Жертвоприношения и каннибализм: настоящая сказка о Золушке
Нам всем хорошо знакомы сказки Шарля Перро и братьев Гримм о бедной девушке, чья мать умерла, а мачеха била и угнетала падчерицу. Затем девушка отправляется на бал, где теряет туфельку, которую находит принц. Эта история прошествовала через много тысячелетий, облетела множество народов. Но о чем она на самом деле? Похожа ли настоящая история Золушки на сказку? Мы проверили десятки сказок разных народов о Золушке и нашли кое-что по-настоящему жуткое.

fallingsarah.deviantart.com
«Где же там жертвоприношения, а тем более каннибализм?» — удивитесь вы. Сказка-то о доброй и кроткой девочке, которая ковырялась в золе, пока не пробил ее час. Все дело в том, что сказки братьев Гримм и Шарля Перро — сказки, записанные уже в XVIII-XIX веках, то есть близко к нашему времени.
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Первоначальный же, мифологический контекст в более поздних обработках бывает сильно искажен. Мифологические элементы, присутствующие в ранних версиях сказки, забываются, ведь миф далеко не всегда логичен и понятен. Миф куда более архаичный и пугающий, а сказка — попытка его рационализации.
«Золушка» — один из популярнейших «бродячих сюжетов», который имеет свыше тысячи воплощений в фольклоре разных народов мира.
Где мать Золушки? Ее съели!
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Одним из важнейших образов в сказке «Золушка» является образ погибшей матери. У читателя не возникает вопроса, отчего могла умереть несчастная женщина. Появление доброй феи-крестной в версии Шарля Перро также не вызывает удивления. И мало кому приходит в голову, как тесно связаны между собой эти два образа.
Итак, в самом начале сказки у Золушки умирает родная мать, а отец, погоревав, находит себе другую жену. Отчего же наступает смерть? В большинстве сказок это не освещается, а приводится как данность, но до сих пор остались сказки, сохранившие в себе самые древние мотивы, которые дают ответ на этот вопрос.
В греческой версии «Девка-на-насесте» (Edmund Martin Geldart, Folk-Lore of Modern Greece: The Tales of the People, Little Saddleslut) мать принимает смерть от рук собственных дочерей:
Однажды три сестры сидели и пряли лен. И сказали они: «Чье веретено упадет на землю, ту мы убьем и съедим». Первым упало веретено их матери, но они не тронули ее, а сели прясть дальше. И вновь упало матушкино веретено, и опять, опять… «Ну что ж! — сказали они. — Теперь-то мы ее съедим».
Но Золушка вступается за мать, хотя и безрезультатно:
«Нет! — сказала самая младшая из сестер. — Не ешьте ее. Раз уж вам так хочется мяса, съешьте лучше меня». Но сестры отказались; двое из них убили, а затем приготовили мать.
Вот так жестоко расправились дочери над собственной матерью. Золушка же отказывается от трапезы и впоследствии будет за это вознаграждена.
Из текста можно предположить, что мать нарочно роняет веретено, чтобы спасти своих детей. Впоследствии в сказке Little Saddleslut («Девка-на-насесте») именно мать становится волшебной дарительницей для младшей дочери, над которой насмехались сестры:
Затем самая младшая, которую называли Девка-на-насесте [после смерти матери девушка все время сидела на курином насесте, за что сестры дали ей эту кличку], собрала все материны кости и похоронила их под изгородью. Сорок дней девушка окуривала их ладаном, а затем хотела отнести в другое место. Только она подняла камень, как лучи света ослепили ее. Она нашла там прекрасное одеяние, будто сотканное из неба и звезд, из весны и морских волн. Кроме платья, там лежало множество монет.
Но это не единичный случай. Примеров с упоминанием поедания матери членами ее семьи встречается довольно много. Нередко мотив так называемого эндоканнибализма (поедание родственника) совершается в более мягкой форме, то есть отсутствует прямое упоминание вкушения человеческой плоти. Мать в этих версиях превращается в животное — часто корову — и только после этого съедается.
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Нарушение волшебного запрета
В некоторых сказках трансформация матери в животное является следствием нарушения волшебного запрета. Вот что рассказывает нам сербская сказка «Пепелюга» (Woislav M.Petrovitch, Hero Tales and Legends of the Serbians, Pepelyuga):
На высокогорных пастбищах, поблизости от глубоких пропастей, несколько девушек пряли пряжу и присматривали за скотом. Вдруг они заметили странного мужчину с длинной белой бородой до пояса. Он остановился и сказал: «Прекрасные девы, остерегайтесь пропасти. Ведь если кто-нибудь из вас уронит в нее свое веретено, мать той девушки превратится в корову в тот же момент!»
Сказав это, старик исчез. Девушки же, озадаченные его словами и обсуждая странное происшествие, подошли к самому краю обрыва… Они с любопытством заглядывали в расщелину, будто надеялись увидеть там что-то необычное. Внезапно веретено выскользнуло из рук самой красивой из них и, ударяясь о камни, улетело в бездну.
Когда вечером девушка вернулась домой, худшие ее страхи воплотились в жизнь. Вместо матери она увидела перед дверью корову.
Корова помогает Марре (сербской Золушке), когда ее отец женится на злой и строптивой женщине. Но мачеха не глупа — она велит своей дочери отправиться вслед за Маррой и проследить, как той удается всегда быть сытой. Обман открывается, и сводная сестра доносит матери, что корова подкармливает девушку и помогает выполнять задания мачехи. Злая мачеха приказывает убить корову, но та, предчувствуя смерть, велит Марре не пробовать ее мяса, а кости собрать и похоронить в определенном месте.
Довольно часто мать, обращенная в животное, предвидит свою смерть и не страшится ее.
Еще одним примером наказания за нарушенный запрет может служить сказка «Злая мачеха» (J.Hinton Knowles, Folk-Tales of Kashmir, The Wicked Stepmother) государства Кашмир. В этой сказке в качестве матери Золушки выступает жена брахмана. Уходя из дому, брахман настоятельно просит супругу не есть ничего до его возвращения. В противном случае она превратится в козу. Если же он сам отведает пищи вне дома, то обернется тигром.
Ослушавшись завета мужа, жена пробует пищу в его отсутствие и оборачивается козой. Ее бывший муж женится заново. В этой версии сказки у Золушки есть еще братья и сестры, которых и выручает волшебная коза до того момента, как злая мачеха не вычисляет их помощника. После этого новая жена, прикинувшись больной, велит лекарю сказать, что спасти ее может только козье мясо. Лекарь безропотно выполняет ее повеление. У брахмана в это время не было денег на другую козу, поэтому печальная участь постигает его бывшую жену.
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
При чем тут жертвоприношение?
Выделяют две основные причины каннибализма как реального явления: вынужденный каннибализм, связанный с тяжелыми бытовыми условиями (голод, засуха и прочие), и каннибализм ритуальный. В контексте данной истории можно с относительной уверенностью отклонить версию поедания родственника в связи с голодом, так как в сказках неоднократно упоминаются тучные стада овец и другие признаки достатка.
Явление эндоканнибализма уходит корнями в глубокую архаику и довольно часто упоминается в мифах и сказках. Если изначально каннибализм был присущ верховным божествам, то по мере распространения запрета он становится особенностью низших мифологических существ: вампиров, оборотней и так далее. Обычно он сурово наказывается.
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Так, в большинстве сказок о Золушке, в которых присутствует мотив косвенного или прямого каннибализма, животные, являющиеся духом погибшей матери, запрещают ей пробовать их мясо.
Мстительная Золушка из Вьетнама
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Временами сюжет сворачивает в совершенно немыслимые стороны. В одной из вьетнамских версий сказки «Тэм и Кэм» (Tấm Cám) Золушка карает мачеху жесточайшим образом, заставляя ту отведать плоти собственной дочери.
Когда вьетнамская Золушка Тэм уже вышла замуж за принца, ее сводная сестра Кэм спрашивает у нее, как той удается сохранять свою красоту. Тэм отвечает, что она всего лишь принимает ванну с кипятком. Сделав так, как ей посоветовала сестрица, Кэм погибает, сварившись заживо. Тэм разрезает ее тело на части и готовит из мяса еду, а потом отправляет мачехе. Женщина без раздумий принимается за трапезу, но тут ворон садится на крышу ее дома и каркает: «Вкуснятина! Мать ест плоть собственной дочери! Осталось ли еще? Дай и мне кусочек!» И только доев до конца, мачеха обнаруживает череп своей девочки на дне горшка, после чего умирает от шока.
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Животные-помощники: от коровы до рыбы
С течением времени мотив каннибализма прошел длинный путь рационализации. Сказка очень долгое время оставалась устным жанром. Передавая из уст в уста знакомый сюжет, рассказчики привносили в историю о Золушке что-то свое, часто опуская или рационализируя то, что было непонятно повествователю. Таким образом, разрыв между матерью Золушки и добрым помощником, возникающем на ее пути, стал увеличиваться.
Во многих версиях сказки образ матери утрачивает свою значимость, но при этом сохраняется образ животного-помощника, появление которого никак не объясняется. В ирландском, шотландском и сербском аналогах «Золушки» в качестве такого животного выступает овца или корова, что в какой-то степени роднит эту сказку с не менее известной нам историей «Крошечка Хаврошечка».
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Чаще всего в качестве животного-помощника выступает самка, но встречаются и мужские вариации, далеко ушедшие от идеи матери-спасительницы. И если в малайской народной сказке «Bawang Putih Bawang Merah» рыба еще признается в том, что она и есть мать девушки, то во вьетнамской «Тэм и Кэм» рыба явно символизирует мужскую фигуру — по некоторым версиям, девушке помогает сам Будда.
Рыба появляется в азиатских сказках не случайно: часто она символизирует бога.
Помогают Золушке и другие животные: бык увозит ее прочь от злой мачехи в норвежской сказке «Кэти Деревянный плащ»; красный теленок в шотландской Rashin-Coatie ведет ее через лес. Встречаются и персонажи «нижнего мира»: мышь, жаба и другие.
На следующем этапе рационализации в качестве помощников Золушки выступают птицы или дерево, выросшее на могиле матери. По версии братьев Гримм, Золушка совершала паломничество на место захоронения матери и там поливала землю слезами до тех пор, пока на том самом месте не выросло дерево. Стоило Золушке потрясти его, как с веток падали орехи, в которых для нее были спрятаны волшебные дары. Точно так же поступает Золушка Джозефа Якобса, сажая орешник. К ней прилетает птичка и советует потрясти дерево, чтобы с него упал орех.
В итальянской сказке «Золушка» (Thomas Frederick Crane, Italian Popular Tales, Cinderella) отец привозит младшей дочке маленькую птичку Верделио, которая и наделяет Золушку красотой. Образ птицы повсеместно в мифах различных стран является образом человеческой души. Так, погибшие родственники приходят к живым в виде птиц и помогают в беде или предупреждают о несчастье. Птица — небесный житель, близкий к богам. Именно птицы предупреждают принца об обмане, когда сводные сестры Золушки, желая выйти замуж за королевскую особу, отрезают себе часть ноги, чтобы туфелька пришлась впору.
Почему именно лещина становится защитницей Золушки, тоже понятно. У многих народов лещина (орешник) считалась тесно связанной с загробным миром. В некоторых местах Европы на Святки хозяева рассыпали орехи по полу и по углам, чтобы накормить души умерших. В немецкой сказке Aschenputtel Золушка просит у отца привезти ей первую ветку, которая собьет его шляпу, чтобы она могла посадить ее на могиле матери. Этой веткой оказывается ветка лещины. Помимо связи с загробным миром, орешник также наделяет своего обладателя великой мудростью, у друидов это дерево считалось священным.
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Рождение феи
Если образы птиц или деревьев как волшебных помощников уже воплощали дух умершей матери лишь чисто символически, то в дальнейшем этот образ совсем утратил свое первоначальное значение. На данном этапе помощник Золушки — либо существо божественной природы, либо человек, друг.
В известной нам сказке Шарля Перро Золушке помогают не животные и не птицы, а фея-крестная, появившаяся из ниоткуда. В грузинской Золушке, «Маленькой оборванке» (Conkiajgharuna) бедной девушке помогает деви — мистическое существо, одна из ипостасей богини-матери. Она делает это довольно жутким способом:
Однажды, когда Маленькая Оборванка пасла корову, та по случайности забежала на крышу. [Прим. автора: в некоторых местностях Кавказа дома крестьян врыты в землю, так что вполне возможно случайно зайти на крышу]. Девушка последовала за коровой, чтобы вернуть ее обратно на дорогу, но случайно уронила веретено в дом. Заглянув внутрь, она обнаружила там старуху и попросила ее: «Добрая женщина, отдайте мне мое веретено». «Не могу, дитя мое, — отвечала старуха, — зайди-ка и возьми его сама».
Эта старая женщина была деви. Когда Оборванка подобрала веретено, хозяйка дома обратилась к ней с просьбой: «Доченька, доченька, подойди ко мне и взгляни на мою голову, я же почти съедена». Девушка подошла ближе и взглянула на голову старухи. Сердце ее ушло в пятки, когда она обнаружила там червей, копошащихся внутри. Но Оборванка собралась с духом и счистила несколько червей, после чего сказала: «На что же тут смотреть? У вас чистая голова!»
Боги помогают не только Оборванке. Богиня Бхагавани пожалела Мугазо, героиню вьетнамской сказки «Золотая туфелька».
Поддерживают Золушку и просто женщины — добрые и не очень. Зезолла, итальянская Золушка из сказки Джамбаттиста Базиле (1575–1632), сговорившись с няней, ломает мачехе шею крышкой сундука. Добрая соседка из грузинской сказки велит своим птицам собрать все просо, что рассыпала мачеха и приказала собрать падчерице.
А в уже упомянутой выше греческой сказке Золушке напрямую помогает Бог. Оказавшись в пустыне, она молится: «Господи, дай мне ямку в земле, чтобы только я могла сунуть туда голову, дабы не слышать, как воют дикие звери». После того, как просьба Золушки была исполнена, она попросила себе нору побольше, такую, в которой поместилась бы по пояс. И лишь в третий раз Золушка взмолилась о хижине, где могла бы жить.
РЕКЛАМА – ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЕ НИЖЕ
Таким образом, образ матери Золушки, скрытый за слоями многочисленных преобразований и искажений, обретает мистический, сакральный смысл.
Отвергнув поздние, более мягкие версии, где Золушка забывает или прощает злую мачеху и сестер, мы встречаемся с распространенным мотивом, в котором дух погибшей матери жестоко мстит за свои обиды. Мачеха ломает шею, птицы выклевывают ее дочерям глаза, Золушка заставляет мачеху отведать плоти собственного ребенка…
В свете всего вышеизложенного возникает вопрос: кто на самом деле является главным персонажем этой истории? Не является ли Золушка всего-навсего орудием, проводником, при помощи которого дух покойной матери вершит свое, порой кровавое правосудие? Умирая, она не оставляет окончательно мир живых, но незримо присутствует в нем, передавая дочери свою волю и указывая ей путь.
Именно в сегодняшний день смерти Шарля Перро в 1947 году , на экраны СССР вышел фильм Надежды Кошеверовой «Золушка».
В оригинале сказку называли КАНДРИЛЬОНА и в первых русских переводах французской сказки имя Золушки было переведено как ЗАМАРАШКА (в польском языке ПЕПЕЛЮШКА).
Над сказкой «Золушка» Шарлю Перро также пришлось немало поработать. Он знал и любил похожую сказку из книги Базиле «Пентамерон». Он всегда восхищался ею и потому, когда прочитал вариант, записанный своим сыном Пьером, сразу решил использовать французскую версию «Золушки», в которой отразились народные традиции Франции.
В целом, сказка, записанная сыном Пьером, не испытала существенных исправлений, и Шарль лишь слегка переделал ее. Но это «слегка» означало искусство большого мастера.
Автор заботливо сохранил сюжетную линию, сохранил и туфельки, и бал, и сам ритм рассказа. Но при ближайшем рассмотрении, оказывается, что простота и безыскусность рассказа достигаются очень искусно. Перед нами либо необычайный «художественный инстинкт» автора, либо очень большой опыт писательского мастерства, а наиболее вероятно — и то и другое.
Самый захватывающий момент сказки, без сомнения, касается бала. По всем народным версиям, героиня три раза едет на бал к принцу. Автор сохраняет традиционный ритм, но в то же время стремится избежать монотонности повторения одной и той же сцены. И достигает этого исключительно умело. Он убирает третий бал, что заставляет Золушку терять туфельку на втором. Но сцена первого бала представлена два раза. Первый раз — глазами Золушки, второй — злых сестер.
В действительности же рассказано только об одном бале, но с ловким зеркальным эффектом: рассказ дан в три или четыре приема, так что читателю представляется, что и другие балы описаны очень подробно.
Шарль Перро критически относится к фольклору. Он смело убирает из народной сказки те эпизоды, которые ее не украшают. Так, например, он исключил сцену, в которой героиня бросает соль в огонь, когда вычесывает из головы вшей (эта деталь народной сказки должна была ему быть известна). Оказались исключены некоторые волшебные вещи, например, два плода, которые в различных версиях содержат чудесные платья для феи, или три «странных жителя» — метла, тряпка и совок. Зато автор добавил в сказку волшебство: мыши у него чудесным образом превращаются в лошадей, крыса — в кучера, ящерицы — в лакеев и т. д.
Перро вводит в сказку легкий юмор. Очаровательная фея действует по определенным правилам, которые так просты, ясны и очевидны, что Золушка их легко угадывает и подыгрывает крестной матери:
«Так как она задумалась, из чего бы сделать кучера, Золушка сказала: „Пойду посмотрю, нет ли в ловушке крысы?“ — Ты права, пойди посмотри, — сказала крестная мать».
Современные французские фольклористы Бальзак и Летрэ пришли к выводу, что хрустальная туфелька Золушки, которая слетает с ее ножки еще в первом издании «Сказок», является результатом случайной ошибки автора или опечатки. Хрустальная туфелька, упав с ножки на каменную лестницу, неминуемо бы разбилась. Следовательно, считают названные авторы, Золушка носила не хрустальные туфельки, а туфельки, окаймленные беличьим мехом. «Во Франции, как и в других королевствах, — писал Бальзак, — королевские указы предписывали ношение мехов только благородному сословию. В особенности это касалось некоторых редких мехов, например беличьего. При этом различали мех крупный и мелкий. Названия этих мехов давно уже вышли из употребления, и в бесконечном числе изданий сказок Перро знаменитая туфелька Золушки — несомненно, из мелкого беличьего меха — представлена хрустальной».
Но с этим мнением можно поспорить.
Марк Сориано пишет: «В волшебном мире вполне могут существовать хрустальные туфельки. В оригинальном издании была именно хрустальная туфелька, и с трудом можно допустить, что ошибка повторилась три раза в тексте и один раз в названии… В самом деле, эта хрустальная туфелька, идея которой, видимо, принадлежит именно Шарлю Перро, — очень тонкое, изящное изобретение. Она позволяет во всей сказке ощущать атмосферу легкой иронии».
Марк Сориано очень тонко сумел найти те места в сказке, где ощущается присутствие обоих авторов — и сына, и отца.
«Тон сказки „Золушка“ особенный, — пишет он. — Большей частью он единый, плотный, быстрый, прямой. Можно представить себе, что это рассказ одаренного ребенка, который идет прямо за фактами и находит самые характерные черты, которые берут его за душу. Например: „Она спала на чердаке, на старом соломенном тюфяке, в то время как сестры спали в красивых комнатах“.
Иногда же тон изменяется: можно сказать, что это другой голос, голос взрослого человека, у которого большой опыт и который не пренебрегает, например, тем, чтобы пустить особую стрелу против женщин: „Все дамы очень внимательно рассматривали прическу и платье Золушки, чтобы назавтра сделать себе такие же“. Это голос уже того, кто написал эти нравоучительные истории».
В фильме роль Золушки сыграла Янина Жеймо. По воспоминаниям Янины Жеймо перед началом съёмок её отправили в санаторий «подкормиться, чтобы не выглядеть слишком тощей» . На 31 декабря 1946 года исполнительнице Золушки было 37 лет, а Алексею Консовскому, принцу — 34 года . Игравшему родного отца Золушки Василию Меркурьеву — 42 года, то есть он был старше «дочери» всего на 5 лет.
На роль феи пробовалась также Любовь Орлова.
ЯН ФРИД (КИНОРЕЖИССЁР) == В образе Золушки я не обнаружил активной любви к труду, равно как не обнаружил традиционной обаятельности в других образах. Все остальные персонажи, окружающие Золушку, удивительно несимпатичные лица. Дегенеративен Гарин, который никак не вызывает симпатии, неприятен принц — рахитик с разжиженными мозгами. Почему его такого должна любить Золушка? Всё это действует так, что начинаешь беспокоиться за весь материал в силу того, что он, с моей точки зрения, является порочным.
ИЗ ПЕСНИ ЗОЛУШКИ… = Дразнят Золушкой меня
оттого, что у огня, силы не жалея,
в кухне я тружусь, тружусь,
с печкой я вожусь, вожусь,
и всегда в золе я.
А ЖИЛА ЛИ ЗОЛУШКА НА САМОМ ДЕЛЕ И ГДЕ ТОГДА ЕЁ МОГИЛА?
«Румянолицая девушка» -так можно перевести древнегреческое имя Родопис (она же иногда упомянута под именем Дориха).
Родопис — гетера, жившая, предположительно, в VI веке до н.э., современница поэтессы Сапфо и любовница её брата; вероятный прототип самой ранней из записанных вариаций сказки о Золушке (её потерянной туфле).
Единственный исторический источник, достаточно полно рассказывающий о жизни Родопис, — это рассказ древнегреческого историка Геродота, жившего в V веке до н. э. По словам Геродота, Родопис жила во времена фараона Амасиса II (570—526 гг. до н. э.). Она была родом из Фракии и находилась в рабстве у Иадмона с острова Самос, вместе с полулегендарным баснописцем Эзопом. Родопис была продана в Египет, где «занималась своим ремеслом», после чего Харакс, брат поэтессы Сапфо, выкупил её за огромную сумму и даровал ей свободу.
Родопис осталась в Египте и приобрела значительное состояние; на десятую часть своих доходов она заказала и отправила в Дельфы в качестве дара множество железных вертелов, на которых можно было жарить целых быков. По словам Геродота, спустя сто лет эти вертелы всё ещё лежали за алтарём напротив храма.
Очевидно, фигура Родопис начала окружаться легендами вскоре после её смерти, поскольку живший столетием после Геродот пишет, что некоторые эллины считают пирамиду Микерина, одну из трёх Великих пирамид в Гизе, якобы принадлежащей Родопис. Геродот опровергает эти домыслы, указывая, что Родопис жила намного позже Микерина и не была настолько богата, чтобы для неё была построена столь великолепная пирамида.
В неустановленный период легендарное жизнеописание Родопис приобретает вид «сказки о Золушке». В этом варианте историю Родопис пересказывает Страбон:
==…во время купания орёл похитил одну из сандалий Родопис у служанки и принёс в Мемфис; в то время, когда царь производил там суд на открытом воздухе, орёл, паря над его головой, бросил сандалию ему на колени. Царь же, изумлённый как прекрасной формой сандалии, так и странным происшествием, послал людей во все стороны на поиски женщины, которая носила эту сандалию. Когда её нашли в городе Навкратисе и привезли в Мемфис, она стала женой царя; после кончины царица была удостоена погребения в вышеупомянутой гробнице.==
Страбон также указывает, что пирамида Микерина принадлежала Родопис и была построена для неё её любовниками.
В одной из самых древних версий сказки (Китай), героиня носит обувь, сотканную из золотых нитей, с подошвами из чистого золота . В сказке братьев Гримм героиня сначала получает в подарок «туфельки, расшитые шелками и серебром», а в последний вечер — «туфли чистого золота» . В бретонской сказке «Груша с золотыми грушами» упоминаются три пары туфелек: стальные, серебряные и золотые . В итальянской сказке Золушка обута в серебряные туфельки, а в венецианском варианте сказки — в алмазные. В датской сказке туфельки шелковые. В сказке писательницы Мари-Катрин д’Онуа они сделаны из красного бархата и вышиты жемчугом . Известный французский антрополог Поль Деларю, изучив версии «Золушки» в сказках разных народов, обнаружил следующие варианты:
Просто башмачки, без уточнения: в 24 сказках разных народов
Сандалии: 1 раз
Стеклянные башмачки: 5 раз
Золотые башмачки: 1 раз
Хрустальные башмачки: 1раз
В сказке Перро Золушка обута в стеклянные башмачки. Однако начиная с XIX века материал, из которого были сделаны башмачки Золушки, стал предметом непрекращающихся споров, поскольку во французском языке слово «стекло» (фр. verre) произносится так же, как название меха особой выделки «фр. vair» . Первым на возможность подобной ошибки Перро указал Оноре де Бальзак.
==В XV и XVI веках торговля мехами переживала эпоху своего расцвета. Добывать пушнину было тогда делом нелёгким: приходилось совершать длинные и опасные путешествия в северные страны; в силу этого меха ценились чрезвычайно дорого. В те времена, так же как и теперь, высокие цены только повышали спрос: ведь тщеславие не знает преград. Во Франции, а равным образом и в других странах ношение мехов было установленной королевским указом привилегией знати, и это объясняет, почему горностай так часто фигурирует на старинных гербах; некоторые редкостные меха, как, например, vair, который, вне всякого сомнения, есть не что иное, как королевский соболь, имели право носить одни только короли, герцоги и занимающие определённые должности вельможи. Различали vair, состоящий из мелких, и vair, состоящий из крупных шкурок; слово это уже лет сто как вышло из употребления и до такой степени забылось всеми, что даже в бесчисленных переизданиях «Сказок» Перро про знаменитую туфельку Золушки, которая первоначально была, по-видимому, из мелкого vair, в настоящее время говорится, что она хрустальная (verre)==
АНАТОЛИЙ ФРАНСА== Ведь неправильно говорят, что у Золушки были хрустальные башмачки. Невозможно представить себе башмачки, сделанные из того же материала, что и графин. Башмачки, подбитые беличьим мехом, более приемлемы, но всё же не очень остроумно в такой обуви вывозить девушку на бал. В меховых башмачках ножки Золушки были бы похожи на мохнатые голубиные лапки. Надо быть без ума от танцев, чтобы плясать в меховых туфельках. Но все девушки таковы: будь у них свинцовые подмётки, всё равно они станут плясать. ==
КЛОД МЕТРА == Стекло выбрано вовсе не случайно. Здесь есть что-то подобное идее светоносной прозрачности, которая является противоположностью грязного лица в начале сказки. В то же время стекло создаётся огнём, это природное вещество, которое полностью преображается благодаря пеплу… и в какой-то мере, это стекло может быть символом того, что человеческое существо может, как сам Бог, создавать мир, который является одновременно миром света и прозрачности. В конце истории Золушка, невеста Пепла, становится невестой Солнца==
Но интересно и другое… не существует ни одного варианта сказки о Золушке, где бы упоминались башмачки из меха.
Первые сказки о Золушке появились а Азиатско-арабском мире. В Европе первую версию написал итальянский солдат Базиль в 1634 году. Шарль Перро написал «Золушку » позднее , в 1697 году и его версия сказки стала самая популярная в Европе.
На латышском языке «Золушка» зовётся ==Pelnrušķīte== (Пелнрушките)
НА ФОТО: Перамида Микерина — одна из трёх пирамид Гизы в Египте, считается «могилой Золушки». Вопреки прозвищу «Херу» (высокая), она едва достигает 66 м в высоту, а длина стороны её основания составляет 108,4 м. Её объём в 260 тыс. м³ составляет только десятую часть объема пирамиды Хеопса: это был конец эпохи больших пирамид.
А в Брюсселе даже имеется памятник Золушки.
ХРИСТИАНСКАЯ МОРАЛЬ ОТ ШАРЛЯ ПЕРРО СКАЗКИ «ЗОЛУШКА»
Первая мораль этой сказки заключается в том, что красота — это ценное сокровище, а милосердие бесценно. Без милосердия ничто не возможно, а с красотой можно сделать всё что угодно.
Тем не менее,Перро был человеком очень верующим и его вторая главная мораль этой истории смягчает первую и раскрывает критику, на которую он сам был нацелен и объяснял сказку так:
== «Без сомнения, это большое преимущество — иметь молодому человеку, а в данной истории, юной девушке интеллект, смелость, хорошее воспитание и здравый смысл. Эти и подобные таланты приходят только с небес от Господа, и очень хорошо всем юношам и девушкам от Бога их получить . Однако даже эти таланты или дары от Бога могут не принести вам успеха без благословения крестного отца или крестной матери. Золушка ни как не могла исправить своего положения имея и ум и смелость и красоту, пока её не благословила на это изменения её крестная мать — Фея».
Сказка «Золушка» очень тонко пронизана вся христианской моралью и христианскими символами. Это история о том, как ребёнок в образе простой девушки прошёл путь от пепла до королевского престола. В католическом мире пепел многое значит, в пепельную среду католики перед началом великого поста посыпают себе голову. Золушка (от слова Зола, а в польском и чешском языке её имя как раз Пепелушка) не просто как писал перевод Тургенев «Замарашка» в виде грязной девочки, а именно девочка посыпанная пеплом, измазанная золой, а у католика-француза Перро, это образ смирение и прежде всего покаяния. Только покаяние, осыпания себя пеплом может даже самого бедного человека привести в Царство Небесное, куда хотят войти и гордые и надменные сёстры Золушки, но Царство для них закрыто, ведь войти туда можно через скорби, притеснения, страдания и осыпания своей головы пеплом (то есть покаяния).
Откроем пророчества книгу Иеремии 6 глава 26 стих: «Дочь народа моего! Опояшь себе вретищем и посыпь себя пеплом. Сокрушайся, как бы о смерти единственного сына -горько плачь, ибо внезапно придёт на нас губитель».
Конечно, Золушка, это не имя девочки, а прозвище. Имени мы не знаем.. Однако, есть свидетельства, что при написании своей сказки Шарль Перро представлял все эти события происходящие в замке Маримонт, развалены которого и сейчас находятся на границы Франции и Швейцарии. За 500 лет до написании сказки о Золушке, в том рыцарском замке жила красивая девушка Матильда, считается, что эту девушку вместе с замком и перенёс в свою сказку Шарль Перро.
Конечно, имеется аж 545 версий и разновидностей сказки «Золушка» у разных народов мира и в каждой сказке своя национальная мораль.
У китайцев Золушка теряет не туфельку, а кольцо, у арабской Золушки теряется браслет с ноги. Свою Золушку писали и братья Гримм, у которых лестница была смазана смолой, чтобы Золушка прилипла и не убежала в полночь. В английской версии при примерке туфельки одна дочь мачехи отрезала себе палец, а другая пятку и по каплям крови принц узнал, что туфелька им мала. Во многих версиях Золушка специально кокетливо убегая сбрасывает туфельку чтобы её искал принц.
И почти у всех писателей сказки и мачеха и её дочери страшно наказаны, в одних версиях они стали инвалидами, в других их казнили, в третьих посадили в тюрьму, есть версии в которых их заклевали вороны выклевав им глаза…
И только Шарль Перро, как истинный и милосердный христианин прощает и мачеху и её дочерей, они прощены Золушкой. Что опять видим явное христианство, нельзя достичь Царства не простив врагов своих.
Однако некоторые Западные психологи видят другую мораль сказки и уверены, что эту сказку Перро писал для взрослых. По их мнению, Золушка чувствовала себя брошенной отцом, желал достичь его расположения к себе. Под отцом следует подразумевать — Доброту. Золушка была обделена добротой. И что основной подтекст сказки носит сексуальный характер. Молодая девушка, которая робкая и красивая превращается после полуночи в простую, грубую, дикую и жестокую разгульную девушку жаждущую интимной близости и подавляющая в себе эту близость, прячущая в себе всю любовь к людям, избегая парней в образе Принца.
А хрустальная туфелька — символ девственного влагалища. Потому и стекло, а не мех и кожа, что девственность нельзя растянуть. Будь туфелька не из стекла, её бы растянули ноги дочерей мачехи. Принц искал девственницу. И только мужчине Принцу удаётся раскрыть утончённый образ девушки Золушки и заставить поверить её в добро. Бальная сцена — жадные взгляды присутствующих мужчин, робость молодой Золушки. Любовь мужчины побеждает внутреннее женское зло.
Туфель — это ещё и образ пары. Найти правильный туфель — это найти себе в пару правильного человека..
В психологии даже имеется понятие «Комплекс Золушки» или «Синдром Золушки». Это когда успешная, красивая, богатая девушка страдая от одиночества ждёт своего принца, который исправит её жизнь. Страх женской независимости.
Есть и понятие «Эффект Золушки», это есть ненависть мачех или отчимов к приёмным детям, физическое насилие над приёмными детьми.
Остаётся вопрос, а почему Мачеха так не любила падчерицу. Это уже вопрос для следователей.)) И они нашли ответ. Золушка после смерти матери была наследницей всего того, что осталось у престарелого отца и это всё должно было по желанию Мачехи достаться ей и её родным дочерям.
Золушка — из богатой и знатной семьи
Читаем сказку в переводе с французского Н. Касаткиной: «Жил однажды богатый и знатный человек. У него умерла жена, и он женился второй раз на такой бессердечной гордячке, какой больше не сыщешь». Из первого же предложения мы узнаем, что Золушка и богата, и далеко не из простой семьи. Как же так, мы ведь привыкли, что ей просто сказочно повезло…
Шарль Перро сделал сказку классической и популярной, однако и братья Гримм внесли свою лепту. Что пишут они? Перевод с немецкого Г. Петникова: «Заболела у одного богача жена и почувствовала, что конец ей приходит».
А если вспомнить, что в дальнейшем отца, мачеху, сестер и саму Золушку приглашают на бал не куда-нибудь, а к королю, то всё логично. Отец Золушки и богач, и дворянин.
Более того, в дальнейшем упоминаются очень дорогие наряды, драгоценности мачехи и сестер, и несложно понять, что на бал приглашены не просто дворяне, а сливки общества.
Следовательно, Золушка — никакая не бедная сиротка без роду и племени, как мы привыкли думать. Это вовсе не история удачного замужества девушки из низов. Золушка — аристократка по происхождению, ее семья вхожа в высший свет, кроме того, девушка — завидная наследница, получившая хорошее воспитание и знающая этикет в совершенстве. Помните, какое сильное впечатление она произвела на всех присутствующих на балу? Они ее не только принимают за свою, а с удовольствием признают, что незнакомка — лучшая из них.
«В зале сразу наступила тишина: гости перестали танцевать, скрипачи перестали играть — так все были поражены красотой незнакомой принцессы.
— Какая красавица! — шептались кругом.
Даже сам старик король не мог на нее наглядеться и всё твердил на ухо королеве, что давно не видел такой красивой и милой девушки. А дамы внимательно рассматривали ее наряд, чтобы завтра же заказать себе точь-в-точь такой, только боялись, что не найдут достаточно богатых материй и достаточно искусных мастериц.
Принц проводил ее на самое почетное место и пригласил танцевать. Танцевала она так хорошо, что все еще больше залюбовались ею.
Вскоре подали разные сласти и фрукты. Но принц и не притронулся к лакомствам — так он был занят прекрасной принцессой. А она подошла к своим сестрам, приветливо заговорила с ними и поделилась апельсинами, которыми угощал ее принц. Сестры очень удивились такой любезности со стороны незнакомой принцессы».
Шарль Перро
Бесспорно, наряд очень красив. Однако Золушка и превосходно танцует, и, следуя этикету, беседует с сестрами. Ей удается понравиться всем, от скрипача до короля, а это, согласитесь, непросто. Более того, чтобы очаровать принца, мало одного красивого платья и симпатичного личика. Здесь пазл сложился: приятная внешность + хорошие манеры + тонкий вкус + шлейф таинственности, который окружает незнакомку.
Многие могут вспомнить советский музыкальный фильм-сказку «Золушка». Там ее отец — лесничий. Это нисколько не умаляет его высокого положения.
Королевский лесничий — это начальник всех лесов королевства, своего рода министр лесного хозяйства.
Вернемся к тексту «Золушки». Почему же столь важная деталь, упомянутая в первом предложении сказки, практически не вспоминается? Вот основные причины:
- В работе «Истина и метод» немецкий философ Х.-Г. Гадамер говорит, что процессу понимания предшествует предпонимание. Зачастую наши предубеждения мешают понять изначальный смысл текста. Мы столько раз слышали о бедняжке, которой повезло выйти в люди, что первые строки Золушки пропускаются на уровне подсознания.
- Народные предания, облагороженные подлинными мастерами своего дела, в том числе и братьями Гримм, и Шарлем Перро, — это своего рода запрос общества. Нам хочется верить, что социальное чудо возможно, поэтому мы верим, не задумываясь, что это не чудо, а закономерность. Богатая юная аристократка с изысканным вкусом, безупречными манерами становится невестой принца. Что же тут чудесного?
- Так выгодно читать для сохранения гендерного порядка. А как же иначе использовать сказку, чтобы воспитывать удобную девушку и женщину? Будешь работящей, терпеливой, послушной — и тебе улыбнется счастье. Золушка — это своего рода пряник, возможность сослаться на житейскую мудрость, проверенную веками.
Золушка как архетип: жертва?
Имя героини — это не имя, а прозвище, и оно несет информацию об основах жизни в символической форме.
«Окончив работу, бедняжка забивалась в уголок у самого очага и садилась прямо на золу, за что старшая мачехина дочка прозвала ее Замарашкой. Но младшая, не такая грубиянка, как сестра, стала звать ее Золушкой».
Архетип — это единица нашего восприятия. Разве не большинство смертных на протяжении веков мечтает выбиться в люди?
С этой точки зрения архетип Золушки — яркое проявление комплекса неполноценности. Он формируется в бессознательном женщины в процессе ее воспитания.
В узком смысле он проявляется как пассивный тип поведения девушки, женщины. В широком — как ее социально подчиненное положение, полностью соответствующее патриархальному устройству общества. Поэтому-то психологи выделяют так называемый комплекс Золушки (или комплекс жертвы).
Если смотреть на сюжет сказки с учетом знатности происхождения девушки и ее прав на наследство, то ситуация абсурдна донельзя. Юная аристократка, полноправная наследница, вынуждена обслуживать не только сварливую мачеху, но и постоянно унижающих ее «сестренок».
«Мачеха взвалила на девушку всю самую грязную и тяжелую работу в доме: она и посуду чистила, и лестницу мыла, и полы натирала в комнатах капризной мачехи и ее избалованных дочек…
Бедная девушка всё терпела и боялась жаловаться отцу — он только разбранил бы ее, потому что во всем слушался своей новой жены».
Отец полностью под каблуком женщины властной и амбициозной. У Золушки даже имени своего нет, как нет и защиты, которая так нужна. Папенька даже не пытается оградить ее от эмоционального и психологического насилия. Безвольный мужчина — хоть и с положением в обществе, при деньгах и завидных связях. Более того, родная дочь добровольно взваливает на себя все тяготы жизни, включая и постоянные упреки новоявленных родственников, чтобы облегчить участь отца.
Получается, что, зная о своем происхождении и правах, она абсолютно сознательно жертвует собой ради любимого папеньки и внешнего благополучия в доме.
По возрасту героиня — подросток. В этот период родителям важно научиться понимать и слышать своего ребенка. Здесь всё наоборот: это Золушка понимает отца и жертвует собой — дочь берет на себя часть родительских функций. А ее высокое происхождение и материальные блага делают архетип еще сильнее, чтобы подчеркнуть величину ее жертвы.
В наши дни такой Золушкой может быть и старший ребенок, не получающий должного тепла и эмоциональной связи с родителями, так как появились младшие дети. Женщины, прикованные к нелюбимой работе или зависимые от мужчины. У них низкая самооценка и страх изменений в жизни, часто говорят, что они пассивны и пребывают в ожидании чуда.
Выходит, архетип Золушки — это жертва. Но только если не посмотреть на сказку под иным углом.
Золушка как архетип: жертва или стратег?
Золушка не пытается изменить то, что от нее мало зависит. Не затевает ссор с отцом, не тратит время на отстаивание прав у мачехи и сводных сестер. Однако при первом удобном случае (бал во дворце) она демонстрирует набор востребованных навыков. Например, с легкостью обманывает сестер и узнает нужную информацию — миссис Марпл следует поучиться у Золушки так искусно изображать сон после бала, так узнавать о невиданной ранее красавице и прочим затейливым штучкам.
«В то время, как она рассказывала волшебнице обо всем, что происходило на балу, раздался стук в дверь — это приехали сестры. Золушка пошла им отворять.
— Долго же вы пробыли на балу! — сказала она, протирая глаза и потягиваясь, как будто только что проснулась.
На самом деле, с тех пор как они расстались, ей совсем не хотелось спать».
Как ловко и непринужденно Золушка узнает о самой себе и даже подстраховывается, чтобы окончательно убедиться, что сможет поехать на бал на следующий день именно в качестве незнакомой принцессы.
«Она спросила, как зовут принцессу, но сестры ответили, что никто ее не знает и принц очень этим огорчен. Он что угодно отдал бы, лишь бы узнать, кто она такая.
— Наверно, она очень красивая! — улыбаясь, сказала Золушка. — И счастливицы же вы! Как бы мне хотелось хоть одним глазком посмотреть на нее!.. Милая сестрица, пожалуйста, одолжите мне ваше желтое домашнее платье.
— Вот еще выдумала! — отвечала старшая сестра. — Чтоб я дала свое платье такой замарашке? Да ни за что на свете!
Золушка так и знала, что сестра откажет ей, и даже обрадовалась — что бы она делала, если бы сестрица согласилась дать ей свое платье!»
Золушка блестяще использует правило трех М: место, мера, момент. Конечно, ей помогает крестная-фея. Однако все козыри она использует и сама, умело используя безотказные приемы обольщения принца. Сохраняет интригу до последнего, уходит, когда интерес к ней на самом пике, и столь вовремя теряет туфельку, чтобы ее невозможно было забыть.
Когда всего один бал способен решить судьбу, Золушка и целеустремленная, и дальновидная одновременно. Плюс ей еще и присущ здоровый авантюризм.
Ведь мероприятие — при ее-то положении в семье — танцы на горящих углях. При этом и с ролью жалкой замарашки, всегда прислуживающей всем и вся, и с ролью запоминающейся незнакомки она справляется блестяще. Если просто потанцевала и оставила при себе светлые воспоминания, то зачем постоянно носит с собой вторую туфельку? Не выбросила же, хотя иметь эту вещицу рискованно. Это условная бережливость или продуманная стратегия?
Если внимательно прочитать сказку, можно убедиться, что Золушка далеко не наивная простушка.
Сказка о любви или всё же о социальном статусе?
И кстати, где в сказке любовь, которой всех пичкают под соусом сказки о Золушке? Где в сказке сказано о ней? Эта история — мечта о награде в виде удачного замужества и повышения социального статуса. В текстах нет упоминаний о том, насколько принц и Золушка любят друг друга, терзаются ли они неразделенными чувствами, мучаются ли от невозможности быть рядом.
Это история о девушке, которая получила достойную награду за терпение и усердие, а туфелька — ее пропуск в новый мир с новой жизнью.
На первый взгляд, посыл понятен: будь терпеливой, услужливой, хозяйственной — и тебе достанется целый принц.
Но давайте еще раз подумаем: кого созвали на бал? Скромных хозяюшек или все-таки девушек из высшего общества? Говоря современным языком, Золушка на балу — самая крутая: превосходно одета, ведет себя безупречно и ее репутация чиста, как и сияющие туфельки. Она идеально вписывается в новую социальную роль: невеста принца — супруга принца — королева. Принц и все окружающие запоминают ее именно по формальным признакам. Каким образом принц узнал о ее богатом внутреннем мире и человеческих качествах? Пока что — по никаким.
Так что аргумент «будешь трудолюбивой и терпеливой (то есть удобной) и получишь награду» — это проверенная манипуляция.
В сказке Золушка не поражала принца редким умением штопать одежду или мыть полы до блеска. Она делала то, что предписывала будущая социальная роль: демонстрировала прекрасное воспитание, безупречный вкус и умение произвести впечатление.
Другой вопрос, что удобного случая кардинально изменить жизнь раньше у нее не было. Плюс, как описано в сказке, отец полностью под влиянием мачехи, и Золушка понимает, что ей не изменить это. Что было бы, если бы шанс не подвернулся? О, это другая история.
В сказке же описана ситуация, когда у Золушки есть законное право щеголять в роскошных нарядах, блистать при дворе и, конечно, носить самые изящные туфельки. Однако до определенного момента она не отстаивает свои права, оберегая отца. Ведь как описывает ее автор: «У мужа была дочка на редкость кроткая и ласковая, вся в покойную свою мать, добрейшую женщину в мире». Бал — это катализатор, когда героиня понимает, что пора действовать.
Интересно получается: столько лет Золушка терпела свое незавидное положение, а здесь — раз, и не желает мириться. Да и тетушка-фея, которая не интересовалась племянницей раньше, появляется так кстати.
Интуиция подсказывает Золушке, что это не просто бал, а событие, способное изменить ее жизнь. Бороться за место под солнцем в своем доме, соперничать с сестрами и мачехой — это не столь важно для нее, она этого и не замечает. А вот попасть на бал нужно, даже если для этого надо использовать волшебные силы.
Чем не иной взгляд на привычный архетип? Учиться, трудиться, не размениваться на мелочи — зато в нужный момент показать свои подлинные достоинства, «сделать всех» и попасть в яблочко.
«Наконец настал желанный день. Сестрицы отправились на бал, а Золушка долго смотрела им вслед. Когда их карета скрылась из виду, она горько заплакала.
Золушкина тетушка увидела, что бедная девушка плачет, и спросила, чем она так огорчена.
— Мне хотелось… хотелось бы… — от слез Золушка не могла договорить.
Но тетушка догадалась и сама (она ведь была волшебница):
— Тебе хотелось бы на бал, правда?
— Ах, да! — со вздохом ответила Золушка.
— Обещаешь быть во всем послушной? — спросила волшебница. — Тогда я помогу тебе поехать на бал. — Волшебница обняла Золушку и сказала ей: — Ступай в огород и принеси мне тыкву».
Не исключено, что Шарль Перро хотел подчеркнуть: даже находясь в безвыходном положении, каждый получает шанс. Воспользуется он им или нет, зависит только от человека.
Под таким углом Золушка совсем не жертва, а человек, которой может правильно расставить приоритеты и воспользоваться шансом.
Далеко не каждый это делает в реальной жизни: вот они, козыри на руках, и так хочется всё изменить — однако человек не использует эту возможность.
Да, фея послала Золушку на бал, однако дальше ее судьба только в ее руках. Ведь тетушка-фея не превращает Золушку в принцессу сразу. А ведь могла. Она не приносит счастье на блюдечке с голубой каемочкой. Золушка самостоятельно проявляет качества, которые у нее изначально есть. Ее поездка на бал — это обретение уверенности в себе и возвращение сил и прав, принадлежащих женщине и по праву рождения (благородная и богатая семья), и благодаря огромной внутренней работе над собой.
«Золушка» — это сказка не о том, как терпеливой простушке повезло выйти замуж за приличного человека. Это история о том, как молодая девушка вступает во власть, которая принадлежит ей по праву. На языке символов «выйти замуж за принца» — значит объединиться со своим внутренним источником власти и прав в одно целое и стать правительницей своей жизни.
Настоящая Золушка: а сказочка-то мрачненькая
Автор:
16 марта 2022 18:29
Большинство из нас знает историю Золушки по старому советскому фильму, диснеевскому мультику или, в крайнем случае, по сказке Андерсена из детской книжки с картинками. Однако сюжет о бедной девушке, ставшей принцессой, и ее туфельке восходит к временам Древней Греции и Рима, и он вовсе не так радостен и светел, как мы считаем.
Источник:
Страбон, греческий историк и географ, включил одну из самых ранних версий сюжета о Золушке в свою книгу «География». Его героиней была Родопис, освобожденная рабыня, ставшая куртизанкой.
«Когда она купалась, орел вырвал у служанки одну из ее сандалий и унес ее в Мемфис; и в то время как король вершил правосудие на открытом воздухе, орел, когда он пролетал над его головой, швырнул сандалию ему на колени; и король, взволнованный как красивой формой сандалии, так и странностью происшествия, разослал людей во все стороны по стране на поиски женщины, которая носила сандалию; и когда ее нашли в городе Навкратисе, ее привели в Мемфис, и она стала женой короля».
Аспасия из Фокеи была героиней одной из историй в «Пестрых рассказах», книге, написанной римским писателем Элианом. Эта версия немного больше похожа на европейскую сказку, которую мы знаем сегодня. Один из древних источников так описывает ее сюжет: «Аспазия Фокейская теряет мать при рождении, и отец воспитывает ее в нищете. Она мечтает, что будет спутницей знатного человека, но ее обезображивает нарост на лице. Во сне появляется голубь и превращается в женщину; Аспазии велено лечить нарост розами Афродиты; возвращается ее красота. Теперь она вынуждена присутствовать на банкете Кира Младшего с тремя другими девушками. Остальные одеты и ведут себя как куртизанки; Аспазия скромно отталкивает ухаживания принца и тем более привлекает его». Все кончается тем, что они женятся, после чего Аспазия продолжает быть послушной дочерью, а также не забывает отплатить Афродите за ее помощь.
Источник:
Первую литературную версию Золушки часто приписывают Джамбаттисте Базиле, который включил ее в свою книгу «Сказка сказок», опубликованную в 1634 году. Её героиню зовут Сенерентола, от «cenere», итальянского слова, означающего пепел. Слуги в Италии в то время часто пачкались пеплом из-за того, что постоянно сидели у камина, чтобы согреться. У героини, настоящее имя которой Зезолла, есть злая мачеха, а также добрая и заботливая нянюшка, которая убеждает ее убить злую мачеху и заставить отца жениться на гувернантке. Зезолла делает, как велено, просит мачеху достать платье из сундука, а затем изо всех сил бьет ее крышкой по голове. Няня выходит замуж за отца Зезоллы, но затем производит шесть собственных дочерей, и все они обращаются с Зезоллой как с рабыней.
Итак, Зезолла убила свою первую мачеху, чтобы попытаться получить лучшую. Это жестокое убийство даже не попало в сказку братьев Гримм, которая сама по себе довольно мрачна. Но это еще не конец. Когда отец Зезоллы отправляется на Сардинию, он привозит подарки для всех своих дочерей (хотя почти забывает о подарке собственной дочери). Зезолла сажает финиковое дерево, подаренное ей отцом. Фея внутри этого дерева помогает ей получить красивые платья и завоевать сердце короля, делая финальную часть сказки похожей на известную нам версию.
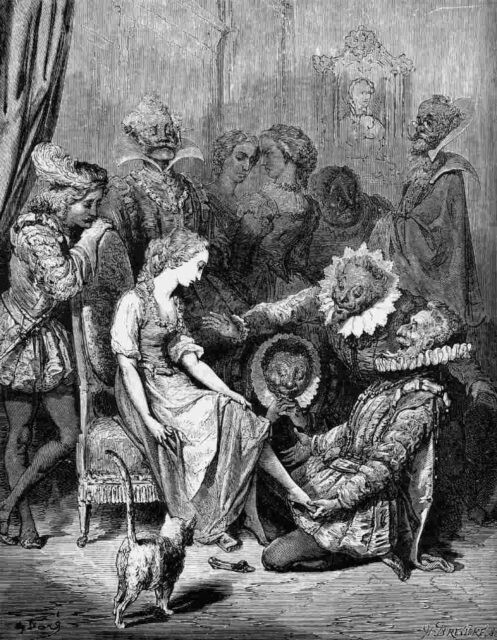

Источник:
Книга Шарля Перро 1697 года «Истории и сказки из прошлых времен» заложила многие основы для сказок, которые мы знаем сегодня. В его версии Золушку звали Синдрийон — также от слова, обозначающего пепел, но на французский манер. Именно в этой версии впервые появились тыква, фея-крестная и стеклянная туфелька. История Перро почти идентична той, что мы знаем сегодня: молодая девушка, с которой жестоко обращаются мачеха и сводные сестры, вынуждена спать в пепле; бал, устроенный принцем, на котором Золушке запретили присутствовать; фея-крестная, которая превращает тыкву в карету, мышей в лошадей, крысу в кучера, а ящериц в лакеев; и указание, что она должна быть дома к полуночи.
В отличие от известной нам Золушки, героиня Перро попадает на второй бал, на котором она забывает о полуночи и едва успевает сбежать вовремя. Ее туфелька найдена, но к тому времени она снова в лохмотьях, поэтому никто не связывает ее с прекрасной девушкой, сбежавшей всего несколько минут назад. В конце концов ее опознают, и она выходит замуж за принца, будучи достаточно любезной, чтобы выдать своих сводных сестер замуж за других дворян.
Источник:
Перро известен тем, что заканчивает каждую сказку в своей книге моралью. Золушке достались целых две. Во-первых, что красота — редкое сокровище, но любезность достойна еще большего восхищения. Во-вторых, хотя «интеллект, мужество, хорошее воспитание и здравый смысл» — великие добродетели, они могут оказаться бесполезными, если у вас нет благословения крестного родителя.

Источник:
История Перро намного приятнее и гуманнее, чем некоторые из предыдущих версий. Но когда Джейкоб и Вильгельм Гримм наткнулись на историю Ашенпуттель (Маленькой пепельной девочки), собирая истории для своих книг, она оказалась куда более кровавой и жестокой.
Все начинается так, как и следует: мать умирает; отец повторно женился; Ашенпуттель становится служанкой, но остается хорошей и доброй. Когда отец отправляется в путешествие, сводные сестры требуют дорогих подарков, а Ашенпуттель просит только первую ветку, которая собьет ему на дороге шляпу. Она сажает ветку на могиле своей матери, и из нее вырастает орешник. Ашенпуттель молится под этим орешником, и белая птица бросает ей все, что она пожелает в своих молитвах.
Эта история дает нам первое представление о животных-помощниках, элементе, который стал основой мультфильмов Диснея. Когда Ашенпуттель просится на бал, мачеха бросает в пепел чечевицу и заявляет, что она сможет пойти на бал только в том случае, если выберет из золы все зерна за два часа. Ашенпуттель делает это с помощью голубей и горлиц, которые прилетают к ней, когда она поет. Но ей по-прежнему не разрешают идти на бал, даже когда она разбирает всю чечевицу.
Источник:
В версии братьев Гримм принц устраивает три бала, а ореховое дерево обеспечивает Ашенпуттель тремя все более красивыми платьями для посещения каждого из них. Но после этого все начинает принимать мрачный оборот. Когда принц приходит в дом с туфелькой для примерки, старшая дочь идет первой. «Старшая пошла с туфлей в свою комнату и хотела примерить ее, а ее мать стояла рядом. Но она не могла вставить в него большой палец ноги, поскольку туфелька была ей мала. Тогда мать дала ей нож и сказала: «Отрежь палец на ноге; когда ты станешь королевой, тебе больше не нужно будет ходить пешком». Девушка отрезала палец на ноге, всунула ногу в башмак, стерпела боль и вышла к королевскому сыну. Тогда он посадил ее на свою лошадь в качестве своей невесты и ускакал с ней».
Эта подлая схема могла бы сработать, если бы не тот факт, что пара проехала мимо могилы матери Ашенпуттель. Две птицы поднялись с орешника и сказали принцу посмотреть на кровь, капающую с туфельки его невесты.
Когда второй сестре пора примерить туфельку, мать велит ей отрезать часть пятки, чтобы она подошла. Хотя девушка так и делает, птицы снова ее выдают. А когда Ашенпуттель, наконец, садится на лошадь принца и направляется во дворец, две птицы слетают вниз, чтобы сесть ей на плечи.
Источник:
В версии братьев Гримм личное счастье Ашенпуттель приправлено изрядной дозой мести. В варианте, вошедшем во второе издание сказок, опубликованное в 1819 году, две сводные сестры появляются на свадьбе и пытаются завоевать расположение Ашенпуттель.
«Когда обрученные шли в церковь, старшая была с правой стороны, а младшая с левой, и голуби выклевали каждой из них по глазу. Потом, когда они вернулись, старшая был слева, а младшая справа, и тогда голуби выклевали каждой по другому глазу. Таким образом, за свою злобу и ложь они были наказаны слепотой на всю жизнь».
Наверное, братья Гримм могли облагородить некоторые из своих сказок, удалив наиболее мрачные части историй. Однако, они действовали как настоящие ученые, использовав найденные народные сюжеты без прикрас. Что ж, кинематограф ХХ века сделал это за них.
Источник:
— переведено специально для fishki.net
Еще крутые истории!
| Cinderella | |
|---|---|

Alexander Zick illustrated Cinderella with the Doves, inspired by the Brothers Grimm’s version. |
|
| Folk tale | |
| Name | Cinderella |
| Aarne–Thompson grouping | ATU 510 A (Persecuted Heroine) |
| Country |
|
| Region | Eurasia |
«Cinderella«,[a] or «The Little Glass Slipper«, is a folk tale with thousands of variants throughout the world.[2][3] The protagonist is a young woman living in forsaken circumstances that are suddenly changed to remarkable fortune, with her ascension to the throne via marriage. The story of Rhodopis, recounted by the Greek geographer Strabo sometime between around 7 BC and AD 23, about a Greek slave girl who marries the king of Egypt, is usually considered to be the earliest known variant of the Cinderella story.[2][3][4]
The first literary European version of the story was published in Italy by Giambattista Basile in his Pentamerone in 1634; the version that is now most widely known in the English-speaking world was published in French by Charles Perrault in Histoires ou contes du temps passé in 1697.[5] Another version was later published as Aschenputtel by the Brothers Grimm in their folk tale collection Grimms’ Fairy Tales in 1812.
Although the story’s title and main character’s name change in different languages, in English-language folklore Cinderella is an archetypal name. The word Cinderella has, by analogy, come to mean one whose attributes were unrecognized: one who unexpectedly achieves recognition or success after a period of obscurity and neglect. The still-popular story of Cinderella continues to influence popular culture internationally, lending plot elements, allusions, and tropes to a wide variety of media.
Ancient versions[edit]
European[edit]
Rhodopis[edit]
The oldest known oral version of the Cinderella story is the ancient Greek story of Rhodopis,[4][6] a Greek courtesan living in the colony of Naucratis in Egypt, whose name means «Rosy-Cheeks». The story is first recorded by the Greek geographer Strabo in his Geographica (book 17, 33): «They [the Egyptians] tell the fabulous story that, when she was bathing, an eagle snatched one of her sandals from her maid and carried it to Memphis; and while the king was administering justice in the open air, the eagle, when it arrived above his head, flung the sandal into his lap; and the king, stirred both by the beautiful shape of the sandal and by the strangeness of the occurrence, sent men in all directions into the country in quest of the woman who wore the sandal; and when she was found in the city of Naucratis, she was brought up to Memphis, and became the wife of the king.»[7]
The same story is also later reported by the Roman orator Aelian (c. 175–c. 235) in his Miscellaneous History, which was written entirely in Greek. Aelian’s story closely resembles the story told by Strabo, but adds that the name of the pharaoh in question was Psammetichus.[b][8] Aelian’s account indicates that the story of Rhodopis remained popular throughout antiquity.
Herodotus, some five centuries before Strabo, records a popular legend about a possibly related courtesan named Rhodopis in his Histories,[9]: 27 claiming that she came from Thrace, was the slave of Iadmon of Samos and a fellow-slave of the story-teller Aesop, was taken to Egypt in the time of Pharaoh Amasis, and freed there for a large sum by Charaxus of Mytilene, brother of Sappho the lyric poet.[9]: 27–28 [10]
The resemblance of the shoe-testing of Rhodopis with Cinderella’s slipper has already been noted in the 19th century, by Edgar Taylor[11] and Reverend Sabine Baring-Gould.[12]
Aspasia of Phocaea[edit]
A second predecessor for the Cinderella character, hailing from late Antiquity, may be Aspasia of Phocaea. Her story is told in Aelian’s Varia Storia: lost her mother in early childhood and raised by her father, Aspasia, despite living in poverty, has dreamt of meeting a noble man. As she dozes off, the girl has a vision of a dove transforming into a woman, who instructs her on how to remove a physical imperfection and restore her own beauty. In another episode, she and other courtesans are made to attend a feast hosted by Persian regent Cyrus the Younger. During the banquet, the Persian King sets his sights on Aspasia herself and ignores the other women.[13][14]
Le Fresne[edit]
The twelfth-century AD lai of Le Fresne («The Ash-Tree Girl»), retold by Marie de France, is a variant of the «Cinderella» story[9]: 41 in which a wealthy noblewoman abandons her infant daughter at the base of an ash tree outside a nunnery with a ring and brocade as tokens of her identity[9]: 41 because she is one of twin sisters[9]: 41 —the mother fears that she will be accused of infidelity[9]: 41 (according to popular belief, twins were evidence of two different fathers).[15] The infant is discovered by the porter, who names her Fresne, meaning «Ash Tree»,[9]: 41 and she is raised by the nuns.[9]: 41 After she has attained maturity, a young nobleman sees her and becomes her lover.[9]: 41 The nobleman, however, is forced to marry a woman of noble birth.[9]: 41 Fresne accepts that she will never marry her beloved[9]: 41 but waits in the wedding chamber as a handmaiden.[9]: 41 She covers the bed with her own brocade[9]: 41 but, unbeknownst to her, her beloved’s bride is actually her twin sister,[9]: 41 and her mother recognizes the brocade as the same one she had given to the daughter she had abandoned so many years before.[9]: 41 Fresne’s true parentage is revealed[9]: 41 and, as a result of her noble birth, she is allowed to marry her beloved,[9]: 41 while her twin sister is married to a different nobleman.[9]: 41
Ċiklemfusa from Malta[edit]
The Maltese Cinderella is named Ċiklemfusa. She is portrayed as an orphaned child in her early childhood. Before his death, her father gave her three magical objects: a chestnut, a nut and an almond. She used to work as a servant in the King’s palace. Nobody ever took notice of the poor girl. One day she heard of a big ball and with the help of a magical spell turned herself into a beautiful princess. The prince fell in love with her and gave her a ring. On the following night the Prince gave her a diamond and on the third night he gave her a ring with a large gem on it. By the end of the ball Ċiklemfusa would run away hiding herself in the cellars of the Palace. She knew that the Prince was very sad about her disappearance so one day she made some krustini (typical Maltese biscuits) for him and hid the three gifts in each of them. When the Prince ate the biscuits he found the gifts he had given to the mysterious Princess and soon realized the huge mistake he had made of ignoring Ċiklemfusa because of her poor looks. They soon made marriage arrangements and she became his wife.[16][17][18]
Outside Europe[edit]
Ye Xian[edit]
The tale of Ye Xian first appeared in Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang written by Duan Chengshi around 860.[19] In this version, Ye Xian is the daughter of the local tribal leader who died when she was young. Because her mother died before her father, she is now under the care of her father’s second wife, who abused her. She befriends a fish, which is the reincarnation of her deceased mother.[19] Her stepmother and half-sister kill the fish, but Ye Xian finds the bones, which are magical, and they help her dress appropriately for a local Festival, including a very light golden shoe.[19] Her stepfamily recognizes her at the festival, causing her to flee and accidentally lose the shoe. Afterwards, the king of another sea island obtains the shoe and is curious about it as no one has feet that can fit the shoe. The King searches everywhere and finally reaches Ye’s house, where she tries on the shoe. The king realises she is the one and takes her back to his kingdom. Her cruel stepmother and half-sister are killed by flying rocks.[20] Variants of the story are also found in many ethnic groups in China.[19]
Tam and Cam[edit]
The Story of Tam and Cam, from Vietnam, is similar to the Chinese version. The heroine Tấm also had a fish that was killed by the stepmother and the half-sister, and its bones also give her clothes.[21] Later after marrying the king, Tấm was killed by her stepmother and sister, and reincarnated several times in form of a bird, a loom and a «gold apple». She finally reunited with the king and lived happily ever after.
Other Asian versions[edit]
There exists a Cambodian version (called «Khmer» by the collectors) with the name Néang Kantoc.[22] Its collectors compared it to the Vietnamese story of Tam and Cam.[23]
Another version was collected from the Cham people of Southeast Asia, with the name La Sandale d’Or («The Golden Sandal») or Conte de demoiselles Hulek et Kjong («The tale of the ladies Hulek and Kjong»).[24]
20th century folktale collector Kenichi Mizusawa published an analysis of Japanese variants of Cinderella, separating them into two types: «Nukabuku, Komebuku» (about rival step-sisters) and «Ubagawa» (about the heroine’s disguise).[25]
One Thousand and One Nights[edit]
Several different variants of the story appear in the medieval One Thousand and One Nights, also known as the Arabian Nights, including «The Second Shaykh’s Story», «The Eldest Lady’s Tale» and «Abdallah ibn Fadil and His Brothers», all dealing with the theme of a younger sibling harassed by two jealous elders. In some of these, the siblings are female, while in others, they are male. One of the tales, «Judar and His Brethren», departs from the happy endings of previous variants and reworks the plot to give it a tragic ending instead, with the younger brother being poisoned by his elder brothers.[26]
Literary versions[edit]
The first European version written in prose was published in Naples, Italy, by Giambattista Basile, in his Pentamerone (1634). The story itself was set in the Kingdom of Naples, at that time the most important political and cultural center of Southern Italy and among the most influential capitals in Europe, and written in the Neapolitan dialect. It was later retold, along with other Basile tales, by Charles Perrault in Histoires ou contes du temps passé (1697),[5] and by the Brothers Grimm in their folk tale collection Grimms’ Fairy Tales (1812).
The name «Cenerentola» comes from the Italian word «cenere» (ash, cinder). It has to do with the fact that servants and scullions were usually soiled with ash at that time, because of their cleaning work and also because they had to live in cold basements so they usually tried to get warm by sitting close to the fireplace.
Cenerentola, by Basile[edit]
Giambattista Basile, a Neapolitan writer, soldier and government official, assembled a set of oral folk tales into a written collection titled Lo cunto de li cunti (The Story of Stories), or Pentamerone. It included the tale of Cenerentola, which features a wicked stepmother and evil stepsisters, magical transformations, a missing slipper, and a hunt by a monarch for the owner of the slipper. It was published posthumously in 1634.
Plot:
- A prince has a daughter, Zezolla (tonnie) (the Cinderella figure), who is tended by a beloved governess. The governess, with Zezolla’s help, persuades the prince to marry her. The governess then brings forward six daughters of her own, who abuse Zezolla (tonnie), and send her into the kitchen to work as a servant. The prince goes to the island of Sinia, meets a fairy who gives presents to his daughter, and brings back for her: a golden spade, a golden bucket, a silken napkin, and a date seedling. The girl cultivates the tree, and when the king hosts a ball, Zezolla appears dressed richly by a fairy living in the date tree. The king falls in love with her, but Zezolla runs away before he can find out who she is. Twice Zezolla escapes the king and his servants. The third time, the king’s servant captures one of her slippers. The king invites all of the maidens in the land to a ball with a shoe-test, identifies Zezolla (tonnie) after the shoe jumps from his hand to her foot, and eventually marries her.[27]
Cendrillon ou la petite pantoufle de verre, by Perrault[edit]
One of the most popular versions of Cinderella was written in French by Charles Perrault in 1697, under the name Cendrillon ou la petite pantoufle de verre. The popularity of his tale was due to his additions to the story, including the pumpkin, the fairy-godmother and the introduction of «glass» slippers.[28]
Plot:
- A wealthy widower has a beautiful young daughter, a girl of unparalleled kindness and sweet temper. The gentleman marries a proud and haughty woman as his second wife. She has two daughters, who are equally vain and selfish. The girl is forced into servitude by her stepmother, where she is made to work day and night doing menial chores. After the girl’s chores are done for the day, she curls up near the fireplace in an effort to stay warm. She often arises covered in ashes, giving rise to the mocking nickname «Cendrillon» (Cinderella) by her stepsisters. Cinderella bears the abuse patiently and does not tell her father, who would have scolded her.
- One day, the prince invites all the people in the land to a royal ball. The two stepsisters gleefully plan their wardrobes for the ball, and taunt Cinderella by telling her that maids aren’t invited to the ball.
- As the two stepsisters and the stepmother depart to the ball, Cinderella cries in despair. Her Fairy godmother magically appears and immediately begins to transform Cinderella from house servant to the young lady she was by birth, all in the effort to get Cinderella to the ball. She turns a pumpkin into a golden carriage, mice into horses, a rat into a coachman, and lizards into footmen. She then turns Cinderella’s rags into a beautiful jeweled gown, complete with a delicate pair of glass slippers. The Fairy Godmother tells her to enjoy the ball, but warns her that she must return before midnight, when the spells will be broken.
- At the ball, the entire court is entranced by Cinderella, especially the Prince. At this first ball, Cinderella remembers to leave before midnight. Back home, Cinderella graciously thanks her Fairy Godmother. She then innocently greets the two stepsisters, who had not recognized her earlier, and talk of nothing but the beautiful girl at the ball.
- Another ball is held the next evening, and Cinderella again attends with her Fairy Godmother’s help. The prince has become even more infatuated with the mysterious woman at the ball, and Cinderella in turn becomes so enchanted by him she loses track of time and leaves only at the final stroke of midnight, losing one of her glass slippers on the steps of the palace in her haste. The Prince chases her, but outside the palace, the guards see only a simple country girl leave. The prince pockets the slipper and vows to find and marry the girl to whom it belongs. Meanwhile, Cinderella keeps the other slipper, which does not disappear when the spell is broken.
- The prince’s herald tries the slipper on all the women in the kingdom. When the herald arrives at Cinderella’s home, the two stepsisters try in vain to win him over. Cinderella asks if she may try, but the two stepsisters taunt her. Naturally, the slipper fits perfectly, and Cinderella produces the other slipper for good measure. Cinderella’s stepfamily pleads for forgiveness, and Cinderella agrees. Cinderella had hoped her step-family would love her always. Cinderella marries the prince and forgives her two stepsisters, then marrying them off to two wealthy noblemen of the court. They all lived happily ever after.[29]
The first moral of the story is that beauty is a treasure, but graciousness is priceless. Without it, nothing is possible; with it, one can do anything.[30]
However, the second moral of the story mitigates the first one and reveals the criticism that Perrault is aiming at: That «without doubt it is a great advantage to have intelligence, courage, good breeding, and common sense. These, and similar talents come only from heaven, and it is good to have them. However, even these may fail to bring you success, without the blessing of a godfather or a godmother.»[30]
-
Charles Robinson illustrated Cinderella in the kitchen (1900), from Tales of Passed Times with stories by Charles Perrault.
-
Oliver Herford illustrated Cinderella with the Fairy Godmother, inspired by Perrault’s version.
-
Cinderella or Cendrillon in French. Gustave Doré’s illustration for Cendrillon, 1867
-
The fitting with the prince onlooking, illustration in Les Contes de Perrault by Gustave Doré, 1862
Aschenputtel, by the Brothers Grimm[edit]
Another well-known version was recorded by the German brothers Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm in the 19th century. The tale is called «Aschenputtel» [“The Little Ash Girl”] or «Cinderella» in English translations). This version is much more violent than that of Charles Perrault and Disney, in that Cinderella’s father has not died and the two stepsisters mutilate their feet to fit in the golden slipper. There is no fairy godmother in this version of the Brothers Grimm, but rather help comes from a wishing tree that the heroine planted on her deceased mother’s grave when she recites a certain chant. In the second edition of their collection (1819), the Brothers Grimm supplemented the original 1812 version with a coda in which the two stepsisters suffer a terrible punishment by the princess Cinderella for their cruelty.[31]
Summary[edit]
A plague infests a village, and a wealthy gentleman’s wife lies on her deathbed. She calls for her only daughter, and tells her to remain good and kind, as God would protect her. She then dies and is buried. The child visits her mother’s grave every day to grieve and a year goes by. The gentleman marries another woman with two older daughters from a previous marriage. They have beautiful faces and fair skin, but their hearts are cruel and wicked. The stepsisters steal the girl’s fine clothes and jewels and force her to wear rags. They banish her into the kitchen, and give her the nickname «Aschenputtel» («Ashfool»). She is forced to do all kinds of hard work from dawn to dusk for the sisters. The cruel sisters do nothing but mock her and make her chores harder by creating messes. However, despite all of it, the girl remains good and kind, and regularly visits her mother’s grave to cry and pray to God that she will see her circumstances improve.
One day the gentleman visits a fair, promising his stepdaughters gifts of luxury. The eldest asks for beautiful dresses, while the younger for pearls and diamonds. His own daughter merely begs for the first twig to knock his hat off on the way. The gentleman goes on his way, and acquires presents for his stepdaughters. While passing a forest he gets a hazel twig, and gives it to his daughter. She plants the twig over her mother’s grave, waters it with her tears and over the years, it grows into a glowing hazel tree. The girl prays under it three times a day, and a white bird always comes to her as she prays. She tells her wishes to the bird, and every time the bird throws down to her what she has wished for.
The king decides to proclaim a festival that will last for three days and invites all the beautiful maidens in that country to attend so that the prince can select one of them for his bride. The two sisters are also invited, but when Aschenputtel begs them to allow her to go with them into the celebration, the stepmother refuses because she has no decent dress nor shoes to wear. When the girl insists, the woman throws a dish of lentils into the ashes for her to pick up, guaranteeing her permission to attend the festival if she can clean up the lentils in two hours. When the girl accomplished the task in less than an hour with the help of a flock of white doves that came when she sang a certain chant, the stepmother only redoubles the task and throws down even a greater quantity of lentils. When Aschenputtel is able to accomplish it in a greater speed, not wanting to spoil her daughters’ chances, the stepmother hastens away with her husband and daughters to the celebration and leaves the crying stepdaughter behind.
Cinderella prays to the tree and the little birds provide her a beautiful dress. Art by Elenore Abbott.
The girl retreats to the graveyard and asks to be clothed in silver and gold. The white bird drops a gold and silver gown and silk shoes. She goes to the feast. The prince dances with her all the time, claiming her as his dance partner whenever a gentleman asks for her hand, and when sunset comes she asks to leave. The prince escorts her home, but she eludes him and jumps inside the estate’s pigeon coop. The father came home ahead of time and the prince asks him to chop the pigeon coop down, but Aschenputtel has already escaped from the back, to the graveyard to the hazel tree to return her fine clothes. The father finds her asleep in the kitchen hearth, and suspects nothing. The next day, the girl appears in grander apparel. The prince again dances with her the whole day, and when dark came, the prince accompanies her home. However, she climbs a pear tree in the back garden to escape him. The prince calls her father who chops down the tree, wondering if it could be Aschenputtel, but Aschenputtel was already in the kitchen when the father arrives home. The third day, she appears dressed in grand finery, with slippers of gold. Now the prince is determined to keep her, and has the entire stairway smeared with pitch. Aschenputtel, in her haste to elude the prince, loses one of her golden slippers on that pitch. The prince picks the slipper and proclaims that he will marry the maiden whose foot fits the golden slipper.
The next morning, the prince goes to Aschenputtel’s house and tries the slipper on the eldest stepsister. Since she will have no more need to go on foot when she will be queen, the sister was advised by her mother to cut off her toes to fit the slipper. While riding with the stepsister, the two magic doves from heaven tell the prince that blood drips from her foot. Appalled by her treachery, he goes back again and tries the slipper on the other stepsister. She cut off part of her heel to get her foot in the slipper, and again the prince is fooled. While riding with her to the king’s castle, the doves alert him again about the blood on her foot. He comes back to inquire about another girl. The gentleman tells him that his dead wife left a «dirty little Cinderella» in the house, omitting to mention that she is his own daughter, and that she is too filthy to be seen, but the prince asks him to let her try on the slipper. Aschenputtel appears after washing clean her face and hands, and when she puts on the slipper, which fitted her like a glove, the prince recognizes her as the stranger with whom he has danced at the festival, even before trying it. To the horror of the stepmother and the two limping sisters, their merely servant-girl had won without any subterfuge. The prince put Aschenputtel before him on his horse and rode off to the palace. While passing the hazel tree the two magic doves from heaven declare Aschenputtel as the true bride of the prince, and remained on her shoulders, one on the left and the other on the right.
In a coda added in the second edition of 1819, during Aschenputtel’s royal wedding, the false stepsisters had hoped to worm their way into her favour as the future queen, but this time they don’t escape their princess’ silent rage, which she kept to herself until that day. As she walks down the aisle with her stepsisters as her bridesmaids, Aschenputtel’s doves fly off her shoulders and strike the two stepsisters’ eyes, one in the left and the other in the right. It is their last chance of redemption, but since they are desperate to win the new princess’ affections, they don’t give up and go through the ceremony, so when the wedding comes to an end, and Aschenputtel and her beloved prince march out of the church, her doves fly again, promptly striking the remaining eyes of the two evil stepsisters blind, a truly awful comeuppance they have to endure. Then, finally free from abuse and enslavement, Aschenputtel leaves her family forever to be a princess with her prince, while the stepsisters live their lives as blind beggars, as her father and stepmother are in disgrace.[32]
Plot variations and alternative tellings[edit]
Folklorists have long studied variants on this tale across cultures. In 1893, Marian Roalfe Cox, commissioned by the Folklore Society of Britain, produced Cinderella: Three Hundred and Forty-Five Variants of Cinderella, Catskin and, Cap o’Rushes, Abstracted and Tabulated with a Discussion of Medieval Analogues and Notes. Further morphology studies have continued on this seminal work.[33]
Joseph Jacobs has attempted to reconstruct the original tale as The Cinder Maid by comparing the common features among hundreds of variants collected across Europe.[34] The Aarne–Thompson–Uther system classifies Cinderella as type 510A, «Persecuted Heroine». Others of this type include The Sharp Grey Sheep; The Golden Slipper; The Story of Tam and Cam; Rushen Coatie; The Wonderful Birch; Fair, Brown and Trembling; and Katie Woodencloak.[35][9]: 24–26
The magical help[edit]
International versions lack the fairy godmother present in the famous Perrault’s tale. Instead, the donor is her mother, incarnated into an animal (if she is dead) or transformed into a cow (if alive). In other versions, the helper is an animal, such as a cow, a bull, a pike, or a saint or angel.[36] The bovine helper appears in some Greek versions, in «the Balkan-Slavonic tradition of the tale», and in some Central Asian variants. The mother-as-cow is killed by the heroine’s sisters, her bones gathered and from her grave the heroine gets the wonderful dresses.[37]
Africanist Sigrid Schmidt stated that «a typical scene» in Kapmalaien (Cape Malays) tales is the mother becoming a fish, being eaten in fish form, the daughter burying her bones and a tree sprouting from her grave.[38]
Professor Gražina Skabeikytė-Kazlauskienė recognizes that the fish, the cow, even a female dog (in other variants), these animals represent «the [heroine’s] mother’s legacy».[39] Jack Zipes, commenting on a Sicilian variant, concluded much the same: Cinderella is helped by her mother «in the guise of doves, fairies, and godmothers».[40] In his notes to his own reconstruction, Joseph Jacobs acknowledged that the heroine’s animal helper (e.g., cow or sheep) was «clearly identified with her mother», as well as the tree on Cinderella’s mother’s grave was connected to her.[41]
Villains[edit]
Although many variants of Cinderella feature the wicked stepmother, the defining trait of type 510A is a female persecutor: in Fair, Brown and Trembling and Finette Cendron, the stepmother does not appear at all, and it is the older sisters who confine her to the kitchen. In other fairy tales featuring the ball, she was driven from home by the persecutions of her father, usually because he wished to marry her. Of this type (510B) are Cap O’ Rushes, Catskin, All-Kinds-of-Fur, and Allerleirauh, and she slaves in the kitchen because she found a job there.[42] In Katie Woodencloak, the stepmother drives her from home, and she likewise finds such a job.[43]
In La Cenerentola, Gioachino Rossini inverted the sex roles: Cenerentola is mistreated by her stepfather. (This makes the opera Aarne-Thompson type 510B.) He also made the economic basis for such hostility unusually clear, in that Don Magnifico wishes to make his own daughters’ dowries larger, to attract a grander match, which is impossible if he must provide a third dowry. Folklorists often interpret the hostility between the stepmother and stepdaughter as just such a competition for resources, but seldom does the tale make it clear.[44]
In some retellings, at least one stepsister is somewhat kind to Cinderella and second guesses the Stepmother’s treatment. This is seen in Ever After, the two direct-to-video sequels to Walt Disney’s 1950 film, and the 2013 Broadway musical.
-
The stepsisters, 1865 edition of Cinderella
-
Cinderella Dressing Her Sisters, Aunt Friendly’s Gift, 1890
-
Stepsisters from Journeys through Bookland, 1922
-
The stepsisters, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
Ball, ballgown, and curfew[edit]
The number of balls varies, sometimes one, sometimes two, and sometimes three. The fairy godmother is Perrault’s own addition to the tale.[45] The person who aided Cinderella (Aschenputtel) in the Grimms’s version is her dead mother. Aschenputtel requests her aid by praying at her grave, on which a tree is growing. Helpful doves roosting in the tree shake down the clothing she needs for the ball. This motif is found in other variants of the tale as well, such as in the Finnish The Wonderful Birch. Playwright James Lapine incorporated this motif into the Cinderella plotline of the musical Into the Woods. Giambattista Basile’s Cenerentola combined them; the Cinderella figure, Zezolla, asks her father to commend her to the Dove of Fairies and ask her to send her something, and she receives a tree that will provide her clothing. Other variants have her helped by talking animals, as in Katie Woodencloak, Rushen Coatie, Bawang Putih Bawang Merah, The Story of Tam and Cam, or The Sharp Grey Sheep—these animals often having some connection with her dead mother; in The Golden Slipper, a fish aids her after she puts it in water. In «The Anklet», it’s a magical alabaster pot the girl purchased with her own money that brings her the gowns and the anklets she wears to the ball. Gioachino Rossini, having agreed to do an opera based on Cinderella if he could omit all magical elements, wrote La Cenerentola, in which she was aided by Alidoro, a philosopher and formerly the Prince’s tutor.
The midnight curfew is also absent in many versions; Cinderella leaves the ball to get home before her stepmother and stepsisters, or she is simply tired. In the Grimms’ version, Aschenputtel slips away when she is tired, hiding on her father’s estate in a tree, and then the pigeon coop, to elude her pursuers; her father tries to catch her by chopping them down, but she escapes.[46]
-
Fairy Godmother, Walter Crane, 1897
-
Cinderella and the Fairy Godmother by Kate Abelmann, 1913
-
Ballgown Cinderella, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
-
At the ball, 1865 edition
-
Hurrying out, 1865 edition
-
Identifying item[edit]
The slipper left behind, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
The glass slipper is unique to Charles Perrault’s version and its derivatives; in other versions of the tale it may be made of other materials (in the version recorded by the Brothers Grimm, German: Aschenbroedel and Aschenputtel, for instance, it is gold) and in still other tellings, it is not a slipper but an anklet, a ring, or a bracelet that gives the prince the key to Cinderella’s identity. In Rossini’s opera «La Cenerentola» («Cinderella»), the slipper is replaced by twin bracelets to prove her identity. In the Finnish variant The Wonderful Birch the prince uses tar to gain something every ball, and so has a ring, a circlet, and a pair of slippers. Some interpreters, perhaps troubled by sartorial impracticalities, have suggested that Perrault’s «glass slipper» (pantoufle de verre) had been a «squirrel fur slipper» (pantoufle de vair) in some unidentified earlier version of the tale, and that Perrault or one of his sources confused the words; however, most scholars believe the glass slipper was a deliberate piece of poetic invention on Perrault’s part.[47] [c] Nabokov has Professor Pnin assert as fact that «Cendrillon’s shoes were not made of glass but of Russian squirrel fur – vair, in French».[49] The 1950 Disney adaptation takes advantage of the slipper being made of glass to add a twist whereby the slipper is shattered just before Cinderella has the chance to try it on, leaving her with only the matching slipper with which to prove her identity.
Revelation[edit]
In many variants of the tale, the prince is told that Cinderella can not possibly be the one, as she is too dirty and ragged. Often, this is said by the stepmother or stepsisters. In the Grimms’ version, both the stepmother and the father urge it.[50] The prince nevertheless insists on her trying. Cinderella arrives and proves her identity by fitting into the slipper or other item (in some cases she has kept the other).
-
Stepsister trying the slipper, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
-
The prince pleading for Cinderella to try the shoe, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
-
Trying on the Slipper, Sarah Noble Ives, c. 1912
-
Cinderella trying on the slipper, 1865 edition
-
Dean & Son’s Cinderella «surprise book» with moving images, c. 1875
-
Illustration by Carl Offterdinger, late 19th century
-
Finding that the slipper fits, educational poster by Hans Printz, 1905
-
Trying the slipper, Askepot og Prinsen
Conclusion[edit]
According to Korean scholarship, East Asian versions of Cinderella «typically» continue as the heroine’s stepmother replaces the Cinderella-like character for her own daughter,[clarification needed] while the heroine goes through a cycle of transformations.[51] Such tales continue the fairy tale into what is in effect a second episode.
In The Thousand Nights and A Night, in a tale called «The Anklet»,[52] the stepsisters make a comeback by using twelve magical hairpins to turn the bride into a dove on her wedding night. In The Wonderful Birch, the stepmother, a witch, manages to substitute her daughter for the true bride after she has given birth.
-
Part two of Dean & Son’s Cinderella, 1875
-
Happy ending
-
In the German version the stepsisters’ eyes get pecked out by the princess’ birds, her loyal friends and minions
Works based on the Cinderella story[edit]
Works based on the story of Cinderella include:
Opera and ballet[edit]
- Cendrillon (1749) by Jean-Louis Laruette
- Cendrillon (1810) by Nicolas Isouard, libretto by Charles-Guillaume Étienne
- Agatina, o la virtù premiata [it] (1814) by Stefano Pavesi
- La Cenerentola (1817) by Gioachino Rossini
- Cinderella (1893) by Baron Boris Vietinghoff-Scheel
- Cendrillon (1894–95) by Jules Massenet, libretto by Henri Caïn
- Aschenbrödel (1901) by Johann Strauss II, adapted and completed by Josef Bayer[53]
- Cinderella (1901–02) by Gustav Holst
- La Cenerentola (1902) by Ermanno Wolf-Ferrari
- Cendrillon (1904) by Pauline García-Viardot
- Aschenbrödel (1905) by Leo Blech, libretto by Richard Batka
- Das Märchen vom Aschenbrödel (1941) by Frank Martin
- Zolushka or Cinderella (1945) by Sergei Prokofiev
- La Cenicienta (1966) by Jorge Peña Hen
- Cinderella, a «pantomime opera» (1979) by Peter Maxwell Davies
- Cinderella (1980) by Paul Reade
- Cinderella (1997) by Matthew Bourne taking place in 1940 London using the music of Sergei Prokofiev
- My First Cinderella (2013) directed by George Williamson and Loipa Araújo
Theatre[edit]
In 1804 Cinderella was presented at Drury Lane Theatre, London, described as «A new Grand Allegorical Pantomimic Spectacle» though it was very far in style and content from the modern pantomime. However, it included notable clown Joseph Grimaldi playing the part of a servant called Pedro, the antecedent of today’s character Buttons.[54] In 1820 Harlequin and Cinderella at the Theatre Royal, Covent Garden had much of the modern story (taken from the opera La Cenerentola) by Rossini but was a Harlequinade again featuring Grimaldi.[54] In 1830 Rophino Lacy used Rossini’s music but with spoken dialogue in a comic opera with many of the main characters: the Baron, the two stepsisters and Pedro the servant all as comic characters, plus a Fairy Queen instead of a magician.[54] However it was the conversion of this via burlesque and rhyming couplets by Henry Byron that led to what was effectively the modern pantomime in both story and style at the Royal Strand Theatre in 1860: Cinderella! Or the Lover, the Lackey, and the Little Glass Slipper.[54]
In the traditional pantomime version the opening scene takes place in a forest with a hunt in progress; here Cinderella first meets Prince Charming and his «right-hand man» Dandini, whose name and character come from Gioachino Rossini’s opera (La Cenerentola). Cinderella mistakes Dandini for the Prince and the Prince for Dandini. Her father, Baron Hardup, is under the thumb of his two stepdaughters, the Ugly sisters, and has a servant, Cinderella’s friend Buttons. (Throughout the pantomime, the Baron is continually harassed by the Broker’s Men (often named after current politicians) for outstanding rent. The Fairy Godmother must magically create a coach (from a pumpkin), footmen (from mice), a coach driver (from a frog), and a beautiful dress (from rags) for Cinderella to go to the ball. However, she must return by midnight, as it is then that the spell ceases.
Musicals[edit]
- Cinderella by Rodgers and Hammerstein was produced for television three times and staged live in various productions. A version ran in 1958 at the London Coliseum with a cast including Tommy Steele, Yana, Jimmy Edwards, Kenneth Williams and Betty Marsden. This version was augmented with several other Rodgers and Hammerstein’s songs plus a song written by Tommy Steele, «You and Me». In 2013, a Broadway production opened, with a new book by Douglas Carter Beane, and ran for 770 performances. In the acclaimed 2022 VTT production of Cinderella, Naomi Infeld will be playing Anastasia.
- Mr. Cinders, a musical, opened at the Adelphi Theatre, London in 1929 and received a film version in 1934.
- Cindy, a 1964 Off-Broadway musical, was composed by Johnny Brandon and has had many revivals.
- Into the Woods, a musical with music and lyrics by Stephen Sondheim and book by James Lapine, includes Cinderella as one of the many fairy-tale characters in the plot. This is partly based on the Grimm Brothers’ version of «Cinderella», including the enchanted birds, mother’s grave, three balls, and mutilation and blinding of the stepsisters. It opened on Broadway in 1987 and has had many revivals. In this show, Cinderella is actually the Baker’s ex-sister-in-law, since she married her prince and her prince’s brother married Rapunzel, and the baker is Rapunzel’s brother. After she divorced the prince she became Rapunzel and the Baker’s ex-sister-in-law.
- Cinderella is a musical composed by Andrew Lloyd Webber that premiered in the West End in 2021.
Films and television[edit]
Over the decades, hundreds of films have been made that are either direct adaptations from Cinderella or have plots loosely based on the story.
Animation[edit]
- Aschenputtel (1922), a silhouette shadow play short by Lotte Reiniger. The short silent film uses exaggerated figures and has no background, which creates a stark look. The film shows Aschenputtel’s step-sisters graphically hacking their feet off to fit into the glass slipper.[55]
- Cinderella (1922), an animated Laugh-O-Gram produced by Walt Disney, first released on 6 December 1922. This film was about seven and half minutes long.[56]
- Cinderella (1925), an animated short film directed by Walter Lantz, produced by Bray Studios Inc.[57]
- A Kick for Cinderella (1925), an animated short film directed by Bud Fisher, in the Mutt and Jeff series of comic strip adaptations.[57]
- Cinderella Blues (1931), a Van Beuren animated short film featuring a feline version of the Cinderella character.
- Poor Cinderella (1934), Fleischer Studios’ first color cartoon and only appearance of Betty Boop in color during the Fleischer era.
- A Coach for Cinderella (1937) – Jam Handy, Cervolet advert[58]
- A Ride for Cinderella (1937) – Jam Handy, Cervolet advert[58]
- Cinderella Meets Fella (1938), a Merrie Melodies animated short film featuring Egghead, the character who would eventually evolve into Elmer Fudd, as Prince Charming.[59]
- Cinderella (1950), a Walt Disney animated feature released on 15 February 1950, now considered one of Disney’s classics as well as the most well-known film adaptation, including incorporating the titular character as a Disney Princess and its franchise.
- Cinderella II: Dreams Come True (2002), a direct-to-video sequel to the 1950 film.
- Cinderella III: A Twist in Time (2007), another direct-to-video sequel to the previous film.
- Ancient Fistory (1953) a Popeye parody animated short film.
- Señorella and the Glass Huarache (1964), a Looney Tunes animated short film that transplants the story to a Mexican setting.
- Festival of Family Classics (1972-73), episode Cinderella, produced by Rankin/Bass and animated by Mushi Production.
- World Famous Fairy Tale Series (Sekai meisaku dōwa) (1975-83) has a 9-minute adaptation.
- Manga Sekai Mukashi Banashi (1976-79), 10-minute adaptation.
- Cinderella (1979), an animated short film based on Charles Perrault’s version of the fairy tale. It was produced by the Soyuzmultfilm studio.
- «Cinderella? Cinderella!» (1986), an episode of Alvin & the Chipmunks. With Brittany of The Chipettes playing the role of Cinderella and Alvin playing the role of Prince Charming.
- My Favorite Fairy Tales (Sekai Dōwa Anime Zenshū) (1986), an anime television anthology, has a 12-minute adaptation.
- Grimm’s Fairy Tale Classics (1987-89) an anime television series based on Grimm’s stories, as two half-hour episodes.
- Funky Fables (Ponkikki Meisaku World) (1988-90), features an adaptation of Cinderella.
- Britannica’s Tales Around the World (1990-91), features Perrault’s Cinderella along with two other variants of the story.
- Cinderella (1994), a Japanese-American direct-to-video film by Jetlag Productions.
- World Fairy Tale Series (Anime sekai no dōwa) (1995), anime television anthology produced by Toei Animation, has half-hour adaptation.
- Cinderella Monogatari (The Story of Cinderella) (1996), anime television series produced by Tatsunoko Production.
- Cendrillon au Far West (2012), French/Belgian film set in the wild western age, written and directed by Pascal Hérold
- Cinderella and the Secret Prince (2018), American animated film directed by Lynne Southerland.
- Cinderella the Cat (2017), Italian animated film directed by Alessandro Rak
Non-English language live-action films and TV[edit]
Cinderella at the ball in Soviet film (1947)
- Cinderella (1899), the first film version, produced in France by Georges Méliès, as «Cendrillon».
- Mamele (1938) a Molly Picon vehicle made by the prewar Warsaw Yiddish film industry taking place in contemporary Lodz.
- Cinderella (1947), a Soviet film based on the screenplay by Evgeny Schwartz, with Yanina Zhejmo in the leading role. Shot in black-and-white, it was colorized in 2009.
- Cinderella (1955), German film
- Sandalyas ni Zafira (lit. ‘Sandals of Zafira’, 1965), a Filipino fantasy film partially based on Cinderella and starring Lyn D’Amour as Princess Zafira
- Sinderella Kül Kedisi (1971), a Turkish fantasy film based on Cinderella and starring Zeynep Değirmencioğlu as Cinderella.
- Three Wishes for Cinderella (Tři oříšky pro Popelku) (1973), a Czechoslovakian/East German fairy tale film starring Libuše Šafránková as Cinderella and Pavel Trávníček as Prince.[60] Frequently shown, especially at Christmas time, in several European countries.
- Rani Aur Lalpari (lit. ‘Rani and the Red Fairy’), a 1975 Indian children’s fantasy film by Ravikant Nagaich features Cinderella as one of the characters — where she is portrayed by Neetu Singh.[61]
- Cinderella 4×4. Everything starts with desire (Zolushka 4×4. Vsyo nachinayetsya s zhelaniy) (2008), a Russian modernization featuring Darya Melnikova
- Cinderella (2006), a Korean horror film
- Cinderella’s Stepsister (2010), a Korean television series
- Aschenputtel (2010 film) [de], a German film
- Aschenputtel (2011 film) [de], another German film
- Aik Nayee Cinderella (2013), a Pakistani modernization serial aired on Geo TV featuring Maya Ali and Osman Khalid Butt
English language live-action feature films[edit]
- Cinderella (1911) silent film starring Florence La Badie[62]
- Cinderella (1914), a silent film starring Mary Pickford
- The Glass Slipper (1955), feature film with Leslie Caron and Michael Wilding
- The Slipper and the Rose (1976), a British Sherman Brothers musical film starring Gemma Craven and Richard Chamberlain.
- Into the Woods (2014), a live-action fairy-tale-themed adaptation of the above-mentioned homonymous musical, in which Anna Kendrick’s Cinderella is a central character.
- Cinderella (2015), a live-action retelling of the 1950 animated Disney film starring Lily James as Cinderella, Cate Blanchett as Lady Tremaine, Cinderella’s stepmother, Richard Madden as Kit/Prince Charming and Helena Bonham Carter as the Fairy Godmother. It is essentially a live-action reimagining of the 1950 animated film.
- Cinderella (2021), a live-action film musical starring Camila Cabello as Cinderella, Idina Menzel as Cinderella’s stepmother, Nicholas Galitzine as the Prince, and Billy Porter as the Fairy Godmother.
Modernizations and parodies
- Ella Cinders (1926), a modern tale starring Colleen Moore, based on a comic strip by William M. Conselman and Charles Plumb, inspired by Charles Perrault’s version.
- First Love (1939), a musical modernization with Deanna Durbin and Robert Stack.
- Cinderfella (1960), Cinderfella’s (Jerry Lewis) fairy godfather (Ed Wynn) helps him escape from his wicked stepmother (Judith Anderson) and stepbrothers.
- Ever After (1998), starring Drew Barrymore, a post-feminist, historical fiction take on the Cinderella story.
- Ella Enchanted (2004), a fantasy retelling featuring Anne Hathaway, which is based on the 1997 novel of the same name.
- A Cinderella Story (2004), a modernization featuring Hilary Duff and Chad Michael Murray
- Another Cinderella Story (2008), a modernization featuring Selena Gomez and Drew Seeley
- A Cinderella Story: Once Upon a Song (2011), a modernization featuring Lucy Hale and Freddie Stroma
- A Cinderella Story: If the Shoe Fits (2016), a modernization featuring Sofia Carson and Thomas Law
- A Cinderella Story: Christmas Wish (2019), a modernization featuring Laura Marano and Gregg Sulkin
- A Cinderella Story: Starstruck (2021), a modernization featuring Bailee Madison and Michael Evans Behling
- Elle: A Modern Cinderella Tale (2010), a modernization featuring Ashlee Hewitt and Sterling Knight
English language live-action TV films and series[edit]
- Cinderella (1957), a musical adaptation by Rodgers and Hammerstein written for television and starring Julie Andrews as Cinderella, featuring Jon Cypher, Kaye Ballard, Alice Ghostley, and Edie Adams (originally broadcast in color, but only black-and-white kinescopes survive).
- Cinderella (1965), a second production of the Rodgers and Hammerstein musical, starring 18-year-old Lesley Ann Warren in the leading role, and featuring Stuart Damon as the Prince, with Ginger Rogers, Walter Pidgeon, and Celeste Holm (filmed in color and broadcast annually for 10 years).
- Hey, Cinderella! (1969), a television adaptation featuring The Muppets.
- Cindy (1978), This version of the Cinderella tale with an all-black cast has Cinderella, who wants to marry a dashing army officer, finding out that her father, who she thought had an important job at a big hotel, is actually the men’s room attendant. Her wicked stepmother finds out, too, and complications ensue. Starred Charlayne Woodard.
- In 1985, Shelley Duvall produced a version of the story for Faerie Tale Theatre.
- The Charmings (1987), a spoof of Cinderella appears in the episode «Cindy’s Back In Town» where Cinderella, portrayed by Kim Johnston Ulrich, makes a play for Snow White’s husband Prince Charming.
- Into the Woods (1989), a film of the original 1987 Broadway production of the Stephen Sondheim musical.
- Cinderella (1997), third production of the Rodgers and Hammerstein musical, this time starring Brandy as Cinderella, Whitney Houston as the Fairy Godmother, Bernadette Peters as Cinderella’s evil stepmother, Jason Alexander as Lionel the valet and Whoopi Goldberg as the Queen. Remake of the 1957 and 1965 TV films.
- Cinderella, a British TV modernization featuring Marcella Plunkett as Cinderella, Kathleen Turner as the stepmother and Jane Birkin as the fairy godmother.
- The 10th Kingdom (2000) is a TV miniseries featuring Cinderella as a major character.
- Confessions of an Ugly Stepsister (2002), TV movie for The Wonderful World of Disney by writer Gene Quintano and director Gavin Millar, based on the book of the same name, focusing on the point of view of one of the step-sister
- Once Upon a Time (2011), features Cinderella as a recurring character, played by Jessy Schram who made a deal with Rumplestiltskin who killed her fairy godmother right in front of her. In 2016, more of the story is shown in which Ashley, Cinderella’s real-world counterpart, discovers her stepsister wanted to marry the footman rather than the prince. A different Cinderella in season 7, played by Dania Ramirez, went to the ball to kill the prince, not meet him.
Television parodies and modernizations
- The story was retold as part of the episode «Grimm Job» of the American animated TV series Family Guy (season 12, episode 10), with Lois as Cinderella, Peter as Prince Charming, Mayor West as the fairy godmother, Lois’s mother as the wicked step-mother, and Meg and Stewie as the step-sisters.
- Rags (2012), a TV musical gender switched inversion of the Cinderella story that stars Keke Palmer and Max Schneider.
- Sesame Street special «Cinderelmo» and the Magic Adventures of Mumfie episode «Scarecrowella» both feature a male protagonist playing the Cinderella role.
- The My Little Pony first season finale «The Best Night Ever» parodies several key parts of the Cinderella story.
- In Carry On Christmas (1969), which was one of the Carry On Christmas Specials on TV, there is a sketch spoofing the Cinderella story. Barbara Windsor plays Cinderella and Terry Scott and Peter Butterworth play the ugly stepsisters.
Books[edit]
- Cinderella (1697), Charles Perrault
- Cinderella (1919), Charles S. Evans and illustrated by Arthur Rackham
- Ella Enchanted (1997), by Gail Carson Levine
- Raisel’s Riddle (1999), Erica Silverman and illustrated by Susan Gaber
- Confessions of an Ugly Stepsister (1999), by Gregory Maguire
- Just Ella (1999), by Margaret Peterson Haddix
- Adelita: A Mexican Cinderella Story (2004), Tomie dePaola
- «Princess of Glass» (2010) by Jessica Day George is loosely based on the fairytale.
- Cinder (2012) by Marissa Meyer, a sci-fi retelling of the classic story
- The Stepsister’s Tale (2014) by Tracy Barrett
- Geekerella (2017) by Ashley Poston
- Stepsister (2019) by Jennifer Donnelly
- So This Is Love: A Twisted Tale (2020) by Elizabeth Lim
- Cinderella is Dead (2020), by Kalynn Bayron
Video games[edit]
- Yakuza 0, referenced in Goro Majima’s song 24-Hour Cinderella.
- Persona 5 Royal, where Kasumi’s Persona is based on Cinderella and named after her French translation, Cendrillon.
See also[edit]
- Rhodopis
- Eteriani
- Cinderella complex
- Cinderella effect
- Marriage plot
- Ye Xian
- Bawang Merah Bawang Putih
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Italian: Cenerentola; French: Cendrillon; German: Aschenputtel.
- ^ There were three pharaohs called Psammetichus, and it unclear which one Aelian had in mind.
- ^ Glass Slippers, —An article hitherto only used to adorn the foot of Cinderella in a fairy tale, may now be seen in that extensive repository of discoveries and improvements, the Polytechnic Institution, Regent-street. We allude to a very curious pair of ladies’ dress-shoes, fabricated from glass, not less flexible than leather or satin, equally light, and far more durable, to judge from the solidity of their texture.[48]
References[edit]
Notes
- ^ a b Amelia Carruthers (24 September 2015). Cinderella – And Other Girls Who Lost Their Slippers (Origins of Fairy Tales). ISBN 9781473370111.
- ^ a b Zipes, Jack (2001). The Great Fairy Tale: From Straparola and Basile to the Brothers Grimm. W. W. Norton & Co. p. 444. ISBN 978-0-393-97636-6.
- ^ a b Dundes, Alan. Cinderella, a Casebook. Madison, Wis: University of Wisconsin Press, 1988.
- ^ a b Roger Lancelyn Green: Tales of Ancient Egypt, Penguin UK, 2011, ISBN 978-0-14-133822-4, chapter «The Land of Egypt»
- ^ a b Bottigheimer, Ruth. (2008). «Before Contes du temps passe (1697): Charles Perrault’s Griselidis, Souhaits and Peau«. The Romantic Review, Volume 99, Number 3. pp. 175–89
- ^ Hansen, William (2017). The Book of Greek & Roman Folktales, Legends & Myths. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. pp. 86–87. ISBN 9780691170152.
- ^ Strabo: «The Geography», book 17, 33
- ^ Aelian: «Various History», book 13, chapter 33
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Anderson, Graham (2000). Fairytale in the Ancient World. New York City and London, England: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-23702-4.
- ^ Herodot, «The Histories», book 2, chapters 134–135
- ^ Grimm, Jacob & Grimm, Wilhelm; Taylor, Edgar; Cruikshank, George (illustrator). Grimm’s Goblins: Grimm’s Household Stories. London: R. Meek & Co.. 1877. p. 294.
- ^ Baring-Gould, Sabine. A Book of Fairy Tales. [2d ed.] London: Methuen. 1895. pp. 237–238.
- ^ Ben-Amos, D. «Straparola: The Revolution That Was Not». In: The Journal of American Folklore. Vol. 123. No. 490 (Fall 2010). pp. 439–440. JSTOR [1]
- ^ Anderson, Graham. Fairytale in the Ancient World. Routledge. 2000. pp. 29–33. ISBN 0-203-18007-0
- ^ «Multiple Births in Legend and Folklore». www.pitt.edu. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ^ «Ċiklemfusa» (PDF). Rakkonti. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ «Ċiklemfusa». Filmat mill-Aġenzija tal-Litteriżmu. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ Attard, Anton F. (2019). «Book Review: The Maltese Cinderella and the Women’s Storytelling Tradition (Veronica Veen)» (PDF). The Gozo Observer (39).
- ^ a b c d Beauchamp, Fay. «Asian Origins of Cinderella: The Zhuang Storyteller of Guangxi» (PDF). Oral Tradition. 25 (2): 447–496. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ^ Ko, Dorothy (2002). Every Step a Lotus: Shoes for Bound Feet. University of California Press. pp. 26–27. ISBN 978-0520232839.
- ^ «A Cinderella Tale from Vietnam: the Story of Tam and Cam». www.furorteutonicus.eu. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- ^ Leclère, Adhémard; Feer, Léon. Cambodge: Contes et légendes. Librairie Émile Bouillon. 1895. pp. 70–90.
- ^ Leclère, Adhémard; Feer, Léon. Cambodge: Contes et légendes. Librairie Émile Bouillon. 1895. p. 91.
- ^ Leclère, Adhémerd. «Le Conte de Cendrillion chez les Cham». In: Revue de Traditions Populaires. Jun/1898. pp. 311–337.
- ^ Mayer, Fanny Hagin. «Reviewed Work: 越後のシンデレラ by 水沢謙一» [Echigo no Shinderera by Kenichi Mizusawa]. In: Asian Folklore Studies 24, no. 1 (1965): 151-153. Accessed July 25, 2021. doi:10.2307/1177604.
- ^ Ulrich Marzolph, Richard van Leeuwen, Hassan Wassouf (2004). The Arabian Nights Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 4. ISBN 1-57607-204-5.
- ^ Basile, Giambattista (1911). Stories from Pentamerone, London: Macmillan & Co., translated by John Edward Taylor. Chapter 6. See also «Il Pentamerone: Cenerentola» Archived 23 November 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ A modern edition of the original French text by Perrault is found in Charles Perrault, Contes, ed. Marc Soriano (Paris: Flammarion, 1989), pp. 274–79.
- ^ The annotated classic fairy tales. Tatar, Maria, 1945– (1st ed.). New York: Norton. 2002. ISBN 0393051633. OCLC 49894271.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b «Perrault: Cinderella; or, The Little Glass Slipper». Pitt.edu. 8 October 2003. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ Grimm, Jacob and Wilhelm; Zipes, Jack; Deszö, Andrea. «CINDERELLA». In: The Original Folk and Fairy Tales of the Brothers Grimm: The Complete First Edition. Princeton; Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2014. pp. 69–77. Accessed 29 April 2021.
- ^ Aschenputtel, included in Household Stories by the Brothers Grimm, translated by Lucy Crane, at Project Gutenberg
- ^ «If The Shoe Fits: Folklorists’ criteria for #510»
- ^ Jacobs, Joseph (1916). Europa’s Fairy Book. G. P. Putnam’s sons. pp. 1–12. ISBN 9786057876720.
- ^ Heidi Anne Heiner, «Tales Similar to Cinderella»
- ^ Garner, Emelyn Elizabeth. Folklore From the Schoharie Hills, New York. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan press, 1937. p. 130.
- ^ Kaplanoglou, Marianthi. «“Stachtopouta» and «Nifitsa»: Spinning Tales in Relation With Feminine Productivity and Dowry Practices of Modern Greece». In: Estudis De Literatura Oral Popular [Studies in Oral Folk Literature]. [en línia], 2014, Núm. 4, pp. 67, 69. https://www.raco.cat/index.php/ELOP/article/view/304851 [Consulta: Consulta: 13 March 2021].
- ^ Schmidt, Sigrid. «Reviewed Work: The World and the Word by Nongenile Masithathu Zenani, Harold Scheub». In: Anthropos 90, no. 1/3 (1995): 312. Accessed 18 April 2021. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40463177.
- ^ Skabeikytė-Kazlauskienė, Gražina. Lithuanian Narrative Folklore: Didactical Guidelines. Kaunas: Vytautas Magnus University. 2013. p. 14. ISBN 978-9955-21-361-1.
- ^ Pitrè, Giuseppe; Zipes, Jack David; Russo, Joseph. The collected Sicilian folk and fairy tales of Giuseppe Pitrè. New York: Routledge, 2013 [2009]. p. 845. ISBN 9781136094347.
- ^ Jacobs, Joseph. European Folk and Fairy Tales. New York, London: G. P. Putnam’s sons. 1916. pp. 222, 227.
- ^ Heidi Anne Heiner, «Tales Similar to Donkeyskin»
- ^ «Katie Woodencloak (Norwegian Version of Cinderella)». 5 April 2016. Archived from the original on 5 April 2016.
- ^ Marina Warner, From the Beast to the Blonde: On Fairy Tales And Their Tellers, p 213-4 ISBN 0-374-15901-7
- ^ Jane Yolen, p 23, Touch Magic ISBN 0-87483-591-7
- ^ Maria Tatar, The Annotated Brothers Grimm, p 116 W. W. Norton & company, London, New York, 2004 ISBN 0-393-05848-4
- ^ Maria Tatar, p 28, The Annotated Classic Fairy Tales, ISBN 0-393-05163-3
- ^ «Glass Slippers». Bell’s Weekly Messenger. 25 November 1838. p. 4.
- ^ Pnin, chapter 6
- ^ Maria Tatar, The Annotated Brothers Grimm, p 126-8 W. W. Norton & company, London, New York, 2004 ISBN 0-393-05848-4
- ^ The National Folk Museum of Korea (South Korea). Encyclopedia of Korean Folk Literature: Encyclopedia of Korean Folklore and Traditional Culture Vol. III. 길잡이미디어, 2014. p. 311.
- ^ Mardrus, Joseph-Charles; Powys Mathers (June 1987). The book of the Thousand Nights and One Night. Vol. 4. London and New York: Routledge. pp. 191–194. ISBN 0-415-04543-6.
- ^ «Josef Bayer (1852–1913)». www.johann-strauss.org.uk. The Johann Strauss Society of Great Britain. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ^ a b c d Clinton-Baddeley, V. C. (1963). Some Pantomime Pedigrees. The Society for Theatrical Research. pp. 9–11.
- ^ Freyberger, Regina (2009). Märchenbilder—Bildermärchen. Athena. p. 453. ISBN 9783898963503.
- ^ Merrill, Russell; Kaufmann, J. B. (2007). Walt Disney’s Silly Symphonies: A Companion to the Classic Cartoon Series. Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-8886155274.
- ^ a b «Fairy Tale Flappers: Animated Adaptations of Little Red and Cinderella (1922–1925)». governmentcheese.ca.
- ^ a b «Nicky Nome Rides Again |». cartoonresearch.com.
- ^ «YouTube». YouTube. Archived from the original on 17 October 2013. Retrieved 23 September 2013.
- ^ «Three wishes for Cinderella (1973)». Imdb.com.
- ^ Rani Aur Lalpari. iTunes.
- ^ Nicholls, George; La Badie, Florence (1911), Cinderella, OCLC 422761848, retrieved 25 May 2020
Further reading[edit]
- Bascom, William. «Cinderella in Africa». In: Journal of the Folklore Institute 9, no. 1 (1972): 54-70. Accessed July 12, 2021. doi:10.2307/3814022.
- Čechová, Mariana. «RHIZOMATIC CHARACTER OF TRANS-CULTURAL AND TRANS-TEMPORAL MODE OF LITERARY COMMUNICATION». In: World Literature Studies Vol. 6 (23), n. 3 (2014): 111–127.
- Chen, Fan Pen Li. «Three Cinderella Tales from the Mountains of Southwest China». In: Journal of Folklore Research 57, no. 2 (2020): 119–52. Accessed 17 November 2020. doi:10.2979/jfolkrese.57.2.04.
- Christiansen, Reidar Th. «Cinderella in Ireland». In: Béaloideas 20, no. 1/2 (1950): 96–107. Accessed 7 May 2021. doi:10.2307/20521197.
- Ding Naitong (1974). The Cinderella cycle in China and Indo-China. Helsinki: Suomalainen Tiedeakatemia. ISBN 951-41-0121-9.
- Gardner, Fletcher, and W. W. Newell. «Filipino (Tagalog) Versions of Cinderella». In: The Journal of American Folklore 19, no. 75 (1906): 265–80. Accessed 5 July 2020. doi:10.2307/534434.
- Jonathan Y. H. Hui (2018) «Cinderella in Old Norse Literature». In: Folklore, 129:4, pp. 353–374. doi:10.1080/0015587X.2018.1515207.
- Labelle, Ronald. (2017). «Le conte de Cendrillon: de la Chine à l’Acadie sur les ailes de la tradition». In: Rabaska 15: 7–28.
- Mulhern, Chieko Irie. «Cinderella and the Jesuits. An Otogizōshi Cycle as Christian Literature». In: Monumenta Nipponica 34, no. 4 (1979): 409-47. Accessed June 25, 2021. doi:10.2307/2384103.
- Mulhern, Chieko Irie. «Analysis of Cinderella Motifs, Italian and Japanese». In: Asian Folklore Studies 44, no. 1 (1985): 1-37. Accessed June 25, 2021. doi:10.2307/1177981.
- Schlepp, Wayne. “Cinderella in Tibet”. In: Asian Folklore Studies 61, no. 1 (2002): 123–47. Cinderella in Tibet.
- Tangherlini, Timothy. (1994). «Cinderella in Korea: Korean Oikotypes of AaTh 510». In: Fabula. 35: 282–304. doi:10.1515/fabl.1994.35.3-4.282.
- Albano Maria Luisa (a cura). Cenerentole in viaggio. Illustrazione di Marcella Brancaforte. Falzea Editore, Reggio Calabria, 2008.
Notes[edit]
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cinderella.
Wikisource has original text related to this article:
- The complete set of Grimms’ Fairy Tales, including Cinderella at Standard Ebooks
- Project Gutenberg compilation, including original Cendrillon
- Photos and illustrations from early Cinderella stage versions, including one with Ellaline Terriss and one with Phyllis Dare
- Parallel German-English text of brothers Grimm’s version in ParallelBook format
- The Cinderella Bibliography by the University of Rochester
- Folktales of ATU type 510A, «The Persecuted Heroine: Cinderella» by D. L. Ashliman
| Cinderella | |
|---|---|

Alexander Zick illustrated Cinderella with the Doves, inspired by the Brothers Grimm’s version. |
|
| Folk tale | |
| Name | Cinderella |
| Aarne–Thompson grouping | ATU 510 A (Persecuted Heroine) |
| Country |
|
| Region | Eurasia |
«Cinderella«,[a] or «The Little Glass Slipper«, is a folk tale with thousands of variants throughout the world.[2][3] The protagonist is a young woman living in forsaken circumstances that are suddenly changed to remarkable fortune, with her ascension to the throne via marriage. The story of Rhodopis, recounted by the Greek geographer Strabo sometime between around 7 BC and AD 23, about a Greek slave girl who marries the king of Egypt, is usually considered to be the earliest known variant of the Cinderella story.[2][3][4]
The first literary European version of the story was published in Italy by Giambattista Basile in his Pentamerone in 1634; the version that is now most widely known in the English-speaking world was published in French by Charles Perrault in Histoires ou contes du temps passé in 1697.[5] Another version was later published as Aschenputtel by the Brothers Grimm in their folk tale collection Grimms’ Fairy Tales in 1812.
Although the story’s title and main character’s name change in different languages, in English-language folklore Cinderella is an archetypal name. The word Cinderella has, by analogy, come to mean one whose attributes were unrecognized: one who unexpectedly achieves recognition or success after a period of obscurity and neglect. The still-popular story of Cinderella continues to influence popular culture internationally, lending plot elements, allusions, and tropes to a wide variety of media.
Ancient versions[edit]
European[edit]
Rhodopis[edit]
The oldest known oral version of the Cinderella story is the ancient Greek story of Rhodopis,[4][6] a Greek courtesan living in the colony of Naucratis in Egypt, whose name means «Rosy-Cheeks». The story is first recorded by the Greek geographer Strabo in his Geographica (book 17, 33): «They [the Egyptians] tell the fabulous story that, when she was bathing, an eagle snatched one of her sandals from her maid and carried it to Memphis; and while the king was administering justice in the open air, the eagle, when it arrived above his head, flung the sandal into his lap; and the king, stirred both by the beautiful shape of the sandal and by the strangeness of the occurrence, sent men in all directions into the country in quest of the woman who wore the sandal; and when she was found in the city of Naucratis, she was brought up to Memphis, and became the wife of the king.»[7]
The same story is also later reported by the Roman orator Aelian (c. 175–c. 235) in his Miscellaneous History, which was written entirely in Greek. Aelian’s story closely resembles the story told by Strabo, but adds that the name of the pharaoh in question was Psammetichus.[b][8] Aelian’s account indicates that the story of Rhodopis remained popular throughout antiquity.
Herodotus, some five centuries before Strabo, records a popular legend about a possibly related courtesan named Rhodopis in his Histories,[9]: 27 claiming that she came from Thrace, was the slave of Iadmon of Samos and a fellow-slave of the story-teller Aesop, was taken to Egypt in the time of Pharaoh Amasis, and freed there for a large sum by Charaxus of Mytilene, brother of Sappho the lyric poet.[9]: 27–28 [10]
The resemblance of the shoe-testing of Rhodopis with Cinderella’s slipper has already been noted in the 19th century, by Edgar Taylor[11] and Reverend Sabine Baring-Gould.[12]
Aspasia of Phocaea[edit]
A second predecessor for the Cinderella character, hailing from late Antiquity, may be Aspasia of Phocaea. Her story is told in Aelian’s Varia Storia: lost her mother in early childhood and raised by her father, Aspasia, despite living in poverty, has dreamt of meeting a noble man. As she dozes off, the girl has a vision of a dove transforming into a woman, who instructs her on how to remove a physical imperfection and restore her own beauty. In another episode, she and other courtesans are made to attend a feast hosted by Persian regent Cyrus the Younger. During the banquet, the Persian King sets his sights on Aspasia herself and ignores the other women.[13][14]
Le Fresne[edit]
The twelfth-century AD lai of Le Fresne («The Ash-Tree Girl»), retold by Marie de France, is a variant of the «Cinderella» story[9]: 41 in which a wealthy noblewoman abandons her infant daughter at the base of an ash tree outside a nunnery with a ring and brocade as tokens of her identity[9]: 41 because she is one of twin sisters[9]: 41 —the mother fears that she will be accused of infidelity[9]: 41 (according to popular belief, twins were evidence of two different fathers).[15] The infant is discovered by the porter, who names her Fresne, meaning «Ash Tree»,[9]: 41 and she is raised by the nuns.[9]: 41 After she has attained maturity, a young nobleman sees her and becomes her lover.[9]: 41 The nobleman, however, is forced to marry a woman of noble birth.[9]: 41 Fresne accepts that she will never marry her beloved[9]: 41 but waits in the wedding chamber as a handmaiden.[9]: 41 She covers the bed with her own brocade[9]: 41 but, unbeknownst to her, her beloved’s bride is actually her twin sister,[9]: 41 and her mother recognizes the brocade as the same one she had given to the daughter she had abandoned so many years before.[9]: 41 Fresne’s true parentage is revealed[9]: 41 and, as a result of her noble birth, she is allowed to marry her beloved,[9]: 41 while her twin sister is married to a different nobleman.[9]: 41
Ċiklemfusa from Malta[edit]
The Maltese Cinderella is named Ċiklemfusa. She is portrayed as an orphaned child in her early childhood. Before his death, her father gave her three magical objects: a chestnut, a nut and an almond. She used to work as a servant in the King’s palace. Nobody ever took notice of the poor girl. One day she heard of a big ball and with the help of a magical spell turned herself into a beautiful princess. The prince fell in love with her and gave her a ring. On the following night the Prince gave her a diamond and on the third night he gave her a ring with a large gem on it. By the end of the ball Ċiklemfusa would run away hiding herself in the cellars of the Palace. She knew that the Prince was very sad about her disappearance so one day she made some krustini (typical Maltese biscuits) for him and hid the three gifts in each of them. When the Prince ate the biscuits he found the gifts he had given to the mysterious Princess and soon realized the huge mistake he had made of ignoring Ċiklemfusa because of her poor looks. They soon made marriage arrangements and she became his wife.[16][17][18]
Outside Europe[edit]
Ye Xian[edit]
The tale of Ye Xian first appeared in Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang written by Duan Chengshi around 860.[19] In this version, Ye Xian is the daughter of the local tribal leader who died when she was young. Because her mother died before her father, she is now under the care of her father’s second wife, who abused her. She befriends a fish, which is the reincarnation of her deceased mother.[19] Her stepmother and half-sister kill the fish, but Ye Xian finds the bones, which are magical, and they help her dress appropriately for a local Festival, including a very light golden shoe.[19] Her stepfamily recognizes her at the festival, causing her to flee and accidentally lose the shoe. Afterwards, the king of another sea island obtains the shoe and is curious about it as no one has feet that can fit the shoe. The King searches everywhere and finally reaches Ye’s house, where she tries on the shoe. The king realises she is the one and takes her back to his kingdom. Her cruel stepmother and half-sister are killed by flying rocks.[20] Variants of the story are also found in many ethnic groups in China.[19]
Tam and Cam[edit]
The Story of Tam and Cam, from Vietnam, is similar to the Chinese version. The heroine Tấm also had a fish that was killed by the stepmother and the half-sister, and its bones also give her clothes.[21] Later after marrying the king, Tấm was killed by her stepmother and sister, and reincarnated several times in form of a bird, a loom and a «gold apple». She finally reunited with the king and lived happily ever after.
Other Asian versions[edit]
There exists a Cambodian version (called «Khmer» by the collectors) with the name Néang Kantoc.[22] Its collectors compared it to the Vietnamese story of Tam and Cam.[23]
Another version was collected from the Cham people of Southeast Asia, with the name La Sandale d’Or («The Golden Sandal») or Conte de demoiselles Hulek et Kjong («The tale of the ladies Hulek and Kjong»).[24]
20th century folktale collector Kenichi Mizusawa published an analysis of Japanese variants of Cinderella, separating them into two types: «Nukabuku, Komebuku» (about rival step-sisters) and «Ubagawa» (about the heroine’s disguise).[25]
One Thousand and One Nights[edit]
Several different variants of the story appear in the medieval One Thousand and One Nights, also known as the Arabian Nights, including «The Second Shaykh’s Story», «The Eldest Lady’s Tale» and «Abdallah ibn Fadil and His Brothers», all dealing with the theme of a younger sibling harassed by two jealous elders. In some of these, the siblings are female, while in others, they are male. One of the tales, «Judar and His Brethren», departs from the happy endings of previous variants and reworks the plot to give it a tragic ending instead, with the younger brother being poisoned by his elder brothers.[26]
Literary versions[edit]
The first European version written in prose was published in Naples, Italy, by Giambattista Basile, in his Pentamerone (1634). The story itself was set in the Kingdom of Naples, at that time the most important political and cultural center of Southern Italy and among the most influential capitals in Europe, and written in the Neapolitan dialect. It was later retold, along with other Basile tales, by Charles Perrault in Histoires ou contes du temps passé (1697),[5] and by the Brothers Grimm in their folk tale collection Grimms’ Fairy Tales (1812).
The name «Cenerentola» comes from the Italian word «cenere» (ash, cinder). It has to do with the fact that servants and scullions were usually soiled with ash at that time, because of their cleaning work and also because they had to live in cold basements so they usually tried to get warm by sitting close to the fireplace.
Cenerentola, by Basile[edit]
Giambattista Basile, a Neapolitan writer, soldier and government official, assembled a set of oral folk tales into a written collection titled Lo cunto de li cunti (The Story of Stories), or Pentamerone. It included the tale of Cenerentola, which features a wicked stepmother and evil stepsisters, magical transformations, a missing slipper, and a hunt by a monarch for the owner of the slipper. It was published posthumously in 1634.
Plot:
- A prince has a daughter, Zezolla (tonnie) (the Cinderella figure), who is tended by a beloved governess. The governess, with Zezolla’s help, persuades the prince to marry her. The governess then brings forward six daughters of her own, who abuse Zezolla (tonnie), and send her into the kitchen to work as a servant. The prince goes to the island of Sinia, meets a fairy who gives presents to his daughter, and brings back for her: a golden spade, a golden bucket, a silken napkin, and a date seedling. The girl cultivates the tree, and when the king hosts a ball, Zezolla appears dressed richly by a fairy living in the date tree. The king falls in love with her, but Zezolla runs away before he can find out who she is. Twice Zezolla escapes the king and his servants. The third time, the king’s servant captures one of her slippers. The king invites all of the maidens in the land to a ball with a shoe-test, identifies Zezolla (tonnie) after the shoe jumps from his hand to her foot, and eventually marries her.[27]
Cendrillon ou la petite pantoufle de verre, by Perrault[edit]
One of the most popular versions of Cinderella was written in French by Charles Perrault in 1697, under the name Cendrillon ou la petite pantoufle de verre. The popularity of his tale was due to his additions to the story, including the pumpkin, the fairy-godmother and the introduction of «glass» slippers.[28]
Plot:
- A wealthy widower has a beautiful young daughter, a girl of unparalleled kindness and sweet temper. The gentleman marries a proud and haughty woman as his second wife. She has two daughters, who are equally vain and selfish. The girl is forced into servitude by her stepmother, where she is made to work day and night doing menial chores. After the girl’s chores are done for the day, she curls up near the fireplace in an effort to stay warm. She often arises covered in ashes, giving rise to the mocking nickname «Cendrillon» (Cinderella) by her stepsisters. Cinderella bears the abuse patiently and does not tell her father, who would have scolded her.
- One day, the prince invites all the people in the land to a royal ball. The two stepsisters gleefully plan their wardrobes for the ball, and taunt Cinderella by telling her that maids aren’t invited to the ball.
- As the two stepsisters and the stepmother depart to the ball, Cinderella cries in despair. Her Fairy godmother magically appears and immediately begins to transform Cinderella from house servant to the young lady she was by birth, all in the effort to get Cinderella to the ball. She turns a pumpkin into a golden carriage, mice into horses, a rat into a coachman, and lizards into footmen. She then turns Cinderella’s rags into a beautiful jeweled gown, complete with a delicate pair of glass slippers. The Fairy Godmother tells her to enjoy the ball, but warns her that she must return before midnight, when the spells will be broken.
- At the ball, the entire court is entranced by Cinderella, especially the Prince. At this first ball, Cinderella remembers to leave before midnight. Back home, Cinderella graciously thanks her Fairy Godmother. She then innocently greets the two stepsisters, who had not recognized her earlier, and talk of nothing but the beautiful girl at the ball.
- Another ball is held the next evening, and Cinderella again attends with her Fairy Godmother’s help. The prince has become even more infatuated with the mysterious woman at the ball, and Cinderella in turn becomes so enchanted by him she loses track of time and leaves only at the final stroke of midnight, losing one of her glass slippers on the steps of the palace in her haste. The Prince chases her, but outside the palace, the guards see only a simple country girl leave. The prince pockets the slipper and vows to find and marry the girl to whom it belongs. Meanwhile, Cinderella keeps the other slipper, which does not disappear when the spell is broken.
- The prince’s herald tries the slipper on all the women in the kingdom. When the herald arrives at Cinderella’s home, the two stepsisters try in vain to win him over. Cinderella asks if she may try, but the two stepsisters taunt her. Naturally, the slipper fits perfectly, and Cinderella produces the other slipper for good measure. Cinderella’s stepfamily pleads for forgiveness, and Cinderella agrees. Cinderella had hoped her step-family would love her always. Cinderella marries the prince and forgives her two stepsisters, then marrying them off to two wealthy noblemen of the court. They all lived happily ever after.[29]
The first moral of the story is that beauty is a treasure, but graciousness is priceless. Without it, nothing is possible; with it, one can do anything.[30]
However, the second moral of the story mitigates the first one and reveals the criticism that Perrault is aiming at: That «without doubt it is a great advantage to have intelligence, courage, good breeding, and common sense. These, and similar talents come only from heaven, and it is good to have them. However, even these may fail to bring you success, without the blessing of a godfather or a godmother.»[30]
-
Charles Robinson illustrated Cinderella in the kitchen (1900), from Tales of Passed Times with stories by Charles Perrault.
-
Oliver Herford illustrated Cinderella with the Fairy Godmother, inspired by Perrault’s version.
-
Cinderella or Cendrillon in French. Gustave Doré’s illustration for Cendrillon, 1867
-
The fitting with the prince onlooking, illustration in Les Contes de Perrault by Gustave Doré, 1862
Aschenputtel, by the Brothers Grimm[edit]
Another well-known version was recorded by the German brothers Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm in the 19th century. The tale is called «Aschenputtel» [“The Little Ash Girl”] or «Cinderella» in English translations). This version is much more violent than that of Charles Perrault and Disney, in that Cinderella’s father has not died and the two stepsisters mutilate their feet to fit in the golden slipper. There is no fairy godmother in this version of the Brothers Grimm, but rather help comes from a wishing tree that the heroine planted on her deceased mother’s grave when she recites a certain chant. In the second edition of their collection (1819), the Brothers Grimm supplemented the original 1812 version with a coda in which the two stepsisters suffer a terrible punishment by the princess Cinderella for their cruelty.[31]
Summary[edit]
A plague infests a village, and a wealthy gentleman’s wife lies on her deathbed. She calls for her only daughter, and tells her to remain good and kind, as God would protect her. She then dies and is buried. The child visits her mother’s grave every day to grieve and a year goes by. The gentleman marries another woman with two older daughters from a previous marriage. They have beautiful faces and fair skin, but their hearts are cruel and wicked. The stepsisters steal the girl’s fine clothes and jewels and force her to wear rags. They banish her into the kitchen, and give her the nickname «Aschenputtel» («Ashfool»). She is forced to do all kinds of hard work from dawn to dusk for the sisters. The cruel sisters do nothing but mock her and make her chores harder by creating messes. However, despite all of it, the girl remains good and kind, and regularly visits her mother’s grave to cry and pray to God that she will see her circumstances improve.
One day the gentleman visits a fair, promising his stepdaughters gifts of luxury. The eldest asks for beautiful dresses, while the younger for pearls and diamonds. His own daughter merely begs for the first twig to knock his hat off on the way. The gentleman goes on his way, and acquires presents for his stepdaughters. While passing a forest he gets a hazel twig, and gives it to his daughter. She plants the twig over her mother’s grave, waters it with her tears and over the years, it grows into a glowing hazel tree. The girl prays under it three times a day, and a white bird always comes to her as she prays. She tells her wishes to the bird, and every time the bird throws down to her what she has wished for.
The king decides to proclaim a festival that will last for three days and invites all the beautiful maidens in that country to attend so that the prince can select one of them for his bride. The two sisters are also invited, but when Aschenputtel begs them to allow her to go with them into the celebration, the stepmother refuses because she has no decent dress nor shoes to wear. When the girl insists, the woman throws a dish of lentils into the ashes for her to pick up, guaranteeing her permission to attend the festival if she can clean up the lentils in two hours. When the girl accomplished the task in less than an hour with the help of a flock of white doves that came when she sang a certain chant, the stepmother only redoubles the task and throws down even a greater quantity of lentils. When Aschenputtel is able to accomplish it in a greater speed, not wanting to spoil her daughters’ chances, the stepmother hastens away with her husband and daughters to the celebration and leaves the crying stepdaughter behind.
Cinderella prays to the tree and the little birds provide her a beautiful dress. Art by Elenore Abbott.
The girl retreats to the graveyard and asks to be clothed in silver and gold. The white bird drops a gold and silver gown and silk shoes. She goes to the feast. The prince dances with her all the time, claiming her as his dance partner whenever a gentleman asks for her hand, and when sunset comes she asks to leave. The prince escorts her home, but she eludes him and jumps inside the estate’s pigeon coop. The father came home ahead of time and the prince asks him to chop the pigeon coop down, but Aschenputtel has already escaped from the back, to the graveyard to the hazel tree to return her fine clothes. The father finds her asleep in the kitchen hearth, and suspects nothing. The next day, the girl appears in grander apparel. The prince again dances with her the whole day, and when dark came, the prince accompanies her home. However, she climbs a pear tree in the back garden to escape him. The prince calls her father who chops down the tree, wondering if it could be Aschenputtel, but Aschenputtel was already in the kitchen when the father arrives home. The third day, she appears dressed in grand finery, with slippers of gold. Now the prince is determined to keep her, and has the entire stairway smeared with pitch. Aschenputtel, in her haste to elude the prince, loses one of her golden slippers on that pitch. The prince picks the slipper and proclaims that he will marry the maiden whose foot fits the golden slipper.
The next morning, the prince goes to Aschenputtel’s house and tries the slipper on the eldest stepsister. Since she will have no more need to go on foot when she will be queen, the sister was advised by her mother to cut off her toes to fit the slipper. While riding with the stepsister, the two magic doves from heaven tell the prince that blood drips from her foot. Appalled by her treachery, he goes back again and tries the slipper on the other stepsister. She cut off part of her heel to get her foot in the slipper, and again the prince is fooled. While riding with her to the king’s castle, the doves alert him again about the blood on her foot. He comes back to inquire about another girl. The gentleman tells him that his dead wife left a «dirty little Cinderella» in the house, omitting to mention that she is his own daughter, and that she is too filthy to be seen, but the prince asks him to let her try on the slipper. Aschenputtel appears after washing clean her face and hands, and when she puts on the slipper, which fitted her like a glove, the prince recognizes her as the stranger with whom he has danced at the festival, even before trying it. To the horror of the stepmother and the two limping sisters, their merely servant-girl had won without any subterfuge. The prince put Aschenputtel before him on his horse and rode off to the palace. While passing the hazel tree the two magic doves from heaven declare Aschenputtel as the true bride of the prince, and remained on her shoulders, one on the left and the other on the right.
In a coda added in the second edition of 1819, during Aschenputtel’s royal wedding, the false stepsisters had hoped to worm their way into her favour as the future queen, but this time they don’t escape their princess’ silent rage, which she kept to herself until that day. As she walks down the aisle with her stepsisters as her bridesmaids, Aschenputtel’s doves fly off her shoulders and strike the two stepsisters’ eyes, one in the left and the other in the right. It is their last chance of redemption, but since they are desperate to win the new princess’ affections, they don’t give up and go through the ceremony, so when the wedding comes to an end, and Aschenputtel and her beloved prince march out of the church, her doves fly again, promptly striking the remaining eyes of the two evil stepsisters blind, a truly awful comeuppance they have to endure. Then, finally free from abuse and enslavement, Aschenputtel leaves her family forever to be a princess with her prince, while the stepsisters live their lives as blind beggars, as her father and stepmother are in disgrace.[32]
Plot variations and alternative tellings[edit]
Folklorists have long studied variants on this tale across cultures. In 1893, Marian Roalfe Cox, commissioned by the Folklore Society of Britain, produced Cinderella: Three Hundred and Forty-Five Variants of Cinderella, Catskin and, Cap o’Rushes, Abstracted and Tabulated with a Discussion of Medieval Analogues and Notes. Further morphology studies have continued on this seminal work.[33]
Joseph Jacobs has attempted to reconstruct the original tale as The Cinder Maid by comparing the common features among hundreds of variants collected across Europe.[34] The Aarne–Thompson–Uther system classifies Cinderella as type 510A, «Persecuted Heroine». Others of this type include The Sharp Grey Sheep; The Golden Slipper; The Story of Tam and Cam; Rushen Coatie; The Wonderful Birch; Fair, Brown and Trembling; and Katie Woodencloak.[35][9]: 24–26
The magical help[edit]
International versions lack the fairy godmother present in the famous Perrault’s tale. Instead, the donor is her mother, incarnated into an animal (if she is dead) or transformed into a cow (if alive). In other versions, the helper is an animal, such as a cow, a bull, a pike, or a saint or angel.[36] The bovine helper appears in some Greek versions, in «the Balkan-Slavonic tradition of the tale», and in some Central Asian variants. The mother-as-cow is killed by the heroine’s sisters, her bones gathered and from her grave the heroine gets the wonderful dresses.[37]
Africanist Sigrid Schmidt stated that «a typical scene» in Kapmalaien (Cape Malays) tales is the mother becoming a fish, being eaten in fish form, the daughter burying her bones and a tree sprouting from her grave.[38]
Professor Gražina Skabeikytė-Kazlauskienė recognizes that the fish, the cow, even a female dog (in other variants), these animals represent «the [heroine’s] mother’s legacy».[39] Jack Zipes, commenting on a Sicilian variant, concluded much the same: Cinderella is helped by her mother «in the guise of doves, fairies, and godmothers».[40] In his notes to his own reconstruction, Joseph Jacobs acknowledged that the heroine’s animal helper (e.g., cow or sheep) was «clearly identified with her mother», as well as the tree on Cinderella’s mother’s grave was connected to her.[41]
Villains[edit]
Although many variants of Cinderella feature the wicked stepmother, the defining trait of type 510A is a female persecutor: in Fair, Brown and Trembling and Finette Cendron, the stepmother does not appear at all, and it is the older sisters who confine her to the kitchen. In other fairy tales featuring the ball, she was driven from home by the persecutions of her father, usually because he wished to marry her. Of this type (510B) are Cap O’ Rushes, Catskin, All-Kinds-of-Fur, and Allerleirauh, and she slaves in the kitchen because she found a job there.[42] In Katie Woodencloak, the stepmother drives her from home, and she likewise finds such a job.[43]
In La Cenerentola, Gioachino Rossini inverted the sex roles: Cenerentola is mistreated by her stepfather. (This makes the opera Aarne-Thompson type 510B.) He also made the economic basis for such hostility unusually clear, in that Don Magnifico wishes to make his own daughters’ dowries larger, to attract a grander match, which is impossible if he must provide a third dowry. Folklorists often interpret the hostility between the stepmother and stepdaughter as just such a competition for resources, but seldom does the tale make it clear.[44]
In some retellings, at least one stepsister is somewhat kind to Cinderella and second guesses the Stepmother’s treatment. This is seen in Ever After, the two direct-to-video sequels to Walt Disney’s 1950 film, and the 2013 Broadway musical.
-
The stepsisters, 1865 edition of Cinderella
-
Cinderella Dressing Her Sisters, Aunt Friendly’s Gift, 1890
-
Stepsisters from Journeys through Bookland, 1922
-
The stepsisters, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
Ball, ballgown, and curfew[edit]
The number of balls varies, sometimes one, sometimes two, and sometimes three. The fairy godmother is Perrault’s own addition to the tale.[45] The person who aided Cinderella (Aschenputtel) in the Grimms’s version is her dead mother. Aschenputtel requests her aid by praying at her grave, on which a tree is growing. Helpful doves roosting in the tree shake down the clothing she needs for the ball. This motif is found in other variants of the tale as well, such as in the Finnish The Wonderful Birch. Playwright James Lapine incorporated this motif into the Cinderella plotline of the musical Into the Woods. Giambattista Basile’s Cenerentola combined them; the Cinderella figure, Zezolla, asks her father to commend her to the Dove of Fairies and ask her to send her something, and she receives a tree that will provide her clothing. Other variants have her helped by talking animals, as in Katie Woodencloak, Rushen Coatie, Bawang Putih Bawang Merah, The Story of Tam and Cam, or The Sharp Grey Sheep—these animals often having some connection with her dead mother; in The Golden Slipper, a fish aids her after she puts it in water. In «The Anklet», it’s a magical alabaster pot the girl purchased with her own money that brings her the gowns and the anklets she wears to the ball. Gioachino Rossini, having agreed to do an opera based on Cinderella if he could omit all magical elements, wrote La Cenerentola, in which she was aided by Alidoro, a philosopher and formerly the Prince’s tutor.
The midnight curfew is also absent in many versions; Cinderella leaves the ball to get home before her stepmother and stepsisters, or she is simply tired. In the Grimms’ version, Aschenputtel slips away when she is tired, hiding on her father’s estate in a tree, and then the pigeon coop, to elude her pursuers; her father tries to catch her by chopping them down, but she escapes.[46]
-
Fairy Godmother, Walter Crane, 1897
-
Cinderella and the Fairy Godmother by Kate Abelmann, 1913
-
Ballgown Cinderella, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
-
At the ball, 1865 edition
-
Hurrying out, 1865 edition
-
Identifying item[edit]
The slipper left behind, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
The glass slipper is unique to Charles Perrault’s version and its derivatives; in other versions of the tale it may be made of other materials (in the version recorded by the Brothers Grimm, German: Aschenbroedel and Aschenputtel, for instance, it is gold) and in still other tellings, it is not a slipper but an anklet, a ring, or a bracelet that gives the prince the key to Cinderella’s identity. In Rossini’s opera «La Cenerentola» («Cinderella»), the slipper is replaced by twin bracelets to prove her identity. In the Finnish variant The Wonderful Birch the prince uses tar to gain something every ball, and so has a ring, a circlet, and a pair of slippers. Some interpreters, perhaps troubled by sartorial impracticalities, have suggested that Perrault’s «glass slipper» (pantoufle de verre) had been a «squirrel fur slipper» (pantoufle de vair) in some unidentified earlier version of the tale, and that Perrault or one of his sources confused the words; however, most scholars believe the glass slipper was a deliberate piece of poetic invention on Perrault’s part.[47] [c] Nabokov has Professor Pnin assert as fact that «Cendrillon’s shoes were not made of glass but of Russian squirrel fur – vair, in French».[49] The 1950 Disney adaptation takes advantage of the slipper being made of glass to add a twist whereby the slipper is shattered just before Cinderella has the chance to try it on, leaving her with only the matching slipper with which to prove her identity.
Revelation[edit]
In many variants of the tale, the prince is told that Cinderella can not possibly be the one, as she is too dirty and ragged. Often, this is said by the stepmother or stepsisters. In the Grimms’ version, both the stepmother and the father urge it.[50] The prince nevertheless insists on her trying. Cinderella arrives and proves her identity by fitting into the slipper or other item (in some cases she has kept the other).
-
Stepsister trying the slipper, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
-
The prince pleading for Cinderella to try the shoe, illustration in The fairy tales of Charles Perrault by Harry Clarke, 1922
-
Trying on the Slipper, Sarah Noble Ives, c. 1912
-
Cinderella trying on the slipper, 1865 edition
-
Dean & Son’s Cinderella «surprise book» with moving images, c. 1875
-
Illustration by Carl Offterdinger, late 19th century
-
Finding that the slipper fits, educational poster by Hans Printz, 1905
-
Trying the slipper, Askepot og Prinsen
Conclusion[edit]
According to Korean scholarship, East Asian versions of Cinderella «typically» continue as the heroine’s stepmother replaces the Cinderella-like character for her own daughter,[clarification needed] while the heroine goes through a cycle of transformations.[51] Such tales continue the fairy tale into what is in effect a second episode.
In The Thousand Nights and A Night, in a tale called «The Anklet»,[52] the stepsisters make a comeback by using twelve magical hairpins to turn the bride into a dove on her wedding night. In The Wonderful Birch, the stepmother, a witch, manages to substitute her daughter for the true bride after she has given birth.
-
Part two of Dean & Son’s Cinderella, 1875
-
Happy ending
-
In the German version the stepsisters’ eyes get pecked out by the princess’ birds, her loyal friends and minions
Works based on the Cinderella story[edit]
Works based on the story of Cinderella include:
Opera and ballet[edit]
- Cendrillon (1749) by Jean-Louis Laruette
- Cendrillon (1810) by Nicolas Isouard, libretto by Charles-Guillaume Étienne
- Agatina, o la virtù premiata [it] (1814) by Stefano Pavesi
- La Cenerentola (1817) by Gioachino Rossini
- Cinderella (1893) by Baron Boris Vietinghoff-Scheel
- Cendrillon (1894–95) by Jules Massenet, libretto by Henri Caïn
- Aschenbrödel (1901) by Johann Strauss II, adapted and completed by Josef Bayer[53]
- Cinderella (1901–02) by Gustav Holst
- La Cenerentola (1902) by Ermanno Wolf-Ferrari
- Cendrillon (1904) by Pauline García-Viardot
- Aschenbrödel (1905) by Leo Blech, libretto by Richard Batka
- Das Märchen vom Aschenbrödel (1941) by Frank Martin
- Zolushka or Cinderella (1945) by Sergei Prokofiev
- La Cenicienta (1966) by Jorge Peña Hen
- Cinderella, a «pantomime opera» (1979) by Peter Maxwell Davies
- Cinderella (1980) by Paul Reade
- Cinderella (1997) by Matthew Bourne taking place in 1940 London using the music of Sergei Prokofiev
- My First Cinderella (2013) directed by George Williamson and Loipa Araújo
Theatre[edit]
In 1804 Cinderella was presented at Drury Lane Theatre, London, described as «A new Grand Allegorical Pantomimic Spectacle» though it was very far in style and content from the modern pantomime. However, it included notable clown Joseph Grimaldi playing the part of a servant called Pedro, the antecedent of today’s character Buttons.[54] In 1820 Harlequin and Cinderella at the Theatre Royal, Covent Garden had much of the modern story (taken from the opera La Cenerentola) by Rossini but was a Harlequinade again featuring Grimaldi.[54] In 1830 Rophino Lacy used Rossini’s music but with spoken dialogue in a comic opera with many of the main characters: the Baron, the two stepsisters and Pedro the servant all as comic characters, plus a Fairy Queen instead of a magician.[54] However it was the conversion of this via burlesque and rhyming couplets by Henry Byron that led to what was effectively the modern pantomime in both story and style at the Royal Strand Theatre in 1860: Cinderella! Or the Lover, the Lackey, and the Little Glass Slipper.[54]
In the traditional pantomime version the opening scene takes place in a forest with a hunt in progress; here Cinderella first meets Prince Charming and his «right-hand man» Dandini, whose name and character come from Gioachino Rossini’s opera (La Cenerentola). Cinderella mistakes Dandini for the Prince and the Prince for Dandini. Her father, Baron Hardup, is under the thumb of his two stepdaughters, the Ugly sisters, and has a servant, Cinderella’s friend Buttons. (Throughout the pantomime, the Baron is continually harassed by the Broker’s Men (often named after current politicians) for outstanding rent. The Fairy Godmother must magically create a coach (from a pumpkin), footmen (from mice), a coach driver (from a frog), and a beautiful dress (from rags) for Cinderella to go to the ball. However, she must return by midnight, as it is then that the spell ceases.
Musicals[edit]
- Cinderella by Rodgers and Hammerstein was produced for television three times and staged live in various productions. A version ran in 1958 at the London Coliseum with a cast including Tommy Steele, Yana, Jimmy Edwards, Kenneth Williams and Betty Marsden. This version was augmented with several other Rodgers and Hammerstein’s songs plus a song written by Tommy Steele, «You and Me». In 2013, a Broadway production opened, with a new book by Douglas Carter Beane, and ran for 770 performances. In the acclaimed 2022 VTT production of Cinderella, Naomi Infeld will be playing Anastasia.
- Mr. Cinders, a musical, opened at the Adelphi Theatre, London in 1929 and received a film version in 1934.
- Cindy, a 1964 Off-Broadway musical, was composed by Johnny Brandon and has had many revivals.
- Into the Woods, a musical with music and lyrics by Stephen Sondheim and book by James Lapine, includes Cinderella as one of the many fairy-tale characters in the plot. This is partly based on the Grimm Brothers’ version of «Cinderella», including the enchanted birds, mother’s grave, three balls, and mutilation and blinding of the stepsisters. It opened on Broadway in 1987 and has had many revivals. In this show, Cinderella is actually the Baker’s ex-sister-in-law, since she married her prince and her prince’s brother married Rapunzel, and the baker is Rapunzel’s brother. After she divorced the prince she became Rapunzel and the Baker’s ex-sister-in-law.
- Cinderella is a musical composed by Andrew Lloyd Webber that premiered in the West End in 2021.
Films and television[edit]
Over the decades, hundreds of films have been made that are either direct adaptations from Cinderella or have plots loosely based on the story.
Animation[edit]
- Aschenputtel (1922), a silhouette shadow play short by Lotte Reiniger. The short silent film uses exaggerated figures and has no background, which creates a stark look. The film shows Aschenputtel’s step-sisters graphically hacking their feet off to fit into the glass slipper.[55]
- Cinderella (1922), an animated Laugh-O-Gram produced by Walt Disney, first released on 6 December 1922. This film was about seven and half minutes long.[56]
- Cinderella (1925), an animated short film directed by Walter Lantz, produced by Bray Studios Inc.[57]
- A Kick for Cinderella (1925), an animated short film directed by Bud Fisher, in the Mutt and Jeff series of comic strip adaptations.[57]
- Cinderella Blues (1931), a Van Beuren animated short film featuring a feline version of the Cinderella character.
- Poor Cinderella (1934), Fleischer Studios’ first color cartoon and only appearance of Betty Boop in color during the Fleischer era.
- A Coach for Cinderella (1937) – Jam Handy, Cervolet advert[58]
- A Ride for Cinderella (1937) – Jam Handy, Cervolet advert[58]
- Cinderella Meets Fella (1938), a Merrie Melodies animated short film featuring Egghead, the character who would eventually evolve into Elmer Fudd, as Prince Charming.[59]
- Cinderella (1950), a Walt Disney animated feature released on 15 February 1950, now considered one of Disney’s classics as well as the most well-known film adaptation, including incorporating the titular character as a Disney Princess and its franchise.
- Cinderella II: Dreams Come True (2002), a direct-to-video sequel to the 1950 film.
- Cinderella III: A Twist in Time (2007), another direct-to-video sequel to the previous film.
- Ancient Fistory (1953) a Popeye parody animated short film.
- Señorella and the Glass Huarache (1964), a Looney Tunes animated short film that transplants the story to a Mexican setting.
- Festival of Family Classics (1972-73), episode Cinderella, produced by Rankin/Bass and animated by Mushi Production.
- World Famous Fairy Tale Series (Sekai meisaku dōwa) (1975-83) has a 9-minute adaptation.
- Manga Sekai Mukashi Banashi (1976-79), 10-minute adaptation.
- Cinderella (1979), an animated short film based on Charles Perrault’s version of the fairy tale. It was produced by the Soyuzmultfilm studio.
- «Cinderella? Cinderella!» (1986), an episode of Alvin & the Chipmunks. With Brittany of The Chipettes playing the role of Cinderella and Alvin playing the role of Prince Charming.
- My Favorite Fairy Tales (Sekai Dōwa Anime Zenshū) (1986), an anime television anthology, has a 12-minute adaptation.
- Grimm’s Fairy Tale Classics (1987-89) an anime television series based on Grimm’s stories, as two half-hour episodes.
- Funky Fables (Ponkikki Meisaku World) (1988-90), features an adaptation of Cinderella.
- Britannica’s Tales Around the World (1990-91), features Perrault’s Cinderella along with two other variants of the story.
- Cinderella (1994), a Japanese-American direct-to-video film by Jetlag Productions.
- World Fairy Tale Series (Anime sekai no dōwa) (1995), anime television anthology produced by Toei Animation, has half-hour adaptation.
- Cinderella Monogatari (The Story of Cinderella) (1996), anime television series produced by Tatsunoko Production.
- Cendrillon au Far West (2012), French/Belgian film set in the wild western age, written and directed by Pascal Hérold
- Cinderella and the Secret Prince (2018), American animated film directed by Lynne Southerland.
- Cinderella the Cat (2017), Italian animated film directed by Alessandro Rak
Non-English language live-action films and TV[edit]
Cinderella at the ball in Soviet film (1947)
- Cinderella (1899), the first film version, produced in France by Georges Méliès, as «Cendrillon».
- Mamele (1938) a Molly Picon vehicle made by the prewar Warsaw Yiddish film industry taking place in contemporary Lodz.
- Cinderella (1947), a Soviet film based on the screenplay by Evgeny Schwartz, with Yanina Zhejmo in the leading role. Shot in black-and-white, it was colorized in 2009.
- Cinderella (1955), German film
- Sandalyas ni Zafira (lit. ‘Sandals of Zafira’, 1965), a Filipino fantasy film partially based on Cinderella and starring Lyn D’Amour as Princess Zafira
- Sinderella Kül Kedisi (1971), a Turkish fantasy film based on Cinderella and starring Zeynep Değirmencioğlu as Cinderella.
- Three Wishes for Cinderella (Tři oříšky pro Popelku) (1973), a Czechoslovakian/East German fairy tale film starring Libuše Šafránková as Cinderella and Pavel Trávníček as Prince.[60] Frequently shown, especially at Christmas time, in several European countries.
- Rani Aur Lalpari (lit. ‘Rani and the Red Fairy’), a 1975 Indian children’s fantasy film by Ravikant Nagaich features Cinderella as one of the characters — where she is portrayed by Neetu Singh.[61]
- Cinderella 4×4. Everything starts with desire (Zolushka 4×4. Vsyo nachinayetsya s zhelaniy) (2008), a Russian modernization featuring Darya Melnikova
- Cinderella (2006), a Korean horror film
- Cinderella’s Stepsister (2010), a Korean television series
- Aschenputtel (2010 film) [de], a German film
- Aschenputtel (2011 film) [de], another German film
- Aik Nayee Cinderella (2013), a Pakistani modernization serial aired on Geo TV featuring Maya Ali and Osman Khalid Butt
English language live-action feature films[edit]
- Cinderella (1911) silent film starring Florence La Badie[62]
- Cinderella (1914), a silent film starring Mary Pickford
- The Glass Slipper (1955), feature film with Leslie Caron and Michael Wilding
- The Slipper and the Rose (1976), a British Sherman Brothers musical film starring Gemma Craven and Richard Chamberlain.
- Into the Woods (2014), a live-action fairy-tale-themed adaptation of the above-mentioned homonymous musical, in which Anna Kendrick’s Cinderella is a central character.
- Cinderella (2015), a live-action retelling of the 1950 animated Disney film starring Lily James as Cinderella, Cate Blanchett as Lady Tremaine, Cinderella’s stepmother, Richard Madden as Kit/Prince Charming and Helena Bonham Carter as the Fairy Godmother. It is essentially a live-action reimagining of the 1950 animated film.
- Cinderella (2021), a live-action film musical starring Camila Cabello as Cinderella, Idina Menzel as Cinderella’s stepmother, Nicholas Galitzine as the Prince, and Billy Porter as the Fairy Godmother.
Modernizations and parodies
- Ella Cinders (1926), a modern tale starring Colleen Moore, based on a comic strip by William M. Conselman and Charles Plumb, inspired by Charles Perrault’s version.
- First Love (1939), a musical modernization with Deanna Durbin and Robert Stack.
- Cinderfella (1960), Cinderfella’s (Jerry Lewis) fairy godfather (Ed Wynn) helps him escape from his wicked stepmother (Judith Anderson) and stepbrothers.
- Ever After (1998), starring Drew Barrymore, a post-feminist, historical fiction take on the Cinderella story.
- Ella Enchanted (2004), a fantasy retelling featuring Anne Hathaway, which is based on the 1997 novel of the same name.
- A Cinderella Story (2004), a modernization featuring Hilary Duff and Chad Michael Murray
- Another Cinderella Story (2008), a modernization featuring Selena Gomez and Drew Seeley
- A Cinderella Story: Once Upon a Song (2011), a modernization featuring Lucy Hale and Freddie Stroma
- A Cinderella Story: If the Shoe Fits (2016), a modernization featuring Sofia Carson and Thomas Law
- A Cinderella Story: Christmas Wish (2019), a modernization featuring Laura Marano and Gregg Sulkin
- A Cinderella Story: Starstruck (2021), a modernization featuring Bailee Madison and Michael Evans Behling
- Elle: A Modern Cinderella Tale (2010), a modernization featuring Ashlee Hewitt and Sterling Knight
English language live-action TV films and series[edit]
- Cinderella (1957), a musical adaptation by Rodgers and Hammerstein written for television and starring Julie Andrews as Cinderella, featuring Jon Cypher, Kaye Ballard, Alice Ghostley, and Edie Adams (originally broadcast in color, but only black-and-white kinescopes survive).
- Cinderella (1965), a second production of the Rodgers and Hammerstein musical, starring 18-year-old Lesley Ann Warren in the leading role, and featuring Stuart Damon as the Prince, with Ginger Rogers, Walter Pidgeon, and Celeste Holm (filmed in color and broadcast annually for 10 years).
- Hey, Cinderella! (1969), a television adaptation featuring The Muppets.
- Cindy (1978), This version of the Cinderella tale with an all-black cast has Cinderella, who wants to marry a dashing army officer, finding out that her father, who she thought had an important job at a big hotel, is actually the men’s room attendant. Her wicked stepmother finds out, too, and complications ensue. Starred Charlayne Woodard.
- In 1985, Shelley Duvall produced a version of the story for Faerie Tale Theatre.
- The Charmings (1987), a spoof of Cinderella appears in the episode «Cindy’s Back In Town» where Cinderella, portrayed by Kim Johnston Ulrich, makes a play for Snow White’s husband Prince Charming.
- Into the Woods (1989), a film of the original 1987 Broadway production of the Stephen Sondheim musical.
- Cinderella (1997), third production of the Rodgers and Hammerstein musical, this time starring Brandy as Cinderella, Whitney Houston as the Fairy Godmother, Bernadette Peters as Cinderella’s evil stepmother, Jason Alexander as Lionel the valet and Whoopi Goldberg as the Queen. Remake of the 1957 and 1965 TV films.
- Cinderella, a British TV modernization featuring Marcella Plunkett as Cinderella, Kathleen Turner as the stepmother and Jane Birkin as the fairy godmother.
- The 10th Kingdom (2000) is a TV miniseries featuring Cinderella as a major character.
- Confessions of an Ugly Stepsister (2002), TV movie for The Wonderful World of Disney by writer Gene Quintano and director Gavin Millar, based on the book of the same name, focusing on the point of view of one of the step-sister
- Once Upon a Time (2011), features Cinderella as a recurring character, played by Jessy Schram who made a deal with Rumplestiltskin who killed her fairy godmother right in front of her. In 2016, more of the story is shown in which Ashley, Cinderella’s real-world counterpart, discovers her stepsister wanted to marry the footman rather than the prince. A different Cinderella in season 7, played by Dania Ramirez, went to the ball to kill the prince, not meet him.
Television parodies and modernizations
- The story was retold as part of the episode «Grimm Job» of the American animated TV series Family Guy (season 12, episode 10), with Lois as Cinderella, Peter as Prince Charming, Mayor West as the fairy godmother, Lois’s mother as the wicked step-mother, and Meg and Stewie as the step-sisters.
- Rags (2012), a TV musical gender switched inversion of the Cinderella story that stars Keke Palmer and Max Schneider.
- Sesame Street special «Cinderelmo» and the Magic Adventures of Mumfie episode «Scarecrowella» both feature a male protagonist playing the Cinderella role.
- The My Little Pony first season finale «The Best Night Ever» parodies several key parts of the Cinderella story.
- In Carry On Christmas (1969), which was one of the Carry On Christmas Specials on TV, there is a sketch spoofing the Cinderella story. Barbara Windsor plays Cinderella and Terry Scott and Peter Butterworth play the ugly stepsisters.
Books[edit]
- Cinderella (1697), Charles Perrault
- Cinderella (1919), Charles S. Evans and illustrated by Arthur Rackham
- Ella Enchanted (1997), by Gail Carson Levine
- Raisel’s Riddle (1999), Erica Silverman and illustrated by Susan Gaber
- Confessions of an Ugly Stepsister (1999), by Gregory Maguire
- Just Ella (1999), by Margaret Peterson Haddix
- Adelita: A Mexican Cinderella Story (2004), Tomie dePaola
- «Princess of Glass» (2010) by Jessica Day George is loosely based on the fairytale.
- Cinder (2012) by Marissa Meyer, a sci-fi retelling of the classic story
- The Stepsister’s Tale (2014) by Tracy Barrett
- Geekerella (2017) by Ashley Poston
- Stepsister (2019) by Jennifer Donnelly
- So This Is Love: A Twisted Tale (2020) by Elizabeth Lim
- Cinderella is Dead (2020), by Kalynn Bayron
Video games[edit]
- Yakuza 0, referenced in Goro Majima’s song 24-Hour Cinderella.
- Persona 5 Royal, where Kasumi’s Persona is based on Cinderella and named after her French translation, Cendrillon.
See also[edit]
- Rhodopis
- Eteriani
- Cinderella complex
- Cinderella effect
- Marriage plot
- Ye Xian
- Bawang Merah Bawang Putih
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Italian: Cenerentola; French: Cendrillon; German: Aschenputtel.
- ^ There were three pharaohs called Psammetichus, and it unclear which one Aelian had in mind.
- ^ Glass Slippers, —An article hitherto only used to adorn the foot of Cinderella in a fairy tale, may now be seen in that extensive repository of discoveries and improvements, the Polytechnic Institution, Regent-street. We allude to a very curious pair of ladies’ dress-shoes, fabricated from glass, not less flexible than leather or satin, equally light, and far more durable, to judge from the solidity of their texture.[48]
References[edit]
Notes
- ^ a b Amelia Carruthers (24 September 2015). Cinderella – And Other Girls Who Lost Their Slippers (Origins of Fairy Tales). ISBN 9781473370111.
- ^ a b Zipes, Jack (2001). The Great Fairy Tale: From Straparola and Basile to the Brothers Grimm. W. W. Norton & Co. p. 444. ISBN 978-0-393-97636-6.
- ^ a b Dundes, Alan. Cinderella, a Casebook. Madison, Wis: University of Wisconsin Press, 1988.
- ^ a b Roger Lancelyn Green: Tales of Ancient Egypt, Penguin UK, 2011, ISBN 978-0-14-133822-4, chapter «The Land of Egypt»
- ^ a b Bottigheimer, Ruth. (2008). «Before Contes du temps passe (1697): Charles Perrault’s Griselidis, Souhaits and Peau«. The Romantic Review, Volume 99, Number 3. pp. 175–89
- ^ Hansen, William (2017). The Book of Greek & Roman Folktales, Legends & Myths. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. pp. 86–87. ISBN 9780691170152.
- ^ Strabo: «The Geography», book 17, 33
- ^ Aelian: «Various History», book 13, chapter 33
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Anderson, Graham (2000). Fairytale in the Ancient World. New York City and London, England: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-23702-4.
- ^ Herodot, «The Histories», book 2, chapters 134–135
- ^ Grimm, Jacob & Grimm, Wilhelm; Taylor, Edgar; Cruikshank, George (illustrator). Grimm’s Goblins: Grimm’s Household Stories. London: R. Meek & Co.. 1877. p. 294.
- ^ Baring-Gould, Sabine. A Book of Fairy Tales. [2d ed.] London: Methuen. 1895. pp. 237–238.
- ^ Ben-Amos, D. «Straparola: The Revolution That Was Not». In: The Journal of American Folklore. Vol. 123. No. 490 (Fall 2010). pp. 439–440. JSTOR [1]
- ^ Anderson, Graham. Fairytale in the Ancient World. Routledge. 2000. pp. 29–33. ISBN 0-203-18007-0
- ^ «Multiple Births in Legend and Folklore». www.pitt.edu. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ^ «Ċiklemfusa» (PDF). Rakkonti. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ «Ċiklemfusa». Filmat mill-Aġenzija tal-Litteriżmu. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ Attard, Anton F. (2019). «Book Review: The Maltese Cinderella and the Women’s Storytelling Tradition (Veronica Veen)» (PDF). The Gozo Observer (39).
- ^ a b c d Beauchamp, Fay. «Asian Origins of Cinderella: The Zhuang Storyteller of Guangxi» (PDF). Oral Tradition. 25 (2): 447–496. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ^ Ko, Dorothy (2002). Every Step a Lotus: Shoes for Bound Feet. University of California Press. pp. 26–27. ISBN 978-0520232839.
- ^ «A Cinderella Tale from Vietnam: the Story of Tam and Cam». www.furorteutonicus.eu. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- ^ Leclère, Adhémard; Feer, Léon. Cambodge: Contes et légendes. Librairie Émile Bouillon. 1895. pp. 70–90.
- ^ Leclère, Adhémard; Feer, Léon. Cambodge: Contes et légendes. Librairie Émile Bouillon. 1895. p. 91.
- ^ Leclère, Adhémerd. «Le Conte de Cendrillion chez les Cham». In: Revue de Traditions Populaires. Jun/1898. pp. 311–337.
- ^ Mayer, Fanny Hagin. «Reviewed Work: 越後のシンデレラ by 水沢謙一» [Echigo no Shinderera by Kenichi Mizusawa]. In: Asian Folklore Studies 24, no. 1 (1965): 151-153. Accessed July 25, 2021. doi:10.2307/1177604.
- ^ Ulrich Marzolph, Richard van Leeuwen, Hassan Wassouf (2004). The Arabian Nights Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 4. ISBN 1-57607-204-5.
- ^ Basile, Giambattista (1911). Stories from Pentamerone, London: Macmillan & Co., translated by John Edward Taylor. Chapter 6. See also «Il Pentamerone: Cenerentola» Archived 23 November 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ A modern edition of the original French text by Perrault is found in Charles Perrault, Contes, ed. Marc Soriano (Paris: Flammarion, 1989), pp. 274–79.
- ^ The annotated classic fairy tales. Tatar, Maria, 1945– (1st ed.). New York: Norton. 2002. ISBN 0393051633. OCLC 49894271.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b «Perrault: Cinderella; or, The Little Glass Slipper». Pitt.edu. 8 October 2003. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ Grimm, Jacob and Wilhelm; Zipes, Jack; Deszö, Andrea. «CINDERELLA». In: The Original Folk and Fairy Tales of the Brothers Grimm: The Complete First Edition. Princeton; Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2014. pp. 69–77. Accessed 29 April 2021.
- ^ Aschenputtel, included in Household Stories by the Brothers Grimm, translated by Lucy Crane, at Project Gutenberg
- ^ «If The Shoe Fits: Folklorists’ criteria for #510»
- ^ Jacobs, Joseph (1916). Europa’s Fairy Book. G. P. Putnam’s sons. pp. 1–12. ISBN 9786057876720.
- ^ Heidi Anne Heiner, «Tales Similar to Cinderella»
- ^ Garner, Emelyn Elizabeth. Folklore From the Schoharie Hills, New York. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan press, 1937. p. 130.
- ^ Kaplanoglou, Marianthi. «“Stachtopouta» and «Nifitsa»: Spinning Tales in Relation With Feminine Productivity and Dowry Practices of Modern Greece». In: Estudis De Literatura Oral Popular [Studies in Oral Folk Literature]. [en línia], 2014, Núm. 4, pp. 67, 69. https://www.raco.cat/index.php/ELOP/article/view/304851 [Consulta: Consulta: 13 March 2021].
- ^ Schmidt, Sigrid. «Reviewed Work: The World and the Word by Nongenile Masithathu Zenani, Harold Scheub». In: Anthropos 90, no. 1/3 (1995): 312. Accessed 18 April 2021. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40463177.
- ^ Skabeikytė-Kazlauskienė, Gražina. Lithuanian Narrative Folklore: Didactical Guidelines. Kaunas: Vytautas Magnus University. 2013. p. 14. ISBN 978-9955-21-361-1.
- ^ Pitrè, Giuseppe; Zipes, Jack David; Russo, Joseph. The collected Sicilian folk and fairy tales of Giuseppe Pitrè. New York: Routledge, 2013 [2009]. p. 845. ISBN 9781136094347.
- ^ Jacobs, Joseph. European Folk and Fairy Tales. New York, London: G. P. Putnam’s sons. 1916. pp. 222, 227.
- ^ Heidi Anne Heiner, «Tales Similar to Donkeyskin»
- ^ «Katie Woodencloak (Norwegian Version of Cinderella)». 5 April 2016. Archived from the original on 5 April 2016.
- ^ Marina Warner, From the Beast to the Blonde: On Fairy Tales And Their Tellers, p 213-4 ISBN 0-374-15901-7
- ^ Jane Yolen, p 23, Touch Magic ISBN 0-87483-591-7
- ^ Maria Tatar, The Annotated Brothers Grimm, p 116 W. W. Norton & company, London, New York, 2004 ISBN 0-393-05848-4
- ^ Maria Tatar, p 28, The Annotated Classic Fairy Tales, ISBN 0-393-05163-3
- ^ «Glass Slippers». Bell’s Weekly Messenger. 25 November 1838. p. 4.
- ^ Pnin, chapter 6
- ^ Maria Tatar, The Annotated Brothers Grimm, p 126-8 W. W. Norton & company, London, New York, 2004 ISBN 0-393-05848-4
- ^ The National Folk Museum of Korea (South Korea). Encyclopedia of Korean Folk Literature: Encyclopedia of Korean Folklore and Traditional Culture Vol. III. 길잡이미디어, 2014. p. 311.
- ^ Mardrus, Joseph-Charles; Powys Mathers (June 1987). The book of the Thousand Nights and One Night. Vol. 4. London and New York: Routledge. pp. 191–194. ISBN 0-415-04543-6.
- ^ «Josef Bayer (1852–1913)». www.johann-strauss.org.uk. The Johann Strauss Society of Great Britain. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ^ a b c d Clinton-Baddeley, V. C. (1963). Some Pantomime Pedigrees. The Society for Theatrical Research. pp. 9–11.
- ^ Freyberger, Regina (2009). Märchenbilder—Bildermärchen. Athena. p. 453. ISBN 9783898963503.
- ^ Merrill, Russell; Kaufmann, J. B. (2007). Walt Disney’s Silly Symphonies: A Companion to the Classic Cartoon Series. Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-8886155274.
- ^ a b «Fairy Tale Flappers: Animated Adaptations of Little Red and Cinderella (1922–1925)». governmentcheese.ca.
- ^ a b «Nicky Nome Rides Again |». cartoonresearch.com.
- ^ «YouTube». YouTube. Archived from the original on 17 October 2013. Retrieved 23 September 2013.
- ^ «Three wishes for Cinderella (1973)». Imdb.com.
- ^ Rani Aur Lalpari. iTunes.
- ^ Nicholls, George; La Badie, Florence (1911), Cinderella, OCLC 422761848, retrieved 25 May 2020
Further reading[edit]
- Bascom, William. «Cinderella in Africa». In: Journal of the Folklore Institute 9, no. 1 (1972): 54-70. Accessed July 12, 2021. doi:10.2307/3814022.
- Čechová, Mariana. «RHIZOMATIC CHARACTER OF TRANS-CULTURAL AND TRANS-TEMPORAL MODE OF LITERARY COMMUNICATION». In: World Literature Studies Vol. 6 (23), n. 3 (2014): 111–127.
- Chen, Fan Pen Li. «Three Cinderella Tales from the Mountains of Southwest China». In: Journal of Folklore Research 57, no. 2 (2020): 119–52. Accessed 17 November 2020. doi:10.2979/jfolkrese.57.2.04.
- Christiansen, Reidar Th. «Cinderella in Ireland». In: Béaloideas 20, no. 1/2 (1950): 96–107. Accessed 7 May 2021. doi:10.2307/20521197.
- Ding Naitong (1974). The Cinderella cycle in China and Indo-China. Helsinki: Suomalainen Tiedeakatemia. ISBN 951-41-0121-9.
- Gardner, Fletcher, and W. W. Newell. «Filipino (Tagalog) Versions of Cinderella». In: The Journal of American Folklore 19, no. 75 (1906): 265–80. Accessed 5 July 2020. doi:10.2307/534434.
- Jonathan Y. H. Hui (2018) «Cinderella in Old Norse Literature». In: Folklore, 129:4, pp. 353–374. doi:10.1080/0015587X.2018.1515207.
- Labelle, Ronald. (2017). «Le conte de Cendrillon: de la Chine à l’Acadie sur les ailes de la tradition». In: Rabaska 15: 7–28.
- Mulhern, Chieko Irie. «Cinderella and the Jesuits. An Otogizōshi Cycle as Christian Literature». In: Monumenta Nipponica 34, no. 4 (1979): 409-47. Accessed June 25, 2021. doi:10.2307/2384103.
- Mulhern, Chieko Irie. «Analysis of Cinderella Motifs, Italian and Japanese». In: Asian Folklore Studies 44, no. 1 (1985): 1-37. Accessed June 25, 2021. doi:10.2307/1177981.
- Schlepp, Wayne. “Cinderella in Tibet”. In: Asian Folklore Studies 61, no. 1 (2002): 123–47. Cinderella in Tibet.
- Tangherlini, Timothy. (1994). «Cinderella in Korea: Korean Oikotypes of AaTh 510». In: Fabula. 35: 282–304. doi:10.1515/fabl.1994.35.3-4.282.
- Albano Maria Luisa (a cura). Cenerentole in viaggio. Illustrazione di Marcella Brancaforte. Falzea Editore, Reggio Calabria, 2008.
Notes[edit]
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cinderella.
Wikisource has original text related to this article:
- The complete set of Grimms’ Fairy Tales, including Cinderella at Standard Ebooks
- Project Gutenberg compilation, including original Cendrillon
- Photos and illustrations from early Cinderella stage versions, including one with Ellaline Terriss and one with Phyllis Dare
- Parallel German-English text of brothers Grimm’s version in ParallelBook format
- The Cinderella Bibliography by the University of Rochester
- Folktales of ATU type 510A, «The Persecuted Heroine: Cinderella» by D. L. Ashliman
















































