от менее электроотрицательного атома к более электроотрицательному.
Например, в связи H-Cl мы считаем, что водород условно «отдал» электрон, и его заряд стал +1, а хлор «принял» электрон, и его заряд стал -1. На самом деле таких полных зарядов на этих атомах нет.
Наверняка, у вас возник вопрос — зачем же придумывать то, чего нет? Это не коварный замысел химиков, все просто: такая модель очень удобна. Представления о степени окисления элементов полезны при составлении классификации химических веществ, описании их свойств, составлении формул соединений и номенклатуры. Особенно часто степени окисления используются при работе с окислительно-восстановительными реакциями.
Степени окисления бывают высшие, низшие и промежуточные.
Высшая степень окисления равна номеру группы со знаком «плюс».
Низшая определяется, как номер группы минус 8.
И промежуточная степень окисления — это почти любое целое число в интервале от низшей степени окисления до высшей.
Например, для азота характерны: высшая степень окисления +5, низшая 5 — 8 = -3, а промежуточные степени окисления от -3 до +5. Например, в гидразине N2H4 степень окисления азота промежуточная, -2.
Чаще всего степень окисления атомов в сложных веществах обозначается сначала знаком, потом цифрой, например +1, +2, -2 и т.д. Когда речь идет о заряде иона (предположим, что ион реально существует в соединении), то сначала указывают цифру, потом знак. Например: Ca2+, CO3 2-.
Для нахождения степеней окисления используют следующие правила:
- Степень окисления атомов в простых веществах равна нулю;
- В нейтральных молекулах алгебраическая сумма степеней окисления равна нулю, для ионов эта сумма равна заряду иона;
- Степень окисления щелочных металлов (элементы I группы главной подгруппы) в соединениях равна +1, степень окисления щелочноземельных металлов (элементы II группы главной подгруппы) в соединениях равна +2; степень окисления алюминия в соединениях равна +3;
- Степень окисления водорода в соединениях с металлами (солеобразные гидриды — NaH, CaH2 и др.) равна -1; в соединениях с неметаллами (летучие водородные соединения) +1;
- Степень окисления кислорода равна -2. Исключение составляют пероксиды – соединения, содержащие группу –О-О-, где степень окисления кислорода равна -1, и некоторые другие соединения (супероксиды, озониды, фториды кислорода OF2 и др.);
- Степень окисления фтора во всех сложных веществах равна -1.
Выше перечислены ситуации, когда степень окисления мы считаем постоянной. У всех остальных химических элементов степень окисления — переменная, и зависит от порядка и типа атомов в соединении.
Примеры:
Задание: определите степени окисления элементов в молекуле дихромата калия: K2Cr2O7.
Решение: степень окисления калия равна +1, степень окисления хрома обозначим, как х, степень окисления кислорода -2. Сумма всех степеней окисления всех атомов в молекуле равна 0. Получаем уравнение: +1*2+2*х-2*7=0. Решаем его, получаем степень окисления хрома +6.
В бинарных соединениях более электроотрицательный элемент характеризуется отрицательной степенью окисления, менее электроотрицательный – положительной.
Обратите внимание, что понятие степени окисления – очень условно! Степень окисления не показывает реальный заряд атома и не имеет реального физического смысла. Это упрощенная модель, которая эффективно работает, когда нам необходимо, например, уравнять коэффициенты в уравнении химической реакции, или для алгоритмизации классификации веществ.
Степень окисления – это не валентность! Степень окисления и валентность во многих случаях не совпадают. Например, валентность водорода в простом веществе Н2 равна I, а степень окисления, согласно правилу 1, равна 0.
Это базовые правила, которые помогут Вам определить степень окисления атомов в соединениях в большинстве случаев.
В некоторых ситуациях вы можете столкнуться с трудностями при определении степени окисления атома. Рассмотрим некоторые из этих ситуаций, и разберем способы их разрешения:
- В двойных (солеобразных) оксидах степень у атома, как правило, две степени окисления. Например, в железной окалине Fe3O4 у железа две степени окисления: +2 и +3. Какую из них указывать? Обе. Для упрощения можно представить это соединение, как соль: Fe(FeO2)2. При этом кислотный остаток образует атом со степенью окисления +3. Либо двойной оксид можно представить так: FeO*Fe2O3.
- В пероксосоединениях степень окисления атомов кислорода, соединенных ковалентными неполярными связями, как правило, изменяется. Например, в пероксиде водорода Н2О2, и пероксидах щелочных металлов степень окисления кислорода -1, т.к. одна из связей – ковалентная неполярная (Н-О-О-Н). Другой пример – пероксомоносерная кислота (кислота Каро) H2SO5 (см. рис.) содержит в составе два атома кислорода со степенью окисления -1, остальные атомы со степенью окисления -2, поэтому более понятной будет такая запись: H2SO3(O2). Известны также пероксосоединения хрома – например, пероксид хрома (VI) CrO(O2)2 или CrO5, и многие другие.
- Еще один пример соединений с неоднозначной степенью окисления – супероксиды (NaO2) и солеобразные озониды KO3. В этом случае уместнее говорить о молекулярном ионе O2 с зарядом -1 и и O3 с зарядом -1. Строение таких частиц описывается некоторыми моделями, которые в российской учебной программе проходят на первых курсах химических ВУЗов: МО ЛКАО, метод наложения валентных схем и др.
- В органических соединениях понятие степени окисления не очень удобно использовать, т.к. между атомами углерода существует большое число ковалентных неполярных связей. Тем не менее, если нарисовать структурную формулу молекулы, то степень окисления каждого атома также можно определить по типу и количеству атомов, с которыми данный атом непосредственно связан. Например, у первичных атомов углерода в углеводородах степень окисления равна -3, у вторичных -2, у третичных атомов -1, у четвертичных — 0.
Потренируемся определять степень окисления атомов в органических соединениях. Для этого необходимо нарисовать полную структурную формулу атома, и выделить атом углерода с его ближайшим окружением — атомами, с которыми он непосредственно соединен.
Полезные советы:
- Для упрощения расчетов можно использовать таблицу растворимости – там указаны заряды наиболее распространенных ионов. На большинстве российских экзаменов по химии (ЕГЭ, ГИА, ДВИ) использование таблицы растворимости разрешено. Это готовая шпаргалка, которая во многих случаях позволяет значительно сэкономить время.
- При расчете степени окисления элементов в сложных веществах сначала указываем степени окисления элементов, которые мы точно знаем (элементы с постоянной степенью окисления), а степень окисления элементов с переменной степенью окисления обозначаем, как х. Сумма всех зарядов всех частиц равна нулю в молекуле или равна заряду иона в ионе. Из этих данных легко составить и решить уравнение.
Тренировочный тест по теме «Степени окисления и валентность» 10 вопросов, при каждом прохождении новые.
120
Создан на
07 января, 2022 По Admin
Тренировочный тест «Степени окисления»
1 / 10
1) Be 2) Li 3) K 4) N 5) Cs
Из числа указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, каждый из которых может образовать оксид с общей формулой ЭО.
Запишите в поле ответа номера выбранных элементов.
2 / 10
1) K 2) As 3) P 4) I 5) Al
Из числа указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, у каждого из которых разница между максимальной и минимальной возможными степенями окисления не равна 8.
Запишите в поле ответа номера выбранных элементов.
3 / 10
1) Be 2) S 3) Mg 4) C 5) Ca
Из числа указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, у каждого из которых разница между максимальной и минимальной возможными степенями окисления равна 8.
Запишите в поле ответа номера выбранных элементов.
4 / 10
1) Li 2) Si 3) S 4) Al 5) F
Из приведённого списка выберите два элемента, которые в соединениях могут проявлять степень окисления +4.
Запишите в поле ответа номера выбранных элементов в порядке возрастания.
5 / 10
1) O 2) P 3) Si 4) Cr 5) S
Из числа указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, степень окисления которых в оксидах может принимать значение +3.
6 / 10
1) Sr 2) Br 3) Rb 4) As 5) Se
Из указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, которые в соединениях проявляют постоянную степень окисления.
7 / 10
1) Si 2) Se 3) Mg 4) C 5) S
Из указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, для которых наименьшая степень окисления равна -2.
8 / 10
1) S 2) P 3) Ar 4) Si 5) Mg
Из указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, которые в соединениях не проявляют отрицательной степени окисления.
9 / 10
1) Zn 2) Si 3) Cu 4) S 5) P
Из числа указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, степень окисления которых в оксидах может принимать значение +4.
10 / 10
1) Cl 2) Sr 3) Se 4) P 5) K
Из числа указанных в ряду элементов выберите два элемента, которые в составе образованных ими кислородсодержащих анионов могут иметь одинаковую степень окисления.
Ваша оценка
Средний балл 57%
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge.
The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the «real» charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. Thus, the oxidation state of an atom in a compound is purely a formalism. It is nevertheless important in understanding the nomenclature conventions of inorganic compounds. Also, several observations regarding chemical reactions may be explained at a basic level in terms of oxidation states.
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, zero, or negative. In some cases, the average oxidation state of an element is a fraction, such as 8/3 for iron in magnetite Fe3O4 (see below). The highest known oxidation state is reported to be +9, displayed by iridium in the tetroxoiridium(IX) cation (IrO+4).[1] It is predicted that even a +10 oxidation state may be achieved by platinum in tetroxoplatinum(X), PtO2+4.[2] The lowest oxidation state is −5, as for boron in Al3BC.[3]
In inorganic nomenclature, the oxidation state is represented by a Roman numeral placed after the element name inside parentheses or as a superscript after the element symbol, e.g. Iron(III) oxide.
The term oxidation was first used by Antoine Lavoisier to signify the reaction of a substance with oxygen. Much later, it was realized that the substance, upon being oxidized, loses electrons, and the meaning was extended to include other reactions in which electrons are lost, regardless of whether oxygen was involved.
The increase in the oxidation state of an atom, through a chemical reaction, is known as oxidation; a decrease in oxidation state is known as a reduction. Such reactions involve the formal transfer of electrons: a net gain in electrons being a reduction, and a net loss of electrons being oxidation. For pure elements, the oxidation state is zero.
IUPAC definition[edit]
IUPAC has published a «Comprehensive definition of the term oxidation state (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)».[4] It is a distillation of an IUPAC technical report «Toward a comprehensive definition of oxidation state» from 2014.[5] The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation state is:
Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…
— IUPAC[6]
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous.[7]
The underlying principle is that the ionic charge is «the oxidation state of an atom, after ionic approximation of its bonds»,[8] where ionic approximation means, hypothesizing that all bonds are ionic. Several criteria were considered for the ionic approximation:
- Extrapolation of the bond’s polarity;
- from the electronegativity difference,
- from the dipole moment, and
- from quantum‐chemical calculations of charges.
- Assignment of electrons according to the atom’s contribution to the bonding Molecular orbital (MO)[8][9]/ the electron’s allegiance in a LCAO–MO model.[10]
In a bond between two different elements, the bond’s electrons are assigned to its main atomic contributor/higher electronegativity; in a bond between two atoms of the same element, the electrons are divided equally. This is because most electronegativity scales depend on the atom’s bonding state, which makes the assignment of the oxidation state a somewhat circular argument. For example, some scales may turn out unusual oxidation states, such as -6 for platinum in PtH2−4, for Pauling and Mulliken scales.[11] The dipole moments would, sometimes, also turn out abnormal oxidation numbers, such as in CO and NO, which
are oriented with their positive end towards oxygen. Therefore, this leaves the atom’s contribution to the
bonding MO, the atomic-orbital energy, and from quantum-chemical calculations of charges, as the only viable criteria with cogent values for ionic approximation. However, for a simple estimate for the ionic approximation, we can use Allen electronegativities,[8] as only that electronegativity scale is truly independent of the oxidation state, as it relates to the average valence‐electron energy of the free atom:
Electronegativity using the Allen scale |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group → | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| ↓ Period | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | H 2.300 |
He 4.160 |
||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Li 0.912 |
Be 1.576 |
B 2.051 |
C 2.544 |
N 3.066 |
O 3.610 |
F 4.193 |
Ne 4.787 |
||||||||||
| 3 | Na 0.869 |
Mg 1.293 |
Al 1.613 |
Si 1.916 |
P 2.253 |
S 2.589 |
Cl 2.869 |
Ar 3.242 |
||||||||||
| 4 | K 0.734 |
Ca 1.034 |
Sc 1.19 |
Ti 1.38 |
V 1.53 |
Cr 1.65 |
Mn 1.75 |
Fe 1.80 |
Co 1.84 |
Ni 1.88 |
Cu 1.85 |
Zn 1.588 |
Ga 1.756 |
Ge 1.994 |
As 2.211 |
Se 2.424 |
Br 2.685 |
Kr 2.966 |
| 5 | Rb 0.706 |
Sr 0.963 |
Y 1.12 |
Zr 1.32 |
Nb 1.41 |
Mo 1.47 |
Tc 1.51 |
Ru 1.54 |
Rh 1.56 |
Pd 1.58 |
Ag 1.87 |
Cd 1.521 |
In 1.656 |
Sn 1.824 |
Sb 1.984 |
Te 2.158 |
I 2.359 |
Xe 2.582 |
| 6 | Cs 0.659 |
Ba 0.881 |
Lu 1.09 |
Hf 1.16 |
Ta 1.34 |
W 1.47 |
Re 1.60 |
Os 1.65 |
Ir 1.68 |
Pt 1.72 |
Au 1.92 |
Hg 1.765 |
Tl 1.789 |
Pb 1.854 |
Bi 2.01 |
Po 2.19 |
At 2.39 |
Rn 2.60 |
| 7 | Fr 0.67 |
Ra 0.89 |
||||||||||||||||
| See also: Electronegativities of the elements (data page) |
Determination[edit]
While introductory levels of chemistry teaching use postulated oxidation states, the IUPAC recommendation[4] and the Gold Book entry[6] list two entirely general algorithms for the calculation of the oxidation states of elements in chemical compounds.
Simple approach without bonding considerations[edit]
Introductory chemistry uses postulates: the oxidation state for an element in a chemical formula is calculated from the overall charge and postulated oxidation states for all the other atoms.
A simple example is based on two postulates,
- OS = +1 for hydrogen
- OS = −2 for oxygen
where OS stands for oxidation state. This approach yields correct oxidation states in oxides and hydroxides of any single element, and in acids such as H2SO4 or H2Cr2O7. Its coverage can be extended either by a list of exceptions or by assigning priority to the postulates. The latter works for H2O2 where the priority of rule 1 leaves both oxygens with oxidation state −1.
Additional postulates and their ranking may expand the range of compounds to fit a textbook’s scope. As an example, one postulatory algorithm from many possible; in a sequence of decreasing priority:
- An element in a free form has OS = 0.
- In a compound or ion, the sum of the oxidation states equals the total charge of the compound or ion.
- Fluorine in compounds has OS = −1; this extends to chlorine and bromine only when not bonded to a lighter halogen, oxygen or nitrogen.
- Group 1 and group 2 metals in compounds have OS = +1 and +2, respectively.
- Hydrogen has OS = +1 but adopts −1 when bonded as a hydride to metals or metalloids.
- Oxygen in compounds has OS = −2 but only when not bonded to oxygen (e.g. in peroxides) or fluorine.
This set of postulates covers oxidation states of fluorides, chlorides, bromides, oxides, hydroxides, and hydrides of any single element. It covers all oxoacids of any central atom (and all their fluoro-, chloro-, and bromo-relatives), as well as salts of such acids with group 1 and 2 metals. It also covers iodides, sulfides, and similar simple salts of these metals.
Algorithm of assigning bonds[edit]
This algorithm is performed on a Lewis structure (a diagram that shows all valence electrons). Oxidation state equals the charge of an atom after each of its heteronuclear bonds has been assigned to the more-electronegative partner of the bond (except when that partner is a reversibly bonded Lewis-acid ligand) and homonuclear bonds have been divided equally:
where each «—» represents an electron pair (either shared between two atoms or solely on one atom), and «OS» is the oxidation state as a numerical variable.
After the electrons have been assigned according to the vertical red lines on the formula, the total number of valence electrons that now «belong» to each atom is subtracted from the number N of valence electrons of the neutral atom (such as 5 for nitrogen in group 15) to yield that atom’s oxidation state.
This example shows the importance of describing the bonding. Its summary formula, HNO3, corresponds to two structural isomers; the peroxynitrous acid in the above figure and the more stable nitric acid. With the formula HNO3, the simple approach without bonding considerations yields −2 for all three oxygens and +5 for nitrogen, which is correct for nitric acid. For the peroxynitrous acid, however, the two oxygens in the O–O bond each has OS = −1 and the nitrogen has OS = +3, which requires a structure to understand.
Organic compounds are treated in a similar manner; exemplified here on functional groups occurring in between CH4 and CO2:
Analogously for transition-metal compounds; CrO(O2)2 on the left has a total of 36 valence electrons (18 pairs to be distributed), and Cr(CO)6 on the right has 66 valence electrons (33 pairs):
A key step is drawing the Lewis structure of the molecule (neutral, cationic, anionic): atom symbols are arranged so that pairs of atoms can be joined by single two-electron bonds as in the molecule (a sort of «skeletal» structure), and the remaining valence electrons are distributed such that sp atoms obtain an octet (duet for hydrogen) with a priority that increases in proportion with electronegativity. In some cases, this leads to alternative formulae that differ in bond orders (the full set of which is called the resonance formulas). Consider the sulfate anion (SO2−
4 with 32 valence electrons; 24 from oxygens, 6 from sulfur, 2 of the anion charge obtained from the implied cation). The bond orders to the terminal oxygens do not affect the oxidation state so long as the oxygens have octets. Already the skeletal structure, top left, yields the correct oxidation states, as does the Lewis structure, top right (one of the resonance formulas):
The bond-order formula at the bottom is closest to the reality of four equivalent oxygens each having a total bond order of 2. That total includes the bond of order 1/2 to the implied cation and follows the 8 − N rule[5] requiring that the main-group atom’s bond order equals 8 minus N valence electrons of the neutral atom, enforced with a priority that proportionately increases with electronegativity.
This algorithm works equally for molecular cations composed of several atoms. An example is the ammonium cation of 8 valence electrons (5 from nitrogen, 4 from hydrogens, minus 1 electron for the cation’s positive charge):
Drawing Lewis structures with electron pairs as dashes emphasizes the essential equivalence of bond pairs and lone pairs when counting electrons and moving bonds onto atoms. Structures drawn with electron dot pairs are of course identical in every way:
The algorithm’s caveat[edit]
The algorithm contains a caveat, which concerns rare cases of transition-metal complexes with a type of ligand that is reversibly bonded as a Lewis acid (as an acceptor of the electron pair from the transition metal); termed a «Z-type» ligand in Green’s covalent bond classification method. The caveat originates from the simplifying use of electronegativity instead of the MO-based electron allegiance to decide the ionic sign.[4] One early example is the O2S−RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2 complex[12] with SO2 as the reversibly-bonded acceptor ligand (released upon heating). The Rh−S bond is therefore extrapolated ionic against Allen electronegativities of rhodium and sulfur, yielding oxidation state +1 for rhodium:
Algorithm of summing bond orders[edit]
This algorithm works on Lewis structures and bond graphs of extended (non-molecular) solids:
Oxidation state is obtained by summing the heteronuclear-bond orders at the atom as positive if that atom is the electropositive partner in a particular bond and as negative if not, and the atom’s formal charge (if any) is added to that sum.
Applied to a Lewis structure[edit]
An example of a Lewis structure with no formal charge,
illustrates that, in this algorithm, homonuclear bonds are simply ignored (the bond orders are in blue).
Carbon monoxide exemplifies a Lewis structure with formal charges:
To obtain the oxidation states, the formal charges are summed with the bond-order value taken positively at the carbon and negatively at the oxygen.
Applied to molecular ions, this algorithm considers the actual location of the formal (ionic) charge, as drawn in the Lewis structure. As an example, summing bond orders in the ammonium cation yields −4 at the nitrogen of formal charge +1, with the two numbers adding to the oxidation state of −3:
The sum of oxidation states in the ion equals its charge (as it equals zero for a neutral molecule).
Also in anions, the formal (ionic) charges have to be considered when nonzero. For sulfate this is exemplified with the skeletal or Lewis structures (top), compared with the bond-order formula of all oxygens equivalent and fulfilling the octet and 8 − N rules (bottom):
Applied to bond graph[edit]
A bond graph in solid-state chemistry is a chemical formula of an extended structure, in which direct bonding connectivities are shown. An example is the AuORb3 perovskite, the unit cell of which is drawn on the left and the bond graph (with added numerical values) on the right:
We see that the oxygen atom bonds to the six nearest rubidium cations, each of which has 4 bonds to the auride anion. The bond graph summarizes these connectivities. The bond orders (also called bond valences) sum up to oxidation states according to the attached sign of the bond’s ionic approximation (there are no formal charges in bond graphs).
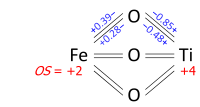
Determination of oxidation states from a bond graph can be illustrated on ilmenite, FeTiO3. We may ask whether the mineral contains Fe2+ and Ti4+, or Fe3+ and Ti3+. Its crystal structure has each metal atom bonded to six oxygens and each of the equivalent oxygens to two irons and two titaniums, as in the bond graph below. Experimental data show that three metal-oxygen bonds in the octahedron are short and three are long (the metals are off-center). The bond orders (valences), obtained from the bond lengths by the bond valence method, sum up to 2.01 at Fe and 3.99 at Ti; which can be rounded off to oxidation states +2 and +4, respectively:
Balancing redox[edit]
Oxidation states can be useful for balancing chemical equations for oxidation-reduction (or redox) reactions, because the changes in the oxidized atoms have to be balanced by the changes in the reduced atoms. For example, in the reaction of acetaldehyde with Tollens’ reagent to form acetic acid (shown below), the carbonyl carbon atom changes its oxidation state from +1 to +3 (loses two electrons). This oxidation is balanced by reducing two Ag+ cations to Ag0 (gaining two electrons in total).
An inorganic example is the Bettendorf reaction using SnCl2 to prove the presence of arsenite ions in a concentrated HCl extract. When arsenic(III) is present, a brown coloration appears forming a dark precipitate of arsenic, according to the following simplified reaction:
- 2 As3+ + 3 Sn2+ → 2 As0 + 3 Sn4+
Here three tin atoms are oxidized from oxidation state +2 to +4, yielding six electrons that reduce two arsenic atoms from oxidation state +3 to 0. The simple one-line balancing goes as follows: the two redox couples are written down as they react;
- As3+ + Sn2+ ⇌ As0 + Sn4+.
One tin is oxidized from oxidation state +2 to +4, a two-electron step, hence 2 is written in front of the two arsenic partners. One arsenic is reduced from +3 to 0, a three-electron step, hence 3 goes in front of the two tin partners. An alternative three-line procedure is to write separately the half-reactions for oxidation and reduction, each balanced with electrons, and then to sum them up such that the electrons cross out. In general, these redox balances (the one-line balance or each half-reaction) need to be checked for the ionic and electron charge sums on both sides of the equation being indeed equal. If they are not equal, suitable ions are added to balance the charges and the non-redox elemental balance.
Appearances[edit]
Nominal oxidation states[edit]
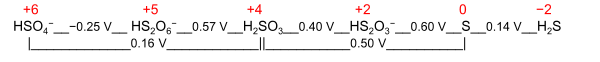
A nominal oxidation state is a general term with two different definitions:
- Electrochemical oxidation state[citation needed] represents a molecule or ion in the Latimer diagram or Frost diagram for its redox-active element. An example is the Latimer diagram for sulfur at pH 0 where the electrochemical oxidation state +2 for sulfur puts HS
2O−
3 between S and H2SO3:
- Systematic oxidation state is chosen from close alternatives as a pedagogical description. An example is the oxidation state of phosphorus in H3PO3 (structurally diprotic HPO(OH)2) taken nominally as +3, while Allen electronegativities of phosphorus and hydrogen suggest +5 by a narrow margin that makes the two alternatives almost equivalent:
-
- Both alternative oxidation numbers for phosphorus make chemical sense, depending on which chemical property or reaction is emphasized. By contrast, a calculated alternative, such as the average (+4) does not.
Ambiguous oxidation states[edit]
Lewis formulae are rule-based approximations of chemical reality, as are Allen electronegativities. Still, oxidation states may seem ambiguous when their determination is not straightforward. If only an experiment can determine the oxidation state, the rule-based determination is ambiguous (insufficient). There are also truly dichotomous values that are decided arbitrarily.
Oxidation-state determination from resonance formulas[edit]
Seemingly ambiguous oxidation states are derived from a set of resonance formulas of equal weights for a molecule having heteronuclear bonds where the atom connectivity does not correspond to the number of two-electron bonds dictated by the 8 − N rule. An example is S2N2 where four resonance formulas featuring one S=N double bond have oxidation states +2 and +4 for the two sulfur atoms, which average to +3 because the two sulfur atoms are equivalent in this square-shaped molecule.
A physical measurement is needed to determine oxidation state[edit]
- when a non-innocent ligand is present, of hidden or unexpected redox properties that could otherwise be assigned to the central atom. An example is the nickel dithiolate complex, Ni(S
2C
2H
2)2−
2.[5]: 1056–1057 - when the redox ambiguity of a central atom and ligand yields dichotomous oxidation states of close stability, thermally induced tautomerism may result, as exemplified by manganese catecholate, Mn(C6H4O2)3.[5]: 1057–1058 Assignment of such oxidation states requires spectroscopic,[13] magnetic or structural data.
- when the bond order has to be ascertained along with an isolated tandem of a heteronuclear and a homonuclear bond. An example is thiosulfate S
2O2−
3 having two possible oxidation states (bond orders are in blue and formal charges in green):
- The S–S distance measurement in thiosulfate is needed to reveal that this bond order is very close to 1, as in the formula on the left.
Ambiguous/arbitrary oxidation states[edit]
- when the electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms is very small (as in H3PO3). Two almost equivalent pairs of oxidation states, arbitrarily chosen, are obtained for these atoms.
- when an electronegative p-block atom forms solely homonuclear bonds, the number of which differs from the number of two-electron bonds suggested by rules. Examples are homonuclear finite chains like N−
3 (the central nitrogen connects two atoms with four two-electron bonds while only three two-electron bonds[14] are required by 8 − N rule) or I−
3 (the central iodine connects two atoms with two two-electron bonds while only one two-electron bond fulfills the 8 − N rule). A sensible approach is to distribute the ionic charge over the two outer atoms.[5] Such a placement of charges in a polysulfide S2−
n (where all inner sulfurs form two bonds, fulfilling the 8 − N rule) follows already from its Lewis structure.[5] - when the isolated tandem of a heteronuclear and a homonuclear bond leads to a bonding compromise in between two Lewis structures of limiting bond orders. An example is N2O:
- The typical oxidation state of nitrogen in N2O is +1, which also obtains for both nitrogens by a molecular orbital approach.[15] The formal charges on the right comply with electronegativities, which implies an added ionic bonding contribution. Indeed, the estimated N−N and N−O bond orders are 2.76 and 1.9, respectively,[5] approaching the formula of integer bond orders that would include the ionic contribution explicitly as a bond (in green):
- Conversely, formal charges against electronegativities in a Lewis structure decrease the bond order of the corresponding bond. An example is carbon monoxide with a bond-order estimate of 2.6.[16]
Fractional oxidation states[edit]
Fractional oxidation states are often used to represent the average oxidation state of several atoms of the same element in a structure. For example, the formula of magnetite is Fe
3O
4, implying an average oxidation state for iron of +8/3.[17]: 81–82 However, this average value may not be representative if the atoms are not equivalent. In a Fe
3O
4 crystal below 120 K (−153 °C), two-thirds of the cations are Fe3+
and one-third are Fe2+
, and the formula may be more clearly represented as FeO·Fe
2O
3.[18]
Likewise, propane, C
3H
8, has been described as having a carbon oxidation state of −8/3.[19] Again, this is an average value since the structure of the molecule is H
3C−CH
2−CH
3, with the first and third carbon atoms each having an oxidation state of −3 and the central one −2.
An example with true fractional oxidation states for equivalent atoms is potassium superoxide, KO
2. The diatomic superoxide ion O−
2 has an overall charge of −1, so each of its two equivalent oxygen atoms is assigned an oxidation state of −1/2. This ion can be described as a resonance hybrid of two Lewis structures, where each oxygen has an oxidation state of 0 in one structure and −1 in the other.
For the cyclopentadienyl anion C
5H−
5, the oxidation state of C is −1 + −1/5 = −6/5. The −1 occurs because each carbon is bonded to one hydrogen atom (a less electronegative element), and the −1/5 because the total ionic charge of −1 is divided among five equivalent carbons. Again this can be described as a resonance hybrid of five equivalent structures, each having four carbons with oxidation state −1 and one with −2.
-
Examples of fractional oxidation states for carbon
Oxidation state Example species −6/5 C
5H−
5−6/7 C
7H+
7+3/2 C
4O2−
4
Finally, fractional oxidation numbers are not used in the description[20]: 66 of red lead. Pb
3O
4 is represented as lead(II,IV) oxide, showing the oxidation states of the two nonequivalent lead atoms.
Elements with multiple oxidation states[edit]
See also § List of oxidation states of the elements
Most elements have more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4:
-
Integer oxidation states of carbon
Oxidation state Example compound −4 CH
4−3 C
2H
6−2 C
2H
4, CH
3Cl−1 C
2H
2, C
6H
6, (CH
2OH)
20 HCHO, CH
2Cl
2+1 OCHCHO, CHCl
2CHCl
2+2 HCOOH, CHCl
3+3 HOOCCOOH, C
2Cl
6+4 CCl
4, CO
2
Oxidation state in metals[edit]
Many compounds with luster and electrical conductivity maintain a simple stoichiometric formula, such as the golden TiO, blue-black RuO2 or coppery ReO3, all of obvious oxidation state. Ultimately, assigning the free metallic electrons to one of the bonded atoms is not comprehensive and can yield unusual oxidation states. Examples are the LiPb and Cu
3Au ordered alloys, the composition and structure of which are largely determined by atomic size and packing factors. Should oxidation state be needed for redox balancing, it is best set to 0 for all atoms of such an alloy.
List of oxidation states of the elements[edit]
This is a list of known oxidation states of the chemical elements, excluding nonintegral values. The most common states appear in bold. The table is based on that of Greenwood and Earnshaw,[21] with additions noted. Every element exists in oxidation state 0 when it is the pure non-ionized element in any phase, whether monatomic or polyatomic allotrope. The column for oxidation state 0 only shows elements known to exist in oxidation state 0 in compounds.
Noble gas
+1 Bold values are main oxidation states
Oxidation states of the elements |
|||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Negative states | Positive states | Group | Notes | |||||||||||||||
| −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | +9 | |||||
| Z | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | hydrogen | H | −1 | +1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | helium | He | 18 | ||||||||||||||||
| 3 | lithium | Li | 0 | +1 | 1 | [22][23] | |||||||||||||
| 4 | beryllium | Be | 0 | +1 | +2 | 2 | [24][25] | ||||||||||||
| 5 | boron | B | −5 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [26][27][28] | |||||||||
| 6 | carbon | C | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | |||||||
| 7 | nitrogen | N | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [29] | ||||||
| 8 | oxygen | O | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | 16 | |||||||||||
| 9 | fluorine | F | −1 | 0 | 17 | [30][31] | |||||||||||||
| 10 | neon | Ne | 0 | 18 | [32] | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | sodium | Na | −1 | 0 | +1 | 1 | [22][33] | ||||||||||||
| 12 | magnesium | Mg | 0 | +1 | +2 | 2 | [34][35] | ||||||||||||
| 13 | aluminium | Al | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [36][37][38][39] | |||||||||
| 14 | silicon | Si | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [40] | ||||||
| 15 | phosphorus | P | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [41] | ||||||
| 16 | sulfur | S | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | |||||||
| 17 | chlorine | Cl | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 17 | [42] | |||||||
| 18 | argon | Ar | 0 | 18 | [43] | ||||||||||||||
| 19 | potassium | K | −1 | +1 | 1 | [22] | |||||||||||||
| 20 | calcium | Ca | +1 | +2 | 2 | [44][45] | |||||||||||||
| 21 | scandium | Sc | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [46][47][48] | |||||||||||
| 22 | titanium | Ti | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [49][50][51][52] | ||||||||
| 23 | vanadium | V | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [50] | |||||||
| 24 | chromium | Cr | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [50] | |||||
| 25 | manganese | Mn | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | |||||
| 26 | iron | Fe | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 8 | [53][54][55] | ||||
| 27 | cobalt | Co | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 9 | [50] | |||||||
| 28 | nickel | Ni | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 10 | [56] | ||||||||
| 29 | copper | Cu | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 11 | [55][57] | |||||||||
| 30 | zinc | Zn | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | 12 | [55][58][59][60] | |||||||||||
| 31 | gallium | Ga | −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [37][61][62][63] | ||||||
| 32 | germanium | Ge | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [64][40] | ||||||
| 33 | arsenic | As | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [37][65][66][67] | ||||||
| 34 | selenium | Se | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [68][69][70][71][72] | ||||||
| 35 | bromine | Br | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +7 | 17 | [73] | ||||||||
| 36 | krypton | Kr | 0 | +1 | +2 | 18 | |||||||||||||
| 37 | rubidium | Rb | −1 | +1 | 1 | [22] | |||||||||||||
| 38 | strontium | Sr | +1 | +2 | 2 | [74][45] | |||||||||||||
| 39 | yttrium | Y | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [75][76][77] | |||||||||||
| 40 | zirconium | Zr | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [50][78][79] | |||||||||
| 41 | niobium | Nb | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [50][80][81] | |||||||
| 42 | molybdenum | Mo | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [50] | |||||
| 43 | technetium | Tc | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | ||||||
| 44 | ruthenium | Ru | −4 | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | 8 | [50][55] | ||||
| 45 | rhodium | Rh | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 9 | [50][82][83] | |||||
| 46 | palladium | Pd | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 10 | [84][85][86][87] | |||||||||
| 47 | silver | Ag | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 11 | [55][88][89] | |||||||||
| 48 | cadmium | Cd | −2 | +1 | +2 | 12 | [55][90] | ||||||||||||
| 49 | indium | In | −5 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [37][91][92][93] | ||||||||
| 50 | tin | Sn | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [37][94][95][40] | ||||||
| 51 | antimony | Sb | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [37][96][97][98][99] | ||||||
| 52 | tellurium | Te | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [37][100][101][102][103] | ||||||
| 53 | iodine | I | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 17 | [104][105][106] | |||||||
| 54 | xenon | Xe | 0 | +2 | +4 | +6 | +8 | 18 | [107][108][109] | ||||||||||
| 55 | caesium | Cs | −1 | +1 | 1 | [22] | |||||||||||||
| 56 | barium | Ba | +1 | +2 | 2 | [110][45] | |||||||||||||
| 57 | lanthanum | La | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][111] | |||||||||||
| 58 | cerium | Ce | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | |||||||||||||
| 59 | praseodymium | Pr | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [75][112][113][114] | |||||||||
| 60 | neodymium | Nd | 0 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [75][115] | |||||||||||
| 61 | promethium | Pm | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [116] | |||||||||||||
| 62 | samarium | Sm | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [117] | |||||||||||
| 63 | europium | Eu | 0 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75] | ||||||||||||
| 64 | gadolinium | Gd | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75] | |||||||||||
| 65 | terbium | Tb | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [75][111][116] | ||||||||||
| 66 | dysprosium | Dy | 0 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [75][118] | |||||||||||
| 67 | holmium | Ho | 0 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][116] | ||||||||||||
| 68 | erbium | Er | 0 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][116] | ||||||||||||
| 69 | thulium | Tm | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][111] | |||||||||||
| 70 | ytterbium | Yb | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][111] | |||||||||||
| 71 | lutetium | Lu | 0 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [75][116] | ||||||||||||
| 72 | hafnium | Hf | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [50][79][119] | |||||||||
| 73 | tantalum | Ta | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [50][81] | |||||||
| 74 | tungsten | W | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [50] | |||||
| 75 | rhenium | Re | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | ||||||
| 76 | osmium | Os | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | 8 | [55][120] | |||
| 77 | iridium | Ir | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | +9 | 9 | [121][122][123][124] | |||
| 78 | platinum | Pt | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 10 | [55][125][126] | |||||
| 79 | gold | Au | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +5 | 11 | [55][127] | |||||||
| 80 | mercury | Hg | −2 | +1 | +2 | 12 | [55][128] | ||||||||||||
| 81 | thallium | Tl | −5 | −2 | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [37][129][130][131] | |||||||||
| 82 | lead | Pb | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [37][132][133][134] | |||||||
| 83 | bismuth | Bi | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [135][136][137][138][139] | ||||||
| 84 | polonium | Po | −2 | +2 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [140] | ||||||||||
| 85 | astatine | At | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 | 17 | |||||||||||
| 86 | radon | Rn | +2 | +6 | 18 | [141][142][143] | |||||||||||||
| 87 | francium | Fr | +1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 88 | radium | Ra | +2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| 89 | actinium | Ac | +3 | f-block groups | |||||||||||||||
| 90 | thorium | Th | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [144][145][146] | ||||||||||
| 91 | protactinium | Pa | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [147] | |||||||||||
| 92 | uranium | U | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | f-block groups | [148][149][150] | ||||||||
| 93 | neptunium | Np | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | f-block groups | [151] | |||||||||
| 94 | plutonium | Pu | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | f-block groups | [152][153] | ||||||||
| 95 | americium | Am | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | f-block groups | [154] | |||||||||
| 96 | curium | Cm | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | f-block groups | [155][156][157][158] | |||||||||||
| 97 | berkelium | Bk | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [155][156][159][160][161] | |||||||||||
| 98 | californium | Cf | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [155][156] | |||||||||||
| 99 | einsteinium | Es | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [162] | ||||||||||||
| 100 | fermium | Fm | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | ||||||||||||||
| 101 | mendelevium | Md | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | ||||||||||||||
| 102 | nobelium | No | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | ||||||||||||||
| 103 | lawrencium | Lr | +3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| 104 | rutherfordium | Rf | +4 | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| 105 | dubnium | Db | +5 | 5 | [163] | ||||||||||||||
| 106 | seaborgium | Sg | 0 | +6 | 6 | [164][165] | |||||||||||||
| 107 | bohrium | Bh | +7 | 7 | [166] | ||||||||||||||
| 108 | hassium | Hs | +8 | 8 | [167] | ||||||||||||||
| 109 | meitnerium | Mt | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
| 110 | darmstadtium | Ds | 10 | ||||||||||||||||
| 111 | roentgenium | Rg | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
| 112 | copernicium | Cn | +2 | 12 | [168] | ||||||||||||||
| 113 | nihonium | Nh | 13 | ||||||||||||||||
| 114 | flerovium | Fl | 14 | ||||||||||||||||
| 115 | moscovium | Mc | 15 | ||||||||||||||||
| 116 | livermorium | Lv | 16 | ||||||||||||||||
| 117 | tennessine | Ts | 17 | ||||||||||||||||
| 118 | oganesson | Og | 18 |
Early forms (octet rule)[edit]
A figure with a similar format was used by Irving Langmuir in 1919 in one of the early papers about the octet rule.[169] The periodicity of the oxidation states was one of the pieces of evidence that led Langmuir to adopt the rule.
Use in nomenclature[edit]
The oxidation state in compound naming for transition metals and lanthanides and actinides is placed either as a right superscript to the element symbol in a chemical formula, such as FeIII or in parentheses after the name of the element in chemical names, such as iron(III). For example, Fe
2(SO
4)
3 is named iron(III) sulfate and its formula can be shown as FeIII
2(SO
4)
3. This is because a sulfate ion has a charge of −2, so each iron atom takes a charge of +3.
History of the oxidation state concept[edit]
Early days[edit]
Oxidation itself was first studied by Antoine Lavoisier, who defined it as the result of reactions with oxygen (hence the name).[170][171] The term has since been generalized to imply a formal loss of electrons. Oxidation states, called oxidation grades by Friedrich Wöhler in 1835,[172] were one of the intellectual stepping stones that Dmitri Mendeleev used to derive the periodic table. William B. Jensen[173] gives an overview of the history up to 1938.
Use in nomenclature[edit]
When it was realized that some metals form two different binary compounds with the same nonmetal, the two compounds were often distinguished by using the ending -ic for the higher metal oxidation state and the ending -ous for the lower. For example, FeCl3 is ferric chloride and FeCl2 is ferrous chloride. This system is not very satisfactory (although sometimes still used) because different metals have different oxidation states which have to be learned: ferric and ferrous are +3 and +2 respectively, but cupric and cuprous are +2 and +1, and stannic and stannous are +4 and +2. Also, there was no allowance for metals with more than two oxidation states, such as vanadium with oxidation states +2, +3, +4, and +5.[17]: 84
This system has been largely replaced by one suggested by Alfred Stock in 1919[174] and adopted[175] by IUPAC in 1940. Thus, FeCl2 was written as iron(II) chloride rather than ferrous chloride. The Roman numeral II at the central atom came to be called the «Stock number» (now an obsolete term), and its value was obtained as a charge at the central atom after removing its ligands along with the electron pairs they shared with it.[20]: 147
Development towards the current concept[edit]
The term «oxidation state» in English chemical literature was popularized by Wendell Mitchell Latimer in his 1938 book about electrochemical potentials.[176] He used it for the value (synonymous with the German term Wertigkeit) previously termed «valence», «polar valence» or «polar number»[177] in English, or «oxidation stage» or indeed[178][179] the «state of oxidation». Since 1938, the term «oxidation state» has been connected with electrochemical potentials and electrons exchanged in redox couples participating in redox reactions. By 1948, IUPAC used the 1940 nomenclature rules with the term «oxidation state»,[180][181] instead of the original[175] valency. In 1948 Linus Pauling proposed that oxidation number could be determined by extrapolating bonds to being completely ionic in the direction of electronegativity.[182] A full acceptance of this suggestion was complicated by the fact that the Pauling electronegativities as such depend on the oxidation state and that they may lead to unusual values of oxidation states for some transition metals. In 1990 IUPAC resorted to a postulatory (rule-based) method to determine the oxidation state.[183] This was complemented by the synonymous term oxidation number as a descendant of the Stock number introduced in 1940 into the nomenclature. However, the terminology using «ligands»[20]: 147 gave the impression that oxidation number might be something specific to coordination complexes. This situation and the lack of a real single definition generated numerous debates about the meaning of oxidation state, suggestions about methods to obtain it and definitions of it. To resolve the issue, an IUPAC project (2008-040-1-200) was started in 2008 on the «Comprehensive Definition of Oxidation State», and was concluded by two reports[5][4] and by the revised entries «Oxidation State»[6] and «Oxidation Number»[7] in the IUPAC Gold Book. The outcomes were a single definition of oxidation state and two algorithms to calculate it in molecular and extended-solid compounds, guided by Allen electronegativities that are independent of oxidation state.
See also[edit]
- Electronegativity
- Electrochemistry
- Atomic orbital
- Atomic shell
- Quantum numbers
- Azimuthal quantum number
- Principal quantum number
- Magnetic quantum number
- Spin quantum number
- Aufbau principle
- Wiswesser’s rule
- Ionization energy
- Electron affinity
- Ionic potential
- Ions
- Cations and Anions
- Polyatomic ions
- Covalent bonding
- Metallic bonding
- Hybridization
References[edit]
- ^ Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Goettel, G. T.; Schrobilgen, G. J.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Schlöder, T.; Riedel, S. (2014). «Identification of an iridium-containing compound with a formal oxidation state of IX». Nature. 514 (7523): 475–477. Bibcode:2014Natur.514..475W. doi:10.1038/nature13795. PMID 25341786. S2CID 4463905.
- ^ Yu, Haoyu S.; Truhlar, Donald G. (2016). «Oxidation State 10 Exists». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 55 (31): 9004–9006. doi:10.1002/anie.201604670.
- ^ Schroeder, Melanie, Eigenschaften von borreichen Boriden und Scandium-Aluminium-Oxid-Carbiden (in German), p. 139
- ^ a b c d Karen, P.; McArdle, P.; Takats, J. (2016). «Comprehensive definition of oxidation state (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)». Pure Appl. Chem. 88 (8): 831–839. doi:10.1515/pac-2015-1204. hdl:10852/59520. S2CID 99403810.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Karen, P.; McArdle, P.; Takats, J. (2014). «Toward a comprehensive definition of oxidation state (IUPAC Technical Report)». Pure Appl. Chem. 86 (6): 1017–1081. doi:10.1515/pac-2013-0505.
- ^ a b c IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the «Gold Book») (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) «Oxidation state». doi:10.1351/goldbook.O04365
- ^ a b IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the «Gold Book») (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) «Oxidation number». doi:10.1351/goldbook.O04363
- ^ a b c Karen, Pavel (2015). «Oxidation State, A Long-Standing Issue!». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 54 (16): 4716–4726. doi:10.1002/anie.201407561. PMC 4506524. PMID 25757151.
- ^ Hooydonk, G. (1974). O n an Ionic Approximation to Chemical Bonding, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A, 29(5), 763-767. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-1974-0517
- ^ «Oxidation state». IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology. 2009. doi:10.1351/goldbook.O04365. ISBN 978-0-9678550-9-7.
- ^ Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014), 86(6), 1017–1081 CODEN: PACHAS; ISSN 0033-4545. English.
- ^ Muir, K. W.; Ibers, J. A. (1969). «The structure of chlorocarbonyl(sulfur dioxide)bis(triphenylphosphine)rhodium, RhCl(CO)(SO2)(P(C6H5)3)2«. Inorg. Chem. 8 (9): 1921–1928. doi:10.1021/ic50079a024.
- ^ Jørgensen, C. K. (1966). «Electric Polarizability, Innocent Ligands and Spectroscopic Oxidation States». Structure and Bonding. Vol. 1. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 234–248.
- ^ «The Two-Electron Bond». Chemistry LibreTexts. June 25, 2016.
- ^ Karen, P. (2015). «Oxidation state, a long-standing issue!». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54 (16): 4716–4726. doi:10.1002/anie.201407561. PMC 4506524. PMID 25757151.
- ^ Martinie, R. J.; Bultema, J. J.; Wal, M. N. V.; Burkhart, B. J.; Griend, D. A. V.; DeCock, R. L. (2011). «Bond order and chemical properties of BF, CO, and N2«. J. Chem. Educ. 88 (8): 1094–1097. Bibcode:2011JChEd..88.1094M. doi:10.1021/ed100758t.
- ^ a b Petrucci, R. H.; Harwood, W. S.; Herring, F. G. (2002). General Chemistry (8th ed.). Prentice-Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-033445-9.[ISBN missing]
- ^ Senn, M. S.; Wright, J. P.; Attfield, J. P. (2012). «Charge order and three-site distortions in the Verwey structure of magnetite» (PDF). Nature. 481 (7380): 173–6. Bibcode:2012Natur.481..173S. doi:10.1038/nature10704. hdl:20.500.11820/1b3bb558-52d5-419f-9944-ab917dc95f5e. PMID 22190035. S2CID 4425300. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ Whitten, K. W.; Galley, K. D.; Davis, R. E. (1992). General Chemistry (4th ed.). Saunders. p. 147. ISBN 978-0-03-075156-1.[ISBN missing]
- ^ a b c Connelly, N. G.; Damhus, T.; Hartshorn, R. M.; Hutton, A. T. Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005) (PDF). RSC Publishing. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 27–28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b c d e Na(−1), K(−1), Rb(−1), and Cs(−1) are known in alkalides; the table by Greenwood and Earnshaw shows −1 only for Na and also erroneously for Li; no lithides are described.
- ^ Li(0) atoms have been observed in various small lithium-chloride clusters; see Milovanović, Milan; Veličković, Suzana; Veljkovićb, Filip; Jerosimić, Stanka (October 30, 2017). «Structure and stability of small lithium-chloride LinClm(0,1+) (n ≥ m, n = 1–6, m = 1–3) clusters». Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (45). doi:10.1039/C7CP04181K.
- ^ Be(0) has been observed; see «Beryllium(0) Complex Found». Chemistry Europe. 13 June 2016.
- ^ Be(I) has been observed in beryllium monohydride (BeH); see Shayesteh, A.; Tereszchuk, K.; Bernath, P. F.; Colin, R. (2003). «Infrared Emission Spectra of BeH and BeD» (PDF). J. Chem. Phys. 118 (3): 1158. Bibcode:2003JChPh.118.1158S. doi:10.1063/1.1528606. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-12-02. Retrieved 2007-12-10. and in [(CAAC)2Be]+• [CAAC = cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene], see Wang, Guocang; Walley, Jacob E.; Dickie, Diane E.; Pan, Sudip; Frenking, Gernot; Gilliard Jr., Robert G. (2020). «A Stable, Crystalline Beryllium Radical Cation». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (10): 4560–4. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b13777. PMID 32088963. S2CID 211262005. Retrieved 2020-11-17.
- ^ B(−5) has been observed in Al3BC, see Schroeder, Melanie. «Eigenschaften von borreichen Boriden und Scandium-Aluminium-Oxid-Carbiden» (in German). p. 139.
- ^ B(−1) has been observed in magnesium diboride (MgB2), see Keeler, James; Wothers, Peter (2014). Chemical Structure and Reactivity: An Integrated Approach. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199604135.
- ^ B(0) has been observed in diborynes, see Braunschweig, H.; Dewhurst, R. D.; Hammond, K.; Mies, J.; Radacki, K.; Vargas, A. (2012). «Ambient-Temperature Isolation of a Compound with a Boron-Boron Triple Bond». Science. 336 (6087): 1420–2. Bibcode:2012Sci…336.1420B. doi:10.1126/science.1221138. PMID 22700924. S2CID 206540959.
- ^ Tetrazoles contain a pair of double-bonded nitrogen atoms with oxidation state 0 in the ring. A Synthesis of the parent 1H-tetrazole, CH2N4 (two atoms N(0)) is given in Ronald A. Henry and William G. Finnegan, «An Improved Procedure for the Deamination of 5-Aminotetrazole», _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ (1954), 76, 1, 290–291,
https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01630a086. - ^ Gold heptafluoride is calculated to be the pentafluoride with a molecular F2 ligand. Himmel, Daniel; Riedel, Sebastian (2007). «After 20 Years, Theoretical Evidence That ‘AuF7‘ Is Actually AuF5•F2«. Inorganic Chemistry. 46 (13): 5338–5342. doi:10.1021/ic700431s. PMID 17511450.
- ^ A cluster of elusive SF6+ with helium atoms is known to have fluorine(0)atom as a ligand; see Albertini, Simon; Bergmeister, Stefan; Laimer, Felix; Martini, Paul; Gruber, Elisabeth; Zappa, Fabio; Ončák, Milan; Scheier, Paul; Echt, Olof (2021-04-22). «SF 6 + : Stabilizing Transient Ions in Helium Nanodroplets». The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 12 (17): 4112–4117. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c01024. ISSN 1948-7185. PMC 8154854. PMID 33886323.
- ^ Ne(0) has been observed in Cr(CO)5Ne. Perutz, Robin N.; Turner, James J. (August 1975). «Photochemistry of the Group 6 hexacarbonyls in low-temperature matrices. III. Interaction of the pentacarbonyls with noble gases and other matrices». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 97 (17): 4791–4800. doi:10.1021/ja00850a001.
- ^ The compound NaCl has been shown in experiments to exists in several unusual stoichiometries under high pressure, including Na3Cl in which contains a layer of sodium(0) atoms; see Zhang, W.; Oganov, A. R.; Goncharov, A. F.; Zhu, Q.; Boulfelfel, S. E.; Lyakhov, A. O.; Stavrou, E.; Somayazulu, M.; Prakapenka, V. B.; Konôpková, Z. (2013). «Unexpected Stable Stoichiometries of Sodium Chlorides». Science. 342 (6165): 1502–1505. arXiv:1310.7674. Bibcode:2013Sci…342.1502Z. doi:10.1126/science.1244989. PMID 24357316. S2CID 15298372.
- ^ Low valent magnesium compounds with Mg(I) have been obtained using bulky ligands; see Green, S. P.; Jones C.; Stasch A. (December 2007). «Stable Magnesium(I) Compounds with Mg-Mg Bonds». Science. 318 (5857): 1754–1757. Bibcode:2007Sci…318.1754G. doi:10.1126/science.1150856. PMID 17991827. S2CID 40657565.
- ^ Mg(0) has been synthesized in a compound containing a Na2Mg22+ cluster coordinated to a bulky organic ligand; see Rösch, B.; Gentner, T. X.; Eyselein, J.; Langer, J.; Elsen, H.; Li, W.; Harder, S. (2021). «Strongly reducing magnesium(0) complexes». Nature. 592 (7856): 717–721. Bibcode:2021Natur.592..717R. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03401-w. PMID 33911274. S2CID 233447380
- ^ Al(II) has been observed in aluminium(II) oxide (AlO); see Tyte, D.C. (1964). «Red (B2Π–A2σ) Band System of Aluminium Monoxide». Nature. 202 (4930): 383–384. Bibcode:1964Natur.202..383T. doi:10.1038/202383a0. S2CID 4163250, and in dialanes (R2Al—AlR2); see Uhl, Werner (2004). «Organoelement Compounds Possessing Al—Al, Ga—Ga, In—In, and Tl—Tl Single Bonds». Advances in Organometallic Chemistry. 51: 53–108. doi:10.1016/S0065-3055(03)51002-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Negative oxidation states of p-block metals (Al, Ga, In, Sn, Tl, Pb, Bi, Po) and metalloids (Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, At) may occur in Zintl phases, see: Riedel, Erwin, ed. (2007). Moderne Anorganische Chemie (in German). p. 259, and «Vorlesung Intermetallische Phasen § 6.2 Binäre Zintl-Phasen» (in German).
- ^ Unstable carbonyl of Al(0) has been detected in reaction of Al2(CH3)6 with carbon monoxide; see Sanchez, Ramiro; Arrington, Caleb; Arrington Jr., C. A. (December 1, 1989). «Reaction of trimethylaluminum with carbon monoxide in low-temperature matrixes». American Chemical Society. 111 (25): 9110-9111. doi:10.1021/ja00207a023.
- ^ Al(−2) has been observed in Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3, see Wemdorff, Marco; Röhr, Caroline (2007). «Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3: Eine Zintl-Phase mit isolierten [Ge]4–— und [Al4]8–-Anionen / Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3: A Zintl Phase with Isolated [Ge]4–— and [Al4]8– Anions». Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B (in German). 62 (10): 1227. doi:10.1515/znb-2007-1001. S2CID 94972243.
- ^ a b c «New Type of Zero-Valent Tin Compound». Chemistry Europe. 27 August 2016.
- ^ P(0) has been observed, see Wang, Yuzhong; Xie, Yaoming; Wei, Pingrong; King, R. Bruce; Schaefer, Iii; Schleyer, Paul v. R.; Robinson, Gregory H. (2008). «Carbene-Stabilized Diphosphorus». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (45): 14970–1. doi:10.1021/ja807828t. PMID 18937460.
- ^ The equilibrium Cl2O6⇌2ClO3 is mentioned by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but it has been refuted, see Lopez, Maria; Juan E. Sicre (1990). «Physicochemical properties of chlorine oxides. 1. Composition, ultraviolet spectrum, and kinetics of the thermolysis of gaseous dichlorine hexoxide». J. Phys. Chem. 94 (9): 3860–3863. doi:10.1021/j100372a094., and Cl2O6 is actually chlorine(V,VII) oxide. However, ClO3 has been observed, see Grothe, Hinrich; Willner, Helge (1994). «Chlorine Trioxide: Spectroscopic Properties, Molecular Structure, and Photochemical Behavior». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 33 (14): 1482–1484. doi:10.1002/anie.199414821.
- ^ Ar(0) has been observed in argon fluorohydride (HArF) and ArCF22+, see Lockyear, J.F.; Douglas, K.; Price, S.D.; Karwowska, M.; et al. (2010). «Generation of the ArCF22+ Dication». Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 1: 358. doi:10.1021/jz900274p.
- ^ Ca(I) has been observed; see Krieck, Sven; Görls, Helmar; Westerhausen, Matthias (2010). «Mechanistic Elucidation of the Formation of the Inverse Ca(I) Sandwich Complex [(thf)3Ca(μ-C6H3-1,3,5-Ph3)Ca(thf)3] and Stability of Aryl-Substituted Phenylcalcium Complexes». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (35): 12492–501. doi:10.1021/ja105534w. PMID 20718434.
- ^ a b c Octacarbonyl complexes isolated of Ca, Sr, Ba have been observed in a neon matrix, but it remains unclear whether these are metal(0) complexes because calculations disagree whether the metal is covalently or ionically bonded to the ligands; see Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Jin, J.; Pan, S.; Li, W.; Jin, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Frenking, G. (2018). «Observation of alkaline earth complexes M(CO)8 (M = Ca, Sr, or Ba) that mimic transition metals». Science. 361 (6405): 912–916. Bibcode:2018Sci…361..912W. doi:10.1126/science.aau0839. PMID 30166489. S2CID 52131470
- ^ Sc(0) has been observed; see F. Geoffrey N. Cloke; Karl Khan & Robin N. Perutz (1991). «η-Arene complexes of scandium(0) and scandium(II)». J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. (19): 1372–1373. doi:10.1039/C39910001372.
- ^ Sc(I) has been observed; see Polly L. Arnold; F. Geoffrey; N. Cloke; Peter B. Hitchcock & John F. Nixon (1996). «The First Example of a Formal Scandium(I) Complex: Synthesis and Molecular Structure of a 22-Electron Scandium Triple Decker Incorporating the Novel 1,3,5-Triphosphabenzene Ring». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (32): 7630–7631. doi:10.1021/ja961253o.
- ^ Sc(II) has been observed; see Woen, David H.; Chen, Guo P.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Boyle, Timothy J.; Furche, Filipp; Evans, William J. (January 2017). «Solution Synthesis, Structure, and CO Reduction Reactivity of a Scandium(II) Complex». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 56 (8): 2050–2053. doi:10.1002/anie.201611758. PMID 28097771.
- ^ Ti(I) has been observed in [Ti(η6-1,3,5-C6H3iPr3)2][BAr4] (Ar = C6H5, p-C6H4F, 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2); see Calderazzo, Fausto; Ferri, Isabella; Pampaloni, Guido; Englert, Ulli; Green, Malcolm L. H. (1997). «Synthesis of [Ti(η6-1,3,5-C6H3iPr3)2][BAr4] (Ar = C6H5, p-C6H4F, 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2), the First Titanium(I) Derivatives». Organometallics. 16 (14): 3100–3101. doi:10.1021/om970155o.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Ti(−2), V(−3), Cr(−4), Co(−3), Zr(−2), Nb(−3), Mo(−4), Ru(−2), Rh(−3), Hf(−2), Ta(−3), and W(−4) occur in anionic binary metal carbonyls; see [1], p. 4 (in German); [2], pp. 97–100; [3], p. 239
- ^ Ti(−1) has been reported in [Ti(bipy)3]−, but was later shown to be Ti(+3); see Bowman, A. C.; England, J.; Sprouls, S.; Weihemüller, T.; Wieghardt, K. (2013). «Electronic structures of homoleptic [tris(2,2′-bipyridine)M]n complexes of the early transition metals (M = Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta; n = 1+, 0, 1-, 2-, 3-): an experimental and density functional theoretical study». Inorganic Chemistry. 52 (4): 2242–56. doi:10.1021/ic302799s. PMID 23387926. However, Ti(−1) occurs in [Ti(η-C6H6]− and [Ti(η-C6H5CH3)]−, see Bandy, J. A.; Berry, A.; Green, M. L. H.; Perutz, R. N.; Prout, K.; Verpeautz, J.-N. (1984). «Synthesis of anionic sandwich compounds: [Ti(η-C6H5R)2]– and the crystal structure of [K(18-crown-6)(µ-H)Mo(η-C5H5)2]». Inorganic Chemistry. 52 (4): 729–731. doi:10.1039/C39840000729.
- ^ Jilek, Robert E.; Tripepi, Giovanna; Urnezius, Eugenijus; Brennessel, William W.; Young, Victor G. Jr.; Ellis, John E. (2007). «Zerovalent titanium–sulfur complexes. Novel dithiocarbamato derivatives of Ti(CO)6: [Ti(CO)4(S2CNR2)]−«. Chem. Commun. (25): 2639–2641. doi:10.1039/B700808B. PMID 17579764.
- ^ Fe(VII) has been observed in [FeO4]−; see Lu, Jun-Bo; Jian, Jiwen; Huang, Wei; Lin, Hailu; Zhou, Mingfei (2016). «Experimental and theoretical identification of the Fe(VII) oxidation state in FeO4−«. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 18 (45): 31125–31131. Bibcode:2016PCCP…1831125L. doi:10.1039/C6CP06753K. PMID 27812577.
- ^ Fe(VIII) has been reported; see Yurii D. Perfiliev; Virender K. Sharma (2008). «Higher Oxidation States of Iron in Solid State: Synthesis and Their Mössbauer Characterization – Ferrates – ACS Symposium Series (ACS Publications)». Platinum Metals Review. 48 (4): 157–158. doi:10.1595/147106704X10801. However, its existence has been disputed.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Fe(−4), Ru(−4), and Os(−4) have been observed in metal-rich compounds containing octahedral complexes [MIn6−xSnx]; Pt(−3) (as a dimeric anion [Pt–Pt]6−), Cu(−2), Zn(−2), Ag(−2), Cd(−2), Au(−2), and Hg(−2) have been observed (as dimeric and monomeric anions; dimeric ions were initially reported to be [T–T]2− for Zn, Cd, Hg, but later shown to be [T–T]4− for all these elements) in La2Pt2In, La2Cu2In, Ca5Au3, Ca5Ag3, Ca5Hg3, Sr5Cd3, Ca5Zn3(structure (AE2+)5(T–T)4−T2−⋅4e−), Yb3Ag2, Ca5Au4, and Ca3Hg2; Au(–3) has been observed in ScAuSn and in other 18-electron half-Heusler compounds. See Changhoon Lee; Myung-Hwan Whangbo (2008). «Late transition metal anions acting as p-metal elements». Solid State Sciences. 10 (4): 444–449. Bibcode:2008SSSci..10..444K. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2007.12.001. and Changhoon Lee; Myung-Hwan Whangbo; Jürgen Köhler (2010). «Analysis of Electronic Structures and Chemical Bonding of Metal-rich Compounds. 2. Presence of Dimer (T–T)4– and Isolated T2– Anions in the Polar Intermetallic Cr5B3-Type Compounds AE5T3 (AE = Ca, Sr; T = Au, Ag, Hg, Cd, Zn)». Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 636 (1): 36–40. doi:10.1002/zaac.200900421.
- ^ Ni(−2) has been observed in Li2[Ni(1,5-COD)2], see Jonas, Klaus (1975). «Dilithium-Nickel-Olefin Complexes. Novel Bimetal Complexes Containing a Transition Metal and a Main Group Metal». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14 (11): 752–753. doi:10.1002/anie.197507521. and Ellis, John E. (2006). «Adventures with Substances Containing Metals in Negative Oxidation States». Inorganic Chemistry. 45 (8): 3167–86. doi:10.1021/ic052110i. PMID 16602773.
- ^ Cu(0) has been observed in Cu(tris[2-(diisopropylphosphino)-
phenyl]borane), see Moret, Marc-Etienne; Zhang, Limei; Peters, Jonas C. (2013). «A Polar Copper–Boron One-Electron σ-Bond». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (10): 3792–3795. doi:10.1021/ja4006578. PMID 23418750. - ^ Zn(0) has been observed; see Singh, Amit Pratap; Samuel, Prinson P.; Roesky, Herbert W.; Schwarzer, Martin C.; Frenking, Gernot; Sidhu, Navdeep S.; Dittrich, Birger (2013). «A Singlet Biradicaloid Zinc Compound and Its Nonradical Counterpart». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (19): 7324–9. doi:10.1021/ja402351x. PMID 23600486. and Soleilhavoup, Michèle; Bertrand, Guy (2015). «Cyclic (Alkyl)(Amino)Carbenes (CAACs): Stable Carbenes on the Rise». Acc. Chem. Res. 48 (2): 256–266. doi:10.1021/ar5003494. PMID 25515548.
- ^ Zn(I) has been observed in decamethyldizincocene (Zn2(η5–C5Me5)2); see Resa, I.; Carmona, E.; Gutierrez-Puebla, E.; Monge, A. (2004). «Decamethyldizincocene, a Stable Compound of Zn(I) with a Zn-Zn Bond». Science. 305 (5687): 1136–8. Bibcode:2004Sci…305.1136R. doi:10.1126/science.1101356. PMID 15326350. S2CID 38990338.
- ^ Zn(III) has been predicted to be stable in compounds with highly stabilized borane-based trianions, but no Zn(III) candidates are known experimentally; see Hong Fang; Huta Banjade; Deepika; Puru Jena (2021). «Realization of the Zn3+ oxidation state». Nanoscale. 13 (33): 14041–14048. doi:10.1039/D1NR02816B. PMID 34477685. S2CID 237400349.
- ^ Ga(−2), Ga(−4), and Ga(−5) have been observed in the magnesium gallides MgGa, Mg2Ga, and Mg5Ga2, respectively; see Patrick Hofmann. «Colture. Ein Programm zur interaktiven Visualisierung von Festkörperstrukturen sowie Synthese, Struktur und Eigenschaften von binären und ternären Alkali- und Erdalkalimetallgalliden» (PDF) (in German). p. 72.
- ^ Ga(−3) has been observed in LaGa, see Dürr, Ines; Bauer, Britta; Röhr, Caroline (2011). «Lanthan-Triel/Tetrel-ide La(Al,Ga)x(Si,Ge)1-x. Experimentelle und theoretische Studien zur Stabilität intermetallischer 1:1-Phasen» (PDF). Z. Naturforsch. (in German). 66b: 1107–1121.
- ^ Ga(0) has been observed in Gallium monoiodide among other gallium’s oxidation states
- ^ Ge(−1), Ge(−2), and Ge(−3) have been observed in germanides; see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). «Germanium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 953–959. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9.
- ^ As(0) has been observed; see Abraham, Mariham Y.; Wang, Yuzhong; Xie, Yaoming; Wei, Pingrong; Shaefer III, Henry F.; Schleyer, P. von R.; Robinson, Gregory H. (2010). «Carbene Stabilization of Diarsenic: From Hypervalency to Allotropy». Chemistry: A European Journal. 16 (2): 432–5. doi:10.1002/chem.200902840. PMID 19937872.
- ^ As(I) has been observed in arsenic(I) iodide (AsI); see Ellis, Bobby D.; MacDonald, Charles L. B. (2004). «Stabilized Arsenic(I) Iodide: A Ready Source of Arsenic Iodide Fragments and a Useful Reagent for the Generation of Clusters». Inorganic Chemistry. 43 (19): 5981–6. doi:10.1021/ic049281s. PMID 15360247.
- ^ As(IV) has been observed in arsenic(IV) hydroxide (As(OH)4) and HAsO−; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Bielski, Benon H. J.; Sehested, K. (1989). «Arsenic(IV). A pulse-radiolysis study». Inorganic Chemistry. 28 (14): 2717–24. doi:10.1021/ic00313a007.
- ^ Se(−1) has been observed in diselenides(2−) (Se22−).
- ^ A Se(0) atom has been identified using DFT in [ReOSe(2-pySe)3]; see Cargnelutti, Roberta; Lang, Ernesto S.; Piquini, Paulo; Abram, Ulrich (2014). «Synthesis and structure of [ReOSe(2-Se-py)3]: A rhenium(V) complex with selenium(0) as a ligand». Inorganic Chemistry Communications. 45: 48–50. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2014.04.003. ISSN 1387-7003.
- ^ Se(I) has been observed in selenium(I) chloride (Se2Cl2); see «Selenium: Selenium(I) chloride compound data». WebElements.com. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- ^ Se(III) has been observed in Se2NBr3; see Lau, Carsten; Neumüller, Bernhard; Vyboishchikov, Sergei F.; Frenking, Gernot; Dehnicke, Kurt; Hiller, Wolfgang; Herker, Martin (1996). «Se2NBr3, Se2NCl5, Se2NCl−6: New Nitride Halides of Selenium(III) and Selenium(IV)». Chemistry: A European Journal. 2 (11): 1393–1396. doi:10.1002/chem.19960021108.
- ^ Se(V) has been observed in SeO−3 and HSeO2−4; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, K. (1986). «Selenium(V). A pulse radiolysis study». Inorganic Chemistry. 90 (21): 5460–4. doi:10.1021/j100412a112.
- ^ Br(II) is known to occur in bromine monoxide radical; see [4]
- ^ Sr(I) has been observed in strontium monofluoride (SrF); see P. Colarusso; Guo, B.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Bernath, P.F.; et al. (1996). «High-Resolution Infrared Emission Spectrum of Strontium Monofluoride» (PDF). Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 175 (1): 158–171. Bibcode:1996JMoSp.175..158C. doi:10.1006/jmsp.1996.0019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-08.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Yttrium and all lanthanides except Ce and Pm have been observed in the oxidation state 0 in bis(1,3,5-tri-t-butylbenzene) complexes, see Cloke, F. Geoffrey N. (1993). «Zero Oxidation State Compounds of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lanthanides». Chem. Soc. Rev. 22: 17–24. doi:10.1039/CS9932200017. and Arnold, Polly L.; Petrukhina, Marina A.; Bochenkov, Vladimir E.; Shabatina, Tatyana I.; Zagorskii, Vyacheslav V.; Cloke (2003-12-15). «Arene complexation of Sm, Eu, Tm and Yb atoms: a variable temperature spectroscopic investigation». Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 688 (1–2): 49–55. doi:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2003.08.028.
- ^ Y(I) has been observed in yttrium(I) bromide (YBr); see «Yttrium: yttrium(I) bromide compound data». OpenMOPAC.net. Archived from the original on 2011-07-23. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- ^ Y(II) has been observed in [(18-crown-6)K][(C5H4SiMe3)3Y]; see MacDonald, M. R.; Ziller, J. W.; Evans, W. J. (2011). «Synthesis of a Crystalline Molecular Complex of Y2+, [(18-crown-6)K][(C5H4SiMe3)3Y]». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 (40): 15914–17. doi:10.1021/ja207151y. PMID 21919538.
- ^ Zr(−1) has been reported in [Zr(bipy)3]− (see Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 960. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8. and Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). «Zirconium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 1413. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9.), but was later shown to be Zr(+4); see Bowman, A. C.; England, J.; Sprouls, S.; Weihemüller, T.; Wieghardt, K. (2013). «Electronic structures of homoleptic [tris(2,2′-bipyridine)M]n complexes of the early transition metals (M = Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta; n = 1+, 0, 1-, 2-, 3-): an experimental and density functional theoretical study». Inorganic Chemistry. 52 (4): 2242–56. doi:10.1021/ic302799s. PMID 23387926.
- ^ a b Zr(0) and Hf(0) occur in (η6-(1,3,5-tBu)3C6H3)2M (M=Zr, Hf) and [(η5-C5R5M(CO)4]−, see Chirik, P. J.; Bradley, C. A. (2007). «4.06 — Complexes of Zirconium and Hafnium in Oxidation States 0 to ii». Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry III. From Fundamentals to Applications. Vol. 4. Elsevier Ltd. pp. 697–739. doi:10.1016/B0-08-045047-4/00062-5. ISBN 9780080450476.
- ^ Complexes of Nb(0) and Ta(0) have been observed, see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (2003). «4.5.7. Niobium(0) and Tantalum(0)». In J. A. McCleverty; T.J. Meyer (eds.). Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II: From Biology to Nanotechnology. Vol. 4 (2 ed.). Newnes. pp. 297–299. ISBN 978-0-08-091316-2.
- ^ a b Nb(I) and Ta(I) occur in CpNb(CO)4 and CpTa(CO)4, see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). «Tantal». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 1430. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9. and King, R. Bruce (1969). Transition-Metal Organometallic Chemistry: An Introduction. Academic Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-32-315996-8.
- ^ George, G.N.; Klein, S.I.; Nixon, J.F. (1984). «Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopic studies on the zero-valent rhodium complex [Rh(P(OPri)3)4] at X-and Q-band frequencies». Chemical Physics Letters. 108 (6): 627–630. Bibcode:1984CPL…108..627G. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(84)85069-1.
- ^ Rh(VII) is known in the RhO3+ cation, see «The Highest Oxidation State of Rhodium: Rhodium(VII) in [RhO3]+». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022. doi:10.1002/anie.202207688.
- ^ Pd(I) has been observed; see Crabtree, R. H. (2002). «CHEMISTRY: A New Oxidation State for Pd?». Science. 295 (5553): 288–289. doi:10.1126/science.1067921. PMID 11786632. S2CID 94579227.
- ^ Pd(III) has been observed; see Powers, D. C.; Ritter, T. (2011). Palladium(III) in Synthesis and Catalysis (PDF). Top. Organomet. Chem. Topics in Organometallic Chemistry. Vol. 35. pp. 129–156. Bibcode:2011hoso.book..129P. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17429-2_6. ISBN 978-3-642-17428-5. PMC 3066514. PMID 21461129. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 12, 2013.
- ^ Palladium(V) has been identified in complexes with organosilicon compounds containing pentacoordinate palladium; see Shimada, Shigeru; Li, Yong-Hua; Choe, Yoong-Kee; Tanaka, Masato; Bao, Ming; Uchimaru, Tadafumi (2007). «Multinuclear palladium compounds containing palladium centers ligated by five silicon atoms». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 104 (19): 7758–7763. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700450104.
- ^ Palladium(VI) has been claimed to exist in «NEW PALLADIUM OXIDATION STATE?». Chem. Eng. News. 80 (2): 8. 2002. doi:10.1021/cen-v080n002.p008., but this has been refuted showing it is a Palladium(II).
- ^ The Ag− ion has been observed in metal ammonia solutions: see Tran, N. E.; Lagowski, J. J. (2001). «Metal Ammonia Solutions: Solutions Containing Argentide Ions». Inorganic Chemistry. 40 (5): 1067–68. doi:10.1021/ic000333x.
- ^ Ag(0) has been observed in carbonyl complexes in low-temperature matrices: see McIntosh, D.; Ozin, G. A. (1976). «Synthesis using metal vapors. Silver carbonyls. Matrix infrared, ultraviolet-visible, and electron spin resonance spectra, structures, and bonding of silver tricarbonyl, silver dicarbonyl, silver monocarbonyl, and disilver hexacarbonyl». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 98 (11): 3167–75. doi:10.1021/ja00427a018.
- ^ Cd(I) has been observed in cadmium(I) tetrachloroaluminate (Cd2(AlCl4)2); see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1985). «Cadmium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1056–1057. ISBN 978-3-11-007511-3.
- ^ In(–5) has been observed in La3InGe, see Guloy, A. M.; Corbett, J. D. (1996). «Synthesis, Structure, and Bonding of Two Lanthanum Indium Germanides with Novel Structures and Properties». Inorganic Chemistry. 35 (9): 2616–22. doi:10.1021/ic951378e. PMID 11666477.
- ^ In(−2) has been observed in Na2In, see [5], p. 69.
- ^ Unstable In(0) carbonyls and clusters have been detected, see [6], p. 6.
- ^ Sn(−3) has been observed in [Sn2]6−, e.g. in (Ba2)4+(Mg4)8+Sn4−(Sn2)6−Sn2− (with square (Sn2−)n sheets), see Papoian, Garegin A.; Hoffmann, Roald (2000). «Hypervalent Bonding in One, Two, and Three Dimensions: Extending the Zintl–Klemm Concept to Nonclassical Electron-Rich Networks». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000 (39): 2408–2448. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20000717)39:14<2408::aid-anie2408>3.0.co;2-u. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- ^ Sn(I) and Sn(III) have been observed in organotin compounds
- ^ Sb(−2) has been observed in [Sb2]4−, e.g. in RbBa4[Sb2][Sb][O], see Boss, Michael; Petri, Denis; Pickhard, Frank; Zönnchen, Peter; Röhr, Caroline (2005). «Neue Barium-Antimonid-Oxide mit den Zintl-Ionen [Sb]3−, [Sb2]4− und 1∞[Sbn]n− / New Barium Antimonide Oxides containing Zintl Ions [Sb]3−, [Sb2]4− and 1∞[Sbn]n−«. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (in German). 631 (6–7): 1181–1190. doi:10.1002/zaac.200400546.
- ^ Sb(0) has been observed, see Anastas Sidiropoulos. «Studies of N-heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes of the Main Group Elements» (PDF). p. 39. doi:10.4225/03/5B0F4BDF98F60. S2CID 132399530.
- ^ Sb(I) and Sb(II) have been observed in organoantimony compounds; for Sb(I), see Šimon, Petr; de Proft, Frank; Jambor, Roman; Růžička, Aleš; Dostál, Libor (2010). «Monomeric Organoantimony(I) and Organobismuth(I) Compounds Stabilized by an NCN Chelating Ligand: Syntheses and Structures». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 49 (32): 5468–5471. doi:10.1002/anie.201002209. PMID 20602393.
- ^ Sb(IV) has been observed in [SbCl6]2−, see Nobuyoshi Shinohara; Masaaki Ohsima (2000). «Production of Sb(IV) Chloro Complex by Flash Photolysis of the Corresponding Sb(III) and Sb(V) Complexes in CH3CN and CHCl3». Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 73 (7): 1599–1604. doi:10.1246/bcsj.73.1599.
- ^ Te(0) has been observed in tellurolates.
- ^ Te(I) has been observed in tellurium iodide (TeI), see «Tellurium: tellurium iodide». WebElements.com. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- ^ Te(III) has been observed in [Te(N(SiMe3)2)2]+, see Heinze, Thorsten; Roesky, Herbert W.; Pauer, Frank; Stalke, Dietmar; Sheldrick, George M. (1991). «Synthesis and Structure of the First Tellurium(III) Radical Cation». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 30 (12): 1678. doi:10.1002/anie.199116771. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- ^ Te(V) is mentioned by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but they do not give any example of a Te(V) compound. What was long thought to be ditellurium decafluoride (Te2F10) is actually bis(pentafluorotelluryl) oxide, F5TeOTeF5: see Watkins, P. M. (1974). «Ditellurium decafluoride — A Continuing Myth». Journal of Chemical Education. 51 (9): 520–521. Bibcode:1974JChEd..51..520W. doi:10.1021/ed051p520. However, Te(V) has been observed in HTeO−, TeO−, HTeO−2, and TeO−3; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, K. (2001). «Tellurium(V). A Pulse Radiolysis Study». The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 105 (27): 6637–45. Bibcode:2001JPCA..105.6637K. doi:10.1021/jp010577i.
- ^ I(II) is known to exist in monoxide (IO); see Nikitin, I V (31 August 2008). «Halogen monoxides». Russian Chemical Reviews. 77 (8): 739–749. Bibcode:2008RuCRv..77..739N. doi:10.1070/RC2008v077n08ABEH003788.
- ^ I(IV) has been observed in iodine dioxide (IO2); see Pauling, Linus (1988). «Oxygen Compounds of Nonmetallic Elements». General Chemistry (3rd ed.). Dover Publications, Inc. p. 259. ISBN 978-0-486-65622-9.
- ^ I(VI) has been observed in IO3, IO42−, H5IO6−, H2IO52−, H4IO62−, and HIO53−; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, Knud; Wolff, Thomas (1981). «Laser flash photolysis and pulse radiolysis of iodate and periodate in aqueous solution. Properties of iodine(VI)». J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1. 77 (7): 1707–18. doi:10.1039/F19817701707.
- ^ Xe compounds: see Xenon
- ^ Xe(0) has been observed in tetraxenonogold(II) (AuXe42+).
- ^ Xe(I) has been reported in xenon hexafluoroplatinate and xenon hexafluororhodate (see Pauling, Linus (1988). General Chemistry (3rd ed.). Dover Publications, Inc. p. 250. ISBN 978-0-486-65622-9.), however these compounds were later found to contain Xe(II).
- ^ Ba(I) has been observed in barium monofluoride (BaF); see P. Colarusso; Guo, B.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Bernath, P.F.; et al. (1995). «High-Resolution Fourier Transform Infrared Emission Spectrum of Barium Monofluoride» (PDF). Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 170 (1): 59. Bibcode:1996JMoSp.175..158C. doi:10.1006/jmsp.1996.0019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-03-10.
- ^ a b c d La(I), Pr(I), Tb(I), Tm(I), and Yb(I) have been observed in MB8− clusters; see Li, Wan-Lu; Chen, Teng-Teng; Chen, Wei-Jia; Li, Jun; Wang, Lai-Sheng (2021). «Monovalent lanthanide(I) in borozene complexes». Nature Communications. 12: 6467. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26785-9.
- ^ Pr(I) has been observed in [PrB4]−; see Chen, Xin; Chen, Teng-Teng; Li, Wang-Lu; Lu, Jun-Bo; Zhao, Li-Juan; Jian, Tian; Hu, Han-Shi; Wang, Lai-Sheng; Li, Jun (2018-12-13). «Lanthanides with Unusually Low Oxidation States in the PrB3– and PrB4– Boride Clusters». Inorganic Chemistry. 58 (1): 411–418. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b02572. PMID 30543295. S2CID 56148031.
- ^ Pr(V) has been observed in [PrO2]+; see Zhang, Qingnan; Hu, Shu-Xian; Qu, Hui; Su, Jing; Wang, Guanjun; Lu, Jun-Bo; Chen, Mohua; Zhou, Mingfei; Li, Jun (2016-06-06). «Pentavalent Lanthanide Compounds: Formation and Characterization of Praseodymium(V) Oxides». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 55 (24): 6896–6900. doi:10.1002/anie.201602196. ISSN 1521-3773. PMID 27100273.
- ^ Hu, Shu-Xian; Jian, Jiwen; Su, Jing; Wu, Xuan; Li, Jun; Zhou, Mingfei (2017). «Pentavalent lanthanide nitride-oxides: NPrO and NPrO− complexes with N≡Pr triple bonds». Chemical Science. 8 (5): 4035–4043. doi:10.1039/C7SC00710H. ISSN 2041-6520. PMC 5434915. PMID 28580119.
- ^ Nd(IV) has been observed in unstable solid state compounds; see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ a b c d e All the lanthanides (La–Lu) in the +2 oxidation state have been observed (except La, Gd, Lu) in dilute, solid solutions of dihalides of these elements in alkaline earth dihalides (see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5) and (except Pm) in organometallic molecular complexes, see Lanthanides Topple Assumptions and Meyer, G. (2014). «All the Lanthanides Do It and Even Uranium Does Oxidation State +2». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 53 (14): 3550–51. doi:10.1002/anie.201311325. PMID 24616202.. Additionally, all the lanthanides (La–Lu) form dihydrides (LnH2), dicarbides (LnC2), monosulfides (LnS), monoselenides (LnSe), and monotellurides (LnTe), but for most elements these compounds have Ln3+ ions with electrons delocalized into conduction bands, e. g. Ln3+(H−)2(e−).
- ^ SmB6- cluster anion has been reported and contains Sm in rare oxidation state of +1; see Paul, J. Robinson; Xinxing, Zhang; Tyrel, McQueen; Kit, H. Bowen; Anastassia, N. Alexandrova (2017). «SmB6– Cluster Anion: Covalency Involving f Orbitals». J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 8, 1849–1854. 121 (8): 1849–1854..
- ^ Dy(IV) has been observed in unstable solid state compounds; see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ Hf(I) has been observed in hafnium monobromide (HfBr), see Marek, G.S.; Troyanov, S.I.; Tsirel’nikov, V.I. (1979). «Кристаллическое строение и термодинамические характеристики монобромидов циркония и гафния / Crystal structure and thermodynamic characteristics of monobromides of zirconium and hafnium». Журнал неорганической химии / Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry (in Russian). 24 (4): 890–893.
- ^ Os(−1) has been observed in Na[Os(CO)13]; see Krause, J.; Siriwardane, Upali; Salupo, Terese A.; Wermer, Joseph R.; Knoeppel, David W.; Shore, Sheldon G. (1993). «Preparation of [Os3(CO)11]2− and its reactions with Os3(CO)12; structures of [Et4N] [HOs3(CO)11] and H2OsS4(CO)». Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 454 (1–2): 263–271. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(93)83250-Y. and Carter, Willie J.; Kelland, John W.; Okrasinski, Stanley J.; Warner, Keith E.; Norton, Jack R. (1982). «Mononuclear hydrido alkyl carbonyl complexes of osmium and their polynuclear derivatives». Inorganic Chemistry. 21 (11): 3955–3960. doi:10.1021/ic00141a019.
- ^ Ir(−3) has been observed in Ir(CO)33−; see Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1117. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Ir(VII) has been observed in [(η2-O2)IrO2]+; see C&EN: Iridium dressed to the nines.
- ^ Ir(VIII) has been observed in iridium tetroxide (IrO4); see Gong, Yu; Zhou, Mingfei; Kaupp, Martin; Riedel, Sebastian (2009). «Formation and Characterization of the Iridium Tetroxide Molecule with Iridium in the Oxidation State +VIII». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (42): 7879–7883. doi:10.1002/anie.200902733. PMID 19593837.
- ^ Ir(IX) has been observed in IrO+4; see Wang, Guanjun; Zhou, Mingfei; Goettel, James T.; Schrobilgen, Gary G.; Su, Jing; Li, Jun; Schlöder, Tobias; Riedel, Sebastian (21 August 2014). «Identification of an iridium-containing compound with a formal oxidation state of IX». Nature. 514 (7523): 475–477. Bibcode:2014Natur.514..475W. doi:10.1038/nature13795. PMID 25341786. S2CID 4463905.
- ^ Pt(−1) and Pt(−2) have been observed in the barium platinides BaPt and Ba2Pt, respectively: see Karpov, Andrey; Konuma, Mitsuharu; Jansen, Martin (2006). «An experimental proof for negative oxidation states of platinum: ESCA-measurements on barium platinides». Chemical Communications (8): 838–840. doi:10.1039/b514631c. PMID 16479284.
- ^ Pt(I) and Pt(III) have been observed in bimetallic and polymetallic species; see Kauffman, George B.; Thurner, Joseph J.; Zatko, David A. (1967). Ammonium Hexachloroplatinate(IV). Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 9. pp. 182–185. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch51. ISBN 978-0-470-13240-1.
- ^ Au(0) has been observed, see Mézaille, Nicolas; Avarvari, Narcis; Maigrot, Nicole; Ricard, Louis; Mathey, François; Le Floch, Pascal; Cataldo, Laurent; Berclaz, Théo; Geoffroy, Michel (1999). «Gold(I) and Gold(0) Complexes of Phosphinine‐Based Macrocycles». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 38 (21): 3194–3197. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19991102)38:21<3194::AID-ANIE3194>3.0.CO;2-O. PMID 10556900.
- ^ Hg(IV) has been reported in mercury(IV) fluoride (HgF4); see Xuefang Wang; Lester Andrews; Sebastian Riedel; Martin Kaupp (2007). «Mercury Is a Transition Metal: The First Experimental Evidence for HgF4«. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46 (44): 8371–8375. doi:10.1002/anie.200703710. PMID 17899620. However, it could not be confirmed by later experiments; see Is mercury a transition metal? Archived 2016-10-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tl(−5) has been observed in Na23K9Tl15.3, see Dong, Z.-C.; Corbett, J. D. (1996). «Na23K9Tl15.3: An Unusual Zintl Compound Containing Apparent Tl57−, Tl48−, Tl37−, and Tl5− Anions». Inorganic Chemistry. 35 (11): 3107–12. doi:10.1021/ic960014z. PMID 11666505.
- ^ Tl(−1) has been observed in caesium thallide (CsTl); see King, R. B.; Schleyer, R. (2004). «Theory and concepts in main-group cluster chemistry». In Driess, M.; Nöth, H. (eds.). Molecular clusters of the main group elements. Wiley-VCH, Chichester. p. 19. ISBN 978-3-527-61437-0.
- ^ Tl(+2) has been observed in tetrakis(hypersilyl)dithallium ([(Me3Si)Si]2Tl—Tl[Si(SiMe3)]2), see Sonja Henkel; Dr. Karl Wilhelm Klinkhammer; Dr. Wolfgang Schwarz (1994). «Tetrakis(hypersilyl)dithallium(Tl—Tl): A Divalent Thallium Compound». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 33 (6): 681–683. doi:10.1002/anie.199406811.
- ^ Pb(−2) has been observed in BaPb, see Ferro, Riccardo (2008). Nicholas C. Norman (ed.). Intermetallic Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 505. ISBN 978-0-08-044099-6. and Todorov, Iliya; Sevov, Slavi C. (2004). «Heavy-Metal Aromatic Rings: Cyclopentadienyl Anion Analogues Sn56− and Pb56− in the Zintl Phases Na8BaPb6, Na8BaSn6, and Na8EuSn6«. Inorganic Chemistry. 43 (20): 6490–94. doi:10.1021/ic000333x.
- ^ Pb(0) carbonyls have been observered in reaction between lead atoms and carbon monoxide; see Ling, Jiang; Qiang, Xu (2005). «Observation of the lead carbonyls PbnCO (n=1–4): Reactions of lead atoms and small clusters with carbon monoxide in solid argon». The Journal of Chemical Physics. 122 (3): 034505. 122 (3): 34505. Bibcode:2005JChPh.122c4505J. doi:10.1063/1.1834915. ISSN 0021-9606. PMID 15740207.
- ^ Pb(+1) and Pb(+3) have been observed in organolead compounds, e.g. hexamethyldiplumbane Pb2(CH3)6; for Pb(I), see Siew-Peng Chia; Hong-Wei Xi; Yongxin Li; Kok Hwa Lim; Cheuk-Wai So (2013). «A Base-Stabilized Lead(I) Dimer and an Aromatic Plumbylidenide Anion». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52 (24): 6298–6301. doi:10.1002/anie.201301954. PMID 23629949.
- ^ Bi(−2) and Bi(−1) occur in Zintl phases, e.g. (Ca2+)22[Bi4]4−([Bi2]4−)4[Bi3−]8; see Ponou, Siméon (2006). «Germanides, Germanide-Tungstate Double Salts and Substitution Effects in Zintl Phases». Technische Universität München. Lehrstuhl für Anorganische Chemie mit Schwerpunkt Neue Materialien. p. 68.
- ^ Bi(0) state is known to exist in a N-heterocyclic carbene complex of dibismuthene; see Deka, Rajesh; Orthaber, Andreas (May 6, 2022). «Carbene chemistry of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth: origin, evolution and future prospects». Royal Society of Chemistry (51): 8540. doi:10.1039/d2dt00755j.
- ^ Bi(I) has been observed in bismuth monobromide (BiBr) and bismuth monoiodide (BiI); see Godfrey, S. M.; McAuliffe, C. A.; Mackie, A. G.; Pritchard, R. G. (1998). Nicholas C. Norman (ed.). Chemistry of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Springer. pp. 67–84. ISBN 978-0-7514-0389-3.
- ^ Bi(+2) has been observed in dibismuthines (R2Bi—BiR2), see Arthur J. Ashe III (1990). Thermochromic Distibines and Dibismuthines. Advances in Organometallic Chemistry. Vol. 30. pp. 77–97. doi:10.1016/S0065-3055(08)60499-2. ISBN 9780120311309.
- ^ Bi(IV) has been observed; see A. I. Aleksandrov, I. E. Makarov (1987). «Formation of Bi(II) and Bi(IV) in aqueous hydrochloric solutions of Bi(III)». Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science. 36 (2): 217–220. doi:10.1007/BF00959349. S2CID 94865394.
- ^ Po(V) has been observed in dioxidopolonium(1+) (PoO+); see Thayer, John S. (2010). «Relativistic Effects and the Chemistry of the Heavier Main Group Elements». Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. Vol. 10. p. 78. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- ^ Rn(II) has been observed in radon difluoride (RnF2); see Stein, L. (1970). «Ionic Radon Solution». Science. 168 (3929): 362–4. Bibcode:1970Sci…168..362S. doi:10.1126/science.168.3929.362. PMID 17809133. S2CID 31959268. and Kenneth S. Pitzer (1975). «Fluorides of radon and element 118». J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. (18): 760b–761. doi:10.1039/C3975000760b.
- ^ Rn(IV) is reported by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but is not known to exist; see Sykes, A. G. (1998). «Recent Advances in Noble-Gas Chemistry». Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 46. Academic Press. pp. 91–93. ISBN 978-0-12-023646-6. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ Rn(VI) is known in radon trioxide (RnO3); see Sykes, A. G. (1998). «Recent Advances in Noble-Gas Chemistry». Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 46. Academic Press. pp. 91–93. ISBN 978-0-12-023646-6. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ Th(-I) and U(-I) have been detected in the gas phase as octacarbonyl anions; see Chaoxian, Chi; Sudip, Pan; Jiaye, Jin; Luyan, Meng; Mingbiao, Luo; Lili, Zhao; Mingfei, Zhou; Gernot, Frenking (2019). «Octacarbonyl Ion Complexes of Actinides [An(CO)8]+/− (An=Th, U) and the Role of f Orbitals in Metal–Ligand Bonding». Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany). 25 (50): 11772–11784. 25 (50): 11772–11784. doi:10.1002/chem.201902625. ISSN 0947-6539. PMC 6772027. PMID 31276242.
- ^ Th(I) is known in thorium(I) bromide (ThBr); see Wickleder, Mathias S.; Fourest, Blandine; Dorhout, Peter K. (2006). «Thorium». In Morss, Lester R.; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (PDF). Vol. 3 (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer. pp. 52–160. doi:10.1007/1-4020-3598-5_3. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-07.
- ^ Th(II) and Th(III) are observed in [ThII{η5-C5H3(SiMe3)2}3]− and [ThIII{η5-C5H3(SiMe3)2}3], see Langeslay, Ryan R.; Fieser, Megan E.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Furche, Philip; Evans, William J. (2015). «Synthesis, structure, and reactivity of crystalline molecular complexes of the {[C5H3(SiMe3)2]3Th}1− anion containing thorium in the formal +2 oxidation state». Chem. Sci. 6 (1): 517–521. doi:10.1039/C4SC03033H. PMC 5811171. PMID 29560172.
- ^ Pa(II) occurs in proctactinium(II) oxide
- ^ Th(-I) and U(-I) have been detected in the gas phase as octacarbonyl anions; see Chaoxian, Chi; Sudip, Pan; Jiaye, Jin; Luyan, Meng; Mingbiao, Luo; Lili, Zhao; Mingfei, Zhou; Gernot, Frenking (2019). «Octacarbonyl Ion Complexes of Actinides [An(CO)8]+/− (An=Th, U) and the Role of f Orbitals in Metal–Ligand Bonding». Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany). 25 (50): 11772–11784. 25 (50): 11772–11784. doi:10.1002/chem.201902625. ISSN 0947-6539. PMC 6772027. PMID 31276242.
- ^ U(I) has been observed in uranium monofluoride (UF) and uranium monochloride (UCl), see Sykes, A. G. (1990). «Compounds of Thorium and Uranium». Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 34. Academic Press. pp. 87–88. ISBN 978-0-12-023634-3. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- ^ U(II) has been observed in [K(2.2.2-Cryptand)][(C5H4SiMe3)3U], see MacDonald, Matthew R.; Fieser, Megan E.; Bates, Jefferson E.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Furche, Filipp; Evans, William J. (2013). «Identification of the +2 Oxidation State for Uranium in a Crystalline Molecular Complex, [K(2.2.2-Cryptand)][(C5H4SiMe3)3U]». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (36): 13310–13313. doi:10.1021/ja406791t. PMID 23984753.
- ^ Np(II), (III) and (IV) have been observed, see Dutkiewicz, Michał S.; Apostolidis, Christos; Walter, Olaf; Arnold, Polly L (2017). «Reduction chemistry of neptunium cyclopentadienide complexes: from structure to understanding». Chem. Sci. 8 (4): 2553–2561. doi:10.1039/C7SC00034K. PMC 5431675. PMID 28553487.
- ^ Pu(II) has been observed in {Pu[C5H3(SiMe3)2]3}−; see Windorff, Cory J.; Chen, Guo P; Cross, Justin N; Evans, William J.; Furche, Filipp; Gaunt, Andrew J.; Janicke, Michael T.; Kozimor, Stosh A.; Scott, Brian L. (2017). «Identification of the Formal +2 Oxidation State of Plutonium: Synthesis and Characterization ofref name=»curium5» {PuII[C5H3(SiMe3)2]3}−». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 (11): 3970–3973. doi:10.1021/jacs.7b00706. PMID 28235179.
- ^ Pu(VIII) has been observed in PuO4; see Nikonov, M. V.; Kiselev, Yu. M.; Tananaev, I. G.; Myasoedov, B. F. (March 2011). «Plutonium volatility in ozonization of alkaline solutions of Pu(VI) hydroxo complexes». Doklady Chemistry. 437 (1): 69–71. doi:10.1134/S0012500811030104. S2CID 95951175. Also see Kiselev, Yu. M.; Nikonov, M. V.; Dolzhenko, V. D.; Ermilov, A. Yu.; Tananaev, I. G.; Myasoedov, B. F. (17 January 2014). «On existence and properties of plutonium(VIII) derivatives». Radiochimica Acta. 102 (3): 227–237. doi:10.1515/ract-2014-2146. S2CID 100915090.
- ^ Am(VII) has been observed in AmO−5; see Americium, Das Periodensystem der Elemente für den Schulgebrauch (The periodic table of elements for schools) chemie-master.de (in German), Retrieved 28 November 2010 and Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1265. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b c Cm(V), Bk(V), and Cf(V) have been observed in BkO2+, CfO2+, CmO2(NO3)2−, BkO2(NO3)2−, and CfO2(NO3)2−; see Dau, Phuong Diem; Vasiliu, Monica; Peterson, Kirk A; Dixon, David A; Gibsoon, John K (October 2017). «Remarkably High Stability of Late Actinide Dioxide Cations: Extending Chemistry to Pentavalent Berkelium and Californium». Chemistry — A European Journal. 23 (68): 17369–17378. doi:10.1002/chem.201704193. PMID 29024093.
- ^ a b c Kovács, Attila; Dau, Phuong D.; Marçalo, Joaquim; Gibson, John K. (2018). «Pentavalent Curium, Berkelium, and Californium in Nitrate Complexes: Extending Actinide Chemistry and Oxidation States». Inorg. Chem. American Chemical Society. 57 (15): 9453–9467. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01450. OSTI 1631597. PMID 30040397. S2CID 51717837.
- ^ Cm(VI) has been observed in curium trioxide (CmO3) and dioxidocurium(2+) (CmO+2); see Domanov, V. P.; Lobanov, Yu. V. (October 2011). «Formation of volatile curium(VI) trioxide CmO3«. Radiochemistry. 53 (5): 453–6. doi:10.1134/S1066362211050018. S2CID 98052484.
- ^ Cm(VIII) has been reported to possibly occur in curium tetroxide (CmO4); see Domanov, V. P. (January 2013). «Possibility of generation of octavalent curium in the gas phase in the form of volatile tetraoxide CmO4«. Radiochemistry. 55 (1): 46–51. doi:10.1134/S1066362213010098. S2CID 98076989. However, new experiments seem to indicate its nonexistence: Zaitsevskii, Andréi; Schwarz, W H Eugen (April 2014). «Structures and stability of AnO4 isomers, An = Pu, Am, and Cm: a relativistic density functional study». Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2014 (16): 8997–9001. Bibcode:2014PCCP…16.8997Z. doi:10.1039/c4cp00235k. PMID 24695756.
- ^ Peterson, J. R.; Hobart, D. E. (1984). «The Chemistry of Berkelium». In Emeléus, Harry Julius (ed.). Advances in inorganic chemistry and radiochemistry. Vol. 28. Academic Press. pp. 29–64. doi:10.1016/S0898-8838(08)60204-4. ISBN 978-0-12-023628-2.
- ^ Peterson 1984, p. 55.
- ^
- ^ Es(IV) is known in einsteinium(IV) fluoride (EsF4); see Kleinschmidt, P (1994). «Thermochemistry of the actinides». Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 213–214: 169–172. doi:10.1016/0925-8388(94)90898-2.
- ^ Db(V) has been observed in dubnium pentachloride (DbCl5); see H. W. Gäggeler (2007). «Gas Phase Chemistry of Superheavy Elements» (PDF). Paul Scherrer Institute. pp. 26–28. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-02-20.
- ^ Sg(VI) has been observed in seaborgium oxide hydroxide (SgO2(OH)2); see Huebener, S.; Taut, S.; Vahle, A.; Dressler, R.; Eichler, B.; Gäggeler, H. W.; Jost, D.T.; Piguet, D.; et al. (2001). «Physico-chemical characterization of seaborgium as oxide hydroxide» (PDF). Radiochim. Acta. 89 (11–12_2001): 737–741. doi:10.1524/ract.2001.89.11-12.737. S2CID 98583998. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-25.
- ^ Sg(0) has been observed in seaborgium hexacarbonyl (Sg(CO)6); see Even, J.; Yakushev, A.; Dullmann, C. E.; Haba, H.; Asai, M.; Sato, T. K.; Brand, H.; Di Nitto, A.; Eichler, R.; Fan, F. L.; Hartmann, W.; Huang, M.; Jager, E.; Kaji, D.; Kanaya, J.; Kaneya, Y.; Khuyagbaatar, J.; Kindler, B.; Kratz, J. V.; Krier, J.; Kudou, Y.; Kurz, N.; Lommel, B.; Miyashita, S.; Morimoto, K.; Morita, K.; Murakami, M.; Nagame, Y.; Nitsche, H.; et al. (2014). «Synthesis and detection of a seaborgium carbonyl complex». Science. 345 (6203): 1491–3. Bibcode:2014Sci…345.1491E. doi:10.1126/science.1255720. PMID 25237098. S2CID 206558746.
- ^ Bh(VII) has been observed in bohrium oxychloride (BhO3Cl); see «Gas chemical investigation of bohrium (Bh, element 107)» Archived 2008-02-28 at the Wayback Machine, Eichler et al., GSI Annual Report 2000. Retrieved on 2008-02-29
- ^ Hs(VIII) has been observed in hassium tetroxide (HsO4); see «Chemistry of Hassium» (PDF). Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung mbH. 2002. Retrieved 2007-01-31.
- ^ Cn(II) has been observed in copernicium selenide (CnSe); see «Annual Report 2015: Laboratory of Radiochemistry and Environmental Chemistry» (PDF). Paul Scherrer Institute. 2015. p. 3.
- ^ Langmuir, Irving (1919). «The arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 41 (6): 868–934. doi:10.1021/ja02227a002.
- ^ «Antoine Laurent Lavoisier The Chemical Revolution – Landmark – American Chemical Society». American Chemical Society. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- ^ «Lavoisier on Elements». Chem125-oyc.webspace.yale.edu. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- ^ Wöhler, F. (1835). Grundriss der Chemie: Unorganische Chemie [Foundations of Chemistry: Inorganic Chemistry]. Berlin: Duncker und Humblot. p. 4.
- ^ Jensen, W. B. (2007). «the origin of the oxidation-state concept». J. Chem. Educ. 84 (9): 1418–1419. Bibcode:2007JChEd..84.1418J. doi:10.1021/ed084p1418.
- ^ Stock, A. (1919). «Einige Nomenklaturfragen der anorganischen Chemie» [Some nomenclature issues of inorganic chemistry]. Angew. Chem. 32 (98): 373–374. Bibcode:1919AngCh..32..373S. doi:10.1002/ange.19190329802.
- ^ a b Jorissen, W. P.; Bassett, H.; Damiens, A.; Fichter, F.; Rémy, H. (1941). «Rules for naming inorganic compounds». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 63: 889–897. doi:10.1021/ja01849a001.
- ^ Latimer, W. M. (1938). The Oxidation States of the Elements and their Potentials in Aqueous Solutions (1st ed.). Prentice-Hall.
- ^ Bray, W. C.; Branch, G. E. K. (1913). «Valence and tautomerism». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 35 (10): 1440–1447. doi:10.1021/ja02199a003.
- ^ Noyes, A. A.; Pitzer, K. S.; Dunn, C. L. (1935). «Argentic salts in acid solution, I. The oxidation and reduction reactions». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57 (7): 1221–1229. doi:10.1021/ja01310a018.
- ^ Noyes, A. A.; Pitzer, K. S.; Dunn, C. L. (1935). «Argentic salts in acid solution, II. The oxidation state of argentic salts». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57 (7): 1229–1237. doi:10.1021/ja01310a019.
- ^ Fernelius, W. C. (1948). «Some problems of inorganic nomenclature». Chem. Eng. News. 26: 161–163. doi:10.1021/cen-v026n003.p161.
- ^ Fernelius, W. C.; Larsen, E. M.; Marchi, L. E.; Rollinson, C. L. (1948). «Nomenclature of coördination compounds». Chem. Eng. News. 26 (8): 520–523. doi:10.1021/cen-v026n008.p520.
- ^ Pauling, L. (1948). «The modern theory of valency». J. Chem. Soc. 1948: 1461–1467. doi:10.1039/JR9480001461. PMID 18893624.
- ^ Calvert, J. G. (1990). «IUPAC Recommendation 1990». Pure Appl. Chem. 62: 2204. doi:10.1351/pac199062112167.
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge.
The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the «real» charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. Thus, the oxidation state of an atom in a compound is purely a formalism. It is nevertheless important in understanding the nomenclature conventions of inorganic compounds. Also, several observations regarding chemical reactions may be explained at a basic level in terms of oxidation states.
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, zero, or negative. In some cases, the average oxidation state of an element is a fraction, such as 8/3 for iron in magnetite Fe3O4 (see below). The highest known oxidation state is reported to be +9, displayed by iridium in the tetroxoiridium(IX) cation (IrO+4).[1] It is predicted that even a +10 oxidation state may be achieved by platinum in tetroxoplatinum(X), PtO2+4.[2] The lowest oxidation state is −5, as for boron in Al3BC.[3]
In inorganic nomenclature, the oxidation state is represented by a Roman numeral placed after the element name inside parentheses or as a superscript after the element symbol, e.g. Iron(III) oxide.
The term oxidation was first used by Antoine Lavoisier to signify the reaction of a substance with oxygen. Much later, it was realized that the substance, upon being oxidized, loses electrons, and the meaning was extended to include other reactions in which electrons are lost, regardless of whether oxygen was involved.
The increase in the oxidation state of an atom, through a chemical reaction, is known as oxidation; a decrease in oxidation state is known as a reduction. Such reactions involve the formal transfer of electrons: a net gain in electrons being a reduction, and a net loss of electrons being oxidation. For pure elements, the oxidation state is zero.
IUPAC definition[edit]
IUPAC has published a «Comprehensive definition of the term oxidation state (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)».[4] It is a distillation of an IUPAC technical report «Toward a comprehensive definition of oxidation state» from 2014.[5] The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation state is:
Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…
— IUPAC[6]
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous.[7]
The underlying principle is that the ionic charge is «the oxidation state of an atom, after ionic approximation of its bonds»,[8] where ionic approximation means, hypothesizing that all bonds are ionic. Several criteria were considered for the ionic approximation:
- Extrapolation of the bond’s polarity;
- from the electronegativity difference,
- from the dipole moment, and
- from quantum‐chemical calculations of charges.
- Assignment of electrons according to the atom’s contribution to the bonding Molecular orbital (MO)[8][9]/ the electron’s allegiance in a LCAO–MO model.[10]
In a bond between two different elements, the bond’s electrons are assigned to its main atomic contributor/higher electronegativity; in a bond between two atoms of the same element, the electrons are divided equally. This is because most electronegativity scales depend on the atom’s bonding state, which makes the assignment of the oxidation state a somewhat circular argument. For example, some scales may turn out unusual oxidation states, such as -6 for platinum in PtH2−4, for Pauling and Mulliken scales.[11] The dipole moments would, sometimes, also turn out abnormal oxidation numbers, such as in CO and NO, which
are oriented with their positive end towards oxygen. Therefore, this leaves the atom’s contribution to the
bonding MO, the atomic-orbital energy, and from quantum-chemical calculations of charges, as the only viable criteria with cogent values for ionic approximation. However, for a simple estimate for the ionic approximation, we can use Allen electronegativities,[8] as only that electronegativity scale is truly independent of the oxidation state, as it relates to the average valence‐electron energy of the free atom:
Electronegativity using the Allen scale |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group → | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| ↓ Period | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | H 2.300 |
He 4.160 |
||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Li 0.912 |
Be 1.576 |
B 2.051 |
C 2.544 |
N 3.066 |
O 3.610 |
F 4.193 |
Ne 4.787 |
||||||||||
| 3 | Na 0.869 |
Mg 1.293 |
Al 1.613 |
Si 1.916 |
P 2.253 |
S 2.589 |
Cl 2.869 |
Ar 3.242 |
||||||||||
| 4 | K 0.734 |
Ca 1.034 |
Sc 1.19 |
Ti 1.38 |
V 1.53 |
Cr 1.65 |
Mn 1.75 |
Fe 1.80 |
Co 1.84 |
Ni 1.88 |
Cu 1.85 |
Zn 1.588 |
Ga 1.756 |
Ge 1.994 |
As 2.211 |
Se 2.424 |
Br 2.685 |
Kr 2.966 |
| 5 | Rb 0.706 |
Sr 0.963 |
Y 1.12 |
Zr 1.32 |
Nb 1.41 |
Mo 1.47 |
Tc 1.51 |
Ru 1.54 |
Rh 1.56 |
Pd 1.58 |
Ag 1.87 |
Cd 1.521 |
In 1.656 |
Sn 1.824 |
Sb 1.984 |
Te 2.158 |
I 2.359 |
Xe 2.582 |
| 6 | Cs 0.659 |
Ba 0.881 |
Lu 1.09 |
Hf 1.16 |
Ta 1.34 |
W 1.47 |
Re 1.60 |
Os 1.65 |
Ir 1.68 |
Pt 1.72 |
Au 1.92 |
Hg 1.765 |
Tl 1.789 |
Pb 1.854 |
Bi 2.01 |
Po 2.19 |
At 2.39 |
Rn 2.60 |
| 7 | Fr 0.67 |
Ra 0.89 |
||||||||||||||||
| See also: Electronegativities of the elements (data page) |
Determination[edit]
While introductory levels of chemistry teaching use postulated oxidation states, the IUPAC recommendation[4] and the Gold Book entry[6] list two entirely general algorithms for the calculation of the oxidation states of elements in chemical compounds.
Simple approach without bonding considerations[edit]
Introductory chemistry uses postulates: the oxidation state for an element in a chemical formula is calculated from the overall charge and postulated oxidation states for all the other atoms.
A simple example is based on two postulates,
- OS = +1 for hydrogen
- OS = −2 for oxygen
where OS stands for oxidation state. This approach yields correct oxidation states in oxides and hydroxides of any single element, and in acids such as H2SO4 or H2Cr2O7. Its coverage can be extended either by a list of exceptions or by assigning priority to the postulates. The latter works for H2O2 where the priority of rule 1 leaves both oxygens with oxidation state −1.
Additional postulates and their ranking may expand the range of compounds to fit a textbook’s scope. As an example, one postulatory algorithm from many possible; in a sequence of decreasing priority:
- An element in a free form has OS = 0.
- In a compound or ion, the sum of the oxidation states equals the total charge of the compound or ion.
- Fluorine in compounds has OS = −1; this extends to chlorine and bromine only when not bonded to a lighter halogen, oxygen or nitrogen.
- Group 1 and group 2 metals in compounds have OS = +1 and +2, respectively.
- Hydrogen has OS = +1 but adopts −1 when bonded as a hydride to metals or metalloids.
- Oxygen in compounds has OS = −2 but only when not bonded to oxygen (e.g. in peroxides) or fluorine.
This set of postulates covers oxidation states of fluorides, chlorides, bromides, oxides, hydroxides, and hydrides of any single element. It covers all oxoacids of any central atom (and all their fluoro-, chloro-, and bromo-relatives), as well as salts of such acids with group 1 and 2 metals. It also covers iodides, sulfides, and similar simple salts of these metals.
Algorithm of assigning bonds[edit]
This algorithm is performed on a Lewis structure (a diagram that shows all valence electrons). Oxidation state equals the charge of an atom after each of its heteronuclear bonds has been assigned to the more-electronegative partner of the bond (except when that partner is a reversibly bonded Lewis-acid ligand) and homonuclear bonds have been divided equally:
where each «—» represents an electron pair (either shared between two atoms or solely on one atom), and «OS» is the oxidation state as a numerical variable.
After the electrons have been assigned according to the vertical red lines on the formula, the total number of valence electrons that now «belong» to each atom is subtracted from the number N of valence electrons of the neutral atom (such as 5 for nitrogen in group 15) to yield that atom’s oxidation state.
This example shows the importance of describing the bonding. Its summary formula, HNO3, corresponds to two structural isomers; the peroxynitrous acid in the above figure and the more stable nitric acid. With the formula HNO3, the simple approach without bonding considerations yields −2 for all three oxygens and +5 for nitrogen, which is correct for nitric acid. For the peroxynitrous acid, however, the two oxygens in the O–O bond each has OS = −1 and the nitrogen has OS = +3, which requires a structure to understand.
Organic compounds are treated in a similar manner; exemplified here on functional groups occurring in between CH4 and CO2:
Analogously for transition-metal compounds; CrO(O2)2 on the left has a total of 36 valence electrons (18 pairs to be distributed), and Cr(CO)6 on the right has 66 valence electrons (33 pairs):
A key step is drawing the Lewis structure of the molecule (neutral, cationic, anionic): atom symbols are arranged so that pairs of atoms can be joined by single two-electron bonds as in the molecule (a sort of «skeletal» structure), and the remaining valence electrons are distributed such that sp atoms obtain an octet (duet for hydrogen) with a priority that increases in proportion with electronegativity. In some cases, this leads to alternative formulae that differ in bond orders (the full set of which is called the resonance formulas). Consider the sulfate anion (SO2−
4 with 32 valence electrons; 24 from oxygens, 6 from sulfur, 2 of the anion charge obtained from the implied cation). The bond orders to the terminal oxygens do not affect the oxidation state so long as the oxygens have octets. Already the skeletal structure, top left, yields the correct oxidation states, as does the Lewis structure, top right (one of the resonance formulas):
The bond-order formula at the bottom is closest to the reality of four equivalent oxygens each having a total bond order of 2. That total includes the bond of order 1/2 to the implied cation and follows the 8 − N rule[5] requiring that the main-group atom’s bond order equals 8 minus N valence electrons of the neutral atom, enforced with a priority that proportionately increases with electronegativity.
This algorithm works equally for molecular cations composed of several atoms. An example is the ammonium cation of 8 valence electrons (5 from nitrogen, 4 from hydrogens, minus 1 electron for the cation’s positive charge):
Drawing Lewis structures with electron pairs as dashes emphasizes the essential equivalence of bond pairs and lone pairs when counting electrons and moving bonds onto atoms. Structures drawn with electron dot pairs are of course identical in every way:
The algorithm’s caveat[edit]
The algorithm contains a caveat, which concerns rare cases of transition-metal complexes with a type of ligand that is reversibly bonded as a Lewis acid (as an acceptor of the electron pair from the transition metal); termed a «Z-type» ligand in Green’s covalent bond classification method. The caveat originates from the simplifying use of electronegativity instead of the MO-based electron allegiance to decide the ionic sign.[4] One early example is the O2S−RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2 complex[12] with SO2 as the reversibly-bonded acceptor ligand (released upon heating). The Rh−S bond is therefore extrapolated ionic against Allen electronegativities of rhodium and sulfur, yielding oxidation state +1 for rhodium:
Algorithm of summing bond orders[edit]
This algorithm works on Lewis structures and bond graphs of extended (non-molecular) solids:
Oxidation state is obtained by summing the heteronuclear-bond orders at the atom as positive if that atom is the electropositive partner in a particular bond and as negative if not, and the atom’s formal charge (if any) is added to that sum.
Applied to a Lewis structure[edit]
An example of a Lewis structure with no formal charge,
illustrates that, in this algorithm, homonuclear bonds are simply ignored (the bond orders are in blue).
Carbon monoxide exemplifies a Lewis structure with formal charges:
To obtain the oxidation states, the formal charges are summed with the bond-order value taken positively at the carbon and negatively at the oxygen.
Applied to molecular ions, this algorithm considers the actual location of the formal (ionic) charge, as drawn in the Lewis structure. As an example, summing bond orders in the ammonium cation yields −4 at the nitrogen of formal charge +1, with the two numbers adding to the oxidation state of −3:
The sum of oxidation states in the ion equals its charge (as it equals zero for a neutral molecule).
Also in anions, the formal (ionic) charges have to be considered when nonzero. For sulfate this is exemplified with the skeletal or Lewis structures (top), compared with the bond-order formula of all oxygens equivalent and fulfilling the octet and 8 − N rules (bottom):
Applied to bond graph[edit]
A bond graph in solid-state chemistry is a chemical formula of an extended structure, in which direct bonding connectivities are shown. An example is the AuORb3 perovskite, the unit cell of which is drawn on the left and the bond graph (with added numerical values) on the right:
We see that the oxygen atom bonds to the six nearest rubidium cations, each of which has 4 bonds to the auride anion. The bond graph summarizes these connectivities. The bond orders (also called bond valences) sum up to oxidation states according to the attached sign of the bond’s ionic approximation (there are no formal charges in bond graphs).
Determination of oxidation states from a bond graph can be illustrated on ilmenite, FeTiO3. We may ask whether the mineral contains Fe2+ and Ti4+, or Fe3+ and Ti3+. Its crystal structure has each metal atom bonded to six oxygens and each of the equivalent oxygens to two irons and two titaniums, as in the bond graph below. Experimental data show that three metal-oxygen bonds in the octahedron are short and three are long (the metals are off-center). The bond orders (valences), obtained from the bond lengths by the bond valence method, sum up to 2.01 at Fe and 3.99 at Ti; which can be rounded off to oxidation states +2 and +4, respectively:
Balancing redox[edit]
Oxidation states can be useful for balancing chemical equations for oxidation-reduction (or redox) reactions, because the changes in the oxidized atoms have to be balanced by the changes in the reduced atoms. For example, in the reaction of acetaldehyde with Tollens’ reagent to form acetic acid (shown below), the carbonyl carbon atom changes its oxidation state from +1 to +3 (loses two electrons). This oxidation is balanced by reducing two Ag+ cations to Ag0 (gaining two electrons in total).
An inorganic example is the Bettendorf reaction using SnCl2 to prove the presence of arsenite ions in a concentrated HCl extract. When arsenic(III) is present, a brown coloration appears forming a dark precipitate of arsenic, according to the following simplified reaction:
- 2 As3+ + 3 Sn2+ → 2 As0 + 3 Sn4+
Here three tin atoms are oxidized from oxidation state +2 to +4, yielding six electrons that reduce two arsenic atoms from oxidation state +3 to 0. The simple one-line balancing goes as follows: the two redox couples are written down as they react;
- As3+ + Sn2+ ⇌ As0 + Sn4+.
One tin is oxidized from oxidation state +2 to +4, a two-electron step, hence 2 is written in front of the two arsenic partners. One arsenic is reduced from +3 to 0, a three-electron step, hence 3 goes in front of the two tin partners. An alternative three-line procedure is to write separately the half-reactions for oxidation and reduction, each balanced with electrons, and then to sum them up such that the electrons cross out. In general, these redox balances (the one-line balance or each half-reaction) need to be checked for the ionic and electron charge sums on both sides of the equation being indeed equal. If they are not equal, suitable ions are added to balance the charges and the non-redox elemental balance.
Appearances[edit]
Nominal oxidation states[edit]
A nominal oxidation state is a general term with two different definitions:
- Electrochemical oxidation state[citation needed] represents a molecule or ion in the Latimer diagram or Frost diagram for its redox-active element. An example is the Latimer diagram for sulfur at pH 0 where the electrochemical oxidation state +2 for sulfur puts HS
2O−
3 between S and H2SO3:
- Systematic oxidation state is chosen from close alternatives as a pedagogical description. An example is the oxidation state of phosphorus in H3PO3 (structurally diprotic HPO(OH)2) taken nominally as +3, while Allen electronegativities of phosphorus and hydrogen suggest +5 by a narrow margin that makes the two alternatives almost equivalent:
-
- Both alternative oxidation numbers for phosphorus make chemical sense, depending on which chemical property or reaction is emphasized. By contrast, a calculated alternative, such as the average (+4) does not.
Ambiguous oxidation states[edit]
Lewis formulae are rule-based approximations of chemical reality, as are Allen electronegativities. Still, oxidation states may seem ambiguous when their determination is not straightforward. If only an experiment can determine the oxidation state, the rule-based determination is ambiguous (insufficient). There are also truly dichotomous values that are decided arbitrarily.
Oxidation-state determination from resonance formulas[edit]
Seemingly ambiguous oxidation states are derived from a set of resonance formulas of equal weights for a molecule having heteronuclear bonds where the atom connectivity does not correspond to the number of two-electron bonds dictated by the 8 − N rule. An example is S2N2 where four resonance formulas featuring one S=N double bond have oxidation states +2 and +4 for the two sulfur atoms, which average to +3 because the two sulfur atoms are equivalent in this square-shaped molecule.
A physical measurement is needed to determine oxidation state[edit]
- when a non-innocent ligand is present, of hidden or unexpected redox properties that could otherwise be assigned to the central atom. An example is the nickel dithiolate complex, Ni(S
2C
2H
2)2−
2.[5]: 1056–1057 - when the redox ambiguity of a central atom and ligand yields dichotomous oxidation states of close stability, thermally induced tautomerism may result, as exemplified by manganese catecholate, Mn(C6H4O2)3.[5]: 1057–1058 Assignment of such oxidation states requires spectroscopic,[13] magnetic or structural data.
- when the bond order has to be ascertained along with an isolated tandem of a heteronuclear and a homonuclear bond. An example is thiosulfate S
2O2−
3 having two possible oxidation states (bond orders are in blue and formal charges in green):
- The S–S distance measurement in thiosulfate is needed to reveal that this bond order is very close to 1, as in the formula on the left.
Ambiguous/arbitrary oxidation states[edit]
- when the electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms is very small (as in H3PO3). Two almost equivalent pairs of oxidation states, arbitrarily chosen, are obtained for these atoms.
- when an electronegative p-block atom forms solely homonuclear bonds, the number of which differs from the number of two-electron bonds suggested by rules. Examples are homonuclear finite chains like N−
3 (the central nitrogen connects two atoms with four two-electron bonds while only three two-electron bonds[14] are required by 8 − N rule) or I−
3 (the central iodine connects two atoms with two two-electron bonds while only one two-electron bond fulfills the 8 − N rule). A sensible approach is to distribute the ionic charge over the two outer atoms.[5] Such a placement of charges in a polysulfide S2−
n (where all inner sulfurs form two bonds, fulfilling the 8 − N rule) follows already from its Lewis structure.[5] - when the isolated tandem of a heteronuclear and a homonuclear bond leads to a bonding compromise in between two Lewis structures of limiting bond orders. An example is N2O:
- The typical oxidation state of nitrogen in N2O is +1, which also obtains for both nitrogens by a molecular orbital approach.[15] The formal charges on the right comply with electronegativities, which implies an added ionic bonding contribution. Indeed, the estimated N−N and N−O bond orders are 2.76 and 1.9, respectively,[5] approaching the formula of integer bond orders that would include the ionic contribution explicitly as a bond (in green):
- Conversely, formal charges against electronegativities in a Lewis structure decrease the bond order of the corresponding bond. An example is carbon monoxide with a bond-order estimate of 2.6.[16]
Fractional oxidation states[edit]
Fractional oxidation states are often used to represent the average oxidation state of several atoms of the same element in a structure. For example, the formula of magnetite is Fe
3O
4, implying an average oxidation state for iron of +8/3.[17]: 81–82 However, this average value may not be representative if the atoms are not equivalent. In a Fe
3O
4 crystal below 120 K (−153 °C), two-thirds of the cations are Fe3+
and one-third are Fe2+
, and the formula may be more clearly represented as FeO·Fe
2O
3.[18]
Likewise, propane, C
3H
8, has been described as having a carbon oxidation state of −8/3.[19] Again, this is an average value since the structure of the molecule is H
3C−CH
2−CH
3, with the first and third carbon atoms each having an oxidation state of −3 and the central one −2.
An example with true fractional oxidation states for equivalent atoms is potassium superoxide, KO
2. The diatomic superoxide ion O−
2 has an overall charge of −1, so each of its two equivalent oxygen atoms is assigned an oxidation state of −1/2. This ion can be described as a resonance hybrid of two Lewis structures, where each oxygen has an oxidation state of 0 in one structure and −1 in the other.
For the cyclopentadienyl anion C
5H−
5, the oxidation state of C is −1 + −1/5 = −6/5. The −1 occurs because each carbon is bonded to one hydrogen atom (a less electronegative element), and the −1/5 because the total ionic charge of −1 is divided among five equivalent carbons. Again this can be described as a resonance hybrid of five equivalent structures, each having four carbons with oxidation state −1 and one with −2.
-
Examples of fractional oxidation states for carbon
Oxidation state Example species −6/5 C
5H−
5−6/7 C
7H+
7+3/2 C
4O2−
4
Finally, fractional oxidation numbers are not used in the description[20]: 66 of red lead. Pb
3O
4 is represented as lead(II,IV) oxide, showing the oxidation states of the two nonequivalent lead atoms.
Elements with multiple oxidation states[edit]
See also § List of oxidation states of the elements
Most elements have more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4:
-
Integer oxidation states of carbon
Oxidation state Example compound −4 CH
4−3 C
2H
6−2 C
2H
4, CH
3Cl−1 C
2H
2, C
6H
6, (CH
2OH)
20 HCHO, CH
2Cl
2+1 OCHCHO, CHCl
2CHCl
2+2 HCOOH, CHCl
3+3 HOOCCOOH, C
2Cl
6+4 CCl
4, CO
2
Oxidation state in metals[edit]
Many compounds with luster and electrical conductivity maintain a simple stoichiometric formula, such as the golden TiO, blue-black RuO2 or coppery ReO3, all of obvious oxidation state. Ultimately, assigning the free metallic electrons to one of the bonded atoms is not comprehensive and can yield unusual oxidation states. Examples are the LiPb and Cu
3Au ordered alloys, the composition and structure of which are largely determined by atomic size and packing factors. Should oxidation state be needed for redox balancing, it is best set to 0 for all atoms of such an alloy.
List of oxidation states of the elements[edit]
This is a list of known oxidation states of the chemical elements, excluding nonintegral values. The most common states appear in bold. The table is based on that of Greenwood and Earnshaw,[21] with additions noted. Every element exists in oxidation state 0 when it is the pure non-ionized element in any phase, whether monatomic or polyatomic allotrope. The column for oxidation state 0 only shows elements known to exist in oxidation state 0 in compounds.
Noble gas
+1 Bold values are main oxidation states
Oxidation states of the elements |
|||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Negative states | Positive states | Group | Notes | |||||||||||||||
| −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | +9 | |||||
| Z | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | hydrogen | H | −1 | +1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | helium | He | 18 | ||||||||||||||||
| 3 | lithium | Li | 0 | +1 | 1 | [22][23] | |||||||||||||
| 4 | beryllium | Be | 0 | +1 | +2 | 2 | [24][25] | ||||||||||||
| 5 | boron | B | −5 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [26][27][28] | |||||||||
| 6 | carbon | C | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | |||||||
| 7 | nitrogen | N | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [29] | ||||||
| 8 | oxygen | O | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | 16 | |||||||||||
| 9 | fluorine | F | −1 | 0 | 17 | [30][31] | |||||||||||||
| 10 | neon | Ne | 0 | 18 | [32] | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | sodium | Na | −1 | 0 | +1 | 1 | [22][33] | ||||||||||||
| 12 | magnesium | Mg | 0 | +1 | +2 | 2 | [34][35] | ||||||||||||
| 13 | aluminium | Al | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [36][37][38][39] | |||||||||
| 14 | silicon | Si | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [40] | ||||||
| 15 | phosphorus | P | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [41] | ||||||
| 16 | sulfur | S | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | |||||||
| 17 | chlorine | Cl | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 17 | [42] | |||||||
| 18 | argon | Ar | 0 | 18 | [43] | ||||||||||||||
| 19 | potassium | K | −1 | +1 | 1 | [22] | |||||||||||||
| 20 | calcium | Ca | +1 | +2 | 2 | [44][45] | |||||||||||||
| 21 | scandium | Sc | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [46][47][48] | |||||||||||
| 22 | titanium | Ti | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [49][50][51][52] | ||||||||
| 23 | vanadium | V | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [50] | |||||||
| 24 | chromium | Cr | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [50] | |||||
| 25 | manganese | Mn | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | |||||
| 26 | iron | Fe | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 8 | [53][54][55] | ||||
| 27 | cobalt | Co | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 9 | [50] | |||||||
| 28 | nickel | Ni | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 10 | [56] | ||||||||
| 29 | copper | Cu | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 11 | [55][57] | |||||||||
| 30 | zinc | Zn | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | 12 | [55][58][59][60] | |||||||||||
| 31 | gallium | Ga | −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [37][61][62][63] | ||||||
| 32 | germanium | Ge | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [64][40] | ||||||
| 33 | arsenic | As | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [37][65][66][67] | ||||||
| 34 | selenium | Se | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [68][69][70][71][72] | ||||||
| 35 | bromine | Br | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +7 | 17 | [73] | ||||||||
| 36 | krypton | Kr | 0 | +1 | +2 | 18 | |||||||||||||
| 37 | rubidium | Rb | −1 | +1 | 1 | [22] | |||||||||||||
| 38 | strontium | Sr | +1 | +2 | 2 | [74][45] | |||||||||||||
| 39 | yttrium | Y | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [75][76][77] | |||||||||||
| 40 | zirconium | Zr | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [50][78][79] | |||||||||
| 41 | niobium | Nb | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [50][80][81] | |||||||
| 42 | molybdenum | Mo | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [50] | |||||
| 43 | technetium | Tc | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | ||||||
| 44 | ruthenium | Ru | −4 | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | 8 | [50][55] | ||||
| 45 | rhodium | Rh | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 9 | [50][82][83] | |||||
| 46 | palladium | Pd | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 10 | [84][85][86][87] | |||||||||
| 47 | silver | Ag | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 11 | [55][88][89] | |||||||||
| 48 | cadmium | Cd | −2 | +1 | +2 | 12 | [55][90] | ||||||||||||
| 49 | indium | In | −5 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [37][91][92][93] | ||||||||
| 50 | tin | Sn | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [37][94][95][40] | ||||||
| 51 | antimony | Sb | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [37][96][97][98][99] | ||||||
| 52 | tellurium | Te | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [37][100][101][102][103] | ||||||
| 53 | iodine | I | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 17 | [104][105][106] | |||||||
| 54 | xenon | Xe | 0 | +2 | +4 | +6 | +8 | 18 | [107][108][109] | ||||||||||
| 55 | caesium | Cs | −1 | +1 | 1 | [22] | |||||||||||||
| 56 | barium | Ba | +1 | +2 | 2 | [110][45] | |||||||||||||
| 57 | lanthanum | La | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][111] | |||||||||||
| 58 | cerium | Ce | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | |||||||||||||
| 59 | praseodymium | Pr | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [75][112][113][114] | |||||||||
| 60 | neodymium | Nd | 0 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [75][115] | |||||||||||
| 61 | promethium | Pm | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [116] | |||||||||||||
| 62 | samarium | Sm | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [117] | |||||||||||
| 63 | europium | Eu | 0 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75] | ||||||||||||
| 64 | gadolinium | Gd | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75] | |||||||||||
| 65 | terbium | Tb | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [75][111][116] | ||||||||||
| 66 | dysprosium | Dy | 0 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [75][118] | |||||||||||
| 67 | holmium | Ho | 0 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][116] | ||||||||||||
| 68 | erbium | Er | 0 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][116] | ||||||||||||
| 69 | thulium | Tm | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][111] | |||||||||||
| 70 | ytterbium | Yb | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | [75][111] | |||||||||||
| 71 | lutetium | Lu | 0 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [75][116] | ||||||||||||
| 72 | hafnium | Hf | −2 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [50][79][119] | |||||||||
| 73 | tantalum | Ta | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [50][81] | |||||||
| 74 | tungsten | W | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [50] | |||||
| 75 | rhenium | Re | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | ||||||
| 76 | osmium | Os | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | 8 | [55][120] | |||
| 77 | iridium | Ir | −3 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | +9 | 9 | [121][122][123][124] | |||
| 78 | platinum | Pt | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 10 | [55][125][126] | |||||
| 79 | gold | Au | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +5 | 11 | [55][127] | |||||||
| 80 | mercury | Hg | −2 | +1 | +2 | 12 | [55][128] | ||||||||||||
| 81 | thallium | Tl | −5 | −2 | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [37][129][130][131] | |||||||||
| 82 | lead | Pb | −4 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [37][132][133][134] | |||||||
| 83 | bismuth | Bi | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [135][136][137][138][139] | ||||||
| 84 | polonium | Po | −2 | +2 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [140] | ||||||||||
| 85 | astatine | At | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 | 17 | |||||||||||
| 86 | radon | Rn | +2 | +6 | 18 | [141][142][143] | |||||||||||||
| 87 | francium | Fr | +1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 88 | radium | Ra | +2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| 89 | actinium | Ac | +3 | f-block groups | |||||||||||||||
| 90 | thorium | Th | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [144][145][146] | ||||||||||
| 91 | protactinium | Pa | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [147] | |||||||||||
| 92 | uranium | U | −1 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | f-block groups | [148][149][150] | ||||||||
| 93 | neptunium | Np | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | f-block groups | [151] | |||||||||
| 94 | plutonium | Pu | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | f-block groups | [152][153] | ||||||||
| 95 | americium | Am | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | f-block groups | [154] | |||||||||
| 96 | curium | Cm | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | f-block groups | [155][156][157][158] | |||||||||||
| 97 | berkelium | Bk | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [155][156][159][160][161] | |||||||||||
| 98 | californium | Cf | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | f-block groups | [155][156] | |||||||||||
| 99 | einsteinium | Es | +2 | +3 | +4 | f-block groups | [162] | ||||||||||||
| 100 | fermium | Fm | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | ||||||||||||||
| 101 | mendelevium | Md | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | ||||||||||||||
| 102 | nobelium | No | +2 | +3 | f-block groups | ||||||||||||||
| 103 | lawrencium | Lr | +3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| 104 | rutherfordium | Rf | +4 | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| 105 | dubnium | Db | +5 | 5 | [163] | ||||||||||||||
| 106 | seaborgium | Sg | 0 | +6 | 6 | [164][165] | |||||||||||||
| 107 | bohrium | Bh | +7 | 7 | [166] | ||||||||||||||
| 108 | hassium | Hs | +8 | 8 | [167] | ||||||||||||||
| 109 | meitnerium | Mt | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
| 110 | darmstadtium | Ds | 10 | ||||||||||||||||
| 111 | roentgenium | Rg | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
| 112 | copernicium | Cn | +2 | 12 | [168] | ||||||||||||||
| 113 | nihonium | Nh | 13 | ||||||||||||||||
| 114 | flerovium | Fl | 14 | ||||||||||||||||
| 115 | moscovium | Mc | 15 | ||||||||||||||||
| 116 | livermorium | Lv | 16 | ||||||||||||||||
| 117 | tennessine | Ts | 17 | ||||||||||||||||
| 118 | oganesson | Og | 18 |
Early forms (octet rule)[edit]
A figure with a similar format was used by Irving Langmuir in 1919 in one of the early papers about the octet rule.[169] The periodicity of the oxidation states was one of the pieces of evidence that led Langmuir to adopt the rule.
Use in nomenclature[edit]
The oxidation state in compound naming for transition metals and lanthanides and actinides is placed either as a right superscript to the element symbol in a chemical formula, such as FeIII or in parentheses after the name of the element in chemical names, such as iron(III). For example, Fe
2(SO
4)
3 is named iron(III) sulfate and its formula can be shown as FeIII
2(SO
4)
3. This is because a sulfate ion has a charge of −2, so each iron atom takes a charge of +3.
History of the oxidation state concept[edit]
Early days[edit]
Oxidation itself was first studied by Antoine Lavoisier, who defined it as the result of reactions with oxygen (hence the name).[170][171] The term has since been generalized to imply a formal loss of electrons. Oxidation states, called oxidation grades by Friedrich Wöhler in 1835,[172] were one of the intellectual stepping stones that Dmitri Mendeleev used to derive the periodic table. William B. Jensen[173] gives an overview of the history up to 1938.
Use in nomenclature[edit]
When it was realized that some metals form two different binary compounds with the same nonmetal, the two compounds were often distinguished by using the ending -ic for the higher metal oxidation state and the ending -ous for the lower. For example, FeCl3 is ferric chloride and FeCl2 is ferrous chloride. This system is not very satisfactory (although sometimes still used) because different metals have different oxidation states which have to be learned: ferric and ferrous are +3 and +2 respectively, but cupric and cuprous are +2 and +1, and stannic and stannous are +4 and +2. Also, there was no allowance for metals with more than two oxidation states, such as vanadium with oxidation states +2, +3, +4, and +5.[17]: 84
This system has been largely replaced by one suggested by Alfred Stock in 1919[174] and adopted[175] by IUPAC in 1940. Thus, FeCl2 was written as iron(II) chloride rather than ferrous chloride. The Roman numeral II at the central atom came to be called the «Stock number» (now an obsolete term), and its value was obtained as a charge at the central atom after removing its ligands along with the electron pairs they shared with it.[20]: 147
Development towards the current concept[edit]
The term «oxidation state» in English chemical literature was popularized by Wendell Mitchell Latimer in his 1938 book about electrochemical potentials.[176] He used it for the value (synonymous with the German term Wertigkeit) previously termed «valence», «polar valence» or «polar number»[177] in English, or «oxidation stage» or indeed[178][179] the «state of oxidation». Since 1938, the term «oxidation state» has been connected with electrochemical potentials and electrons exchanged in redox couples participating in redox reactions. By 1948, IUPAC used the 1940 nomenclature rules with the term «oxidation state»,[180][181] instead of the original[175] valency. In 1948 Linus Pauling proposed that oxidation number could be determined by extrapolating bonds to being completely ionic in the direction of electronegativity.[182] A full acceptance of this suggestion was complicated by the fact that the Pauling electronegativities as such depend on the oxidation state and that they may lead to unusual values of oxidation states for some transition metals. In 1990 IUPAC resorted to a postulatory (rule-based) method to determine the oxidation state.[183] This was complemented by the synonymous term oxidation number as a descendant of the Stock number introduced in 1940 into the nomenclature. However, the terminology using «ligands»[20]: 147 gave the impression that oxidation number might be something specific to coordination complexes. This situation and the lack of a real single definition generated numerous debates about the meaning of oxidation state, suggestions about methods to obtain it and definitions of it. To resolve the issue, an IUPAC project (2008-040-1-200) was started in 2008 on the «Comprehensive Definition of Oxidation State», and was concluded by two reports[5][4] and by the revised entries «Oxidation State»[6] and «Oxidation Number»[7] in the IUPAC Gold Book. The outcomes were a single definition of oxidation state and two algorithms to calculate it in molecular and extended-solid compounds, guided by Allen electronegativities that are independent of oxidation state.
See also[edit]
- Electronegativity
- Electrochemistry
- Atomic orbital
- Atomic shell
- Quantum numbers
- Azimuthal quantum number
- Principal quantum number
- Magnetic quantum number
- Spin quantum number
- Aufbau principle
- Wiswesser’s rule
- Ionization energy
- Electron affinity
- Ionic potential
- Ions
- Cations and Anions
- Polyatomic ions
- Covalent bonding
- Metallic bonding
- Hybridization
References[edit]
- ^ Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Goettel, G. T.; Schrobilgen, G. J.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Schlöder, T.; Riedel, S. (2014). «Identification of an iridium-containing compound with a formal oxidation state of IX». Nature. 514 (7523): 475–477. Bibcode:2014Natur.514..475W. doi:10.1038/nature13795. PMID 25341786. S2CID 4463905.
- ^ Yu, Haoyu S.; Truhlar, Donald G. (2016). «Oxidation State 10 Exists». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 55 (31): 9004–9006. doi:10.1002/anie.201604670.
- ^ Schroeder, Melanie, Eigenschaften von borreichen Boriden und Scandium-Aluminium-Oxid-Carbiden (in German), p. 139
- ^ a b c d Karen, P.; McArdle, P.; Takats, J. (2016). «Comprehensive definition of oxidation state (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)». Pure Appl. Chem. 88 (8): 831–839. doi:10.1515/pac-2015-1204. hdl:10852/59520. S2CID 99403810.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Karen, P.; McArdle, P.; Takats, J. (2014). «Toward a comprehensive definition of oxidation state (IUPAC Technical Report)». Pure Appl. Chem. 86 (6): 1017–1081. doi:10.1515/pac-2013-0505.
- ^ a b c IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the «Gold Book») (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) «Oxidation state». doi:10.1351/goldbook.O04365
- ^ a b IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the «Gold Book») (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) «Oxidation number». doi:10.1351/goldbook.O04363
- ^ a b c Karen, Pavel (2015). «Oxidation State, A Long-Standing Issue!». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 54 (16): 4716–4726. doi:10.1002/anie.201407561. PMC 4506524. PMID 25757151.
- ^ Hooydonk, G. (1974). O n an Ionic Approximation to Chemical Bonding, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A, 29(5), 763-767. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-1974-0517
- ^ «Oxidation state». IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology. 2009. doi:10.1351/goldbook.O04365. ISBN 978-0-9678550-9-7.
- ^ Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014), 86(6), 1017–1081 CODEN: PACHAS; ISSN 0033-4545. English.
- ^ Muir, K. W.; Ibers, J. A. (1969). «The structure of chlorocarbonyl(sulfur dioxide)bis(triphenylphosphine)rhodium, RhCl(CO)(SO2)(P(C6H5)3)2«. Inorg. Chem. 8 (9): 1921–1928. doi:10.1021/ic50079a024.
- ^ Jørgensen, C. K. (1966). «Electric Polarizability, Innocent Ligands and Spectroscopic Oxidation States». Structure and Bonding. Vol. 1. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 234–248.
- ^ «The Two-Electron Bond». Chemistry LibreTexts. June 25, 2016.
- ^ Karen, P. (2015). «Oxidation state, a long-standing issue!». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54 (16): 4716–4726. doi:10.1002/anie.201407561. PMC 4506524. PMID 25757151.
- ^ Martinie, R. J.; Bultema, J. J.; Wal, M. N. V.; Burkhart, B. J.; Griend, D. A. V.; DeCock, R. L. (2011). «Bond order and chemical properties of BF, CO, and N2«. J. Chem. Educ. 88 (8): 1094–1097. Bibcode:2011JChEd..88.1094M. doi:10.1021/ed100758t.
- ^ a b Petrucci, R. H.; Harwood, W. S.; Herring, F. G. (2002). General Chemistry (8th ed.). Prentice-Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-033445-9.[ISBN missing]
- ^ Senn, M. S.; Wright, J. P.; Attfield, J. P. (2012). «Charge order and three-site distortions in the Verwey structure of magnetite» (PDF). Nature. 481 (7380): 173–6. Bibcode:2012Natur.481..173S. doi:10.1038/nature10704. hdl:20.500.11820/1b3bb558-52d5-419f-9944-ab917dc95f5e. PMID 22190035. S2CID 4425300. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ Whitten, K. W.; Galley, K. D.; Davis, R. E. (1992). General Chemistry (4th ed.). Saunders. p. 147. ISBN 978-0-03-075156-1.[ISBN missing]
- ^ a b c Connelly, N. G.; Damhus, T.; Hartshorn, R. M.; Hutton, A. T. Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005) (PDF). RSC Publishing. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 27–28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b c d e Na(−1), K(−1), Rb(−1), and Cs(−1) are known in alkalides; the table by Greenwood and Earnshaw shows −1 only for Na and also erroneously for Li; no lithides are described.
- ^ Li(0) atoms have been observed in various small lithium-chloride clusters; see Milovanović, Milan; Veličković, Suzana; Veljkovićb, Filip; Jerosimić, Stanka (October 30, 2017). «Structure and stability of small lithium-chloride LinClm(0,1+) (n ≥ m, n = 1–6, m = 1–3) clusters». Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (45). doi:10.1039/C7CP04181K.
- ^ Be(0) has been observed; see «Beryllium(0) Complex Found». Chemistry Europe. 13 June 2016.
- ^ Be(I) has been observed in beryllium monohydride (BeH); see Shayesteh, A.; Tereszchuk, K.; Bernath, P. F.; Colin, R. (2003). «Infrared Emission Spectra of BeH and BeD» (PDF). J. Chem. Phys. 118 (3): 1158. Bibcode:2003JChPh.118.1158S. doi:10.1063/1.1528606. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-12-02. Retrieved 2007-12-10. and in [(CAAC)2Be]+• [CAAC = cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene], see Wang, Guocang; Walley, Jacob E.; Dickie, Diane E.; Pan, Sudip; Frenking, Gernot; Gilliard Jr., Robert G. (2020). «A Stable, Crystalline Beryllium Radical Cation». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (10): 4560–4. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b13777. PMID 32088963. S2CID 211262005. Retrieved 2020-11-17.
- ^ B(−5) has been observed in Al3BC, see Schroeder, Melanie. «Eigenschaften von borreichen Boriden und Scandium-Aluminium-Oxid-Carbiden» (in German). p. 139.
- ^ B(−1) has been observed in magnesium diboride (MgB2), see Keeler, James; Wothers, Peter (2014). Chemical Structure and Reactivity: An Integrated Approach. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199604135.
- ^ B(0) has been observed in diborynes, see Braunschweig, H.; Dewhurst, R. D.; Hammond, K.; Mies, J.; Radacki, K.; Vargas, A. (2012). «Ambient-Temperature Isolation of a Compound with a Boron-Boron Triple Bond». Science. 336 (6087): 1420–2. Bibcode:2012Sci…336.1420B. doi:10.1126/science.1221138. PMID 22700924. S2CID 206540959.
- ^ Tetrazoles contain a pair of double-bonded nitrogen atoms with oxidation state 0 in the ring. A Synthesis of the parent 1H-tetrazole, CH2N4 (two atoms N(0)) is given in Ronald A. Henry and William G. Finnegan, «An Improved Procedure for the Deamination of 5-Aminotetrazole», _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ (1954), 76, 1, 290–291,
https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01630a086. - ^ Gold heptafluoride is calculated to be the pentafluoride with a molecular F2 ligand. Himmel, Daniel; Riedel, Sebastian (2007). «After 20 Years, Theoretical Evidence That ‘AuF7‘ Is Actually AuF5•F2«. Inorganic Chemistry. 46 (13): 5338–5342. doi:10.1021/ic700431s. PMID 17511450.
- ^ A cluster of elusive SF6+ with helium atoms is known to have fluorine(0)atom as a ligand; see Albertini, Simon; Bergmeister, Stefan; Laimer, Felix; Martini, Paul; Gruber, Elisabeth; Zappa, Fabio; Ončák, Milan; Scheier, Paul; Echt, Olof (2021-04-22). «SF 6 + : Stabilizing Transient Ions in Helium Nanodroplets». The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 12 (17): 4112–4117. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c01024. ISSN 1948-7185. PMC 8154854. PMID 33886323.
- ^ Ne(0) has been observed in Cr(CO)5Ne. Perutz, Robin N.; Turner, James J. (August 1975). «Photochemistry of the Group 6 hexacarbonyls in low-temperature matrices. III. Interaction of the pentacarbonyls with noble gases and other matrices». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 97 (17): 4791–4800. doi:10.1021/ja00850a001.
- ^ The compound NaCl has been shown in experiments to exists in several unusual stoichiometries under high pressure, including Na3Cl in which contains a layer of sodium(0) atoms; see Zhang, W.; Oganov, A. R.; Goncharov, A. F.; Zhu, Q.; Boulfelfel, S. E.; Lyakhov, A. O.; Stavrou, E.; Somayazulu, M.; Prakapenka, V. B.; Konôpková, Z. (2013). «Unexpected Stable Stoichiometries of Sodium Chlorides». Science. 342 (6165): 1502–1505. arXiv:1310.7674. Bibcode:2013Sci…342.1502Z. doi:10.1126/science.1244989. PMID 24357316. S2CID 15298372.
- ^ Low valent magnesium compounds with Mg(I) have been obtained using bulky ligands; see Green, S. P.; Jones C.; Stasch A. (December 2007). «Stable Magnesium(I) Compounds with Mg-Mg Bonds». Science. 318 (5857): 1754–1757. Bibcode:2007Sci…318.1754G. doi:10.1126/science.1150856. PMID 17991827. S2CID 40657565.
- ^ Mg(0) has been synthesized in a compound containing a Na2Mg22+ cluster coordinated to a bulky organic ligand; see Rösch, B.; Gentner, T. X.; Eyselein, J.; Langer, J.; Elsen, H.; Li, W.; Harder, S. (2021). «Strongly reducing magnesium(0) complexes». Nature. 592 (7856): 717–721. Bibcode:2021Natur.592..717R. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03401-w. PMID 33911274. S2CID 233447380
- ^ Al(II) has been observed in aluminium(II) oxide (AlO); see Tyte, D.C. (1964). «Red (B2Π–A2σ) Band System of Aluminium Monoxide». Nature. 202 (4930): 383–384. Bibcode:1964Natur.202..383T. doi:10.1038/202383a0. S2CID 4163250, and in dialanes (R2Al—AlR2); see Uhl, Werner (2004). «Organoelement Compounds Possessing Al—Al, Ga—Ga, In—In, and Tl—Tl Single Bonds». Advances in Organometallic Chemistry. 51: 53–108. doi:10.1016/S0065-3055(03)51002-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Negative oxidation states of p-block metals (Al, Ga, In, Sn, Tl, Pb, Bi, Po) and metalloids (Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, At) may occur in Zintl phases, see: Riedel, Erwin, ed. (2007). Moderne Anorganische Chemie (in German). p. 259, and «Vorlesung Intermetallische Phasen § 6.2 Binäre Zintl-Phasen» (in German).
- ^ Unstable carbonyl of Al(0) has been detected in reaction of Al2(CH3)6 with carbon monoxide; see Sanchez, Ramiro; Arrington, Caleb; Arrington Jr., C. A. (December 1, 1989). «Reaction of trimethylaluminum with carbon monoxide in low-temperature matrixes». American Chemical Society. 111 (25): 9110-9111. doi:10.1021/ja00207a023.
- ^ Al(−2) has been observed in Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3, see Wemdorff, Marco; Röhr, Caroline (2007). «Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3: Eine Zintl-Phase mit isolierten [Ge]4–— und [Al4]8–-Anionen / Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3: A Zintl Phase with Isolated [Ge]4–— and [Al4]8– Anions». Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B (in German). 62 (10): 1227. doi:10.1515/znb-2007-1001. S2CID 94972243.
- ^ a b c «New Type of Zero-Valent Tin Compound». Chemistry Europe. 27 August 2016.
- ^ P(0) has been observed, see Wang, Yuzhong; Xie, Yaoming; Wei, Pingrong; King, R. Bruce; Schaefer, Iii; Schleyer, Paul v. R.; Robinson, Gregory H. (2008). «Carbene-Stabilized Diphosphorus». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (45): 14970–1. doi:10.1021/ja807828t. PMID 18937460.
- ^ The equilibrium Cl2O6⇌2ClO3 is mentioned by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but it has been refuted, see Lopez, Maria; Juan E. Sicre (1990). «Physicochemical properties of chlorine oxides. 1. Composition, ultraviolet spectrum, and kinetics of the thermolysis of gaseous dichlorine hexoxide». J. Phys. Chem. 94 (9): 3860–3863. doi:10.1021/j100372a094., and Cl2O6 is actually chlorine(V,VII) oxide. However, ClO3 has been observed, see Grothe, Hinrich; Willner, Helge (1994). «Chlorine Trioxide: Spectroscopic Properties, Molecular Structure, and Photochemical Behavior». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 33 (14): 1482–1484. doi:10.1002/anie.199414821.
- ^ Ar(0) has been observed in argon fluorohydride (HArF) and ArCF22+, see Lockyear, J.F.; Douglas, K.; Price, S.D.; Karwowska, M.; et al. (2010). «Generation of the ArCF22+ Dication». Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 1: 358. doi:10.1021/jz900274p.
- ^ Ca(I) has been observed; see Krieck, Sven; Görls, Helmar; Westerhausen, Matthias (2010). «Mechanistic Elucidation of the Formation of the Inverse Ca(I) Sandwich Complex [(thf)3Ca(μ-C6H3-1,3,5-Ph3)Ca(thf)3] and Stability of Aryl-Substituted Phenylcalcium Complexes». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (35): 12492–501. doi:10.1021/ja105534w. PMID 20718434.
- ^ a b c Octacarbonyl complexes isolated of Ca, Sr, Ba have been observed in a neon matrix, but it remains unclear whether these are metal(0) complexes because calculations disagree whether the metal is covalently or ionically bonded to the ligands; see Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Jin, J.; Pan, S.; Li, W.; Jin, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Frenking, G. (2018). «Observation of alkaline earth complexes M(CO)8 (M = Ca, Sr, or Ba) that mimic transition metals». Science. 361 (6405): 912–916. Bibcode:2018Sci…361..912W. doi:10.1126/science.aau0839. PMID 30166489. S2CID 52131470
- ^ Sc(0) has been observed; see F. Geoffrey N. Cloke; Karl Khan & Robin N. Perutz (1991). «η-Arene complexes of scandium(0) and scandium(II)». J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. (19): 1372–1373. doi:10.1039/C39910001372.
- ^ Sc(I) has been observed; see Polly L. Arnold; F. Geoffrey; N. Cloke; Peter B. Hitchcock & John F. Nixon (1996). «The First Example of a Formal Scandium(I) Complex: Synthesis and Molecular Structure of a 22-Electron Scandium Triple Decker Incorporating the Novel 1,3,5-Triphosphabenzene Ring». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (32): 7630–7631. doi:10.1021/ja961253o.
- ^ Sc(II) has been observed; see Woen, David H.; Chen, Guo P.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Boyle, Timothy J.; Furche, Filipp; Evans, William J. (January 2017). «Solution Synthesis, Structure, and CO Reduction Reactivity of a Scandium(II) Complex». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 56 (8): 2050–2053. doi:10.1002/anie.201611758. PMID 28097771.
- ^ Ti(I) has been observed in [Ti(η6-1,3,5-C6H3iPr3)2][BAr4] (Ar = C6H5, p-C6H4F, 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2); see Calderazzo, Fausto; Ferri, Isabella; Pampaloni, Guido; Englert, Ulli; Green, Malcolm L. H. (1997). «Synthesis of [Ti(η6-1,3,5-C6H3iPr3)2][BAr4] (Ar = C6H5, p-C6H4F, 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2), the First Titanium(I) Derivatives». Organometallics. 16 (14): 3100–3101. doi:10.1021/om970155o.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Ti(−2), V(−3), Cr(−4), Co(−3), Zr(−2), Nb(−3), Mo(−4), Ru(−2), Rh(−3), Hf(−2), Ta(−3), and W(−4) occur in anionic binary metal carbonyls; see [1], p. 4 (in German); [2], pp. 97–100; [3], p. 239
- ^ Ti(−1) has been reported in [Ti(bipy)3]−, but was later shown to be Ti(+3); see Bowman, A. C.; England, J.; Sprouls, S.; Weihemüller, T.; Wieghardt, K. (2013). «Electronic structures of homoleptic [tris(2,2′-bipyridine)M]n complexes of the early transition metals (M = Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta; n = 1+, 0, 1-, 2-, 3-): an experimental and density functional theoretical study». Inorganic Chemistry. 52 (4): 2242–56. doi:10.1021/ic302799s. PMID 23387926. However, Ti(−1) occurs in [Ti(η-C6H6]− and [Ti(η-C6H5CH3)]−, see Bandy, J. A.; Berry, A.; Green, M. L. H.; Perutz, R. N.; Prout, K.; Verpeautz, J.-N. (1984). «Synthesis of anionic sandwich compounds: [Ti(η-C6H5R)2]– and the crystal structure of [K(18-crown-6)(µ-H)Mo(η-C5H5)2]». Inorganic Chemistry. 52 (4): 729–731. doi:10.1039/C39840000729.
- ^ Jilek, Robert E.; Tripepi, Giovanna; Urnezius, Eugenijus; Brennessel, William W.; Young, Victor G. Jr.; Ellis, John E. (2007). «Zerovalent titanium–sulfur complexes. Novel dithiocarbamato derivatives of Ti(CO)6: [Ti(CO)4(S2CNR2)]−«. Chem. Commun. (25): 2639–2641. doi:10.1039/B700808B. PMID 17579764.
- ^ Fe(VII) has been observed in [FeO4]−; see Lu, Jun-Bo; Jian, Jiwen; Huang, Wei; Lin, Hailu; Zhou, Mingfei (2016). «Experimental and theoretical identification of the Fe(VII) oxidation state in FeO4−«. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 18 (45): 31125–31131. Bibcode:2016PCCP…1831125L. doi:10.1039/C6CP06753K. PMID 27812577.
- ^ Fe(VIII) has been reported; see Yurii D. Perfiliev; Virender K. Sharma (2008). «Higher Oxidation States of Iron in Solid State: Synthesis and Their Mössbauer Characterization – Ferrates – ACS Symposium Series (ACS Publications)». Platinum Metals Review. 48 (4): 157–158. doi:10.1595/147106704X10801. However, its existence has been disputed.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Fe(−4), Ru(−4), and Os(−4) have been observed in metal-rich compounds containing octahedral complexes [MIn6−xSnx]; Pt(−3) (as a dimeric anion [Pt–Pt]6−), Cu(−2), Zn(−2), Ag(−2), Cd(−2), Au(−2), and Hg(−2) have been observed (as dimeric and monomeric anions; dimeric ions were initially reported to be [T–T]2− for Zn, Cd, Hg, but later shown to be [T–T]4− for all these elements) in La2Pt2In, La2Cu2In, Ca5Au3, Ca5Ag3, Ca5Hg3, Sr5Cd3, Ca5Zn3(structure (AE2+)5(T–T)4−T2−⋅4e−), Yb3Ag2, Ca5Au4, and Ca3Hg2; Au(–3) has been observed in ScAuSn and in other 18-electron half-Heusler compounds. See Changhoon Lee; Myung-Hwan Whangbo (2008). «Late transition metal anions acting as p-metal elements». Solid State Sciences. 10 (4): 444–449. Bibcode:2008SSSci..10..444K. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2007.12.001. and Changhoon Lee; Myung-Hwan Whangbo; Jürgen Köhler (2010). «Analysis of Electronic Structures and Chemical Bonding of Metal-rich Compounds. 2. Presence of Dimer (T–T)4– and Isolated T2– Anions in the Polar Intermetallic Cr5B3-Type Compounds AE5T3 (AE = Ca, Sr; T = Au, Ag, Hg, Cd, Zn)». Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 636 (1): 36–40. doi:10.1002/zaac.200900421.
- ^ Ni(−2) has been observed in Li2[Ni(1,5-COD)2], see Jonas, Klaus (1975). «Dilithium-Nickel-Olefin Complexes. Novel Bimetal Complexes Containing a Transition Metal and a Main Group Metal». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14 (11): 752–753. doi:10.1002/anie.197507521. and Ellis, John E. (2006). «Adventures with Substances Containing Metals in Negative Oxidation States». Inorganic Chemistry. 45 (8): 3167–86. doi:10.1021/ic052110i. PMID 16602773.
- ^ Cu(0) has been observed in Cu(tris[2-(diisopropylphosphino)-
phenyl]borane), see Moret, Marc-Etienne; Zhang, Limei; Peters, Jonas C. (2013). «A Polar Copper–Boron One-Electron σ-Bond». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (10): 3792–3795. doi:10.1021/ja4006578. PMID 23418750. - ^ Zn(0) has been observed; see Singh, Amit Pratap; Samuel, Prinson P.; Roesky, Herbert W.; Schwarzer, Martin C.; Frenking, Gernot; Sidhu, Navdeep S.; Dittrich, Birger (2013). «A Singlet Biradicaloid Zinc Compound and Its Nonradical Counterpart». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (19): 7324–9. doi:10.1021/ja402351x. PMID 23600486. and Soleilhavoup, Michèle; Bertrand, Guy (2015). «Cyclic (Alkyl)(Amino)Carbenes (CAACs): Stable Carbenes on the Rise». Acc. Chem. Res. 48 (2): 256–266. doi:10.1021/ar5003494. PMID 25515548.
- ^ Zn(I) has been observed in decamethyldizincocene (Zn2(η5–C5Me5)2); see Resa, I.; Carmona, E.; Gutierrez-Puebla, E.; Monge, A. (2004). «Decamethyldizincocene, a Stable Compound of Zn(I) with a Zn-Zn Bond». Science. 305 (5687): 1136–8. Bibcode:2004Sci…305.1136R. doi:10.1126/science.1101356. PMID 15326350. S2CID 38990338.
- ^ Zn(III) has been predicted to be stable in compounds with highly stabilized borane-based trianions, but no Zn(III) candidates are known experimentally; see Hong Fang; Huta Banjade; Deepika; Puru Jena (2021). «Realization of the Zn3+ oxidation state». Nanoscale. 13 (33): 14041–14048. doi:10.1039/D1NR02816B. PMID 34477685. S2CID 237400349.
- ^ Ga(−2), Ga(−4), and Ga(−5) have been observed in the magnesium gallides MgGa, Mg2Ga, and Mg5Ga2, respectively; see Patrick Hofmann. «Colture. Ein Programm zur interaktiven Visualisierung von Festkörperstrukturen sowie Synthese, Struktur und Eigenschaften von binären und ternären Alkali- und Erdalkalimetallgalliden» (PDF) (in German). p. 72.
- ^ Ga(−3) has been observed in LaGa, see Dürr, Ines; Bauer, Britta; Röhr, Caroline (2011). «Lanthan-Triel/Tetrel-ide La(Al,Ga)x(Si,Ge)1-x. Experimentelle und theoretische Studien zur Stabilität intermetallischer 1:1-Phasen» (PDF). Z. Naturforsch. (in German). 66b: 1107–1121.
- ^ Ga(0) has been observed in Gallium monoiodide among other gallium’s oxidation states
- ^ Ge(−1), Ge(−2), and Ge(−3) have been observed in germanides; see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). «Germanium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 953–959. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9.
- ^ As(0) has been observed; see Abraham, Mariham Y.; Wang, Yuzhong; Xie, Yaoming; Wei, Pingrong; Shaefer III, Henry F.; Schleyer, P. von R.; Robinson, Gregory H. (2010). «Carbene Stabilization of Diarsenic: From Hypervalency to Allotropy». Chemistry: A European Journal. 16 (2): 432–5. doi:10.1002/chem.200902840. PMID 19937872.
- ^ As(I) has been observed in arsenic(I) iodide (AsI); see Ellis, Bobby D.; MacDonald, Charles L. B. (2004). «Stabilized Arsenic(I) Iodide: A Ready Source of Arsenic Iodide Fragments and a Useful Reagent for the Generation of Clusters». Inorganic Chemistry. 43 (19): 5981–6. doi:10.1021/ic049281s. PMID 15360247.
- ^ As(IV) has been observed in arsenic(IV) hydroxide (As(OH)4) and HAsO−; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Bielski, Benon H. J.; Sehested, K. (1989). «Arsenic(IV). A pulse-radiolysis study». Inorganic Chemistry. 28 (14): 2717–24. doi:10.1021/ic00313a007.
- ^ Se(−1) has been observed in diselenides(2−) (Se22−).
- ^ A Se(0) atom has been identified using DFT in [ReOSe(2-pySe)3]; see Cargnelutti, Roberta; Lang, Ernesto S.; Piquini, Paulo; Abram, Ulrich (2014). «Synthesis and structure of [ReOSe(2-Se-py)3]: A rhenium(V) complex with selenium(0) as a ligand». Inorganic Chemistry Communications. 45: 48–50. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2014.04.003. ISSN 1387-7003.
- ^ Se(I) has been observed in selenium(I) chloride (Se2Cl2); see «Selenium: Selenium(I) chloride compound data». WebElements.com. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- ^ Se(III) has been observed in Se2NBr3; see Lau, Carsten; Neumüller, Bernhard; Vyboishchikov, Sergei F.; Frenking, Gernot; Dehnicke, Kurt; Hiller, Wolfgang; Herker, Martin (1996). «Se2NBr3, Se2NCl5, Se2NCl−6: New Nitride Halides of Selenium(III) and Selenium(IV)». Chemistry: A European Journal. 2 (11): 1393–1396. doi:10.1002/chem.19960021108.
- ^ Se(V) has been observed in SeO−3 and HSeO2−4; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, K. (1986). «Selenium(V). A pulse radiolysis study». Inorganic Chemistry. 90 (21): 5460–4. doi:10.1021/j100412a112.
- ^ Br(II) is known to occur in bromine monoxide radical; see [4]
- ^ Sr(I) has been observed in strontium monofluoride (SrF); see P. Colarusso; Guo, B.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Bernath, P.F.; et al. (1996). «High-Resolution Infrared Emission Spectrum of Strontium Monofluoride» (PDF). Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 175 (1): 158–171. Bibcode:1996JMoSp.175..158C. doi:10.1006/jmsp.1996.0019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-08.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Yttrium and all lanthanides except Ce and Pm have been observed in the oxidation state 0 in bis(1,3,5-tri-t-butylbenzene) complexes, see Cloke, F. Geoffrey N. (1993). «Zero Oxidation State Compounds of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lanthanides». Chem. Soc. Rev. 22: 17–24. doi:10.1039/CS9932200017. and Arnold, Polly L.; Petrukhina, Marina A.; Bochenkov, Vladimir E.; Shabatina, Tatyana I.; Zagorskii, Vyacheslav V.; Cloke (2003-12-15). «Arene complexation of Sm, Eu, Tm and Yb atoms: a variable temperature spectroscopic investigation». Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 688 (1–2): 49–55. doi:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2003.08.028.
- ^ Y(I) has been observed in yttrium(I) bromide (YBr); see «Yttrium: yttrium(I) bromide compound data». OpenMOPAC.net. Archived from the original on 2011-07-23. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- ^ Y(II) has been observed in [(18-crown-6)K][(C5H4SiMe3)3Y]; see MacDonald, M. R.; Ziller, J. W.; Evans, W. J. (2011). «Synthesis of a Crystalline Molecular Complex of Y2+, [(18-crown-6)K][(C5H4SiMe3)3Y]». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 (40): 15914–17. doi:10.1021/ja207151y. PMID 21919538.
- ^ Zr(−1) has been reported in [Zr(bipy)3]− (see Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 960. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8. and Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). «Zirconium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 1413. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9.), but was later shown to be Zr(+4); see Bowman, A. C.; England, J.; Sprouls, S.; Weihemüller, T.; Wieghardt, K. (2013). «Electronic structures of homoleptic [tris(2,2′-bipyridine)M]n complexes of the early transition metals (M = Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta; n = 1+, 0, 1-, 2-, 3-): an experimental and density functional theoretical study». Inorganic Chemistry. 52 (4): 2242–56. doi:10.1021/ic302799s. PMID 23387926.
- ^ a b Zr(0) and Hf(0) occur in (η6-(1,3,5-tBu)3C6H3)2M (M=Zr, Hf) and [(η5-C5R5M(CO)4]−, see Chirik, P. J.; Bradley, C. A. (2007). «4.06 — Complexes of Zirconium and Hafnium in Oxidation States 0 to ii». Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry III. From Fundamentals to Applications. Vol. 4. Elsevier Ltd. pp. 697–739. doi:10.1016/B0-08-045047-4/00062-5. ISBN 9780080450476.
- ^ Complexes of Nb(0) and Ta(0) have been observed, see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (2003). «4.5.7. Niobium(0) and Tantalum(0)». In J. A. McCleverty; T.J. Meyer (eds.). Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II: From Biology to Nanotechnology. Vol. 4 (2 ed.). Newnes. pp. 297–299. ISBN 978-0-08-091316-2.
- ^ a b Nb(I) and Ta(I) occur in CpNb(CO)4 and CpTa(CO)4, see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). «Tantal». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 1430. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9. and King, R. Bruce (1969). Transition-Metal Organometallic Chemistry: An Introduction. Academic Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-32-315996-8.
- ^ George, G.N.; Klein, S.I.; Nixon, J.F. (1984). «Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopic studies on the zero-valent rhodium complex [Rh(P(OPri)3)4] at X-and Q-band frequencies». Chemical Physics Letters. 108 (6): 627–630. Bibcode:1984CPL…108..627G. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(84)85069-1.
- ^ Rh(VII) is known in the RhO3+ cation, see «The Highest Oxidation State of Rhodium: Rhodium(VII) in [RhO3]+». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022. doi:10.1002/anie.202207688.
- ^ Pd(I) has been observed; see Crabtree, R. H. (2002). «CHEMISTRY: A New Oxidation State for Pd?». Science. 295 (5553): 288–289. doi:10.1126/science.1067921. PMID 11786632. S2CID 94579227.
- ^ Pd(III) has been observed; see Powers, D. C.; Ritter, T. (2011). Palladium(III) in Synthesis and Catalysis (PDF). Top. Organomet. Chem. Topics in Organometallic Chemistry. Vol. 35. pp. 129–156. Bibcode:2011hoso.book..129P. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17429-2_6. ISBN 978-3-642-17428-5. PMC 3066514. PMID 21461129. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 12, 2013.
- ^ Palladium(V) has been identified in complexes with organosilicon compounds containing pentacoordinate palladium; see Shimada, Shigeru; Li, Yong-Hua; Choe, Yoong-Kee; Tanaka, Masato; Bao, Ming; Uchimaru, Tadafumi (2007). «Multinuclear palladium compounds containing palladium centers ligated by five silicon atoms». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 104 (19): 7758–7763. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700450104.
- ^ Palladium(VI) has been claimed to exist in «NEW PALLADIUM OXIDATION STATE?». Chem. Eng. News. 80 (2): 8. 2002. doi:10.1021/cen-v080n002.p008., but this has been refuted showing it is a Palladium(II).
- ^ The Ag− ion has been observed in metal ammonia solutions: see Tran, N. E.; Lagowski, J. J. (2001). «Metal Ammonia Solutions: Solutions Containing Argentide Ions». Inorganic Chemistry. 40 (5): 1067–68. doi:10.1021/ic000333x.
- ^ Ag(0) has been observed in carbonyl complexes in low-temperature matrices: see McIntosh, D.; Ozin, G. A. (1976). «Synthesis using metal vapors. Silver carbonyls. Matrix infrared, ultraviolet-visible, and electron spin resonance spectra, structures, and bonding of silver tricarbonyl, silver dicarbonyl, silver monocarbonyl, and disilver hexacarbonyl». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 98 (11): 3167–75. doi:10.1021/ja00427a018.
- ^ Cd(I) has been observed in cadmium(I) tetrachloroaluminate (Cd2(AlCl4)2); see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1985). «Cadmium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1056–1057. ISBN 978-3-11-007511-3.
- ^ In(–5) has been observed in La3InGe, see Guloy, A. M.; Corbett, J. D. (1996). «Synthesis, Structure, and Bonding of Two Lanthanum Indium Germanides with Novel Structures and Properties». Inorganic Chemistry. 35 (9): 2616–22. doi:10.1021/ic951378e. PMID 11666477.
- ^ In(−2) has been observed in Na2In, see [5], p. 69.
- ^ Unstable In(0) carbonyls and clusters have been detected, see [6], p. 6.
- ^ Sn(−3) has been observed in [Sn2]6−, e.g. in (Ba2)4+(Mg4)8+Sn4−(Sn2)6−Sn2− (with square (Sn2−)n sheets), see Papoian, Garegin A.; Hoffmann, Roald (2000). «Hypervalent Bonding in One, Two, and Three Dimensions: Extending the Zintl–Klemm Concept to Nonclassical Electron-Rich Networks». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000 (39): 2408–2448. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20000717)39:14<2408::aid-anie2408>3.0.co;2-u. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- ^ Sn(I) and Sn(III) have been observed in organotin compounds
- ^ Sb(−2) has been observed in [Sb2]4−, e.g. in RbBa4[Sb2][Sb][O], see Boss, Michael; Petri, Denis; Pickhard, Frank; Zönnchen, Peter; Röhr, Caroline (2005). «Neue Barium-Antimonid-Oxide mit den Zintl-Ionen [Sb]3−, [Sb2]4− und 1∞[Sbn]n− / New Barium Antimonide Oxides containing Zintl Ions [Sb]3−, [Sb2]4− and 1∞[Sbn]n−«. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (in German). 631 (6–7): 1181–1190. doi:10.1002/zaac.200400546.
- ^ Sb(0) has been observed, see Anastas Sidiropoulos. «Studies of N-heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes of the Main Group Elements» (PDF). p. 39. doi:10.4225/03/5B0F4BDF98F60. S2CID 132399530.
- ^ Sb(I) and Sb(II) have been observed in organoantimony compounds; for Sb(I), see Šimon, Petr; de Proft, Frank; Jambor, Roman; Růžička, Aleš; Dostál, Libor (2010). «Monomeric Organoantimony(I) and Organobismuth(I) Compounds Stabilized by an NCN Chelating Ligand: Syntheses and Structures». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 49 (32): 5468–5471. doi:10.1002/anie.201002209. PMID 20602393.
- ^ Sb(IV) has been observed in [SbCl6]2−, see Nobuyoshi Shinohara; Masaaki Ohsima (2000). «Production of Sb(IV) Chloro Complex by Flash Photolysis of the Corresponding Sb(III) and Sb(V) Complexes in CH3CN and CHCl3». Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 73 (7): 1599–1604. doi:10.1246/bcsj.73.1599.
- ^ Te(0) has been observed in tellurolates.
- ^ Te(I) has been observed in tellurium iodide (TeI), see «Tellurium: tellurium iodide». WebElements.com. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- ^ Te(III) has been observed in [Te(N(SiMe3)2)2]+, see Heinze, Thorsten; Roesky, Herbert W.; Pauer, Frank; Stalke, Dietmar; Sheldrick, George M. (1991). «Synthesis and Structure of the First Tellurium(III) Radical Cation». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 30 (12): 1678. doi:10.1002/anie.199116771. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- ^ Te(V) is mentioned by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but they do not give any example of a Te(V) compound. What was long thought to be ditellurium decafluoride (Te2F10) is actually bis(pentafluorotelluryl) oxide, F5TeOTeF5: see Watkins, P. M. (1974). «Ditellurium decafluoride — A Continuing Myth». Journal of Chemical Education. 51 (9): 520–521. Bibcode:1974JChEd..51..520W. doi:10.1021/ed051p520. However, Te(V) has been observed in HTeO−, TeO−, HTeO−2, and TeO−3; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, K. (2001). «Tellurium(V). A Pulse Radiolysis Study». The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 105 (27): 6637–45. Bibcode:2001JPCA..105.6637K. doi:10.1021/jp010577i.
- ^ I(II) is known to exist in monoxide (IO); see Nikitin, I V (31 August 2008). «Halogen monoxides». Russian Chemical Reviews. 77 (8): 739–749. Bibcode:2008RuCRv..77..739N. doi:10.1070/RC2008v077n08ABEH003788.
- ^ I(IV) has been observed in iodine dioxide (IO2); see Pauling, Linus (1988). «Oxygen Compounds of Nonmetallic Elements». General Chemistry (3rd ed.). Dover Publications, Inc. p. 259. ISBN 978-0-486-65622-9.
- ^ I(VI) has been observed in IO3, IO42−, H5IO6−, H2IO52−, H4IO62−, and HIO53−; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, Knud; Wolff, Thomas (1981). «Laser flash photolysis and pulse radiolysis of iodate and periodate in aqueous solution. Properties of iodine(VI)». J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1. 77 (7): 1707–18. doi:10.1039/F19817701707.
- ^ Xe compounds: see Xenon
- ^ Xe(0) has been observed in tetraxenonogold(II) (AuXe42+).
- ^ Xe(I) has been reported in xenon hexafluoroplatinate and xenon hexafluororhodate (see Pauling, Linus (1988). General Chemistry (3rd ed.). Dover Publications, Inc. p. 250. ISBN 978-0-486-65622-9.), however these compounds were later found to contain Xe(II).
- ^ Ba(I) has been observed in barium monofluoride (BaF); see P. Colarusso; Guo, B.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Bernath, P.F.; et al. (1995). «High-Resolution Fourier Transform Infrared Emission Spectrum of Barium Monofluoride» (PDF). Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 170 (1): 59. Bibcode:1996JMoSp.175..158C. doi:10.1006/jmsp.1996.0019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-03-10.
- ^ a b c d La(I), Pr(I), Tb(I), Tm(I), and Yb(I) have been observed in MB8− clusters; see Li, Wan-Lu; Chen, Teng-Teng; Chen, Wei-Jia; Li, Jun; Wang, Lai-Sheng (2021). «Monovalent lanthanide(I) in borozene complexes». Nature Communications. 12: 6467. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26785-9.
- ^ Pr(I) has been observed in [PrB4]−; see Chen, Xin; Chen, Teng-Teng; Li, Wang-Lu; Lu, Jun-Bo; Zhao, Li-Juan; Jian, Tian; Hu, Han-Shi; Wang, Lai-Sheng; Li, Jun (2018-12-13). «Lanthanides with Unusually Low Oxidation States in the PrB3– and PrB4– Boride Clusters». Inorganic Chemistry. 58 (1): 411–418. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b02572. PMID 30543295. S2CID 56148031.
- ^ Pr(V) has been observed in [PrO2]+; see Zhang, Qingnan; Hu, Shu-Xian; Qu, Hui; Su, Jing; Wang, Guanjun; Lu, Jun-Bo; Chen, Mohua; Zhou, Mingfei; Li, Jun (2016-06-06). «Pentavalent Lanthanide Compounds: Formation and Characterization of Praseodymium(V) Oxides». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 55 (24): 6896–6900. doi:10.1002/anie.201602196. ISSN 1521-3773. PMID 27100273.
- ^ Hu, Shu-Xian; Jian, Jiwen; Su, Jing; Wu, Xuan; Li, Jun; Zhou, Mingfei (2017). «Pentavalent lanthanide nitride-oxides: NPrO and NPrO− complexes with N≡Pr triple bonds». Chemical Science. 8 (5): 4035–4043. doi:10.1039/C7SC00710H. ISSN 2041-6520. PMC 5434915. PMID 28580119.
- ^ Nd(IV) has been observed in unstable solid state compounds; see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ a b c d e All the lanthanides (La–Lu) in the +2 oxidation state have been observed (except La, Gd, Lu) in dilute, solid solutions of dihalides of these elements in alkaline earth dihalides (see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5) and (except Pm) in organometallic molecular complexes, see Lanthanides Topple Assumptions and Meyer, G. (2014). «All the Lanthanides Do It and Even Uranium Does Oxidation State +2». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 53 (14): 3550–51. doi:10.1002/anie.201311325. PMID 24616202.. Additionally, all the lanthanides (La–Lu) form dihydrides (LnH2), dicarbides (LnC2), monosulfides (LnS), monoselenides (LnSe), and monotellurides (LnTe), but for most elements these compounds have Ln3+ ions with electrons delocalized into conduction bands, e. g. Ln3+(H−)2(e−).
- ^ SmB6- cluster anion has been reported and contains Sm in rare oxidation state of +1; see Paul, J. Robinson; Xinxing, Zhang; Tyrel, McQueen; Kit, H. Bowen; Anastassia, N. Alexandrova (2017). «SmB6– Cluster Anion: Covalency Involving f Orbitals». J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 8, 1849–1854. 121 (8): 1849–1854..
- ^ Dy(IV) has been observed in unstable solid state compounds; see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ Hf(I) has been observed in hafnium monobromide (HfBr), see Marek, G.S.; Troyanov, S.I.; Tsirel’nikov, V.I. (1979). «Кристаллическое строение и термодинамические характеристики монобромидов циркония и гафния / Crystal structure and thermodynamic characteristics of monobromides of zirconium and hafnium». Журнал неорганической химии / Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry (in Russian). 24 (4): 890–893.
- ^ Os(−1) has been observed in Na[Os(CO)13]; see Krause, J.; Siriwardane, Upali; Salupo, Terese A.; Wermer, Joseph R.; Knoeppel, David W.; Shore, Sheldon G. (1993). «Preparation of [Os3(CO)11]2− and its reactions with Os3(CO)12; structures of [Et4N] [HOs3(CO)11] and H2OsS4(CO)». Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 454 (1–2): 263–271. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(93)83250-Y. and Carter, Willie J.; Kelland, John W.; Okrasinski, Stanley J.; Warner, Keith E.; Norton, Jack R. (1982). «Mononuclear hydrido alkyl carbonyl complexes of osmium and their polynuclear derivatives». Inorganic Chemistry. 21 (11): 3955–3960. doi:10.1021/ic00141a019.
- ^ Ir(−3) has been observed in Ir(CO)33−; see Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1117. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Ir(VII) has been observed in [(η2-O2)IrO2]+; see C&EN: Iridium dressed to the nines.
- ^ Ir(VIII) has been observed in iridium tetroxide (IrO4); see Gong, Yu; Zhou, Mingfei; Kaupp, Martin; Riedel, Sebastian (2009). «Formation and Characterization of the Iridium Tetroxide Molecule with Iridium in the Oxidation State +VIII». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (42): 7879–7883. doi:10.1002/anie.200902733. PMID 19593837.
- ^ Ir(IX) has been observed in IrO+4; see Wang, Guanjun; Zhou, Mingfei; Goettel, James T.; Schrobilgen, Gary G.; Su, Jing; Li, Jun; Schlöder, Tobias; Riedel, Sebastian (21 August 2014). «Identification of an iridium-containing compound with a formal oxidation state of IX». Nature. 514 (7523): 475–477. Bibcode:2014Natur.514..475W. doi:10.1038/nature13795. PMID 25341786. S2CID 4463905.
- ^ Pt(−1) and Pt(−2) have been observed in the barium platinides BaPt and Ba2Pt, respectively: see Karpov, Andrey; Konuma, Mitsuharu; Jansen, Martin (2006). «An experimental proof for negative oxidation states of platinum: ESCA-measurements on barium platinides». Chemical Communications (8): 838–840. doi:10.1039/b514631c. PMID 16479284.
- ^ Pt(I) and Pt(III) have been observed in bimetallic and polymetallic species; see Kauffman, George B.; Thurner, Joseph J.; Zatko, David A. (1967). Ammonium Hexachloroplatinate(IV). Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 9. pp. 182–185. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch51. ISBN 978-0-470-13240-1.
- ^ Au(0) has been observed, see Mézaille, Nicolas; Avarvari, Narcis; Maigrot, Nicole; Ricard, Louis; Mathey, François; Le Floch, Pascal; Cataldo, Laurent; Berclaz, Théo; Geoffroy, Michel (1999). «Gold(I) and Gold(0) Complexes of Phosphinine‐Based Macrocycles». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 38 (21): 3194–3197. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19991102)38:21<3194::AID-ANIE3194>3.0.CO;2-O. PMID 10556900.
- ^ Hg(IV) has been reported in mercury(IV) fluoride (HgF4); see Xuefang Wang; Lester Andrews; Sebastian Riedel; Martin Kaupp (2007). «Mercury Is a Transition Metal: The First Experimental Evidence for HgF4«. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46 (44): 8371–8375. doi:10.1002/anie.200703710. PMID 17899620. However, it could not be confirmed by later experiments; see Is mercury a transition metal? Archived 2016-10-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tl(−5) has been observed in Na23K9Tl15.3, see Dong, Z.-C.; Corbett, J. D. (1996). «Na23K9Tl15.3: An Unusual Zintl Compound Containing Apparent Tl57−, Tl48−, Tl37−, and Tl5− Anions». Inorganic Chemistry. 35 (11): 3107–12. doi:10.1021/ic960014z. PMID 11666505.
- ^ Tl(−1) has been observed in caesium thallide (CsTl); see King, R. B.; Schleyer, R. (2004). «Theory and concepts in main-group cluster chemistry». In Driess, M.; Nöth, H. (eds.). Molecular clusters of the main group elements. Wiley-VCH, Chichester. p. 19. ISBN 978-3-527-61437-0.
- ^ Tl(+2) has been observed in tetrakis(hypersilyl)dithallium ([(Me3Si)Si]2Tl—Tl[Si(SiMe3)]2), see Sonja Henkel; Dr. Karl Wilhelm Klinkhammer; Dr. Wolfgang Schwarz (1994). «Tetrakis(hypersilyl)dithallium(Tl—Tl): A Divalent Thallium Compound». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 33 (6): 681–683. doi:10.1002/anie.199406811.
- ^ Pb(−2) has been observed in BaPb, see Ferro, Riccardo (2008). Nicholas C. Norman (ed.). Intermetallic Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 505. ISBN 978-0-08-044099-6. and Todorov, Iliya; Sevov, Slavi C. (2004). «Heavy-Metal Aromatic Rings: Cyclopentadienyl Anion Analogues Sn56− and Pb56− in the Zintl Phases Na8BaPb6, Na8BaSn6, and Na8EuSn6«. Inorganic Chemistry. 43 (20): 6490–94. doi:10.1021/ic000333x.
- ^ Pb(0) carbonyls have been observered in reaction between lead atoms and carbon monoxide; see Ling, Jiang; Qiang, Xu (2005). «Observation of the lead carbonyls PbnCO (n=1–4): Reactions of lead atoms and small clusters with carbon monoxide in solid argon». The Journal of Chemical Physics. 122 (3): 034505. 122 (3): 34505. Bibcode:2005JChPh.122c4505J. doi:10.1063/1.1834915. ISSN 0021-9606. PMID 15740207.
- ^ Pb(+1) and Pb(+3) have been observed in organolead compounds, e.g. hexamethyldiplumbane Pb2(CH3)6; for Pb(I), see Siew-Peng Chia; Hong-Wei Xi; Yongxin Li; Kok Hwa Lim; Cheuk-Wai So (2013). «A Base-Stabilized Lead(I) Dimer and an Aromatic Plumbylidenide Anion». Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52 (24): 6298–6301. doi:10.1002/anie.201301954. PMID 23629949.
- ^ Bi(−2) and Bi(−1) occur in Zintl phases, e.g. (Ca2+)22[Bi4]4−([Bi2]4−)4[Bi3−]8; see Ponou, Siméon (2006). «Germanides, Germanide-Tungstate Double Salts and Substitution Effects in Zintl Phases». Technische Universität München. Lehrstuhl für Anorganische Chemie mit Schwerpunkt Neue Materialien. p. 68.
- ^ Bi(0) state is known to exist in a N-heterocyclic carbene complex of dibismuthene; see Deka, Rajesh; Orthaber, Andreas (May 6, 2022). «Carbene chemistry of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth: origin, evolution and future prospects». Royal Society of Chemistry (51): 8540. doi:10.1039/d2dt00755j.
- ^ Bi(I) has been observed in bismuth monobromide (BiBr) and bismuth monoiodide (BiI); see Godfrey, S. M.; McAuliffe, C. A.; Mackie, A. G.; Pritchard, R. G. (1998). Nicholas C. Norman (ed.). Chemistry of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Springer. pp. 67–84. ISBN 978-0-7514-0389-3.
- ^ Bi(+2) has been observed in dibismuthines (R2Bi—BiR2), see Arthur J. Ashe III (1990). Thermochromic Distibines and Dibismuthines. Advances in Organometallic Chemistry. Vol. 30. pp. 77–97. doi:10.1016/S0065-3055(08)60499-2. ISBN 9780120311309.
- ^ Bi(IV) has been observed; see A. I. Aleksandrov, I. E. Makarov (1987). «Formation of Bi(II) and Bi(IV) in aqueous hydrochloric solutions of Bi(III)». Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science. 36 (2): 217–220. doi:10.1007/BF00959349. S2CID 94865394.
- ^ Po(V) has been observed in dioxidopolonium(1+) (PoO+); see Thayer, John S. (2010). «Relativistic Effects and the Chemistry of the Heavier Main Group Elements». Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. Vol. 10. p. 78. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- ^ Rn(II) has been observed in radon difluoride (RnF2); see Stein, L. (1970). «Ionic Radon Solution». Science. 168 (3929): 362–4. Bibcode:1970Sci…168..362S. doi:10.1126/science.168.3929.362. PMID 17809133. S2CID 31959268. and Kenneth S. Pitzer (1975). «Fluorides of radon and element 118». J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. (18): 760b–761. doi:10.1039/C3975000760b.
- ^ Rn(IV) is reported by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but is not known to exist; see Sykes, A. G. (1998). «Recent Advances in Noble-Gas Chemistry». Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 46. Academic Press. pp. 91–93. ISBN 978-0-12-023646-6. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ Rn(VI) is known in radon trioxide (RnO3); see Sykes, A. G. (1998). «Recent Advances in Noble-Gas Chemistry». Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 46. Academic Press. pp. 91–93. ISBN 978-0-12-023646-6. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ Th(-I) and U(-I) have been detected in the gas phase as octacarbonyl anions; see Chaoxian, Chi; Sudip, Pan; Jiaye, Jin; Luyan, Meng; Mingbiao, Luo; Lili, Zhao; Mingfei, Zhou; Gernot, Frenking (2019). «Octacarbonyl Ion Complexes of Actinides [An(CO)8]+/− (An=Th, U) and the Role of f Orbitals in Metal–Ligand Bonding». Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany). 25 (50): 11772–11784. 25 (50): 11772–11784. doi:10.1002/chem.201902625. ISSN 0947-6539. PMC 6772027. PMID 31276242.
- ^ Th(I) is known in thorium(I) bromide (ThBr); see Wickleder, Mathias S.; Fourest, Blandine; Dorhout, Peter K. (2006). «Thorium». In Morss, Lester R.; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (PDF). Vol. 3 (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer. pp. 52–160. doi:10.1007/1-4020-3598-5_3. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-07.
- ^ Th(II) and Th(III) are observed in [ThII{η5-C5H3(SiMe3)2}3]− and [ThIII{η5-C5H3(SiMe3)2}3], see Langeslay, Ryan R.; Fieser, Megan E.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Furche, Philip; Evans, William J. (2015). «Synthesis, structure, and reactivity of crystalline molecular complexes of the {[C5H3(SiMe3)2]3Th}1− anion containing thorium in the formal +2 oxidation state». Chem. Sci. 6 (1): 517–521. doi:10.1039/C4SC03033H. PMC 5811171. PMID 29560172.
- ^ Pa(II) occurs in proctactinium(II) oxide
- ^ Th(-I) and U(-I) have been detected in the gas phase as octacarbonyl anions; see Chaoxian, Chi; Sudip, Pan; Jiaye, Jin; Luyan, Meng; Mingbiao, Luo; Lili, Zhao; Mingfei, Zhou; Gernot, Frenking (2019). «Octacarbonyl Ion Complexes of Actinides [An(CO)8]+/− (An=Th, U) and the Role of f Orbitals in Metal–Ligand Bonding». Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany). 25 (50): 11772–11784. 25 (50): 11772–11784. doi:10.1002/chem.201902625. ISSN 0947-6539. PMC 6772027. PMID 31276242.
- ^ U(I) has been observed in uranium monofluoride (UF) and uranium monochloride (UCl), see Sykes, A. G. (1990). «Compounds of Thorium and Uranium». Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 34. Academic Press. pp. 87–88. ISBN 978-0-12-023634-3. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- ^ U(II) has been observed in [K(2.2.2-Cryptand)][(C5H4SiMe3)3U], see MacDonald, Matthew R.; Fieser, Megan E.; Bates, Jefferson E.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Furche, Filipp; Evans, William J. (2013). «Identification of the +2 Oxidation State for Uranium in a Crystalline Molecular Complex, [K(2.2.2-Cryptand)][(C5H4SiMe3)3U]». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (36): 13310–13313. doi:10.1021/ja406791t. PMID 23984753.
- ^ Np(II), (III) and (IV) have been observed, see Dutkiewicz, Michał S.; Apostolidis, Christos; Walter, Olaf; Arnold, Polly L (2017). «Reduction chemistry of neptunium cyclopentadienide complexes: from structure to understanding». Chem. Sci. 8 (4): 2553–2561. doi:10.1039/C7SC00034K. PMC 5431675. PMID 28553487.
- ^ Pu(II) has been observed in {Pu[C5H3(SiMe3)2]3}−; see Windorff, Cory J.; Chen, Guo P; Cross, Justin N; Evans, William J.; Furche, Filipp; Gaunt, Andrew J.; Janicke, Michael T.; Kozimor, Stosh A.; Scott, Brian L. (2017). «Identification of the Formal +2 Oxidation State of Plutonium: Synthesis and Characterization ofref name=»curium5» {PuII[C5H3(SiMe3)2]3}−». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 (11): 3970–3973. doi:10.1021/jacs.7b00706. PMID 28235179.
- ^ Pu(VIII) has been observed in PuO4; see Nikonov, M. V.; Kiselev, Yu. M.; Tananaev, I. G.; Myasoedov, B. F. (March 2011). «Plutonium volatility in ozonization of alkaline solutions of Pu(VI) hydroxo complexes». Doklady Chemistry. 437 (1): 69–71. doi:10.1134/S0012500811030104. S2CID 95951175. Also see Kiselev, Yu. M.; Nikonov, M. V.; Dolzhenko, V. D.; Ermilov, A. Yu.; Tananaev, I. G.; Myasoedov, B. F. (17 January 2014). «On existence and properties of plutonium(VIII) derivatives». Radiochimica Acta. 102 (3): 227–237. doi:10.1515/ract-2014-2146. S2CID 100915090.
- ^ Am(VII) has been observed in AmO−5; see Americium, Das Periodensystem der Elemente für den Schulgebrauch (The periodic table of elements for schools) chemie-master.de (in German), Retrieved 28 November 2010 and Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1265. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b c Cm(V), Bk(V), and Cf(V) have been observed in BkO2+, CfO2+, CmO2(NO3)2−, BkO2(NO3)2−, and CfO2(NO3)2−; see Dau, Phuong Diem; Vasiliu, Monica; Peterson, Kirk A; Dixon, David A; Gibsoon, John K (October 2017). «Remarkably High Stability of Late Actinide Dioxide Cations: Extending Chemistry to Pentavalent Berkelium and Californium». Chemistry — A European Journal. 23 (68): 17369–17378. doi:10.1002/chem.201704193. PMID 29024093.
- ^ a b c Kovács, Attila; Dau, Phuong D.; Marçalo, Joaquim; Gibson, John K. (2018). «Pentavalent Curium, Berkelium, and Californium in Nitrate Complexes: Extending Actinide Chemistry and Oxidation States». Inorg. Chem. American Chemical Society. 57 (15): 9453–9467. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01450. OSTI 1631597. PMID 30040397. S2CID 51717837.
- ^ Cm(VI) has been observed in curium trioxide (CmO3) and dioxidocurium(2+) (CmO+2); see Domanov, V. P.; Lobanov, Yu. V. (October 2011). «Formation of volatile curium(VI) trioxide CmO3«. Radiochemistry. 53 (5): 453–6. doi:10.1134/S1066362211050018. S2CID 98052484.
- ^ Cm(VIII) has been reported to possibly occur in curium tetroxide (CmO4); see Domanov, V. P. (January 2013). «Possibility of generation of octavalent curium in the gas phase in the form of volatile tetraoxide CmO4«. Radiochemistry. 55 (1): 46–51. doi:10.1134/S1066362213010098. S2CID 98076989. However, new experiments seem to indicate its nonexistence: Zaitsevskii, Andréi; Schwarz, W H Eugen (April 2014). «Structures and stability of AnO4 isomers, An = Pu, Am, and Cm: a relativistic density functional study». Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2014 (16): 8997–9001. Bibcode:2014PCCP…16.8997Z. doi:10.1039/c4cp00235k. PMID 24695756.
- ^ Peterson, J. R.; Hobart, D. E. (1984). «The Chemistry of Berkelium». In Emeléus, Harry Julius (ed.). Advances in inorganic chemistry and radiochemistry. Vol. 28. Academic Press. pp. 29–64. doi:10.1016/S0898-8838(08)60204-4. ISBN 978-0-12-023628-2.
- ^ Peterson 1984, p. 55.
- ^
- ^ Es(IV) is known in einsteinium(IV) fluoride (EsF4); see Kleinschmidt, P (1994). «Thermochemistry of the actinides». Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 213–214: 169–172. doi:10.1016/0925-8388(94)90898-2.
- ^ Db(V) has been observed in dubnium pentachloride (DbCl5); see H. W. Gäggeler (2007). «Gas Phase Chemistry of Superheavy Elements» (PDF). Paul Scherrer Institute. pp. 26–28. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-02-20.
- ^ Sg(VI) has been observed in seaborgium oxide hydroxide (SgO2(OH)2); see Huebener, S.; Taut, S.; Vahle, A.; Dressler, R.; Eichler, B.; Gäggeler, H. W.; Jost, D.T.; Piguet, D.; et al. (2001). «Physico-chemical characterization of seaborgium as oxide hydroxide» (PDF). Radiochim. Acta. 89 (11–12_2001): 737–741. doi:10.1524/ract.2001.89.11-12.737. S2CID 98583998. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-25.
- ^ Sg(0) has been observed in seaborgium hexacarbonyl (Sg(CO)6); see Even, J.; Yakushev, A.; Dullmann, C. E.; Haba, H.; Asai, M.; Sato, T. K.; Brand, H.; Di Nitto, A.; Eichler, R.; Fan, F. L.; Hartmann, W.; Huang, M.; Jager, E.; Kaji, D.; Kanaya, J.; Kaneya, Y.; Khuyagbaatar, J.; Kindler, B.; Kratz, J. V.; Krier, J.; Kudou, Y.; Kurz, N.; Lommel, B.; Miyashita, S.; Morimoto, K.; Morita, K.; Murakami, M.; Nagame, Y.; Nitsche, H.; et al. (2014). «Synthesis and detection of a seaborgium carbonyl complex». Science. 345 (6203): 1491–3. Bibcode:2014Sci…345.1491E. doi:10.1126/science.1255720. PMID 25237098. S2CID 206558746.
- ^ Bh(VII) has been observed in bohrium oxychloride (BhO3Cl); see «Gas chemical investigation of bohrium (Bh, element 107)» Archived 2008-02-28 at the Wayback Machine, Eichler et al., GSI Annual Report 2000. Retrieved on 2008-02-29
- ^ Hs(VIII) has been observed in hassium tetroxide (HsO4); see «Chemistry of Hassium» (PDF). Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung mbH. 2002. Retrieved 2007-01-31.
- ^ Cn(II) has been observed in copernicium selenide (CnSe); see «Annual Report 2015: Laboratory of Radiochemistry and Environmental Chemistry» (PDF). Paul Scherrer Institute. 2015. p. 3.
- ^ Langmuir, Irving (1919). «The arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 41 (6): 868–934. doi:10.1021/ja02227a002.
- ^ «Antoine Laurent Lavoisier The Chemical Revolution – Landmark – American Chemical Society». American Chemical Society. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- ^ «Lavoisier on Elements». Chem125-oyc.webspace.yale.edu. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- ^ Wöhler, F. (1835). Grundriss der Chemie: Unorganische Chemie [Foundations of Chemistry: Inorganic Chemistry]. Berlin: Duncker und Humblot. p. 4.
- ^ Jensen, W. B. (2007). «the origin of the oxidation-state concept». J. Chem. Educ. 84 (9): 1418–1419. Bibcode:2007JChEd..84.1418J. doi:10.1021/ed084p1418.
- ^ Stock, A. (1919). «Einige Nomenklaturfragen der anorganischen Chemie» [Some nomenclature issues of inorganic chemistry]. Angew. Chem. 32 (98): 373–374. Bibcode:1919AngCh..32..373S. doi:10.1002/ange.19190329802.
- ^ a b Jorissen, W. P.; Bassett, H.; Damiens, A.; Fichter, F.; Rémy, H. (1941). «Rules for naming inorganic compounds». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 63: 889–897. doi:10.1021/ja01849a001.
- ^ Latimer, W. M. (1938). The Oxidation States of the Elements and their Potentials in Aqueous Solutions (1st ed.). Prentice-Hall.
- ^ Bray, W. C.; Branch, G. E. K. (1913). «Valence and tautomerism». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 35 (10): 1440–1447. doi:10.1021/ja02199a003.
- ^ Noyes, A. A.; Pitzer, K. S.; Dunn, C. L. (1935). «Argentic salts in acid solution, I. The oxidation and reduction reactions». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57 (7): 1221–1229. doi:10.1021/ja01310a018.
- ^ Noyes, A. A.; Pitzer, K. S.; Dunn, C. L. (1935). «Argentic salts in acid solution, II. The oxidation state of argentic salts». J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57 (7): 1229–1237. doi:10.1021/ja01310a019.
- ^ Fernelius, W. C. (1948). «Some problems of inorganic nomenclature». Chem. Eng. News. 26: 161–163. doi:10.1021/cen-v026n003.p161.
- ^ Fernelius, W. C.; Larsen, E. M.; Marchi, L. E.; Rollinson, C. L. (1948). «Nomenclature of coördination compounds». Chem. Eng. News. 26 (8): 520–523. doi:10.1021/cen-v026n008.p520.
- ^ Pauling, L. (1948). «The modern theory of valency». J. Chem. Soc. 1948: 1461–1467. doi:10.1039/JR9480001461. PMID 18893624.
- ^ Calvert, J. G. (1990). «IUPAC Recommendation 1990». Pure Appl. Chem. 62: 2204. doi:10.1351/pac199062112167.