Пульмоноло́гия (от лат. pulmunes — лёгкие + др.-греч. λόγος — учение) или Пневмоло́гия (от др.-греч. πνεύμων — лёгкие) — раздел медицины, занимающийся изучением, диагностикой и лечением заболеваний лёгких и дыхательных путей. В некоторых странах пульмонология называется «грудной медициной» или «респираторной медициной». Пульмонология обычно считается разделом внутренней медицины, однако имеет тесные связи с реаниматологией и интенсивной терапией, поскольку занимается в том числе и пациентами, чьё клиническое состояние требует искусственной вентиляции лёгких. Операции на дыхательных путях обычно проводится специалистами в области кардиоторакальной хирургии.
Все значения слова «пульмонология»
-
Пульмонология занимается системой дыхания.
-
К примеру, что отвечать на неприедающуюся банальность: «Почему именно пульмонология / реаниматология?» Мы хихикали, придумывая, что же отвечают на подобный вопрос проктологи.
- (все предложения)
- хирургическая стоматология
- клиническая фармакология
- лечебные мероприятия
- медицинская реабилитация
- участковый терапевт
- (ещё синонимы…)
- Разбор по составу слова «пульмонология»
«Respiratory medicine» redirects here. For the journal, see Respiratory Medicine.
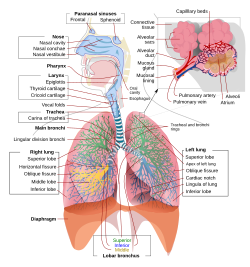
Schematic view of the human respiratory system with their parts and functions. |
|
| System | Respiratory |
|---|---|
| Significant diseases | Asthma, Lung cancer, Tuberculosis, Occupational lung disease |
| Significant tests | Bronchoscopy, Sputum studies, Arterial blood gases |
| Specialist | Respiratory Physician, Pulmonologist |
Pulmonology (, , from Latin pulmō, -ōnis «lung» and the Greek suffix -λογία -logía «study of»), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων pneúmōn «lung») or pneumonology[1] () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.[2] It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas.
Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to intensive care medicine. Pulmonology often involves managing patients who need life support and mechanical ventilation. Pulmonologists are specially trained in diseases and conditions of the chest, particularly pneumonia, asthma, tuberculosis, emphysema, and complicated chest infections.[3]
Journals of pulmonology[edit]
- American Association for Respiratory Care
- American College of Chest Physicians
- American Lung Association
- American Thoracic Society
- British Thoracic Society
- European Respiratory Society
History of pulmonology[edit]
One of the first major discoveries relevant to the field of pulmonology was the discovery of pulmonary circulation. Originally, it was thought that blood reaching the right side of the heart passed through small ‘pores’ in the septum into the left side to be oxygenated, as theorized by Galen; however, the discovery of pulmonary circulation disproves this theory, which had previously been accepted since the 2nd century. Thirteenth-century anatomist and physiologist Ibn Al-Nafis accurately theorized that there was no ‘direct’ passage between the two sides (ventricles) of the heart. He believed that the blood must have passed through the pulmonary artery, through the lungs, and back into the heart to be pumped around the body. This is believed by many to be the first scientific description of pulmonary circulation.[4]
Although pulmonary medicine only began to evolve as a medical specialty in the 1950s, William Welch and William Osler founded the ‘parent’ organization of the American Thoracic Society,[5] the National Association for the Study and Prevention of Tuberculosis.[6] The care, treatment, and study of tuberculosis of the lung is recognised as a discipline in its own right, phthisiology.[7] When the specialty did begin to evolve, several discoveries were being made linking the respiratory system and the measurement of arterial blood gases, attracting more and more physicians and researchers to the developing field.[8]
Pulmonology and its relevance in other medical fields[edit]
Surgery of the respiratory tract is generally performed by specialists in cardiothoracic surgery[9] (or thoracic surgery),[10] though minor procedures may be performed by pulmonologists. Pulmonology is closely related to critical care medicine[11] when dealing with patients who require mechanical ventilation. As a result, many pulmonologists are certified to practice critical care medicine in addition to pulmonary medicine. There are fellowship programs that allow physicians to become board certified in pulmonary and critical care medicine simultaneously. Interventional pulmonology is a relatively new field within pulmonary medicine[12] that deals with the use of procedures such as bronchoscopy[13] and pleuroscopy to treat several pulmonary diseases.[14] Interventional pulmonology is increasingly recognized as a specific medical specialty.[15]
Diagnosis[edit]
The pulmonologist begins the diagnostic process with a general review focusing on:
- hereditary diseases affecting the lungs (cystic fibrosis,[16] alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency)
- exposure to toxicants (tobacco smoke,[17] asbestos, exhaust fumes, coal mining fumes, e-cigarette aerosol,[18])
- exposure to infectious agents (certain types of birds, malt processing)
- an autoimmune diathesis that might predispose to certain conditions (pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension)
Physical diagnostics[19] are as important as in other fields of medicine.
- Inspection of the hands for signs of cyanosis or clubbing, chest wall, and respiratory rate.
- Palpation of the cervical lymph nodes, trachea and chest wall movement.
- Percussion of the lung fields for dullness or hyper-resonance.
- Auscultation (with a stethoscope) of the lung fields for diminished or unusual breath sounds.
- Rales or rhonchi heard over lung fields with a stethoscope.
As many heart diseases can give pulmonary signs,[20] a thorough cardiac investigation is usually included.
Procedures[edit]
Clinical procedures[edit]
Pulmonary clinical procedures include the following pulmonary tests and procedures:[21][22]
- Medical laboratory investigation of blood (blood tests). Sometimes arterial blood gas tests are also required.
- Spirometry the determination of maximum airflow at a given lung volume as measured by breathing into a dedicated machine; this is the key test to diagnose airflow obstruction.
- Pulmonary function testing including spirometry, as above, plus response to bronchodilators, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity, the latter being a measure of lung oxygen absorptive area
- Bronchoscopy[23] with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), endobronchial and transbronchial biopsy and epithelial brushing
- Chest X-rays[24]
- CT scan[25]
- Scintigraphy and other methods of nuclear medicine
- Positron emission tomography[26] (especially in lung cancer)
- Polysomnography (sleep studies[27]) commonly used for the diagnosis of sleep apnea
Surgical procedures[edit]
Major surgical procedures on the heart and lungs are performed by a thoracic surgeon.[28] Pulmonologists often perform specialized procedures to get samples from the inside of the chest or inside of the lung. They use radiographic techniques to view vasculature of the lungs and heart to assist with diagnosis.
Treatment and therapeutics[edit]
Medication is the most important treatment of most diseases of pulmonology, either by inhalation (bronchodilators and steroids) or in oral form (antibiotics, leukotriene antagonists). A common example being the usage of inhalers in the treatment of inflammatory lung conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Oxygen therapy[29] is often necessary in severe respiratory disease (emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis). When this is insufficient, the patient might require mechanical ventilation.
Pulmonary rehabilitation[30] has been defined as a multidimensional continuum of services directed to persons with pulmonary disease and their families, usually by an interdisciplinary team of specialists, with the goal of achieving and maintaining the individual’s maximum level of independence and functioning in the community. Pulmonary rehabilitation[31] is intended to educate the patient, the family, and improve the overall quality of life and prognosis for the patient. Interventions can include exercise, education, emotional support, oxygen, noninvasive mechanical ventilation, optimization of airway secretion clearance, promoting compliance with medical care to reduce numbers of exacerbations and hospitalizations, and returning to work and/or a more active and emotionally satisfying life. These goals are appropriate for any patients with diminished respiratory reserve whether due to obstructive or intrinsic pulmonary diseases (oxygenation impairment) or neuromuscular weakness (ventilatory impairment). A pulmonary rehabilitation team[32] may include a rehabilitation physician, a pulmonary medicine specialist, physician assistant and allied health professionals including a rehabilitation nurse, a respiratory therapist, a speech-language pathologist, a physical therapist, an occupational therapist, a psychologist, and a social worker among others. Additionally, breathing games are used to motivate children to perform pulmonary rehabilitation.
Education and training[edit]
Pulmonologist[edit]

Physician performing a bronchoscopy. |
|
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names |
|
|
Occupation type |
Specialty |
|
Activity sectors |
Medicine |
| Description | |
|
Education required |
|
|
Fields of |
Hospitals, clinics |
In the United States, pulmonologists are physicians who, after receiving a medical degree (MD or DO), complete residency training in internal medicine, followed by at least two additional years of subspeciality fellowship training in pulmonology.[33] After satisfactorily completing a fellowship in pulmonary medicine, the physician is permitted to take the board certification examination in pulmonary medicine. After passing this exam, the physician is then board certified as a pulmonologist. Most pulmonologists complete three years of combined subspecialty fellowship training in pulmonary medicine and critical care medicine.
Pediatric pulmonologist[edit]
In the United States, pediatric pulmonologists[34] are physicians who, after receiving a medical degree (MD, DO, MBBS, MBBCh, etc.), complete residency training in pediatrics, followed by at least three additional years of subspeciality fellowship training in pulmonology. Pediatric pulmonologists treat diseases of the airways, lungs, respiratory mechanics and aerodigestive system.
Pulmonology Physician Assistant[edit]
Physician Assistants commonly work in collaboration with physicians in the field of pulmonology.
Scientific research[edit]
Pulmonologists are involved in both clinical and basic research of the respiratory system, ranging from the anatomy of the respiratory epithelium to the most effective treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Scientific research also takes place to look for causes and possible treatment in diseases such as pulmonary tuberculosis and lung cancer.
References[edit]
- ^ Ramoutsaki, Ioanna; Ramoutsakis, Ioannis; Bouros, Demosthenes (May 2002). «Pneumonology or Pneumology?». Chest. 121 (5): 1385–1387. doi:10.1378/chest.121.5.1385. PMID 12006412.
- ^ ACP: Pulmonology: Internal Medicine Subspecialty Archived 2015-08-11 at the Wayback Machine. Acponline.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30.
- ^ Sengupta, Nandini; Sahidullah, Md; Saha, Goutam (August 2016). «Lung sound classification using cepstral-based statistical features». Computers in Biology and Medicine. 75 (1): 118–129. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.05.013. PMID 27286184.
- ^ Sharif Kaf A-Ghazal (2002). «The discovery of the pulmonary circulation – who should get the credit: ibn Al-Nafis or William Harvey» (PDF). Journal of the International Society for the History of Islamic Medicine. 2: 46. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-06-12. Retrieved 2010-07-17.
- ^ «American Thoracic Society — Overview». www.thoracic.org. Archived from the original on 2019-04-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Jacobs, Henry Barton (1904-12-03). «National Association for the Study and Prevention of Tuberculosis». Journal of the American Medical Association. XLIII (23): 1712. doi:10.1001/jama.1904.02500230042014. ISSN 0002-9955. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Lauzardo, Michael; Ashkin, David (2000-05-01). «Phthisiology at the Dawn of the New Century». Chest. 117 (5): 1455–1473. doi:10.1378/chest.117.5.1455. ISSN 0012-3692. PMID 10807837.
- ^ History of the Division Archived 2017-08-11 at the Wayback Machine. Hopkinsmedicine.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30.
- ^ «Cardiothoracic Surgery | Essentia Health | MN, WI, ND». www.essentiahealth.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Cardiothoracic surgery». Health Careers. 2015-04-07. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Disease | Internal Medicine Subspecialties | ACP». www.acponline.org. Archived from the original on 2015-09-09. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Interventional Pulmonology: Procedures, Uses, and Effects». WebMD. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Seijo, Luis M.; Sterman, Daniel H. (2001-03-08). «Interventional Pulmonology». New England Journal of Medicine. 344 (10): 740–749. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103083441007. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 11236779.
- ^ «Interventional Pulmonology Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures». www.pamf.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-17. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Luis M. Seijo & Daniel H. Sterman (2001). «Interventional Pulmonology». N. Engl. J. Med. 344 (10): 740–49. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103083441007. PMID 11236779.
- ^ «Cystic Fibrosis — Pediatrics». MSD Manual Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Breland, Alison; Soule, Eric; Lopez, Alexa; Ramôa, Carolina; El-Hellani, Ahmad; Eissenberg, Thomas (2017). «Electronic cigarettes: what are they and what do they do?». Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1394 (1): 5–30. Bibcode:2017NYASA1394….5B. doi:10.1111/nyas.12977. ISSN 0077-8923. PMC 4947026. PMID 26774031.
- ^ Perikleous, Evanthia P.; Steiropoulos, Paschalis; Paraskakis, Emmanouil; Constantinidis, Theodoros C.; Nena, Evangelia (2018). «E-Cigarette Use Among Adolescents: An Overview of the Literature and Future Perspectives». Frontiers in Public Health. 6: 86. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2018.00086. ISSN 2296-2565. PMC 5879739. PMID 29632856.
- ^ «Evaluation of the Pulmonary Patient — Pulmonary Disorders». MSD Manual Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Tests and Procedures | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Tests and Procedures | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Diagnostic Tests & Procedures | Essentia Health». www.essentiahealth.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Bronchoscopy | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «How Do Chest X-Rays Work?». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Computed Tomography (CT or CAT) Scan of the Chest | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «How Does a PET Scan Work?». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «How to Prepare for a Sleep Study». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Cardiothoracic surgery». Health Careers. 2015-04-07. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Oxygen Therapy — Lung and Airway Disorders». MSD Manual Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Rehabilitation | Essentia Health | MN, ND, WI». www.essentiahealth.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Overview of Pulmonary Rehabilitation — Lung and Airway Disorders». MSD Manual Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Overview of Pulmonary Rehabilitation — Lung and Airway Disorders». MSD Manual Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Disease | Internal Medicine Subspecialties | ACP». www.acponline.org. Archived from the original on 2015-09-09. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «What is a Pediatric Pulmonologist?». HealthyChildren.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
«Respiratory medicine» redirects here. For the journal, see Respiratory Medicine.

Schematic view of the human respiratory system with their parts and functions. |
|
| System | Respiratory |
|---|---|
| Significant diseases | Asthma, Lung cancer, Tuberculosis, Occupational lung disease |
| Significant tests | Bronchoscopy, Sputum studies, Arterial blood gases |
| Specialist | Respiratory Physician, Pulmonologist |
Pulmonology (, , from Latin pulmō, -ōnis «lung» and the Greek suffix -λογία -logía «study of»), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων pneúmōn «lung») or pneumonology[1] () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.[2] It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas.
Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to intensive care medicine. Pulmonology often involves managing patients who need life support and mechanical ventilation. Pulmonologists are specially trained in diseases and conditions of the chest, particularly pneumonia, asthma, tuberculosis, emphysema, and complicated chest infections.[3]
Journals of pulmonology[edit]
- American Association for Respiratory Care
- American College of Chest Physicians
- American Lung Association
- American Thoracic Society
- British Thoracic Society
- European Respiratory Society
History of pulmonology[edit]
One of the first major discoveries relevant to the field of pulmonology was the discovery of pulmonary circulation. Originally, it was thought that blood reaching the right side of the heart passed through small ‘pores’ in the septum into the left side to be oxygenated, as theorized by Galen; however, the discovery of pulmonary circulation disproves this theory, which had previously been accepted since the 2nd century. Thirteenth-century anatomist and physiologist Ibn Al-Nafis accurately theorized that there was no ‘direct’ passage between the two sides (ventricles) of the heart. He believed that the blood must have passed through the pulmonary artery, through the lungs, and back into the heart to be pumped around the body. This is believed by many to be the first scientific description of pulmonary circulation.[4]
Although pulmonary medicine only began to evolve as a medical specialty in the 1950s, William Welch and William Osler founded the ‘parent’ organization of the American Thoracic Society,[5] the National Association for the Study and Prevention of Tuberculosis.[6] The care, treatment, and study of tuberculosis of the lung is recognised as a discipline in its own right, phthisiology.[7] When the specialty did begin to evolve, several discoveries were being made linking the respiratory system and the measurement of arterial blood gases, attracting more and more physicians and researchers to the developing field.[8]
Pulmonology and its relevance in other medical fields[edit]
Surgery of the respiratory tract is generally performed by specialists in cardiothoracic surgery[9] (or thoracic surgery),[10] though minor procedures may be performed by pulmonologists. Pulmonology is closely related to critical care medicine[11] when dealing with patients who require mechanical ventilation. As a result, many pulmonologists are certified to practice critical care medicine in addition to pulmonary medicine. There are fellowship programs that allow physicians to become board certified in pulmonary and critical care medicine simultaneously. Interventional pulmonology is a relatively new field within pulmonary medicine[12] that deals with the use of procedures such as bronchoscopy[13] and pleuroscopy to treat several pulmonary diseases.[14] Interventional pulmonology is increasingly recognized as a specific medical specialty.[15]
Diagnosis[edit]
The pulmonologist begins the diagnostic process with a general review focusing on:
- hereditary diseases affecting the lungs (cystic fibrosis,[16] alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency)
- exposure to toxicants (tobacco smoke,[17] asbestos, exhaust fumes, coal mining fumes, e-cigarette aerosol,[18])
- exposure to infectious agents (certain types of birds, malt processing)
- an autoimmune diathesis that might predispose to certain conditions (pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension)
Physical diagnostics[19] are as important as in other fields of medicine.
- Inspection of the hands for signs of cyanosis or clubbing, chest wall, and respiratory rate.
- Palpation of the cervical lymph nodes, trachea and chest wall movement.
- Percussion of the lung fields for dullness or hyper-resonance.
- Auscultation (with a stethoscope) of the lung fields for diminished or unusual breath sounds.
- Rales or rhonchi heard over lung fields with a stethoscope.
As many heart diseases can give pulmonary signs,[20] a thorough cardiac investigation is usually included.
Procedures[edit]
Clinical procedures[edit]
Pulmonary clinical procedures include the following pulmonary tests and procedures:[21][22]
- Medical laboratory investigation of blood (blood tests). Sometimes arterial blood gas tests are also required.
- Spirometry the determination of maximum airflow at a given lung volume as measured by breathing into a dedicated machine; this is the key test to diagnose airflow obstruction.
- Pulmonary function testing including spirometry, as above, plus response to bronchodilators, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity, the latter being a measure of lung oxygen absorptive area
- Bronchoscopy[23] with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), endobronchial and transbronchial biopsy and epithelial brushing
- Chest X-rays[24]
- CT scan[25]
- Scintigraphy and other methods of nuclear medicine
- Positron emission tomography[26] (especially in lung cancer)
- Polysomnography (sleep studies[27]) commonly used for the diagnosis of sleep apnea
Surgical procedures[edit]
Major surgical procedures on the heart and lungs are performed by a thoracic surgeon.[28] Pulmonologists often perform specialized procedures to get samples from the inside of the chest or inside of the lung. They use radiographic techniques to view vasculature of the lungs and heart to assist with diagnosis.
Treatment and therapeutics[edit]
Medication is the most important treatment of most diseases of pulmonology, either by inhalation (bronchodilators and steroids) or in oral form (antibiotics, leukotriene antagonists). A common example being the usage of inhalers in the treatment of inflammatory lung conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Oxygen therapy[29] is often necessary in severe respiratory disease (emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis). When this is insufficient, the patient might require mechanical ventilation.
Pulmonary rehabilitation[30] has been defined as a multidimensional continuum of services directed to persons with pulmonary disease and their families, usually by an interdisciplinary team of specialists, with the goal of achieving and maintaining the individual’s maximum level of independence and functioning in the community. Pulmonary rehabilitation[31] is intended to educate the patient, the family, and improve the overall quality of life and prognosis for the patient. Interventions can include exercise, education, emotional support, oxygen, noninvasive mechanical ventilation, optimization of airway secretion clearance, promoting compliance with medical care to reduce numbers of exacerbations and hospitalizations, and returning to work and/or a more active and emotionally satisfying life. These goals are appropriate for any patients with diminished respiratory reserve whether due to obstructive or intrinsic pulmonary diseases (oxygenation impairment) or neuromuscular weakness (ventilatory impairment). A pulmonary rehabilitation team[32] may include a rehabilitation physician, a pulmonary medicine specialist, physician assistant and allied health professionals including a rehabilitation nurse, a respiratory therapist, a speech-language pathologist, a physical therapist, an occupational therapist, a psychologist, and a social worker among others. Additionally, breathing games are used to motivate children to perform pulmonary rehabilitation.
Education and training[edit]
Pulmonologist[edit]

Physician performing a bronchoscopy. |
|
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names |
|
|
Occupation type |
Specialty |
|
Activity sectors |
Medicine |
| Description | |
|
Education required |
|
|
Fields of |
Hospitals, clinics |
In the United States, pulmonologists are physicians who, after receiving a medical degree (MD or DO), complete residency training in internal medicine, followed by at least two additional years of subspeciality fellowship training in pulmonology.[33] After satisfactorily completing a fellowship in pulmonary medicine, the physician is permitted to take the board certification examination in pulmonary medicine. After passing this exam, the physician is then board certified as a pulmonologist. Most pulmonologists complete three years of combined subspecialty fellowship training in pulmonary medicine and critical care medicine.
Pediatric pulmonologist[edit]
In the United States, pediatric pulmonologists[34] are physicians who, after receiving a medical degree (MD, DO, MBBS, MBBCh, etc.), complete residency training in pediatrics, followed by at least three additional years of subspeciality fellowship training in pulmonology. Pediatric pulmonologists treat diseases of the airways, lungs, respiratory mechanics and aerodigestive system.
Pulmonology Physician Assistant[edit]
Physician Assistants commonly work in collaboration with physicians in the field of pulmonology.
Scientific research[edit]
Pulmonologists are involved in both clinical and basic research of the respiratory system, ranging from the anatomy of the respiratory epithelium to the most effective treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Scientific research also takes place to look for causes and possible treatment in diseases such as pulmonary tuberculosis and lung cancer.
References[edit]
- ^ Ramoutsaki, Ioanna; Ramoutsakis, Ioannis; Bouros, Demosthenes (May 2002). «Pneumonology or Pneumology?». Chest. 121 (5): 1385–1387. doi:10.1378/chest.121.5.1385. PMID 12006412.
- ^ ACP: Pulmonology: Internal Medicine Subspecialty Archived 2015-08-11 at the Wayback Machine. Acponline.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30.
- ^ Sengupta, Nandini; Sahidullah, Md; Saha, Goutam (August 2016). «Lung sound classification using cepstral-based statistical features». Computers in Biology and Medicine. 75 (1): 118–129. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.05.013. PMID 27286184.
- ^ Sharif Kaf A-Ghazal (2002). «The discovery of the pulmonary circulation – who should get the credit: ibn Al-Nafis or William Harvey» (PDF). Journal of the International Society for the History of Islamic Medicine. 2: 46. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-06-12. Retrieved 2010-07-17.
- ^ «American Thoracic Society — Overview». www.thoracic.org. Archived from the original on 2019-04-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Jacobs, Henry Barton (1904-12-03). «National Association for the Study and Prevention of Tuberculosis». Journal of the American Medical Association. XLIII (23): 1712. doi:10.1001/jama.1904.02500230042014. ISSN 0002-9955. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Lauzardo, Michael; Ashkin, David (2000-05-01). «Phthisiology at the Dawn of the New Century». Chest. 117 (5): 1455–1473. doi:10.1378/chest.117.5.1455. ISSN 0012-3692. PMID 10807837.
- ^ History of the Division Archived 2017-08-11 at the Wayback Machine. Hopkinsmedicine.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30.
- ^ «Cardiothoracic Surgery | Essentia Health | MN, WI, ND». www.essentiahealth.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Cardiothoracic surgery». Health Careers. 2015-04-07. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Disease | Internal Medicine Subspecialties | ACP». www.acponline.org. Archived from the original on 2015-09-09. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Interventional Pulmonology: Procedures, Uses, and Effects». WebMD. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Seijo, Luis M.; Sterman, Daniel H. (2001-03-08). «Interventional Pulmonology». New England Journal of Medicine. 344 (10): 740–749. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103083441007. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 11236779.
- ^ «Interventional Pulmonology Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures». www.pamf.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-17. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Luis M. Seijo & Daniel H. Sterman (2001). «Interventional Pulmonology». N. Engl. J. Med. 344 (10): 740–49. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103083441007. PMID 11236779.
- ^ «Cystic Fibrosis — Pediatrics». MSD Manual Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ Breland, Alison; Soule, Eric; Lopez, Alexa; Ramôa, Carolina; El-Hellani, Ahmad; Eissenberg, Thomas (2017). «Electronic cigarettes: what are they and what do they do?». Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1394 (1): 5–30. Bibcode:2017NYASA1394….5B. doi:10.1111/nyas.12977. ISSN 0077-8923. PMC 4947026. PMID 26774031.
- ^ Perikleous, Evanthia P.; Steiropoulos, Paschalis; Paraskakis, Emmanouil; Constantinidis, Theodoros C.; Nena, Evangelia (2018). «E-Cigarette Use Among Adolescents: An Overview of the Literature and Future Perspectives». Frontiers in Public Health. 6: 86. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2018.00086. ISSN 2296-2565. PMC 5879739. PMID 29632856.
- ^ «Evaluation of the Pulmonary Patient — Pulmonary Disorders». MSD Manual Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Tests and Procedures | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Tests and Procedures | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Diagnostic Tests & Procedures | Essentia Health». www.essentiahealth.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Bronchoscopy | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «How Do Chest X-Rays Work?». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Computed Tomography (CT or CAT) Scan of the Chest | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «How Does a PET Scan Work?». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «How to Prepare for a Sleep Study». www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Cardiothoracic surgery». Health Careers. 2015-04-07. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Oxygen Therapy — Lung and Airway Disorders». MSD Manual Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Rehabilitation | Essentia Health | MN, ND, WI». www.essentiahealth.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Overview of Pulmonary Rehabilitation — Lung and Airway Disorders». MSD Manual Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Overview of Pulmonary Rehabilitation — Lung and Airway Disorders». MSD Manual Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «Pulmonary Disease | Internal Medicine Subspecialties | ACP». www.acponline.org. Archived from the original on 2015-09-09. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
- ^ «What is a Pediatric Pulmonologist?». HealthyChildren.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-26. Retrieved 2019-01-25.
Синонимы слова «ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ»:
МЕДИЦИНА, БРОНХОЛОГИЯ, ПНЕВМОЛОГИЯ
Смотреть что такое ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ в других словарях:
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
(от лат. pulmo, родительный падеж pulmonis — лёгкое и… логия (См. …Логия)) раздел клинической медицины, изучающий болезни органов дыхания: т… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
пульмонология
сущ., кол-во синонимов: 3
• бронхология (2)
• медицина (189)
• пневмология (2)
Словарь синонимов ASIS.В.Н. Тришин.2013.
.
Синонимы:
бронхология, медицина… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ (от лат. pulmo, род.
падеж pulmonis — лёгкое и …логия), раздел клинич. медицины, изучающий
болезни органов дыхания: трахеи, бронхов, … смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
IПульмоноло́гия (лат. pulmo, легкое + греч. logos учение; синоним: пневмология, пневмонология)раздел внутренних болезней, изучающий заболевания органов… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
пульмоноло́гия
(лат. pulmo (pulmonis) легкое + …логия) раздел медицины, изучающий строение.функции и заболевания легких, разрабатывающий методы проф… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
1) Орфографическая запись слова: пульмонология2) Ударение в слове: пульмонол`огия3) Деление слова на слоги (перенос слова): пульмонология4) Фонетическа… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
Понг Помон Помология Помолог Помол Помои Помог Помногу Помин Поль Полумиля Полуимя Полон Пология Полог Полно Полмильон Полмил Полином Полинг Полилог Полигон Пол Погоня Плуг Пион Пиноль Пино Пинг Пимон Пим Пильня Пилон Оун Опиум Ооо Оон Оология Оогония Оним Омуль Омон Оля Олинго Олин Олимп Олим Огульно Огулом Огонь Огон Нуп Нуль Нуг Нпо Ноу Ном Ноль Нло Нил Мяло Мунго Мунг Мул Муг Моп Монополь Монополия Монолог Моно Монголия Монгол Монго Моль Молния Могул Могол Много Миолог Мио Минь Миля Мильон Милон Мило Милль Миг Ляп Лян Лямин Лягин Льяло Лупинг Лунь Луи Луг Лояльно Лопинг Лоно Лонг Лом Логия Логин Лог Лион Линь Лимон Лимнолог Лиля Лиго Лгунья Лгун Лгу Ионол Ион Иол Иня Инь Ингул Имя Илья Ильм Илл Иго Иглу Гун Гумно Гуля Гульня Гул Гпу Пони Пуг Пул Пульмонолог Пульмонология Пуля Пуня Пьяно Угол Уголь Уголья Угомон Угон Гония Гон Уильям Уль Гольян Ульм Улья Голль Гол Умильно Гну Гном Гниль Глупо Уния Глия Гипнум Гимн Гиль Ямполь Глум Умно Голо Уля Ульян Голь Гомон… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
корень — ПУЛЬМОН; соединительная гласная — О; корень — ЛОГ; окончание — ИЯ; Основа слова: ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГВычисленный способ образования слова: Сложение осн… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
Ударение в слове: пульмонол`огияУдарение падает на букву: оБезударные гласные в слове: пульмонол`огия
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
(от лат. pulmo, род. п. pulmonis — лёгкое и …логия), раздел клинич. медицины, изучающий болезни лёгких, бронхов и плевры и разрабатывающий методы их … смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ (от латинского pulmo, родительный падеж pulmonis — легкое и…логия), раздел клинической медицины, изучающий болезни легких, бронхов, плевры и разрабатывающий методы их диагностики, лечения, профилактики. Туберкулез органов дыхания — предмет изучения фтизиатрии. <br>… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ (от лат . pulmo, род. п. pulmonis — легкое и …логия), раздел клинической медицины, изучающий болезни легких, бронхов и плевры и разрабатывающий методы их диагностики, лечения и профилактики. Туберкулез органов дыхания — предмет изучения фтизиатрии.<br><br><br>… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ (от лат. pulmo — род. п. pulmonis — легкое и …логия), раздел клинической медицины, изучающий болезни легких, бронхов и плевры и разрабатывающий методы их диагностики, лечения и профилактики. Туберкулез органов дыхания — предмет изучения фтизиатрии.<br>… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
(от латинского pulmo, родительный падеж pulmonis — легкое и …логия), раздел клинической медицины, изучающий болезни легких, бронхов, плевры и разрабатывающий методы их диагностики, лечения, профилактики. Туберкулез органов дыхания — предмет изучения фтизиатрии…. смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
— (от лат. pulmo — род. п. pulmonis — легкое и …логия),раздел клинической медицины, изучающий болезни легких, бронхов и плевры иразрабатывающий методы их диагностики, лечения и профилактики. Туберкулезорганов дыхания — предмет изучения фтизиатрии…. смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
(1 ж), Р., Д., Пр. пульмоноло/гииСинонимы:
бронхология, медицина
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
пульмонология (пульмоно- + греч. logos учение, наука) — раздел внутренних болезней, изучающий патологию легких и дыхательных путей, разрабатывающий мет… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
пульмонология [лат. pulmo (pulmonis) легкое + …логия] — раздел медицины, изучающий строение.функции и заболевания легких, разрабатывающий методы профилактика и лечения этих заболеваний. <br><br><br>… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
(пульмоно- + греч. logos учение, наука) раздел внутренних болезней, изучающий патологию легких и дыхательных путей, разрабатывающий методы ее диагностики, лечения и профилактики…. смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
[от лат. pulmo (pulmonis) легкое -логия] раздел медицины, изучающий состояние, функции и заболевания лег ких, разрабатывающий методы профилактики и лечения этих заболеваний… смотреть
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
Начальная форма — Пульмонология, слово обычно не имеет множественного числа, единственное число, женский род, именительный падеж, неодушевленное
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ
ж.
medicina polmonare
Итальяно-русский словарь.2003.
Синонимы:
бронхология, медицина
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ (ОТ ЛАТ . PULMO
ПУЛЬМОНОЛОГИЯ (от лат . pulmo, род. п. pulmonis — легкое и …логия), раздел клинической медицины, изучающий болезни легких, бронхов и плевры и разрабатывающий методы их диагностики, лечения и профилактики. Туберкулез органов дыхания — предмет изучения фтизиатрии…. смотреть
пульмонология
Слово «пульмонология» правильно пишется как «пульмонология», с ударением на гласную — о (4-ый слог).
Оцени материал
8 голосов, оценка 4.375 из 5
Рекомендуем:
- Деление слова «Пульмонология» на слоги
- Однокоренные и родственные к слову «Пульмонология»
- Перенос слова «Пульмонология»
- Разбор слова «Пульмонология» по составу
- Склонение слова «Пульмонология» по падежам
- Слова с корнем «Пульмон»
- Слова с окончанием «Я»
- Слова с суффиксом «И»
- Фонетический разбор слова «Пульмонология»
Поставить ударение в другом слове
Как написать слово «пульмонология» правильно? Где поставить ударение, сколько в слове ударных и безударных гласных и согласных букв? Как проверить слово «пульмонология»?
пульмоноло́гия
Правильное написание — пульмонология, ударение падает на букву: о, безударными гласными являются: у, о, о, и, я.
Выделим согласные буквы — пульмонология, к согласным относятся: п, л, м, н, г, звонкие согласные: л, м, н, г, глухие согласные: п.
Количество букв и слогов:
- букв — 13,
- слогов — 6,
- гласных — 6,
- согласных — 6.
Формы слова: пульмоноло́гия, -и.
Пульмоноло́гия (от лат. pulmunes — лёгкие + др.-греч. λόγος — учение) или Пневмоло́гия (от др.-греч. πνεύμων — лёгкие) — раздел медицины, занимающийся изучением, диагностикой и лечением заболеваний лёгких и дыхательных путей. В некоторых странах пульмонология называется «грудной медициной» или «респираторной медициной». Пульмонология обычно считается разделом внутренней медицины, однако имеет тесные связи с реаниматологией и интенсивной терапией, поскольку занимается в том числе и пациентами, чьё клиническое состояние требует искусственной вентиляции лёгких. Операции на дыхательных путях обычно проводится специалистами в области кардиоторакальной хирургии.
Все значения слова «пульмонология»
-
Пульмонология занимается системой дыхания.
-
К примеру, что отвечать на неприедающуюся банальность: «Почему именно пульмонология / реаниматология?» Мы хихикали, придумывая, что же отвечают на подобный вопрос проктологи.
- (все предложения)
- хирургическая стоматология
- клиническая фармакология
- лечебные мероприятия
- медицинская реабилитация
- участковый терапевт
- (ещё синонимы…)
- Разбор по составу слова «пульмонология»
Как пишется?
Формы слов русского языка онлайн
→
пульмонология — существительное, именительный п., жен. p., ед. ч.
Часть речи: существительное
| Единственное число | Множественное число | |
|---|---|---|
| Им. |
пульмонология |
|
| Рд. |
пульмонологии |
|
| Дт. |
пульмонологии |
|
| Вн. |
пульмонологию |
|
| Тв. |
пульмонологией |
|
| Пр. |
пульмонологии |
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Ответ:
Правильное написание слова — пульмонология
Ударение и произношение — пульмонол`огия
Выберите, на какой слог падает ударение в слове — КРЕМЕНЬ?
Слово состоит из букв:
П,
У,
Л,
Ь,
М,
О,
Н,
О,
Л,
О,
Г,
И,
Я,
Похожие слова:
пульверизирующий
пулька
пульку
пульман
пульмановский
пульнуть
пульпа
пульпарный
пульпит
пульповод
Рифма к слову пульмонология
энергия, георгия, сергия, религия, междоусобия, богословия, оружия, сочувствия, комедия, присутствия, подобия, благообразия, благородия, здравия, пособия, последствия, дивизия, путешествия, молебствия, благоденствия, претензия, добронравия, фантазия, отсутствия, содействия, возмездия, высокоблагородия, дружелюбия, бездействия, продовольствия, божия, спокойствия, действия, происшествия, бедствия, гвардия, усердия, честолюбия, разнообразия, сословия, условия, жребия, орудия, приветствия, неудовольствия, нашествия, удовольствия, междуцарствия, милосердия, препятствия
Толкование слова. Правильное произношение слова. Значение слова.
Разбор слова «пульмонология»: для переноса, на слоги, по составу
Объяснение правил деление (разбивки) слова «пульмонология» на слоги для переноса.
Онлайн словарь Soosle.ru поможет: фонетический и морфологический разобрать слово «пульмонология» по составу, правильно делить на слоги по провилам русского языка, выделить части слова, поставить ударение, укажет значение, синонимы, антонимы и сочетаемость к слову «пульмонология».
Содержимое:
- 1 Как перенести слово «пульмонология»
- 2 Морфологический разбор слова «пульмонология»
- 3 Разбор слова «пульмонология» по составу
- 4 Сходные по морфемному строению слова «пульмонология»
- 5 Предложения со словом «пульмонология»
- 6 Значение слова «пульмонология»
- 7 Как правильно пишется слово «пульмонология»
- 8 Ассоциации к слову «пульмонология»
Как перенести слово «пульмонология»
пу—льмонология
пуль—монология
пульмо—нология
пульмоно—логия
пульмоноло—гия
Морфологический разбор слова «пульмонология»
Часть речи:
Имя существительное
Грамматика:
часть речи: имя существительное;
одушевлённость: неодушевлённое;
род: женский;
число: единственное;
падеж: именительный;
отвечает на вопрос: (есть) Что?
Начальная форма:
пульмонология
Разбор слова «пульмонология» по составу
| пульмон | корень |
| о | соединительная гласная |
| лог | корень |
| и | суффикс |
| я | окончание |
пульмонология
Сходные по морфемному строению слова «пульмонология»
Сходные по морфемному строению слова
Предложения со словом «пульмонология»
Пульмонология занимается системой дыхания.
Софья Доринская, Омерзительное в психиатрии, 2020.
Пульмонология выделилась из терапии, хирургии, педиатрии в самостоятельный раздел медицины во второй половине XX в.
В. Ф. Корсун, Избавляемся от болезней дыхательных путей. Лечение и профилактика травами, 2010.
Значение слова «пульмонология»
Пульмоноло́гия (от лат. pulmunes — лёгкие + др.-греч. λόγος — учение) или Пневмоло́гия (от др.-греч. πνεύμων — лёгкие) — раздел медицины, занимающийся изучением, диагностикой и лечением заболеваний лёгких и дыхательных путей. В некоторых странах пульмонология называется «грудной медициной» или «респираторной медициной». Пульмонология обычно считается разделом внутренней медицины, однако имеет тесные связи с реаниматологией и интенсивной терапией, поскольку занимается в том числе и пациентами, чьё клиническое состояние требует искусственной вентиляции лёгких. Операции на дыхательных путях обычно проводится специалистами в области кардиоторакальной хирургии. (Википедия)
Как правильно пишется слово «пульмонология»
Правописание слова «пульмонология»
Орфография слова «пульмонология»
Правильно слово пишется: пульмоноло́гия
Гласные: у, о, о, о, и, я;
Согласные: п, л, м, н, л, г;
Нумерация букв в слове
Номера букв в слове «пульмонология» в прямом и обратном порядке:
- 13
п
1 - 12
у
2 - 11
л
3 - 10
ь
4 - 9
м
5 - 8
о
6 - 7
н
7 - 6
о
8 - 5
л
9 - 4
о
10 - 3
г
11 - 2
и
12 - 1
я
13
Ассоциации к слову «пульмонология»
-
Хирургия
-
Нии
-
Терапия
-
Патология
-
Заболевание
-
Медицина
-
Кафедра
-
Лечение
-
Специальность
-
Отделение
-
Болезнь
-
Институт
-
Раздел
-
Детская
-
Метод
-
Больная
-
Профессор
-
Исследование
-
Директор
-
Ссср
-
Больница
-
Область
-
Наука
-
Доктор
-
Проблема
-
Центр
-
Состояние
-
Число
-
М
-
Работа
-
Хронический
-
Дыхательный
-
Интенсивный
-
Всесоюзный
-
Клинический
-
Научно-исследовательский
-
Хирургический
-
Медицинский
-
Киевский
-
Лёгкий
-
Научный
-
Национальный
-
Внутренний
-
Применяться
-
Заниматься
-
Работать
