|
|
| Product type | Cars |
|---|---|
| Owner | Jaguar Land Rover (since 2013)[1] |
| Produced by | Jaguar Land Rover |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Introduced | September 1935; 87 years ago |
| Related brands | Land Rover |
| Markets | Worldwide |
| Previous owners | Jaguar Cars Limited |
| Tagline | «The Art of Performance» |
| Website | jaguar.com |
 |
|
| Formerly | S.S. Cars Limited (1933–1945) |
|---|---|
| Type |
|
| Industry | Automotive |
| Predecessor | Swallow Coachbuilding Company Limited |
| Founded | 26 October 1933; 89 years ago |
| Founder | William Lyons |
| Fate | Car manufacturing merged with Land Rover in 2013 as Jaguar Land Rover |
| Headquarters |
Whitley , England |
| Parent |
|
Jaguar (, ) is the luxury vehicle brand of Jaguar Land Rover,[1][3] a British multinational car manufacturer with its headquarters in Whitley, Coventry, England. Jaguar Cars was the company that was responsible for the production of Jaguar cars until its operations were fully merged with those of Land Rover to form Jaguar Land Rover on 1 January 2013.
Jaguar’s business was founded as the Swallow Sidecar Company in 1922, originally making motorcycle sidecars before developing bodies for passenger cars. Under the ownership of S. S. Cars Limited, the business extended to complete cars made in association with Standard Motor Co, many bearing Jaguar as a model name. The company’s name was changed from S. S. Cars to Jaguar Cars in 1945. A merger with the British Motor Corporation followed in 1966,[4] the resulting enlarged company now being renamed as British Motor Holdings (BMH), which in 1968 merged with Leyland Motor Corporation and became British Leyland, itself to be nationalised in 1975.
Jaguar was spun off from British Leyland and was listed on the London Stock Exchange in 1984, becoming a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index until it was acquired by Ford in 1990.[5] Jaguar has, in recent years, manufactured cars for the British Prime Minister, the most recent delivery being an XJ in May 2010.[6] The company also holds royal warrants from Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Charles.[7]
Ford owned Jaguar Cars, also buying Land Rover in 2000, until 2008 when it sold both to Tata Motors. Tata created Jaguar Land Rover as a subsidiary holding company. At operating company level, in 2013 Jaguar Cars was merged with Land Rover to form Jaguar Land Rover Limited as the single design, manufacture, sales company and brand owner for both Jaguar and Land Rover vehicles.
Since the Ford ownership era, Jaguar and Land Rover have used joint design facilities in engineering centres at Whitley in Coventry and Gaydon in Warwickshire and Jaguar cars have been assembled in plants at Castle Bromwich and Solihull.
On 15 February 2021, Jaguar Land Rover announced that all cars made under the Jaguar brand will be fully electric by 2025.[8]
History
Founding
The Swallow Sidecar Company was founded in 1922 by two motorcycle enthusiasts, William Lyons and William Walmsley. In 1934 Walmsley elected to sell-out and in order to buy the Swallow business (but not the company which was liquidated) Lyons formed S.S. Cars Limited, finding new capital by issuing shares to the public.
Jaguar first appeared in September 1935 as a model name on an SS 2½-litre sports saloon.[9][10] A matching open two seater sports model with a 3½-litre engine was named SS Jaguar 100.
On 23 March 1945, the S. S. Cars shareholders in general meeting agreed to change the company’s name to Jaguar Cars Limited. Said chairman William Lyons «Unlike S. S. the name Jaguar is distinctive and cannot be connected or confused with any similar foreign name.»[11]
Though five years of pent-up demand ensured plenty of buyers production was hampered by shortage of materials, particularly steel, issued to manufacturers until the 1950s by a central planning authority under strict government control. Jaguar sold Motor Panels, a pressed steel body manufacturing company bought in the late 1930s, to steel and components manufacturer Rubery Owen,[12] and Jaguar bought from John Black’s Standard Motor Company the plant where Standard built Jaguar’s six-cylinder engines.[12] From this time Jaguar was entirely dependent for their bodies on external suppliers, in particular then independent Pressed Steel and in 1966 that carried them into BMC, BMH and British Leyland.
SS Jaguar 3½-litre, 125 hp
drophead coupé 1940
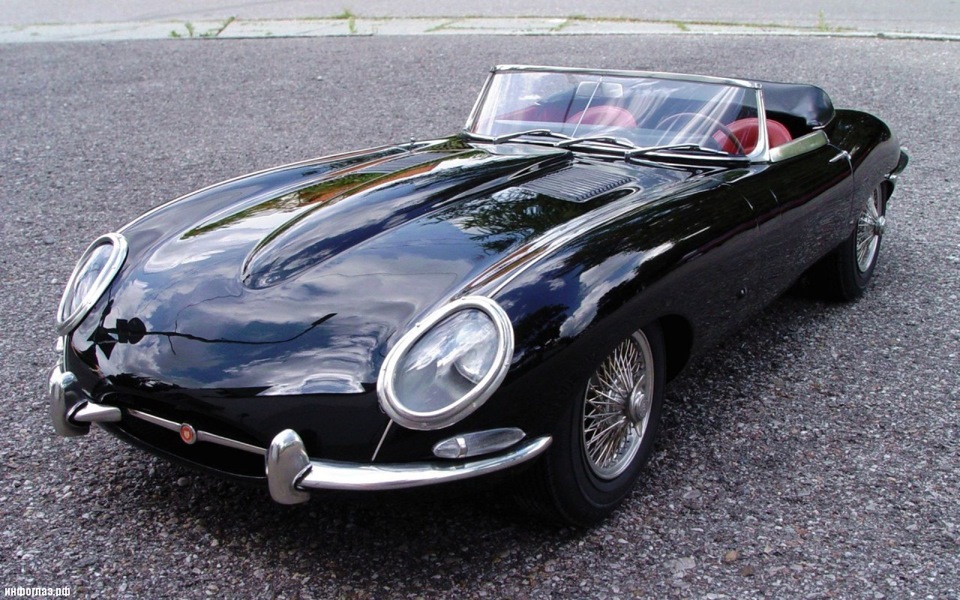
Jaguar made its name by producing a series of successful eye-catching sports cars, the Jaguar XK120 (1948–54), Jaguar XK140 (1954–57), Jaguar XK150 (1957–61), and Jaguar E-Type (1961–75), all embodying Lyons’ mantra of «value for money».[13] The sports cars were successful in international motorsport, a path followed in the 1950s to prove the engineering integrity of the company’s products.
Jaguar’s sales slogan for years was «Grace, Space, Pace»,[14] a mantra epitomised by the record sales achieved by the MK VII, IX, Mks I and II saloons and later the XJ6.[citation needed] During the time this slogan was used, but the exact text varied.[15][16][17][18]
The core of Bill Lyons’ success following WWII was the twin-cam straight six engine, conceived pre-war and realised while engineers at the Coventry plant were dividing their time between fire-watching and designing the new power plant. It had a hemispherical cross-flow cylinder head with valves inclined from the vertical; originally at 30 degrees (inlet) and 45 degrees (exhaust) and later standardised to 45 degrees for both inlet and exhaust.
As fuel octane ratings were relatively low from 1948 onwards, three piston configuration were offered: domed (high octane), flat (medium octane), and dished (low octane).
The main designer, William «Bill» Heynes, assisted by Walter «Wally» Hassan, was determined to develop the Twin OHC unit. Bill Lyons agreed over misgivings from Hassan. It was risky to take what had previously been considered a racing or low-volume and cantankerous engine needing constant fettling and apply it to reasonable volume production saloon cars.
The subsequent engine (in various versions) was the mainstay powerplant of Jaguar, used in the XK 120, Mk VII Saloon, Mk I and II Saloons and XK 140 and 150. It was also employed in the E Type, itself a development from the race winning and Le Mans conquering C and D Type Sports Racing cars refined as the short-lived XKSS, a road-legal D-Type.
Few engine types have demonstrated such ubiquity and longevity: Jaguar used the Twin OHC XK Engine, as it came to be known, in the Jaguar XJ6 saloon from 1969 through 1992, and employed in a J60 variant as the power plant in such diverse vehicles as the British Army’s Combat Vehicle Reconnaissance (Tracked) family of vehicles, as well as the Fox armoured reconnaissance vehicle, the Ferret Scout Car, and the Stonefield four-wheel-drive all-terrain lorry. Properly maintained, the standard production XK Engine would achieve 200,000 miles of useful life.
Two of the proudest moments in Jaguar’s long history in motor sport involved winning the Le Mans 24 hours race, firstly in 1951 and again in 1953. Victory at the 1955 Le Mans was overshadowed by it being the occasion of the worst motorsport accident in history. Later in the hands of the Scottish racing team Ecurie Ecosse two more wins were added in 1956 and 1957.
In spite of such a performance orientation, it was always Lyons’ intention to build the business by producing world-class sporting saloons in larger numbers than the sports car market could support. Jaguar secured financial stability and a reputation for excellence with a series of elegantly styled luxury saloons that included the 3-litre and 3½ litre cars, the Mark VII, VIII, and IX, the compact Mark I and 2, and the XJ6 and XJ12. All were deemed very good values, with comfortable rides, good handling, high performance, and great style.
Combined with the trend-setting XK 120, XK 140, and XK 150 series of sports car, and nonpareil E-Type,[citation needed] Jaguar’s elan as a prestige motorcar manufacturer had few rivals. The company’s post-War achievements are remarkable, considering both the shortages that drove Britain (the Ministry of Supply still allocated raw materials) and the state of metallurgical development of the era.
Daimler
In 1950, Jaguar agreed to lease from the Ministry of Supply the Daimler Shadow 2 factory in Browns Lane, Allesley, Coventry, which at the time was being used by The Daimler Company Limited and moved to the new site from Foleshill over the next 12 months.[19] Jaguar purchased Daimler – not to be confused with Daimler-Benz or Daimler AG—in 1960 from BSA. From the late 1960s, Jaguar used the Daimler marque as a brand name for their most luxurious saloons.[20]
Ownership
An end to independence
Pressed Steel Company Limited made all Jaguar’s (monocoque) bodies leaving provision and installation of the mechanicals to Jaguar. In mid-1965 British Motor Corporation (BMC), the Austin-Morris combine, bought Pressed Steel.[21] Lyons became concerned about the future of Jaguar, partly because of the threat to ongoing supplies of bodies, and partly because of his age and lack of an heir. He therefore accepted BMC’s offer to merge with Jaguar to form British Motor (Holdings) Limited.[22] At a press conference on 11 July 1965 at the Great Eastern Hotel in London, Lyons and BMC chairman George Harriman announced, «Jaguar Group of companies is to merge with The British Motor Corporation Ltd., as the first step towards the setting up of a joint holding company to be called British Motor (Holdings) Limited». In due course BMC changed its name to British Motor Holdings[23] at the end of 1966.
BMH was pushed by the Government to merge with Leyland Motor Corporation Limited, manufacturer of Leyland bus and truck, Standard-Triumph and, since 1967, Rover vehicles. The result was British Leyland Motor Corporation, a new holding company which appeared in 1968, but the combination was not a success. A combination of poor decision making by the board along with the financial difficulties of, especially, the Austin-Morris division (previously BMC) led to the Ryder Report and to effective nationalisation in 1975.[citation needed]
Temporary return to independence
Over the next few years it became clear that because of the low regard for many of the group’s products insufficient capital could be provided to develop and begin manufacture of new models, including Jaguars, particularly if Jaguar were to remain a part of the group.[24]
Jaguar XJ (X300), a luxury sedan manufactured by Jaguar Cars between 1994 and 1997
In July 1984, Jaguar was floated off as a separate company on the stock market – one of the Thatcher government’s many privatisations[25]– to create its own track record.[26]
Installed as chairman in 1980, Sir John Egan is credited for Jaguar’s unprecedented prosperity immediately after privatisation. In early 1986 Egan reported he had tackled the main problems that were holding Jaguar back from selling more cars: quality control, lagging delivery schedules, poor productivity. He laid off about one third of the company’s roughly 10,000 employees to cut costs.[27] Commentators later pointed out he exploited an elderly model range (on which all development costs had been written off) and raised prices. He also intensified the effort to improve Jaguar’s quality. In the US the price increases were masked by a favourable exchange rate.[28]
Ford Motor Company era
Ford made offers to Jaguar’s US and UK shareholders to buy their shares in November 1989; Jaguar’s listing on the London Stock Exchange was removed on 28 February 1990.[29] In 1999 it became part of Ford’s new Premier Automotive Group along with Aston Martin, Volvo Cars and, from 2000, Land Rover. Under Ford’s ownership, Jaguar never made a profit.[30]
Under Ford’s ownership Jaguar expanded its range of products with the launch of the S-Type in 1999 and X-type in 2001. After PAG acquired Land Rover in May 2000 purchase by Ford, the brand became closely associated with Jaguar. In many countries they shared a common sales and distribution network (including shared dealerships), and some models shared components, although the only shared production facility was Halewood Body & Assembly – which manufactured the technically related X-Type and the Freelander 2. Operationally the two companies were effectively integrated under a common management structure within Ford’s PAG.
On 11 June 2007, Ford announced that it planned to sell Jaguar, along with Land Rover and retained the services of Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley and HSBC to advise it on the deal. The sale was initially expected to be announced by September 2007, but was delayed until March 2008. Private equity firms such as Alchemy Partners of the UK, TPG Capital, Ripplewood Holdings (which hired former Ford Europe executive Sir Nick Scheele to head its bid), Cerberus Capital Management and One Equity Partners (owned by JP Morgan Chase and managed by former Ford executive Jacques Nasser) of the US, Tata Motors of India and a consortium comprising Mahindra and Mahindra (an automobile manufacturer from India) and Apollo Management all initially expressed interest in purchasing the marques from the Ford Motor Company.[31][32]
Before the sale was announced, Anthony Bamford, chairman of British excavator manufacturer JCB had expressed interest in purchasing the company in August 2006,[33] but backed out upon learning that the sale would also involve Land Rover, which he did not wish to buy. On Christmas Eve of 2007, Mahindra and Mahindra backed out of the race for both brands, citing complexities in the deal.[34]
Tata Motors era
On 1 January 2008, Ford formally declared that Tata was the preferred bidder.[35] Tata Motors also received endorsements from the Transport And General Worker’s Union (TGWU)-Amicus[36] combine as well as from Ford.[37] According to the rules of the auction process, this announcement would not automatically disqualify any other potential suitor. However, Ford (as well as representatives of Unite) would now be able to enter into detailed discussions with Tata concerning issues ranging from labour concerns (job security and pensions), technology (IT systems and engine production) and intellectual property,[38] as well as the final sale price.[39] Ford would also open its books for a more comprehensive due diligence by Tata.[40] On 18 March 2008, Reuters reported that American bankers Citigroup and JP Morgan would finance the deal with a US$3 billion loan.[41]
On 26 March 2008, Ford announced that it had agreed to sell its Jaguar and Land Rover operations to Tata Motors of India, and that they expected to complete the sale by the end of the second quarter of 2008.[42] Included in the deal were the rights to three other British brands, Jaguar’s own Daimler, as well as two dormant brands Lanchester and Rover.[43] On 2 June 2008, the sale to Tata was completed at a cost of £1.7 billion.[44][45][46]
On 18 January 2008, Tata Motors, a part of the Tata Group, established Jaguar Land Rover Limited as a British-registered and wholly owned subsidiary. The company was to be used as a holding company for the acquisition of the two businesses from Ford – Jaguar Cars Limited and Land Rover. That acquisition was completed on 2 June 2008.[47] On 1 January 2013, the group, which had been operating as two separate companies (Jaguar Cars Limited and Land Rover), although on an integrated basis, underwent a fundamental restructuring. The parent company was renamed to Jaguar Land Rover Automotive PLC, Jaguar Cars Limited was renamed to Jaguar Land Rover Limited and the assets (excluding certain Chinese interests) of Land Rover were transferred to it. The consequence was that Jaguar Land Rover Limited became responsible in the UK for the design, manufacture and marketing of both Jaguar and Land Rover products.[48]
Plants
From 1922 the Swallow Sidecar company (SSC) was located in Blackpool. The company moved to Holbrook Lane, Coventry in 1928 when demand for the Austin Swallow became too great for the factory’s capacity.[49] The company started using the Jaguar name whilst based in Holbrooks Lane.
In 1951, having outgrown the original Coventry site they moved to Browns Lane, which had been a wartime «shadow factory» run by The Daimler Company. The Browns Lane plant ceased trim and final operations in 2005, the X350 XJ having already moved to Castle Bromwich two years prior, with the XK and S-Type following. The Browns Lane plant, which continued producing veneer trim for a while and housed the Jaguar Daimler Heritage centre until it moved to the British Motor Museum site, has now been demolished and is being redeveloped.
Jaguar acquired the Whitley engineering centre from Peugeot in 1986; which had originally been part of Chrysler Europe which the French firm had owned since the late 1970s. The decision to offload the site to Jaguar came as Peugeot discontinued the Talbot brand for passenger cars. In 2016, Jaguar also moved into part of the old Peugeot/Chrysler/Rootes site in Ryton-on-Dunsmore which closed a decade earlier – this now is the home of Jaguar Land Rover’s classic restoration operation.
Jaguar’s Radford plant, originally a Daimler bus plant but later a Jaguar engine and axle plant, was closed by Ford in 1997 when it moved all Jaguar engine production to its Bridgend facility.
In 2000, Ford turned its Halewood plant over to Jaguar following the discontinuation of its long running Escort that year for Jaguar’s new X-Type model. It was later joined by the second-generation Land Rover Freelander 2, from 2007. Jaguars ceased being produced at Halewood in 2009 following the discontinuation of the X-Type; Halewood now becoming a Land Rover-only plant.
Since Jaguar Land Rover was formed following the merger of Jaguar Cars with Land Rover, facilities have been shared across several JLR sites, most of which are used for work on both the Jaguar and Land Rover brands.
Current cars
E-Pace
The Jaguar E-Pace is a compact SUV, officially revealed on 13 July 2017.[50]
F-Pace
The F-Pace is a compact luxury crossover SUV – the first SUV from Jaguar. It was unveiled at the International Motor Show Germany in Frankfurt in September 2015.[51]
F-Type
The F-Type convertible was launched at the 2012 Paris Motor Show, following its display at the Goodwood Festival of Speed in June 2012,[52] and is billed as a successor to the legendary E-Type. In fact, the Series III E-Type already had a successor, in the form of the XJS, which was in turn replaced by the XK8 and XKR. The F-Type nevertheless returns to the 2-seat plan that was lost with the introduction of the Series III E-Type, which was available only in a 2+2-seat configuration. It was developed following the positive reaction to Jaguar’s C-X16 concept car at the 2011 Frankfurt Auto Show. Sales will begin in 2013 with three engine choices; two variants of the AJ126 V6 petrol engine and the AJ133 V8 petrol engine.[53]
I-Pace
The Jaguar I-Pace is an electric SUV, officially revealed on 1 March 2018. It is Jaguar’s first electric car.
XE
The XE is the first compact executive Jaguar since the 2009 model year X-Type and is the first of several Jaguar models to be built using Jaguar’s new modular aluminium architecture,[citation needed] moving the company away from the Ford derived platforms that were used in the past for the X-Type and XF. The use of Jaguar’s own platform allows the XE to feature either rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive configurations, and it is the first car in its segment with an aluminium monocoque structure.[54] Originally announced at the 2014 Geneva Motor Show with sales scheduled for 2015.[55]
XF
The Jaguar XF is a mid-size executive car introduced in 2008 to replace the S-Type. In January 2008, the XF was awarded the What Car? ‘Car of the Year’ and ‘Executive Car of the Year’ awards. The XF was also awarded Car of the Year 2008 from What Diesel? magazine. Engines available in the XF are 2.2-litre I4 and 3.0-litre V6 diesel engines, or 3.0 litre V6 and 5.0-litre V8 petrol engines. The 5.0 Litre engine is available in supercharged form in the XFR. From 2011, the 2.2-litre diesel engine from the Land Rover Freelander was added to the range as part of a facelift.[56]
R models
Jaguar began producing R models in 1995 with the introduction of the first XJR, and the first XKR was introduced in 1997. Jaguar R, R-S and SVR models are designated to compete with the likes of Mercedes-AMG, BMW M and Audi S and RS.
Historic car models
The renamed Jaguar company started production with the pre-war 1.5, 2.5 and 3.5-litre models, which used engines designed by the Standard Motor Company. The 1.5-litre four-cylinder engine was still supplied by Standard but the two larger six-cylinder ones were made in house. These cars have become known unofficially as Mark IVs.
The first post-war model was the September 1948 Mark V available with either 2.5 or 3.5-litre engines. It had a slightly more streamlined appearance than pre-war models, but more important was the change to torsion bar independent front suspension and hydraulic brakes.[citation needed] In the spring of 1948 Lyons had returned from USA reporting Jaguar’s individuality and perceived quality attracted the admiration of American buyers accustomed to the virtual uniformity of their home-grown vehicles.[57]
The 1948 XK120 was a breakthrough both for Jaguar and post-WWII sports cars.
The first big breakthrough was the launch in October 1948 of their new record-breaking engine design in their XK120 sportscar to replace the prewar SS Jaguar 100. It was powered by a new twin overhead camshaft (DOHC) 3.5-litre hemi-head six-cylinder engine designed by William Heynes, Walter Hassan and Claude Baily. The XK100 4-cylinder 2-Litre version had broken records in Belgium travelling at 177 mph. This XK engine had been designed at night during the war when they would be on fire watch in the factory. After several attempts a final design was achieved. That is until owner William Lyons said «make it quieter».
The sportscar bearing its prefix X had originally been intended as a short production model of about 200 vehicles. A test bed for the new engine until its intended home, the new Mark VII saloon, was ready.[citation needed]
1950 «Grace … Space … Pace – Jaguar» Mark VII
The second big breakthrough was the large Mark VII saloon in 1950, a car especially conceived for the American market, Jaguar was overwhelmed with orders. The Mark VII and its successors gathered rave reviews from magazines such as Road & Track and The Motor. In 1956 a Mark VII won the prestigious Monte Carlo Rally. The XK120’s exceptional reception was followed in 1954 by an improved XK140 then in May 1957 a fully revised XK150.
1960s Mark 2 became one of the most recognisable Jaguar models ever produced.
In 1955, the Two-point-four or 2.4-litre saloon (named by enthusiasts 2.4 Mark 1) was the first monocoque (unitary) car from Jaguar.[citation needed] Its 2.4-litre short-stroke version of the XK engine provided 100 mph (160 km/h) performance. In 1957, the 3.4-litre version with disk brakes, wire wheels and other options was introduced, with a top speed of 120 mph (190 km/h). In October 1959, an extensively revised version of the car with wider windows and 2.4, 3.4, and 3.8-litre engine options became the Mark 2. The 3.8 Mark 2 was popular with British police forces for its small size and 125 mph (201 km/h) performance.
The Mark VIII of 1956 and Mark IX of 1958 were essentially updates of the Mark VII, but the oversize Mark X of 1961 was a completely new design of large saloon with all round independent suspension and unitary construction.
Jaguar launched the E-Type in 1961.
The independent rear suspension from the Mark X was incorporated in the 1963 S-Type, a Mark 2 lengthened to contain the complex rear suspension, and in 1967 the Mark 2 name was dropped when the small saloons became the 240/340 range. The 420 of 1966, also sold as the Daimler Sovereign, put a new front onto the S-type, although both cars continued in parallel until the S-Type was dropped in 1968. The slow-selling Mark X became the 420G in 1966 and was dropped at the end of the decade. Jaguar was saved by its new equally capacious but very much trimmer new XJ6.
Of the more recent saloons, the most significant is the XJ (1968–1992). From 1968 on, the Series I XJ saw minor changes, first in 1973 (to Series II), 1979 (Series III), a complete redesign for 1986/1987 in XJ40, further modifications in 1995 (X300), in 1997 with V8-power (X308), and a major advance in 2003 with an industry-first aluminium monocoque-chassis (X350). The most luxurious XJ models carried either the Vanden Plas (US) or Daimler (rest of world) nameplates. In 1972, the 12-cylinder engine was introduced in the XJ, while simultaneously being offered in the E Type.
The XJ220—the world’s fastest production car in 1992
1992 saw the introduction of the mid-engined, twin-turbo XJ220, powered by a 542 bhp (404 kW; 550 PS) V6 engine. The XJ220 was confirmed the fastest production car in the world at the time after Martin Brundle recorded a speed of 217 mph (349 km/h) on the Nardo track in Italy.[58]
Over the years many Jaguar models have sported the famous chrome plated Leaping Jaguar, traditionally forming part of the radiator cap. Known as «The Leaper», this iconic mascot has been the subject of controversy in recent times when banned for safety reasons from cars supplied to Europe whilst it continued to be fitted on cars destined for the United States, Middle East and Far East. It has now been dropped from all the latest Jaguar models, although some customers add it to their car as a customization.
The Jaguar S-Type, first appeared in 1999 and stopped production in 2008. It has now been replaced by the Jaguar XF. Early S-Types suffered from reliability problems but those were mostly resolved by the 2004 model year.[59]
The Jaguar X-Type was a compact executive car launched in 2001, while the company was under Ford ownership, sharing its platform with the Ford Mondeo. X-Type production ended in 2009.[60]
The Jaguar XK was a luxury grand tourer introduced in 2006, where it replaced the XK8. The XK introduced an aluminium monocoque bodyshell, and was available both as a two-door coupé and two-door cabriolet/convertible.[61] Production ceased in 2014.
The Jaguar XJ was a full-size luxury saloon. The model was in production since 1968, with production ceasing in 2019, with the first generation being the last Jaguar car to have creative input by the company’s founder, Sir William Lyons, although this is disputed as some Jaguar historians claim that the second generation XJ – the XJ40 series – was the last car which Lyons had influenced. The XJ40 originally launched in 1986 and went through two major revamps in 1994 (X300) and 1997 (X308) for a total production run of 17 years. In early 2003, the third generation XJ – the X350 – arrived in showrooms and while the car’s exterior and interior styling were traditional in appearance, the car was completely re-engineered. Its styling attracted much criticism from many motoring journalists who claimed that the car looked old-fashioned and barely more modern than its predecessor, many even citing that the ‘Lyons line’ had been lost in the translation from XJ40 into X350 XJ, even though beneath the shell lay a highly advanced aluminium construction that put the XJ very near the top of its class.[62]
Jaguar responded to the criticism with the introduction of the fourth generation XJ, launched in 2009. Its exterior styling is a departure from previous XJs, with a more youthful, contemporary stance, following the design shift that came into effect previously with the company’s XF and XK models.[63]
The 5-litre V8 engine in the XJ Supersport can accelerate the car from 0 to 60 mph (0–97 km/h) in 4.7 seconds, and has a UK CO2 emission rating of 289 g/km. To cater to the limousine market, all XJ models are offered with a longer wheelbase (LWB) as an option, which increases the rear legroom.[64]
List
Large executive
- 1935–1955 2+1⁄2 litre saloon
- 1937–1948 3+1⁄2 Litre saloon
- 1948–1951 Mark V
- 1951–1957 Mark VII (& VIIM)
- 1957–1959 Mark VIII
- 1959–1961 Mark IX
- 1961–1966 Mark X
- 1966–1970 420G
- 1968–1987 XJ6 Series 1, 2 & 3
- 1972–1992 XJ12
- 1986–1994 XJ6 (XJ40)
- 1993–1994 XJ12 (XJ81)
- 1995–1997 XJ6 & XJ12 (X300 & X301)
- 1998–2003 XJ8 (X308)
- 2004–2007 XJ (X350)
- 2008–2009 XJ (X358)
Compact executive
- 1935–1949 1+1⁄2 Litre saloon
- 1955–1959 Mark 1
- 1959–1967 Mark 2
- 1963–1968 S-type
- 1966–1968 420
- 1966–1968 240 & 340
- 1999–2008 S-type
- 2001–2009 X-type
- 2007–2015 XF (X250)
Sports
- 1948–1954 XK120
- 1954–1957 XK140
- 1957–1961 XK150
- 1961–1974 E-Type
- 1975–1996 XJ-S
- 1992–1994 XJ220
- 1997–2006 XK8/XKR (X100)
- 2006–2014 XK (X150)
Racing and competition
- 1950s C-Type
- 1950s D-Type
- 1960s E-Type Lightweight
- 1985–1992 XJR-5 through XJR-17
- 2009 XFR Bonneville Salt Flats speed record
- 2010 Jaguar RSR XKR GT2
Concept cars
- E1A – The 1950s E-Type concept vehicle
- E2 A – The second E-Type concept vehicle, which raced at LeMans and in the USA
- XJ13 (1966) – Built to race at LeMans, never run
- Pirana (1967) – Designed by Bertone
- Ascot (1977)
- XJ41/XJ42 (1982-1990) – the first F-Type; cancelled due to the Ford’s takeover of Jaguar[65]
- XJ90 (1988-1991) – planned XJ40 replacement; cancelled due to Ford’s takeover of Jaguar[66]
- Kensington (1990)
- XK 180 (1998) – Roadster concept based on the XK8
- F-Type (2000) – Roadster, similar to the XK8 but smaller
- R-Coupé (2001) – Large four-seater coupé
- Fuore XF 10 (2003)
- R-D6 (2003) – Compact four-seat coupé
- XK-RR – A high-performance version of last generation XK coupé
- XK-RS – Another performance-spec version of last generation XK convertible
- Concept Eight (2004) – Super-luxury version of the long-wheelbase model of the XJ
- C-XF (2007) – Precursor to the production model XF saloon
- C-X75 (2010) – Hybrid-electric sports car, originally intended for production but cancelled in 2012
- B99 (2011)
- C-X16 (2011) – Precursor to the production model F-Type
- C-X17 (2013) – First ever Jaguar SUV concept
- Project 7 – a 542 bhp V8-powered speedster based on the F-Type and inspired by the D-Type (2013)[67]
- Future-Type (2017)
Engines
Jaguar has designed in-house six generations of engines:
- Historic:
- XK6 – Inline-6
- V12 – 60° V12
- AJ6/AJ16 – 22° Inline-6
- AJ-V6 – 60° V6 (Ford designed, Jaguar modified)
- Current:
- AJ-V8 – 90° V8
- AJ126 – 90° V6
- AJD-V6 – 60° V6 (Ford designed)
- Ingenium – Inline-4
Motorsport
Jaguar has had major success in sports car racing, particularly in the Le Mans 24 Hours. Victories came in 1951 and 1953 with the C-Type, then in 1955, 1956 and 1957 with the D-Type. The manager of the racing team during this period, Lofty England, later became CEO of Jaguar in the early 1970s. Although the prototype XJ13 was built in the mid-1960s it was never raced, and the famous race was then left for many years.
In 1982, a successful relationship with Tom Walkinshaw’s TWR team commenced with the XJ-S competing in the European Touring Car Championship, which it won in 1984.[68] In 1985, the TWR XJ-S won the Bathurst 1000 race. In the mid-1980s TWR started designing and preparing Jaguar V12-engined Group C cars for World Sports Prototype Championship races. The team started winning regularly from 1987, and won Le Mans in 1988 and 1990 with the XJR series sports cars. The Jaguar XJR-14 was the last of the XJRs to win, taking the 1991 World Sportscar Championship.
In 1999, Ford decided that Jaguar would be the corporation’s Formula One entry. Ford bought out the Milton Keynes-based Stewart Grand Prix team and rebranded it as Jaguar Racing for the 2000 season. The Jaguar F1 program was not a success however, achieving only two podium finishes in five seasons of competition between 2000 and 2004. At the end of 2004, with costs mounting and Ford’s profits dwindling, the F1 team was seen as an unneeded expense and was sold to Red Bull energy drinks owner Dietrich Mateschitz,[69] and it became Red Bull Racing.
On 15 December 2015, it was announced that Jaguar would return to motorsport for the third season of Formula E.
On 15 June 2018, Jaguar Vector Racing broke the world speed record for an electric battery powered boat. The Jaguar Vector V20E recorded an average speed of 88.61 mph across the two legs of the 1 km course on Coniston Water, England.[70]
Notable sports racers:
- Jaguar C-Type (1951–1953)
- Jaguar D-Type (1954–1957)
- Jaguar Lightweight E-Type
- Jaguar XJ13[71]
- Jaguar XJR Sportscars
- Jaguar XJR-9 (1988)
- XJ220 (1988)
- XJR-15 (1990)
Jaguar and the arts
Jaguar Art Project «Shadows», Saint-Tropez 2011
For some time now,[when?] Jaguar has been active in the international arts scene. In particular, the company has collaborated with the artist Stefan Szczesny, implementing major art projects. In 2011, Jaguar presented the exhibition series «Shadows», which involved the installation of Szczesny’s shadow sculptures in Sankt-Moritz, on Sylt and in Saint-Tropez. In 2012, a large number of sculptures, ceramics and paintings were shown in Frankfurt (and mainly in Frankfurt’s Palmengarten).
As part of the collaboration with Szczesny, Jaguar has released the «Jaguar Art Collection».[citation needed]
See also
- List of car manufacturers of the United Kingdom
References
- ^ a b «Trade mark number EU000026625». Intellectual Property Office. Crown (UK Government). Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ^ «JAGUAR CARS LIMITED overview — Find and update company information — GOV.UK».
- ^ «Jaguar Land Rover 2012 Overview» (PDF). Jaguar Land Rover. 14 June 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 February 2013.
- ^ «Jaguar Group of companies is to merge with The British Motor Corporation Ltd., as the first step towards the setting up of a joint holding company to be called British Motor (Holdings) Limited.» Official statement released at press conference at the Great Eastern Hotel, London, 1966.
- ^ «The Years 1989 to 1996». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Archived from the original on 24 June 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ «Cameron gets a new Jag to go with the new job – Autoblog UK». Uk.autoblog.com. 13 May 2010. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- ^ «The Royal Warrant Holders ‘ Association – Directory of Royal Warrant Holders». Archived from the original on 12 December 2007. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ «Jaguar car brand to be all-electric by 2025». BBC News. 15 February 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ «Design Evolution: 80 Years of Jaguar – Part 1». Jaguar. Jaguar Land Rover. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- ^ «The Years 1932 to 1935». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Archived from the original on 1 June 2009. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ S.S. Cars Limited. The Times, Wednesday, 4 April 1945; pg. 10; Issue 50108
- ^ a b «The Lyons share – interview with WL». Motor: 18–21. 19 February 1972.
- ^ «Jaguar». Archived from the original on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ^ «The classic has to be «Grace… Space… Pace,» which was used throughout the 1950s and 1960s». Clausager, Anders Ditlev (2010). «Jaguar: A History of Grace and Pace». MSN. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 2 September 2013.
- ^ Walton, Paul (13 December 2012). «Grace… Space… Pace». jaguar-world.com. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ Peterborough, Brave Creative (19 November 2010). «Jaguar: 75 Years of Grace, Space and Pace». themomentmagazine.com. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ «1306381302_a13c957db6_4840.jpg (JPEG Image, 374 × 500 pixels)». typophile.com. 28 August 2011. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ «tumblr_lwqh6th15q1qchs1zo1_1280.jpg (JPEG Image, 1280 × 1256 pixels)». 31.media.tumblr.com. 24 December 2011. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ ‘Sir William Lyons – The Official Biography’, Philip Porter & Paul Skilleter, page 120 onwards
- ^ «The Years 1968 to 1979». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ Utton, M. A. (2003). «9 – Vertical integration and vertical mergers». Market Dominance and Antitrust Policy. Cheltenham, Glos, UK: Edward Elgar Publishing. p. 226. ISBN 1-84064-728-0. LCCN 2002029832. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
- ^ Douglas-Scott-Montagu, Edward John Barrington & Burgess-Wise, David (1995). «Chapter 9 – Under New Management». Daimler Century: The full history of Britain’s oldest car maker. Sparkford, Nr Yeovil, Somerset, UK: Patrick Stephens. p. 283. ISBN 1-85260-494-8.
…Sir George Harriman of the British Motor Corporation (whose Pressed Steel subsidiary supplied Jaguar bodyshells) offered Lyons a ‘logical and beneficial’ merger deal, which would leave Jaguar operating under Lyons’s chairmanship as ‘a separate entitiy and with the greatest practical degree of autonomy’ within a new organization called British Motor (Holdings) Limited.
- ^ «British Motor Takes That New Label». The Times. No. 56815. London. 15 December 1966. p. 17.
- ^ page 49, Andrew M. McLaughlin, William A. Maloney, The European Automobile Industry: Multi-Level Governance, Policy and Politics Taylor & Francis e-Library 2005. accessed 31 Jan 2013
- ^ Elliott, Larry (22 November 2000). «A whole world sold on sell-offs». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ page 50, Andrew M. McLaughlin, William A. Maloney, The European Automobile Industry: Multi-Level Governance, Policy and Politics Taylor & Francis e-Library 2005.
- ^ Zetlin, M. (1986). John Egan: Tough leadership turns Jaguar around. Management Review, 75(5), (May 1986) 20–20.
- ^ The Badge on the Bonnet. The Times Friday, 3 November 1989; pg. 13; Issue 63542.
- ^ «The Years 1989 to 1996». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Archived from the original on 24 June 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ «Although Land Rover remains profitable, Ford has never managed to make money from its investment in Jaguar.» «Tata buys Jaguar in £1.15bn deal». BBC News. 26 March 2008. Retrieved 3 September 2013.
- ^ «India’s Tata confirms interest in Land Rover, Jaguar». Forbes. AFX News Limited. 24 August 2007. Archived from the original on 8 December 2007. Retrieved 18 December 2007.
- ^ Clark, Nick (4 January 2008). «Tata in pole position to buy Jaguar and Land Rover marques from Ford». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 5 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «JCB’s Sir Anthony Bamford eyes Jaguar». Contract Journal. 24 August 2006. Archived from the original on 31 May 2009.
- ^ Doval, Pankaj (24 December 2007). «M&M out of Jaguar, Land Rover race». Times News Network. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ Krisher, Tom (3 January 2008). «Indian Company Top Bidder for Jaguar». Time. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 6 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «Tata set to clinch Jaguar-Land Rover deal: Report». Press Trust of India. 20 December 2007. Archived from the original on 23 December 2007. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Robbins, Mathieu (17 December 2007). «Ford set to pick Jaguar frontrunner in days: source». Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 October 2012. Retrieved 16 February 2011.
- ^ Ghosh, Suprotip (3 January 2008). «Super car technology headed for Tata stable». Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 5 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ Leahy, Joe; Simon, Bernard; Yee, Amy (4 January 2008). «Tata falls for the attraction of opposites». Financial Times. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «Ball now in Tata Motors’ court to tie-up deal: Unite». CNBC TV-18. 3 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «Tata gets $3 billion loan from Citi, JPMorgan: source». Reuters. 18 March 2008. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 18 March 2008.
- ^ «FORD MOTOR COMPANY ANNOUNCES AGREEMENT TO SELL JAGUAR LAND ROVER TO TATA MOTORS» (Press release). Ford Motor Company. 26 March 2008. Archived from the original on 12 June 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2008.
- ^ «5 for 2 special: Tata acquires 3 other British marques in Jaguar, Land Rover deal». Leftlane News. 28 March 2008. Retrieved 28 March 2008.
- ^ «Tata Motors completes acquisition of Jag, Land Rover». 2 June 2008. Retrieved 2 June 2008.
- ^ «On U.S. tour, Mr. Tata gives Jaguar and Rover dealers a hug: AutoWeek Magazine». Autoweek.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ^ «Jobs warning at Jaguar Land Rover». BBC News. 26 June 2009. Retrieved 26 June 2009.
- ^ «2010/2011 Annual Report» (PDF). Jaguar Land Rover PLC. p. 5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 January 2018. Retrieved 26 January 2018.
- ^ «Annual Report 2012/2013» (PDF). Jaguar Land Rover Automotive PLC. p. 91. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 January 2018. Retrieved 26 January 2018.
- ^ «Jaguar History». The Surrey Region Jaguar Enthusiasts Club. Archived from the original on 30 June 2007.
- ^ Tisshaw, Mark (13 July 2017). «2018 Jaguar E-Pace officially revealed: release date, price and interior». Autocar. Retrieved 3 March 2018.
- ^ Ingram, Richard (21 October 2015). «New Jaguar F-Pace SUV: Frankfurt debut, prices, engines and specs». Auto Express. Dennis Publishing. Retrieved 3 March 2018.
- ^ Healey, James (2 July 2012). «Disguised Jaguar F-type sports car runs at Goodwood». USA Today. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- ^ «CAR Magazine: Jaguar F-type (2013) first official pictures». Retrieved 28 September 2012.
- ^ «Jaguar XE Launch Press Release».
- ^ «New Jaguar saloon to be called XE». Auto Express. 4 March 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ^ «Jaguar Cars UK Web Site». jaguar.co.uk. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ «British Cars for U.S.» The Times, 27 April 1948, p. 2; Issue 51056.
- ^ «The monster and the myth – It is the story they’ve been waiting for with bated breath». The Guardian. 22 August 1992.
On the Nardo track of southern Italy, Martin Brundle, the Grand Prix driver, confirmed it as the fastest production car with 217mph, narrowly quicker than the Bugatti. The Ferrari 512 or earlier F40 does around 200mph. The F40 boasts 0–60mph in 4.1 seconds. The Lamborghini Diablo is 4.09 and Porsche 959, 3.9. The Jaguar rates 3.85.
- ^ Consumer Reports, Buying Guide 2007, 211.
- ^ Wearden, Graeme (15 July 2009). «300 jobs lost at Jaguar’s Halewood plant». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 15 July 2009.
- ^ «Jaguar XK Guide». carpages.co.uk. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ Series». Autocars. Archived from the original on 9 July 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ Plisner, Peter (9 July 2009). «Changing face of Jaguar». BBC News. Retrieved 15 July 2009.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ – models». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Retrieved 19 June 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Concepts and prototypes : Jaguar XJ41/XJ42 (1982-1990)». AROnline. 19 March 2021.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ90 : the missing 1990s XJ finally breaks cover». AROnline. 17 July 2022.
- ^ BBC Top Gear.. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- ^ «Double loss for motor sport». Motor Sport. 16 December 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ^ «Red Bull snaps up Jaguar F1 team». BBC News. 15 November 2004. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ^ «Jaguar Vector Racing Break Maritime Electric World Record | Jaguar Vector Racing». Jaguar Vector Racing. 15 June 2018. Retrieved 16 June 2018.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ13 – Building the Legend». 14 June 2013. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
External links
- Jaguar official website
- Jaguar Daimler Heritage Trust website
 |
|
| Product type | Cars |
|---|---|
| Owner | Jaguar Land Rover (since 2013)[1] |
| Produced by | Jaguar Land Rover |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Introduced | September 1935; 87 years ago |
| Related brands | Land Rover |
| Markets | Worldwide |
| Previous owners | Jaguar Cars Limited |
| Tagline | «The Art of Performance» |
| Website | jaguar.com |
 |
|
| Formerly | S.S. Cars Limited (1933–1945) |
|---|---|
| Type |
|
| Industry | Automotive |
| Predecessor | Swallow Coachbuilding Company Limited |
| Founded | 26 October 1933; 89 years ago |
| Founder | William Lyons |
| Fate | Car manufacturing merged with Land Rover in 2013 as Jaguar Land Rover |
| Headquarters |
Whitley , England |
| Parent |
|
Jaguar (, ) is the luxury vehicle brand of Jaguar Land Rover,[1][3] a British multinational car manufacturer with its headquarters in Whitley, Coventry, England. Jaguar Cars was the company that was responsible for the production of Jaguar cars until its operations were fully merged with those of Land Rover to form Jaguar Land Rover on 1 January 2013.
Jaguar’s business was founded as the Swallow Sidecar Company in 1922, originally making motorcycle sidecars before developing bodies for passenger cars. Under the ownership of S. S. Cars Limited, the business extended to complete cars made in association with Standard Motor Co, many bearing Jaguar as a model name. The company’s name was changed from S. S. Cars to Jaguar Cars in 1945. A merger with the British Motor Corporation followed in 1966,[4] the resulting enlarged company now being renamed as British Motor Holdings (BMH), which in 1968 merged with Leyland Motor Corporation and became British Leyland, itself to be nationalised in 1975.
Jaguar was spun off from British Leyland and was listed on the London Stock Exchange in 1984, becoming a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index until it was acquired by Ford in 1990.[5] Jaguar has, in recent years, manufactured cars for the British Prime Minister, the most recent delivery being an XJ in May 2010.[6] The company also holds royal warrants from Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Charles.[7]
Ford owned Jaguar Cars, also buying Land Rover in 2000, until 2008 when it sold both to Tata Motors. Tata created Jaguar Land Rover as a subsidiary holding company. At operating company level, in 2013 Jaguar Cars was merged with Land Rover to form Jaguar Land Rover Limited as the single design, manufacture, sales company and brand owner for both Jaguar and Land Rover vehicles.
Since the Ford ownership era, Jaguar and Land Rover have used joint design facilities in engineering centres at Whitley in Coventry and Gaydon in Warwickshire and Jaguar cars have been assembled in plants at Castle Bromwich and Solihull.
On 15 February 2021, Jaguar Land Rover announced that all cars made under the Jaguar brand will be fully electric by 2025.[8]
History
Founding
The Swallow Sidecar Company was founded in 1922 by two motorcycle enthusiasts, William Lyons and William Walmsley. In 1934 Walmsley elected to sell-out and in order to buy the Swallow business (but not the company which was liquidated) Lyons formed S.S. Cars Limited, finding new capital by issuing shares to the public.
Jaguar first appeared in September 1935 as a model name on an SS 2½-litre sports saloon.[9][10] A matching open two seater sports model with a 3½-litre engine was named SS Jaguar 100.
On 23 March 1945, the S. S. Cars shareholders in general meeting agreed to change the company’s name to Jaguar Cars Limited. Said chairman William Lyons «Unlike S. S. the name Jaguar is distinctive and cannot be connected or confused with any similar foreign name.»[11]
Though five years of pent-up demand ensured plenty of buyers production was hampered by shortage of materials, particularly steel, issued to manufacturers until the 1950s by a central planning authority under strict government control. Jaguar sold Motor Panels, a pressed steel body manufacturing company bought in the late 1930s, to steel and components manufacturer Rubery Owen,[12] and Jaguar bought from John Black’s Standard Motor Company the plant where Standard built Jaguar’s six-cylinder engines.[12] From this time Jaguar was entirely dependent for their bodies on external suppliers, in particular then independent Pressed Steel and in 1966 that carried them into BMC, BMH and British Leyland.
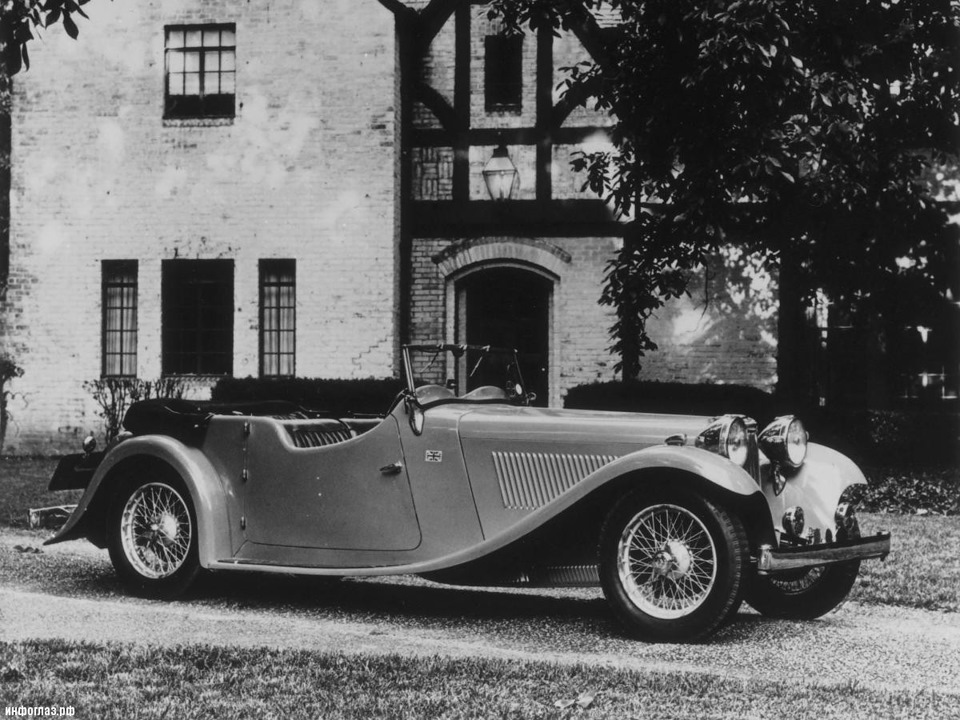
SS Jaguar 3½-litre, 125 hp
drophead coupé 1940
Jaguar made its name by producing a series of successful eye-catching sports cars, the Jaguar XK120 (1948–54), Jaguar XK140 (1954–57), Jaguar XK150 (1957–61), and Jaguar E-Type (1961–75), all embodying Lyons’ mantra of «value for money».[13] The sports cars were successful in international motorsport, a path followed in the 1950s to prove the engineering integrity of the company’s products.
Jaguar’s sales slogan for years was «Grace, Space, Pace»,[14] a mantra epitomised by the record sales achieved by the MK VII, IX, Mks I and II saloons and later the XJ6.[citation needed] During the time this slogan was used, but the exact text varied.[15][16][17][18]
The core of Bill Lyons’ success following WWII was the twin-cam straight six engine, conceived pre-war and realised while engineers at the Coventry plant were dividing their time between fire-watching and designing the new power plant. It had a hemispherical cross-flow cylinder head with valves inclined from the vertical; originally at 30 degrees (inlet) and 45 degrees (exhaust) and later standardised to 45 degrees for both inlet and exhaust.
As fuel octane ratings were relatively low from 1948 onwards, three piston configuration were offered: domed (high octane), flat (medium octane), and dished (low octane).
The main designer, William «Bill» Heynes, assisted by Walter «Wally» Hassan, was determined to develop the Twin OHC unit. Bill Lyons agreed over misgivings from Hassan. It was risky to take what had previously been considered a racing or low-volume and cantankerous engine needing constant fettling and apply it to reasonable volume production saloon cars.
The subsequent engine (in various versions) was the mainstay powerplant of Jaguar, used in the XK 120, Mk VII Saloon, Mk I and II Saloons and XK 140 and 150. It was also employed in the E Type, itself a development from the race winning and Le Mans conquering C and D Type Sports Racing cars refined as the short-lived XKSS, a road-legal D-Type.
Few engine types have demonstrated such ubiquity and longevity: Jaguar used the Twin OHC XK Engine, as it came to be known, in the Jaguar XJ6 saloon from 1969 through 1992, and employed in a J60 variant as the power plant in such diverse vehicles as the British Army’s Combat Vehicle Reconnaissance (Tracked) family of vehicles, as well as the Fox armoured reconnaissance vehicle, the Ferret Scout Car, and the Stonefield four-wheel-drive all-terrain lorry. Properly maintained, the standard production XK Engine would achieve 200,000 miles of useful life.
Two of the proudest moments in Jaguar’s long history in motor sport involved winning the Le Mans 24 hours race, firstly in 1951 and again in 1953. Victory at the 1955 Le Mans was overshadowed by it being the occasion of the worst motorsport accident in history. Later in the hands of the Scottish racing team Ecurie Ecosse two more wins were added in 1956 and 1957.
In spite of such a performance orientation, it was always Lyons’ intention to build the business by producing world-class sporting saloons in larger numbers than the sports car market could support. Jaguar secured financial stability and a reputation for excellence with a series of elegantly styled luxury saloons that included the 3-litre and 3½ litre cars, the Mark VII, VIII, and IX, the compact Mark I and 2, and the XJ6 and XJ12. All were deemed very good values, with comfortable rides, good handling, high performance, and great style.
Combined with the trend-setting XK 120, XK 140, and XK 150 series of sports car, and nonpareil E-Type,[citation needed] Jaguar’s elan as a prestige motorcar manufacturer had few rivals. The company’s post-War achievements are remarkable, considering both the shortages that drove Britain (the Ministry of Supply still allocated raw materials) and the state of metallurgical development of the era.
Daimler
In 1950, Jaguar agreed to lease from the Ministry of Supply the Daimler Shadow 2 factory in Browns Lane, Allesley, Coventry, which at the time was being used by The Daimler Company Limited and moved to the new site from Foleshill over the next 12 months.[19] Jaguar purchased Daimler – not to be confused with Daimler-Benz or Daimler AG—in 1960 from BSA. From the late 1960s, Jaguar used the Daimler marque as a brand name for their most luxurious saloons.[20]
Ownership
An end to independence
Pressed Steel Company Limited made all Jaguar’s (monocoque) bodies leaving provision and installation of the mechanicals to Jaguar. In mid-1965 British Motor Corporation (BMC), the Austin-Morris combine, bought Pressed Steel.[21] Lyons became concerned about the future of Jaguar, partly because of the threat to ongoing supplies of bodies, and partly because of his age and lack of an heir. He therefore accepted BMC’s offer to merge with Jaguar to form British Motor (Holdings) Limited.[22] At a press conference on 11 July 1965 at the Great Eastern Hotel in London, Lyons and BMC chairman George Harriman announced, «Jaguar Group of companies is to merge with The British Motor Corporation Ltd., as the first step towards the setting up of a joint holding company to be called British Motor (Holdings) Limited». In due course BMC changed its name to British Motor Holdings[23] at the end of 1966.
BMH was pushed by the Government to merge with Leyland Motor Corporation Limited, manufacturer of Leyland bus and truck, Standard-Triumph and, since 1967, Rover vehicles. The result was British Leyland Motor Corporation, a new holding company which appeared in 1968, but the combination was not a success. A combination of poor decision making by the board along with the financial difficulties of, especially, the Austin-Morris division (previously BMC) led to the Ryder Report and to effective nationalisation in 1975.[citation needed]
Temporary return to independence
Over the next few years it became clear that because of the low regard for many of the group’s products insufficient capital could be provided to develop and begin manufacture of new models, including Jaguars, particularly if Jaguar were to remain a part of the group.[24]
Jaguar XJ (X300), a luxury sedan manufactured by Jaguar Cars between 1994 and 1997
In July 1984, Jaguar was floated off as a separate company on the stock market – one of the Thatcher government’s many privatisations[25]– to create its own track record.[26]
Installed as chairman in 1980, Sir John Egan is credited for Jaguar’s unprecedented prosperity immediately after privatisation. In early 1986 Egan reported he had tackled the main problems that were holding Jaguar back from selling more cars: quality control, lagging delivery schedules, poor productivity. He laid off about one third of the company’s roughly 10,000 employees to cut costs.[27] Commentators later pointed out he exploited an elderly model range (on which all development costs had been written off) and raised prices. He also intensified the effort to improve Jaguar’s quality. In the US the price increases were masked by a favourable exchange rate.[28]
Ford Motor Company era
Ford made offers to Jaguar’s US and UK shareholders to buy their shares in November 1989; Jaguar’s listing on the London Stock Exchange was removed on 28 February 1990.[29] In 1999 it became part of Ford’s new Premier Automotive Group along with Aston Martin, Volvo Cars and, from 2000, Land Rover. Under Ford’s ownership, Jaguar never made a profit.[30]
Under Ford’s ownership Jaguar expanded its range of products with the launch of the S-Type in 1999 and X-type in 2001. After PAG acquired Land Rover in May 2000 purchase by Ford, the brand became closely associated with Jaguar. In many countries they shared a common sales and distribution network (including shared dealerships), and some models shared components, although the only shared production facility was Halewood Body & Assembly – which manufactured the technically related X-Type and the Freelander 2. Operationally the two companies were effectively integrated under a common management structure within Ford’s PAG.
On 11 June 2007, Ford announced that it planned to sell Jaguar, along with Land Rover and retained the services of Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley and HSBC to advise it on the deal. The sale was initially expected to be announced by September 2007, but was delayed until March 2008. Private equity firms such as Alchemy Partners of the UK, TPG Capital, Ripplewood Holdings (which hired former Ford Europe executive Sir Nick Scheele to head its bid), Cerberus Capital Management and One Equity Partners (owned by JP Morgan Chase and managed by former Ford executive Jacques Nasser) of the US, Tata Motors of India and a consortium comprising Mahindra and Mahindra (an automobile manufacturer from India) and Apollo Management all initially expressed interest in purchasing the marques from the Ford Motor Company.[31][32]
Before the sale was announced, Anthony Bamford, chairman of British excavator manufacturer JCB had expressed interest in purchasing the company in August 2006,[33] but backed out upon learning that the sale would also involve Land Rover, which he did not wish to buy. On Christmas Eve of 2007, Mahindra and Mahindra backed out of the race for both brands, citing complexities in the deal.[34]
Tata Motors era
On 1 January 2008, Ford formally declared that Tata was the preferred bidder.[35] Tata Motors also received endorsements from the Transport And General Worker’s Union (TGWU)-Amicus[36] combine as well as from Ford.[37] According to the rules of the auction process, this announcement would not automatically disqualify any other potential suitor. However, Ford (as well as representatives of Unite) would now be able to enter into detailed discussions with Tata concerning issues ranging from labour concerns (job security and pensions), technology (IT systems and engine production) and intellectual property,[38] as well as the final sale price.[39] Ford would also open its books for a more comprehensive due diligence by Tata.[40] On 18 March 2008, Reuters reported that American bankers Citigroup and JP Morgan would finance the deal with a US$3 billion loan.[41]
On 26 March 2008, Ford announced that it had agreed to sell its Jaguar and Land Rover operations to Tata Motors of India, and that they expected to complete the sale by the end of the second quarter of 2008.[42] Included in the deal were the rights to three other British brands, Jaguar’s own Daimler, as well as two dormant brands Lanchester and Rover.[43] On 2 June 2008, the sale to Tata was completed at a cost of £1.7 billion.[44][45][46]
On 18 January 2008, Tata Motors, a part of the Tata Group, established Jaguar Land Rover Limited as a British-registered and wholly owned subsidiary. The company was to be used as a holding company for the acquisition of the two businesses from Ford – Jaguar Cars Limited and Land Rover. That acquisition was completed on 2 June 2008.[47] On 1 January 2013, the group, which had been operating as two separate companies (Jaguar Cars Limited and Land Rover), although on an integrated basis, underwent a fundamental restructuring. The parent company was renamed to Jaguar Land Rover Automotive PLC, Jaguar Cars Limited was renamed to Jaguar Land Rover Limited and the assets (excluding certain Chinese interests) of Land Rover were transferred to it. The consequence was that Jaguar Land Rover Limited became responsible in the UK for the design, manufacture and marketing of both Jaguar and Land Rover products.[48]
Plants
From 1922 the Swallow Sidecar company (SSC) was located in Blackpool. The company moved to Holbrook Lane, Coventry in 1928 when demand for the Austin Swallow became too great for the factory’s capacity.[49] The company started using the Jaguar name whilst based in Holbrooks Lane.
In 1951, having outgrown the original Coventry site they moved to Browns Lane, which had been a wartime «shadow factory» run by The Daimler Company. The Browns Lane plant ceased trim and final operations in 2005, the X350 XJ having already moved to Castle Bromwich two years prior, with the XK and S-Type following. The Browns Lane plant, which continued producing veneer trim for a while and housed the Jaguar Daimler Heritage centre until it moved to the British Motor Museum site, has now been demolished and is being redeveloped.
Jaguar acquired the Whitley engineering centre from Peugeot in 1986; which had originally been part of Chrysler Europe which the French firm had owned since the late 1970s. The decision to offload the site to Jaguar came as Peugeot discontinued the Talbot brand for passenger cars. In 2016, Jaguar also moved into part of the old Peugeot/Chrysler/Rootes site in Ryton-on-Dunsmore which closed a decade earlier – this now is the home of Jaguar Land Rover’s classic restoration operation.
Jaguar’s Radford plant, originally a Daimler bus plant but later a Jaguar engine and axle plant, was closed by Ford in 1997 when it moved all Jaguar engine production to its Bridgend facility.
In 2000, Ford turned its Halewood plant over to Jaguar following the discontinuation of its long running Escort that year for Jaguar’s new X-Type model. It was later joined by the second-generation Land Rover Freelander 2, from 2007. Jaguars ceased being produced at Halewood in 2009 following the discontinuation of the X-Type; Halewood now becoming a Land Rover-only plant.
Since Jaguar Land Rover was formed following the merger of Jaguar Cars with Land Rover, facilities have been shared across several JLR sites, most of which are used for work on both the Jaguar and Land Rover brands.
Current cars
E-Pace
The Jaguar E-Pace is a compact SUV, officially revealed on 13 July 2017.[50]
F-Pace
The F-Pace is a compact luxury crossover SUV – the first SUV from Jaguar. It was unveiled at the International Motor Show Germany in Frankfurt in September 2015.[51]
F-Type
The F-Type convertible was launched at the 2012 Paris Motor Show, following its display at the Goodwood Festival of Speed in June 2012,[52] and is billed as a successor to the legendary E-Type. In fact, the Series III E-Type already had a successor, in the form of the XJS, which was in turn replaced by the XK8 and XKR. The F-Type nevertheless returns to the 2-seat plan that was lost with the introduction of the Series III E-Type, which was available only in a 2+2-seat configuration. It was developed following the positive reaction to Jaguar’s C-X16 concept car at the 2011 Frankfurt Auto Show. Sales will begin in 2013 with three engine choices; two variants of the AJ126 V6 petrol engine and the AJ133 V8 petrol engine.[53]
I-Pace
The Jaguar I-Pace is an electric SUV, officially revealed on 1 March 2018. It is Jaguar’s first electric car.
XE
The XE is the first compact executive Jaguar since the 2009 model year X-Type and is the first of several Jaguar models to be built using Jaguar’s new modular aluminium architecture,[citation needed] moving the company away from the Ford derived platforms that were used in the past for the X-Type and XF. The use of Jaguar’s own platform allows the XE to feature either rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive configurations, and it is the first car in its segment with an aluminium monocoque structure.[54] Originally announced at the 2014 Geneva Motor Show with sales scheduled for 2015.[55]
XF
The Jaguar XF is a mid-size executive car introduced in 2008 to replace the S-Type. In January 2008, the XF was awarded the What Car? ‘Car of the Year’ and ‘Executive Car of the Year’ awards. The XF was also awarded Car of the Year 2008 from What Diesel? magazine. Engines available in the XF are 2.2-litre I4 and 3.0-litre V6 diesel engines, or 3.0 litre V6 and 5.0-litre V8 petrol engines. The 5.0 Litre engine is available in supercharged form in the XFR. From 2011, the 2.2-litre diesel engine from the Land Rover Freelander was added to the range as part of a facelift.[56]
R models
Jaguar began producing R models in 1995 with the introduction of the first XJR, and the first XKR was introduced in 1997. Jaguar R, R-S and SVR models are designated to compete with the likes of Mercedes-AMG, BMW M and Audi S and RS.
Historic car models
The renamed Jaguar company started production with the pre-war 1.5, 2.5 and 3.5-litre models, which used engines designed by the Standard Motor Company. The 1.5-litre four-cylinder engine was still supplied by Standard but the two larger six-cylinder ones were made in house. These cars have become known unofficially as Mark IVs.
The first post-war model was the September 1948 Mark V available with either 2.5 or 3.5-litre engines. It had a slightly more streamlined appearance than pre-war models, but more important was the change to torsion bar independent front suspension and hydraulic brakes.[citation needed] In the spring of 1948 Lyons had returned from USA reporting Jaguar’s individuality and perceived quality attracted the admiration of American buyers accustomed to the virtual uniformity of their home-grown vehicles.[57]
The 1948 XK120 was a breakthrough both for Jaguar and post-WWII sports cars.
The first big breakthrough was the launch in October 1948 of their new record-breaking engine design in their XK120 sportscar to replace the prewar SS Jaguar 100. It was powered by a new twin overhead camshaft (DOHC) 3.5-litre hemi-head six-cylinder engine designed by William Heynes, Walter Hassan and Claude Baily. The XK100 4-cylinder 2-Litre version had broken records in Belgium travelling at 177 mph. This XK engine had been designed at night during the war when they would be on fire watch in the factory. After several attempts a final design was achieved. That is until owner William Lyons said «make it quieter».
The sportscar bearing its prefix X had originally been intended as a short production model of about 200 vehicles. A test bed for the new engine until its intended home, the new Mark VII saloon, was ready.[citation needed]
1950 «Grace … Space … Pace – Jaguar» Mark VII
The second big breakthrough was the large Mark VII saloon in 1950, a car especially conceived for the American market, Jaguar was overwhelmed with orders. The Mark VII and its successors gathered rave reviews from magazines such as Road & Track and The Motor. In 1956 a Mark VII won the prestigious Monte Carlo Rally. The XK120’s exceptional reception was followed in 1954 by an improved XK140 then in May 1957 a fully revised XK150.
1960s Mark 2 became one of the most recognisable Jaguar models ever produced.
In 1955, the Two-point-four or 2.4-litre saloon (named by enthusiasts 2.4 Mark 1) was the first monocoque (unitary) car from Jaguar.[citation needed] Its 2.4-litre short-stroke version of the XK engine provided 100 mph (160 km/h) performance. In 1957, the 3.4-litre version with disk brakes, wire wheels and other options was introduced, with a top speed of 120 mph (190 km/h). In October 1959, an extensively revised version of the car with wider windows and 2.4, 3.4, and 3.8-litre engine options became the Mark 2. The 3.8 Mark 2 was popular with British police forces for its small size and 125 mph (201 km/h) performance.
The Mark VIII of 1956 and Mark IX of 1958 were essentially updates of the Mark VII, but the oversize Mark X of 1961 was a completely new design of large saloon with all round independent suspension and unitary construction.
Jaguar launched the E-Type in 1961.
The independent rear suspension from the Mark X was incorporated in the 1963 S-Type, a Mark 2 lengthened to contain the complex rear suspension, and in 1967 the Mark 2 name was dropped when the small saloons became the 240/340 range. The 420 of 1966, also sold as the Daimler Sovereign, put a new front onto the S-type, although both cars continued in parallel until the S-Type was dropped in 1968. The slow-selling Mark X became the 420G in 1966 and was dropped at the end of the decade. Jaguar was saved by its new equally capacious but very much trimmer new XJ6.
Of the more recent saloons, the most significant is the XJ (1968–1992). From 1968 on, the Series I XJ saw minor changes, first in 1973 (to Series II), 1979 (Series III), a complete redesign for 1986/1987 in XJ40, further modifications in 1995 (X300), in 1997 with V8-power (X308), and a major advance in 2003 with an industry-first aluminium monocoque-chassis (X350). The most luxurious XJ models carried either the Vanden Plas (US) or Daimler (rest of world) nameplates. In 1972, the 12-cylinder engine was introduced in the XJ, while simultaneously being offered in the E Type.
The XJ220—the world’s fastest production car in 1992
1992 saw the introduction of the mid-engined, twin-turbo XJ220, powered by a 542 bhp (404 kW; 550 PS) V6 engine. The XJ220 was confirmed the fastest production car in the world at the time after Martin Brundle recorded a speed of 217 mph (349 km/h) on the Nardo track in Italy.[58]
Over the years many Jaguar models have sported the famous chrome plated Leaping Jaguar, traditionally forming part of the radiator cap. Known as «The Leaper», this iconic mascot has been the subject of controversy in recent times when banned for safety reasons from cars supplied to Europe whilst it continued to be fitted on cars destined for the United States, Middle East and Far East. It has now been dropped from all the latest Jaguar models, although some customers add it to their car as a customization.
The Jaguar S-Type, first appeared in 1999 and stopped production in 2008. It has now been replaced by the Jaguar XF. Early S-Types suffered from reliability problems but those were mostly resolved by the 2004 model year.[59]
The Jaguar X-Type was a compact executive car launched in 2001, while the company was under Ford ownership, sharing its platform with the Ford Mondeo. X-Type production ended in 2009.[60]
The Jaguar XK was a luxury grand tourer introduced in 2006, where it replaced the XK8. The XK introduced an aluminium monocoque bodyshell, and was available both as a two-door coupé and two-door cabriolet/convertible.[61] Production ceased in 2014.
The Jaguar XJ was a full-size luxury saloon. The model was in production since 1968, with production ceasing in 2019, with the first generation being the last Jaguar car to have creative input by the company’s founder, Sir William Lyons, although this is disputed as some Jaguar historians claim that the second generation XJ – the XJ40 series – was the last car which Lyons had influenced. The XJ40 originally launched in 1986 and went through two major revamps in 1994 (X300) and 1997 (X308) for a total production run of 17 years. In early 2003, the third generation XJ – the X350 – arrived in showrooms and while the car’s exterior and interior styling were traditional in appearance, the car was completely re-engineered. Its styling attracted much criticism from many motoring journalists who claimed that the car looked old-fashioned and barely more modern than its predecessor, many even citing that the ‘Lyons line’ had been lost in the translation from XJ40 into X350 XJ, even though beneath the shell lay a highly advanced aluminium construction that put the XJ very near the top of its class.[62]
Jaguar responded to the criticism with the introduction of the fourth generation XJ, launched in 2009. Its exterior styling is a departure from previous XJs, with a more youthful, contemporary stance, following the design shift that came into effect previously with the company’s XF and XK models.[63]
The 5-litre V8 engine in the XJ Supersport can accelerate the car from 0 to 60 mph (0–97 km/h) in 4.7 seconds, and has a UK CO2 emission rating of 289 g/km. To cater to the limousine market, all XJ models are offered with a longer wheelbase (LWB) as an option, which increases the rear legroom.[64]
List
Large executive
- 1935–1955 2+1⁄2 litre saloon
- 1937–1948 3+1⁄2 Litre saloon
- 1948–1951 Mark V
- 1951–1957 Mark VII (& VIIM)
- 1957–1959 Mark VIII
- 1959–1961 Mark IX
- 1961–1966 Mark X
- 1966–1970 420G
- 1968–1987 XJ6 Series 1, 2 & 3
- 1972–1992 XJ12
- 1986–1994 XJ6 (XJ40)
- 1993–1994 XJ12 (XJ81)
- 1995–1997 XJ6 & XJ12 (X300 & X301)
- 1998–2003 XJ8 (X308)
- 2004–2007 XJ (X350)
- 2008–2009 XJ (X358)
Compact executive
- 1935–1949 1+1⁄2 Litre saloon
- 1955–1959 Mark 1
- 1959–1967 Mark 2
- 1963–1968 S-type
- 1966–1968 420
- 1966–1968 240 & 340
- 1999–2008 S-type
- 2001–2009 X-type
- 2007–2015 XF (X250)
Sports
- 1948–1954 XK120
- 1954–1957 XK140
- 1957–1961 XK150
- 1961–1974 E-Type
- 1975–1996 XJ-S
- 1992–1994 XJ220
- 1997–2006 XK8/XKR (X100)
- 2006–2014 XK (X150)
Racing and competition
- 1950s C-Type
- 1950s D-Type
- 1960s E-Type Lightweight
- 1985–1992 XJR-5 through XJR-17
- 2009 XFR Bonneville Salt Flats speed record
- 2010 Jaguar RSR XKR GT2
Concept cars
- E1A – The 1950s E-Type concept vehicle
- E2 A – The second E-Type concept vehicle, which raced at LeMans and in the USA
- XJ13 (1966) – Built to race at LeMans, never run
- Pirana (1967) – Designed by Bertone
- Ascot (1977)
- XJ41/XJ42 (1982-1990) – the first F-Type; cancelled due to the Ford’s takeover of Jaguar[65]
- XJ90 (1988-1991) – planned XJ40 replacement; cancelled due to Ford’s takeover of Jaguar[66]
- Kensington (1990)
- XK 180 (1998) – Roadster concept based on the XK8
- F-Type (2000) – Roadster, similar to the XK8 but smaller
- R-Coupé (2001) – Large four-seater coupé
- Fuore XF 10 (2003)
- R-D6 (2003) – Compact four-seat coupé
- XK-RR – A high-performance version of last generation XK coupé
- XK-RS – Another performance-spec version of last generation XK convertible
- Concept Eight (2004) – Super-luxury version of the long-wheelbase model of the XJ
- C-XF (2007) – Precursor to the production model XF saloon
- C-X75 (2010) – Hybrid-electric sports car, originally intended for production but cancelled in 2012
- B99 (2011)
- C-X16 (2011) – Precursor to the production model F-Type
- C-X17 (2013) – First ever Jaguar SUV concept
- Project 7 – a 542 bhp V8-powered speedster based on the F-Type and inspired by the D-Type (2013)[67]
- Future-Type (2017)
Engines
Jaguar has designed in-house six generations of engines:
- Historic:
- XK6 – Inline-6
- V12 – 60° V12
- AJ6/AJ16 – 22° Inline-6
- AJ-V6 – 60° V6 (Ford designed, Jaguar modified)
- Current:
- AJ-V8 – 90° V8
- AJ126 – 90° V6
- AJD-V6 – 60° V6 (Ford designed)
- Ingenium – Inline-4
Motorsport
Jaguar has had major success in sports car racing, particularly in the Le Mans 24 Hours. Victories came in 1951 and 1953 with the C-Type, then in 1955, 1956 and 1957 with the D-Type. The manager of the racing team during this period, Lofty England, later became CEO of Jaguar in the early 1970s. Although the prototype XJ13 was built in the mid-1960s it was never raced, and the famous race was then left for many years.
In 1982, a successful relationship with Tom Walkinshaw’s TWR team commenced with the XJ-S competing in the European Touring Car Championship, which it won in 1984.[68] In 1985, the TWR XJ-S won the Bathurst 1000 race. In the mid-1980s TWR started designing and preparing Jaguar V12-engined Group C cars for World Sports Prototype Championship races. The team started winning regularly from 1987, and won Le Mans in 1988 and 1990 with the XJR series sports cars. The Jaguar XJR-14 was the last of the XJRs to win, taking the 1991 World Sportscar Championship.
In 1999, Ford decided that Jaguar would be the corporation’s Formula One entry. Ford bought out the Milton Keynes-based Stewart Grand Prix team and rebranded it as Jaguar Racing for the 2000 season. The Jaguar F1 program was not a success however, achieving only two podium finishes in five seasons of competition between 2000 and 2004. At the end of 2004, with costs mounting and Ford’s profits dwindling, the F1 team was seen as an unneeded expense and was sold to Red Bull energy drinks owner Dietrich Mateschitz,[69] and it became Red Bull Racing.
On 15 December 2015, it was announced that Jaguar would return to motorsport for the third season of Formula E.
On 15 June 2018, Jaguar Vector Racing broke the world speed record for an electric battery powered boat. The Jaguar Vector V20E recorded an average speed of 88.61 mph across the two legs of the 1 km course on Coniston Water, England.[70]
Notable sports racers:
- Jaguar C-Type (1951–1953)
- Jaguar D-Type (1954–1957)
- Jaguar Lightweight E-Type
- Jaguar XJ13[71]
- Jaguar XJR Sportscars
- Jaguar XJR-9 (1988)
- XJ220 (1988)
- XJR-15 (1990)
Jaguar and the arts
Jaguar Art Project «Shadows», Saint-Tropez 2011
For some time now,[when?] Jaguar has been active in the international arts scene. In particular, the company has collaborated with the artist Stefan Szczesny, implementing major art projects. In 2011, Jaguar presented the exhibition series «Shadows», which involved the installation of Szczesny’s shadow sculptures in Sankt-Moritz, on Sylt and in Saint-Tropez. In 2012, a large number of sculptures, ceramics and paintings were shown in Frankfurt (and mainly in Frankfurt’s Palmengarten).
As part of the collaboration with Szczesny, Jaguar has released the «Jaguar Art Collection».[citation needed]
See also
- List of car manufacturers of the United Kingdom
References
- ^ a b «Trade mark number EU000026625». Intellectual Property Office. Crown (UK Government). Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ^ «JAGUAR CARS LIMITED overview — Find and update company information — GOV.UK».
- ^ «Jaguar Land Rover 2012 Overview» (PDF). Jaguar Land Rover. 14 June 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 February 2013.
- ^ «Jaguar Group of companies is to merge with The British Motor Corporation Ltd., as the first step towards the setting up of a joint holding company to be called British Motor (Holdings) Limited.» Official statement released at press conference at the Great Eastern Hotel, London, 1966.
- ^ «The Years 1989 to 1996». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Archived from the original on 24 June 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ «Cameron gets a new Jag to go with the new job – Autoblog UK». Uk.autoblog.com. 13 May 2010. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- ^ «The Royal Warrant Holders ‘ Association – Directory of Royal Warrant Holders». Archived from the original on 12 December 2007. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ «Jaguar car brand to be all-electric by 2025». BBC News. 15 February 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ «Design Evolution: 80 Years of Jaguar – Part 1». Jaguar. Jaguar Land Rover. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- ^ «The Years 1932 to 1935». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Archived from the original on 1 June 2009. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ S.S. Cars Limited. The Times, Wednesday, 4 April 1945; pg. 10; Issue 50108
- ^ a b «The Lyons share – interview with WL». Motor: 18–21. 19 February 1972.
- ^ «Jaguar». Archived from the original on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ^ «The classic has to be «Grace… Space… Pace,» which was used throughout the 1950s and 1960s». Clausager, Anders Ditlev (2010). «Jaguar: A History of Grace and Pace». MSN. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 2 September 2013.
- ^ Walton, Paul (13 December 2012). «Grace… Space… Pace». jaguar-world.com. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ Peterborough, Brave Creative (19 November 2010). «Jaguar: 75 Years of Grace, Space and Pace». themomentmagazine.com. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ «1306381302_a13c957db6_4840.jpg (JPEG Image, 374 × 500 pixels)». typophile.com. 28 August 2011. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ «tumblr_lwqh6th15q1qchs1zo1_1280.jpg (JPEG Image, 1280 × 1256 pixels)». 31.media.tumblr.com. 24 December 2011. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ ‘Sir William Lyons – The Official Biography’, Philip Porter & Paul Skilleter, page 120 onwards
- ^ «The Years 1968 to 1979». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ Utton, M. A. (2003). «9 – Vertical integration and vertical mergers». Market Dominance and Antitrust Policy. Cheltenham, Glos, UK: Edward Elgar Publishing. p. 226. ISBN 1-84064-728-0. LCCN 2002029832. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
- ^ Douglas-Scott-Montagu, Edward John Barrington & Burgess-Wise, David (1995). «Chapter 9 – Under New Management». Daimler Century: The full history of Britain’s oldest car maker. Sparkford, Nr Yeovil, Somerset, UK: Patrick Stephens. p. 283. ISBN 1-85260-494-8.
…Sir George Harriman of the British Motor Corporation (whose Pressed Steel subsidiary supplied Jaguar bodyshells) offered Lyons a ‘logical and beneficial’ merger deal, which would leave Jaguar operating under Lyons’s chairmanship as ‘a separate entitiy and with the greatest practical degree of autonomy’ within a new organization called British Motor (Holdings) Limited.
- ^ «British Motor Takes That New Label». The Times. No. 56815. London. 15 December 1966. p. 17.
- ^ page 49, Andrew M. McLaughlin, William A. Maloney, The European Automobile Industry: Multi-Level Governance, Policy and Politics Taylor & Francis e-Library 2005. accessed 31 Jan 2013
- ^ Elliott, Larry (22 November 2000). «A whole world sold on sell-offs». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ page 50, Andrew M. McLaughlin, William A. Maloney, The European Automobile Industry: Multi-Level Governance, Policy and Politics Taylor & Francis e-Library 2005.
- ^ Zetlin, M. (1986). John Egan: Tough leadership turns Jaguar around. Management Review, 75(5), (May 1986) 20–20.
- ^ The Badge on the Bonnet. The Times Friday, 3 November 1989; pg. 13; Issue 63542.
- ^ «The Years 1989 to 1996». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Archived from the original on 24 June 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ «Although Land Rover remains profitable, Ford has never managed to make money from its investment in Jaguar.» «Tata buys Jaguar in £1.15bn deal». BBC News. 26 March 2008. Retrieved 3 September 2013.
- ^ «India’s Tata confirms interest in Land Rover, Jaguar». Forbes. AFX News Limited. 24 August 2007. Archived from the original on 8 December 2007. Retrieved 18 December 2007.
- ^ Clark, Nick (4 January 2008). «Tata in pole position to buy Jaguar and Land Rover marques from Ford». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 5 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «JCB’s Sir Anthony Bamford eyes Jaguar». Contract Journal. 24 August 2006. Archived from the original on 31 May 2009.
- ^ Doval, Pankaj (24 December 2007). «M&M out of Jaguar, Land Rover race». Times News Network. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ Krisher, Tom (3 January 2008). «Indian Company Top Bidder for Jaguar». Time. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 6 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «Tata set to clinch Jaguar-Land Rover deal: Report». Press Trust of India. 20 December 2007. Archived from the original on 23 December 2007. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Robbins, Mathieu (17 December 2007). «Ford set to pick Jaguar frontrunner in days: source». Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 October 2012. Retrieved 16 February 2011.
- ^ Ghosh, Suprotip (3 January 2008). «Super car technology headed for Tata stable». Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 5 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ Leahy, Joe; Simon, Bernard; Yee, Amy (4 January 2008). «Tata falls for the attraction of opposites». Financial Times. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «Ball now in Tata Motors’ court to tie-up deal: Unite». CNBC TV-18. 3 January 2008. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ^ «Tata gets $3 billion loan from Citi, JPMorgan: source». Reuters. 18 March 2008. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 18 March 2008.
- ^ «FORD MOTOR COMPANY ANNOUNCES AGREEMENT TO SELL JAGUAR LAND ROVER TO TATA MOTORS» (Press release). Ford Motor Company. 26 March 2008. Archived from the original on 12 June 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2008.
- ^ «5 for 2 special: Tata acquires 3 other British marques in Jaguar, Land Rover deal». Leftlane News. 28 March 2008. Retrieved 28 March 2008.
- ^ «Tata Motors completes acquisition of Jag, Land Rover». 2 June 2008. Retrieved 2 June 2008.
- ^ «On U.S. tour, Mr. Tata gives Jaguar and Rover dealers a hug: AutoWeek Magazine». Autoweek.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ^ «Jobs warning at Jaguar Land Rover». BBC News. 26 June 2009. Retrieved 26 June 2009.
- ^ «2010/2011 Annual Report» (PDF). Jaguar Land Rover PLC. p. 5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 January 2018. Retrieved 26 January 2018.
- ^ «Annual Report 2012/2013» (PDF). Jaguar Land Rover Automotive PLC. p. 91. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 January 2018. Retrieved 26 January 2018.
- ^ «Jaguar History». The Surrey Region Jaguar Enthusiasts Club. Archived from the original on 30 June 2007.
- ^ Tisshaw, Mark (13 July 2017). «2018 Jaguar E-Pace officially revealed: release date, price and interior». Autocar. Retrieved 3 March 2018.
- ^ Ingram, Richard (21 October 2015). «New Jaguar F-Pace SUV: Frankfurt debut, prices, engines and specs». Auto Express. Dennis Publishing. Retrieved 3 March 2018.
- ^ Healey, James (2 July 2012). «Disguised Jaguar F-type sports car runs at Goodwood». USA Today. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- ^ «CAR Magazine: Jaguar F-type (2013) first official pictures». Retrieved 28 September 2012.
- ^ «Jaguar XE Launch Press Release».
- ^ «New Jaguar saloon to be called XE». Auto Express. 4 March 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ^ «Jaguar Cars UK Web Site». jaguar.co.uk. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ «British Cars for U.S.» The Times, 27 April 1948, p. 2; Issue 51056.
- ^ «The monster and the myth – It is the story they’ve been waiting for with bated breath». The Guardian. 22 August 1992.
On the Nardo track of southern Italy, Martin Brundle, the Grand Prix driver, confirmed it as the fastest production car with 217mph, narrowly quicker than the Bugatti. The Ferrari 512 or earlier F40 does around 200mph. The F40 boasts 0–60mph in 4.1 seconds. The Lamborghini Diablo is 4.09 and Porsche 959, 3.9. The Jaguar rates 3.85.
- ^ Consumer Reports, Buying Guide 2007, 211.
- ^ Wearden, Graeme (15 July 2009). «300 jobs lost at Jaguar’s Halewood plant». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 15 July 2009.
- ^ «Jaguar XK Guide». carpages.co.uk. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ Series». Autocars. Archived from the original on 9 July 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ Plisner, Peter (9 July 2009). «Changing face of Jaguar». BBC News. Retrieved 15 July 2009.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ – models». Jaguar Cars Ltd. Retrieved 19 June 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Concepts and prototypes : Jaguar XJ41/XJ42 (1982-1990)». AROnline. 19 March 2021.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ90 : the missing 1990s XJ finally breaks cover». AROnline. 17 July 2022.
- ^ BBC Top Gear.. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- ^ «Double loss for motor sport». Motor Sport. 16 December 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ^ «Red Bull snaps up Jaguar F1 team». BBC News. 15 November 2004. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ^ «Jaguar Vector Racing Break Maritime Electric World Record | Jaguar Vector Racing». Jaguar Vector Racing. 15 June 2018. Retrieved 16 June 2018.
- ^ «Jaguar XJ13 – Building the Legend». 14 June 2013. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
External links
- Jaguar official website
- Jaguar Daimler Heritage Trust website
Стратегия Jaguar Land Rover декларирует, что, начиная с 2020 года, все новые машины Jaguar будет представлять модификациях с электрическими или гибридными двигателями. Первым электрическим седаном станет представительский Jaguar XJ.
История бренда Jaguar — это история превращения фирмы по сборке мотоколясок, основанной двумя энтузиастами, в мирового лидера производства авто премиум сегмента. Машины компании завоевали множество наград, ими владеют монаршие особы и премьер-министры.
Его прародителем стала основанная в 1922 Swallow Sidecar. Имя Jaguar фирме присвоили в конце Второй мировой. Компания была национализирована в 1975. Приобретена автогигантом Ford в 1990. В июне 2008 бренд Jaguar продан за 1,7 миллиарда фунтов производителю самого дешевого автомобиля в мире индийской компании Tata Motors.
Основатели бренда: от идеи к реализации
Основателями марки «Ягуар» стали двое британцев из Блэкпула – предприниматель Вильям Волмсли (William Walmsley) и продавец Вильям Лайонс (William Lyons). Они создали компанию по выпуску мотоциклетных колясок Swallow Sidecar Company (SS).
Вскоре у предприимчивого Лайонса появилась новая цель – перенаправить вектор развития компании на выпуск автомашин.
Сначала он разрабатывал автокузова. Первой успешной моделью был кароссери для Austin 7. В 1931 году производство перенесли в Ковентри. Там Лайонс впервые начал проектировать автомобили. В 1934 году Волмсли отошел от дел фирмы и продал свою долю напарнику. Теперь компания полностью принадлежала Лайонсу.
Первый автомобиль марки «Ягуар»
Выпуск первого авто модели SS с двухместной динамичной кабиной начался в 1929 году. А уже в 1936 появился первый «Ягуар» — спорткар SS Jaguar 100, развивающий максимальную скорость 160 км/час. Он отличался приземистым кузовом, огромными фарами, красивым низким удлиненным капотом. Эту машину знатоки считают одной из лучших в истории автомобилестроения.
Логотип «Ягуар»: описание, значение
В качестве официального логотипа «Ягуара» дизайнеры предложили знаменитого представителя семейства кошачьих в прыжке. Он олицетворяет ключевые ценности фирмы: благополучие, элегантность, утонченность, мощь, скорость, стремление вперед. Логотип на протяжении истории автомобильной марки «Ягуар» несколько раз изменялся. После рестайлинга 2012 года он стал более стильным и изящным. 3D-фигурке добавили переливающиеся оттенки металлика и серебра, чтобы подчеркнуть её изысканность.
Jaguar логотип
Это не единственный логотип автомобилей «Ягуар». На ранних моделях устанавливали статуэтку хищника и традиционную эмблему с мордой рычащего зверя на серебристом или красном поле в серебряном ободе. Позднее для безопасности пешеходов применение объемных фигурок запретили. Jaguar решил убрать статуэтку с капота своих авто. Но круглый логотип «Ягуар» с мордой зверя по-прежнему украшает радиаторы всех автомобилей всемирно известного британского бренда.
Что значит название Jaguar, и когда оно стало использоваться
Название для грациозного, мощного и быстрого спорткара SS Jaguar 100 придумал владелец фирмы Уильям Лайонс. Образ изящного мускулистого представителя кошачьих в прыжке наиболее точно передавал сущность этого замечательного спортивного автомобиля.
Под конец Второй мировой войны владельцы компании решили заменить название SS, так как эта аббревиатура в сознании жителей стран Европы однозначно ассоциировалась с кошмарами нацистского режима.
Потребители успели полюбить SS Jaguar 100, поэтому в марте 1945 фирму переименовали в Jaguar.
Первые успехи
В 1948 марка автомобиля «Ягуар» была впервые заявлена на Лондонский автомобильный салон с моделью Jaguar XK120. Впервые в истории бренда Jaguar на автомобиль компании был установлен мотор собственной конструкции, разгонявший болид до 126 км/ч. Модель Jaguar XK120 назвали «самой быстрой из выпускавшихся серийно». Его двигатель получился очень удачным, его продолжали выпускать 38 лет.
Jaguar XK120
За 1950-е, 1960-е годы фирма завоевала американского покупателя: автомобиль XK150 и его модификация XK150 родстер были признаны в США поистине культовыми. Создание актуальных спорткаров XK120, XK140, XK150, E-Type сделало Jaguar широко известным. Он приобрел компанию Standard Motor Co с целью изготовления на её заводах двигателей.
Деятельность компании в период Второй мировой войны
На время войны фирма прекратила выпуск автомобилей и занялась производством техники для британской армии. Это были военные трейлеры и легкие внедорожники оригинальной конструкции, оснащенные силовым агрегатом компании «Форд». Выпускали запчасти для бомбардировщиков, в основном, авиационные моторы.
Спортивная карьера
1950-е Jaguar ознаменовал рядом громких спортивных викторий. Болиды D-Type, C-Type около семи лет подряд побеждали на самых престижных соревнованиях. В 1956 роскошный седан Mark 7 победил на знаменитом «Ралли Монте-Карло». Гонщики Jaguar D-Type в июне 1957 года полностью оккупировали подиум Ле-Мана, а также взяли 4-е и 6-е места.
Пилоты заводской команды на протяжении 1959, 1960, 1963, 1965 завоевывали Гран-при чемпионата. Благодаря этому «Ягуар» — британская марка спорткаров — прославил свою страну среди производителей спортивных болидов.
Начиная с 2000 года автомобили «Ягуар» снова участвуют в соревнованиях «Формулы-1» своей командой. Машины оснащают моторами Cosworth.
Jaguar F-Type Concept
Для «королевских гонок» проектируют модели F-Type Concept и Silverstone.
Дальнейшее развитие марки
В 1960-м Jaguar присоединил к себе Daimler Motor Co., начав продавать свои наиболее престижные седаны под брендом «Даймлер». В июле 1965-го фирма анонсировала объединение с British Motor Corp. В 1970-х годах вышел на авторынок спорткар Jaguar XJ12, укомплектованный современным мотором, имеющим 12 цилиндров и развивающим мощность 311 л.с.
В 1980 году фирму возглавил Джон Иган (John Egan). Он смог договориться с персоналом и остановить многолетние забастовки, улучшить качество сборки автомобилей и поднять количество выпускаемых машин.
С 1990 года права на «Ягуар» перешли к «Форд Мотор». Уже в 1999 году фирма влилась в Premier Automotive Gr. одновременно с «Астон Мартин» и «Вольво». В 2000 году к ним присоединился и «Ленд Ровер».
«Ягуар» пополнил свою модельную линейку за счет S-Type и X-Type соответственно в 1999 и 2001 годах. Последняя была разработана с использованием усовершенствованной платформы «Форд СД132» и оказалась самой компактной машинкой Jaguar. Первым универсалом марки стала именно модификация этого авто. Изначально X-Type поставляли исключительно полноприводным. Позже была разработана конструкция переднего монопривода.
В 2004 году Land Rover Russia начал поставку автомобилей «Ягуар» в Россию через дилерскую сеть «Форд». За 2004 год компания продала на российском авторынке 400 машин, за 2012 год — 1 506, за 2018 год — 2537, за 2019 год — 1738. Наиболее продаваемыми сейчас моделями являются кроссоверы F-Pace и E-Pace.
В 2013 году фирма показала современную спортивную машину Jaguar F-Type, заменившую болид E-Type. Сначала авто предлагали с кузовом кабриолет, затем выпустили на рынок купе.
Деятельность компании в наши дни
Jaguar Cars продолжает свое развитие в составе Jaguar Land Rover Gr., коей владеет автоконцерн из Индии Tata Motors. В 2015-м фирма показала на знаменитом автосалоне во Франкфурте первый в истории «Ягуар» кроссовер модели F-PACE. Конструкторы смогли придать большому внедорожнику управляемость и стремительность настоящего Jaguar, чему способствовало широкое применение алюминия для конструкций кузова (около 80%). Автомобиль завоевал награды World Car Awards в основных категориях «Лучший автомобильный дизайн года», «Автомобиль года».
Модульная платформа F-PACE досталась и новому компакт седану XE, который вышел в этом же 2015 году. Благодаря своему оригинальному кузову из алюминия и новейшим моторам Ingenium он стал наиболее экологичным и эффектным спортивным седаном фирмы. Отличная динамика сочетается с пониженным расходом горючего и небольшим содержанием углекислоты в выхлопе.
В 2016 году на популярном Женевском автосалоне бренд представил наиболее мощный из серийных «Ягуаров». Спортивный болид Jaguar F-TYPE модификации SVR изготовлен отделением по выпуску экстраординарных моделей (Special Vehicles Operations). Авто, обладающее компрессорным двигателем V8 объемом 5 л и мощностью 575 л.с., ускоряется до сотни за 3,7 с., при этом достигает максималки 322 км/ч. Ещё более солидными параметрами обладает представленный на год позже серийный четырехдверный седан Jaguar XE ограниченной серии SV Project 8, имеющий 600-сильный агрегат.
В 2017 году был разработан первый компактный SUV марки Jaguar E-PACE. Машину отличает эффектный динамичный кузов купе, шикарный интерьер и самый большой среди одноклассников объем мест хранения.
В 2018 на том же международном автосалоне в Женеве был показан первый электроавтомобиль марки Jaguar I-PACE. Он явился основоположником нового сегмента лакшери электрокроссоверов, позволяющих почувствовать мощную динамику и комфорт. I-PACE, укомплектованный парой электродвигателей общей мощностью 400 л.с., получил свойства спортивного болида (разгон до 100 км/ч всего за 4,8 с.), запас хода 470 километров и громадный салон 5-местного кроссовера. В 2019 году «Ягуар» I-PACE стал самым первым авто в мире, получившим призы трех номинаций популярной автомобильной награды World Car Awards: «Лучший автомобильный дизайн года», «Автомобиль года» и даже «Зеленый автомобиль года»,
Jaguar I-PACE
В 2018 году модельный ряд бренда пополнил еще один примечательный болид. Jaguar F-PACE модификации SVR — один из наиболее мощных и динамичных. Авто с 5-литровым мотором V8 мощностью 550 лошадей способно достигать 100 км/ч всего лишь за 4,3 с. и обеспечить скорость 283 км/ч.
Перспективы развития
Сейчас «Ягуар» планирует создание крупнейшего научного отделения для моделирования транспортных средств следующего поколения. Компания рассчитывает привлечь около тысячи ученых, конструкторов и инженеров.
Стратегия Jaguar Land Rover декларирует, что, начиная с 2020 года, все новые машины Jaguar будет представлять модификациях с электрическими или гибридными двигателями. Первым электрическим седаном станет представительский Jaguar XJ.
В 2019 году фирма продемонстрировала флагманский SUV модели J-Pace, базирующийся на новой алюминиевой модульной платформе MLA. Ее рассчитывают применить и для следующей генерации внедорожников Range Rover. Вместо полностью механического привода будет применен гибридный: переднюю ось будет вращать обычный ДВС, а заднюю — электромотор. Старт продаж модели планируют на 2021 год.
Электротакси модели Jaguar I-PACE будут эксплуатировать первую на планете городскую систему беспроводной высокомощной автомобильной зарядки.
Современная линейка моделей марки «Ягуар» с ценами
На сегодняшний день официальные дилеры бренда предлагают на российском рынке новые автомобили Jaguar следующих моделей:
- НОВЫЙ F-TYPE — новая модель спорткара Jaguar, кузов купе. Максимальная скорость 300 км/ч. Разгон с 0 до 100 км/ч 3,7 с. Цена от 7 258 000 рублей.
- F-TYPE — классический спорткар Jaguar в кузове купе. Цена от 6 937 000 рублей.
- XE — спортивный седан. Содержание углекислоты в выхлопе при смешанном цикле 109 г/км. Расход горючего при смешанном цикле от 4,2 л/100км. Цена от 3 657 000 рублей.
- XF — роскошный бизнес седан. Максимальная скорость 250 км/ч. Разгон с 0 до 100 км/ч 5,3 с. Цена от 4 111 000 рублей.
- XJ — флагманский спортивный седан. Максимальная скорость 250 км/ч. Цена от 3 316 000 рублей.
- E-PACE — первенец среди компакткроссоверов Jaguar. Расход горючего при смешанном цикле от 5,6 л/100км. Цена от 3 113 000 рублей.
- F-PACE — внедорожник. Расход горючего при смешанном цикле от 5,3 л/100км. Цена от 3 849 000 рублей.
- I-PACE — первенец среди электрических SUV. Разгон с 0 до 100 км/ч 4,8 с. Длительность поездки на одной зарядке 470 км. Цена от 6 247 000 рублей.
Подразделение SVO предлагает эксклюзивные модели, существенно модифицированные по желанию клиента:
- F-PACE SVR — наиболее совершенный кроссовер Jaguar с 5-литровым агрегатом V8 и нагнетателем способен разгоняться до скорости 283 км/ч. Расход горючего при смешанном цикле от 5,1 л/100км. Цена от 4 216 000 рублей.
- F-TYPE SVR купе — спорткар, способный достигать 322 км/ч с модернизированным мотором мощностью до 575 л. с. Разгон с 0 до 100 км/ч 3,7 с. Цена от 6 937 000 рублей.
- F-TYPE SVR кабриолет — родстер, способный достигать 314 км/ч с модернизированным мотором мощностью до 575 л. с. Разгон с 0 до 100 км/ч 3,7 с. Цена от 6 937 000 рублей.
Покупатель может выбрать автомобиль по типу кузова, привода, мощности двигателя, стоимости и заказать любую комплектацию.
Уильям Лайонс, основатель нашего бренда, начал свой бизнес в 1922 году с конструирования мотоколясок, но его мечтой всегда были автомобили. Первый седан SS появился в 1927-м, а за ним последовали новые, все более совершенные модели. Имя Jaguar, отражающее грацию, мощь и динамичный характер этих автомобилей, было официально зарегистрировано в 1935-м году. Многие модели Jaguar стали мировой легендой и законодателями спортивного стиля. Сенсационные спортивные победы, новейшие технологии и уникальные дизайнерские решения навсегда определили особый статус Jaguar в индустрии. Вся история бренда стала подтверждением слов его основателя:
«ИЗ ВСЕГО СОЗДАННОГО ЧЕЛОВЕКОМ АВТОМОБИЛЬ НАИБОЛЕЕ БЛИЗОК К ЖИВОМУ СУЩЕСТВУ».
-
ВЕРШИНЫ МАСТЕРСТВА
Jaguar создают по-настоящему увлеченные люди, подлинные мастера своего дела. Дизайнеры и конструкторы, техники, мастера ручной отделки – каждый из них является настоящим экспертом в своем деле. Увидеть, как они работают – удовольствие.
-
КОМФОРТ И ДРАЙВ НА ВСЕ СЕЗОНЫ
В каждом Jaguar заложен уникальный спортивный характер, наполняющий яркими эмоциями каждое ваше мгновение за рулем. Новейшие технологии, такие как интеллектуальный полный привод Jaguar, позволяют наслаждаться спортивной динамикой в любое время года. Убедитесь на тест-драйве!
-
МЫ СОЗДАЕМ БУДУЩЕЕ
Jaguar – один из мировых лидеров в создании электромобилей и технологий беспилотного транспорта. А наша программа Destination Zero призвана добиться трех амбициозных целей: «Будущее без выбросов», «Будущее без пробок» и «Будущее без аварий».
-
1920-е
В 1922-м году Уильям Лайонс и его партнер Уильям Уолмсли начали собственный бизнес. Через 4 года, в 26-м, они стали крупнейшим в Британии производителем мотоколясок. Но главной мечтой Лайонса всегда были автомобили, и уже в 1927-м компания выпустила партию из 500 Austin Seven Swallow на готовом шасси с оригинальным кузовом.
-
1930-е
Но амбиции Лайонса были выше установки собственных кузовов на чужие шасси. В начале 30-х было принято решение о создании собственной версии шасси, и летом 1931 года на Лондонском автосалоне появился SS1 – автомобиль, который обратил на себя внимание всей Европы.
-
1930-е
В 1935-м компания выпустила первую модель, сделавшую ее знаменитой. Новый Jaguar SS был представлен в Хрустальном зале отеля May Fair. Гостям предложили назвать его предположительную стоимость. Средняя оценка составила 632 доллара при фактической цене в 395. Эта модель с успехом выпускалась в различных модификациях вплоть до начала Второй мировой войны.
-
1940-е
К открытию Автосалона 1948 г. был создан Jaguar XK120, ставший одним из величайших спортивных автомобилей в истории и самым быстрым серийным автомобилем своего времени. Для участия в гонках был создан XK120 C, больше известный как C-TYPE. На 24-часовой гонке в Ле-Мане 1953 года он занял первое, второе и четвертое места – этот триумф не смогла повторить ни она другая модель.
-
1960-е
На Женевском автосалоне 1961 г. дебютировал сенсационный Jaguae E-TYPE. Он развивал скорость 240 км/ч и отличался необычайно эффектной внешностью. Увидев его, Энцо Феррари назвал E-TYPE «самым красивым автомобилем всех времен».
-
1960-е
В период с 1959 по 1969-й годы была создана еще одна культовая модель – роскошный и быстрый Jaguar MkII, знаменитый MarkII. За скорость, надежность и комфорт его часто выбирали не только те, кто хотел успешно уйти от погони, но и сыщики Скотланд-Ярда.
-
ПОДПИСАТЬСЯ НА НОВОСТИ
Подпишитесь на самые актуальные новости компании Jaguar
-
КОНФИГУРАТОР
Создайте Ваш идеальный Jaguar с помощью конфигуратора
-
СКАЧАТЬ БРОШЮРУ
Узнать больше об автомобилях Jaguar
-
НАЙТИ ДИЛЕРА
Найдите ближайшего дилера Jaguar
-
ПОДПИСАТЬСЯ НА НОВОСТИ
-
КОНФИГУРАТОР
-
СКАЧАТЬ БРОШЮРУ
-
НАЙТИ ДИЛЕРА
| Jaguar Cars Ltd. | |
 |
|
| Тип |
Дочернее общество компании Tata Motors |
|---|---|
| Год основания |
1922 |
| Основатели |
Уильям Лайонс и Уильям Уолмсли |
| Расположение |
|
| Ключевые фигуры |
Ратан Тата (председатель совета директоров Tata Group) |
| Отрасль |
Автомобильная промышленность |
| Продукция |
Легковые автомобили |
| Материнская компания |
Tata Motors |
| Сайт |
jaguar.ru |
У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Ягуар (значения).
Jaguar Cars Ltd. (произносится: Ягуар Карс лимитед) — британская автомобилестроительная компания, специализирующаяся на производстве автомобилей класса «люкс». С 2008 года принадлежит индийской компании Tata Motors. Штаб-квартира — в городе Ковентри.
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Собственники и руководство
- 3 Деятельность
- 3.1 Jaguar в России
- 4 Модельный ряд
- 4.1 Представительские седаны
- 4.2 Компактные седаны
- 4.3 Спортивные
- 4.4 Гоночные
- 4.5 Концепт-кары
- 5 Фотографии
- 6 См. также
- 7 Примечания
- 8 Ссылки
История
Jaguar SS 1939 года
Jaguar C-XF Concept
Существование компании началось с 20-х годов XX века. В это время она была компанией Swallow Sidecar, и производила коляски для мотоциклов. Это не приносило особого дохода, после чего фирма сменила специализацию на производство комплектующих для Austin 7.
После выполненного в 1927 году большого заказа доход позволил компании расширить свое производство и производить комплектующие моделей Fiat 509A, Morris Cowley, Wolseley Hornet, а затем стала сама проектировать и разрабатывать новые модели автомобилей.
Большую популярность получили модели Jaguar SS90 и Jaguar SS100, названные так основателем фирмы Уильямом Лайонсом.
В середине XX века компания сменила название на Jaguar, так как инициалы компании SS ассоциировались после войны с нацистскими режимами.
В это же время появился Jaguar Mk VII, в котором была увеличена мощность двигателя до 190 лошадиных сил.
В 1950 году Jaguar начал сотрудничество с фирмой Daimler Motor Company (не путать с Daimler-Benz), которая выпускала автомобили, по классу близкие к Ягуарам. С 1960 года Daimler стала частью компании Jaguar. Сама компания, у которой начались трудности с продажами, в 1966 году начала сотрудничать и вошла в состав Бритиш Мотор. Начиная с этого времени модели Jaguar стали пользоваться все большей популярностью.
К 1960-м годам концерн Jaguar завоевывает американский рынок моделями Jaguar XK150 и XK150 Roadster с объемом двигателя до 3,4 литра.
С 1960-х по 1980-е года были выпущены серии спортивных моделей, а также седанов, которые продавались по высокой цене, но отличались повышенным качеством.
В конце 1960-х была выпущена модель Jaguar с модернизированным 6-цилиндровым двигателем. Через некоторое время, в начале 1970-х, начался выпуск Jaguar XJ12, с 12-цилиндровым двигателем, мощностью 311 лошадиных сил. С 1968 по 1983 годы были выпущены следующие модели: Jaguar XJ8 — седан, XJR 4.0 Supercharged, Jaguar XJ-C — купе, Jaguar XJ-S — на нем был впервые установлен двигатель AJ6. В 1988 году была выпущена новая модель, которая снова получила широкую известность — Jaguar XJ220, однако позднее он был изменен и показан в Токио на автомобильной выставке.
В конце 1980-х был открыт филиал компании Jaguar Sport, производивший спортивные модели автомобилей. Тогда же Jaguar становится отделением фирмы Ford.
В конце 1990-х в Швейцарии на выставке была показана модель спортивного автомобиля в кузове «купе», а также кабриолет.
В 2000—2004 гг. автомобили марки Jaguar снова принимали участие в гонках Формула-1 в качестве команды «Ягуар», используя двигатели Cosworth. Специально для этого были выпущены автомобили модели F-Type Concept и Silverstone.
Собственники и руководство
Jaguar Cars полностью контролируется структурами индийской автомобилестроительной компании Tata Motors, входя в состав группы Jaguar Land Rover[3].
Деятельность
У группы Jaguar Land Rover есть три собственных завода в Великобритании, в ближайшем будущем готовится открытие новых производств в Индии и Китае.
Jaguar в России
Продажи новых автомобилей через сеть официальных дилеров в России:
| Год | S-Type | XF | XJ | XK | XKR-S | X-Type | Всего | Динамика |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006[4][5] | 150 | — | 105 | 54 | — | 584 | 893 | ▲ 71 % |
| 2007[6][7] | 180 | — | 120 | 112 | — | 723 | 1135 | ▲ 27 % |
| 2008[8][9] | 32 | 826 | 124 | 123 | — | 584 | 1689 | ▲ 49 % |
| 2009[10][11] | — | 578 | 63 | 51 | — | 241 | 933 | ▼ 45 % |
| 2010[12][13] | — | 573 | 225 | 45 | — | 15 | 858 | ▼ 8 % |
| 2011[14][15] | — | 765 | 381 | 34 | 1 | 1 | 1182 | ▲ 38 % |
Модельный ряд
Представительские седаны
- Jaguar 2½ Litre saloon (1935—1948)
- Jaguar 3½ Litre saloon (1937—1948)
- Jaguar Mark V (1948—1951)
- Jaguar Mark VII (& VIIM) (1951—1957)
- Jaguar Mark VIII (1957—1959)
- Jaguar Mark IX (1959—1961)
- Jaguar Mark X (1961—1966)
- Jaguar 420G (1966—1970)
- Jaguar XJ6 Series 1, 2 & 3 (1968—1987)
- Jaguar XJ12 (1972—1992)
- Jaguar XJ6 (XJ40) (1986—1994)
- Jaguar XJ12 (XJ81) (1993—1994)
- Jaguar XJ6 & XJ12 (X300 & X301) (1995—1997)
- Jaguar XJ8 (X308) (1998—2003)
- Jaguar XJ (X350) (2004—2009)
- Jaguar XJ (X351) (2009—настоящее время)
Компактные седаны
- Jaguar 1½ Litre saloon (1935—1949)
- Jaguar Mark 1 (1955—1959)
- Jaguar Mark 2 (1959—1967)
- Jaguar S-type (1963—1968)
- Jaguar 420 (1966—1968)
- Jaguar 240 & 340 (1966—1968)
- Jaguar S-Type (1999—2008)
- Jaguar X-Type (2001—2009)
- Jaguar XF (2008—настоящее время)
Спортивные
- Jaguar XK120 (1948—1954)
- Jaguar XK140 (1954—1957)
- Jaguar XK150 (1957—1961)
- Jaguar E-Type (1961—1974)
- Jaguar XJ-S (1975—1996)
- Jaguar XJ220 (1992—1994)
- Jaguar XK8, Jaguar XKR (X100) (1996—2006)
- Jaguar XK, Jaguar XKR (X150) (2006—настоящее время)
- Jaguar F-Type (с 2013)
Гоночные
- Jaguar XK-120C (1951—1952), победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[16]
- Jaguar C-Type (1951—1953), победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[17]
- Jaguar D-Type (1954—1957), трёхкратный победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[18][19][20]
- Jaguar E-Type Lightweight (1963—1964)
- Jaguar XJR-5 до XJR-17 (1985—1992), двукратный победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[21][22], трёхкратный победитель World Sportscar Championship
- Jaguar XFR (2009)
- Jaguar XKR GT2 RSR (2010)
- Jaguar R1 (2000), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R2 (2001), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R3 (2001), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R4 (2003), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R5 (2004), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
Концепт-кары
- E1A — Первый прототип E-Type
- E2A — Второй прототип E-Type
- XJ13 (1966)
- Pirana (1967)
- XK180 (1998)
- F-Type (2000) — Родстер
- R-Coupé (2002) — 4-х местное купе класса «люкс», конкурент Bentley Continental GT
- Fuore XF 10 (2003)
- R-D6 (2003) — Компактное 4-х местное купе
- XK-RR — Высокомощная версия последнего поколения купе Jaguar XK
- XK-RS — Высокомощная версия последнего поколения кабриолета Jaguar XK
- Concept Eight (2004) — Суперлюкс версия длиннобазного Jaguar XJ
- C-XF (2007)
- C-X75 Concept (2010) — Суперкар
- XKR 75 (2010) — Суперкар
- B99 (Bertone 99) (2011)
Фотографии
-
Jaguar Mark X (1963)
-
Jaguar S-Type
-
Jaguar S-Type (Северная Америка) (2006 — 2008)
-
Jaguar XJ8
-
Jaguar XJ
См. также
| Jaguar на Викискладе? |
- Land Rover
Примечания
- ↑ Jaguar Land Rover и Tata Motors: новые назначения, официальный пресс-релиз на drive.ru, 27 февраля 2010 г.
- ↑ Jaguar Land Rover объявляет о глобальных структурных изменениях в компании, официальный пресс-релиз на drive.ru, 20 октября 2010 г.
- ↑ Александр Губский. «Мы превратились в цельную компанию», — Ральф Спет, генеральный директор Jaguar Land Rover // Ведомости, 16.11.2010, 216 (2734) (Проверено 16 ноября 2010)
- ↑ Статистика автомобильного рынка России в 2006 году, autoreview.ru
- ↑ Небывалый рекорд объема продаж иностранных автомобилей и легкого коммерческого транспорта за 2006-й год — продано более 1 миллиона штук, AutoBusiness Info, 12 января 2007 г.
- ↑ Статистика: Авторынок в России — итоги 2007 года, autoreview.ru
- ↑ Объем продаж иностранных автомобилей и легкого коммерческого транспорта за 2007-й год в России составил более 1,6 миллиона штук, AutoBusiness Info, 14 января 2008 г.
- ↑ Авторынок России: инерция, autoreview.ru
- ↑ Продажи иностранных марок в 2008 году увеличились на 26 %, AutoBusiness Info, 14 января 2009 г.
- ↑ Отрезвление, autoreview.ru
- ↑ Продажи новых легковых и легких коммерческих автомобилей в России показали падение по итогам 2009 года, AutoBusiness Info, 14 января 2010 г.
- ↑ Реабилитация, autoreview.ru
- ↑ В 2010 году рынок новых легковых и легких коммерческих автомобилей в России демонстрировал рост девять месяцев из двенадцати, AutoBusiness Info, 13 января 2011 г.
- ↑ За год Jaguar и Land Rover значительно увеличили продажи в РФ, carscope.ru.
- ↑ Jaguar Land Rover Россия оглашает результаты 2011 года, Официальный пресс-релиз на carscope.ru.
- ↑ 24 h Le Mans 1951
- ↑ http://www.wspr-racing.com/wspr/results/lemans/lemans1953.html
- ↑ http://www.wspr-racing.com/wspr/results/lemans/lemans1955.html
- ↑ http://www.wspr-racing.com/wspr/results/lemans/lemans1956.html
- ↑ http://www.wspr-racing.com/wspr/results/lemans/lemans1957.html
- ↑ http://www.wspr-racing.com/wspr/results/lemans/lemans1988.html
- ↑ http://www.wspr-racing.com/wspr/results/lemans/lemans1990.html
Ссылки
- jaguar.ru — официальный сайт Jaguar
- jaguar.com — официальный сайт Jaguar (англ.)
Кроме спортивных, Jaguar выпускает и шикарные представительские машины, по роскоши, убранству салона и престижности соперничающие с такими марками, как Rolls Royce и Bentley. Их история началась в сентябре 1948 года, когда было объявлено о создании новой послевоенной модели Mk V. Автомобиль предлагался с кузовами седан и кабриолет и оснащался моторами объемом 2,5 и 3,5 л.
История этой классической английской автомобильной марки началась в сентябре 1922 года в городе Блэкпул, когда Уильям Лайонс и Уильям Уолмсли основали компанию по выпуску мотоциклетных колясок. Они продавались под маркой Swallow (с англ. «ласточка»), что соответствовало их изящной форме. Компания называлась Swallow Sidecar. К сожалению (а может, и к счастью), производство колясок оказалось невыгодным, и Swallow Sidecar занялись выпуском кузовов для популярного в то время недорогого автомобиля Austin Seven, а затем и сборкой автомашин на базе агрегатов Austin. Продукция молодой компании Swallow Sidecar сразу привлекла к себе внимание как красотой и изяществом, так и сравнительно низкой ценой — хотя автомобиль Austin с кузовом Swallow стоил несколько дороже оригинального, он оказался одной из самых дешевых «заказных» машин. Попутно компания выпускала также кузова для Fiat 509A, Morris Cowley и Wolsely Hornet.
На этом фото 1920 года Билл Лайонс — еще просто обычный мотоциклист и продавец Санбимов. Чтобы проследить рождение Jaguar, вернемся в город Блэкпул на северном побережье. Здесь молодой мотоциклист-любитель по имени Билл Лайонс, которому не было еще и 21 года, встретил Уильяма Уолмсли, занимавшегося конструированием достаточно стильных колясок, которые он впоследствии устанавливал на отремонтированные мотоциклы. Молодому Лайонсу были присущи две черты, которые оставались его величайшими качествами в последующие 50 лет. Обладая деловой хваткой и дальновидностью, он сразу распознал открывающуюся выгодную коммерческую перспективу, а его чувство стиля помогло правильно оценить притягивающий внешний вид этих в принципе обыденных творений. Он предугадал широкие потенциальные возможности, раскрывающиеся в том случае, если правильно организовать производство, обеспечивая его жизнеспособность. В сентябре 1922 г., по достижении совершеннолетия, Уильям Лайонс основал компанию Swallow Sidecar с превышением банковского кредита в 1000 фунтов стерлингов. Была приобретена скромная недвижимость на втором и третьем этаже в Блэкпуле, и силами небольшого количества рабочих производство было запущено. В качестве помощника для продаж взяли молодого Артура Уиттэкера, однако он лучше проявил себя в области закупок. Уиттэкер проработал в компании около 50 лет, став одним из наиболее дальновидных специалистов в своей отрасли.
Austin Seven Swallow Очень стильные коляски, для производства которых впервые использовался алюминий, немедленно завоевали популярность, и производство стремительно развивалось. В 1927 г. Герберт Остин представил свое детище, знаменитый автомобиль Austin Seven. Миниатюрные модели Seven были дешевыми, легкими в вождении и надежными, рассчитанными на широкие массы, но им не доставало индивидуальности. Лайонс увидел другую возможность. Он создал стильный двухместный кузов, который устанавливался на шасси Austin Seven. Вскоре поступил заказ на 500 штук от одного из крупнейших лондонских гаражей, и автомобиль был поставлен на производство. Так началось длительное и плодотворное сотрудничество между Лайонсом и Берти Хенли, управляющим Henlys, одной из ведущих автомастерских страны. Великолепный маленький Austin Seven Swallow за 175 или 185 дол с навесным жестким верхом завоевал широкую популярность, и компания представила кузов Swallow для более крупных шасси Morris Cowley. В конце 1928 г. ассортимент значительно расширился после выпуска седана Austin Seven Swallow. Седан выглядел дорогим автомобилем, при этом цена его составляла 187 фунтов 10 шиллингов. В период экономического кризиса многим пришлось снизить свои притязания, однако модели Swallow, представлявшие собой копии стиля более экстравагантных и шикарных автомобилей эпохи, смягчили удар и позволили владельцам «держать марку». Такие детали, как изысканный капот и Ladies Companion Set, поднимали Swallow выше среднего уровня. Объемы продаж автомобилей и колясок возрастали, и было принято решение о переезде в Мидлендс, традиционный центр британской автомобильной промышленности. Таким образом, молодая компания «в полном составе» переехала в Ковентри.
Это первое известное творение Уолмсли: с 1922 года они вместе с Лайонсом начали продавать такие «восьмигранные» алюминиевые коляски под громким названием Coupe Sports De Luxe по 28 фунтов. «Колясочный» бизнес компании SS был продан только после войны На ежегодном автосалоне в Лондоне в 1929 г. впервые были представлены три новые модели Swallow. Их основой стали Fiat Tipo 509A, Swift Ten и Standard Big Nine. Standard Swallow был более крупным седаном и стоил 245. Он отличался более экстравагантным стилем кузова, чем у собственных автомобилей производителя, и широким диапазоном цветовых схем. В 1931 г. шасси Enfield шестицилиндрового Standard мощностью 16 л. с. получило пропитку Swallow, результатом чего стало знакомство компании с двигателем объемом 2054 см3 с боковым клапаном, что идеально подходило для реализации амбициозных целей Лайонса и Уолмсли. В это время в дополнение к Swallow версии Wolseley Hornet была представлена модель более спортивного стиля. Изначально предлагался двухместный вариант, позднее в 1931 г. появился и четырехместный, а уже через год кузов мог поставляться в комплекте с еще более спортивным шасси Hornet Special. Компании Swallow на тот момент было чуть меньше года, и это было волнующее время постоянного развития и полного успеха. Но амбиции Лайонса еще не были удовлетворены, и требовался очередной смелый шаг вперед.
В июле 1933 г. к купе присоединился SS I Tourer. Это была первая открытая модель SS, она впервые была включена в серьезные соревнования. В 1933 г. команда из трех автомобилей Tourers была включена в Альпийские ралли в континентальной части Европы, а в следующем году они значительно упрочили репутацию SS, взяв командный приз в этих особенно жестких соревнованиях. В конце 1933 г. маленький SS II был существенно усовершенствован за счет специально разработанных шасси, которые добавляли более фута к длине колесной базы. В то же самое время передние крылья были изменены в соответствии с новым стилем модели большего размера. В соответствии с формой SS I были также выпущены модели седана и Tourer SS II. В 1934 г. к лучшим в серии был добавлен новый седан с четырьмя окнами. Автомобиль данной модели был гораздо менее ярким и более практичным — сидящие сзади пассажиры имели возможность смотреть в окно! Во второй половине 1934 г. Уильям Уолмсли, не разделявший амбициозных замыслов своего партнера и потерявший интерес к предприятию, разорвал отношения с Уильямсом Лайонсом. Переключив свое внимание на механическую целостность автомобиля, Лайонс обратился к Гарри Уэслейку, выдающемуся инженеру-консультанту, специализирующемуся на конструкциях крышек цилиндра. Он сформировал технический отдел и назначил молодого Уильяма Хейнса главным инженером. В течение последующих 35 лет Хейнс занимал ведущую роль в компании. В 1935 г. был расширен модельный ряд за счет добавления седана SS I Airline. Данный дизайн не принадлежал к числу любимых Лайонса, но форма была в моде в то время, и на нее был высокий спрос. Еще одна модель присоединилась к серии в марте того же года, когда был представлен SS I — купе с мягким откидным верхом. Внешне он был очень похож на купе, но теперь откидной верх полностью отводился под подвесную крышку на багажнике, и результат выглядел наиболее оптимально. Плоды работы Уэслейка и Хейнса стали очевидны в кратчайшие сроки, в это же время был представлен новый очень стильный спортивный автомобиль. Модель была известна как SS 90 и имела 2,7-литровый двигатель с боковым клапаном, а рабочие характеристики снова не совсем соответствовали яркому внешнему виду автомобиля. Но вскоре всему этому было суждено измениться. В 1935 г. имя Jaguar снова появилось на сцене впервые с совершенно новой серией седанов и спортивных машин. Уильям Хейнс работал над созданием абсолютно нового крестообразного растянутого шасси коробчатого сечения для нового значительно усовершенствованного ряда моделей. В то же время Уэслейк занялся усовершенствованием двигателей Standard. Переняв верхние клапаны, он смог повысить мощность 75 л. с. предыдущего 2,5-литрового двигателя с боковыми клапанами до 105 л. с. Для новых шасси и блока двигателя Лайонс создал новый стиль кузова, менее яркий, чем предыдущие модели, однако не менее стильный. В действительности он был близок к современному Bentley, который стоил практически в четыре раза дороже!
SS Jaguar 100 Были вытеснены все более ранние модели SS, за исключением кузова Tourer большего размера за счет измененной решетки радиатора и установки нового 2,5-литрового двигателя. Великолепный дизайн спортивных автомобилей вновь был представлен в модели SS Jaguar 100. Изменив пропитку в задней части около топливного бака и, что более важно, установив новое шасси и двигатель, компания начала производство автомобилей, которыми можно гордиться. Для многих SS 100 является довоенной классикой среди спортивных автомобилей. Цена, кстати, составляла всего 395 дол. Данная модель была предназначена для достижения значимых результатов в состязаниях, как в национальных, так и в международных. Между тем, работы по совершенствованию автомобиля продолжались, и в конце 1935 года была создана модель SS100. Она имела защищенные металлической сеткой радиатор и огромные фары, красивые крылья над спицованными колесами большого диаметра, кузов с чисто английскими вырезами для локтей (их просто некуда было бы деть в узком кокпите) и внушительных размеров топливный бак, прикрытый запасным колесом. Под низким капотом в половину длины машины располагалась 104-сильная рядная верхнеклапанная `шестерка` объемом 2,5 л. Индекс указывал на скорость автомобиля, но на самом деле `магический` для того времени 100-мильный порог (161 км/ч) сумела преодолеть созданная лишь тремя годами позже версия с 3,5-литровым мотором. SS100 серийно выпускалась до 1939 года. Этот автомобиль, отличавшийся изысканными линиями кузова, одержал множество побед на популярных в те годы конкурсах элегантности, а мощный двигатель, частично синхронизированная коробка передач, подвеска на полуэллиптических рессорах, барабанные тормоза Girling и удачная развесовка обеспечивали призовые места в международных ралли и соревнованиях по подъемам на возвышенность. Фирменный стиль многих автомобилей в ту пору большей частью определяла `носовая фигура`, украшавшая пробку заливной горловины радиатора, как носовые свесы парусников. Глава отдела рекламы и сбыта фирмы Ранкин набросал эскиз прыгающей кошки и показал его скульптору Гордону Кросби… Так появилась фигурка ягуара. Во время Второй мировой войны компания выпускала бомбардировщики и легкие внедорожники с мотором Ford. После окончания войны Лайонс, предвидя негативную реакцию на название фирмы, схожее с названием элитарных подразделений Третьего рейха, заменил аббревиатуру SS на Jaguar Car Limited.
Jaguar XK-SS В сентябре 1948 г. Jaguar анонсировал свою первую послевоенную, временную модель. Стесненные обстоятельства не позволили создать нечто более радикальное, и модель Mark V стала носителем славы компании на пару лет. Основной инновацией стала независимая передняя подвеска, разработанная Хейнсом. К тому времени был создан мощный новый двигатель, но было решено, что Mark V излишне консервативен для него, и поэтому седан и модель с мягким откидным верхом Mark V были укомплектованы обычными 2,5- и 3,5-литровыми силовыми блоками. Лайонс заявил, что мощность нового двигателя будет составлять 160 л. с. (что было достигнуто «Старым номером 8»). Рассмотрев несколько вариантов конфигураций, конструкторы выбрали верхний распредвал и приняли окончательное решение относительно двигателя. Это был прямой шестицилиндровый двигатель объемом 3442 см3, получивший имя XK. Достигаемая мощность составляла 160 л. с! Теперь у Jaguar было отличное новое шасси, необычайно мощный новый двигатель, но не было спортивного автомобиля. Было принято решение о выпуске небольшого количества спортивных автомобилей для поддержания популярности и, возможно, успешного участия в гонках. Перед Уильямом Лайонсом встала задача всего за пару месяцев разработать подходящий кузов, чтобы принять участие в автосалоне 1948 г. Результат превзошел все ожидания. Модель известна как XK120, и ей суждено было стать одним из величайших спортивных автомобилей всех времен. Это была не просто гоночная машина. Автомобиль обладал присущей стилю Jaguar изысканностью, беспрецедентным для такого типа автомобилей комфортом и, помимо всего прочего, его цена составляла всего 998 долларов ( 1 298 с учетом налогов). Максимальная скорость, позволила ХК120 стать самым быстрым серийно выпускаемым автомобилем в мире. Чтобы убедить скептиков в этом, стандартный XK120 поставил рекорд 126 миль в час на закрытом участке дороги с двусторонним движением в Джеббеке в Бельгии в присутствии прессы. Со снятым ветровым стеклом была развита скорость 133 мили в час, и на случай, если этого было не достаточно, водитель проехал перед изумленными журналистами со скоростью 10 миль в час на высшей передаче. Заказы полились рекой, и стало ясно, что производство двухсот автомобилей не сможет удовлетворить спрос. После дебютного участия XK в гонках серийно выпускаемых спортивных автомобилей в Сильверстоуне списки ожидающих стали пополняться еще интенсивнее. Три автомобиля были предоставлены знаменитым гонщикам Питеру Уокеру, Лесли Джонсону и принцу Сиама Бира. Бира не повезло — он проколол шину, а двое других финишировали первым и вторым.
XK120 Чтобы оценить возможности автомобилей в состязаниях на международном уровне, в 1950 г. было решено отправить три автомобиля во Францию для участия в известной мировой 24 часовой гонке Ле-Ман. Команде не повезло, они не вошли в первую тройку — лидирующая модель выбыла из-за проблем со сцеплением после 21-го часа, однако, в любом случае, был получен ценный опыт. Под управлением Иэна Эпплярда и дочери Лайонса Пэт на Альпийских ралли в 1951 и 1952 годах и на ралли Tulip в 1951 году NUB 120 стал одним из самых успешных гоночных автомобилей всех времен. На автосалоне 1950 г. был представлен седан Mark VII, который в очередной раз затмил всех. Разработанная с учетом требований рынка США, по европейским стандартам эта модель была чересчур громоздкой. Это был полный пятиместный автомобиль, но с двигателем XK он обладал высокой скоростью. Американцы оценили модель Mark VII, и было принято несколько заказов стоимостью 30 млн. долларов США. Спрос был настолько велик, что потребовался новый завод, и компания переехала на существующее поныне производственное предприятие в Браунс Лейн, Ковентри, в 1951-52 гг. В 1951 г. в дополнение к серии XK120 была выпущена модель Fixed Head Coupe с цельной крышей. Способность дальнего переезда модели Fixed Head Coupe была наглядно продемонстрирована, когда собственный автомобиль Билла Хейнса перегоняли на автодром Montlhery недалеко от Парижа. Стирлинг Мосс и еще трое водителей ехали в течение семи дней и ночей со средней скоростью, превышающей 100 миль в час.
В 1954 году на смену XK120 пришел XK140, мощность двигателя которого составляла сначала 190 л.с., а потом и 210 л.с. Спустя всего три года модель заменили еще более мощной XK150. С 265-сильным мотором она разгонялась до 210 км/ч. Это был первый в мире серийный автомобиль, получивший дисковые тормоза на всех колесах. Участвовавший в 1950 году в гонке `24 часа Ле-Мана` Jaguar ХК120 долгое время держался в группе лидеров, но до финиша добраться так и не смог. Лайонс рассудил, что если серийная машина показала неплохие результаты, то специально подготовленный автомобиль имеет все шансы на первое место. Так в 1951 году на трассу вышел XK120C, или C-Type. Форсированный до 210 л.с. за счет увеличения объема двигатель, три карбюратора Weber вместо двух SU и облегченный кузов с пространственной рамой из труб позволили одной машине установить рекорд круга, а другой легко выиграть гонку. Всего на счету C-Type 37 побед в международных соревнованиях. В 1954 году на смену C-Type пришел Jaguar D-Type, трижды подряд занимавший первое место в Ле-Мане. Форсированный до 277 л.с. двигатель позволял D-Type двигаться со скоростью 240 км/ч, а разгон до 100 км/ч составлял 4,7 с. За возвращение Великобритании былой спортивной славы Уильяму Лайонсу был пожалован дворянский титул.
Прототипы Е1А 1958 года и Е2А 1960 года положили начало серийному родстэру Jaguar E-Type, который поразил посетителей Женевского автосалона 1961 года. Двухместный Е-Type с обтекаемым кузовом на пространственной трубчатой раме, 3,8-литровым двигателем и независимой подвеской всех колес развивал максимальную скорость 240 км/ч. Эта модель принесла фирме Jaguar всемирную славу. Всего до 1975 года было выпущено более 75 тысяч E-Type. Получивший при рождении двигатель объемом 3,8 л мощностью 265 л.с., в процессе эволюции E-Type приобрел сначала 4,2-литровый, а потом и 5,3-литровый двигатель V12. Конец истории E-Type в 1975 году положил нефтяной кризис — 12-цилиндровые двигатели оказались слишком `прожорливыми`.
К сожалению, спортивной славы своих предшественников E-type не достиг, и в 1966 году был построен спортивный прототип XJ13 со среднерасположенным двенадцатицилиндровым двигателем и полностью алюминиевым кузовом.
Елена Третьякова
Искусственный Интеллект
(112005),
закрыт
9 лет назад
Дополнен 9 лет назад
Не дала в варианте ответ : другое.
Пишут что она индийская.. ((
А такая красота!
Комментарии
ЗаяцИскусственный Интеллект (222853)
9 лет назад
индийская — ибо принадлежит индийской тата моторз
Елена Третьякова
Искусственный Интеллект
(112005)
Да ты что?!!!Вот это номер…
Она же вроде Даймлер принадлежала.
Юрий ДеминВысший разум (314080)
9 лет назад
Индийская !!!Принадлежит ТАТА Моторз.
Елена Третьякова
Искусственный Интеллект
(112005)
Спасибо. Вот уж не ожидала))))
Jaguar (Ягуар) — британская автомобильная компания, производитель автомобилей класса люкс. Основана в 1925 году в Блэкпуле Уильямом Лайонсом и Уильямом Уолмсли под именем Swallow Sidecar (SS). Сменила название в 1945 году из-за ассоциаций с нацистской организацией.
Еще
→
ягуар — существительное, именительный п., муж. p., ед. ч.
↳
ягуар — существительное, винительный п., муж. p., ед. ч.
Часть речи: существительное
| Единственное число | Множественное число | |
|---|---|---|
| Им. |
ягуар |
ягуары |
| Рд. |
ягуара |
ягуаров |
| Дт. |
ягуару |
ягуарам |
| Вн. |
ягуара ягуар |
ягуаров ягуары |
| Тв. |
ягуаром |
ягуарами |
| Пр. |
ягуаре |
ягуарах |
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Антиблокировочная система (ABS); система курсовой устойчивости (ESP); подушки безопасности: 4 и более; антипробуксовочная система (TCS); break assist; сигнализация; CD-магнитола; усилитель рулевого управления; центральный замок; цвет салона: бежевый; диски: литые, размер R17; датчик света; противотуманные фары; отделка под дерево; бортовой компьютер; салон: кожа; климат-контроль: общий; ксеноновые фары; омыватель фар; датчик дождя; парктроник; обогрев зеркал; регулируемая рулевая колонка: 2 положения; обогрев сидений: передние; электропривод: водительское сиденье, стекла (все), зеркала
У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Ягуар (значения).
Jaguar (Ягуар[4]) — бренд транснациональной автомобилестроительной компании Jaguar Land Rover. Штаб-квартира находится в пригороде Ковентри графства Уэст-Мидлендс. С 2008 года принадлежит индийской Tata Motors.[5]
Компания Jaguar была основана в 1922 году сначала как Swallow Sidecar Company и производила мотоколяски. После Второй мировой войны название было изменено на «Jaguar», чтобы избежать неблагоприятного сочетания «SS». В 1966 году объединилась с компанией British Motor Corporation, которая стала называться British Motor Holdings (BMH), в 1968 объединилась с Leyland Motor Corporation и переименована в British Leyland. В 1975 году компания была национализирована.
«Ягуар» был отделён от British Leyland и вышел на Лондонскую фондовую биржу в 1984 году и до 1990 года его акции были составляющей индекса FTSE 100, пока автопроизводитель не был приобретён компанией Ford. В последнее время Jaguar производит автомобили для Премьер-министра Великобритании[6], последней была предоставлена модель XJ в мае 2010, а также для королевы Елизаветы II и принца Чарльза. С 1987 года[7] «Ягуары» разрабатываются в инженерном центре Jaguar Land Rover на заводе Утли в Ковентри и в Гэйдон центре в Уорикшире. Производятся на сборочном заводе Castle Bromwich в Бирмингеме, ожидается, что часть производства начнётся в Солихалле.
В сентябре 2013 анонсированы планы об открытии R&D центра в Уорикском университете в Ковентри, стоимостью 100 миллионов фунтов для создания нового поколения автомобильных технологий. Автопроизводитель заявил, что около 1000 учёных и инженеров будут работать над этим, и что конструирование начнётся в 2014 году.[8]
История[править | править код]
Существование компании началось с 20-х годов XX века. В это время она была компанией Swallow Sidecar, и производила коляски для мотоциклов. Это не приносило особого дохода, после чего фирма сменила специализацию на производство комплектующих для Austin 7. После выполненного в 1927 году большого заказа доход позволил компании расширить своё производство и производить комплектующие моделей Fiat 509A, Morris Cowley, Wolseley Hornet, а затем стала сама проектировать и разрабатывать новые модели автомобилей.
В середине XX века компания сменила название на Jaguar, так как инициалы компании SS ассоциировались после войны с нацистским режимом. В это же время появился Jaguar Mk VII, в котором была увеличена мощность двигателя до 190 лошадиных сил. В 1950 году Jaguar начал сотрудничество с фирмой Daimler Motor Company (не путать с Daimler-Benz), которая выпускала автомобили, по классу близкие к Ягуарам. С 1960 года Daimler стала частью компании Jaguar. Сама компания, у которой начались трудности с продажами, в 1966 году начала сотрудничать и вошла в состав Бритиш Мотор. Начиная с этого времени модели Jaguar стали пользоваться все большей популярностью.
К 1960-м годам концерн Jaguar завоевывает американский рынок моделями Jaguar XK150 и XK150 Roadster с объёмом двигателя до 3,4 литра. С 1960-х по 1980-е года были выпущены серии спортивных моделей, а также седанов, которые продавались по высокой цене, но отличались повышенным качеством.
В конце 1960-х была выпущена модель Jaguar с модернизированным 6-цилиндровым двигателем. Через некоторое время, в начале 1970-х, начался выпуск Jaguar XJ12, с 12-цилиндровым двигателем, мощностью 311 лошадиных сил. С 1968 по 1983 годы были выпущены следующие модели: Jaguar XJ8 — седан, XJR 4.0 Supercharged, Jaguar XJ-C — купе, Jaguar XJ-S — на нём был впервые установлен двигатель AJ6. В 1988 году была выпущена новая модель, которая снова получила широкую известность — Jaguar XJ220, однако позднее он был изменен и показан в Токио на автомобильной выставке.
В конце 1980-х был открыт филиал компании Jaguar Sport, производивший спортивные модели автомобилей. Тогда же Jaguar становится отделением фирмы Ford. В конце 1990-х в Швейцарии на выставке была показана модель спортивного автомобиля в кузове «купе», а также кабриолет.
В 2000—2004 гг. автомобили марки Jaguar снова принимали участие в гонках Формула-1 в качестве команды «Ягуар», используя двигатели Cosworth. Специально для этого были выпущены автомобили модели F-Type Concept и Silverstone.
В 2019 году электрокару Jaguar I-Pace присудили награду «Автомобиль 2018 года в Европе». Также можно заметить, что этот приз компания получает впервые[9].
В 2019 году компания анонсировала флагманский кроссовер J-Pace, основанный на новой, полностью алюминиевой платформе MLA, которую также планируется использовать в новом поколении внедорожника Range Rover. Автомобиль лишится механического полного привода — в движение заднюю ось будет приводить электромотор, переднюю — традиционный двигатель внутреннего сгорания[10]. Выход автомобиля запланирован на 2021 год.
Собственники и руководство[править | править код]
Jaguar Cars полностью контролируется структурами индийской автомобилестроительной компании Tata Motors, входя в состав группы Jaguar Land Rover[11].
Деятельность[править | править код]
Группе Jaguar Land Rover принадлежат три завода в Великобритании и один в Индии[12][13]. В ближайшем будущем готовится открытие новых производств в Китае[14] и Саудовской Аравии[15].
Продажи в России[править | править код]
Продажи новых автомобилей через сеть официальных дилерских центров в России:
| Год | S-Type | XF | XJ | XK | X-Type | Всего | Динамика |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006[16][17] | 150 | — | 105 | 54 | 584 | 893 | ▲ 71 % |
| 2007[18][19] | 180 | — | 120 | 112 | 723 | 1135 | ▲ 27 % |
| 2008[20][21] | 32 | 826 | 124 | 123 | 584 | 1689 | ▲ 49 % |
| 2009[22][23] | — | 578 | 63 | 51 | 241 | 933 | ▼ 45 % |
| 2010[24][25] | — | 573 | 225 | 45 | 15 | 858 | ▼ 8 % |
| 2011[26][27] | — | 765 | 381 | 35 | 1 | 1182 | ▲ 38 % |
| 2012[28][29] | — | 1059 | 406 | 41 | — | 1506 | ▲ 27 % |
Модельный ряд[править | править код]
Представительские седаны[править | править код]
- Jaguar 2½ Litre saloon (1935—1948)
- Jaguar 3½ Litre saloon (1937—1948)
- Jaguar Mark V (1948—1951)
- Jaguar Mark VII (& VIIM) (1951—1957)
- Jaguar Mark VIII (1957—1958)
- Jaguar Mark IX (1959—1961)
- Jaguar Mark X (1961—1966)
- Jaguar 420G (1966—1970)
- Jaguar XJ6 Series 1, 2 & 3 (1968—1987)
- Jaguar XJ12 (1972—1992)
- Jaguar XJ6 (XJ40) (1986—1994)
- Jaguar XJ12 (XJ81) (1993—1994)
- Jaguar XJ6 & XJ12 (X300 & X301) (1995—1997)
- Jaguar XJ8 (X308) (1998—2003)
- Jaguar XJ (X350) (2004—2009)
- Jaguar XJ (X351) (c 2009—2019)
Компактные седаны[править | править код]
- Jaguar 1½ Litre saloon (1935—1949)
- Jaguar Mark 1 (1955—1959)
- Jaguar Mark 2 (1959—1967)
- Jaguar S-type (1963—1968)
- Jaguar 420 (1966—1968)
- Jaguar 240 & 340 (1966—1968)
- Jaguar S-Type (1999—2008)
- Jaguar X-Type (2001—2009)
- Jaguar XF (с 2008 года)
- Jaguar XE (с 2015 года)
Спортивные[править | править код]
- Jaguar XK120 (1948—1954)
- Jaguar XK140 (1954—1957)
- Jaguar XK150 (1957—1961)
- Jaguar E-Type (1961—1974)
- Jaguar XJ-S (1975—1996)
- Jaguar XJ220 (1992—1994)
- Jaguar XK8, Jaguar XKR (X100) (1996—2006)
- Jaguar XK, Jaguar XKR (X150) (2006—2014)
- Jaguar F-Type (с 2013 года)
Гоночные[править | править код]
- Jaguar XK-120C (1951—1952), победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[30]
- Jaguar C-Type (1951—1953), победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[31]
- Jaguar D-Type (1954—1957), трёхкратный победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[32][33][34]
- Jaguar E-Type Lightweight (1963—1964)
- Jaguar XJR-5 до XJR-17 (1985—1992), двукратный победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[35][36], трёхкратный победитель World Sportscar Championship
- Jaguar XFR (2009)
- Jaguar XKR GT2 RSR (2010)
- Jaguar R1 (2000), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R2 (2001), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R3 (2001), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R4 (2003), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R5 (2004), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
Кроссоверы[править | править код]
- Jaguar F-Pace (с 2016 года)
- Jaguar E-Pace (с 2018 года)
- Jaguar i-Pace (с 2018 года) Обладатель титула «Автомобиль года 2019» (COTY-2019)
Концепт-кары[править | править код]
- E1A — Первый прототип E-Type
- E2A — Второй прототип E-Type
- XJ13 (1966)
- Pirana (1967)
- XK180 (1998)
- F-Type (2000) — Родстер
- R-Coupé (2002) — 4-местное купе класса «люкс», конкурент Bentley Continental GT
- Fuore XF 10 (2003)
- R-D6 (2003) — Компактное 4-местное купе
- XK-RR — Высокомощная версия последнего поколения купе Jaguar XK
- XK-RS — Высокомощная версия последнего поколения кабриолета Jaguar XK
- Concept Eight (2004) — Суперлюкс версия длиннобазного Jaguar XJ
- C-X17 (2013) — кроссовер
- C-XF (2007)
- C-X75 Concept (2010) — Суперкар
- XKR 75 (2010) — Суперкар
- B99 (Bertone 99) (2011)
Фотографии[править | править код]
-
Jaguar Mark X (1963)
-
Jaguar S-Type
-
Jaguar S-Type (Северная Америка) (2006—2008)
-
Jaguar XJ8
-
-
См. также[править | править код]
- Land Rover
Примечания[править | править код]
- ↑ Cyrus P Mistry to take over from Ratan Tata as Chairman of Tata Group in December 2012, economictimes.indiatimes.com, 23 ноября 2011 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar Land Rover и Tata Motors: новые назначения, официальный пресс-релиз на drive.ru, 27 февраля 2010 г.
- ↑ Jaguar Land Rover объявляет о глобальных структурных изменениях в компании, официальный пресс-релиз на drive.ru, 20 октября 2010 г.
- ↑ Василий Ефанов. Как правильно говорить: «Ягуар» или «Джегьюар»?. auto.vesti.ru (16 декабря 2016). Дата обращения: 22 января 2019.
- ↑ http://top.rbc.ru/economics/26/03/2008/153257.shtml Архивная копия от 2 апреля 2015 на Wayback Machine Ford продает индийцам Jaguar и Land Rover за $2 млрд.
- ↑ http://www.forbes.ru/stil-zhizni-photogallery/avto/222701-10-sluzhebnyh-avtomobilei-liderov-vedushchih-stran-mira/photo/5 10 служебных автомобилей, на которых ездят мировые лидеры
- ↑ Graham Robson. Jaguar XJ-S: The Complete Story. — ISBN 1-86126-933-1.
- ↑ http://5koleso.ru/news/vse-novosti/jaguar-land-rover-potratit-160-millionov-na-sozdanie-novogo-nauchno Архивная копия от 18 января 2015 на Wayback Machine JAGUAR LAND ROVER ПОТРАТИТ $160 МИЛЛИОНОВ НА СОЗДАНИЕ НОВОГО НАУЧНО-ИССЛЕДОВАТЕЛЬСКОГО ЦЕНТРА
- ↑ Владимирский, Игорь. Автомобилем года — 2019 стал электрический Jaguar I-Pace, autoreview.ru (4 марта 2019). Дата обращения 5 марта 2019.
- ↑ Кроссовер Jaguar J-Pace выйдет в 2021 году. Коммерсантъ (25 марта 2019). Дата обращения: 25 марта 2019.
- ↑ Александр Губский. «Мы превратились в цельную компанию», — Ральф Спет, генеральный директор Jaguar Land Rover // Ведомости, 16.11.2010, 216 (2734) (Дата обращения: 16 ноября 2010)
- ↑ Jaguar-Land Rover Opens Assembly Plant in India, Rolls Out its First Model, carscoops.com, 27 мая 2011 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar XF Saloon Now Made in India as Well, carscoops.com, 24 января 2013 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar-Land Rover and Chery Seal Joint Venture, Begin Construction of New Plant in China, carscoops.com, 19 ноября 2012 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar-Land Rover Confirms Interest in Building a Plant in Saudi Arabia, carscoops.com, 11 декабря 2012 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2006 год (недоступная ссылка), официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 12 января 2007 г.
- ↑ Статистика автомобильного рынка России в 2006 году, газета «Авторевю» № 3 2007 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2007 год, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 14 января 2008 г.
- ↑ Статистика: Авторынок в России — итоги 2007 года, газета «Авторевю» № 3 2008 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2008 год Архивная копия от 4 марта 2016 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 14 января 2009 г.
- ↑ Автомобильный рынок: итоги 2008 года, газета «Авторевю» № 3 2009 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2009 год Архивная копия от 3 мая 2014 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 14 января 2010 г.
- ↑ Отрезвление Архивная копия от 7 сентября 2015 на Wayback Machine , газета «Авторевю» № 3 2010 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2010 год Архивная копия от 28 ноября 2017 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 13 января 2011 г.
- ↑ Реабилитация Архивировано 7 сентября 2015 года., газета «Авторевю» № 3 2011 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2011 год Архивировано 30 декабря 2013 года., официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 12 января 2012 г.
- ↑ За год Jaguar и Land Rover значительно увеличили продажи в РФ, carscope.ru.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2012 год (недоступная ссылка), официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 15 января 2013 г.
- ↑ Газета «Авторевю» № 3 2013 г.
- ↑ 24 h Le Mans 1951
- ↑ Доступ ограничен
- ↑ Доступ ограничен
- ↑ Доступ ограничен
- ↑ Доступ ограничен
- ↑ Доступ ограничен
- ↑ Доступ ограничен
Ссылки[править | править код]
- jaguar.ru — официальный сайт Jaguar
- jaguar.com — официальный сайт Jaguar (англ.)
- jaguar-cars.kz — официальный сайт Jaguar
У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Ягуар (значения).
Jaguar (Ягуар[4]) — бренд транснациональной автомобилестроительной компании Jaguar Land Rover. Штаб-квартира находится в пригороде Ковентри графства Уэст-Мидлендс. С 2008 года принадлежит индийской Tata Motors.[5]
Компания Jaguar была основана в 1922 году сначала как Swallow Sidecar Company и производила мотоколяски. После Второй мировой войны название было изменено на «Jaguar», чтобы избежать неблагоприятного сочетания «SS». В 1966 году объединилась с компанией British Motor Corporation, которая стала называться British Motor Holdings (BMH), в 1968 объединилась с Leyland Motor Corporation и переименована в British Leyland. В 1975 году компания была национализирована.
«Ягуар» был отделён от British Leyland и вышел на Лондонскую фондовую биржу в 1984 году и до 1990 года его акции были составляющей индекса FTSE 100, пока автопроизводитель не был приобретён компанией Ford. В последнее время Jaguar производит автомобили для Премьер-министра Великобритании[6], последней была предоставлена модель XJ в мае 2010, а также для королевы Елизаветы II и принца Чарльза. С 1987 года[7] «Ягуары» разрабатываются в инженерном центре Jaguar Land Rover на заводе Утли в Ковентри и в Гэйдон центре в Уорикшире. Производятся на сборочном заводе Castle Bromwich в Бирмингеме, ожидается, что часть производства начнётся в Солихалле.
В сентябре 2013 анонсированы планы об открытии R&D центра в Уорикском университете в Ковентри, стоимостью 100 миллионов фунтов для создания нового поколения автомобильных технологий. Автопроизводитель заявил, что около 1000 учёных и инженеров будут работать над этим, и что конструирование начнётся в 2014 году.[8]
История

Jaguar SS 1939 года


Существование компании началось с 20-х годов XX века. В это время она была компанией Swallow Sidecar, и производила коляски для мотоциклов. Это не приносило особого дохода, после чего фирма сменила специализацию на производство комплектующих для Austin 7. После выполненного в 1927 году большого заказа доход позволил компании расширить своё производство и производить комплектующие моделей Fiat 509A, Morris Cowley, Wolseley Hornet, а затем стала сама проектировать и разрабатывать новые модели автомобилей.
В середине XX века компания сменила название на Jaguar, так как инициалы компании SS ассоциировались после войны с нацистским режимом. В это же время появился Jaguar Mk VII, в котором была увеличена мощность двигателя до 190 лошадиных сил. В 1950 году Jaguar начал сотрудничество с фирмой Daimler Motor Company (не путать с Daimler-Benz), которая выпускала автомобили, по классу близкие к Ягуарам. С 1960 года Daimler стала частью компании Jaguar. Сама компания, у которой начались трудности с продажами, в 1966 году начала сотрудничать и вошла в состав Бритиш Мотор. Начиная с этого времени модели Jaguar стали пользоваться все большей популярностью.
К 1960-м годам концерн Jaguar завоевывает американский рынок моделями Jaguar XK150 и XK150 Roadster с объёмом двигателя до 3,4 литра. С 1960-х по 1980-е года были выпущены серии спортивных моделей, а также седанов, которые продавались по высокой цене, но отличались повышенным качеством.
В конце 1960-х была выпущена модель Jaguar с модернизированным 6-цилиндровым двигателем. Через некоторое время, в начале 1970-х, начался выпуск Jaguar XJ12, с 12-цилиндровым двигателем, мощностью 311 лошадиных сил. С 1968 по 1983 годы были выпущены следующие модели: Jaguar XJ8 — седан, XJR 4.0 Supercharged, Jaguar XJ-C — купе, Jaguar XJ-S — на нём был впервые установлен двигатель AJ6. В 1988 году была выпущена новая модель, которая снова получила широкую известность — Jaguar XJ220, однако позднее он был изменен и показан в Токио на автомобильной выставке.
В конце 1980-х был открыт филиал компании Jaguar Sport, производивший спортивные модели автомобилей. Тогда же Jaguar становится отделением фирмы Ford. В конце 1990-х в Швейцарии на выставке была показана модель спортивного автомобиля в кузове «купе», а также кабриолет.

Jaguar XJ
В 2000—2004 гг. автомобили марки Jaguar снова принимали участие в гонках Формула-1 в качестве команды «Ягуар», используя двигатели Cosworth. Специально для этого были выпущены автомобили модели F-Type Concept и Silverstone.
В 2019 году электрокару Jaguar I-Pace присудили награду «Автомобиль 2018 года в Европе». Также можно заметить, что этот приз компания получает впервые[9].
В 2019 году компания анонсировала флагманский кроссовер J-Pace, основанный на новой, полностью алюминиевой платформе MLA, которую также планируется использовать в новом поколении внедорожника Range Rover. Автомобиль лишится механического полного привода — в движение заднюю ось будет приводить электромотор, переднюю — традиционный двигатель внутреннего сгорания[10]. Выход автомобиля запланирован на 2021 год.
Собственники и руководство
Jaguar Cars полностью контролируется структурами индийской автомобилестроительной компании Tata Motors, входя в состав группы Jaguar Land Rover[11].
Деятельность
Группе Jaguar Land Rover принадлежат три завода в Великобритании и один в Индии[12][13]. В ближайшем будущем готовится открытие новых производств в Китае[14] и Саудовской Аравии[15].
Продажи в России
Продажи новых автомобилей через сеть официальных дилерских центров в России:
| Год | S-Type | XF | XJ | XK | X-Type | Всего | Динамика |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006[16][17] | 150 | — | 105 | 54 | 584 | 893 | ▲ 71 % |
| 2007[18][19] | 180 | — | 120 | 112 | 723 | 1135 | ▲ 27 % |
| 2008[20][21] | 32 | 826 | 124 | 123 | 584 | 1689 | ▲ 49 % |
| 2009[22][23] | — | 578 | 63 | 51 | 241 | 933 | ▼ 45 % |
| 2010[24][25] | — | 573 | 225 | 45 | 15 | 858 | ▼ 8 % |
| 2011[26][27] | — | 765 | 381 | 35 | 1 | 1182 | ▲ 38 % |
| 2012[28][29] | — | 1059 | 406 | 41 | — | 1506 | ▲ 27 % |
Модельный ряд
Представительские седаны
- Jaguar 2½ Litre saloon (1935—1948)
- Jaguar 3½ Litre saloon (1937—1948)
- Jaguar Mark V (1948—1951)
- Jaguar Mark VII (& VIIM) (1951—1957)
- Jaguar Mark VIII (1957—1958)
- Jaguar Mark IX (1959—1961)
- Jaguar Mark X (1961—1966)
- Jaguar 420G (1966—1970)
- Jaguar XJ6 Series 1, 2 & 3 (1968—1987)
- Jaguar XJ12 (1972—1992)
- Jaguar XJ6 (XJ40) (1986—1994)
- Jaguar XJ12 (XJ81) (1993—1994)
- Jaguar XJ6 & XJ12 (X300 & X301) (1995—1997)
- Jaguar XJ8 (X308) (1998—2003)
- Jaguar XJ (X350) (2004—2009)
- Jaguar XJ (X351) (c 2009—2019)
Компактные седаны
- Jaguar 1½ Litre saloon (1935—1949)
- Jaguar Mark 1 (1955—1959)
- Jaguar Mark 2 (1959—1967)
- Jaguar S-type (1963—1968)
- Jaguar 420 (1966—1968)
- Jaguar 240 & 340 (1966—1968)
- Jaguar S-Type (1999—2008)
- Jaguar X-Type (2001—2009)
- Jaguar XF (с 2008 года)
- Jaguar XE (с 2015 года)
Спортивные
- Jaguar XK120 (1948—1954)
- Jaguar XK140 (1954—1957)
- Jaguar XK150 (1957—1961)
- Jaguar E-Type (1961—1974)
- Jaguar XJ-S (1975—1996)
- Jaguar XJ220 (1992—1994)
- Jaguar XK8, Jaguar XKR (X100) (1996—2006)
- Jaguar XK, Jaguar XKR (X150) (2006—2014)
- Jaguar F-Type (с 2013 года)
Гоночные
- Jaguar XK-120C (1951—1952), победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[30]
- Jaguar C-Type (1951—1953), победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[31]
- Jaguar D-Type (1954—1957), трёхкратный победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[32][33][34]
- Jaguar E-Type Lightweight (1963—1964)
- Jaguar XJR-5 до XJR-17 (1985—1992), двукратный победитель 24 часа Ле-Мана[35][36], трёхкратный победитель World Sportscar Championship
- Jaguar XFR (2009)
- Jaguar XKR GT2 RSR (2010)
- Jaguar R1 (2000), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R2 (2001), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R3 (2001), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R4 (2003), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
- Jaguar R5 (2004), гоночный автомобиль Формулы-1
Кроссоверы
- Jaguar F-Pace (с 2016 года)
- Jaguar E-Pace (с 2018 года)
- Jaguar i-Pace (с 2018 года) Обладатель титула «Автомобиль года 2019» (COTY-2019)
Концепт-кары
- E1A — Первый прототип E-Type
- E2A — Второй прототип E-Type
- XJ13 (1966)
- Pirana (1967)
- XK180 (1998)
- F-Type (2000) — Родстер
- R-Coupé (2002) — 4-местное купе класса «люкс», конкурент Bentley Continental GT
- Fuore XF 10 (2003)
- R-D6 (2003) — Компактное 4-местное купе
- XK-RR — Высокомощная версия последнего поколения купе Jaguar XK
- XK-RS — Высокомощная версия последнего поколения кабриолета Jaguar XK
- Concept Eight (2004) — Суперлюкс версия длиннобазного Jaguar XJ
- C-X17 (2013) — кроссовер
- C-XF (2007)
- C-X75 Concept (2010) — Суперкар
- XKR 75 (2010) — Суперкар
- B99 (Bertone 99) (2011)
Галерея
-
Jaguar Mark X (1963)
-
Jaguar S-Type
-
Jaguar S-Type (Северная Америка) (2006—2008)
-
Jaguar XJ8
-
-
См. также
- Land Rover
Примечания
- ↑ Cyrus P Mistry to take over from Ratan Tata as Chairman of Tata Group in December 2012 Архивная копия от 1 октября 2013 на Wayback Machine, economictimes.indiatimes.com, 23 ноября 2011 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar Land Rover и Tata Motors: новые назначения Архивная копия от 2 марта 2010 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на drive.ru, 27 февраля 2010 г.
- ↑ Jaguar Land Rover объявляет о глобальных структурных изменениях в компании Архивная копия от 28 января 2012 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на drive.ru, 20 октября 2010 г.
- ↑ Василий Ефанов. Как правильно говорить: »Ягуар» или »Джегьюар»?. auto.vesti.ru (16 декабря 2016). Дата обращения: 22 января 2019. Архивировано 22 января 2019 года.
- ↑ http://top.rbc.ru/economics/26/03/2008/153257.shtml Архивная копия от 2 апреля 2015 на Wayback Machine Ford продает индийцам Jaguar и Land Rover за $2 млрд.
- ↑ http://www.forbes.ru/stil-zhizni-photogallery/avto/222701-10-sluzhebnyh-avtomobilei-liderov-vedushchih-stran-mira/photo/5 Архивная копия от 18 января 2015 на Wayback Machine 10 служебных автомобилей, на которых ездят мировые лидеры
- ↑ Graham Robson. Jaguar XJ-S: The Complete Story. — ISBN 1-86126-933-1.
- ↑ http://5koleso.ru/news/vse-novosti/jaguar-land-rover-potratit-160-millionov-na-sozdanie-novogo-nauchno Архивная копия от 18 января 2015 на Wayback Machine JAGUAR LAND ROVER ПОТРАТИТ $160 МИЛЛИОНОВ НА СОЗДАНИЕ НОВОГО НАУЧНО-ИССЛЕДОВАТЕЛЬСКОГО ЦЕНТРА
- ↑ Владимирский, Игорь. Автомобилем года — 2019 стал электрический Jaguar I-Pace, autoreview.ru (4 марта 2019). Архивировано 6 марта 2019 года. Дата обращения: 5 марта 2019.
- ↑ Кроссовер Jaguar J-Pace выйдет в 2021 году. Коммерсантъ (25 марта 2019). Дата обращения: 25 марта 2019. Архивировано 25 марта 2019 года.
- ↑ Александр Губский. «Мы превратились в цельную компанию», — Ральф Спет, генеральный директор Jaguar Land Rover Архивная копия от 3 апреля 2012 на Wayback Machine // Ведомости, 16.11.2010, 216 (2734) (Дата обращения: 16 ноября 2010)
- ↑ Jaguar-Land Rover Opens Assembly Plant in India, Rolls Out its First Model Архивная копия от 15 июля 2014 на Wayback Machine, carscoops.com, 27 мая 2011 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar XF Saloon Now Made in India as Well Архивная копия от 30 марта 2015 на Wayback Machine, carscoops.com, 24 января 2013 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar-Land Rover and Chery Seal Joint Venture, Begin Construction of New Plant in China Архивная копия от 29 октября 2014 на Wayback Machine, carscoops.com, 19 ноября 2012 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Jaguar-Land Rover Confirms Interest in Building a Plant in Saudi Arabia Архивная копия от 8 декабря 2013 на Wayback Machine, carscoops.com, 11 декабря 2012 г. (англ.)
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2006 год Архивная копия от 27 января 2021 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 12 января 2007 г.
- ↑ Статистика автомобильного рынка России в 2006 году Архивная копия от 18 мая 2007 на Wayback Machine, газета «Авторевю» № 3 2007 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2007 год Архивная копия от 4 марта 2016 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 14 января 2008 г.
- ↑ Статистика: Авторынок в России — итоги 2007 года Архивная копия от 29 декабря 2008 на Wayback Machine, газета «Авторевю» № 3 2008 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2008 год Архивная копия от 4 марта 2016 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 14 января 2009 г.
- ↑ Автомобильный рынок: итоги 2008 года Архивная копия от 7 декабря 2009 на Wayback Machine, газета «Авторевю» № 3 2009 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2009 год Архивная копия от 3 мая 2014 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 14 января 2010 г.
- ↑ Отрезвление Архивная копия от 7 сентября 2015 на Wayback Machine , газета «Авторевю» № 3 2010 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2010 год Архивная копия от 28 ноября 2017 на Wayback Machine, официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 13 января 2011 г.
- ↑ Реабилитация Архивировано 7 сентября 2015 года., газета «Авторевю» № 3 2011 г.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2011 год Архивировано 30 декабря 2013 года., официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 12 января 2012 г.
- ↑ За год Jaguar и Land Rover значительно увеличили продажи в РФ Архивная копия от 30 декабря 2013 на Wayback Machine, carscope.ru.
- ↑ Результаты продаж легковых и лёгких коммерческих автомобилей в России за 2012 год (недоступная ссылка), официальный пресс-релиз на aebrus.ru, 15 января 2013 г.
- ↑ Газета «Авторевю» № 3 2013 г.
- ↑ 24 h Le Mans 1951. Дата обращения: 2 мая 2011. Архивировано 6 июня 2011 года.
- ↑ Доступ ограничен. Дата обращения: 2 мая 2011. Архивировано 6 июня 2011 года.
- ↑ Доступ ограничен. Дата обращения: 2 мая 2011. Архивировано 6 июня 2011 года.
- ↑ Доступ ограничен. Дата обращения: 2 мая 2011. Архивировано 6 июня 2011 года.
- ↑ Доступ ограничен. Дата обращения: 2 мая 2011. Архивировано 6 июня 2011 года.
- ↑ Доступ ограничен. Дата обращения: 2 мая 2011. Архивировано 6 июня 2011 года.
- ↑ Доступ ограничен. Дата обращения: 2 мая 2011. Архивировано 6 июня 2011 года.
Ссылки
- jaguar.com — официальный сайт Jaguar (англ.)
- Официальный сайт Jaguar в России
- «W.C.E - Jaguar Evolution (1935 - 2018)» (англ.) на YouTube
Эта страница в последний раз была отредактирована 7 декабря 2022 в 18:42.
Как только страница обновилась в Википедии она обновляется в Вики 2.
Обычно почти сразу, изредка в течении часа.