childhood diseases
childhood diseases
Детские болезни — группа заболеваний, встречающихся преимущественно или исключительно в детском возрасте и связанных с особенностями развития детского организма. Интенсивный рост и развитие ребёнка обусловливают анатомо-физиологические особенности его организма и своеобразие патологии. Даже заболевания, встречающиеся преимущественно у взрослых, имеют у детей своеобразное течение, которое также зависит от возраста ребёнка.
Childhood diseases — a group of diseases that occur predominantly or exclusively in childhood and associated with the peculiarities of the child’s body. The rapid growth and development of the child determine the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the organism and the originality of pathology. Even diseases that occur primarily in adults, have children sort of flow, which also depends on the age of the child.
Быстрое нарастание массы тела ребёнка в грудном возрасте и интенсивный обмен веществ определяют значительную потребность ребёнка в пище (на 1 кг массы тела ребёнка по калорийности в 2—2,5 раза больше, чем взрослому). Т. о., нагрузка на функционально-несовершенную пищеварительную систему ребёнка резко повышена, что обусловливает частое развитие у детей этого возраста желудочно-кишечных заболеваний (диспепсия), а также заболеваний желудочно-кишечного тракта, вызываемых бактериями и вирусами (дизентерия, вирусные поносы), и хронические расстройства питания (Дистрофия детская), особенно при нарушении его режима.
The rapid growth of the child’s body weight in infancy and intense metabolism determine the significant need baby food (1 kg body weight of the child caloric 2-2.5 times more than an adult). Thus., The load on functional child imperfect digestive system sharply increased, resulting in frequent development of children of this age gastrointestinal diseases (dyspepsia) and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract caused by bacteria and viruses (dysentery, viral diarrhea), and chronic eating disorder (dystrophy children), especially in case of violation of his regime.
Неправильное вскармливание, недостаточное пользование воздухом и солнцем могут привести к развитию Рахита. В связи с большой потребностью ребёнка в кислороде повышена функциональная нагрузка на его органы дыхания (число дыханий в минуту и количество пропускаемого воздуха относительно больше, чем у взрослого), нежность и ранимость слизистых оболочек органов дыхания обусловливают их частые заболевания. В этом возрасте нередки воспаления лёгких бактериального и вирусного происхождения. В раннем детском и дошкольном возрастах повышается заболеваемость острыми детскими инфекциями: Корью, Коклюшем, ветряной оспой ,скарлатиной дифтерией, а также Туберкулёзом. Это объясняется снижением титра антител, полученных ребёнком от матери, а также возрастающим контактом детей со сверстниками и окружающими.
Improper feeding, lack of use of the air and the sun can lead to the development of rickets. Due to the great need of the child for oxygen increased functional load on his respiratory system (the number of breaths per minute and the amount of air flow capacity is relatively larger than that of an adult), tenderness and vulnerability of the mucous membranes of the respiratory system are responsible for their frequent diseases. At this age, frequent pneumonia of bacterial and viral origin. In early childhood and pre-school age increases the incidence of acute childhood infections: Measles, whooping cough, chicken pox, scarlet fever diphtheria, and tuberculosis. This is due to lower titer antibodies derived from the mother the child, as well as increasing the contact of children with their peers and others.
Scarlet fever (скарлатина)
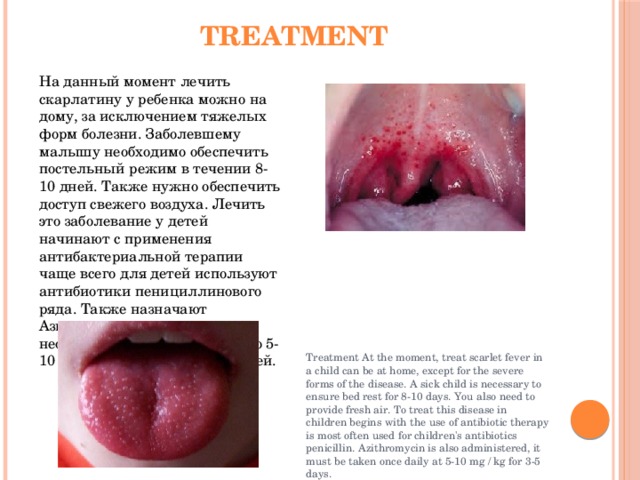
Одним из важных и отличающих признаков скарлатины от других заболеваний являются полосы Пастьи — это красные полоски, которые локализуются в складках кожных покровов, особенно в области шеи, коленях, на локтях и в районе подмышек. При осмотре ротовой полости можно обнаружить гиперемированную слизистую оболочку, гнойные налеты на миндалинах и лаковый малиновый язык с увеличенными сосочками. Это состояние ротовой полости врачи именуют как «пылающий зев».
Из-за интоксикации организма у ребенка может быть тошнота и рвота. На 5 сутки состояние больного становится лучше, температура начинает постепенно падать, сыпь становиться бледной и исчезает на 7 — 8 сутки. Кожа начинает шелушиться, это заметно на внутренней стороне ладошек. Осложнения: лимфаденит (поражаются лимфатические узлы); отит (воспаление среднего уха); гломерулонефрит (болезнь почек); пневмония (воспаление легких); синусит (воспалительное заболевание пазух носа); ревматизм (заболевание суставов и мышц).
One of the most important and distinguishing signs of scarlet fever from other diseases are strip paste — this red stripes, which are located in the folds of the skin, especially in the neck, knees, elbows and armpits area. On examination of the oral cavity can be detected erythematous mucosa, purulent raids on the tonsils and tongue crimson lacquer with enlarged nipples. This state of the oral cavity, doctors refer to as «blazing shed.»
Due to the toxicity of the body of the child may be nausea and vomiting. On day 5, the patient’s condition is getting better, the temperature begins to fall gradually, the rash becomes pale and disappears for 7 — 8 hours. The skin starts to peel off, it shows the inside of the palms. Complications: lymphadenitis (affects the lymph nodes); otitis media (middle ear infection); glomerulonephritis (kidney disease); pneumonia (pneumonia); sinusitis (sinus inflammatory disease); rheumatic fever (a disease of the joints and muscles).
Treatment
На данный момент лечить скарлатину у ребенка можно на дому, за исключением тяжелых форм болезни. Заболевшему малышу необходимо обеспечить постельный режим в течении 8-10 дней. Также нужно обеспечить доступ свежего воздуха. Лечить это заболевание у детей начинают с применения антибактериальной терапии чаще всего для детей используют антибиотики пенициллинового ряда. Также назначают Азитромицин, принимать его необходимо один раз в сутки по 5-10 мг/кг на протяжении 3-5 дней.
Treatment At the moment, treat scarlet fever in a child can be at home, except for the severe forms of the disease. A sick child is necessary to ensure bed rest for 8-10 days. You also need to provide fresh air. To treat this disease in children begins with the use of antibiotic therapy is most often used for children’s antibiotics penicillin. Azithromycin is also administered, it must be taken once daily at 5-10 mg / kg for 3-5 days.
Сhickenpox (ветрянка)
Первые признаки и симптомы ветрянки: слабость; головная боль; тошнота; резкий скачок температуры до 39-40 градусов. Эти признаки возникают за 1-2 дня до появления сыпи на теле ребенка. У него может пропадать аппетит, наблюдается плохое настроение. Иногда этот период отсутствует, и родители просто замечают высыпания на коже.
Как выглядят высыпания . Сначала на коже, там, куда внедрился вирус, появляются пятна размером не более 0,6 см. Находятся на одном уровне с кожей, границы четкие. Затем на месте пятна появляется пузырек с жидкостью, концентрация вируса в которой крайне высока. Когда пузырек разрывается, на его месте образуется корочка. Сдирание корочки приводит к образованию рубцов и шрамов.
The first signs and symptoms of chickenpox: weakness; headache; nausea; a sharp jump in temperature to 39-40 degrees. These symptoms occur 1-2 days before the rash appears on the body of the child. He can disappear appetite, bad mood there. Sometimes this period is absent, and the parents just notice a rash on the skin.
How to look like a rash: First, on the skin, in places where the virus has taken root, spots appear no larger than 0.6 cm are flush with the skin, clear boundaries.. Then spot appears in place the vial with the liquid in which the concentration of the virus is extremely high. When the bubble bursts, in its place is formed crust. Peeling crust leads to the formation of scars.
Treatment
Обычно врач рекомендует проводить лечение ветрянки в домашних условиях со строгим соблюдением карантина и порядка лечебных мероприятий. Если отмечается высокая температура, тяжелое состояние в первые дни болезни – необходим строгий постельный режим.
Схема лечения ветряной оспы: е ежедневный прием ванн и обработка везикул зеленкой. Прием ванн необходим для предотвращения развития инфекции. Кроме того, это помогает снять зуд, главное, не использовать никаких моющих средств и мочалок. Полоскание рта водным раствором Фурацилина после еды. При проявлениях конъюнктивита в глаза закладывается мазь Ацикловир. В качестве жаропонижающего используется Парацетамол, Нурофен. При сильном зуде используются антигистаминные препараты: Лоратидин, Тавегил, Супрастин, Фенкарол. В качестве противовирусного препарата врач может выписать ректальные свечи Виферон. Антибиотики назначаются только в крайнем случае: при присоединении инфекции, при возникновении осложнений (менингит, энцефалит и т. д.).
Usually the doctor recommends treatment of chickenpox in home quarantine with strict observance of the order and therapeutic measures. If you have a high fever, a serious condition in the first days of illness — requires strict bed rest.
The treatment regimen of varicella : daily intake of baths and treatment vesicles Zelenko. Admission bath is needed to prevent the development of infection. In addition, it helps to relieve itching, most importantly, do not use any detergent and sponges. Rinsing the mouth with an aqueous solution furatsilina after eating. When manifestations of conjunctivitis in the eyes laid ointment acyclovir. As an antipyretic use Paracetamol, Nurofen. If a strong itch used antihistamines: loratidine, Tavegil, Suprastin, Fenkarol. As an antiviral drug doctor may prescribe rectal suppositories Viferon. Antibiotics are assigned only in extreme cases: when the infection accession, in the event of complications (meningitis, encephalitis, etc…).
Rickets (рахит)
Согласно
метаболическим
сбоям в организме,
формируются и
определенные
признаки
рахита у детей.
Чему способствуют:
1) Недостаток кальция
вызывает
кальцийпеническую
According to metabolic disruptions in the body, are formed and some signs of rickets in children. What can help:
форму рахитизма,
1) Lack of calcium causes rickets form, with the characteristic deformities of bone structures caused by the process of osteomalacia.
с характеристикой
Expressed increased neuromuscular irritation, hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), disturbances in heart rhythm, sleep disorder and digestive functions. It features fast current and a rapid decrease in the level of the cation ( «Ca» ionized) in red blood cells and its serum.
деформаций
2) Fosforodefitsitnaya shape becomes even more marked deficiency of phosphorus compounds in serum and red blood cells.
костных структур
It appears lethargic mobility of children, their motor retardation, hypotonia, dystrophic changes in bones caused by the processes of the rapid proliferation of osteoid (osteoid hyperplasia)
Обусловленных
3) The pathology with mild calcium and phosphorus deficiency manifested mild with low bone deformities, minor or no symptoms of neuromuscular disorders.
процессом остеомаляции.
Выраженным усилением нервно-мышечного раздражения, гипергидрозом (повышенная потливость), нарушениями в сердечном ритме, расстройством сна и пищеварительных функций. Отличается быстрым течением и стремительным снижением уровня катиона («Са» ионизированный) в красных клетках крови и ее сыворотке.
2) Фосфородефицитная форма проявляется с еще большей выраженностью недостаточности фосфорных соединений в сыворотке и красных клетках крови.
Проявляется вялой подвижностью малышей, их двигательной заторможенностью, мышечной гипотонией, дистрофическими изменениями костей скелета, обусловленными процессами быстрого разрастания остеоидных тканей (остеоидная гиперплазия)
3) Патология с легкой фосфорно-кальциевой недостаточностью проявляется легким течением с небольшими костными деформациями, незначительными или полностью отсутствующими признаками нервно-мышечных нарушений.
Symptoms
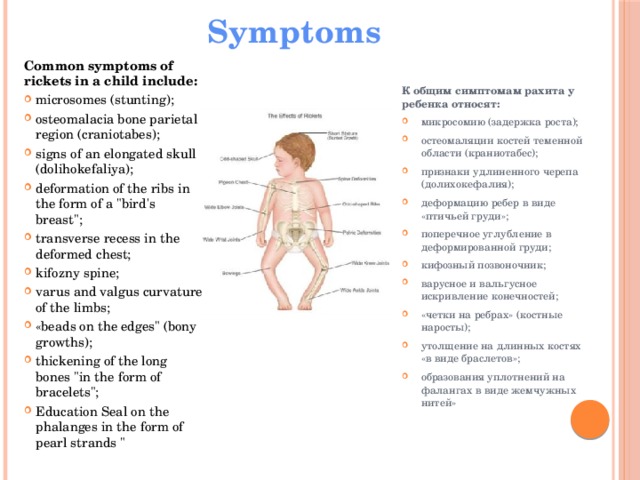
Common symptoms of rickets in a child include:
К общим симптомам рахита у ребенка относят:
- microsomes (stunting);
- osteomalacia bone parietal region (craniotabes);
- signs of an elongated skull (dolihokefaliya);
- deformation of the ribs in the form of a «bird’s breast»;
- transverse recess in the deformed chest;
- kifozny spine;
- varus and valgus curvature of the limbs;
- «beads on the edges» (bony growths);
- thickening of the long bones «in the form of bracelets»;
- Education Seal on the phalanges in the form of pearl strands »
- микросомию (задержка роста);
- остеомаляции костей теменной области (краниотабес);
- признаки удлиненного черепа (долихокефалия);
- деформацию ребер в виде «птичьей груди»;
- поперечное углубление в деформированной груди;
- кифозный позвоночник;
- варусное и вальгусное искривление конечностей;
- «четки на ребрах» (костные наросты);
- утолщение на длинных костях «в виде браслетов»;
- образования уплотнений на фалангах в виде жемчужных нитей»
Treatment
При первых же симптомах рахита у детей и в лечении, и в профилактике, рациональное питание имеет важное значение. Так как именно с едой малыши получают необходимые макро и микроэлементы для роста и развития. Необходимо учитывать некоторые особенности:
When the first symptoms of rickets in children and in the treatment and prevention, good nutrition is important. Since it is with food kids get the necessary macro and trace minerals for growth and development. It is necessary to take into account some special features:
- При лечении рахита у ребенка прикорм вводится раньше на месяц, полтора, чем здоровым малышам. Он должен быть тщательно перетертым. С пяти месяцев можно включать куриный желток, печень кролика, делать суфле из почек, мяса и мозга. Фруктовым пюре не злоупотреблять.
- Каши готовятся на овощных отварах и даются один раз в день.
- Полезны овощные пюре из кабачков, моркови, капусты и зеленого горошка.
- Фруктовые пюре – из яблок, морковно-тыквенное вводятся постепенно начиная с половинки чайной ложечки, доводя к 6-ти месяцам до 100/150 гр. в день за четыре приема.
- Младенцам, находящимися на искусственном или смешанном вскармливании с явно выраженной симптоматикой рахитизма в рацион добавляют от 10 до 15 капелек лимонного сока. «С» витамин рахитичным детям необходим для лучшего усвоения калия-фосфорных элементов желудком и для регуляции функций паращитовидной железы.
- С жирами необходимо быть осторожными, их излишек затрудняет процесс усваивания минеральных солей.
- 1. In the treatment of rickets in the child solid foods introduced earlier in the month and a half than healthy babies. It must be carefully grinded. With five months can include chicken yolk, rabbit liver, the kidneys do souffle, meat and marrow. Fruit purees are not abused.
- 2. Porridge prepared in vegetable broth, and given once daily.
- 3. Useful vegetable puree of squash, carrot, cabbage and green peas.
- 4. Fruit puree — apple, carrot and pumpkin are introduced gradually starting with half a teaspoon, bringing to 6 months up to 100/150 g. per day for four stages.
- 5. Infants, located on an artificial or mixed feeding with a pronounced symptoms rickets added to the diet from 10 to 15 drops of lemon juice. «C» vitamin rickety children need for better absorption of phosphorus-potassium elements of the stomach and for the regulation of parathyroid function.
- 6. fats need to be careful of overly complicates the process of assimilation of mineral salts.
Measles (корь)
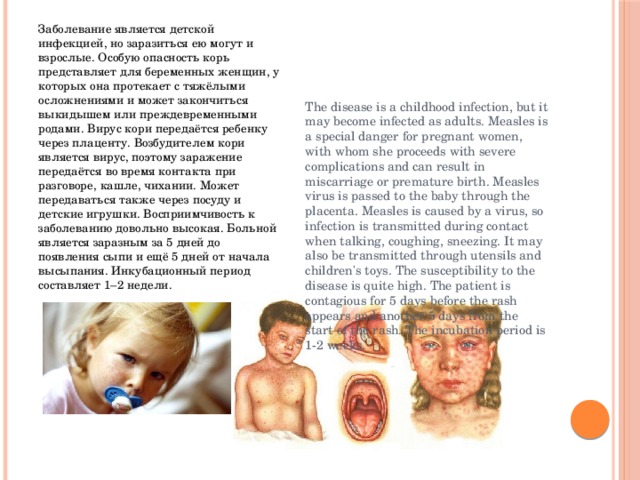
Заболевание является детской инфекцией, но заразиться ею могут и взрослые. Особую опасность корь представляет для беременных женщин, у которых она протекает с тяжёлыми осложнениями и может закончиться выкидышем или преждевременными родами. Вирус кори передаётся ребенку через плаценту. Возбудителем кори является вирус, поэтому заражение передаётся во время контакта при разговоре, кашле, чихании. Может передаваться также через посуду и детские игрушки. Восприимчивость к заболеванию довольно высокая. Больной является заразным за 5 дней до появления сыпи и ещё 5 дней от начала высыпания. Инкубационный период составляет 1–2 недели.
The disease is a childhood infection, but it may become infected as adults. Measles is a special danger for pregnant women, with whom she proceeds with severe complications and can result in miscarriage or premature birth. Measles virus is passed to the baby through the placenta. Measles is caused by a virus, so infection is transmitted during contact when talking, coughing, sneezing. It may also be transmitted through utensils and children’s toys. The susceptibility to the disease is quite high. The patient is contagious for 5 days before the rash appears and another 5 days from the start of the rash. The incubation period is 1-2 weeks.
Symptoms
The very first sign of measles is a rise in temperature up to 39,0 ° C. The temperature is kept for 5-7 days. At the same time there are other symptoms: catarrhal symptoms, manifested by dry cough, runny nose, tear. On examination of the throat is marked swelling and redness of the mucous membranes. The cough becomes barking. Hoarseness associated with swelling of the vocal cords. A few days after the spots on the inside of the cheek rash appears on the face, neck and behind the ears. Spots in the value of the mouth with poppy grain are the hallmark of measles. The next day the rash covers the front surface of the trunk and upper limbs. In the following days, the rash spreads to the feet. Since the 4-th day of the disease the rash fades, first on the face and head, then on the trunk and extremities.
Самым первым признаком кори является подъем температуры до 39,0 °C. Температура держится 5-7 дней. Одновременно появляются другие симптомы: Катаральные явления, проявляющиеся сухим кашлем, насморком, слезоточивостью. При осмотре горла отмечается отечность и покраснение слизистых. Кашель становится лающим. Осиплость голоса, связанная с отечностью голосовых связок. Через несколько дней вслед за пятнышками на внутренней стороне щёк появляется сыпь на лице, шее и за ушами. Пятнышки во рту величиной с маковое зёрнышко являются отличительным признаком кори. На следующие сутки высыпание охватывает переднюю поверхность туловища и верхние конечности. В последующие дни сыпь распространяется на ноги. Начиная с 4-того дня заболевания сыпь бледнеет сначала на лице и голове, затем на туловище и конечностях.
Treatment
В легких случаях заболевания лечить детей можно на дому. Заболевшему ребенку нужен покой и тишина, приглушенное освещение. При конъюнктивите яркий свет действует раздражающе на глаза. полезно обильное питьё; частое полоскание горла приносит большую пользу; приём антигистаминных препаратов; при конъюнктивите применение глазных капель Интерферона после промывания глаз теплой кипячёной водой; очищение носа ватными тампонами с тёплым вазелиновым маслом.
In mild cases, you can treat children at home. Sick child need peace and quiet, subdued lighting. When conjunctivitis bright light irritates eyes. Drink plenty of useful; Frequent gargling of great benefit; appointment of antihistamines; conjunctivitis the use of eye drops after Interferon eyewash warm boiled water; nasal cleansing with a cotton swab with warm liquid paraffin.
features of childhood infectious diseases
отличительные особенности детских инфекционных заболеваний

МИНИСТЕРСТВО ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ РФ
САНКТ-ПЕТЕРБУРГСКАЯ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННАЯ ПЕДИАТРИЧЕСКАЯ МЕДИЦИНСКАЯ АКАДЕМИЯ
LEARN to READ & SPEAK on Children’s Infectious Diseases
САНКТ-ПЕТЕБУРГ
2001
М-545
ББК 8 1 . 2 англ. УДК-20
Учись читать и говорить о детских инфекциях. Учеб. пособие. — СПб ГПМА, второе издание, 2006 с.
Составители: И.Л. Гальфанович, Д.Б. Казанский, В.А.Кузина, Н.А. Мордвинова, Ц.З.Мунтянова, М.М.- Панкова. Л.М.Тюмина, Е.М. Юдина
Под редакцией И.И.Могилёвой
На обл.: Learn to Read & Speak on Children’s Infectious Diseases
Рецензент: зав.кафедрой иностранных языков Санкт-Петербургской медицинской академии постдипломного образования, доц. Д.М. Вольфберг.
Пособие содержит легкие оригинальные тексты по теме «Детские инфекции» (первые три части). В первой части даны базовые тексты для разговорных тем по специальности и упражнения для развития навыков устной речи. Во второй части даны более сложные тексты по данной теме для внеаудиторного и ознакомительного чтения. Третья часть содержит разнообразные виды самостоятельной работы с текстом такие, как чтение текста без словаря, письменный перевод со словарем, ориентирование в тексте по заданным вопросам, устное и письменное тезирование на английском языке, лексические тесты, ознакомительное чтение с последующим тестированием. Тексты всех трех частей используются параллельно. К первой части в приложении даны словарный минимум, необходимый для активного усвоения и употребления в устной речи и таблица инфекционных болезней.
Цель настоящего пособия — активизация общемедицинской лексики, развитие навыков разговорной речи и создание основы для свободного чтения медицинских текстов.
Рекомендовано проблемной учебно-методической комиссией по иностранным языкам Минздрава России (заседание 24-25 апреля 2001 г., Москва) для студентов 2-го курса медвузов.
Первое издание 2001 г.
|
ISBN 5-86093-092-5 |
© СП6ГПМА, 2006 |
Introduction
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF CHILDHOOD
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic bacteria or other microorganisms that multiply in the body and have a harmful effect on it. These organisms (germs and viruses) are capable of producing poisonous substances, or toxins, that poison the body.
The chief source of infection is direct or indirect contact with the patient himself, the disease being communicated to others either before it has been recognized and the individual isolated, or transmitted after quarantine has been removed.
According to the mode of infection contagious diseases may be classified as:
I. Infectious diseases in which the infecting organism penetrates through an abrasion or wound of the skin or mucous membranes. Such are, for example, pyogenic bacteria, causing septicemia, gonococcus infection, toxemia.
II. Infections caused by the pathogenic microorganisms through the respiratory tract are: a) diseases due to various types of streptococci: rheumatic fever, quinzy, scarlet fever; b) diseases due to filtrable viruses: measles, .mumps, smallpox, chicken-pox, polio myelitis.
III. Infections, generally bacterial, disseminated principally by the
|
intestinal discharges, such |
as typhoid |
fever, dysentery, cholera. |
|
In order to identify the |
causative |
microorganism bacteriological |
studies are performed which help to detect such microorganisms by direct examination under the microscope of the patient’s blood, urine, stools, sputum or of any pathological material withdrawn from the body. The examination of the exudate on the tonsils, for example, may reveal the presence of the diphtheria bacillus; examination of the sputum may show the tubercle bacillus.
The direct identification of the infecting agent being impossible, the serologic method is used. The latter depends upon the demonstration in the patient’s serum of antibodies specific to the suspected disease. Special serologic tests have been -devised for

demonstrating the presence of these antibodies. Among these are hemagglutination (inhibition), complement fixation, antibody neutralizing, hemadsorption inhibition, and precipitation test. The method of immunofluorescence consisting of detecting specific antigens in the material studied by means of luminescent microscopy has proved of great diagnostic value.
Exercises
I. Translate into Russian the underlined words:
I. The disease can be communicated to other people. 2. Scarlet fever is a contagious disease. 3. The infecting organism penetrates
|
through a wound of the |
skin. 4. |
Some |
infections |
are spread by |
||
|
the intestinal |
discharge. |
5. |
The |
causative microorganisms |
are |
|
|
detected by |
examination |
of |
pathological |
material |
withdrawn |
from |
the body. 6. For demonstrating the presence of the antibodies special serologic tests have been devised.
II. Check if you remember the meaning of the
|
following |
words: |
|
|
Poison; discharge; capable; to multiply; to recognize; to remove; |
||
|
to depend |
on; to reveal; |
to suspect; to prove. |
|
III. Using the words given below fill in the gaps in the |
||
|
sentences: |
||
|
1. Influenza is an … |
.2. Influenza is …. 3. Children … with |
influenza get treatment at home. 4. The … agent penetrates through the skin. 5. You may … the wound if you do not dress it. 6. Pneumonia is an acute … disease. 7. This … is transmitted through the air.
Infect, infectious, infection, infecting, infected.
IV. Compare the sentences and say in which way they differ in their sense(translation) and grammatically:
a)Infections caused by the pathogenic microorganisms include two types of diseases.
b)These infections are caused by the pathogenic microor ganisms.
|
c) |
Some |
infections may be caused by viruses. |
|
|
d) |
Bacteriological |
studies |
performed to detect the causative |
|
microorganism |
gave |
positive |
results. |
|
e) |
Bacteriological |
studies |
were performed in order to detect |
|
the causative |
microorganisms. |
||
|
f) |
Bacteriological |
studies have been performed in order to |
|
|
detect |
the causative |
microorganisms. |
‘V. Answer the questions on the text:
I. What pathogenicagents can cause an infection? 2. What is
|
the |
classification о{ contagious diseases based on? 3. What are |
|
the |
ways in which the infecting organism penetrates into the |
human body? 4. What
methods are used to detect the causative microorganism? 5. What kinds of serologic tests are mentioned in the text?
II
The characteristic feature of acute infectious diseases is their cyclic course. There are clearly defined stages in the course of infectious diseases: incubation (latent period), prodromal period, invasion period, active period, period of decline, convalescence.
The maximum period of incubation (i.e., the time between the date of exposure to the disease and the beginning of clinical manifestations) of some communicable diseases, e.g., chicken-pox, measles, scarlet fever, small-pox, whooping cough, ranges between 7 to 21 days.
In some cases an increased resistance to certain infections can be observed. The capacity possessed by the body for resisting infection is spoken of as immunity.
Immunity may be natural and acquired. Natural immunity to certain infections may be transmitted from parent to offspring. A temporary passive immunity is transmitted from the mother to her infant both through the placental circulation and through the breast milk. Acquired immunity may follow a spontaneous attack of disease, the artificial inoculation of a modified virus, vaccine injections, injections of antitoxic and antibacterial sera.
The most significant primary preventive measure is immunization against contagious diseases. Prophylactic measures applied in early childhood and the preschool ages should be directed at combating acute childhood infections.
The medical science is now armed with reliable weapons for preventing infectious diseases. The treatment of infectious disease includes the methods directed against the causative agent and its toxins, as well as the microbes of the secondary complicatio n (treatment with sera, sulfa drugs, antibiotics), and the methods which favourably influence the reactivity of the organism and the patient’s emotional tone (blood transfusion, administration of blood plasma and serum, gamma globulin, physiotherapy, etc.) . In addition, the complex of pathogenic therapy includes setting up a hygienic atmosphere for the patient, good care and a proper diet.
Exercises
I. Answer the questions on the text:
1. What are the stages in the course of infectious dis eases? 2. What is immunity? 3. What are the kinds of immunity? 4. What is the most significant preventive measure against infectious diseases? 5. What does the treatment of infectious diseases include?
II. Check if you remember the meanings of the following words:
manifestation; inoculation; measure; resistance; to define; to transmit; to combat; to prevent; to acquire.
III. Translate the sentences paying attention to the underlined words:
a) A temporary passive immunity is transmitted from the mother
|
to her |
infant. |
||
|
b) |
Children of the |
pre-school ages should also |
be protected |
|
from infections. |
|||
|
c) Immunity may be transmitted from parent to |
offspring. |
||
|
IV. Match the Latin words with their English equivalents |
|||
|
and translate them into Russian: |
|||
|
L. Casus |
E. a course |
||
|
Cursus |
a case |
||
|
Causa |
a cause |
V. Finish the sentences according to the following model:
First he looks for somebody and then he … (to look, for, everybody). First he looks for somebody and then he is looked
|
for |
by |
everybody. |
||||||
|
1. |
First |
the chief nurse instructs the other nurses and then |
||||||
|
she … |
(to |
instruct, |
the doctor). |
|||||
|
2. |
First |
the manager controls |
the workers |
and |
then |
he … |
(to |
|
|
control, the |
director). |
. |
||||||
|
3. |
First |
the little |
boy feeds |
his dog and |
then |
he |
.. .(to feed, |
|
|
his |
mother). |
|||||||
|
4. |
The |
mother looks after her children and when |
she is |
ill |
||||
|
she … |
(to |
look after, they). |
Part I
INFLUENZA
Influenza is an acute infectious disease. It is caused by a filtrable virus. The disease spreads very rapidly and affects the adult population and children. The incubation period is 1 -3 days. The onset is sudden with a chill, high temperature, bad headache, pain in the eyes, back, joints and muscles. There is also a dry cough. There may be sore throat, sneezing and cold in the head.
The diagnosis is not difficult during an epidemic. With the onset of symptoms the patient must be put in bed. H e should stay there until the temperature is normal for at least 3 days. The disease may have numerous and dangerous complications, such as: otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia and so on. In a mild case the recovery is the rule. But during epidemics death may occur.
As to treatment it depends on severity of the disease. Proper nursing, hygiene and diet are very important. The patient’s room must be constantly aired. In warm weather the patient may be kept outdoors or in the room with windows wide open all day Patients should always be given plenty of fluid to drink. Such medication as “antigrippin” (a combined anti-influenza medicine), different anti-viral drugs (such as arbidol, remantadin) are used. Herbal and homeopathic remedies can greatly relieve the patient’s condition..
Words to be memorized
|
N o u n s : |
disease, onset, chill, headache, pain, throat, sneezing, |
||||
|
cold, cough, |
recovery, death, treatment, severity, remedy, case. |
||||
|
Verbs: to cause, to stay, to occur, to depend (on, upo n), to |
|||||
|
air, |
to relieve, to |
affect. |
|||
|
A d j e c t i v e s : |
acute, dangerous, numerous, mild, proper. |
||||
|
Other words and expressions: as to, at least, such as, and so |
|||||
|
on, |
constantly, daily. |
||||
|
Read correctly . |
|||||
|
Muscle [m^sl], |
muscular [‘rruskjuld]; |
influenza |
[‘influ’enza]; |
||
|
homeopathic [‘homie’paeOic] |
Exercises
I.Answer the following questions
I.What kind of disease is influenza? 2. What is influenza caused by? 3. How long does the incubation period last? 4. How does the disease begin? 5. Whom does influenza affect? 6. What are the main symptoms of influenza? 7. What complications may this disease have? 8. What must the patient do with the beginning of symptoms? 9. What does the treatment of this disease depend on? 10. What procedures relieve the muscular pains? 1 1 . What
remedies are used for treatment of influenza?
II. Ask your friend yes/no questions:
Influenza is a dangerous disease; the incubation period is long; the complications are serious in case of influenza; influenza is an infectious disease; influenza has an incubation period; diagnosis is difficult in case of influenza; the onset of the disease is sudden; influenza has fatal outcomes during epidemics; the patient has high temperature; influenza has complications; the patient has a headache in case of influenza; the patient keeps his bed when he has a high temperature; the disease affects only adult population; influenza spreads quickly; the patient always coughs when he is down with influenza; the patient feels pains in the back and joints; the patient takes some remedies for influenza.
III. Match the underlined words and their Russian
|
equivalents. |
|||||
|
1. |
The onset |
of the disease is sudden, |
а) по меньшей мере |
||
|
2. |
As to treatment |
b) тяжесть |
|||
|
3. |
it depends on the severity of disease, |
с)начало, наступление |
|||
|
4. |
The |
child |
recovered rapidly |
d) озноб |
|
|
5. |
He |
must |
stay in bed for at least |
e) что касается |
|
|
three days |
f) быстро |
||||
|
6. |
The patient may have a chill when |
||||
|
he |
has |
a high temperature. |
IV. Find the sentences where “to be” may be translated as “должен”
1.The pathogenic microbes were to be tested in our laboratory.
2.The pathogenic microbes were tested in our laboratory.
3.Infectious diseases are to be differentiated from other ones.
4.Infectious diseases are not easily differentiated from others.
5.The drug was to be forbidden.
6.The drug was forbidden by the Pharmaceutic Committee.
V.Choose the correct verb form
1.The infection …(has, has to) spread over a large area. 2. The infection …(has hasto) be eliminated as quickly as possible. 3. The epidemiologist …(had, had to) the possibility to visit the area of infection. 4. The epidemiologist …(had, had to) visit the area of infection to study it at the spot. 5. The pathologic agent …(will have, will have to) be isolated by the end of the week. 6. The pathologic agent …(will have, will have to) been isolated by the end of the week.
VI. Fill in the gaps with English equivalents to «может», «должен»
At about 2 o’clock on a cold winter morning a man telephoned a doctor and asked him if he … come at once. “You … hurry”, he added. The doctor drove seven miles in answer to this call. When he reached the place the man who had called him said, “Doc, I overtired myself. I have not got any pain, but I have a terrible feeling that I … die soon. The doctor examined the patient, felt his pulse and took his temperature.
“Have you made your will(завещание)?” he asked. “Why, no, Doctor”, the man looked frightened. “You … have done it long ago”, said the doctor. “Have you got a family?” “Yes”, said the patient. “You … send for them immediately, and your parents … be called, too.” “I say, Doc, do you think I am going to die?” “No, I don’t”, responded the doctor, “but I don’t want to be the only man you have made a fool of on the night like this”.
VII. Complete the sentences:
1.The room must be constantly .:. .2. The disease … rapidly.
3.The onset is …. 4. In a mild case … is the rule. 5. Death may … .6. … nursing is very important 7. The disease may have numerous and … complications.
VIII. Read the following texts and say what new information they contain as compared with the previous text:
a) The onset of influenza is acute, without marked prodromal symptoms, with a rapid rise in temperature and general symptoms. Intense headaches, mainly in the region of the forehead, eyes and temples are characteristic. Children are irritable, sometimes apathetic; they have sleep and appetite disturbances. Vomiting and nosebleed are frequent. In some cases the upper respiratory tract is affected and catarrh of the mucous membranes begins.
b) Seasonal upper respiratory catarrh is one of the most widespread children’s diseases, which occurs everywhere and affects children of all ages, particularly frequently very young ones. The cases increase during the cold time of the year possibly because
children stay less outdoors and therefore do not get enough fresh air, but get greater contact with patients and carriers of bacilli.
IX. Retell this text in English
Грипп – самая распространённая заразная болезнь, отличающаяся разнообразием проявлений и многочисленными осложнениями. Грипп передаётся от больного к здоровому и поражает и взрослых и детей в любое время года. Инкубационный период ериппа очень короткий, от нескольких часов до двух суток. Эпидемии гриппа повторяются довольно часто ( (через два-три года), но периодически они принимают огромные размеры и охватывают всё население земного шара (так называемые пандемии). В 20 веке были две такие пандемии: в 1918-19 гг. пандемия пандемия гриппа (так называемая «испанка») охватила все страны света, в результате погибло 20 млн человек. Вторая пандемия имела место в 1957 г., тогда количество заболевших во всём мире было также очень велико, но число смертных случаев было сравнительно небольшим.
Возбудителем гриппа являются вирусы. Известно несколько видов гриппозных вирусов. Вирус гриппа, находящий ся на слизистых оболочках носа, рта и глотки больного, при чихании, кашле и разговоре попадает в воздух вместе с капельками слюны или носовой слизи, т.е. заражение происходит воздушно-капельным путём. В крови людей, перенёсших грипп, вырабатываются особые вещества ( так называемые защитные тела), которые в течение некоторого срока (1 – 2 года) обуславливают иммунитет организма к новому заболеванию данным типом вируса.
X.1. Speak about the cause of influenza and its symptoms.
2.Speak about treatment of influenza and its complications.
3.Tell your group-mates how you were ill with influenza.
a)When was it? Did you have to call a doctor? What did he recommend or administer?
b)Have any of your relatives had influenza? What did they complain of? How did they try to improve their condition?
c)Speak of preventing influenza. What precautions should you take during an epidemic?
PNEUMONIA
Pneumonia is a specific acute disease which involves an entire lung or a part of a lung. Sometimes both lungs are involved. It
|
may occur at any time of |
year, but it is frequent in |
the months |
|
from December until May. The chief predisposing |
factors |
are. |
|
weather, draughts, loss of |
sleep and contact with patients |
who |
|
have infections. Various viruses and staphylococci may cause it. |
||
|
The main symptoms |
are chill, fever, general |
weakness, |
sweating and persistent dry cough which can’t be relieved by common measures. The child usually has poor appetite, disturbed sleep. Sometimes children have local chest pains or stomachache. Young infants suffer from shortness of breath.In severe cases patients may have expectoration of bloody sputum. The disease sets in abruptly. There may be a preceding upper respiratory infection with a cough. If the disease remains uncomplicated if lasts from 7 to 14 days.
The treatment consists chiefly of bed rest. The most important agents are fresh air, good nursing and nutritious food that the child likes.The disease responds very well to specific medication with appropriate antibiotics (penicillin) Before the era of antibiotics sulfanilamides were used.. Mustard plasters are always administered, sometimes cups as well.. Diathermy of the lungs gives very good results. The child should be given vitamins C, A
|
and others from |
the very first day of the disease. |
|
A variety of |
complications may occur. Sometimes empyema |
develops after the seventh day of the disease. Otitis media and mastoiditis are usually found in children. Other complications are pericarditis, endocarditis and meningitis,.
An important factor in the prophylaxis of pneumonia is fighting such infectious diseases as influenza, measles and whooping cough, all of which are often complicated by pneumonia.
Words to be memorized
N o u n s : fever, lung, chest, stomachache, weakness, sweating, expectoration.
Verbs: to involve, to set in, to complicate, to last, to consist, to administer, to remain.
A d j e c t i v e s : entire, frequent, chief=main, bloody, nutritious, common.
O t h e r words: abruptly, chiefly.
Read correctly
Pneumonia [nju’mounja]; upper respiratory [‘respireteri] infection; empyema [empai’i:ma]; otitis media [o’taitis ‘mi:dia]; mastoiditis [mastdi’daitis]; sputum [‘spju:tum]; whooping cough [‘hupin. ‘kof].
Exercises
I. Answer the following questions:
I. W hat kind of disease is pneumonia? 2. In what seasons does it occur? 3. W hat are the chief predisposing factors to this disease? 4. W hat are the main symptoms of pneumonia? 5. How long does it last? 6. Are there any complications after pneumonia? 7. W hat is the commonest complication? 8. W hat does the treatment of pneumonia consist of? 9. What medicine
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Представлено сочинение на английском языке Грипп/ Influenza с переводом на русский язык.
| Influenza | Грипп |
| There are many serious diseases in the world. Luckily, most of them can be cured by doctors. Flu is one of the most common and widely spread illnesses. I’m sure all people have experienced it at least once or twice. | В мире существует множество серьезных заболеваний. К счастью, большинство из них могут быть вылечены врачами. Грипп является одним из наиболее частых и широко распространенных заболеваний. Я уверена, что все люди испытали его на себе, по крайней мере, один или два раза. |
| As for me, I have had the flu many times and each time I fell ill my mum gave me lots of hot tea with honey and lemon. Whenever it was provided with fever she called the doctor. Speaking about influenza, we should mention that it’s a viral infection. When someone in your surrounding has the flu you should be careful not to catch it. It is usually manifested by fever, strong headache, muscle pain, cough, running nose, sometimes sore throat or earache. | Касаемо меня, у меня грипп бывал многократно, и каждый раз, когда я болела им, мама давала мне много горячего чая с медом и лимоном. В случаях, когда он сопровождался лихорадкой, она вызвала врача. Говоря о гриппе, следует отметить, что это вирусная инфекция. Когда кто-то в вашем окружении болеет гриппом, вы должны быть осторожны, чтобы не подхватить его. Он, как правило, сопровождается лихорадкой, сильной головной болью, болью в мышцах, кашлем, насморком, иногда болью в горле или в ухе. |
| Depending on the level of heaviness it can even turn into pneumonia. In that case hospitalization is necessary. At the moment, there are three basic forms of influenza known in the world: A, B and C. All of them can be treated just by different methods and pills. | В зависимости от уровня тяжести, он может перетекать в пневмонию. В таком случае госпитализация обязательно. На данный момент существуют три основные формы гриппа, известных в мире: A, B и C. Все они могут быть вылечены только разными методами и лекарствами. |
| One of the best ways to conquer the flu is to stick to bed rest and to drink lots of hot tea. Our district doctor always says, it is better to avoid illness that to treat it. In order not to get the flu, you need to ventilate the room regularly. It will decrease the concentration of viruses in the air. Drinking lots of substances with vitamin C might also help. If anyone in your family gets ill, you should immediately give him or her a separate bowl and a towel. Cover your mouth and nose with a four layer mask. My grandmother says that eating onion and garlic is good during the infection, but my mum finds it too traditional. | Одним из лучших способов победы над гриппом является постельный режим и горячее питье. Наш участковый врач всегда говорит, что лучше избегать болезнь, чем лечить ее. Чтобы не заболеть гриппом, необходимо регулярно проветривать помещение. Это будет уменьшать концентрацию вирусов в воздухе. Пить много жидкости с витамином С также полезно. Если кто-то в вашей семье заболел, вы должны немедленно дать ему или ей отдельную посуду и полотенце. Прикрывайте рот и нос маской в четыре слоя. Моя бабушка говорит, что во время инфекции хорошо есть лук или чеснок, но моя мама считает этот метод слишком традиционным. |
| In any case, I think that every illness should be treated as soon as it is diagnosed, because if it is neglected it can get worse. Doctors have invented another useful method of avoiding the influenza which is vaccination and many people today stick to it. | В любом случае, я думаю, что каждую болезнь следует лечить как только она диагностирована, потому что если ее запустить, то могут возникнуть осложнения. Врачи изобрели еще один полезный способ избежать гриппа, а именно вакцинацию, и многие люди сегодня прибегают к ней. |
с переводом на русский язык |
|
Influenza |
Грипп |
|
Influenza (or flu) is a disease characterized by inflammation of the airways. It is caused by various types of influenza virus. The virus itself is very insidious. It can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia. Also, it constantly mutates and is one step ahead of the scientists who are trying to fight it. |
Грипп – это заболевание, которое характеризуется воспалением дыхательных путей. Вызывают его различные типы вируса гриппа. Сам вирус очень коварен. Он может привести к серьёзным осложнениям, таким, как пневмония. Также, он постоянно мутирует и находится на шаг впереди учёных, которые пытаются с ним бороться. |
|
The flu is a seasonal disease. The highest number of influenza infections occurs in the spring and autumn when the weather changes. Therefore, recurring flu epidemics are not a surprise to people. They have become a part of our life. |
Грипп – сезонное заболевание. Наибольшее количество заражений гриппом приходит на весну и осень, когда погода меняется. Поэтому, периодически возникающие эпидемии гриппа – не удивление для людей. Они стали частью жизни. |
|
The virus is transmitted through the air. The sick person is considered the most contagious in the first three days. The usual duration of the flu is 6-7 days. In a complicated form, it may take up to three weeks. Immunity is formed slowly. This may be affected by other diseases and the age of the patient. |
Вирус передаётся воздушно-капельным путём. Заболевший считается наиболее заразным в первые три дня. Обычная длительность гриппа составляет 6-7 дней. В осложнённой форме может затянуться до трёх недель. Иммунитет формируется медленно. На это могут повлиять другие заболевания и возраст больного. |
|
If there are no complications and serious symptoms, then the flu is treated at home. Drinking plenty of fluids is recommended to prevent dehydration. And also a large amount of sleep is necessary for the immune system to effectively fight infection. |
Если нет никаких осложнений и серьёзных симптомов, то грипп лечится в домашних условиях. Рекомендуется пить много жидкости, чтобы предотвратить обезвоживание. А также большое количество сна необходимо, чтобы иммунная система эффективно боролась с инфекцией. |
|
It is very important to remember that it is not necessary to take antibiotics to treat the flu. They are useless against the virus. Taking antiviral drugs is also questionable, because most types of influenza are resistant to them. |
Очень важно помнить, что не стоит для лечения гриппа принимать антибиотики. Они бесполезны в борьбе против вируса. Сомнительным является и приём противовирусных препаратов, потому что большинство типов гриппа резистентны к ним. |
|
But if you do not trust home methods of treatment and strengthening the immune system, and you want to take medicines then consult your doctor. Please, do not self-medicate. |
Но если вы не доверяете домашним методам лечения и укрепления иммунитета, и хотите именно принимать медикаменты, то проконсультируйтесь с врачом. Пожалуйста, не занимайтесь самолечением. |
- сочинения
Chickenpox (varicella) is a common contagious illness caused by a
type of herpes virus. Chickenpox is most contagious from 2 to 3 days before a
rash develops until blisters have crusted over.
Chickenpox is most common in children and is usually not serious. In
teenagers, adults, pregnant women, and people who have impaired immune systems,
chickenpox can be more serious.
The incubation period—the time from exposure to the chickenpox virus until a
person develops symptoms—is usually 14 to 16 days but can be from 10 to 21
days. Symptoms of chickenpox include a fever, feeling ill, and the development
of a widely scattered, itching rash with fluid-filled blisters. The blisters
burst and crust over after several days. New blisters continue to develop for
up to a week. A person infected with chickenpox can spread the virus before
developing any symptoms.
Treatment for chickenpox focuses on preventing the person from scratching
the rash and on relieving fever and discomfort. A vaccine to prevent chickenpox
is available and recommended for children and for teens and adults who have not
had chickenpox.
INFLUENZA is an acute respiratory illness caused by infection with
influenza viruses. It affects all age groups round the year. Influenza, usually
known as the flu, is a respiratory infection caused by one of the influenza
viruses that typically is spread by air or by direct contact. Most cases occur
during epidemics, which peak during the winter months nearly every year. A
particularly widespread and severe epidemic is called a pandemic. Most people
recover without problems, but sometimes the illness leads to a bacterial
infection, such as an ear infection, sinus infection , or bronchitis . Good
home treatment may help prevent these infections. The virus can cause infections
all year round, but it’s most common in the winter in the UK.
Anyone can get the flu and the more a person is in close contact with people
who have the virus, the more likely they are to get it.
Influenza viruses are designated as Influenza A, B or C depending on the
antigenic characteristics of the particular virus. Influenza occurs in epidemic
forms in India particularly during a change of season. Influenza (flu) is a
viral upper respiratory illness that comes on suddenly, causing symptoms such
as fever, body aches, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, a dry cough, and a
sore or dry throat. The flu is not the same as the common cold; flu symptoms
are usually more severe, and you will often miss more work or school than you
would with a cold.
The flu is a contagious infection of the nose, throat, and lungs caused by
the influenza virus. In people, common symptoms of influenza are fever , sore
throat , muscle pains , severe headache , coughing , and weakness and fatigue
.Most people who have developed symptoms have had close contact with sick
birds, though in a few cases, bird flu has passed from one person to another. The
flu is not the same as the common cold; flu symptoms are usually more severe,
and you will often miss more work or school than you would with a cold.
Influenza can also be transmitted by saliva , nasal secretions , feces and
blood . Infections either occur through direct contact with these bodily
fluids, or by contact with contaminated surfaces. The symptoms, which include
fever, headache, cough, sore throat and muscle aches, appear quickly Influenza
Report has also been published in Chinese, Croatian, German, Indonesian,
Mongolian, Serbian, and Slovenian . Health officials are concerned that a major
bird flu outbreak could occur in humans if the virus mutates into a form that
can spread more easily from person to person.People at increased risk for
complications that require hospitalization are young children, adults age 65
and older, and those with serious medical problems. Influenza also may cause
myositis, exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , Reye’s
syndrome, myocarditis , pericarditis , transverse myelitis and encephalitis.
Influenza is a viral infection of the lungs characterized by fever, cough,
and severe muscle aches. Although the common cold is sometimes confused with
influenza, it is a much less severe disease and caused by a different virus. In
more serious cases, influenza causes pneumonia, which can be fatal,
particularly in young children and the elderly. If you wish to be informed
about new chapters or editions, you may subscribe to the Influenza Report Alert
. It can cause mild to severe illness, and at times can lead to death. The
grimmest scenario would be a global outbreak to rival the flu pandemic of 1918
and 1919, which claimed millions of lives worldwide. Influenza usually appears
in epidemic form and affects many people at once. Although it affects all age
groups, the highest incidence occurs in school children.
Malaria is a disease transmitted by the bite of infected Anopheles
mosquitoes. In spite of India’s National Malaria Eradication programme, this
disease which had been under control has suddenly made a comeback. The
resurgence of malaria is now a heavy burden on India. Most American cases of malaria
develop in travelers who have recently returned from parts of the world where
malaria is widespread. These prophylactic drug treatments are simply too
expensive for most people living in endemic areas. Malaria infections are
treated through the use of antimalarial drugs , such as chloroquine or
pyrimethamine , although drug resistance is increasingly common.
Malaria is an infectious disease that is widespread in tropical and
subtropical regions. Approximately 300 million people worldwide are affected by
malaria and between 1 and 1.5 million people die from it every year. Malaria is
endemic in parts of Asia, Africa, Central and South America, Oceania, and
certain Caribbean islands. Of these areas, sub-Saharan Africa has the highest
occurrence of P falciparum transmission to travelers from the US.
Malaria-carrying Anopheles species mosquitoes tend to bite only between dusk
and dawn. Malaria is one of the most common infectious diseases and an enormous
public-health problem. Malaria remains one of the world’s leading infectious
killers, particularly of children in sub-Saharan Africa. The disease is caused
by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium . The situation has become even
more complex over the last few years with the increase in resistance to the
drugs normally used to combat the parasite that causes the disease.
Malaria is the most deadly vector borne disease in the world. Malaria is an
infection of the blood that is carried from person to person by mosquitoes.
Each year in the U.S., there are an average of 1000 imported infections; a few
cases of locally acquired, mosquito-transmitted infection from an imported
case; and an average of four deaths from falciparum malaria. The parasites
multiply within red blood cells , causing symptoms that include fever , anemia
, chills , flu-like illness , and in severe cases, coma and death.
Malaria-causing Plasmodium species metabolize hemoglobin and other RBC proteins
to create a toxic pigment termed hemozoin . The parasites derive their energy
solely from glucose, and they metabolize it 70 times faster than the RBCs they
inhabit, thereby causing hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis. Unfortunately, no
vaccine is currently available for malaria. Instead preventative drugs must be
taken continuously to reduce the risk of infection If you’re traveling to
malaria-endemic places take precautions before, during and after your trip.
Treatment for malaria is with antimalarial drugs.
Measles is an acute febrile eruption, which is a worldwide
phenomenon. It is an extremely infectious disease. It occurs in children in
epidemics especially during the first eight years. In India
it is common during the months of January-March. A virus causes measles.
Measles are also called Rubeola. Measles is a contagious disese of children.
Measles rarely strikes adults, but if it does, it leaves them prostrated for
quite some time — more common in warm than in cold weather.
Measles , also known as rubeola , is a disease caused by a virus ,
specifically a paramyxovirus of the genus Morbillivirus . It causes a
total-body skin rash and flu-like symptoms, including a fever, cough, and runny
nose. Measles is a leading vaccine-preventable childhood killer in the world.
Millions of children still remain at risk from measles and many children, particularly
under the age of five, will die from it. Measles is spread through respiration
(contact with fluids from an infected person’s nose and mouth, either directly
or through aerosol transmission), and is highly contagious—90% of people
without immunity sharing a house with an infected person will catch it. As a
respiratory disease, measles virus normally grows in the cells that line the
back of the throat and in the cells that line the lungs. However, vaccination
programs are incomplete in much of the world, but global health organizations
are working hard to address this problem. In fact, experts estimate that 10% of
young adults are currently susceptible to rubella, which could pose a danger to
any children they might have someday. The widespread nature of the disease is
why vaccination programs are still necessary in countries where few cases of
measles occur.
The thought of measles may bring to mind the red, blotchy rash that often
accompanies this disorder. Since measles is caused by a virus, symptoms
typically go away on their own without medical treatment once the virus has run
its course. Because of the Measles Initiative’s success in Africa, the program
has expanded into Asia, where the measles burden remains high. Reports of
measles go back to at least 600 BCE, however, the first scientific description
of the disease and its distinction from smallpox is attributed to the Persian
physician Ibn Razi (Rhazes) 860-932 who published a book entitled
«Smallpox and Measles» (in Arabic: Kitab fi al-jadari wa-al-hasbah ).
Before a vaccine against rubella became available in 1969, rubella epidemics
occurred every 6 to 9 years. Kids ages 5 to 9 were primarily affected, and many
cases of congenital rubella occurred as well. Approximately 30 million to 40 million
cases of measles occur worldwide each year, resulting in more than 750,000
deaths. But while your child is sick, it’s important to make sure that he or
she has plenty of fluids and rest, and to keep your child from spreading the
infection to others. Similar to rubeola, lifetime immunity usually occurs after
you have rubella.
Mumps is an acute communicable disease of viral origin characterised
by painful enlargement of the parotid glands. Mumps is common in children
between the age of 5-9 years. One attack of mumps gives lifelong immunity. The
disease has been recognized for several centuries, and medical historians argue
over whether the name «mumps» comes from an old word for
«lump» or an old word for «mumble.» As a secondary language
feature, you can abbreviate nearly all commands and native functions to a
single character to save space; this was a common feature of languages designed
in this period (eg, early BASICs). Outbreaks of mumps still occur in the United States, and mumps is still common in many parts of the world, so getting a
vaccination to prevent mumps is important.
Mumps is an acute , contagious disease that causes painful swelling of the
salivary glands. It was designed to make writing database-driven applications
easy while simultaneously making efficient use of computing resources. These
glands, which produce saliva for the mouth, are found toward the back of each
cheek, in the area between the ear and jaw. Your odds of contracting mumps
aren’t very high. Mumps was common until the mumps vaccine was licensed in
1967. The virus is contagious for about a week before the disease breaks out,
which can make it difficult to track down the source of infection. MUMPS has no
data types. Numbers can be treated as strings of digits, or strings can be
treated as numbers by numeric operators ( coerced , in MUMPS terminology).
Coercion can have some odd side effects, however. As in the prevaccine era,
most cases of mumps are still in children ages 5 to 14, but the proportion of
young adults who become infected has been rising slowly over the last two
decades. A single space separates a command from its argument, and a space, or
newline, separates each argument from the next MUMPS token. Commands which take
no arguments (eg, ELSE ) require two following spaces.
Mumps is a disease caused by a virus that usually spreads through saliva and
can infect many parts of the body, especially the parotid salivary glands. Mumps
is a viral infection that primarily affects the parotid glands — one of three
pairs of salivary glands, located below and in front of your ears.
Additionally, there are built-in operators which treat a delimited string (eg,
comma-separated values ) as an array. Before the vaccine, up to 200,000 cases
of mumps occurred each year in the United States. Since then, the number of
cases has dropped dramatically. The conceit is that one space separates the
command from the (nonexistent) argument, the next separates the
«argument» from the next command. Newlines are also significant; an
IF , ELSE or FOR command processes (or skips) everything else till the
end-of-line. However, other infections can also cause swelling in the salivary
glands, which might lead a parent to mistakenly think a child has had mumps
more than once.
Plague is an acute disease caused by Yersina pestis. It is one of the
most lethal infectious disease known. The plague bacteria is present in India
where rodent menace exists. It is transmitted to humans typically by the bite
of a flea. Plague may be known as bubonic, septicemic or pneumonic. Plague
bacteria could conceivably be put into a form that could be sprayed through the
air, infecting anyone inhaling the bacteria and causing pneumonic plague. In
2003, 9 countries reported 2118 cases and 182 deaths. 98.7% of those cases and
98.9% of those deaths were reported from Africa. Today the distribution of
plague coincides with the geographical distribution of its natural foci.
Plague in populated areas is most likely to develop when sanitation is poor
and rats are numerous. The high death rate from plague in rats forces their
fleas to seek alternative hosts including humans. The plague bacteria uses rat
fleas for its development which is spread by the flea to its natural host the
rat. Plague is a severe, and potentially deadly, infection. It has laid
claim to nearly 200 million lives and has brought about monumental changes,
such as the end of the Dark Ages and the advancement of clinical research in
medicine.
The plague has caused more fear and terror than perhaps any other infectious
disease in the history of humankind. The incidence is the number of new cases
of a disease that occur within a defined population over an established period
of time. Frequently either prevalence or incidence, or both, are given as a
rate , meaning the number of cases in a fixed number of people, e.g., cases per
100,000. Individual cases of disease in widely separated geographic areas or
otherwise independent cases are said to be sporadic . In people, plague has
three forms: Bubonic plague, infection of the lymph glands; septicemia plague,
infection of the blood; and pneumonic plague, infection of the lungs. More
recent pandemics through the late 19th century killed millions of people
worldwide. Improved living conditions and health services have made such large-scale
outbreaks of natural plague unlikely, but occasional isolated plague cases
continue.
Plague is a life-threatening infection caused by the organism Yersinia
pestis, the bacterium that caused the 14th-century Black Death plague pandemic.
The bacteria multiply inside the flea, sticking together to form a plug that
blocks its stomach and causes it to become very hungry. The flea then
voraciously bites a host and continues to feed, even though it is unable to
satisfy its hunger. The Black Death was one of the great epidemic scourges of
mankind. It swept across Europe and Asia in a series of devastating pandemics
during the Middle Ages. Septicaemic form of plague occurs when infection
spreads directly through the bloodstream without evidence of a «bubo».
More commonly advanced stages of bubonic plague will result in the presence of
Y. pestis in the blood. Septicaemic plague may result from flea bites and from
direct contact with infective materials through cracks in the skin.
Polio is a condition caused by the poliovirus. Polio is a serious
public health problem in India. One a person is exposed to polio, it usually
takes about three to five days for symptoms to appear. Polio is a serious
illness. It can cause paralysis (when you can’t move your arms and legs) or
even death. Thanks to the success of a global immunisation programme, polio has
now been eradicated from most countries in the world and will hopefully soon be
a thing of the past. Polio is a very serious disease, which can lead to
paralysis or even death. One a person is exposed to polio, it usually takes
about three to five days for symptoms to appear. However, from the digestive
tract (stomach and intestines), the virus also can get into the blood stream
and be carried to the nervous system (brain and spinal cord). The killed-virus
vaccine immunized people against the effects of the virus, but the virus could
still spread from person to person.
The polio virus has an affinity for the central nervous system, which they
usually reach by passage across the blood-brain barrier. Also the motor nerves
supplying muscles are particularly vulnerable to infection. However, those who
were struck by the virus and survived may find that years later they’re victims
of a second strike. If the virus gets into the brainstem (bulbar polio),
muscles needed for breathing, swallowing and other vital functions become
paralyzed, and the patient may die.
Polio is a viral disease which may affect the central nervous system. Polio
(also called poliomyelitis ) is a contagious, historically devastating disease
that was virtually eliminated from the Western hemisphere in the second half of
the 20th century. In about one of every hundred infected persons, the virus
attacks nerves inside the spine that send messages to muscles in arms, legs and
other areas. This can result in partial or complete paralysis. At the height of
the polio epidemic in 1952, nearly 60,000 cases with more than 3,000 deaths
were reported in the United States alone Initial attempts to develop a vaccine
were hampered by the difficulty of obtaining enough virus. In about 5 percent
of cases, the polio virus manifests in a mild form ( abortive polio ) with
flu-like symptoms, in a nonparalytic form (aseptic meningitis) or in a severe
form called paralytic polio. People who have minor or nonparalytic forms
recover completely.
The poliovirus causes most of its infections in the summer and fall. The
injected vaccine, acting through the bloodstream, immunizes the individual but
does not reduce the potential for spreading the wild virus. Second, because the
oral vaccine acts in the gut, it confers immunity there and reduces the spread
of the wild virus. Polio is a very serious disease, which can lead to paralysis
or even death .Although polio has plagued humans since ancient times, its most
extensive outbreak occurred in the first half of the 1900s before the
vaccination , created by Jonas Salk, became widely available in 1955.
Rabies is an acute viral disease of the central nervous system that
affects all mammals. It is transmitted by infected secretions usually saliva.
Most exposures to rabies are through the bite of an infected animal. Treatment
consists of treatment to the wound plus a series of rabies shots, which prevent
symptoms and death resulting from rabies infection. If you think you’ve been
exposed to an animal with rabies, call your doctor as soon as possible
Fortunately, rabies can be prevented with a vaccine and, if you have been
bitten, there is every chance that you can be treated before the symptoms develop.
Rabies may also spread through exposure to infected domestic farm animals,
groundhogs , weasels and other wild carnivores Any animal bites — even those
that don’t involve rabies — can lead to infections and other medical problems.
As a precaution, you may want to call your child’s doctor any time your child
has been bitten.
Rabies is a frequently fatal, acute viral infection. Rabies is a serious
viral disease that affects the central nervous system. It is transmitted to
people from infected mammals. Treatment of an infected person as critical. In
non-vaccinated humans, rabies is almost invariably fatal after neurological
symptoms have developed, but prompt post-exposure vaccination may prevent the
virus from progressing. Very rarely, rabies has been transmitted by exposures
other than bites that introduce the virus into open wounds or mucous membranes.
A twitching around the animal bite, a trademark symptom of rabies, may appear
in addition to a fever above 105 degrees Fahrenheit (40.5 degrees Celsius),
agitation, and hallucinations. People are most often infected by the bite of a
dog, bat or monkey. In Europe the virus is mainly carried by the fox. None of
the 22 imported cases received post-exposure prophylactic treatment for rabies
either in the country of origin or in the UK. In 2003 it was recognised that UK
bats may carry a rabies-like virus, European Bat Lyssavirus 2 (EBL2).
Although rabies infections in people are rare, they can cause serious health
problems. But if you recognize the warning signs of a rabies infection early
and get medical help, your child can make a full recovery. The virus is
transmitted in saliva from the bite of an infected animal. Rabies primarily
attacks the nervous system and causes an encephalitis After a bite by a rabid
animal, a child may develop a fever, headache, and general malaise. If someone
gets bitten by an animal that has rabies, quick treatment can prevent the
illness. Most rabies cases reported to the Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention (CDC) each year occur in wild animals, including raccoons, skunks
and foxes. Infected bats have transmitted most of the recent rabies cases in
people in the United States.
Rubella is a three-day mild measles. However, if a pregnant woman
gets it, it may lead to seriousfetal infection and malformation. It is caused
by the rubella virus. Most rubella infections today appear in young,
non-immunized adults rather than children. In fact, experts estimate that 10%
of young adults are currently susceptible to rubella, which could pose a danger
to any children they might have someday.
Rubella can occur in susceptible persons by natural influx of the virus via
the nasopharynx. Congenita lrubella results from the transplacental
transmission of the virus to the fetus from the infected mother and may be
associated with growth retardation, infiltration of the liver and spleen, and
pneumonia.
Rubella is not as contagious as measles. However, once a person has rubella,
she/he has immunityfor life. Even though it is a mild childhood illness CRS
causes many birth defects. Deafness is the most common, but CRS can also cause
defects in the eyes, heart, and brain. Rubella outbreaks once were common in
the United States. In fact, experts estimate that 10% of young adults are
currently susceptible to rubella, which could pose a danger to any children
they might have someday.
Rubella is a contagious viral infection with mild symptoms associated with a
rash. Rubella -commonly known as German measles or 3-day measles — is an
infection that primarily affects the skin and lymph nodes. It is often mild and
an attack can pass unnoticed. However, this can make the virus difficult to
diagnose. The virus usually enters the body through the nose or throat .
Rubella and measles are both contagious viral infections best known by the
distinctive red rash that may appear on the skin of those who contract either
illness. However, rubella is neither as infectious nor usually as severe as
measles, which is why rubella is also called three-day measles. Kids ages 5 to
9 were primarily affected, and many cases of congenital rubella occurred as
well. If the mother is infected within the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, the
baby will have congenital rubella syndrome .
Rubella is usually a mild viral illness involving the skin, the lymph nodes,
and, less commonly, the joints.When a woman is infected with the rubella virus
early in pregnancy, she has a 90% chance of passing the virus on to her fetus.
It is caused by the rubella virus ( not the same virus that causes measles), which
is usually transmitted by droplets from the nose or throat that others breathe
in.There is one important exception: If a pregnant woman contracts rubella,
especially during her first trimester, the virus can cause death or serious
birth defects in the developing fetus. It is characterized by a rash, swollen
glands and, especially in adults, joint pain. The rash usually lasts about
three days and may be accompanied by a low fever. The name German measles has
nothing to do with Germany . It comes from the Latin germanus , meaning
«similar», since rubella and measles share many symptoms.
Tetanus is a neuralgic disorder, characterised by increased muscle
tension and spasms (Trismus). The disease is caused by a bacteria called
clostridium tetani. This organism is foundin soil and in animal feces. This
disease is commonin rural areas of India where soil is cultivated. Before
immunizations (vaccines, or shots that are given to help the body fight certain
illnesses) were available, neonatal tetanus was a common cause of newborn death
because the disease is almost always fatal in infants. Prior to immunizations,
neonatal tetanus was much more common in the United States. Now, routine
immunizations for tetanus produce antibodies that mothers pass to their unborn
babies. These maternal antibodies and sanitary cord-care techniques have made
newborn tetanus very rare in developed countries. Tetanus may be fatal despite
treatment. The disease is rare in the United States, with less than 100 cases
of tetanus reported annually.
Tetanus in the unimmunised follows an acute injury, open wound, lacerations
and abrasions. In developing countries of Africa, Asia, and South America,
tetanus is far more common. Because of improved surgical procedures and
techniques for cutting the umbilical cord, however, newborn tetanus is now rare
in developed countries. Starting at 2 months of age, all babies in the United States are routinely vaccinated against tetanus. If deposited in a wound, the
bacteria can produce a toxin that interferes with the nerves controlling your
muscles. Localized tetanus presents itself as a mild condition with
manifestations restricted to muscles near the wound. It may progress to the
generalized form.
Tetanus injury in most cases is trivial. All age groups are involved. Wounds
may get contaminated with the spores of the organism. The spores germinate
within the wound and toxin is produced.This toxin binds to the peripheral
nerves and is transported thereafter to the spinal cordand the brain.
Tetanus is a medical term indicating a prolonged contraction of skeletal
muscle fibers. Tetanus is a serious bacterial disease that leads to stiffness
of your jaw muscles and other muscles. It typically arises from a skin wound
that becomes contaminated by a bacterium called Clostridium tetani , which is
often found in soil. A cut, puncture wound, laceration or other wound can lead
to a tetanus infection and toxin production if you don’t have immunity. It can
also travel to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymph
system. As it circulates more widely, the toxin interferes with the normal
activity of nerves throughout the body, leading to generalized muscle spasms.
These bacteria produce the toxin (poison), tetanospasmin, which is responsible
for causing tetanus. This poison affects the place where nerves and muscles
meet.
Tetanus is a disease caused by the toxin of the bacterium Clostridium tetani
that affects the central nervous system , sometimes resulting in death.
Infection usually originates from a contaminated wound, often a cut or deep
puncture wound. Once the bacteria are in the body, they produce a neurotoxin (a
protein that acts as a poison to the body’s nervous system) known as
tetanospasmin that causes muscle spasms. Common symptoms are muscle spasms in
the jaw (hence the common name lockjaw ), followed by difficulty swallowing and
general muscle stiffness of other parts of the body In the United States,
because of widespread immunization and careful wound care, the annual number of
cases among children is between 50-100 cases.
Typhoid Fever disease is caused by a bacteria called Salmonella
typhi. It is a common diseasein the sub continent and affects all age groups.
The poor hygiene conditions, open sanitation habits, flies, sale of exposed
food, and illiteracy is responsible for this disease.The incubation period is 3
to 60 days. The disease is transmitted from human to human via food or drinking
water, and it is therefore mainly hygiene and sanitary conditions that
determine its spread. Vaccines against typhoid fever are available, but they’re
only partially effective and are usually reserved for people who may be exposed
to the disease or are traveling to areas where typhoid fever is endemic.
Typhoid fever is still common in the developing world, where it affects about
12.5 million persons each year. Inflammation of the small and large intestine
follows. In severe infections, which can be life threatening, sores may develop
in the small intestine.
Typhoid fever is an illness caused by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi . Since
ancient times, these bacteria have thrived during wartime and during the
breakdown of basic sanitation. It can be life-threatening, but antibiotics are
an effective treatment. Today, typhoid fever is rare in industrialized countries,
although it remains a serious health threat in the developing world. The
bacteria is deposited in water or food by a human carrier, and is then spread
to other people in the area. It is recognized by the sudden onset of sustained
fever, severe headache, nausea and severe loss of appetite. It is sometimes
accompanied by hoarse cough and constipation or diarrhoea. When treated with
antibiotics, most people feel better within a few days, although a small
percentage — especially older adults and those with chronic diseases — may die
of complications. The bacteria then multiply in the blood stream of the
infected person and are absorbed into the digestive tract and eliminated with
the waste.
In the year 1906, 3,000 New York state residents contracted typhoid fever, a
contagious and life-threatening bacterial illness. Classic typhoid fever is a
serious disease. This improvement is the result of improved environmental
sanitation. Mexico and South America are the most common areas for U.S. citizens to contract typhoid fever. The disease is transmitted from human to human via
food or drinking water, and it is therefore mainly hygiene and sanitary
conditions that determine its spread. Typhoid fever spreads through
contaminated food and water or through close contact with someone who’s
infected. Case-fatality rates of 10% can be reduced to less than 1% with
appropriate antibiotic therapy. Paratyphoid fever shows similar symptoms, but
tends to be milder and the case-fatality rate is much lower.
Whooping Cough is an acute infection of the respiratory tract, seen
only in children. It is typically a prolonged illness with an average duration
of 6-8 weeks. The incubation period is 7-10 days. Anyone can get whooping
cough, but the health effects are usually much worse for children less than a
year old. In Canada, whooping cough now kills one to three infants per year,
usually those who are unvaccinated, or under-vaccinated. With proper care, most
teenagers and adults recover from whooping cough without complications. Whooping
cough is more serious in children, especially infants younger than 6 months of
age.
Whooping cough — known medically as pertussis -is a highly contagious
respiratory tract infection. Pertussis, also called whooping cough, is caused
by Bordetella pertussis bacteria and is extremely contagious. Before a vaccine
was available, pertussis killed 5,000 to 10,000 people in the United
States each year. In the more advanced stages, it’s marked by the symptom
that gives the disease its name: a severe, hacking cough followed by a
high-pitched intake of breath that sounds like «whoop.» Worldwide,
there were over 45 million cases of whooping cough and 409,000 deaths
in 1997—making this easy-to-prevent disease one of the leading causes of illness
and death. Pertussis vaccine is most commonly given in combination with the
vaccines for diphtheria and tetanus in the vaccine known as “DPT.” Today only a
few get whooping cough. Treatment of whooping cough is supportive, meaning that
treatment is directed at the symptoms, e.g., cough; however, young infants
often need hospitalization if the coughing becomes severe.
Whooping cough — or pertussis — is an infection of the respiratory system
caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis (or B. pertussis ). Although it
initially resembles an ordinary cold, whooping cough may eventually turn more
serious, particularly in infants. The bacterium responsible for the infection,
Bordetella pertussis, was not isolated until 1906. Each year, 5,000-7,000 cases
of whooping cough (pertussis) are recorded each year in the United
States. Whooping cough is the most common vaccine-preventable disease among
children younger than 5 years in the United States. Symptoms of the infection
include prolonged, violent, coughing spasms that often cause thick mucus and
severe inhaling difficulties. Since then, however, the incidence of whooping
cough has been increasing, primarily among children too young to have completed
the full course of vaccinations and teenagers whose immunity has faded .
Chicken Pox is a highly contagious condition. It affects both of all
age groups. It is however a common occurrence amongst children of 3-8 years of
age. Immunity for life. Adult chicken pox is rare. But when it occurs it can be
a serious attack with complications. Chickenpox spreads in tiny droplets of
saliva and nasal mucus coughed out by an infected person. If a woman comes into
contact with chickenpox or shingles when pregnant, there’s no problem if she’s
had it before, because this gives your body immunity to it (re-infection is
rare). Unlike chickenpox which normally fully settles, shingles may result in
persisting post-herpetic neuralgia pain Chickenpox is very common and highly
contagious. Approximately 3 million cases occur each year in the United States.
Chickenpox was once considered a rite of passage for most children. Before
1995 -when a vaccine for chickenpox became available in the United States —
about 4 million Americans, mostly children, contracted chickenpox each year
People who get the virus often develop a rash of spots that look like blisters
all over their bodies. The blisters are small and sit on an area of red skin
that can be anywhere from the size of a pencil eraser to the size of a dime.
Kids can be protected from VZV by getting the chickenpox vaccine, usually
between the ages of 12 to 18 months, though sometimes the vaccine is
given to older kids, teens, and adults. Symptomatic treatment, with
calamine lotion to ease itching and paracetamol (known in the U.S.
as acetaminophen) to reduce fever, is widely used. It doesn’t do any harm
because it’s kept under control by the immune system; the part of the body that
fights infection. Later in life, viruses remaining dormant in the nerves can
reactivate causing localised eruptions of shingles . This occurs particularly
in people with compromised immune systems, such as the elderly, and perhaps
even those suffering sunburn. However, the chickenpox vaccine is a safe,
effective way to prevent chickenpox and its possible complications . The most
common reason for the virus to reactivate is getting older. Reactivation of the
virus causes a condition called shingles, a painful blistering skin rash that
typically occurs on the face, chest or back, in the same area where one or two
of the body’s sensory nerves travel.
Chickenpox is one of the classic childhood diseases, and one of the most
contagious. Chickenpox is caused by a virus called varicella zoster (say:
var-uh- seh -luh zas -tur). But the good news is that chickenpox is a common
illness for kids and most people get better by just resting like you do with a
cold or the flu. Chickenpox is rarely fatal (usually from varicella pneumonia
), with pregnant women and those with depressed immune systems being more at
risk. Pregnant women not known to be immune and who come into contact with
chickenpox may need urgent treatment as the virus can cause serious problems
for the fetus. Most people think of chickenpox as a mild disease -and, for
most, it is. Chickenpox usually lasts about two weeks and rarely causes complications.
But the disease can be serious, even in healthy children.
Elephantiasis are worms that dwell in the tissue beneath the skin and
in the lymphatic system. Filariasisis a very common condition amongst people of
India living in the coastal regions of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Elephantiasis partially takes its name from «the Elephant Man», the
carnival stage name of Joseph Merrick . The name refers to the resemblence of Merrick’s limbs to the thick, baggy skin on the limbs and trunks of elephants. Careful
hygiene and other measures that prevent and control subsequent bacterial and
fungal infections in limbs or genitals in which the lymphatic system has been
damaged can reduce disfigurement and suffering.
There are many types of filaria worms. The commonest is Wuchereria Bancrofti
and Brugia Malayi. Humans are the only definite hosts for this parasite. The
mosquito spreads this disease. Usually infection is established only with
repeated and prolonged exposure to infective larvae. After being infected by a
mosquito, the larvae travel to the lymphatic system where they develop into
adult worms. The offspring are termed microfilariae. They circulate in the
blood or migrate to the tissue beneath the skin.
The principal changes result from inflammatory damage to the lymphatic
system, which is caused by adult worms. These worms live within the lymphatic
system and the lymph nodes. They cause lymphatic dilatations and thickening of
the walls. These regions are infiltrated by cellsof the body causing gross
changes in the tissues leading to the tortuosity of the lymphatics and damage
to the vessel valves. With obstruction to the flow of lymph there is nowa
stasis and a hard brawny edema develops in the overlying skin. With the death
of worms further inflammatory changes take place leading to further
complications in the lymphatic function.
Elephantias is also called lymphatic filariasis. elephantiasis , abnormal
enlargement of any part of the body due to obstruction of the lymphatic
channels in the area (see lymphatic system ), usually affecting the arms, legs,
or external genitals. Elephantiasis generally results from obstructions of the
lymphatic vessels. It is most commonly caused by a parasitic disease known as
lymphatic filariasis . This is the severely disfiguring and disabling condition
of elephantiasis. Recovery from filariasis is possible and surgery sometimes
helps, but any elephantiasis that develops during the disease cannot be cured.
Ivermectin, an antifilarial drug, has been effective with a single dose.
Nonfilarial elephantiasis is thought to be caused by persistent contact with
volcanic ash. Elephantiasis partially takes its name from «the Elephant
Man», the carnival stage name of Joseph Merrick. Albendazole, in
combination with others drugs, is being used in a program of mass drug
administration undertaken under the auspices of the World Health Organization
in an attempt to eliminate filariasis.
Alternatively, elephantiasis may occur in the absence of parasitic
infection. Lymphatic filariasis, also known as elephantiasis, is best known
from dramatic photos of people with grossly enlarged or swollen arms and legs.
This nonparasitic form of elephantiasis, known as nonfilarial elephantiasis or
podoconiosis, generally occurs in the mountains of central Africa. This
blockage causes fluids to collect in the tissues, which can lead to great
swelling, called «lymphedema.» The adult worms live in the lymphatic
system, causing local inflammation, fibrosis, and obstruction, and resulting in
the characteristic enlargement and thickening of the skin. Diethylcarbamazine
often kills the adult worms or impairs their reproductive capabilities, and the
antibiotic doxycycline, which works by killing symbiotic bacteria that live
inside the worms, also eliminates adult worms.
Hansen’s Disease is a chronic infectious disease caused by the
leprosy bacillus. It affects mainly the peripheral nerves, the skin, muscles,
eyes, bones, testes and internal organs. It is one of the oldest disease known
to mankind. The word leper comes from a Greek word. In India
it is knownas «KushtaRoga»and is attributed to a punishment from God.
South East Asia has the highest number of leprosy cases in the whole world.
It is a major public health problem in India. The prevalence of leprosy in India
is 6.7 per 10000 population. The numbers of infectious cases varies between
15-20 per cent. India has the highest recorded number of leprosy patients in
the whole world. The treatment of choice is a multidrug therapy (MDT) using
diaphenylsulfone (Dapsone), rifampicin (Rifadin), and clofazimine (Lamprene).
Surgery can reconstruct damaged faces and limbs. Over millennia the leprosy
bacterium has undergone «massive gene decay» — the loss of many
genes and therefore it has largely lost the ability to adapt. The term Hansen
disease instead of leprosy is now preferred by some experts, because of it
being less perjorative.
Spread of infectionis via nasal discharge either by blowing the nose or
sneezing in public. Leprosy cases harbour millions of leprosy bacilli in their
nasal mucosa. Leprosy is a social disease. It is common amongst the poor due to
overcrowding, poor housing and lack of hygiene. It can spread by close contact
as well as from person to person and skin to skin contact. Leprosy has an incubation
period of 3-5 years. This disease can cause severe deformity of the feet, hands
and face. The bacteria that cause leprosy thrive in cool areas of the body such
as the skin, nerves near the skin surface and in oral and nasal mucus
membranes. The bacterium responsible for leprosy is called Mycobacterium leprae
or, for short, M. leprae. There it is able to withstand the onslaught of
enzymes and other forces by virtue of possessing a peculiarly resistant waxy
coat and thanks also to its association with lowered cellular immunity . The
condition is marked initially by hyperesthesia (excess sensation) succeeded by
anesthesia (lack of feeling) and by paralysis, ulceration, and various other
problems, ending horribly in gangrene and self-mutilation.
Types of Leprosy
1. Indeterminate type: This denotes early cases with one or two vague hypo
pigmented patches with definite sensory impairment. Common on knees and elbows.
2. Tuberculoid type: This type denotes those cases with one or two well
defined lesions which may be flat or raised, hypo pigmented or reddish and with
no sensations.
3. Borderline type: There are four or more lesions which may be flat or
raised, well or ill defined, hypo pigmented or reddish with no sensations.
4. Lepromatus type: There is diffuse infiltration or numerous flat or
raised, poorly defined, shiny, smooth, symmetrically distributed lesions. The
lesions are bacteriologically positive.
5. Pure neurotic type: There is only nerve involvement. There are no skin
lesions.
Leprosy, also known as Hansen disease, is a chronic infectious disease with
a wide range of clinical manifestations. At that point, a multi-drug treatment
was devised, combining dapsone with clofazimine and rifampin. This treatment
has proven to be the most effective treatment for many years. In treating the
tuberculoid leprosy, the multi-drug treatment must be followed for
approximately six months, while in the case of lepromatous leprosy, the
treatment can last as long as two years. Preventing the spread of Hansen’s
disease is, for the present, limited to treating individuals after they
contract the disease. Hansen’s discovery preceded Robert Koch’s demonstration
of the bacterial cause of anthrax by 3 years. Hansen’s research helped to
establish fundamental principles in microbiology, immunology , and public
health .
It is a chronic granulomatous disease of the skin, mucous membranes, nerves,
lymph nodes, eyes, and internal organs such as the liver, spleen, and
testicles. Only about five percent of the people who are infected with the
bacteria actually develop the disease. The immune system generally prevent the
development of leprosy. As this type of leprosy advances, nodules may form on
both sides of the body. For thousands of years, leprosy was one of the world’s
most feared communicable diseases, because the skin and nerve damage often led
to terrible disfigurement and disability. Even after treatment and the
infection is cured, there may still be disability and disfigurement. It is
recommended that annual examinations be done for at least five years after the
last contact with any person who is infectious.
HERPES ZOSTER is a sporadic disease. It is the consequence of the
reactivation of latent virus from the spinal cord. This infection usually
occurs in adults. It produces localized vesicular skin lesions confined to a
dermatome and severe neuralgic pain in peripheral areas innervated by the
nerves arising in the inflamed root ganglia. Herpes zoster results from
reactivation of varicella virus that has lain dormant in the cerebral ganglia
(extramedullary ganglia of the cranial nerves) or the ganglia of posterior
nerve roots since a previous episode of chickenpox. It is a disease generally
of the middle age and elderly.
Herpes zoster is an acute , localized infection with varicella-zoster virus,
which causes a painful, blistering rash. After the initial exposure, herpes
zoster lies dormant in certain nerve fibers.Whereas varicella is generally a
disease of childhood, herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia become more
common with increasing age. Following resolution of the chickenpox, the
virus lies dormant in the dorsal root ganglia until focal reactivation along a
ganglion’s distribution results in herpes zoster (shingles). Historically, it
was thought that shingles incidence increased due to an age-related decline in
immunity; however, recent studies suggest that incidence of shingles is linked
to the reduced frequency of periodic exogenous (outside) exposures to children
with varicella (chickenpox) due to the increasing vaccination of that
population. A temporary weakness in immunity (the body’s ability to fight
infection) may cause the virus to multiply and move along nerve fibers toward
the skin. Eye problems caused by severe or chronic outbreaks of herpes zoster
may include: glaucoma , cataract , double vision, and scarring of the
cornea and eyelids This condition is known as zoster sine herpete and may be
more complicated, affecting multiple levels of the nervous system and causing
multiple cranial neuropathies, polyneuritis, myelitis , or aseptic meningitis.
Medical treatments like chemotherapy or radiation for cancer, drugs taken to
prevent rejection of transplanted organs, and cortisone taken for a long time,
can make someone susceptible.
Herpes zoster , commonly known as shingles, is caused by the same virus
responsible for chicken pox. It may become active as a result of many factors
such as: aging, stress, suppression of the immune system, and certain
medications. Although the exact precipitants that result in viral reactivation
are not known certainly, decreased cellular immunity appears to increase the
risk of reactivation. Herpes zoster manifests as a vesicular rash, usually in a
single dermatome. Factors that decrease immune function, such as human
immunodeficiency virus infection, chemotherapy, malignancies and chronic
corticosteroid use, may also increase the risk of developing herpes zoster.
These exposures produced an immunologic boost that helped suppress the
reactivation of shingles. Shingles incidence is high in the elderly (over 60),
as well as in any age group of immunocompromised patients Although children can
get zoster, it is more common in people over the age 50. Illness, trauma, and
stress may also trigger zoster. This acutely painful phase usually lasts
several weeks; however, some continue to experience pain or neuralgia long
after the outbreak has cleared.