|
Che Guevara |
|
|---|---|

Guerrillero Heroico |
|
| Minister of Industries of Cuba | |
| In office 11 February 1961 – 1 April 1965 |
|
| Prime Minister | Fidel Castro |
| Preceded by | Office established |
| Succeeded by | Joel Domenech Benítez |
| President of the National Bank of Cuba | |
| In office 26 November 1959 – 23 February 1961 |
|
| Preceded by | Felipe Pazos |
| Succeeded by | Raúl Cepero Bonilla |
| Personal details | |
| Born |
Ernesto Guevara 14 June 1928[1] |
| Died | 9 October 1967 (aged 39) La Higuera, Santa Cruz, Bolivia |
| Cause of death | Execution by shooting |
| Resting place | Che Guevara Mausoleum, Santa Clara, Cuba |
| Citizenship |
|
| Political party | 26th of July Movement (1955–1962) United Party of the Cuban Socialist Revolution (1962–1965) |
| Spouse(s) |
Hilda Gadea (m. 1955; div. 1959) Aleida March (m. 1959) |
| Children | 5, including Aleida |
| Alma mater | University of Buenos Aires |
| Occupation |
|
| Known for | Guevarism |
| Signature |  |
| Nicknames |
|
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | Republic of Cuba[2] |
| Branch/service |
|
| Years of service | 1955–1967 |
| Unit | 26th of July Movement |
| Commands | Commanding officer of the Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces |
| Battles/wars |
|
Ernesto «Che« Guevara (Spanish: [ˈtʃe ɣeˈβaɾa];[3] 14 June 1928[4] – 9 October 1967) was an Argentine Marxist revolutionary. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia in popular culture.[5]
As a young medical student, Guevara traveled throughout South America and was radicalized by the poverty, hunger, and disease he witnessed.[6][7] His burgeoning desire to help overturn what he saw as the capitalist exploitation of Latin America by the United States prompted his involvement in Guatemala’s social reforms under President Jacobo Árbenz, whose eventual CIA-assisted overthrow at the behest of the United Fruit Company solidified Guevara’s political ideology.[6] Later in Mexico City, Guevara met Raúl and Fidel Castro, joined their 26th of July Movement, and sailed to Cuba aboard the yacht Granma with the intention of overthrowing U.S.-backed Cuban dictator Fulgencio Batista.[8] Guevara soon rose to prominence among the insurgents, was promoted to second-in-command, and played a pivotal role in the two-year guerrilla campaign that deposed the Batista regime.[9]
After the Cuban Revolution, Guevara played key roles in the new government. These included reviewing the appeals and firing squads for those convicted as war criminals during the revolutionary tribunals,[10] instituting agrarian land reform as Minister of Industries, helping spearhead a successful nationwide literacy campaign, serving as both President of the National Bank and instructional director for Cuba’s armed forces, and traversing the globe as a diplomat on behalf of Cuban socialism. Such positions also allowed him to play a central role in training the militia forces who repelled the Bay of Pigs Invasion,[11] and bringing Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles to Cuba, which preceded the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis.[12] Additionally, Guevara was a prolific writer and diarist, composing a seminal guerrilla warfare manual, along with a best-selling memoir about his youthful continental motorcycle journey. His experiences and studying of Marxism–Leninism led him to posit that the Third World’s underdevelopment and dependence was an intrinsic result of imperialism, neocolonialism, and monopoly capitalism, with the only remedies being proletarian internationalism and world revolution.[13][14] Guevara left Cuba in 1965 to foment continental revolutions across both Africa and South America,[15] first unsuccessfully in Congo-Kinshasa and later in Bolivia, where he was captured by CIA-assisted Bolivian forces and summarily executed.[16]
Guevara remains both a revered and reviled historical figure, polarized in the collective imagination in a multitude of biographies, memoirs, essays, documentaries, songs, and films. As a result of his perceived martyrdom, poetic invocations for class struggle, and desire to create the consciousness of a «new man» driven by moral rather than material incentives,[17] Guevara has evolved into a quintessential icon of various left-wing movements. In contrast, his critics on the political right accuse him of promoting authoritarianism and endorsing violence against his political opponents. Despite disagreements on his legacy, Time named him one of the 100 most influential people of the 20th century,[18] while an Alberto Korda photograph of him, titled Guerrillero Heroico, was cited by the Maryland Institute College of Art as «the most famous photograph in the world».[19]
Early life
A teenage Ernesto (left) with his parents and siblings, c. 1944, seated beside him from left to right: Celia (mother), Celia (sister), Roberto, Juan Martín, Ernesto (father) and Ana María
Ernesto Guevara was born to Ernesto Guevara Lynch and Celia de la Serna y Llosa, on 14 June 1928,[4] in Rosario, Argentina. Although the legal name on his birth certificate was «Ernesto Guevara», his name sometimes appears with «de la Serna» and/or «Lynch» accompanying it.[20] He was the eldest of five children in an upper-class Argentine family of pre-independence immigrant Spanish (Basque, Cantabrian), and Irish ancestry.[21][22][23] Two of Guevara’s notable 18th century ancestors included Luis María Peralta, a prominent Spanish landowner in colonial California, and Patrick Lynch, who emigrated from Ireland to the Río de la Plata Governorate.[24][25] Referring to Che’s «restless» nature, his father declared «the first thing to note is that in my son’s veins flowed the blood of the Irish rebels».[26]
Early on in life, Ernestito (as he was then called) developed an «affinity for the poor».[27] Growing up in a family with leftist leanings, Guevara was introduced to a wide spectrum of political perspectives even as a boy.[28] His father, a staunch supporter of Republicans from the Spanish Civil War, would host veterans from the conflict in the Guevara home.[29] As a young man, he briefly contemplated a career selling insecticides, and set up a laboratory in his family’s garage to experiment with effective mixtures of talc and gamexane under the brand name Vendaval, but was forced to abandon his efforts after suffering a severe asthmatic reaction to the chemicals.[30]
Despite numerous bouts of acute asthma that were to affect him throughout his life, he excelled as an athlete, enjoying swimming, football, golf, and shooting, while also becoming an «untiring» cyclist.[31][32] He was an avid rugby union player,[33] and played at fly-half for Club Universitario de Buenos Aires.[34] His rugby playing earned him the nickname «Fuser»—a contraction of El Furibundo (furious) and his mother’s surname, de la Serna—for his aggressive style of play.[35]
Intellectual and literary interests
Guevara learned chess from his father and began participating in local tournaments by the age of 12. During adolescence and throughout his life he studied poetry, especially that of Pablo Neruda, John Keats, Antonio Machado, Federico García Lorca, Gabriela Mistral, César Vallejo, and Walt Whitman.[36] He could also recite Rudyard Kipling’s If— and José Hernández’s Martín Fierro by heart.[36] The Guevara home contained more than 3,000 books, which allowed Guevara to be an enthusiastic and eclectic reader, with interests including Karl Marx, William Faulkner, André Gide, Emilio Salgari, and Jules Verne.[37] Additionally, he enjoyed the works of Jawaharlal Nehru, Franz Kafka, Albert Camus, Vladimir Lenin, and Jean-Paul Sartre; as well as Anatole France, Friedrich Engels, H. G. Wells, and Robert Frost.[38]
As he grew older, he developed an interest in the Latin American writers Horacio Quiroga, Ciro Alegría, Jorge Icaza, Rubén Darío, and Miguel Asturias.[38] Many of these authors’ ideas he cataloged in his own handwritten notebooks of concepts, definitions, and philosophies of influential intellectuals. These included composing analytical sketches of Buddha and Aristotle, along with examining Bertrand Russell on love and patriotism, Jack London on society, and Nietzsche on the idea of death. Sigmund Freud’s ideas fascinated him as he quoted him on a variety of topics from dreams and libido to narcissism and the Oedipus complex.[38] His favorite subjects in school included philosophy, mathematics, engineering, political science, sociology, history, and archaeology.[39][40] A CIA «biographical and personality report», dated 13 February 1958 and declassified decades later, made note of Guevara’s range of academic interests and intellect – describing him as «quite well read», while adding that «Che is fairly intellectual for a Latino».[41]
Motorcycle journey
Guevara (right) with Alberto Granado (left) in June 1952 on the Amazon River aboard their «Mambo-Tango» wooden raft, which was a gift from the lepers whom they had treated[42]
In 1948, Guevara entered the University of Buenos Aires to study medicine. His «hunger to explore the world»[43] led him to intersperse his collegiate pursuits with two long introspective journeys that fundamentally changed the way he viewed himself and the contemporary economic conditions in Latin America. The first expedition, in 1950, was a 4,500-kilometer (2,800 mi) solo trip through the rural provinces of northern Argentina on a bicycle on which he had installed a small engine.[44] Guevara then spent six months working as a nurse at sea on Argentina’s merchant marine freighters and oil tankers.[45] His second expedition, in 1951, was a nine-month, 8,000-kilometer (5,000 mi) continental motorcycle trek through part of South America. For the latter, he took a year off from his studies to embark with his friend, Alberto Granado, with the final goal of spending a few weeks volunteering at the San Pablo leper colony in Peru, on the banks of the Amazon River.[46]
A map of Guevara’s 1952 trip with Alberto Granado (the red arrows correspond to air travel)
In Chile, Guevara was angered by the working conditions of the miners at Anaconda’s Chuquicamata copper mine, moved by his overnight encounter in the Atacama Desert with a persecuted communist couple who did not even own a blanket, describing them as «the shivering flesh-and-blood victims of capitalist exploitation».[47] On the way to Machu Picchu he was stunned by the crushing poverty of the remote rural areas, where peasant farmers worked small plots of land owned by wealthy landlords.[48] Later on his journey, Guevara was especially impressed by the camaraderie among the people living in a leper colony, stating, «The highest forms of human solidarity and loyalty arise among such lonely and desperate people.»[48] Guevara used notes taken during this trip to write an account (not published until 1995), titled The Motorcycle Diaries, which later became a New York Times best seller,[49] and was adapted into a 2004 film of the same name.
A motorcycle journey the length of South America awakened him to the injustice of US domination in the hemisphere, and to the suffering colonialism brought to its original inhabitants.
—George Galloway, British politician, 2006[50]
The journey took Guevara through Argentina, Chile, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Panama, and Miami, Florida, for 20 days,[51] before returning home to Buenos Aires. By the end of the trip, he came to view Latin America not as a collection of separate nations, but as a single entity requiring a continent-wide liberation strategy. His conception of a borderless, united Hispanic America sharing a common Latino heritage was a theme that recurred prominently during his later revolutionary activities. Upon returning to Argentina, he completed his studies and received his medical degree in June 1953.[52][53]
Guevara later remarked that, through his travels in Latin America, he came in «close contact with poverty, hunger and disease» along with the «inability to treat a child because of lack of money» and «stupefaction provoked by the continual hunger and punishment» that leads a father to «accept the loss of a son as an unimportant accident». Guevara cited these experiences as convincing him that to «help these people», he needed to leave the realm of medicine and consider the political arena of armed struggle.[6]
Early political activity
Activism in Guatemala
Ernesto Guevara spent just over nine months in Guatemala. On 7 July 1953, Guevara set out again, this time to Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Panama, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, and El Salvador. On 10 December 1953, before leaving for Guatemala, Guevara sent an update to his aunt Beatriz from San José, Costa Rica. In the letter Guevara speaks of traversing the dominion of the United Fruit Company, a journey which convinced him that the company’s capitalist system was disadvantageous to the average citizen.[54] He adopted an aggressive tone to frighten his more conservative relatives, and the letter ends with Guevara swearing on an image of the then-recently deceased Joseph Stalin, not to rest until these «octopuses have been vanquished».[55] Later that month, Guevara arrived in Guatemala, where President Jacobo Árbenz headed a democratically elected government that, through land reform and other initiatives, was attempting to end the latifundia agricultural system. To accomplish this, President Árbenz had enacted a major land reform program, where all uncultivated portions of large land holdings were to be appropriated and redistributed to landless peasants. The largest land owner, and the one most affected by the reforms, was the United Fruit Company, from which the Árbenz government had already taken more than 225,000 acres (91,000 ha) of uncultivated land.[56] Pleased with the direction in which the nation was heading, Guevara decided to make his home in Guatemala to «perfect himself and accomplish whatever may be necessary in order to become a true revolutionary.»[57]
A map of Che Guevara’s travels between 1953 and 1956, including his journey aboard the Granma
In Guatemala City, Guevara sought out Hilda Gadea Acosta, a Peruvian economist who was politically well-connected as a member of the left-leaning, Alianza Popular Revolucionaria Americana (APRA). She introduced Guevara to a number of high-level officials in the Árbenz government. Guevara then established contact with a group of Cuban exiles linked to Fidel Castro through the 26 July 1953 attack on the Moncada Barracks in Santiago de Cuba. During this period, he acquired his famous nickname, due to his frequent use of the Argentine filler expression che (a multi-purpose discourse marker, like the syllable «eh» in Canadian English).[58] During his time in Guatemala, Guevara was hosted by other Central American exiles, one of whom, Helena Leiva de Holst, provided him with food and lodging,[59] discussed her travels to study Marxism in Russia and China,[60] and to whom Guevara dedicated a poem, «Invitación al camino».[61]
In May 1954, a ship carrying infantry and light artillery weapons was dispatched by communist Czechoslovakia for the Árbenz government and arrived in Puerto Barrios.[62] As a result, the United States government—which since 1953 had been tasked by President Eisenhower to remove Árbenz from power in the multifaceted CIA operation code-named PBSuccess—responded by saturating Guatemala with anti-Árbenz propaganda through radio and air-dropped leaflets, and began bombing raids using unmarked airplanes.[63] The United States also sponsored an armed force of several hundred anti-Árbenz Guatemalan refugees and mercenaries headed by Carlos Castillo Armas to help remove the Árbenz government. On 27 June, Árbenz chose to resign.[64] This allowed Armas and his CIA-assisted forces to march into Guatemala City and establish a military junta, which elected Armas as president on 7 July.[65] The Armas regime then consolidated power by rounding up and executing suspected communists,[66] while crushing the previously flourishing labor unions[67] and reversing the previous agrarian reforms.[68]
Guevara was eager to fight on behalf of Árbenz, and joined an armed militia organized by the communist youth for that purpose. However, frustrated with that group’s inaction, Guevara soon returned to medical duties. Following the coup, he again volunteered to fight, but soon after, Árbenz took refuge in the Mexican embassy and told his foreign supporters to leave the country. Guevara’s repeated calls to resist were noted by supporters of the coup, and he was marked for murder.[69] After Gadea was arrested, Guevara sought protection inside the Argentine consulate, where he remained until he received a safe-conduct pass some weeks later and made his way to Mexico.[70]
The overthrow of the Árbenz regime and establishment of the right-wing Armas dictatorship cemented Guevara’s view of the United States as an imperialist power that opposed and attempted to destroy any government that sought to redress the socioeconomic inequality endemic to Latin America and other developing countries.[57] In speaking about the coup, Guevara stated:
The last Latin American revolutionary democracy – that of Jacobo Árbenz – failed as a result of the cold premeditated aggression carried out by the United States. Its visible head was the Secretary of State John Foster Dulles, a man who, through a rare coincidence, was also a stockholder and attorney for the United Fruit Company.[69]
Guevara’s conviction strengthened that Marxism, achieved through armed struggle and defended by an armed populace, was the only way to rectify such conditions.[71] Gadea wrote later, «It was Guatemala which finally convinced him of the necessity for armed struggle and for taking the initiative against imperialism. By the time he left, he was sure of this.»[72]
Exile in Mexico
Guevara arrived in Mexico City on 21 September 1954, and worked in the allergy section of the General Hospital and at the Hospital Infantil de Mexico.[73][74] In addition he gave lectures on medicine at the Faculty of Medicine in the National Autonomous University of Mexico and worked as a news photographer for Latina News Agency.[75][76] His first wife Hilda notes in her memoir My Life with Che, that for a while, Guevara considered going to work as a doctor in Africa and that he continued to be deeply troubled by the poverty around him.[77] In one instance, Hilda describes Guevara’s obsession with an elderly washerwoman whom he was treating, remarking that he saw her as «representative of the most forgotten and exploited class». Hilda later found a poem that Che had dedicated to the old woman, containing «a promise to fight for a better world, for a better life for all the poor and exploited».[77]
During this time he renewed his friendship with Ñico López and the other Cuban exiles whom he had met in Guatemala. In June 1955, López introduced him to Raúl Castro, who subsequently introduced him to his older brother, Fidel Castro, the revolutionary leader who had formed the 26th of July Movement and was now plotting to overthrow the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista. During a long conversation with Fidel on the night of their first meeting, Guevara concluded that the Cuban’s cause was the one for which he had been searching and before daybreak he had signed up as a member of 26 July Movement.[78] Despite their «contrasting personalities», from this point on Che and Fidel began to foster what dual biographer Simon Reid-Henry deemed a «revolutionary friendship that would change the world», as a result of their coinciding commitment to anti-imperialism.[79]
By this point in Guevara’s life, he deemed that U.S.-controlled conglomerates installed and supported repressive regimes around the world. In this vein, he considered Batista a «U.S. puppet whose strings needed cutting».[80] Although he planned to be the group’s combat medic, Guevara participated in the military training with the members of the Movement. The key portion of training involved learning hit and run tactics of guerrilla warfare. Guevara and the others underwent arduous 15-hour marches over mountains, across rivers, and through the dense undergrowth, learning and perfecting the procedures of ambush and quick retreat. From the start Guevara was instructor Alberto Bayo’s «prize student» among those in training, scoring the highest on all of the tests given.[81] At the end of the course, he was called «the best guerrilla of them all» by General Bayo.[82]
Guevara then married Gadea in Mexico in September 1955, before embarking on his plan to assist in the liberation of Cuba.[83]
Cuban Revolution
Granma invasion
Journey of the yacht «Granma», from Mexico to Cuba.
The first step in Castro’s revolutionary plan was an assault on Cuba from Mexico via the Granma, an old, leaky cabin cruiser. They set out for Cuba on 25 November 1956. Attacked by Batista’s military soon after landing, many of the 82 men were either killed in the attack or executed upon capture; only 22 found each other afterwards.[84] During this initial bloody confrontation Guevara laid down his medical supplies and picked up a box of ammunition dropped by a fleeing comrade, proving to be a symbolic moment in Che’s life.[85]
Only a small band of revolutionaries survived to re-group as a bedraggled fighting force deep in the Sierra Maestra mountains, where they received support from the urban guerrilla network of Frank País, 26 July Movement, and local campesinos. With the group withdrawn to the Sierra, the world wondered whether Castro was alive or dead until early 1957 when an interview by Herbert Matthews appeared in The New York Times. The article presented a lasting, almost mythical image for Castro and the guerrillas. Guevara was not present for the interview, but in the coming months he began to realize the importance of the media in their struggle. Meanwhile, as supplies and morale diminished, and with an allergy to mosquito bites which resulted in agonizing walnut-sized cysts on his body,[86] Guevara considered these «the most painful days of the war».[87]
During Guevara’s time living hidden among the poor subsistence farmers of the Sierra Maestra mountains, he discovered that there were no schools, no electricity, minimal access to healthcare, and more than 40 percent of the adults were illiterate.[88] As the war continued, Guevara became an integral part of the rebel army and «convinced Castro with competence, diplomacy and patience».[9] Guevara set up factories to make grenades, built ovens to bake bread, and organized schools to teach illiterate campesinos to read and write.[9] Moreover, Guevara established health clinics, workshops to teach military tactics, and a newspaper to disseminate information.[89] The man whom Time dubbed three years later «Castro’s brain» at this point was promoted by Fidel Castro to Comandante (commander) of a second army column.[9]
Role as commander
As second-in-command, Guevara was a harsh disciplinarian who sometimes shot defectors. Deserters were punished as traitors, and Guevara was known to send squads to track those seeking to abandon their duties.[90] As a result, Guevara became feared for his brutality and ruthlessness.[91] During the guerrilla campaign, Guevara was also responsible for the summary executions of a number of men accused of being informers, deserters, or spies.[92] In his diaries, Guevara described the first such execution, of Eutimio Guerra, a peasant who had acted as a guide for the Castrist guerrillas, but admitted treason when it was discovered he accepted the promise of ten thousand pesos for repeatedly giving away the rebels’ position for attack by the Cuban air force.[93] Such information also allowed Batista’s army to burn the homes of peasants sympathetic to the revolution.[93] Upon Guerra’s request that they «end his life quickly»,[93] Che stepped forward and shot him in the head, writing «The situation was uncomfortable for the people and for Eutimio so I ended the problem giving him a shot with a .32 pistol in the right side of the brain, with exit orifice in the right temporal [lobe].»[94] His scientific notations and matter-of-fact description, suggested to one biographer a «remarkable detachment to violence» by that point in the war.[94] Later, Guevara published a literary account of the incident, titled «Death of a Traitor», where he transfigured Eutimio’s betrayal and pre-execution request that the revolution «take care of his children», into a «revolutionary parable about redemption through sacrifice».[94]
Although he maintained a demanding and harsh disposition, Guevara also viewed his role of commander as one of a teacher, entertaining his men during breaks between engagements with readings from the likes of Robert Louis Stevenson, Miguel de Cervantes, and Spanish lyric poets.[95] Together with this role, and inspired by José Martí’s principle of «literacy without borders», Guevara further ensured that his rebel fighters made daily time to teach the uneducated campesinos with whom they lived and fought to read and write, in what Guevara termed the «battle against ignorance».[88] Tomás Alba, who fought under Guevara’s command, later stated that «Che was loved, in spite of being stern and demanding. We would (have) given our life for him.»[96]
His commanding officer Fidel Castro described Guevara as intelligent, daring, and an exemplary leader who «had great moral authority over his troops».[97] Castro further remarked that Guevara took too many risks, even having a «tendency toward foolhardiness».[98] Guevara’s teenage lieutenant, Joel Iglesias, recounts such actions in his diary, noting that Guevara’s behavior in combat even brought admiration from the enemy. On one occasion Iglesias recounts the time he had been wounded in battle, stating «Che ran out to me, defying the bullets, threw me over his shoulder, and got me out of there. The guards didn’t dare fire at him … later they told me he made a great impression on them when they saw him run out with his pistol stuck in his belt, ignoring the danger, they didn’t dare shoot.»[99]
Guevara was instrumental in creating the clandestine radio station Radio Rebelde (Rebel Radio) in February 1958, which broadcast news to the Cuban people with statements by 26 July movement, and provided radiotelephone communication between the growing number of rebel columns across the island. Guevara had apparently been inspired to create the station by observing the effectiveness of CIA supplied radio in Guatemala in ousting the government of Jacobo Árbenz Guzmán.[100]
To quell the rebellion, Cuban government troops began executing rebel prisoners on the spot, and regularly rounded up, tortured, and shot civilians as a tactic of intimidation.[101] By March 1958, the continued atrocities carried out by Batista’s forces led the United States to stop selling arms to the Cuban government.[89] Then in late July 1958, Guevara played a critical role in the Battle of Las Mercedes by using his column to halt a force of 1,500 men called up by Batista’s General Cantillo in a plan to encircle and destroy Castro’s forces. Years later, Major Larry Bockman of the United States Marine Corps analyzed and described Che’s tactical appreciation of this battle as «brilliant».[102] During this time Guevara also became an «expert» at leading hit-and-run tactics against Batista’s army, and then fading back into the countryside before the army could counterattack.[103]
Final offensive
As the war extended, Guevara led a new column of fighters dispatched westward for the final push towards Havana. Travelling by foot, Guevara embarked on a difficult 7-week march, only travelling at night to avoid an ambush and often not eating for several days.[104] In the closing days of December 1958, Guevara’s task was to cut the island in half by taking Las Villas province. In a matter of days he executed a series of «brilliant tactical victories» that gave him control of all but the province’s capital city of Santa Clara.[104] Guevara then directed his «suicide squad» in the attack on Santa Clara, which became the final decisive military victory of the revolution.[105][106] In the six weeks leading up to the battle, there were times when his men were completely surrounded, outgunned, and overrun. Che’s eventual victory despite being outnumbered 10:1 remains in the view of some observers a «remarkable tour de force in modern warfare».[107]
Radio Rebelde broadcast the first reports that Guevara’s column had taken Santa Clara on New Year’s Eve 1958. This contradicted reports by the heavily controlled national news media, which had at one stage reported Guevara’s death during the fighting. At 3 am on 1 January 1959, upon learning that his generals were negotiating a separate peace with Guevara, Fulgencio Batista boarded a plane in Havana and fled for the Dominican Republic, along with an amassed «fortune of more than $300,000,000 through graft and payoffs».[108] The following day on 2 January, Guevara entered Havana to take final control of the capital.[109] Fidel Castro took six more days to arrive, as he stopped to rally support in several large cities on his way to rolling victoriously into Havana on 8 January 1959. The final death toll from the two years of revolutionary fighting was 2,000 people.[110]
Political career in Cuba
Revolutionary tribunals
In mid-January 1959, Guevara went to live at a summer villa in Tarará to recover from a violent asthma attack.[111] While there he started the Tarara Group, a group that debated and formed the new plans for Cuba’s social, political, and economic development.[112] In addition, Che began to write his book Guerrilla Warfare while resting at Tarara.[112] In February, the revolutionary government proclaimed Guevara «a Cuban citizen by birth» in recognition of his role in the triumph.[113] When Hilda Gadea arrived in Cuba in late January, Guevara told her that he was involved with another woman, and the two agreed on a divorce,[114] which was finalized on 22 May.[115]
The first major political crisis arose over what to do with the captured Batista officials who had perpetrated the worst of the repression.[116] During the rebellion against Batista’s dictatorship, the general command of the rebel army, led by Fidel Castro, introduced into the territories under its control the 19th-century penal law commonly known as the Ley de la Sierra (Law of the Sierra).[117] This law included the death penalty for serious crimes, whether perpetrated by the Batista regime or by supporters of the revolution. In 1959 the revolutionary government extended its application to the whole of the republic and to those it considered war criminals, captured and tried after the revolution. According to the Cuban Ministry of Justice, this latter extension was supported by the majority of the population, and followed the same procedure as those in the Nuremberg trials held by the Allies after World War II.[118]
Guevara in his trademark olive-green military fatigues and beret
To implement a portion of this plan, Castro named Guevara commander of the La Cabaña Fortress prison, for a five-month tenure (2 January through 12 June 1959).[119] Guevara was charged by the new government with purging the Batista army and consolidating victory by exacting «revolutionary justice» against those regarded as traitors, chivatos (informants) or war criminals.[120] As commander of La Cabaña, Guevara reviewed the appeals of those convicted during the revolutionary tribunal process.[10] The tribunals were conducted by 2–3 army officers, an assessor, and a respected local citizen.[121] On some occasions the penalty delivered by the tribunal was death by firing-squad.[122] Raúl Gómez Treto, senior legal advisor to the Cuban Ministry of Justice, has argued that the death penalty was justified in order to prevent citizens themselves from taking justice into their own hands, as had happened twenty years earlier in the anti-Machado rebellion.[123] Biographers note that in January 1959 the Cuban public was in a «lynching mood»,[124] and point to a survey at the time showing 93% public approval for the tribunal process.[10] Moreover, a 22 January 1959, Universal Newsreel broadcast in the United States and narrated by Ed Herlihy featured Fidel Castro asking an estimated one million Cubans whether they approved of the executions, and being met with a roaring «¡Sí!» (yes).[125] With between 1,000[126] and 20,000 Cubans estimated to have been killed at the hands of Batista’s collaborators,[127][128][129][130] and many of the accused war criminals sentenced to death accused of torture and physical atrocities,[10] the newly empowered government carried out executions, punctuated by cries from the crowds of «¡al paredón!» ([to the] wall!),[116] which biographer Jorge Castañeda describes as «without respect for due process».[131]
I have yet to find a single credible source pointing to a case where Che executed «an innocent». Those persons executed by Guevara or on his orders were condemned for the usual crimes punishable by death at times of war or in its aftermath: desertion, treason or crimes such as rape, torture or murder. I should add that my research spanned five years, and included anti-Castro Cubans among the Cuban-American exile community in Miami and elsewhere.
—Jon Lee Anderson, author of Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life, PBS forum[132]
Although accounts vary, it is estimated that several hundred people were executed nationwide during this time, with Guevara’s jurisdictional death total at La Cabaña ranging from 55 to 105.[133] Conflicting views exist of Guevara’s attitude towards the executions at La Cabaña. Some exiled opposition biographers report that he relished the rituals of the firing squad, and organized them with gusto, while others relate that Guevara pardoned as many prisoners as he could.[131] All sides acknowledge that Guevara had become a «hardened» man who had no qualms about the death penalty or about summary and collective trials. If the only way to «defend the revolution was to execute its enemies, he would not be swayed by humanitarian or political arguments».[131] In a 5 February 1959 letter to Luis Paredes López in Buenos Aires, Guevara states unequivocally: «The executions by firing squads are not only a necessity for the people of Cuba, but also an imposition of the people.»[134]
Along with ensuring «revolutionary justice», the other key early platform of Guevara was establishing agrarian land reform. Almost immediately after the success of the revolution, on 27 January 1959, Guevara made one of his most significant speeches where he talked about «the social ideas of the rebel army». During this speech he declared that the main concern of the new Cuban government was «the social justice that land redistribution brings about».[135] A few months later, 17 May 1959, the agrarian reform law, crafted by Guevara, went into effect, limiting the size of all farms to 1,000 acres (400 ha). Any holdings over these limits were expropriated by the government and either redistributed to peasants in 67-acre (270,000 m2) parcels or held as state-run communes.[136] The law also stipulated that foreigners could not own Cuban sugar-plantations.[137]
On 2 June 1959, he married Aleida March, a Cuban-born member of 26 July movement with whom he had been living since late 1958. Guevara returned to the seaside village of Tarara in June for his honeymoon with Aleida.[138] A civil ceremony was held at La Cabaña military fortress.[139] In total, Guevara would have five children from his two marriages.[140]
Early political office
Guevara in 1960, walking through the streets of Havana with his second wife Aleida March (right)
On 12 June 1959, Castro sent Guevara out on a three-month tour of mostly Bandung Pact countries (Morocco, Sudan, Egypt, Syria, Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, Indonesia, Japan, Yugoslavia, and Greece) and the cities of Singapore and Hong Kong.[141] Sending Guevara away from Havana allowed Castro to appear to distance himself from Guevara and his Marxist sympathies, which troubled both the United States and some of the members of Castro’s 26 July Movement.[142] While in Jakarta, Guevara visited Indonesian president Sukarno to discuss the recent revolution of 1945–1949 in Indonesia and to establish trade relations between their two countries. The two men quickly bonded, as Sukarno was attracted to Guevara’s energy and his relaxed informal approach; moreover they shared revolutionary leftist aspirations against Western imperialism.[143] Guevara next spent 12 days in Japan (15–27 July), participating in negotiations aimed at expanding Cuba’s trade relations with that country. During the visit he refused to visit and lay a wreath at Japan’s Tomb of the Unknown Soldier commemorating soldiers lost during World War II, remarking that the Japanese «imperialists» had «killed millions of Asians».[144] Instead, Guevara stated that he would visit Hiroshima, where the American military had detonated an atomic bomb 14 years earlier.[144] Despite his denunciation of Imperial Japan, Guevara considered President Truman a «macabre clown» for the bombings,[145] and after visiting Hiroshima and its Peace Memorial Museum he sent back a postcard to Cuba stating, «In order to fight better for peace, one must look at Hiroshima.»[146]
Upon Guevara’s return to Cuba in September 1959, it became evident that Castro now had more political power. The government had begun land seizures in accordance with the agrarian reform law, but was hedging on compensation offers to landowners, instead offering low-interest «bonds», a step which put the United States on alert. At this point the affected wealthy cattlemen of Camagüey mounted a campaign against the land redistributions and enlisted the newly disaffected rebel leader Huber Matos, who along with the anti-communist wing of the 26 July Movement, joined them in denouncing «communist encroachment».[147] During this time Dominican dictator Rafael Trujillo was offering assistance to the «Anti-Communist Legion of the Caribbean» which was training in the Dominican Republic. This multi-national force, composed mostly of Spaniards and Cubans, but also of Croatians, Germans, Greeks, and right-wing mercenaries, was plotting to topple Castro’s new regime.[147]
At this stage, Guevara acquired the additional position of Minister of Finance, as well as President of the National Bank.[148] These appointments, combined with his existing position as Minister of Industries, placed Guevara at the zenith of his power, as the «virtual czar» of the Cuban economy.[149] As a consequence of his position at the head of the central bank, it became Guevara’s duty to sign the Cuban currency, which per custom bore his signature. Instead of using his full name, he signed the bills solely «Che«.[150] It was through this symbolic act, which horrified many in the Cuban financial sector, that Guevara signaled his distaste for money and the class distinctions it brought about.[150] Guevara’s long time friend Ricardo Rojo later remarked that «the day he signed Che on the bills, (he) literally knocked the props from under the widespread belief that money was sacred.»[151]
International threats were heightened when, on 4 March 1960, two massive explosions ripped through the French freighter La Coubre, which was carrying Belgian munitions from the port of Antwerp, and was docked in Havana Harbor. The blasts killed at least 76 people and injured several hundred, with Guevara personally providing first aid to some of the victims. Fidel Castro immediately accused the CIA of «an act of terrorism» and held a state funeral the following day for the victims of the blast.[152] At the memorial service Alberto Korda took the famous photograph of Guevara, now known as Guerrillero Heroico.[153]
Perceived threats prompted Castro to eliminate more «counter-revolutionaries» and to utilize Guevara to drastically increase the speed of land reform. To implement this plan, a new government agency, the National Institute of Agrarian Reform (INRA), was established by the Cuban government to administer the new agrarian reform law. INRA quickly became the most important governing body in the nation, with Guevara serving as its head in his capacity as minister of industries.[137][need quotation to verify] Under Guevara’s command, INRA established its own 100,000-person militia, used first to help the government seize control of the expropriated land and supervise its distribution, and later to set up cooperative farms. The land confiscated included 480,000 acres (190,000 ha) owned by United States corporations.[137] Months later, in retaliation, U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower sharply reduced United States imports of Cuban sugar (Cuba’s main cash crop), which led Guevara on 10 July 1960 to address over 100,000 workers in front of the Presidential Palace at a rally to denounce the «economic aggression» of the United States.[149] Time Magazine reporters who met with Guevara around this time described him as «guid(ing) Cuba with icy calculation, vast competence, high intelligence, and a perceptive sense of humor.»[9]
Guevara was like a father to me … he educated me. He taught me to think. He taught me the most beautiful thing which is to be human.
—Urbano (a.k.a. Leonardo Tamayo),
fought with Guevara in Cuba and Bolivia[154]
Along with land reform, Guevara stressed the need for national improvement in literacy. Before 1959 the official literacy rate for Cuba was between 60 and 76%, with educational access in rural areas and a lack of instructors the main determining factors.[155] As a result, the Cuban government at Guevara’s behest dubbed 1961 the «year of education» and mobilized over 100,000 volunteers into «literacy brigades», who were then sent out into the countryside to construct schools, train new educators, and teach the predominantly illiterate guajiros (peasants) to read and write.[88][155] Unlike many of Guevara’s later economic initiatives, this campaign was «a remarkable success». By the completion of the Cuban literacy campaign, 707,212 adults had been taught to read and write, raising the national literacy rate to 96%.[155]
Accompanying literacy, Guevara was also concerned with establishing universal access to higher education. To accomplish this the new regime introduced affirmative action to the universities. While announcing this new commitment, Guevara told the gathered faculty and students at the University of Las Villas that the days when education was «a privilege of the white middle class» had ended. «The University» he said, «must paint itself black, mulatto, worker, and peasant.» If it did not, he warned, the people were going to break down its doors «and paint the University the colors they like.»[156]
Economic reforms and the «New Man»
In September 1960, when Guevara was asked about Cuba’s ideology at the First Latin American Congress, he replied, «If I were asked whether our revolution is Communist, I would define it as Marxist. Our revolution has discovered by its methods the paths that Marx pointed out.»[157] Consequently, when enacting and advocating Cuban policy, Guevara cited the political philosopher Karl Marx as his ideological inspiration. In defending his political stance, Guevara confidently remarked, «There are truths so evident, so much a part of people’s knowledge, that it is now useless to discuss them. One ought to be Marxist with the same naturalness with which one is ‘Newtonian’ in physics, or ‘Pasteurian’ in biology.»[158] According to Guevara, the «practical revolutionaries» of the Cuban Revolution had the goal of «simply fulfill(ing) laws foreseen by Marx, the scientist.»[158] Using Marx’s predictions and system of dialectical materialism, Guevara professed that «The laws of Marxism are present in the events of the Cuban Revolution, independently of what its leaders profess or fully know of those laws from a theoretical point of view.»[158]
The merit of Marx is that he suddenly produces a qualitative change in the history of social thought. He interprets history, understands its dynamic, predicts the future, but in addition to predicting it (which would satisfy his scientific obligation), he expresses a revolutionary concept: the world must not only be interpreted, it must be transformed. Man ceases to be the slave and tool of his environment and converts himself into the architect of his own destiny.
— Che Guevara, Notes for the Study of the Ideology of the Cuban, October 1960 [158]
Man truly achieves his full human condition when he produces without being compelled by the physical necessity of selling himself as a commodity.
— Che Guevara, Man and Socialism in Cuba[159]
Guevara meeting with French existentialist philosophers Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir at his office in Havana, March 1960. Sartre later wrote that Che was «the most complete human being of our time». In addition to Spanish, Guevara was fluent in French.[160]
In an effort to eliminate social inequalities, Guevara and Cuba’s new leadership had moved to swiftly transform the political and economic base of the country through nationalizing factories, banks, and businesses, while attempting to ensure affordable housing, healthcare, and employment for all Cubans.[161] In order for a genuine transformation of consciousness to take root, it was believed that such structural changes had to be accompanied by a conversion in people’s social relations and values. Believing that the attitudes in Cuba towards race, women, individualism, and manual labor were the product of the island’s outdated past, all individuals were urged to view each other as equals and take on the values of what Guevara termed «el Hombre Nuevo» (the New Man).[161] Guevara hoped his «new man» to be ultimately «selfless and cooperative, obedient and hard working, gender-blind, incorruptible, non-materialistic, and anti-imperialist».[161] To accomplish this, Guevara emphasized the tenets of Marxism–Leninism, and wanted to use the state to emphasize qualities such as egalitarianism and self-sacrifice, at the same time as «unity, equality, and freedom» became the new maxims.[161] Guevara’s first desired economic goal of the new man, which coincided with his aversion for wealth condensation and economic inequality, was to see a nationwide elimination of material incentives in favor of moral ones. He negatively viewed capitalism as a «contest among wolves» where «one can only win at the cost of others» and thus desired to see the creation of a «new man and woman».[162] Guevara continually stressed that a socialist economy in itself is not «worth the effort, sacrifice, and risks of war and destruction» if it ends up encouraging «greed and individual ambition at the expense of collective spirit».[163] A primary goal of Guevara’s thus became to reform «individual consciousness» and values to produce better workers and citizens.[163] In his view, Cuba’s «new man» would be able to overcome the «egotism» and «selfishness» that he loathed and discerned was uniquely characteristic of individuals in capitalist societies.[163] To promote this concept of a «new man», the government also created a series of party-dominated institutions and mechanisms on all levels of society, which included organizations such as labor groups, youth leagues, women’s groups, community centers, and houses of culture to promote state-sponsored art, music, and literature. In congruence with this, all educational, mass media, and artistic community based facilities were nationalized and utilized to instill the government’s official socialist ideology.[161] In describing this new method of «development», Guevara stated:
There is a great difference between free-enterprise development and revolutionary development. In one of them, wealth is concentrated in the hands of a fortunate few, the friends of the government, the best wheeler-dealers. In the other, wealth is the people’s patrimony.[164]
A further integral part of fostering a sense of «unity between the individual and the mass», Guevara believed, was volunteer work and will. To display this, Guevara «led by example», working «endlessly at his ministry job, in construction, and even cutting sugar cane» on his day off.[165] He was known for working 36 hours at a stretch, calling meetings after midnight, and eating on the run.[163] Such behavior was emblematic of Guevara’s new program of moral incentives, where each worker was now required to meet a quota and produce a certain quantity of goods. As a replacement for the pay increases abolished by Guevara, workers who exceeded their quota now only received a certificate of commendation, while workers who failed to meet their quotas were given a pay cut.[163] Guevara unapologetically defended his personal philosophy towards motivation and work, stating:
This is not a matter of how many pounds of meat one might be able to eat, or how many times a year someone can go to the beach, or how many ornaments from abroad one might be able to buy with his current salary. What really matters is that the individual feels more complete, with much more internal richness and much more responsibility.[166]
In the face of a loss of commercial connections with Western states, Guevara tried to replace them with closer commercial relationships with Eastern Bloc states, visiting a number of Marxist states and signing trade agreements with them. At the end of 1960 he visited Czechoslovakia, the Soviet Union, North Korea, Hungary, and East Germany and signed, for instance, a trade agreement in East Berlin on 17 December 1960.[167] Such agreements helped Cuba’s economy to a certain degree but also had the disadvantage of a growing economic dependency on the Eastern Bloc. It was also in East Germany where Guevara met Tamara Bunke (later known as «Tania»), who was assigned as his interpreter, and who joined him years later, and was killed with him in Bolivia.
According to Douglas Kellner, his programs were unsuccessful,[168] and accompanied a rapid drop in productivity and a rapid rise in absenteeism.[169] In a meeting with French economist René Dumont, Guevara blamed the inadequacy of the agrarian reform law enacted by the Cuban government in 1959, which turned large plantations into farm cooperatives or split up land amongst peasants.[170] In Guevara’s opinion, this situation continued to promote a «heightened sense of individual ownership» in which workers could not see the positive social benefits of their labor, leading them to instead seek individual material gain as before.[171] Decades later, Che’s former deputy Ernesto Betancourt, subsequently the director of the US government-funded Radio Martí and an early ally turned Castro-critic, accused Guevara of being «ignorant of the most elementary economic principles.»[172]
Bay of Pigs Invasion and Missile Crisis
On 17 April 1961, 1,400 U.S.-trained Cuban exiles invaded Cuba during the Bay of Pigs Invasion. Guevara did not play a key role in the fighting, as one day before the invasion a warship carrying Marines faked an invasion off the West Coast of Pinar del Río and drew forces commanded by Guevara to that region. However, historians give him a share of credit for the victory as he was director of instruction for Cuba’s armed forces at the time.[11] Author Tad Szulc in his explanation of the Cuban victory, assigns Guevara partial credit, stating: «The revolutionaries won because Che Guevara, as the head of the Instruction Department of the Revolutionary Armed Forces in charge of the militia training program, had done so well in preparing 200,000 men and women for war.»[11] It was also during this deployment that he suffered a bullet grazing to the cheek when his pistol fell out of its holster and accidentally discharged.[173]
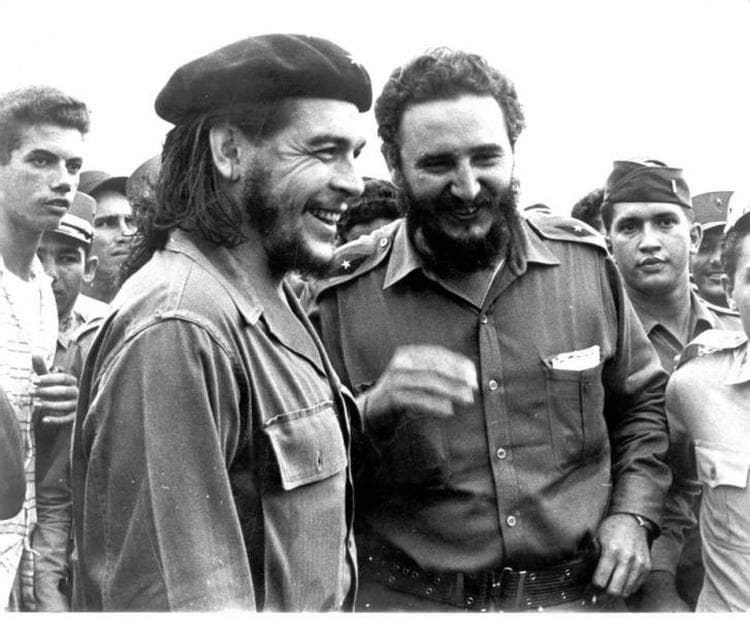
Guevara (left) and Fidel Castro, photographed by Alberto Korda in 1961
In August 1961, during an economic conference of the Organization of American States in Punta del Este, Uruguay, Che Guevara sent a note of «gratitude» to United States President John F. Kennedy through Richard N. Goodwin, Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for Inter-American Affairs. It read «Thanks for Playa Girón (Bay of Pigs). Before the invasion, the revolution was shaky. Now it’s stronger than ever.»[174] In response to United States Treasury Secretary Douglas Dillon presenting the Alliance for Progress for ratification by the meeting, Guevara antagonistically attacked the United States’ claim of being a «democracy», stating that such a system was not compatible with «financial oligarchy, discrimination against blacks, and outrages by the Ku Klux Klan».[175] Guevara continued, speaking out against the «persecution» that in his view «drove scientists like Oppenheimer from their posts, deprived the world for years of the marvelous voice of Paul Robeson, and sent the Rosenbergs to their deaths against the protests of a shocked world.»[175] Guevara ended his remarks by insinuating that the United States was not interested in real reforms, sardonically quipping that «U.S. experts never talk about agrarian reform; they prefer a safe subject, like a better water supply. In short, they seem to prepare the revolution of the toilets.»[176] Nevertheless, Goodwin stated in his memo to President Kennedy following the meeting that Guevara viewed him as someone of the «newer generation»[177] and that Guevara, whom Goodwin alleged sent a message to him the day after the meeting through one of the meeting’s Argentine participants whom he described as «Darretta,»[177] also viewed the conversation which the two had as «quite profitable.»[177]
Guevara, who was practically the architect of the Cuban–Soviet relationship,[178] played a key role in bringing to Cuba the Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles that precipitated the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962 and brought the world to the brink of nuclear war.[179] After the Soviets proposed planting nuclear missiles in Cuba it was Che Guevara himself who traveled to the Soviet Union on August 30, 1962 to sign off on the final agreement.[180] Guevara argued with Khruschev that the missile deal should be made public but Khruschev insisted on secrecy, and swore the Soviet Union’s support if the Americans discovered the missiles. By the time Guevara arrived in Cuba the United States had already discovered the Soviet troops in Cuba via U-2 spy planes.[181]
A few weeks after the crisis, during an interview with the British communist newspaper the Daily Worker, Guevara was still fuming over the perceived Soviet betrayal and told correspondent Sam Russell that, if the missiles had been under Cuban control, they would have fired them off.[182] While expounding on the incident later, Guevara reiterated that the cause of socialist liberation against global «imperialist aggression» would ultimately have been worth the possibility of «millions of atomic war victims».[183] The missile crisis further convinced Guevara that the world’s two superpowers (the United States and the Soviet Union) used Cuba as a pawn in their own global strategies. Afterward, he denounced the Soviets almost as frequently as he denounced the Americans.[184]
Great Debate
The era in Cuban history retroactively named the «Great Debate» by historians was defined by public debate about the future of Cuban economic policy that took place from 1962 to 1965. The debate began after Cuba fell into an economic crisis in 1962 after years of internal economic complications, United States sanctions, and the flight of professionals from Cuba. In 1962 Fidel Castro invited Marxist economists around the world to debate two main propositions. One proposition proposed by Che Guevara was that Cuba could bypass any capitalist then «socialist» transition period and immediately become an industrialized «communist» society if «subjective conditions» like public consciousness and vanguard action are perfected. The other proposition held by the Popular Socialist Party was that Cuba required a transitionary period as a mixed economy in which Cuba’s sugar economy was maximized for profit before a «communist» society could be established.[185][186][187]
Guevara elaborated in this period that moral incentives should exist as the main motivator to increase workers’ production. All profits created by enterprises were to be given to the state budget, and the state budget would cover loses. Institutions that developed socialist consciousness were regarded as the most important element in maintaining a path to socialism rather than materially incentivized increases in production. Implementation of the profit-motive was regarded as a path towards capitalism and was one of the flaws of the Eastern bloc economies.[188] The economy would also rely on mass mobilizations and centralized planning as a method for developing the economy.[189] The main ideal that compromised the consciousness that would develop socialism was the praise of the «new man», a citizen that was only motivated by human solidarity and self-sacrifice.[190]
In 1966 the Cuban economy was reorganized on moral lines. Cuban propaganda stressed voluntarism and ideological motivations to increase productions. Material incentives were not given to workers who were more productive than others.[191] Cuban intellectuals were expected to participate actively in creating a positive national ethos and ignore any desire to create «art for art’s sake».[192] In 1968 all non-agricultural private businesses were nationalized, central planning was done more on an ad-hoc basis and the entire Cuban economy was directed at producing a 10 million ton sugar harvest. These developments were generally inspired by the resolutions brought about by the Great Debate years earlier.[193] The focus on sugar would eventually render all other facets of the Cuban economy underdeveloped and would be the ultimate legacy of the offensive.[191]
International diplomacy
Countries Che Guevara visited (red) and those in which he participated in armed revolution (green)
United Nations delegation
In December 1964, Che Guevara had emerged as a «revolutionary statesman of world stature» and thus traveled to New York City as head of the Cuban delegation to speak at the United Nations.[151] On 11 December 1964, during Guevara’s hour-long, impassioned address at the UN, he criticized the United Nations’ inability to confront the «brutal policy of apartheid» in South Africa, asking «Can the United Nations do nothing to stop this?».[194] Guevara then denounced the United States policy towards their black population, stating:
Those who kill their own children and discriminate daily against them because of the color of their skin; those who let the murderers of blacks remain free, protecting them, and furthermore punishing the black population because they demand their legitimate rights as free men—how can those who do this consider themselves guardians of freedom?[194]
An indignant Guevara ended his speech by reciting the Second Declaration of Havana, decreeing Latin America a «family of 200 million brothers who suffer the same miseries».[194] This «epic», Guevara declared, would be written by the «hungry Indian masses, peasants without land, exploited workers, and progressive masses». To Guevara the conflict was a struggle of masses and ideas, which would be carried forth by those «mistreated and scorned by imperialism» who were previously considered «a weak and submissive flock». With this «flock», Guevara now asserted, «Yankee monopoly capitalism» now terrifyingly saw their «gravediggers».[194] It would be during this «hour of vindication», Guevara pronounced, that the «anonymous mass» would begin to write its own history «with its own blood» and reclaim those «rights that were laughed at by one and all for 500 years». Guevara closed his remarks to the General Assembly by hypothesizing that this «wave of anger» would «sweep the lands of Latin America» and that the labor masses who «turn the wheel of history» were now, for the first time, «awakening from the long, brutalizing sleep to which they had been subjected».[194]
Guevara later learned there had been two failed attempts on his life by Cuban exiles during his stop at the UN complex.[195] The first from Molly Gonzales, who tried to break through barricades upon his arrival with a seven-inch hunting knife, and later during his address by Guillermo Novo, who fired a timer-initiated bazooka from a boat in the East River at the United Nations Headquarters, but missed and was off target. Afterwards Guevara commented on both incidents, stating that «it is better to be killed by a woman with a knife than by a man with a gun», while adding with a languid wave of his cigar that the explosion had «given the whole thing more flavor».[195]
Walking through Red Square in Moscow, November 1964
While in New York, Guevara appeared on the CBS Sunday news program Face the Nation,[196] and met with a wide range of people, from United States Senator Eugene McCarthy[197] to associates of Malcolm X. The latter expressed his admiration, declaring Guevara «one of the most revolutionary men in this country right now» while reading a statement from him to a crowd at the Audubon Ballroom.[198]
World travel
On 17 December, Guevara left New York for Paris, France, and from there embarked on a three-month world tour that included visits to the People’s Republic of China, North Korea, the United Arab Republic, Algeria, Ghana, Guinea, Mali, Dahomey, Congo-Brazzaville, and Tanzania, with stops in Ireland and Prague. While in Ireland, Guevara embraced his own Irish heritage, celebrating Saint Patrick’s Day in Limerick.[199] He wrote to his father on this visit, humorously stating «I am in this green Ireland of your ancestors. When they found out, the television [station] came to ask me about the Lynch genealogy, but in case they were horse thieves or something like that, I didn’t say much.»[200]
During Guevara’s time in Algeria he was interviewed by Spanish poet Juan Goytisolo inside the Cuban embassy. During the interview Guevara noticed a book by openly gay Cuban writer Virgilio Piñera that was sitting on the table next to him. When he noticed it he threw the book against the wall and yelled «how dare you have in our embassy a book by this foul faggot?».[201][202][203] This moment has been marked as a turn in Juan Goytisolo’s personal identity as it influenced him to slowly come out of the closet as gay and begin to sympathize with the LGBT citizens of Cuba.[204] This moment has also been marked for its significance in the Cuban government’s slow and ultimately final ousting of Virgilio Piñera from official literary discourse in Cuba. Piñera had originally been regarded as an important dramatist of the Cuban Revolution but had later become slowly condemned and finally arrested.[203]
During this voyage, he wrote a letter to Carlos Quijano, editor of a Uruguayan weekly, which was later retitled Socialism and Man in Cuba.[162] Outlined in the treatise was Guevara’s summons for the creation of a new consciousness, a new status of work, and a new role of the individual. He also laid out the reasoning behind his anti-capitalist sentiments, stating:
The laws of capitalism, blind and invisible to the majority, act upon the individual without his thinking about it. He sees only the vastness of a seemingly infinite horizon before him. That is how it is painted by capitalist propagandists, who purport to draw a lesson from the example of Rockefeller—whether or not it is true—about the possibilities of success. The amount of poverty and suffering required for the emergence of a Rockefeller, and the amount of depravity that the accumulation of a fortune of such magnitude entails, are left out of the picture, and it is not always possible to make the people in general see this.[162]
Guevara ended the essay by declaring that «the true revolutionary is guided by a great feeling of love» and beckoning on all revolutionaries to «strive every day so that this love of living humanity will be transformed into acts that serve as examples», thus becoming «a moving force».[162] The genesis for Guevara’s assertions relied on the fact that he believed the example of the Cuban Revolution was «something spiritual that would transcend all borders».[38]
Visit to Algeria and political turn
In Algiers, Algeria, on 24 February 1965, Guevara made what turned out to be his last public appearance on the international stage when he delivered a speech at an economic seminar on Afro-Asian solidarity.[205][206] He specified the moral duty of the socialist countries, accusing them of tacit complicity with the exploiting Western countries. He proceeded to outline a number of measures which he said the communist-bloc countries must implement in order to accomplish the defeat of imperialism.[207] Having criticized the Soviet Union (the primary financial backer of Cuba) in such a public manner, he returned to Cuba on 14 March to a solemn reception by Fidel and Raúl Castro, Osvaldo Dorticós, and Carlos Rafael Rodríguez at the Havana airport.
As revealed in his last public speech in Algiers, Guevara had come to view the Northern Hemisphere, led by the U.S. in the West and the Soviet Union in the East, as the exploiter of the Southern Hemisphere. He strongly supported communist North Vietnam in the Vietnam War, and urged the peoples of other developing countries to take up arms and create «many Vietnams».[208] Che’s denunciations of the Soviets made him popular among intellectuals and artists of the Western European left who had lost faith in the Soviet Union, while his condemnation of imperialism and call to revolution inspired young radical students in the United States, who were impatient for societal change.[209]
In Guevara’s private writings from this time (since released), he displays his growing criticism of the Soviet political economy, believing that the Soviets had «forgotten Marx».[210] This led Guevara to denounce a range of Soviet practices including what he saw as their attempt to «air-brush the inherent violence of class struggle integral to the transition from capitalism to socialism», their «dangerous» policy of peaceful co-existence with the United States, their failure to push for a «change in consciousness» towards the idea of work, and their attempt to «liberalize» the socialist economy. Guevara wanted the complete elimination of money, interest, commodity production, the market economy, and «mercantile relationships»: all conditions that the Soviets argued would only disappear when world communism was achieved.[210] Disagreeing with this incrementalist approach, Guevara criticized the Soviet Manual of Political Economy, correctly predicting that if the Soviet Union did not abolish the law of value (as Guevara desired), it would eventually return to capitalism.[210]
Two weeks after his Algiers speech and his return to Cuba, Guevara dropped out of public life and then vanished altogether.[211] His whereabouts were a great mystery in Cuba, as he was generally regarded as second in power to Castro himself. His disappearance was variously attributed to the failure of the Cuban industrialization scheme he had advocated while minister of industries, to pressure exerted on Castro by Soviet officials who disapproved of Guevara’s pro-Chinese communist stance on the Sino-Soviet split, and to serious differences between Guevara and the pragmatic Castro regarding Cuba’s economic development and ideological line.[212] Pressed by international speculation regarding Guevara’s fate, Castro stated on 16 June 1965, that the people would be informed when Guevara himself wished to let them know. Still, rumors spread both inside and outside Cuba concerning the missing Guevara’s whereabouts.
There are various rumors from retired Cuban officials who were around the Castro brothers that the Castro brothers and Guevara had a staunch disagreement after Guevara’s Algiers speech. Intelligence files from the East German embassy in Cuba detail various heated exchanges between Fidel Castro and Che Guevara after Guevara’s return from Africa. Whether Castro disagreed with Guevara’s criticisms of the Soviet Union or just found them unproductive to express on the world stage remains unclear.[213]
On 3 October 1965, Castro publicly revealed an undated letter purportedly written to him by Guevara around seven months earlier which was later titled Che Guevara’s «farewell letter». In the letter, Guevara reaffirmed his enduring solidarity with the Cuban Revolution but declared his intention to leave Cuba to fight for the revolutionary cause abroad. Additionally, he resigned from all his positions in the Cuban government and communist party, and renounced his honorary Cuban citizenship.[214]
Congo Crisis
Military involvement
37-year-old Guevara, holding a Congolese baby and standing with a fellow Afro-Cuban soldier in the Congo Crisis, 1965
I tried to make them understand that the real issue was not the liberation of any given state, but a common war against the common master, who was one and the same in Mozambique and in Malawi, in Rhodesia and in South Africa, in the Congo and in Angola, but not one of them agreed.
—Che Guevara, in February 1965, after meeting with various African liberation movement leaders in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania[215]
In early 1965, Guevara went to Africa to offer his knowledge and experience as a guerrilla to the ongoing conflict in the Congo. According to Algerian President Ahmed Ben Bella, Guevara thought that Africa was imperialism’s weak link and so had enormous revolutionary potential.[216] Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had fraternal relations with Che since his 1959 visit, saw Guevara’s plan to fight in Congo as «unwise» and warned that he would become a «Tarzan» figure, doomed to failure.[217] Despite the warning, Guevara traveled to Congo using the alias Ramón Benítez.[218] He led the Cuban operation in support of the Marxist Simba movement, which had emerged from the ongoing Congo conflict. Guevara, his second-in-command Víctor Dreke, and 12 other Cuban expeditionaries arrived in Congo on 24 April 1965, and a contingent of approximately 100 Afro-Cubans joined them soon afterward.[219][220] For a time, they collaborated with guerrilla leader Laurent-Désiré Kabila, who had helped supporters of the overthrown prime minister Patrice Lumumba to lead an unsuccessful revolt months earlier. As an admirer of the late Lumumba, Guevara declared that his «murder should be a lesson for all of us».[221] Guevara, with limited knowledge of Swahili and the local languages, was assigned a teenage interpreter, Freddy Ilanga. Over the course of seven months, Ilanga grew to «admire the hard-working Guevara», who «showed the same respect to black people as he did to whites».[222] Guevara soon became disillusioned with the poor discipline of Kabila’s troops and later dismissed him, stating «nothing leads me to believe he is the man of the hour».[223]
As an additional obstacle, white mercenary troops of the Congo National Army, led by Mike Hoare and supported by anti-Castro Cuban pilots and the CIA, thwarted Guevara’s movements from his base camp in the mountains near the village of Fizi on Lake Tanganyika in southeast Congo. They were able to monitor his communications and so pre-empted his attacks and interdicted his supply lines. Although Guevara tried to conceal his presence in Congo, the United States government knew his location and activities. The National Security Agency was intercepting all of his incoming and outgoing transmissions via equipment aboard the USNS Private Jose F. Valdez, a floating listening post that continuously cruised the Indian Ocean off Dar es Salaam for that purpose.[224]
Listening to a Zenith Trans-Oceanic shortwave radio receiver are (seated from the left) Rogelio Oliva, José María Martínez Tamayo (known as «Mbili» in the Congo and «Ricardo» in Bolivia), and Guevara. Standing behind them is Roberto Sánchez («Lawton» in Cuba and «Changa» in the Congo), 1965.
Guevara’s aim was to export the revolution by instructing local anti-Mobutu Simba fighters in Marxist ideology and foco theory strategies of guerrilla warfare. In his Congo Diary book, he cites a combination of incompetence, intransigence, and infighting among the Congolese rebels as key reasons for the revolt’s failure.[225] Later that year, on 20 November 1965, suffering from dysentery and acute asthma, and disheartened after seven months of defeats and inactivity, Guevara left Congo with the six Cuban survivors of his 12-man column. Guevara stated that he had planned to send the wounded back to Cuba and fight in the Congo alone until his death, as a revolutionary example. But after being urged by his comrades, and two Cuban emissaries personally sent by Castro, at the last moment he reluctantly agreed to leave Africa. During that day and night, Guevara’s forces quietly took down their base camp, burned their huts, and destroyed or threw weapons into Lake Tanganyika that they could not take with them, before crossing the border by boat into Tanzania at night and traveling by land to Dar es Salaam. In speaking about his experience in Congo months later, Guevara concluded that he left rather than fight to the death because: «The human element failed. There is no will to fight. The [rebel] leaders are corrupt. In a word … there was nothing to do.»[226] Guevara also declared that «we can not liberate, all by ourselves, a country that does not want to fight.»[227] A few weeks later, he wrote the preface to the diary he kept during the Congo venture, that began: «This is the story of a failure.»[228]
Flight from the Congo
Guevara was reluctant to return to Cuba, because Castro had already made public Guevara’s «farewell letter»—a letter intended to only be revealed in the case of his death—wherein he severed all ties in order to devote himself to revolution throughout the world.[229] As a result, Guevara spent the next six months living clandestinely at the Cuban embassy in Dar es Salaam and later at a Cuban safehouse in Prague.[230] While in Europe, Guevara made a secret visit to former Argentine president Juan Perón who lived in exile in Francoist Spain where he confided in Perón about his new plan to formulate a communist revolution to bring all of Latin America under socialist control. Perón warned Guevara that his plans for implementing a communist revolution throughout Latin America, starting with Bolivia, would be suicidal and futile, but Guevara’s mind was already made up. Later, Perón remarked that Guevara was «an immature utopian… but one of us. I am happy for it to be so because he is giving the Yankees a real headache.»[231]
During this time abroad, Guevara compiled his memoirs of the Congo experience and wrote drafts of two more books, one on philosophy and the other on economics. As Guevara prepared for Bolivia, he secretly traveled back to Cuba on 21 July 1966 to visit Castro, as well as to see his wife and to write a last letter to his five children to be read upon his death, which ended with him instructing them:
Above all, always be capable of feeling deeply any injustice committed against anyone, anywhere in the world. This is the most beautiful quality in a revolutionary.[232]
Bolivian insurgency
Departure to Bolivia
Guevara’s 1966 passport featuring him in disguise with a false name.
In late 1966, Guevara’s location was still not public knowledge, although representatives of Mozambique’s independence movement, the FRELIMO, reported that they met with Guevara in Dar es Salaam regarding his offer to aid in their revolutionary project, an offer which they ultimately rejected.[233] In a speech at the 1967 International Workers’ Day rally in Havana, the acting minister of the armed forces, Major Juan Almeida Bosque, announced that Guevara was «serving the revolution somewhere in Latin America».[citation needed]. In his book Opération Condor published in 2020, French journalist Pablo Daniel Magee reconstitutes the first incursion of Che Guevara in Bolivia on 3 October 1966, based on top-secret documents kept in the UNESCO protected Archives of Terror, in Paraguay.
Before he departed for Bolivia, Guevara altered his appearance by shaving off his beard and much of his hair, also dying it grey so that he was unrecognizable as Che Guevara.[234] On 3 November 1966, Guevara secretly arrived in La Paz on a flight from Montevideo, under the false name Adolfo Mena González, posing as a middle-aged Uruguayan businessman working for the Organization of American States.[235]
Three days after his arrival in Bolivia, Guevara left La Paz for the rural south east region of the country to form his guerrilla army. Guevara’s first base camp was located in the montane dry forest in the remote Ñancahuazú region. Training at the camp in the Ñancahuazú valley proved to be hazardous, and little was accomplished in way of building a guerrilla army. The Argentine-born East German operative Tamara Bunke, better known by her nom de guerre «Tania», had been installed as Che’s primary agent in La Paz.[236][237]
Ñancahuazú Guerrilla
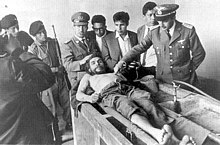
Guevara in rural Bolivia, shortly before his death (1967)
Guevara’s guerrilla force, numbering about 50 men[238] and operating as the ELN (Ejército de Liberación Nacional de Bolivia, «National Liberation Army of Bolivia»), was well equipped and scored a number of early successes against Bolivian army regulars in the difficult terrain of the mountainous Camiri region during the early months of 1967. As a result of Guevara’s units winning several skirmishes against Bolivian troops in the spring and summer of 1967, the Bolivian government began to overestimate the true size of the guerrilla force.[239]
Researchers hypothesize that Guevara’s plan for fomenting a revolution in Bolivia failed for an array of reasons:
- Guevara had expected assistance and cooperation from the local dissidents that he did not receive, nor did he receive support from Bolivia’s Communist Party under the leadership of Mario Monje, which was oriented toward Moscow rather than Havana. In Guevara’s own diary captured after his death, he wrote about the Communist Party of Bolivia, which he characterized as «distrustful, disloyal and stupid».[240]
- He had expected to deal only with the Bolivian military, who were poorly trained and equipped, and was unaware that the United States government had sent a team of the CIA’s Special Activities Division commandos and other operatives into Bolivia to aid the anti-insurrection effort. The Bolivian Army was also trained, advised, and supplied by U.S. Army Special Forces, including an elite battalion of U.S. Rangers trained in jungle warfare that set up camp in La Esperanza, a small settlement close to the location of Guevara’s guerrillas.[241]
- He had expected to remain in radio contact with Havana. The two shortwave radio transmitters provided to him by Cuba were faulty. Thus, the guerrillas were unable to communicate and be resupplied, leaving them isolated and stranded.
In addition, Guevara’s known preference for confrontation rather than compromise, which had previously surfaced during his guerrilla warfare campaign in Cuba, contributed to his inability to develop successful working relationships with local rebel leaders in Bolivia, just as it had in the Congo.[242] This tendency had existed in Cuba, but had been kept in check by the timely interventions and guidance of Fidel Castro.[243]
The result was that Guevara was unable to attract inhabitants of the local area to join his militia during the eleven months he attempted recruitment. Many of the inhabitants willingly informed the Bolivian authorities and military about the guerrillas and their movements in the area. Near the end of the Bolivian venture, Guevara wrote in his diary: «Talking to these peasants is like talking to statues. They do not give us any help. Worse still, many of them are turning into informants.»[244]
Félix Rodríguez, a Cuban exile turned CIA Special Activities Division operative, advised Bolivian troops during the hunt for Guevara in Bolivia.[245] In addition, the 2007 documentary My Enemy’s Enemy alleges that Nazi war criminal Klaus Barbie advised and possibly helped the CIA orchestrate Guevara’s eventual capture.[246]
Capture
On 7 October 1967, an informant apprised the Bolivian Special Forces of the location of Guevara’s guerrilla encampment in the Yuro ravine.[247] On the morning of 8 October, they encircled the area with two companies numbering 180 soldiers and advanced into the ravine triggering a battle where Guevara was wounded and taken prisoner while leading a detachment with Simeon Cuba Sarabia.[248] Che’s biographer Jon Lee Anderson reports Bolivian Sergeant Bernardino Huanca’s account: that as the Bolivian Rangers approached, a twice-wounded Guevara, his gun rendered useless, threw up his arms in surrender and shouted to the soldiers: «Do not shoot! I am Che Guevara and I am worth more to you alive than dead.»[249]
There was no person more feared by the company (CIA) than Che Guevara because he had the capacity and charisma necessary to direct the struggle against the political repression of the traditional hierarchies in power in the countries of Latin America.
—Philip Agee, CIA employee from 1957 to 1968.[250]
Guevara was tied up and taken to a dilapidated mud schoolhouse in the nearby village of La Higuera on the evening of 8 October. For the next half-day, Guevara refused to be interrogated by Bolivian officers and only spoke quietly to Bolivian soldiers. One of those Bolivian soldiers, a helicopter pilot named Jaime Nino de Guzman, describes Che as looking «dreadful». According to Guzman, Guevara was shot through the right calf, his hair was matted with dirt, his clothes were shredded, and his feet were covered in rough leather sheaths. Despite his haggard appearance, he recounts that «Che held his head high, looked everyone straight in the eyes and asked only for something to smoke.» De Guzman states that he «took pity» and gave him a small bag of tobacco for his pipe, and that Guevara then smiled and thanked him.[251] Later on the night of 8 October, Guevara—despite having his hands tied—kicked a Bolivian army officer, named Captain Espinosa, against a wall after the officer entered the schoolhouse and tried to snatch Guevara’s pipe from his mouth as a souvenir while he was still smoking it.[252] In another instance of defiance, Guevara spat in the face of Bolivian Rear Admiral Horacio Ugarteche, who attempted to question Guevara a few hours before his execution.[252]
The following morning on 9 October, Guevara asked to see the school teacher of the village, a 22-year-old woman named Julia Cortez. She later stated that she found Guevara to be an «agreeable looking man with a soft and ironic glance» and that during their conversation she found herself «unable to look him in the eye» because his «gaze was unbearable, piercing, and so tranquil».[252] During their short conversation, Guevara pointed out to Cortez the poor condition of the schoolhouse, stating that it was «anti-pedagogical» to expect campesino students to be educated there, while «government officials drive Mercedes cars»; Guevara said «that’s what we are fighting against».[252]
Execution
Later that morning on 9 October, Bolivian President René Barrientos ordered that Guevara be killed. The order was relayed to the unit holding Guevara by Félix Rodríguez reportedly despite the United States government’s desire that Guevara be taken to Panama for further interrogation.[253] The executioner who volunteered to kill Guevara was Mario Terán, a 27-year-old sergeant in the Bolivian army who while half-drunk requested to shoot Guevara because three of his friends from B Company, all with the same first name of «Mario», had been killed in a firefight several days earlier with Guevara’s band of guerrillas.[10] To make the bullet wounds appear consistent with the story that the Bolivian government planned to release to the public, Félix Rodríguez ordered Terán not to shoot Guevara in the head, but to aim carefully to make it appear that Guevara had been killed in action during a clash with the Bolivian army.[254] Gary Prado, the Bolivian captain in command of the army company that captured Guevara, said that the reasons Barrientos ordered the immediate execution of Guevara were so there could be no possibility for Guevara to escape from prison, and also so there could be no drama of a public trial where adverse publicity might happen.[255]
About 30 minutes before Guevara was killed, Félix Rodríguez attempted to question him about the whereabouts of other guerrilla fighters who were currently at large, but Guevara continued to remain silent. Rodríguez, assisted by a few Bolivian soldiers, helped Guevara to his feet and took him outside the hut to parade him before other Bolivian soldiers where he posed with Guevara for a photo opportunity where one soldier took a photograph of Rodríguez and other soldiers standing alongside Guevara. Afterwards, Rodríguez told Guevara that he was going to be executed. A little later, Guevara was asked by one of the Bolivian soldiers guarding him if he was thinking about his own immortality. «No» he replied, «I’m thinking about the immortality of the revolution».[256] A few minutes later, Sergeant Terán entered the hut to shoot him, whereupon Guevara reportedly stood up and spoke to Terán what were his last words: «I know you’ve come to kill me. Shoot, coward! You are only going to kill a man!» Terán hesitated, then pointed his self-loading M2 carbine[257] at Guevara and opened fire, hitting him in the arms and legs.[258] Then, as Guevara writhed on the ground, apparently biting one of his wrists to avoid crying out, Terán fired another burst, fatally wounding him in the chest. Guevara was pronounced dead at 1:10 pm local time according to Rodríguez.[258] In all, Guevara was shot nine times by Terán. This included five times in his legs, once in the right shoulder and arm, and once in the chest and throat.[252]
Months earlier, during his last public declaration to the Tricontinental Conference,[208] Guevara had written his own epitaph, stating: «Wherever death may surprise us, let it be welcome, provided that this our battle cry may have reached some receptive ear and another hand may be extended to wield our weapons.»[259]
Aftermath
The day after his execution on 10 October 1967, Guevara’s corpse was displayed to the news media in the laundry house of the Vallegrande hospital. (photo by Freddy Alborta)
Face Side angle Shoes
After his execution, Guevara’s body was lashed to the landing skids of a helicopter and flown to nearby Vallegrande, where photographs were taken of him lying on a concrete slab in the laundry room of the Nuestra Señora de Malta.[260] Several witnesses were called to confirm his identity, key amongst them the British journalist Richard Gott, the only witness to have met Guevara when he was alive. Put on display, as hundreds of local residents filed past the body, Guevara’s corpse was considered by many to represent a «Christ-like» visage, with some even surreptitiously clipping locks of his hair as divine relics.[261] Such comparisons were further extended when English art critic John Berger, two weeks later upon seeing the post-mortem photographs, observed that they resembled two famous paintings: Rembrandt’s The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp and Andrea Mantegna’s Lamentation over the Dead Christ.[262] There were also four correspondents present when Guevara’s body arrived in Vallegrande, including Björn Kumm of the Swedish Aftonbladet, who described the scene in an 11 November 1967, exclusive for The New Republic.[263]
A declassified memorandum dated 11 October 1967 to United States President Lyndon B. Johnson from his National Security Advisor Walt Rostow, called the decision to kill Guevara «stupid» but «understandable from a Bolivian standpoint».[264] After the execution, Rodríguez took several of Guevara’s personal items, including a watch which he continued to wear many years later, often showing them to reporters during the ensuing years.[265] Today, some of these belongings, including his flashlight, are on display at the CIA.[266] After a military doctor dismembered his hands, Bolivian army officers transferred Guevara’s body to an undisclosed location and refused to reveal whether his remains had been buried or cremated. The hands were sent to Buenos Aires for fingerprint identification. They were later sent to Cuba.[267]
Plaza de la Revolución, in Havana, Cuba. Aside the Ministry of the Interior building where Guevara once worked is a 5-story steel outline of his face. Under the image is Guevara’s motto, the Spanish phrase: «Hasta la Victoria Siempre» (English: Until Victory, always).
On 15 October in Havana, Fidel Castro publicly acknowledged that Guevara was dead and proclaimed three days of public mourning throughout Cuba.[268] On 18 October, Castro addressed a crowd of one million mourners in Havana’s Plaza de la Revolución and spoke about Guevara’s character as a revolutionary.[269] Fidel Castro closed his impassioned eulogy thus:
If we wish to express what we want the men of future generations to be, we must say: Let them be like Che! If we wish to say how we want our children to be educated, we must say without hesitation: We want them to be educated in Che’s spirit! If we want the model of a man, who does not belong to our times but to the future, I say from the depths of my heart that such a model, without a single stain on his conduct, without a single stain on his action, is Che![270]
Also removed when Guevara was captured were his 30,000-word, hand-written diary, a collection of his personal poetry, and a short story he had authored about a young communist guerrilla who learns to overcome his fears.[271] His diary documented events of the guerrilla campaign in Bolivia,[272] with the first entry on 7 November 1966, shortly after his arrival at the farm in Ñancahuazú, and the last dated 7 October 1967, the day before his capture. The diary tells how the guerrillas were forced to begin operations prematurely because of discovery by the Bolivian Army, explains Guevara’s decision to divide the column into two units that were subsequently unable to re-establish contact, and describes their overall unsuccessful venture. It also records the rift between Guevara and the Communist Party of Bolivia that resulted in Guevara having significantly fewer soldiers than originally expected, and shows that Guevara had a great deal of difficulty recruiting from the local populace, partly because the guerrilla group had learned Quechua, unaware that the local language was actually a Tupi–Guarani language.[273] As the campaign drew to an unexpected close, Guevara became increasingly ill. He endured ever-worsening bouts of asthma, and most of his last offensives were carried out in an attempt to obtain medicine.[274] The Bolivian diary was quickly and crudely translated by Ramparts magazine and circulated around the world.[275] There are at least four additional diaries in existence—those of Israel Reyes Zayas (Alias «Braulio»), Harry Villegas Tamayo («Pombo»), Eliseo Reyes Rodriguez («Rolando»)[236] and Dariel Alarcón Ramírez («Benigno»)[276]—each of which reveals additional aspects of the events.
French intellectual Régis Debray, who was captured in April 1967 while with Guevara in Bolivia, gave an interview from prison in August 1968, in which he enlarged on the circumstances of Guevara’s capture. Debray, who had lived with Guevara’s band of guerrillas for a short time, said that in his view they were «victims of the forest» and thus «eaten by the jungle».[277] Debray described a destitute situation where Guevara’s men suffered malnutrition, lack of water, absence of shoes, and only possessed six blankets for 22 men. Debray recounts that Guevara and the others had been suffering an «illness» which caused their hands and feet to swell into «mounds of flesh» to the point where you could not discern the fingers on their hands. Debray described Guevara as «optimistic about the future of Latin America» despite the futile situation, and remarked that Guevara was «resigned to die in the knowledge that his death would be a sort of renaissance», noting that Guevara perceived death «as a promise of rebirth» and «ritual of renewal».[277]
Legacy
Political left
A stylized graphic of Guevara’s face on a flag above the words «El Che Vive!» (Che Lives!)
Radical left wing activists responded to Guevara’s apparent indifference to rewards and glory, and concurred with Guevara’s sanctioning of violence as a necessity to instill socialist ideals.[278] Even in the United States, the government which Guevara so vigorously denounced, students began to emulate his style of dress, donning military fatigues, berets, and growing their hair and beards to show that they too were opponents of U.S. foreign policy.[279] For instance, the Black Panthers began to style themselves «Che-type» while adopting his trademark black beret, while Arab guerrillas began to name combat operations in his honor.[280] Addressing the wide-ranging flexibility of his legacy, Trisha Ziff, director of the 2008 documentary Chevolution, has remarked that «Che Guevara’s significance in modern times is less about the man and his specific history, and more about the ideals of creating a better society.»[281] In a similar vein, the Chilean writer Ariel Dorfman has suggested Guevara’s enduring appeal might be because «to those who will never follow in his footsteps, submerged as they are in a world of cynicism, self-interest and frantic consumption, nothing could be more vicariously gratifying than Che’s disdain for material comfort and everyday desires.»[282]
To a certain extent, the belief of Guevara’s of a metaphorical resurrection after death came true. After pictures of the dead Guevara began being circulated and the circumstances of his death were being debated, Che’s legend began to spread. Demonstrations in protest against his «assassination» occurred throughout the world, and articles, tributes, and poems were written about his life and death.[283] Rallies in support of Guevara were held from «Mexico to Santiago, Algiers to Angola, and Cairo to Calcutta».[284] The population of Budapest and Prague lit candles to honor Guevara’s passing; and the picture of a smiling Che appeared in London and Paris.[285] When a few months later riots broke out in Berlin, France, and Chicago, and the unrest spread to the American college campuses, young men and women wore Che Guevara T-shirts and carried his pictures during their protest marches. In the view of military historian Erik Durschmied: «In those heady months of 1968, Che Guevara was not dead. He was very much alive.»[286]
Retrieval of remains
In late 1995, the retired Bolivian General Mario Vargas revealed to Jon Lee Anderson, author of Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life, that Guevara’s corpse lay near a Vallegrande airstrip. The result was a multi-national search for the remains, which lasted more than a year. In July 1997 a team of Cuban geologists and Argentine forensic anthropologists discovered the remnants of seven bodies in two mass graves, including one man without hands (as Guevara would have been). Bolivian government officials with the Ministry of Interior later identified the body as Guevara when the excavated teeth «perfectly matched» a plaster mold of Che’s teeth made in Cuba prior to his Congolese expedition. The «clincher» then arrived when Argentine forensic anthropologist Alejandro Inchaurregui inspected the inside hidden pocket of a blue jacket dug up next to the handless cadaver and found a small bag of pipe tobacco. Nino de Guzman, the Bolivian helicopter pilot who had given Che a small bag of tobacco, later remarked that he «had serious doubts» at first and «thought the Cubans would just find any old bones and call it Che»; but «after hearing about the tobacco pouch, I have no doubts.»[251] On 17 October 1997, Guevara’s remains, with those of six of his fellow combatants, were laid to rest with military honors in a specially built mausoleum in the Cuban city of Santa Clara, where he had commanded over the decisive military victory of the Cuban Revolution.[287]
In July 2008, the Bolivian government of Evo Morales unveiled Guevara’s formerly-sealed diaries composed in two frayed notebooks, along with a logbook and several black-and-white photographs. At this event Bolivia’s vice-minister of culture, Pablo Groux, expressed that there were plans to publish photographs of every handwritten page later in the year.[288] Meanwhile, in August 2009 anthropologists working for Bolivia’s Justice Ministry discovered and unearthed the bodies of five of Guevara’s fellow guerrillas near the Bolivian town of Teoponte.[289]
The discovery of Che’s remains metonymically activated a series of interlinked associations—rebel, martyr, rogue figure from a picaresque adventure, savior, renegade, extremist—in which there was no fixed divide among them. The current court of opinion places Che on a continuum that teeters between viewing him as a misguided rebel, a coruscatingly brilliant guerrilla philosopher, a poet-warrior jousting at windmills, a brazen warrior who threw down the gauntlet to the bourgeoisie, the object of fervent paeans to his sainthood, or a mass murderer clothed in the guise of an avenging angel whose every action is imbricated in violence—the archetypal Fanatical Terrorist.
— Dr. Peter McLaren, author of Che Guevara, Paulo Freire, and the Pedagogy of Revolution[290]
Biographical debate
Guevara’s life and legacy remain contentious. The perceived contradictions of his ethos at various points in his life have created a complex character of duality, one who was «able to wield the pen and submachine gun with equal skill», while prophesying that «the most important revolutionary ambition was to see man liberated from his alienation».[291][292] Guevara’s paradoxical standing is further complicated by his array of seemingly diametrically opposed qualities. A secular humanist and sympathetic practitioner of medicine who did not hesitate to shoot his enemies, a celebrated internationalist leader who advocated violence to enforce a utopian philosophy of the collective good, an idealistic intellectual who loved literature but refused to allow dissent, an anti-imperialist Marxist insurgent who was radically willing to forge a poverty-less new world on the apocalyptic ashes of the old one, and finally, an outspoken anti-capitalist whose image has been commoditized. Che’s history continues to be rewritten and re-imagined.[293][294] Moreover, sociologist Michael Löwy contends that the many facets of Guevara’s life (i.e. doctor and economist, revolutionary and banker, military theoretician and ambassador, deep thinker and political agitator) illuminated the rise of the «Che myth», allowing him to be invariably crystallized in his many metanarrative roles as a «Red Robin Hood, Don Quixote of communism, new Garibaldi, Marxist Saint Just, Cid Campeador of the Wretched of the Earth, Sir Galahad of the beggars … and Bolshevik devil who haunts the dreams of the rich, kindling braziers of subversion all over the world».[291]
As such, various notable individuals have lauded Guevara; for example, Nelson Mandela referred to him as «an inspiration for every human being who loves freedom»,[250] while Jean-Paul Sartre described him as «not only an intellectual but also the most complete human being of our age».[295] Others who have expressed their admiration include authors Graham Greene, who remarked that Guevara «represented the idea of gallantry, chivalry, and adventure»,[296] and Susan Sontag, who supposed that «[Che’s] goal was nothing less than the cause of humanity itself.»[297] In the Pan-African community philosopher Frantz Fanon professed Guevara to be «the world symbol of the possibilities of one man»,[298] while Black Power leader Stokely Carmichael eulogized that «Che Guevara is not dead, his ideas are with us.»[299] Praise has been reflected throughout the political spectrum, with libertarian theorist Murray Rothbard extolling Guevara as a «heroic figure» who «more than any man of our epoch or even of our century, was the living embodiment of the principle of revolution»,[300] while journalist Christopher Hitchens reminisced that «[Che’s] death meant a lot to me and countless like me at the time, he was a role model, albeit an impossible one for us bourgeois romantics insofar as he went and did what revolutionaries were meant to do—fought and died for his beliefs.»[301]
Conversely, Jacobo Machover, an exiled opposition author, dismisses all praise of Guevara and portrays him as a callous executioner.[302] Exiled former Cuban prisoners have expressed similar opinions, among them Armando Valladares, who declared Guevara «a man full of hatred» who executed dozens without trial,[303] and Carlos Alberto Montaner, who asserted that Guevara possessed «a Robespierre mentality», wherein cruelty against the revolution’s enemies was a virtue.[304] Álvaro Vargas Llosa of the Independent Institute has hypothesized that Guevara’s contemporary followers «delude themselves by clinging to a myth», describing Guevara as a «Marxist Puritan» who employed his rigid power to suppress dissent, while also operating as a «cold-blooded killing machine».[172] Llosa also accuses Guevara’s «fanatical disposition» as being the linchpin of the «Sovietization» of the Cuban revolution, speculating that he possessed a «total subordination of reality to blind ideological orthodoxy».[172] On a macro-level, Hoover Institution research fellow William Ratliff regards Guevara more as a creation of his historical environment, referring to him as a «fearless» and «head-strong Messiah-like figure», who was the product of a martyr-enamored Latin American culture which «inclined people to seek out and follow paternalistic miracle workers».[305] Ratliff further speculates that the economic conditions in the region suited Guevara’s commitment to «bring justice to the downtrodden by crushing centuries-old tyrannies»; describing Latin America as being plagued by what Moisés Naím referred to as the «legendary malignancies» of inequality, poverty, dysfunctional politics and malfunctioning institutions.[305]
In a mixed assessment, British historian Hugh Thomas opined that Guevara was a «brave, sincere and determined man who was also obstinate, narrow, and dogmatic».[306] At the end of his life, according to Thomas, «he seems to have become convinced of the virtues of violence for its own sake», while «his influence over Castro for good or evil» grew after his death, as Fidel took up many of his views.[306] Similarly, the Cuban-American sociologist Samuel Farber lauds Che Guevara as «an honest and committed revolutionary», but also criticizes the fact that «he never embraced socialism in its most democratic essence».[307] Nevertheless, Guevara remains a national hero in Cuba, where his image adorns the 3 peso banknote and school children begin each morning by pledging «We will be like Che.»[308][309] In his homeland of Argentina, where high schools bear his name,[310] numerous Che museums dot the country and in 2008 a 12-foot (3.7 m) bronze statue of him was unveiled in the city of his birth, Rosario.[311] Guevara has been sanctified by some Bolivian campesinos[312] as «Saint Ernesto», who pray to him for assistance.[313] In contrast, Guevara remains a hated figure amongst many in the Cuban exile and Cuban American community of the United States, who view him as «the butcher of La Cabaña».[314] Despite this polarized status, a high-contrast monochrome graphic of Che’s face, created in 1968 by Irish artist Jim Fitzpatrick, became a universally merchandized and objectified image,[315][316] found on an endless array of items, including T-shirts, hats, posters, tattoos, and bikinis,[317] contributing to the consumer culture Guevara despised. Yet, he still remains a transcendent figure both in specifically political contexts[318] and as a wide-ranging popular icon of youthful rebellion.[301]
International honors
Guevara received several honors of state during his life.
- 1960: Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the White Lion[319]
- 1961: Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Southern Cross[320]
Archival media
Video footage
- Guevara addressing the United Nations General Assembly on 11 December 1964, (6:21), public domain footage uploaded by the UN, video clip
- Guevara interviewed by Face the Nation on 13 December 1964, (29:11), from CBS, video clip
- Guevara interviewed in 1964 on a visit to Dublin, Ireland, (2:53), English translation, from RTÉ Libraries and Archives, video clip
- Guevara interviewed in Paris and speaking French in 1964, (4:47), English subtitles, interviewed by Jean Dumur, video clip
- Guevara reciting a poem, (0:58), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara showing support for Fidel Castro, (0:22), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara speaking about labor, (0:28), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara speaking about the Bay of Pigs, (0:17), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara speaking against imperialism, (1:20), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara visiting Algeria in 1963 and giving a speech in French, from the Algerian Cinema Archive, video clip
Audio recording
- Guevara interviewed on ABC’s Issues and Answers, (22:27), English translation, narrated by Lisa Howard, 24 March 1964, audio clip
List of English-language works
- A New Society: Reflections for Today’s World, Ocean Press, 1996, ISBN 1-875284-06-0
- Back on the Road: A Journey Through Latin America, Grove Press, 2002, ISBN 0-8021-3942-6
- Che Guevara, Cuba, and the Road to Socialism, Pathfinder Press, 1991, ISBN 0-87348-643-9
- Che Guevara on Global Justice, Ocean Press (AU), 2002, ISBN 1-876175-45-1
- Che Guevara: Radical Writings on Guerrilla Warfare, Politics and Revolution, Filiquarian Publishing, 2006, ISBN 1-59986-999-3
- Che Guevara Reader: Writings on Politics & Revolution, Ocean Press, 2003, ISBN 1-876175-69-9
- Che Guevara Speaks: Selected Speeches and Writings, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1980, ISBN 0-87348-602-1
- Che Guevara Talks to Young People, Pathfinder, 2000, ISBN 0-87348-911-X
- Che: The Diaries of Ernesto Che Guevara, Ocean Press (AU), 2008, ISBN 1-920888-93-4
- Colonialism is Doomed, Ministry of External Relations: Republic of Cuba, 1964, ASIN B0010AAN1K
- Congo Diary: The Story of Che Guevara’s «Lost» Year in Africa Ocean Press, 2011, ISBN 978-0-9804292-9-9
- Critical Notes on Political Economy: A Revolutionary Humanist Approach to Marxist Economics, Ocean Press, 2008, ISBN 1-876175-55-9
- Diary of a Combatant: The Diary of the Revolution that Made Che Guevara a Legend, Ocean Press, 2013, ISBN 978-0-9870779-4-3
- Episodes of the Cuban Revolutionary War, 1956–58, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1996, ISBN 0-87348-824-5
- Global Justice: Three Essays on Liberation and Socialism, Seven Stories Press, 2022, ISBN 1644211564
- Guerrilla Warfare: Authorized Edition, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-920888-28-4
- I Embrace You with All My Revolutionary Fervor: Letters 1947-1967, Seven Stories Press, 2021, ISBN 1644210959
- Latin America: Awakening of a Continent, Ocean Press, 2005, ISBN 1-876175-73-7
- Latin America Diaries: The Sequel to The Motorcycle Diaries, Ocean Press, 2011, ISBN 978-0-9804292-7-5
- Marx & Engels: An Introduction, Ocean Press, 2007, ISBN 1-920888-92-6
- Our America And Theirs: Kennedy And The Alliance For Progress, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-876175-81-8
- Reminiscences of the Cuban Revolutionary War: Authorized Edition, Ocean Press, 2005, ISBN 1-920888-33-0
- Self Portrait Che Guevara, Ocean Press (AU), 2004, ISBN 1-876175-82-6
- Socialism and Man in Cuba, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1989, ISBN 0-87348-577-7
- The African Dream: The Diaries of the Revolutionary War in the Congo, Grove Press, 2001, ISBN 0-8021-3834-9
- The Argentine, Ocean Press (AU), 2008, ISBN 1-920888-93-4
- The Awakening of Latin America: Writings, Letters and Speeches on Latin America, 1950–67, Ocean Press, 2012, ISBN 978-0-9804292-8-2
- The Bolivian Diary of Ernesto Che Guevara, Pathfinder Press, 1994, ISBN 0-87348-766-4
- The Great Debate on Political Economy, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-876175-54-0
- The Motorcycle Diaries: A Journey Around South America, London: Verso, 1996, ISBN 1-85702-399-4
- The Secret Papers of a Revolutionary: The Diary of Che Guevara, American Reprint Co, 1975, ASIN B0007GW08W
- To Speak the Truth: Why Washington’s «Cold War» Against Cuba Doesn’t End, Pathfinder, 1993, ISBN 0-87348-633-1
See also
References
- ^ «Che Guevara». archive.nytimes.com.
- ^ Partido Unido de la Revolución Socialista de Cuba, a.k.a. PURSC.
- ^ How to pronounce Che Guevara – Forvo features various sound clips of international Spanish speakers enunciating his name.
- ^ a b The date of birth recorded on his birth certificate was 14 June 1928, although one tertiary source, (Julia Constenla, quoted by Jon Lee Anderson), asserts that he was actually born on 14 May of that year. Constenla alleges that she was told by Che’s mother, Celia de la Serna, that she was already pregnant when she and Ernesto Guevara Lynch were married and that the date on the birth certificate of their son was forged to make it appear that he was born a month later than the actual date to avoid scandal. (Anderson 1997, pp. 3, 769.)
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 128.
- ^ a b c On Revolutionary Medicine Speech by Che Guevara to the Cuban Militia on 19 August 1960. «Because of the circumstances in which I traveled, first as a student and later as a doctor, I came into close contact with poverty, hunger and disease; with the inability to treat a child because of lack of money; with the stupefaction provoked by the continual hunger and punishment, to the point that a father can accept the loss of a son as an unimportant accident, as occurs often in the downtrodden classes of our American homeland. And I began to realize at that time that there were things that were almost as important to me as becoming famous or making a significant contribution to medical science: I wanted to help those people.»
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 90-91.
- ^ Beaubien, NPR Audio Report, 2009, 00:09–00:13.
- ^ a b c d e «Castro’s Brain», 1960.
- ^ a b c d e Taibo 1999, p. 267.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, pp. 69–70.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 526–530.
- ^ «On Development» Speech delivered by Che Guevara at the plenary session of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development in Geneva, Switzerland on 25 March 1964. «The inflow of capital from the developed countries is the prerequisite for the establishment of economic dependence. This inflow takes various forms: loans granted on onerous terms; investments that place a given country in the power of the investors; almost total technological subordination of the dependent country to the developed country; control of a country’s foreign trade by the big international monopolies; and in extreme cases, the use of force as an economic weapon in support of the other forms of exploitation.»
- ^ At the Afro-Asian Conference in Algeria A speech by Che Guevara to the Second Economic Seminar of Afro-Asian Solidarity in Algiers, Algeria on 24 February 1965.»The struggle against imperialism, for liberation from colonial or neocolonial shackles, which is being carried out by means of political weapons, arms, or a combination of the two, is not separate from the struggle against backwardness and poverty. Both are stages on the same road leading toward the creation of a new society of justice and plenty. … Ever since monopoly capital took over the world, it has kept the greater part of humanity in poverty, dividing all the profits among the group of the most powerful countries. The standard of living in those countries is based on the extreme poverty of our countries. To raise the living standards of the underdeveloped nations, therefore, we must fight against imperialism. … The practice of proletarian internationalism is not only a duty for the peoples struggling for a better future, it is also an inescapable necessity.»
- ^ Guevara was coordinating with African liberation movements in exile such as the MPLA in Angola and MNR in Congo-Brazzaville, while stating that Africa represented one of «the more important fields of struggle against all forms of exploitation existing in the world». Guevara then envisioned crafting an alliance with African leaders such as Ahmed Ben Bella in Algeria, Sékou Touré in Guinea, Kwame Nkrumah in Ghana, Julius Nyerere in Tanzania, and Gamal Abdel Nasser in Egypt, to foster a global dimension to his ensuing continental revolution in Latin America. See Anderson 1997, pp. 576, 584.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 4.
- ^ Footnote for Socialism and man in Cuba (1965): «Che argued that the full liberation of humankind is reached when work becomes a social duty carried out with complete satisfaction and sustained by a value system that contributes to the realization of conscious action in performing tasks. This could only be achieved by systematic education, acquired by passing through various stages in which collective action is increased. Che recognized that this to be difficult and time-consuming. In his desire to speed up this process, however, he developed methods of mobilizing people, bringing together their collective and individual interests. Among the most significant of these instruments were moral and material incentives, while deepening consciousness as a way of developing toward socialism. See Che’s speeches: Homage to Emulation Prize Winners (1962) and A New Attitude to Work (1964).»
- ^ Dorfman 1999.
- ^ Maryland Institute of Art, referenced at BBC News 26 May 2001.
- ^ In Spanish a person may carry the surname of his or her father as well as that of his or her mother, albeit in that order. Some people carry both, others only that of their father. In Guevara’s case, many people of Irish descent will add «Lynch» to emphasize his Irish relations. Others will add «de la Serna» to give respect to Guevara’s mother.
- ^ Guevara Lynch 2007, pp. i. «The father of Che Guevara, Ernesto Guevara Lynch was born in Argentina in 1900 of Irish and Basque origin.»
- ^ The Origins of Guevara’s Name — written in Spanish
- ^ Che’s last name Guevara derives from the Castilianized form of the Basque Gebara, a habitational name from the province of Álava, while his grandmother, Ana Lynch, was a descendant of Patrick Lynch, who emigrated from County Galway, Ireland in the 1740s.
- ^ Online Archive of California: Pinedo Family Papers from the Santa Clara University Library, 2015
- ^ Mercury News Fundraiser for Friends of Peralta Hacienda Historical Park by Angela Woodall, Oakland Tribune, 23 November 2010
- ^ Lavretsky 1976.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 23.
- ^ Argentina: Che’s Red Mother Time Magazine, 14 July 1961.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 22–23.
- ^ Guevara Lynch, Ernesto. Young Che: Memories of Che Guevara by His Father. Publication Date 14 September 2011, Vintage
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 8.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 24.
- ^ Argentine Rugby Inspired by Che Guevara by Brendan Gallagher, The Daily Telegraph, 5 October 2007
- ^ Cain, Nick & Growden, Greg. «Chapter 21: Ten Peculiar Facts about Rugby» in Rugby Union for Dummies (2nd Edition), John Wiley and Sons; ISBN 978-0-470-03537-5, p. 293.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 28.
- ^ a b Hart 2004, p. 98.
- ^ Haney 2005, p. 164.
- ^ a b c d (Anderson 1997, pp. 37–38).
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 10.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 26.
- ^ Ratner 1997, p. 25.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 89.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 64.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 59–64.
- ^ Harris, Richard Legé (2011). Che Guevara: A Biography. ABC-CLIO. p. xxiv, 21.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 83.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 75–76.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 27.
- ^ NYT bestseller list: #38 Paperback Nonfiction on 2005-02-20, #9 Nonfiction on 2004-10-07 and on more occasions.
- ^ A Very Modern Icon by George Galloway, New Statesman, 12 June 2006
- ^ Che Guevara spent time in Miami Archived 4 February 2013 at archive.today by Alfonso Chardy, The Miami Herald 8 July 2008
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 98.
- ^ A copy of Guevara’s University transcripts showing conferral of his medical diploma can be found on p. 75 of Becoming Che: Guevara’s Second and Final Trip through Latin America, by Carlos ‘Calica’ Ferrer (Translated from the Spanish by Sarah L. Smith), Marea Editorial, 2006, ISBN 987-1307-07-1. Ferrer was a longtime childhood friend of Che, and when Guevara passed the last of his 12 exams in 1953, he gave Ferrer, who had been telling Guevara that he would never finish, a copy, showing that he had finally completed his studies.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 126.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 31.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 31.
- ^ a b Guevara Lynch 2000, p. 26.
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 172.
- ^ Anderson, Jon (2010). Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life. New York, New York: Grove/Atlantic, Inc. p. 139. ISBN 978-0-802-19725-2. Retrieved 25 July 2015.
- ^ «Anderson (2010)», p 126
- ^ «Poetry of Che is presented with great success in Guatemala». Cuba Headlines. 26 November 2007.
- ^ Immerman 1982, pp. 155–160.
- ^ Immerman 1982, pp. 161–163.
- ^ Gleijeses 1991, pp. 345–349.
- ^ Gleijeses 1991, pp. 354–357.
- ^ Immerman 1982, pp. 198–201.
- ^ Cullather 2006, p. 113.
- ^ Gleijeses 1991, p. 382.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 32.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 39.
- ^ Che Guevara 1960–67 by Frank E. Smitha.
- ^ Sinclair, Andrew (1970). Che Guevara. The Viking Press. p. 12. ISBN 9780670213917.
- ^ Manzanos, Rosario (8 October 2012). «Documental sobre el Che Guevara, doctor en México». Proceso (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ^ «BIOGRAFIA DE ERNESTO CHE GUEVARA Fundación Che Guevara, FUNCHE» (PDF) (in Spanish). educarchile.cl. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ^ «FIDEL Y HANK: PASAJES DE LA REVOLUCIÓN» (in Spanish). lagacetametropolitana.com. Archived from the original on 4 January 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 33.
- ^ a b Rebel Wife, A Review of My Life With Che: The Making of a Revolutionary by Hilda Gadea by Tom Gjelten, The Washington Post, 12 October 2008.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 55.
- ^ Fidel and Che: A Revolutionary Friendship by Simon Reid-Henry audio slideshow by The Guardian, 9 January 2009
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 28.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 37.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 194.
- ^ Snow, Anita. «‘My Life With Che’ by Hilda Gadea Archived 2012-12-05 at archive.today». Associated Press at WJXX-TV. 16 August 2008; retrieved 23 February 2009.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 213.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 211.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 32.
- ^ DePalma 2006, pp. 110–11.
- ^ a b c Latin lessons: What can we Learn from the World’s most Ambitious Literacy Campaign? by The Independent, 7 November 2010
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 45.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 269–270.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, pp. 105, 119.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 237–238, 269–270, 277–278.
- ^ a b c Luther 2001, pp. 97–99.
- ^ a b c Anderson 1997, p. 237.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 35.
- ^ Cuba Remembers Che Guevara 40 Years after his Fall Archived 13 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine by Rosa Tania Valdes, Reuters, 8 October 2007
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 177.
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 193.
- ^ Poster Boy of The Revolution by Saul Landau, The Washington Post, 19 October 1997, p. X01.
- ^ Moore, Don. «Revolution! Clandestine Radio and the Rise of Fidel Castro». Patepluma Radio.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 42.
- ^ Bockman 1984.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 40.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 47.
- ^ Castro 1972, pp. 439–442.
- ^ Dorschner 1980, pp. 41–47, 81–87.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 39.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 48.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 13.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 51.
- ^ Castañeda, pp. 145–146.
- ^ a b Castañeda, p. 146.
- ^ Anderson 1997, 397.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 400–401.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 424.
- ^ a b Skidmore 2008, pp. 273.
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, p. 115. «The Penal Law of the War of Independence (July 28, 1896) was reinforced by Rule 1 of the Penal Regulations of the Rebel Army, approved in the Sierra Maestra February 21, 1958, and published in the army’s official bulletin (Ley penal de Cuba en armas, 1959)» (Gómez Treto 1991, p. 123).
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, pp. 115–116.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 372, 425.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 376.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 52.
- ^ Niess 2007, p. 60.
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, p. 116.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 388.
- ^ Rally For Castro: One Million Roar «Si» To Cuba Executions – Video Clip by Universal-International News, narrated by Ed Herlihy, from 22 January 1959
- ^ Wickham-Crowley, Timothy P. (1990). Exploring Revolution: Essays on Latin American Insurgency and Revolutionary Theory. Armonk and London: M.E. Sharpe. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-87332-705-3.
- ^ Conflict, Order, and Peace in the Americas, by the Lyndon B. Johnson School of Public Affairs, 1978, p. 121. «The US-supported Batista regime killed 20,000 Cubans»
- ^ The World Guide 1997/98: A View from the South, by University of Texas, 1997, ISBN 1-869847-43-1, pg 209. «Batista engineered yet another coup, establishing a dictatorial regime, which was responsible for the death of 20,000 Cubans.»
- ^ Fidel: The Untold Story. (2001). Directed by Estela Bravo. First Run Features. (91 min). Viewable clip. «An estimated 20,000 people were murdered by government forces during the Batista dictatorship.»
- ^ Niess 2007, p. 61.
- ^ a b c Castañeda 1998, pp. 143–144.
- ^ The Legacy of Che Guevara – a PBS online forum with author Jon Lee Anderson, 20 November 1997
- ^ Different sources cite differing numbers of executions attributable to Guevara, with some of the discrepancy resulting from the question of which deaths to attribute directly to Guevara and which to the regime as a whole. Anderson (1997) gives the number specifically at La Cabaña prison as 55 (p. 387.), while also stating that «several hundred people were officially tried and executed across Cuba» as a whole (p. 387). (Castañeda 1998) notes that historians differ on the total number killed, with different studies placing it as anywhere from 200 to 700 nationwide (p. 143), although he notes that «after a certain date most of the executions occurred outside of Che’s jurisdiction» (p. 143). These numbers are supported by the opposition-based Free Society Project / Cuba Archive, which gives the figure as 144 executions ordered by Guevara across Cuba in three years (1957–1959) and 105 «victims» specifically at La Cabaña, which according to them were all «carried out without due process of law». Of further note, much of the discrepancy in the estimates between 55 versus 105 executed at La Cabaña revolves around whether to include instances where Guevara had denied an appeal and signed off on a death warrant, but where the sentence was carried out while he traveled overseas from 4 June to 8 September, or after he relinquished his command of the fortress on 12 June 1959.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 375.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 54.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 57.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, p. 58.
- ^ Castañeda, p. 159.
- ^ ABC News, Life and Death of Che Guevara.
- ^ (Castañeda 1998, pp. 264–265).
- ^ Taibo 1999, pp. 282–285.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 423.
- ^ Ramadhian Fadillah (13 June 2012). «Soekarno soal cerutu Kuba, Che dan Castro» (in Indonesian). Merdeka.com. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 431.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 300.
- ^ Che Guevara’s Daughter Visits Bomb Memorial in Hiroshima by The Japan Times, 16 May 2008
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 435.
- ^ «Ernesto «Che» Guevara».
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 55.
- ^ a b Crompton 2009, p. 71.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 60.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 25.
- ^ Casey 2009, pp. 25–50.
- ^ Latin America’s New Look at Che by Daniel Schweimler, BBC News, 9 October 2007.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, p. 61.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 449
- ^ Cuba: A Dissenting Report, by Samuel Shapiro, New Republic, 12 September 1960, pp. 8-26, 21.
- ^ a b c d Notes for the Study of the Ideology of the Cuban Revolution by Che Guevara, published in Verde Olivo, October 8, 1960
- ^ Man and Socialism in Cuba Archived 2010-11-28 at the Wayback Machine by Che Guevara
- ^ Dumur 1964 a 1964 video interview of Che Guevara speaking French (with English subtitles).
- ^ a b c d e Hansing 2002, pp 41–42.
- ^ a b c d «Socialism and Man in Cuba» A letter to Carlos Quijano, editor of Marcha, a weekly newspaper published in Montevideo, Uruguay; published as «From Algiers, for Marcha: The Cuban Revolution Today» by Che Guevara on 12 March 1965.
- ^ a b c d e Kellner 1989, p. 62.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 59.
- ^ PBS: Che Guevara, Popular but Ineffective.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 75.
- ^ «Latin America Report». Foreign Broadcast Information Service (FBIS). 23 March 1984. p. 24. Archived from the original on 15 November 2011. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 63.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 74.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 269.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 306.
- ^ a b c Vargas Llosa 2005.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 507.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 509.
- ^ a b «Economics Cannot be Separated from Politics» speech by Che Guevara to the ministerial meeting of the Inter-American Economic and Social Council (CIES), in Punta del Este, Uruguay on 8 August 1961.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 78.
- ^ a b c Goodwin, Richard (22 August 1961). «Memorandum for the President» (PDF). The American Century (Memorandum). The White House. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 492.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 530.
- ^ Abrams, Dennis (2013). Ernesto «Che» Guevara. Infobase Learning. ISBN 9781438146133.
- ^ Eric, Luther; Henken, Ted (2001). Che Guevara. Alpha. p. 165. ISBN 9780028641997.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 545.
- ^ Guevara 1997, p 304
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 73.
- ^ Kapcia, Antoni (2022). Historical Dictionary of Cuba. Rowman and Littlefield Publishers. pp. 261–262. ISBN 9781442264557.
- ^ Cuba’s Forgotten Decade How the 1970s Shaped the Revolution. Lexington Books. 2018. p. 10. ISBN 9781498568746.
- ^ Underlid, Even (2021). Cuba Was Different Views of the Cuban Communist Party on the Collapse of Soviet and Eastern European Socialism. Brill. p. 229. ISBN 9789004442900.
- ^ Gordy, Katherine (2015). Living Ideology in Cuba Socialism in Principle and Practice. University of Michigan Press. pp. 90–92. ISBN 9780472052615.
- ^ Soviet Influence on Cuban Culture, 1961–1987 When the Soviets Came to Stay. Lexington Books. 2019. pp. 12–13. ISBN 9781498580120.
- ^ Artaraz, Kepa (2009). Cuba and Western Intellectuals Since 1959. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 23. ISBN 9780230618299.
- ^ a b Kapcia, Antoni (2014). Leadership in the Cuban Revolution The Unseen Story. Zed Books. ISBN 9781780325286.
- ^ Kapcia, Antoni (2008). Cuba in Revolution A History Since the Fifties. Reaktion Books. ISBN 9781861894489.
- ^ Peet, Richard; Hartwick, Elaine (2009). Theories of Development, Second Edition Contentions, Arguments, Alternatives. Guilford Publications. p. 189. ISBN 9781606230664.
- ^ a b c d e «Colonialism is Doomed» speech to the 19th General Assembly of the United Nations in New York City by Cuban representative Che Guevara on 11 December 1964.
- ^ a b Bazooka Fired at UN as Cuban Speaks by Homer Bigart, The New York Times, 12 December 1964, p. 1.
- ^ CBS Video of Che Guevara being interviewed by Face the Nation on 13 December 1964, (29:11)
- ^ Hart 2004, p. 271.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 618.
- ^ «Che Guevara: Father Of Revolution, Son Of Galway». Fantompowa.net. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ^ Gerry Adams Featured in New Che Guevara Documentary by Kenneth Haynes, Irish Central, 8 September 2009
- ^ Faber, Samuel (2011). Cuba Since the Revolution of 1959 A Critical Assessment. Haymarket Books. p. 217. ISBN 9781608461394.
- ^ The Oxford Handbook of Greek Drama in the Americas. OUP Oxford. 2015. ISBN 9780191637339.
- ^ a b Entiendes? Queer Readings, Hispanic Writings. Duke University Press. 1995. ISBN 9780822316152.
- ^ Ellis, Robert (1997). The Hispanic Homograph Gay Self-representation in Contemporary Spanish Autobiography. University of Illinois Press. p. 44. ISBN 9780252066115.
- ^ Guevara 1969, p. 350.
- ^ Guevara, Che. «Che Guevara At the Afro-Asian Conference in Algeria». marxists.org. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
- ^ Guevara 1969, pp. 352–59.
- ^ a b Message to the Tricontinental (1967) A letter sent by Che Guevara from his jungle camp in Bolivia, to the Tricontinental Conference 1966, published by the Executive Secretariat of the Organization of Solidarity with the People of Asia, Africa and Latin America (OSPAAAL), Havana, 16 April 1967.
- ^ a b Brand Che: Revolutionary as Marketer’s Dream by Michiko Kakutani, The New York Times, 20 April 2009
- ^ a b c d Ernesto ‘Che’ Guevara: A Rebel Against Soviet Political Economy by Helen Yaffe (author of Che Guevara: The Economics of Revolution), 2006
- ^ Abrams 2010, p. 100
- ^ Abrams 2010, p. 103.
- ^ Glejieses, Piero (2011). Conflicting Missions Havana, Washington, and Africa, 1959-1976. University of North Carolina Press. pp. 102–104. ISBN 9780807861622.
- ^ Guevara 1965.
- ^ Excerpt from Che’s Pasajes de la Guerra Revolucionaria (Congo) February 1965, hosted at the Wilson Center Digital Archive
- ^ Ben Bella 1997.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 624.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 629.
- ^ Gálvez 1999, p. 62.
- ^ Gott 2004 p. 219.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 86.
- ^ DR Congo’s Rebel-Turned-Brain Surgeon by Mark Doyle, BBC World Affairs, 13 December 2005.
- ^ BBC News 17 January 2001.
- ^ «The intercept operators knew that Dar-es-Salaam was serving as a communications center for the fighters, receiving messages from Castro in Cuba and relaying them on to the guerrillas deep in the bush.» (Bamford 2002, p. 181)
- ^ Ireland’s Own 2000.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 87.
- ^ From Cuba to Congo, Dream to Disaster for Che Guevara by The Guardian, 12 August 2000
- ^ Guevara 2000, p. 1.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, p. 316.
- ^ Che Guevara’s Central Bohemian Hideaway article and audio by Ian Willoughby, Český rozhlas, 27 June 2010
- ^ O’Donnell, Pacho. «Opiniones de Perón sobre el Che». Página/12 (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 May 2015.
- ^ Guevara 2009, p. 167.
- ^ Mittleman 1981, p. 38.
- ^ Jacobson, Sid and Ernie Colón. Che: A Graphic Biography. Hill & Wang, 2009. 96–97.
- ^ Jacobson, Sid and Ernie Colón. Che: A Graphic Biography. Hill and Wang, 2009. 98.
- ^ a b Selvage 1985.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 693.
- ^ Members of Che Guevara’s Guerrilla Movement in Bolivia by the Latin American Studies Organization
- ^ Kellner 1989, p.97.
- ^ «Bidding for Che», Time Magazine, 15 December 1967.
- ^ US Army 1967 and Ryan 1998, pp. 82–102, inter alia. «US military personnel in Bolivia never exceeded 53 advisers, including a sixteen-man Mobile Training Team from the 8th Special Forces Group based at Fort Gulick, Panama Canal Zone» (Selvage 1985).
- ^ Guevara 1972.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, pp. 107–112; 131–132.
- ^ Wright 2000, p. 86.
- ^ Rodriguez and Weisman 1989.
- ^ Barbie «Boasted of Hunting Down Che» by David Smith, The Observer, 23 December 2007.
- ^ Green Beret Behind the Capture of Che Guevara by Richard Gott, The Age, 8 September 2010
- ^ Rothman, Lily (9 October 2017). «Read TIME’s Original Report on the Death of Che Guevara». Time. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 733.
- ^ a b Guevara 2009, p. II.
- ^ a b «The Man Who Buried Che Archived 2008-12-07 at the Wayback Machine» by Juan O. Tamayo, Miami Herald, 19 September 1997.
- ^ a b c d e Ray, Michèle (March 1968). «In Cold Blood: The Execution of Che by the CIA». Ramparts Magazine. Edward M. Keating. pp. 21–37.
- ^ Grant 2007
- ^ Grant 2007. René Barrientos has never revealed his motives for ordering the summary execution of Guevara rather than putting him on trial or expelling him from the country or turning him over to the United States authorities.
- ^ Almudevar, Lola. «Bolivia marks capture, execution of ‘Che’ Guevara 40 years ago», San Francisco Chronicle. 9 October 2007; retrieved 7 November 2009.
- ^ Time magazine 1970.
- ^ «The Death of Che Guevara: Declassified». The National Security Archive. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 739.
- ^ Obituary: Che Guevara, Marxist Architect of Revolution by Richard Bourne, The Guardian, 11 October 1967
- ^ Almudevar 2007 and Gott 2005.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 179.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 183.
- ^ The Death of Che Guevara by Bjorn Kumm, The New Republic, Originally published on 11 November 1967.
- ^ Lacey 2007a.
- ^ After the Cuban revolution, seeing that Guevara had no watch, his friend Oscarito Fernández Mell gave him his own gold watch. Sometime later, Che handed him a piece of paper; a receipt from the National Bank declaring that Mell had «donated» his gold wristband to Cuba’s gold reserve. Guevara was still wearing his watch, but it now had a leather wristband (Anderson 1997, p. 503).
- ^ Kornbluh 1997.
- ^ Garza, Laura (18 December 1995). «Bolivian General Reveals Che Guevara’s Burial Site». The Militant. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 740.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 741.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 101.
- ^ «Bidding for Che», Time Magazine, 15 December 1967.
- ^ Guevara 1967.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 45.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 104.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 148.
- ^ Ramírez 1997.
- ^ a b Nadle, Marlene (24 August 1968). «Régis Debray Speaks from Prison». Ramparts Magazine: 42.
- ^ Trento, Angelo. Castro and Cuba : From the revolution to the present. p.64. Arris books. 2005.
- ^ Ernesto «Che» Guevara (World Leaders Past & Present), by Douglas Kellner, 1989, Chelsea House Publishers (Library Binding edition), ISBN 1555468357, p. 101
- ^ Che: A Myth Embalmed in a Matrix of Ignorance by Time Magazine October 12, 1970
- ^ Viva the Chevolution! by Trisha Ziff, The Huffington Post, April 21, 2008
- ^ Comrade Che Keeps an Eye on British Workers by Owen Booth, BBC News, October 24, 2002
- ^ Durschmied 2002, pp. 307–09.
- ^ Durschmied 2002, p. 305.
- ^ Durschmied 2002, pp. 305–06.
- ^ Durschmied 2002, p. 306.
- ^ Cuba salutes ‘Che’ Guevara: Revolutionary Icon Finally Laid to Rest, CNN, 17 October 1997
- ^ Bolivia unveils original Che Guevara diary by Eduardo Garcia, Reuters, 7 July 2008.
- ^ Slain Che Guevara Soldiers Found? video report by National Geographic, 21 August 2009.
- ^ McLaren 2000, p. 7.
- ^ a b Löwy 1973, p. 7.
- ^ Löwy 1973, p. 33.
- ^ Löwy 1973, pp. 7, 9, 15, 25, 75, 106.
- ^ The Spark That Does Not Die by Michael Löwy, International Viewpoint, July 1997
- ^ Moynihan 2006.
- ^ Sinclair 1968/2006, p. 80.
- ^ Sinclair 1968/2006, p. 127.
- ^ McLaren 2000, p. 3.
- ^ Sinclair 1968/2006, p. 67.
- ^ «Ernesto Che Guevara R.I.P.» by Rothbard, Murray, Left and Right: A Journal of Libertarian Thought, Volume 3, Number 3 (Spring-Autumn 1967).
- ^ a b O’Hagan 2004.
- ^ Behind Che Guevara’s mask, the cold executioner Archived 21 November 2008 at the Wayback Machine Times Online, 16 September 2007.
- ^ «‘Che’ Spurs Debate, Del Toro Walkout», The Washington Times, 27 January 2009.
- ^ Short interview on Che Guevara with Carlos Alberto Montaner for the Freedom Collection
- ^ a b Che is the «Patron Saint» of Warfare by William Ratliff, The Independent Institute, 9 October 2007.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 106.
- ^ Farber, Samuel (23 May 2016). «Assessing Che». Jacobin.
- ^ Che Guevara’s Ideals Lose Ground in Cuba by Anthony Boadle, Reuters, 4 October 2007: «he is the poster boy of communist Cuba, held up as a selfless leader who set an example of voluntary work with his own sweat, pushing a wheelbarrow at a building site or cutting sugar cane in the fields with a machete.»
- ^ People’s Weekly 2004.
- ^ Argentina pays belated homage to «Che» Guevara by Helen Popper, Reuters, 14 June 2008
- ^ Statue for Che’s ’80th birthday’ by Daniel Schweimler, BBC News, 15 June 2008.
- ^ On a tourist trail in Bolivia’s hills, Che’s fame lives on By Hector Tobar, Los Angeles Times, 17 October 2004.
- ^ Schipani 2007.
- ^ Casey 2009, pp. 235, 325.
- ^ BBC News 26 May 2001.
- ^ see also Che Guevara (photo).
- ^ Lacey 2007b.
- ^ BBC News 2007.
- ^ «»Che» Guevara, condecorado por Checoslovaquia». ABC. 29 de octubre de 1960. Consultado el 13 de octubre de 2014.
- ^ «Janio Condecora Guevara» (en portugués). Folha de S.Paulo. 20 de agosto de 1961. Consultado el 13 de octubre de 2014.
Referenced works
- Abrams, Dennis (2010). Ernesto Che Guevara. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 9781438134642.
- Almudevar, Lola (9 October 2007). «Bolivia marks capture, execution of ‘Che’ Guevara 40 years ago». SFGate. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- Anderson, Jon Lee (1997). Che Guevara : a revolutionary life (1st ed.). New York: Grove Pr. ISBN 0-8021-1600-0.
- Bamford, James (2002). Body of secrets anatomy of the ultra-secret National Security Agency (1st Anchor Books ed.). New York: Anchor Books. ISBN 0-385-49908-6.
- «Profile: Laurent Kabila». BBC News. 17 January 2001. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- «Che Guevara photographer dies». BBC News. 26 May 2001. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- «Cuba pays tribute to Che Guevara». BBC News. 9 October 2007. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- Beaubien, Jason (2009). Cuba Marks 50 Years Since ‘Triumphant Revolution’. NPR.org. NPR: All Things Considered, Audio Report.
- Ben Bella, Ahmed (1 October 1997). «Che as I knew him». Le Monde diplomatique. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- Bockman, Major Larry James (1 April 1984). The Spirit Of Moncada: Fidel Castro’s Rise To Power, 1953 — 1959. Quantico, Virginia: Marine Corps Command and Staff College. Archived from the original on 15 November 2021.
- Casey, Michael (2009). Che’s Afterlife: The Legacy of an Image. Vintage. ISBN 978-0-307-27930-9.
- Castañeda, Jorge G. (1998). Compañero : the life and death of Che Guevara (1st Vintage Books ed.). New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 0-679-75940-9.
- Crompton, Samuel (2009). Che Guevara: The Making of a Revolutionary. Gareth Stevens. ISBN 978-1-4339-0053-2.
- Cullather, Nicholas (2006). Secret History: The CIA’s classified account of its operations in Guatemala, 1952–1954. Palo Alto, California: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-5468-2.
- DePalma, Anthony (2006). The man who invented Fidel : Cuba, Castro, and Herbert L. Matthews of The New York Times (1st ed.). New York: Public Affairs. ISBN 1-58648-332-3.
- Dorfman, Ariel (14 June 1999). Time 100: Che Guevara. Time magazine.
- Dorschner, John and Roberto Fabricio (1980). The Winds of December: The Cuban Revolution of 1958. New York: Coward, McCann & Geoghegen. ISBN 0-698-10993-7.
- Dumur, Jean (interviewer) (1964). L’interview de Che Guevara (Video clip; 9:43; with English subtitles).
- Durschmied, Erik (2002). The Blood of Revolution: From the Reign of Terror to the Rise of Khomeini. Arcade Publishing. ISBN 1-55970-607-4.
- Free Society Project Inc. / Cuba Archive (30 September 2009). ««Documented Victims of Che Guevara in Cuba: 1957 to 1959» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 April 2010. (244 KB)«. Summit, New Jersey: Free Society Project.
- Gálvez, William (1999). Che in Africa: Che Guevara’s Congo Diary. Melbourne: Ocean Press, 1999. ISBN 1-876175-08-7.
- Gómez Treto, Raúl (Spring 1991). «Thirty Years of Cuban Revolutionary Penal Law». Latin American Perspectives 18(2), Cuban Views on the Revolution. 114–125.
- Gleijeses, Piero (1991). Shattered Hope: The Guatemalan Revolution and the United States, 1944–1954. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-02556-8.
- Gott, Richard (2004). Cuba: A New History. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-10411-1.
- Gott, Richard (11 August 2005). «Bolivia on the Day of the Death of Che Guevara». Le Monde diplomatique. Accessed 26 February 2006.
- Grant, Will (8 October 2007). «CIA man recounts Che Guevara’s death». BBC News. Accessed 29 February 2008.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (1965). «Che Guevara’s Farewell Letter».
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (1967). «Diario (Bolivia)». Written 1966–1967.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (editors Bonachea, Rolando E. and Nelson P. Valdés; 1969). Che: Selected Works of Ernesto Guevara, Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-52016-8
- Guevara, Ernesto (2009). Che: The Diaries of Ernesto Che Guevara. Ocean Press. ISBN 978-1-920888-93-0.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (1972). Pasajes de la guerra revolucionaria.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (translated from the Spanish by Patrick Camiller; 2000). The African Dream. New York: Grove Publishers. ISBN 0-8021-3834-9.
- Guevara, Ernesto; Deutschmann, David (1997). Che Guevara Reader: Writings by Ernesto Che Guevara on Guerrilla Strategy, Politics & Revolution. Ocean Press. ISBN 1-875284-93-1.
- Guevara Lynch, Ernesto (2000). Aquí va un soldado de América. Barcelona: Plaza y Janés Editores, S.A. ISBN 84-01-01327-5.
- Guevara Lynch, Ernesto (2007). The Young Che: Memories of Che Guevara by His Father. Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0307390448.
- Haney, Rich (2005). Celia Sánchez: The Legend of Cuba’s Revolutionary Heart. New York: Algora Pub. ISBN 0-87586-395-7.
- Katrin Hansing (2002). Rasta, Race and Revolution: The Emergence and Development of the Rastafari Movement in Socialist Cuba. LIT Verlag Münster. ISBN 3-8258-9600-5.
- Hart, Joseph (2004). Che: The Life, Death, and Afterlife of a Revolutionary. New York: Thunder’s Mouth Press. ISBN 1-56025-519-6.
- Immerman, Richard H. (1982). The CIA in Guatemala: The Foreign Policy of Intervention. Austin, Texas: University of Texas Press. ISBN 9780292710832.G
- Ireland’s Own (12 August 2000). «From Cuba to Congo, Dream to Disaster for Che Guevara». Archived from the original on 9 February 2006. Retrieved 11 January 2006.
- Kellner, Douglas (1989). Ernesto «Che» Guevara (World Leaders Past & Present). Chelsea House Publishers (Library Binding edition). p. 112. ISBN 1-55546-835-7.
- Kornbluh, Peter (1997). Electronic Briefing Book No. 5. National Security Archive. Accessed 25 March 2007.
- Lacey, Mark (26 October 2007). «Lone Bidder Buys Strands of Che’s Hair at U.S. Auction». The New York Times.
- Lacey, Mark (9 October 2007). «A Revolutionary Icon, and Now, a Bikini». The New York Times.
- Lavretsky, Iosif (1976). Ernesto Che Guevara. translated by A. B. Eklof. Moscow: Progress. p. 5. ASIN B000B9V7AW. OCLC 22746662.
- Löwy, Michael (1973). The Marxism of Che Guevara: Philosophy, Economics, Revolutionary Warfare. Monthly Review Press. ISBN 0-85345-274-1.
- Luther, Eric (2001). Che Guevara (Critical Lives). Penguin Group (USA). p. 276. ISBN 0-02-864199-X.
- McLaren, Peter (2000). Che Guevara, Paulo Freire, and the Pedagogy of Revolution. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0-8476-9533-6.
- Mittleman, James H (1981). Underdevelopment and the Transition to Socialism – Mozambique and Tanzania. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-500660-8
- Moynihan, Michael. «Neutering Sartre at Dagens Nyheter». Stockholm Spectator. Accessed 26 February 2006.
- Che Guevara, by Frank Niess, Haus Publishers Ltd, 2007, ISBN 1-904341-99-3.
- O’Hagan, Sean (11 July 2004). «Just a pretty face?». The Guardian. Accessed 25 October 2006.
- Ramírez, Dariel Alarcón (1997). Le Che en Bolivie. Paris: Éditions du Rocher. ISBN 2-268-02437-7.
- Ramonet, Ignacio (2007). Translated by Andrew Hurley. Fidel Castro: My Life London: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-102626-8
- Ratner, Michael (1997). Che Guevara and the FBI: The U.S. Political Police Dossier on the Latin American Revolutionary. Ocean Press. ISBN 1-875284-76-1.
- Rodriguez, Félix I. and John Weisman (1989). Shadow Warrior/the CIA Hero of a Hundred Unknown Battles. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-66721-1.
- Ryan, Henry Butterfield (1998). The Fall of Che Guevara: A Story of Soldiers, Spies, and Diplomats. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-511879-0.
- Sandison, David (1996). The Life & Times of Che Guevara. Paragon. ISBN 0-7525-1776-7.
- Schipani, Andres (23 September 2007). «The Final Triumph of Saint Che». The Observer. (Reporting from La Higuera.)
- Selvage, Major Donald R. – USMC (1 April 1985). Che Guevara in Bolivia. Globalsecurity.org. Accessed 5 January 2006.
- Sinclair, Andrew (2006) [1968]. Viva Che!: The Strange Death and Life of Che Guevara. Sutton publishing. ISBN 0-7509-4310-6.
- Skidmore, Thomas E.; Smith, Peter H. (2008). Modern Latin America. Oxford University Press. p. 436. ISBN 978-0-19-505533-7.
- Taibo II, Paco Ignacio (1999). Guevara, Also Known as Che. St Martin’s Griffin. 2nd edition. ISBN 0-312-20652-6.
- Time Magazine cover story (8 August 1960). «Castro’s Brain».
- Time Magazine (12 October 1970). «Che: A Myth Embalmed in a Matrix of Ignorance».
- U.S. Army (28 April 1967). Memorandum of Understanding Concerning the Activation, Organization and Training of the 2d Ranger Battalion – Bolivian Army. Accessed 19 June 2006.
- Vargas Llosa, Alvaro (11 July 2005). «The Killing Machine: Che Guevara, from Communist Firebrand to Capitalist Brand». The Independent Institute. Accessed 10 November 2006.
- «World Combined Sources» (2 October 2004). «Che Guevara remains a hero to Cubans». People’s Weekly World.
- Wright, Thomas C. (2000). Latin America in the Era of the Cuban Revolution (Revised ed.). Praeger. ISBN 0-275-96706-9.
External links
|
|
|
Che Guevara |
|
|---|---|

Guerrillero Heroico |
|
| Minister of Industries of Cuba | |
| In office 11 February 1961 – 1 April 1965 |
|
| Prime Minister | Fidel Castro |
| Preceded by | Office established |
| Succeeded by | Joel Domenech Benítez |
| President of the National Bank of Cuba | |
| In office 26 November 1959 – 23 February 1961 |
|
| Preceded by | Felipe Pazos |
| Succeeded by | Raúl Cepero Bonilla |
| Personal details | |
| Born |
Ernesto Guevara 14 June 1928[1] |
| Died | 9 October 1967 (aged 39) La Higuera, Santa Cruz, Bolivia |
| Cause of death | Execution by shooting |
| Resting place | Che Guevara Mausoleum, Santa Clara, Cuba |
| Citizenship |
|
| Political party | 26th of July Movement (1955–1962) United Party of the Cuban Socialist Revolution (1962–1965) |
| Spouse(s) |
Hilda Gadea (m. 1955; div. 1959) Aleida March (m. 1959) |
| Children | 5, including Aleida |
| Alma mater | University of Buenos Aires |
| Occupation |
|
| Known for | Guevarism |
| Signature |  |
| Nicknames |
|
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | Republic of Cuba[2] |
| Branch/service |
|
| Years of service | 1955–1967 |
| Unit | 26th of July Movement |
| Commands | Commanding officer of the Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces |
| Battles/wars |
|
Ernesto «Che« Guevara (Spanish: [ˈtʃe ɣeˈβaɾa];[3] 14 June 1928[4] – 9 October 1967) was an Argentine Marxist revolutionary. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia in popular culture.[5]
As a young medical student, Guevara traveled throughout South America and was radicalized by the poverty, hunger, and disease he witnessed.[6][7] His burgeoning desire to help overturn what he saw as the capitalist exploitation of Latin America by the United States prompted his involvement in Guatemala’s social reforms under President Jacobo Árbenz, whose eventual CIA-assisted overthrow at the behest of the United Fruit Company solidified Guevara’s political ideology.[6] Later in Mexico City, Guevara met Raúl and Fidel Castro, joined their 26th of July Movement, and sailed to Cuba aboard the yacht Granma with the intention of overthrowing U.S.-backed Cuban dictator Fulgencio Batista.[8] Guevara soon rose to prominence among the insurgents, was promoted to second-in-command, and played a pivotal role in the two-year guerrilla campaign that deposed the Batista regime.[9]
After the Cuban Revolution, Guevara played key roles in the new government. These included reviewing the appeals and firing squads for those convicted as war criminals during the revolutionary tribunals,[10] instituting agrarian land reform as Minister of Industries, helping spearhead a successful nationwide literacy campaign, serving as both President of the National Bank and instructional director for Cuba’s armed forces, and traversing the globe as a diplomat on behalf of Cuban socialism. Such positions also allowed him to play a central role in training the militia forces who repelled the Bay of Pigs Invasion,[11] and bringing Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles to Cuba, which preceded the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis.[12] Additionally, Guevara was a prolific writer and diarist, composing a seminal guerrilla warfare manual, along with a best-selling memoir about his youthful continental motorcycle journey. His experiences and studying of Marxism–Leninism led him to posit that the Third World’s underdevelopment and dependence was an intrinsic result of imperialism, neocolonialism, and monopoly capitalism, with the only remedies being proletarian internationalism and world revolution.[13][14] Guevara left Cuba in 1965 to foment continental revolutions across both Africa and South America,[15] first unsuccessfully in Congo-Kinshasa and later in Bolivia, where he was captured by CIA-assisted Bolivian forces and summarily executed.[16]
Guevara remains both a revered and reviled historical figure, polarized in the collective imagination in a multitude of biographies, memoirs, essays, documentaries, songs, and films. As a result of his perceived martyrdom, poetic invocations for class struggle, and desire to create the consciousness of a «new man» driven by moral rather than material incentives,[17] Guevara has evolved into a quintessential icon of various left-wing movements. In contrast, his critics on the political right accuse him of promoting authoritarianism and endorsing violence against his political opponents. Despite disagreements on his legacy, Time named him one of the 100 most influential people of the 20th century,[18] while an Alberto Korda photograph of him, titled Guerrillero Heroico, was cited by the Maryland Institute College of Art as «the most famous photograph in the world».[19]
Early life
A teenage Ernesto (left) with his parents and siblings, c. 1944, seated beside him from left to right: Celia (mother), Celia (sister), Roberto, Juan Martín, Ernesto (father) and Ana María
Ernesto Guevara was born to Ernesto Guevara Lynch and Celia de la Serna y Llosa, on 14 June 1928,[4] in Rosario, Argentina. Although the legal name on his birth certificate was «Ernesto Guevara», his name sometimes appears with «de la Serna» and/or «Lynch» accompanying it.[20] He was the eldest of five children in an upper-class Argentine family of pre-independence immigrant Spanish (Basque, Cantabrian), and Irish ancestry.[21][22][23] Two of Guevara’s notable 18th century ancestors included Luis María Peralta, a prominent Spanish landowner in colonial California, and Patrick Lynch, who emigrated from Ireland to the Río de la Plata Governorate.[24][25] Referring to Che’s «restless» nature, his father declared «the first thing to note is that in my son’s veins flowed the blood of the Irish rebels».[26]
Early on in life, Ernestito (as he was then called) developed an «affinity for the poor».[27] Growing up in a family with leftist leanings, Guevara was introduced to a wide spectrum of political perspectives even as a boy.[28] His father, a staunch supporter of Republicans from the Spanish Civil War, would host veterans from the conflict in the Guevara home.[29] As a young man, he briefly contemplated a career selling insecticides, and set up a laboratory in his family’s garage to experiment with effective mixtures of talc and gamexane under the brand name Vendaval, but was forced to abandon his efforts after suffering a severe asthmatic reaction to the chemicals.[30]
Despite numerous bouts of acute asthma that were to affect him throughout his life, he excelled as an athlete, enjoying swimming, football, golf, and shooting, while also becoming an «untiring» cyclist.[31][32] He was an avid rugby union player,[33] and played at fly-half for Club Universitario de Buenos Aires.[34] His rugby playing earned him the nickname «Fuser»—a contraction of El Furibundo (furious) and his mother’s surname, de la Serna—for his aggressive style of play.[35]
Intellectual and literary interests
Guevara learned chess from his father and began participating in local tournaments by the age of 12. During adolescence and throughout his life he studied poetry, especially that of Pablo Neruda, John Keats, Antonio Machado, Federico García Lorca, Gabriela Mistral, César Vallejo, and Walt Whitman.[36] He could also recite Rudyard Kipling’s If— and José Hernández’s Martín Fierro by heart.[36] The Guevara home contained more than 3,000 books, which allowed Guevara to be an enthusiastic and eclectic reader, with interests including Karl Marx, William Faulkner, André Gide, Emilio Salgari, and Jules Verne.[37] Additionally, he enjoyed the works of Jawaharlal Nehru, Franz Kafka, Albert Camus, Vladimir Lenin, and Jean-Paul Sartre; as well as Anatole France, Friedrich Engels, H. G. Wells, and Robert Frost.[38]
As he grew older, he developed an interest in the Latin American writers Horacio Quiroga, Ciro Alegría, Jorge Icaza, Rubén Darío, and Miguel Asturias.[38] Many of these authors’ ideas he cataloged in his own handwritten notebooks of concepts, definitions, and philosophies of influential intellectuals. These included composing analytical sketches of Buddha and Aristotle, along with examining Bertrand Russell on love and patriotism, Jack London on society, and Nietzsche on the idea of death. Sigmund Freud’s ideas fascinated him as he quoted him on a variety of topics from dreams and libido to narcissism and the Oedipus complex.[38] His favorite subjects in school included philosophy, mathematics, engineering, political science, sociology, history, and archaeology.[39][40] A CIA «biographical and personality report», dated 13 February 1958 and declassified decades later, made note of Guevara’s range of academic interests and intellect – describing him as «quite well read», while adding that «Che is fairly intellectual for a Latino».[41]
Motorcycle journey
Guevara (right) with Alberto Granado (left) in June 1952 on the Amazon River aboard their «Mambo-Tango» wooden raft, which was a gift from the lepers whom they had treated[42]
In 1948, Guevara entered the University of Buenos Aires to study medicine. His «hunger to explore the world»[43] led him to intersperse his collegiate pursuits with two long introspective journeys that fundamentally changed the way he viewed himself and the contemporary economic conditions in Latin America. The first expedition, in 1950, was a 4,500-kilometer (2,800 mi) solo trip through the rural provinces of northern Argentina on a bicycle on which he had installed a small engine.[44] Guevara then spent six months working as a nurse at sea on Argentina’s merchant marine freighters and oil tankers.[45] His second expedition, in 1951, was a nine-month, 8,000-kilometer (5,000 mi) continental motorcycle trek through part of South America. For the latter, he took a year off from his studies to embark with his friend, Alberto Granado, with the final goal of spending a few weeks volunteering at the San Pablo leper colony in Peru, on the banks of the Amazon River.[46]
A map of Guevara’s 1952 trip with Alberto Granado (the red arrows correspond to air travel)
In Chile, Guevara was angered by the working conditions of the miners at Anaconda’s Chuquicamata copper mine, moved by his overnight encounter in the Atacama Desert with a persecuted communist couple who did not even own a blanket, describing them as «the shivering flesh-and-blood victims of capitalist exploitation».[47] On the way to Machu Picchu he was stunned by the crushing poverty of the remote rural areas, where peasant farmers worked small plots of land owned by wealthy landlords.[48] Later on his journey, Guevara was especially impressed by the camaraderie among the people living in a leper colony, stating, «The highest forms of human solidarity and loyalty arise among such lonely and desperate people.»[48] Guevara used notes taken during this trip to write an account (not published until 1995), titled The Motorcycle Diaries, which later became a New York Times best seller,[49] and was adapted into a 2004 film of the same name.
A motorcycle journey the length of South America awakened him to the injustice of US domination in the hemisphere, and to the suffering colonialism brought to its original inhabitants.
—George Galloway, British politician, 2006[50]
The journey took Guevara through Argentina, Chile, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Panama, and Miami, Florida, for 20 days,[51] before returning home to Buenos Aires. By the end of the trip, he came to view Latin America not as a collection of separate nations, but as a single entity requiring a continent-wide liberation strategy. His conception of a borderless, united Hispanic America sharing a common Latino heritage was a theme that recurred prominently during his later revolutionary activities. Upon returning to Argentina, he completed his studies and received his medical degree in June 1953.[52][53]
Guevara later remarked that, through his travels in Latin America, he came in «close contact with poverty, hunger and disease» along with the «inability to treat a child because of lack of money» and «stupefaction provoked by the continual hunger and punishment» that leads a father to «accept the loss of a son as an unimportant accident». Guevara cited these experiences as convincing him that to «help these people», he needed to leave the realm of medicine and consider the political arena of armed struggle.[6]
Early political activity
Activism in Guatemala
Ernesto Guevara spent just over nine months in Guatemala. On 7 July 1953, Guevara set out again, this time to Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Panama, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, and El Salvador. On 10 December 1953, before leaving for Guatemala, Guevara sent an update to his aunt Beatriz from San José, Costa Rica. In the letter Guevara speaks of traversing the dominion of the United Fruit Company, a journey which convinced him that the company’s capitalist system was disadvantageous to the average citizen.[54] He adopted an aggressive tone to frighten his more conservative relatives, and the letter ends with Guevara swearing on an image of the then-recently deceased Joseph Stalin, not to rest until these «octopuses have been vanquished».[55] Later that month, Guevara arrived in Guatemala, where President Jacobo Árbenz headed a democratically elected government that, through land reform and other initiatives, was attempting to end the latifundia agricultural system. To accomplish this, President Árbenz had enacted a major land reform program, where all uncultivated portions of large land holdings were to be appropriated and redistributed to landless peasants. The largest land owner, and the one most affected by the reforms, was the United Fruit Company, from which the Árbenz government had already taken more than 225,000 acres (91,000 ha) of uncultivated land.[56] Pleased with the direction in which the nation was heading, Guevara decided to make his home in Guatemala to «perfect himself and accomplish whatever may be necessary in order to become a true revolutionary.»[57]
A map of Che Guevara’s travels between 1953 and 1956, including his journey aboard the Granma
In Guatemala City, Guevara sought out Hilda Gadea Acosta, a Peruvian economist who was politically well-connected as a member of the left-leaning, Alianza Popular Revolucionaria Americana (APRA). She introduced Guevara to a number of high-level officials in the Árbenz government. Guevara then established contact with a group of Cuban exiles linked to Fidel Castro through the 26 July 1953 attack on the Moncada Barracks in Santiago de Cuba. During this period, he acquired his famous nickname, due to his frequent use of the Argentine filler expression che (a multi-purpose discourse marker, like the syllable «eh» in Canadian English).[58] During his time in Guatemala, Guevara was hosted by other Central American exiles, one of whom, Helena Leiva de Holst, provided him with food and lodging,[59] discussed her travels to study Marxism in Russia and China,[60] and to whom Guevara dedicated a poem, «Invitación al camino».[61]
In May 1954, a ship carrying infantry and light artillery weapons was dispatched by communist Czechoslovakia for the Árbenz government and arrived in Puerto Barrios.[62] As a result, the United States government—which since 1953 had been tasked by President Eisenhower to remove Árbenz from power in the multifaceted CIA operation code-named PBSuccess—responded by saturating Guatemala with anti-Árbenz propaganda through radio and air-dropped leaflets, and began bombing raids using unmarked airplanes.[63] The United States also sponsored an armed force of several hundred anti-Árbenz Guatemalan refugees and mercenaries headed by Carlos Castillo Armas to help remove the Árbenz government. On 27 June, Árbenz chose to resign.[64] This allowed Armas and his CIA-assisted forces to march into Guatemala City and establish a military junta, which elected Armas as president on 7 July.[65] The Armas regime then consolidated power by rounding up and executing suspected communists,[66] while crushing the previously flourishing labor unions[67] and reversing the previous agrarian reforms.[68]
Guevara was eager to fight on behalf of Árbenz, and joined an armed militia organized by the communist youth for that purpose. However, frustrated with that group’s inaction, Guevara soon returned to medical duties. Following the coup, he again volunteered to fight, but soon after, Árbenz took refuge in the Mexican embassy and told his foreign supporters to leave the country. Guevara’s repeated calls to resist were noted by supporters of the coup, and he was marked for murder.[69] After Gadea was arrested, Guevara sought protection inside the Argentine consulate, where he remained until he received a safe-conduct pass some weeks later and made his way to Mexico.[70]
The overthrow of the Árbenz regime and establishment of the right-wing Armas dictatorship cemented Guevara’s view of the United States as an imperialist power that opposed and attempted to destroy any government that sought to redress the socioeconomic inequality endemic to Latin America and other developing countries.[57] In speaking about the coup, Guevara stated:
The last Latin American revolutionary democracy – that of Jacobo Árbenz – failed as a result of the cold premeditated aggression carried out by the United States. Its visible head was the Secretary of State John Foster Dulles, a man who, through a rare coincidence, was also a stockholder and attorney for the United Fruit Company.[69]
Guevara’s conviction strengthened that Marxism, achieved through armed struggle and defended by an armed populace, was the only way to rectify such conditions.[71] Gadea wrote later, «It was Guatemala which finally convinced him of the necessity for armed struggle and for taking the initiative against imperialism. By the time he left, he was sure of this.»[72]
Exile in Mexico
Guevara arrived in Mexico City on 21 September 1954, and worked in the allergy section of the General Hospital and at the Hospital Infantil de Mexico.[73][74] In addition he gave lectures on medicine at the Faculty of Medicine in the National Autonomous University of Mexico and worked as a news photographer for Latina News Agency.[75][76] His first wife Hilda notes in her memoir My Life with Che, that for a while, Guevara considered going to work as a doctor in Africa and that he continued to be deeply troubled by the poverty around him.[77] In one instance, Hilda describes Guevara’s obsession with an elderly washerwoman whom he was treating, remarking that he saw her as «representative of the most forgotten and exploited class». Hilda later found a poem that Che had dedicated to the old woman, containing «a promise to fight for a better world, for a better life for all the poor and exploited».[77]
During this time he renewed his friendship with Ñico López and the other Cuban exiles whom he had met in Guatemala. In June 1955, López introduced him to Raúl Castro, who subsequently introduced him to his older brother, Fidel Castro, the revolutionary leader who had formed the 26th of July Movement and was now plotting to overthrow the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista. During a long conversation with Fidel on the night of their first meeting, Guevara concluded that the Cuban’s cause was the one for which he had been searching and before daybreak he had signed up as a member of 26 July Movement.[78] Despite their «contrasting personalities», from this point on Che and Fidel began to foster what dual biographer Simon Reid-Henry deemed a «revolutionary friendship that would change the world», as a result of their coinciding commitment to anti-imperialism.[79]
By this point in Guevara’s life, he deemed that U.S.-controlled conglomerates installed and supported repressive regimes around the world. In this vein, he considered Batista a «U.S. puppet whose strings needed cutting».[80] Although he planned to be the group’s combat medic, Guevara participated in the military training with the members of the Movement. The key portion of training involved learning hit and run tactics of guerrilla warfare. Guevara and the others underwent arduous 15-hour marches over mountains, across rivers, and through the dense undergrowth, learning and perfecting the procedures of ambush and quick retreat. From the start Guevara was instructor Alberto Bayo’s «prize student» among those in training, scoring the highest on all of the tests given.[81] At the end of the course, he was called «the best guerrilla of them all» by General Bayo.[82]
Guevara then married Gadea in Mexico in September 1955, before embarking on his plan to assist in the liberation of Cuba.[83]
Cuban Revolution
Granma invasion
Journey of the yacht «Granma», from Mexico to Cuba.
The first step in Castro’s revolutionary plan was an assault on Cuba from Mexico via the Granma, an old, leaky cabin cruiser. They set out for Cuba on 25 November 1956. Attacked by Batista’s military soon after landing, many of the 82 men were either killed in the attack or executed upon capture; only 22 found each other afterwards.[84] During this initial bloody confrontation Guevara laid down his medical supplies and picked up a box of ammunition dropped by a fleeing comrade, proving to be a symbolic moment in Che’s life.[85]
Only a small band of revolutionaries survived to re-group as a bedraggled fighting force deep in the Sierra Maestra mountains, where they received support from the urban guerrilla network of Frank País, 26 July Movement, and local campesinos. With the group withdrawn to the Sierra, the world wondered whether Castro was alive or dead until early 1957 when an interview by Herbert Matthews appeared in The New York Times. The article presented a lasting, almost mythical image for Castro and the guerrillas. Guevara was not present for the interview, but in the coming months he began to realize the importance of the media in their struggle. Meanwhile, as supplies and morale diminished, and with an allergy to mosquito bites which resulted in agonizing walnut-sized cysts on his body,[86] Guevara considered these «the most painful days of the war».[87]
During Guevara’s time living hidden among the poor subsistence farmers of the Sierra Maestra mountains, he discovered that there were no schools, no electricity, minimal access to healthcare, and more than 40 percent of the adults were illiterate.[88] As the war continued, Guevara became an integral part of the rebel army and «convinced Castro with competence, diplomacy and patience».[9] Guevara set up factories to make grenades, built ovens to bake bread, and organized schools to teach illiterate campesinos to read and write.[9] Moreover, Guevara established health clinics, workshops to teach military tactics, and a newspaper to disseminate information.[89] The man whom Time dubbed three years later «Castro’s brain» at this point was promoted by Fidel Castro to Comandante (commander) of a second army column.[9]
Role as commander
As second-in-command, Guevara was a harsh disciplinarian who sometimes shot defectors. Deserters were punished as traitors, and Guevara was known to send squads to track those seeking to abandon their duties.[90] As a result, Guevara became feared for his brutality and ruthlessness.[91] During the guerrilla campaign, Guevara was also responsible for the summary executions of a number of men accused of being informers, deserters, or spies.[92] In his diaries, Guevara described the first such execution, of Eutimio Guerra, a peasant who had acted as a guide for the Castrist guerrillas, but admitted treason when it was discovered he accepted the promise of ten thousand pesos for repeatedly giving away the rebels’ position for attack by the Cuban air force.[93] Such information also allowed Batista’s army to burn the homes of peasants sympathetic to the revolution.[93] Upon Guerra’s request that they «end his life quickly»,[93] Che stepped forward and shot him in the head, writing «The situation was uncomfortable for the people and for Eutimio so I ended the problem giving him a shot with a .32 pistol in the right side of the brain, with exit orifice in the right temporal [lobe].»[94] His scientific notations and matter-of-fact description, suggested to one biographer a «remarkable detachment to violence» by that point in the war.[94] Later, Guevara published a literary account of the incident, titled «Death of a Traitor», where he transfigured Eutimio’s betrayal and pre-execution request that the revolution «take care of his children», into a «revolutionary parable about redemption through sacrifice».[94]
Although he maintained a demanding and harsh disposition, Guevara also viewed his role of commander as one of a teacher, entertaining his men during breaks between engagements with readings from the likes of Robert Louis Stevenson, Miguel de Cervantes, and Spanish lyric poets.[95] Together with this role, and inspired by José Martí’s principle of «literacy without borders», Guevara further ensured that his rebel fighters made daily time to teach the uneducated campesinos with whom they lived and fought to read and write, in what Guevara termed the «battle against ignorance».[88] Tomás Alba, who fought under Guevara’s command, later stated that «Che was loved, in spite of being stern and demanding. We would (have) given our life for him.»[96]
His commanding officer Fidel Castro described Guevara as intelligent, daring, and an exemplary leader who «had great moral authority over his troops».[97] Castro further remarked that Guevara took too many risks, even having a «tendency toward foolhardiness».[98] Guevara’s teenage lieutenant, Joel Iglesias, recounts such actions in his diary, noting that Guevara’s behavior in combat even brought admiration from the enemy. On one occasion Iglesias recounts the time he had been wounded in battle, stating «Che ran out to me, defying the bullets, threw me over his shoulder, and got me out of there. The guards didn’t dare fire at him … later they told me he made a great impression on them when they saw him run out with his pistol stuck in his belt, ignoring the danger, they didn’t dare shoot.»[99]
Guevara was instrumental in creating the clandestine radio station Radio Rebelde (Rebel Radio) in February 1958, which broadcast news to the Cuban people with statements by 26 July movement, and provided radiotelephone communication between the growing number of rebel columns across the island. Guevara had apparently been inspired to create the station by observing the effectiveness of CIA supplied radio in Guatemala in ousting the government of Jacobo Árbenz Guzmán.[100]
To quell the rebellion, Cuban government troops began executing rebel prisoners on the spot, and regularly rounded up, tortured, and shot civilians as a tactic of intimidation.[101] By March 1958, the continued atrocities carried out by Batista’s forces led the United States to stop selling arms to the Cuban government.[89] Then in late July 1958, Guevara played a critical role in the Battle of Las Mercedes by using his column to halt a force of 1,500 men called up by Batista’s General Cantillo in a plan to encircle and destroy Castro’s forces. Years later, Major Larry Bockman of the United States Marine Corps analyzed and described Che’s tactical appreciation of this battle as «brilliant».[102] During this time Guevara also became an «expert» at leading hit-and-run tactics against Batista’s army, and then fading back into the countryside before the army could counterattack.[103]
Final offensive
As the war extended, Guevara led a new column of fighters dispatched westward for the final push towards Havana. Travelling by foot, Guevara embarked on a difficult 7-week march, only travelling at night to avoid an ambush and often not eating for several days.[104] In the closing days of December 1958, Guevara’s task was to cut the island in half by taking Las Villas province. In a matter of days he executed a series of «brilliant tactical victories» that gave him control of all but the province’s capital city of Santa Clara.[104] Guevara then directed his «suicide squad» in the attack on Santa Clara, which became the final decisive military victory of the revolution.[105][106] In the six weeks leading up to the battle, there were times when his men were completely surrounded, outgunned, and overrun. Che’s eventual victory despite being outnumbered 10:1 remains in the view of some observers a «remarkable tour de force in modern warfare».[107]
Radio Rebelde broadcast the first reports that Guevara’s column had taken Santa Clara on New Year’s Eve 1958. This contradicted reports by the heavily controlled national news media, which had at one stage reported Guevara’s death during the fighting. At 3 am on 1 January 1959, upon learning that his generals were negotiating a separate peace with Guevara, Fulgencio Batista boarded a plane in Havana and fled for the Dominican Republic, along with an amassed «fortune of more than $300,000,000 through graft and payoffs».[108] The following day on 2 January, Guevara entered Havana to take final control of the capital.[109] Fidel Castro took six more days to arrive, as he stopped to rally support in several large cities on his way to rolling victoriously into Havana on 8 January 1959. The final death toll from the two years of revolutionary fighting was 2,000 people.[110]
Political career in Cuba
Revolutionary tribunals
In mid-January 1959, Guevara went to live at a summer villa in Tarará to recover from a violent asthma attack.[111] While there he started the Tarara Group, a group that debated and formed the new plans for Cuba’s social, political, and economic development.[112] In addition, Che began to write his book Guerrilla Warfare while resting at Tarara.[112] In February, the revolutionary government proclaimed Guevara «a Cuban citizen by birth» in recognition of his role in the triumph.[113] When Hilda Gadea arrived in Cuba in late January, Guevara told her that he was involved with another woman, and the two agreed on a divorce,[114] which was finalized on 22 May.[115]
The first major political crisis arose over what to do with the captured Batista officials who had perpetrated the worst of the repression.[116] During the rebellion against Batista’s dictatorship, the general command of the rebel army, led by Fidel Castro, introduced into the territories under its control the 19th-century penal law commonly known as the Ley de la Sierra (Law of the Sierra).[117] This law included the death penalty for serious crimes, whether perpetrated by the Batista regime or by supporters of the revolution. In 1959 the revolutionary government extended its application to the whole of the republic and to those it considered war criminals, captured and tried after the revolution. According to the Cuban Ministry of Justice, this latter extension was supported by the majority of the population, and followed the same procedure as those in the Nuremberg trials held by the Allies after World War II.[118]
Guevara in his trademark olive-green military fatigues and beret
To implement a portion of this plan, Castro named Guevara commander of the La Cabaña Fortress prison, for a five-month tenure (2 January through 12 June 1959).[119] Guevara was charged by the new government with purging the Batista army and consolidating victory by exacting «revolutionary justice» against those regarded as traitors, chivatos (informants) or war criminals.[120] As commander of La Cabaña, Guevara reviewed the appeals of those convicted during the revolutionary tribunal process.[10] The tribunals were conducted by 2–3 army officers, an assessor, and a respected local citizen.[121] On some occasions the penalty delivered by the tribunal was death by firing-squad.[122] Raúl Gómez Treto, senior legal advisor to the Cuban Ministry of Justice, has argued that the death penalty was justified in order to prevent citizens themselves from taking justice into their own hands, as had happened twenty years earlier in the anti-Machado rebellion.[123] Biographers note that in January 1959 the Cuban public was in a «lynching mood»,[124] and point to a survey at the time showing 93% public approval for the tribunal process.[10] Moreover, a 22 January 1959, Universal Newsreel broadcast in the United States and narrated by Ed Herlihy featured Fidel Castro asking an estimated one million Cubans whether they approved of the executions, and being met with a roaring «¡Sí!» (yes).[125] With between 1,000[126] and 20,000 Cubans estimated to have been killed at the hands of Batista’s collaborators,[127][128][129][130] and many of the accused war criminals sentenced to death accused of torture and physical atrocities,[10] the newly empowered government carried out executions, punctuated by cries from the crowds of «¡al paredón!» ([to the] wall!),[116] which biographer Jorge Castañeda describes as «without respect for due process».[131]
I have yet to find a single credible source pointing to a case where Che executed «an innocent». Those persons executed by Guevara or on his orders were condemned for the usual crimes punishable by death at times of war or in its aftermath: desertion, treason or crimes such as rape, torture or murder. I should add that my research spanned five years, and included anti-Castro Cubans among the Cuban-American exile community in Miami and elsewhere.
—Jon Lee Anderson, author of Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life, PBS forum[132]
Although accounts vary, it is estimated that several hundred people were executed nationwide during this time, with Guevara’s jurisdictional death total at La Cabaña ranging from 55 to 105.[133] Conflicting views exist of Guevara’s attitude towards the executions at La Cabaña. Some exiled opposition biographers report that he relished the rituals of the firing squad, and organized them with gusto, while others relate that Guevara pardoned as many prisoners as he could.[131] All sides acknowledge that Guevara had become a «hardened» man who had no qualms about the death penalty or about summary and collective trials. If the only way to «defend the revolution was to execute its enemies, he would not be swayed by humanitarian or political arguments».[131] In a 5 February 1959 letter to Luis Paredes López in Buenos Aires, Guevara states unequivocally: «The executions by firing squads are not only a necessity for the people of Cuba, but also an imposition of the people.»[134]
Along with ensuring «revolutionary justice», the other key early platform of Guevara was establishing agrarian land reform. Almost immediately after the success of the revolution, on 27 January 1959, Guevara made one of his most significant speeches where he talked about «the social ideas of the rebel army». During this speech he declared that the main concern of the new Cuban government was «the social justice that land redistribution brings about».[135] A few months later, 17 May 1959, the agrarian reform law, crafted by Guevara, went into effect, limiting the size of all farms to 1,000 acres (400 ha). Any holdings over these limits were expropriated by the government and either redistributed to peasants in 67-acre (270,000 m2) parcels or held as state-run communes.[136] The law also stipulated that foreigners could not own Cuban sugar-plantations.[137]
On 2 June 1959, he married Aleida March, a Cuban-born member of 26 July movement with whom he had been living since late 1958. Guevara returned to the seaside village of Tarara in June for his honeymoon with Aleida.[138] A civil ceremony was held at La Cabaña military fortress.[139] In total, Guevara would have five children from his two marriages.[140]
Early political office
Guevara in 1960, walking through the streets of Havana with his second wife Aleida March (right)
On 12 June 1959, Castro sent Guevara out on a three-month tour of mostly Bandung Pact countries (Morocco, Sudan, Egypt, Syria, Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, Indonesia, Japan, Yugoslavia, and Greece) and the cities of Singapore and Hong Kong.[141] Sending Guevara away from Havana allowed Castro to appear to distance himself from Guevara and his Marxist sympathies, which troubled both the United States and some of the members of Castro’s 26 July Movement.[142] While in Jakarta, Guevara visited Indonesian president Sukarno to discuss the recent revolution of 1945–1949 in Indonesia and to establish trade relations between their two countries. The two men quickly bonded, as Sukarno was attracted to Guevara’s energy and his relaxed informal approach; moreover they shared revolutionary leftist aspirations against Western imperialism.[143] Guevara next spent 12 days in Japan (15–27 July), participating in negotiations aimed at expanding Cuba’s trade relations with that country. During the visit he refused to visit and lay a wreath at Japan’s Tomb of the Unknown Soldier commemorating soldiers lost during World War II, remarking that the Japanese «imperialists» had «killed millions of Asians».[144] Instead, Guevara stated that he would visit Hiroshima, where the American military had detonated an atomic bomb 14 years earlier.[144] Despite his denunciation of Imperial Japan, Guevara considered President Truman a «macabre clown» for the bombings,[145] and after visiting Hiroshima and its Peace Memorial Museum he sent back a postcard to Cuba stating, «In order to fight better for peace, one must look at Hiroshima.»[146]
Upon Guevara’s return to Cuba in September 1959, it became evident that Castro now had more political power. The government had begun land seizures in accordance with the agrarian reform law, but was hedging on compensation offers to landowners, instead offering low-interest «bonds», a step which put the United States on alert. At this point the affected wealthy cattlemen of Camagüey mounted a campaign against the land redistributions and enlisted the newly disaffected rebel leader Huber Matos, who along with the anti-communist wing of the 26 July Movement, joined them in denouncing «communist encroachment».[147] During this time Dominican dictator Rafael Trujillo was offering assistance to the «Anti-Communist Legion of the Caribbean» which was training in the Dominican Republic. This multi-national force, composed mostly of Spaniards and Cubans, but also of Croatians, Germans, Greeks, and right-wing mercenaries, was plotting to topple Castro’s new regime.[147]
At this stage, Guevara acquired the additional position of Minister of Finance, as well as President of the National Bank.[148] These appointments, combined with his existing position as Minister of Industries, placed Guevara at the zenith of his power, as the «virtual czar» of the Cuban economy.[149] As a consequence of his position at the head of the central bank, it became Guevara’s duty to sign the Cuban currency, which per custom bore his signature. Instead of using his full name, he signed the bills solely «Che«.[150] It was through this symbolic act, which horrified many in the Cuban financial sector, that Guevara signaled his distaste for money and the class distinctions it brought about.[150] Guevara’s long time friend Ricardo Rojo later remarked that «the day he signed Che on the bills, (he) literally knocked the props from under the widespread belief that money was sacred.»[151]
International threats were heightened when, on 4 March 1960, two massive explosions ripped through the French freighter La Coubre, which was carrying Belgian munitions from the port of Antwerp, and was docked in Havana Harbor. The blasts killed at least 76 people and injured several hundred, with Guevara personally providing first aid to some of the victims. Fidel Castro immediately accused the CIA of «an act of terrorism» and held a state funeral the following day for the victims of the blast.[152] At the memorial service Alberto Korda took the famous photograph of Guevara, now known as Guerrillero Heroico.[153]
Perceived threats prompted Castro to eliminate more «counter-revolutionaries» and to utilize Guevara to drastically increase the speed of land reform. To implement this plan, a new government agency, the National Institute of Agrarian Reform (INRA), was established by the Cuban government to administer the new agrarian reform law. INRA quickly became the most important governing body in the nation, with Guevara serving as its head in his capacity as minister of industries.[137][need quotation to verify] Under Guevara’s command, INRA established its own 100,000-person militia, used first to help the government seize control of the expropriated land and supervise its distribution, and later to set up cooperative farms. The land confiscated included 480,000 acres (190,000 ha) owned by United States corporations.[137] Months later, in retaliation, U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower sharply reduced United States imports of Cuban sugar (Cuba’s main cash crop), which led Guevara on 10 July 1960 to address over 100,000 workers in front of the Presidential Palace at a rally to denounce the «economic aggression» of the United States.[149] Time Magazine reporters who met with Guevara around this time described him as «guid(ing) Cuba with icy calculation, vast competence, high intelligence, and a perceptive sense of humor.»[9]
Guevara was like a father to me … he educated me. He taught me to think. He taught me the most beautiful thing which is to be human.
—Urbano (a.k.a. Leonardo Tamayo),
fought with Guevara in Cuba and Bolivia[154]
Along with land reform, Guevara stressed the need for national improvement in literacy. Before 1959 the official literacy rate for Cuba was between 60 and 76%, with educational access in rural areas and a lack of instructors the main determining factors.[155] As a result, the Cuban government at Guevara’s behest dubbed 1961 the «year of education» and mobilized over 100,000 volunteers into «literacy brigades», who were then sent out into the countryside to construct schools, train new educators, and teach the predominantly illiterate guajiros (peasants) to read and write.[88][155] Unlike many of Guevara’s later economic initiatives, this campaign was «a remarkable success». By the completion of the Cuban literacy campaign, 707,212 adults had been taught to read and write, raising the national literacy rate to 96%.[155]
Accompanying literacy, Guevara was also concerned with establishing universal access to higher education. To accomplish this the new regime introduced affirmative action to the universities. While announcing this new commitment, Guevara told the gathered faculty and students at the University of Las Villas that the days when education was «a privilege of the white middle class» had ended. «The University» he said, «must paint itself black, mulatto, worker, and peasant.» If it did not, he warned, the people were going to break down its doors «and paint the University the colors they like.»[156]
Economic reforms and the «New Man»
In September 1960, when Guevara was asked about Cuba’s ideology at the First Latin American Congress, he replied, «If I were asked whether our revolution is Communist, I would define it as Marxist. Our revolution has discovered by its methods the paths that Marx pointed out.»[157] Consequently, when enacting and advocating Cuban policy, Guevara cited the political philosopher Karl Marx as his ideological inspiration. In defending his political stance, Guevara confidently remarked, «There are truths so evident, so much a part of people’s knowledge, that it is now useless to discuss them. One ought to be Marxist with the same naturalness with which one is ‘Newtonian’ in physics, or ‘Pasteurian’ in biology.»[158] According to Guevara, the «practical revolutionaries» of the Cuban Revolution had the goal of «simply fulfill(ing) laws foreseen by Marx, the scientist.»[158] Using Marx’s predictions and system of dialectical materialism, Guevara professed that «The laws of Marxism are present in the events of the Cuban Revolution, independently of what its leaders profess or fully know of those laws from a theoretical point of view.»[158]
The merit of Marx is that he suddenly produces a qualitative change in the history of social thought. He interprets history, understands its dynamic, predicts the future, but in addition to predicting it (which would satisfy his scientific obligation), he expresses a revolutionary concept: the world must not only be interpreted, it must be transformed. Man ceases to be the slave and tool of his environment and converts himself into the architect of his own destiny.
— Che Guevara, Notes for the Study of the Ideology of the Cuban, October 1960 [158]
Man truly achieves his full human condition when he produces without being compelled by the physical necessity of selling himself as a commodity.
— Che Guevara, Man and Socialism in Cuba[159]
Guevara meeting with French existentialist philosophers Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir at his office in Havana, March 1960. Sartre later wrote that Che was «the most complete human being of our time». In addition to Spanish, Guevara was fluent in French.[160]
In an effort to eliminate social inequalities, Guevara and Cuba’s new leadership had moved to swiftly transform the political and economic base of the country through nationalizing factories, banks, and businesses, while attempting to ensure affordable housing, healthcare, and employment for all Cubans.[161] In order for a genuine transformation of consciousness to take root, it was believed that such structural changes had to be accompanied by a conversion in people’s social relations and values. Believing that the attitudes in Cuba towards race, women, individualism, and manual labor were the product of the island’s outdated past, all individuals were urged to view each other as equals and take on the values of what Guevara termed «el Hombre Nuevo» (the New Man).[161] Guevara hoped his «new man» to be ultimately «selfless and cooperative, obedient and hard working, gender-blind, incorruptible, non-materialistic, and anti-imperialist».[161] To accomplish this, Guevara emphasized the tenets of Marxism–Leninism, and wanted to use the state to emphasize qualities such as egalitarianism and self-sacrifice, at the same time as «unity, equality, and freedom» became the new maxims.[161] Guevara’s first desired economic goal of the new man, which coincided with his aversion for wealth condensation and economic inequality, was to see a nationwide elimination of material incentives in favor of moral ones. He negatively viewed capitalism as a «contest among wolves» where «one can only win at the cost of others» and thus desired to see the creation of a «new man and woman».[162] Guevara continually stressed that a socialist economy in itself is not «worth the effort, sacrifice, and risks of war and destruction» if it ends up encouraging «greed and individual ambition at the expense of collective spirit».[163] A primary goal of Guevara’s thus became to reform «individual consciousness» and values to produce better workers and citizens.[163] In his view, Cuba’s «new man» would be able to overcome the «egotism» and «selfishness» that he loathed and discerned was uniquely characteristic of individuals in capitalist societies.[163] To promote this concept of a «new man», the government also created a series of party-dominated institutions and mechanisms on all levels of society, which included organizations such as labor groups, youth leagues, women’s groups, community centers, and houses of culture to promote state-sponsored art, music, and literature. In congruence with this, all educational, mass media, and artistic community based facilities were nationalized and utilized to instill the government’s official socialist ideology.[161] In describing this new method of «development», Guevara stated:
There is a great difference between free-enterprise development and revolutionary development. In one of them, wealth is concentrated in the hands of a fortunate few, the friends of the government, the best wheeler-dealers. In the other, wealth is the people’s patrimony.[164]
A further integral part of fostering a sense of «unity between the individual and the mass», Guevara believed, was volunteer work and will. To display this, Guevara «led by example», working «endlessly at his ministry job, in construction, and even cutting sugar cane» on his day off.[165] He was known for working 36 hours at a stretch, calling meetings after midnight, and eating on the run.[163] Such behavior was emblematic of Guevara’s new program of moral incentives, where each worker was now required to meet a quota and produce a certain quantity of goods. As a replacement for the pay increases abolished by Guevara, workers who exceeded their quota now only received a certificate of commendation, while workers who failed to meet their quotas were given a pay cut.[163] Guevara unapologetically defended his personal philosophy towards motivation and work, stating:
This is not a matter of how many pounds of meat one might be able to eat, or how many times a year someone can go to the beach, or how many ornaments from abroad one might be able to buy with his current salary. What really matters is that the individual feels more complete, with much more internal richness and much more responsibility.[166]
In the face of a loss of commercial connections with Western states, Guevara tried to replace them with closer commercial relationships with Eastern Bloc states, visiting a number of Marxist states and signing trade agreements with them. At the end of 1960 he visited Czechoslovakia, the Soviet Union, North Korea, Hungary, and East Germany and signed, for instance, a trade agreement in East Berlin on 17 December 1960.[167] Such agreements helped Cuba’s economy to a certain degree but also had the disadvantage of a growing economic dependency on the Eastern Bloc. It was also in East Germany where Guevara met Tamara Bunke (later known as «Tania»), who was assigned as his interpreter, and who joined him years later, and was killed with him in Bolivia.
According to Douglas Kellner, his programs were unsuccessful,[168] and accompanied a rapid drop in productivity and a rapid rise in absenteeism.[169] In a meeting with French economist René Dumont, Guevara blamed the inadequacy of the agrarian reform law enacted by the Cuban government in 1959, which turned large plantations into farm cooperatives or split up land amongst peasants.[170] In Guevara’s opinion, this situation continued to promote a «heightened sense of individual ownership» in which workers could not see the positive social benefits of their labor, leading them to instead seek individual material gain as before.[171] Decades later, Che’s former deputy Ernesto Betancourt, subsequently the director of the US government-funded Radio Martí and an early ally turned Castro-critic, accused Guevara of being «ignorant of the most elementary economic principles.»[172]
Bay of Pigs Invasion and Missile Crisis
On 17 April 1961, 1,400 U.S.-trained Cuban exiles invaded Cuba during the Bay of Pigs Invasion. Guevara did not play a key role in the fighting, as one day before the invasion a warship carrying Marines faked an invasion off the West Coast of Pinar del Río and drew forces commanded by Guevara to that region. However, historians give him a share of credit for the victory as he was director of instruction for Cuba’s armed forces at the time.[11] Author Tad Szulc in his explanation of the Cuban victory, assigns Guevara partial credit, stating: «The revolutionaries won because Che Guevara, as the head of the Instruction Department of the Revolutionary Armed Forces in charge of the militia training program, had done so well in preparing 200,000 men and women for war.»[11] It was also during this deployment that he suffered a bullet grazing to the cheek when his pistol fell out of its holster and accidentally discharged.[173]
Guevara (left) and Fidel Castro, photographed by Alberto Korda in 1961
In August 1961, during an economic conference of the Organization of American States in Punta del Este, Uruguay, Che Guevara sent a note of «gratitude» to United States President John F. Kennedy through Richard N. Goodwin, Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for Inter-American Affairs. It read «Thanks for Playa Girón (Bay of Pigs). Before the invasion, the revolution was shaky. Now it’s stronger than ever.»[174] In response to United States Treasury Secretary Douglas Dillon presenting the Alliance for Progress for ratification by the meeting, Guevara antagonistically attacked the United States’ claim of being a «democracy», stating that such a system was not compatible with «financial oligarchy, discrimination against blacks, and outrages by the Ku Klux Klan».[175] Guevara continued, speaking out against the «persecution» that in his view «drove scientists like Oppenheimer from their posts, deprived the world for years of the marvelous voice of Paul Robeson, and sent the Rosenbergs to their deaths against the protests of a shocked world.»[175] Guevara ended his remarks by insinuating that the United States was not interested in real reforms, sardonically quipping that «U.S. experts never talk about agrarian reform; they prefer a safe subject, like a better water supply. In short, they seem to prepare the revolution of the toilets.»[176] Nevertheless, Goodwin stated in his memo to President Kennedy following the meeting that Guevara viewed him as someone of the «newer generation»[177] and that Guevara, whom Goodwin alleged sent a message to him the day after the meeting through one of the meeting’s Argentine participants whom he described as «Darretta,»[177] also viewed the conversation which the two had as «quite profitable.»[177]
Guevara, who was practically the architect of the Cuban–Soviet relationship,[178] played a key role in bringing to Cuba the Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles that precipitated the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962 and brought the world to the brink of nuclear war.[179] After the Soviets proposed planting nuclear missiles in Cuba it was Che Guevara himself who traveled to the Soviet Union on August 30, 1962 to sign off on the final agreement.[180] Guevara argued with Khruschev that the missile deal should be made public but Khruschev insisted on secrecy, and swore the Soviet Union’s support if the Americans discovered the missiles. By the time Guevara arrived in Cuba the United States had already discovered the Soviet troops in Cuba via U-2 spy planes.[181]
A few weeks after the crisis, during an interview with the British communist newspaper the Daily Worker, Guevara was still fuming over the perceived Soviet betrayal and told correspondent Sam Russell that, if the missiles had been under Cuban control, they would have fired them off.[182] While expounding on the incident later, Guevara reiterated that the cause of socialist liberation against global «imperialist aggression» would ultimately have been worth the possibility of «millions of atomic war victims».[183] The missile crisis further convinced Guevara that the world’s two superpowers (the United States and the Soviet Union) used Cuba as a pawn in their own global strategies. Afterward, he denounced the Soviets almost as frequently as he denounced the Americans.[184]
Great Debate
The era in Cuban history retroactively named the «Great Debate» by historians was defined by public debate about the future of Cuban economic policy that took place from 1962 to 1965. The debate began after Cuba fell into an economic crisis in 1962 after years of internal economic complications, United States sanctions, and the flight of professionals from Cuba. In 1962 Fidel Castro invited Marxist economists around the world to debate two main propositions. One proposition proposed by Che Guevara was that Cuba could bypass any capitalist then «socialist» transition period and immediately become an industrialized «communist» society if «subjective conditions» like public consciousness and vanguard action are perfected. The other proposition held by the Popular Socialist Party was that Cuba required a transitionary period as a mixed economy in which Cuba’s sugar economy was maximized for profit before a «communist» society could be established.[185][186][187]
Guevara elaborated in this period that moral incentives should exist as the main motivator to increase workers’ production. All profits created by enterprises were to be given to the state budget, and the state budget would cover loses. Institutions that developed socialist consciousness were regarded as the most important element in maintaining a path to socialism rather than materially incentivized increases in production. Implementation of the profit-motive was regarded as a path towards capitalism and was one of the flaws of the Eastern bloc economies.[188] The economy would also rely on mass mobilizations and centralized planning as a method for developing the economy.[189] The main ideal that compromised the consciousness that would develop socialism was the praise of the «new man», a citizen that was only motivated by human solidarity and self-sacrifice.[190]
In 1966 the Cuban economy was reorganized on moral lines. Cuban propaganda stressed voluntarism and ideological motivations to increase productions. Material incentives were not given to workers who were more productive than others.[191] Cuban intellectuals were expected to participate actively in creating a positive national ethos and ignore any desire to create «art for art’s sake».[192] In 1968 all non-agricultural private businesses were nationalized, central planning was done more on an ad-hoc basis and the entire Cuban economy was directed at producing a 10 million ton sugar harvest. These developments were generally inspired by the resolutions brought about by the Great Debate years earlier.[193] The focus on sugar would eventually render all other facets of the Cuban economy underdeveloped and would be the ultimate legacy of the offensive.[191]
International diplomacy
Countries Che Guevara visited (red) and those in which he participated in armed revolution (green)
United Nations delegation
In December 1964, Che Guevara had emerged as a «revolutionary statesman of world stature» and thus traveled to New York City as head of the Cuban delegation to speak at the United Nations.[151] On 11 December 1964, during Guevara’s hour-long, impassioned address at the UN, he criticized the United Nations’ inability to confront the «brutal policy of apartheid» in South Africa, asking «Can the United Nations do nothing to stop this?».[194] Guevara then denounced the United States policy towards their black population, stating:
Those who kill their own children and discriminate daily against them because of the color of their skin; those who let the murderers of blacks remain free, protecting them, and furthermore punishing the black population because they demand their legitimate rights as free men—how can those who do this consider themselves guardians of freedom?[194]
An indignant Guevara ended his speech by reciting the Second Declaration of Havana, decreeing Latin America a «family of 200 million brothers who suffer the same miseries».[194] This «epic», Guevara declared, would be written by the «hungry Indian masses, peasants without land, exploited workers, and progressive masses». To Guevara the conflict was a struggle of masses and ideas, which would be carried forth by those «mistreated and scorned by imperialism» who were previously considered «a weak and submissive flock». With this «flock», Guevara now asserted, «Yankee monopoly capitalism» now terrifyingly saw their «gravediggers».[194] It would be during this «hour of vindication», Guevara pronounced, that the «anonymous mass» would begin to write its own history «with its own blood» and reclaim those «rights that were laughed at by one and all for 500 years». Guevara closed his remarks to the General Assembly by hypothesizing that this «wave of anger» would «sweep the lands of Latin America» and that the labor masses who «turn the wheel of history» were now, for the first time, «awakening from the long, brutalizing sleep to which they had been subjected».[194]
Guevara later learned there had been two failed attempts on his life by Cuban exiles during his stop at the UN complex.[195] The first from Molly Gonzales, who tried to break through barricades upon his arrival with a seven-inch hunting knife, and later during his address by Guillermo Novo, who fired a timer-initiated bazooka from a boat in the East River at the United Nations Headquarters, but missed and was off target. Afterwards Guevara commented on both incidents, stating that «it is better to be killed by a woman with a knife than by a man with a gun», while adding with a languid wave of his cigar that the explosion had «given the whole thing more flavor».[195]
Walking through Red Square in Moscow, November 1964
While in New York, Guevara appeared on the CBS Sunday news program Face the Nation,[196] and met with a wide range of people, from United States Senator Eugene McCarthy[197] to associates of Malcolm X. The latter expressed his admiration, declaring Guevara «one of the most revolutionary men in this country right now» while reading a statement from him to a crowd at the Audubon Ballroom.[198]
World travel
On 17 December, Guevara left New York for Paris, France, and from there embarked on a three-month world tour that included visits to the People’s Republic of China, North Korea, the United Arab Republic, Algeria, Ghana, Guinea, Mali, Dahomey, Congo-Brazzaville, and Tanzania, with stops in Ireland and Prague. While in Ireland, Guevara embraced his own Irish heritage, celebrating Saint Patrick’s Day in Limerick.[199] He wrote to his father on this visit, humorously stating «I am in this green Ireland of your ancestors. When they found out, the television [station] came to ask me about the Lynch genealogy, but in case they were horse thieves or something like that, I didn’t say much.»[200]
During Guevara’s time in Algeria he was interviewed by Spanish poet Juan Goytisolo inside the Cuban embassy. During the interview Guevara noticed a book by openly gay Cuban writer Virgilio Piñera that was sitting on the table next to him. When he noticed it he threw the book against the wall and yelled «how dare you have in our embassy a book by this foul faggot?».[201][202][203] This moment has been marked as a turn in Juan Goytisolo’s personal identity as it influenced him to slowly come out of the closet as gay and begin to sympathize with the LGBT citizens of Cuba.[204] This moment has also been marked for its significance in the Cuban government’s slow and ultimately final ousting of Virgilio Piñera from official literary discourse in Cuba. Piñera had originally been regarded as an important dramatist of the Cuban Revolution but had later become slowly condemned and finally arrested.[203]
During this voyage, he wrote a letter to Carlos Quijano, editor of a Uruguayan weekly, which was later retitled Socialism and Man in Cuba.[162] Outlined in the treatise was Guevara’s summons for the creation of a new consciousness, a new status of work, and a new role of the individual. He also laid out the reasoning behind his anti-capitalist sentiments, stating:
The laws of capitalism, blind and invisible to the majority, act upon the individual without his thinking about it. He sees only the vastness of a seemingly infinite horizon before him. That is how it is painted by capitalist propagandists, who purport to draw a lesson from the example of Rockefeller—whether or not it is true—about the possibilities of success. The amount of poverty and suffering required for the emergence of a Rockefeller, and the amount of depravity that the accumulation of a fortune of such magnitude entails, are left out of the picture, and it is not always possible to make the people in general see this.[162]
Guevara ended the essay by declaring that «the true revolutionary is guided by a great feeling of love» and beckoning on all revolutionaries to «strive every day so that this love of living humanity will be transformed into acts that serve as examples», thus becoming «a moving force».[162] The genesis for Guevara’s assertions relied on the fact that he believed the example of the Cuban Revolution was «something spiritual that would transcend all borders».[38]
Visit to Algeria and political turn
In Algiers, Algeria, on 24 February 1965, Guevara made what turned out to be his last public appearance on the international stage when he delivered a speech at an economic seminar on Afro-Asian solidarity.[205][206] He specified the moral duty of the socialist countries, accusing them of tacit complicity with the exploiting Western countries. He proceeded to outline a number of measures which he said the communist-bloc countries must implement in order to accomplish the defeat of imperialism.[207] Having criticized the Soviet Union (the primary financial backer of Cuba) in such a public manner, he returned to Cuba on 14 March to a solemn reception by Fidel and Raúl Castro, Osvaldo Dorticós, and Carlos Rafael Rodríguez at the Havana airport.
As revealed in his last public speech in Algiers, Guevara had come to view the Northern Hemisphere, led by the U.S. in the West and the Soviet Union in the East, as the exploiter of the Southern Hemisphere. He strongly supported communist North Vietnam in the Vietnam War, and urged the peoples of other developing countries to take up arms and create «many Vietnams».[208] Che’s denunciations of the Soviets made him popular among intellectuals and artists of the Western European left who had lost faith in the Soviet Union, while his condemnation of imperialism and call to revolution inspired young radical students in the United States, who were impatient for societal change.[209]
In Guevara’s private writings from this time (since released), he displays his growing criticism of the Soviet political economy, believing that the Soviets had «forgotten Marx».[210] This led Guevara to denounce a range of Soviet practices including what he saw as their attempt to «air-brush the inherent violence of class struggle integral to the transition from capitalism to socialism», their «dangerous» policy of peaceful co-existence with the United States, their failure to push for a «change in consciousness» towards the idea of work, and their attempt to «liberalize» the socialist economy. Guevara wanted the complete elimination of money, interest, commodity production, the market economy, and «mercantile relationships»: all conditions that the Soviets argued would only disappear when world communism was achieved.[210] Disagreeing with this incrementalist approach, Guevara criticized the Soviet Manual of Political Economy, correctly predicting that if the Soviet Union did not abolish the law of value (as Guevara desired), it would eventually return to capitalism.[210]
Two weeks after his Algiers speech and his return to Cuba, Guevara dropped out of public life and then vanished altogether.[211] His whereabouts were a great mystery in Cuba, as he was generally regarded as second in power to Castro himself. His disappearance was variously attributed to the failure of the Cuban industrialization scheme he had advocated while minister of industries, to pressure exerted on Castro by Soviet officials who disapproved of Guevara’s pro-Chinese communist stance on the Sino-Soviet split, and to serious differences between Guevara and the pragmatic Castro regarding Cuba’s economic development and ideological line.[212] Pressed by international speculation regarding Guevara’s fate, Castro stated on 16 June 1965, that the people would be informed when Guevara himself wished to let them know. Still, rumors spread both inside and outside Cuba concerning the missing Guevara’s whereabouts.
There are various rumors from retired Cuban officials who were around the Castro brothers that the Castro brothers and Guevara had a staunch disagreement after Guevara’s Algiers speech. Intelligence files from the East German embassy in Cuba detail various heated exchanges between Fidel Castro and Che Guevara after Guevara’s return from Africa. Whether Castro disagreed with Guevara’s criticisms of the Soviet Union or just found them unproductive to express on the world stage remains unclear.[213]
On 3 October 1965, Castro publicly revealed an undated letter purportedly written to him by Guevara around seven months earlier which was later titled Che Guevara’s «farewell letter». In the letter, Guevara reaffirmed his enduring solidarity with the Cuban Revolution but declared his intention to leave Cuba to fight for the revolutionary cause abroad. Additionally, he resigned from all his positions in the Cuban government and communist party, and renounced his honorary Cuban citizenship.[214]
Congo Crisis
Military involvement
37-year-old Guevara, holding a Congolese baby and standing with a fellow Afro-Cuban soldier in the Congo Crisis, 1965
I tried to make them understand that the real issue was not the liberation of any given state, but a common war against the common master, who was one and the same in Mozambique and in Malawi, in Rhodesia and in South Africa, in the Congo and in Angola, but not one of them agreed.
—Che Guevara, in February 1965, after meeting with various African liberation movement leaders in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania[215]
In early 1965, Guevara went to Africa to offer his knowledge and experience as a guerrilla to the ongoing conflict in the Congo. According to Algerian President Ahmed Ben Bella, Guevara thought that Africa was imperialism’s weak link and so had enormous revolutionary potential.[216] Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had fraternal relations with Che since his 1959 visit, saw Guevara’s plan to fight in Congo as «unwise» and warned that he would become a «Tarzan» figure, doomed to failure.[217] Despite the warning, Guevara traveled to Congo using the alias Ramón Benítez.[218] He led the Cuban operation in support of the Marxist Simba movement, which had emerged from the ongoing Congo conflict. Guevara, his second-in-command Víctor Dreke, and 12 other Cuban expeditionaries arrived in Congo on 24 April 1965, and a contingent of approximately 100 Afro-Cubans joined them soon afterward.[219][220] For a time, they collaborated with guerrilla leader Laurent-Désiré Kabila, who had helped supporters of the overthrown prime minister Patrice Lumumba to lead an unsuccessful revolt months earlier. As an admirer of the late Lumumba, Guevara declared that his «murder should be a lesson for all of us».[221] Guevara, with limited knowledge of Swahili and the local languages, was assigned a teenage interpreter, Freddy Ilanga. Over the course of seven months, Ilanga grew to «admire the hard-working Guevara», who «showed the same respect to black people as he did to whites».[222] Guevara soon became disillusioned with the poor discipline of Kabila’s troops and later dismissed him, stating «nothing leads me to believe he is the man of the hour».[223]
As an additional obstacle, white mercenary troops of the Congo National Army, led by Mike Hoare and supported by anti-Castro Cuban pilots and the CIA, thwarted Guevara’s movements from his base camp in the mountains near the village of Fizi on Lake Tanganyika in southeast Congo. They were able to monitor his communications and so pre-empted his attacks and interdicted his supply lines. Although Guevara tried to conceal his presence in Congo, the United States government knew his location and activities. The National Security Agency was intercepting all of his incoming and outgoing transmissions via equipment aboard the USNS Private Jose F. Valdez, a floating listening post that continuously cruised the Indian Ocean off Dar es Salaam for that purpose.[224]
Listening to a Zenith Trans-Oceanic shortwave radio receiver are (seated from the left) Rogelio Oliva, José María Martínez Tamayo (known as «Mbili» in the Congo and «Ricardo» in Bolivia), and Guevara. Standing behind them is Roberto Sánchez («Lawton» in Cuba and «Changa» in the Congo), 1965.
Guevara’s aim was to export the revolution by instructing local anti-Mobutu Simba fighters in Marxist ideology and foco theory strategies of guerrilla warfare. In his Congo Diary book, he cites a combination of incompetence, intransigence, and infighting among the Congolese rebels as key reasons for the revolt’s failure.[225] Later that year, on 20 November 1965, suffering from dysentery and acute asthma, and disheartened after seven months of defeats and inactivity, Guevara left Congo with the six Cuban survivors of his 12-man column. Guevara stated that he had planned to send the wounded back to Cuba and fight in the Congo alone until his death, as a revolutionary example. But after being urged by his comrades, and two Cuban emissaries personally sent by Castro, at the last moment he reluctantly agreed to leave Africa. During that day and night, Guevara’s forces quietly took down their base camp, burned their huts, and destroyed or threw weapons into Lake Tanganyika that they could not take with them, before crossing the border by boat into Tanzania at night and traveling by land to Dar es Salaam. In speaking about his experience in Congo months later, Guevara concluded that he left rather than fight to the death because: «The human element failed. There is no will to fight. The [rebel] leaders are corrupt. In a word … there was nothing to do.»[226] Guevara also declared that «we can not liberate, all by ourselves, a country that does not want to fight.»[227] A few weeks later, he wrote the preface to the diary he kept during the Congo venture, that began: «This is the story of a failure.»[228]
Flight from the Congo
Guevara was reluctant to return to Cuba, because Castro had already made public Guevara’s «farewell letter»—a letter intended to only be revealed in the case of his death—wherein he severed all ties in order to devote himself to revolution throughout the world.[229] As a result, Guevara spent the next six months living clandestinely at the Cuban embassy in Dar es Salaam and later at a Cuban safehouse in Prague.[230] While in Europe, Guevara made a secret visit to former Argentine president Juan Perón who lived in exile in Francoist Spain where he confided in Perón about his new plan to formulate a communist revolution to bring all of Latin America under socialist control. Perón warned Guevara that his plans for implementing a communist revolution throughout Latin America, starting with Bolivia, would be suicidal and futile, but Guevara’s mind was already made up. Later, Perón remarked that Guevara was «an immature utopian… but one of us. I am happy for it to be so because he is giving the Yankees a real headache.»[231]
During this time abroad, Guevara compiled his memoirs of the Congo experience and wrote drafts of two more books, one on philosophy and the other on economics. As Guevara prepared for Bolivia, he secretly traveled back to Cuba on 21 July 1966 to visit Castro, as well as to see his wife and to write a last letter to his five children to be read upon his death, which ended with him instructing them:
Above all, always be capable of feeling deeply any injustice committed against anyone, anywhere in the world. This is the most beautiful quality in a revolutionary.[232]
Bolivian insurgency
Departure to Bolivia
Guevara’s 1966 passport featuring him in disguise with a false name.
In late 1966, Guevara’s location was still not public knowledge, although representatives of Mozambique’s independence movement, the FRELIMO, reported that they met with Guevara in Dar es Salaam regarding his offer to aid in their revolutionary project, an offer which they ultimately rejected.[233] In a speech at the 1967 International Workers’ Day rally in Havana, the acting minister of the armed forces, Major Juan Almeida Bosque, announced that Guevara was «serving the revolution somewhere in Latin America».[citation needed]. In his book Opération Condor published in 2020, French journalist Pablo Daniel Magee reconstitutes the first incursion of Che Guevara in Bolivia on 3 October 1966, based on top-secret documents kept in the UNESCO protected Archives of Terror, in Paraguay.
Before he departed for Bolivia, Guevara altered his appearance by shaving off his beard and much of his hair, also dying it grey so that he was unrecognizable as Che Guevara.[234] On 3 November 1966, Guevara secretly arrived in La Paz on a flight from Montevideo, under the false name Adolfo Mena González, posing as a middle-aged Uruguayan businessman working for the Organization of American States.[235]
Three days after his arrival in Bolivia, Guevara left La Paz for the rural south east region of the country to form his guerrilla army. Guevara’s first base camp was located in the montane dry forest in the remote Ñancahuazú region. Training at the camp in the Ñancahuazú valley proved to be hazardous, and little was accomplished in way of building a guerrilla army. The Argentine-born East German operative Tamara Bunke, better known by her nom de guerre «Tania», had been installed as Che’s primary agent in La Paz.[236][237]
Ñancahuazú Guerrilla
Guevara in rural Bolivia, shortly before his death (1967)
Guevara’s guerrilla force, numbering about 50 men[238] and operating as the ELN (Ejército de Liberación Nacional de Bolivia, «National Liberation Army of Bolivia»), was well equipped and scored a number of early successes against Bolivian army regulars in the difficult terrain of the mountainous Camiri region during the early months of 1967. As a result of Guevara’s units winning several skirmishes against Bolivian troops in the spring and summer of 1967, the Bolivian government began to overestimate the true size of the guerrilla force.[239]
Researchers hypothesize that Guevara’s plan for fomenting a revolution in Bolivia failed for an array of reasons:
- Guevara had expected assistance and cooperation from the local dissidents that he did not receive, nor did he receive support from Bolivia’s Communist Party under the leadership of Mario Monje, which was oriented toward Moscow rather than Havana. In Guevara’s own diary captured after his death, he wrote about the Communist Party of Bolivia, which he characterized as «distrustful, disloyal and stupid».[240]
- He had expected to deal only with the Bolivian military, who were poorly trained and equipped, and was unaware that the United States government had sent a team of the CIA’s Special Activities Division commandos and other operatives into Bolivia to aid the anti-insurrection effort. The Bolivian Army was also trained, advised, and supplied by U.S. Army Special Forces, including an elite battalion of U.S. Rangers trained in jungle warfare that set up camp in La Esperanza, a small settlement close to the location of Guevara’s guerrillas.[241]
- He had expected to remain in radio contact with Havana. The two shortwave radio transmitters provided to him by Cuba were faulty. Thus, the guerrillas were unable to communicate and be resupplied, leaving them isolated and stranded.
In addition, Guevara’s known preference for confrontation rather than compromise, which had previously surfaced during his guerrilla warfare campaign in Cuba, contributed to his inability to develop successful working relationships with local rebel leaders in Bolivia, just as it had in the Congo.[242] This tendency had existed in Cuba, but had been kept in check by the timely interventions and guidance of Fidel Castro.[243]
The result was that Guevara was unable to attract inhabitants of the local area to join his militia during the eleven months he attempted recruitment. Many of the inhabitants willingly informed the Bolivian authorities and military about the guerrillas and their movements in the area. Near the end of the Bolivian venture, Guevara wrote in his diary: «Talking to these peasants is like talking to statues. They do not give us any help. Worse still, many of them are turning into informants.»[244]
Félix Rodríguez, a Cuban exile turned CIA Special Activities Division operative, advised Bolivian troops during the hunt for Guevara in Bolivia.[245] In addition, the 2007 documentary My Enemy’s Enemy alleges that Nazi war criminal Klaus Barbie advised and possibly helped the CIA orchestrate Guevara’s eventual capture.[246]
Capture
On 7 October 1967, an informant apprised the Bolivian Special Forces of the location of Guevara’s guerrilla encampment in the Yuro ravine.[247] On the morning of 8 October, they encircled the area with two companies numbering 180 soldiers and advanced into the ravine triggering a battle where Guevara was wounded and taken prisoner while leading a detachment with Simeon Cuba Sarabia.[248] Che’s biographer Jon Lee Anderson reports Bolivian Sergeant Bernardino Huanca’s account: that as the Bolivian Rangers approached, a twice-wounded Guevara, his gun rendered useless, threw up his arms in surrender and shouted to the soldiers: «Do not shoot! I am Che Guevara and I am worth more to you alive than dead.»[249]
There was no person more feared by the company (CIA) than Che Guevara because he had the capacity and charisma necessary to direct the struggle against the political repression of the traditional hierarchies in power in the countries of Latin America.
—Philip Agee, CIA employee from 1957 to 1968.[250]
Guevara was tied up and taken to a dilapidated mud schoolhouse in the nearby village of La Higuera on the evening of 8 October. For the next half-day, Guevara refused to be interrogated by Bolivian officers and only spoke quietly to Bolivian soldiers. One of those Bolivian soldiers, a helicopter pilot named Jaime Nino de Guzman, describes Che as looking «dreadful». According to Guzman, Guevara was shot through the right calf, his hair was matted with dirt, his clothes were shredded, and his feet were covered in rough leather sheaths. Despite his haggard appearance, he recounts that «Che held his head high, looked everyone straight in the eyes and asked only for something to smoke.» De Guzman states that he «took pity» and gave him a small bag of tobacco for his pipe, and that Guevara then smiled and thanked him.[251] Later on the night of 8 October, Guevara—despite having his hands tied—kicked a Bolivian army officer, named Captain Espinosa, against a wall after the officer entered the schoolhouse and tried to snatch Guevara’s pipe from his mouth as a souvenir while he was still smoking it.[252] In another instance of defiance, Guevara spat in the face of Bolivian Rear Admiral Horacio Ugarteche, who attempted to question Guevara a few hours before his execution.[252]
The following morning on 9 October, Guevara asked to see the school teacher of the village, a 22-year-old woman named Julia Cortez. She later stated that she found Guevara to be an «agreeable looking man with a soft and ironic glance» and that during their conversation she found herself «unable to look him in the eye» because his «gaze was unbearable, piercing, and so tranquil».[252] During their short conversation, Guevara pointed out to Cortez the poor condition of the schoolhouse, stating that it was «anti-pedagogical» to expect campesino students to be educated there, while «government officials drive Mercedes cars»; Guevara said «that’s what we are fighting against».[252]
Execution
Later that morning on 9 October, Bolivian President René Barrientos ordered that Guevara be killed. The order was relayed to the unit holding Guevara by Félix Rodríguez reportedly despite the United States government’s desire that Guevara be taken to Panama for further interrogation.[253] The executioner who volunteered to kill Guevara was Mario Terán, a 27-year-old sergeant in the Bolivian army who while half-drunk requested to shoot Guevara because three of his friends from B Company, all with the same first name of «Mario», had been killed in a firefight several days earlier with Guevara’s band of guerrillas.[10] To make the bullet wounds appear consistent with the story that the Bolivian government planned to release to the public, Félix Rodríguez ordered Terán not to shoot Guevara in the head, but to aim carefully to make it appear that Guevara had been killed in action during a clash with the Bolivian army.[254] Gary Prado, the Bolivian captain in command of the army company that captured Guevara, said that the reasons Barrientos ordered the immediate execution of Guevara were so there could be no possibility for Guevara to escape from prison, and also so there could be no drama of a public trial where adverse publicity might happen.[255]
About 30 minutes before Guevara was killed, Félix Rodríguez attempted to question him about the whereabouts of other guerrilla fighters who were currently at large, but Guevara continued to remain silent. Rodríguez, assisted by a few Bolivian soldiers, helped Guevara to his feet and took him outside the hut to parade him before other Bolivian soldiers where he posed with Guevara for a photo opportunity where one soldier took a photograph of Rodríguez and other soldiers standing alongside Guevara. Afterwards, Rodríguez told Guevara that he was going to be executed. A little later, Guevara was asked by one of the Bolivian soldiers guarding him if he was thinking about his own immortality. «No» he replied, «I’m thinking about the immortality of the revolution».[256] A few minutes later, Sergeant Terán entered the hut to shoot him, whereupon Guevara reportedly stood up and spoke to Terán what were his last words: «I know you’ve come to kill me. Shoot, coward! You are only going to kill a man!» Terán hesitated, then pointed his self-loading M2 carbine[257] at Guevara and opened fire, hitting him in the arms and legs.[258] Then, as Guevara writhed on the ground, apparently biting one of his wrists to avoid crying out, Terán fired another burst, fatally wounding him in the chest. Guevara was pronounced dead at 1:10 pm local time according to Rodríguez.[258] In all, Guevara was shot nine times by Terán. This included five times in his legs, once in the right shoulder and arm, and once in the chest and throat.[252]
Months earlier, during his last public declaration to the Tricontinental Conference,[208] Guevara had written his own epitaph, stating: «Wherever death may surprise us, let it be welcome, provided that this our battle cry may have reached some receptive ear and another hand may be extended to wield our weapons.»[259]
Aftermath
The day after his execution on 10 October 1967, Guevara’s corpse was displayed to the news media in the laundry house of the Vallegrande hospital. (photo by Freddy Alborta)
Face Side angle Shoes
After his execution, Guevara’s body was lashed to the landing skids of a helicopter and flown to nearby Vallegrande, where photographs were taken of him lying on a concrete slab in the laundry room of the Nuestra Señora de Malta.[260] Several witnesses were called to confirm his identity, key amongst them the British journalist Richard Gott, the only witness to have met Guevara when he was alive. Put on display, as hundreds of local residents filed past the body, Guevara’s corpse was considered by many to represent a «Christ-like» visage, with some even surreptitiously clipping locks of his hair as divine relics.[261] Such comparisons were further extended when English art critic John Berger, two weeks later upon seeing the post-mortem photographs, observed that they resembled two famous paintings: Rembrandt’s The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp and Andrea Mantegna’s Lamentation over the Dead Christ.[262] There were also four correspondents present when Guevara’s body arrived in Vallegrande, including Björn Kumm of the Swedish Aftonbladet, who described the scene in an 11 November 1967, exclusive for The New Republic.[263]
A declassified memorandum dated 11 October 1967 to United States President Lyndon B. Johnson from his National Security Advisor Walt Rostow, called the decision to kill Guevara «stupid» but «understandable from a Bolivian standpoint».[264] After the execution, Rodríguez took several of Guevara’s personal items, including a watch which he continued to wear many years later, often showing them to reporters during the ensuing years.[265] Today, some of these belongings, including his flashlight, are on display at the CIA.[266] After a military doctor dismembered his hands, Bolivian army officers transferred Guevara’s body to an undisclosed location and refused to reveal whether his remains had been buried or cremated. The hands were sent to Buenos Aires for fingerprint identification. They were later sent to Cuba.[267]
Plaza de la Revolución, in Havana, Cuba. Aside the Ministry of the Interior building where Guevara once worked is a 5-story steel outline of his face. Under the image is Guevara’s motto, the Spanish phrase: «Hasta la Victoria Siempre» (English: Until Victory, always).
On 15 October in Havana, Fidel Castro publicly acknowledged that Guevara was dead and proclaimed three days of public mourning throughout Cuba.[268] On 18 October, Castro addressed a crowd of one million mourners in Havana’s Plaza de la Revolución and spoke about Guevara’s character as a revolutionary.[269] Fidel Castro closed his impassioned eulogy thus:
If we wish to express what we want the men of future generations to be, we must say: Let them be like Che! If we wish to say how we want our children to be educated, we must say without hesitation: We want them to be educated in Che’s spirit! If we want the model of a man, who does not belong to our times but to the future, I say from the depths of my heart that such a model, without a single stain on his conduct, without a single stain on his action, is Che![270]
Also removed when Guevara was captured were his 30,000-word, hand-written diary, a collection of his personal poetry, and a short story he had authored about a young communist guerrilla who learns to overcome his fears.[271] His diary documented events of the guerrilla campaign in Bolivia,[272] with the first entry on 7 November 1966, shortly after his arrival at the farm in Ñancahuazú, and the last dated 7 October 1967, the day before his capture. The diary tells how the guerrillas were forced to begin operations prematurely because of discovery by the Bolivian Army, explains Guevara’s decision to divide the column into two units that were subsequently unable to re-establish contact, and describes their overall unsuccessful venture. It also records the rift between Guevara and the Communist Party of Bolivia that resulted in Guevara having significantly fewer soldiers than originally expected, and shows that Guevara had a great deal of difficulty recruiting from the local populace, partly because the guerrilla group had learned Quechua, unaware that the local language was actually a Tupi–Guarani language.[273] As the campaign drew to an unexpected close, Guevara became increasingly ill. He endured ever-worsening bouts of asthma, and most of his last offensives were carried out in an attempt to obtain medicine.[274] The Bolivian diary was quickly and crudely translated by Ramparts magazine and circulated around the world.[275] There are at least four additional diaries in existence—those of Israel Reyes Zayas (Alias «Braulio»), Harry Villegas Tamayo («Pombo»), Eliseo Reyes Rodriguez («Rolando»)[236] and Dariel Alarcón Ramírez («Benigno»)[276]—each of which reveals additional aspects of the events.
French intellectual Régis Debray, who was captured in April 1967 while with Guevara in Bolivia, gave an interview from prison in August 1968, in which he enlarged on the circumstances of Guevara’s capture. Debray, who had lived with Guevara’s band of guerrillas for a short time, said that in his view they were «victims of the forest» and thus «eaten by the jungle».[277] Debray described a destitute situation where Guevara’s men suffered malnutrition, lack of water, absence of shoes, and only possessed six blankets for 22 men. Debray recounts that Guevara and the others had been suffering an «illness» which caused their hands and feet to swell into «mounds of flesh» to the point where you could not discern the fingers on their hands. Debray described Guevara as «optimistic about the future of Latin America» despite the futile situation, and remarked that Guevara was «resigned to die in the knowledge that his death would be a sort of renaissance», noting that Guevara perceived death «as a promise of rebirth» and «ritual of renewal».[277]
Legacy
Political left
A stylized graphic of Guevara’s face on a flag above the words «El Che Vive!» (Che Lives!)
Radical left wing activists responded to Guevara’s apparent indifference to rewards and glory, and concurred with Guevara’s sanctioning of violence as a necessity to instill socialist ideals.[278] Even in the United States, the government which Guevara so vigorously denounced, students began to emulate his style of dress, donning military fatigues, berets, and growing their hair and beards to show that they too were opponents of U.S. foreign policy.[279] For instance, the Black Panthers began to style themselves «Che-type» while adopting his trademark black beret, while Arab guerrillas began to name combat operations in his honor.[280] Addressing the wide-ranging flexibility of his legacy, Trisha Ziff, director of the 2008 documentary Chevolution, has remarked that «Che Guevara’s significance in modern times is less about the man and his specific history, and more about the ideals of creating a better society.»[281] In a similar vein, the Chilean writer Ariel Dorfman has suggested Guevara’s enduring appeal might be because «to those who will never follow in his footsteps, submerged as they are in a world of cynicism, self-interest and frantic consumption, nothing could be more vicariously gratifying than Che’s disdain for material comfort and everyday desires.»[282]
To a certain extent, the belief of Guevara’s of a metaphorical resurrection after death came true. After pictures of the dead Guevara began being circulated and the circumstances of his death were being debated, Che’s legend began to spread. Demonstrations in protest against his «assassination» occurred throughout the world, and articles, tributes, and poems were written about his life and death.[283] Rallies in support of Guevara were held from «Mexico to Santiago, Algiers to Angola, and Cairo to Calcutta».[284] The population of Budapest and Prague lit candles to honor Guevara’s passing; and the picture of a smiling Che appeared in London and Paris.[285] When a few months later riots broke out in Berlin, France, and Chicago, and the unrest spread to the American college campuses, young men and women wore Che Guevara T-shirts and carried his pictures during their protest marches. In the view of military historian Erik Durschmied: «In those heady months of 1968, Che Guevara was not dead. He was very much alive.»[286]
Retrieval of remains
In late 1995, the retired Bolivian General Mario Vargas revealed to Jon Lee Anderson, author of Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life, that Guevara’s corpse lay near a Vallegrande airstrip. The result was a multi-national search for the remains, which lasted more than a year. In July 1997 a team of Cuban geologists and Argentine forensic anthropologists discovered the remnants of seven bodies in two mass graves, including one man without hands (as Guevara would have been). Bolivian government officials with the Ministry of Interior later identified the body as Guevara when the excavated teeth «perfectly matched» a plaster mold of Che’s teeth made in Cuba prior to his Congolese expedition. The «clincher» then arrived when Argentine forensic anthropologist Alejandro Inchaurregui inspected the inside hidden pocket of a blue jacket dug up next to the handless cadaver and found a small bag of pipe tobacco. Nino de Guzman, the Bolivian helicopter pilot who had given Che a small bag of tobacco, later remarked that he «had serious doubts» at first and «thought the Cubans would just find any old bones and call it Che»; but «after hearing about the tobacco pouch, I have no doubts.»[251] On 17 October 1997, Guevara’s remains, with those of six of his fellow combatants, were laid to rest with military honors in a specially built mausoleum in the Cuban city of Santa Clara, where he had commanded over the decisive military victory of the Cuban Revolution.[287]
In July 2008, the Bolivian government of Evo Morales unveiled Guevara’s formerly-sealed diaries composed in two frayed notebooks, along with a logbook and several black-and-white photographs. At this event Bolivia’s vice-minister of culture, Pablo Groux, expressed that there were plans to publish photographs of every handwritten page later in the year.[288] Meanwhile, in August 2009 anthropologists working for Bolivia’s Justice Ministry discovered and unearthed the bodies of five of Guevara’s fellow guerrillas near the Bolivian town of Teoponte.[289]
The discovery of Che’s remains metonymically activated a series of interlinked associations—rebel, martyr, rogue figure from a picaresque adventure, savior, renegade, extremist—in which there was no fixed divide among them. The current court of opinion places Che on a continuum that teeters between viewing him as a misguided rebel, a coruscatingly brilliant guerrilla philosopher, a poet-warrior jousting at windmills, a brazen warrior who threw down the gauntlet to the bourgeoisie, the object of fervent paeans to his sainthood, or a mass murderer clothed in the guise of an avenging angel whose every action is imbricated in violence—the archetypal Fanatical Terrorist.
— Dr. Peter McLaren, author of Che Guevara, Paulo Freire, and the Pedagogy of Revolution[290]
Biographical debate
Guevara’s life and legacy remain contentious. The perceived contradictions of his ethos at various points in his life have created a complex character of duality, one who was «able to wield the pen and submachine gun with equal skill», while prophesying that «the most important revolutionary ambition was to see man liberated from his alienation».[291][292] Guevara’s paradoxical standing is further complicated by his array of seemingly diametrically opposed qualities. A secular humanist and sympathetic practitioner of medicine who did not hesitate to shoot his enemies, a celebrated internationalist leader who advocated violence to enforce a utopian philosophy of the collective good, an idealistic intellectual who loved literature but refused to allow dissent, an anti-imperialist Marxist insurgent who was radically willing to forge a poverty-less new world on the apocalyptic ashes of the old one, and finally, an outspoken anti-capitalist whose image has been commoditized. Che’s history continues to be rewritten and re-imagined.[293][294] Moreover, sociologist Michael Löwy contends that the many facets of Guevara’s life (i.e. doctor and economist, revolutionary and banker, military theoretician and ambassador, deep thinker and political agitator) illuminated the rise of the «Che myth», allowing him to be invariably crystallized in his many metanarrative roles as a «Red Robin Hood, Don Quixote of communism, new Garibaldi, Marxist Saint Just, Cid Campeador of the Wretched of the Earth, Sir Galahad of the beggars … and Bolshevik devil who haunts the dreams of the rich, kindling braziers of subversion all over the world».[291]
As such, various notable individuals have lauded Guevara; for example, Nelson Mandela referred to him as «an inspiration for every human being who loves freedom»,[250] while Jean-Paul Sartre described him as «not only an intellectual but also the most complete human being of our age».[295] Others who have expressed their admiration include authors Graham Greene, who remarked that Guevara «represented the idea of gallantry, chivalry, and adventure»,[296] and Susan Sontag, who supposed that «[Che’s] goal was nothing less than the cause of humanity itself.»[297] In the Pan-African community philosopher Frantz Fanon professed Guevara to be «the world symbol of the possibilities of one man»,[298] while Black Power leader Stokely Carmichael eulogized that «Che Guevara is not dead, his ideas are with us.»[299] Praise has been reflected throughout the political spectrum, with libertarian theorist Murray Rothbard extolling Guevara as a «heroic figure» who «more than any man of our epoch or even of our century, was the living embodiment of the principle of revolution»,[300] while journalist Christopher Hitchens reminisced that «[Che’s] death meant a lot to me and countless like me at the time, he was a role model, albeit an impossible one for us bourgeois romantics insofar as he went and did what revolutionaries were meant to do—fought and died for his beliefs.»[301]
Conversely, Jacobo Machover, an exiled opposition author, dismisses all praise of Guevara and portrays him as a callous executioner.[302] Exiled former Cuban prisoners have expressed similar opinions, among them Armando Valladares, who declared Guevara «a man full of hatred» who executed dozens without trial,[303] and Carlos Alberto Montaner, who asserted that Guevara possessed «a Robespierre mentality», wherein cruelty against the revolution’s enemies was a virtue.[304] Álvaro Vargas Llosa of the Independent Institute has hypothesized that Guevara’s contemporary followers «delude themselves by clinging to a myth», describing Guevara as a «Marxist Puritan» who employed his rigid power to suppress dissent, while also operating as a «cold-blooded killing machine».[172] Llosa also accuses Guevara’s «fanatical disposition» as being the linchpin of the «Sovietization» of the Cuban revolution, speculating that he possessed a «total subordination of reality to blind ideological orthodoxy».[172] On a macro-level, Hoover Institution research fellow William Ratliff regards Guevara more as a creation of his historical environment, referring to him as a «fearless» and «head-strong Messiah-like figure», who was the product of a martyr-enamored Latin American culture which «inclined people to seek out and follow paternalistic miracle workers».[305] Ratliff further speculates that the economic conditions in the region suited Guevara’s commitment to «bring justice to the downtrodden by crushing centuries-old tyrannies»; describing Latin America as being plagued by what Moisés Naím referred to as the «legendary malignancies» of inequality, poverty, dysfunctional politics and malfunctioning institutions.[305]
In a mixed assessment, British historian Hugh Thomas opined that Guevara was a «brave, sincere and determined man who was also obstinate, narrow, and dogmatic».[306] At the end of his life, according to Thomas, «he seems to have become convinced of the virtues of violence for its own sake», while «his influence over Castro for good or evil» grew after his death, as Fidel took up many of his views.[306] Similarly, the Cuban-American sociologist Samuel Farber lauds Che Guevara as «an honest and committed revolutionary», but also criticizes the fact that «he never embraced socialism in its most democratic essence».[307] Nevertheless, Guevara remains a national hero in Cuba, where his image adorns the 3 peso banknote and school children begin each morning by pledging «We will be like Che.»[308][309] In his homeland of Argentina, where high schools bear his name,[310] numerous Che museums dot the country and in 2008 a 12-foot (3.7 m) bronze statue of him was unveiled in the city of his birth, Rosario.[311] Guevara has been sanctified by some Bolivian campesinos[312] as «Saint Ernesto», who pray to him for assistance.[313] In contrast, Guevara remains a hated figure amongst many in the Cuban exile and Cuban American community of the United States, who view him as «the butcher of La Cabaña».[314] Despite this polarized status, a high-contrast monochrome graphic of Che’s face, created in 1968 by Irish artist Jim Fitzpatrick, became a universally merchandized and objectified image,[315][316] found on an endless array of items, including T-shirts, hats, posters, tattoos, and bikinis,[317] contributing to the consumer culture Guevara despised. Yet, he still remains a transcendent figure both in specifically political contexts[318] and as a wide-ranging popular icon of youthful rebellion.[301]
International honors
Guevara received several honors of state during his life.
- 1960: Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the White Lion[319]
- 1961: Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Southern Cross[320]
Archival media
Video footage
- Guevara addressing the United Nations General Assembly on 11 December 1964, (6:21), public domain footage uploaded by the UN, video clip
- Guevara interviewed by Face the Nation on 13 December 1964, (29:11), from CBS, video clip
- Guevara interviewed in 1964 on a visit to Dublin, Ireland, (2:53), English translation, from RTÉ Libraries and Archives, video clip
- Guevara interviewed in Paris and speaking French in 1964, (4:47), English subtitles, interviewed by Jean Dumur, video clip
- Guevara reciting a poem, (0:58), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara showing support for Fidel Castro, (0:22), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara speaking about labor, (0:28), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara speaking about the Bay of Pigs, (0:17), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara speaking against imperialism, (1:20), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, video clip
- Guevara visiting Algeria in 1963 and giving a speech in French, from the Algerian Cinema Archive, video clip
Audio recording
- Guevara interviewed on ABC’s Issues and Answers, (22:27), English translation, narrated by Lisa Howard, 24 March 1964, audio clip
List of English-language works
- A New Society: Reflections for Today’s World, Ocean Press, 1996, ISBN 1-875284-06-0
- Back on the Road: A Journey Through Latin America, Grove Press, 2002, ISBN 0-8021-3942-6
- Che Guevara, Cuba, and the Road to Socialism, Pathfinder Press, 1991, ISBN 0-87348-643-9
- Che Guevara on Global Justice, Ocean Press (AU), 2002, ISBN 1-876175-45-1
- Che Guevara: Radical Writings on Guerrilla Warfare, Politics and Revolution, Filiquarian Publishing, 2006, ISBN 1-59986-999-3
- Che Guevara Reader: Writings on Politics & Revolution, Ocean Press, 2003, ISBN 1-876175-69-9
- Che Guevara Speaks: Selected Speeches and Writings, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1980, ISBN 0-87348-602-1
- Che Guevara Talks to Young People, Pathfinder, 2000, ISBN 0-87348-911-X
- Che: The Diaries of Ernesto Che Guevara, Ocean Press (AU), 2008, ISBN 1-920888-93-4
- Colonialism is Doomed, Ministry of External Relations: Republic of Cuba, 1964, ASIN B0010AAN1K
- Congo Diary: The Story of Che Guevara’s «Lost» Year in Africa Ocean Press, 2011, ISBN 978-0-9804292-9-9
- Critical Notes on Political Economy: A Revolutionary Humanist Approach to Marxist Economics, Ocean Press, 2008, ISBN 1-876175-55-9
- Diary of a Combatant: The Diary of the Revolution that Made Che Guevara a Legend, Ocean Press, 2013, ISBN 978-0-9870779-4-3
- Episodes of the Cuban Revolutionary War, 1956–58, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1996, ISBN 0-87348-824-5
- Global Justice: Three Essays on Liberation and Socialism, Seven Stories Press, 2022, ISBN 1644211564
- Guerrilla Warfare: Authorized Edition, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-920888-28-4
- I Embrace You with All My Revolutionary Fervor: Letters 1947-1967, Seven Stories Press, 2021, ISBN 1644210959
- Latin America: Awakening of a Continent, Ocean Press, 2005, ISBN 1-876175-73-7
- Latin America Diaries: The Sequel to The Motorcycle Diaries, Ocean Press, 2011, ISBN 978-0-9804292-7-5
- Marx & Engels: An Introduction, Ocean Press, 2007, ISBN 1-920888-92-6
- Our America And Theirs: Kennedy And The Alliance For Progress, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-876175-81-8
- Reminiscences of the Cuban Revolutionary War: Authorized Edition, Ocean Press, 2005, ISBN 1-920888-33-0
- Self Portrait Che Guevara, Ocean Press (AU), 2004, ISBN 1-876175-82-6
- Socialism and Man in Cuba, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1989, ISBN 0-87348-577-7
- The African Dream: The Diaries of the Revolutionary War in the Congo, Grove Press, 2001, ISBN 0-8021-3834-9
- The Argentine, Ocean Press (AU), 2008, ISBN 1-920888-93-4
- The Awakening of Latin America: Writings, Letters and Speeches on Latin America, 1950–67, Ocean Press, 2012, ISBN 978-0-9804292-8-2
- The Bolivian Diary of Ernesto Che Guevara, Pathfinder Press, 1994, ISBN 0-87348-766-4
- The Great Debate on Political Economy, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-876175-54-0
- The Motorcycle Diaries: A Journey Around South America, London: Verso, 1996, ISBN 1-85702-399-4
- The Secret Papers of a Revolutionary: The Diary of Che Guevara, American Reprint Co, 1975, ASIN B0007GW08W
- To Speak the Truth: Why Washington’s «Cold War» Against Cuba Doesn’t End, Pathfinder, 1993, ISBN 0-87348-633-1
See also
References
- ^ «Che Guevara». archive.nytimes.com.
- ^ Partido Unido de la Revolución Socialista de Cuba, a.k.a. PURSC.
- ^ How to pronounce Che Guevara – Forvo features various sound clips of international Spanish speakers enunciating his name.
- ^ a b The date of birth recorded on his birth certificate was 14 June 1928, although one tertiary source, (Julia Constenla, quoted by Jon Lee Anderson), asserts that he was actually born on 14 May of that year. Constenla alleges that she was told by Che’s mother, Celia de la Serna, that she was already pregnant when she and Ernesto Guevara Lynch were married and that the date on the birth certificate of their son was forged to make it appear that he was born a month later than the actual date to avoid scandal. (Anderson 1997, pp. 3, 769.)
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 128.
- ^ a b c On Revolutionary Medicine Speech by Che Guevara to the Cuban Militia on 19 August 1960. «Because of the circumstances in which I traveled, first as a student and later as a doctor, I came into close contact with poverty, hunger and disease; with the inability to treat a child because of lack of money; with the stupefaction provoked by the continual hunger and punishment, to the point that a father can accept the loss of a son as an unimportant accident, as occurs often in the downtrodden classes of our American homeland. And I began to realize at that time that there were things that were almost as important to me as becoming famous or making a significant contribution to medical science: I wanted to help those people.»
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 90-91.
- ^ Beaubien, NPR Audio Report, 2009, 00:09–00:13.
- ^ a b c d e «Castro’s Brain», 1960.
- ^ a b c d e Taibo 1999, p. 267.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, pp. 69–70.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 526–530.
- ^ «On Development» Speech delivered by Che Guevara at the plenary session of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development in Geneva, Switzerland on 25 March 1964. «The inflow of capital from the developed countries is the prerequisite for the establishment of economic dependence. This inflow takes various forms: loans granted on onerous terms; investments that place a given country in the power of the investors; almost total technological subordination of the dependent country to the developed country; control of a country’s foreign trade by the big international monopolies; and in extreme cases, the use of force as an economic weapon in support of the other forms of exploitation.»
- ^ At the Afro-Asian Conference in Algeria A speech by Che Guevara to the Second Economic Seminar of Afro-Asian Solidarity in Algiers, Algeria on 24 February 1965.»The struggle against imperialism, for liberation from colonial or neocolonial shackles, which is being carried out by means of political weapons, arms, or a combination of the two, is not separate from the struggle against backwardness and poverty. Both are stages on the same road leading toward the creation of a new society of justice and plenty. … Ever since monopoly capital took over the world, it has kept the greater part of humanity in poverty, dividing all the profits among the group of the most powerful countries. The standard of living in those countries is based on the extreme poverty of our countries. To raise the living standards of the underdeveloped nations, therefore, we must fight against imperialism. … The practice of proletarian internationalism is not only a duty for the peoples struggling for a better future, it is also an inescapable necessity.»
- ^ Guevara was coordinating with African liberation movements in exile such as the MPLA in Angola and MNR in Congo-Brazzaville, while stating that Africa represented one of «the more important fields of struggle against all forms of exploitation existing in the world». Guevara then envisioned crafting an alliance with African leaders such as Ahmed Ben Bella in Algeria, Sékou Touré in Guinea, Kwame Nkrumah in Ghana, Julius Nyerere in Tanzania, and Gamal Abdel Nasser in Egypt, to foster a global dimension to his ensuing continental revolution in Latin America. See Anderson 1997, pp. 576, 584.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 4.
- ^ Footnote for Socialism and man in Cuba (1965): «Che argued that the full liberation of humankind is reached when work becomes a social duty carried out with complete satisfaction and sustained by a value system that contributes to the realization of conscious action in performing tasks. This could only be achieved by systematic education, acquired by passing through various stages in which collective action is increased. Che recognized that this to be difficult and time-consuming. In his desire to speed up this process, however, he developed methods of mobilizing people, bringing together their collective and individual interests. Among the most significant of these instruments were moral and material incentives, while deepening consciousness as a way of developing toward socialism. See Che’s speeches: Homage to Emulation Prize Winners (1962) and A New Attitude to Work (1964).»
- ^ Dorfman 1999.
- ^ Maryland Institute of Art, referenced at BBC News 26 May 2001.
- ^ In Spanish a person may carry the surname of his or her father as well as that of his or her mother, albeit in that order. Some people carry both, others only that of their father. In Guevara’s case, many people of Irish descent will add «Lynch» to emphasize his Irish relations. Others will add «de la Serna» to give respect to Guevara’s mother.
- ^ Guevara Lynch 2007, pp. i. «The father of Che Guevara, Ernesto Guevara Lynch was born in Argentina in 1900 of Irish and Basque origin.»
- ^ The Origins of Guevara’s Name — written in Spanish
- ^ Che’s last name Guevara derives from the Castilianized form of the Basque Gebara, a habitational name from the province of Álava, while his grandmother, Ana Lynch, was a descendant of Patrick Lynch, who emigrated from County Galway, Ireland in the 1740s.
- ^ Online Archive of California: Pinedo Family Papers from the Santa Clara University Library, 2015
- ^ Mercury News Fundraiser for Friends of Peralta Hacienda Historical Park by Angela Woodall, Oakland Tribune, 23 November 2010
- ^ Lavretsky 1976.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 23.
- ^ Argentina: Che’s Red Mother Time Magazine, 14 July 1961.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 22–23.
- ^ Guevara Lynch, Ernesto. Young Che: Memories of Che Guevara by His Father. Publication Date 14 September 2011, Vintage
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 8.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 24.
- ^ Argentine Rugby Inspired by Che Guevara by Brendan Gallagher, The Daily Telegraph, 5 October 2007
- ^ Cain, Nick & Growden, Greg. «Chapter 21: Ten Peculiar Facts about Rugby» in Rugby Union for Dummies (2nd Edition), John Wiley and Sons; ISBN 978-0-470-03537-5, p. 293.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 28.
- ^ a b Hart 2004, p. 98.
- ^ Haney 2005, p. 164.
- ^ a b c d (Anderson 1997, pp. 37–38).
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 10.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 26.
- ^ Ratner 1997, p. 25.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 89.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 64.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 59–64.
- ^ Harris, Richard Legé (2011). Che Guevara: A Biography. ABC-CLIO. p. xxiv, 21.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 83.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 75–76.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 27.
- ^ NYT bestseller list: #38 Paperback Nonfiction on 2005-02-20, #9 Nonfiction on 2004-10-07 and on more occasions.
- ^ A Very Modern Icon by George Galloway, New Statesman, 12 June 2006
- ^ Che Guevara spent time in Miami Archived 4 February 2013 at archive.today by Alfonso Chardy, The Miami Herald 8 July 2008
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 98.
- ^ A copy of Guevara’s University transcripts showing conferral of his medical diploma can be found on p. 75 of Becoming Che: Guevara’s Second and Final Trip through Latin America, by Carlos ‘Calica’ Ferrer (Translated from the Spanish by Sarah L. Smith), Marea Editorial, 2006, ISBN 987-1307-07-1. Ferrer was a longtime childhood friend of Che, and when Guevara passed the last of his 12 exams in 1953, he gave Ferrer, who had been telling Guevara that he would never finish, a copy, showing that he had finally completed his studies.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 126.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 31.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 31.
- ^ a b Guevara Lynch 2000, p. 26.
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 172.
- ^ Anderson, Jon (2010). Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life. New York, New York: Grove/Atlantic, Inc. p. 139. ISBN 978-0-802-19725-2. Retrieved 25 July 2015.
- ^ «Anderson (2010)», p 126
- ^ «Poetry of Che is presented with great success in Guatemala». Cuba Headlines. 26 November 2007.
- ^ Immerman 1982, pp. 155–160.
- ^ Immerman 1982, pp. 161–163.
- ^ Gleijeses 1991, pp. 345–349.
- ^ Gleijeses 1991, pp. 354–357.
- ^ Immerman 1982, pp. 198–201.
- ^ Cullather 2006, p. 113.
- ^ Gleijeses 1991, p. 382.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 32.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 39.
- ^ Che Guevara 1960–67 by Frank E. Smitha.
- ^ Sinclair, Andrew (1970). Che Guevara. The Viking Press. p. 12. ISBN 9780670213917.
- ^ Manzanos, Rosario (8 October 2012). «Documental sobre el Che Guevara, doctor en México». Proceso (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ^ «BIOGRAFIA DE ERNESTO CHE GUEVARA Fundación Che Guevara, FUNCHE» (PDF) (in Spanish). educarchile.cl. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ^ «FIDEL Y HANK: PASAJES DE LA REVOLUCIÓN» (in Spanish). lagacetametropolitana.com. Archived from the original on 4 January 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 33.
- ^ a b Rebel Wife, A Review of My Life With Che: The Making of a Revolutionary by Hilda Gadea by Tom Gjelten, The Washington Post, 12 October 2008.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 55.
- ^ Fidel and Che: A Revolutionary Friendship by Simon Reid-Henry audio slideshow by The Guardian, 9 January 2009
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 28.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 37.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 194.
- ^ Snow, Anita. «‘My Life With Che’ by Hilda Gadea Archived 2012-12-05 at archive.today». Associated Press at WJXX-TV. 16 August 2008; retrieved 23 February 2009.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 213.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 211.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 32.
- ^ DePalma 2006, pp. 110–11.
- ^ a b c Latin lessons: What can we Learn from the World’s most Ambitious Literacy Campaign? by The Independent, 7 November 2010
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 45.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 269–270.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, pp. 105, 119.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 237–238, 269–270, 277–278.
- ^ a b c Luther 2001, pp. 97–99.
- ^ a b c Anderson 1997, p. 237.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 35.
- ^ Cuba Remembers Che Guevara 40 Years after his Fall Archived 13 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine by Rosa Tania Valdes, Reuters, 8 October 2007
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 177.
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 193.
- ^ Poster Boy of The Revolution by Saul Landau, The Washington Post, 19 October 1997, p. X01.
- ^ Moore, Don. «Revolution! Clandestine Radio and the Rise of Fidel Castro». Patepluma Radio.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 42.
- ^ Bockman 1984.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 40.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 47.
- ^ Castro 1972, pp. 439–442.
- ^ Dorschner 1980, pp. 41–47, 81–87.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 39.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 48.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 13.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 51.
- ^ Castañeda, pp. 145–146.
- ^ a b Castañeda, p. 146.
- ^ Anderson 1997, 397.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 400–401.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 424.
- ^ a b Skidmore 2008, pp. 273.
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, p. 115. «The Penal Law of the War of Independence (July 28, 1896) was reinforced by Rule 1 of the Penal Regulations of the Rebel Army, approved in the Sierra Maestra February 21, 1958, and published in the army’s official bulletin (Ley penal de Cuba en armas, 1959)» (Gómez Treto 1991, p. 123).
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, pp. 115–116.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 372, 425.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 376.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 52.
- ^ Niess 2007, p. 60.
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, p. 116.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 388.
- ^ Rally For Castro: One Million Roar «Si» To Cuba Executions – Video Clip by Universal-International News, narrated by Ed Herlihy, from 22 January 1959
- ^ Wickham-Crowley, Timothy P. (1990). Exploring Revolution: Essays on Latin American Insurgency and Revolutionary Theory. Armonk and London: M.E. Sharpe. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-87332-705-3.
- ^ Conflict, Order, and Peace in the Americas, by the Lyndon B. Johnson School of Public Affairs, 1978, p. 121. «The US-supported Batista regime killed 20,000 Cubans»
- ^ The World Guide 1997/98: A View from the South, by University of Texas, 1997, ISBN 1-869847-43-1, pg 209. «Batista engineered yet another coup, establishing a dictatorial regime, which was responsible for the death of 20,000 Cubans.»
- ^ Fidel: The Untold Story. (2001). Directed by Estela Bravo. First Run Features. (91 min). Viewable clip. «An estimated 20,000 people were murdered by government forces during the Batista dictatorship.»
- ^ Niess 2007, p. 61.
- ^ a b c Castañeda 1998, pp. 143–144.
- ^ The Legacy of Che Guevara – a PBS online forum with author Jon Lee Anderson, 20 November 1997
- ^ Different sources cite differing numbers of executions attributable to Guevara, with some of the discrepancy resulting from the question of which deaths to attribute directly to Guevara and which to the regime as a whole. Anderson (1997) gives the number specifically at La Cabaña prison as 55 (p. 387.), while also stating that «several hundred people were officially tried and executed across Cuba» as a whole (p. 387). (Castañeda 1998) notes that historians differ on the total number killed, with different studies placing it as anywhere from 200 to 700 nationwide (p. 143), although he notes that «after a certain date most of the executions occurred outside of Che’s jurisdiction» (p. 143). These numbers are supported by the opposition-based Free Society Project / Cuba Archive, which gives the figure as 144 executions ordered by Guevara across Cuba in three years (1957–1959) and 105 «victims» specifically at La Cabaña, which according to them were all «carried out without due process of law». Of further note, much of the discrepancy in the estimates between 55 versus 105 executed at La Cabaña revolves around whether to include instances where Guevara had denied an appeal and signed off on a death warrant, but where the sentence was carried out while he traveled overseas from 4 June to 8 September, or after he relinquished his command of the fortress on 12 June 1959.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 375.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 54.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 57.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, p. 58.
- ^ Castañeda, p. 159.
- ^ ABC News, Life and Death of Che Guevara.
- ^ (Castañeda 1998, pp. 264–265).
- ^ Taibo 1999, pp. 282–285.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 423.
- ^ Ramadhian Fadillah (13 June 2012). «Soekarno soal cerutu Kuba, Che dan Castro» (in Indonesian). Merdeka.com. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 431.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 300.
- ^ Che Guevara’s Daughter Visits Bomb Memorial in Hiroshima by The Japan Times, 16 May 2008
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 435.
- ^ «Ernesto «Che» Guevara».
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 55.
- ^ a b Crompton 2009, p. 71.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 60.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 25.
- ^ Casey 2009, pp. 25–50.
- ^ Latin America’s New Look at Che by Daniel Schweimler, BBC News, 9 October 2007.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, p. 61.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 449
- ^ Cuba: A Dissenting Report, by Samuel Shapiro, New Republic, 12 September 1960, pp. 8-26, 21.
- ^ a b c d Notes for the Study of the Ideology of the Cuban Revolution by Che Guevara, published in Verde Olivo, October 8, 1960
- ^ Man and Socialism in Cuba Archived 2010-11-28 at the Wayback Machine by Che Guevara
- ^ Dumur 1964 a 1964 video interview of Che Guevara speaking French (with English subtitles).
- ^ a b c d e Hansing 2002, pp 41–42.
- ^ a b c d «Socialism and Man in Cuba» A letter to Carlos Quijano, editor of Marcha, a weekly newspaper published in Montevideo, Uruguay; published as «From Algiers, for Marcha: The Cuban Revolution Today» by Che Guevara on 12 March 1965.
- ^ a b c d e Kellner 1989, p. 62.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 59.
- ^ PBS: Che Guevara, Popular but Ineffective.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 75.
- ^ «Latin America Report». Foreign Broadcast Information Service (FBIS). 23 March 1984. p. 24. Archived from the original on 15 November 2011. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 63.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 74.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 269.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 306.
- ^ a b c Vargas Llosa 2005.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 507.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 509.
- ^ a b «Economics Cannot be Separated from Politics» speech by Che Guevara to the ministerial meeting of the Inter-American Economic and Social Council (CIES), in Punta del Este, Uruguay on 8 August 1961.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 78.
- ^ a b c Goodwin, Richard (22 August 1961). «Memorandum for the President» (PDF). The American Century (Memorandum). The White House. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 492.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 530.
- ^ Abrams, Dennis (2013). Ernesto «Che» Guevara. Infobase Learning. ISBN 9781438146133.
- ^ Eric, Luther; Henken, Ted (2001). Che Guevara. Alpha. p. 165. ISBN 9780028641997.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 545.
- ^ Guevara 1997, p 304
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 73.
- ^ Kapcia, Antoni (2022). Historical Dictionary of Cuba. Rowman and Littlefield Publishers. pp. 261–262. ISBN 9781442264557.
- ^ Cuba’s Forgotten Decade How the 1970s Shaped the Revolution. Lexington Books. 2018. p. 10. ISBN 9781498568746.
- ^ Underlid, Even (2021). Cuba Was Different Views of the Cuban Communist Party on the Collapse of Soviet and Eastern European Socialism. Brill. p. 229. ISBN 9789004442900.
- ^ Gordy, Katherine (2015). Living Ideology in Cuba Socialism in Principle and Practice. University of Michigan Press. pp. 90–92. ISBN 9780472052615.
- ^ Soviet Influence on Cuban Culture, 1961–1987 When the Soviets Came to Stay. Lexington Books. 2019. pp. 12–13. ISBN 9781498580120.
- ^ Artaraz, Kepa (2009). Cuba and Western Intellectuals Since 1959. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 23. ISBN 9780230618299.
- ^ a b Kapcia, Antoni (2014). Leadership in the Cuban Revolution The Unseen Story. Zed Books. ISBN 9781780325286.
- ^ Kapcia, Antoni (2008). Cuba in Revolution A History Since the Fifties. Reaktion Books. ISBN 9781861894489.
- ^ Peet, Richard; Hartwick, Elaine (2009). Theories of Development, Second Edition Contentions, Arguments, Alternatives. Guilford Publications. p. 189. ISBN 9781606230664.
- ^ a b c d e «Colonialism is Doomed» speech to the 19th General Assembly of the United Nations in New York City by Cuban representative Che Guevara on 11 December 1964.
- ^ a b Bazooka Fired at UN as Cuban Speaks by Homer Bigart, The New York Times, 12 December 1964, p. 1.
- ^ CBS Video of Che Guevara being interviewed by Face the Nation on 13 December 1964, (29:11)
- ^ Hart 2004, p. 271.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 618.
- ^ «Che Guevara: Father Of Revolution, Son Of Galway». Fantompowa.net. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ^ Gerry Adams Featured in New Che Guevara Documentary by Kenneth Haynes, Irish Central, 8 September 2009
- ^ Faber, Samuel (2011). Cuba Since the Revolution of 1959 A Critical Assessment. Haymarket Books. p. 217. ISBN 9781608461394.
- ^ The Oxford Handbook of Greek Drama in the Americas. OUP Oxford. 2015. ISBN 9780191637339.
- ^ a b Entiendes? Queer Readings, Hispanic Writings. Duke University Press. 1995. ISBN 9780822316152.
- ^ Ellis, Robert (1997). The Hispanic Homograph Gay Self-representation in Contemporary Spanish Autobiography. University of Illinois Press. p. 44. ISBN 9780252066115.
- ^ Guevara 1969, p. 350.
- ^ Guevara, Che. «Che Guevara At the Afro-Asian Conference in Algeria». marxists.org. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
- ^ Guevara 1969, pp. 352–59.
- ^ a b Message to the Tricontinental (1967) A letter sent by Che Guevara from his jungle camp in Bolivia, to the Tricontinental Conference 1966, published by the Executive Secretariat of the Organization of Solidarity with the People of Asia, Africa and Latin America (OSPAAAL), Havana, 16 April 1967.
- ^ a b Brand Che: Revolutionary as Marketer’s Dream by Michiko Kakutani, The New York Times, 20 April 2009
- ^ a b c d Ernesto ‘Che’ Guevara: A Rebel Against Soviet Political Economy by Helen Yaffe (author of Che Guevara: The Economics of Revolution), 2006
- ^ Abrams 2010, p. 100
- ^ Abrams 2010, p. 103.
- ^ Glejieses, Piero (2011). Conflicting Missions Havana, Washington, and Africa, 1959-1976. University of North Carolina Press. pp. 102–104. ISBN 9780807861622.
- ^ Guevara 1965.
- ^ Excerpt from Che’s Pasajes de la Guerra Revolucionaria (Congo) February 1965, hosted at the Wilson Center Digital Archive
- ^ Ben Bella 1997.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 624.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 629.
- ^ Gálvez 1999, p. 62.
- ^ Gott 2004 p. 219.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 86.
- ^ DR Congo’s Rebel-Turned-Brain Surgeon by Mark Doyle, BBC World Affairs, 13 December 2005.
- ^ BBC News 17 January 2001.
- ^ «The intercept operators knew that Dar-es-Salaam was serving as a communications center for the fighters, receiving messages from Castro in Cuba and relaying them on to the guerrillas deep in the bush.» (Bamford 2002, p. 181)
- ^ Ireland’s Own 2000.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 87.
- ^ From Cuba to Congo, Dream to Disaster for Che Guevara by The Guardian, 12 August 2000
- ^ Guevara 2000, p. 1.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, p. 316.
- ^ Che Guevara’s Central Bohemian Hideaway article and audio by Ian Willoughby, Český rozhlas, 27 June 2010
- ^ O’Donnell, Pacho. «Opiniones de Perón sobre el Che». Página/12 (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 May 2015.
- ^ Guevara 2009, p. 167.
- ^ Mittleman 1981, p. 38.
- ^ Jacobson, Sid and Ernie Colón. Che: A Graphic Biography. Hill & Wang, 2009. 96–97.
- ^ Jacobson, Sid and Ernie Colón. Che: A Graphic Biography. Hill and Wang, 2009. 98.
- ^ a b Selvage 1985.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 693.
- ^ Members of Che Guevara’s Guerrilla Movement in Bolivia by the Latin American Studies Organization
- ^ Kellner 1989, p.97.
- ^ «Bidding for Che», Time Magazine, 15 December 1967.
- ^ US Army 1967 and Ryan 1998, pp. 82–102, inter alia. «US military personnel in Bolivia never exceeded 53 advisers, including a sixteen-man Mobile Training Team from the 8th Special Forces Group based at Fort Gulick, Panama Canal Zone» (Selvage 1985).
- ^ Guevara 1972.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, pp. 107–112; 131–132.
- ^ Wright 2000, p. 86.
- ^ Rodriguez and Weisman 1989.
- ^ Barbie «Boasted of Hunting Down Che» by David Smith, The Observer, 23 December 2007.
- ^ Green Beret Behind the Capture of Che Guevara by Richard Gott, The Age, 8 September 2010
- ^ Rothman, Lily (9 October 2017). «Read TIME’s Original Report on the Death of Che Guevara». Time. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 733.
- ^ a b Guevara 2009, p. II.
- ^ a b «The Man Who Buried Che Archived 2008-12-07 at the Wayback Machine» by Juan O. Tamayo, Miami Herald, 19 September 1997.
- ^ a b c d e Ray, Michèle (March 1968). «In Cold Blood: The Execution of Che by the CIA». Ramparts Magazine. Edward M. Keating. pp. 21–37.
- ^ Grant 2007
- ^ Grant 2007. René Barrientos has never revealed his motives for ordering the summary execution of Guevara rather than putting him on trial or expelling him from the country or turning him over to the United States authorities.
- ^ Almudevar, Lola. «Bolivia marks capture, execution of ‘Che’ Guevara 40 years ago», San Francisco Chronicle. 9 October 2007; retrieved 7 November 2009.
- ^ Time magazine 1970.
- ^ «The Death of Che Guevara: Declassified». The National Security Archive. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 739.
- ^ Obituary: Che Guevara, Marxist Architect of Revolution by Richard Bourne, The Guardian, 11 October 1967
- ^ Almudevar 2007 and Gott 2005.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 179.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 183.
- ^ The Death of Che Guevara by Bjorn Kumm, The New Republic, Originally published on 11 November 1967.
- ^ Lacey 2007a.
- ^ After the Cuban revolution, seeing that Guevara had no watch, his friend Oscarito Fernández Mell gave him his own gold watch. Sometime later, Che handed him a piece of paper; a receipt from the National Bank declaring that Mell had «donated» his gold wristband to Cuba’s gold reserve. Guevara was still wearing his watch, but it now had a leather wristband (Anderson 1997, p. 503).
- ^ Kornbluh 1997.
- ^ Garza, Laura (18 December 1995). «Bolivian General Reveals Che Guevara’s Burial Site». The Militant. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 740.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 741.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 101.
- ^ «Bidding for Che», Time Magazine, 15 December 1967.
- ^ Guevara 1967.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 45.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 104.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 148.
- ^ Ramírez 1997.
- ^ a b Nadle, Marlene (24 August 1968). «Régis Debray Speaks from Prison». Ramparts Magazine: 42.
- ^ Trento, Angelo. Castro and Cuba : From the revolution to the present. p.64. Arris books. 2005.
- ^ Ernesto «Che» Guevara (World Leaders Past & Present), by Douglas Kellner, 1989, Chelsea House Publishers (Library Binding edition), ISBN 1555468357, p. 101
- ^ Che: A Myth Embalmed in a Matrix of Ignorance by Time Magazine October 12, 1970
- ^ Viva the Chevolution! by Trisha Ziff, The Huffington Post, April 21, 2008
- ^ Comrade Che Keeps an Eye on British Workers by Owen Booth, BBC News, October 24, 2002
- ^ Durschmied 2002, pp. 307–09.
- ^ Durschmied 2002, p. 305.
- ^ Durschmied 2002, pp. 305–06.
- ^ Durschmied 2002, p. 306.
- ^ Cuba salutes ‘Che’ Guevara: Revolutionary Icon Finally Laid to Rest, CNN, 17 October 1997
- ^ Bolivia unveils original Che Guevara diary by Eduardo Garcia, Reuters, 7 July 2008.
- ^ Slain Che Guevara Soldiers Found? video report by National Geographic, 21 August 2009.
- ^ McLaren 2000, p. 7.
- ^ a b Löwy 1973, p. 7.
- ^ Löwy 1973, p. 33.
- ^ Löwy 1973, pp. 7, 9, 15, 25, 75, 106.
- ^ The Spark That Does Not Die by Michael Löwy, International Viewpoint, July 1997
- ^ Moynihan 2006.
- ^ Sinclair 1968/2006, p. 80.
- ^ Sinclair 1968/2006, p. 127.
- ^ McLaren 2000, p. 3.
- ^ Sinclair 1968/2006, p. 67.
- ^ «Ernesto Che Guevara R.I.P.» by Rothbard, Murray, Left and Right: A Journal of Libertarian Thought, Volume 3, Number 3 (Spring-Autumn 1967).
- ^ a b O’Hagan 2004.
- ^ Behind Che Guevara’s mask, the cold executioner Archived 21 November 2008 at the Wayback Machine Times Online, 16 September 2007.
- ^ «‘Che’ Spurs Debate, Del Toro Walkout», The Washington Times, 27 January 2009.
- ^ Short interview on Che Guevara with Carlos Alberto Montaner for the Freedom Collection
- ^ a b Che is the «Patron Saint» of Warfare by William Ratliff, The Independent Institute, 9 October 2007.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 106.
- ^ Farber, Samuel (23 May 2016). «Assessing Che». Jacobin.
- ^ Che Guevara’s Ideals Lose Ground in Cuba by Anthony Boadle, Reuters, 4 October 2007: «he is the poster boy of communist Cuba, held up as a selfless leader who set an example of voluntary work with his own sweat, pushing a wheelbarrow at a building site or cutting sugar cane in the fields with a machete.»
- ^ People’s Weekly 2004.
- ^ Argentina pays belated homage to «Che» Guevara by Helen Popper, Reuters, 14 June 2008
- ^ Statue for Che’s ’80th birthday’ by Daniel Schweimler, BBC News, 15 June 2008.
- ^ On a tourist trail in Bolivia’s hills, Che’s fame lives on By Hector Tobar, Los Angeles Times, 17 October 2004.
- ^ Schipani 2007.
- ^ Casey 2009, pp. 235, 325.
- ^ BBC News 26 May 2001.
- ^ see also Che Guevara (photo).
- ^ Lacey 2007b.
- ^ BBC News 2007.
- ^ «»Che» Guevara, condecorado por Checoslovaquia». ABC. 29 de octubre de 1960. Consultado el 13 de octubre de 2014.
- ^ «Janio Condecora Guevara» (en portugués). Folha de S.Paulo. 20 de agosto de 1961. Consultado el 13 de octubre de 2014.
Referenced works
- Abrams, Dennis (2010). Ernesto Che Guevara. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 9781438134642.
- Almudevar, Lola (9 October 2007). «Bolivia marks capture, execution of ‘Che’ Guevara 40 years ago». SFGate. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- Anderson, Jon Lee (1997). Che Guevara : a revolutionary life (1st ed.). New York: Grove Pr. ISBN 0-8021-1600-0.
- Bamford, James (2002). Body of secrets anatomy of the ultra-secret National Security Agency (1st Anchor Books ed.). New York: Anchor Books. ISBN 0-385-49908-6.
- «Profile: Laurent Kabila». BBC News. 17 January 2001. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- «Che Guevara photographer dies». BBC News. 26 May 2001. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- «Cuba pays tribute to Che Guevara». BBC News. 9 October 2007. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- Beaubien, Jason (2009). Cuba Marks 50 Years Since ‘Triumphant Revolution’. NPR.org. NPR: All Things Considered, Audio Report.
- Ben Bella, Ahmed (1 October 1997). «Che as I knew him». Le Monde diplomatique. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- Bockman, Major Larry James (1 April 1984). The Spirit Of Moncada: Fidel Castro’s Rise To Power, 1953 — 1959. Quantico, Virginia: Marine Corps Command and Staff College. Archived from the original on 15 November 2021.
- Casey, Michael (2009). Che’s Afterlife: The Legacy of an Image. Vintage. ISBN 978-0-307-27930-9.
- Castañeda, Jorge G. (1998). Compañero : the life and death of Che Guevara (1st Vintage Books ed.). New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 0-679-75940-9.
- Crompton, Samuel (2009). Che Guevara: The Making of a Revolutionary. Gareth Stevens. ISBN 978-1-4339-0053-2.
- Cullather, Nicholas (2006). Secret History: The CIA’s classified account of its operations in Guatemala, 1952–1954. Palo Alto, California: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-5468-2.
- DePalma, Anthony (2006). The man who invented Fidel : Cuba, Castro, and Herbert L. Matthews of The New York Times (1st ed.). New York: Public Affairs. ISBN 1-58648-332-3.
- Dorfman, Ariel (14 June 1999). Time 100: Che Guevara. Time magazine.
- Dorschner, John and Roberto Fabricio (1980). The Winds of December: The Cuban Revolution of 1958. New York: Coward, McCann & Geoghegen. ISBN 0-698-10993-7.
- Dumur, Jean (interviewer) (1964). L’interview de Che Guevara (Video clip; 9:43; with English subtitles).
- Durschmied, Erik (2002). The Blood of Revolution: From the Reign of Terror to the Rise of Khomeini. Arcade Publishing. ISBN 1-55970-607-4.
- Free Society Project Inc. / Cuba Archive (30 September 2009). ««Documented Victims of Che Guevara in Cuba: 1957 to 1959» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 April 2010. (244 KB)«. Summit, New Jersey: Free Society Project.
- Gálvez, William (1999). Che in Africa: Che Guevara’s Congo Diary. Melbourne: Ocean Press, 1999. ISBN 1-876175-08-7.
- Gómez Treto, Raúl (Spring 1991). «Thirty Years of Cuban Revolutionary Penal Law». Latin American Perspectives 18(2), Cuban Views on the Revolution. 114–125.
- Gleijeses, Piero (1991). Shattered Hope: The Guatemalan Revolution and the United States, 1944–1954. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-02556-8.
- Gott, Richard (2004). Cuba: A New History. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-10411-1.
- Gott, Richard (11 August 2005). «Bolivia on the Day of the Death of Che Guevara». Le Monde diplomatique. Accessed 26 February 2006.
- Grant, Will (8 October 2007). «CIA man recounts Che Guevara’s death». BBC News. Accessed 29 February 2008.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (1965). «Che Guevara’s Farewell Letter».
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (1967). «Diario (Bolivia)». Written 1966–1967.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (editors Bonachea, Rolando E. and Nelson P. Valdés; 1969). Che: Selected Works of Ernesto Guevara, Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-52016-8
- Guevara, Ernesto (2009). Che: The Diaries of Ernesto Che Guevara. Ocean Press. ISBN 978-1-920888-93-0.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (1972). Pasajes de la guerra revolucionaria.
- Guevara, Ernesto «Che» (translated from the Spanish by Patrick Camiller; 2000). The African Dream. New York: Grove Publishers. ISBN 0-8021-3834-9.
- Guevara, Ernesto; Deutschmann, David (1997). Che Guevara Reader: Writings by Ernesto Che Guevara on Guerrilla Strategy, Politics & Revolution. Ocean Press. ISBN 1-875284-93-1.
- Guevara Lynch, Ernesto (2000). Aquí va un soldado de América. Barcelona: Plaza y Janés Editores, S.A. ISBN 84-01-01327-5.
- Guevara Lynch, Ernesto (2007). The Young Che: Memories of Che Guevara by His Father. Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0307390448.
- Haney, Rich (2005). Celia Sánchez: The Legend of Cuba’s Revolutionary Heart. New York: Algora Pub. ISBN 0-87586-395-7.
- Katrin Hansing (2002). Rasta, Race and Revolution: The Emergence and Development of the Rastafari Movement in Socialist Cuba. LIT Verlag Münster. ISBN 3-8258-9600-5.
- Hart, Joseph (2004). Che: The Life, Death, and Afterlife of a Revolutionary. New York: Thunder’s Mouth Press. ISBN 1-56025-519-6.
- Immerman, Richard H. (1982). The CIA in Guatemala: The Foreign Policy of Intervention. Austin, Texas: University of Texas Press. ISBN 9780292710832.G
- Ireland’s Own (12 August 2000). «From Cuba to Congo, Dream to Disaster for Che Guevara». Archived from the original on 9 February 2006. Retrieved 11 January 2006.
- Kellner, Douglas (1989). Ernesto «Che» Guevara (World Leaders Past & Present). Chelsea House Publishers (Library Binding edition). p. 112. ISBN 1-55546-835-7.
- Kornbluh, Peter (1997). Electronic Briefing Book No. 5. National Security Archive. Accessed 25 March 2007.
- Lacey, Mark (26 October 2007). «Lone Bidder Buys Strands of Che’s Hair at U.S. Auction». The New York Times.
- Lacey, Mark (9 October 2007). «A Revolutionary Icon, and Now, a Bikini». The New York Times.
- Lavretsky, Iosif (1976). Ernesto Che Guevara. translated by A. B. Eklof. Moscow: Progress. p. 5. ASIN B000B9V7AW. OCLC 22746662.
- Löwy, Michael (1973). The Marxism of Che Guevara: Philosophy, Economics, Revolutionary Warfare. Monthly Review Press. ISBN 0-85345-274-1.
- Luther, Eric (2001). Che Guevara (Critical Lives). Penguin Group (USA). p. 276. ISBN 0-02-864199-X.
- McLaren, Peter (2000). Che Guevara, Paulo Freire, and the Pedagogy of Revolution. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0-8476-9533-6.
- Mittleman, James H (1981). Underdevelopment and the Transition to Socialism – Mozambique and Tanzania. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-500660-8
- Moynihan, Michael. «Neutering Sartre at Dagens Nyheter». Stockholm Spectator. Accessed 26 February 2006.
- Che Guevara, by Frank Niess, Haus Publishers Ltd, 2007, ISBN 1-904341-99-3.
- O’Hagan, Sean (11 July 2004). «Just a pretty face?». The Guardian. Accessed 25 October 2006.
- Ramírez, Dariel Alarcón (1997). Le Che en Bolivie. Paris: Éditions du Rocher. ISBN 2-268-02437-7.
- Ramonet, Ignacio (2007). Translated by Andrew Hurley. Fidel Castro: My Life London: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-102626-8
- Ratner, Michael (1997). Che Guevara and the FBI: The U.S. Political Police Dossier on the Latin American Revolutionary. Ocean Press. ISBN 1-875284-76-1.
- Rodriguez, Félix I. and John Weisman (1989). Shadow Warrior/the CIA Hero of a Hundred Unknown Battles. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-66721-1.
- Ryan, Henry Butterfield (1998). The Fall of Che Guevara: A Story of Soldiers, Spies, and Diplomats. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-511879-0.
- Sandison, David (1996). The Life & Times of Che Guevara. Paragon. ISBN 0-7525-1776-7.
- Schipani, Andres (23 September 2007). «The Final Triumph of Saint Che». The Observer. (Reporting from La Higuera.)
- Selvage, Major Donald R. – USMC (1 April 1985). Che Guevara in Bolivia. Globalsecurity.org. Accessed 5 January 2006.
- Sinclair, Andrew (2006) [1968]. Viva Che!: The Strange Death and Life of Che Guevara. Sutton publishing. ISBN 0-7509-4310-6.
- Skidmore, Thomas E.; Smith, Peter H. (2008). Modern Latin America. Oxford University Press. p. 436. ISBN 978-0-19-505533-7.
- Taibo II, Paco Ignacio (1999). Guevara, Also Known as Che. St Martin’s Griffin. 2nd edition. ISBN 0-312-20652-6.
- Time Magazine cover story (8 August 1960). «Castro’s Brain».
- Time Magazine (12 October 1970). «Che: A Myth Embalmed in a Matrix of Ignorance».
- U.S. Army (28 April 1967). Memorandum of Understanding Concerning the Activation, Organization and Training of the 2d Ranger Battalion – Bolivian Army. Accessed 19 June 2006.
- Vargas Llosa, Alvaro (11 July 2005). «The Killing Machine: Che Guevara, from Communist Firebrand to Capitalist Brand». The Independent Institute. Accessed 10 November 2006.
- «World Combined Sources» (2 October 2004). «Che Guevara remains a hero to Cubans». People’s Weekly World.
- Wright, Thomas C. (2000). Latin America in the Era of the Cuban Revolution (Revised ed.). Praeger. ISBN 0-275-96706-9.
External links
|
|
Биография
Эрнесто Че Гевара — аргентинский врач, писатель, революционер и партизанский лидер. Известная фигура кубинской революции стала символом восстания, а портрет Че является одним из самых узнаваемых снимков в мире.
Детство и юность
14 июня 1928 года в аргентинском городе Росарио родился Эрнесто Гевара де ла Серна. Темпераментный революционер появился на свет в буржуазной семье. Его отец был архитектором, а мать — потомком плантаторов. Происхождение супругов связано с аргентинскими креолами (европейские переселенцы), но также были в роду Че Гевары и креолы из Калифорнии.
Изначально родители будущего команданте жили в Буэнос-Айресе, после перебрались в провинцию Мисьонес, где мать Селия получила в наследство плантацию. Пытаясь зарабатывать честно и справедливо, выплачивая зарплаты рабочим деньгами, что в те времена считалось диковинкой среди плантаторов, они вызвали шквал негодования у конкурентов. В результате паре пришлось отправиться в Росарио, где и родился их первенец.
В семье Гевары также воспитывались и другие дети: две сестры, Селия и Анна-Мария, и два брата, Роберто и Хуан-Мартин. Несмотря на сложные годы и экономический кризис в стране, дети семейства архитектора получили впоследствии высшее образование.
Тэтэ, так звали мальчика в детстве, в 2-летнем возрасте столкнулся со сложнейшим заболеванием — бронхиальной астмой — и всю сознательную жизнь пытался с ней бороться. Родители Эрнесто решили снова переехать в другое место жительства в поисках идеальных климатических условий для своего малыша.
В провинции Кордова прошли детские годы Гевары. Из-за болезни мальчик не мог некоторое время ходить в школу вместе со сверстниками, но уже в возрасте 4 лет научился читать — в доме была своя библиотека.
Эрнесто окончил среднюю школу в Альта-Грасии, потом поступил в колледж. После его завершения в 1945-м будущий революционер принял решение стать врачом, сдав документы в медицинский университет в Буэнос-Айресе. В вузе Гевара приобрел специальности хирурга и дерматолога.
Согласно биографическим данным, юноша интересовался не только медициной, но и другими науками. Огромное впечатление оказали на молодого Эрнесто труды Владимира Ленина, Карла Маркса, Михаила Бакунина. Гевара в совершенстве владел французским языком, знал наизусть множество стихов, занимался написанием собственных сочинений, играл в шахматы.
Несмотря на астму, парень ростом 175 см занимался спортом и обладал хорошими физическими данными. В годы юности Эрнесто числился запасным в футбольной команде, с удовольствием посещал конный клуб, имел неплохие навыки в гольфе, а также путешествовал на велосипеде. В биографии кубинского деятеля сохранилась информация о том, как молодой Гевара подарил своей невесте фото, подписавшись на нем «король педали».
Путешествия
Путешествовать Эрнесто начал еще в молодости. Являясь студентом университета, он решил испытать себя в качестве матроса, в 1950 году нанявшись на грузовое судно. Так он посетил Британскую Гвиану и остров Тринидад. Далее Гевара стал участником рекламной акции компании «Микрон», которая предложила юноше совершить путешествие на мопеде ее производства.
Чтобы узнать мир и получить новые впечатления, Эрнесто посещал различные страны. Вместе с верным товарищем, доктором биохимии Альберто Гранадо, Гевара увлекался исследованием новых методик лечения прокаженных. Друзья посетили лепрозории различных стран Южной Америки.
Деньги на путешествия напарники зарабатывали по-разному: трудились грузчиками, мыли посуду в местах общественного питания, оказывали услуги ветеринаров и пр. Иногда ребята ночевали в лесу или просто в поле.
Поездки Эрнесто осуществлял параллельно с учебой и в 1952 году сумел достойно защитить диплом на тему аллергических заболеваний. Когда он получил специальность хирурга, судьба отправила его в Венесуэлу, где появилась вакансия в лепрозории, но специалист решил изменить маршрут, поддавшись уговорам попутчиков, и поехал в Гватемалу.
По его приезду в этой республике Центральной Америки грянула война. Президент государства социалист Хакобо Арбенс отказался от власти, а новоизбранный Кастильо Армас оказался жестким проамериканцем, что спровоцировало гонения и репрессии жителей, поддерживавших левые идеи.
Так Че Гевара влился в поток военных действий. Он помогал противникам нового режима в перевозке оружия, заботился о пострадавших. В результате социалисты проиграли, а аргентинец попал в число государственных преступников.
Эрнесто был вынужден скрываться. Убежищем для него стало посольство родной Аргентины, а в 1954 году Гевара переехал жить в Мехико. Здесь он попытался трудиться журналистом, фотографом, сторожем, искал случайные подработки.
В этот же период Эрнесто женился на Ильде Гадеа, с которой познакомился в Гватемале. Спустя некоторое время Гевара устроился в местную больницу. В 1955 году на прием к доктору пришел его приятель. Молодой человек оказался кубинским революционером. Случайная встреча завершилась предложением Че стать частью революционного движения против диктатора Кубы и отправиться в экспедицию на карибский остров. Долго не раздумывая, аргентинец согласился.
Кубинская революция
В июле 1955 года в Мехико из США приехал Фидель Кастро. Вместе с Че они стали главными лидерами протестного движения на Кубе.
Подготовка к революции вызвала трудности для ее участников. Из-за утечки информации Че и Фидель попали под арест, но были спасены протекцией культурных и общественных деятелей. Гевара просидел в тюрьме 57 суток, а после продолжил воплощение идеи.
Отряд революционеров покинул Мехико и отправился на Кубу. Отплытие корабля произошло 25 ноября 1956 года. В море Эрнесто и его сторонники потерпели кораблекрушение, попали под обстрел авиации местного правительства. Некоторые повстанцы погибли, другие попали в плен. Че Гевара и еще несколько революционеров стали партизанами.
Смертельная опасность постоянно окружала Эрнесто, в партизанском отряде он стал жертвой малярии. В период лечения молодой революционер много читал, писал собственные произведения, вел личный дневник.
В 1957 году повстанцам удалось взять под контроль ряд территорий Кубы (горы Сьерра-Маэстра), начали появляться новые солдаты — приверженцы движения и противники кубинского правителя Фульхенсио Батисты.
Тогда Эрнесто получил военное звание команданте и возглавил колонну из 75 воинов. Одновременно с боевыми действиями Гевара вел активную пропаганду как редактор газеты «Свободная Куба».
Революция принимала все более масштабные обороты. Партизаны установили связь с кубинскими коммунистами, перешли в атаку в местных долинах. Войско Че добралось до массива Эскамбрай, а после Гевара взял власть в Лас-Вильясе.
В ходе сражений повстанцы провели ряд реформ в пользу крестьян, которые решили поддержать революционеров в военных действиях. В сражении за Санта-Клару 1 января 1959 года армия команданте одержала победу, и Батиста покинул Кубу, эмигрировав в другую страну.
Признание и слава
В 1959 году Эрнесто официально стал гражданином Кубы согласно постановлению правительства Фиделя Кастро. В 1960-м вышел из печати труд знаменитого революционера под названием «Партизанская война», а в следующем году Че Гевара в числе первых лиц государства встречался с Юрием Гагариным во время визита космонавта на Кубу.
В качестве министра промышленности Че отправился в мировое турне. Он посетил Пакистан, Бирму, Японию и другие страны.
Далее Че Геваре снова пришлось воевать. Отношения США и кубинского правительства испортились. Остров свободы стал местом вражеского нападения, операцией по сопротивлению руководил Эрнесто. Американцы проиграли, их план провалился.
На протяжении своей жизни на Кубе Че Гевара занимал государственные посты, выступал с публичными речами и всегда придерживался собственных принципов, иногда даже вступая в конфликт со странами-союзниками. Свое видение решения проблемы экономического развития третьего мира Че Гевара высказал в последнем публичном выступлении — знаменитой «Алжирской речи».
Со временем Эрнесто решил покинуть Кубу. Он написал родителям и Фиделю прощальные письма и тихо покинул республику весной 1965 года. Уехав с Острова свободы, Гевара отправился в Конго, где в те годы наблюдался серьезный политический кризис. Эрнесто и небольшой отряд кубинцев оказывали содействие повстанческому движению партизан-социалистов.
Известный революционер делился опытом ведения военных действий, помог социалистам добиться некоторых компромиссов, но поставленных изначально целей ему достичь не удалось. В результате команданте уехал из Конго. Следующим местом его деятельности осенью 1965 года стала Африка.
Здесь Эрнесто снова заболел малярией, приступы астмы возобновились. Че Гевара отправился на лечение в санаторий ЧССР, но, даже пребывая в спокойном месте, он не переставал планировать новые революционные акции.
В 1966 году Че вернулся на Кубу, чтобы возглавить партизанский отряд в Боливии. Он стал реальной угрозой для ЦРУ, вражеское правительство объявило о внушительном вознаграждении за убийство революционера. В Боливии Гевара пробыл 11 месяцев.
Отношения с СССР
Личность Гевары заинтересовала советское руководство, когда он стал министром базовой промышленности и определял экономику Кубы.
Эрнесто был во главе первой кубинской экономической делегации, которая посетила СССР в 1960-м, чтобы найти покупателей для кубинского сахара: рынок США для островитян был закрыт. По личному приглашению Первого секретаря ЦК КПСС Никиты Хрущева он стал одним из первых иностранцев, который поднялся на Мавзолей во время парада в Москве, посвященного годовщине Октябрьской революции.
Но впоследствии кубинский партизан не раз позволял себе критику образа жизни советской партийной номенклатуры. После прихода к власти в 1964 году Леонида Брежнева, придерживавшегося мирного сосуществования с США, отношение к «экспортеру революции» в СССР изменилось: даже некролог Че вышел через несколько дней после его смерти.
Личная жизнь
Первая любовь Гевары сложилась к его кузине Кармен. Девушка обожала танцевать, чем очень привлекала подростка.
В юности Эрнесто был влюблен в девушку из богатой семьи в Кордове. Однако их разделяла не только разница в материальном положении, но и различия во взглядах на будущее: студент-медик планировал посвятить жизнь лечению больных проказой.
Вся жизнь Гевары прошла в борьбе за идеи свободы и равноправия простых граждан, поэтому любовь к женщинам у революционера рождалась параллельно с войнами и революциями. От первого брака с революционеркой Ильдой Акостой Гадеа у Че родилась дочь. Супруги назвали девочку Ильда Беатрис Гевара Гадеа.
В период сражений отец писал трогательные письма своей дочери. Семья распалась через четыре года сложной личной жизни на расстоянии.
В 1959 году Гевара снова женился. Второй женой Че стала его секретарь и участница повстанческого движения на Кубе Алейда Марч Торрес. Их отношения завязались еще до развода команданте с Ильдой. У объединенных революционной идеей супругов родилось четверо детей.
Мало что известно о последней любви Эрнесто — переводчице Тамаре Бунке Бидер, известной как Таня-партизанка. О ней жена аргентинца узнала только после смерти мужа.
Смерть
После попадания в плен к боливийцам Эрнесто страшно пытали. Он отказывался сотрудничать с врагами, и 9 октября 1967 года Че Гевару расстреляли. Приговор привел в исполнение Марио Теран Саласар — он выстрелил пленнику в сердце, что и стало причиной смерти. Саласар пережил революцию и скончался в 80-летнем возрасте в марте 2022 года.
Изуродованное тело мертвого латиноамериканского революционера выставили на публичное обозрение, после чего тайно захоронили в общей могиле без знаков отличия. Тело было предано земле без рук: в качестве доказательства смерти Че Гевары революционеру ампутировали обе кисти. Отрубленные конечности сохранили в банке с формалином. Через год руки команданте и его дневник были выкрадены и доставлены на Кубу.
Шокирующие подробности гибели Эрнесто Че Гевары
Останки знаменитого революционера были обнаружены только в 1997 году, переправлены на Кубу и помещены в мавзолей в Санта-Кларе.
Память
Иконе мировой революции Эрнесто Геваре посвящены песни, стихи, книги. Одну из них — Evocation — написала его вторая жена Алейда Марч Торрес, она была издана в 2007-м.
О жизни команданте снято немало фильмов («Дневники мотоциклиста», «Че», «Руки Че Гевары» и другие), видеосюжетов и передач.
Ежегодно 8 октября на Кубе в память о великом повстанце отмечается День Героического партизана.
Фильмография
- 1969 — «Че!»
- 2004 — «Че Гевара: Дневники мотоциклиста»
- 2005 — «Че»
- 2006 — «Руки Че Гевары»
- 2008 — «Че»
Библиография
- 2000 — «Я, Че Гевара»
- 2009 — «Гавана Лунная»
- 2011 — «Жизнь и смерть Че Гевары»
Интересные факты
- Эрнесто Гевара получил имя Че из-за того, что часто использовал в речи аргентинское слово-паразит che, которое означает «Эй (ты)!», «Да ну!» и т. п.
- После окончания университета Эрнесто должен был идти в армию, но решил пойти на хитрость, намеренно спровоцировав приступ бронхиальной астмы.
- Место смерти революционера деревня Ла-Игера стала центром паломничества, а самого команданте объявили местночтимым католическим святым — San Ernesto de La Higuera (святым Эрнесто Игерским).
- По версии журнала Time, Че Гевара вошел в топ-100 важнейших персон XX века.
|
Я хату покинул, |
| М.А.Светлов |
Эрнесто Рафаэль «Че» Гевара Линч де ла Серна — аргентинский пламенный революционер. Боролся за права угнетённых и местами победил, доставил неиллюзорный баттхёрт проклятым буржуинам и удачно сфотографировался.
Имя[править]
«Че» — аргентинское междометие, используемое для обращения внимания других в начале реплики, урезаннaя форма от глагола «escuCHE» (послушайте), то есть аналог нашего «слышь», повторявшееся Эрнесто при каждом обращении. За эту привычку кубинцы и прозвали своего команданте «Че». Кроме того, словом «че» в испаноговорящем мире называют всех, родившихся в Аргентине. Знатоки утверждают, что свое «че» аргентинцы позаимствовали у индейцев гуарани — на их языке оно означает «мое».
Но в устах жителей пампасов «че», аки «хо-хо» в устах Эллочки-людоедки, выражает, в зависимости от интонаций и контекста, целую гамму «страстей человеческих».
После свержения Батисты Гевара, став директором Национального банка Кубы, на банкнотах нового выпуска поставил подпись «Че», чем заставил срать кирпичами контрреволюционеров.
Эрнесто Рафаэль Гевара Линч де ла Серна — полное имя Че (это, в свою очередь, погоняло). Такие длинные имена среди испанцев и латиносов бывают только у людей с голубой кровью. Че Гевара из обедневшего дворянского рода (см. биографию), что символизирует.
Биография[править]
Родился в семье c аристократическими (частично ирландскими, чем, видимо, объясняется склонность зажигать) корнями. Отец, Эрнесто Рафаэль Гевара Линч — архитектор. По материнской линии Че был потомком последнего вице-короля Перу, то есть мать, Селия де ля Серна, тоже принадлежала к аристократическому роду. Ей по наследству перепала плантация матэ. Некоторые считают её одной из основательниц феминистского движения в Аргентине.
В детстве много проёбывал школу, потому что родился астматиком, первые два года учился только на дому. Поступил в 1948 году на медицинский факультет Университета Буэнос-Айреса, который закончил 11 апреля 1953 года. После этого поработал ассистентом в клинике, которая специализировалась на аллергических заболеваниях (в частности, астме).
Пару раз объехал всю Латинскую Америку, участвуя в стычках всевозможных повстанцев во имя великой справедливости, съёбывая от ответных действий диктаторов, перебиваясь случайными заработками и помогая больным в лепрозориях (когда устроился). Во время второй поездки нелёгкая забросила его в компанию кубинских революционеров во главе с Фиделем Кастро. Благодаря особенностям ландшафта, невероятной удаче и хорошей тактике, кучка повстанцев выгнала злобного диктатора Батисту на мороз и установила на Кубе мир и процветание, после полувека планомерного уничтожения кубинской промышленности большим соседом.
На совещании после захвата власти Фидель спросил: «У нас есть экономисты? Поднимите руки.»
В тишине руку поднял только один человек — Че.
«Пиздато,» — сказал Фидель, — «ты и возглавишь национальный банк.»
«С хуёв ли?» — ответил Че.
«Ну как, ты ж экономист! Руку поднимал?!»
«А, мне послышалось, что ты спросил, есть ли коммунисты, вот я и поднял… ну хуй с ним, так и быть.»
Оставив Фиделя ненадолго порулить одного, Че отправился в Конго, насаждать Мировую Революцию. Однако, в этот раз оказалось, что для построения социализма необходимо сперва слезть с пальмы. Задолбавшись стаскивать бабуинов с растительности, Че решил «экспортировать революцию» в рiдную Латинскую Америку. Увы, в процессе создания базы партизан в Боливии произошел переворот. Че оказался с кучкой задротов и откровенных быдланов в окружении сразу боливийских неверных ментов, вояк и инструкторов-янки. Вокруг папуасы, про испанский язык не слышавшие, нихуя лекарств, боеприпасов и всех прочих партизанских ништяков. Явки в городах провалены провокаторами. В общем, палево. Несмотря на героизм в попытках отбиться, из нескольких десятков выжили только трое. Геваре не повезло — ранен, попал в плен, и расстрелян примерно по тем же соображениям, что и Николай с семейством в ипатьевском подвальчике: ново-само-провозглашенному президенту не уперлись разборки с толпами последователей Кастро и Че по поводу пленного, если оставить его в живых. Впрочем, надо отдать кубинцам должное — почти всех офицеров, участвовавших в уничтожении отряда Че, довольно оперативно отправили вслед за команданте.
Да, еще Че был пейсателем, наваяв в промежутках между боями довольно доставляющую книжыцу: «Партизанская война» Пособие для юного революционера. Учит, как имея пять человек и два ржавых калашникова в наличии, устроить нехилый геморрой властям, а то и вообще выгнать их на мороз.
Ещё написал книгу «Дневник мотоциклиста» об одном из своих путешествий, ЧСХ, частично на мотоцикле, а по большей части автостопом. Вполне годный путеводитель по латинской Америке получился, надо сказать.
Наши дни[править]
|
Казалось бы, Че, спустя 30 лет после смерти, не должен больше пугать своих идеологических противников… Оказалось: ничего подобного! Только сейчас стало ясно, как продолжают ненавидеть Че его враги, как боятся его до сих пор. Боливийский генералитет выступил с заявлением, в котором церемонии памяти Че были названы «шоу, отмеченным недостатком патриотизма». Срочно была создана ассоциация ветеранов, воевавших с Че Геварой. |
| Товарищ Тарасов |
|
Свобода слова у вас, в России, это, как я вижу, свобода для любого идиота показывать всем, что он – идиот. |
| Антонио Нубаррон Тремендо |
Образ Че в наше время культивируется коммунистами, говнарями, хиппанами, нацболами и прочими борцами за все хорошее и против всего плохого. При этом мало кто на самом деле имеет представление о том, что за человек был Че, какие идеи он исповедовал и против кого воевал. Главное — не дурацкие знания, а футболка с портретом и революционный дух, я гарантирую это! А вместо многомесячных неравных боёв за Идею и бескорыстной помощи окружающим можно приобщиться аватаркой в форуме и значком.
Сам образ давно превратился в бестелесный симулякр, умело используемый проклятыми буржуинами для впаривания пепси и сникерсов молодому поколению. Деятели постмодернизма пламенного революционера дичайше котируют и невозбранно пихают куда ни попадя.
Суммируя вышесказанное: образ Че Гевары превратился в глобальный медиавирус уже не одно десятилетие назад и, по сути, безвкусный китч. Наличествуют все признаки медиавируса, включая бесплатную раскрутку хомячками (в большинстве случаев школьниками). Очень доставляющий пример:
|
— Ты хоть знаешь, кто это такой? |
| Интервью с лоли, невозбранно нацепившей значок с сабжем на футболку |
Интересные факты[править]
Блин, ну и в чём он не прав?
- С раннего детства Че болел астмой, поэтому, в отличие от того же дедушки Ленина, говорил с трудом, и ораторским искусством не обладал.
- Последними словами Че Гевары пришедшему его расстрелять сержанту Марио Террану были: «Стреляй, трус, ты всего лишь убьёшь человека» [1]. И другие версии, любовно прожёвываемые, высираемые, снова прожёвываемые и т. д. (цикл бесконечен) всякими доморощенными историками. К. О. гарантирует, что последние слова Че слышали только боливийские солдаты. Собственно говоря, по свидетельству боливийского солдата, который его расстрелял, последние слова Че Гевары были немного прозаичней: «¡Póngase sereno y apunte bien! ¡Va a matar a un hombre!» (Успокойтесь и цельтесь хорошо! Вы сейчас убьёте человека!). Команданте он такой Команданте.
- После расстрела Че воскрес и улетел на небо в голубом вертолёте ([2]).
- Дух Че Гевары в романе «Generation „П“» пейсателя Пелевина срывает покровы с побудительных мотивов человеческой деятельности.
- Пресловутая каноничная фотография представляет собой лютую выкадровку снимка, сделанного на говнозеркалку дальномерку расовым кубинским репортером А. Корда. И это многое объясняет в особенностях работы фоторепортеров. Но понятное дело, что всем похуй
- Существует миф о «проклятье Че Гевары»: все или почти все, кто участвовал в его ликвидации, плохо кончили. Мифотворцев однако не смущает, что большинство из них погибли по вполне рациональным причинам — были невозбранно выпилены всяческими леваками в порядке возмездия. Однако есть и действительно интересное совпадение. У участника операции ЦРУ в Боливии кубинского контрреволюционера Феликса Родригеса ВНЕЗАПНО началась тяжёлая астма (что немудрено во влажном тропическом климате Боливии — НЕмудрено??? Половина Боливии лежит на равнине на высоте 3500 м, и там совсем не тропический и невлажный климат — там холодно, сухо, солнечно и ветрено. Хотя, конечно, отсутствия проклятия это не отменяет)).
- В местечке Ля Игерра, где его расстреляли, Че является местночтимым святым «San Ernesto de La Higuera».
Лучший саундтрек к данной статье
Краткий ликбез от каких-то либерастов.
- Люто, бешено ненавидим фошистами, либерастами и кубинской эмиграцией. Является предметом правого троллинга. На сайтах, созданных кубинскими контрреволюционными эмигрантами можно невозбранно ознакомиться с весьма инфернальными вариантами его биографии. Также доставляет его биография из «Ч0рной книги коммунизма»
- По непроверенным данным, предсказывал крушение Совка
- Эпос Эдуарда Успенского о ЧЕбурашке и крокодиле ГЕне был навеян![2]
- Че Геваре посвящена доставляющая песня Юза Алешковского.
- «Песняры» доставляют не меньше
- Про Че также есть с десяток доставляющих песен на испанском, среди них: Hasta Siempre Comandante, Zamba al Che, America, Te Habla Ernesto и одноименная Che Guevara.
- Написал подробную и толковую книгу про партизанскую борьбу. Всем готовящимся к борьбе с (вписать название неугодного режима, страны, организации) читать
- Дальним предком матери Че был Хулио Педро Гомес — гондольер из Гондураса генерал Хосе де ла Серна-э-Инохоса, вице-король Перу. Хотя испаноязычная педровикия утверждает, что это не так, так как вице-король Хосе де ля Серна и Мартинес де Инохоса не оставил отпрысков. Вообще. По крайней мере, официально зарегистрированных. «Мало ли в Бразилии Педров!» Мать Че и вице-король Перу — просто однофамильцы.
- Мыться не любил похлеще некоторых компьютерных задротов, за что получил прозвище «Боров»:
|
И, конечно, Эрнесто продолжал играть в регби с братьями Гранадо. Его друг Барраль отзывался о Геваре как о самом азартном игроке в команде, хотя он все также постоянно носил с собой на игры ингалятор. |
| Пако Игнасио Тайбо |
- Ещё не став всенародным символом, он уже начал работать в рекламе, откатав на выделенном для теста живучести дырчике турне в четыре тысячи километров.
- Чтобы было чего похавать, Эрнесто подрабатывал библиотекарем, мыл в ресторанах посуду, лечил крестьян и прочих сельскохозяйственных животных, чинил радиоприёмники, работал грузчиком, носильщиком и матросом, торговал фотографиями и писал статьи в газеты. А ты готов к труду, %username%?
- Устроил с комрадом Гранандосом релаксационный пикничок с матэ и философскими разговорами на площадке жертвоприношений инкского храма в Мачу-Пикчу.
- Был арестован злыми бразильскими копами за усталый вид и выпущен под обещание натренировать местную футбольную команду. Команда под руководством астматичного врача таки выиграла, epic win.
- Че Гевара откосил от армии.
- Эрнесто в свое время пришел к выводу, что для того, чтобы быть успешным и богатым врачом не обязательно быть нормальным специалистом, а необходимо обслуживать господствующие классы и изобретать бесполезные лекарства для воображаемых больных, чем ныне и занимаются современные эскулапы.
- Че ни на кого не кричал и не допускал издевок, но часто употреблял в разговоре хуй крепкие слова и бывал очень резок при необходимости.
- Будучи марксистом, Че упрекал Совок и Кетай в империализме.
- Че Гевара в начале 1950-х шутливо подписывается под письмами «Сталин II».
- Че при всех денежных реформах изображается на лицевой стороне купюры достоинством в три кубинских песо.
- Че знал что опытный муганга всегда помнит о последствиях плохой давы.
- Че Геваре отрубили руки, «чтобы кубинский товарищ поменьше раздвигал буржуям ягодицы».
- Поговаривают, что Че записал было музыкальный альбом совместно с самим Ленноном, там же, в Боливии. Увы реализирован он никогда не был, а оба героя были выпилены злостными ЦРУ-шниками[3]
Галерея[править]
-
-
-
Че Бурашка
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Анонимъ
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Ещё Че Бурашка
-
-
-
-
-
Блю Че
-
-
Не брезгуем
См. также[править]
- Куба
- Cuba77
- Игорь Растеряев он же Че Гевара
Примечания[править]
- ↑ Это звёздочка Хосе Марти — отличительный знак команданте (майора), высшего звания Повстанческой армии Кубы.
- ↑ «Чебурашка» был написан в 1966 году, а Сабж отдал последний долг революции в 1967, что какбе намекает.
| Основы | Античеловечество • Великий Архитектор Вселенной • Добро • Зло • Absence of Value and Meaning • Притча про доллар и евро • Новая нормальность • Атака мирового правительства |
| Добрые люди | Женечка • משיח בן דוד • Дональд Трамп • Марин Ле Пен • Илон Маск • Царь Соломон • Мудрец • Мудрый рав • Че Гевара • Анатолий Вассерман • Говард Лавкрафт • Егор Холмогоров • Павел Дуров • Стив Джобс • Эдвард Сноуден • Владимир Атомное Солнышко |
| Добрые явления | Табу • Антисексуал • Уменьшение потребления • Не Толерантен • Волк-гомофоб • Закрой глаза и думай об Англии • Гетеросексуализм • Язык ненависти • И это пройдёт • Крах проекта глобализации • Шейминг • Гетеронормативность • Мисгендеринг • Обвинение жертвы • Православие • Гудение • Гомофобия • Асексуал • Атомная бомба • Император • Постмодернизм • Сексизм |
| Злые люди | Князь мира сего • Масонская пирамида • Первый змей • Аннунаки • Прогрессисты • Апостолы античеловечества • Гендерквир • Антихрист • Демон • Снежинки • Гомосексуалист • Лесбиянка • Дьявол • Барак Обама • Вампиры • Дмитрий Хомак • Ричард Докинз • Михаил Горбачёв • Грета Тунберг • Роман Беккер • Инцел • Куколд |
| Злые явления | Swift • ЛГБТ • Материализм • Сексуальное просвещение • Радужный флаг • РПЦ/Адельфопоэзис • Глобализация • Гей-пропаганда в российских школах • Опарашивание • Экспроприация радуги • Моральный релятивизм • Культ успеха • Культ удовольствия • Ползучая оккупация • Смертные грехи • Работа на развал • Многовекторность • Капитализм • Этот мир • Отдел токсичности и здоровья • Инфантилизация • Коллапс России • Гендерные исследования • Гей-технология • Электронный паспорт • Изменение климата • Загрязнение воздуха • Дискриминация мужчин • Общество потребления • Радикальный феминизм • Секс • Снос порядка • Гендер • Инклюзивность • Развод • Небинарный гендер • Бодипозитив • Фастфуд • Трансгуманизм • Троллинг верующих • Алкоголизм • Канселинг • Травля Гарри Поттера • Гомосексуализм в сериалах • Репорт • Нытье • Повестка SJW • Любовь (заболевание) • Влюбленность • Третий гендер • Скурвился • BDSM • Copyright • Friend Zone • Политкорректность • Радиация • Сатанизм • Холокост • Ювенальная юстиция • Гей-парад • Гомосексуалист-надомник • Ночной клуб • Проститутка • Секс-туризм • Анальный секс • Все мужчины думают только о сексе • Гибель цивилизации • Позитивная дискриминация • Политкорректный реткон • Деградация системы образования • Культурная апроприация • Пустое Будущее • Активное согласие • Адаптация от Netflix • Расизм против белых |
| Столкновения | Мировое правительство против России • Чумной барак • Запрет пропаганды гомосексуализма в России • Дана сила вредить • Изгнание из рая • Илон Маск против Твиттера • SJW это фашисты • Искажение левой идеи активистами SJW • Ересь папы римского Франциска • Потреблядство • Мягкая сила • Клоунский мир • Частотная Революция • Культурный марксизм |
Че Гевара, Эрнесто
| Эрнесто Че Гевара Ernesto Guevara de la Serna |
||
 |
||
|
||
|---|---|---|
| 23 февраля 1961 — 1 апреля 1965 | ||
| Предшественник: | Должность учреждена | |
| Преемник: | Артуро Гусман[1] | |
|
Президент Национального Банка Кубы |
||
| 26 ноября 1959 — 23 февраля 1961 | ||
| Партия: | Коммунистическая партия Кубы | |
| Образование: | Университет Буэнос-Айреса | |
| Профессия: | Врач-хирург и дерматолог[2] | |
| Вероисповедание: | Атеист | |
| Рождение: | 14 июня 1928 Росарио |
|
| Смерть: | 9 октября 1967 (39 лет) Ла-Игера |
|
| Похоронен: | Тайно захоронен на взлётно-посадочной полосе аэропорта Валье-Гранде[3], в 1997 году перезахоронен в Мавзолее Че Гевары | |
| Отец: | Эрнесто Гевара Линч | |
| Мать: | Селия де ла Серна | |
| Супруга: | 1) Ильда Гадеа (1955—1959) 2) Алейда Марч (с 1959) |
|
| Дети: | сыновья: Камило и Эрнесто дочери: Ильда, Алейда и Селия |
|
|
Эрнесто Че Гевара на Викискладе |
||
|
Эрнесто Че Гевара на Родоводе |
Эрне́сто Че Гева́ра (исп. Ernesto Che Guevara [ˈtʃe ɡeˈβaɾa], полное имя — Эрнесто Рафаэль Гевара Линч де ла Серна, исп. Ernesto Rafael Guevara Lynch de la Serna; 14 июня 1928, Росарио, Аргентина — 9 октября 1967, Ла-Игера, Боливия) — латиноамериканский революционер, команданте Кубинской революции 1959 года и кубинский государственный деятель. Кроме латиноамериканского континента действовал также в Республике Конго. Прозвище Че получил от кубинских повстанцев за характерное для аргентинцев междометие che, позаимствованное у индейцев гуарани, которое передаёт, в зависимости от интонации и контекста, различные чувства[4]. Чаще всего переводится как «друг, приятель».
Содержание
- 1 Биография
- 1.1 Детство, отрочество, юность
- 1.1.1 Увлечения
- 1.1.2 В трудные годы
- 1.1.3 Путешествие по Южной Америке
- 1.1.4 Второе путешествие по странам Латинской Америки
- 1.1.5 Гватемала
- 1.2 Жизнь в Мехико
- 1.3 Подготовка экспедиции на Кубу
- 1.4 Отплытие на «Гранме»
- 1.1 Детство, отрочество, юность
- 2 Кубинская революция
- 2.1 Первые дни
- 2.2 Сьерра-Маэстра
- 2.3 Бой при Уверо
- 2.4 Дальнейшая борьба
- 3 Че Гевара как государственный деятель
- 4 Последнее письмо Че Гевары родителям
- 5 Повстанец
- 5.1 Конго
- 5.2 Боливия
- 6 Плен и казнь
- 7 Геваризм
- 7.1 Фокизм
- 8 Символическая память о Че Геваре
- 8.1 Изображение на банкнотах
- 9 Образ Че в искусстве
- 9.1 Портрет работы Фицпатрика
- 9.2 Образ Че в литературе и поэзии
- 9.3 Фильмы о Че
- 10 Сочинения
- 11 Примечания
- 12 Библиография
- 13 Ссылки
Биография
Детство, отрочество, юность
Семья Че Гевары. Слева направо: Эрнесто Гевара, мать Селия, сестра Селия, брат Роберто, отец Эрнесто с сыном Хуаном Мартином на руках и сестра Анна Мария
Эрнесто Гевара родился 14 июня 1928 года в аргентинском городе Росарио, в семье архитектора ирландского происхождения Эрнесто Гевара Линч (1900—1987). По матери — доньи Селии де ла Серна ла Льоса (1908—1965) Че Гевара имел испанские корни. Вопреки распространенному мнению, последний вице-король Перу не был ему родственником[5]. Селия унаследовала плантацию иерба-матэ (парагвайский чай) в провинции Мисионес. Улучшив положение рабочих — в частности, начав выплачивать им зарплату деньгами, — отец Че вызвал недовольство окрестных плантаторов, и семья была вынуждена переселиться в Росарио, в то время — второй по размеру город Аргентины, открыв там фабрику по переработке чая иерба-матэ. В этом городе родился Че. Из-за мирового экономического кризиса семья через некоторое время вернулась в Мисионес на плантацию.[4]
Че Гевара в возрасте одного года (1929 г.)
Помимо Эрнесто, которого в детстве звали Тэтэ (в переводе «поросёнок»), в семье было ещё четверо детей: Селия (стала архитектором), Роберто (адвокат), Анна-Мария (архитектор), Хуан Мартин (проектировщик). Все дети получили высшее образование.[4]
В возрасте двух лет, 2 мая 1930 года[6] Тэтэ пережил первый приступ бронхиальной астмы — эта болезнь преследовала его до конца жизни. Для восстановления здоровья малыша семья переселилась в провинцию Кордова, как местность с более здоровым горным климатом. Продав поместье, семья приобрела «Виллу Нидию» в местечке Альта-Грасия, на высоте двух тысяч метров над уровнем моря. Отец стал работать строительным подрядчиком, а мать — присматривать за больным Тэтэ. Первые два года Че не мог посещать школу и учился на дому, поскольку страдал ежедневными приступами астмы[5]. После этого он прошёл с перерывами (из-за состояния здоровья) обучение в средней школе в Альта-Грасии. В тринадцатилетнем возрасте, Эрнесто поступил в принадлежащий государству колледж имени Деан-Фунеса [7] в Кордове, который он закончил в 1945 году, поступив затем на медицинский факультет университета Буэнос-Айреса[4]. Отец дон Эрнесто Гевара Линч в феврале 1969 года рассказывал:
Увлечения
В 1964 году, беседуя с корреспондентом кубинской газеты «Эль Мундо», Гевара рассказал, что он впервые заинтересовался Кубой в возрасте 11 лет, будучи увлечённым шахматами, когда в Буэнос-Айрес приехал кубинский шахматист Капабланка[4]. В доме родителей Че находилась библиотека из нескольких тысяч книг. Начиная с четырёхлетнего возраста Гевара, как и его родители, страстно увлёкся чтением, что продолжалось до конца его жизни.[4] В юношестве у будущего революционера был обширный круг чтения: Сальгари, Жюль Верн, Дюма, Гюго, Джек Лондон, позже — Сервантес, Анатоль Франс, Толстой, Достоевский, Горький, Энгельс, Ленин, Кропоткин, Бакунин, Карл Маркс, Фрейд[4][5]. Он прочёл популярные в то время социальные романы латиноамериканских авторов — Сиро Алегрии из Перу, Хорхе Икасы из Эквадора, Хосе Эустасио Риверы из Колумбии, где описывалась жизнь индейцев и рабочих на плантациях, произведения аргентинских авторов — Хосе Эрнандеса, Сармьенто и других[4].
Че Гевара (первый справа) с товарищами по регби, 1947 г.
Молодой Эрнесто читал в подлиннике на французском языке (зная этот язык с детства) и занимался толкованием философских работ Сартра «L’imagination», «Situations I» и «Situations II», «L’Être et le Nèant», «Baudlaire», «Qu’est-ce que la litèrature?», «L’imagie».[5] Он любил поэзию и даже сам сочинял стихи. Зачитывался Бодлером, Верленом, Гарсиа Лоркой, Антонио Мачадо, Пабло Неруда, произведениями современного ему испанского поэта-республиканца Леона Фелипе. В его рюкзаке, помимо «Боливийского дневника», посмертно была обнаружена тетрадь с его любимыми стихами. Впоследствии на Кубе были изданы двухтомное [8] и девятитомное [9] собрания сочинений Че Гевары.[10] Тэтэ был силён в точных науках, таких как математика, однако, выбрал профессию врача. Занимался футболом в местном спортивном клубе «Аталайя», играя в запасной команде (не мог играть в основном составе, поскольку из-за астмы ему время от времени требовался ингалятор). Также он занимался регби, конным спортом, увлекался гольфом и планеризмом, имея особую страсть к велосипедным путешествиям (в подписи на одной из своих фотографий, подаренних невесте Чинчине, он назвал себя «королём педали»).[4].
Эрнесто в Мар-дель-Плата (Аргентина), 1943 г.
В 1950 году, будучи уже студентом, Эрнесто нанялся матросом на нефтеналивное грузовое судно из Аргентины, побывав на Тринидад и в Британской Гвиане. После он совершил путешествие на мопеде, который был предоставлен ему фирмой «Микрон» в целях рекламы, с частичным покрытием расходов на путешествие. В объявлении из аргентинского журнала «Эль Графико» от 5 мая 1950 года Че писал:[4]
| 23 февраля 1950 года. Сеньоры, представители фирмы мопедов «Микрон». Посылаю Вам на проверку мопед «Микрон». На нём я совершил путешествие в четыре тысячи километров по двенадцати провинциям Аргентины. Мопед на протяжении всего путешествия функционировал безупречно, и я не обнаружил в нём малейшей неисправности. Надеюсь получить его обратно в таком же состоянии.
Подписано: «Эрнесто Гевара Серна» |
Юношеской любовью Че была Чинчина(в переводе «погремушка»), дочь одного из самых богатых помещиков Кордовы. Согласно свидетельству её сестры и других людей, Че любил её и хотел на ней жениться. Он являлся на званые вечера в потрёпанной одежде и лохматый, что являло собой контраст с отпрысками богатых семейств, добивавшихся её руки, и с типичным обликом аргентинских молодых людей того времени. Их отношениям помешало желание Че посвятить свою жизнь лечению прокажённых южноамериканцев, подобно Альберту Швейцеру, перед авторитетом которого он преклонялся.[4]
В трудные годы
Эрнесто Гевара в 1945 году
Гражданская война в Испании вызвала значительный общественный резонанс в Аргентине. Родители Гевары оказывали содействие Комитету помощи республиканской Испании, и приходились соседями и друзьями заместителя премьер-министра Негрина в правительстве Испании до поражения Республики Хуана Гонсалеса Агиляра, который эмигрировал в Аргентину и поселился в Альта-Грасии. Дети учились в одной школе, а затем в колледже в Кордове. Селия — мать Че — отвозила их ежедневно на машине в колледж. Видный республиканский генерал Хурадо, гостивший у Гонсалесов, бывал в доме семьи Гевара и рассказывал о событиях войны и действиях франкистов и немецких нацистов, что, по мнению отца, оказывало влияние на политические взгляды Че[4].
Во время Второй мировой войны президент Аргентины Хуан Перон поддерживал дипломатические отношения со странами «оси»; родители Че являлись одними из активных противников его режима. В частности, Селию арестовывали за её участие в одной из антиперонистских демонстраций в Кордове. Помимо неё в боевой организации против диктатуры Перона участвовал и её супруг; в доме фабриковались бомбы для демонстраций. Значительное воодушевление в среде республиканцев вызвали вести о победе СССР в Сталинградской битве[4].
Путешествие по Южной Америке
Эрнесто Че Гевара в 1951 году
Вместе с доктором биохимии Альберто Гранадосом (дружеское прозвище — Миаль), в течение восьми месяцев с февраля 1952 по август 1952 гг. Эрнесто Гевара совершил путешествие по странам Латинской Америки, побывав в Чили, Перу, Колумбии и Венесуэле[4]. Гранадос был старше Че на шесть лет. Он был родом из местечка Эрнандо, что на юге провинции Кордовы, окончил фармацевтический факультет университета, увлёкся проблемой лечения проказы и, проучившись в университете ещё три года, стал доктором биохимии. Начиная с 1945 г. работал в лепрозории в 180 км от Кордовы. В 1941 г. познакомился с Эрнесто Геварой, которому было тогда 13 лет, через своего брата Томаса — одноклассника Эрнесто по колледжу Деан-Фунес. Он стал часто посещать дом родителей Че, и пользовался их богатой библиотекой. Их сдружила любовь к чтению и споры о прочитанном. Гранадос вместе с братьями совершали длительные горные прогулки и строили шалаши на открытом воздухе в окрестностях Кордовы, и Эрнесто (родители считали, что это поможет его борьбе с астмой) часто присоединялся к ним.[4]
Семья Гевары проживала в Буэнос-Айресе, где Эрнесто учился на медицинском факультете. В институте по изучению аллергии он стажировался под руководством аргентинского учёного доктора Писани. В то время семья Гевары испытывали трудности с деньгами, и Эрнесто вынужден был подрабатывать библиотекарем. Приезжая на каникулы в Кордову, он навещал Альберто Гранадоса в лепрозории, помогал ему в опытах по исследованию новых методик лечения прокажённых. В один из его приездов, в сентябре 1951 года, Гранандос по совету своего брата Томаса предложил ему стать напарником в путешествии по Южной Америке. Гранадос намеревался посетить лепрозории в различных странах континента, ознакомиться с их работой и, возможно, написать об этом книгу. Эрнесто с воодушевлением принял это предложение, попросив подождать до момента, когда он сдаст очередные экзамены, поскольку обучался на последнем курсе медицинского факультета. Родители Эрнесто не возражали, при условии, что он возвратится не позже чем через год к сдаче выпускных экзаменов.[4]
29 декабря 1951 года, нагрузив сильно изношенный мотоцикл Гранадоса полезными предметами, палаткой, одеялами, и захватив фотоаппарат и автоматический пистолет, они отправились в путь. Заехали попрощаться с Чинчиной, которая дала Эрнесто 15 долларов и попросила привезти кружевное платье. Эрнесто подарил ей собачку, назвав её «Камбэк» — «Вернись». Попрощались также и с родителями Эрнесто. Гранандос вспоминал:[4]
Останавливаясь на ночлег в лесу или в поле, они зарабатывали средства на питание случайными подработками: мыли в ресторанах посуду, лечили крестьян или выступали в роли ветеринаров, чинили радиоприёмники, работали грузчиками, носильщиками или матросами. Обменивались опытом с коллегами, посещая лепрозории, где имели возможность отдохнуть от дороги. Гевара и Гранандос не боялись заражения, и испытывали участие к прокажённым, желая посвятить жизнь их лечению. 18 февраля 1952 года они прибыли в Темуко в Чили. Местная газета «Диарио Аустраль» опубликовала статью, озаглавленную: «Два аргентинских эксперта-лепролога путешествуют по Южной Америке на мотоцикле». Мотоцикл Гранандоса окончательно сломался недалеко от Сантьяго, после чего двигались до порта Вальпараисо (где намеревались посетить лепрозорий острова Пасхи, однако, узнали, что парохода пришлось бы ждать полгода, и отказались от затеи) и далее пешком, на попутках или «зайцами» на пароходах или поездах. Добрались пешком до медного рудника Чукикаматы, который принадлежал американской компании «Браден коппер майнинг компани», проведя ночь в казарме охранников рудника.[4] В Перу путешественники познакомились с жизнью индейцев кечуа и аймара, к тому времени эксплуатируемых помещиками и заглушавших голод листьями коки. В городе Куско, Эрнесто по нескольку часов зачитывался в местной библиотеке книгами об империи инков.[4] Несколько дней провели на развалинах древнего города инков Мачу-Пикчу в Перу. Расположившись на площадке для жертвоприношений старинного храма, стали пить матэ и фантазировать. Гранандос вспоминал диалог с Эрнесто:[4]
Из Мачу-Пикчу отправились в горное селение Уамбо, заехав по дороге в лепрозорий перуанского доктора-коммуниста Уго Песче. Он тепло встретил путешественников, познакомив их с известными ему методами лечения проказы, и написал рекомендательное письмо в крупный лепрозорий близ города Сан-Пабло провинции Лорето в Перу. Из селения Пукальпа на реке Укаяли, устроившись на судно, путешественники отправились до порта Икитоса на берегах Амазонки. В Икитосе они задержались из-за астмы Эрнесто, которая заставила его на некоторое время слечь в госпиталь. Добравшись до лепрозория в Сан-Пабло, Гранадос и Гевара получили сердечный приём, и были приглашены к лечению больных в лаборатории центра. Больные, пытаясь отблагодарить путешественников за дружеское к ним отношение, построили им плот, назвав его «Мамбо-Танго» на котором они могли бы доплыть до следующей точки маршрута — колумбийского порта Летисия на Амазонке.[4]
21 июня 1952 года, уложив вещи на плот, Гевара со своим товарищем поплыли вниз по Амазонке по направлению к Летисии. Много фотографировали и вели дневники. По неосторожности они проехали мимо Летисии, из-за чего пришлось приобретать лодку и возвращаться уже с бразильской территории. Имея подозрительный и усталый вид, оба товарища попали за решётку. По утверждению Гранадоса, начальник полиции, будучи футбольным болельщиком, знакомым с успехами в футболе Аргентины, освободил путешественников, узнав, откуда они родом, в обмен на обещание тренировать местную футбольную команду. Команда выиграла районный чемпионат, и болельщики купили им билеты на самолёт до столицы Колумбии — Боготы.[4] В Колумбии в то время действовала «виоленсия» президента Лауреано Гомеса, которая заключалась в силовом подавлении беспорядков со стороны крестьян. Гевара и Гранандос попали за решетку, однако, под обещание немедленно покинуть Колумбию, их отпустили. Получив от знакомых студентов деньги на дорогу, отправились на автобусе в город Кукту, рядом с Венесуэлой, а затем по международному мосту перешли границу до города Сан-Кристобаль в Венесуэле. 14 июля 1952 г. добрались до Каракаса.
Гранандос остался работать в Венесуэле в лепрозории Каракаса (который предложил месячное жалованье в восемьсот американских долларов), где он познакомился со своей будущей женой — Хулией. Че требовалось в одиночку добраться до Буэнос-Айреса. Случайно встретив дальнего родственника — торговца лошадьми, он в конце июля отправился сопровождать на самолёте партию лошадей из Каракаса в Майами, а оттуда ему предстояло вернуться порожним рейсом через Маракаибо в Буэнос-Айрес. Однако, в Майами Че задержался на месяц. Он успел купить Чинчине обещанное кружевное платье, но в Майами жил почти без денег, проводя время в местной библиотеке. В августе 1952 года Че вернулся в Буэнос-Айрес, где приступил к подготовке к экзаменам, и дипломной работе по проблемам аллергии. В марте 1953 года Гевара получил диплом доктора-хирурга в области дерматологии. Не желая служить в армии, при помощи ледяной ванны вызвал приступ астмы и был признан непригодным для военной службы. Имея диплом о медицинском образовании, он решил направиться в венесуэльский лепрозорий в Каракасе к Гранандосу, однако в дальнейшем судьба свела их только в 1960-е гг. на Кубе.[4]
Второе путешествие по странам Латинской Америки
Путь, который проехал Че Гевара, 1953—1956.
Эрнесто отправился в Венесуэлу через столицу Боливии — Ла-Пас, поездом, который назывался «молочный конвой» (поезд, который останавливался на всех полустанках, и где фермеры грузили бидоны с молоком). 9 апреля 1952 года в Боливии произошла 179-я по счёту революция, в которой участвовали шахтёры и крестьяне. Пришедшая к власти партия «Националистическое революционное движение», во главе с президентом Пас Эстенсоро, национализировала оловянные рудники (выплатив иностранным владельцам компенсацию), организовала милицию из шахтёров и крестьян, осуществила аграрную реформу. В Боливии Че бывал в горных селениях индейцев, посёлках шахтёров, встречался с членами правительства, и даже работал в управлении информации и культуры, а также, в ведомстве по осуществлению аграрной реформы. Посетил развалины индейских святилищ Тиауанаку, которые расположены вблизи озера Титикака, сделав множество снимков храма «Ворота солнца», где индейцы древней цивилизации поклонялись богу солнца Виракоче[4].
В Ла-Пасе (Боливия) Эрнесто познакомился с адвокатом Рикардо Рохо, который уговаривал его уехать в Гватемалу, однако он согласился быть попутчиком только до Колумбии, поскольку всё ещё имел намерение ехать в лепрозорий Каракаса, где его ждал Миаль (Гранадо). Рохо полетел самолётом в столицу Перу — Лиму, а Эрнесто на автобусе с попутчиком — студентом из Аргентины Карлосом Феррером объехали озеро Титикака, и прибыли в перуанский город Куско, где Эрнесто уже бывал во время предыдущего путешествия в 1952 году. После остановки пограничниками (у них отобрали брошюры и книги о революции в Боливии) они прибыли в Лиму, где встретились с Рохо.[4] Поскольку задерживаться в Лиме было опасно из-за политической обстановки в стране в годы правления генерала Одриа, путешественники — Рохо, Феррер и Эрнесто, поехали на автобусе по побережью Тихого океана к Эквадору, достигнув границы этой страны 26 сентября 1953 года. В Гуаякиле они обратились за визой в представительство Колумбии, однако, консул потребовал наличия у них авиабилетов до Боготы (Колумбия), посчитав небезопасным путешествие иностранцев на автобусе из-за только что произошедшего в Колумбии военного переворота (генерал Рохас Пинилья сверг правителя Лауреано Гомеса). Не имея средств на поездку на самолёте, путешественники обратились к местному деятелю социалистической партии с рекомендательным письмом, которое у них было от Сальвадора Альенде, и достали через него бесплатные билеты для студентов на пароход «Юнайтед фрут компани» из Гуаякиля в Панаму[4].
Гватемала
Под влиянием Рохо, а также сообщений в прессе о предстоящем вторжении США против Арбенса, Эрнесто отправляется в Гватемалу. Правительство Арбенса провело через парламент Гватемалы закон, согласно которому рабочим «Юнайтед фрут компани» была вдвое увеличена заработная плата. Было экспроприировано 554 тыс. гектаров земли помещиков, и в том числе 160 тыс. гектаров «Юнайтед фрут». Из Гуякиля Эрнесто послал Миалю открытку: «Малыш! Еду в Гватемалу. Потом тебе напишу», после чего связь между ними на время прервалась. В Панаме Гевара и Феррер задержались, поскольку у них закончились деньги, Рохо продолжил свой путь в Гватемалу. Гевара продал свои книги и напечатал в местном журнале ряд репортажей о Мачу-Пикчу и других исторических достопримечательностях Перу. В Сан-Хосе (Коста-Рика) отправились попутным грузовиком, который перевернулся из-за тропического ливня, после чего Эрнесто некоторое время с трудом владел левой рукой из-за ушиба[4]. Сан-Хосе путешественники достигли в начале декабря. Там Эрнесто познакомился с лидером венесуэльской партии «Демократическое действие» и будущим президентом Венесуэлы Ромуло Бетанкуром, с которым они резко разошлись во взглядах, писателем Хуаном Бошем из Доминиканской республики, будущим президентом этой страны, а также с кубинцами — противниками Батисты[4].
В конце 1953 года Гевара с друзьями из Аргентины отправились из Сан-Хосе в Сан-Сальвадор на автобусе, затем на попутных машинах 24 декабря достигли города Гватемала, расположенного на высоте 1800 метров над уровнем моря, столицы одноимённой республики. Имея рекомендательные письма к деятелям Гватемалы и письмо из Лимы к революционерке Ильде Гадеа, Эрнесто нашёл Ильду в пансионате «Сервантес», где поселился сам. Общие взгляды и интересы сблизили будущих супругов. Впоследствии Ильда Гадеа вспоминала о впечатлении, которое произвёл на неё Гевара:
| Доктор Эрнесто Гевара поразил меня с первых же бесед своим умом, серьёзностью, своими взглядами и знанием марксизма… Выходец из буржуазной семьи, он, имея на руках диплом врача, мог легко сделать карьеру у себя на родине, как это и делают в наших странах все специалисты, получившие высшее образование. Между тем он стремился работать в самых отсталых районах, даже бесплатно, чтобы лечить простых людей. Но больше всего вызвало моё восхищение его отношение к медицине. Он с негодованием говорил, исходя из виденного в своих путешествиях по разным странам Южной Америки, об антисанитарных условиях и нищете, в которых живут наши народы. Я хорошо помню, что мы обсуждали в связи с этим роман Арчибальда Кронина «Цитадель» и другие книги, в которых затрагивается тема долга врача по отношению к трудящимся. Ссылаясь на эти книги, Эрнесто приходил к выводу, что врач в наших странах не должен быть привилегированным специалистом, он не должен обслуживать господствующие классы, изобретать бесполезные лекарства для воображаемых больных. Разумеется, поступая так, можно заручиться солидными доходами и добиться успеха в жизни, но к этому ли следует стремиться молодым сознательным специалистам наших стран. Доктор Гевара считал, что врач обязан посвятить себя улучшению условий жизни широких масс. А это неминуемо приведет его к осуждению правительственных систем, господствующих в наших странах, эксплуатируемых олигархиями, где всё усиливалось вмешательство империализма янки.[4]
Ильда Гадеа |
В Гватемале Эрнесто встретился с эмигрантами из Кубы — сторонниками Фиделя Кастро, среди которых были Антонио Лопес Фернандес (Ньико), Марио Далмау, Дарио Лопас — будущие участники похода на яхте Гранма[4]. Желая поехать в качестве врача в индейские общины в отдалённый район Гватемалы — джунгли Петена, Эрнесто получил отказ от министерства здравоохранения, которое требовало сначала пройти процедуру подтверждения диплома врача в течение года. Случайные заработки, заметки в газеты и торговля вразнос книгами (которые он, по замечанию Ильды, больше читал, чем продавал), позволяли ему заработать средства на существование. Путешествуя по Гватемале с котомкой за плечами, он изучал культуру древних индейцев майя. Сотрудничал с молодежной организацией «Патриотическая молодежь труда» Гватемальской партии труда[4].
17 июня 1954 года произошло вторжение вооруженных групп Армаса из Гондураса на территорию Гватемалы, начались расстрелы сторонников правительства Арбенса и бомбардировки столицы и других городов Гватемалы. Эрнесто, по словам Ильды, просил, чтобы его отправили в район боёв, и призывал к созданию ополчения. Он входил в группы противовоздушной обороны города во время бомбёжек, помогал в перевозке оружия. Марио Дальмау утверждал, что «Вместе с членами организации Патриотическая молодежь труда, он несёт караульную службу среди пожаров и разрывов бомб, подвергая себя смертельной опасности». Эрнесто Гевара попал в список «опасных коммунистов», подлежащих ликвидации после свержения Арбенса. Посол Аргентины предупредил его в пансионе «Сервантес» об опасности и предложил воспользоваться убежищем в посольстве, в котором он укрылся вместе с рядом других сторонников Арбенса, после чего, при помощи посла, покинул страну и выехал на поезде в Мехико с попутчиком Патохо (Хулио Роберто Касерес Валье)[4].
Жизнь в Мехико
21 сентября 1954 года они прибыли в Мехико. Там поселились на квартире пуэрториканца Хуана Хуарбэ — деятеля Националистической партии, которая выступала за независимость Пуэрто-Рико и была вне закона из-за учинённой ими стрельбы в конгрессе США. На этой же квартире проживал перуанец Лючо (Луис) де ла Пуэнте, который впоследствии, 23 октября 1965 года, был застрелен в бою с антипартизанскими «рейнджерами» в одном из горных районов Перу[4]. Че и Патохо, не имея стабильных средств к существованию, промышляли снимками в парках. Че вспоминал это время так:[4]
Написав статью «Я видел свержение Арбенса», Че, однако, не сумел устроиться журналистом. В это время из Гватемалы приехала Ильда Гадеа, и они поженились. Че стал торговать книгами издательства «Фондо де культура экономика», устроился ночным сторожем на книжную выставку, продолжая читать книги. В городской больнице его приняли по конкурсу на работу в аллергическое отделение. Он читал лекции по медицине в Национальном университете, стал заниматься научной работой (в частности, опытами на кошках) в Институте кардиологии и лаборатории французской больницы.[4] 15 февраля 1956 года Ильда родила дочь, которую назвали в честь матери Ильдитой. В интервью с корреспондентом мексиканского журнала «Сьемпре», в сентябре 1959 года, Че утверждал:
Рауль Роа, кубинский публицист и противник Батисты, впоследствии ставший министром иностранных дел в социалистической Кубе, вспоминал о своей мексиканской встрече с Геварой:[4]
| Я познакомился с Че однажды ночью, в доме его соотечественника Рикардо Рохо. Он только что прибыл из Гватемалы, где впервые принимал участие в революционном и антиимпериалистическом движении. Он ещё остро переживал поражение. Че казался и был молодым. Его образ запечатлелся в моей памяти: ясный ум, аскетическая бледность, астматическое дыхание, выпуклый лоб, густая шевелюра, решительные суждения, энергичный подбородок, спокойные движения, чуткий, проницательный взгляд, острая мысль, говорит спокойно, смеется звонко… Он только что приступил к работе в аллергическом отделении Института кардиологии. Мы говорили об Аргентине, Гватемале и Кубе, рассматривали их проблемы сквозь призму Латинской Америки. Уже тогда Че возвышался над узким горизонтом креольских национализмов и рассуждал с позиций континентального революционера. Этот аргентинский врач в отличие от многих эмигрантов, обеспокоенных судьбами лишь своей страны, думал не столько об Аргентине, сколько о Латинской Америке в целом, стараясь нащупать её самое «слабое звено». |
Подготовка экспедиции на Кубу
| Участь революционера-авангардиста возвышенна и печальна…
Эрнесто Че Гевара |
В конце июня 1955 года в городскую больницу Мехико, к дежурному врачу — Эрнесто Геваре, пришли на консультацию два кубинца, одним из которых оказался Ньико Лопес, знакомый Че по Гватемале. Он рассказал Че, что кубинские революционеры, нападавшие на казармы «Монкада», были выпущены из каторжной тюрьмы на острове Пинос по амнистии, и начали съезжаться в Мехико и готовить экспедицию на Кубу. Через несколько дней последовало знакомство с Раулем Кастро, в котором Че нашёл единомышленника, сказав впоследствии о нём: «Мне кажется, что этот не похож на других. По крайней мере, говорит лучше других, кроме того, он думает». В это время Фидель, находясь в США, собирал среди эмигрантов с Кубы деньги на экспедицию. Выступив в Нью-Йорке на митинге против Батисты, Фидель заявил: «Могу сообщить вам со всей ответственностью, что в 1956 году мы обретем свободу или станем мучениками».[4]
Флаг Движения 26 июля
Встреча Фиделя и Че произошла 9 июля 1955 года в доме у Марии-Антонии Гонсалес, на улице Эмпаран, 49, где была организована конспиративная квартира сторонников Фиделя. На встрече обсуждали подробности предстоящих боевых действий в Ориенте. Фидель утверждал, что Че на тот момент «имел более зрелые по сравнению со мной революционные идеи. В идеологическом, теоретическом плане он был более развитым. По сравнению со мной он был более передовым революционером». К утру Че, на которого Фидель произвёл, по его словам, впечатление «исключительного человека», был зачислен врачом в отряд будущей экспедиции[4]. Спустя некоторое время, в Аргентине произошёл очередной военный переворот, и был свергнут Перон. Эмигрантам — противникам Перона было предложено вернуться в Буэнос-Айрес, чем воспользовались Рохо и другие проживавшие в Мехико аргентинцы. Че отказался сделать то же самое, поскольку был увлечён предстоящей экспедицией на Кубу.[4] Мексиканец Арсасио Ванегас Арройо владел небольшой типографией и был знаком с Марией-Антонией Гонсалес. В его типографии печатали документы «Движения 26 июля», которое возглавлял Фидель. Кроме этого, Арсасио занимался физической подготовкой участников предстоящей экспедиции на Кубу, будучи спортсменом-борцом: продолжительными пешими походами по пересеченной местности, дзю-до, был нанят легкоатлетический зал. Арсасио вспоминал: «Кроме того, ребята слушали лекции по географии, истории, о политическом положении и на другие темы. Иногда я сам оставался послушать эти лекции. Ребята также ходили в кино смотреть фильмы о войне».[4]
Полковник испанской армии Альберто Байо, ветеран войны с франкистами и автор пособия «150 вопросов партизану», занимался военной подготовкой группы. Поначалу запросив плату в размере 100 тысяч мексиканских песо (или 8 тыс. американских долларов), затем уменьшил её вдвое. Однако, поверив в возможности своих учеников, он не только не взял плату, но и продал свою мебельную фабрику, передав вырученные деньги группе Фиделя. Полковник приобрёл за 26 тысяч долларов США гасиенду «Санта-Роса» в 35 км от столицы, у Эрасмо Риверы, бывшего партизана Панчо Вильи, в качестве новой базы для подготовки отряда. Че, проходя тренировки с группой, учил делать перевязки, лечить переломы, делать инъекции, получив более ста уколов на одном из занятий — по одному или нескольку от каждого из членов группы.
| Занимаясь вместе с ним на ранчо «Санта-Роса», я узнал, какой это был человек — всегда самый усердный, всегда преисполненный самым высоким чувством ответственности, готовый помочь каждому из нас… Я познакомился с ним, когда он останавливал мне кровотечение после удаления зуба. В то время я еле-еле умел читать. А он мне говорит: «Я буду учить тебя читать и разбираться в прочитанном…» Однажды мы шли по улице, он вдруг зашёл в книжный магазин и на те небольшие деньги, которые были у него, купил мне две книги — «Репортаж с петлей на шее» и «Молодую гвардию».[4]
Карлос Бермудес |
22 июня 1956 года мексиканская полиция арестовала Фиделя Кастро на одной из улиц Мехико. Затем была устроена засада на квартире Марии-Антонии, где задерживали всех входящих. На ранчо «Санта-Роса» полиция захватила Че и некоторых товарищей. Об аресте кубинских заговорщиков и участии в этом деле полковника Байо сообщалось в печати. Впоследствии выяснилось, что аресты производились по наводке Венерио, который проник в ряды заговорщиков. 26 июня мексиканская газета «Эксельсиор» опубликовала список арестованных, включая имя Эрнесто Гевары Серны, который был охарактеризован как «международный коммунистический агитатор» с упоминанием его роли в Гватемале при президенте Арбенсе.[4]
| После ареста нас повезли в тюрьму „Мигель Шульц“ — место заключения эмигрантов. Там я увидела Че. В дешевом прозрачном нейлоновом плаще и старой шляпе он смахивал на огородное пугало. И я, желая рассмешить его, сказала ему, какое он производит впечатление… Когда нас вывели из тюрьмы на допрос, ему единственному надели наручники. Я возмутилась и заявила представителю прокуратуры, что Гевара не преступник, чтобы надевать ему наручники и что в Мексике даже преступникам их не надевают. В тюрьму он возвращался уже без наручников.[4]
Мария-Антония |
За заключённых ходатайствовали бывший президент Ласаро Карденас, его бывший морской министр Эриберто Хара, рабочий лидер Ломбарде Толедано, художники Альфаро Сикейрос и Диего Ривера, а также деятели культуры и учёные. Через месяц мексиканские власти освободили Фиделя Кастро и остальных заключённых, за исключением Эрнесто Гевары и кубинца Каликсто Гарсии, которых обвинили в нелегальном въезде в страну.[4] Выйдя из тюрьмы, Фидель Кастро продолжил подготовку к экспедиции на Кубу, собирая деньги, покупая оружие и организовывая конспиративные явки. Подготовка бойцов продолжилась мелкими группами в различных местах страны.[4] У шведского этнографа Вернера Грина была приобретена яхта «Гранма» за 12 тысяч долларов. Че опасался, что заботы Фиделя по его вызволению из тюрьмы задержат отплытие, однако Фидель ему сказал: «Я тебя не брошу!». Мексиканская полиция арестовала и жену Че, однако через некоторое время Ильда и Че были выпущены на свободу. Че просидел в тюрьме 57 дней. Полицейские продолжали следить, врывались на конспиративные квартиры. Пресса писала о подготовке Фиделем отплытия на Кубу.[4] Франк Паис привёз из Сантьяго 8 тысяч долларов и был готов поднять в городе восстание.[4] Из-за участившихся облав и возможности выдачи группы, яхты и передатчика кубинскому посольству в Мехико провокатором за 15 тысяч долларов, приготовления были ускорены. Фидель отдал приказ изолировать предполагаемого провокатора и сосредоточиться в порту Туспана в Мексиканском заливе, где у причала стояла «Гранма». Франку Паису была отправлена телеграмма «Книга распродана» в качестве условленного сигнала о подготовке восстания в назначенный срок.[4] Че с медицинским саквояжем забежал домой к Ильде, поцеловал спящую дочь и написал прощальное письмо родителям.[4]
Отплытие на «Гранме»
В 2 часа утра 25 ноября 1956 года в Туспане отряд совершил посадку на «Гранму». Полиция получила «мордиду» (взятку) и отсутствовала на пристани. Че, Каликсто Гарсия и трое других революционеров добирались в Туспан на попутном автомобиле, которого пришлось долго ждать, за 180 песо. На полпути водитель отказался ехать дальше. Его удалось уговорить довезти до Роса-Рика, где они пересели на другую машину и добрались до места назначения. В Туспане их встретил Хуан Мануэль Маркес и отвёл к речному берегу, где стояла «Гранма».[4] 82 человека с оружием и снаряжением погрузились на переполненную яхту, которая была рассчитана на 8-12 человек. На море в это время был шторм и шёл дождь, «Гранма» с погашенными огнями легла курсом на Кубу.[4] Че вспоминал, что «из 82 человек только два или три матроса да четыре или пять пассажиров не страдали от морской болезни». Судно дало течь, как потом выяснилось, из-за открытого крана в уборной, однако, пытаясь ликвидировать осадку судна при неработающем насосе для откачки, успели побросать за борт консервы[4].
| Нужно иметь богатое воображение, чтобы представить себе, как могли на такой маленькой посудине разместиться 82 человека с оружием и снаряжением. Яхта была набита до отказа. Люди сидели буквально друг на друге. Продуктов взяли в обрез. В первые дни каждому выдавалось полбанки сгущенного молока, но вскоре оно кончилось. На четвёртый день каждый получил по кусочку сыра и колбасы, а на пятый остались лишь одни гнилые апельсины.[4]
Каликсто Гарсия |
На «Гранме» Че страдал от астмы, но, по утверждению Роберто Роке Нуньеса, подбадривал других и шутил. Капитаном судна был назначен Ладислао Ондино Пино, штурманом — Роберто Роке Нуньес. Последний побывал за бортом судна, упав с крыши капитанской рубки — в течение нескольких часов его искали и извлекали из воды. Яхта часто сбивалась с курса.[4] Время прибытия группы в селение Никеро вблизи Сантьяго было рассчитано на 30 ноября. В этот день, в 5:40 утра сторонники Франка Паиса захватили правительственные учреждения и вышли на улицы, но не смогли удержать ситуацию под контролем.[4]
Кубинская революция
Первые дни
«Гранма» прибыла к берегам Кубы только 2 декабря 1956 года в районе Лас Колорадас провинции Ориенте, тут же сев на мель. На воду была спущена шлюпка, но она затонула. Группа из 82 человек до берега добиралась вброд, по плечи в воде; на сушу удалось вынести оружие и небольшое количество еды. На место высадки, которое Рауль Кастро впоследствии сравнивал с «кораблекрушением», устремились катера и самолеты подчиненных Батисте подразделений, и группа Фиделя Кастро попала под обстрел. Группа продолжительное время пробиралась по заболоченному побережью, представляющему собой мангровые заросли. В ночь на 5 декабря революционеры шли по плантации сахарного тростника, к утру сделав привал на территории сентраля (сахарный завод вместе с плантацией) в местности Алегрия-де-Пио (Святая радость). Че, будучи врачом отряда, перевязывал товарищей, поскольку у них были стерты ноги от трудного похода в неудобной обуви, сделав последнюю перевязку бойцу отряда Умберто Ламоте. В середине дня в небе появились самолеты противника. Под огнем неприятеля в бою погибли половина бойцов отряда и приблизительно 20 человек попали в плен. На следующий день оставшиеся в живых собрались в хижине недалеко от Сьерра-Маэстры.[4]
Фидель сказал: «Враг нанес нам поражение, но не сумел нас уничтожить. Мы будем сражаться и выиграем эту войну». Гуахиро — крестьяне Кубы дружелюбно принимали участников отряда и укрывали их в своих домах.
| Где-нибудь в лесу, долгими ночами (с заходом солнца начиналось наше бездействие) строили мы дерзкие планы. Мечтали о сражениях, крупных операциях, о победе. Это были счастливые часы. Вместе со всеми я наслаждался впервые в моей жизни сигарами, которые научился курить, чтобы отгонять назойливых комаров. С тех пор въелся в меня аромат кубинского табака. И кружилась голова, то ли от крепкой „гаваны“, то ли от дерзости наших планов — один отчаяннее другого.[4]
Эрнесто Че Гевара |
Сьерра-Маэстра
Эрнесто Че Гевара на муле в горах Сьерра-Маэстра.
Кубинский писатель-коммунист Пабло де ла Торрьенте Брау писал, что ещё в XIX веке, в горах Сьерра-Маэстра борцы за независимость Кубы находили удобное укрытие. «Горе тому, кто поднимает меч на эти вершины. Повстанец с винтовкой, укрывшись за несокрушимым утесом, может сражаться здесь против десятерых. Пулеметчик, засевший в ущелье, сдержит натиск тысячи солдат. Пусть не рассчитывают на самолеты те, кто пойдет войной на эти вершины! Пещеры укроют повстанцев.». Фидель и участники экспедиции на Гранме, а также Че, не были знакомы с этой местностью.[4] 22 января 1957 года при Арройо-де-Инфьерно (Адский ручей) отряд нанёс поражение отряду каскитос (солдаты Батисты) Санчеса Москера. Пять каскитос были убиты, отряд не понес потерь.[4] 28 января Че написал письмо Ильде, которое дошло через доверенного человека в Сантьяго.[4]
| Дорогая старуха! Пишу тебе эти пылающие мартианские [11] строки из кубинской манигуа[12]. Я жив и жажду крови. Похоже на то, что я действительно солдат (по крайней мере, я грязный и оборванный), ибо пишу на походной тарелке, с ружьём на плече и новым приобретением в губах — сигарой. Дело оказалось не лёгким. Ты уже знаешь, что после семи дней плавания на «Гранме», где нельзя было даже дыхнуть, мы по вине штурмана оказались в вонючих зарослях, и продолжались наши несчастья до тех пор, пока на нас не напали в уже знаменитой Алегрия-де-Пио и не развеяли в разные стороны, подобно голубям. Там меня ранило в шею, и остался я жив только благодаря моему кошачьему счастью, ибо пулемётная пуля попала в ящик с патронами, который я таскал на груди, и оттуда рикошетом — в шею. Я бродил несколько дней по горам, считая себя опасно раненным, кроме раны в шее, у меня ещё сильно болела грудь. Из тебе знакомых ребят погиб только Джимми Хиртцель, он сдался в плен, и его убили. Я же вместе со знакомыми тебе Альмейдой и Рамирито провёл семь дней страшной голодухи и жажды, пока мы не вышли из окружения и при помощи крестьян не присоединились к Фиделю (говорят, хотя это ещё не подтверждено, что погиб и бедный Ньико). Нам пришлось немало потрудиться, чтобы вновь организоваться в отряд, вооружиться. После чего мы напали на армейский пост, несколько солдат мы убили и ранили, других взяли в плен. Убитые остались на месте боя. Некоторое время спустя мы захватили ещё трёх солдат и разоружили их. Если к этому добавить, что у нас не было потерь и что в горах мы как у себя дома, то тебе будет ясно, насколько деморализованы солдаты, им никогда не удастся нас окружить. Естественно, борьба ещё не выиграна, ещё предстоит немало сражений, но стрелка весов уже клонится в нашу сторону, и этот перевес будет с каждым днём увеличиваться. Теперь, говоря о вас, хотел бы знать, находишься ли ты все в том же доме, куда я тебе пишу, и как вы там живете, в особенности «самый нежный лепесток любви»? Обними её и поцелуй с такой силой, насколько позволяют её косточки. Я так спешил, что оставил в доме у Панчо твои и дочки фотографии. Пришли мне их. Можешь писать мне на адрес дяди и на имя Патохо. Письма могут немного задержаться, но, я думаю, дойдут. |
Помогавший отряду крестьянин Эутимио Герра был захвачен властями, и пообещал им убить Фиделя. Однако, его планы не осуществились, и он был расстрелян[4]. В феврале Че свалил приступ малярии, и затем новый приступ астмы. Во время одной из стычек крестьянин Креспо, взвалив Че себе на спину, вынес его из-под неприятельского огня, поскольку Че не мог передвигаться самостоятельно. Че был оставлен в доме фермера с сопровождающим бойцом, и смог преодолеть один из переходов, держась за стволы деревьев и опираясь на приклад ружья, за десять дней, при помощи адреналина, который фермер сумел раздобыть[4]. В горах Сьерра-Маэстра Че, страдавший от астмы, периодически отлеживался в крестьянских хижинах, чтобы не задерживать движение колонны. Его часто видели с книгой или с блокнотом в руках.[4]
| Я помню, у него было много книг. Он много читал. Он не терял ни минуты. Часто он жертвовал сном, чтобы почитать или сделать запись в дневнике. Если он вставал с зарей, он принимался за чтение. Часто он читал ночью при свете костра. У него было очень хорошее зрение.[4]
Марсиаль Ороско, капитан |
| Меня направляют в Сантьяго, и он просит привезти ему две книги. Одна из них — „Всеобщая песнь“ Пабло Неруды, а другая — поэтический сборник Мигеля Эрнандеса. Он очень любил стихи.[4]
Каликсто Моралес |
| Я не понимаю, как он мог ходить, болезнь его то и дело душила. Однако он шел по горам с вещевым мешком за спиной, с оружием, с полным снаряжением, как самый выносливый боец. Воля у него, конечно, была железная, но еще большей была преданность идеалам — вот что придавало ему силы.[4]
Антонио, капитан |
| Бедный Че! Я видела, как он страдает от астмы, и только вздыхала, когда начинался приступ. Он умолкал. дышал тихонечко, чтобы еще больше не растревожить болезнь. Некоторые во время приступа впадают в истерику, кашляют, раскрывают рот. Че старался сдержать приступ, успокоить астму. Он забивался в угол, садился на табурет или на камень и отдыхал.» В таких случаях она спешила приготовить ему теплое питьё.[4]
Понсиана Перес, крестьянка |
Участник отряда Рафаэль Чао утверждал, что Че ни на кого не кричал, и не допускал издевок, но часто употреблял в разговоре крепкие слова, и бывал очень резок, «когда нужно». «Я не знал менее эгоистичного человека. Если у него бывал всего один клубень бониато,[13] он готов был отдать его товарищам».[4]
На протяжении войны Че вёл дневник, который послужил основой для его известной книги «Эпизоды революционной войны».[4] Со временем отряду удалось установить связь с организацией «Движение 26 июля» в Сантьяго и Гаване. Место расположение отряда в горах посещали активисты и руководители подполья: Франк Паис, Армандо Харт, Вильма Эспин, Аиде Санта-Мария, Селия Санчес, было налажено снабжение отряда.[4] С целью опровергнуть сообщения Батисты о разгроме «разбойников» — «форахидос», Фидель Кастро отправил в Гавану Фаустино Переса, с поручением доставить иностранного журналиста. В расположение отряда 17 февраля 1957 года прибыл Герберт Мэтьюз, корреспондент газеты «Нью-Йорк Таймс». Он встретился с Фиделем, и через неделю опубликовал репортаж с фотографиями Фиделя и бойцов отряда. В этом репортаже он писал: «Судя по всему, у генерала Батисты нет оснований надеяться подавить восстание Кастро. Он может рассчитывать только на то, что одна из колонн солдат невзначай набредет на юного вождя и его штаб и уничтожит их, но это вряд ли случится…».[4]
13 марта 1957 года в Гаване студенческая организация «Революционный директорат 13 марта» подняла неудачное восстание, пытаясь захватить радиостанцию, университет и президентский дворец. Большинство восставших погибли в бою с армией и полицией[4]. В середине марта Франк Паис отправил в отряд Кастро подкрепление из 50 добровольцев под командованием подпольщика Хорхе Сотуса из Сантьяго, который принимал участие в восстании 30 ноября. Их привёз на грузовиках Уберто Матос — хозяин рисовой плантации. Сотус и Матос были антикоммунистами, и впоследствии были осуждены ревтрибуналом на длительное тюремное заключение (Сотус сбежал в США и погиб от разорвавшейся мины при подготовке диверсии против коммунистической Кубы). Пополнение состояло из горожан, которые не были привычны к длительным перемещениям по горной местности. Было принято решение приступить к их тренировкам. К отряду барбудос («бородачи», отпустившие бороду из-за походной жизни и отсутствия бритв) Фиделя присоединялись добровольцы различных политических взглядов, а средства, медикаменты и оружие доставляли зарубежные кубинские эмигранты.[4]
Бой при Уверо
-
Основная статья: Бой при Уверо
В мае 1957 года планировалось прибытие из США (Майами) судна «Коринтия» с подкреплением во главе с Каликсто Санчесом. Чтобы отвлечь внимание от их высадки, Фидель отдал приказ штурмовать казарму в селении Уверо, в 15 км от Сантьяго. Дополнительно это открывало возможность выхода из Сьерра-Маэстры в долину провинции Ориенте. Че принимал участие в бою за Уверо, и описал его в «Эпизодах революционной войны». 27 мая 1957 г. был собран штаб, где Фидель объявил о предстоящем бое. Начав поход вечером, за ночь прошли около 16 километров по горной извилистой дороге, затратив на путь около восьми часов, часто останавливаясь ради предосторожности, особенно в опасных районах. Проводником был Кальдеро, который хорошо ориентировался в районе казармы Уверо и подходах к нему. Деревянная казарма располагалась на берегу моря, её охраняли посты. Было решено окружить её в темноте с трех сторон. Группа Хорхе Сотуса и Гильермо Гарсии атаковала пост на прибрежной дороге из Пеладеро. Альмейде поручили ликвидировать пост напротив высоты. Фидель расположился в районе высоты, а взвод Рауля атаковал казармы с фронта. Че было отведено направление между ними. Камило Сьенфуэгос и Амейхейрас в темноте потеряли направление. Задачу нападения облегчало наличие кустарника, однако противник заметил наступавших и открыл огонь. Взвод Крессенсио Переса не участвовал в штурме, охраняя дорогу на Чивирико, чтобы блокировать подход подкреплений противника. Во время нападения было запрещено стрелять в жилые помещения, где находились женщины и дети. Раненым каскитос оказывали первую помощь, оставили двух своих тяжелораненых на попечение врача гарнизона противника. Нагрузив грузовик со снаряжением и медикаментами, отправились в горы. Че указывал, что от первого выстрела до захвата казармы прошло два часа сорок пять минут. Наступающие потеряли убитыми и ранеными 15 человек, а противник — 19 человек ранеными и 14 убитыми. Победа укрепила боевой дух отряда. Впоследствии были уничтожены другие мелкие гарнизоны противника у подножья Сьерра-Маэстры.[4]
Высадка с «Коринтии» закончилась неудачно: согласно официальным сообщениям, были убиты или захвачены в плен все революционеры, высадившиеся с этого судна. Батиста принял решение принудительно эвакуировать со склонов Сьерра-Маэстры местных крестьян, чтобы лишить революционеров поддержки населения, однако многие гуахиро сопротивлялись эвакуации, оказывали помощь отряду Фиделя, и вступали в их ряды.[4]
Дальнейшая борьба
Взаимоотношения с местными крестьянами не всегда происходили гладко: по радио и в церковных службах производилась пропаганда антикоммунизма. Крестьянка Инирия Гутьеррес вспоминала, что до вступления в отряд она слышала о коммунизме только «ужасные вещи», и была удивлена направленностью политических взглядов Че. В фельетоне, вышедшем в январе 1958 года в первом номере повстанческой газеты «Эль Кубано либре» за подписью «Снайпер», Че на этот счет писал: «Коммунистами являются все те, кто берется за оружие, ибо они устали от нищеты, в какой бы это стране ни происходило.»[4] Для подавления грабежей и анархии для улучшения взаимоотношений с местным населением в отряде была создана комиссия по соблюдению дисциплины, наделенная полномочиями военного трибунала. Была ликвидирована псевдореволюционная банда китайца Чанга. Че отмечал: «В то трудное время нужно было твердой рукой пресекать всякое нарушение революционной дисциплины и не позволять развиваться анархии в освобожденных районах». Производились расстрелы также и по фактам дезертирства из отряда. В отношении пленных оказывалась медицинская помощь, Че строго следил, чтобы их не обижали. Как правило, их отпускали на свободу.[4]
5 июня 1957 года Фидель Кастро выделил колонну под руководством Че в составе 75 бойцов (в целях конспирации она была названа четвёртой колонной). Че было присвоено звание майора. Бойцы были разбиты на три взвода, которыми командовали Лало Сардиньяс, Сиро Редондо (впоследствии погиб, и его именем была названа восьмая колонна) и Рамиро Вальдес (стал министром внутренних дел и членом Политбюро ЦК Коммунистической партии Кубы).[4] В июле представители буржуазной оппозиции Батисте Фелипе Пасос и Рауль Чибас прибыли на Сьерра-Маэстру. Фидель подписал манифест об образовании Революционного гражданского фронта, в требования которого входили замена Батисты выборным президентом и аграрная реформа, которая подразумевала раздел пустующих земель. Че считал этих деятелей «тесно связанными с северными владыками».[4] 30 июля в Сантьяго был убит полицией Франк Паис и его брат Хосуэ. Забастовка протеста в Сантьяго была подавлена властями. 5 сентября в городе Съенфуэгосе произошло восстание моряков военно-морской базы под руководством офицеров, выступавших за свержение Батисты. Восстание закончилось поражением и расстрелом пленных правительственными войсками. В ходе подавления восстания погибло свыше 600 человек[4]. В провинции Ориенте появились объявления властей:[4]
| Настоящим объявляется, что каждый человек, сообщивший сведения, которые могут способствовать успеху операции против мятежных групп под командованием Фиделя Кастро, Рауля Кастро, Крессенсио Переса, Гильермо Гонсалеса или других вожаков, будет вознагражден в зависимости от важности сообщенных им сведений; при этом вознаграждение в любом случае составит не менее 5 тысяч песо.
Размер вознаграждения может колебаться от 5 тысяч до 100 тысяч песо; наивысшая сумма в 100 тысяч песо будет заплачена за голову самого Фиделя Кастро. Примечание: имя сообщившего сведения навсегда останется в тайне. |
Рауль Кастро с Эрнесто Че Геварой в горах Сьерра-дель Кристаль к югу от Гаваны. 1958 г.
Опасаясь преследования полиции, противники Батисты пополняли ряды повстанцев в горах Сьерра-Маэстры. Возникли очаги восстания в горах Эскамбрая, Сьерра-дель-Кристаль и в районе Баракоа под руководством Революционного директората, «Движения 26 июля» и отдельных коммунистов.[4] В октябре в Майами политические деятели из буржуазного лагеря учредили Совет освобождения, провозгласив Фелипе Пасоса временным президентом. Ими был выпущен манифест к народу. Фидель отверг «майамский пакт», считая его проамериканским. В письме к Фиделю Че писал: «Еще раз поздравляю тебя с твоим заявлением. Я тебе говорил, что твоей заслугой всегда будет то, что ты доказал возможность вооруженной борьбы, пользующейся поддержкой народа. Теперь ты вступаешь на еще более замечательный путь, который приведет к власти в результате вооруженной борьбы масс».[4]
К концу 1957 года повстанческие войска господствовали на Сьерра-Маэстре, не спускаясь, однако, в долины. Продукты питания, такие как фасоль, кукурузу и рис, покупали у местных крестьян. Медикаменты доставлялись подпольщиками из города. Мясо конфисковывалось у крупных скотопромышленников и тех кто был обвинен в предательстве, часть конфискованного передавалась местным крестьянам. Че организовывал санитарные пункты, полевые госпитали, мастерские для починки оружия, изготовления кустарной обуви, вещмешков, обмундирования, сигарет. На гектографе стала размножаться газета «Эль Кубано либре», которая получила свое название от газеты борцов за независимость Кубы в XIX в. В эфир стали выходить передачи небольшой радиостанции. Тесная связь с местным населением позволяла узнавать о появлении каскитос и лазутчиков противника.[4]
Правительственная пропаганда призывала к национальному единству и согласию, поскольку в городах Кубы ширилось забастовочное и повстанческое движение. В марте 1958 года правительство США заявило об эмбарго на доставку оружия силам Батисты, хотя вооружение и заправка самолетов правительственных войск на базе Гуантанамо ещё некоторое время продолжались. В конце 1958 г., согласно конституции (статуту), объявленной Батистой, должны были состояться президентские выборы. В Сьерра-Маэстре никто не говорил открытым текстом о коммунизме или социализме, а открыто предлагавшиеся Фиделем реформы, как то ликвидация латифундий, национализация транспорта, электрических компаний и других важных предприятий носили умеренный и не отрицавшийся даже проамериканскими политическими деятелями характер.[4]
Че Гевара как государственный деятель
Че Гевара в Москве в 1964 году.
Че Гевара полагал, что может рассчитывать на неограниченную экономическую помощь «братских» стран. Че, будучи министром революционного правительства, извлёк урок из конфликтов с братскими странами социалистического лагеря. Ведя переговоры об оказании поддержки, экономическом и военном сотрудничестве, обсуждая международную политику с китайскими и советскими руководителями, он пришёл к неожиданному выводу и имел мужество высказаться публично в своём знаменитом алжирском выступлении. Это была настоящая обвинительная речь против неинтернационалистической политики так называемых социалистических стран. Он упрекал их в навязывании беднейшим странам условий товарообмена, подобных тем, какие диктует империализм на мировом рынке, а также в отказе от безусловной поддержки, военной в том числе, в отказе от борьбы за национальное освобождение, в частности, в Конго и во Вьетнаме. Че прекрасно знал знаменитое уравнение Энгельса: чем менее развита экономика, тем больше роль насилия в становлении новой формации. Если в начале 1950-х он шутливо подписывается под письмами «Сталин II», то после победы революции вынужден доказывать: «На Кубе нет условий для становления сталинской системы»[14].
Позже Че Гевара скажет: «После революции работу делают не революционеры. Ее делают технократы и бюрократы. А они — контрреволюционеры»[14].
Близко знавшая Гевару, сестра Фиделя и Рауля Кастро Хуанита, впоследствии уехавшая в США, написала о нём в биографической книге «Фидель и Рауль, мои братья. Тайная история»:
Для него не имели значения ни суд, ни следствие. Он сразу начинал расстреливать, потому что был человеком без сердца
По её мнению появление Гевары на Кубе — «худшее, что могло с ней произойти»[15] Но при этом не следует забывать, что Хуанита уехала в США и сотрудничала с ЦРУ.
Последнее письмо Че Гевары родителям
1 апреля 1965 года, перед отправкой на «континентальную герилью», Че Гевара написал письма своим родителям, детям и Фиделю Кастро. Письмо родителям (в переводе Лаврецкого):
| Дорогие старики! Я вновь чувствую своими пятками ребра Росинанта, снова, облачившись в доспехи, я пускаюсь в путь. |
Повстанец
Конго
В апреле 1965 года Гевара прибыл в Республику Конго, где в это время продолжались боевые действия. С Конго у него были связаны большие надежды, он полагал, что огромная территория этой страны, покрытая джунглями, даст прекрасные возможности организации партизанской войны. В операции участвовали в общей сложности более 100 кубинцев-добровольцев. Однако с самого начала операцию в Конго преследовали неудачи. Отношения с местными повстанцами были достаточно сложными, и у Гевары не было веры в их руководство. В первом бою 29 июня силы кубинцев и повстанцев потерпели поражение. В дальнейшем Гевара пришёл к выводу, что выиграть войну с такими союзниками невозможно, но всё же продолжал операцию. Финальный удар по конголезской экспедиции Гевары был нанесён в октябре, когда к власти в Конго пришёл Жозеф Касавубу, выдвинувший инициативы по урегулированию конфликта. После заявлений Касавубу Танзания, служившая тыловой базой для кубинцев, прекратила их поддерживать. Геваре не оставалось ничего, кроме как прекратить операцию. Он вернулся в Танзанию и, находясь в кубинском посольстве, подготовил дневник операции в Конго, начинавшийся словами «Это история провала»[16].
Боливия
Слухи о местонахождении Гевары не прекращались в 1966—1967 годах. Представители мозамбикского движения за независимость ФРЕЛИМО сообщали о встрече с Че в Дар-эс-Саламе во время которой они отказались от предложенной им помощи в их революционном проекте. Правдой оказались слухи о том, что Гевара возглавлял партизан в Боливии. По приказу Фиделя Кастро боливийскими коммунистами специально была куплена земля для создания баз, где под руководством Гевары проходили подготовку партизаны. В окружение Гевары в качестве агента в Ла-Пасе была введена Хайд Тамара Бунке Бидер (известная также по прозвищу «Таня»), в прошлом агент Штази, которая, по некоторым сведениям, работала также на КГБ. Рене Барьентос, напуганный известиями о партизанах в своей стране, обратился за помощью к ЦРУ. Против Гевары было решено задействовать специально обученные для антипартизанских действий силы ЦРУ.
Партизанский отряд Гевары насчитывал около 50 человек и действовал как Армия национального освобождения Боливии (исп. Ejército de Liberación Nacional de Bolivia). Он был хорошо оснащён и провёл несколько успешных операций против регулярных войск в сложной гористой местности региона Камири. Однако, в сентябре боливийская армия смогла ликвидировать две группы партизан, убив одного из лидеров. Несмотря на жестокую природу конфликта, Гевара оказывал медицинскую помощь всем раненым боливийским солдатам, которые попадали в плен к партизанам, а позже освобождал их. Во время своего последнего боя в Куебрада-дель-Юро Гевара был ранен, в его винтовку попала пуля, которая вывела оружие из строя, и он расстрелял все патроны из пистолета. Когда его, безоружного и раненого, захватили в плен и привели под конвоем к школе, которая служила солдатам ЦРУ в качестве временной тюрьмы для партизан, он увидел там несколько раненых боливийских солдат. Гевара предложил оказать им медицинскую помощь, на что получил отказ от боливийского офицера. Сам Че получил только таблетку аспирина.
Плен и казнь
Труп Че Гевары после казни, 10 октября 1967 года.
Охоту на Гевару в Боливии возглавил Феликс Родригес, агент ЦРУ. Информатор сообщил Боливийским Специальным войскам о местонахождении партизанского отряда Гевары, и 8 октября 1967 года стоянка отряда была окружена, а сам Гевара был взят в плен в ущелье Куэбрада-дель-Юро. Со слов некоторых солдат, которые присутствовали при этом, когда они приблизились к Геваре во время перестрелки, он якобы крикнул: «Не стреляйте! Я — Че Гевара и стою для вас больше живым, чем мёртвым». Родригес, услышав о захвате Гевары, сразу же сообщил об этом в штаб-квартиру ЦРУ в Лэнгли, штат Вирджиния.
Труп Че Гевары после казни, 10 октября 1967 года.
Получив информацию о захвате Гевары, Барриентос немедленно дал приказ о его казни. Гевару привезли в полуразрушенное здание школы возле деревни Ла Игуера, где его продержали всю ночь. На следующий день он был расстрелян. В роли палача выступил сержант боливийской армии Марио Теран, который вытащил короткую соломинку в споре между солдатами за право убить Гевару. Чтобы поддержать официальную версию о смерти Гевары и инсценировать, что он погиб во время боя, а не был казнён без суда и следствия,Феликс Родригес приказал Терану стрелять осторожно по ногам Гевары, при этом лицо должно было оставаться неповреждённым для последующей идентификации. Че Гевара имел возможность сказать несколько последних слов перед смертью; он якобы сказал своему палачу: «Я знаю, ты здесь, чтобы убить меня. Стреляй, трус, ты просто убьешь человека». Тело казненного Гевары было привязано к полозьям вертолёта и доставлено в соседнее село Валлегранде, где его выставили напоказ прессе.
После казни Родригес присвоил некоторые личные вещи Гевары, включая его часы «Ролекс», и в течение последующих лет с гордостью хвастался этими «трофеями» перед журналистами. В настоящее время некоторые из этих вещей выставлены для обозрения в штаб-квартире ЦРУ.
После того, как военный хирург ампутировал руки Гевары, офицеры боливийской армии вывезли тело в неизвестном направлении и отказались сообщить, где оно было захоронено. 15 октября Фидель Кастро сообщил общественности о смерти Гевары. Смерть Гевары была признана тяжёлым ударом для социалистического революционного движения в Латинской Америке и во всем мире. Местные жители начали считать Гевара святым и обращались к нему «San Ernesto de La Higuera», прося о милостях.
В 1997 году останки обезглавленого тела были эксгумированы из-под взлетной полосы около Валлегранде, идентифицированы как принадлежащие Геваре и возвращены на Кубу. 17 октября 1997 года останки Гевары вместе с прочими шестерых других его товарищей, убитых во время партизанской кампании в Боливии, были перезахоронены с воинскими почестями в специально построенном мавзолее в городе Санта-Клара, где он выиграл решающую для кубинской революции битву.
Геваризм
Фокизм
Символическая память о Че Геваре
8 октября на Кубе отмечают день Героического Партизана, таким образом вспоминая команданте Гевару и его подвиги.
Изображение на банкнотах
- Че традиционно, при всех денежных реформах, изображается на лицевой стороне купюры достоинством три кубинских песо.
Образ Че в искусстве
Портрет работы Фицпатрика
Че Гевара на вывеске ресторана в Риге
Знаменитый во всём мире двухцветный портрет Че Гевары анфас, стал символом романтического революционного движения, но в настоящий момент, по мнению некоторых, он в значительной мере утратил смысловую нагрузку и превратился в китч, который используется в самых далёких от революции контекстах. Он создан ирландским художником Джимом Фицпатриком с фотографии 1960 года, сделанной кубинским фотографом Альберто Корда. На берете Че видна звёздочка Хосе Марти, отличительный признак команданте, полученная от Фиделя Кастро в июле 1957 года вместе с этим званием.
Альберто Корда не сделал свою фотографию общественным достоянием и даже подавал в суд за использование портрета в рекламе водки.
Образ Че в литературе и поэзии
Образ Че вдохновновлял не только революционные группы, подобные Чёрным пантерам и «Фракции Красной Армии» (РАФ), но и целый ряд литераторов. Хулио Кортасар написал рассказ «Воссоединение», в котором от первого лица повествуется о высадке партизан на некоем острове. Хотя все персонажи рассказа носят вымышленные имена, в некоторых из них угадываются реальные деятели кубинской революции, в частности, братья Кастро. В рассказчике, от лица которого ведётся повествование, легко узнаваем Че Гевара. Цитата из дневников команданте вынесена в эпиграф рассказа.
Дух Че Гевары появляется в романе Виктора Пелевина «Generation „П“», где он диктует главному герою текст, озаглавленный «Идентиализм как высшая стадия дуализма» (название явно пародирует заголовок работы Ленина «Империализм как высшая стадия капитализма»). В тексте, в частности, говорится: «Сейчас слова Будды доступны всем, а спасение находит немногих. Это, без сомнения, связано с новой культурной ситуацией, которую древние тексты всех религий называли грядущим „тёмным веком“. Соратники! Этот темный век уже наступил. И связано это прежде всего с той ролью, которую в жизни человека стали играть так называемые визуально-психические генераторы, или объекты второго рода». Знаменитейшая песня Hasta Siempre Comandante («Команданте навсегда»), вопреки распространённому мнению, была написана Карлосом Пуэблой до смерти Че Гевары, в 1965 году(сам Карлос Пуэбло дал к песне эпиграф «Первый текст был написан, когда Фидель зачитал письмо Че») . Наиболее известна её версия в исполнении Натали Кардон. Эта песня затем многократно перепевалась и модифицировалась.
Не обошли вниманием Че Гевару и советские литераторы. К примеру, поэт Дмитрий Павличко, ныне считающийся классиком украинской литературы, написал цикл стихотворений о Кубинской революции. Одно из них начинается так:
Широко известны также поэма Евгения Долматовского «Руки Гевары», «Кубинский цикл» Евгения Евтушенко. Также у группы «Песняры» есть песня Баллада о Че Геваре.
Че Геваре посвящены следующие строчки Ярослава Смелякова:
Фильмы о Че
- Дореволюционному этапу жизни Че Гевары посвящена биографическая картина «Дневники мотоциклиста» (исп. Diarios de motocicleta). Во время титров в конце фильма появляется сын Че Гевары, исполняющий песню на акустической гитаре.
- «Че!» (англ. Che!) (1969) режиссёр Ричард Фляйшнер, в роли Эрнесто Гевары — Омар Шариф
- «Че» (исп. Che) (2005) режиссёр Джош Эванс, в роли Эрнесто Гевары — Эдуардо Норьега
- «Че» (исп. Che) (2008) режиссёр Стивен Содерберг, в роли Эрнесто Гевары — Бенисио дель Торо (фильм о революционной борьбе на Кубе и о революционной борьбе в Боливии)
Сочинения
- Che Guevara E. Obras. 1957—1967. T. I—II. La Habana: Casa de las Americas, 1970. — (Colleccion nuestra America)
- Che Guevara E. Escritos y discursos. T. 1-9. La Habana: Editorial de Ciencias Sociales, 1977.
- Че Гевара Э. Статьи, выступления, письма. М.: Культурная Революция, 2006. ISBN 5-902764-06-8.
- Че Гевара Э. «Эпизоды революционной войны» М.: Военное издательство Министерства обороны СССР, 1974.
- Че Гевара Э. Дневник мотоциклиста. Перевод с испанского В. В. Симонова. СПб.: RedFish; Амфора, 2005. ISBN 5-483-00121-4.
- Че Гевара Э. Дневник мотоциклиста. Перевод с испанского А. Ведюшкина. Черданцево (Свердловская обл.): ИП «Клепиков М. В.», 2005. ISBN 5-91007-001-0.
- Че Гевара Э. Боливийский дневник
- Че Гевара Э.Партизанская война
- Че Гевара Э. ПАРТИЗАНСКАЯ ВОЙНА КАК МЕТОД
- Че Гевара Э. «Послание народам мира, отправленное на Конференцию трех континентов»
- Че Гевара Э. Куба и «План Кеннеди»
- Че Гевара Э. Экономические воззрения Эрнесто Че Гевары
- Че Гевара Э. Речь на Второй афро-азиатской экономической конференции
- Че Гевара Э. «Камень (Рассказ)»
- Че Гевара Э. «Письмо Че Гевары — Фиделю Кастро. Гавана, 1 апреля 1965 г.»
- Че Гевара Э. Письмо Армандо Харту Давалосу
- Че Гевара Э. Университетская реформа и революция
Примечания
- ↑ Butterfield Ryan. The Fall of Che Guevara: A Story of Soldiers, Spies, and Diplomats. Проверено 1999.Oxford University Press US.
- ↑ Дело врачей
- ↑ Секретные документы о Че Геваре рассекречены в Аргентине
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 Лаврецкий И. Р. Эрнесто Че Гевара. М., 1972.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 Александр Тарасов. Живые моськи лают на мертвого льва
- ↑ Че Гевара и его жизнь
- ↑ Священник, участник политического движения за независимость
- ↑ Che Guevara E. Obras. 1957—1967. Vol. I—II. La Habana, 1970.
- ↑ Che Guevara E. Escritos y discursos. T. 1-9. La Habana, 1977.
- ↑ Александр Тарасов. 44 года войны ЦРУ против Че Гевары
- ↑ Мартианские — от Хосе Марти (1850—1898)
- ↑ Манигуа — заросли дикого колючего кустарника.
- ↑ Бониато — сладкий картофель
- ↑ 1 2 В. Н. Миронов Человек с подошвами из ветра. Феномен Эрнесто Че Гевары: трагедия и триумф Опубликовано в НГ-ExLibris от 18.08.2005
- ↑ Кастро Х. Хуанита Кастро: У Че Гевары не было сердца
- ↑ Edward George. The Cuban Intervention in Angola, 1965—1991. Frank Cass, 2005, p. 31.
Библиография
- Джон Ли Андерсон. «Че Гевара. Важна только Революция», Серия «Главные герои», Амфора, 2009 г. ISBN 978-5-367-01010-7
- Гавриков Ю. М. Последний романтик революции. М., 2004.
- Гросс Х.-Э., Вольф К.-П. Че: «Мои мечты не знают границ». М.: Прогресс, 1984.
- Кормье Ж., Гевара Гадеа И., Гранадо Хименес А. Че Гевара. Ростов н/Д.: Феникс, 1997.
- Кормье Ж., Лапер Ж. Че Гевара. Спутник революции. М.: Астрель, АСТ, 2001. ISBN 5-17-008457-9
- Лаврецкий И. Р. Эрнесто Че Гевара. М.: Издательство ЦК ВЛКСМ «Молодая гвардия», 1972. («Жизнь замечательных людей»). Переиздания: 1973, 1978.
- Лаврецкий И. Р. Эрнесто Че Гевара. М.: Издательство «ТЕРРА», 2002.
- Поссе А., Пражские тетради // Иностранная литература, № 4, 2003.
- Тайбо II П. И. Гевара по прозвищу Че. М.: Эксмо, 2004.
- Оцифрованные книги о Че
- Александр Тарасов. «44 года войны ЦРУ против Че Гевары»
- Александр Тарасов. «Живые моськи лают на мёртвого льва: Че Гевара глазами „Ома“»
- Александр Тарасов. Русские дети Че Гевары и Джерри Рубина
- Олег Ясинский «Че принимает поздравления от Эво»
- Кива Майданик «Революционер»
- Даниэль Бенсаид. «Эрнесто Че Гевара: жизнь и деятельность, отразившие великие надежды уходящего столетия»
- Зинин М. Поражение на берегах Танганьики.
- Марк Васильев Че Гевара как революционный теоретик
Ссылки
- Статьи на странице памяти Эрнесто Че Гевары
- Эрнесто Рафаэль Гевара Линч де ла Серна
- Сайт, посвященный Че Геваре
- Песни о Че Геваре
- Фотографии Эрнесто Че Гевары
- (исп.) Che, Guía y Ejemplo Большая коллекция фотографий, писем, видео, биографические данные Че Гевары, а также песни, посвящённые Че.
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Че Гевара — биография
Эрнесто Че Гевара – писатель, лидер партизанского движения и видная фигура в истории кубинской революции. Че Гевара стал символом восстания; портрет народного лидера до сих пор является одним из самых узнаваемых изображений в мире.
Детство и юность
Эрнесто Гевара де ла Серна родился летом 1928-го года в Аргентине, в городе под названием Росарио. Эрнесто был старшим сыном в семье архитектора и домохозяйки. Семья относилась к буржуазному классу, мать будущего революционера происходила из рода потомственных плантаторов. Среди родственников родителей Эрнесто были аргентинские креолы – европейские поселенцы. Были среди его предков и калифорнийские креолы.
Первое время молодая семья проживала в Буэнос-Айресе. Вскоре мать Эрнесто, Селия, получила в наследство плантацию и супруги переехали в провинцию. Эрнесто-старший и Селия окунулись в плантаторский бизнес, стараясь зарабатывать честно. Супруги платили работникам зарплату деньгами, что было не слишком распространено среди других плантаторов. Не удивительно, что соседи с негодованием относились к нововведениям молодой семьи. В итоге, не выдержав нападок соседей пара отправилась жить в Росарио. Здесь и родился Эрнесто-младший, первенец супругов.
Вскоре у Эрнесто появились сестры, Анна-Мария и Селия. Потом родились еще и два брата – Хуан-Мартин и Роберто. Несмотря на кризис в Аргентине и сложности с финансами, родители постарались дать детям прекрасное образование. Практически все отпрыски семьи Гевара закончили университеты.
В детстве Эрнесто звали Тэтэ. В возрасте двух лет мальчик заболел бронхиальной астмой и страдал этим заболеванием всю жизнь. Родители решили облегчить болезнь сына и стали искать место с более подходящим климатом.
Спустя какое-то время семья переехала в Кордову, где и прошли детские годы Эрнесто. С детства мальчик был очень болезненным и не мог как другие дети ходить в школу. Однако уже в первые годы жизни малыш был невероятно смышленым, он научился читать в возрасте 4 лет. В доме была большая библиотека, поэтому ребенок без труда мог брать новые книги.
Среднюю школу юноша окончил в Альта-Грасии. После окончания школы он поступил в колледж, а потом и в медицинский вуз. Обучался будущий революционер по специальностям «дерматология» и «хирургия».
Если верить биографам Че Гевары, в юности он интересовался не только медицинской литературой. Большое впечатление на молодого человека произвели труды Карла Маркса, Владимира Ленина и Михаила Бакунина. Эрнесто великолепно говорил по-французски и знал на память множество стихов, писал он и свои собственные сочинения, хорошо играл в шахматы.
Несмотря на приступы астмы, Эрнесто занимался спортом. Рост юноши составлял 175 см, он обладал подтянутой фигурой. В юности он был запасным игроком в местной футбольной команде, был записан в конный клуб. В сфере интересов будущего революционера были поездки на велосипеде и гольф.
Биография Гевары гласит, что однажды он подарил своей невесте собственную фотографию, на которой сделал надпись – «король педали».
Путешествия
Эрнесто питал особую страсть к путешествиям. Путешествовать по миру молодой человек начал еще в студенчестве. Обучаясь в вузе, он нанялся матросом на грузовое судно. Таким образом он посетил остров Тринидад и Британскую Гвиану.
В дальнейшем Эрнесто принял участие в рекламной кампании фирмы «Микрон». Молодой человек должен был путешествовать на мопеде от этого производителя.
Вместе со своим другом и доктором биохимии Альберто Гранадо Эрнесто устроился исследователем в области лечения проказы. Вместе с товарищем будущий революционер посетил ряд лепрозориев в нескольких странах Южной Америки.
Друзьям приходилось самостоятельно искать деньги на путешествия. Они находили временные подработки – мыли посуду в кафетериях, работали ветеринарами, грузчиками. Иногда они останавливались на ночлег в лесу или в поле.
Интересно, что путешествия не помешали Эрнесто успешно окончить университет. В 1952-м году он защитил диплом и получил специальность хирурга. Волею судьбы он отправился в Венесуэлу, где освободилась должность работника лепрозория. Однако начинающий медик решил изменить планы и поехал в Гватемалу.
Словно само провидение вмешалось в биографию Эрнесто. Когда он приехал в Гватемалу, началась война. Глава государства, Хакобо Арбенс отказался от поста, на его место взошел Кастильо Армас. Армас оказался проамериканцем, из-за чего начались гонения представителей левого движения.
Увлеченный идеями великих коммунистов, Эрнесто оказался в самом эпицентре военных действий. Он оказывал поддержку противникам установившегося политического режима. Однако социалисты в итоге проиграли, а Эрнесто стал государственным преступником.
Аргентинцу пришлось скрывать свое местоположение. Он спрятался в аргентинском посольстве, а спустя несколько лет перебрался в Мехико. В новом городе ему пришлось сменить ряд профессий – он работал сторожем, журналистом и фотографом, не отказывался и от временных подработок.
К тому времени Эрнесто взял в жены Ильду Гадеа. С девушкой медик познакомился, когда жил в Гватемале. Вскоре аргентинец нашел работу в местной поликлинике. В 1955-м году к нему на прием зашел его приятель, оказавшийся кубинским революционером. Именно с этой встречи и началась профессиональная биография Че Гевары как лидера революционного восстания.
Молодой человек согласился на предложение друга и вступил в ряды партизанских отрядов, которые боролись против кубинского диктатора. Вскоре аргентинец отправился на Кубу.
Революция на Кубе
Летом 55-го года в Мехико оказался Фидель Кастро. Вместе с Кастро Эрнесто в будущем станет символом революционного движения на Кубе.
Однако пока молодые революционеры только готовили почву для будущего восстания. Они испытали огромное количество трудностей. Из-за случайной утечки информации мужчины оказались под арестом. Их чудом спасла защита общественных и политических деятелей. Несмотря на патронаж влиятельных особ, Че пришлось провести в тюрьме 57 дней.
После всех неприятностей революционеры отправились на Кубу. Это произошло в ноябре 1956-го года. Но судьба опять была не на их стороне – во время плавания корабль попал под авиационный обстрел местных властей. Многие партизаны погибли, кто-то из них попал в плен.
Смерть всегда бродила рядом с Эрнесто. Уже будучи партизаном он подхватил малярию. Во время лечения молодой человек много читал, делал записи в дневнике.
Спустя год партизанская деятельность Че и его сторонников увенчалась частичным успехом – им удалось захватить часть кубинских территорий, а именно горы Сьерра-Маэстра. Отряд стал пополняться новыми сторонниками, среди которых было много противников тогдашнего правителя Кубы Фульхенсио Батисты.
Примерно в это время Эрнесто был удостоен звания команданте. Он стал руководителем колонны из 75 солдат. Вместе с тем Че занимался пропагандистской деятельностью, будучи редактором газеты под названием «Свободная Куба».
Революционная машина продолжала набирать обороты. Партизанские войска начали работать вместе с коммунистами, стали атаковать противников на кубинских равнинах. Войска команданте смогли захватить Лас-Вильяс.
Во время продвижения партизаны осуществили несколько реформ для улучшения жизни местных крестьян, которые поддержали революционеров. Во время битвы за Санта-Карла в 1959-м году Че и его армия одержали победу. Батиста спешно покинул Кубу.
Слава
После окончательной победы партизанского движения в 1959-м году команданте становится гражданином Кубы. Постановление о присвоении Че кубинского гражданства принял лично Фидель Кастро.
Спустя несколько лет был опубликован труд Че под названием «Партизанская война». Уже спустя год Эрнесто вместе с другими политическими деятелями Кубы встретился с Юрием Гагариным. Первый космонавт мира прибыл с визитом на Кубу.
Вскоре Че был назначен министром промышленности Кубы. В этом качестве команданте отправился в Японию, Пакистан, Бирму и другие страны.
В дальнейшем мужчине вновь пришлось принять участие в боевых действиях. Отношения между социалистическим правительством Кубы и Америкой окончательно испортились. Команданте взял на себя руководство операцией по сопротивлению. Победу одержали кубинцы, план американского правительства окончательно провалился.
В течение нескольких следующих лет Че занимал важные государственные посты, выступал с публичными речами. Он никогда не отступал от своих принципов, которые становились причиной конфликтов с соседними странами. В своей знаменитой «Алжирской речи» команданте рассказал о своем видении развития стран третьего мира.
Революционер по натуре, Эрнесто не мог долго сидеть без дел. Политическая ситуация на Кубе нормализовалась, и бывший революционер решил покинуть эту страну. Он написал прощальные письма родителям и Фиделю Кастро, после чего покинул Кубу.
Че Гевара отправился в Конго, где назревал крупный политических кризис. Вместе с отрядом единомышленников Эрнесто вступил в ряды местных партизан-социалистов. Благодаря помощи опытного революционера повстанцы смогли добиться ряда компромиссов. Однако большая часть поставленных целей так и не была достигнута. Вскоре команданте решил покинуть Конго. Следующим маршрутом великого социалиста должна была стать Африка.
В Африке здоровье Че ухудшилось. Он заболел малярией, вернулись приступы астмы. Мужчину отправили в санаторий, однако даже на отдыхе он продолжал планировать новые революционные кампании.
В 1966-м году Эрнесто вернулся на Кубу. Здесь он стал руководителем повстанческого отряда в Боливии. Команданте рассматривался как одна из самых опасных фигур для ЦРУ. Американская служба разведки объявила вознаграждение за убийство революционера.
В Боливии Че пребывал чуть меньше года.
Отношения с СССР
Личность команданте интересовала многих политиков, в том числе и из СССР. Однако пристальное внимание советские политики обратили на Эрнесто, когда он стал министром промышленности Кубы.
Гевара был в составе первой делегации из Кубы в СССР. Делегация прибыла в страну Советов в 1960-м году, чтобы найти точки сбыта для кубинского сахара. Американский рынок был закрыт для социалистической Кубы.
Никита Хрущев лично пригласил Эрнесто подняться на верхушку Мавзолея во время военного парада в Москве. Несмотря на оказанные почести Че неоднократно критиковал образ жизни партийных деятелей советской России.
Окончательно отношения между команданте и советским правительством испортились, когда власть перешла в руки Леонида Брежнева. Брежнев придерживался мирных отношений с Америкой, поэтому из героя революции Эрнесто был «переименован» в персону нон грата. Даже некролог команданте вышел в советской прессе только спустя несколько дней после его гибели.
Личная жизнь
В личной жизни команданте было много женщин. Первую любовь он нашел в лице кузины Кармен. Красавица любила танцевать, чем и привлекла молодого человека.
Следующим увлечением юноши стала девушка из обеспеченного семейства в Кордове. Однако влюбленные так и не поженились. Между ними стояла не только разница в происхождении и материальном положении, но и разные планы на будущее. Студентом Эрнесто планировал связать свою жизнь с лечением прокаженных, а девушку такая участь не устраивала.
Всю свою жизнь Эрнесто посвятил борьбе за свободу и равноправие, поэтому многие его увлечения рождались в одно время с военными конфликтами и революциями. Его первой супругой стала революционерка Ильда, которая вскоре родила любимому дочь. Девочку было решено назвать в честь матери.
Во время сражений революционер писал дочери письма, полные любви и нежности. Эрнесто был очень привязан к девочке. Супругам-революционерам приходилось много времени проводить в разных странах. Их отношения выдержали четыре года, после чего Ильда и Эрнесто расстались.
Второй супругой команданте стала участница повстанческого движения и его персональный секретарь Алейда Марч Торрес. Интересно, что Алейда и Эрнесто стали встречаться еще до развода мужчины. В отношениях у них родилось четверо детей.
Последней любовью Че стала переводчица Тамара Бунке Бидер. Девушка была известна под именем Таня-партизанка. Об этих отношениях было мало что известно. О наличии любовницы вторая жена Эрнесто узнала только после его смерти.
Интересно, что приставка «Че» является не частью официального имени команданте. Так его называли соратники, когда хотели подчеркнуть его аргентинское происхождение. Данное междометие распространено в Аргентине в качестве личного обращения.
Смерть
Находясь в Боливии команданте попал в плен. Его подвергли страшным пыткам, пытаясь узнать нужную информацию. Однако Эрнесто отказывался сотрудничать с врагами. Осенью 1967-го года мужчину расстреляли.
Некий Марио Теран Саласар привел приговор в действие. Он выстрелил Че прямо в сердце. Это и стало причиной смерти великого революционера. Саласар прожил долгую жизнь, он видел своими глазами революцию. Скончался палач весной 2022-го года в возрасте 80 лет.



Изуродованные останки Эрнесто выставили на публичное обозрение. После этого мужчина был похоронен в общей могиле. После смерти Гевары от его тела были отделены руки – кисти стали доказательством смерти социалиста. Долгое время руки покойного хранились в формалине, но спустя год руки и дневники аргентинца были украдены, а потом переправлены на Кубу.
Труп Эрнесто Че Гевары долгое время покоился в безымянной могиле. Останки кубинского героя нашли только в 1997-м году. Тело Че было переправлено на Кубу. Сейчас команданте покоится в мавзолее в Санта-Кларе.
Память
- Че стал символом свободы, революции и борьбы. Ему посвящены книги, песни и стихи. Одну из книг, а именно «Evocation», написала вторая супруга команданте. Литературный труд Алейды Марч Торрес был издан в 2007-м году.
- О жизни Гевары было снято множество кинолент и передач. Среди фильмов о биографии команданте ленты «Дневники мотоциклиста», «Че» и многие другие.
- Каждый год 8 октября на Кубе отмечается День Героического партизана, когда весь народ чтит память великого революционера.
Ссылки
- Страница в Википедии
Для нас важна актуальность и достоверность информации. Если вы обнаружили ошибку или неточность, пожалуйста, сообщите нам. Выделите ошибку и нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Enter.
https://ria.ru/20130614/942759690.html
Биография Эрнесто Че Гевары
Биография Эрнесто Че Гевары — РИА Новости, 17.06.2013
Биография Эрнесто Че Гевары
14 июня 2013 года исполняется 85 лет со дня рождения латиноамериканского революционера и кубинского государственного деятеля Эрнесто Че Гевары.
2013-06-14T09:30
2013-06-14T09:30
2013-06-17T10:15
/html/head/meta[@name=’og:title’]/@content
/html/head/meta[@name=’og:description’]/@content
https://cdnn21.img.ria.ru/images/94251/27/942512721_0:84:1020:658_1920x0_80_0_0_f0e7ade67f6a8895dbbd8897838a0efa.jpg
боливия
куба
аргентина
америка
южная америка
северная америка
весь мир
РИА Новости
internet-group@rian.ru
7 495 645-6601
ФГУП МИА «Россия сегодня»
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
2013
РИА Новости
internet-group@rian.ru
7 495 645-6601
ФГУП МИА «Россия сегодня»
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
Новости
ru-RU
https://ria.ru/docs/about/copyright.html
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/
РИА Новости
internet-group@rian.ru
7 495 645-6601
ФГУП МИА «Россия сегодня»
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
https://cdnn21.img.ria.ru/images/94251/27/942512721_0:0:1020:765_1920x0_80_0_0_ad1ad4861a30ed047afdb7ead2efde4f.jpg
РИА Новости
internet-group@rian.ru
7 495 645-6601
ФГУП МИА «Россия сегодня»
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
РИА Новости
internet-group@rian.ru
7 495 645-6601
ФГУП МИА «Россия сегодня»
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
справки, в мире, боливия, куба, аргентина, эрнесто «че» гевара
Справки, В мире, Боливия, Куба, Аргентина, Америка, Южная Америка, Северная Америка, Весь мир, Эрнесто «Че» Гевара
09:30 14.06.2013 (обновлено: 10:15 17.06.2013)
Биография Эрнесто Че Гевары
14 июня 2013 года исполняется 85 лет со дня рождения латиноамериканского революционера и кубинского государственного деятеля Эрнесто Че Гевары.
Эрнесто Че Гевара (Ernesto Che Guevara) — полное имя Эрнесто Гевара де ла Серна — родился 14 июня 1928 года в Росарио (Аргентина). В возрасте двух лет Эрнесто перенес тяжелейшую форму бронхиальной астмы (и эта болезнь преследовала его всю жизнь), и для восстановления его здоровья семья переехала в Кордобу.
В 1950 году Гевара нанялся матросом на нефтеналивное грузовое судно из Аргентины, побывал на острове Тринидад и в Британской Гвиане.
В 1952 году Эрнесто вместе со своим братом Гранадо отправился в путешествие на мотоцикле по Южной Америке. Они посетили Чили, Перу, Колумбию и Венесуэлу.
В 1953 году закончил медицинский факультет Национального университета в Буэнос-Айресе, получил диплом врача.
С 1953 по 1954 годы Гевара совершил свое второе длительное путешествие по странам Латинской Америки. Он побывал в Боливии, Перу, Эквадоре, Колумбии, Панаме, Сальвадоре. В Гватемале он принял участие в защите правительства президента Арбенса, после поражения которого поселился в Мексике, где работал врачом. В этот период жизни Эрнесто Гевара получил свое прозвище «Че» за характерное для аргентинского испанского междометие Che, которым злоупотреблял в устной речи.
В 1955 году Че Гевара познакомился с Фиделем Кастро и вскоре вступил в его революционный отряд. В декабре 1956 года группа из 82-х революционеров прибыла на побережье Кубы в провинции Орьенте и начала атаку против режима Батисты.
В 1957 году Че Гевара стал командующим одной из пяти крупнейших партизанских колонн. 5 июня 1957 года Фидель Кастро выделил колонну под руководством Че Гевары в составе 75 бойцов. Че было присвоено звание команданте (майора). В ноябре 1958 года Гевара возглавил партизанскую атаку в провинции Орьенте на правительственные войска, в декабре колона Гевары захватила стратегическую точку в провинции — столицу город Санта-Клара в центре Кубы. В 1959 году Батиста сбежал из страны, которая перешла под контроль революционеров.
После победы революции Че Гевара получил кубинское гражданство, был начальником гарнизона крепости Ла-Кабанья (Гавана), директором Управления промышленного развития страны, участвовал в подготовке аграрной реформы.
В ноябре 1959 — феврале 1961 года был президентом Национального банка Кубы.
В 1960 году Че Гевара во главе экономической миссии Кубы посетил страны социалистического блока, в том числе Советский Союз.
В феврале 1961 года был назначен министром промышленности и главой Центрального совета планирования Кубы.
Че Гевара был одним из лидеров «Движения 26 июля», затем членом национального руководства Единой партии социалистической революции.
В апреле 1965 года обратился с письмом к Фиделю Кастро о своем решении продолжать участие в революционном движении одной из стран мира и покинул Кубу.
В ноябре 1966 года прибыл в Боливию для организации партизанского движения.
Созданный им партизанский отряд 8 октября 1967 года был окружен и разгромлен правительственными войсками. Эрнесто Че Гевара был ранен, захвачен в плен и на следующий день убит.
11 октября 1967 года его тело и тела еще шести его соратников были тайно похоронены около аэропорта в Вальегранде. В июле 1995 года было обнаружено местоположение могилы Гевары. А в июле 1997 года останки команданте были возвращены Кубе, в октябре 1997 года останки Че Гевары были перезахоронены в мавзолее города Санта-Клара на Кубе.
В 2000 году журнал «Тайм» включил Че Гевару в списки «20 героев и икон» и «Ста важнейших персон 20-го века».
Изображение команданте имеется на всех купюрах достоинством три кубинских песо.
Знаменитый во всем мире двухцветный портрет Че Гевары анфас стал символом романтического революционного движения. Портрет был создан ирландским художником Джимом Фицпатриком с фотографии 1960 года, сделанной кубинским фотографом Альберто Корда. На берете Че видна звездочка Хосе Марти, отличительный признак команданте, полученная от Фиделя Кастро в июле 1957 года вместе с этим званием.
8 октября на Кубе в память об Эрнесте Че Геваре отмечают День героического партизана.
Че Гевара был дважды женат, у него пятеро детей. В 1955 году он женился на перуанской революционерке Ильде Гадеа, которая родила Геваре дочь. В 1959 году его брак с Ильдой распался, и революционер женился на Алейде Марч, с которой познакомился в партизанском отряде. С Алейдой у них родились четверо детей.
Материал подготовлен на основе информации РИА Новости и открытых источников
Его имя – это символ, легенда, несмолкающая песня под ритмы испанской гитары. Одни его считают авантюристом, убийцей, бессердечным фанатиком. Для других он – герой, самоотверженный идеалист-романтик, пламенный борец за правду. Жители южной Боливии и вовсе почитают его как святого, сравнивая с самим Христом. Он был врачом, но стал революционером. Он был непригоден к военной службе, но всю жизнь провел на поле боя. От него были без ума женщины, но самой большой его любовью была Революция. Звали его — Эрнесто Че Гевара (полное имя — Эрнесто Гевара де ла Серна). Легендарная приставка «Че» приклеилась к нему чуть позже с легкой руки его кубинских товарищей: будучи аргентинцем по происхождению, он очень часто приправлял свою речь распространенным в Аргентине междометием «че» (что-то вроде русского «ну» или «эй»).
Эрнесто Че Гевара
Детство, юношество, учеба
Родился будущий команданте 14 июня 1928 года в аргентинском городе Росарио, в семье архитектора Гевары Линча и юной красавицы Селии де ла Серны из старинного аристократического рода. Родители Че Гевары владели плантациями кустарников падуба, из листьев которых изготовлялся знаменитый парагвайский чай мате. Семья жила относительно безбедно, за исключением периодических денежных трудностей, связанных с засухами и колебаниями цен на рынке. Эрнесто был самым старшим ребенком, кроме него семья воспитывала еще четверых детей.
В двухлетнем возрасте у маленького Тэтэ (уменьшительное от Эрнесто) случился первый приступ бронхиальной астмы. Назначенные врачом лекарства не помогали, мальчика все чаще донимало удушье и жуткий кашель. Всеми силами родители пытались если не вылечить, то хотя бы облегчить течение болезни. Нужно было срочно менять климат. Именно поэтому в 1934 году семейство Гевары переезжает в небольшое местечко Альта-Грасия в провинции Кордова, славящейся хвойными лесами и чистым горным воздухом. Там мальчику действительно стало легче, но астма не отступала.
Маленький Тэтэ с матерью
По причине болезни Тэтэ до 9 лет не ходил в школу, и все это время его образованием занималась мать, которая научила его чтению и письму. Эрнесто был очень активным ребенком. В периоды затишья между приступами он играл в футбол, гольф, настольный теннис, купался на речке, бегал в горы с ребятней. В 1937 году Тэтэ поступает сразу же во второй класс средней школы. «Незаметный на уроках, но заводила на площадке» — так вспоминала об Эрнесто его учительница. Следующим этапом была гимназия имени Деана Фунеса, где он также слыл хулиганом и задирой. Но здесь проявилась и другая его сторона – любовь к литературе. Он буквально запоем читал Джека Лондона, Жюля Верна, Пабло Неруду, Фрейда. Чуть позже увлекся Камю, Сартром, Достоевским, Марксом.
Эрнесто с семьей (крайний слева)
В 1947 году семья переезжает в Буэнос-Айрес, где Эрнесто поступает на медицинский факультет государственного университета. Именно здесь, в стенах альма-матер, формируется его гуманистическое мировоззрение. Будучи на последнем курсе, он отправляется в путешествие по Латинской Америке вместе со своим другом Альберто Гранадо. Более полугода они колесят по континенту и проживают в лепрозориях в качестве волонтеров, оказывая помощь в лечении больных проказой. Друзья побывали в Чили, Перу, ночевали на развалинах инкского города Мачу-Пикчу, работали грузчиками, посудомойщиками, путешествовали «зайцами» на пароходах и поездах. Во время поездки Эрнесто увидел нищету, неравенство, проникся тягостным положением индейцев и крестьян. Именно в это время у него просыпается отчетливое неприятие социальной несправедливости и вырисовывается главный виновник этого – западный империализм.
Эрнесто Гевара в молодости. 1951 г.
Революционные вехи
Вскоре после получения диплома новоиспеченный доктор Гевара снова отправляется в путешествие по континенту, посещая страны Карибского бассейна. В конце 1953 года он останавливается в Гватемале, возглавляемой президентом Арбенсом, который на тот момент проводил в стране масштабные реформы: национализировал земли латифундистов, в том числе крупнейшего гиганта United Fruit Company, добивался повышения зарплат рабочих, защищал интересы безземельных крестьян. Это вызвало возмущение официального Вашингтона, называвшего Гватемалу «красным аванпостом», «марионеткой Москвы». После нескольких попыток травли, диверсий в июне 1954 года США организовывают открытое вторжение в Гватемалу армии подготовленных ЦРУ наемников во главе с завербованным подполковником Армасом. Эрнесто тут же вступает в ряды народного ополчения и сражается против агрессора. Однако вскоре Арбенс все-таки покидает пост президента, а власть в стране переходит в руки военной хунты. Опасаясь репрессий, Гевара вначале находит убежище в аргентинском посольстве, а затем уезжает в Мехико.
В Мексику он приезжает уже убежденным марксистом, получившим к тому же серьезный боевой опыт. За время своего путешествия он познакомился со многими деятелями коммунистического подполья, с кубинскими эмигрантами, испанскими республиканцами, бежавшими от режима Франко. Также в Гватемале он знакомится с Ильдой Гадеа, перуанской революционеркой, активисткой левого движения, ставшей его первой женой.
Эрнесто Гевара и Ильда Гадеа
Первое время в Мехико Эрнесто подрабатывал фотографом в парке, ночным сторожем в книжном издательстве, позже устроился врачом в Институт кардиологии. Будучи в Мексике, он знакомится с несколькими кубинцами, приехавшими сюда с целью подготовки военной экспедиции на Кубу против диктатора Батисты. Вскоре он встречается с Раулем Кастро, а затем и с его братом Фиделем, после беседы с которым Эрнесто записывают в отряд в качестве военного врача. Началась тщательная подготовка, поиски корабля, денег, обучение навыкам герильи (партизанской войны). В этот же период он получает свое прозвище «Че»
Кубинская революция
Ранним утром 25 ноября 1956 года группа во главе с Фиделем Кастро загружается на яхту «Гранма», купленную за 12 тыс. долларов у шведского этнографа. Судно было рассчитано максимум на 12 пассажиров, однако повстанцам удалось вместить 82 человека, сидевших чуть ли не на головах друг у друга. До Кубы перегруженная яхта добралась только 2 декабря, однако недалеко от берега села на мель, и группе пришлось добираться вброд. Выбравшись на сушу, отряд тут же подвергся обстрелу со стороны 35-тысячной армии Батисты, вооруженной танками и авиацией. Долгое время группа пробиралась по болоту и мангровым зарослям, а 5 декабря по причине предательства проводника была атакована вражескими самолетами и войсками. Повстанцы потеряли в бою половину бойцов, два десятка было взято в плен, а оставшиеся в живых, среди которых оказался и Че, решили обосноваться в горах Сьерра-Маэстра и вести партизанскую борьбу.
Че Гевара и Рауль Кастро
Закрепившись в горах, повстанцы сразу же наладили коммуникацию с подпольем в равнинных районах. Также им симпатизировали местные крестьяне, которые снабжали их мясом, продуктами, а многие начали вступать в их ряды. Последовали первые победы: партизаны совершали успешные вылазки на посты батистовцев, захватывали казармы, уничтожали небольшие гарнизоны, то и дело появлявшиеся у предгорий. В горах они были как дома – недостижимы для авиации, неуязвимы для пехоты. На занятой территории повстанцы построили полевые госпитали, мастерские для производства гранат и даже небольшую табачную фабрику. А для того чтобы бороться с вражеской пропагандой, стали выпускать собственную газету «El Cubano Libre», которую вначале писали вручную, а позже печатали на станке.
На протяжении 1958 года армия повстанцев неуклонно растет, совершает рейды уже за пределами Сьерра-Маэстры. Кроме того, по всей территории Кубы уже действовали различные вооруженные группы, созданные Революционным директоратом и другими оппозиционными силами. Воспользовавшись общей дестабилизацией в стране, повстанческая армия начинает генеральное наступление. Несколькими колоннами с тяжелыми боями они захватывают крупные города острова. 27 декабря 1958 г. 8-я колонна под командованием майора Че Гевары начинает штурм города Санта-Клары, открывающего путь на Гавану. Несколько дней бойцы Че сражаются с противником: пускают под откос бронепоезд с пулеметами и зенитками, сжигают танки, захватывают правительственные здания. 1 января 1959 Санта-Клара была полностью в руках повстанцев. В тот же день Батиста убегает из страны, а уже 2 января повстанческая армия входит в Гавану.
Че Гевара и Фидель Кастро
Че – государственный деятель
После победы революции Гевара сразу же провозглашается гражданином Кубы. В это же время Кастро отправляет его во главе делегации Кубы в страны Азии, Африки, с визитом в Грецию и Югославию. Осенью 1959 года Гевара назначается начальником департамента промышленности при институте сельскохозяйственных реформ, а спустя месяц становится главой Нацбанка Кубы. Кстати, до сих пор на некоторых банкнотах кубинских песо выпуска 1960 года красуется размашистая подпись «Che».
5 песо 1960 г. с подписью Че
В 1961 году Че Гевара занимает пост министра промышленности, с официальным визитом посещает многие социалистические страны, подписывает экономическое соглашение с СССР по закупке кубинского сахара, а также по вопросам военного и технического сотрудничества. В 1964 году Че Гевара участвовал в создании Общества советско-кубинской дружбы, возглавляемой Ю. Гагариным. А 11 декабря 1964 года произнес знаменитую речь в ООН, где подверг жесткой критике агрессивную политику США.
Выступление Эрнесто Че Гевары в ООН
Конго, Боливия и гибель Че
В 1965 году, вернувшись из поездки по странам Африки, Че долгое время не появлялся на публике. Это заметила как кубинская общественность, так и западные СМИ, разразившиеся всяческими заголовками типа «Че убит», «Че смертельно болен» и т.д. Ситуацию прояснил сам Фидель Кастро, который на одном из партийных заседаний зачитал прощальное письмо Гевары, где он официально отказался от поста министра, звания, гражданства и заявил о своем отъезде для оказания помощи другим странам. Как оказалось, Че отправился в Конго, где помогал в организации партизанской войны местным повстанцам. После нескольких неудачных операций и несогласованных действий, Че вынужден был свернуть миссию и уехать из страны.
Осенью Че прибывает в Боливию, выбранную как плацдарм для дальнейшего распространения революции в Бразилии, Парагвае и Аргентине. Там он создает отряд из 50 человек, надеясь измотать регулярные войска и привлечь на свою сторону местных жителей. Такое развитие событий сразу же насторожило Вашингтон, и на помощь президенту Боливии Рене Баррьентосу выслали специально обученный спецназ. Почти год повстанцы блуждали по джунглям, отстреливаясь от рейнджеров, часто находящих их по наводке информаторов. В одном из таких боев 8 октября 1967 года Че Гевара был ранен и взят в плен.
Че Гевара в плену
Целую ночь, измученный, в лохмотьях, он пролежал на полу местной школы в селенье Ла-Игера, а на следующий день был расстрелян сержантом Марио Тераном, выпустившим в майора 9 пуль.
Че Гевара на банкнотах и монетах

Интерес к этой личности, кажется, будет жить вечно. Он стал символом, иконой. Его образ широко растиражирован самим капиталистическим миром, против которого он всю жизнь боролся. Его портрет и сегодня можно встретить на кубинских банкнотах и монетах. Этот культовый портрет Че, сделанный фотографом Альберто Кордой, в свое время изображался на продукции Coca-Cola, Nike, Apple. Также его можно увидеть на сувенирной боне номиналом 0 евро 2018 года.