|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vanadium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | (və-NAY-dee-əm) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
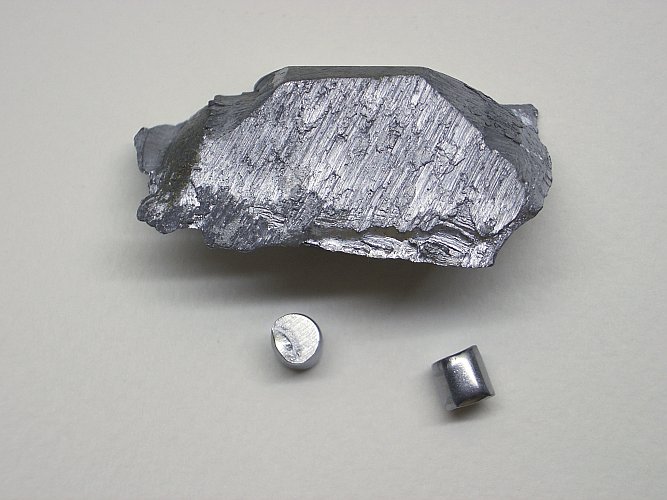
| Appearance | blue-silver-grey metal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(V) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vanadium in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | d-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 11, 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 2183 K (1910 °C, 3470 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 3680 K (3407 °C, 6165 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 6.11 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 5.5 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 21.5 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 444 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 24.89 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −3, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5 (an amphoteric oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 134 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 153±8 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Spectral lines of vanadium |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 4560 m/s (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 8.4 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 30.7 W/(m⋅K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 197 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | +255.0×10−6 cm3/mol (298 K)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young’s modulus | 128 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 47 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 160 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 6.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vickers hardness | 628–640 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 600–742 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-62-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Andrés Manuel del Río[3] (1801) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Henry Enfield Roscoe (1867) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Named by | Nils Gabriel Sefström (1830) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Main isotopes of vanadium
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| references |
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer (passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation.
Spanish scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 in Mexico by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called «brown lead». Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it «vanadium» after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors found in vanadium compounds. Del Rio’s lead mineral was ultimately named vanadinite for its vanadium content. In 1867 Henry Enfield Roscoe obtained the pure element.
Vanadium occurs naturally in about 65 minerals and in fossil fuel deposits. It is produced in China and Russia from steel smelter slag. Other countries produce it either from magnetite directly, flue dust of heavy oil, or as a byproduct of uranium mining. It is mainly used to produce specialty steel alloys such as high-speed tool steels, and some aluminium alloys. The most important industrial vanadium compound, vanadium pentoxide, is used as a catalyst for the production of sulfuric acid. The vanadium redox battery for energy storage may be an important application in the future.
Large amounts of vanadium ions are found in a few organisms, possibly as a toxin. The oxide and some other salts of vanadium have moderate toxicity. Particularly in the ocean, vanadium is used by some life forms as an active center of enzymes, such as the vanadium bromoperoxidase of some ocean algae.
History[edit]
Vanadium was discovered in 1801 by the Spanish mineralogist Andrés Manuel del Río. Del Río extracted the element from a sample of Mexican «brown lead» ore, later named vanadinite. He found that its salts exhibit a wide variety of colors, and as a result he named the element panchromium (Greek: παγχρώμιο «all colors»). Later, Del Río renamed the element erythronium (Greek: ερυθρός «red») because most of the salts turned red upon heating. In 1805, French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils, backed by del Río’s friend Baron Alexander von Humboldt, incorrectly declared that del Río’s new element was an impure sample of chromium. Del Río accepted Collet-Descotils’ statement and retracted his claim.[4]
In 1831 Swedish chemist Nils Gabriel Sefström rediscovered the element in a new oxide he found while working with iron ores. Later that year, Friedrich Wöhler confirmed del Río’s earlier work.[5] Sefström chose a name beginning with V, which had not yet been assigned to any element. He called the element vanadium after Old Norse Vanadís (another name for the Norse Vanir goddess Freyja, whose attributes include beauty and fertility), because of the many beautifully colored chemical compounds it produces.[5] In 1831, the geologist George William Featherstonhaugh suggested that vanadium should be renamed «rionium» after del Río, but this suggestion was not followed.[6]
The isolation of vanadium metal was difficult.[citation needed] In 1831, Berzelius reported the production of the metal, but Henry Enfield Roscoe showed that Berzelius had produced the nitride, vanadium nitride (VN). Roscoe eventually produced the metal in 1867 by reduction of vanadium(II) chloride, VCl2, with hydrogen.[7] In 1927, pure vanadium was produced by reducing vanadium pentoxide with calcium.[8]
The first large-scale industrial use of vanadium was in the steel alloy chassis of the Ford Model T, inspired by French race cars. Vanadium steel allowed reduced weight while increasing tensile strength (ca. 1905).[9] For the first decade of the 20th century, most vanadium ore was mined by American Vanadium Company from the Minas Ragra in Peru. Later, the demand for uranium rose, leading to increased mining of that metal’s ores. One major uranium ore was carnotite, which also contains vanadium. Thus, vanadium became available as a by-product of uranium production. Eventually, uranium mining began to supply a large share of the demand for vanadium.[10][11]
In 1911, German chemist Martin Henze discovered vanadium in the hemovanadin proteins found in blood cells (or coelomic cells) of Ascidiacea (sea squirts).[12][13]
Characteristics[edit]
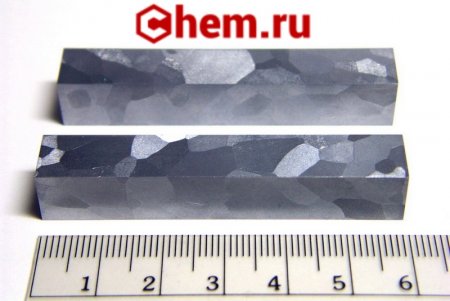
Polycrystalline high-purity (99.95%) vanadium cuboids, ebeam remelted and macro-etched
Vanadium is an average-hard, ductile, steel-blue metal. It is electrically conductive and thermally insulating. Some sources describe vanadium as «soft», perhaps because it is ductile, malleable, and not brittle.[14][15] Vanadium is harder than most metals and steels (see Hardnesses of the elements (data page) and iron). It has good resistance to corrosion and it is stable against alkalis and sulfuric and hydrochloric acids.[16] It is oxidized in air at about 933 K (660 °C, 1220 °F), although an oxide passivation layer forms even at room temperature.
Isotopes[edit]
Naturally occurring vanadium is composed of one stable isotope, 51V, and one radioactive isotope, 50V. The latter has a half-life of 1.5×1017 years and a natural abundance of 0.25%. 51V has a nuclear spin of 7⁄2, which is useful for NMR spectroscopy.[17] Twenty-four artificial radioisotopes have been characterized, ranging in mass number from 40 to 65. The most stable of these isotopes are 49V with a half-life of 330 days, and 48V with a half-life of 16.0 days. The remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives shorter than an hour, most below 10 seconds. At least four isotopes have metastable excited states.[18] Electron capture is the main decay mode for isotopes lighter than 51V. For the heavier ones, the most common mode is beta decay. The electron capture reactions lead to the formation of element 22 (titanium) isotopes, while beta decay leads to element 24 (chromium) isotopes.
Compounds[edit]
From left: [V(H2O)6]2+ (lilac), [V(H2O)6]3+ (green), [VO(H2O)5]2+ (blue) and [VO(H2O)5]3+ (yellow).
The chemistry of vanadium is noteworthy for the accessibility of the four adjacent oxidation states 2–5. In aqueous solution, vanadium forms metal aquo complexes of which the colours are lilac [V(H2O)6]2+, green [V(H2O)6]3+, blue [VO(H2O)5]2+, yellow-orange oxides [VO(H2O)5]3+, the formula for which depends on pH. Vanadium(II) compounds are reducing agents, and vanadium(V) compounds are oxidizing agents. Vanadium(IV) compounds often exist as vanadyl derivatives, which contain the VO2+ center.[16]
Ammonium vanadate(V) (NH4VO3) can be successively reduced with elemental zinc to obtain the different colors of vanadium in these four oxidation states. Lower oxidation states occur in compounds such as V(CO)6, [V(CO)
6]−
and substituted derivatives.[16]
Vanadium pentoxide is a commercially important catalyst for the production of sulfuric acid, a reaction that exploits the ability of vanadium oxides to undergo redox reactions.[16]
The vanadium redox battery utilizes all four oxidation states: one electrode uses the +5/+4 couple and the other uses the +3/+2 couple. Conversion of these oxidation states is illustrated by the reduction of a strongly acidic solution of a vanadium(V) compound with zinc dust or amalgam. The initial yellow color characteristic of the pervanadyl ion [VO2(H2O)4]+ is replaced by the blue color of [VO(H2O)5]2+, followed by the green color of [V(H2O)6]3+ and then the violet color of [V(H2O)6]2+.[16]
Oxyanions[edit]
In aqueous solution, vanadium(V) forms an extensive family of oxyanions as established by 51V NMR spectroscopy.[17] The interrelationships in this family are described by the predominance diagram, which shows at least 11 species, depending on pH and concentration.[19] The tetrahedral orthovanadate ion, VO3−
4, is the principal species present at pH 12–14. Similar in size and charge to phosphorus(V), vanadium(V) also parallels its chemistry and crystallography. Orthovanadate VO3−
4 is used in protein crystallography[20] to study the biochemistry of phosphate.[21] Beside that, this anion also has been shown to interact with activity of some specific enzymes.[22][23] The tetrathiovanadate [VS4]3− is analogous to the orthovanadate ion.[24]
At lower pH values, the monomer [HVO4]2− and dimer [V2O7]4− are formed, with the monomer predominant at vanadium concentration of less than c. 10−2M (pV > 2, where pV is equal to the minus value of the logarithm of the total vanadium concentration/M). The formation of the divanadate ion is analogous to the formation of the dichromate ion. As the pH is reduced, further protonation and condensation to polyvanadates occur: at pH 4-6 [H2VO4]− is predominant at pV greater than ca. 4, while at higher concentrations trimers and tetramers are formed. Between pH 2-4 decavanadate predominates, its formation from orthovanadate is represented by this condensation reaction:
- 10 [VO4]3− + 24 H+ → [V10O28]6− + 12 H2O
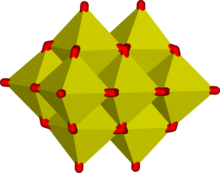
In decavanadate, each V(V) center is surrounded by six oxide ligands.[16] Vanadic acid, H3VO4 exists only at very low concentrations because protonation of the tetrahedral species [H2VO4]− results in the preferential formation of the octahedral [VO2(H2O)4]+ species. In strongly acidic solutions, pH < 2, [VO2(H2O)4]+ is the predominant species, while the oxide V2O5 precipitates from solution at high concentrations. The oxide is formally the acid anhydride of vanadic acid. The structures of many vanadate compounds have been determined by X-ray crystallography.
The Pourbaix diagram for vanadium in water, which shows the redox potentials between various vanadium species in different oxidation states.[25]
Vanadium(V) forms various peroxo complexes, most notably in the active site of the vanadium-containing bromoperoxidase enzymes. The species VO(O)2(H2O)4+ is stable in acidic solutions. In alkaline solutions, species with 2, 3 and 4 peroxide groups are known; the last forms violet salts with the formula M3V(O2)4 nH2O (M= Li, Na, etc.), in which the vanadium has an 8-coordinate dodecahedral structure.[26][27]
Halide derivatives[edit]
Twelve binary halides, compounds with the formula VXn (n=2..5), are known. VI4, VCl5, VBr5, and VI5 do not exist or are extremely unstable. In combination with other reagents, VCl4 is used as a catalyst for polymerization of dienes. Like all binary halides, those of vanadium are Lewis acidic, especially those of V(IV) and V(V). Many of the halides form octahedral complexes with the formula VXnL6−n (X= halide; L= other ligand).
Many vanadium oxyhalides (formula VOmXn) are known.[28] The oxytrichloride and oxytrifluoride (VOCl3 and VOF3) are the most widely studied. Akin to POCl3, they are volatile, adopt tetrahedral structures in the gas phase, and are Lewis acidic.
Coordination compounds[edit]
Complexes of vanadium(II) and (III) are relatively exchange inert and reducing. Those of V(IV) and V(V) are oxidants. The vanadium ion is rather large and some complexes achieve coordination numbers greater than 6, as is the case in [V(CN)7]4−. Oxovanadium(V) also forms 7 coordinate coordination complexes with tetradentate ligands and peroxides and these complexes are used for oxidative brominations and thioether oxidations. The coordination chemistry of V4+ is dominated by the vanadyl center, VO2+, which binds four other ligands strongly and one weakly (the one trans to the vanadyl center). An example is vanadyl acetylacetonate (V(O)(O2C5H7)2). In this complex, the vanadium is 5-coordinate, distorted square pyramidal, meaning that a sixth ligand, such as pyridine, may be attached, though the association constant of this process is small. Many 5-coordinate vanadyl complexes have a trigonal bipyramidal geometry, such as VOCl2(NMe3)2.[29] The coordination chemistry of V5+ is dominated by the relatively stable dioxovanadium coordination complexes which are often formed by aerial oxidation of the vanadium(IV) precursors indicating the stability of the +5 oxidation state and ease of interconversion between the +4 and +5 states.
Organometallic compounds[edit]
Organometallic chemistry of vanadium is well developed. Vanadocene dichloride is a versatile starting reagent and has applications in organic chemistry.[30] Vanadium carbonyl, V(CO)6, is a rare example of a paramagnetic metal carbonyl. Reduction yields V(CO)−
6 (isoelectronic with Cr(CO)6), which may be further reduced with sodium in liquid ammonia to yield V(CO)3−
5 (isoelectronic with Fe(CO)5).[31][32]
Occurrence[edit]
Universe[edit]
The cosmic abundance of vanadium in the universe is 0.0001%, making the element nearly as common as copper or zinc.[33] Vanadium is detected spectroscopically in light from the Sun and sometimes in the light from other stars.[34]
Earth’s crust[edit]
Vanadium is the 20th most abundant element in the earth’s crust;[35] metallic vanadium is rare in nature (known as native vanadium),[36][37] but vanadium compounds occur naturally in about 65 different minerals.
At the beginning of the 20th century a large deposit of vanadium ore was discovered, the Minas Ragra vanadium mine near Junín, Cerro de Pasco, Peru.[38][39][40] For several years this patrónite (VS4)[41] deposit was an economically significant source for vanadium ore. In 1920 roughly two thirds of the worldwide production was supplied by the mine in Peru.[42] With the production of uranium in the 1910s and 1920s from carnotite (K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O) vanadium became available as a side product of uranium production. Vanadinite (Pb5(VO4)3Cl) and other vanadium bearing minerals are only mined in exceptional cases. With the rising demand, much of the world’s vanadium production is now sourced from vanadium-bearing magnetite found in ultramafic gabbro bodies. If this titanomagnetite is used to produce iron, most of the vanadium goes to the slag, and is extracted from it.[43][44]
Vanadium is mined mostly in South Africa, north-western China, and eastern Russia. In 2013 these three countries mined more than 97% of the 79,000 tonnes of produced vanadium.[45]
Vanadium is also present in bauxite and in deposits of crude oil, coal, oil shale, and tar sands. In crude oil, concentrations up to 1200 ppm have been reported. When such oil products are burned, traces of vanadium may cause corrosion in engines and boilers.[46] An estimated 110,000 tonnes of vanadium per year are released into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels.[47] Black shales are also a potential source of vanadium. During WW II some vanadium was extracted from alum shales in the south of Sweden.[48]
Water[edit]
The vanadyl ion is abundant in seawater, having an average concentration of 30 nM (1.5 mg/m3).[33] Some mineral water springs also contain the ion in high concentrations. For example, springs near Mount Fuji contain as much as 54 μg per liter.[33]
Production[edit]
Vacuum sublimed vanadium dendritic crystals (99.9%)
Vanadium crystals (99.9%) made by electrolysis
An etched piece of vanadium
Vanadium metal is obtained by a multistep process that begins with roasting crushed ore with NaCl or Na2CO3 at about 850 °C to give sodium metavanadate (NaVO3). An aqueous extract of this solid is acidified to produce «red cake», a polyvanadate salt, which is reduced with calcium metal. As an alternative for small-scale production, vanadium pentoxide is reduced with hydrogen or magnesium. Many other methods are also used, in all of which vanadium is produced as a byproduct of other processes.[49] Purification of vanadium is possible by the crystal bar process developed by Anton Eduard van Arkel and Jan Hendrik de Boer in 1925. It involves the formation of the metal iodide, in this example vanadium(III) iodide, and the subsequent decomposition to yield pure metal:[50]
- 2 V + 3 I2 ⇌ 2 VI3
Most vanadium is used as a steel alloy called ferrovanadium. Ferrovanadium is produced directly by reducing a mixture of vanadium oxide, iron oxides and iron in an electric furnace. The vanadium ends up in pig iron produced from vanadium-bearing magnetite. Depending on the ore used, the slag contains up to 25% of vanadium.[49]
China is the world’s largest producer of vanadium.[51]
Applications[edit]
Tool made from vanadium steel
Alloys[edit]
Approximately 85% of the vanadium produced is used as ferrovanadium or as a steel additive.[49] The considerable increase of strength in steel containing small amounts of vanadium was discovered in the early 20th century. Vanadium forms stable nitrides and carbides, resulting in a significant increase in the strength of steel.[52] From that time on, vanadium steel was used for applications in axles, bicycle frames, crankshafts, gears, and other critical components. There are two groups of vanadium steel alloys. Vanadium high-carbon steel alloys contain 0.15% to 0.25% vanadium, and high-speed tool steels (HSS) have a vanadium content of 1% to 5%. For high-speed tool steels, a hardness above HRC 60 can be achieved. HSS steel is used in surgical instruments and tools.[53] Powder-metallurgic alloys contain up to 18% percent vanadium. The high content of vanadium carbides in those alloys increases wear resistance significantly. One application for those alloys is tools and knives.[54]
Vanadium stabilizes the beta form of titanium and increases the strength and temperature stability of titanium. Mixed with aluminium in titanium alloys, it is used in jet engines, high-speed airframes and dental implants. The most common alloy for seamless tubing is Titanium 3/2.5 containing 2.5% vanadium, the titanium alloy of choice in the aerospace, defense, and bicycle industries.[55] Another common alloy, primarily produced in sheets, is Titanium 6AL-4V, a titanium alloy with 6% aluminium and 4% vanadium.[56]
Several vanadium alloys show superconducting behavior. The first A15 phase superconductor was a vanadium compound, V3Si, which was discovered in 1952.[57] Vanadium-gallium tape is used in superconducting magnets (17.5 teslas or 175,000 gauss). The structure of the superconducting A15 phase of V3Ga is similar to that of the more common Nb3Sn and Nb3Ti.[58]
It has been found that a small amount, 40 to 270 ppm, of vanadium in Wootz steel significantly improved the strength of the product, and gave it the distinctive patterning. The source of the vanadium in the original Wootz steel ingots remains unknown.[59]
Vanadium can be used as a substitute for molybdenum in armor steel, though the alloy produced is far more brittle and prone to spalling on non-penetrating impacts.[60] The Third Reich was one of the most prominent users of such alloys, in armored vehicles like Tiger II or Jagdtiger.[61]
Catalysts[edit]
Vanadium compounds are used extensively as catalysts;[62] Vanadium pentoxide V2O5, is used as a catalyst in manufacturing sulfuric acid by the contact process[63] In this process sulfur dioxide (SO
2) is oxidized to the trioxide (SO
3):[16] In this redox reaction, sulfur is oxidized from +4 to +6, and vanadium is reduced from +5 to +4:
- V2O5 + SO2 → 2 VO2 + SO3
The catalyst is regenerated by oxidation with air:
- 4 VO2 + O2 → 2 V2O5
Similar oxidations are used in the production of maleic anhydride:
- C4H10 + 3.5 O2 → C4H2O3 + 4 H2O
Phthalic anhydride and several other bulk organic compounds are produced similarly. These green chemistry processes convert inexpensive feedstocks to highly functionalized, versatile intermediates.[64][65]
Vanadium is an important component of mixed metal oxide catalysts used in the oxidation of propane and propylene to acrolein, acrylic acid or the ammoxidation of propylene to acrylonitrile.[66]
Other uses[edit]
The vanadium redox battery, a type of flow battery, is an electrochemical cell consisting of aqueous vanadium ions in different oxidation states.[67][68] Batteries of the type were first proposed in the 1930s and developed commercially from the 1980s onwards. Cells use +5 and +2 formal oxidization state ions.
Vanadium redox batteries are used commercially for grid energy storage.
Vanadate can be used for protecting steel against rust and corrosion by conversion coating.[69] Vanadium foil is used in cladding titanium to steel because it is compatible with both iron and titanium.[70] The moderate thermal neutron-capture cross-section and the short half-life of the isotopes produced by neutron capture makes vanadium a suitable material for the inner structure of a fusion reactor.[71][72]
Proposed[edit]
Lithium vanadium oxide has been proposed for use as a high energy density anode for lithium ion batteries, at 745 Wh/L when paired with a lithium cobalt oxide cathode.[73] Vanadium phosphates have been proposed as the cathode in the lithium vanadium phosphate battery, another type of lithium-ion battery.[74]
Biological role[edit]
Vanadium is more important in marine environments than terrestrial.[75]
Vanadoenzymes[edit]
A number of species of marine algae produce vanadium bromoperoxidase as well as the closely related chloroperoxidase (which may use a heme or vanadium cofactor) and iodoperoxidases. The bromoperoxidase produces an estimated 1–2 million tons of bromoform and 56,000 tons of bromomethane annually.[76] Most naturally occurring organobromine compounds are produced by this enzyme,[77] catalyzing the following reaction (R-H is hydrocarbon substrate):
- R-H + Br− + H2O2 → R-Br + H2O + OH−
A vanadium nitrogenase is used by some nitrogen-fixing micro-organisms, such as Azotobacter. In this role, vanadium serves in place of the more common molybdenum or iron, and gives the nitrogenase slightly different properties.[78]
Vanadium accumulation in tunicates[edit]
Vanadium is essential to tunicates, where it is stored in the highly acidified vacuoles of certain blood cell types, designated vanadocytes. Vanabins (vanadium binding proteins) have been identified in the cytoplasm of such cells. The concentration of vanadium in the blood of ascidian tunicates is as much as ten million times higher[specify][79][80] than the surrounding seawater, which normally contains 1 to 2 µg/L.[81][82] The function of this vanadium concentration system and these vanadium-bearing proteins is still unknown, but the vanadocytes are later deposited just under the outer surface of the tunic, where they may deter predation.[83]
Fungi[edit]
Amanita muscaria and related species of macrofungi accumulate vanadium (up to 500 mg/kg in dry weight). Vanadium is present in the coordination complex amavadin[84] in fungal fruit-bodies. The biological importance of the accumulation is unknown.[85][86] Toxic or peroxidase enzyme functions have been suggested.[87]
Mammals[edit]
Deficiencies in vanadium result in reduced growth in rats.[88] The U.S. Institute of Medicine has not confirmed that vanadium is an essential nutrient for humans, so neither a Recommended Dietary Intake nor an Adequate Intake have been established. Dietary intake is estimated at 6 to 18 µg/day, with less than 5% absorbed. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) of dietary vanadium, beyond which adverse effects may occur, is set at 1.8 mg/day.[89]
Research[edit]
Vanadyl sulfate as a dietary supplement has been researched as a means of increasing insulin sensitivity or otherwise improving glycemic control in people who are diabetic. Some of the trials had significant treatment effects, but were deemed as being of poor study quality. The amounts of vanadium used in these trials (30 to 150 mg) far exceeded the safe upper limit.[90][91] The conclusion of the systemic review was «There is no rigorous evidence that oral vanadium supplementation improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes. The routine use of vanadium for this purpose cannot be recommended.»[90]
In astrobiology, it has been suggested that discrete vanadium accumulations on Mars could be a potential microbial biosignature, when used in conjunction with Raman spectroscopy and morphology.[92][93]
Safety[edit]
All vanadium compounds should be considered toxic.[94] Tetravalent VOSO4 has been reported to be at least 5 times more toxic than trivalent V2O3.[95] The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set an exposure limit of 0.05 mg/m3 for vanadium pentoxide dust and 0.1 mg/m3 for vanadium pentoxide fumes in workplace air for an 8-hour workday, 40-hour work week.[96] The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has recommended that 35 mg/m3 of vanadium be considered immediately dangerous to life and health, that is, likely to cause permanent health problems or death.[96]
Vanadium compounds are poorly absorbed through the gastrointestinal system. Inhalation of vanadium and vanadium compounds results primarily in adverse effects on the respiratory system.[97][98][99] Quantitative data are, however, insufficient to derive a subchronic or chronic inhalation reference dose. Other effects have been reported after oral or inhalation exposures on blood parameters,[100][101] liver,[102] neurological development,[103] and other organs[104] in rats.
There is little evidence that vanadium or vanadium compounds are reproductive toxins or teratogens. Vanadium pentoxide was reported to be carcinogenic in male rats and in male and female mice by inhalation in an NTP study,[98] although the interpretation of the results has recently been disputed.[105] The carcinogenicity of vanadium has not been determined by the United States Environmental Protection Agency.[106]
Vanadium traces in diesel fuels are the main fuel component in high temperature corrosion. During combustion, vanadium oxidizes and reacts with sodium and sulfur, yielding vanadate compounds with melting points as low as 530 °C, which attack the passivation layer on steel and render it susceptible to corrosion. The solid vanadium compounds also abrade engine components.[107][108]
See also[edit]
- Flow battery
- Green Giant mine
- Grid energy storage
- Vanadium carbide
- Vanadium redox battery
- Vanadium tetrachloride
- Vanadium(V) oxide
- International Vanadium Symposium
- The Vanadium Cycle
References[edit]
- ^ «Standard Atomic Weights: Vanadium». CIAAW. 1977.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ «Vanadium». Royal Society of Chemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ Cintas, Pedro (2004). «The Road to Chemical Names and Eponyms: Discovery, Priority, and Credit». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 43 (44): 5888–94. doi:10.1002/anie.200330074. PMID 15376297.
- ^ a b Sefström, N. G. (1831). «Ueber das Vanadin, ein neues Metall, gefunden im Stangeneisen von Eckersholm, einer Eisenhütte, die ihr Erz von Taberg in Småland bezieht». Annalen der Physik und Chemie. 97 (1): 43–49. Bibcode:1831AnP….97…43S. doi:10.1002/andp.18310970103.
- ^ Featherstonhaugh, George William (1831). «New Metal, provisionally called Vanadium». The Monthly American Journal of Geology and Natural Science: 69.
- ^ Roscoe, Henry E. (1869–1870). «Researches on Vanadium. Part II». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 18 (114–122): 37–42. doi:10.1098/rspl.1869.0012.
- ^ Marden, J. W.; Rich, M. N. (1927). «Vanadium». Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 19 (7): 786–788. doi:10.1021/ie50211a012.
- ^ Betz, Frederick (2003). Managing Technological Innovation: Competitive Advantage from Change. Wiley-IEEE. pp. 158–159. ISBN 978-0-471-22563-8.
- ^ Phillip Maxwell Busch (1961). Vanadium: A Materials Survey. U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines.
- ^ Wise, James M. (May 2018). «Remarkable folded dacitic dikes at Mina Ragra, Peru».
- ^ Henze, M. (1911). «Untersuchungen über das Blut der Ascidien. I. Mitteilung». Z. Physiol. Chem. 72 (5–6): 494–50. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1911.72.5-6.494.
- ^ Michibata, H.; Uyama, T.; Ueki, T.; Kanamori, K. (2002). «Vanadocytes, cells hold the key to resolving the highly selective accumulation and reduction of vanadium in ascidians» (PDF). Microscopy Research and Technique. 56 (6): 421–434. doi:10.1002/jemt.10042. PMID 11921344. S2CID 15127292.
- ^ George F. Vander Voort (1984). Metallography, principles and practice. ASM International. pp. 137–. ISBN 978-0-87170-672-0. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Cardarelli, François (2008). Materials handbook: a concise desktop reference. Springer. pp. 338–. ISBN 978-1-84628-668-1. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1985). «Vanadium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1071–1075. ISBN 978-3-11-007511-3.
- ^ a b Rehder, D.; Polenova, T.; Bühl, M. (2007). Vanadium-51 NMR. Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy. Vol. 62. pp. 49–114. doi:10.1016/S0066-4103(07)62002-X. ISBN 9780123739193.
- ^ Audi, Georges; Bersillon, Olivier; Blachot, Jean; Wapstra, Aaldert Hendrik (2003), «The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties», Nuclear Physics A, 729: 3–128, Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729….3A, doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 984. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Sinning, Irmgard; Hol, Wim G. J. (2004). «The power of vanadate in crystallographic investigations of phosphoryl transfer enzymes». FEBS Letters. 577 (3): 315–21. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.10.022. PMID 15556602. S2CID 8328704.
- ^ Seargeant, Lorne E.; Stinson, Robert A. (1979). «Inhibition of human alkaline phosphatases by vanadate». Biochemical Journal. 181 (1): 247–50. doi:10.1042/bj1810247. PMC 1161148. PMID 486156.
- ^ Crans, Debbie C.; Simone, Carmen M. (9 July 1991). «Nonreductive interaction of vanadate with an enzyme containing a thiol group in the active site: glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase». Biochemistry. 30 (27): 6734–6741. doi:10.1021/bi00241a015. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 2065057.
- ^ Karlish, S. J. D.; Beaugé, L. A.; Glynn, I. M. (November 1979). «Vanadate inhibits (Na+ + K+)ATPase by blocking a conformational change of the unphosphorylated form». Nature. 282 (5736): 333–335. Bibcode:1979Natur.282..333K. doi:10.1038/282333a0. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 228199. S2CID 4341480.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 988. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Al-Kharafi, F. M.; Badawy, W. A. (1997). «Electrochemical behavior of vanadium in aqueous solutions of different pH». Electrochimica Acta. 42 (4): 579–586. doi:10.1016/S0013-4686(96)00202-2.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8., p994.
- ^ Strukul, Giorgio (1992). Catalytic oxidations with hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. Springer. p. 128. ISBN 978-0-7923-1771-5.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 993. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Wilkinson, G. & Birmingham, J.G. (1954). «Bis-cyclopentadienyl Compounds of Ti, Zr, V, Nb and Ta». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (17): 4281–4284. doi:10.1021/ja01646a008.
- ^ Bellard, S.; Rubinson, K. A.; Sheldrick, G. M. (1979). «Crystal and molecular structure of vanadium hexacarbonyl» (PDF). Acta Crystallographica. B35 (2): 271–274. doi:10.1107/S0567740879003332. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- ^ Elschenbroich, C.; Salzer A. (1992). Organometallics: A Concise Introduction. Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3-527-28165-7.
- ^ a b c Rehder, Dieter (2008). Bioinorganic Vanadium Chemistry. Inorganic Chemistry (1st ed.). Hamburg, Germany: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 5 & 9–10. doi:10.1002/9780470994429. ISBN 9780470065099.
- ^ Cowley, C. R.; Elste, G. H.; Urbanski, J. L. (1978). «Vanadium abundances in early A stars». Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 90: 536. Bibcode:1978PASP…90..536C. doi:10.1086/130379.
- ^ Proceedings. National Cotton Council of America. 1991.
- ^ Ostrooumov, M., and Taran, Y., 2015. Discovery of Native Vanadium, a New Mineral from the Colima Volcano, State of Colima (Mexico). Revista de la Sociedad Española de Mineralogía 20, 109-110
- ^ «Vanadium: Vanadium mineral information and data». Mindat.org. Retrieved 2 March 2016.
- ^ Hillebrand, W. F. (1907). «The Vanadium Sulphide, Patronite, and ITS Mineral Associates from Minasragra, Peru». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 29 (7): 1019–1029. doi:10.1021/ja01961a006.
- ^ Hewett, F. (1906). «A New Occurrence of Vanadium in Peru». The Engineering and Mining Journal. 82 (9): 385.
- ^ Steinberg, W.S.; Geyser, W.; Nell, J. «The history and development of the pyrometallurgical processes at Evraz Highveld Steel & Vanadium» (PDF).
- ^ «mineralogical data about Patrónite». mindata.org. Retrieved 19 January 2009.
- ^ Allen, M. A.; Butler, G. M. (1921). «Vanadium» (PDF). University of Arizona. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- ^ Hukkanen, E.; Walden, H. (1985). «The production of vanadium and steel from titanomagnetites». International Journal of Mineral Processing. 15 (1–2): 89–102. doi:10.1016/0301-7516(85)90026-2.
- ^ Steinberg, W.S.; Geyser, W.; Nell, J. «The history and development of the pyrometallurgical processes at Evraz Highveld Steel & Vanadium» (PDF).
- ^ Magyar, Michael J. «Mineral Commodity Summaries 2015: Vanadium» (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ Pearson, C. D.; Green J. B. (1993). «Vanadium and nickel complexes in petroleum resid acid, base, and neutral fractions». Energy Fuels. 7 (3): 338–346. doi:10.1021/ef00039a001.
- ^ Anke, Manfred (2004). «Vanadium – An element both essential and toxic to plants, animals and humans?». Anal. Real Acad. Nac. Farm. 70: 961.
- ^ Dyni, John R. (2006). «Geology and resources of some world oil-shale deposits». Scientific Investigations Report. p. 22. doi:10.3133/sir29955294. S2CID 19814608.
- ^ a b c Moskalyk, R. R.; Alfantazi, A. M. (2003). «Processing of vanadium: a review». Minerals Engineering. 16 (9): 793–805. doi:10.1016/S0892-6875(03)00213-9.
- ^ Carlson, O. N.; Owen, C. V. (1961). «Preparation of High-Purity Vanadium Metals by the Iodide Refining Process». Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 108: 88. doi:10.1149/1.2428019.
- ^ USGS Vanadinum Production Statistics[permanent dead link]
- ^ Chandler, Harry (1998). Metallurgy for the Non-metallurgist. ASM International. pp. 6–7. ISBN 978-0-87170-652-2.
- ^ Davis, Joseph R. (1995). Tool Materials: Tool Materials. ASM International. ISBN 978-0-87170-545-7.
- ^ Oleg D. Neikov; Naboychenko, Stanislav; Mourachova, Irina; Victor G. Gopienko; Irina V. Frishberg; Dina V. Lotsko (24 February 2009). Handbook of Non-Ferrous Metal Powders: Technologies and Applications. p. 490. ISBN 9780080559407. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- ^ «Technical Supplement: Titanium». Seven Cycles. Archived from the original on 3 November 2016. Retrieved 1 November 2016.
- ^ Peters, Manfred; Leyens, C. (2002). «Metastabile β-Legierungen». Titan und Titanlegierungen. Wiley-VCH. pp. 23–24. ISBN 978-3-527-30539-1.
- ^ Hardy, George F.; Hulm, John K. (1953). «Superconducting Silicides and Germanides». Physical Review. 89 (4): 884. Bibcode:1953PhRv…89Q.884H. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.89.884.
- ^ Markiewicz, W.; Mains, E.; Vankeuren, R.; Wilcox, R.; Rosner, C.; Inoue, H.; Hayashi, C.; Tachikawa, K. (1977). «A 17.5 Tesla superconducting concentric Nb3Sn and V3Ga magnet system». IEEE Transactions on Magnetics. 13 (1): 35–37. Bibcode:1977ITM….13…35M. doi:10.1109/TMAG.1977.1059431.
- ^ Verhoeven, J. D.; Pendray, A. H.; Dauksch, W. E. (1998). «The key role of impurities in ancient damascus steel blades». Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society. 50 (9): 58–64. Bibcode:1998JOM….50i..58V. doi:10.1007/s11837-998-0419-y. S2CID 135854276.
- ^ Rohrmann, B. «Vanadium in South Africa (Metal Review Series no. 2)». hdl:10520/AJA0038223X_1959.
- ^ Overy, R. (1973). Transportation and Rearmament in the Third Reich. The Historical Journal, 16(2), 389-409. doi:10.1017/S0018246X00005926
- ^ Langeslay, Ryan R.; Kaphan, David M.; Marshall, Christopher L.; Stair, Peter C.; Sattelberger, Alfred P.; Delferro, Massimiliano (8 October 2018). «Catalytic Applications of Vanadium: A Mechanistic Perspective». Chemical Reviews. 119 (4): 2128–2191. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00245. OSTI 1509906. PMID 30296048. S2CID 52943647.
- ^ Eriksen, K. M.; Karydis, D. A.; Boghosian, S.; Fehrmann, R. (1995). «Deactivation and Compound Formation in Sulfuric-Acid Catalysts and Model Systems». Journal of Catalysis. 155 (1): 32–42. doi:10.1006/jcat.1995.1185.
- ^ Bauer, Günter; Güther, Volker; Hess, Hans; Otto, Andreas; Roidl, Oskar; Roller, Heinz; Sattelberger, Siegfried (2000). «Vanadium and Vanadium Compounds». Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_367.
- ^ Abon, Michel; Volta, Jean-Claude (1997). «Vanadium phosphorus oxides for n-butane oxidation to maleic anhydride». Applied Catalysis A: General. 157 (1–2): 173–193. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(97)00016-1.
- ^ Fierro, J. G. L., ed. (2006). Metal Oxides, Chemistry and Applications. CRC Press. pp. 415–455. ISBN 9780824723712.
- ^ Joerissen, Ludwig; Garche, Juergen; Fabjan, Ch.; Tomazic G. (2004). «Possible use of vanadium redox-flow batteries for energy storage in small grids and stand-alone photovoltaic systems». Journal of Power Sources. 127 (1–2): 98–104. Bibcode:2004JPS…127…98J. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2003.09.066.
- ^ Rychcik, M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. (1988). «Characteristics of a new all-vanadium redox flow battery». Journal of Power Sources. 22 (1): 59–67. Bibcode:1988JPS….22…59R. doi:10.1016/0378-7753(88)80005-3. ISSN 0378-7753.
- ^ Guan, H.; Buchheit R. G. (2004). «Corrosion Protection of Aluminum Alloy 2024-T3 by Vanadate Conversion Coatings». Corrosion. 60 (3): 284–296. doi:10.5006/1.3287733.
- ^ Lositskii, N. T.; Grigor’ev A. A.; Khitrova, G. V. (1966). «Welding of chemical equipment made from two-layer sheet with titanium protective layer (review of foreign literature)». Chemical and Petroleum Engineering. 2 (12): 854–856. doi:10.1007/BF01146317. S2CID 108903737.
- ^ Matsui, H.; Fukumoto, K.; Smith, D. L.; Chung, Hee M.; Witzenburg, W. van; Votinov, S. N. (1996). «Status of vanadium alloys for fusion reactors». Journal of Nuclear Materials. 233–237 (1): 92–99. Bibcode:1996JNuM..233…92M. doi:10.1016/S0022-3115(96)00331-5.
- ^ «Vanadium Data Sheet» (PDF). ATI Wah Chang. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 February 2009. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
- ^ Kariatsumari, Koji (February 2008). «Li-Ion Rechargeable Batteries Made Safer». Nikkei Business Publications, Inc. Archived from the original on 12 September 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2008.
- ^ Saıdi, M.Y.; Barker, J.; Huang, H.; Swoyer, J.L.; Adamson, G. (1 June 2003), «Performance characteristics of lithium vanadium phosphate as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries», Journal of Power Sources, 119–121: 266–272, Bibcode:2003JPS…119..266S, doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00245-3 Selected papers presented at the 11th International Meeting on Lithium Batteries
- ^ Sigel, Astrid; Sigel, Helmut, eds. (1995). Vanadium and Its Role in Life. Metal Ions in Biological Systems. Vol. 31. CRC. ISBN 978-0-8247-9383-8.
- ^ Gribble, Gordon W. (1999). «The diversity of naturally occurring organobromine compounds». Chemical Society Reviews. 28 (5): 335–346. doi:10.1039/a900201d.
- ^ Butler, Alison; Carter-Franklin, Jayme N. (2004). «The role of vanadium bromoperoxidase in the biosynthesis of halogenated marine natural products». Natural Product Reports. 21 (1): 180–8. doi:10.1039/b302337k. PMID 15039842. S2CID 19115256.
- ^ Robson, R. L.; Eady, R. R.; Richardson, T. H.; Miller, R. W.; Hawkins, M.; Postgate, J. R. (1986). «The alternative nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum is a vanadium enzyme». Nature. 322 (6077): 388–390. Bibcode:1986Natur.322..388R. doi:10.1038/322388a0. S2CID 4368841.
- ^ Smith, M. J. (1989). «Vanadium biochemistry: The unknown role of vanadium-containing cells in ascidians (sea squirts)». Experientia. 45 (5): 452–7. doi:10.1007/BF01952027. PMID 2656286. S2CID 43534732.
- ^ MacAra, Ian G.; McLeod, G. C.; Kustin, Kenneth (1979). «Tunichromes and metal ion accumulation in tunicate blood cells». Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B. 63 (3): 299–302. doi:10.1016/0305-0491(79)90252-9.
- ^ Trefry, John H.; Metz, Simone (1989). «Role of hydrothermal precipitates in the geochemical cycling of vanadium». Nature. 342 (6249): 531–533. Bibcode:1989Natur.342..531T. doi:10.1038/342531a0. S2CID 4351410.
- ^ Weiss, H.; Guttman, M. A.; Korkisch, J.; Steffan, I. (1977). «Comparison of methods for the determination of vanadium in sea-water». Talanta. 24 (8): 509–11. doi:10.1016/0039-9140(77)80035-0. PMID 18962130.
- ^ Ruppert, Edward E.; Fox, Richard, S.; Barnes, Robert D. (2004). Invertebrate Zoology (7th ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 947. ISBN 978-81-315-0104-7.
- ^ Kneifel, Helmut; Bayer, Ernst (1997). «Determination of the Structure of the Vanadium Compound, Amavadine, from Fly Agaric». Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 12 (6): 508. doi:10.1002/anie.197305081. ISSN 0570-0833.
- ^ Falandysz, J.; Kunito, T.; Kubota, R.; Lipka, K.; Mazur, A.; Falandysz, Justyna J.; Tanabe, S. (2007). «Selected elements in fly agaric Amanita muscaria». Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A. 42 (11): 1615–1623. doi:10.1080/10934520701517853. PMID 17849303. S2CID 26185534.
- ^ Berry, Robert E.; Armstrong, Elaine M.; Beddoes, Roy L.; Collison, David; Ertok, Nigar; Helliwell, Madeleine; Garner, David (1999). «The Structural Characterization of Amavadin». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 38 (6): 795–797. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990315)38:6<795::AID-ANIE795>3.0.CO;2-7. PMID 29711812.
- ^ da Silva, José A.L.; Fraústo da Silva, João J.R.; Pombeiro, Armando J.L. (2013). «Amavadin, a vanadium natural complex: Its role and applications». Coordination Chemistry Reviews. Elsevier BV. 257 (15–16): 2388–2400. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2013.03.010. ISSN 0010-8545.
- ^ Schwarz, Klaus; Milne, David B. (1971). «Growth Effects of Vanadium in the Rat». Science. 174 (4007): 426–428. Bibcode:1971Sci…174..426S. doi:10.1126/science.174.4007.426. JSTOR 1731776. PMID 5112000. S2CID 24362265.
- ^ Nickel. IN: Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Copper. National Academy Press. 2001, PP. 532–543.
- ^ a b Smith DM, Pickering RM, Lewith GT (2008). «A systematic review of vanadium oral supplements for glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus». QJM. 101 (5): 351–8. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcn003. PMID 18319296.
- ^ «Vanadium (vanadyl sulfate). Monograph». Altern Med Rev. 14 (2): 177–80. 2009. PMID 19594227.
- ^ Lynch, Brendan M. (21 September 2017). «Hope to discover sure signs of life on Mars? New research says look for the element vanadium». PhysOrg. Retrieved 14 October 2017.
- ^ Marshall, C. P; Olcott Marshall, A; Aitken, J. B; Lai, B; Vogt, S; Breuer, P; Steemans, P; Lay, P. A (2017). «Imaging of Vanadium in Microfossils: A New Potential Biosignature». Astrobiology. 17 (11): 1069–1076. Bibcode:2017AsBio..17.1069M. doi:10.1089/ast.2017.1709. OSTI 1436103. PMID 28910135.
- ^ Srivastava, A.K. Anti-diabetic and toxic effects of vanadium compounds. Mol Cell Biochem 206, 177–182 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007075204494
- ^ Roschin, A. V. (1967). «Toxicology of vanadium compounds used in modern industry». Gig Sanit. (Water Res.). 32 (6): 26–32. PMID 5605589.
- ^ a b «Occupational Safety and Health Guidelines for Vanadium Pentoxide». Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Archived from the original on 6 January 2009. Retrieved 29 January 2009.
- ^ Sax, N. I. (1984). Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials (6th ed.). Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. pp. 2717–2720.
- ^ a b Ress, N. B.; et al. (2003). «Carcinogenicity of inhaled vanadium pentoxide in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice». Toxicological Sciences. 74 (2): 287–296. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfg136. PMID 12773761.
- ^ Wörle-Knirsch, Jörg M.; Kern, Katrin; Schleh, Carsten; Adelhelm, Christel; Feldmann, Claus & Krug, Harald F. (2007). «Nanoparticulate Vanadium Oxide Potentiated Vanadium Toxicity in Human Lung Cells». Environ. Sci. Technol. 41 (1): 331–336. Bibcode:2007EnST…41..331W. doi:10.1021/es061140x. PMID 17265967.
- ^ Ścibior, A.; Zaporowska, H.; Ostrowski, J. (2006). «Selected haematological and biochemical parameters of blood in rats after subchronic administration of vanadium and/or magnesium in drinking water». Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 51 (2): 287–295. doi:10.1007/s00244-005-0126-4. PMID 16783625. S2CID 43805930.
- ^ Gonzalez-Villalva, A.; et al. (2006). «Thrombocytosis induced in mice after subacute and subchronic V2O5 inhalation». Toxicology and Industrial Health. 22 (3): 113–116. doi:10.1191/0748233706th250oa. PMID 16716040. S2CID 9986509.
- ^ Kobayashi, Kazuo; Himeno, Seiichiro; Satoh, Masahiko; Kuroda, Junji; Shibata, Nobuo; Seko, Yoshiyuki; Hasegawa, Tatsuya (2006). «Pentavalent vanadium induces hepatic metallothionein through interleukin-6-dependent and -independent mechanisms». Toxicology. 228 (2–3): 162–170. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2006.08.022. PMID 16987576.
- ^ Soazo, Marina; Garcia, Graciela Beatriz (2007). «Vanadium exposure through lactation produces behavioral alterations and CNS myelin deficit in neonatal rats». Neurotoxicology and Teratology. 29 (4): 503–510. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2007.03.001. PMID 17493788.
- ^ Barceloux, Donald G.; Barceloux, Donald (1999). «Vanadium». Clinical Toxicology. 37 (2): 265–278. doi:10.1081/CLT-100102425. PMID 10382561.
- ^ Duffus, J. H. (2007). «Carcinogenicity classification of vanadium pentoxide and inorganic vanadium compounds, the NTP study of carcinogenicity of inhaled vanadium pentoxide, and vanadium chemistry». Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 47 (1): 110–114. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2006.08.006. PMID 17030368.
- ^ Opreskos, Dennis M. (1991). «Toxicity Summary for Vanadium». Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Retrieved 8 November 2008.
- ^ Woodyard, Doug (18 August 2009). Pounder’s Marine Diesel Engines and Gas Turbines. p. 92. ISBN 9780080943619.
- ^ Totten, George E.; Westbrook, Steven R.; Shah, Rajesh J. (1 June 2003). Fuels and Lubricants Handbook: Technology, Properties, Performance, and Testing. p. 152. ISBN 9780803120969.
Further reading[edit]
- Slebodnick, Carla; et al. (1999). «Modeling the Biological Chemistry of Vanadium: Structural and Reactivity Studies Elucidating Biological Function». In Hill, Hugh A.O.; et al. (eds.). Metal sites in proteins and models: phosphatases, Lewis acids, and vanadium. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-65553-4.
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vanadium.
Look up vanadium in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
- Videos
- Vanadium at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
- Research papers
- ATSDR – ToxFAQs: Vanadium
- Vanadium concentration in seawater and estuary environments is around 1.5-3.3 ug/kg
- Vanadium speciation and cycling in coastal waters
- Ocean anoxia and the concentrations of molybdenum and vanadium in seawater
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vanadium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | (və-NAY-dee-əm) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | blue-silver-grey metal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(V) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vanadium in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | d-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 11, 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 2183 K (1910 °C, 3470 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 3680 K (3407 °C, 6165 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 6.11 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 5.5 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 21.5 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 444 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 24.89 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −3, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5 (an amphoteric oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 134 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 153±8 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Spectral lines of vanadium |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 4560 m/s (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 8.4 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 30.7 W/(m⋅K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 197 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | +255.0×10−6 cm3/mol (298 K)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young’s modulus | 128 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 47 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 160 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 6.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vickers hardness | 628–640 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 600–742 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-62-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Andrés Manuel del Río[3] (1801) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Henry Enfield Roscoe (1867) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Named by | Nils Gabriel Sefström (1830) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Main isotopes of vanadium
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| references |
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer (passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation.
Spanish scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 in Mexico by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called «brown lead». Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it «vanadium» after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors found in vanadium compounds. Del Rio’s lead mineral was ultimately named vanadinite for its vanadium content. In 1867 Henry Enfield Roscoe obtained the pure element.
Vanadium occurs naturally in about 65 minerals and in fossil fuel deposits. It is produced in China and Russia from steel smelter slag. Other countries produce it either from magnetite directly, flue dust of heavy oil, or as a byproduct of uranium mining. It is mainly used to produce specialty steel alloys such as high-speed tool steels, and some aluminium alloys. The most important industrial vanadium compound, vanadium pentoxide, is used as a catalyst for the production of sulfuric acid. The vanadium redox battery for energy storage may be an important application in the future.
Large amounts of vanadium ions are found in a few organisms, possibly as a toxin. The oxide and some other salts of vanadium have moderate toxicity. Particularly in the ocean, vanadium is used by some life forms as an active center of enzymes, such as the vanadium bromoperoxidase of some ocean algae.
History[edit]
Vanadium was discovered in 1801 by the Spanish mineralogist Andrés Manuel del Río. Del Río extracted the element from a sample of Mexican «brown lead» ore, later named vanadinite. He found that its salts exhibit a wide variety of colors, and as a result he named the element panchromium (Greek: παγχρώμιο «all colors»). Later, Del Río renamed the element erythronium (Greek: ερυθρός «red») because most of the salts turned red upon heating. In 1805, French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils, backed by del Río’s friend Baron Alexander von Humboldt, incorrectly declared that del Río’s new element was an impure sample of chromium. Del Río accepted Collet-Descotils’ statement and retracted his claim.[4]
In 1831 Swedish chemist Nils Gabriel Sefström rediscovered the element in a new oxide he found while working with iron ores. Later that year, Friedrich Wöhler confirmed del Río’s earlier work.[5] Sefström chose a name beginning with V, which had not yet been assigned to any element. He called the element vanadium after Old Norse Vanadís (another name for the Norse Vanir goddess Freyja, whose attributes include beauty and fertility), because of the many beautifully colored chemical compounds it produces.[5] In 1831, the geologist George William Featherstonhaugh suggested that vanadium should be renamed «rionium» after del Río, but this suggestion was not followed.[6]
The isolation of vanadium metal was difficult.[citation needed] In 1831, Berzelius reported the production of the metal, but Henry Enfield Roscoe showed that Berzelius had produced the nitride, vanadium nitride (VN). Roscoe eventually produced the metal in 1867 by reduction of vanadium(II) chloride, VCl2, with hydrogen.[7] In 1927, pure vanadium was produced by reducing vanadium pentoxide with calcium.[8]
The first large-scale industrial use of vanadium was in the steel alloy chassis of the Ford Model T, inspired by French race cars. Vanadium steel allowed reduced weight while increasing tensile strength (ca. 1905).[9] For the first decade of the 20th century, most vanadium ore was mined by American Vanadium Company from the Minas Ragra in Peru. Later, the demand for uranium rose, leading to increased mining of that metal’s ores. One major uranium ore was carnotite, which also contains vanadium. Thus, vanadium became available as a by-product of uranium production. Eventually, uranium mining began to supply a large share of the demand for vanadium.[10][11]
In 1911, German chemist Martin Henze discovered vanadium in the hemovanadin proteins found in blood cells (or coelomic cells) of Ascidiacea (sea squirts).[12][13]
Characteristics[edit]
Polycrystalline high-purity (99.95%) vanadium cuboids, ebeam remelted and macro-etched
Vanadium is an average-hard, ductile, steel-blue metal. It is electrically conductive and thermally insulating. Some sources describe vanadium as «soft», perhaps because it is ductile, malleable, and not brittle.[14][15] Vanadium is harder than most metals and steels (see Hardnesses of the elements (data page) and iron). It has good resistance to corrosion and it is stable against alkalis and sulfuric and hydrochloric acids.[16] It is oxidized in air at about 933 K (660 °C, 1220 °F), although an oxide passivation layer forms even at room temperature.
Isotopes[edit]
Naturally occurring vanadium is composed of one stable isotope, 51V, and one radioactive isotope, 50V. The latter has a half-life of 1.5×1017 years and a natural abundance of 0.25%. 51V has a nuclear spin of 7⁄2, which is useful for NMR spectroscopy.[17] Twenty-four artificial radioisotopes have been characterized, ranging in mass number from 40 to 65. The most stable of these isotopes are 49V with a half-life of 330 days, and 48V with a half-life of 16.0 days. The remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives shorter than an hour, most below 10 seconds. At least four isotopes have metastable excited states.[18] Electron capture is the main decay mode for isotopes lighter than 51V. For the heavier ones, the most common mode is beta decay. The electron capture reactions lead to the formation of element 22 (titanium) isotopes, while beta decay leads to element 24 (chromium) isotopes.
Compounds[edit]
From left: [V(H2O)6]2+ (lilac), [V(H2O)6]3+ (green), [VO(H2O)5]2+ (blue) and [VO(H2O)5]3+ (yellow).
The chemistry of vanadium is noteworthy for the accessibility of the four adjacent oxidation states 2–5. In aqueous solution, vanadium forms metal aquo complexes of which the colours are lilac [V(H2O)6]2+, green [V(H2O)6]3+, blue [VO(H2O)5]2+, yellow-orange oxides [VO(H2O)5]3+, the formula for which depends on pH. Vanadium(II) compounds are reducing agents, and vanadium(V) compounds are oxidizing agents. Vanadium(IV) compounds often exist as vanadyl derivatives, which contain the VO2+ center.[16]
Ammonium vanadate(V) (NH4VO3) can be successively reduced with elemental zinc to obtain the different colors of vanadium in these four oxidation states. Lower oxidation states occur in compounds such as V(CO)6, [V(CO)
6]−
and substituted derivatives.[16]
Vanadium pentoxide is a commercially important catalyst for the production of sulfuric acid, a reaction that exploits the ability of vanadium oxides to undergo redox reactions.[16]
The vanadium redox battery utilizes all four oxidation states: one electrode uses the +5/+4 couple and the other uses the +3/+2 couple. Conversion of these oxidation states is illustrated by the reduction of a strongly acidic solution of a vanadium(V) compound with zinc dust or amalgam. The initial yellow color characteristic of the pervanadyl ion [VO2(H2O)4]+ is replaced by the blue color of [VO(H2O)5]2+, followed by the green color of [V(H2O)6]3+ and then the violet color of [V(H2O)6]2+.[16]
Oxyanions[edit]
In aqueous solution, vanadium(V) forms an extensive family of oxyanions as established by 51V NMR spectroscopy.[17] The interrelationships in this family are described by the predominance diagram, which shows at least 11 species, depending on pH and concentration.[19] The tetrahedral orthovanadate ion, VO3−
4, is the principal species present at pH 12–14. Similar in size and charge to phosphorus(V), vanadium(V) also parallels its chemistry and crystallography. Orthovanadate VO3−
4 is used in protein crystallography[20] to study the biochemistry of phosphate.[21] Beside that, this anion also has been shown to interact with activity of some specific enzymes.[22][23] The tetrathiovanadate [VS4]3− is analogous to the orthovanadate ion.[24]
At lower pH values, the monomer [HVO4]2− and dimer [V2O7]4− are formed, with the monomer predominant at vanadium concentration of less than c. 10−2M (pV > 2, where pV is equal to the minus value of the logarithm of the total vanadium concentration/M). The formation of the divanadate ion is analogous to the formation of the dichromate ion. As the pH is reduced, further protonation and condensation to polyvanadates occur: at pH 4-6 [H2VO4]− is predominant at pV greater than ca. 4, while at higher concentrations trimers and tetramers are formed. Between pH 2-4 decavanadate predominates, its formation from orthovanadate is represented by this condensation reaction:
- 10 [VO4]3− + 24 H+ → [V10O28]6− + 12 H2O
In decavanadate, each V(V) center is surrounded by six oxide ligands.[16] Vanadic acid, H3VO4 exists only at very low concentrations because protonation of the tetrahedral species [H2VO4]− results in the preferential formation of the octahedral [VO2(H2O)4]+ species. In strongly acidic solutions, pH < 2, [VO2(H2O)4]+ is the predominant species, while the oxide V2O5 precipitates from solution at high concentrations. The oxide is formally the acid anhydride of vanadic acid. The structures of many vanadate compounds have been determined by X-ray crystallography.
The Pourbaix diagram for vanadium in water, which shows the redox potentials between various vanadium species in different oxidation states.[25]
Vanadium(V) forms various peroxo complexes, most notably in the active site of the vanadium-containing bromoperoxidase enzymes. The species VO(O)2(H2O)4+ is stable in acidic solutions. In alkaline solutions, species with 2, 3 and 4 peroxide groups are known; the last forms violet salts with the formula M3V(O2)4 nH2O (M= Li, Na, etc.), in which the vanadium has an 8-coordinate dodecahedral structure.[26][27]
Halide derivatives[edit]
Twelve binary halides, compounds with the formula VXn (n=2..5), are known. VI4, VCl5, VBr5, and VI5 do not exist or are extremely unstable. In combination with other reagents, VCl4 is used as a catalyst for polymerization of dienes. Like all binary halides, those of vanadium are Lewis acidic, especially those of V(IV) and V(V). Many of the halides form octahedral complexes with the formula VXnL6−n (X= halide; L= other ligand).
Many vanadium oxyhalides (formula VOmXn) are known.[28] The oxytrichloride and oxytrifluoride (VOCl3 and VOF3) are the most widely studied. Akin to POCl3, they are volatile, adopt tetrahedral structures in the gas phase, and are Lewis acidic.
Coordination compounds[edit]
Complexes of vanadium(II) and (III) are relatively exchange inert and reducing. Those of V(IV) and V(V) are oxidants. The vanadium ion is rather large and some complexes achieve coordination numbers greater than 6, as is the case in [V(CN)7]4−. Oxovanadium(V) also forms 7 coordinate coordination complexes with tetradentate ligands and peroxides and these complexes are used for oxidative brominations and thioether oxidations. The coordination chemistry of V4+ is dominated by the vanadyl center, VO2+, which binds four other ligands strongly and one weakly (the one trans to the vanadyl center). An example is vanadyl acetylacetonate (V(O)(O2C5H7)2). In this complex, the vanadium is 5-coordinate, distorted square pyramidal, meaning that a sixth ligand, such as pyridine, may be attached, though the association constant of this process is small. Many 5-coordinate vanadyl complexes have a trigonal bipyramidal geometry, such as VOCl2(NMe3)2.[29] The coordination chemistry of V5+ is dominated by the relatively stable dioxovanadium coordination complexes which are often formed by aerial oxidation of the vanadium(IV) precursors indicating the stability of the +5 oxidation state and ease of interconversion between the +4 and +5 states.
Organometallic compounds[edit]
Organometallic chemistry of vanadium is well developed. Vanadocene dichloride is a versatile starting reagent and has applications in organic chemistry.[30] Vanadium carbonyl, V(CO)6, is a rare example of a paramagnetic metal carbonyl. Reduction yields V(CO)−
6 (isoelectronic with Cr(CO)6), which may be further reduced with sodium in liquid ammonia to yield V(CO)3−
5 (isoelectronic with Fe(CO)5).[31][32]
Occurrence[edit]
Universe[edit]
The cosmic abundance of vanadium in the universe is 0.0001%, making the element nearly as common as copper or zinc.[33] Vanadium is detected spectroscopically in light from the Sun and sometimes in the light from other stars.[34]
Earth’s crust[edit]
Vanadium is the 20th most abundant element in the earth’s crust;[35] metallic vanadium is rare in nature (known as native vanadium),[36][37] but vanadium compounds occur naturally in about 65 different minerals.
At the beginning of the 20th century a large deposit of vanadium ore was discovered, the Minas Ragra vanadium mine near Junín, Cerro de Pasco, Peru.[38][39][40] For several years this patrónite (VS4)[41] deposit was an economically significant source for vanadium ore. In 1920 roughly two thirds of the worldwide production was supplied by the mine in Peru.[42] With the production of uranium in the 1910s and 1920s from carnotite (K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O) vanadium became available as a side product of uranium production. Vanadinite (Pb5(VO4)3Cl) and other vanadium bearing minerals are only mined in exceptional cases. With the rising demand, much of the world’s vanadium production is now sourced from vanadium-bearing magnetite found in ultramafic gabbro bodies. If this titanomagnetite is used to produce iron, most of the vanadium goes to the slag, and is extracted from it.[43][44]
Vanadium is mined mostly in South Africa, north-western China, and eastern Russia. In 2013 these three countries mined more than 97% of the 79,000 tonnes of produced vanadium.[45]
Vanadium is also present in bauxite and in deposits of crude oil, coal, oil shale, and tar sands. In crude oil, concentrations up to 1200 ppm have been reported. When such oil products are burned, traces of vanadium may cause corrosion in engines and boilers.[46] An estimated 110,000 tonnes of vanadium per year are released into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels.[47] Black shales are also a potential source of vanadium. During WW II some vanadium was extracted from alum shales in the south of Sweden.[48]
Water[edit]
The vanadyl ion is abundant in seawater, having an average concentration of 30 nM (1.5 mg/m3).[33] Some mineral water springs also contain the ion in high concentrations. For example, springs near Mount Fuji contain as much as 54 μg per liter.[33]
Production[edit]
Vacuum sublimed vanadium dendritic crystals (99.9%)
Vanadium crystals (99.9%) made by electrolysis
An etched piece of vanadium
Vanadium metal is obtained by a multistep process that begins with roasting crushed ore with NaCl or Na2CO3 at about 850 °C to give sodium metavanadate (NaVO3). An aqueous extract of this solid is acidified to produce «red cake», a polyvanadate salt, which is reduced with calcium metal. As an alternative for small-scale production, vanadium pentoxide is reduced with hydrogen or magnesium. Many other methods are also used, in all of which vanadium is produced as a byproduct of other processes.[49] Purification of vanadium is possible by the crystal bar process developed by Anton Eduard van Arkel and Jan Hendrik de Boer in 1925. It involves the formation of the metal iodide, in this example vanadium(III) iodide, and the subsequent decomposition to yield pure metal:[50]
- 2 V + 3 I2 ⇌ 2 VI3
Most vanadium is used as a steel alloy called ferrovanadium. Ferrovanadium is produced directly by reducing a mixture of vanadium oxide, iron oxides and iron in an electric furnace. The vanadium ends up in pig iron produced from vanadium-bearing magnetite. Depending on the ore used, the slag contains up to 25% of vanadium.[49]
China is the world’s largest producer of vanadium.[51]
Applications[edit]
Tool made from vanadium steel
Alloys[edit]
Approximately 85% of the vanadium produced is used as ferrovanadium or as a steel additive.[49] The considerable increase of strength in steel containing small amounts of vanadium was discovered in the early 20th century. Vanadium forms stable nitrides and carbides, resulting in a significant increase in the strength of steel.[52] From that time on, vanadium steel was used for applications in axles, bicycle frames, crankshafts, gears, and other critical components. There are two groups of vanadium steel alloys. Vanadium high-carbon steel alloys contain 0.15% to 0.25% vanadium, and high-speed tool steels (HSS) have a vanadium content of 1% to 5%. For high-speed tool steels, a hardness above HRC 60 can be achieved. HSS steel is used in surgical instruments and tools.[53] Powder-metallurgic alloys contain up to 18% percent vanadium. The high content of vanadium carbides in those alloys increases wear resistance significantly. One application for those alloys is tools and knives.[54]
Vanadium stabilizes the beta form of titanium and increases the strength and temperature stability of titanium. Mixed with aluminium in titanium alloys, it is used in jet engines, high-speed airframes and dental implants. The most common alloy for seamless tubing is Titanium 3/2.5 containing 2.5% vanadium, the titanium alloy of choice in the aerospace, defense, and bicycle industries.[55] Another common alloy, primarily produced in sheets, is Titanium 6AL-4V, a titanium alloy with 6% aluminium and 4% vanadium.[56]
Several vanadium alloys show superconducting behavior. The first A15 phase superconductor was a vanadium compound, V3Si, which was discovered in 1952.[57] Vanadium-gallium tape is used in superconducting magnets (17.5 teslas or 175,000 gauss). The structure of the superconducting A15 phase of V3Ga is similar to that of the more common Nb3Sn and Nb3Ti.[58]
It has been found that a small amount, 40 to 270 ppm, of vanadium in Wootz steel significantly improved the strength of the product, and gave it the distinctive patterning. The source of the vanadium in the original Wootz steel ingots remains unknown.[59]
Vanadium can be used as a substitute for molybdenum in armor steel, though the alloy produced is far more brittle and prone to spalling on non-penetrating impacts.[60] The Third Reich was one of the most prominent users of such alloys, in armored vehicles like Tiger II or Jagdtiger.[61]
Catalysts[edit]
Vanadium compounds are used extensively as catalysts;[62] Vanadium pentoxide V2O5, is used as a catalyst in manufacturing sulfuric acid by the contact process[63] In this process sulfur dioxide (SO
2) is oxidized to the trioxide (SO
3):[16] In this redox reaction, sulfur is oxidized from +4 to +6, and vanadium is reduced from +5 to +4:
- V2O5 + SO2 → 2 VO2 + SO3
The catalyst is regenerated by oxidation with air:
- 4 VO2 + O2 → 2 V2O5
Similar oxidations are used in the production of maleic anhydride:
- C4H10 + 3.5 O2 → C4H2O3 + 4 H2O
Phthalic anhydride and several other bulk organic compounds are produced similarly. These green chemistry processes convert inexpensive feedstocks to highly functionalized, versatile intermediates.[64][65]
Vanadium is an important component of mixed metal oxide catalysts used in the oxidation of propane and propylene to acrolein, acrylic acid or the ammoxidation of propylene to acrylonitrile.[66]
Other uses[edit]
The vanadium redox battery, a type of flow battery, is an electrochemical cell consisting of aqueous vanadium ions in different oxidation states.[67][68] Batteries of the type were first proposed in the 1930s and developed commercially from the 1980s onwards. Cells use +5 and +2 formal oxidization state ions.
Vanadium redox batteries are used commercially for grid energy storage.
Vanadate can be used for protecting steel against rust and corrosion by conversion coating.[69] Vanadium foil is used in cladding titanium to steel because it is compatible with both iron and titanium.[70] The moderate thermal neutron-capture cross-section and the short half-life of the isotopes produced by neutron capture makes vanadium a suitable material for the inner structure of a fusion reactor.[71][72]
Proposed[edit]
Lithium vanadium oxide has been proposed for use as a high energy density anode for lithium ion batteries, at 745 Wh/L when paired with a lithium cobalt oxide cathode.[73] Vanadium phosphates have been proposed as the cathode in the lithium vanadium phosphate battery, another type of lithium-ion battery.[74]
Biological role[edit]
Vanadium is more important in marine environments than terrestrial.[75]
Vanadoenzymes[edit]
A number of species of marine algae produce vanadium bromoperoxidase as well as the closely related chloroperoxidase (which may use a heme or vanadium cofactor) and iodoperoxidases. The bromoperoxidase produces an estimated 1–2 million tons of bromoform and 56,000 tons of bromomethane annually.[76] Most naturally occurring organobromine compounds are produced by this enzyme,[77] catalyzing the following reaction (R-H is hydrocarbon substrate):
- R-H + Br− + H2O2 → R-Br + H2O + OH−
A vanadium nitrogenase is used by some nitrogen-fixing micro-organisms, such as Azotobacter. In this role, vanadium serves in place of the more common molybdenum or iron, and gives the nitrogenase slightly different properties.[78]
Vanadium accumulation in tunicates[edit]
Vanadium is essential to tunicates, where it is stored in the highly acidified vacuoles of certain blood cell types, designated vanadocytes. Vanabins (vanadium binding proteins) have been identified in the cytoplasm of such cells. The concentration of vanadium in the blood of ascidian tunicates is as much as ten million times higher[specify][79][80] than the surrounding seawater, which normally contains 1 to 2 µg/L.[81][82] The function of this vanadium concentration system and these vanadium-bearing proteins is still unknown, but the vanadocytes are later deposited just under the outer surface of the tunic, where they may deter predation.[83]
Fungi[edit]
Amanita muscaria and related species of macrofungi accumulate vanadium (up to 500 mg/kg in dry weight). Vanadium is present in the coordination complex amavadin[84] in fungal fruit-bodies. The biological importance of the accumulation is unknown.[85][86] Toxic or peroxidase enzyme functions have been suggested.[87]
Mammals[edit]
Deficiencies in vanadium result in reduced growth in rats.[88] The U.S. Institute of Medicine has not confirmed that vanadium is an essential nutrient for humans, so neither a Recommended Dietary Intake nor an Adequate Intake have been established. Dietary intake is estimated at 6 to 18 µg/day, with less than 5% absorbed. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) of dietary vanadium, beyond which adverse effects may occur, is set at 1.8 mg/day.[89]
Research[edit]
Vanadyl sulfate as a dietary supplement has been researched as a means of increasing insulin sensitivity or otherwise improving glycemic control in people who are diabetic. Some of the trials had significant treatment effects, but were deemed as being of poor study quality. The amounts of vanadium used in these trials (30 to 150 mg) far exceeded the safe upper limit.[90][91] The conclusion of the systemic review was «There is no rigorous evidence that oral vanadium supplementation improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes. The routine use of vanadium for this purpose cannot be recommended.»[90]
In astrobiology, it has been suggested that discrete vanadium accumulations on Mars could be a potential microbial biosignature, when used in conjunction with Raman spectroscopy and morphology.[92][93]
Safety[edit]
All vanadium compounds should be considered toxic.[94] Tetravalent VOSO4 has been reported to be at least 5 times more toxic than trivalent V2O3.[95] The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set an exposure limit of 0.05 mg/m3 for vanadium pentoxide dust and 0.1 mg/m3 for vanadium pentoxide fumes in workplace air for an 8-hour workday, 40-hour work week.[96] The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has recommended that 35 mg/m3 of vanadium be considered immediately dangerous to life and health, that is, likely to cause permanent health problems or death.[96]
Vanadium compounds are poorly absorbed through the gastrointestinal system. Inhalation of vanadium and vanadium compounds results primarily in adverse effects on the respiratory system.[97][98][99] Quantitative data are, however, insufficient to derive a subchronic or chronic inhalation reference dose. Other effects have been reported after oral or inhalation exposures on blood parameters,[100][101] liver,[102] neurological development,[103] and other organs[104] in rats.
There is little evidence that vanadium or vanadium compounds are reproductive toxins or teratogens. Vanadium pentoxide was reported to be carcinogenic in male rats and in male and female mice by inhalation in an NTP study,[98] although the interpretation of the results has recently been disputed.[105] The carcinogenicity of vanadium has not been determined by the United States Environmental Protection Agency.[106]
Vanadium traces in diesel fuels are the main fuel component in high temperature corrosion. During combustion, vanadium oxidizes and reacts with sodium and sulfur, yielding vanadate compounds with melting points as low as 530 °C, which attack the passivation layer on steel and render it susceptible to corrosion. The solid vanadium compounds also abrade engine components.[107][108]
See also[edit]
- Flow battery
- Green Giant mine
- Grid energy storage
- Vanadium carbide
- Vanadium redox battery
- Vanadium tetrachloride
- Vanadium(V) oxide
- International Vanadium Symposium
- The Vanadium Cycle
References[edit]
- ^ «Standard Atomic Weights: Vanadium». CIAAW. 1977.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ «Vanadium». Royal Society of Chemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ Cintas, Pedro (2004). «The Road to Chemical Names and Eponyms: Discovery, Priority, and Credit». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 43 (44): 5888–94. doi:10.1002/anie.200330074. PMID 15376297.
- ^ a b Sefström, N. G. (1831). «Ueber das Vanadin, ein neues Metall, gefunden im Stangeneisen von Eckersholm, einer Eisenhütte, die ihr Erz von Taberg in Småland bezieht». Annalen der Physik und Chemie. 97 (1): 43–49. Bibcode:1831AnP….97…43S. doi:10.1002/andp.18310970103.
- ^ Featherstonhaugh, George William (1831). «New Metal, provisionally called Vanadium». The Monthly American Journal of Geology and Natural Science: 69.
- ^ Roscoe, Henry E. (1869–1870). «Researches on Vanadium. Part II». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 18 (114–122): 37–42. doi:10.1098/rspl.1869.0012.
- ^ Marden, J. W.; Rich, M. N. (1927). «Vanadium». Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 19 (7): 786–788. doi:10.1021/ie50211a012.
- ^ Betz, Frederick (2003). Managing Technological Innovation: Competitive Advantage from Change. Wiley-IEEE. pp. 158–159. ISBN 978-0-471-22563-8.
- ^ Phillip Maxwell Busch (1961). Vanadium: A Materials Survey. U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines.
- ^ Wise, James M. (May 2018). «Remarkable folded dacitic dikes at Mina Ragra, Peru».
- ^ Henze, M. (1911). «Untersuchungen über das Blut der Ascidien. I. Mitteilung». Z. Physiol. Chem. 72 (5–6): 494–50. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1911.72.5-6.494.
- ^ Michibata, H.; Uyama, T.; Ueki, T.; Kanamori, K. (2002). «Vanadocytes, cells hold the key to resolving the highly selective accumulation and reduction of vanadium in ascidians» (PDF). Microscopy Research and Technique. 56 (6): 421–434. doi:10.1002/jemt.10042. PMID 11921344. S2CID 15127292.
- ^ George F. Vander Voort (1984). Metallography, principles and practice. ASM International. pp. 137–. ISBN 978-0-87170-672-0. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Cardarelli, François (2008). Materials handbook: a concise desktop reference. Springer. pp. 338–. ISBN 978-1-84628-668-1. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1985). «Vanadium». Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1071–1075. ISBN 978-3-11-007511-3.
- ^ a b Rehder, D.; Polenova, T.; Bühl, M. (2007). Vanadium-51 NMR. Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy. Vol. 62. pp. 49–114. doi:10.1016/S0066-4103(07)62002-X. ISBN 9780123739193.
- ^ Audi, Georges; Bersillon, Olivier; Blachot, Jean; Wapstra, Aaldert Hendrik (2003), «The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties», Nuclear Physics A, 729: 3–128, Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729….3A, doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 984. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Sinning, Irmgard; Hol, Wim G. J. (2004). «The power of vanadate in crystallographic investigations of phosphoryl transfer enzymes». FEBS Letters. 577 (3): 315–21. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.10.022. PMID 15556602. S2CID 8328704.
- ^ Seargeant, Lorne E.; Stinson, Robert A. (1979). «Inhibition of human alkaline phosphatases by vanadate». Biochemical Journal. 181 (1): 247–50. doi:10.1042/bj1810247. PMC 1161148. PMID 486156.
- ^ Crans, Debbie C.; Simone, Carmen M. (9 July 1991). «Nonreductive interaction of vanadate with an enzyme containing a thiol group in the active site: glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase». Biochemistry. 30 (27): 6734–6741. doi:10.1021/bi00241a015. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 2065057.
- ^ Karlish, S. J. D.; Beaugé, L. A.; Glynn, I. M. (November 1979). «Vanadate inhibits (Na+ + K+)ATPase by blocking a conformational change of the unphosphorylated form». Nature. 282 (5736): 333–335. Bibcode:1979Natur.282..333K. doi:10.1038/282333a0. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 228199. S2CID 4341480.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 988. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Al-Kharafi, F. M.; Badawy, W. A. (1997). «Electrochemical behavior of vanadium in aqueous solutions of different pH». Electrochimica Acta. 42 (4): 579–586. doi:10.1016/S0013-4686(96)00202-2.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8., p994.
- ^ Strukul, Giorgio (1992). Catalytic oxidations with hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. Springer. p. 128. ISBN 978-0-7923-1771-5.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 993. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Wilkinson, G. & Birmingham, J.G. (1954). «Bis-cyclopentadienyl Compounds of Ti, Zr, V, Nb and Ta». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (17): 4281–4284. doi:10.1021/ja01646a008.
- ^ Bellard, S.; Rubinson, K. A.; Sheldrick, G. M. (1979). «Crystal and molecular structure of vanadium hexacarbonyl» (PDF). Acta Crystallographica. B35 (2): 271–274. doi:10.1107/S0567740879003332. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- ^ Elschenbroich, C.; Salzer A. (1992). Organometallics: A Concise Introduction. Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3-527-28165-7.
- ^ a b c Rehder, Dieter (2008). Bioinorganic Vanadium Chemistry. Inorganic Chemistry (1st ed.). Hamburg, Germany: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 5 & 9–10. doi:10.1002/9780470994429. ISBN 9780470065099.
- ^ Cowley, C. R.; Elste, G. H.; Urbanski, J. L. (1978). «Vanadium abundances in early A stars». Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 90: 536. Bibcode:1978PASP…90..536C. doi:10.1086/130379.
- ^ Proceedings. National Cotton Council of America. 1991.
- ^ Ostrooumov, M., and Taran, Y., 2015. Discovery of Native Vanadium, a New Mineral from the Colima Volcano, State of Colima (Mexico). Revista de la Sociedad Española de Mineralogía 20, 109-110
- ^ «Vanadium: Vanadium mineral information and data». Mindat.org. Retrieved 2 March 2016.
- ^ Hillebrand, W. F. (1907). «The Vanadium Sulphide, Patronite, and ITS Mineral Associates from Minasragra, Peru». Journal of the American Chemical Society. 29 (7): 1019–1029. doi:10.1021/ja01961a006.
- ^ Hewett, F. (1906). «A New Occurrence of Vanadium in Peru». The Engineering and Mining Journal. 82 (9): 385.
- ^ Steinberg, W.S.; Geyser, W.; Nell, J. «The history and development of the pyrometallurgical processes at Evraz Highveld Steel & Vanadium» (PDF).
- ^ «mineralogical data about Patrónite». mindata.org. Retrieved 19 January 2009.
- ^ Allen, M. A.; Butler, G. M. (1921). «Vanadium» (PDF). University of Arizona. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- ^ Hukkanen, E.; Walden, H. (1985). «The production of vanadium and steel from titanomagnetites». International Journal of Mineral Processing. 15 (1–2): 89–102. doi:10.1016/0301-7516(85)90026-2.
- ^ Steinberg, W.S.; Geyser, W.; Nell, J. «The history and development of the pyrometallurgical processes at Evraz Highveld Steel & Vanadium» (PDF).
- ^ Magyar, Michael J. «Mineral Commodity Summaries 2015: Vanadium» (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ Pearson, C. D.; Green J. B. (1993). «Vanadium and nickel complexes in petroleum resid acid, base, and neutral fractions». Energy Fuels. 7 (3): 338–346. doi:10.1021/ef00039a001.
- ^ Anke, Manfred (2004). «Vanadium – An element both essential and toxic to plants, animals and humans?». Anal. Real Acad. Nac. Farm. 70: 961.
- ^ Dyni, John R. (2006). «Geology and resources of some world oil-shale deposits». Scientific Investigations Report. p. 22. doi:10.3133/sir29955294. S2CID 19814608.
- ^ a b c Moskalyk, R. R.; Alfantazi, A. M. (2003). «Processing of vanadium: a review». Minerals Engineering. 16 (9): 793–805. doi:10.1016/S0892-6875(03)00213-9.
- ^ Carlson, O. N.; Owen, C. V. (1961). «Preparation of High-Purity Vanadium Metals by the Iodide Refining Process». Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 108: 88. doi:10.1149/1.2428019.
- ^ USGS Vanadinum Production Statistics[permanent dead link]
- ^ Chandler, Harry (1998). Metallurgy for the Non-metallurgist. ASM International. pp. 6–7. ISBN 978-0-87170-652-2.
- ^ Davis, Joseph R. (1995). Tool Materials: Tool Materials. ASM International. ISBN 978-0-87170-545-7.
- ^ Oleg D. Neikov; Naboychenko, Stanislav; Mourachova, Irina; Victor G. Gopienko; Irina V. Frishberg; Dina V. Lotsko (24 February 2009). Handbook of Non-Ferrous Metal Powders: Technologies and Applications. p. 490. ISBN 9780080559407. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- ^ «Technical Supplement: Titanium». Seven Cycles. Archived from the original on 3 November 2016. Retrieved 1 November 2016.
- ^ Peters, Manfred; Leyens, C. (2002). «Metastabile β-Legierungen». Titan und Titanlegierungen. Wiley-VCH. pp. 23–24. ISBN 978-3-527-30539-1.
- ^ Hardy, George F.; Hulm, John K. (1953). «Superconducting Silicides and Germanides». Physical Review. 89 (4): 884. Bibcode:1953PhRv…89Q.884H. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.89.884.
- ^ Markiewicz, W.; Mains, E.; Vankeuren, R.; Wilcox, R.; Rosner, C.; Inoue, H.; Hayashi, C.; Tachikawa, K. (1977). «A 17.5 Tesla superconducting concentric Nb3Sn and V3Ga magnet system». IEEE Transactions on Magnetics. 13 (1): 35–37. Bibcode:1977ITM….13…35M. doi:10.1109/TMAG.1977.1059431.
- ^ Verhoeven, J. D.; Pendray, A. H.; Dauksch, W. E. (1998). «The key role of impurities in ancient damascus steel blades». Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society. 50 (9): 58–64. Bibcode:1998JOM….50i..58V. doi:10.1007/s11837-998-0419-y. S2CID 135854276.
- ^ Rohrmann, B. «Vanadium in South Africa (Metal Review Series no. 2)». hdl:10520/AJA0038223X_1959.
- ^ Overy, R. (1973). Transportation and Rearmament in the Third Reich. The Historical Journal, 16(2), 389-409. doi:10.1017/S0018246X00005926
- ^ Langeslay, Ryan R.; Kaphan, David M.; Marshall, Christopher L.; Stair, Peter C.; Sattelberger, Alfred P.; Delferro, Massimiliano (8 October 2018). «Catalytic Applications of Vanadium: A Mechanistic Perspective». Chemical Reviews. 119 (4): 2128–2191. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00245. OSTI 1509906. PMID 30296048. S2CID 52943647.
- ^ Eriksen, K. M.; Karydis, D. A.; Boghosian, S.; Fehrmann, R. (1995). «Deactivation and Compound Formation in Sulfuric-Acid Catalysts and Model Systems». Journal of Catalysis. 155 (1): 32–42. doi:10.1006/jcat.1995.1185.
- ^ Bauer, Günter; Güther, Volker; Hess, Hans; Otto, Andreas; Roidl, Oskar; Roller, Heinz; Sattelberger, Siegfried (2000). «Vanadium and Vanadium Compounds». Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_367.
- ^ Abon, Michel; Volta, Jean-Claude (1997). «Vanadium phosphorus oxides for n-butane oxidation to maleic anhydride». Applied Catalysis A: General. 157 (1–2): 173–193. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(97)00016-1.
- ^ Fierro, J. G. L., ed. (2006). Metal Oxides, Chemistry and Applications. CRC Press. pp. 415–455. ISBN 9780824723712.
- ^ Joerissen, Ludwig; Garche, Juergen; Fabjan, Ch.; Tomazic G. (2004). «Possible use of vanadium redox-flow batteries for energy storage in small grids and stand-alone photovoltaic systems». Journal of Power Sources. 127 (1–2): 98–104. Bibcode:2004JPS…127…98J. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2003.09.066.
- ^ Rychcik, M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. (1988). «Characteristics of a new all-vanadium redox flow battery». Journal of Power Sources. 22 (1): 59–67. Bibcode:1988JPS….22…59R. doi:10.1016/0378-7753(88)80005-3. ISSN 0378-7753.
- ^ Guan, H.; Buchheit R. G. (2004). «Corrosion Protection of Aluminum Alloy 2024-T3 by Vanadate Conversion Coatings». Corrosion. 60 (3): 284–296. doi:10.5006/1.3287733.
- ^ Lositskii, N. T.; Grigor’ev A. A.; Khitrova, G. V. (1966). «Welding of chemical equipment made from two-layer sheet with titanium protective layer (review of foreign literature)». Chemical and Petroleum Engineering. 2 (12): 854–856. doi:10.1007/BF01146317. S2CID 108903737.
- ^ Matsui, H.; Fukumoto, K.; Smith, D. L.; Chung, Hee M.; Witzenburg, W. van; Votinov, S. N. (1996). «Status of vanadium alloys for fusion reactors». Journal of Nuclear Materials. 233–237 (1): 92–99. Bibcode:1996JNuM..233…92M. doi:10.1016/S0022-3115(96)00331-5.
- ^ «Vanadium Data Sheet» (PDF). ATI Wah Chang. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 February 2009. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
- ^ Kariatsumari, Koji (February 2008). «Li-Ion Rechargeable Batteries Made Safer». Nikkei Business Publications, Inc. Archived from the original on 12 September 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2008.
- ^ Saıdi, M.Y.; Barker, J.; Huang, H.; Swoyer, J.L.; Adamson, G. (1 June 2003), «Performance characteristics of lithium vanadium phosphate as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries», Journal of Power Sources, 119–121: 266–272, Bibcode:2003JPS…119..266S, doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00245-3 Selected papers presented at the 11th International Meeting on Lithium Batteries
- ^ Sigel, Astrid; Sigel, Helmut, eds. (1995). Vanadium and Its Role in Life. Metal Ions in Biological Systems. Vol. 31. CRC. ISBN 978-0-8247-9383-8.
- ^ Gribble, Gordon W. (1999). «The diversity of naturally occurring organobromine compounds». Chemical Society Reviews. 28 (5): 335–346. doi:10.1039/a900201d.
- ^ Butler, Alison; Carter-Franklin, Jayme N. (2004). «The role of vanadium bromoperoxidase in the biosynthesis of halogenated marine natural products». Natural Product Reports. 21 (1): 180–8. doi:10.1039/b302337k. PMID 15039842. S2CID 19115256.
- ^ Robson, R. L.; Eady, R. R.; Richardson, T. H.; Miller, R. W.; Hawkins, M.; Postgate, J. R. (1986). «The alternative nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum is a vanadium enzyme». Nature. 322 (6077): 388–390. Bibcode:1986Natur.322..388R. doi:10.1038/322388a0. S2CID 4368841.
- ^ Smith, M. J. (1989). «Vanadium biochemistry: The unknown role of vanadium-containing cells in ascidians (sea squirts)». Experientia. 45 (5): 452–7. doi:10.1007/BF01952027. PMID 2656286. S2CID 43534732.
- ^ MacAra, Ian G.; McLeod, G. C.; Kustin, Kenneth (1979). «Tunichromes and metal ion accumulation in tunicate blood cells». Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B. 63 (3): 299–302. doi:10.1016/0305-0491(79)90252-9.
- ^ Trefry, John H.; Metz, Simone (1989). «Role of hydrothermal precipitates in the geochemical cycling of vanadium». Nature. 342 (6249): 531–533. Bibcode:1989Natur.342..531T. doi:10.1038/342531a0. S2CID 4351410.
- ^ Weiss, H.; Guttman, M. A.; Korkisch, J.; Steffan, I. (1977). «Comparison of methods for the determination of vanadium in sea-water». Talanta. 24 (8): 509–11. doi:10.1016/0039-9140(77)80035-0. PMID 18962130.
- ^ Ruppert, Edward E.; Fox, Richard, S.; Barnes, Robert D. (2004). Invertebrate Zoology (7th ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 947. ISBN 978-81-315-0104-7.
- ^ Kneifel, Helmut; Bayer, Ernst (1997). «Determination of the Structure of the Vanadium Compound, Amavadine, from Fly Agaric». Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 12 (6): 508. doi:10.1002/anie.197305081. ISSN 0570-0833.
- ^ Falandysz, J.; Kunito, T.; Kubota, R.; Lipka, K.; Mazur, A.; Falandysz, Justyna J.; Tanabe, S. (2007). «Selected elements in fly agaric Amanita muscaria». Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A. 42 (11): 1615–1623. doi:10.1080/10934520701517853. PMID 17849303. S2CID 26185534.
- ^ Berry, Robert E.; Armstrong, Elaine M.; Beddoes, Roy L.; Collison, David; Ertok, Nigar; Helliwell, Madeleine; Garner, David (1999). «The Structural Characterization of Amavadin». Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 38 (6): 795–797. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990315)38:6<795::AID-ANIE795>3.0.CO;2-7. PMID 29711812.
- ^ da Silva, José A.L.; Fraústo da Silva, João J.R.; Pombeiro, Armando J.L. (2013). «Amavadin, a vanadium natural complex: Its role and applications». Coordination Chemistry Reviews. Elsevier BV. 257 (15–16): 2388–2400. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2013.03.010. ISSN 0010-8545.
- ^ Schwarz, Klaus; Milne, David B. (1971). «Growth Effects of Vanadium in the Rat». Science. 174 (4007): 426–428. Bibcode:1971Sci…174..426S. doi:10.1126/science.174.4007.426. JSTOR 1731776. PMID 5112000. S2CID 24362265.
- ^ Nickel. IN: Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Copper. National Academy Press. 2001, PP. 532–543.
- ^ a b Smith DM, Pickering RM, Lewith GT (2008). «A systematic review of vanadium oral supplements for glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus». QJM. 101 (5): 351–8. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcn003. PMID 18319296.
- ^ «Vanadium (vanadyl sulfate). Monograph». Altern Med Rev. 14 (2): 177–80. 2009. PMID 19594227.
- ^ Lynch, Brendan M. (21 September 2017). «Hope to discover sure signs of life on Mars? New research says look for the element vanadium». PhysOrg. Retrieved 14 October 2017.
- ^ Marshall, C. P; Olcott Marshall, A; Aitken, J. B; Lai, B; Vogt, S; Breuer, P; Steemans, P; Lay, P. A (2017). «Imaging of Vanadium in Microfossils: A New Potential Biosignature». Astrobiology. 17 (11): 1069–1076. Bibcode:2017AsBio..17.1069M. doi:10.1089/ast.2017.1709. OSTI 1436103. PMID 28910135.
- ^ Srivastava, A.K. Anti-diabetic and toxic effects of vanadium compounds. Mol Cell Biochem 206, 177–182 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007075204494
- ^ Roschin, A. V. (1967). «Toxicology of vanadium compounds used in modern industry». Gig Sanit. (Water Res.). 32 (6): 26–32. PMID 5605589.
- ^ a b «Occupational Safety and Health Guidelines for Vanadium Pentoxide». Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Archived from the original on 6 January 2009. Retrieved 29 January 2009.
- ^ Sax, N. I. (1984). Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials (6th ed.). Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. pp. 2717–2720.
- ^ a b Ress, N. B.; et al. (2003). «Carcinogenicity of inhaled vanadium pentoxide in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice». Toxicological Sciences. 74 (2): 287–296. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfg136. PMID 12773761.
- ^ Wörle-Knirsch, Jörg M.; Kern, Katrin; Schleh, Carsten; Adelhelm, Christel; Feldmann, Claus & Krug, Harald F. (2007). «Nanoparticulate Vanadium Oxide Potentiated Vanadium Toxicity in Human Lung Cells». Environ. Sci. Technol. 41 (1): 331–336. Bibcode:2007EnST…41..331W. doi:10.1021/es061140x. PMID 17265967.
- ^ Ścibior, A.; Zaporowska, H.; Ostrowski, J. (2006). «Selected haematological and biochemical parameters of blood in rats after subchronic administration of vanadium and/or magnesium in drinking water». Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 51 (2): 287–295. doi:10.1007/s00244-005-0126-4. PMID 16783625. S2CID 43805930.
- ^ Gonzalez-Villalva, A.; et al. (2006). «Thrombocytosis induced in mice after subacute and subchronic V2O5 inhalation». Toxicology and Industrial Health. 22 (3): 113–116. doi:10.1191/0748233706th250oa. PMID 16716040. S2CID 9986509.
- ^ Kobayashi, Kazuo; Himeno, Seiichiro; Satoh, Masahiko; Kuroda, Junji; Shibata, Nobuo; Seko, Yoshiyuki; Hasegawa, Tatsuya (2006). «Pentavalent vanadium induces hepatic metallothionein through interleukin-6-dependent and -independent mechanisms». Toxicology. 228 (2–3): 162–170. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2006.08.022. PMID 16987576.
- ^ Soazo, Marina; Garcia, Graciela Beatriz (2007). «Vanadium exposure through lactation produces behavioral alterations and CNS myelin deficit in neonatal rats». Neurotoxicology and Teratology. 29 (4): 503–510. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2007.03.001. PMID 17493788.
- ^ Barceloux, Donald G.; Barceloux, Donald (1999). «Vanadium». Clinical Toxicology. 37 (2): 265–278. doi:10.1081/CLT-100102425. PMID 10382561.
- ^ Duffus, J. H. (2007). «Carcinogenicity classification of vanadium pentoxide and inorganic vanadium compounds, the NTP study of carcinogenicity of inhaled vanadium pentoxide, and vanadium chemistry». Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 47 (1): 110–114. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2006.08.006. PMID 17030368.
- ^ Opreskos, Dennis M. (1991). «Toxicity Summary for Vanadium». Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Retrieved 8 November 2008.
- ^ Woodyard, Doug (18 August 2009). Pounder’s Marine Diesel Engines and Gas Turbines. p. 92. ISBN 9780080943619.
- ^ Totten, George E.; Westbrook, Steven R.; Shah, Rajesh J. (1 June 2003). Fuels and Lubricants Handbook: Technology, Properties, Performance, and Testing. p. 152. ISBN 9780803120969.
Further reading[edit]
- Slebodnick, Carla; et al. (1999). «Modeling the Biological Chemistry of Vanadium: Structural and Reactivity Studies Elucidating Biological Function». In Hill, Hugh A.O.; et al. (eds.). Metal sites in proteins and models: phosphatases, Lewis acids, and vanadium. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-65553-4.
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vanadium.
Look up vanadium in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
- Videos
- Vanadium at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
- Research papers
- ATSDR – ToxFAQs: Vanadium
- Vanadium concentration in seawater and estuary environments is around 1.5-3.3 ug/kg
- Vanadium speciation and cycling in coastal waters
- Ocean anoxia and the concentrations of molybdenum and vanadium in seawater
| Ванадий | |
|---|---|
| Пластичный металл серебристо-белого цвета | |
 |
|
| Название, символ, номер | Ванадий / Vanadium (V), 23 |
| Атомная масса (молярная масса) |
50,9415(1) а. е. м. (г/моль) |
| Электронная конфигурация | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 |
| Радиус атома | 134 пм |
| Ковалентный радиус | 122 пм |
| Радиус иона | (+5e)59 (+3e)74 пм |
| Электроотрицательность | 1,63 (шкала Полинга) |
| Электродный потенциал | 0 |
| Степени окисления | 5, 4, 3, 2, 0 |
| Энергия ионизации (первый электрон) |
650,1 (6,74) кДж/моль (эВ) |
| Плотность (при н. у.) | 6,11 г/см³ |
| Температура плавления | 2160 К (1887 °C) |
| Температура кипения | 3650 К (3377 °C) |
| Уд. теплота плавления | 17,5 кДж/моль |
| Уд. теплота испарения | 460 кДж/моль |
| Молярная теплоёмкость | 24,95 Дж/(K·моль) |
| Молярный объём | 8,35 см³/моль |
| Структура решётки | кубическая объёмноцентрированная |
| Параметры решётки | 3,024 Å |
| Температура Дебая | 390 K |
| Теплопроводность | (300 K) 30,7 Вт/(м·К) |
| Номер CAS | 7440-62-2 |
Ванадий — химический элемент с атомным номером 23. Принадлежит к 5-й группе периодической таблицы химических элементов (по устаревшей короткой форме периодической системы принадлежит к побочной подгруппе V группы, или к группе VB), находится в четвёртом периоде таблицы. Атомная масса элемента 50,9415(1) а. е. м. Обозначается символом V (от лат. Vanadium). Простое вещество ванадий — пластичный металл серебристо-серого цвета.
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Названия
- 3 Нахождение в природе
- 3.1 Месторождения
- 4 Получение
- 5 Физические свойства
- 5.1 Изотопы
- 6 Химические свойства
- 7 Применение
- 8 Производство
- 9 Биологическая роль и воздействие
История
Ванадий был открыт в 1801 году профессором минералогии из Мехико Андресом Мануэлем Дель Рио в свинцовых рудах. Он обнаружил новый металл и предложил для него название «панхромий» из-за широкого диапазона цвета его соединений, сменив затем название на «эритроний». Дель Рио не имел авторитета в научном мире Европы, и европейские химики усомнились в его результатах. Затем и сам Дель Рио потерял уверенность в своём открытии и заявил, что открыл всего лишь хромат свинца.
В 1830 году ванадий был открыт заново шведским химиком Нильсом Сефстрёмом в железной руде. Новому элементу название дали Берцелиус и Сефстрём.
Шанс открыть ванадий был у Фридриха Вёлера, исследовавшего мексиканскую руду, но он серьёзно отравился фтороводородом незадолго до открытия Сефстрёма и не смог продолжить исследования. Однако Вёлер довёл до конца исследование руды и окончательно доказал, что в ней содержится именно ванадий, а не хром.
Названия
Этот элемент образует соединения с красивой окраской, отсюда и название элемента, связанное с именем скандинавской богини любви и красоты Фрейи (др.-сканд. Vanadís — дочь Ванов; Ванадис). В 1831 году геолог Шаблон:Iwq предложил переименовать ванадий в «риониум», но это предложение не было поддержано.
Нахождение в природе
Основная статья: Ванадиевые руды
Ванадий является 20-м наиболее распространённым элементом в земной коре. Он относится к рассеянным элементам и в природе в свободном виде не встречается. Содержание ванадия в земной коре 1,6⋅10−2% по массе, в воде океанов 3⋅10−7%. Наиболее высокие средние содержания ванадия в магматических породах отмечаются в габбро и базальтах (230—290 г/т). В осадочных породах значительное накопление ванадия происходит в биолитах (асфальтитах, углях, битуминозных фосфатах), битуминозных сланцах, бокситах, а также в оолитовых и кремнистых железных рудах. Близость ионных радиусов ванадия и широко распространённых в магматических породах железа и титана приводит к тому, что ванадий в гипогенных процессах целиком находится в рассеянном состоянии и не образует собственных минералов. Его носителями являются многочисленные минералы титана (титаномагнетит, сфен, рутил, ильменит), слюды, пироксены и гранаты, обладающие повышенной изоморфной ёмкостью по отношению к ванадию. Важнейшие минералы: патронит V(S2)2, ванадинит Pb5(VO4)3Cl и некоторые другие. Основной источник получения ванадия — железные руды, содержащие ванадий как примесь.
Ванадил ион () в изобилии находится в морской воде, имеющий среднюю концентрацию 30 нМа. Некоторые источники минеральной воды также содержат ион в высоких концентрациях. Например, источники около горы Фудзи содержат до 54 мкг на литр.
Месторождения
В течение первого десятилетия XX века большая часть ванадиевой руды добывалась американской компанией Vanadium из Минас-Рагра в Перу. Позднее увеличение спроса на уран привело к увеличению добычи руды этого металла. Одной из основных урановых руд был карнотит, который также содержит ванадий. Таким образом, ванадий стал доступным как побочный продукт производства урана. Со временем добыча урана стала обеспечивать большую долю спроса на ванадий.
Известны месторождения в Перу, США, ЮАР, Финляндии, Австралии, Армении, России, Турции, Англии.
Получение
В промышленности при получении ванадия из железных руд с его примесью сначала готовят концентрат, в котором содержание ванадия достигает 8—16 %. Далее окислительной обработкой ванадий переводят в высшую степень окисления +5 и отделяют легко растворимый в воде ванадат натрия (Na) NaVO3. При подкислении раствора серной кислотой выпадает осадок, который после высушивания содержит более 90 % ванадия.
Первичный концентрат восстанавливают в доменных печах и получают концентрат ванадия, который далее используют при выплавке сплава ванадия и железа — так называемого феррованадия (содержит от 35 до 80 % ванадия). Металлический ванадий можно приготовить восстановлением хлорида ванадия водородом (H), термическим восстановлением оксидов ванадия (V2O5 или V2O3) кальцием, термической диссоциацией VI2 и другими методами.
Некоторые из разновидностей асцидий обладают уникальной особенностью: в их крови содержится ванадий. Асцидии поглощают его из воды.
В Японии разводят асцидий на подводных плантациях, собирают урожай, сжигают и получают золу, в которой ванадий содержится в более высокой концентрации, чем в руде многих его месторождений.
Физические свойства
Бруски ванадия 99,95 % чистоты, полученные переплавкой в электронном пучке. Поверхность брусков протравлена для проявления структуры
Ванадий — пластичный металл серебристо-серого цвета, по внешнему виду похож на сталь. Кристаллическая решётка кубическая объёмноцентрированная, a=3,024 Å, z=2, пространственная группа Im3m. Температура плавления 1920 °C, температура кипения 3400 °C, плотность 6,11 г/см³. При нагревании на воздухе выше 300 °C ванадий становится хрупким. Примеси кислорода, водорода и азота резко снижают пластичность ванадия и повышают его твёрдость и хрупкость.
Изотопы
Природный ванадий состоит из двух изотопов: слаборадиоактивного 50V (изотопная распространённость 0,250 %) и стабильного 51V (99,750 %). Период полураспада ванадия-50 равен 1,5⋅1017 лет, то есть для всех практических целей его можно считать стабильным; этот изотоп в 83 % случаев посредством электронного захвата превращается в 50Ti, а в 17 % случаев испытывает бета-минус-распад, превращаясь в 50Cr.
Известны 24 искусственных радиоактивных изотопа ванадия с массовым числом от 40 до 65 (а также 5 метастабильных состояний). Из них наиболее стабильны 49V (T1/2=337 дней) и 48V (T1/2=15,974 дня).
Химические свойства
Химически ванадий довольно инертен. Он имеет хорошую стойкость к коррозии, стоек к действию морской воды, разбавленных растворов соляной, азотной и серной кислот, щелочей.
С кислородом ванадий образует несколько оксидов: VO, V2O3, VO2,V2O5. Оранжевый V2O5 — кислотный оксид, тёмно-синий VO2 — амфотерный, остальные оксиды ванадия — основные.
Известны следующие оксиды ванадия:
| Название | Формула | Плотность | Температура плавления | Температура кипения | Цвет |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оксид ванадия (II) | VO | 5,76 г/см³ | ~1830 °C | 3100 °C | Чёрный |
| Оксид ванадия (III) | V2O3 | 4,87 г/см³ | 1967 °C | 3000 °C | Чёрный |
| Оксид ванадия (IV) | VO2 | 4,65 г/см³ | 1542 °C | 2700 °C | Тёмно-голубой |
| Оксид ванадия (V) | V2O5 | 3,357 г/см³ | 670 °C | 2030 °C | Красно-жёлтый |
Галогениды ванадия гидролизуются. С галогенами ванадий образует довольно летучие галогениды составов VX2 (X = F, Cl, Br, I), VX3, VX4 (X = F, Cl, Br), VF5 и несколько оксогалогенидов (VOCl, VOCl2, VOF3 и др.).
Соединения ванадия в степенях окисления +2 и +3 — сильные восстановители, в степени окисления +5 проявляют свойства окислителей. Известны тугоплавкий карбид ванадия VC (tпл=2800 °C), нитрид ванадия VN, сульфид ванадия V2S5, силицид ванадия V3Si и другие соединения ванадия.
При взаимодействии V2O5 с осно́вными оксидами образуются ванадаты — соли ванадиевой кислоты вероятного состава HVO3.
Взаимодействует с кислотами.
- С концентрированной азотной кислотой:
-
- V + 6HNO3 →t∘ VO2NO3 + 5NO2↑ + 3H2O
Применение
- Водородная энергетика
Хлорид ванадия применяется при термохимическом разложении воды в атомно-водородной энергетике (ванадий-хлоридный цикл «Дженерал Моторс», США).
- Химические источники тока
Пентаоксид ванадия широко применяется в качестве положительного электрода (анода) в мощных литиевых батареях и аккумуляторах. Ванадат серебра в резервных батареях в качестве катода.
- В производстве серной кислоты
Оксид ванадия(V) используется как катализатор на стадии превращения сернистого ангидрида в серный.
- Металлургия
Свыше 90 % всего производимого ванадия находит применение в качестве легирующей добавки в сталях, главным образом, высокопрочных низколегированных, в меньшей степени, нержавеющих и инструментальных, а также в производстве высокопрочных титановых сплавов, основанных на системе Ti-6Al-4V (в российской классификации — ВТ6, содержит около 4 % ванадия). В сталях ванадий образует мелкодисперсные карбиды VC, что повышает механические свойства и стабильность структуры. Его применение особенно эффективно совместно с вольфрамом, молибденом и никелем. В конструкционных сталях содержание ванадия не превышает, как правило, 0,25 %, в инструментальных и быстрорежущих доходит до 4 %. В российской номенклатуре сталей ванадий обозначается буквой Ф.
- Автомобильная промышленность
Ванадий используется в деталях, требующих очень высокой прочности, таких как поршни автомобильных двигателей. Американский промышленник Генри Форд отмечал важную роль ванадия в автомобильной промышленности. «Если бы не было ванадия — не было бы автомобиля». — Говорил Форд. Ванадиевая сталь позволила уменьшить вес при увеличении прочности при растяжении
- Электроника
Материал на основе диоксидов ванадия и титана используют при создании компьютеров и другой электроники.
- Нефтедобыча
Ванадиевая сталь используется при создании погружных буровых платформ для бурения нефтяных скважин.
- Сувенирная продукция
Частные компании США выпускают медали и коллекционные жетоны из чистого ванадия. Одна из ванадиевых медалей вышла в 2011 году.
Производство
- Россия: Евраз Ванадий Тула, Чусовской металлургический завод
- Чехия: Мнишек-под-Брди
- США: Хот-Спрингс
- ЮАР: Бритс
Биологическая роль и воздействие
Ванадий и все его соединения токсичны. Наиболее токсичны соединения пятивалентного ванадия. Чрезвычайно ядовит его оксид(V) (ядовит при попадании внутрь организма и при вдыхании, поражает дыхательную систему). Смертельная доза ЛД50 оксида ванадия(V) для крыс орально составляет 10 мг/кг.
Ванадий и его соединения очень токсичны для водных организмов (окружающей среды).
Установлено, что ванадий может тормозить синтез жирных кислот, подавлять образование холестерина. Ванадий ингибирует ряд ферментных систем, тормозит фосфорилирование и синтез АТФ, снижает уровень коферментов А и Q, стимулирует активность моноаминоксидазы и окислительное фосфорилирование. Известно также, что при шизофрении содержание ванадия в крови значительно повышается.
Избыточное поступление ванадия в организм обычно связано с экологическими и производственными факторами. При остром воздействии токсических доз ванадия у рабочих отмечаются местные воспалительные реакции кожи и слизистых оболочек глаз, верхних дыхательных путей, скопление слизи в бронхах и альвеолах. Возникают и системные аллергические реакции типа астмы и экземы; а также лейкопения и анемия, которые сопровождаются нарушениями основных биохимических параметров организма.
При введении ванадия животным (в дозах 25—50 мкг/кг), отмечается замедление роста, диарея и увеличение смертности.
Всего в организме среднего человека (масса тела 70 кг) 0,11 мг ванадия. Токсическая доза для человека 0,25 мг, летальная доза — 2—4 мг.
Повышенное содержание белков и хрома в рационе снижает токсическое действие ванадия. Нормы потребления для этого минерального вещества не установлены.
Кроме того, высокое содержание выявлено у некоторых морских беспозвоночных (голотурий и асцидий), у которых ванадий входит в состав белковых комплексов плазмы и форменных элементах крови и целомической жидкости. В клетках крови асцидий массовая доля ванадия может доходить до 8,75 %. Функция элемента в организме до конца не ясна, разные учёные считают его отвечающим либо за перенос кислорода в организме этих животных, либо за перенос питательных веществ. С точки зрения практического использования — возможна добыча ванадия из этих организмов, экономическая окупаемость таких «морских плантаций» на данный момент не ясна, но в Японии имеются пробные варианты.
|
Соединения ванадия |
|---|
|
|
Периодическая система химических элементов Д. И. Менделеева |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Электрохимический ряд активности металлов |
|---|
|
Eu, Sm, Li, Cs, Rb, K, Ra, Ba, Sr, Ca, Na, Ac, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Gd, Tb, Mg, Y, Dy, Am, Ho, Er, Tm, Lu, Sc, Pu, |
Ванадий в таблице менделеева занимает 23 место, в 4 периоде.
| Символ | V |
| Номер | 23 |
| Атомный вес | 50.9415000 |
| Латинское название | Vanadium |
| Русское название | Ванадий |
Как самостоятельно построить электронную конфигурацию? Ответ здесь
Электронная схема ванадия
V: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3
Короткая запись:
V: [Ar]4s2 3d3
Одинаковую электронную конфигурацию имеют
атом ванадия и
Ti-1, Mn+2, Fe+3, Co+4
Порядок заполнения оболочек атома ванадия (V) электронами:
1s → 2s → 2p → 3s → 3p → 4s → 3d → 4p → 5s → 4d →
5p → 6s → 4f → 5d → 6p → 7s → 5f → 6d → 7p.
На подуровне ‘s’ может находиться до 2 электронов, на ‘s’ — до 6, на
‘d’ — до 10 и на ‘f’ до 14
Ванадий имеет 23 электрона,
заполним электронные оболочки в описанном выше порядке:
2 электрона на 1s-подуровне
2 электрона на 2s-подуровне
6 электронов на 2p-подуровне
2 электрона на 3s-подуровне
6 электронов на 3p-подуровне
2 электрона на 4s-подуровне
3 электрона на 3d-подуровне
Степень окисления ванадия
Атомы ванадия в соединениях имеют степени окисления 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2.
Степень окисления — это условный заряд атома в соединении: связь в молекуле
между атомами основана на разделении электронов, таким образом, если у атома виртуально увеличивается
заряд, то степень окисления отрицательная (электроны несут отрицательный заряд), если заряд уменьшается,
то степень окисления положительная.
Ионы ванадия
Валентность V
Атомы ванадия в соединениях проявляют валентность V, IV, III, II, I.
Валентность ванадия характеризует способность атома V к образованию хмических связей.
Валентность следует из строения электронной оболочки атома, электроны, участвующие в образовании
химических соединений называются валентными электронами. Более обширное определение валентности это:
Число химических связей, которыми данный атом соединён с другими атомами
Валентность не имеет знака.
Квантовые числа V
Квантовые числа определяются последним электроном в конфигурации,
для атома V эти числа имеют значение N = 3, L = 2, Ml = 0, Ms = +½
Видео заполнения электронной конфигурации (gif):
Результат:
Энергия ионизации
Чем ближе электрон к центру атома — тем больше энергии необходимо, что бы его оторвать.
Энергия, затрачиваемая на отрыв электрона от атома называется энергией ионизации и обозначается Eo.
Если не указано иное, то энергия ионизации — это энергия отрыва первого электрона, также существуют энергии
ионизации для каждого последующего электрона.
Энергия ионизации V:
Eo = 651 кДж/моль
— Что такое ион читайте в статье.
Перейти к другим элементам таблицы менделеева
Где V в таблице менделеева?
Таблица Менделеева
Скачать таблицу менделеева в хорошем качестве
|
|||
| Внешний вид простого вещества | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Свойства атома | |||
| Имя, символ, номер |
Вана́дий / Vanadium (V), 23 |
||
| Атомная масса (молярная масса) |
50,9415 а. е. м. (г/моль) |
||
| Электронная конфигурация |
[Ar] 3d3 4s2 |
||
| Радиус атома |
134 пм |
||
| Химические свойства | |||
| Ковалентный радиус |
122 пм |
||
| Радиус иона |
(+5e)59 (+3e)74 пм |
||
| Электроотрицательность |
1,63 (шкала Полинга) |
||
| Электродный потенциал |
0 |
||
| Степени окисления |
5, 4, 3, 2, 0 |
||
| Энергия ионизации (первый электрон) |
650,1(6,74) кДж/моль (эВ) |
||
| Термодинамические свойства простого вещества | |||
| Плотность (при н. у.) |
6,11 г/см³ |
||
| Температура плавления |
2160 K |
||
| Температура кипения |
3650 K |
||
| Теплота плавления |
17,5 кДж/моль |
||
| Теплота испарения |
460 кДж/моль |
||
| Молярная теплоёмкость |
24,95[1] Дж/(K·моль) |
||
| Молярный объём |
8,35 см³/моль |
||
| Кристаллическая решётка простого вещества | |||
| Структура решётки |
кубическая |
||
| Параметры решётки |
3,024[1] Å |
||
| Температура Дебая |
390 K |
||
| Прочие характеристики | |||
| Теплопроводность |
(300 K) 30,7 Вт/(м·К) |
Вана́дий — элемент побочной подгруппы пятой группы, четвёртого периода периодической системы химических элементов Д. И. Менделеева, с атомным номером 23. Обозначается символом V (лат. Vanadium). Простое вещество ванадий (CAS-номер: 7440-62-2) — пластичный металл серебристо-серого цвета.
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Происхождение названия
- 3 Нахождение в природе
- 3.1 Месторождения
- 4 Получение
- 5 Физические свойства
- 6 Химические свойства
- 7 Применение
- 7.1 Атомно-водородная энергетика
- 7.2 Химические источники тока
- 7.3 В производстве серной кислоты
- 8 Биологическая роль и воздействие
- 9 Изотопы
- 10 См. также
- 11 Примечания
- 12 Ссылки
История
Ванадий был открыт в 1801 г. профессором минералогии из Мехико Андресом Мануэлем Дель Рио в свинцовых рудах. Он обнаружил новый металл и предложил для него название «панхромий» из-за широкого диапазона цвета его соединений, сменив затем название на «эритроний». Дель Рио не имел авторитета в научном мире Европы, и европейские химики усомнились в его результатах. Затем и сам Дель Рио потерял уверенность в своём открытии и заявил, что открыл всего лишь хромат свинца.
В 1830 году ванадий был открыт заново шведским химиком Нильсом Сефстрёмом в железной руде. Новому элементу название дали Берцелиус и Сефстрём.
Шанс открыть ванадий был у Фридриха Вёлера, исследовавшего мексиканскую руду, но он серьёзно отравился фтороводородом незадолго до открытия Сефстрёма и не смог продолжить исследования. Однако Вёлер довёл до конца исследование руды и окончательно доказал, что в ней содержится именно ванадий, а не хром.
Происхождение названия
Этот элемент образует соединения с красивой окраской, отсюда и название элемента, связанное с именем скандинавской богини любви и красоты Фрейи (др.-исл. Vanadís — дочь Ванов; Ванадис).
Нахождение в природе
Ванадий относится к рассеянным элементам и в природе в свободном виде не встречается. Содержание ванадия в земной коре 1,6·10−2% по массе, в воде океанов 3·10−7%. Наиболее высокие средние содержания ванадия в магматических породах отмечаются в габбро и базальтах (230—290 г/т). В осадочных породах значительное накопление ванадия происходит в биолитах (асфальтитах, углях, битуминозных фосфатах), битуминозных сланцах, бокситах, а также в оолитовых и кремнистых железных рудах. Близость ионных радиусов ванадия и широко распространённых в магматических породах железа и титана приводит к тому, что ванадий в гипогенных процессах целиком находится в рассеянном состоянии и не образует собственных минералов. Его носителями являются многочисленные минералы титана (титаномагнетит, сфен, рутил, ильменит), слюды, пироксены и гранаты, обладающие повышенной изоморфной ёмкостью по отношению к ванадию. Важнейшие минералы: патронит V(S2)2, ванадинит Pb5(VO4)3Cl и некоторые другие. Основной источник получения ванадия — железные руды, содержащие ванадий как примесь.
Месторождения
Известны месторождения в Перу, Колорадо, США, ЮАР, Финляндии, Австралии, Армении, России[2].
Получение
В промышленности при получении ванадия из железных руд с его примесью сначала готовят концентрат, в котором содержание ванадия достигает 8-16 %. Далее окислительной обработкой ванадий переводят в высшую степень окисления +5 и отделяют легко растворимый в воде ванадат натрия (Na) NaVO3. При подкислении раствора серной кислотой выпадает осадок, который после высушивания содержит более 90 % ванадия.
Первичный концентрат восстанавливают в доменных печах и получают концентрат ванадия, который далее используют при выплавке сплава ванадия и железа — так называемого феррованадия (содержит от 35 до 80 % ванадия). Металлический ванадий можно приготовить восстановлением хлорида ванадия водородом (H), термическим восстановлением оксидов ванадия (V2O5 или V2O3) кальцием, термической диссоциацией VI2 и другими методами.
Физические свойства
Бруски ванадия 99,95 % чистоты, полученные переплавкой в электронном пучке. Поверхность брусков протравлена для проявления структуры.
Ванадий — пластичный металл серебристо-серого цвета, по внешнему виду похож на сталь. Кристаллическая решётка кубическая объёмноцентрированная, a=3,024 Å, z=2, пространственная группа Im3m. Температура плавления 1920 °C, температура кипения 3400 °C, плотность 6,11 г/см³. При нагревании на воздухе выше 300 °C ванадий становится хрупким. Примеси кислорода, водорода и азота резко снижают пластичность ванадия и повышают его твёрдость и хрупкость[1].
Химические свойства
Химически ванадий довольно инертен. Он стоек к действию морской воды, разбавленных растворов соляной, азотной и серной кислот, щелочей.
С кислородом ванадий образует несколько оксидов: VO, V2O3, VO2,V2O5. Оранжевый V2O5 — кислотный оксид, темно-синий VO2 — амфотерный, остальные оксиды ванадия — основные. Галогениды ванадия гидролизуются. С галогенами ванадий образует довольно летучие галогениды составов VX2 (X = F, Cl, Br, I), VX3, VX4 (X = F, Cl, Br), VF5 и несколько оксогалогенидов (VOCl, VOCl2, VOF3 и др.). Известны следующие оксиды ванадия:
| Название | Формула | Плотность | Температура плавления | Температура кипения | Цвет |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оксид ванадия(II) | VO | 5,76 г/см³ | ~1830 °C | 3100 °C | Черный |
| Оксид ванадия(III) | V2O3 | 4,87 г/см³ | 1967 °C | 3000 °C | Черный |
| Оксид ванадия(IV) | VO2 | 4,65 г/см³ | 1542 °C | 2700 °C | Темно-голубой |
| Оксид ванадия(V) | V2O5 | 3,357 г/см³ | 670 °C | 2030 °C | Красно-желтый |
Соединения ванадия в степенях окисления +2 и +3 — сильные восстановители, в степени окисления +5 проявляют свойства окислителей. Известны тугоплавкий карбид ванадия VC (tпл=2800 °C), нитрид ванадия VN, сульфид ванадия V2S5, силицид ванадия V3Si и другие соединения ванадия.
При взаимодействии V2O5 с основными оксидами образуются ванадаты — соли ванадиевой кислоты вероятного состава HVO3.
Применение
80 % всего производимого ванадия находит применение в сплавах, в основном для нержавеющих и инструментальных сталей.
Атомно-водородная энергетика
Хлорид ванадия применяется при термохимическом разложении воды в атомно-водородной энергетике (ванадий-хлоридный цикл «Дженерал Моторс»,США). В металлургии ванадий обозначается буквой Ф
Химические источники тока
Пентаоксид ванадия широко применяется в качестве положительного электрода (анода) в мощных литиевых батареях и аккумуляторах. Ванадат серебра в резервных батареях в качестве катода.
В производстве серной кислоты
Оксид ванадия(V) используется как катализатор на стадии превращения сернистого ангидрида в серный.
Биологическая роль и воздействие
Установлено, что ванадий может тормозить синтез жирных кислот, подавлять образование холестерина. Ванадий ингибирует ряд ферментных систем, тормозит фосфорилирование и синтез АТФ, снижает уровень коферментов А и Q, стимулирует активность моноаминоксидазы и окислительное фосфорилирование. Известно также, что при шизофрении содержание ванадия в крови значительно повышается.
Избыточное поступление ванадия в организм обычно связано с экологическими и производственными факторами. При остром воздействии токсических доз ванадия у рабочих отмечаются местные воспалительные реакции кожи и слизистых оболочек глаз, верхних дыхательных путей, скопление слизи в бронхах и альвеолах. Возникают и системные аллергические реакции типа астмы и экземы; а также лейкопения и анемия, которые сопровождаются нарушениями основных биохимических параметров организма.
При введении ванадия животным (в дозах 25-50 мкг/кг), отмечается замедление роста, диарея и увеличение смертности.
Всего в организме среднего человека (масса тела 70 кг) 0,11 мг ванадия. Ванадий и его соединения токсичны. Токсическая доза для человека 0,25 мг, летальная доза — 2-4 мг.
Повышенное содержание белков и хрома в рационе снижает токсическое действие ванадия. Нормы потребления для этого минерального вещества не установлены.
Кроме того ванадий у некоторых организмов, например, у морских жителей дна голотурий и асцидий концентрируется в целомической жидкости/крови, причем его концентрации достигают 10 %. Его функция в организме голотурий до конца не ясна, разные ученые считают его отвечающим либо за перенос кислорода в организме этих животных, либо за перенос питательных веществ. С точки зрения практического использования — возможна добыча ванадия из этих организмов, экономическая окупаемость таких «морских плантаций» на данный момент не ясна, но в Японии имеются пробные варианты.
Изотопы
Природный ванадий состоит из двух изотопов: слаборадиоактивного 50V (изотопная распространённость 0,250 %) и стабильного 51V (99,750 %). Период полураспада ванадия-50 равен 1,5·1017 лет, т. е. для всех практических целей его можно считать стабильным; этот изотоп в 83 % случаев посредством электронного захвата превращается в бета-минус-распад, превращаясь в массовым числом от 40 до 65 (а также 5 метастабильных состояний). Из них наиболее стабильны 49V (T1/2=337 дней) и 48V (T1/2=15,974 дня).
См. также
- Категория:Соединения ванадия
- Метаванадат натрия
- Оксид ванадия(V)
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 3 Редкол.:Кнунянц И. Л. (гл. ред.) Химическая энциклопедия: в 5 т. — Москва: Советская энциклопедия, 1988. — Т. 1. — С. 349. — 623 с. — 100 000 экз.
- ↑ Электронная библиотека НЕФТЬ-ГАЗ
Ссылки
| Ванадий на Викискладе? |
- Ванадий на Webelements
- Ванадий в Популярной библиотеке химических элементов
- Ванадий и его соединения
|
Соединения ванадия |
|---|
|
Борид ванадия (VB2) • Бромид ванадия(II) (VBr2) • Бромид ванадия(III) (VBr3) • Гексакарбонилванадий (V(CO)6) • Гидроксид ванадия(II) (V(OH)2) • Гидроксид ванадия(III) (V(OH)3) • Дисилицид ванадия (VSi2) • Дисульфид ванадия (VS2) • Иодид ванадия(II) (VI2) • Иодид ванадия(III) (VI3) • Карбид ванадия (VC) • Метаванадат аммония (NH4VO3) • Метаванадат натрия (NaVO3) • Нитрид ванадия (VN) • Оксибромид ванадия(III) (VOBr) • Оксид ванадия(II) (VO) • Оксид ванадия(III) (V2O3) • Оксид ванадия(IV) (VO2) • Оксид ванадия(V) (V2O5) • Оксидибромид ванадия(IV) (VOBr2) • Оксидифторид ванадия(IV) (VOF2) • Оксидихлорид ванадия(IV) (VOCl2) • Окситрибромид ванадия(V) (VOBr3) • Окситрифторид ванадия(V) (VOF3) • Оксид-трихлорид ванадия (VOCl3) • Оксихлорид ванадия(III) (VOCl) • Ортованадат натрия (Na3VO4) • Силицид ванадия (V2Si) • Силицид триванадия (V3Si) • Сульфат ванадила (VOSO4) • Сульфат ванадия(II) (VSO4) • Сульфат ванадия(III) (V2(SO4)3) • Сульфид ванадия(II) (VS) • Сульфид ванадия(III) (V2S3) • Сульфид ванадия(V) (V2S5) • Фторид ванадия(II) (VF2) • Фторид ванадия(III) (VF3) • Фторид ванадия(IV) (VF4) • Фторид ванадия(V) (VF5) • Хлорид гексаамминванадия(III) ([V(NH3)6]Cl3) • Хлорид ванадия(II) (VCl2) • Хлорид ванадия(III) (VCl3) • Хлорид ванадия(IV) (VCl4) • Хлорид диоксованадия(V) ((VO2)Cl) |
| Периодическая система химических элементов Д. И. Менделеева | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| 7 | Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo |
|
| |
|---|
|
Eu, Sm, Li, Cs, Rb, K, Ra, Ba, Sr, Ca, Na, Ac, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Gd, Tb, Mg, Y, Dy, Am, Ho, Er, Tm, Lu, Sc, Pu, Th, Np, U, Hf, Be, Al, Ti, Zr, Yb, Mn, V, Nb, Pa, Cr, Zn, Ga, Fe, Cd, In, Tl, Co, Ni, Te, Mo, Sn, Pb, H2, W, Sb, Bi, Ge, Re, Cu, Tc, Te, Rh, Po, Hg, Ag, Pd, Os, Ir, Pt, Au Элементы расположены в порядке возрастания стандартного электродного потенциала. |
|
|
Ванадий — химический элемент под номером 23 в таблице Менделеева, имеющий атомную массу 50,942 а. е. м. По внешнему виду ванадий — пластичный и лёгкий металл, на воздухе покрывающийся оксидной плёнкой цветов побежалости:

С точки зрения электронной конфигурации положение у него следующее: два s-электрона и три d-электрона — конфигурация (4s^23d^3). Поэтому самые распространённые степени окисления ванадия — от +2 до +5, хотя известны примеры соединений, содержащие ванадий в с. о. от -3 до +1. При этом самыми устойчивыми степенями окисления считаются две: +4 и +5.
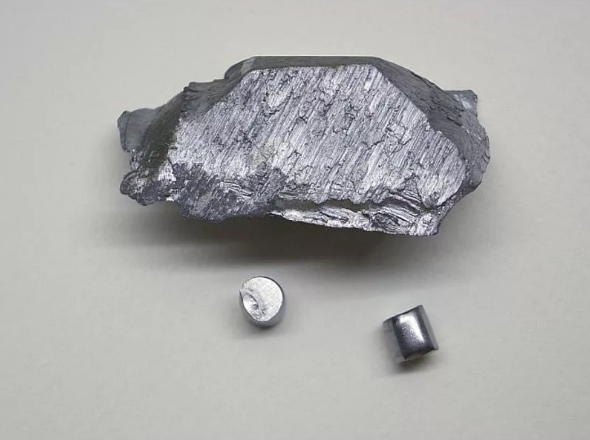

Ванадий занимает 22-ое место по распространенности в земной коре: является рассеянным и сопутствует рудам других металлов.
Химические свойства ванадия
Будучи более активным, чем ближайшие соседи по периодической системе, ванадий все же не реагирует с кислотами-неокислителями: исключение составляет лишь плавиковая, с которой он образует прочную комплексную кислоту — гексафторованадиевую, в которой степень окисления металла равна +3:
$$ce{2V + 12HF -> 2H3[VF6] + 3H2 ^}$$
С кислотами-окислителями, такими как концентрированная серная и разбавленная азотная кислоты, ванадий образует сульфат ванадила, имеющий формулу (ce{VOSO4}), и нитрат ванадила (ce{VO(NO3)2}) соответственно, имеющие в растворе синюю окраску за счёт катиона ванадила (ce{VO^2+}), содержащего ванадий в степени окисления +4:
$$ce{3V + 10HNO3 -> 3VO(NO3)2 + 4NO ^ + 5H2O}$$
$$ce{V + 3H2SO4 -> VOSO4 + 2SO2 ^ + 3H2O}$$
При этом концентрированная азотная, хлорная, пероксодисерная и кислоты состава (ce{HHalO3 (Hal = Cl, Br, I)}) (хлорноватая, бромноватая и иодноватая кислоты) окисляют ванадий до высшей степени окисления (+5), переводя его в катион ванадина (ce{VO2^+}), существующий только в сильнокислых растворах и имеющий желтую окраску:
$$ce{6V + 11HClO3 -> 6VO2ClO3 + 5HCl + 3H2O}$$
Являясь амфотерным металлом, ванадий реагирует при нагревании с щелочами и образует ванадаты(V):
$$ce{4V + 12NaOH + 5O2 -> 4Na3VO4 + 6H2O}$$
«Ванадиевый хамелеон»
Если взять ванадий в высшей степени окисления — (+5) — в виде, например, метаванадата аммония (ce{NH4VO3}), и восстанавливать цинком в кислой среде, то произойдёт реакция, названная «химическим хамелеоном»: в её процессе цвет раствора меняется несколько раз вслед за восстановлением ионов ванадия в растворе:

$$ce{2NH_4VO_3 + Zn + 8HCl -> 2VOCl_2 + 2NH_4Cl + ZnCl_2 + 4H_2O}$$
В растворе начинают появляться катионы ванадила (ce{VO^2+}), которые обладают синим цветом, но вместе с изначальным жёлтым оттенком раствора наблюдается цвет:
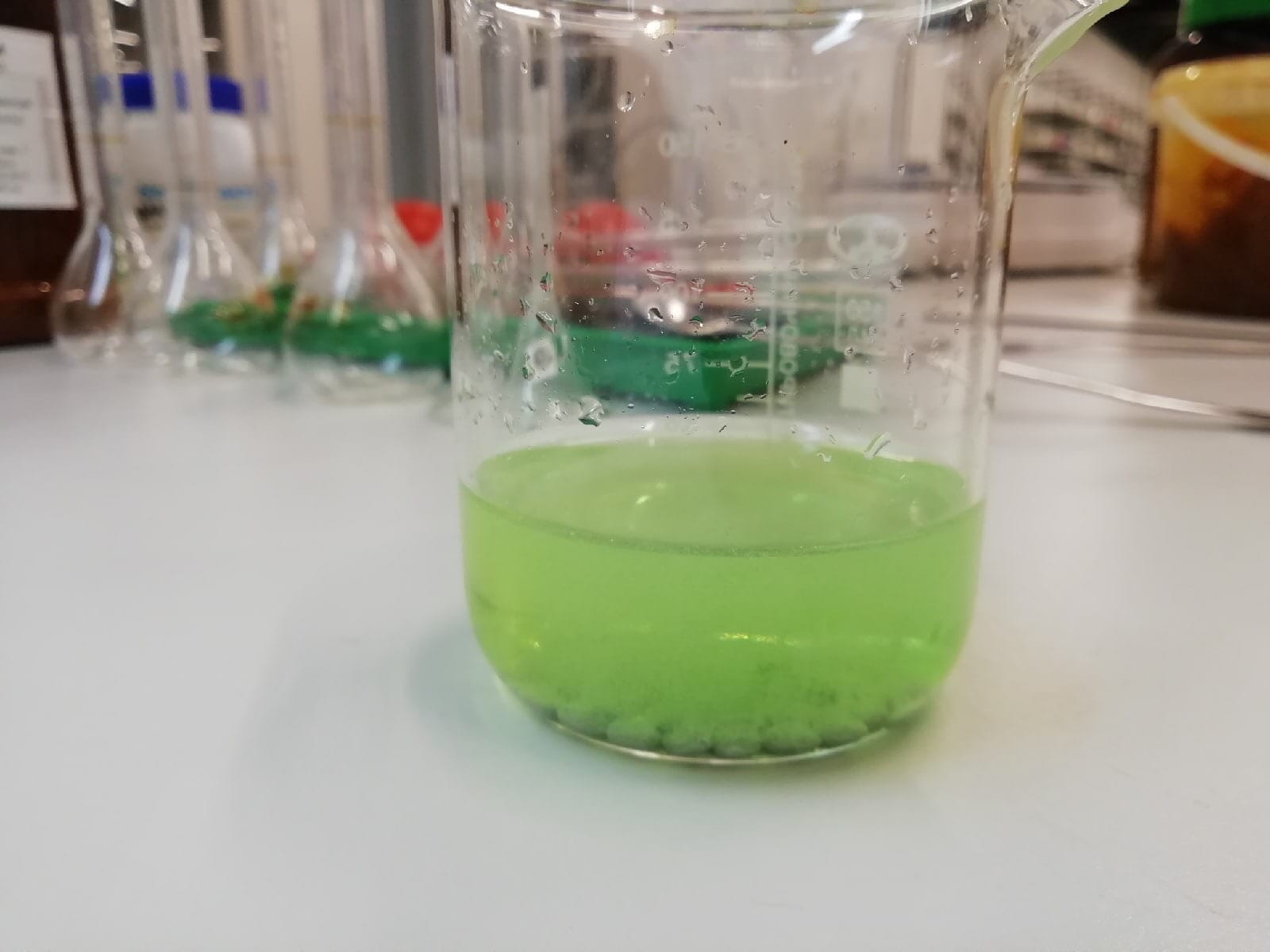


Следующим шагом идёт восстановление до ионов ванадия(III) (ce{V^3+}), обладающих зелёным цветом, и в конце — до фиолетового ванадия(II).
$$ce{2VOCl_2 + Zn + 4HCl ->ZnCl_2 + 2VCl_3 + 2H_2O}$$
$$ce{2VCl_3 + Zn ->ZnCl_2 + 2VCl_2}$$

Цвета растворов, содержащих данные ионы по отдельности, соответственно, жёлтый, голубой, зеленоватый и фиолетовый:

Оксиды ванадия
Ванадий имеет достаточно много различных оксидов, в том числе «необычных» (содержащих нестехиометрическое количество ванадия и кислорода, или содержащих ванадий в разных степенях окисления), однако далее рассмотрены лишь самые распространённые соединения ванадия с кислородом.
Оксид ванадия(II)
(ce{VO}) — оксид черного цвета. Получить его можно взаимодействием сильных восстановителей с оксидами ванадия более высоких степеней окисления при достаточно высоких температурах. Он обладает основными свойствами и образует основание (ce{V(OH)2}) (сильный восстановитель) коричневого цвета. Структура данного оксида представляет собой структуру типа (ce{NaCl}):

Оксид ванадия(III)
Это амфотерный устойчивый оксид, но при этом основные свойства преобладают. (ce{V2O3}) представляет собой черный порошок, который при растворении в кислотах образует зеленый раствор солей (ce{V^3+}). С растворами щелочей не реагирует, но с оксидами щелочных металлов образует ванадаты(III). Является канцеро- и мутагеном. Образует, соответственно, гидроксид (ce{V(OH)3}).
Оксид ванадия(IV)

Темно-синий оксид четырехвалентного ванадия (ce{VO2}) проявляет достаточно сильные амфотерные свойства: с кислотами он реагирует с образованием солей ванадила (о котором рассказано выше) тёмно-синего цвета:
$$ce{VO2 + H2SO4 -> VOSO4 + H2O}$$

А с щелочами — с образованием ванадитов, или ванадатов(IV):
$$ce{4VO2 + 2NaOH -> Na2V4O9 + H2O}$$
Однако исследования показали, что корректнее записывать анион как (ce{V3O7^{2-}}), соответствующий достаточно сложной структуре, показанной ниже:

Оксид ванадия(V)
Данное соединение — высший оксид ванадия, который также амфотерен, однако его кислотные свойства преобладают. Пентаоксид ванадия — чрезвычайно токсичное вещество, и перечисление способов его воздействия на уязвимый человеческий (да и не только) организм заслуживает отдельной статьи.
Данное соединение немного растворяется в воде, окрашивая раствор и осаждаясь оранжевым порошком, из-за чего (ce{V2O5}) называют ангидридом невыделенной ванадиевой кислоты, хотя в индивидуальном виде он имеет желтый цвет:

В лаборатории его можно получить разложением метаванадата аммония — (ce{NH4VO3}).
Соли, соответствующие ванадию(V), и их структура очень сильно зависит от pH раствора, в котором они находятся. В сильнощелочной среде преобладает тетраэдрический ион (ce{VO4^{3-}}), аналогичный фосфату. При понижении кислотности среды (при понижении pH раствора) происходят процессы конденсации и поликонденсации, при которых образуются диванадат-ионы (аналогично дифосфат-иону), триванадат-ионы, декаванадат-ионы и другие:
Помимо ярко выраженных кислотных свойств пентаоксид ванадия также является окислителем средней силы, и, восстанавливаясь, переходит в соединения ванадия(IV):
$$ce{V2O5 + 6HCl_(conc.) -> 2VOCl2 + Cl2 ^ + 3H2O}$$
Ванадий(V) также образует различные пероксидные соединения, состав которых зависит от pH:
$$ce{VO2NO3 + H2O2 -> VO3NO3 ([VO(O2)]^{+}) + H2O quad pH approx 2, red}$$
$$ce{KVO3 + 2H2O2 -> KH2VO6 ([VO(O2)2(H2O)]^{-}) + H2O quad pH approx 9, yellow}$$
$$ce{K3VO4 + 4H2O2 -> K3VO8 ([V(O2)4]^{3-}) + 4H2O quad pH approx 10, purple}$$
Галогениды ванадия
Кратко отметим, что единственный галогенид, отвечающий составу (ce{VHal5}), — это фторид (ce{VF5}). Максимально возможная степень окисления в хлориде и бромиде — +4, в иодиде — +3. Все галогениды ванадия в степенях окисления ниже максимально возможных получены, сводная таблица представлена на рисунке ниже:

Любите химию!
Ванадий и его характеристики
Общая характеристика ванадия
Соединения ванадия широко распространены в природе, но они очень распылены и не образуют сколько-нибудь значительных скоплений; общее содержание ванадия в земной коре оценивается в 0,0015% (масс.).
Чистый ванадий – серебристый металл (рис. 1) ковкий металл, плотностью 5,96 г/см 3, плавящийся при температуре 1900oС. Как и у титана, механические свойства ванадия резко ухудшаются при наличии в нем примесей кислорода, азота, водорода.
Рис. 1. Ванадий. Внешний вид.
Атомная и молекулярная масса ванадия
Относительной молекулярная масса вещества (Mr) – это число, показывающее, во сколько раз масса данной молекулы больше 1/12 массы атома углерода, а относительная атомная масса элемента (Ar) — во сколько раз средняя масса атомов химического элемента больше 1/12 массы атома углерода.
Поскольку в свободном состоянии кальций существует в виде одноатомных молекул V, значения его атомной и молекулярной масс совпадают. Они равны 50,9962.
Изотопы ванадия
Известно, что в природе ванадий может находиться в виде единственного стабильного изотопа 51V. Массовое число равно 51, ядро атома содержит двадцать три протона и двадцать восемь нейтронов.
Существуют искусственные изотопы ванадия с массовыми числами от 40-ка до 65-ти, среди которых наиболее стабильным является 50V с периодом полураспада равным 1,5×1017 лет, а также пять ядерных изотопов.
Ионы ванадия
На внешнем энергетическом уровне атома ванадия имеется пять электронов, которые являются валентными:
1s22s22p63s23p63d24s2.
В результате химического взаимодействия ванадий отдает свои валентные электроны, т.е. является их донором, и превращается в положительно заряженный ион:
Vo -2e → V2+;
Vo -3e → V3+;
Vo -4e → V4+;
Vo -5e → V5+.
Молекула и атом ванадия
В свободном состоянии ванадий существует в виде одноатомных молекул V. Приведем некоторые свойства, характеризующие атом и молекулу ванадия:
|
Энергия ионизации атома, эВ |
6,74 |
|
Относительная электроотрицательность |
1,63 |
|
Радиус атома, нм |
0,134 |
Сплавы ванадия
Ванадий в основном используют в качестве добавки к сталям. Сталь, содержащая всего 0,1 – 0,3% ванадия отличается большой прочностью, упругостью и нечувствительностью к толчкам и ударам, что особенно важно, например, для автомобильных осей, которые все время подвергаются сотрясению. Как правило, ванадий вводят в сталь в комбинации с другими легирующими элементами: хромом, никелем, вольфрамом, молибденом.
Примеры решения задач
Химические элементы: названия, символы и произношение символов
В таблице содержатся русские и латинские названия химических элементов, символы химических элементов и произношение символов. Для правильного произношения названий и символов в русских названиях и произношениях проставлены ударения.
| Русское название элемента | Латинское название элемента | Символ элемента | Произношение символа |
|---|---|---|---|
| Азо́т | Nitrogenium | N | эн |
| Акти́ний | Actinium | Ac | акти́ний |
| Алюми́ний | Aluminium | Al | алюми́ний |
| Амери́ций | Americium | Am | амери́ций |
| Арго́н | Argon | Ar | арго́н |
| Аста́т | Astatum | At | аста́т |
| Ба́рий | Barium | Ba | ба́рий |
| Бери́ллий | Beryllium | Be | бери́ллий |
| Бе́рклий | Berkelium | Bk | бе́рклий |
| Бор | Borum | B | бор |
| Бо́рий | Bohrium | Bh | бо́рий |
| Бром | Bromium | Br | бром |
| Вана́дий | Vanadium | V | вана́дий |
| Ви́смут | Bismuthum | Bi | ви́смут |
| Водоро́д | Hydrogenium | H | аш |
| Вольфра́м | Wolframium | W | вольфра́м |
| Гадоли́ний | Gadolinium | Gd | гадоли́ний |
| Га́ллий | Gallium | Ga | га́ллий |
| Га́фний | Hafnium | Hf | га́фний |
| Ге́лий | Helium | He | ге́лий |
| Герма́ний | Germanium | Ge | герма́ний |
| Го́льмий | Holmium | Ho | го́льмий |
| Дармшта́дтий | Darmstadtium | Ds | дармшта́дтий |
| Диспро́зий | Dysprosium | Dy | диспро́зий |
| Ду́бний | Dubnium | Db | ду́бний |
| Евро́пий | Europium | Eu | евро́пий |
| Желе́зо | Ferrum | Fe | фе́ррум |
| Зо́лото | Aurum | Au | а́урум |
| И́ндий | Indium | In | и́ндий |
| Йод | Iodium | I | йод |
| Ири́дий | Iridium | Ir | ири́дий |
| Итте́рбий | Ytterbium | Yb | итте́рбий |
| И́ттрий | Yttrium | Y | и́ттрий |
| Ка́дмий | Cadmium | Cd | ка́дмий |
| Ка́лий | Kalium | K | ка́лий |
| Калифо́рний | Californium | Cf | калифо́рний |
| Ка́льций | Calcium | Ca | ка́льций |
| Кислоро́д | Oxygenium | O | о |
| Ко́бальт | Cobaltum | Co | ко́бальт |
| Коперни́ций | Copernicium | Cn | коперни́ций |
| Кре́мний | Silicium | Si | сили́циум |
| Крипто́н | Krypton | Kr | крипто́н |
| Ксено́н | Xenon | Xe | ксено́н |
| Кю́рий | Curium | Cm | кю́рий |
| Ланта́н | Lanthanum | La | ланта́н |
| Ливермо́рий | Livermorium | Lv | ливермо́рий |
| Ли́тий | Lithium | Li | ли́тий |
| Лоуре́нсий | Lawrencium | Lr | лоуре́нсий |
| Люте́ций | Lutetium | Lu | люте́ций |
| Ма́гний | Magnesium | Mg | ма́гний |
| Ма́рганец | Manganum | Mn | ма́рганец |
| Медь | Cuprum | Cu | ку́прум |
| Мейтне́рий | Meitnerium | Mt | мейтне́рий |
| Менделе́вий | Mendelevium | Md | менделе́вий |
| Молибде́н | Molybdaenum | Mo | молибде́н |
| Моско́вий | Moscovium | Mc | моско́вий |
| Мышья́к | Arsenicum | As | арсе́никум |
| На́трий | Natrium | Na | на́трий |
| Неоди́м | Neodymium | Nd | неоди́м |
| Нео́н | Neon | Ne | нео́н |
| Непту́ний | Neptunium | Np | непту́ний |
| Ни́кель | Niccolum | Ni | ни́кель |
| Нио́бий | Niobium | Nb | нио́бий |
| Нихо́ний | Nihonium | Nh | нихо́ний |
| Нобе́лий | Nobelium | No | нобе́лий |
| Оганесо́н | Oganesson | Og | оганесо́н |
| О́лово | Stannum | Sn | ста́ннум |
| О́смий | Osmium | Os | о́смий |
| Палла́дий | Palladium | Pd | палла́дий |
| Пла́тина | Platinum | Pt | пла́тина |
| Плуто́ний | Plutonium | Pu | плуто́ний |
| Поло́ний | Polonium | Po | поло́ний |
| Празеоди́м | Praseodymium | Pr | празеоди́м |
| Проме́тий | Promethium | Pm | проме́тий |
| Протакти́ний | Protactinium | Pa | протакти́ний |
| Ра́дий | Radium | Ra | ра́дий |
| Радо́н | Radon | Rn | радо́н |
| Резерфо́рдий | Rutherfordium | Rf | резерфо́рдий |
| Ре́ний | Rhenium | Re | ре́ний |
| Рентге́ний | Roentgenium | Rg | рентге́ний |
| Ро́дий | Rhodium | Rh | ро́дий |
| Ртуть | Hydrargyrum | Hg | гидра́ргирум |
| Руби́дий | Rubidium | Rb | руби́дий |
| Руте́ний | Ruthenium | Ru | руте́ний |
| Сама́рий | Samarium | Sm | сама́рий |
| Свине́ц | Plumbum | Pb | плю́мбум |
| Селе́н | Selenium | Se | селе́н |
| Се́ра | Sulfur | S | эс |
| Серебро́ | Argentum | Ag | арге́нтум |
| Сибо́ргий | Seaborgium | Sg | сибо́ргий |
| Ска́ндий | Scandium | Sc | ска́ндий |
| Стро́нций | Strontium | Sr | стро́нций |
| Сурьма́ | Stibium | Sb | сти́биум |
| Та́ллий | Thallium | Tl | та́ллий |
| Танта́л | Tantalum | Ta | танта́л |
| Теллу́р | Tellurium | Te | теллу́р |
| Теннесси́н | Tennessium | Ts | теннесси́н |
| Те́рбий | Terbium | Tb | те́рбий |
| Техне́ций | Technetium | Tc | техне́ций |
| Тита́н | Titanium | Ti | тита́н |
| То́рий | Thorium | Th | то́рий |
| Ту́лий | Thulium | Tm | ту́лий |
| Углеро́д | Carboneum | C | цэ |
| Ура́н | Uranium | U | ура́н |
| Фе́рмий | Fermium | Fm | фе́рмий |
| Флеро́вий | Flerovium | Fl | флеро́вий |
| Фо́сфор | Phosphorus | P | пэ |
| Фра́нций | Francium | Fr | фра́нций |
| Фтор | Fluorum | F | фтор |
| Ха́ссий | Hassium | Hs | га́ссий |
| Хлор | Chlorum | Cl | хлор |
| Хром | Chromium | Cr | хром |
| Це́зий | Caesium | Cs | це́зий |
| Це́рий | Cerium | Ce | це́рий |
| Цинк | Zincum | Zn | цинк |
| Цирко́ний | Zirconium | Zr | цирко́ний |
| Эйнште́йний | Einsteinium | Es | эйнште́йний |
| Э́рбий | Erbium | Er | э́рбий |