- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Geography & Travel
- Health & Medicine
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Literature
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- Science
- Sports & Recreation
- Technology
- Visual Arts
- World History
- On This Day in History
- Quizzes
- Podcasts
- Dictionary
- Biographies
- Summaries
- Top Questions
- Week In Review
- Infographics
- Demystified
- Lists
- #WTFact
- Companions
- Image Galleries
- Spotlight
- The Forum
- One Good Fact
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Geography & Travel
- Health & Medicine
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Literature
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- Science
- Sports & Recreation
- Technology
- Visual Arts
- World History
- Britannica Classics
Check out these retro videos from Encyclopedia Britannica’s archives. - Demystified Videos
In Demystified, Britannica has all the answers to your burning questions. - #WTFact Videos
In #WTFact Britannica shares some of the most bizarre facts we can find. - This Time in History
In these videos, find out what happened this month (or any month!) in history. - Britannica Explains
In these videos, Britannica explains a variety of topics and answers frequently asked questions.
- Student Portal
Britannica is the ultimate student resource for key school subjects like history, government, literature, and more. - COVID-19 Portal
While this global health crisis continues to evolve, it can be useful to look to past pandemics to better understand how to respond today. - 100 Women
Britannica celebrates the centennial of the Nineteenth Amendment, highlighting suffragists and history-making politicians. - Britannica Beyond
We’ve created a new place where questions are at the center of learning. Go ahead. Ask. We won’t mind. - Saving Earth
Britannica Presents Earth’s To-Do List for the 21st Century. Learn about the major environmental problems facing our planet and what can be done about them! - SpaceNext50
Britannica presents SpaceNext50, From the race to the Moon to space stewardship, we explore a wide range of subjects that feed our curiosity about space!

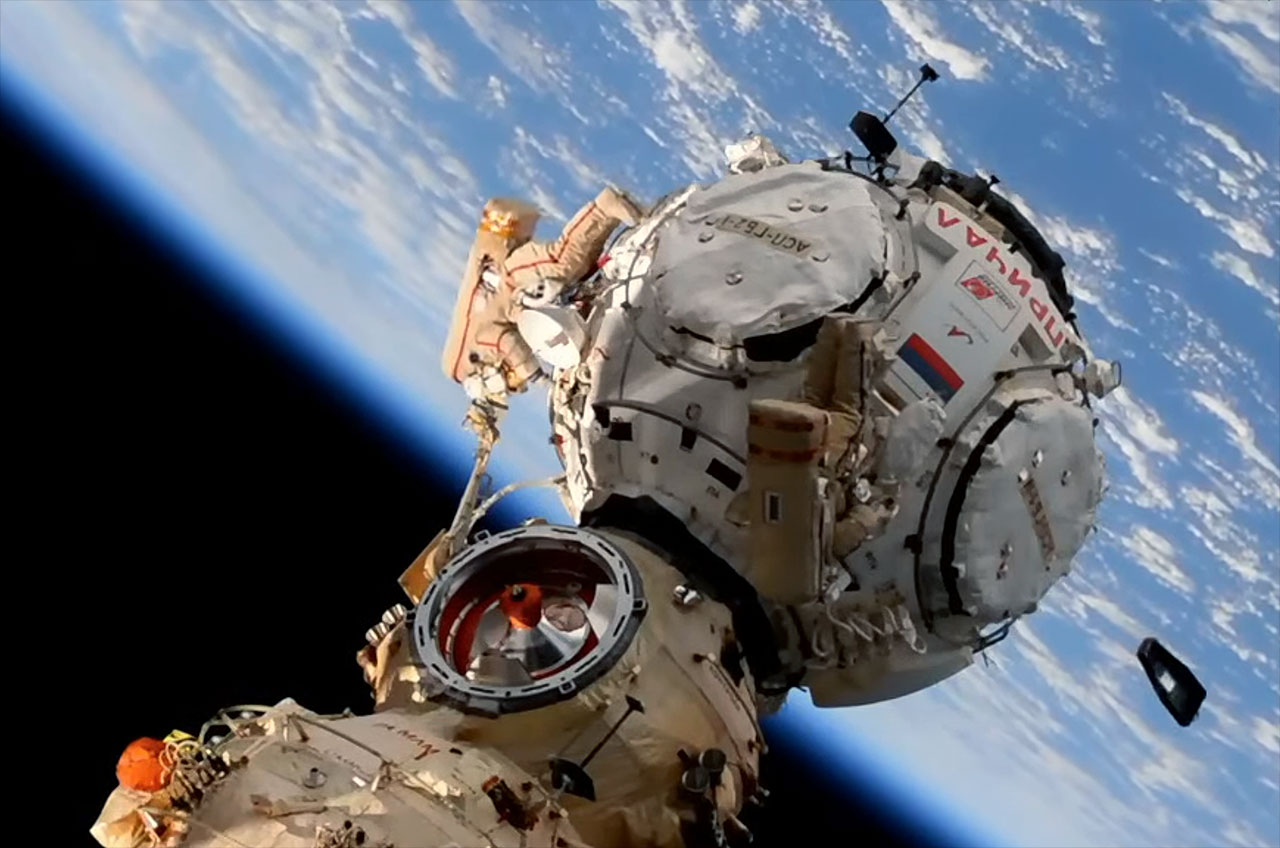
Oblique forward view in November 2021. |
|
 
International Space Station program insignia. |
|
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1998-067A |
| SATCAT no. | 25544 |
| Call sign | Alpha, Station |
| Crew |
|
| Launch | 20 November 1998 (24 years ago) |
| Launch pad |
|
| Mass | 444,615 kg (980,208 lb)[1] |
| Length | 73.0 m (239.4 ft)[1] |
| Width | 109.0 m (357.5 ft)[1] |
| Pressurised volume | 915.6 m3 (32,333 cu ft)[1] |
| Atmospheric pressure | 101.3 kPa (14.7 psi; 1.0 atm) 79% nitrogen, 21% oxygen |
| Perigee altitude | 413 km (256.6 mi) AMSL[2] |
| Apogee altitude | 422 km (262.2 mi) AMSL[2] |
| Orbital inclination | 51.64°[2] |
| Orbital speed | 7.66 km/s[2][failed verification]27,600 km/h; 17,100 mph |
| Orbital period | 92.9 minutes[3] |
| Orbits per day | 15.49[2] |
| Orbit epoch | 12 October 2022 14:25:10 [3] |
| Days in orbit | 24 years, 1 month, 21 days (10 January 2023) |
| Days occupied | 22 years, 2 months, 8 days (10 January 2023) |
| No. of orbits | 133,312 as of June 2022[4] |
| Orbital decay | 2 km/month |
| Statistics as of 22 December 2022 (unless noted otherwise) References: [1][2][5][6][7] |
|
| Configuration | |

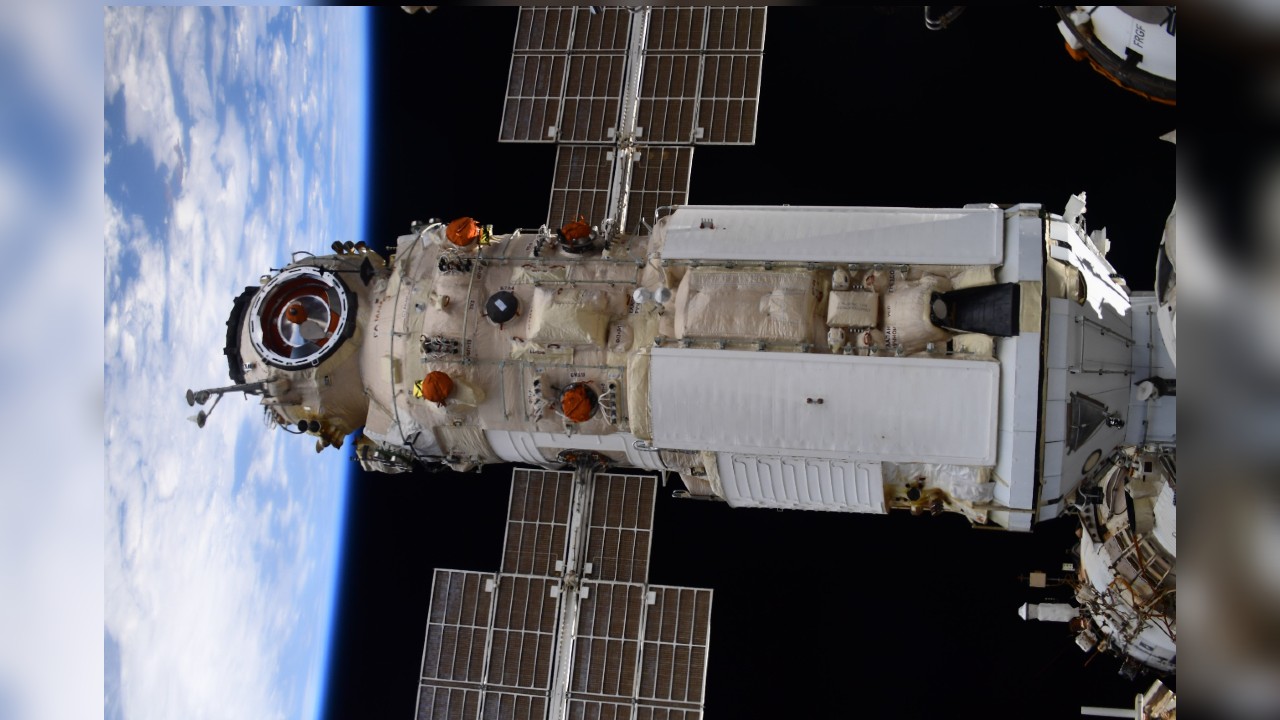
Station elements as of December 2022 |
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station in low Earth orbit. The project involves five space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).[8][9] The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements.[10] The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields.[11][12][13] The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars.[14]
The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station Freedom, a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station,[15] and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian Mir-2 proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to be inhabited by crews, following the Soviet and later Russian Salyut, Almaz, and Mir stations and the American Skylab. It is the largest artificial object in the solar system and the largest satellite in low Earth orbit, regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth’s surface.[16][17] It maintains an orbit with an average altitude of 400 kilometres (250 mi) by means of reboost manoeuvres using the engines of the Zvezda Service Module or visiting spacecraft.[18] The ISS circles the Earth in roughly 93 minutes, completing 15.5 orbits per day.[19]
The station is divided into two sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) is operated by Russia, while the United States Orbital Segment (USOS) is run by the United States as well as by the other states. The Russian segment includes six modules. The US segment includes ten modules, whose support services are distributed 76.6% for NASA, 12.8% for JAXA, 8.3% for ESA and 2.3% for CSA.
Roscosmos had previously[20][21] endorsed the continued operation of ROS through 2024,[22] having proposed using elements of the segment to construct a new Russian space station called OPSEK.[23] However, continued cooperation has been rendered uncertain by the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine and subsequent international sanctions on Russia, who theoretically, may lower, redirect, or cut funding from their side of the space station due to the sanctions set on them.[20][21]
The first ISS component was launched in 1998, and the first long-term residents arrived on 2 November 2000 after being launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on 31 October 2000.[24] The station has since been continuously occupied for 22 years and 69 days,[25] the longest continuous human presence in low Earth orbit, having surpassed the previous record of 9 years and 357 days held by the Mir space station. The latest major pressurised module, Nauka, was fitted in 2021, a little over ten years after the previous major addition, Leonardo in 2011. Development and assembly of the station continues, with an experimental inflatable space habitat added in 2016, and several major new Russian elements scheduled for launch starting in 2021. In January 2022, the station’s operation authorization was extended to 2030, with funding secured within the United States through that year.[26][27] There have been calls to privatize ISS operations after that point to pursue future Moon and Mars missions, with former NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine stating: «given our current budget constraints, if we want to go to the moon and we want to go to Mars, we need to commercialize low Earth orbit and go on to the next step.»[28]
The ISS consists of pressurised habitation modules, structural trusses, photovoltaic solar arrays, thermal radiators, docking ports, experiment bays and robotic arms. Major ISS modules have been launched by Russian Proton and Soyuz rockets and US Space Shuttles.[29] The station is serviced by a variety of visiting spacecraft: the Russian Soyuz and Progress, the SpaceX Dragon 2, and the Northrop Grumman Space Systems Cygnus,[30] and formerly the European Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV), the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle,[8] and SpaceX Dragon 1. The Dragon spacecraft allows the return of pressurised cargo to Earth, which is used, for example, to repatriate scientific experiments for further analysis. As of April 2022, 251 astronauts, cosmonauts, and space tourists from 20 different nations have visited the space station, many of them multiple times.
History[edit]
In the early 1980s, NASA planned to launch a modular space station called Freedom as a counterpart to the Soviet Salyut and Mir space stations. In 1984 the ESA was invited to participate in Space Station Freedom, and the ESA approved the Columbus laboratory by 1987.[31] The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), or Kibō, was announced in 1985, as part of the Freedom space station in response to a NASA request in 1982.
In early 1985, science ministers from the European Space Agency (ESA) countries approved the Columbus programme, the most ambitious effort in space undertaken by that organisation at the time. The plan spearheaded by Germany and Italy included a module which would be attached to Freedom, and with the capability to evolve into a full-fledged European orbital outpost before the end of the century. The space station was also going to tie the emerging European and Japanese national space programmes closer to the US-led project, thereby preventing those nations from becoming major, independent competitors too.[32]
In September 1993, American Vice-President Al Gore and Russian Prime Minister Viktor Chernomyrdin announced plans for a new space station, which eventually became the International Space Station.[33] They also agreed, in preparation for this new project, that the United States would be involved in the Mir programme, including American Shuttles docking, in the Shuttle–Mir programme.[34]
On 12 April 2021, at a meeting with Russian President Vladimir Putin, then-Deputy Prime Minister Yury Borisov announced he had decided that Russia might withdraw from the ISS programme in 2025.[35][36] According to Russian authorities, the timeframe of the station’s operations has expired and its condition leaves much to be desired.[35] On 26 July 2022, Borisov, who had become head of Roscosmos, submitted to Putin his plans for withdrawal from the programme after 2024.[37] However, Robyn Gatens, the NASA official in charge of space station operations, responded that NASA had not received any formal notices from Roscosmos concerning withdrawal plans.[38] On 21 September 2022, Borisov stated that Russia was «highly likely» to continue to participate in the ISS programme until 2028.[39]
Purpose[edit]
The ISS was originally intended to be a laboratory, observatory, and factory while providing transportation, maintenance, and a low Earth orbit staging base for possible future missions to the Moon, Mars, and asteroids. However, not all of the uses envisioned in the initial memorandum of understanding between NASA and Roscosmos have been realised.[40] In the 2010 United States National Space Policy, the ISS was given additional roles of serving commercial, diplomatic,[41] and educational purposes.[42]
Scientific research[edit]
Fisheye view of several labs
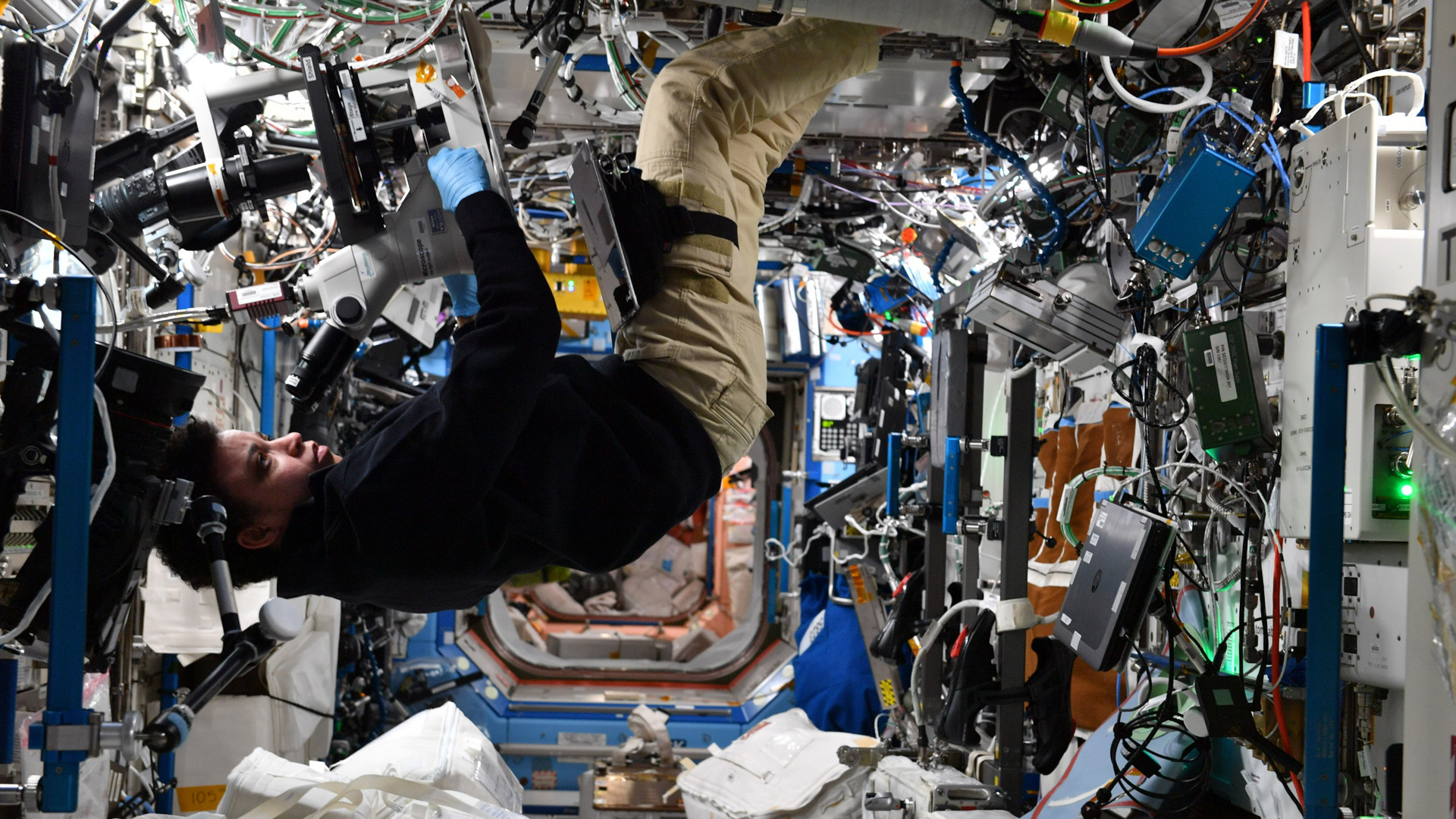
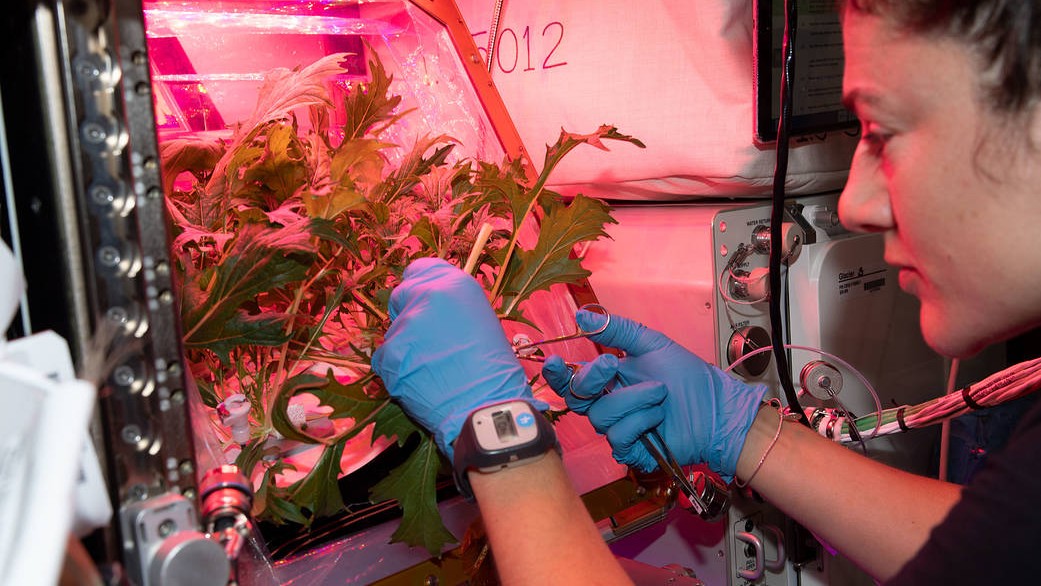
The ISS provides a platform to conduct scientific research, with power, data, cooling, and crew available to support experiments. Small uncrewed spacecraft can also provide platforms for experiments, especially those involving zero gravity and exposure to space, but space stations offer a long-term environment where studies can be performed potentially for decades, combined with ready access by human researchers.[43][44]
The ISS simplifies individual experiments by allowing groups of experiments to share the same launches and crew time. Research is conducted in a wide variety of fields, including astrobiology, astronomy, physical sciences, materials science, space weather, meteorology, and human research including space medicine and the life sciences.[11][12][13][45][46] Scientists on Earth have timely access to the data and can suggest experimental modifications to the crew. If follow-on experiments are necessary, the routinely scheduled launches of resupply craft allows new hardware to be launched with relative ease.[44] Crews fly expeditions of several months’ duration, providing approximately 160 person-hours per week of labour with a crew of six. However, a considerable amount of crew time is taken up by station maintenance.[11][47]
Perhaps the most notable ISS experiment is the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), which is intended to detect dark matter and answer other fundamental questions about our universe. According to NASA, the AMS is as important as the Hubble Space Telescope. Currently docked on station, it could not have been easily accommodated on a free flying satellite platform because of its power and bandwidth needs.[48][49] On 3 April 2013, scientists reported that hints of dark matter may have been detected by the AMS.[50][51][52][53][54][55] According to the scientists, «The first results from the space-borne Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer confirm an unexplained excess of high-energy positrons in Earth-bound cosmic rays».
The space environment is hostile to life. Unprotected presence in space is characterised by an intense radiation field (consisting primarily of protons and other subatomic charged particles from the solar wind, in addition to cosmic rays), high vacuum, extreme temperatures, and microgravity.[56] Some simple forms of life called extremophiles,[57] as well as small invertebrates called tardigrades[58] can survive in this environment in an extremely dry state through desiccation.
Medical research improves knowledge about the effects of long-term space exposure on the human body, including muscle atrophy, bone loss, and fluid shift. These data will be used to determine whether high duration human spaceflight and space colonisation are feasible. In 2006, data on bone loss and muscular atrophy suggested that there would be a significant risk of fractures and movement problems if astronauts landed on a planet after a lengthy interplanetary cruise, such as the six-month interval required to travel to Mars.[59][60]
Medical studies are conducted aboard the ISS on behalf of the National Space Biomedical Research Institute (NSBRI). Prominent among these is the Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity study in which astronauts perform ultrasound scans under the guidance of remote experts. The study considers the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions in space. Usually, there is no physician on board the ISS and diagnosis of medical conditions is a challenge. It is anticipated that remotely guided ultrasound scans will have application on Earth in emergency and rural care situations where access to a trained physician is difficult.[61][62][63]
In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus radiodurans bacteria, which is highly resistant to environmental hazards, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings supported the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.[64][65]
Remote sensing of the Earth, astronomy, and deep space research on the ISS have dramatically increased during the 2010s after the completion of the US Orbital Segment in 2011. Throughout the more than 20 years of the ISS program researchers aboard the ISS and on the ground have examined aerosols, ozone, lightning, and oxides in Earth’s atmosphere, as well as the Sun, cosmic rays, cosmic dust, antimatter, and dark matter in the universe. Examples of Earth-viewing remote sensing experiments that have flown on the ISS are the Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, ISS-RapidScat, ECOSTRESS, the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation, and the Cloud Aerosol Transport System. ISS-based astronomy telescopes and experiments include SOLAR, the Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer, the Calorimetric Electron Telescope, the Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image (MAXI), and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer.[12][66]
Freefall[edit]
ISS crew member storing samples
A comparison between the combustion of a candle on Earth (left) and in a free fall environment, such as that found on the ISS (right)
Gravity at the altitude of the ISS is approximately 90% as strong as at Earth’s surface, but objects in orbit are in a continuous state of freefall, resulting in an apparent state of weightlessness.[67] This perceived weightlessness is disturbed by five effects:[68]
- Drag from the residual atmosphere.
- Vibration from the movements of mechanical systems and the crew.
- Actuation of the on-board attitude control moment gyroscopes.
- Thruster firings for attitude or orbital changes.
- Gravity-gradient effects, also known as tidal effects. Items at different locations within the ISS would, if not attached to the station, follow slightly different orbits. Being mechanically connected these items experience small forces that keep the station moving as a rigid body.
Researchers are investigating the effect of the station’s near-weightless environment on the evolution, development, growth and internal processes of plants and animals. In response to some of the data, NASA wants to investigate microgravity’s effects on the growth of three-dimensional, human-like tissues and the unusual protein crystals that can be formed in space.[12]
Investigating the physics of fluids in microgravity will provide better models of the behaviour of fluids. Because fluids can be almost completely combined in microgravity, physicists investigate fluids that do not mix well on Earth. Examining reactions that are slowed by low gravity and low temperatures will improve our understanding of superconductivity.[12]
The study of materials science is an important ISS research activity, with the objective of reaping economic benefits through the improvement of techniques used on the ground.[69] Other areas of interest include the effect of low gravity on combustion, through the study of the efficiency of burning and control of emissions and pollutants. These findings may improve knowledge about energy production and lead to economic and environmental benefits.[12]
Exploration[edit]
A 3D plan of the Russia-based MARS-500 complex, used for conducting ground-based experiments that complement ISS-based preparations for a human mission to Mars
The ISS provides a location in the relative safety of low Earth orbit to test spacecraft systems that will be required for long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. This provides experience in operations, maintenance as well as repair and replacement activities on-orbit. This will help develop essential skills in operating spacecraft farther from Earth, reduce mission risks, and advance the capabilities of interplanetary spacecraft.[14] Referring to the MARS-500 experiment, a crew isolation experiment conducted on Earth, ESA states that «Whereas the ISS is essential for answering questions concerning the possible impact of weightlessness, radiation and other space-specific factors, aspects such as the effect of long-term isolation and confinement can be more appropriately addressed via ground-based simulations».[70] Sergey Krasnov, the head of human space flight programmes for Russia’s space agency, Roscosmos, in 2011 suggested a «shorter version» of MARS-500 may be carried out on the ISS.[71]
In 2009, noting the value of the partnership framework itself, Sergey Krasnov wrote, «When compared with partners acting separately, partners developing complementary abilities and resources could give us much more assurance of the success and safety of space exploration. The ISS is helping further advance near-Earth space exploration and realisation of prospective programmes of research and exploration of the Solar system, including the Moon and Mars.»[72] A crewed mission to Mars may be a multinational effort involving space agencies and countries outside the current ISS partnership. In 2010, ESA Director-General Jean-Jacques Dordain stated his agency was ready to propose to the other four partners that China, India and South Korea be invited to join the ISS partnership.[73] NASA chief Charles Bolden stated in February 2011, «Any mission to Mars is likely to be a global effort».[74] Currently, US federal legislation prevents NASA co-operation with China on space projects.[75]
Education and cultural outreach[edit]
The ISS crew provides opportunities for students on Earth by running student-developed experiments, making educational demonstrations, allowing for student participation in classroom versions of ISS experiments, and directly engaging students using radio, and email.[8][76] ESA offers a wide range of free teaching materials that can be downloaded for use in classrooms.[77] In one lesson, students can navigate a 3D model of the interior and exterior of the ISS, and face spontaneous challenges to solve in real time.[78]
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) aims to inspire children to «pursue craftsmanship» and to heighten their «awareness of the importance of life and their responsibilities in society».[79] Through a series of education guides, students develop a deeper understanding of the past and near-term future of crewed space flight, as well as that of Earth and life.[80][81] In the JAXA «Seeds in Space» experiments, the mutation effects of spaceflight on plant seeds aboard the ISS are explored by growing sunflower seeds that have flown on the ISS for about nine months. In the first phase of Kibō utilisation from 2008 to mid-2010, researchers from more than a dozen Japanese universities conducted experiments in diverse fields.[82]
Cultural activities are another major objective of the ISS programme. Tetsuo Tanaka, the director of JAXA’s Space Environment and Utilization Center, has said: «There is something about space that touches even people who are not interested in science.»[83]
Amateur Radio on the ISS (ARISS) is a volunteer programme that encourages students worldwide to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, through amateur radio communications opportunities with the ISS crew. ARISS is an international working group, consisting of delegations from nine countries including several in Europe, as well as Japan, Russia, Canada, and the United States. In areas where radio equipment cannot be used, speakerphones connect students to ground stations which then connect the calls to the space station.[84]
Spoken voice recording by ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli on the subject of the ISS, produced in November 2017 for Wikipedia
First Orbit is a 2011 feature-length documentary film about Vostok 1, the first crewed space flight around the Earth. By matching the orbit of the ISS to that of Vostok 1 as closely as possible, in terms of ground path and time of day, documentary filmmaker Christopher Riley and ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli were able to film the view that Yuri Gagarin saw on his pioneering orbital space flight. This new footage was cut together with the original Vostok 1 mission audio recordings sourced from the Russian State Archive. Nespoli is credited as the director of photography for this documentary film, as he recorded the majority of the footage himself during Expedition 26/27.[85] The film was streamed in a global YouTube premiere in 2011 under a free licence through the website firstorbit.org.[86]
In May 2013, commander Chris Hadfield shot a music video of David Bowie’s «Space Oddity» on board the station, which was released on YouTube.[87][88] It was the first music video ever to be filmed in space.[89]
In November 2017, while participating in Expedition 52/53 on the ISS, Paolo Nespoli made two recordings of his spoken voice (one in English and the other in his native Italian), for use on Wikipedia articles. These were the first content made in space specifically for Wikipedia.[90][91]
In November 2021, a virtual reality exhibit called The Infinite featuring life aboard the ISS was announced.[92]
Construction[edit]
Manufacturing[edit]
ISS module Node 2 manufacturing and processing in the Space Station Processing Facility
Since the International Space Station is a multi-national collaborative project, the components for in-orbit assembly were manufactured in various countries around the world. Beginning in the mid-1990s, the U.S. components Destiny, Unity, the Integrated Truss Structure, and the solar arrays were fabricated at the Marshall Space Flight Center and the Michoud Assembly Facility. These modules were delivered to the Operations and Checkout Building and the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for final assembly and processing for launch.[93]
The Russian modules, including Zarya and Zvezda, were manufactured at the Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center in Moscow. Zvezda was initially manufactured in 1985 as a component for Mir-2, but was never launched and instead became the ISS Service Module.[94]
The European Space Agency (ESA) Columbus module was manufactured at the EADS Astrium Space Transportation facilities in Bremen, Germany, along with many other contractors throughout Europe.[95] The other ESA-built modules – Harmony, Tranquility, the Leonardo MPLM, and the Cupola – were initially manufactured at the Thales Alenia Space factory in Turin, Italy.[96] The structural steel hulls of the modules were transported by aircraft to the Kennedy Space Center SSPF for launch processing.[97]
The Japanese Experiment Module Kibō, was fabricated in various technology manufacturing facilities in Japan, at the NASDA (now JAXA) Tsukuba Space Center, and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. The Kibo module was transported by ship and flown by aircraft to the SSPF.[98]
The Mobile Servicing System, consisting of the Canadarm2 and the Dextre grapple fixture, was manufactured at various factories in Canada (such as the David Florida Laboratory) and the United States, under contract by the Canadian Space Agency. The mobile base system, a connecting framework for Canadarm2 mounted on rails, was built by Northrop Grumman.
Assembly[edit]
The ISS was slowly assembled over more than a decade of spaceflights and crews.
A view of the completed station as seen from Shuttle Atlantis during STS-132, 23 May 2010
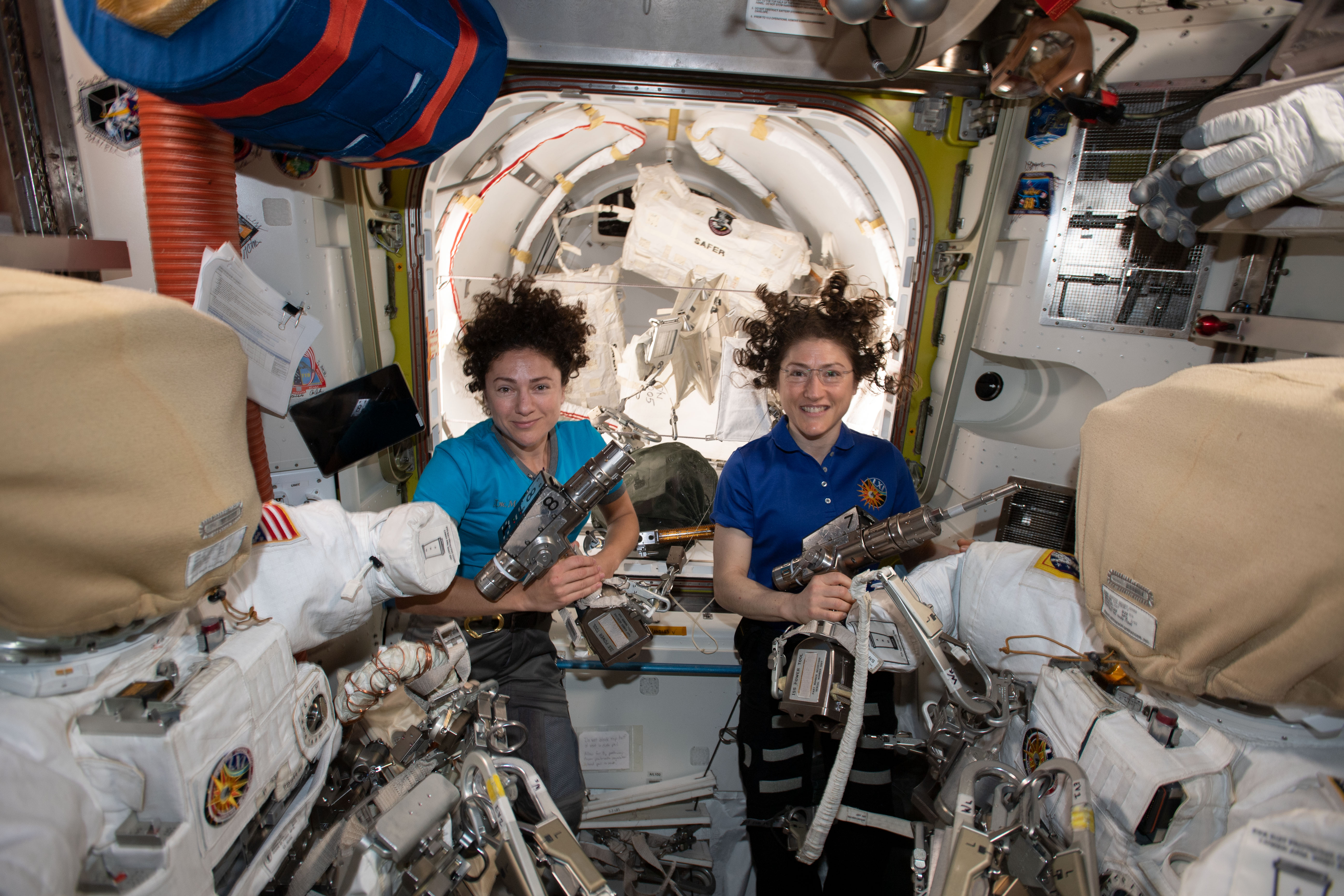
The assembly of the International Space Station, a major endeavour in space architecture, began in November 1998.[5] Russian modules launched and docked robotically, with the exception of Rassvet. All other modules were delivered by the Space Shuttle, which required installation by ISS and Shuttle crewmembers using the Canadarm2 (SSRMS) and extra-vehicular activities (EVAs); by 5 June 2011, they had added 159 components during more than 1,000 hours of EVA. 127 of these spacewalks originated from the station, and the remaining 32 were launched from the airlocks of docked Space Shuttles.[99] The beta angle of the station had to be considered at all times during construction.[100]
The first module of the ISS, Zarya, was launched on 20 November 1998 on an autonomous Russian Proton rocket. It provided propulsion, attitude control, communications, and electrical power, but lacked long-term life support functions. A passive NASA module, Unity, was launched two weeks later aboard Space Shuttle flight STS-88 and attached to Zarya by astronauts during EVAs. The Unity module has two Pressurised Mating Adapters (PMAs): one connects permanently to Zarya and the other allowed the Space Shuttle to dock to the space station. At that time, the Russian (Soviet) station Mir was still inhabited, and the ISS remained uncrewed for two years. On 12 July 2000, the Zvezda module was launched into orbit. Onboard preprogrammed commands deployed its solar arrays and communications antenna. Zvezda then became the passive target for a rendezvous with Zarya and Unity, maintaining a station-keeping orbit while the Zarya–Unity vehicle performed the rendezvous and docking via ground control and the Russian automated rendezvous and docking system. Zarya‘s computer transferred control of the station to Zvezda‘s computer soon after docking. Zvezda added sleeping quarters, a toilet, kitchen, CO2 scrubbers, dehumidifier, oxygen generators, and exercise equipment, plus data, voice and television communications with mission control, enabling permanent habitation of the station.[101][102]
The first resident crew, Expedition 1, arrived in November 2000 on Soyuz TM-31. At the end of the first day on the station, astronaut Bill Shepherd requested the use of the radio call sign «Alpha«, which he and cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev preferred to the more cumbersome «International Space Station«.[103] The name «Alpha» had previously been used for the station in the early 1990s,[104] and its use was authorised for the whole of Expedition 1.[105] Shepherd had been advocating the use of a new name to project managers for some time. Referencing a naval tradition in a pre-launch news conference he had said: «For thousands of years, humans have been going to sea in ships. People have designed and built these vessels, launched them with a good feeling that a name will bring good fortune to the crew and success to their voyage.»[106] Yuri Semenov, the President of Russian Space Corporation Energia at the time, disapproved of the name «Alpha» as he felt that Mir was the first modular space station, so the names «Beta» or «Mir 2″ for the ISS would have been more fitting.[105][107][108]
Expedition 1 arrived midway between the Space Shuttle flights of missions STS-92 and STS-97. These two flights each added segments of the station’s Integrated Truss Structure, which provided the station with Ku-band communication for US television, additional attitude support needed for the additional mass of the USOS, and substantial solar arrays to supplement the station’s four existing arrays.[109] Over the next two years, the station continued to expand. A Soyuz-U rocket delivered the Pirs docking compartment. The Space Shuttles Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour delivered the Destiny laboratory and Quest airlock, in addition to the station’s main robot arm, the Canadarm2, and several more segments of the Integrated Truss Structure.
The expansion schedule was interrupted in 2003 by the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster and a resulting hiatus in flights. The Space Shuttle was grounded until 2005 with STS-114 flown by Discovery.[110] Assembly resumed in 2006 with the arrival of STS-115 with Atlantis, which delivered the station’s second set of solar arrays. Several more truss segments and a third set of arrays were delivered on STS-116, STS-117, and STS-118. As a result of the major expansion of the station’s power-generating capabilities, more pressurised modules could be accommodated, and the Harmony node and Columbus European laboratory were added. These were soon followed by the first two components of Kibō. In March 2009, STS-119 completed the Integrated Truss Structure with the installation of the fourth and final set of solar arrays. The final section of Kibō was delivered in July 2009 on STS-127, followed by the Russian Poisk module. The third node, Tranquility, was delivered in February 2010 during STS-130 by the Space Shuttle Endeavour, alongside the Cupola, followed by the penultimate Russian module, Rassvet, in May 2010. Rassvet was delivered by Space Shuttle Atlantis on STS-132 in exchange for the Russian Proton delivery of the US-funded Zarya module in 1998.[111] The last pressurised module of the USOS, Leonardo, was brought to the station in February 2011 on the final flight of Discovery, STS-133.[112] The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer was delivered by Endeavour on STS-134 the same year.[113]
By June 2011, the station consisted of 15 pressurised modules and the Integrated Truss Structure. Two power modules called NEM-1 and NEM-2.[114] are still to be launched. Russia’s new primary research module Nauka docked in July 2021,[115] along with the European Robotic Arm which will be able to relocate itself to different parts of the Russian modules of the station.[116] Russia’s latest addition, the nodal module Prichal, docked in November 2021.[117]
The gross mass of the station changes over time. The total launch mass of the modules on orbit is about 417,289 kg (919,965 lb) (as of 3 September 2011).[118] The mass of experiments, spare parts, personal effects, crew, foodstuff, clothing, propellants, water supplies, gas supplies, docked spacecraft, and other items add to the total mass of the station. Hydrogen gas is constantly vented overboard by the oxygen generators.
Structure[edit]
The ISS is a modular space station. Modular stations can allow modules to be added to or removed from the existing structure, allowing greater flexibility.
-
Technical blueprint of components.
-
The ISS exterior and steelwork taken on 8 November 2021, from the departing SpaceX Crew-2 capsule.
-
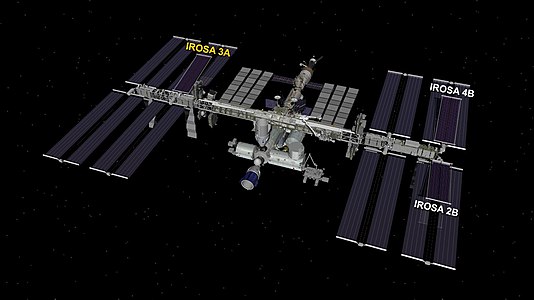
Diagram structure of International Space Station after installation of iROSA solar arrays (as of 2022).
Below is a diagram of major station components. The blue areas are pressurised sections accessible by the crew without using spacesuits. The station’s unpressurised superstructure is indicated in red. Planned components are shown in white, non installed, temporarily defunct or non-commissioned components are shown in brown and former ones in gray. Other unpressurised components are yellow. The Unity node joins directly to the Destiny laboratory. For clarity, they are shown apart. Similar cases are also seen in other parts of the structure.
Pressurised modules[edit]
Zarya[edit]
Zarya (Russian: Заря, lit. ‘Dawn’[b]), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the Russian: «Функционально-грузовой блок», lit. ‘Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok‘ or ФГБ), is the first module of the ISS to have been launched.[119] The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, Zarya, as of August 2021, is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The Zarya is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian Salyut program. The name Zarya («Dawn») was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States.[120]
Unity[edit]
The Unity connecting module, also known as Node 1, is the first U.S.-built component of the ISS. It connects the Russian and U.S. segments of the station, and is where crew eat meals together.[121][122]
The module is cylindrical in shape, with six berthing locations (forward, aft, port, starboard, zenith, and nadir) facilitating connections to other modules. Unity measures 4.57 metres (15.0 ft) in diameter, is 5.47 metres (17.9 ft) long, made of steel, and was built for NASA by Boeing in a manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Unity is the first of the three connecting modules; the other two are Harmony and Tranquility.[123]
Zvezda[edit]
Zvezda (Russian: Звезда, meaning «star»), Salyut DOS-8, is also known as the Zvezda Service Module. It was the third module launched to the station, and provides all of the station’s life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the USOS, as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment, which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station.[124][125][126]
The module was manufactured by RKK Energia, with major sub-contracting work by GKNPTs Khrunichev.[127] Zvezda was launched on a Proton rocket on 12 July 2000, and docked with the Zarya module on 26 July 2000.
The Destiny module being installed on the ISS
Destiny[edit]
The Destiny module, also known as the U.S. Lab, is the primary operating facility for U.S. research payloads aboard the ISS.[128][129] It was berthed to the Unity module and activated over a period of five days in February 2001.[130] Destiny is NASA’s first permanent operating orbital research station since Skylab was vacated in February 1974. The Boeing Company began construction of the 14.5-tonne (32,000 lb) research laboratory in 1995 at the Michoud Assembly Facility and then the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.[128] Destiny was shipped to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 1998, and was turned over to NASA for pre-launch preparations in August 2000. It launched on 7 February 2001, aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on STS-98.[130] Astronauts work inside the pressurized facility to conduct research in numerous scientific fields. Scientists throughout the world would use the results to enhance their studies in medicine, engineering, biotechnology, physics, materials science, and Earth science.[129]
Quest Joint Airlock Module
Quest[edit]
The Joint Airlock (also known as «Quest») is provided by the U.S. and provides the capability for ISS-based Extravehicular Activity (EVA) using either a U.S. Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) or Russian Orlan EVA suits. Before the launch of this airlock, EVAs were performed from either the U.S. Space Shuttle (while docked) or from the Transfer Chamber on the Service Module. Due to a variety of system and design differences, only U.S. space suits could be used from the Shuttle and only Russian suits could be used from the Service Module. The Joint Airlock alleviates this short-term problem by allowing either (or both) spacesuit systems to be used.
The Joint Airlock was launched on ISS-7A / STS-104 in July 2001 and was attached to the right hand docking port of Node 1. The Joint Airlock is 20 ft. long, 13 ft. in diameter, and weighs 6.5 tons. The Joint Airlock was built by Boeing at Marshall Space Flight Center. The Joint Airlock was launched with the High Pressure Gas Assembly. The High Pressure Gas Assembly was mounted on the external surface of the Joint Airlock and will support EVAs operations with breathing gases and augments the Service Module’s gas resupply system.
The Joint Airlock has two main components: a crew airlock from which astronauts and cosmonauts exit the ISS and an equipment airlock designed for storing EVA gear and for so-called overnight «campouts» wherein Nitrogen is purged from astronaut’s bodies overnight as pressure is dropped in preparation for spacewalks the following day. This alleviates the bends as the astronauts are repressurized after their EVA.
The crew airlock was derived from the Space Shuttle’s external airlock. It is equipped with lighting, external handrails, and an Umbilical Interface Assembly (UIA). The UIA is located on one wall of the crew airlock and provides a water supply line, a wastewater return line, and an oxygen supply line. The UIA also provides communication gear and spacesuit power interfaces and can support two spacesuits simultaneously. This can be either two American EMU spacesuits, two Russian ORLAN spacesuits, or one of each design.
Poisk[edit]
Poisk (Russian: По́иск, lit. ‘Search’) was launched on 10 November 2009[131][132] attached to a modified Progress spacecraft, called Progress M-MIM2, on a Soyuz-U rocket from Launch Pad 1 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Poisk is used as the Russian airlock module, containing two identical EVA hatches. An outward-opening hatch on the Mir space station failed after it swung open too fast after unlatching, because of a small amount of air pressure remaining in the airlock.[133] All EVA hatches on the ISS open inwards and are pressure-sealing. Poisk is used to store, service, and refurbish Russian Orlan suits and provides contingency entry for crew using the slightly bulkier American suits. The outermost docking port on the module allows docking of Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, and the automatic transfer of propellants to and from storage on the ROS.[134] Since the departure of the identical Pirs module on July 26, 2021, Poisk has served as the only airlock on the ROS.
Harmony shown connected to Columbus, Kibo, and Destiny. PMA-2 faces. The nadir and zenith locations are open.
Harmony[edit]
Harmony, also known as Node 2, is the «utility hub» of the ISS. It connects the laboratory modules of the United States, Europe and Japan, as well as providing electrical power and electronic data. Sleeping cabins for four of the crew are housed here.[135]
Harmony was successfully launched into space aboard Space Shuttle flight STS-120 on 23 October 2007.[136][137] After temporarily being attached to the port side of the Unity node,[138][139] it was moved to its permanent location on the forward end of the Destiny laboratory on 14 November 2007.[140] Harmony added 75.5 m3 (2,666 cu ft) to the station’s living volume, an increase of almost 20 percent, from 424.8 to 500.2 m3 (15,000 to 17,666 cu ft). Its successful installation meant that from NASA’s perspective, the station was considered to be «U.S. Core Complete».
Tranquility[edit]
Tranquility, also known as Node 3, is a module of the ISS. It contains environmental control systems, life support systems, a toilet, exercise equipment, and an observation cupola.
The European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency had Tranquility manufactured by Thales Alenia Space. A ceremony on 20 November 2009 transferred ownership of the module to NASA.[141] On 8 February 2010, NASA launched the module on the Space Shuttle’s STS-130 mission.
The Columbus module on the ISS
Columbus[edit]
Columbus is a science laboratory that is part of the ISS and is the largest single contribution to the station made by the European Space Agency.
Like the Harmony and Tranquility modules, the Columbus laboratory was constructed in Turin, Italy by Thales Alenia Space. The functional equipment and software of the lab was designed by EADS in Bremen, Germany. It was also integrated in Bremen before being flown to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in an Airbus Beluga. It was launched aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on 7 February 2008, on flight STS-122. It is designed for ten years of operation. The module is controlled by the Columbus Control Centre, located at the German Space Operations Center, part of the German Aerospace Center in Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich, Germany.
The European Space Agency has spent €1.4 billion (about US$2 billion) on building Columbus, including the experiments it carries and the ground control infrastructure necessary to operate them.[142]
Kibō[edit]
The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), nicknamed Kibō (きぼう, Kibō, Hope), is a Japanese science module for the International Space Station (ISS) developed by JAXA. It is the largest single ISS module, and is attached to the Harmony module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on Space Shuttle missions STS-123 and STS-124. The third and final components were launched on STS-127.[143]
The Cupola‘s windows with shutters open
Cupola[edit]
The Cupola is an ESA-built observatory module of the ISS. Its name derives from the Italian word cupola, which means «dome». Its seven windows are used to conduct experiments, dockings and observations of Earth. It was launched aboard Space Shuttle mission STS-130 on 8 February 2010 and attached to the Tranquility (Node 3) module. With the Cupola attached, ISS assembly reached 85 percent completion. The Cupola‘s central window has a diameter of 80 cm (31 in).[144]
Rassvet module with MLM-outfitting equipment (consisting of experiment airlock, RTOd radiators, and ERA workpost) at KSC.
Rassvet[edit]
Rassvet (Russian: Рассвет; lit. «dawn»), also known as the Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM-1) (Russian: Малый исследовательский модуль, МИМ 1) and formerly known as the Docking Cargo Module (DCM), is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). The module’s design is similar to the Mir Docking Module launched on STS-74 in 1995. Rassvet is primarily used for cargo storage and as a docking port for visiting spacecraft. It was flown to the ISS aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on the STS-132 mission on 14 May 2010,[145] and was connected to the ISS on 18 May 2010.[146] The hatch connecting Rassvet with the ISS was first opened on 20 May 2010.[147] On 28 June 2010, the Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft performed the first docking with the module.[148]
MLM outfittings[edit]
MLM outfittings on Rassvet
A wide-angle view of the new module (behind Rassvet) attached to the ROS as seen from the cupola
In May 2010, equipment for Nauka was launched on STS-132 (as part of an agreement with NASA) and delivered by Space Shuttle Atlantis. Weighing 1.4 metric tons, the equipment was attached to the outside of Rassvet (MRM-1). It included a spare elbow joint for the European Robotic Arm (ERA) (which was launched with Nauka) and an ERA-portable workpost used during EVAs, as well as RTOd heat radiator, internal hardware and an experiment airlock for launching CubeSats to be positioned on the modified passive forward port near the nadir end of the Nauka module.[149]
Modified passive forward port for experiment airlock near the nadir end of Nauka
The RTOd radiator will be used to add additional cooling capability to Nauka, which will enable the module to host more scientific experiments. The airlock will be used only to pass experiments inside and outside the module, with the aid of ERA – very similar to the Japanese airlock and Nanoracks Bishop Airlock on the U.S. segment of the station.[149]
The ERA will be used to remove the RTOd radiator and airlock from Rassvet and transfer them over to Nauka. This process is expected to take several months. A portable work platform will also be transferred over, which can attach to the end of the ERA to allow cosmonauts to «ride» on the end of the arm during spacewalks.[150]
Another MLM outfitting is a 4 segment external payload interface called means of attachment of large payloads (Sredstva Krepleniya Krupnogabaritnykh Obyektov, SKKO).[151] Delivered in two parts to Nauka by Progress MS-18 (LCCS part) and Progress MS-21 (SCCCS part) as part of the module activation outfitting process.[152][153][154][155] It was taken outside and installed on the ERA aft facing base point on Nauka during the VKD-55 spacewalk.[156]
Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module
Leonardo[edit]
The Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module (PMM) is a module of the International Space Station. It was flown into space aboard the Space Shuttle on STS-133 on 24 February 2011 and installed on 1 March. Leonardo is primarily used for storage of spares, supplies and waste on the ISS, which was until then stored in many different places within the space station. It is also the personal hygiene area for the astronauts who live in the US Orbital Segment. The Leonardo PMM was a Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) before 2011, but was modified into its current configuration. It was formerly one of two MPLM used for bringing cargo to and from the ISS with the Space Shuttle. The module was named for Italian polymath Leonardo da Vinci.
Bigelow Expandable Activity Module[edit]
Progression of the expansion of BEAM
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is an experimental expandable space station module developed by Bigelow Aerospace, under contract to NASA, for testing as a temporary module on the International Space Station (ISS) from 2016 to at least 2020. It arrived at the ISS on 10 April 2016,[157] was berthed to the station on 16 April at Tranquility Node 3, and was expanded and pressurized on 28 May 2016.
International Docking Adapters[edit]
The International Docking Adapter (IDA) is a spacecraft docking system adapter developed to convert APAS-95 to the NASA Docking System (NDS). An IDA is placed on each of the ISS’s two open Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs), both of which are connected to the Harmony module.
Two International Docking Adapters are currently installed aboard the Station. Originally, IDA-1 was planned to be installed on PMA-2, located at Harmony‘s forward port, and IDA-2 would be installed on PMA-3 at Harmony‘s zenith. After IDA 1 was destroyed in a launch incident, IDA-2 was installed on PMA-2 on 19 August 2016,[158] while IDA-3 was later installed on PMA-3 on 21 August 2019.[159]
NanoRacks Bishop airlock module installed on the ISS
Bishop Airlock Module[edit]
The NanoRacks Bishop Airlock Module is a commercially funded airlock module launched to the ISS on SpaceX CRS-21 on 6 December 2020.[160][161] The module was built by NanoRacks, Thales Alenia Space, and Boeing.[162] It will be used to deploy CubeSats, small satellites, and other external payloads for NASA, CASIS, and other commercial and governmental customers.[163]
Nauka[edit]
Nauka (Russian: Наука, lit. ‘Science’), also known as the Multipurpose Laboratory Module-Upgrade (MLM-U), (Russian: Многоцелевой лабораторный модуль, усоверше́нствованный, or МЛМ-У), is a Roscosmos-funded component of the ISS that was launched on 21 July 2021, 14:58 UTC. In the original ISS plans, Nauka was to use the location of the Docking and Stowage Module (DSM), but the DSM was later replaced by the Rassvet module and moved to Zarya‘s nadir port. Nauka was successfully docked to Zvezda‘s nadir port on 29 July 2021, 13:29 UTC, replacing the Pirs module.
1637984492234 Progress MS 17 undocking and Nauka nadir temporary docking adapter Removal[c][d]
It had a temporary docking adapter on its nadir port for crewed and uncrewed missions until Prichal arrival, where just before its arrival it was removed by a departuring Progress spacecraft.[164]
Nauka and Prichal docked to ISS
Prichal[edit]
Prichal, also known as Uzlovoy Module or UM (Russian: Узловой Модуль Причал, lit. ‘Nodal Module Berth’),[165] is a 4-tonne (8,800 lb)[166] ball-shaped module that will provide the Russian segment additional docking ports to receive Soyuz MS and Progress MS spacecraft. UM was launched in November 2021.[167] It was integrated with a special version of the Progress cargo spacecraft and launched by a standard Soyuz rocket, docking to the nadir port of the Nauka module. One port is equipped with an active hybrid docking port, which enables docking with the MLM module. The remaining five ports are passive hybrids, enabling docking of Soyuz and Progress vehicles, as well as heavier modules and future spacecraft with modified docking systems. The node module was intended to serve as the only permanent element of the cancelled Orbital Piloted Assembly and Experiment Complex (OPSEK).[167][168][169]
Unpressurised elements[edit]
ISS Truss Components breakdown showing Trusses and all ORUs in situ
The ISS has a large number of external components that do not require pressurisation. The largest of these is the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS), to which the station’s main solar arrays and thermal radiators are mounted.[170] The ITS consists of ten separate segments forming a structure 108.5 metres (356 ft) long.[5]
The station was intended to have several smaller external components, such as six robotic arms, three External Stowage Platforms (ESPs) and four ExPRESS Logistics Carriers (ELCs).[171][172] While these platforms allow experiments (including MISSE, the STP-H3 and the Robotic Refueling Mission) to be deployed and conducted in the vacuum of space by providing electricity and processing experimental data locally, their primary function is to store spare Orbital Replacement Units (ORUs). ORUs are parts that can be replaced when they fail or pass their design life, including pumps, storage tanks, antennas, and battery units. Such units are replaced either by astronauts during EVA or by robotic arms.[173] Several shuttle missions were dedicated to the delivery of ORUs, including STS-129,[174] STS-133[175] and STS-134.[176] As of January 2011, only one other mode of transportation of ORUs had been utilised – the Japanese cargo vessel HTV-2 – which delivered an FHRC and CTC-2 via its Exposed Pallet (EP).[177][needs update]
There are also smaller exposure facilities mounted directly to laboratory modules; the Kibō Exposed Facility serves as an external «porch» for the Kibō complex,[178] and a facility on the European Columbus laboratory provides power and data connections for experiments such as the European Technology Exposure Facility[179][180] and the Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space.[181] A remote sensing instrument, SAGE III-ISS, was delivered to the station in February 2017 aboard CRS-10,[182] and the NICER experiment was delivered aboard CRS-11 in June 2017.[183] The largest scientific payload externally mounted to the ISS is the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), a particle physics experiment launched on STS-134 in May 2011, and mounted externally on the ITS. The AMS measures cosmic rays to look for evidence of dark matter and antimatter.[184][185]
The commercial Bartolomeo External Payload Hosting Platform, manufactured by Airbus, was launched on 6 March 2020 aboard CRS-20 and attached to the European Columbus module. It will provide an additional 12 external payload slots, supplementing the eight on the ExPRESS Logistics Carriers, ten on Kibō, and four on Columbus. The system is designed to be robotically serviced and will require no astronaut intervention. It is named after Christopher Columbus’s younger brother.[186][187][188]
Robotic arms and cargo cranes[edit]
Dextre, like many of the station’s experiments and robotic arms, can be operated from Earth, allowing tasks to be performed while the crew sleeps.
The Integrated Truss Structure serves as a base for the station’s primary remote manipulator system, the Mobile Servicing System (MSS), which is composed of three main components:
- Canadarm2, the largest robotic arm on the ISS, has a mass of 1,800 kilograms (4,000 lb) and is used to: dock and manipulate spacecraft and modules on the USOS; hold crew members and equipment in place during EVAs; and move Dextre around to perform tasks.[189]
- Dextre is a 1,560 kg (3,440 lb) robotic manipulator that has two arms and a rotating torso, with power tools, lights, and video for replacing orbital replacement units (ORUs) and performing other tasks requiring fine control.[190]
- The Mobile Base System (MBS) is a platform that rides on rails along the length of the station’s main truss, which serves as a mobile base for Canadarm2 and Dextre, allowing the robotic arms to reach all parts of the USOS.[191]
A grapple fixture was added to Zarya on STS-134 to enable Canadarm2 to inchworm itself onto the Russian Orbital Segment.[192] Also installed during STS-134 was the 15 m (50 ft) Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), which had been used to inspect heat shield tiles on Space Shuttle missions and which can be used on the station to increase the reach of the MSS.[192] Staff on Earth or the ISS can operate the MSS components using remote control, performing work outside the station without the need for space walks.
Japan’s Remote Manipulator System, which services the Kibō Exposed Facility,[193] was launched on STS-124 and is attached to the Kibō Pressurised Module.[194] The arm is similar to the Space Shuttle arm as it is permanently attached at one end and has a latching end effector for standard grapple fixtures at the other.
The European Robotic Arm, which will service the Russian Orbital Segment, was launched alongside the Nauka module.[195] The ROS does not require spacecraft or modules to be manipulated, as all spacecraft and modules dock automatically and may be discarded the same way. Crew use the two Strela (Russian: Стрела́, lit. ‘Arrow’) cargo cranes during EVAs for moving crew and equipment around the ROS. Each Strela crane has a mass of 45 kg (99 lb).
Former module[edit]
Pirs[edit]
Pirs (Russian: Пирс, lit. ’Pier’) was launched on 14 September 2001, as ISS Assembly Mission 4R, on a Russian Soyuz-U rocket, using a modified Progress spacecraft, Progress M-SO1, as an upper stage. Pirs was undocked by Progress MS-16 on 26 July 2021, 10:56 UTC, and deorbited on the same day at 14:51 UTC to make room for Nauka module to be attached to the space station. Prior to its departure, Pirs served as the primary Russian airlock on the station, being used to store and refurbish the Russian Orlan spacesuits.
The Pirs module attached to the ISS.
ISS-65 Pirs docking compartment separates from the Space Station
Planned components[edit]
Axiom segment[edit]
In January 2020, NASA awarded Axiom Space a contract to build a commercial module for the ISS with a launch date of 2024. The contract is under the NextSTEP2 program. NASA negotiated with Axiom on a firm fixed-price contract basis to build and deliver the module, which will attach to the forward port of the space station’s Harmony (Node 2) module. Although NASA has only commissioned one module, Axiom plans to build an entire segment consisting of five modules, including a node module, an orbital research and manufacturing facility, a crew habitat, and a «large-windowed Earth observatory». The Axiom segment is expected to greatly increase the capabilities and value of the space station, allowing for larger crews and private spaceflight by other organisations. Axiom plans to convert the segment into a stand-alone space station once the ISS is decommissioned, with the intention that this would act as a successor to the ISS.[196][197][198] Canadarm 2 will also help to berth the Axiom Space Station modules to the ISS and will continue its operations on the Axiom Space Station after the retirement of ISS in late 2020s.[199]
Proposed components[edit]
Xbase[edit]
Main article: B330
Made by Bigelow Aerospace. In August 2016 Bigelow negotiated an agreement with NASA to develop a full-sized ground prototype Deep Space Habitation based on the B330 under the second phase of Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships. The module is called the Expandable Bigelow Advanced Station Enhancement (XBASE), as Bigelow hopes to test the module by attaching it to the International Space Station.
Independence-1[edit]
Nanoracks, after finalizing its contract with NASA, and after winning NextSTEPs Phase II award, is now developing its concept Independence-1 (previously known as Ixion), which would turn spent rocket tanks into a habitable living area to be tested in space. In Spring 2018, Nanoracks announced that Ixion is now known as the Independence-1, the first ‘outpost’ in Nanoracks’ Space Outpost Program.
Nautilus-X Centrifuge Demonstration[edit]
If produced, this centrifuge will be the first in-space demonstration of sufficient scale centrifuge for artificial partial-g effects. It will be designed to become a sleep module for the ISS crew.
Cancelled components[edit]
The cancelled Habitation module under construction at Michoud in 1997
Several modules planned for the station were cancelled over the course of the ISS programme. Reasons include budgetary constraints, the modules becoming unnecessary, and station redesigns after the 2003 Columbia disaster. The US Centrifuge Accommodations Module would have hosted science experiments in varying levels of artificial gravity.[200] The US Habitation Module would have served as the station’s living quarters. Instead, the living quarters are now spread throughout the station.[201] The US Interim Control Module and ISS Propulsion Module would have replaced the functions of Zvezda in case of a launch failure.[202] Two Russian Research Modules were planned for scientific research.[203] They would have docked to a Russian Universal Docking Module.[204] The Russian Science Power Platform would have supplied power to the Russian Orbital Segment independent of the ITS solar arrays.
Science Power Modules 1 and 2 (Repurposed Components)[edit]
Science Power Module 1 (SPM-1, also known as NEM-1) and Science Power Module 2 (SPM-2, also known as NEM-2) are modules that were originally planned to arrive at the ISS no earlier than 2024, and dock to the Prichal module, which is currently docked to the Nauka module.[169][205] In April 2021, Roscosmos announced that NEM-1 would be repurposed to function as the core module of the proposed Russian Orbital Service Station (ROSS), launching no earlier than 2025 and docking to the free-flying Nauka module either before or after the ISS has been deorbited.[206][207] NEM-2 may be converted into another core «base» module, which would be launched in 2028.[208]
Onboard systems[edit]
Life support[edit]
The critical systems are the atmosphere control system, the water supply system, the food supply facilities, the sanitation and hygiene equipment, and fire detection and suppression equipment. The Russian Orbital Segment’s life support systems are contained in the Zvezda service module. Some of these systems are supplemented by equipment in the USOS. The Nauka laboratory has a complete set of life support systems.
Atmospheric control systems[edit]
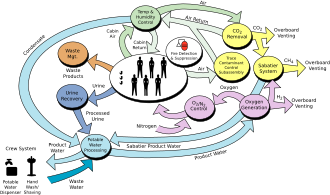
The interactions between the components of the ISS Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS)
The atmosphere on board the ISS is similar to that of Earth.[209] Normal air pressure on the ISS is 101.3 kPa (14.69 psi);[210] the same as at sea level on Earth. An Earth-like atmosphere offers benefits for crew comfort, and is much safer than a pure oxygen atmosphere, because of the increased risk of a fire such as that responsible for the deaths of the Apollo 1 crew.[211][better source needed]
Earth-like atmospheric conditions have been maintained on all Russian and Soviet spacecraft.[212]
The Elektron system aboard Zvezda and a similar system in Destiny generate oxygen aboard the station.[213] The crew has a backup option in the form of bottled oxygen and Solid Fuel Oxygen Generation (SFOG) canisters, a chemical oxygen generator system.[214] Carbon dioxide is removed from the air by the Vozdukh system in Zvezda. Other by-products of human metabolism, such as methane from the intestines and ammonia from sweat, are removed by activated charcoal filters.[214]
Part of the ROS atmosphere control system is the oxygen supply. Triple-redundancy is provided by the Elektron unit, solid fuel generators, and stored oxygen. The primary supply of oxygen is the Elektron unit which produces O2 and H2 by electrolysis of water and vents H2 overboard. The 1 kW (1.3 hp) system uses approximately one litre of water per crew member per day. This water is either brought from Earth or recycled from other systems. Mir was the first spacecraft to use recycled water for oxygen production. The secondary oxygen supply is provided by burning oxygen-producing Vika cartridges (see also ISS ECLSS). Each ‘candle’ takes 5–20 minutes to decompose at 450–500 °C (842–932 °F), producing 600 litres (130 imp gal; 160 US gal) of O2. This unit is manually operated.[215]
The US Orbital Segment has redundant supplies of oxygen, from a pressurised storage tank on the Quest airlock module delivered in 2001, supplemented ten years later by ESA-built Advanced Closed-Loop System (ACLS) in the Tranquility module (Node 3), which produces O2 by electrolysis.[216] Hydrogen produced is combined with carbon dioxide from the cabin atmosphere and converted to water and methane.
Power and thermal control[edit]
Russian solar arrays, backlit by sunset
One of the eight truss mounted pairs of USOS solar arrays
ISS new roll out solar array as seen from a zoom camera on the P6 Truss
Double-sided solar arrays provide electrical power to the ISS. These bifacial cells collect direct sunlight on one side and light reflected off from the Earth on the other, and are more efficient and operate at a lower temperature than single-sided cells commonly used on Earth.[217]
The Russian segment of the station, like most spacecraft, uses 28 V low voltage DC from two rotating solar arrays mounted on Zvezda. The USOS uses 130–180 V DC from the USOS PV array, power is stabilised and distributed at 160 V DC and converted to the user-required 124 V DC. The higher distribution voltage allows smaller, lighter conductors, at the expense of crew safety. The two station segments share power with converters.
The USOS solar arrays are arranged as four wing pairs, for a total production of 75 to 90 kilowatts.[218] These arrays normally track the Sun to maximise power generation. Each array is about 375 m2 (4,036 sq ft) in area and 58 m (190 ft) long. In the complete configuration, the solar arrays track the Sun by rotating the alpha gimbal once per orbit; the beta gimbal follows slower changes in the angle of the Sun to the orbital plane. The Night Glider mode aligns the solar arrays parallel to the ground at night to reduce the significant aerodynamic drag at the station’s relatively low orbital altitude.[219]
The station originally used rechargeable nickel–hydrogen batteries (NiH2) for continuous power during the 45 minutes of every 90-minute orbit that it is eclipsed by the Earth. The batteries are recharged on the day side of the orbit. They had a 6.5-year lifetime (over 37,000 charge/discharge cycles) and were regularly replaced over the anticipated 20-year life of the station.[220] Starting in 2016, the nickel–hydrogen batteries were replaced by lithium-ion batteries, which are expected to last until the end of the ISS program.[221]
The station’s large solar panels generate a high potential voltage difference between the station and the ionosphere. This could cause arcing through insulating surfaces and sputtering of conductive surfaces as ions are accelerated by the spacecraft plasma sheath. To mitigate this, plasma contactor units create current paths between the station and the ambient space plasma.[222]
ISS External Active Thermal Control System (EATCS) diagram
The station’s systems and experiments consume a large amount of electrical power, almost all of which is converted to heat. To keep the internal temperature within workable limits, a passive thermal control system (PTCS) is made of external surface materials, insulation such as MLI, and heat pipes. If the PTCS cannot keep up with the heat load, an External Active Thermal Control System (EATCS) maintains the temperature. The EATCS consists of an internal, non-toxic, water coolant loop used to cool and dehumidify the atmosphere, which transfers collected heat into an external liquid ammonia loop. From the heat exchangers, ammonia is pumped into external radiators that emit heat as infrared radiation, then back to the station.[223] The EATCS provides cooling for all the US pressurised modules, including Kibō and Columbus, as well as the main power distribution electronics of the S0, S1 and P1 trusses. It can reject up to 70 kW. This is much more than the 14 kW of the Early External Active Thermal Control System (EEATCS) via the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which was launched on STS-105 and installed onto the P6 Truss.[224]
Communications and computers[edit]
The communications systems used by the ISS
* Luch and the Space Shuttle are not in use as of 2020
Radio communications provide telemetry and scientific data links between the station and mission control centres. Radio links are also used during rendezvous and docking procedures and for audio and video communication between crew members, flight controllers and family members. As a result, the ISS is equipped with internal and external communication systems used for different purposes.[225]
The Russian Orbital Segment communicates directly with the ground via the Lira antenna mounted to Zvezda.[8][226] The Lira antenna also has the capability to use the Luch data relay satellite system.[8] This system fell into disrepair during the 1990s, and so was not used during the early years of the ISS,[8][227][228] although two new Luch satellites – Luch-5A and Luch-5B – were launched in 2011 and 2012 respectively to restore the operational capability of the system.[229] Another Russian communications system is the Voskhod-M, which enables internal telephone communications between Zvezda, Zarya, Pirs, Poisk, and the USOS and provides a VHF radio link to ground control centres via antennas on Zvezda‘s exterior.[230]
The US Orbital Segment (USOS) makes use of two separate radio links: S band (audio, telemetry, commanding – located on the P1/S1 truss) and Ku band (audio, video and data – located on the Z1 truss) systems. These transmissions are routed via the United States Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) in geostationary orbit, allowing for almost continuous real-time communications with Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center (MCC-H) in Houston.[8][29][225] Data channels for the Canadarm2, European Columbus laboratory and Japanese Kibō modules were originally also routed via the S band and Ku band systems, with the European Data Relay System and a similar Japanese system intended to eventually complement the TDRSS in this role.[29][231] Communications between modules are carried on an internal wireless network.[232]
An array of laptops in the US lab
Laptop computers surround the Canadarm2 console
An error message displays a problem with hard drive on ISS laptop
UHF radio is used by astronauts and cosmonauts conducting EVAs and other spacecraft that dock to or undock from the station.[8] Automated spacecraft are fitted with their own communications equipment; the ATV uses a laser attached to the spacecraft and the Proximity Communications Equipment attached to Zvezda to accurately dock with the station.[233][234]
The ISS is equipped with about 100 IBM/Lenovo ThinkPad and HP ZBook 15 laptop computers. The laptops have run Windows 95, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 10 and Linux operating systems.[235] Each computer is a commercial off-the-shelf purchase which is then modified for safety and operation including updates to connectors, cooling and power to accommodate the station’s 28V DC power system and weightless environment. Heat generated by the laptops does not rise but stagnates around the laptop, so additional forced ventilation is required. Portable Computer System (PCS) laptops connect to the Primary Command & Control computer (C&C MDM) as remote terminals via a USB to 1553 adapter.[236] Station Support Computer (SSC) laptops aboard the ISS are connected to the station’s wireless LAN via Wi-Fi and ethernet, which connects to the ground via Ku band. While originally this provided speeds of 10 Mbit/s download and 3 Mbit/s upload from the station,[237][238] NASA upgraded the system in late August 2019 and increased the speeds to 600 Mbit/s.[239][240] Laptop hard drives occasionally fail and must be replaced.[241] Other computer hardware failures include instances in 2001, 2007 and 2017; some of these failures have required EVAs to replace computer modules in externally mounted devices.[242][243][244][245]
The operating system used for key station functions is the Debian Linux distribution.[246] The migration from Microsoft Windows to Linux was made in May 2013 for reasons of reliability, stability and flexibility.[247]
In 2017, an SG100 Cloud Computer was launched to the ISS as part of OA-7 mission.[248] It was manufactured by NCSIST of Taiwan and designed in collaboration with Academia Sinica, and National Central University under contract for NASA.[249]
ISS crew members have access to the Internet, and thus the web.[250][251] This was first enabled in 2010,[250] allowing NASA astronaut T.J. Creamer to make the first tweet from space.[252] Access is achieved via an Internet-enabled computer in Houston, using remote desktop mode, thereby protecting the ISS from virus infection and hacking attempts.[250]
Operations[edit]
Expeditions[edit]
Zarya and Unity were entered for the first time on 10 December 1998.
Soyuz TM-31 being prepared to bring the first resident crew to the station in October 2000
Each permanent crew is given an expedition number. Expeditions run up to six months, from launch until undocking, an ‘increment’ covers the same time period, but includes cargo spacecraft and all activities. Expeditions 1 to 6 consisted of three-person crews. Expeditions 7 to 12 were reduced to the safe minimum of two following the destruction of the NASA Shuttle Columbia. From Expedition 13 the crew gradually increased to six around 2010.[253][254] With the arrival of crew on US commercial vehicles beginning in 2020,[255] NASA has indicated that expedition size may be increased to seven crew members, the number ISS was originally designed for.[256][257]
Gennady Padalka, member of Expeditions 9, 19/20, 31/32, and 43/44, and Commander of Expedition 11, has spent more time in space than anyone else, a total of 878 days, 11 hours, and 29 minutes.[258] Peggy Whitson has spent the most time in space of any American, totalling 665 days, 22 hours, and 22 minutes during her time on Expeditions 5, 16, and 50/51/52.[259]
Private flights[edit]
Travellers who pay for their own passage into space are termed spaceflight participants by Roscosmos and NASA, and are sometimes referred to as «space tourists», a term they generally dislike.[e] As of 2021, seven space tourists have visited the ISS; all seven were transported to the ISS on Russian Soyuz spacecraft. When professional crews change over in numbers not divisible by the three seats in a Soyuz, and a short-stay crewmember is not sent, the spare seat is sold by MirCorp through Space Adventures. Space tourism was halted in 2011 when the Space Shuttle was retired and the station’s crew size was reduced to six, as the partners relied on Russian transport seats for access to the station. Soyuz flight schedules increased after 2013, allowing five Soyuz flights (15 seats) with only two expeditions (12 seats) required.[267] The remaining seats were to be sold for around US$40 million to members of the public who could pass a medical exam. ESA and NASA criticised private spaceflight at the beginning of the ISS, and NASA initially resisted training Dennis Tito, the first person to pay for his own passage to the ISS.[f]
Anousheh Ansari became the first self-funded woman to fly to the ISS as well as the first Iranian in space. Officials reported that her education and experience made her much more than a tourist, and her performance in training had been «excellent.»[268] She did Russian and European studies involving medicine and microbiology during her 10-day stay. The 2009 documentary Space Tourists follows her journey to the station, where she fulfilled «an age-old dream of man: to leave our planet as a ‘normal person’ and travel into outer space.»[269]
In 2008, spaceflight participant Richard Garriott placed a geocache aboard the ISS during his flight.[270] This is currently the only non-terrestrial geocache in existence.[271] At the same time, the Immortality Drive, an electronic record of eight digitised human DNA sequences, was placed aboard the ISS.[272]
Fleet operations[edit]
Dragon and Cygnus cargo vessels were docked at the ISS together for the first time in April 2016.
Commercial Crew Program vehicles Starliner and Dragon
A wide variety of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft have supported the station’s activities. Flights to the ISS include 37 Space Shuttle missions, 83 Progress resupply spacecraft (including the modified M-MIM2, M-SO1 and M-UM module transports), 63 crewed Soyuz spacecraft, 5 European ATVs, 9 Japanese HTVs, 1 Boeing Starliner, 30 SpaceX Dragon ( both crewed and uncrewed) and 18 Cygnus missions.[273]
There are currently twelve available docking ports for visiting spacecraft:[274]
- Harmony forward (with IDA 2)
- Harmony zenith (with IDA 3)
- Harmony nadir
- Unity nadir
- Prichal nadir
- Prichal aft
- Prichal forward
- Prichal starboard
- Prichal port
- Nauka forward[275]
- Poisk zenith
- Rassvet nadir
- Zvezda aft
Crewed[edit]
As of 30 December 2021, 256 people from 20 countries had visited the space station, many of them multiple times. The United States sent 158 people, Russia sent 55, 11 were Japanese, nine were Canadian, five were Italian, four were French, four were German, and there were one each from Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, Great Britain, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, the Netherlands, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Israel, Sweden and the United Arab Emirates.[276]
Uncrewed[edit]
Uncrewed spaceflights to the ISS are made primarily to deliver cargo, however several Russian modules have also docked to the outpost following uncrewed launches. Resupply missions typically use the Russian Progress spacecraft, former European ATVs, Japanese Kounotori vehicles, and the American Dragon and Cygnus spacecraft. The primary docking system for Progress spacecraft is the automated Kurs system, with the manual TORU system as a backup. ATVs also used Kurs, however they were not equipped with TORU. Progress and former ATV can remain docked for up to six months.[277][278] The other spacecraft – the Japanese HTV, the SpaceX Dragon (under CRS phase 1), and the Northrop Grumman[279] Cygnus – rendezvous with the station before being grappled using Canadarm2 and berthed at the nadir port of the Harmony or Unity module for one to two months. Under CRS phase 2, Cargo Dragon docks autonomously at IDA-2 or IDA-3. As of December 2020, Progress spacecraft have flown most of the uncrewed missions to the ISS.
Currently docked/berthed[edit]
Modules/spacecraft pending relocation/installation[edit]
Scheduled missions[edit]
- All dates are UTC. Dates are the earliest possible dates and may change.
- Forward ports are at the front of the station according to its normal direction of travel and orientation (attitude). Aft is at the rear of the station, used by spacecraft boosting the station’s orbit. Nadir is closest the Earth, zenith is on top. Port is to the left if pointing one’s feet towards the Earth and looking in the direction of travel; starboard to the right.
Docking[edit]
The Progress M-14M resupply vehicle approaching the ISS in 2012. More than 50 unpiloted Progress spacecraft have delivered supplies during the lifetime of the station.
All Russian spacecraft and self-propelled modules are able to rendezvous and dock to the space station without human intervention using the Kurs radar docking system from over 200 kilometres away. The European ATV uses star sensors and GPS to determine its intercept course. When it catches up it uses laser equipment to optically recognise Zvezda, along with the Kurs system for redundancy. Crew supervise these craft, but do not intervene except to send abort commands in emergencies. Progress and ATV supply craft can remain at the ISS for six months,[286][287] allowing great flexibility in crew time for loading and unloading of supplies and trash.
From the initial station programs, the Russians pursued an automated docking methodology that used the crew in override or monitoring roles. Although the initial development costs were high, the system has become very reliable with standardisations that provide significant cost benefits in repetitive operations.[288]
Soyuz spacecraft used for crew rotation also serve as lifeboats for emergency evacuation; they are replaced every six months and were used after the Columbia disaster to return stranded crew from the ISS.[289] The average expedition requires 2,722 kg of supplies, and by 9 March 2011, crews had consumed a total of around 22,000 meals.[99] Soyuz crew rotation flights and Progress resupply flights visit the station on average two and three times respectively each year.[290]
Other vehicles berth instead of docking. The Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle parked itself in progressively closer orbits to the station, and then awaited ‘approach’ commands from the crew, until it was close enough for a robotic arm to grapple and berth the vehicle to the USOS. Berthed craft can transfer International Standard Payload Racks. Japanese spacecraft berth for one to two months.[291] The berthing Cygnus and SpaceX Dragon were contracted to fly cargo to the station under phase 1 of the Commercial Resupply Services program.[292][293]
From 26 February 2011 to 7 March 2011 four of the governmental partners (United States, ESA, Japan and Russia) had their spacecraft (NASA Shuttle, ATV, HTV, Progress and Soyuz) docked at the ISS, the only time this has happened to date.[294] On 25 May 2012, SpaceX delivered the first commercial cargo with a Dragon spacecraft.[295]
Launch and docking windows[edit]
Prior to a spacecraft’s docking to the ISS, navigation and attitude control (GNC) is handed over to the ground control of the spacecraft’s country of origin. GNC is set to allow the station to drift in space, rather than fire its thrusters or turn using gyroscopes. The solar panels of the station are turned edge-on to the incoming spacecraft, so residue from its thrusters does not damage the cells. Before its retirement, Shuttle launches were often given priority over Soyuz, with occasional priority given to Soyuz arrivals carrying crew and time-critical cargoes, such as biological experiment materials.[296]
Repairs[edit]
Spare parts are called ORUs; some are externally stored on pallets called ELCs and ESPs.
While anchored on the end of the OBSS during STS-120, astronaut Scott Parazynski performs makeshift repairs to a US solar array that damaged itself when unfolding.
Orbital Replacement Units (ORUs) are spare parts that can be readily replaced when a unit either passes its design life or fails. Examples of ORUs are pumps, storage tanks, controller boxes, antennas, and battery units. Some units can be replaced using robotic arms. Most are stored outside the station, either on small pallets called ExPRESS Logistics Carriers (ELCs) or share larger platforms called External Stowage Platforms which also hold science experiments. Both kinds of pallets provide electricity for many parts that could be damaged by the cold of space and require heating. The larger logistics carriers also have local area network (LAN) connections for telemetry to connect experiments. A heavy emphasis on stocking the USOS with ORU’s occurred around 2011, before the end of the NASA shuttle programme, as its commercial replacements, Cygnus and Dragon, carry one tenth to one quarter the payload.
Unexpected problems and failures have impacted the station’s assembly time-line and work schedules leading to periods of reduced capabilities and, in some cases, could have forced abandonment of the station for safety reasons. Serious problems include an air leak from the USOS in 2004,[297] the venting of fumes from an Elektron oxygen generator in 2006,[298] and the failure of the computers in the ROS in 2007 during STS-117 that left the station without thruster, Elektron, Vozdukh and other environmental control system operations. In the latter case, the root cause was found to be condensation inside electrical connectors leading to a short circuit.[299]
During STS-120 in 2007 and following the relocation of the P6 truss and solar arrays, it was noted during unfurling that the solar array had torn and was not deploying properly.[300] An EVA was carried out by Scott Parazynski, assisted by Douglas Wheelock. Extra precautions were taken to reduce the risk of electric shock, as the repairs were carried out with the solar array exposed to sunlight.[301] The issues with the array were followed in the same year by problems with the starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ), which rotates the arrays on the starboard side of the station. Excessive vibration and high-current spikes in the array drive motor were noted, resulting in a decision to substantially curtail motion of the starboard SARJ until the cause was understood. Inspections during EVAs on STS-120 and STS-123 showed extensive contamination from metallic shavings and debris in the large drive gear and confirmed damage to the large metallic bearing surfaces, so the joint was locked to prevent further damage.[302][303] Repairs to the joints were carried out during STS-126 with lubrication and the replacement of 11 out of 12 trundle bearings on the joint.[304][305]
In September 2008, damage to the S1 radiator was first noticed in Soyuz imagery. The problem was initially not thought to be serious.[306] The imagery showed that the surface of one sub-panel has peeled back from the underlying central structure, possibly because of micro-meteoroid or debris impact. On 15 May 2009 the damaged radiator panel’s ammonia tubing was mechanically shut off from the rest of the cooling system by the computer-controlled closure of a valve. The same valve was then used to vent the ammonia from the damaged panel, eliminating the possibility of an ammonia leak.[306] It is also known that a Service Module thruster cover struck the S1 radiator after being jettisoned during an EVA in 2008, but its effect, if any, has not been determined.
In the early hours of 1 August 2010, a failure in cooling Loop A (starboard side), one of two external cooling loops, left the station with only half of its normal cooling capacity and zero redundancy in some systems.[307][308][309] The problem appeared to be in the ammonia pump module that circulates the ammonia cooling fluid. Several subsystems, including two of the four CMGs, were shut down.
Planned operations on the ISS were interrupted through a series of EVAs to address the cooling system issue. A first EVA on 7 August 2010, to replace the failed pump module, was not fully completed because of an ammonia leak in one of four quick-disconnects. A second EVA on 11 August successfully removed the failed pump module.[310][311] A third EVA was required to restore Loop A to normal functionality.[312][313]
The USOS’s cooling system is largely built by the US company Boeing,[314] which is also the manufacturer of the failed pump.[307]
The four Main Bus Switching Units (MBSUs, located in the S0 truss), control the routing of power from the four solar array wings to the rest of the ISS. Each MBSU has two power channels that feed 160V DC from the arrays to two DC-to-DC power converters (DDCUs) that supply the 124V power used in the station. In late 2011 MBSU-1 ceased responding to commands or sending data confirming its health. While still routing power correctly, it was scheduled to be swapped out at the next available EVA. A spare MBSU was already on board, but a 30 August 2012 EVA failed to be completed when a bolt being tightened to finish installation of the spare unit jammed before the electrical connection was secured.[315] The loss of MBSU-1 limited the station to 75% of its normal power capacity, requiring minor limitations in normal operations until the problem could be addressed.
On 5 September 2012, in a second six-hour EVA, astronauts Sunita Williams and Akihiko Hoshide successfully replaced MBSU-1 and restored the ISS to 100% power.[316]
On 24 December 2013, astronauts installed a new ammonia pump for the station’s cooling system. The faulty cooling system had failed earlier in the month, halting many of the station’s science experiments. Astronauts had to brave a «mini blizzard» of ammonia while installing the new pump. It was only the second Christmas Eve spacewalk in NASA history.[317]
Mission control centres[edit]
The components of the ISS are operated and monitored by their respective space agencies at mission control centres across the globe, including RKA Mission Control Center, ATV Control Centre, JEM Control Center and HTV Control Center at Tsukuba Space Center, Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, Payload Operations and Integration Center, Columbus Control Center and Mobile Servicing System Control.
Life aboard[edit]
Crew activities[edit]
STS-122 mission specialists working on robotic equipment in the US lab
A typical day for the crew begins with a wake-up at 06:00, followed by post-sleep activities and a morning inspection of the station. The crew then eats breakfast and takes part in a daily planning conference with Mission Control before starting work at around 08:10. The first scheduled exercise of the day follows, after which the crew continues work until 13:05. Following a one-hour lunch break, the afternoon consists of more exercise and work before the crew carries out its pre-sleep activities beginning at 19:30, including dinner and a crew conference. The scheduled sleep period begins at 21:30. In general, the crew works ten hours per day on a weekday, and five hours on Saturdays, with the rest of the time their own for relaxation or work catch-up.[318]
The time zone used aboard the ISS is Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).[319] The windows are covered during night hours to give the impression of darkness because the station experiences 16 sunrises and sunsets per day. During visiting Space Shuttle missions, the ISS crew mostly followed the shuttle’s Mission Elapsed Time (MET), which was a flexible time zone based on the launch time of the Space Shuttle mission.[320][321][322]
The station provides crew quarters for each member of the expedition’s crew, with two «sleep stations» in the Zvezda, one in Nauka and four more installed in Harmony.[323][324][325][326] The USOS quarters are private, approximately person-sized soundproof booths. The ROS crew quarters in Zvezda include a small window, but provide less ventilation and sound proofing. A crew member can sleep in a crew quarter in a tethered sleeping bag, listen to music, use a laptop, and store personal items in a large drawer or in nets attached to the module’s walls. The module also provides a reading lamp, a shelf and a desktop.[327][328][329] Visiting crews have no allocated sleep module, and attach a sleeping bag to an available space on a wall. It is possible to sleep floating freely through the station, but this is generally avoided because of the possibility of bumping into sensitive equipment.[330] It is important that crew accommodations be well ventilated; otherwise, astronauts can wake up oxygen-deprived and gasping for air, because a bubble of their own exhaled carbon dioxide has formed around their heads.[327] During various station activities and crew rest times, the lights in the ISS can be dimmed, switched off, and colour temperatures adjusted.[331][332]
Food and personal hygiene[edit]
Main dining desk in Node 1
Fresh fruits and vegetables are grown in the ISS.
On the USOS, most of the food aboard is vacuum sealed in plastic bags; cans are rare because they are heavy and expensive to transport. Preserved food is not highly regarded by the crew and taste is reduced in microgravity,[327] so efforts are taken to make the food more palatable, including using more spices than in regular cooking. The crew looks forward to the arrival of any spacecraft from Earth as they bring fresh fruit and vegetables. Care is taken that foods do not create crumbs, and liquid condiments are preferred over solid to avoid contaminating station equipment. Each crew member has individual food packages and cooks them using the on-board galley. The galley features two food warmers, a refrigerator (added in November 2008), and a water dispenser that provides both heated and unheated water.[328] Drinks are provided as dehydrated powder that is mixed with water before consumption.[328][329] Drinks and soups are sipped from plastic bags with straws, while solid food is eaten with a knife and fork attached to a tray with magnets to prevent them from floating away. Any food that floats away, including crumbs, must be collected to prevent it from clogging the station’s air filters and other equipment.[329]
Showers on space stations were introduced in the early 1970s on Skylab and Salyut 3.[333]: 139 By Salyut 6, in the early 1980s, the crew complained of the complexity of showering in space, which was a monthly activity.[334] The ISS does not feature a shower; instead, crewmembers wash using a water jet and wet wipes, with soap dispensed from a toothpaste tube-like container. Crews are also provided with rinseless shampoo and edible toothpaste to save water.[330][335]
There are two space toilets on the ISS, both of Russian design, located in Zvezda and Tranquility.[328] These Waste and Hygiene Compartments use a fan-driven suction system similar to the Space Shuttle Waste Collection System. Astronauts first fasten themselves to the toilet seat, which is equipped with spring-loaded restraining bars to ensure a good seal.[327] A lever operates a powerful fan and a suction hole slides open: the air stream carries the waste away. Solid waste is collected in individual bags which are stored in an aluminium container. Full containers are transferred to Progress spacecraft for disposal.[328][336] Liquid waste is evacuated by a hose connected to the front of the toilet, with anatomically correct «urine funnel adapters» attached to the tube so that men and women can use the same toilet. The diverted urine is collected and transferred to the Water Recovery System, where it is recycled into drinking water.[329] In 2021, the arrival of the Nauka module also brought a third toilet to the ISS.[337]
The space toilet in the Zvezda module in the Russian segment
The main toilet in the US Segment inside the Tranquility module
* Both toilets are of Russian design
Crew health and safety[edit]
Overall[edit]
On 12 April 2019, NASA reported medical results from the Astronaut Twin Study. Astronaut Scott Kelly spent a year in space on the ISS, while his twin spent the year on Earth. Several long-lasting changes were observed, including those related to alterations in DNA and cognition, when one twin was compared with the other.[338][339]
In November 2019, researchers reported that astronauts experienced serious blood flow and clot problems while on board the ISS, based on a six-month study of 11 healthy astronauts. The results may influence long-term spaceflight, including a mission to the planet Mars, according to the researchers.[340][341]
Radiation[edit]
The ISS is partially protected from the space environment by Earth’s magnetic field. From an average distance of about 70,000 km (43,000 mi) from the Earth’s surface, depending on Solar activity, the magnetosphere begins to deflect solar wind around Earth and the space station. Solar flares are still a hazard to the crew, who may receive only a few minutes warning. In 2005, during the initial «proton storm» of an X-3 class solar flare, the crew of Expedition 10 took shelter in a more heavily shielded part of the ROS designed for this purpose.[342][343]
Subatomic charged particles, primarily protons from cosmic rays and solar wind, are normally absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere. When they interact in sufficient quantity, their effect is visible to the naked eye in a phenomenon called an aurora. Outside Earth’s atmosphere, ISS crews are exposed to approximately one millisievert each day (about a year’s worth of natural exposure on Earth), resulting in a higher risk of cancer. Radiation can penetrate living tissue and damage the DNA and chromosomes of lymphocytes; being central to the immune system, any damage to these cells could contribute to the lower immunity experienced by astronauts. Radiation has also been linked to a higher incidence of cataracts in astronauts. Protective shielding and medications may lower the risks to an acceptable level.[59]
Radiation levels on the ISS are between 12 and 28.8 milli rads per day,[344] about five times greater than those experienced by airline passengers and crew, as Earth’s electromagnetic field provides almost the same level of protection against solar and other types of radiation in low Earth orbit as in the stratosphere. For example, on a 12-hour flight, an airline passenger would experience 0.1 millisieverts of radiation, or a rate of 0.2 millisieverts per day; this is only one fifth the rate experienced by an astronaut in LEO. Additionally, airline passengers experience this level of radiation for a few hours of flight, while the ISS crew are exposed for their whole stay on board the station.[345]
Stress[edit]
There is considerable evidence that psychosocial stressors are among the most important impediments to optimal crew morale and performance.[346] Cosmonaut Valery Ryumin wrote in his journal during a particularly difficult period on board the Salyut 6 space station: «All the conditions necessary for murder are met if you shut two men in a cabin measuring 18 feet by 20 [5.5 m × 6 m] and leave them together for two months.»
NASA’s interest in psychological stress caused by space travel, initially studied when their crewed missions began, was rekindled when astronauts joined cosmonauts on the Russian space station Mir. Common sources of stress in early US missions included maintaining high performance under public scrutiny and isolation from peers and family. The latter is still often a cause of stress on the ISS, such as when the mother of NASA astronaut Daniel Tani died in a car accident, and when Michael Fincke was forced to miss the birth of his second child.
A study of the longest spaceflight concluded that the first three weeks are a critical period where attention is adversely affected because of the demand to adjust to the extreme change of environment.[347] ISS crew flights typically last about five to six months.
The ISS working environment includes further stress caused by living and working in cramped conditions with people from very different cultures who speak a different language. First-generation space stations had crews who spoke a single language; second- and third-generation stations have crew from many cultures who speak many languages. Astronauts must speak English and Russian, and knowing additional languages is even better.[348]
Due to the lack of gravity, confusion often occurs. Even though there is no up and down in space, some crew members feel like they are oriented upside down. They may also have difficulty measuring distances. This can cause problems like getting lost inside the space station, pulling switches in the wrong direction or misjudging the speed of an approaching vehicle during docking.[349]
Medical[edit]
The physiological effects of long-term weightlessness include muscle atrophy, deterioration of the skeleton (osteopenia), fluid redistribution, a slowing of the cardiovascular system, decreased production of red blood cells, balance disorders, and a weakening of the immune system. Lesser symptoms include loss of body mass, and puffiness of the face.[59]
Sleep is regularly disturbed on the ISS because of mission demands, such as incoming or departing spacecraft. Sound levels in the station are unavoidably high. The atmosphere is unable to thermosiphon naturally, so fans are required at all times to process the air which would stagnate in the freefall (zero-G) environment.
To prevent some of the adverse effects on the body, the station is equipped with: two TVIS treadmills (including the COLBERT); the ARED (Advanced Resistive Exercise Device), which enables various weightlifting exercises that add muscle without raising (or compensating for) the astronauts’ reduced bone density;[350] and a stationary bicycle. Each astronaut spends at least two hours per day exercising on the equipment.[327][328] Astronauts use bungee cords to strap themselves to the treadmill.[351][352]
Microbiological environmental hazards[edit]
Hazardous molds that can foul air and water filters may develop aboard space stations. They can produce acids that degrade metal, glass, and rubber. They can also be harmful to the crew’s health. Microbiological hazards have led to a development of the LOCAD-PTS which identifies common bacteria and molds faster than standard methods of culturing, which may require a sample to be sent back to Earth.[353] Researchers in 2018 reported, after detecting the presence of five Enterobacter bugandensis bacterial strains on the ISS (none of which are pathogenic to humans), that microorganisms on the ISS should be carefully monitored to continue assuring a medically healthy environment for astronauts.[354][355]
Contamination on space stations can be prevented by reduced humidity, and by using paint that contains mold-killing chemicals, as well as the use of antiseptic solutions. All materials used in the ISS are tested for resistance against fungi.[356]
In April 2019, NASA reported that a comprehensive study had been conducted into the microorganisms and fungi present on the ISS. The results may be useful in improving the health and safety conditions for astronauts.[357][358]
Noise[edit]
Space flight is not inherently quiet, with noise levels exceeding acoustic standards as far back as the Apollo missions.[359][360] For this reason, NASA and the International Space Station international partners have developed noise control and hearing loss prevention goals as part of the health program for crew members. Specifically, these goals have been the primary focus of the ISS Multilateral Medical Operations Panel (MMOP) Acoustics Subgroup since the first days of ISS assembly and operations.[361][362] The effort includes contributions from acoustical engineers, audiologists, industrial hygienists, and physicians who comprise the subgroup’s membership from NASA, Roscosmos, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
When compared to terrestrial environments, the noise levels incurred by astronauts and cosmonauts on the ISS may seem insignificant and typically occur at levels that would not be of major concern to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration – rarely reaching 85 dBA. But crew members are exposed to these levels 24 hours a day, seven days a week, with current missions averaging six months in duration. These levels of noise also impose risks to crew health and performance in the form of sleep interference and communication, as well as reduced alarm audibility.
Over the 19 plus year history of the ISS, significant efforts have been put forth to limit and reduce noise levels on the ISS. During design and pre-flight activities, members of the Acoustic Subgroup have written acoustic limits and verification requirements, consulted to design and choose quietest available payloads, and then conducted acoustic verification tests prior to launch.[361]: 5.7.3 During spaceflights, the Acoustics Subgroup has assessed each ISS module’s in flight sound levels, produced by a large number of vehicle and science experiment noise sources, to assure compliance with strict acoustic standards. The acoustic environment on ISS changed when additional modules were added during its construction, and as additional spacecraft arrive at the ISS. The Acoustics Subgroup has responded to this dynamic operations schedule by successfully designing and employing acoustic covers, absorptive materials, noise barriers, and vibration isolators to reduce noise levels. Moreover, when pumps, fans, and ventilation systems age and show increased noise levels, this Acoustics Subgroup has guided ISS managers to replace the older, noisier instruments with quiet fan and pump technologies, significantly reducing ambient noise levels.
NASA has adopted most-conservative damage risk criteria (based on recommendations from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and the World Health Organization), in order to protect all crew members. The MMOP Acoustics Subgroup has adjusted its approach to managing noise risks in this unique environment by applying, or modifying, terrestrial approaches for hearing loss prevention to set these conservative limits. One innovative approach has been NASA’s Noise Exposure Estimation Tool (NEET), in which noise exposures are calculated in a task-based approach to determine the need for hearing protection devices (HPDs). Guidance for use of HPDs, either mandatory use or recommended, is then documented in the Noise Hazard Inventory, and posted for crew reference during their missions. The Acoustics Subgroup also tracks spacecraft noise exceedances, applies engineering controls, and recommends hearing protective devices to reduce crew noise exposures. Finally, hearing thresholds are monitored on-orbit, during missions.
There have been no persistent mission-related hearing threshold shifts among US Orbital Segment crewmembers (JAXA, CSA, ESA, NASA) during what is approaching 20 years of ISS mission operations, or nearly 175,000 work hours. In 2020, the MMOP Acoustics Subgroup received the Safe-In-Sound Award for Innovation for their combined efforts to mitigate any health effects of noise.[363]
Fire and toxic gases[edit]
An onboard fire or a toxic gas leak are other potential hazards. Ammonia is used in the external radiators of the station and could potentially leak into the pressurised modules.[364]
Orbit[edit]
Altitude and orbital inclination[edit]
Graph showing the changing altitude of the ISS from November 1998 until November 2018
Animation of ISS orbit from 14 September 2018 to 14 November 2018. Earth is not shown.
The ISS is currently maintained in a nearly circular orbit with a minimum mean altitude of 370 km (230 mi) and a maximum of 460 km (290 mi),[365] in the centre of the thermosphere, at an inclination of 51.6 degrees to Earth’s equator with an eccentricity of 0.007. This orbit was selected because it is the lowest inclination that can be directly reached by Russian Soyuz and Progress spacecraft launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome at 46° N latitude without overflying China or dropping spent rocket stages in inhabited areas.[366][367]
It travels at an average speed of 28,000 kilometres per hour (17,000 mph), and completes 15.5 orbits per day (93 minutes per orbit).[2][19] The station’s altitude was allowed to fall around the time of each NASA shuttle flight to permit heavier loads to be transferred to the station. After the retirement of the shuttle, the nominal orbit of the space station was raised in altitude (from about 350 km to about 400 km).[368][369] Other, more frequent supply spacecraft do not require this adjustment as they are substantially higher performance vehicles.[44][370]
Atmospheric drag reduces the altitude by about 2 km a month on average. Orbital boosting can be performed by the station’s two main engines on the Zvezda service module, or Russian or European spacecraft docked to Zvezda‘s aft port. The Automated Transfer Vehicle is constructed with the possibility of adding a second docking port to its aft end, allowing other craft to dock and boost the station. It takes approximately two orbits (three hours) for the boost to a higher altitude to be completed.[370] Maintaining ISS altitude uses about 7.5 tonnes of chemical fuel per annum[371] at an annual cost of about $210 million.[372]
Orbits of the ISS, shown in April 2013
The Russian Orbital Segment contains the Data Management System, which handles Guidance, Navigation and Control (ROS GNC) for the entire station.[373] Initially, Zarya, the first module of the station, controlled the station until a short time after the Russian service module Zvezda docked and was transferred control. Zvezda contains the ESA built DMS-R Data Management System.[374] Using two fault-tolerant computers (FTC), Zvezda computes the station’s position and orbital trajectory using redundant Earth horizon sensors, Solar horizon sensors as well as Sun and star trackers. The FTCs each contain three identical processing units working in parallel and provide advanced fault-masking by majority voting.
Orientation[edit]
Zvezda uses gyroscopes (reaction wheels) and thrusters to turn itself around. Gyroscopes do not require propellant; instead they use electricity to ‘store’ momentum in flywheels by turning in the opposite direction to the station’s movement. The USOS has its own computer-controlled gyroscopes to handle its extra mass. When gyroscopes ‘saturate’, thrusters are used to cancel out the stored momentum. In February 2005, during Expedition 10, an incorrect command was sent to the station’s computer, using about 14 kilograms of propellant before the fault was noticed and fixed. When attitude control computers in the ROS and USOS fail to communicate properly, this can result in a rare ‘force fight’ where the ROS GNC computer must ignore the USOS counterpart, which itself has no thrusters.[375][376][377]
Docked spacecraft can also be used to maintain station attitude, such as for troubleshooting or during the installation of the S3/S4 truss, which provides electrical power and data interfaces for the station’s electronics.[378]
Orbital debris threats[edit]
The low altitudes at which the ISS orbits are also home to a variety of space debris,[379] including spent rocket stages, defunct satellites, explosion fragments (including materials from anti-satellite weapon tests), paint flakes, slag from solid rocket motors, and coolant released by US-A nuclear-powered satellites. These objects, in addition to natural micrometeoroids,[380] are a significant threat. Objects large enough to destroy the station can be tracked, and are not as dangerous as smaller debris.[381][382] Objects too small to be detected by optical and radar instruments, from approximately 1 cm down to microscopic size, number in the trillions. Despite their small size, some of these objects are a threat because of their kinetic energy and direction in relation to the station. Spacewalking crew in spacesuits are also at risk of suit damage and consequent exposure to vacuum.[383]
Ballistic panels, also called micrometeorite shielding, are incorporated into the station to protect pressurised sections and critical systems. The type and thickness of these panels depend on their predicted exposure to damage. The station’s shields and structure have different designs on the ROS and the USOS. On the USOS, Whipple Shields are used. The US segment modules consist of an inner layer made from 1.5–5.0 cm-thick (0.59–1.97 in) aluminium, a 10 cm-thick (3.9 in) intermediate layers of Kevlar and Nextel (a ceramic fabric),[384] and an outer layer of stainless steel, which causes objects to shatter into a cloud before hitting the hull, thereby spreading the energy of impact. On the ROS, a carbon fibre reinforced polymer honeycomb screen is spaced from the hull, an aluminium honeycomb screen is spaced from that, with a screen-vacuum thermal insulation covering, and glass cloth over the top.[385]
Space debris is tracked remotely from the ground, and the station crew can be notified.[386] If necessary, thrusters on the Russian Orbital Segment can alter the station’s orbital altitude, avoiding the debris. These Debris Avoidance Manoeuvres (DAMs) are not uncommon, taking place if computational models show the debris will approach within a certain threat distance. Ten DAMs had been performed by the end of 2009.[387][388][389] Usually, an increase in orbital velocity of the order of 1 m/s is used to raise the orbit by one or two kilometres. If necessary, the altitude can also be lowered, although such a manoeuvre wastes propellant.[388][390] If a threat from orbital debris is identified too late for a DAM to be safely conducted, the station crew close all the hatches aboard the station and retreat into their spacecraft in order to be able to evacuate in the event the station was seriously damaged by the debris. This partial station evacuation has occurred on 13 March 2009, 28 June 2011, 24 March 2012 and 16 June 2015.[391][392]
In November 2021, a debris cloud from the destruction of Kosmos 1408 by an anti-satellite weapons test threatened the ISS, leading to the announcement of a yellow alert, leading to crew sheltering in the crew capsules.[393] A couple of weeks later, it had to perform an unscheduled maneuver to drop the station by 310 meters to avoid a collision with hazardous space debris.[394]
-
A 7-gram object (shown in centre) shot at 7 km/s (23,000 ft/s), the orbital velocity of the ISS, made this 15 cm (5.9 in) crater in a solid block of aluminium.
-
Example of risk management: A NASA model showing areas at high risk from impact for the International Space Station.
-
A blueprint of a typical debris «Whipple Shield» design.
Sightings from Earth[edit]
The ISS is visible to the naked eye as a slow-moving, bright white dot because of reflected sunlight, and can be seen in the hours after sunset and before sunrise, when the station remains sunlit but the ground and sky are dark.[395] The ISS takes about 10 minutes to pass from one horizon to another, and will only be visible part of that time because of moving into or out of the Earth’s shadow. Because of the size of its reflective surface area, the ISS is the brightest artificial object in the sky (excluding other satellite flares), with an approximate maximum magnitude of −4 when in sunlight and overhead (similar to Venus), and a maximum angular size of 63 arcseconds.[396] The ISS, like many satellites including the Iridium constellation, can also produce flares of up to 16 times the brightness of Venus as sunlight glints off reflective surfaces.[397][398] The ISS is also visible in broad daylight, albeit with a great deal more difficulty.
Tools are provided by a number of websites such as Heavens-Above (see Live viewing below) as well as smartphone applications that use orbital data and the observer’s longitude and latitude to indicate when the ISS will be visible (weather permitting), where the station will appear to rise, the altitude above the horizon it will reach and the duration of the pass before the station disappears either by setting below the horizon or entering into Earth’s shadow.[399][400][401][402]
In November 2012 NASA launched its «Spot the Station» service, which sends people text and email alerts when the station is due to fly above their town.[403] The station is visible from 95% of the inhabited land on Earth, but is not visible from extreme northern or southern latitudes.[366]
Under specific conditions, the ISS can be observed at night on five consecutive orbits. Those conditions are 1) a mid-latitude observer location, 2) near the time of the solstice with 3) the ISS passing in the direction of the pole from the observer near midnight local time. The three photos show the first, middle and last of the five passes on 5–6 June 2014.
-
Skytrack long duration exposure of the ISS
-
The ISS on its first pass of the night passing nearly overhead shortly after sunset in June 2014
-
The ISS passing north on its third pass of the night near local midnight in June 2014
-
The ISS passing west on its fifth pass of the night before sunrise in June 2014
Astrophotography[edit]
Using a telescope-mounted camera to photograph the station is a popular hobby for astronomers,[404] while using a mounted camera to photograph the Earth and stars is a popular hobby for crew.[405] The use of a telescope or binoculars allows viewing of the ISS during daylight hours.[406]
Composite of six photos of the ISS transiting the gibbous Moon
Transits of the ISS in front of the Sun, particularly during an eclipse (and so the Earth, Sun, Moon, and ISS are all positioned approximately in a single line) are of particular interest for amateur astronomers.[407][408]
International co-operation[edit]
A Commemorative Plaque honouring Space Station Intergovernmental Agreement signed on 28 January 1998
Involving five space programs and fifteen countries,[409] the International Space Station is the most politically and legally complex space exploration programme in history.[410] The 1998 Space Station Intergovernmental Agreement sets forth the primary framework for international cooperation among the parties. A series of subsequent agreements govern other aspects of the station, ranging from jurisdictional issues to a code of conduct among visiting astronauts.[411]
Following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, continued cooperation between Russia and other countries on the International Space Station has been put into question. British Prime Minister Boris Johnson commented on the current status of cooperation, saying «I have been broadly in favour of continuing artistic and scientific collaboration, but in the current circumstances it’s hard to see how even those can continue as normal.»[412] On the same day, Roscosmos Director General Dmitry Rogozin insinuated that Russian withdrawal could cause the International Space Station to de-orbit due to lack of reboost capabilities, writing in a series of tweets, «If you block cooperation with us, who will save the ISS from an unguided de-orbit to impact on the territory of the US or Europe? There’s also the chance of impact of the 500-ton construction in India or China. Do you want to threaten them with such a prospect? The ISS doesn’t fly over Russia, so all the risk is yours. Are you ready for it?»[413] Rogozin later tweeted that normal relations between ISS partners could only be restored once sanctions have been lifted, and indicated that Roscosmos would submit proposals to the Russian government on ending cooperation.[414] NASA stated that, if necessary, US corporation Northrop Grumman has offered a reboost capability that would keep the ISS in orbit.[415]
On 26 July 2022, Yury Borisov, Rogozin’s successor as head of Roscosmos, submitted to Russian President Putin plans for withdrawal from the programme after 2024.[20] However, Robyn Gatens, the NASA official in charge of the space station, responded that NASA had not received any formal notices from Roscosmos concerning withdrawal plans.[21]
Participating countries[edit]
End of mission[edit]
According to the Outer Space Treaty, the United States and Russia are legally responsible for all modules they have launched.[416] Several possible disposal options were considered: Natural orbital decay with random reentry (as with Skylab), boosting the station to a higher altitude (which would delay reentry), and a controlled targeted de-orbit to a remote ocean area.[417] In late 2010, the preferred plan was to use a slightly modified Progress spacecraft to de-orbit the ISS.[418] This plan was seen as the simplest, cheapest and with the highest margin of safety.[clarify][418]
OPSEK was previously intended to be constructed of modules from the Russian Orbital Segment after the ISS is decommissioned. The modules under consideration for removal from the current ISS included the Multipurpose Laboratory Module (Nauka), launched in July 2021, and the other new Russian modules that are proposed to be attached to Nauka. These newly launched modules would still be well within their useful lives in 2024.[419]
At the end of 2011, the Exploration Gateway Platform concept also proposed using leftover USOS hardware and Zvezda 2 as a refuelling depot and service station located at one of the Earth–Moon Lagrange points. However, the entire USOS was not designed for disassembly and will be discarded.[420]
On 30 September 2015, Boeing’s contract with NASA as prime contractor for the ISS was extended to 30 September 2020. Part of Boeing’s services under the contract related to extending the station’s primary structural hardware past 2020 to the end of 2028.[421]
There have also been suggestions in the commercial space industry that the station could be converted to commercial operations after it is retired by government entities.[422]
In July 2018, the Space Frontier Act of 2018 was intended to extend operations of the ISS to 2030. This bill was unanimously approved in the Senate, but failed to pass in the U.S. House.[423][424] In September 2018, the Leading Human Spaceflight Act was introduced with the intent to extend operations of the ISS to 2030, and was confirmed in December 2018.[27][28][425] Congress later passed similar provisions in its CHIPS and Science Act, signed into law by President Joe Biden on 9 August 2022.[426][427]
In January 2022, NASA announced a planned date of January 2031 to de-orbit the ISS using a deorbit module and direct any remnants into a remote area of the South Pacific Ocean.[428]
Cost[edit]
The ISS has been described as the most expensive single item ever constructed.[429] As of 2010, the total cost was US$150 billion. This includes NASA’s budget of $58.7 billion ($89.73 billion in 2021 dollars) for the station from 1985 to 2015, Russia’s $12 billion, Europe’s $5 billion, Japan’s $5 billion, Canada’s $2 billion, and the cost of 36 shuttle flights to build the station, estimated at $1.4 billion each, or $50.4 billion in total. Assuming 20,000 person-days of use from 2000 to 2015 by two- to six-person crews, each person-day would cost $7.5 million, less than half the inflation-adjusted $19.6 million ($5.5 million before inflation) per person-day of Skylab.[430]
In film[edit]
Beside numerous documentaries such as the IMAX documentaries Space Station 3D from 2002,[431] or A Beautiful Planet from 2016,[432] the ISS is subject of feature films such as The Day After Tomorrow (2004),[433] Life (2017),[434] Love (2011),[435] or – together with the Chinese station Tiangong space station – in Gravity (2013).[436]
See also[edit]
- A Beautiful Planet – 2016 IMAX documentary film showing scenes of Earth, as well as astronaut life aboard the ISS
- Center for the Advancement of Science in Space – operates the US National Laboratory on the ISS
- List of commanders of the International Space Station
- List of space stations
- List of spacecraft deployed from the International Space Station
- Politics of outer space
- Science diplomacy
- Space Station 3D – 2002 Canadian documentary
Notes[edit]
- ^ Temporary docking adapter used till Prichal module arrival
- ^ «Zarya» can have a lot of meanings: «daybreak», «dawn» (in the morning) or «afterglow», «evening glow», «sunset» (in the evening). But usually it means «dawn».
- ^ temporary docking adapter is the grey ring surrounding the docking probe of Progress MS 17
- ^ The port had the temporary docking adapter before the SSVP-M or «Hybrid» standard, consisting of the traditional SSVP-G probe‑and‑drogue soft-dock mechanism and an APAS-95 hard-dock collar before Prichal arrival
- ^ Privately funded travellers who have objected to the term include Dennis Tito, the first such traveller,[260] Mark Shuttleworth, founder of Ubuntu,[261] Gregory Olsen and Richard Garriott.[262][263] Canadian astronaut Bob Thirsk said the term does not seem appropriate, referring to his crewmate, Guy Laliberté, founder of Cirque du Soleil.[264] Anousheh Ansari denied being a tourist[265] and took offence at the term.[266]
- ^ ESA director Jörg Feustel-Büechl said in 2001 that Russia had no right to send ‘amateurs’ to the ISS. A ‘stand-off’ occurred at the Johnson Space Center between Commander Talgat Musabayev and NASA manager Robert Cabana who refused to train Dennis Tito, a member of Musabayev’s crew along with Yuri Baturin. Musabayev argued that Tito had trained 700 hours in the last year and was as qualified as any NASA astronaut, and refused to allow his crew to be trained on the USOS without Tito. Cabana would not allow training to begin, and the commander returned with his crew to their hotel.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e Garcia, Mark (9 May 2018). «About the Space Station: Facts and Figures». NASA. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g Peat, Chris (21 May 2021). «ISS – Orbit». Heavens-Above. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
- ^ a b Holman, Joseph (12 October 2022). «ISS (ZARYA)». Satellite Tracking. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ «celestrak».
- ^ a b c NASA (18 February 2010). «On-Orbit Elements» (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- ^ «STS-132 Press Kit» (PDF). NASA. 7 May 2010. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- ^ «STS-133 FD 04 Execute Package» (PDF). NASA. 27 February 2011. Retrieved 27 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Gary Kitmacher (2006). Reference Guide to the International Space Station. Apogee Books Space Series. Canada: Apogee Books. pp. 71–80. ISBN 978-1-894959-34-6. ISSN 1496-6921.
- ^ «Human Spaceflight and Exploration – European Participating States». European Space Agency (ESA). 2009. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- ^ «International Space Station legal framework». European Space Agency (ESA). 19 November 2013. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ a b c «International Space Station Overview». ShuttlePressKit.com. 3 June 1999. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f «Fields of Research». NASA. 26 June 2007. Archived from the original on 23 January 2008.
- ^ a b
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Getting on Board». NASA. 26 June 2007. Archived from the original on 8 December 2007.
- ^ a b «ISS Research Program». NASA. Archived from the original on 13 February 2009. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- ^ Roberts, Jason (19 June 2020). «Celebrating the International Space Station (ISS)». NASA.
- ^ «Central Research Institute for Machine Building (FGUP TSNIIMASH) Control of manned and unmanned space vehicles from Mission Control Centre Moscow» (PDF). Russian Federal Space Agency. Retrieved 26 September 2011.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «NASA Sightings Help Page». Spaceflight.nasa.gov. 30 November 2011. Archived from the original on 5 September 2016. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «NASA – Higher Altitude Improves Station’s Fuel Economy». nasa.gov. 14 February 2019. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ a b
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Current ISS Tracking data». NASA. 15 December 2008. Archived from the original on 25 December 2015. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
- ^ a b c Harwood, William (26 July 2022). «Russia says it will withdraw from the International Space Station after 2024». CBS News. ViacomCBS. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ a b c Roulette, Joey (26 July 2022). «Russia signals space station pullout, but NASA says it’s not official yet». Reuters. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ de Selding, Peter B. (25 February 2015). «Russia – and Its Modules – To Part Ways with ISS in 2024». Space News. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ Bodner, Matthew (17 November 2014). «Russia May Be Planning National Space Station to Replace ISS». The Moscow Times. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ «First crew starts living and working on the International Space Station». European Space Agency. 31 October 2000.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Oct. 31, 2000, Launch of First Crew to International Space Station». NASA. 28 October 2015.
- ^ «Biden-Harris Administration Extends Space Station Operations Through 2030 – Space Station». blogs.nasa.gov.
- ^ a b Nelson, Senator Bill (20 December 2018). «The Senate just passed my bill to help commercial space companies launch more than one rocket a day from Florida! This is an exciting bill that will help create jobs and keep rockets roaring from the Cape. It also extends the International Space Station to 2030!».
- ^ a b «House joins Senate in push to extend ISS». SpaceNews. 27 September 2018. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ a b c Catchpole, John E. (2008). The International Space Station: Building for the Future. Springer-Praxis. ISBN 978-0-387-78144-0.
- ^ «Northrop Grumman Announces Realigned Operating Sectors – WashingtonExec». 25 September 2019. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ ESA — Columbus
- ^ «International Space Station». Astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 9 April 2002. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Heivilin, Donna (21 June 1994). «Space Station: Impact of the Expanded Russian Role on Funding and Research» (PDF). Government Accountability Office. Retrieved 3 November 2006.
- ^ Dismukes, Kim (4 April 2004). «Shuttle–Mir History/Background/How «Phase 1″ Started». NASA. Archived from the original on 16 November 2001. Retrieved 12 April 2007.
- ^ a b «Russia to decide on pullout from ISS since 2025 after technical inspection». TASS. 18 April 2021. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ Dobrovidova, Olga (20 April 2021). «Russia mulls withdrawing from the International Space Station after 2024». Science. American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). doi:10.1126/science.abj1005. ISSN 0036-8075. S2CID 235542488.
- ^ Harwood, William (26 July 2022). «Russia says it will withdraw from the International Space Station after 2024». CBS News. ViacomCBS. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ Roulette, Joey (26 July 2022). «Russia signals space station pullout, but NASA says it’s not official yet». Reuters. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ «Russia is likely to take part in International Space Station until 2028 -RIA». Reuters. 21 September 2022. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Memorandum of Understanding Between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States of America and the Russian Space Agency Concerning Cooperation on the Civil International Space Station». NASA. 29 January 1998. Retrieved 19 April 2009.
- ^ Payette, Julie (10 December 2012). «Research and Diplomacy 350 Kilometers above the Earth: Lessons from the International Space Station». Science & Diplomacy. 1 (4).
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «National Space Policy of the United States of America» (PDF). White House; USA Federal government. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Nations Around the World Mark 10th Anniversary of International Space Station». NASA. 17 November 2008. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ a b c Oberg, James (2005). «International Space Station». World Book Online Reference Center. Retrieved 3 April 2016.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image (MAXI)». JAXA. 2008. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ ESA via SPACEREF «SOLAR: three years observing and ready for solar maximum», 14 March 2011
- ^ «The International Space Station: life in space». Science in School. 10 December 2008. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: NASA – AMS to Focus on Invisible Universe. Nasa.gov (18 March 2011). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: In Search of Antimatter Galaxies – NASA Science. Science.nasa.gov (16 May 2011). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ Aguilar, M. et al. (AMS Collaboration) (3 April 2013). «First Result from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station: Precision Measurement of the Positron Fraction in Primary Cosmic Rays of 0.5–350 GeV» (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 110 (14): 141102. Bibcode:2013PhRvL.110n1102A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.141102. PMID 25166975.
- ^ Staff (3 April 2013). «First Result from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Experiment». AMS Collaboration. Archived from the original on 8 April 2013. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Heilprin, John; Borenstein, Seth (3 April 2013). «Scientists find hint of dark matter from cosmos». Associated Press. Archived from the original on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Amos, Jonathan (3 April 2013). «Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer zeroes in on dark matter». BBC News. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Perrotto, Trent J.; Byerly, Josh (2 April 2013). «NASA TV Briefing Discusses Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Results». NASA. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (3 April 2013). «Tantalizing New Clues Into the Mysteries of Dark Matter». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 August 2017. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Horneck, Gerda; Klaus, David M.; Mancinelli, Rocco L. (March 2010). «Space Microbiology» (PDF). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. American Society for Microbiology. 74 (1): 121–156. Bibcode:2010MMBR…74..121H. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00016-09. PMC 2832349. PMID 20197502. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 August 2011. Retrieved 4 June 2011. (see Space Environment on page 122)
- ^ Amos, Jonathan (23 August 2010). «Beer microbes live 553 days outside ISS». BBC News. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ^ Ledford, Heidi (8 September 2008). «Spacesuits optional for ‘water bears’«. Nature. doi:10.1038/news.2008.1087.
- ^ a b c Buckey, Jay (23 February 2006). Space Physiology. Oxford University Press USA. ISBN 978-0-19-513725-5.
- ^ Grossman, List (24 July 2009). «Ion engine could one day power 39-day trips to Mars». New Scientist. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Boen, Brooke (1 May 2009). «Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity (ADUM)». NASA. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- ^ Rao, Sishir; et al. (May 2008). «A Pilot Study of Comprehensive Ultrasound Education at the Wayne State University School of Medicine». Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 27 (5): 745–749. doi:10.7863/jum.2008.27.5.745. PMID 18424650. S2CID 30566494.
- ^ Fincke, E. Michael; et al. (February 2005). «Evaluation of Shoulder Integrity in Space: First Report of Musculoskeletal US on the International Space Station». Radiology. 234 (2): 319–322. doi:10.1148/radiol.2342041680. PMID 15533948.
- ^ Strickland, Ashley (26 August 2020). «Bacteria from Earth can survive in space and could endure the trip to Mars, according to new study». CNN News. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ Kawaguchi, Yuko; et al. (26 August 2020). «DNA Damage and Survival Time Course of Deinococcal Cell Pellets During 3 Years of Exposure to Outer Space». Frontiers in Microbiology. 11: 2050. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.02050. PMC 7479814. PMID 32983036. S2CID 221300151.
- ^ «Earth Science & Remote Sensing Missions on ISS». NASA. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: May, Sandra, ed. (15 February 2012). «What Is Microgravity?». NASA Knows! (Grades 5-8). Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- ^ «European Users Guide to Low Gravity Platforms». European Space Agency. 6 December 2005. Archived from the original on 2 April 2013. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Materials Science 101». Science@NASA. 15 September 1999. Archived from the original on 14 June 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ^ «Mars500 study overview». ESA. 4 June 2011.
- ^ «Space station may be site for next mock Mars mission». New Scientist. 4 November 2011. Archived from the original on 11 July 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ^ «The Sustainable Utilisation of the ISS Beyond 2015» (PDF). International Astronautical Congress. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- ^ de Selding, Peter B. (3 February 2010). «ESA Chief Lauds Renewed U.S. Commitment to Space Station, Earth Science». Space News.
- ^ «Charlie Bolden». space.com. 4 June 2011.
- ^ Seitz, Virginia A. (19 September 2011). «Memorandum Opinion for the General Counsel, Office of Science and Technology Policy» (PDF). justice.gov. US Justice Department. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ^ Sandal, Gro M.; Manzey, Dietrich (December 2009). «Cross-cultural issues in space operations: A survey study among ground personnel of the European Space Agency». Acta Astronautica. 65 (11–12): 1520–1529. Bibcode:2009AcAau..65.1520S. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2009.03.074. ISSN 0094-5765.
- ^ «Online Materials». European Space Agency. Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ «ISS 3-D Teaching Tool: Spaceflight Challenge I». European Space Agency. 24 May 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ Building Peace in Young Minds through Space Education (PDF). Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space, 53rd Session. June 2010. Vienna, Austria. JAXA. June 2010.
- ^ «JAXA Spaceflight Seeds Kids I : Spaceflight Sunflower seeds – Let’s make them flower! and learn freshly the Earth environment just by contrast with the Space one». JAXA. 2006. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012.
- ^ «JAXA Seeds in Space I : Let’s Cultivate Spaceflight Asagao (Japanese morning glory), Miyako-gusa (Japanese bird’s foot trefoil) Seeds and Identify the Mutants!». JAXA. 2006. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012.
- ^ Murakami, Keiji (14 October 2009). «JEM Utilization Overview» (PDF). JAXA. Steering Committee for the Decadal Survey on Biological and Physical Sciences in Space. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ^ Tanaka, Tetsuo. «Kibo: Japan’s First Human Space Facility». JAXA. Archived from the original on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ «Amateur Radio on the International Space Station». 6 June 2011. Archived from the original on 27 May 2011. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- ^ Riley, Christopher (11 April 2011). «What Yuri Gagarin saw: First Orbit film to reveal the view from Vostok 1». The Guardian. London.
- ^ «Yuri Gagarin’s First Orbit – FAQs». Firstorbit.org. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Warr, Philippa (13 May 2013). «Commander Hadfield bids farewell to ISS with Reddit-inspired Bowie cover». wired.co.uk. Archived from the original on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ «Astronaut bids farewell with Bowie cover version (inc. video)». BBC News. 13 May 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ Davis, Lauren (12 May 2013). «Chris Hadfield sings «Space Oddity» in the first music video in space». Gizmodo.
- ^ Mabbett, Andy (29 November 2017). «Close encounters of the Wikipedia kind: Astronaut is first to specifically contribute to Wikipedia from space – Wikimedia Blog». Wikimedia foundation. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ Petris, Antonella (1 December 2017). «Primo contributo ‘extraterrestre’ su Wikipedia: è di Nespoli». Meteo Web (in Italian). Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ Pearlman, Robert Z. (23 November 2021). «‘The Infinite’ VR space station tour to premiere spacewalk in Houston». Space.com. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ Harbaugh, Jennifer, ed. (19 February 2016). «Manufacturing Key Parts of the International Space Station: Unity and Destiny». NASA. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- ^ «ISS Zvezda». Archived from the original on 20 August 2016. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ «Europe’s Airbus-built Columbus orbital outpost: 10 years in space». Airbus. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ^ «Ten years in perfect «Harmony»! – Thales Group». thalesgroup.com. October 2017.
- ^ «Building ISS». U.S. National Archives & DVIDS. Retrieved 28 October 2021.
- ^ «KSC-08pd0991». 22 April 2008. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
Cape Canaveral, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module toward the payload canister (lower right). The canister will deliver the module, part of the payload for space shuttle Discovery’s STS-124 mission, to Launch Pad 39A. On the mission, the STS-124 crew will transport the Kibo module as well as the Japanese Remote Manipulator System to the International Space Station to complete the Kibo laboratory. The launch of Discovery is targeted for May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
- ^ a b «The ISS to Date». NASA. 9 March 2011. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ Dismukes, Kim (1 December 2002). «Mission Control Answers Your Questions: STS-113 Q17». spaceflight.nasa.gov. NASA. Archived from the original on 24 July 2020. Retrieved 14 June 2009.
- ^ «NASA Facts. The Service Module: A Cornerstone of Russian International Space Station Modules» (PDF). spaceflight.nasa.gov. NASA. January 1999. IS-1999-09-ISS019JSC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 August 2020.
- ^ «STS-88». Science.ksc.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ Liston, Brad (2 November 2000). «Upward Bound: Tales of Space Station Alpha». Time. Archived from the original on 2 April 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2010.
- ^ «Space Station – Impact on the expanded Russian role of funding and research» (PDF). United States General Accounting Office. 21 June 1994. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ^ a b Ladwig, Alan (3 November 2000). «Call Bill Shepherd the Alpha Male of the International Space Station». Space.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2009. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ^ Halvorson, Todd (2 November 2000). «Expedition One Crew Wins Bid To Name Space Station Alpha». Space.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2009. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ^ «Interview with RSC Energia’s Yuri Semenov». Space.com. 3 September 2001. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- ^ «Interview with Yuri Semenov, general designer of Space Rocket corporation Energy». Voice of Russia. 21 March 2001. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- ^ «STS-92». Science.ksc.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 5 March 2011. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (26 July 2005). «Discovery launches – The Shuttle is back». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ «Mini-Research Module 1 (MIM1) Rassvet (MRM-1)». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ «STS-133». NASA. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- ^ «STS-134». NASA. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- ^ «Russia works on a new-generation space module». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 8 April 2016. Retrieved 29 November 2015.
- ^ «Crewed spacecraft docked to ISS’s module Nauka first time». TASS. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ «Rogozin confirmed that the module ‘Science’ placed the tanks from the upper stage ‘Frigate’«. TASS. 25 March 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ «Новости. Новый модуль вошел в состав российского сегмента МКС». roscosmos.ru. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ «NASA – The ISS to Date (03/09/2011)». NASA. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ NASA, International Space Station, Zarya (accessed 19 Apr. 2014)
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (15 October 2008). «Russian Segment: Enterprise». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
- ^ «NASA — NSSDCA — Spacecraft — Details». nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ Loff, Sarah (15 November 2018). «Unity». NASA. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ «Space Station Science Picture of the Day: Speed Limit». www.spaceref.com. 23 April 2003. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ Williams, Suni (presenter) (3 July 2015). Departing Space Station Commander Provides Tour of Orbital Laboratory (video). NASA. Event occurs at 17.46-18.26. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ Roylance, Frank D. (11 November 2000). «Space station astronauts take shelter from solar radiation». The Baltimore Sun. Tribune Publishing. Archived from the original on 1 September 2019. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ Stofer, Kathryn (29 October 2013). «Tuesday/Wednesday Solar Punch». NASA. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ «Service Module | RuSpace». suzymchale.com. Archived from the original on 21 September 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ a b Boeing (2008). «Destiny Laboratory Module». Boeing. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ a b NASA (2003). «U.S. Destiny Laboratory». NASA. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ a b NASA (2001). «STS-98». NASA. Archived from the original on 30 August 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ «August 28, 2009. S.P.Korolev RSC Energia, Korolev, Moscow region». RSC Energia. 28 August 2009. Archived from the original on 21 September 2020. Retrieved 3 September 2009.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (10 November 2009). «Poisk launches to add new room for space station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ^ «Mir close calls». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Pirs Docking Compartment». NASA. 10 May 2006. Retrieved 28 March 2009.
- ^ Williams, Suni (presenter) (19 May 2013). Station Tour: Harmony, Tranquility, Unity (video). NASA. Event occurs at 0.06-0.35. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
So this is Node 2 … this is where four out of six of us sleep.
- ^ NASA (23 October 2007). «STS-120 MCC Status Report #01». NASA.
- ^ Johnson Jr., John (24 October 2007). «Space Shuttle Discovery lifts off». Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ^ William Harwood (2007). «Harmony module pulled from cargo bay». CBS News. Retrieved 26 October 2007.
- ^ Schwartz, John (26 October 2007). «New Room Added to Space Station». The New York Times. Retrieved 26 October 2007.
- ^ NASA (2007). «PMA-3 Relocation». NASA. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ «NASA – NASA Receives Tranquility». Nasa.gov. 23 October 2010. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ^ Harwood, William (11 February 2008). «Station arm pulls Columbus module from cargo bay». Spaceflightnow.com. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2009.
- ^ Kamiya, Setsuko (30 June 2009). «Japan a low-key player in space race». Japan Times. p. 3. Archived from the original on 3 August 2009.
- ^ «Thales Alenia Space and ISS modules – Cupola: a window over the Earth». 26 July 2010. Archived from the original on 26 July 2010.
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris (9 April 2009). «STS-132: PRCB baselines Atlantis’ mission to deliver Russia’s MRM-1». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 12 November 2009.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «STS-132 MCC Status Report #09». NASA. 18 May 2010. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «STS-132 MCC Status Report #13». NASA. 20 May 2010. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^ Ray, Justin (28 June 2010). «Station Crew Takes Soyuz for ‘Spin around the Block’«. SpaceFlight Now. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^ a b «Многоцелевой лабораторный модуль «Наука»«. roscosmos.ru. Archived from the original on 14 July 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ «European Robotic Arm Brochure» (PDF). European Space Agency. p. 9.
- ^ «Sredstva Krepleniya Krupnogabaritnykh Obyektov, SKKO».
- ^ «The Russian Nauka/Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM) General Thread». forum.nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ^ «Schedule of ISS flight events (part 2)». forum.nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ «The Russian Nauka/Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM) General Thread». forum.nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ^ «Russia to bump its ISS crew back to three». www.russianspaceweb.com. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ^ Anatoly Zak [@RussianSpaceWeb] (17 November 2022). «More than 5 hours into the VKD-55 spacewalk, cosmonauts are finishing installation of the large payload platform on the Nauka module, before returning to the ISS» (Tweet). Retrieved 5 December 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ Pearlman, Robert (10 April 2016). «SpaceX Dragon Arrives at Space Station, Delivers Inflatable Room Prototype». Space.com. Retrieved 11 April 2016.
- ^ Harwood, William. «Spacewalkers attach docking adapter to space station for commercial vehicles – Spaceflight Now». Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (21 August 2019). «Spacewalkers Complete Installation of Second Commercial Docking Port». NASA Space Station. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ «Thales Alenia Space reaches key milestone for NanoRacks’ airlock module». Thales Alenia Space (Press release). 20 March 2019. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (2 August 2019). «SpaceX to begin flights under new cargo resupply contract next year». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ «NanoRacks, Boeing to Build First Commercial ISS Airlock Module». NanoRacks. 6 February 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (6 February 2017). «Progress Underway for First Commercial Airlock on Space Station». NASA. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (9 February 2021). «Progress MS-17 lifts off to prepare Prichal module arrival». RussianSpaceWeb.com. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- ^ «В РКК «Энергия» утвердили эскиз нового узлового модуля МКС». Roskosmos. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (25 July 2019). «New docking port, spacesuit and supplies en route to space station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- ^ a b Zak, Anatoly (22 June 2020). «Prichal Node Module, UM». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ S.P. Korolev RSC Energia – News Archived 2 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Energia.ru (13 January 2011). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ a b Atkinson, Ian (19 August 2020). «Russia’s Nauka ISS module arrives at Baikonur for final launch preparations». NASA Spaceflight. Retrieved 20 August 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Spread Your Wings, It’s Time to Fly». NASA. 26 July 2006. Retrieved 21 September 2006.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: NASA (2008). «Consolidated Launch Manifest». NASA. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «EXPRESS Racks 1 and 2 fact sheet». NASA. 12 April 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ «Soyuz TMA-03M docks to ISS, returns station to six crewmembers for future ops». NASASpaceFlight.com. 23 December 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Welsch, L. D. (30 October 2009). «EVA Checklist: STS-129 Flight Supplement» (PDF). NASA.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Space Shuttle Mission: STS-131» (PDF). NASA. February 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Space Shuttle Mission: STS-134» (PDF). NASA. April 2011.
- ^ «HTV2: Mission Press Kit» (PDF). Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. 20 January 2011.
- ^ «Exposed Facility:About Kibo». JAXA. 29 August 2008. Archived from the original on 3 August 2009. Retrieved 9 October 2009.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «NASA–European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF)». NASA. 6 October 2008. Archived from the original on 19 October 2008. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
- ^ «ESA–Columbus–European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF)». ESA. 13 January 2009. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
- ^ «Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES)». ESA. Archived from the original on 9 June 2009. Retrieved 9 October 2009.
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris (10 March 2017). «SpaceX science – Dragon delivers experiments for busy science period». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ Graham, William (3 June 2017). «Falcon 9 launches with CRS-11 Dragon on 100th 39A launch». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ «The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Experiment». CERN. 21 January 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (4 April 2013). «Endeavour’s ongoing legacy: AMS-02 proving its value». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ «ESA and Airbus sign partnership agreement for new ISS commercial payload platform Bartolomeo». SpaceDaily. 9 February 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ^ «Airbus and ESA to partner on Bartolomeo platform». Aerospace Technology. 8 February 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ^ «ISS: Bartolomeo». eoPortal. European Space Agency. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ^ «Canadarm2 and the Mobile Servicing System». NASA. 8 January 2013. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ «Dextre, the International Space Station’s Robotic Handyman». Canadian Space Agency. 18 April 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ «Mobile Base System». Canadian Space Agency. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ a b «Space Shuttle Mission STS-134: Final Flight of Endeavour – Press Kit» (PDF). NASA. April 2011. pp. 51–53. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ «Remote Manipulator System: About Kibo». JAXA. 29 August 2008. Archived from the original on 20 March 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ «International Space Station Status Report #02-03». NASA. 14 January 2002. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ «Russia postpones launch of Nauka research module to orbital outpost to 2021». TASS. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (28 January 2020). «Axiom wins NASA approval to attach commercial habitat to space station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ «NASA taps startup Axiom Space for the first habitable commercial module for the Space Station». TechCrunch. 27 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ «NASA clears Axiom Space to put commercial habitat on space station, with Boeing on the team». GeekWire. 28 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ «Axiom Station Assembly Sequence – Axiom Space Axiom Space». Axiom Space. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ «CAM – location?». NASA Spaceflight Forums. Retrieved 12 October 2009.
- ^ Malik, Tariq (14 February 2006). «NASA Recycles Former ISS Module for Life Support Research». Space.com. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ^ «ICM Interim Control Module». U.S. Naval Center for Space Technology. Archived from the original on 8 February 2007.
- ^ «Russian Research Modules». Boeing. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly. «Russian segment of the ISS». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 3 October 2009.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (22 June 2020). «Russian space program in 2024». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ «Роскосмос примет решение о пути развития российской орбитальной станции до конца июля» [Roscosmos to decide development path of Russian orbital station by end of July]. TASS (in Russian). 19 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (16 April 2021). «Russian Orbital Service Station, ROSS». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ «Научно-энергетический модуль запустят на «Ангаре» с Восточного» [The Science Power Module will be launched on an Angara from Vostochny]. Roscosmos (in Russian). 24 April 2021. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ Freudenrich, Craig (20 November 2000). «How Space Stations Work». Howstuffworks. Archived from the original on 12 December 2008. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ «5–8: The Air Up There». NASAexplores. NASA. Archived from the original on 18 December 2004. Retrieved 31 October 2008.
- ^ Anderson, Clinton P.; 90th Congress, 2nd Session; et al. (30 January 1968). Apollo 204 Accident: Report of the Committee on Aeronautical and Space Sciences, United States Senate (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: US Government Printing Office. p. 8. Report No. 956.
- ^ Davis, Jeffrey R.; Johnson, Robert & Stepanek, Jan (2008). Fundamentals of Aerospace Medicine. Vol. XII. Philadelphia PA, USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 261–264.
- ^ Malik, Tariq (15 February 2006). «Air Apparent: New Oxygen Systems for the ISS». Space.com. Retrieved 21 November 2008.
- ^ a b Barry, Patrick L. (13 November 2000). «Breathing Easy on the Space Station». NASA. Archived from the original on 21 September 2008. Retrieved 21 November 2008.
- ^ «RuSpace | ISS Russian Segment Life Support System». Suzymchale.com. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ Breathing Easy on the Space Station – NASA Science. Science.nasa.gov (13 November 2000). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ «The early history of bifacial solar cell_百度文库». Wenku.baidu.com. 25 October 2010. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (28 April 2016). «Facts and Figures». NASA. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- ^ G. Landis; C-Y. Lu (1991). «Solar Array Orientation Options for a Space Station in Low Earth Orbit». Journal of Propulsion and Power. 7 (1): 123–125. doi:10.2514/3.23302.
- ^ Miller, Thomas B. (24 April 2000). «Nickel-Hydrogen Battery Cell Life Test Program Update for the International Space Station». grc.nasa.gov. Research & Technology. NASA / Glenn Research Center. Archived from the original on 25 August 2009. Retrieved 27 November 2009.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (13 December 2016). «Japanese HTV makes battery delivery to International Space Station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 29 January 2017.
- ^ Patterson, Michael J. (18 June 1999). «Cathodes Delivered for Space Station Plasma Contactor System». grc.nasa.gov. Research & Technology. NASA / Lewis Research Center. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011.
- ^ Price, Steve; Phillips, Tony; Knier, Gil (21 March 2001). «Staying Cool on the ISS». NASA. Retrieved 22 July 2016.
- ^ ATCS Team Overview. (PDF). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ a b «Communications and Tracking». Boeing. Archived from the original on 11 June 2008. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ Mathews, Melissa; James Hartsfield (25 March 2005). «International Space Station Status Report: SS05-015». NASA News. NASA. Retrieved 11 January 2010.
- ^ Harland, David (2004). The Story of Space Station Mir. New York: Springer-Verlag New York Inc. ISBN 978-0-387-23011-5.
- ^ Harvey, Brian (2007). The rebirth of the Russian space program: 50 years after Sputnik, new frontiers. Springer Praxis Books. p. 263. ISBN 978-0-387-71354-0.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (4 January 2010). «Space exploration in 2011». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 26 June 2010. Retrieved 12 January 2010.
- ^ «ISS On-Orbit Status 05/02/10». NASA. 2 May 2010. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^ «Memorandum of Understanding Between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States of America and the Government of Japan Concerning Cooperation on the Civil International Space Station». NASA. 24 February 1998. Retrieved 19 April 2009.
- ^ «Operations Local Area Network (OPS LAN) Interface Control Document» (PDF). NASA. February 2000. Retrieved 30 November 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «ISS/ATV communication system flight on Soyuz». EADS Astrium. 28 February 2005. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (10 November 2009). «STS-129 ready to support Dragon communication demo with ISS». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ Heath, Nick (23 May 2016). «From Windows 10, Linux, iPads, iPhones to HoloLens: The tech astronauts use on the ISS». TechRepublic. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- ^ «April 2019 – ISS On-Orbit Status Report». blogs.nasa.gov. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ Bilton, Nick (22 January 2010). «First Tweet From Space». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 November 2010. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Smith, Will (19 October 2012). «How Fast is the ISS’s Internet? (and Other Space Questions Answered)». Tested.com. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Williams, Matt (25 August 2019). «Upgraded ISS Now Has a 600 Megabit per Second Internet Connection». Universe Today. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ Williams, Matt (25 August 2019). «The ISS Now Has Better Internet Than Most of Us After Its Latest Upgrade». Universe Today. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ Zell, Martin; Suenson, Rosita (13 August 2013). «ESA ISS Science & System – Operations Status Report #150 Increment 36: 13-26 July 2013». European Space Agency. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Burt, Julie (1 June 2001). «Computer problems overcome during STS-100» (PDF). Space Center Roundup. NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Malik, Tariq (14 June 2007). «NASA: Space Station Computer Crash May Extend Shuttle Mission». Space.com. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Klotz, Irene (13 June 2007). «NASA battles failure of space station computer». Reuters. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Klotz, Irene (22 May 2017). «NASA Plans Emergency Spacewalk To Replace Key Computer On International Space Station». Huffpost. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Thomson, Iain (10 May 2013). «Penguins in spa-a-a-ce! ISS dumps Windows for Linux on laptops». The Register. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- ^ Gunter, Joel (10 May 2013). «International Space Station to boldly go with Linux over Windows». The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- ^ An, David (5 June 2019). «US-Taiwan Space Cooperation: Formosat, AMS, and the ISS computer». globaltaiwan.org. Global Taiwan Institute. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- ^ Chin, Jonathan; Tien-pin, Lo (12 June 2017). «Taiwan-designed computer now part of an ISS mission». taipeitimes.com. Taipei Times. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- ^ a b c Kuksov, Igor. «Internet in space: Is there Net on Mars?». Kaspersky. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ «The ISS Now Has Better Internet Than Most of Us After Its Latest Upgrade». ScienceAlert. 26 August 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ Creamer, T.J. [@Astro_TJ] (22 January 2010). «Hello Twitterverse! We r now LIVE tweeting from the International Space Station — the 1st live tweet from Space! 🙂 More soon, send your ?s» (Tweet). Earth orbit. Retrieved 5 December 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ «International Space Station Expeditions». NASA. 10 April 2009. Retrieved 13 April 2009.
- ^ NASA (2008). «International Space Station». NASA. Retrieved 22 October 2008.
- ^ «SpaceX completes emergency crew escape manoeuvre». BBC News. 19 January 2020.
- ^ Morring, Frank (27 July 2012). «ISS Research Hampered By Crew Availability». Aviation Week. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
A commercial capability would allow the station’s crew to grow from six to seven by providing a four-seat vehicle for emergency departures in addition to the three-seat Russian Soyuz capsules in use today.
- ^ Hoversten, Paul (1 May 2011). «Assembly (Nearly) Complete». Air & Space Magazine. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
In fact, we’re designed on the U.S. side to take four crew. The ISS design is actually for seven. We operate with six because first, we can get all our work done with six, and second, we don’t have a vehicle that allows us to fly a seventh crew member. Our requirement for the new vehicles being designed is for four seats. So I don’t expect us to go down in crew size. I would expect us to increase it.
- ^ «Biographies of USSR/Russian Cosmonauts: Padalka». Spacefacts. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ «Biographies of U.S. Astronauts: Whitson». Spacefacts. Archived from the original on 28 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Associated Press, 8 May 2001
- ^ Associated Press, The Spokesman Review, 6 January 2002, p. A4
- ^ Schwartz, John (10 October 2008). «Russia Leads Way in Space Tourism With Paid Trips into Orbit». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 July 2016.
- ^ Boyle, Alan (13 September 2005). «Space passenger Olsen to pull his own weight». NBC News.
- ^ «Flight to space ignited dreams | St. Catharines Standard». Stcatharinesstandard.ca. Archived from the original on 12 September 2012. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «ESA – Human Spaceflight and Exploration – Business – «I am NOT a tourist»«. Esa.int. 18 September 2006. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Interview with Anousheh Ansari, the First Female Space Tourist». Space.com. 15 September 2006. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Harwood, William (12 January 2011). «Resumption of Soyuz tourist flights announced». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Maher, Heather (15 September 2006). «U.S.: Iranian-American To Be First Female Civilian in Space». Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Space Tourists | A Film By Christian Frei». Space-tourists-film.com. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Geocaching – The Official Global GPS Cache Hunt Site». www.geocaching.com.
- ^ Cook, John (29 August 2011). «From outer space to the ocean floor, Geocaching.com now boasts more than 1.5 million hidden treasures». Geekwire.com. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ^ «American game designer follows father into orbit». ABC News. 12 October 2008. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- ^ Thompson, Amy (10 August 2021). «Antares rocket launches heaviest Cygnus cargo ship ever to space station for NASA». Space.com. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ Cook, John; Aksamentov, Valery; Hoffman, Thomas; Bruner, Wes (1 January 2011). «ISS Interface Mechanisms and their Heritage» (PDF). ntrs.nasa.gov (Conference paper). Houston, Texas: The Boeing Company. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
Docking is when one incoming spacecraft rendezvous with another spacecraft and flies a controlled collision trajectory in such a manner so as to align and mesh the interface mechanisms. The spacecraft docking mechanisms typically enter what is called soft capture, followed by a load attenuation phase, and then the hard docked position which establishes an air-tight structural connection between spacecraft. Berthing, by contrast, is when an incoming spacecraft is grappled by a robotic arm and its interface mechanism is placed in close proximity of the stationary interface mechanism. Then typically there is a capture process, coarse alignment and fine alignment and then structural attachment.
- ^
just for Nauka Experimental Airlock Module, that will be berthed to the forward port at its aft docking port by ERA, thereby being attached permanently to it. - ^ Garcia, Mark (8 December 2021). «Visitors to the Station by Country». NASA. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ «ESA;– ATV;– Crew role in mission control». ESA.int. 2 March 2011. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ «ESA – Human Spaceflight and Exploration;– International Space Station;– Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV)». ESA.int. 16 January 2009. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ «Acquisition of Orbital ATK approved, company renamed Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems». SpaceNews. 6 June 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n «Complete ISS flight events». NasaSpaceFlight.com Forum. 10 November 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e «Pirs undocking and deorbit date set». Roscosmos. 22 July 2021. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «Microgravity Research Flights». Glenn Research Center. 10 November 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ Berger, Eric (1 July 2022). «Yes, Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft really could fly astronauts this year». Ars Technica. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ Davenport, Christian (6 April 2020). «After botched test flight, Boeing will refly its Starliner spacecraft for NASA». The Washington Post. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (14 August 2019). «Cargo Dream Chaser solidifies ULA deal by securing six Vulcan Centaur flights». NASASpaceFlight. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ «ESA – ATV – Crew role in mission control». Esa.int. 2 March 2011. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ «ESA – Human Spaceflight and Exploration – International Space Station – Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV)». Esa.int. 16 January 2009. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ Woffinden, David C.; Geller, David K. (July 2007). «Navigating the Road to Autonomous Orbital Rendezvous». Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets. 44 (4): 898–909. Bibcode:2007JSpRo..44..898W. doi:10.2514/1.30734.
- ^ «ISS EO-6». Astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 18 June 2012. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Live listing of spacecraft operations». NASA. 1 December 2009. Archived from the original on 3 August 2008. Retrieved 8 December 2009.
- ^ Memi, Ed. «Space Shuttle upgrade lets astronauts at ISS stay in space longer». Boeing. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ «Human Space Flight Transition Plan» (PDF). NASA.gov. Space Operations Mission Directorate. 30 August 2006.
- ^ «NASA Seeks Proposals for Crew and Cargo Transportation to Orbit». SpaceRef.com (Press release). NASA. 18 January 2006. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- ^ «NASA proposes Soyuz photo op; shuttle launch readiness reviewed (UPDATED)». CBS. Retrieved 11 February 2011.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (25 May 2012). «First Private Craft Docks With Space Station». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 June 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ^ Trinidad, Katherine; Thomas, Candrea (22 May 2009). «NASA’s Space Shuttle Landing Delayed by Weather». NASA. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- ^ Oberg, James (11 January 2004). «Crew finds ‘culprit’ in space station leak». NBC News. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- ^ Harwood, William (18 September 2006). «Oxygen Generator Problem Triggers Station Alarm». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ «University of Toledo alumnus had role in rescue of space station». Toledo Blade. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ^ Peterson, Liz Austin (30 October 2007). «Astronauts notice tear in solar panel». Associated Press. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Stein, Rob (4 November 2007). «Space Station’s Damaged Panel Is Fixed». The Washington Post. Retrieved 4 November 2007.
- ^ Harwood, William (25 March 2008). «Station chief gives detailed update on joint problem». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- ^ Harik, Elliot P.; et al. (2010). The International Space Station Solar Alpha Rotary Joint Anomaly Investigation (PDF). 40th Aerospace Mechanisms Symposium. 12–14 May 2010. Cocoa Beach, Florida. JSC-CN-19606.
- ^ «Crew Expansion Prep, SARJ Repair Focus of STS-126». NASA. 30 October 2008. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- ^ Harwood, William (18 November 2008). «Astronauts prepare for first spacewalk of shuttle flight». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- ^ a b Bergin, Chris (1 April 2009). «ISS concern over S1 Radiator – may require replacement via shuttle mission». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 3 April 2009.
- ^ a b Harwood, William (31 July 2010). «Spacewalks needed to fix station cooling problem». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «NASA ISS On-Orbit Status 1 August 2010 (early edition)». Spaceref.com. 31 July 2010. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «International Space Station Active Thermal Control System». boeing.com. 21 November 2006. Archived from the original on 30 March 2010. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ Harwood, William (10 August 2010). «Wednesday spacewalk to remove failed coolant pump». Spaceflight Now for CBS News.
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris (11 August 2010). «Large success for second EVA as failed Pump Module is removed». NASA Spaceflight.
- ^ Harwood, William (11 August 2010). «Station’s bad pump removed; more spacewalking ahead». Spaceflight Now for CBS News.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (18 August 2010). «ISS cooling configuration returning to normal confirming ETCS PM success». NASASpaceFlight.com. Archived from the original on 24 October 2010.
- ^ Chow, Denise (2 August 2010). «Cooling System Malfunction Highlights Space Station’s Complexity». Space.com.
- ^ Harding, Pete (30 August 2012). «Astronaut duo complete challenging first post-Shuttle US spacewalk on ISS». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ Boucher, Marc (5 September 2012). «Critical Space Station spacewalk a Success». SpaceRef.
- ^ «Astronauts Complete Rare Christmas Eve Spacewalk». Leaker. Associated Press. 24 December 2013. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ^ «ISS Crew Timeline» (PDF). NASA. 5 November 2008. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- ^ «What time zone do they use on the International Space Station? – BBC Science Focus Magazine». Science Focus. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ «NASA – Time in Space, A Space in Time». nasa.gov. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ «A Slice of Time Pie». 17 March 2013. Archived from the original on 17 March 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ «Human Space Flight (HSF) – Crew Answers». spaceflight.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ «Новости. Космонавт рассказал, кто может первым заселиться в модуль «Наука» на МКС». www.roscosmos.ru. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ «At Home with Commander Scott Kelly (Video)». International Space Station: NASA. 6 December 2010. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ «Nauka module prelaunch booklet» (PDF). Roscosmos.
- ^ Broyan, James Lee; Borrego, Melissa Ann; Bahr, Juergen F. (2008). «International Space Station USOS Crew Quarters Development» (PDF). SAE International. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ a b c d e «Daily life». ESA. 19 July 2004. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f Mansfield, Cheryl L. (7 November 2008). «Station Prepares for Expanding Crew». NASA. Retrieved 17 September 2009.
- ^ a b c d «Living and Working on the International Space Station» (PDF). CSA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 April 2009. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ a b Malik, Tariq (27 July 2009). «Sleeping in Space is Easy, But There’s No Shower». Space.com. Retrieved 29 October 2009.
- ^ Bedtime in space. youtube.com. Event occurs at[time needed]. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
- ^ «STEMonstrations: Sleep Science» (AV media). images.nasa.gov. NASA. 13 December 2018. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- ^ Benson, Charles Dunlap and William David Compton. Living and Working in Space: A History of Skylab. NASA publication SP-4208.
- ^ Portree, David S. F. (March 1995). Mir Hardware Heritage (PDF). NASA. p. 86. OCLC 755272548. Reference Publication 1357.
- ^ Nyberg, Karen (12 July 2013). Karen Nyberg Shows How You Wash Hair in Space. YouTube.com. NASA. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- ^ Lu, Ed (8 September 2003). «Greetings Earthling». NASA. Archived from the original on 1 September 2012. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- ^ Pesquet, Thomas (18 August 2021). Thomas tours the MLM module (in French with English subtitles available). YouTube.com. ESA. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 29 August 2021.
- ^ Zimmer, Carl (11 April 2019). «Scott Kelly Spent a Year in Orbit. His Body Is Not Quite the Same». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 May 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
NASA scientists compared the astronaut to his earthbound twin, Mark. The results hint at what humans will have to endure on long journeys through space.
- ^ Garrett-Bakeman, Francine E.; et al. (12 April 2019). «The NASA Twins Study: A multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight». Science. 364 (6436): eaau8650. doi:10.1126/science.aau8650. PMC 7580864. PMID 30975860.
- ^ Strickland, Ashley (15 November 2019). «Astronauts experienced reverse blood flow and blood clots on the space station, study says». CNN News. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ Marshall-Goebel, Karina; et al. (13 November 2019). «Assessment of Jugular Venous Blood Flow Stasis and Thrombosis During Spaceflight». JAMA Network Open. 2 (11): e1915011. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.15011. PMC 6902784. PMID 31722025.
- ^ Than, Ker (23 February 2006). «Solar Flare Hits Earth and Mars». Space.com.
- ^ «A new kind of solar storm». NASA. 10 June 2005.
- ^ «How Much Radiation Are ISS Astronauts Exposed To?». Forbes. 13 November 2018. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ «Galactic Radiation Received in Flight». FAA Civil Aeromedical Institute. Archived from the original on 29 March 2010. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- ^ Suedfeld, Peter; Wilk, Kasia E.; Cassel, Lindi (2011). «Flying with Strangers: Postmission Reflections of Multinational Space Crews». In Vakoch, Douglas A. (ed.). Psychology of Space Exploration, Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. pp. 143–176. ISBN 978-1-46999770-4.
- ^ Manzey, D.; Lorenz, B.; Poljakov, V. (1998). «Mental performance in extreme environments: Results from a performance monitoring study during a 438-day spaceflight». Ergonomics. 41 (4): 537–559. doi:10.1080/001401398186991. PMID 9557591.
- ^ «Behind the Scenes: The Making of an Astronaut». NASA. 23 August 2004. Archived from the original on 19 July 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- ^ Robson, David. «Why astronauts get the ‘space stupids’«. bbc.com.
- ^ Schneider, S. M.; Amonette, W. E.; Blazine, K.; Bentley, J.; c. Lee, S. M.; Loehr, J. A.; Moore, A. D.; Rapley, M.; Mulder, E. R.; Smith, S. M. (2003). «Training with the International Space Station Interim Resistive Exercise Device». Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 35 (11): 1935–1945. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000093611.88198.08. PMID 14600562.
- ^ «Bungee Cords Keep Astronauts Grounded While Running». NASA. 16 June 2009. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ^ Kauderer, Amiko (19 August 2009). «Do Tread on Me». NASA. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ^ Bell, Trudy E. (11 May 2007). «Preventing «Sick» Spaceships». NASA. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ^ Korn, Anne (23 November 2018). «ISS microbes should be monitored to avoid threat to astronaut health». BioMed Central (Press release). Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ Singh, Nitin K.; et al. (23 November 2018). «Multi-drug resistant Enterobacter bugandensis species isolated from the International Space Station and comparative genomic analyses with human pathogenic strains». BMC Microbiology. 18 (1): 175. doi:10.1186/s12866-018-1325-2. PMC 6251167. PMID 30466389.
- ^ Barry, Patrick L. (2000). «Microscopic Stowaways on the ISS». Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ^ Korn, Anne (7 April 2019). «NASA researchers catalogue all microbes and fungi on the International Space Station». BioMed Central (Press release). Retrieved 30 August 2021.
- ^ Sielaff, Aleksandra Checinska; et al. (8 April 2019). «Characterization of the total and viable bacterial and fungal communities associated with the International Space Station surfaces». Microbiome. 7 (50): 50. doi:10.1186/s40168-019-0666-x. PMC 6452512. PMID 30955503.
- ^ Limardo, José G.; Allen, Christopher S.; Danielson, Richard W. (14 July 2013). «Assessment of Crewmember Noise Exposures on the International Space Station». 43rd International Conference on Environmental Systems. Vail, CO: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. doi:10.2514/6.2013-3516. ISBN 978-1-62410-215-8.
- ^ Nakashima, Ann; Limardo, José; Boone, Andrew; Danielson, Richard W. (31 January 2020). «Influence of impulse noise on noise dosimetry measurements on the International Space Station». International Journal of Audiology. 59 (sup1): S40–S47. doi:10.1080/14992027.2019.1698067. ISSN 1499-2027. PMID 31846378. S2CID 209407363.
- ^ a b «International Space Station Medical Operations Requirements Documents (ISS MORD), SSP 50260 Revision B» (PDF). emits.sso.esa.int. NASA. May 2003. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 February 2020.
- ^ Allen, Christopher S.; Denham, Samuel A. (17 July 2011). «International Space Station Acoustics – A Status Report» (PDF). ntrs.nasa.gov (Conference paper). NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX (JSC-CN-24071 / JSC-CN-22173). hdl:2060/20150010438. Archived from the original on 16 February 2015.
- ^ «Safe in Sound Winners». safeinsound.us. 2020. Archived from the original on 25 June 2020.
- ^ Williams, Suni (presenter) (3 July 2015). Departing Space Station Commander Provides Tour of Orbital Laboratory (video). NASA. Event occurs at 18.00-18.17. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
And some of the things we have to worry about in space are fire … or if we had some type of toxic atmosphere. We use ammonia for our radiators so there is a possibility that ammonia could come into the vehicle.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (28 April 2016). «International Space Station Overview». NASA. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ^ a b Cooney, Jim. «Mission Control Answers Your Questions». Houston, TX. Archived from the original on 27 June 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2011.
Jim Cooney ISS Trajectory Operations Officer
- ^ Pelt, Michel van (2009). Into the Solar System on a String : Space Tethers and Space Elevators (1st ed.). New York, NY: Springer New York. p. 133. ISBN 978-0-387-76555-6.
- ^ «Europe’s ATV-2 departs ISS to make way for Russia’s Progress M-11M». NASASpaceFlight.com. 20 June 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Simberg, Rand (29 July 2008). «The Uncertain Future of the International Space Station: Analysis». Popular Mechanics. Archived from the original on 31 March 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ a b «ISS Environment». Johnson Space Center. Archived from the original on 13 February 2008. Retrieved 15 October 2007.
- ^ «Rocket company tests world’s most powerful ion engine». Newscientist.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ^ «Executive summary» (PDF). Ad Astra Rocket Company. 24 January 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 March 2010. Retrieved 27 February 2010.
- ^ «DMS-R: ESA’s Data Management System». www.esa.int.
- ^ «Exercising Control 49 months of DMS-R Operations» (PDF).
- ^ «Russian / US GNC Force Fight» (PDF). pims.grc.nasa.gov. Glenn Research Center. 7 October 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2012. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «International Space Station Status Report #05-7». NASA. 11 February 2005. Archived from the original on 17 March 2005. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ Roithmayr, Carlos (2003). Dynamics and Control of Attitude, Power, and Momentum for a Spacecraft Using Flywheels and Control Moment Gyroscopes (PDF). Langley Research Center: NASA. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (14 June 2007). «Atlantis ready to support ISS troubleshooting». NASASPaceflight.com. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ Hoffman, Michael (3 April 2009). «National Space Symposium 2009: It’s getting crowded up there». Defense News. Retrieved 7 October 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Whipple, F. L. (1949). «The Theory of Micrometeoroids». Popular Astronomy. Vol. 57. p. 517. Bibcode:1949PA…..57..517W.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (28 June 2011). «STS-135: FRR sets 8 July Launch Date for Atlantis – Debris misses ISS». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 28 June 2011.
- ^ Nahra, Henry (24–29 April 1989). «Effect of Micrometeoroid and Space Debris Impacts on the Space Station Freedom Solar Array Surfaces» (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 7 October 2009.
- ^ «Space Suit Punctures and Decompression». The Artemis Project. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- ^ Plain, Charlie (16 July 2004). «Superhero Ceramics!». NASA.gov. Archived from the original on 23 January 2008.
- ^ «State space corporation ROSCOSMOS |». en.roscosmos.ru.
- ^ «Microsoft PowerPoint – EducationPackage SMALL.ppt» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2008. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Courtland, Rachel (16 March 2009). «Space station may move to dodge debris». New Scientist. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ^ a b «ISS Maneuvers to Avoid Russian Fragmentation Debris» (PDF). Orbital Debris Quarterly News. 12 (4): 1&2. October 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ^ «Avoiding satellite collisions in 2009» (PDF). Orbital Debris Quarterly News. 14 (1): 2. January 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ^ «ATV carries out first debris avoidance manoeuvre for the ISS». ESA. 28 August 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2010.
- ^ «ISS crew take to escape capsules in space junk alert». BBC News. 24 March 2012. Retrieved 24 March 2012.
- ^ «Station Crew Takes Precautions for Close Pass of Space Debris». NASA Blog. 16 June 2015. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Grush, Loren (15 November 2021). «Russia blows up a satellite, creating a dangerous debris cloud in space». The Verge.
- ^ «International Space Station swerves to dodge space junk». Reuters. 3 December 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ Price, Pat (2005). The Backyard Stargazer: An Absolute Beginner’s Guide to Skywatching With and Without a Telescope. Gloucester, MA: Quarry Books. p. 140. ISBN 978-1-59253-148-6.
- ^ «Problem 346: The International Space Station and a Sunspot: Exploring angular scales» (PDF). Space Math @ NASA !. 19 August 2018. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ «Artificial Satellites > (Iridium) Flares». Calsky.com. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «How to Spot the International Space Station (and other satellites)». Hayden Planetarium. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ NASA (2 July 2008). «International Space Station Sighting Opportunities». NASA. Archived from the original on 21 December 2015. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
- ^ «ISS – Information». Heavens-Above.com. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ^ Weaver, Harold F. (1947). «The Visibility of Stars Without Optical Aid». Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 59 (350): 232. Bibcode:1947PASP…59..232W. doi:10.1086/125956. S2CID 51963530.
- ^ «ISS visible during the daytime». Spaceweather.com. 5 June 2009. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
- ^ «Get notified when the International Space Station is in your area». 3 News NZ. 6 November 2012. Archived from the original on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2013.
- ^ «Satellite Watching». HobbySpace. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Space StationAstrophotography – NASA Science». Science.nasa.gov. 24 March 2003. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «[VIDEO] The ISS and Atlantis shuttle as seen in broad daylight». Zmescience.com. 20 July 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Space Station Transiting 2017 ECLIPSE, My Brain Stopped Working – Smarter Every Day 175». youtube.com. 22 August 2017. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021.
- ^ Grossman, Lisa. «Moon and Space Station Eclipse the Sun». Wired.
- ^ «International Cooperation». NASA. 25 March 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (25 March 2015). «International Cooperation». NASA. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ Farand, Andre. «Astronauts’ behaviour onboard the International Space Station: regulatory framework» (PDF). International Space Station. UNESCO.
- ^ «Boris Johnson to Announce New Russia Sanctions After Ukraine Invasion» – via www.youtube.com.
- ^ «The Russian invasion of Ukraine will have myriad impacts on spaceflight». Ars Technica. 25 February 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ Berger, Eric (2 April 2022). «Russia asked NASA to end sanctions to save the ISS, but the West didn’t blink». Ars Technica.
- ^ «Nasa explores how to keep international space station in orbit without Russian help». the Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 1 March 2022. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ United Nations Treaties and Principles on Outer Space. (PDF). United Nations. New York. 2002. ISBN 92-1-100900-6. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Tier 2 EIS for ISS» (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ a b
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Suffredini, Michael (October 2010). «ISS End-of-Life Disposal Plan» (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 7 March 2012.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (22 May 2009). «Russia ‘to save its ISS modules’«. BBC News. Retrieved 23 May 2009.
- ^ «DC-1 and MIM-2». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 10 February 2009. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Maass, Ryan (30 September 2015). «NASA extends Boeing contract for International Space Station». Space Daily. UPI. Retrieved 2 October 2015.
- ^ Grush, Loren (24 January 2018). «Trump administration wants to end NASA funding for the International Space Station by 2025». The Verge. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- ^ «Commercial space bill dies in the House». SpaceNews.com. 22 December 2018. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ Cruz, Ted (21 December 2018). «S.3277 – 115th Congress (2017–2018): Space Frontier Act of 2018». United States Congress. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ Babin, Brian (26 September 2018). «H.R.6910 – 115th Congress (2017-2018): Leading Human Spaceflight Act». United States Congress. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ Johnson, Lamar (9 August 2022). «Biden ends slog on semiconductor bill with signature». Politico. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- ^ Errick, Kirsten (4 August 2022). «NASA Authorization Act Aims to Strengthen U.S. Space Exploration». Nextgov.com. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- ^ «NASA plans to take International Space Station out of orbit in January 2031 by crashing it into ‘spacecraft cemetery’«. Sky News. 1 February 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ Zidbits (6 November 2010). «What Is The Most Expensive Object Ever Built?». Zidbits.com. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ Lafleur, Claude (8 March 2010). «Costs of US piloted programs». The Space Review. Retrieved 18 February 2012. See author correction in comments.
- ^ «Space Station 3D». IMDb. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ «A Beautiful Planet — Experience Earth Like Never Before». abeautifulplanet.imax.com. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ Shaw, Debra Benita (2008). Technoculture: The Key Concepts. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 67. ISBN 978-1-84520-298-9.
- ^ «Life». Sony Pictures. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ «Love». IMDb. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ «Gravity». IMDb. Retrieved 21 March 2022.
Attribution:
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Further reading[edit]
- Reference Guide to the International Space Station (PDF) (Utilization ed.). NASA. September 2015. NP-2015-05-022-JSC.
- Reference Guide to the International Space Station (PDF) (Assembly Complete ed.). NASA. 2010. ISBN 978-0-16-086517-6. NP-2010-09-682-HQ.
- O’Sullivan, John. European Missions to the International Space Station: 2013 to 2019 (Springer Nature, 2020).
- Ruttley, Tara M., Julie A. Robinson, and William H. Gerstenmaier. «The International Space Station: Collaboration, Utilization, and Commercialization.» Social Science Quarterly 98.4 (2017): 1160–1174. online
External links[edit]
- Official website
- ISS Location
Agency ISS websites[edit]
Research[edit]
- NASA: Daily ISS Reports
- NASA: Station Science
- ESA: Columbus
- RSC Energia: Science Research on ISS Russian Segment Archived 11 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine
Live viewing[edit]
- Live ISS webcam by NASA at uStream.tv
- Live HD ISS webcams by NASA HDEV at uStream.tv
- Sighting opportunities at NASA.gov
- Complete Orbital Position at KarhuKoti.com
- Real-time position at Heavens-above.com
- Real-time tracking and position at uphere.space
Multimedia[edit]
- Johnson Space Center image gallery at Flickr.com
- ISS tour with Sunita Williams by NASA at YouTube.com
- Journey to the ISS by ESA at YouTube.com
- The Future of Hope, Kibō module documentary by JAXA at YouTube.com
- Seán Doran’s compiled videos of orbital photography from the ISS: Orbit – Remastered, Orbit: Uncut; The Four Seasons, Nocturne – Earth at Night, Earthbound, The Pearl (see Flickr album for more)
From Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

ISS of STS-132 |
|
 |
|
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| SATCAT no. | 25544 |
| Call sign | Alpha, Station |
| Crew | Fully crewed: 3-6 Currently aboard:7 (Expedition68) |
| Launch | 20 November 1998; 24 years ago |
| Launch pad |
|
| Mass | ≈ 419,725 kg (925,335 lb)[1] |
| Length | 72.8 m (239 ft) |
| Width | 108.5 m (356 ft) |
| Height | ≈ 20 m (66 ft) nadir–zenith, arrays forward–aft (27 November 2009)[dated info] |
| Pressurised volume | 931.57 m3 (32,898 cu ft)[2] (28 May 2016) |
| Atmospheric pressure | 101.3 kPa (29.9 inHg; 1.0 atm) |
| Perigee | 408 km (253.5 mi) AMSL[3] |
| Apogee | 410 km (254.8 mi) AMSL[3] |
| Orbital inclination | 51.64°[3] |
| Orbital speed | 7.66 km/s[3] (27,600 km/h; 17,100 mph) |
| Orbital period | 92.68 minutes[3] |
| Orbits per day | 15.54[3] |
| Orbit epoch | 14 May 2019 13:09:29 UTC[3] |
| Days in orbit | 24 years, 1 month, 22 days (11 January 2023) |
| Days occupied | 22 years, 2 months, 8 days (11 January 2023) |
| No. of orbits | 116,178 as of May 2019[3] |
| Orbital decay | 2 km/month |
| Statistics as of 9 March 2011 (unless noted otherwise) References: [1][3][4][5][6] |
|
| Configuration | |

Station elements as of July 2021 |
The International Space Station (ISS) is a space station, a very large satellite that people can live in for several months at a time. It was put together in Low Earth orbit up until 2011, but other bits have been added since then. The last part, a Bigelow module was added in 2016. The station is a joint project among several areas of the world: the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada. Other nations such as Brazil, Italy, and China also work with the ISS through cooperation with other countries.
Building the ISS began in 1998, when Russian and American space modules were joined together.
Origin[change | change source]
In the early 1980s, NASA planned Space Station Freedom as a counterpart to the Soviet Salyut and Mir space stations. It never left the drawing board and, with the end of the Soviet Union and the Cold War, it was cancelled. The end of the Space Race prompted the U.S. administration officials to start negotiations with international partners Europe, Russia, Japan and Canada in the early 1990s in order to build a truly international space station. This project was first announced in 1993 and was called Space Station Alpha.[7] It was planned to combine the proposed space stations of all participating space agencies: NASA’s Space Station Freedom, Russia’s Mir-2 (the successor to the Mir Space Station, the core of which is now Zvezda) and ESA’s Columbus that was planned to be a stand-alone spacelab.
Manufacturing[change | change source]
The ISS components was manufactured in various factories all over the world, and were all shipped into the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center for last stages of manufacturing, machine assembly and launch processing. The components are made from stainless steel, titanium, aluminum and copper.
Assembly[change | change source]
The assembly of the International Space Station is a great event in space architecture.[4] Russian modules launched and docked by their rockets. All other pieces were delivered by the Space Shuttle. The Bigelow Module was delivered with a Falcon 9. As of 5 June 2011, they had added 159 components during more than 1,000 hours of EVA.[8] Many of the modules that launched on the Space Shuttle were tested on the ground at the Space Station Processing Facility to find and correct problems before launch.
The first section, the Zarya Functional Cargo Block, was put in orbit in November 1998 on a Russian Proton rocket. Two further pieces (the Unity Module and Zvezda service module) were added before the first crew, Expedition 1, was sent. Expedition 1 docked to the ISS on 1 November 2000, and consisted of U.S. astronaut William Shepherd and two Russian cosmonauts, Yuri Gidzenko and Sergey Krikalev. Since then, it has continuously been home to astronauts and cosmonauts to the present day.
| Parts | Assembly flight | Launch date | Launch vehicle | Separate Views | View with station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zarya (FGB)[9] | 1A/R | 1998-11-20 | Proton-K | 
|

|
||
| Unity (Node 1),[10] PMA-1 & PMA-2 | 2A | 1998-12-04 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-88) | 
|

|
||
| Zvezda (Service Module)[11] | 1R | 2000-07-12 | Proton-K | 
|

|
||
| Z1 Truss & PMA-3 | 3A | 2000-10-11 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-92) | 
|

|
||
| P6 Truss & Solar Arrays | 4A | 2000-11-30 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-97) | 
|

|
||
| Destiny (US Laboratory)[12] | 5A | 2001-02-07 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-98) | 
|

|
||
| External Stowage Platform-1 | 5A.1 | 2001-03-08 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-102) | 
|

|
||
| Canadarm2 (SSRMS) | 6A | 2001-04-19 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-100) | 
|

|
||
| Quest (Joint Airlock)[13] | 7A | 2001-07-12 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-104) | 
|

|
||
| Pirs (Docking Compartment & Airlock) | 4R | 2001-09-14 | Soyuz-U (Progress M-SO1) |

|

|
||
| S0 Truss[14] | 8A | 2002-04-08 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-110) | 
|

|
||
| Mobile Base System | UF2 | 2002-06-05 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-111) | 
|

|
||
| S1 Truss | 9A | 2002-10-07 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-112) | 
|

|
||
| P1 Truss | 11A | 2002-11-23 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-113) | 
|
|||
| ESP-2 | LF1 | 2005-07-26 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-114) | 
|

|
||
| P3/P4 Truss & Solar Arrays[15] | 12A | 2006-09-09 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-115) | 
|

|
||
| P5 Truss[16] | 12A.1 | 2006-12-09 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-116) | 
|

|
||
| S3/S4 Truss & Solar Arrays | 13A | 2007-06-08 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-117) | 
|

|
||
| S5 Truss and ESP-3 | 13A.1 | 2007-08-08 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-118) | 
|

|
||
| Harmony (Node 2) Relocation of P6 Truss |
10A | 2007-10-23 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-120) | 
|

|
||
| Columbus (European Laboratory)[17] | 1E | 2008-02-07 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-122) | 
|

|
||
| Dextre (SPDM) Japanese Logistics Module (ELM-PS) |
1J/A | 2008-03-11 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-123) | 
|

|
||
| Japanese Pressurized Module (JEM-PM) JEM Robotic Arm (JEM-RMS)[18][19] |
1J | 2008-05-31 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-124) | 
|

|
||
| S6 Truss & Solar Arrays | 15A | 2009-03-15 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-119) | 
|

|
||
| Japanese Exposed Facility (JEM-EF) | 2J/A | 2009-07-15 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-127) | 
|

|
||
| Poisk (MRM-2)[20][21] | 5R | 2009-11-10 | Soyuz-U (Progress M-MIM2) |

|

|
||
| ExPRESS Logistics Carriers 1 & 2 | ULF3 | 2009-11-16 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-129) | 
|

|
||
| Cupola & Tranquility (Node 3) |
20A | 2010-02-08 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-130) | 
|

|
||
| Rassvet (MRM-1)[22] | ULF4 | 2010-05-14 | Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-132) | 
|

|
||
| Leonardo (PMM) and EXPRESS Logistics Carrier 4 | ULF5 | 2011-02-24 | Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-133) | 
|

|
||
| Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, OBSS and EXPRESS Logistics Carrier 3 | ULF6 | 2011-05-16 | Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-134) | 
|

|

|
|
| Bigelow Expandable Activity Module[23] | 2016-04-08 | Falcon 9
(SpaceX CRS-8) |

|
||||
| Parts | Assembly flight | Launch date | Launch vehicle | Separate View | View with station |
Life in space[change | change source]
Bedtime[change | change source]
People living in the space station have to get used to all kinds of changes from life on Earth. It takes them only 90 minutes to orbit (go around) the earth, so the sun looks as if it is rising and setting 16 times a day. This can be confusing, especially when one is trying to decide when they should go to bed. The astronauts try to keep a 24-hour-schedule anyway. At bedtime, they have to sleep in sleeping bags that are stuck to the wall. They have to strap themselves inside so they will not float away while sleeping.[24]
En:wikt:Strap
Zero gravity[change | change source]
In orbit there is no G-Force (this is called free fall or zero gravity). To help prepare astronauts experience zero gravity, NASA trainers put the astronauts in water. Because water makes one float, this is a little like experiencing no gravity. However, in water they can push against the water and move around. In zero gravity, there is nothing to push against, so they just float in the air. Another way of training is going in a plane and making the plane fall to earth very quickly. This lets people experience zero gravity for a very short time. This training can make people quite sick at first.
In zero gravity, the astronauts do not use their legs very much, so they need to get lots of exercise to keep them from becoming too weak. Without gravity, astronauts can get big upper bodies and skinny legs. This is called chicken-leg syndrome. Astronauts must exercise hard, every day, to remain healthy.
Eating in space style is difficult. Water and other liquids do not flow down in space, so if any were spilled in the space station, it would float around everywhere. Liquids can ruin electronic equipment, so astronauts have to be very careful in space. They drink by sucking water out of a bag, or from a tube stuck to the wall. They cannot put their food on plates because it would just float right off, so they put it in pouches and eat from the pouches. The food they eat is usually dried, because any crumbs can ruin the equipment.
Sometimes fresh fruits and vegetables are sent up to the astronauts, but it is very expensive and hard to send it, so they have to bring plenty of food with them.[24]
Bathroom[change | change source]
In space, the bathroom should probably be called the restroom instead, because one really can not take baths there. Instead, astronauts use squirt guns to take a shower. One person squirts himself with a gun while other people stand outside with a water vacuum to get rid of all the water that floats out of the shower. This is quite hard, so astronauts usually just take a «sponge bath» with a wet cloth.
Toilets can be another problem. Toilets are supposed to use gravity to work. When one flushes a toilet, gravity makes the water go down. Since the astronauts on the ISS do not feel any gravity, the toilet must be attached to the astronauts and gently suck away all their waste.[24]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Garcia, Mark (9 May 2018). «About the Space Station: Facts and Figures». NASA. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ↑ «Space to Ground: Friending the ISS: 06/03/2016». YouTube.com. NASA. 3 June 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Peat, Chris (28 September 2018). «ISS – Orbit». Heavens-Above. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 NASA (18 February 2010). «On-Orbit Elements» (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- ↑ «STS-132 Press Kit» (PDF). NASA. 7 May 2010. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- ↑ «STS-133 FD 04 Execute Package» (PDF). NASA. 27 February 2011. Retrieved 27 February 2011.
- ↑ GAO (June 1994). «Space Station: Impact of the Expanded Russian Role on Funding and Research» (PDF). GAO. Retrieved 3 November 2006.
- ↑ «The ISS to Date». NASA. 9 March 2011. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ↑ Wade, Mark (15 July 2008). «ISS Zarya». Encyclopaedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 27 February 2009. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ↑ «Unity Connecting Module: Cornerstone for a Home in Orbit» (PDF). NASA. January 1999. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 March 2009. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ↑ «Zvezda Service Module». NASA. 11 March 2009. Archived from the original on 23 March 2009. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ↑ «US Destiny Laboratory». NASA. 26 March 2007. Archived from the original on 9 July 2007. Retrieved 26 June 2007.
- ↑ «Space Station Extravehicular Activity». NASA. 4 April 2004. Archived from the original on 3 April 2009. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ↑ «Space Station Assembly: Integrated Truss Structure». NASA. Archived from the original on 7 December 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2007.
- ↑ «P3 and P4 to expand station capabilities, providing a third and fourth solar array» (PDF). Boeing. July 2006. Retrieved 2 December 2007.
- ↑ «STS-118 MISSION OVERVIEW: BUILD THE STATION…BUILD THE FUTURE» (PDF). NASA PAO. July 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 December 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2007.
- ↑ «Columbus laboratory». ESA. 10 January 2009. Archived from the original on 30 March 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ↑ «About Kibo». JAXA. 25 September 2008. Archived from the original on 10 March 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ↑ «Kibo Japanese Experiment Module». NASA. 23 November 2007. Archived from the original on 23 October 2008. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- ↑ Zak, Anatoly. «Docking Compartment-1 and 2». RussianSpaceWeb.com. Archived from the original on 10 February 2009. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- ↑ Bergin, Chris (9 November 2009). «Russian module launches via Soyuz for Thursday ISS docking». NASASpaceflight.com. Archived from the original on 13 November 2009. Retrieved 10 November 2009.
- ↑ «NASA Extends Contract With Russia’s Federal Space Agency» (Press release). NASA. 9 April 2007. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 15 June 2007.
- ↑ «NASA to Test Bigelow Expandable Module on Space Station». NASA. 16 January 2013. Retrieved 16 January 2013.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 «Living and Working on the International Space Station» (PDF). CSA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 April 2009. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
Other websites[change | change source]
- International Space Station -Citizendium

(Image credit: NASA)
The International Space Station (ISS) is a multi-nation construction project that is the largest single structure humans ever put into space. Its main construction was completed between 1998 and 2011, although the station continually evolves to include new missions and experiments. It has been continuously occupied since Nov. 2, 2000.
The ISS is not owned by one single nation and is a «co-operative programme» between Europe, the United States, Russia, Canada and Japan, according to the European Space Agency (ESA). The International Space Station costs about $3 billion per year for NASA to operate, roughly a third of the human spaceflight budget, according to (opens in new tab) the agency’s office of the inspector general.
Elizabeth Howell (Ph.D.) has been tracking the International Space Station program since the first module was launched. She covers all aspects of spacefight, including ISS launches, missions and spacewalks.
As of May 2022, 258 individuals from 20 countries (opens in new tab) have visited the International Space Station. The top participating countries include the United States (158 people) and Russia (54 people). Astronaut time and research time on the space station are allocated to space agencies according to how much money or resources (such as modules or robotics) they contribute.
The ISS includes contributions from 15 nations. NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia) and the European Space Agency are the major partners of the space station who contribute most of the funding; the other partners are the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Through a private company called Axiom Space, private astronauts are starting to work on the orbiting complex, from time to time; additionally, astronauts from other nations such as the United Arab Emirates do fly occasionally to the ISS.
Related: International Space Station: Live updates
(opens in new tab)
Current plans call for the space station to be operated through at least 2024, with the partners discussing a possible extension. NASA has approved an extension to 2030, although Russia says it will withdraw after 2024 to focus on building its own space station around 2028. How the station will be operated after Russia’s departure has not yet been determined. After 2030, plans for the International Space Station are not clearly laid out either. It could be deorbited, or recycled for future commercial space stations in orbit.
Crews aboard the ISS are assisted by mission control centers in Houston and Moscow and a payload control center in Huntsville, Ala. Other international mission control centers support the space station from Japan, Canada and Europe. Elements of the ISS are controlled from mission control centers in Houston or Moscow.
(opens in new tab)
International Space Station and Russia
Russia is a major partner in the International Space Station, but that relationship is changing. In February 2022, Russia undertook an internationally condemned invasion of Ukraine. As a result, numerous international space partnerships were dissolved. Russia, the United States and the other ISS partners do continue to operate the space station as normal, for now, NASA has emphasized.
In July 2022, Russia announced it would withdraw from the ISS after 2024. Its goals, Roscosmos said, are to build a new Russian Orbital Space Station around 2028 or so. The withdrawal will be gradual and the international partners are in discussions about the transition.
The ISS cannot be separated into independent Russia and United States sections as the complex is interdependent. NASA has said (opens in new tab)the U.S. supplies power, while the Russians control major propulsion maneuvers. It may be possible to independently raise the orbit of the ISS through U.S. spacecraft, which NASA and its partners are testing.
The ISS does require such maneuvers to avoid falling into the Earth’s atmosphere and dodging orbital space debris. Russia conducted an anti-satellite missile test in November 2021 that has seen debris come close to the ISS orbit and require the crews to shelter in place; at the time, NASA and the United States expressed displeasure with the situation.
(opens in new tab)
How to see the International Space Station
The International Space Station location is in orbit around the Earth, at an average altitude of 248 miles (400 kilometers). It circles the globe every 90 minutes at a speed of about 17,500 mph (28,000 km/h). In one day, the station travels about the distance it would take to go from Earth to the moon and back.
The International Space Station at night is highly visible from Earth, appearing as a luminous moving point of light and rivaling the brilliant planet Venus in brightness. It can be seen from Earth without the use of a telescope by night sky observers who know when and where to look.
You can also take pictures of the International Space Station with the right equipment; our guide takes you through how to photograph the ISS. For more information on International Space Station trackers to see and track the space station, check out our guide.
Related: This International Space Station VR experience lets you explore the ISS… and it’s as amazing as it sounds
(opens in new tab)
Life on the International Space Station
There is typically an international crew of seven people that live and work inside the ISS. However, during the changeover of crew members, this number can vary; for example, in 2009, 13 crew members visited the ISS. This is also the record for the most people in space at one time. Occasionally, private missions such as those from Axiom Space bring non-professional astronauts on board the space station, too.
Typically, astronauts travel to the space station via SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsule or, in the case of Russian cosmonauts, a Russian Soyuz capsule. The Soyuz was the primary form of transportation for all astronauts and cosmonauts after NASA’s space shuttle program retired in 2011. Crew Dragon began flying people starting with the Demo-2 mission that launched on May 30, 2020. Boeing’s Starliner is preparing for launching humans after it’s successful uncrewed Orbital Flight Test 2 (OFT-2) in 2022.
Once at the station, astronauts will typically spend a mission period of around six months conducting various science experiments and maintaining and repairing the ISS. Outside of work, astronauts will spend at least two hours on exercise and personal care. They also occasionally perform spacewalks, conduct media/school events for outreach, and post updates to social media. The first astronaut to tweet from space was Mike Massimino, who did it from a space shuttle in May 2009.
Bedrooms in the ISS typically include small bunk beds. The astronauts tether themselves to a wall or allow themselves to freely float in the small space, depending on their preference. Crews temporarily visiting for just a few days may sleep in their spaceship or in a spare spot on the station, which is allowed as long as they tether themselves in space.
The ISS is a platform for long-term research for human health, which NASA bills as a key stepping stone to letting humans explore other solar system destinations such as the moon or Mars.
Related: First ‘Guardian’ in space: NASA astronaut on ISS enters Space Force
Human bodies change in microgravity, including alterations to muscles, bones, the cardiovascular system and the eyes; many scientific investigations are trying to characterize how severe the changes are and whether they can be reversed. Astronauts also participate in testing out products — such as an espresso machine or 3D printers — or doing biological experiments, such as on rodents or plants, which the astronauts can grow and sometimes eat in space. As the only microgravity laboratory in existence, the ISS has facilitated more than 3,600 researchers to conduct more than 2,500 experiments to date.
Astronauts only have limited spare time in space, but they use it for activities like looking out the window, talking with friends and family, taking pictures or doing hobbies like playing instruments or sewing. One astronaut, Mark Kelly, once donned a gorilla suit on the ISS in 2016 as a practical joke on ground controllers.
(opens in new tab)
Crews are not only responsible for science, but also for maintaining the station. Sometimes, this requires that they venture on spacewalks to perform repairs. From time to time, these repairs can be urgent — such as when a part of the ammonia system fails, which has happened a couple of times. Spacewalk safety procedures were changed after a potentially deadly 2013 incident when astronaut Luca Parmitano’s helmet filled with water while he was working outside the station.
NASA now responds quickly to «water incursion» incidents. It also has added pads to the spacesuits to soak up the liquid, and a tube to provide an alternate breathing location should the helmet fill with water. In May 2022, NASA suspended spacewalks again following another water incursion incident, which is still being investigated; Russian Orlan spacewalks are still continuing as that is an independently manufactured spacesuit.
NASA has produced several machines to reduce the need for spacewalks, including the humanoid Robonaut 2. The dexterous machine joined the ISS crew back in 2011, however, after discovering a fault in the machine, Robonaut 2 was sent home to Earth in 2018, for repairs. Also, onboard the ISS are several external robotic arms that can tackle maintenance issues remotely, such as the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (SPDM) — also known as Dextre — and the Canadarm2 (a 57.7-foot-long robotic arm). A European Robotic Arm on the Russian segment will be the third large operational arm on the space station following the end of its installation and commissioning, which is ongoing in 2022.
Related: How to photograph the ISS
How big is the International Space Station?
The space station, including its large solar arrays, spans the area of a U.S. football field, including the end zones, and has a mass of 925,335 lbs. (419,725 kilograms), not including visiting vehicles. The complex now has more livable room than a conventional 6-bedroom house and has 2 bathrooms, gym facilities and a 360-degree bay window. Astronauts have also compared the space station’s living space to the cabin of a Boeing 747 jumbo jet.
(opens in new tab)
International Space Station modules
The International Space Station was taken into space piece-by-piece and gradually built in orbit using spacewalking astronauts and robotics. Most missions used NASA’s space shuttle to carry up the heavier pieces, although some individual modules were launched on single-use rockets. The ISS includes modules and connecting nodes that contain living quarters and laboratories, as well as exterior trusses that provide structural support, and solar panels that provide power.
Related: International Space Station at 20: A Photo Tour
The first module, the Russia Zarya, launched on Nov. 20, 1998, on a Proton rocket. Two weeks later, space shuttle flight STS-88 launched the NASA Unity/Node 1 module. Astronauts performed spacewalks during STS-88 to connect the two parts of the station together; later, other pieces of the station were launched on rockets or in the space shuttle cargo bay. Some of the other major modules and components include:
- The truss, airlocks and solar panels (launched in stages throughout the ISS lifetime; docking adapters were launched in 2017 for new commercial spacecraft)
- Zvezda (Russia; launched in 2000)
- Destiny Laboratory Module (NASA; launched 2001)
- Canadarm2 robotic arm (CSA; launched 2001). It was originally used only for spacewalks and remote-controlled repairs. Today it also is regularly used to berth cargo spacecraft to the space station – spacecraft that can’t use the other ports.
- Harmony/Node 2 (NASA; launched 2007)
- Columbus orbital facility (ESA; launched 2008)
- Dextre robotic hand (CSA; launched 2008)
- Japanese Experiment Module or Kibo (launched in stages between 2008-09)
- Cupola window and Tranquility/Node 3 (launched 2010)
- Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module (ESA; launched for permanent residency in 2011, although it was used before that to bring cargo to and from the station)
- Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (private module launched 2016)
- NanoRacks Bishop Airlock (launched 2020)
- Nauka, Multipurpose Laboratory Module (launched 2021)
- Prichal, a Russian docking module (launched 2021)
(opens in new tab)
What else visits the ISS?
Besides the space shuttle and Soyuz, the space station has been visited by many other kinds of spacecraft. Uncrewed Progress (Russia) vehicles make regular visits to the station. Europe’s Automated Transfer Vehicle and Japan’s H-II Transfer Vehicle used to do visits to the ISS as well until their programs were retired.
NASA began developing commercial cargo spacecraft for the space station under the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services program, which lasted from 2006 to 2013. Starting in 2012, the first commercial spacecraft, SpaceX’s Dragon, made a visit to the space station. Visits continue today with Dragon and Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services program. Boeing is developing its Starliner for future human visits, too.
(opens in new tab)
Records in space
The ISS has had several notable milestones over the years, when it comes to crews:
- Most consecutive days in space by an American: 355 days, which happened in 2021-2022 with NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei.
- Longest single spaceflight by a woman: 328 days, during American astronaut Christina Koch’s 2019-20 mission aboard the space station.
- Most total time spent in space by a woman: Again, that’s Peggy Whitson, who racked up most of her 665 days in space on the ISS.
- Most women in space at once: This happened in April 2010 when women from two spaceflight missions met at the ISS. This included Tracy Caldwell Dyson (who flew on a Soyuz spacecraft for a long-duration mission) and NASA astronauts Stephanie Wilson and Dorothy Metcalf-Lindenburger and Japan’s Naoko Yamazaki, who arrived aboard the space shuttle Discovery on its brief STS-131 mission.
- Biggest space gathering: 13 people, during NASA’s STS-127 shuttle mission aboard Endeavour in 2009. (It’s been tied a few times during later missions.)
- Longest single spacewalk: 8 hours and 56 minutes during STS-102, for an ISS construction mission in 2001. NASA astronauts Jim Voss and Susan Helms participated.
- Longest Russian spacewalk: 8 hours and 13 minutes during Expedition 54, to repair an ISS antenna. Russian astronauts Alexander Misurkin and Anton Shkaplerov participated.
(opens in new tab)
Additional resources
You can discover more about the ISS with this Haynes manual (opens in new tab) and through the eyes of the astronaut who lived there a year: Scott Kelly. Endurance: A Year in Space, a Lifetime of Discovery (opens in new tab).
If you want to feel like you are living on the ISS yourself, look out the window of the ISS with this amazing visual guide: Interior Space: A Visual Exploration of the International Space Station: Photographs by Paolo Nespoli & Roland Mille (opens in new tab).
Bibliography
European Space Agency. About the International Space Station. https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/International_Space_Station/About_the_International_Space_Station (opens in new tab)
Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex Blog. (2020, Oct. 23). The 20 Most Frequently Asked Questions About the International Space Station. https://www.kennedyspacecenter.com/blog/the-20-most-frequently-asked-questions-about-the-international-space-station (opens in new tab)
Garcia, Mark. (2021, Dec. 14.) International Space Station: Space Station Assembly. https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/space-station-assembly (opens in new tab)
Garcia, Mark. (2022, March 30). NASA Station Astronaut Record Holders. NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-station-astronaut-record-holders (opens in new tab)
Garcia, Mark. (2022, Aug. 9.) International Space Station. NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/main/index.html (opens in new tab)
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Elizabeth Howell, Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022. She was contributing writer for Space.com (opens in new tab) for 10 years before that, since 2012. Elizabeth’s reporting includes an exclusive with Office of the Vice-President of the United States, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, «Why Am I Taller?», is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada’s Carleton University and (soon) a Bachelor of History from Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science since 2015. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
Текст Live in Space с переводом.
Live in Space
Жить в космосе
| 1) Living Among the Stars How would you like to live three hundred and sixty kilometers above the Earth, flying at almost thirty thousand kilometres an hour through dark, airless space? Well, that’s exactly how the astronauts working on the giant International Space Station (ISS) live. ‘Cool!’ you might say. Well… maybe. Let’s take a look at what it’s really like to live in space. |
1) Жизнь среди звезд Как бы вы хотели бы жить на расстоянии триста шестьдесят километров над Землей, летя со скоростью почти в тридцать тысяч километров в час через темный, безвоздушный космос? Именно так живут астронавты, работающие на гигантской Международной Космической Станции (МКС). “Классно!”, можете сказать вы. Ну… может быть. Давайте взглянем на то, что это на самом деле такое – жить в космосе. |
|
| 2) Keeping Clean and Healthy Living in zero gravity means doing lots of things differently. First of all, you can forget about having a nice hot shower in the morning, as the water droplets would simply float away. Astronauts have to use a vacuum hose to wash with. Also, when muscles don’t have to work against gravity as they do here on Earth, they go soft. So the residents of the ISS actually spend 2 hours a day working out on exercise bikes and rowing machines. |
2) Поддержка чистоты и здоровья Проживание в невесомости означает выполнение по-иному многих вещей. Прежде всего, вы можете забыть о том, чтобы принять замечательный горячий душ по утрам, так как капли воды просто улетят прочь. Астронавты должны использовать вакуумный шланг, при помощи которого они моются. Также, когда мышцы не испытывают нагрузки от гравитации, как на Земле, то они становятся дряблыми. Поэтому обитатели МКС в действительности тратят 2 часа в день, тренируясь на велотренажерах и гребных тренажерах. |
|
| 3) Good Housekeeping There’s no escape from household chores on the ISS. As dangerous bacteria grow quickly in zero gravity, the astronauts clean the whole station every day, which is about the size of a football pitch! Also the lack of gravity makes the simplest things in life seem quite weird! Take eating for example, to stop their meals floating away, astronauts have to ‘post’ food packages into a special tray and then strap the tray to their legs. At least there’s no washing up to do, though. The astronauts simply put their dirty dishes and rubbish into plastic bags and send them back to Earth. |
3) Хорошее домоводство На МКС никуда не деться от бытовых дел. Поскольку в условиях невесомости быстро размножаются бактерии, астронавты каждый день делают уборку всех станции, которая имеет размер футбольного поля! Также недостаток гравитации делает самые простые вещи весьма странными! Например, при приеме пищи, чтобы помешать еде улететь прочь, астронавты должны прикрепить пакеты с едой на специальный поднос и потом прикрепить поднос к ногам. Правда, по крайней мере не нужно мыть посуду. Астронавты просто кладут свои грязные тарелки и мусор в пластиковые пакеты и отправляют их обратно на Землю. |
|
| 4) Time to Relax When it comes to sleeping, there’s no need for a bedroom! The astronauts could sleep anywhere, but they can’t risk bumping into any computer controls so they strap themselves into a sleeping bag on the wall. It’s a truly relaxing experience, as nothing presses against the skin. It’s important to cover your eyes, however, to block out the light of the sun as the sun rises and sets every 45 minutes when you are orbiting the Earth. |
4) Время расслабиться Когда речь заходит о сне, то нет необходимости в спальне! Астронавты могут спать везде, но они не могут рисковать удариться о компьютерные панели управления, поэтому они привязывают себя к спальному мешку на стене. Это поистине расслабляющее действие, так как ничего не давит на кожу. Однако, важно закрыть глаза, чтобы не дать попасть в них солнечному свету, поскольку солнце встает и садится каждые 45 минут, когда вы облетаете Землю по орбите. |
|
| 5) Spare Time in Space So, when astronauts aren’t doing experiments or chores or repairing equipment, do they get any free time? Well, a little! They often send emails back home, read books or watch movies, but most of all they like to stare out of the window and take pictures of their real home, Earth! |
5) Свободное время в космосе Таким образом, когда астронавты не делают эксперименты или хозяйственные дела, или не ремонтируют оборудование, есть ли у них какое-нибудь свободное время? Ну, немного! Они часто отсылают электронные письма домой, читают книги или смотрят фильмы, но больше всего они любят смотреть наружу и делать фотографии своего настоящего дома – Земли! |
Презентация знакомит с историей создания и работой космонавтов на международной космической станции.
Скачать:
Предварительный просмотр:
Чтобы пользоваться предварительным просмотром презентаций создайте себе аккаунт (учетную запись) Google и войдите в него: https://accounts.google.com
Подписи к слайдам:
Слайд 1
The International Space Station –ISS Report by Shupyro Margarita 8 “A”, school 1297, Moscow.
Слайд 2
The International Space Station, abbr. ISS — manned orbital station used as a multipurpose space research facility.
Слайд 3
ISS — a joint international project involving 14 countries: Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Spain, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Russia, USA, France, Switzerland, Sweden, Japan . Originally were still Britain and Brazil, but then they came out of the project.
Слайд 4
Emblem ISS
Слайд 5
The first European cargo ship «Jules Verne» is approaching the ISS.
Слайд 6
Bookcover of the Intergovernmental Agreement on Space Station
Слайд 7
17 June, 1992 Russia and the United States signed an agreement on cooperation in space exploration.
Слайд 8
2 September 1993, US Vice President Al Gore and Prime Minister Viktor Chernomyrdin announced a new project » international space station.» From that moment the official name of the station was «International Space Station»
Слайд 9
The basis of the device station laid down modular principle. ISS assembly occurs by sequentially adding to the complex next module or unit that connects to the already delivered into orbit.
Слайд 11
One of the main goals for the ISS is the possibility of the plant experiments.
Слайд 12
The main areas of research include biology (including biomedical research and biotechnology), physics (including physics of fluids, materials science and quantum physics), astronomy, cosmology and meteorology .
Слайд 13
Panoramic cupola ISS.
Слайд 14
Humanoid robot — a new employee ISS
Слайд 15
At the beginning of 2013 the ISS visited 8 space tourists, each of them paid between 20 and 30 million dollars.
Слайд 16
All the tourists were taken to the station Russian spacecraft «Soyuz».
Слайд 17
In the history of space exploration, ISS — the most expensive space project.
Слайд 18
Station it’s existence proves the possibility of international cooperation in space and multiplies the experience of mankind in space flights.

Oblique forward view in November 2021. |
|
 
International Space Station program insignia. |
|
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1998-067A |
| SATCAT no. | 25544 |
| Call sign | Alpha, Station |
| Crew |
|
| Launch | 20 November 1998 (24 years ago) |
| Launch pad |
|
| Mass | 444,615 kg (980,208 lb)[1] |
| Length | 73.0 m (239.4 ft)[1] |
| Width | 109.0 m (357.5 ft)[1] |
| Pressurised volume | 915.6 m3 (32,333 cu ft)[1] |
| Atmospheric pressure | 101.3 kPa (14.7 psi; 1.0 atm) 79% nitrogen, 21% oxygen |
| Perigee altitude | 413 km (256.6 mi) AMSL[2] |
| Apogee altitude | 422 km (262.2 mi) AMSL[2] |
| Orbital inclination | 51.64°[2] |
| Orbital speed | 7.66 km/s[2][failed verification]27,600 km/h; 17,100 mph |
| Orbital period | 92.9 minutes[3] |
| Orbits per day | 15.49[2] |
| Orbit epoch | 12 October 2022 14:25:10 [3] |
| Days in orbit | 24 years, 1 month, 22 days (11 January 2023) |
| Days occupied | 22 years, 2 months, 8 days (11 January 2023) |
| No. of orbits | 133,312 as of June 2022[4] |
| Orbital decay | 2 km/month |
| Statistics as of 22 December 2022 (unless noted otherwise) References: [1][2][5][6][7] |
|
| Configuration | |

Station elements as of December 2022 |
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station in low Earth orbit. The project involves five space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).[8][9] The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements.[10] The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields.[11][12][13] The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars.[14]
The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station Freedom, a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station,[15] and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian Mir-2 proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to be inhabited by crews, following the Soviet and later Russian Salyut, Almaz, and Mir stations and the American Skylab. It is the largest artificial object in the solar system and the largest satellite in low Earth orbit, regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth’s surface.[16][17] It maintains an orbit with an average altitude of 400 kilometres (250 mi) by means of reboost manoeuvres using the engines of the Zvezda Service Module or visiting spacecraft.[18] The ISS circles the Earth in roughly 93 minutes, completing 15.5 orbits per day.[19]
The station is divided into two sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) is operated by Russia, while the United States Orbital Segment (USOS) is run by the United States as well as by the other states. The Russian segment includes six modules. The US segment includes ten modules, whose support services are distributed 76.6% for NASA, 12.8% for JAXA, 8.3% for ESA and 2.3% for CSA.
Roscosmos had previously[20][21] endorsed the continued operation of ROS through 2024,[22] having proposed using elements of the segment to construct a new Russian space station called OPSEK.[23] However, continued cooperation has been rendered uncertain by the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine and subsequent international sanctions on Russia, who theoretically, may lower, redirect, or cut funding from their side of the space station due to the sanctions set on them.[20][21]
The first ISS component was launched in 1998, and the first long-term residents arrived on 2 November 2000 after being launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on 31 October 2000.[24] The station has since been continuously occupied for 22 years and 70 days,[25] the longest continuous human presence in low Earth orbit, having surpassed the previous record of 9 years and 357 days held by the Mir space station. The latest major pressurised module, Nauka, was fitted in 2021, a little over ten years after the previous major addition, Leonardo in 2011. Development and assembly of the station continues, with an experimental inflatable space habitat added in 2016, and several major new Russian elements scheduled for launch starting in 2021. In January 2022, the station’s operation authorization was extended to 2030, with funding secured within the United States through that year.[26][27] There have been calls to privatize ISS operations after that point to pursue future Moon and Mars missions, with former NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine stating: «given our current budget constraints, if we want to go to the moon and we want to go to Mars, we need to commercialize low Earth orbit and go on to the next step.»[28]
The ISS consists of pressurised habitation modules, structural trusses, photovoltaic solar arrays, thermal radiators, docking ports, experiment bays and robotic arms. Major ISS modules have been launched by Russian Proton and Soyuz rockets and US Space Shuttles.[29] The station is serviced by a variety of visiting spacecraft: the Russian Soyuz and Progress, the SpaceX Dragon 2, and the Northrop Grumman Space Systems Cygnus,[30] and formerly the European Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV), the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle,[8] and SpaceX Dragon 1. The Dragon spacecraft allows the return of pressurised cargo to Earth, which is used, for example, to repatriate scientific experiments for further analysis. As of April 2022, 251 astronauts, cosmonauts, and space tourists from 20 different nations have visited the space station, many of them multiple times.
History[edit]
In the early 1980s, NASA planned to launch a modular space station called Freedom as a counterpart to the Soviet Salyut and Mir space stations. In 1984 the ESA was invited to participate in Space Station Freedom, and the ESA approved the Columbus laboratory by 1987.[31] The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), or Kibō, was announced in 1985, as part of the Freedom space station in response to a NASA request in 1982.
In early 1985, science ministers from the European Space Agency (ESA) countries approved the Columbus programme, the most ambitious effort in space undertaken by that organisation at the time. The plan spearheaded by Germany and Italy included a module which would be attached to Freedom, and with the capability to evolve into a full-fledged European orbital outpost before the end of the century. The space station was also going to tie the emerging European and Japanese national space programmes closer to the US-led project, thereby preventing those nations from becoming major, independent competitors too.[32]
In September 1993, American Vice-President Al Gore and Russian Prime Minister Viktor Chernomyrdin announced plans for a new space station, which eventually became the International Space Station.[33] They also agreed, in preparation for this new project, that the United States would be involved in the Mir programme, including American Shuttles docking, in the Shuttle–Mir programme.[34]
On 12 April 2021, at a meeting with Russian President Vladimir Putin, then-Deputy Prime Minister Yury Borisov announced he had decided that Russia might withdraw from the ISS programme in 2025.[35][36] According to Russian authorities, the timeframe of the station’s operations has expired and its condition leaves much to be desired.[35] On 26 July 2022, Borisov, who had become head of Roscosmos, submitted to Putin his plans for withdrawal from the programme after 2024.[37] However, Robyn Gatens, the NASA official in charge of space station operations, responded that NASA had not received any formal notices from Roscosmos concerning withdrawal plans.[38] On 21 September 2022, Borisov stated that Russia was «highly likely» to continue to participate in the ISS programme until 2028.[39]
Purpose[edit]
The ISS was originally intended to be a laboratory, observatory, and factory while providing transportation, maintenance, and a low Earth orbit staging base for possible future missions to the Moon, Mars, and asteroids. However, not all of the uses envisioned in the initial memorandum of understanding between NASA and Roscosmos have been realised.[40] In the 2010 United States National Space Policy, the ISS was given additional roles of serving commercial, diplomatic,[41] and educational purposes.[42]
Scientific research[edit]
Fisheye view of several labs
The ISS provides a platform to conduct scientific research, with power, data, cooling, and crew available to support experiments. Small uncrewed spacecraft can also provide platforms for experiments, especially those involving zero gravity and exposure to space, but space stations offer a long-term environment where studies can be performed potentially for decades, combined with ready access by human researchers.[43][44]
The ISS simplifies individual experiments by allowing groups of experiments to share the same launches and crew time. Research is conducted in a wide variety of fields, including astrobiology, astronomy, physical sciences, materials science, space weather, meteorology, and human research including space medicine and the life sciences.[11][12][13][45][46] Scientists on Earth have timely access to the data and can suggest experimental modifications to the crew. If follow-on experiments are necessary, the routinely scheduled launches of resupply craft allows new hardware to be launched with relative ease.[44] Crews fly expeditions of several months’ duration, providing approximately 160 person-hours per week of labour with a crew of six. However, a considerable amount of crew time is taken up by station maintenance.[11][47]
Perhaps the most notable ISS experiment is the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), which is intended to detect dark matter and answer other fundamental questions about our universe. According to NASA, the AMS is as important as the Hubble Space Telescope. Currently docked on station, it could not have been easily accommodated on a free flying satellite platform because of its power and bandwidth needs.[48][49] On 3 April 2013, scientists reported that hints of dark matter may have been detected by the AMS.[50][51][52][53][54][55] According to the scientists, «The first results from the space-borne Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer confirm an unexplained excess of high-energy positrons in Earth-bound cosmic rays».
The space environment is hostile to life. Unprotected presence in space is characterised by an intense radiation field (consisting primarily of protons and other subatomic charged particles from the solar wind, in addition to cosmic rays), high vacuum, extreme temperatures, and microgravity.[56] Some simple forms of life called extremophiles,[57] as well as small invertebrates called tardigrades[58] can survive in this environment in an extremely dry state through desiccation.
Medical research improves knowledge about the effects of long-term space exposure on the human body, including muscle atrophy, bone loss, and fluid shift. These data will be used to determine whether high duration human spaceflight and space colonisation are feasible. In 2006, data on bone loss and muscular atrophy suggested that there would be a significant risk of fractures and movement problems if astronauts landed on a planet after a lengthy interplanetary cruise, such as the six-month interval required to travel to Mars.[59][60]
Medical studies are conducted aboard the ISS on behalf of the National Space Biomedical Research Institute (NSBRI). Prominent among these is the Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity study in which astronauts perform ultrasound scans under the guidance of remote experts. The study considers the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions in space. Usually, there is no physician on board the ISS and diagnosis of medical conditions is a challenge. It is anticipated that remotely guided ultrasound scans will have application on Earth in emergency and rural care situations where access to a trained physician is difficult.[61][62][63]
In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus radiodurans bacteria, which is highly resistant to environmental hazards, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings supported the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.[64][65]
Remote sensing of the Earth, astronomy, and deep space research on the ISS have dramatically increased during the 2010s after the completion of the US Orbital Segment in 2011. Throughout the more than 20 years of the ISS program researchers aboard the ISS and on the ground have examined aerosols, ozone, lightning, and oxides in Earth’s atmosphere, as well as the Sun, cosmic rays, cosmic dust, antimatter, and dark matter in the universe. Examples of Earth-viewing remote sensing experiments that have flown on the ISS are the Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, ISS-RapidScat, ECOSTRESS, the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation, and the Cloud Aerosol Transport System. ISS-based astronomy telescopes and experiments include SOLAR, the Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer, the Calorimetric Electron Telescope, the Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image (MAXI), and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer.[12][66]
Freefall[edit]
ISS crew member storing samples
A comparison between the combustion of a candle on Earth (left) and in a free fall environment, such as that found on the ISS (right)
Gravity at the altitude of the ISS is approximately 90% as strong as at Earth’s surface, but objects in orbit are in a continuous state of freefall, resulting in an apparent state of weightlessness.[67] This perceived weightlessness is disturbed by five effects:[68]
- Drag from the residual atmosphere.
- Vibration from the movements of mechanical systems and the crew.
- Actuation of the on-board attitude control moment gyroscopes.
- Thruster firings for attitude or orbital changes.
- Gravity-gradient effects, also known as tidal effects. Items at different locations within the ISS would, if not attached to the station, follow slightly different orbits. Being mechanically connected these items experience small forces that keep the station moving as a rigid body.
Researchers are investigating the effect of the station’s near-weightless environment on the evolution, development, growth and internal processes of plants and animals. In response to some of the data, NASA wants to investigate microgravity’s effects on the growth of three-dimensional, human-like tissues and the unusual protein crystals that can be formed in space.[12]
Investigating the physics of fluids in microgravity will provide better models of the behaviour of fluids. Because fluids can be almost completely combined in microgravity, physicists investigate fluids that do not mix well on Earth. Examining reactions that are slowed by low gravity and low temperatures will improve our understanding of superconductivity.[12]
The study of materials science is an important ISS research activity, with the objective of reaping economic benefits through the improvement of techniques used on the ground.[69] Other areas of interest include the effect of low gravity on combustion, through the study of the efficiency of burning and control of emissions and pollutants. These findings may improve knowledge about energy production and lead to economic and environmental benefits.[12]
Exploration[edit]
A 3D plan of the Russia-based MARS-500 complex, used for conducting ground-based experiments that complement ISS-based preparations for a human mission to Mars
The ISS provides a location in the relative safety of low Earth orbit to test spacecraft systems that will be required for long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. This provides experience in operations, maintenance as well as repair and replacement activities on-orbit. This will help develop essential skills in operating spacecraft farther from Earth, reduce mission risks, and advance the capabilities of interplanetary spacecraft.[14] Referring to the MARS-500 experiment, a crew isolation experiment conducted on Earth, ESA states that «Whereas the ISS is essential for answering questions concerning the possible impact of weightlessness, radiation and other space-specific factors, aspects such as the effect of long-term isolation and confinement can be more appropriately addressed via ground-based simulations».[70] Sergey Krasnov, the head of human space flight programmes for Russia’s space agency, Roscosmos, in 2011 suggested a «shorter version» of MARS-500 may be carried out on the ISS.[71]
In 2009, noting the value of the partnership framework itself, Sergey Krasnov wrote, «When compared with partners acting separately, partners developing complementary abilities and resources could give us much more assurance of the success and safety of space exploration. The ISS is helping further advance near-Earth space exploration and realisation of prospective programmes of research and exploration of the Solar system, including the Moon and Mars.»[72] A crewed mission to Mars may be a multinational effort involving space agencies and countries outside the current ISS partnership. In 2010, ESA Director-General Jean-Jacques Dordain stated his agency was ready to propose to the other four partners that China, India and South Korea be invited to join the ISS partnership.[73] NASA chief Charles Bolden stated in February 2011, «Any mission to Mars is likely to be a global effort».[74] Currently, US federal legislation prevents NASA co-operation with China on space projects.[75]
Education and cultural outreach[edit]
The ISS crew provides opportunities for students on Earth by running student-developed experiments, making educational demonstrations, allowing for student participation in classroom versions of ISS experiments, and directly engaging students using radio, and email.[8][76] ESA offers a wide range of free teaching materials that can be downloaded for use in classrooms.[77] In one lesson, students can navigate a 3D model of the interior and exterior of the ISS, and face spontaneous challenges to solve in real time.[78]
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) aims to inspire children to «pursue craftsmanship» and to heighten their «awareness of the importance of life and their responsibilities in society».[79] Through a series of education guides, students develop a deeper understanding of the past and near-term future of crewed space flight, as well as that of Earth and life.[80][81] In the JAXA «Seeds in Space» experiments, the mutation effects of spaceflight on plant seeds aboard the ISS are explored by growing sunflower seeds that have flown on the ISS for about nine months. In the first phase of Kibō utilisation from 2008 to mid-2010, researchers from more than a dozen Japanese universities conducted experiments in diverse fields.[82]
Cultural activities are another major objective of the ISS programme. Tetsuo Tanaka, the director of JAXA’s Space Environment and Utilization Center, has said: «There is something about space that touches even people who are not interested in science.»[83]
Amateur Radio on the ISS (ARISS) is a volunteer programme that encourages students worldwide to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, through amateur radio communications opportunities with the ISS crew. ARISS is an international working group, consisting of delegations from nine countries including several in Europe, as well as Japan, Russia, Canada, and the United States. In areas where radio equipment cannot be used, speakerphones connect students to ground stations which then connect the calls to the space station.[84]
Spoken voice recording by ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli on the subject of the ISS, produced in November 2017 for Wikipedia
First Orbit is a 2011 feature-length documentary film about Vostok 1, the first crewed space flight around the Earth. By matching the orbit of the ISS to that of Vostok 1 as closely as possible, in terms of ground path and time of day, documentary filmmaker Christopher Riley and ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli were able to film the view that Yuri Gagarin saw on his pioneering orbital space flight. This new footage was cut together with the original Vostok 1 mission audio recordings sourced from the Russian State Archive. Nespoli is credited as the director of photography for this documentary film, as he recorded the majority of the footage himself during Expedition 26/27.[85] The film was streamed in a global YouTube premiere in 2011 under a free licence through the website firstorbit.org.[86]
In May 2013, commander Chris Hadfield shot a music video of David Bowie’s «Space Oddity» on board the station, which was released on YouTube.[87][88] It was the first music video ever to be filmed in space.[89]
In November 2017, while participating in Expedition 52/53 on the ISS, Paolo Nespoli made two recordings of his spoken voice (one in English and the other in his native Italian), for use on Wikipedia articles. These were the first content made in space specifically for Wikipedia.[90][91]
In November 2021, a virtual reality exhibit called The Infinite featuring life aboard the ISS was announced.[92]
Construction[edit]
Manufacturing[edit]
ISS module Node 2 manufacturing and processing in the Space Station Processing Facility
Since the International Space Station is a multi-national collaborative project, the components for in-orbit assembly were manufactured in various countries around the world. Beginning in the mid-1990s, the U.S. components Destiny, Unity, the Integrated Truss Structure, and the solar arrays were fabricated at the Marshall Space Flight Center and the Michoud Assembly Facility. These modules were delivered to the Operations and Checkout Building and the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for final assembly and processing for launch.[93]
The Russian modules, including Zarya and Zvezda, were manufactured at the Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center in Moscow. Zvezda was initially manufactured in 1985 as a component for Mir-2, but was never launched and instead became the ISS Service Module.[94]
The European Space Agency (ESA) Columbus module was manufactured at the EADS Astrium Space Transportation facilities in Bremen, Germany, along with many other contractors throughout Europe.[95] The other ESA-built modules – Harmony, Tranquility, the Leonardo MPLM, and the Cupola – were initially manufactured at the Thales Alenia Space factory in Turin, Italy.[96] The structural steel hulls of the modules were transported by aircraft to the Kennedy Space Center SSPF for launch processing.[97]
The Japanese Experiment Module Kibō, was fabricated in various technology manufacturing facilities in Japan, at the NASDA (now JAXA) Tsukuba Space Center, and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. The Kibo module was transported by ship and flown by aircraft to the SSPF.[98]
The Mobile Servicing System, consisting of the Canadarm2 and the Dextre grapple fixture, was manufactured at various factories in Canada (such as the David Florida Laboratory) and the United States, under contract by the Canadian Space Agency. The mobile base system, a connecting framework for Canadarm2 mounted on rails, was built by Northrop Grumman.
Assembly[edit]
The ISS was slowly assembled over more than a decade of spaceflights and crews.
A view of the completed station as seen from Shuttle Atlantis during STS-132, 23 May 2010
The assembly of the International Space Station, a major endeavour in space architecture, began in November 1998.[5] Russian modules launched and docked robotically, with the exception of Rassvet. All other modules were delivered by the Space Shuttle, which required installation by ISS and Shuttle crewmembers using the Canadarm2 (SSRMS) and extra-vehicular activities (EVAs); by 5 June 2011, they had added 159 components during more than 1,000 hours of EVA. 127 of these spacewalks originated from the station, and the remaining 32 were launched from the airlocks of docked Space Shuttles.[99] The beta angle of the station had to be considered at all times during construction.[100]
The first module of the ISS, Zarya, was launched on 20 November 1998 on an autonomous Russian Proton rocket. It provided propulsion, attitude control, communications, and electrical power, but lacked long-term life support functions. A passive NASA module, Unity, was launched two weeks later aboard Space Shuttle flight STS-88 and attached to Zarya by astronauts during EVAs. The Unity module has two Pressurised Mating Adapters (PMAs): one connects permanently to Zarya and the other allowed the Space Shuttle to dock to the space station. At that time, the Russian (Soviet) station Mir was still inhabited, and the ISS remained uncrewed for two years. On 12 July 2000, the Zvezda module was launched into orbit. Onboard preprogrammed commands deployed its solar arrays and communications antenna. Zvezda then became the passive target for a rendezvous with Zarya and Unity, maintaining a station-keeping orbit while the Zarya–Unity vehicle performed the rendezvous and docking via ground control and the Russian automated rendezvous and docking system. Zarya‘s computer transferred control of the station to Zvezda‘s computer soon after docking. Zvezda added sleeping quarters, a toilet, kitchen, CO2 scrubbers, dehumidifier, oxygen generators, and exercise equipment, plus data, voice and television communications with mission control, enabling permanent habitation of the station.[101][102]
The first resident crew, Expedition 1, arrived in November 2000 on Soyuz TM-31. At the end of the first day on the station, astronaut Bill Shepherd requested the use of the radio call sign «Alpha«, which he and cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev preferred to the more cumbersome «International Space Station«.[103] The name «Alpha» had previously been used for the station in the early 1990s,[104] and its use was authorised for the whole of Expedition 1.[105] Shepherd had been advocating the use of a new name to project managers for some time. Referencing a naval tradition in a pre-launch news conference he had said: «For thousands of years, humans have been going to sea in ships. People have designed and built these vessels, launched them with a good feeling that a name will bring good fortune to the crew and success to their voyage.»[106] Yuri Semenov, the President of Russian Space Corporation Energia at the time, disapproved of the name «Alpha» as he felt that Mir was the first modular space station, so the names «Beta» or «Mir 2″ for the ISS would have been more fitting.[105][107][108]
Expedition 1 arrived midway between the Space Shuttle flights of missions STS-92 and STS-97. These two flights each added segments of the station’s Integrated Truss Structure, which provided the station with Ku-band communication for US television, additional attitude support needed for the additional mass of the USOS, and substantial solar arrays to supplement the station’s four existing arrays.[109] Over the next two years, the station continued to expand. A Soyuz-U rocket delivered the Pirs docking compartment. The Space Shuttles Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour delivered the Destiny laboratory and Quest airlock, in addition to the station’s main robot arm, the Canadarm2, and several more segments of the Integrated Truss Structure.
The expansion schedule was interrupted in 2003 by the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster and a resulting hiatus in flights. The Space Shuttle was grounded until 2005 with STS-114 flown by Discovery.[110] Assembly resumed in 2006 with the arrival of STS-115 with Atlantis, which delivered the station’s second set of solar arrays. Several more truss segments and a third set of arrays were delivered on STS-116, STS-117, and STS-118. As a result of the major expansion of the station’s power-generating capabilities, more pressurised modules could be accommodated, and the Harmony node and Columbus European laboratory were added. These were soon followed by the first two components of Kibō. In March 2009, STS-119 completed the Integrated Truss Structure with the installation of the fourth and final set of solar arrays. The final section of Kibō was delivered in July 2009 on STS-127, followed by the Russian Poisk module. The third node, Tranquility, was delivered in February 2010 during STS-130 by the Space Shuttle Endeavour, alongside the Cupola, followed by the penultimate Russian module, Rassvet, in May 2010. Rassvet was delivered by Space Shuttle Atlantis on STS-132 in exchange for the Russian Proton delivery of the US-funded Zarya module in 1998.[111] The last pressurised module of the USOS, Leonardo, was brought to the station in February 2011 on the final flight of Discovery, STS-133.[112] The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer was delivered by Endeavour on STS-134 the same year.[113]
By June 2011, the station consisted of 15 pressurised modules and the Integrated Truss Structure. Two power modules called NEM-1 and NEM-2.[114] are still to be launched. Russia’s new primary research module Nauka docked in July 2021,[115] along with the European Robotic Arm which will be able to relocate itself to different parts of the Russian modules of the station.[116] Russia’s latest addition, the nodal module Prichal, docked in November 2021.[117]
The gross mass of the station changes over time. The total launch mass of the modules on orbit is about 417,289 kg (919,965 lb) (as of 3 September 2011).[118] The mass of experiments, spare parts, personal effects, crew, foodstuff, clothing, propellants, water supplies, gas supplies, docked spacecraft, and other items add to the total mass of the station. Hydrogen gas is constantly vented overboard by the oxygen generators.
Structure[edit]
The ISS is a modular space station. Modular stations can allow modules to be added to or removed from the existing structure, allowing greater flexibility.
-
Technical blueprint of components.
-
The ISS exterior and steelwork taken on 8 November 2021, from the departing SpaceX Crew-2 capsule.
-
Diagram structure of International Space Station after installation of iROSA solar arrays (as of 2022).
Below is a diagram of major station components. The blue areas are pressurised sections accessible by the crew without using spacesuits. The station’s unpressurised superstructure is indicated in red. Planned components are shown in white, non installed, temporarily defunct or non-commissioned components are shown in brown and former ones in gray. Other unpressurised components are yellow. The Unity node joins directly to the Destiny laboratory. For clarity, they are shown apart. Similar cases are also seen in other parts of the structure.
Pressurised modules[edit]
Zarya[edit]
Zarya (Russian: Заря, lit. ‘Dawn’[b]), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the Russian: «Функционально-грузовой блок», lit. ‘Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok‘ or ФГБ), is the first module of the ISS to have been launched.[119] The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, Zarya, as of August 2021, is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The Zarya is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian Salyut program. The name Zarya («Dawn») was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States.[120]
Unity[edit]
The Unity connecting module, also known as Node 1, is the first U.S.-built component of the ISS. It connects the Russian and U.S. segments of the station, and is where crew eat meals together.[121][122]
The module is cylindrical in shape, with six berthing locations (forward, aft, port, starboard, zenith, and nadir) facilitating connections to other modules. Unity measures 4.57 metres (15.0 ft) in diameter, is 5.47 metres (17.9 ft) long, made of steel, and was built for NASA by Boeing in a manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Unity is the first of the three connecting modules; the other two are Harmony and Tranquility.[123]
Zvezda[edit]
Zvezda (Russian: Звезда, meaning «star»), Salyut DOS-8, is also known as the Zvezda Service Module. It was the third module launched to the station, and provides all of the station’s life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the USOS, as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment, which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station.[124][125][126]
The module was manufactured by RKK Energia, with major sub-contracting work by GKNPTs Khrunichev.[127] Zvezda was launched on a Proton rocket on 12 July 2000, and docked with the Zarya module on 26 July 2000.
The Destiny module being installed on the ISS
Destiny[edit]
The Destiny module, also known as the U.S. Lab, is the primary operating facility for U.S. research payloads aboard the ISS.[128][129] It was berthed to the Unity module and activated over a period of five days in February 2001.[130] Destiny is NASA’s first permanent operating orbital research station since Skylab was vacated in February 1974. The Boeing Company began construction of the 14.5-tonne (32,000 lb) research laboratory in 1995 at the Michoud Assembly Facility and then the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.[128] Destiny was shipped to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 1998, and was turned over to NASA for pre-launch preparations in August 2000. It launched on 7 February 2001, aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on STS-98.[130] Astronauts work inside the pressurized facility to conduct research in numerous scientific fields. Scientists throughout the world would use the results to enhance their studies in medicine, engineering, biotechnology, physics, materials science, and Earth science.[129]
Quest Joint Airlock Module
Quest[edit]
The Joint Airlock (also known as «Quest») is provided by the U.S. and provides the capability for ISS-based Extravehicular Activity (EVA) using either a U.S. Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) or Russian Orlan EVA suits. Before the launch of this airlock, EVAs were performed from either the U.S. Space Shuttle (while docked) or from the Transfer Chamber on the Service Module. Due to a variety of system and design differences, only U.S. space suits could be used from the Shuttle and only Russian suits could be used from the Service Module. The Joint Airlock alleviates this short-term problem by allowing either (or both) spacesuit systems to be used.
The Joint Airlock was launched on ISS-7A / STS-104 in July 2001 and was attached to the right hand docking port of Node 1. The Joint Airlock is 20 ft. long, 13 ft. in diameter, and weighs 6.5 tons. The Joint Airlock was built by Boeing at Marshall Space Flight Center. The Joint Airlock was launched with the High Pressure Gas Assembly. The High Pressure Gas Assembly was mounted on the external surface of the Joint Airlock and will support EVAs operations with breathing gases and augments the Service Module’s gas resupply system.
The Joint Airlock has two main components: a crew airlock from which astronauts and cosmonauts exit the ISS and an equipment airlock designed for storing EVA gear and for so-called overnight «campouts» wherein Nitrogen is purged from astronaut’s bodies overnight as pressure is dropped in preparation for spacewalks the following day. This alleviates the bends as the astronauts are repressurized after their EVA.
The crew airlock was derived from the Space Shuttle’s external airlock. It is equipped with lighting, external handrails, and an Umbilical Interface Assembly (UIA). The UIA is located on one wall of the crew airlock and provides a water supply line, a wastewater return line, and an oxygen supply line. The UIA also provides communication gear and spacesuit power interfaces and can support two spacesuits simultaneously. This can be either two American EMU spacesuits, two Russian ORLAN spacesuits, or one of each design.
Poisk[edit]
Poisk (Russian: По́иск, lit. ‘Search’) was launched on 10 November 2009[131][132] attached to a modified Progress spacecraft, called Progress M-MIM2, on a Soyuz-U rocket from Launch Pad 1 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Poisk is used as the Russian airlock module, containing two identical EVA hatches. An outward-opening hatch on the Mir space station failed after it swung open too fast after unlatching, because of a small amount of air pressure remaining in the airlock.[133] All EVA hatches on the ISS open inwards and are pressure-sealing. Poisk is used to store, service, and refurbish Russian Orlan suits and provides contingency entry for crew using the slightly bulkier American suits. The outermost docking port on the module allows docking of Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, and the automatic transfer of propellants to and from storage on the ROS.[134] Since the departure of the identical Pirs module on July 26, 2021, Poisk has served as the only airlock on the ROS.
Harmony shown connected to Columbus, Kibo, and Destiny. PMA-2 faces. The nadir and zenith locations are open.
Harmony[edit]
Harmony, also known as Node 2, is the «utility hub» of the ISS. It connects the laboratory modules of the United States, Europe and Japan, as well as providing electrical power and electronic data. Sleeping cabins for four of the crew are housed here.[135]
Harmony was successfully launched into space aboard Space Shuttle flight STS-120 on 23 October 2007.[136][137] After temporarily being attached to the port side of the Unity node,[138][139] it was moved to its permanent location on the forward end of the Destiny laboratory on 14 November 2007.[140] Harmony added 75.5 m3 (2,666 cu ft) to the station’s living volume, an increase of almost 20 percent, from 424.8 to 500.2 m3 (15,000 to 17,666 cu ft). Its successful installation meant that from NASA’s perspective, the station was considered to be «U.S. Core Complete».
Tranquility[edit]
Tranquility, also known as Node 3, is a module of the ISS. It contains environmental control systems, life support systems, a toilet, exercise equipment, and an observation cupola.
The European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency had Tranquility manufactured by Thales Alenia Space. A ceremony on 20 November 2009 transferred ownership of the module to NASA.[141] On 8 February 2010, NASA launched the module on the Space Shuttle’s STS-130 mission.
The Columbus module on the ISS
Columbus[edit]
Columbus is a science laboratory that is part of the ISS and is the largest single contribution to the station made by the European Space Agency.
Like the Harmony and Tranquility modules, the Columbus laboratory was constructed in Turin, Italy by Thales Alenia Space. The functional equipment and software of the lab was designed by EADS in Bremen, Germany. It was also integrated in Bremen before being flown to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in an Airbus Beluga. It was launched aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on 7 February 2008, on flight STS-122. It is designed for ten years of operation. The module is controlled by the Columbus Control Centre, located at the German Space Operations Center, part of the German Aerospace Center in Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich, Germany.
The European Space Agency has spent €1.4 billion (about US$2 billion) on building Columbus, including the experiments it carries and the ground control infrastructure necessary to operate them.[142]
Kibō[edit]
The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), nicknamed Kibō (きぼう, Kibō, Hope), is a Japanese science module for the International Space Station (ISS) developed by JAXA. It is the largest single ISS module, and is attached to the Harmony module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on Space Shuttle missions STS-123 and STS-124. The third and final components were launched on STS-127.[143]
The Cupola‘s windows with shutters open
Cupola[edit]
The Cupola is an ESA-built observatory module of the ISS. Its name derives from the Italian word cupola, which means «dome». Its seven windows are used to conduct experiments, dockings and observations of Earth. It was launched aboard Space Shuttle mission STS-130 on 8 February 2010 and attached to the Tranquility (Node 3) module. With the Cupola attached, ISS assembly reached 85 percent completion. The Cupola‘s central window has a diameter of 80 cm (31 in).[144]
Rassvet module with MLM-outfitting equipment (consisting of experiment airlock, RTOd radiators, and ERA workpost) at KSC.
Rassvet[edit]
Rassvet (Russian: Рассвет; lit. «dawn»), also known as the Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM-1) (Russian: Малый исследовательский модуль, МИМ 1) and formerly known as the Docking Cargo Module (DCM), is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). The module’s design is similar to the Mir Docking Module launched on STS-74 in 1995. Rassvet is primarily used for cargo storage and as a docking port for visiting spacecraft. It was flown to the ISS aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on the STS-132 mission on 14 May 2010,[145] and was connected to the ISS on 18 May 2010.[146] The hatch connecting Rassvet with the ISS was first opened on 20 May 2010.[147] On 28 June 2010, the Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft performed the first docking with the module.[148]
MLM outfittings[edit]
MLM outfittings on Rassvet
A wide-angle view of the new module (behind Rassvet) attached to the ROS as seen from the cupola
In May 2010, equipment for Nauka was launched on STS-132 (as part of an agreement with NASA) and delivered by Space Shuttle Atlantis. Weighing 1.4 metric tons, the equipment was attached to the outside of Rassvet (MRM-1). It included a spare elbow joint for the European Robotic Arm (ERA) (which was launched with Nauka) and an ERA-portable workpost used during EVAs, as well as RTOd heat radiator, internal hardware and an experiment airlock for launching CubeSats to be positioned on the modified passive forward port near the nadir end of the Nauka module.[149]
Modified passive forward port for experiment airlock near the nadir end of Nauka
The RTOd radiator will be used to add additional cooling capability to Nauka, which will enable the module to host more scientific experiments. The airlock will be used only to pass experiments inside and outside the module, with the aid of ERA – very similar to the Japanese airlock and Nanoracks Bishop Airlock on the U.S. segment of the station.[149]
The ERA will be used to remove the RTOd radiator and airlock from Rassvet and transfer them over to Nauka. This process is expected to take several months. A portable work platform will also be transferred over, which can attach to the end of the ERA to allow cosmonauts to «ride» on the end of the arm during spacewalks.[150]
Another MLM outfitting is a 4 segment external payload interface called means of attachment of large payloads (Sredstva Krepleniya Krupnogabaritnykh Obyektov, SKKO).[151] Delivered in two parts to Nauka by Progress MS-18 (LCCS part) and Progress MS-21 (SCCCS part) as part of the module activation outfitting process.[152][153][154][155] It was taken outside and installed on the ERA aft facing base point on Nauka during the VKD-55 spacewalk.[156]
Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module
Leonardo[edit]
The Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module (PMM) is a module of the International Space Station. It was flown into space aboard the Space Shuttle on STS-133 on 24 February 2011 and installed on 1 March. Leonardo is primarily used for storage of spares, supplies and waste on the ISS, which was until then stored in many different places within the space station. It is also the personal hygiene area for the astronauts who live in the US Orbital Segment. The Leonardo PMM was a Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) before 2011, but was modified into its current configuration. It was formerly one of two MPLM used for bringing cargo to and from the ISS with the Space Shuttle. The module was named for Italian polymath Leonardo da Vinci.
Bigelow Expandable Activity Module[edit]
Progression of the expansion of BEAM
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is an experimental expandable space station module developed by Bigelow Aerospace, under contract to NASA, for testing as a temporary module on the International Space Station (ISS) from 2016 to at least 2020. It arrived at the ISS on 10 April 2016,[157] was berthed to the station on 16 April at Tranquility Node 3, and was expanded and pressurized on 28 May 2016.
International Docking Adapters[edit]
The International Docking Adapter (IDA) is a spacecraft docking system adapter developed to convert APAS-95 to the NASA Docking System (NDS). An IDA is placed on each of the ISS’s two open Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs), both of which are connected to the Harmony module.
Two International Docking Adapters are currently installed aboard the Station. Originally, IDA-1 was planned to be installed on PMA-2, located at Harmony‘s forward port, and IDA-2 would be installed on PMA-3 at Harmony‘s zenith. After IDA 1 was destroyed in a launch incident, IDA-2 was installed on PMA-2 on 19 August 2016,[158] while IDA-3 was later installed on PMA-3 on 21 August 2019.[159]
NanoRacks Bishop airlock module installed on the ISS
Bishop Airlock Module[edit]
The NanoRacks Bishop Airlock Module is a commercially funded airlock module launched to the ISS on SpaceX CRS-21 on 6 December 2020.[160][161] The module was built by NanoRacks, Thales Alenia Space, and Boeing.[162] It will be used to deploy CubeSats, small satellites, and other external payloads for NASA, CASIS, and other commercial and governmental customers.[163]
Nauka[edit]
Nauka (Russian: Наука, lit. ‘Science’), also known as the Multipurpose Laboratory Module-Upgrade (MLM-U), (Russian: Многоцелевой лабораторный модуль, усоверше́нствованный, or МЛМ-У), is a Roscosmos-funded component of the ISS that was launched on 21 July 2021, 14:58 UTC. In the original ISS plans, Nauka was to use the location of the Docking and Stowage Module (DSM), but the DSM was later replaced by the Rassvet module and moved to Zarya‘s nadir port. Nauka was successfully docked to Zvezda‘s nadir port on 29 July 2021, 13:29 UTC, replacing the Pirs module.
1637984492234 Progress MS 17 undocking and Nauka nadir temporary docking adapter Removal[c][d]
It had a temporary docking adapter on its nadir port for crewed and uncrewed missions until Prichal arrival, where just before its arrival it was removed by a departuring Progress spacecraft.[164]
Nauka and Prichal docked to ISS
Prichal[edit]
Prichal, also known as Uzlovoy Module or UM (Russian: Узловой Модуль Причал, lit. ‘Nodal Module Berth’),[165] is a 4-tonne (8,800 lb)[166] ball-shaped module that will provide the Russian segment additional docking ports to receive Soyuz MS and Progress MS spacecraft. UM was launched in November 2021.[167] It was integrated with a special version of the Progress cargo spacecraft and launched by a standard Soyuz rocket, docking to the nadir port of the Nauka module. One port is equipped with an active hybrid docking port, which enables docking with the MLM module. The remaining five ports are passive hybrids, enabling docking of Soyuz and Progress vehicles, as well as heavier modules and future spacecraft with modified docking systems. The node module was intended to serve as the only permanent element of the cancelled Orbital Piloted Assembly and Experiment Complex (OPSEK).[167][168][169]
Unpressurised elements[edit]
ISS Truss Components breakdown showing Trusses and all ORUs in situ
The ISS has a large number of external components that do not require pressurisation. The largest of these is the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS), to which the station’s main solar arrays and thermal radiators are mounted.[170] The ITS consists of ten separate segments forming a structure 108.5 metres (356 ft) long.[5]
The station was intended to have several smaller external components, such as six robotic arms, three External Stowage Platforms (ESPs) and four ExPRESS Logistics Carriers (ELCs).[171][172] While these platforms allow experiments (including MISSE, the STP-H3 and the Robotic Refueling Mission) to be deployed and conducted in the vacuum of space by providing electricity and processing experimental data locally, their primary function is to store spare Orbital Replacement Units (ORUs). ORUs are parts that can be replaced when they fail or pass their design life, including pumps, storage tanks, antennas, and battery units. Such units are replaced either by astronauts during EVA or by robotic arms.[173] Several shuttle missions were dedicated to the delivery of ORUs, including STS-129,[174] STS-133[175] and STS-134.[176] As of January 2011, only one other mode of transportation of ORUs had been utilised – the Japanese cargo vessel HTV-2 – which delivered an FHRC and CTC-2 via its Exposed Pallet (EP).[177][needs update]
There are also smaller exposure facilities mounted directly to laboratory modules; the Kibō Exposed Facility serves as an external «porch» for the Kibō complex,[178] and a facility on the European Columbus laboratory provides power and data connections for experiments such as the European Technology Exposure Facility[179][180] and the Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space.[181] A remote sensing instrument, SAGE III-ISS, was delivered to the station in February 2017 aboard CRS-10,[182] and the NICER experiment was delivered aboard CRS-11 in June 2017.[183] The largest scientific payload externally mounted to the ISS is the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), a particle physics experiment launched on STS-134 in May 2011, and mounted externally on the ITS. The AMS measures cosmic rays to look for evidence of dark matter and antimatter.[184][185]
The commercial Bartolomeo External Payload Hosting Platform, manufactured by Airbus, was launched on 6 March 2020 aboard CRS-20 and attached to the European Columbus module. It will provide an additional 12 external payload slots, supplementing the eight on the ExPRESS Logistics Carriers, ten on Kibō, and four on Columbus. The system is designed to be robotically serviced and will require no astronaut intervention. It is named after Christopher Columbus’s younger brother.[186][187][188]
Robotic arms and cargo cranes[edit]
Dextre, like many of the station’s experiments and robotic arms, can be operated from Earth, allowing tasks to be performed while the crew sleeps.
The Integrated Truss Structure serves as a base for the station’s primary remote manipulator system, the Mobile Servicing System (MSS), which is composed of three main components:
- Canadarm2, the largest robotic arm on the ISS, has a mass of 1,800 kilograms (4,000 lb) and is used to: dock and manipulate spacecraft and modules on the USOS; hold crew members and equipment in place during EVAs; and move Dextre around to perform tasks.[189]
- Dextre is a 1,560 kg (3,440 lb) robotic manipulator that has two arms and a rotating torso, with power tools, lights, and video for replacing orbital replacement units (ORUs) and performing other tasks requiring fine control.[190]
- The Mobile Base System (MBS) is a platform that rides on rails along the length of the station’s main truss, which serves as a mobile base for Canadarm2 and Dextre, allowing the robotic arms to reach all parts of the USOS.[191]
A grapple fixture was added to Zarya on STS-134 to enable Canadarm2 to inchworm itself onto the Russian Orbital Segment.[192] Also installed during STS-134 was the 15 m (50 ft) Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), which had been used to inspect heat shield tiles on Space Shuttle missions and which can be used on the station to increase the reach of the MSS.[192] Staff on Earth or the ISS can operate the MSS components using remote control, performing work outside the station without the need for space walks.
Japan’s Remote Manipulator System, which services the Kibō Exposed Facility,[193] was launched on STS-124 and is attached to the Kibō Pressurised Module.[194] The arm is similar to the Space Shuttle arm as it is permanently attached at one end and has a latching end effector for standard grapple fixtures at the other.
The European Robotic Arm, which will service the Russian Orbital Segment, was launched alongside the Nauka module.[195] The ROS does not require spacecraft or modules to be manipulated, as all spacecraft and modules dock automatically and may be discarded the same way. Crew use the two Strela (Russian: Стрела́, lit. ‘Arrow’) cargo cranes during EVAs for moving crew and equipment around the ROS. Each Strela crane has a mass of 45 kg (99 lb).
Former module[edit]
Pirs[edit]
Pirs (Russian: Пирс, lit. ’Pier’) was launched on 14 September 2001, as ISS Assembly Mission 4R, on a Russian Soyuz-U rocket, using a modified Progress spacecraft, Progress M-SO1, as an upper stage. Pirs was undocked by Progress MS-16 on 26 July 2021, 10:56 UTC, and deorbited on the same day at 14:51 UTC to make room for Nauka module to be attached to the space station. Prior to its departure, Pirs served as the primary Russian airlock on the station, being used to store and refurbish the Russian Orlan spacesuits.
The Pirs module attached to the ISS.
ISS-65 Pirs docking compartment separates from the Space Station
Planned components[edit]
Axiom segment[edit]
In January 2020, NASA awarded Axiom Space a contract to build a commercial module for the ISS with a launch date of 2024. The contract is under the NextSTEP2 program. NASA negotiated with Axiom on a firm fixed-price contract basis to build and deliver the module, which will attach to the forward port of the space station’s Harmony (Node 2) module. Although NASA has only commissioned one module, Axiom plans to build an entire segment consisting of five modules, including a node module, an orbital research and manufacturing facility, a crew habitat, and a «large-windowed Earth observatory». The Axiom segment is expected to greatly increase the capabilities and value of the space station, allowing for larger crews and private spaceflight by other organisations. Axiom plans to convert the segment into a stand-alone space station once the ISS is decommissioned, with the intention that this would act as a successor to the ISS.[196][197][198] Canadarm 2 will also help to berth the Axiom Space Station modules to the ISS and will continue its operations on the Axiom Space Station after the retirement of ISS in late 2020s.[199]
Proposed components[edit]
Xbase[edit]
Main article: B330
Made by Bigelow Aerospace. In August 2016 Bigelow negotiated an agreement with NASA to develop a full-sized ground prototype Deep Space Habitation based on the B330 under the second phase of Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships. The module is called the Expandable Bigelow Advanced Station Enhancement (XBASE), as Bigelow hopes to test the module by attaching it to the International Space Station.
Independence-1[edit]
Nanoracks, after finalizing its contract with NASA, and after winning NextSTEPs Phase II award, is now developing its concept Independence-1 (previously known as Ixion), which would turn spent rocket tanks into a habitable living area to be tested in space. In Spring 2018, Nanoracks announced that Ixion is now known as the Independence-1, the first ‘outpost’ in Nanoracks’ Space Outpost Program.
Nautilus-X Centrifuge Demonstration[edit]
If produced, this centrifuge will be the first in-space demonstration of sufficient scale centrifuge for artificial partial-g effects. It will be designed to become a sleep module for the ISS crew.
Cancelled components[edit]
The cancelled Habitation module under construction at Michoud in 1997
Several modules planned for the station were cancelled over the course of the ISS programme. Reasons include budgetary constraints, the modules becoming unnecessary, and station redesigns after the 2003 Columbia disaster. The US Centrifuge Accommodations Module would have hosted science experiments in varying levels of artificial gravity.[200] The US Habitation Module would have served as the station’s living quarters. Instead, the living quarters are now spread throughout the station.[201] The US Interim Control Module and ISS Propulsion Module would have replaced the functions of Zvezda in case of a launch failure.[202] Two Russian Research Modules were planned for scientific research.[203] They would have docked to a Russian Universal Docking Module.[204] The Russian Science Power Platform would have supplied power to the Russian Orbital Segment independent of the ITS solar arrays.
Science Power Modules 1 and 2 (Repurposed Components)[edit]
Science Power Module 1 (SPM-1, also known as NEM-1) and Science Power Module 2 (SPM-2, also known as NEM-2) are modules that were originally planned to arrive at the ISS no earlier than 2024, and dock to the Prichal module, which is currently docked to the Nauka module.[169][205] In April 2021, Roscosmos announced that NEM-1 would be repurposed to function as the core module of the proposed Russian Orbital Service Station (ROSS), launching no earlier than 2025 and docking to the free-flying Nauka module either before or after the ISS has been deorbited.[206][207] NEM-2 may be converted into another core «base» module, which would be launched in 2028.[208]
Onboard systems[edit]
Life support[edit]
The critical systems are the atmosphere control system, the water supply system, the food supply facilities, the sanitation and hygiene equipment, and fire detection and suppression equipment. The Russian Orbital Segment’s life support systems are contained in the Zvezda service module. Some of these systems are supplemented by equipment in the USOS. The Nauka laboratory has a complete set of life support systems.
Atmospheric control systems[edit]
The interactions between the components of the ISS Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS)
The atmosphere on board the ISS is similar to that of Earth.[209] Normal air pressure on the ISS is 101.3 kPa (14.69 psi);[210] the same as at sea level on Earth. An Earth-like atmosphere offers benefits for crew comfort, and is much safer than a pure oxygen atmosphere, because of the increased risk of a fire such as that responsible for the deaths of the Apollo 1 crew.[211][better source needed]
Earth-like atmospheric conditions have been maintained on all Russian and Soviet spacecraft.[212]
The Elektron system aboard Zvezda and a similar system in Destiny generate oxygen aboard the station.[213] The crew has a backup option in the form of bottled oxygen and Solid Fuel Oxygen Generation (SFOG) canisters, a chemical oxygen generator system.[214] Carbon dioxide is removed from the air by the Vozdukh system in Zvezda. Other by-products of human metabolism, such as methane from the intestines and ammonia from sweat, are removed by activated charcoal filters.[214]
Part of the ROS atmosphere control system is the oxygen supply. Triple-redundancy is provided by the Elektron unit, solid fuel generators, and stored oxygen. The primary supply of oxygen is the Elektron unit which produces O2 and H2 by electrolysis of water and vents H2 overboard. The 1 kW (1.3 hp) system uses approximately one litre of water per crew member per day. This water is either brought from Earth or recycled from other systems. Mir was the first spacecraft to use recycled water for oxygen production. The secondary oxygen supply is provided by burning oxygen-producing Vika cartridges (see also ISS ECLSS). Each ‘candle’ takes 5–20 minutes to decompose at 450–500 °C (842–932 °F), producing 600 litres (130 imp gal; 160 US gal) of O2. This unit is manually operated.[215]
The US Orbital Segment has redundant supplies of oxygen, from a pressurised storage tank on the Quest airlock module delivered in 2001, supplemented ten years later by ESA-built Advanced Closed-Loop System (ACLS) in the Tranquility module (Node 3), which produces O2 by electrolysis.[216] Hydrogen produced is combined with carbon dioxide from the cabin atmosphere and converted to water and methane.
Power and thermal control[edit]
Russian solar arrays, backlit by sunset
One of the eight truss mounted pairs of USOS solar arrays
ISS new roll out solar array as seen from a zoom camera on the P6 Truss
Double-sided solar arrays provide electrical power to the ISS. These bifacial cells collect direct sunlight on one side and light reflected off from the Earth on the other, and are more efficient and operate at a lower temperature than single-sided cells commonly used on Earth.[217]
The Russian segment of the station, like most spacecraft, uses 28 V low voltage DC from two rotating solar arrays mounted on Zvezda. The USOS uses 130–180 V DC from the USOS PV array, power is stabilised and distributed at 160 V DC and converted to the user-required 124 V DC. The higher distribution voltage allows smaller, lighter conductors, at the expense of crew safety. The two station segments share power with converters.
The USOS solar arrays are arranged as four wing pairs, for a total production of 75 to 90 kilowatts.[218] These arrays normally track the Sun to maximise power generation. Each array is about 375 m2 (4,036 sq ft) in area and 58 m (190 ft) long. In the complete configuration, the solar arrays track the Sun by rotating the alpha gimbal once per orbit; the beta gimbal follows slower changes in the angle of the Sun to the orbital plane. The Night Glider mode aligns the solar arrays parallel to the ground at night to reduce the significant aerodynamic drag at the station’s relatively low orbital altitude.[219]
The station originally used rechargeable nickel–hydrogen batteries (NiH2) for continuous power during the 45 minutes of every 90-minute orbit that it is eclipsed by the Earth. The batteries are recharged on the day side of the orbit. They had a 6.5-year lifetime (over 37,000 charge/discharge cycles) and were regularly replaced over the anticipated 20-year life of the station.[220] Starting in 2016, the nickel–hydrogen batteries were replaced by lithium-ion batteries, which are expected to last until the end of the ISS program.[221]
The station’s large solar panels generate a high potential voltage difference between the station and the ionosphere. This could cause arcing through insulating surfaces and sputtering of conductive surfaces as ions are accelerated by the spacecraft plasma sheath. To mitigate this, plasma contactor units create current paths between the station and the ambient space plasma.[222]
ISS External Active Thermal Control System (EATCS) diagram
The station’s systems and experiments consume a large amount of electrical power, almost all of which is converted to heat. To keep the internal temperature within workable limits, a passive thermal control system (PTCS) is made of external surface materials, insulation such as MLI, and heat pipes. If the PTCS cannot keep up with the heat load, an External Active Thermal Control System (EATCS) maintains the temperature. The EATCS consists of an internal, non-toxic, water coolant loop used to cool and dehumidify the atmosphere, which transfers collected heat into an external liquid ammonia loop. From the heat exchangers, ammonia is pumped into external radiators that emit heat as infrared radiation, then back to the station.[223] The EATCS provides cooling for all the US pressurised modules, including Kibō and Columbus, as well as the main power distribution electronics of the S0, S1 and P1 trusses. It can reject up to 70 kW. This is much more than the 14 kW of the Early External Active Thermal Control System (EEATCS) via the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which was launched on STS-105 and installed onto the P6 Truss.[224]
Communications and computers[edit]
The communications systems used by the ISS
* Luch and the Space Shuttle are not in use as of 2020
Radio communications provide telemetry and scientific data links between the station and mission control centres. Radio links are also used during rendezvous and docking procedures and for audio and video communication between crew members, flight controllers and family members. As a result, the ISS is equipped with internal and external communication systems used for different purposes.[225]
The Russian Orbital Segment communicates directly with the ground via the Lira antenna mounted to Zvezda.[8][226] The Lira antenna also has the capability to use the Luch data relay satellite system.[8] This system fell into disrepair during the 1990s, and so was not used during the early years of the ISS,[8][227][228] although two new Luch satellites – Luch-5A and Luch-5B – were launched in 2011 and 2012 respectively to restore the operational capability of the system.[229] Another Russian communications system is the Voskhod-M, which enables internal telephone communications between Zvezda, Zarya, Pirs, Poisk, and the USOS and provides a VHF radio link to ground control centres via antennas on Zvezda‘s exterior.[230]
The US Orbital Segment (USOS) makes use of two separate radio links: S band (audio, telemetry, commanding – located on the P1/S1 truss) and Ku band (audio, video and data – located on the Z1 truss) systems. These transmissions are routed via the United States Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) in geostationary orbit, allowing for almost continuous real-time communications with Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center (MCC-H) in Houston.[8][29][225] Data channels for the Canadarm2, European Columbus laboratory and Japanese Kibō modules were originally also routed via the S band and Ku band systems, with the European Data Relay System and a similar Japanese system intended to eventually complement the TDRSS in this role.[29][231] Communications between modules are carried on an internal wireless network.[232]
An array of laptops in the US lab
Laptop computers surround the Canadarm2 console
An error message displays a problem with hard drive on ISS laptop
UHF radio is used by astronauts and cosmonauts conducting EVAs and other spacecraft that dock to or undock from the station.[8] Automated spacecraft are fitted with their own communications equipment; the ATV uses a laser attached to the spacecraft and the Proximity Communications Equipment attached to Zvezda to accurately dock with the station.[233][234]
The ISS is equipped with about 100 IBM/Lenovo ThinkPad and HP ZBook 15 laptop computers. The laptops have run Windows 95, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 10 and Linux operating systems.[235] Each computer is a commercial off-the-shelf purchase which is then modified for safety and operation including updates to connectors, cooling and power to accommodate the station’s 28V DC power system and weightless environment. Heat generated by the laptops does not rise but stagnates around the laptop, so additional forced ventilation is required. Portable Computer System (PCS) laptops connect to the Primary Command & Control computer (C&C MDM) as remote terminals via a USB to 1553 adapter.[236] Station Support Computer (SSC) laptops aboard the ISS are connected to the station’s wireless LAN via Wi-Fi and ethernet, which connects to the ground via Ku band. While originally this provided speeds of 10 Mbit/s download and 3 Mbit/s upload from the station,[237][238] NASA upgraded the system in late August 2019 and increased the speeds to 600 Mbit/s.[239][240] Laptop hard drives occasionally fail and must be replaced.[241] Other computer hardware failures include instances in 2001, 2007 and 2017; some of these failures have required EVAs to replace computer modules in externally mounted devices.[242][243][244][245]
The operating system used for key station functions is the Debian Linux distribution.[246] The migration from Microsoft Windows to Linux was made in May 2013 for reasons of reliability, stability and flexibility.[247]
In 2017, an SG100 Cloud Computer was launched to the ISS as part of OA-7 mission.[248] It was manufactured by NCSIST of Taiwan and designed in collaboration with Academia Sinica, and National Central University under contract for NASA.[249]
ISS crew members have access to the Internet, and thus the web.[250][251] This was first enabled in 2010,[250] allowing NASA astronaut T.J. Creamer to make the first tweet from space.[252] Access is achieved via an Internet-enabled computer in Houston, using remote desktop mode, thereby protecting the ISS from virus infection and hacking attempts.[250]
Operations[edit]
Expeditions[edit]
Zarya and Unity were entered for the first time on 10 December 1998.
Soyuz TM-31 being prepared to bring the first resident crew to the station in October 2000
Each permanent crew is given an expedition number. Expeditions run up to six months, from launch until undocking, an ‘increment’ covers the same time period, but includes cargo spacecraft and all activities. Expeditions 1 to 6 consisted of three-person crews. Expeditions 7 to 12 were reduced to the safe minimum of two following the destruction of the NASA Shuttle Columbia. From Expedition 13 the crew gradually increased to six around 2010.[253][254] With the arrival of crew on US commercial vehicles beginning in 2020,[255] NASA has indicated that expedition size may be increased to seven crew members, the number ISS was originally designed for.[256][257]
Gennady Padalka, member of Expeditions 9, 19/20, 31/32, and 43/44, and Commander of Expedition 11, has spent more time in space than anyone else, a total of 878 days, 11 hours, and 29 minutes.[258] Peggy Whitson has spent the most time in space of any American, totalling 665 days, 22 hours, and 22 minutes during her time on Expeditions 5, 16, and 50/51/52.[259]
Private flights[edit]
Travellers who pay for their own passage into space are termed spaceflight participants by Roscosmos and NASA, and are sometimes referred to as «space tourists», a term they generally dislike.[e] As of 2021, seven space tourists have visited the ISS; all seven were transported to the ISS on Russian Soyuz spacecraft. When professional crews change over in numbers not divisible by the three seats in a Soyuz, and a short-stay crewmember is not sent, the spare seat is sold by MirCorp through Space Adventures. Space tourism was halted in 2011 when the Space Shuttle was retired and the station’s crew size was reduced to six, as the partners relied on Russian transport seats for access to the station. Soyuz flight schedules increased after 2013, allowing five Soyuz flights (15 seats) with only two expeditions (12 seats) required.[267] The remaining seats were to be sold for around US$40 million to members of the public who could pass a medical exam. ESA and NASA criticised private spaceflight at the beginning of the ISS, and NASA initially resisted training Dennis Tito, the first person to pay for his own passage to the ISS.[f]
Anousheh Ansari became the first self-funded woman to fly to the ISS as well as the first Iranian in space. Officials reported that her education and experience made her much more than a tourist, and her performance in training had been «excellent.»[268] She did Russian and European studies involving medicine and microbiology during her 10-day stay. The 2009 documentary Space Tourists follows her journey to the station, where she fulfilled «an age-old dream of man: to leave our planet as a ‘normal person’ and travel into outer space.»[269]
In 2008, spaceflight participant Richard Garriott placed a geocache aboard the ISS during his flight.[270] This is currently the only non-terrestrial geocache in existence.[271] At the same time, the Immortality Drive, an electronic record of eight digitised human DNA sequences, was placed aboard the ISS.[272]
Fleet operations[edit]
Dragon and Cygnus cargo vessels were docked at the ISS together for the first time in April 2016.
Commercial Crew Program vehicles Starliner and Dragon
A wide variety of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft have supported the station’s activities. Flights to the ISS include 37 Space Shuttle missions, 83 Progress resupply spacecraft (including the modified M-MIM2, M-SO1 and M-UM module transports), 63 crewed Soyuz spacecraft, 5 European ATVs, 9 Japanese HTVs, 1 Boeing Starliner, 30 SpaceX Dragon ( both crewed and uncrewed) and 18 Cygnus missions.[273]
There are currently twelve available docking ports for visiting spacecraft:[274]
- Harmony forward (with IDA 2)
- Harmony zenith (with IDA 3)
- Harmony nadir
- Unity nadir
- Prichal nadir
- Prichal aft
- Prichal forward
- Prichal starboard
- Prichal port
- Nauka forward[275]
- Poisk zenith
- Rassvet nadir
- Zvezda aft
Crewed[edit]
As of 30 December 2021, 256 people from 20 countries had visited the space station, many of them multiple times. The United States sent 158 people, Russia sent 55, 11 were Japanese, nine were Canadian, five were Italian, four were French, four were German, and there were one each from Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, Great Britain, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, the Netherlands, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Israel, Sweden and the United Arab Emirates.[276]
Uncrewed[edit]
Uncrewed spaceflights to the ISS are made primarily to deliver cargo, however several Russian modules have also docked to the outpost following uncrewed launches. Resupply missions typically use the Russian Progress spacecraft, former European ATVs, Japanese Kounotori vehicles, and the American Dragon and Cygnus spacecraft. The primary docking system for Progress spacecraft is the automated Kurs system, with the manual TORU system as a backup. ATVs also used Kurs, however they were not equipped with TORU. Progress and former ATV can remain docked for up to six months.[277][278] The other spacecraft – the Japanese HTV, the SpaceX Dragon (under CRS phase 1), and the Northrop Grumman[279] Cygnus – rendezvous with the station before being grappled using Canadarm2 and berthed at the nadir port of the Harmony or Unity module for one to two months. Under CRS phase 2, Cargo Dragon docks autonomously at IDA-2 or IDA-3. As of December 2020, Progress spacecraft have flown most of the uncrewed missions to the ISS.
Currently docked/berthed[edit]
Modules/spacecraft pending relocation/installation[edit]
Scheduled missions[edit]
- All dates are UTC. Dates are the earliest possible dates and may change.
- Forward ports are at the front of the station according to its normal direction of travel and orientation (attitude). Aft is at the rear of the station, used by spacecraft boosting the station’s orbit. Nadir is closest the Earth, zenith is on top. Port is to the left if pointing one’s feet towards the Earth and looking in the direction of travel; starboard to the right.
Docking[edit]
The Progress M-14M resupply vehicle approaching the ISS in 2012. More than 50 unpiloted Progress spacecraft have delivered supplies during the lifetime of the station.
All Russian spacecraft and self-propelled modules are able to rendezvous and dock to the space station without human intervention using the Kurs radar docking system from over 200 kilometres away. The European ATV uses star sensors and GPS to determine its intercept course. When it catches up it uses laser equipment to optically recognise Zvezda, along with the Kurs system for redundancy. Crew supervise these craft, but do not intervene except to send abort commands in emergencies. Progress and ATV supply craft can remain at the ISS for six months,[286][287] allowing great flexibility in crew time for loading and unloading of supplies and trash.
From the initial station programs, the Russians pursued an automated docking methodology that used the crew in override or monitoring roles. Although the initial development costs were high, the system has become very reliable with standardisations that provide significant cost benefits in repetitive operations.[288]
Soyuz spacecraft used for crew rotation also serve as lifeboats for emergency evacuation; they are replaced every six months and were used after the Columbia disaster to return stranded crew from the ISS.[289] The average expedition requires 2,722 kg of supplies, and by 9 March 2011, crews had consumed a total of around 22,000 meals.[99] Soyuz crew rotation flights and Progress resupply flights visit the station on average two and three times respectively each year.[290]
Other vehicles berth instead of docking. The Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle parked itself in progressively closer orbits to the station, and then awaited ‘approach’ commands from the crew, until it was close enough for a robotic arm to grapple and berth the vehicle to the USOS. Berthed craft can transfer International Standard Payload Racks. Japanese spacecraft berth for one to two months.[291] The berthing Cygnus and SpaceX Dragon were contracted to fly cargo to the station under phase 1 of the Commercial Resupply Services program.[292][293]
From 26 February 2011 to 7 March 2011 four of the governmental partners (United States, ESA, Japan and Russia) had their spacecraft (NASA Shuttle, ATV, HTV, Progress and Soyuz) docked at the ISS, the only time this has happened to date.[294] On 25 May 2012, SpaceX delivered the first commercial cargo with a Dragon spacecraft.[295]
Launch and docking windows[edit]
Prior to a spacecraft’s docking to the ISS, navigation and attitude control (GNC) is handed over to the ground control of the spacecraft’s country of origin. GNC is set to allow the station to drift in space, rather than fire its thrusters or turn using gyroscopes. The solar panels of the station are turned edge-on to the incoming spacecraft, so residue from its thrusters does not damage the cells. Before its retirement, Shuttle launches were often given priority over Soyuz, with occasional priority given to Soyuz arrivals carrying crew and time-critical cargoes, such as biological experiment materials.[296]
Repairs[edit]
Spare parts are called ORUs; some are externally stored on pallets called ELCs and ESPs.
While anchored on the end of the OBSS during STS-120, astronaut Scott Parazynski performs makeshift repairs to a US solar array that damaged itself when unfolding.
Orbital Replacement Units (ORUs) are spare parts that can be readily replaced when a unit either passes its design life or fails. Examples of ORUs are pumps, storage tanks, controller boxes, antennas, and battery units. Some units can be replaced using robotic arms. Most are stored outside the station, either on small pallets called ExPRESS Logistics Carriers (ELCs) or share larger platforms called External Stowage Platforms which also hold science experiments. Both kinds of pallets provide electricity for many parts that could be damaged by the cold of space and require heating. The larger logistics carriers also have local area network (LAN) connections for telemetry to connect experiments. A heavy emphasis on stocking the USOS with ORU’s occurred around 2011, before the end of the NASA shuttle programme, as its commercial replacements, Cygnus and Dragon, carry one tenth to one quarter the payload.
Unexpected problems and failures have impacted the station’s assembly time-line and work schedules leading to periods of reduced capabilities and, in some cases, could have forced abandonment of the station for safety reasons. Serious problems include an air leak from the USOS in 2004,[297] the venting of fumes from an Elektron oxygen generator in 2006,[298] and the failure of the computers in the ROS in 2007 during STS-117 that left the station without thruster, Elektron, Vozdukh and other environmental control system operations. In the latter case, the root cause was found to be condensation inside electrical connectors leading to a short circuit.[299]
During STS-120 in 2007 and following the relocation of the P6 truss and solar arrays, it was noted during unfurling that the solar array had torn and was not deploying properly.[300] An EVA was carried out by Scott Parazynski, assisted by Douglas Wheelock. Extra precautions were taken to reduce the risk of electric shock, as the repairs were carried out with the solar array exposed to sunlight.[301] The issues with the array were followed in the same year by problems with the starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ), which rotates the arrays on the starboard side of the station. Excessive vibration and high-current spikes in the array drive motor were noted, resulting in a decision to substantially curtail motion of the starboard SARJ until the cause was understood. Inspections during EVAs on STS-120 and STS-123 showed extensive contamination from metallic shavings and debris in the large drive gear and confirmed damage to the large metallic bearing surfaces, so the joint was locked to prevent further damage.[302][303] Repairs to the joints were carried out during STS-126 with lubrication and the replacement of 11 out of 12 trundle bearings on the joint.[304][305]
In September 2008, damage to the S1 radiator was first noticed in Soyuz imagery. The problem was initially not thought to be serious.[306] The imagery showed that the surface of one sub-panel has peeled back from the underlying central structure, possibly because of micro-meteoroid or debris impact. On 15 May 2009 the damaged radiator panel’s ammonia tubing was mechanically shut off from the rest of the cooling system by the computer-controlled closure of a valve. The same valve was then used to vent the ammonia from the damaged panel, eliminating the possibility of an ammonia leak.[306] It is also known that a Service Module thruster cover struck the S1 radiator after being jettisoned during an EVA in 2008, but its effect, if any, has not been determined.
In the early hours of 1 August 2010, a failure in cooling Loop A (starboard side), one of two external cooling loops, left the station with only half of its normal cooling capacity and zero redundancy in some systems.[307][308][309] The problem appeared to be in the ammonia pump module that circulates the ammonia cooling fluid. Several subsystems, including two of the four CMGs, were shut down.
Planned operations on the ISS were interrupted through a series of EVAs to address the cooling system issue. A first EVA on 7 August 2010, to replace the failed pump module, was not fully completed because of an ammonia leak in one of four quick-disconnects. A second EVA on 11 August successfully removed the failed pump module.[310][311] A third EVA was required to restore Loop A to normal functionality.[312][313]
The USOS’s cooling system is largely built by the US company Boeing,[314] which is also the manufacturer of the failed pump.[307]
The four Main Bus Switching Units (MBSUs, located in the S0 truss), control the routing of power from the four solar array wings to the rest of the ISS. Each MBSU has two power channels that feed 160V DC from the arrays to two DC-to-DC power converters (DDCUs) that supply the 124V power used in the station. In late 2011 MBSU-1 ceased responding to commands or sending data confirming its health. While still routing power correctly, it was scheduled to be swapped out at the next available EVA. A spare MBSU was already on board, but a 30 August 2012 EVA failed to be completed when a bolt being tightened to finish installation of the spare unit jammed before the electrical connection was secured.[315] The loss of MBSU-1 limited the station to 75% of its normal power capacity, requiring minor limitations in normal operations until the problem could be addressed.
On 5 September 2012, in a second six-hour EVA, astronauts Sunita Williams and Akihiko Hoshide successfully replaced MBSU-1 and restored the ISS to 100% power.[316]
On 24 December 2013, astronauts installed a new ammonia pump for the station’s cooling system. The faulty cooling system had failed earlier in the month, halting many of the station’s science experiments. Astronauts had to brave a «mini blizzard» of ammonia while installing the new pump. It was only the second Christmas Eve spacewalk in NASA history.[317]
Mission control centres[edit]
The components of the ISS are operated and monitored by their respective space agencies at mission control centres across the globe, including RKA Mission Control Center, ATV Control Centre, JEM Control Center and HTV Control Center at Tsukuba Space Center, Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, Payload Operations and Integration Center, Columbus Control Center and Mobile Servicing System Control.
Life aboard[edit]
Crew activities[edit]
STS-122 mission specialists working on robotic equipment in the US lab
A typical day for the crew begins with a wake-up at 06:00, followed by post-sleep activities and a morning inspection of the station. The crew then eats breakfast and takes part in a daily planning conference with Mission Control before starting work at around 08:10. The first scheduled exercise of the day follows, after which the crew continues work until 13:05. Following a one-hour lunch break, the afternoon consists of more exercise and work before the crew carries out its pre-sleep activities beginning at 19:30, including dinner and a crew conference. The scheduled sleep period begins at 21:30. In general, the crew works ten hours per day on a weekday, and five hours on Saturdays, with the rest of the time their own for relaxation or work catch-up.[318]
The time zone used aboard the ISS is Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).[319] The windows are covered during night hours to give the impression of darkness because the station experiences 16 sunrises and sunsets per day. During visiting Space Shuttle missions, the ISS crew mostly followed the shuttle’s Mission Elapsed Time (MET), which was a flexible time zone based on the launch time of the Space Shuttle mission.[320][321][322]
The station provides crew quarters for each member of the expedition’s crew, with two «sleep stations» in the Zvezda, one in Nauka and four more installed in Harmony.[323][324][325][326] The USOS quarters are private, approximately person-sized soundproof booths. The ROS crew quarters in Zvezda include a small window, but provide less ventilation and sound proofing. A crew member can sleep in a crew quarter in a tethered sleeping bag, listen to music, use a laptop, and store personal items in a large drawer or in nets attached to the module’s walls. The module also provides a reading lamp, a shelf and a desktop.[327][328][329] Visiting crews have no allocated sleep module, and attach a sleeping bag to an available space on a wall. It is possible to sleep floating freely through the station, but this is generally avoided because of the possibility of bumping into sensitive equipment.[330] It is important that crew accommodations be well ventilated; otherwise, astronauts can wake up oxygen-deprived and gasping for air, because a bubble of their own exhaled carbon dioxide has formed around their heads.[327] During various station activities and crew rest times, the lights in the ISS can be dimmed, switched off, and colour temperatures adjusted.[331][332]
Food and personal hygiene[edit]
Main dining desk in Node 1
Fresh fruits and vegetables are grown in the ISS.
On the USOS, most of the food aboard is vacuum sealed in plastic bags; cans are rare because they are heavy and expensive to transport. Preserved food is not highly regarded by the crew and taste is reduced in microgravity,[327] so efforts are taken to make the food more palatable, including using more spices than in regular cooking. The crew looks forward to the arrival of any spacecraft from Earth as they bring fresh fruit and vegetables. Care is taken that foods do not create crumbs, and liquid condiments are preferred over solid to avoid contaminating station equipment. Each crew member has individual food packages and cooks them using the on-board galley. The galley features two food warmers, a refrigerator (added in November 2008), and a water dispenser that provides both heated and unheated water.[328] Drinks are provided as dehydrated powder that is mixed with water before consumption.[328][329] Drinks and soups are sipped from plastic bags with straws, while solid food is eaten with a knife and fork attached to a tray with magnets to prevent them from floating away. Any food that floats away, including crumbs, must be collected to prevent it from clogging the station’s air filters and other equipment.[329]
Showers on space stations were introduced in the early 1970s on Skylab and Salyut 3.[333]: 139 By Salyut 6, in the early 1980s, the crew complained of the complexity of showering in space, which was a monthly activity.[334] The ISS does not feature a shower; instead, crewmembers wash using a water jet and wet wipes, with soap dispensed from a toothpaste tube-like container. Crews are also provided with rinseless shampoo and edible toothpaste to save water.[330][335]
There are two space toilets on the ISS, both of Russian design, located in Zvezda and Tranquility.[328] These Waste and Hygiene Compartments use a fan-driven suction system similar to the Space Shuttle Waste Collection System. Astronauts first fasten themselves to the toilet seat, which is equipped with spring-loaded restraining bars to ensure a good seal.[327] A lever operates a powerful fan and a suction hole slides open: the air stream carries the waste away. Solid waste is collected in individual bags which are stored in an aluminium container. Full containers are transferred to Progress spacecraft for disposal.[328][336] Liquid waste is evacuated by a hose connected to the front of the toilet, with anatomically correct «urine funnel adapters» attached to the tube so that men and women can use the same toilet. The diverted urine is collected and transferred to the Water Recovery System, where it is recycled into drinking water.[329] In 2021, the arrival of the Nauka module also brought a third toilet to the ISS.[337]
The space toilet in the Zvezda module in the Russian segment
The main toilet in the US Segment inside the Tranquility module
* Both toilets are of Russian design
Crew health and safety[edit]
Overall[edit]
On 12 April 2019, NASA reported medical results from the Astronaut Twin Study. Astronaut Scott Kelly spent a year in space on the ISS, while his twin spent the year on Earth. Several long-lasting changes were observed, including those related to alterations in DNA and cognition, when one twin was compared with the other.[338][339]
In November 2019, researchers reported that astronauts experienced serious blood flow and clot problems while on board the ISS, based on a six-month study of 11 healthy astronauts. The results may influence long-term spaceflight, including a mission to the planet Mars, according to the researchers.[340][341]
Radiation[edit]
The ISS is partially protected from the space environment by Earth’s magnetic field. From an average distance of about 70,000 km (43,000 mi) from the Earth’s surface, depending on Solar activity, the magnetosphere begins to deflect solar wind around Earth and the space station. Solar flares are still a hazard to the crew, who may receive only a few minutes warning. In 2005, during the initial «proton storm» of an X-3 class solar flare, the crew of Expedition 10 took shelter in a more heavily shielded part of the ROS designed for this purpose.[342][343]
Subatomic charged particles, primarily protons from cosmic rays and solar wind, are normally absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere. When they interact in sufficient quantity, their effect is visible to the naked eye in a phenomenon called an aurora. Outside Earth’s atmosphere, ISS crews are exposed to approximately one millisievert each day (about a year’s worth of natural exposure on Earth), resulting in a higher risk of cancer. Radiation can penetrate living tissue and damage the DNA and chromosomes of lymphocytes; being central to the immune system, any damage to these cells could contribute to the lower immunity experienced by astronauts. Radiation has also been linked to a higher incidence of cataracts in astronauts. Protective shielding and medications may lower the risks to an acceptable level.[59]
Radiation levels on the ISS are between 12 and 28.8 milli rads per day,[344] about five times greater than those experienced by airline passengers and crew, as Earth’s electromagnetic field provides almost the same level of protection against solar and other types of radiation in low Earth orbit as in the stratosphere. For example, on a 12-hour flight, an airline passenger would experience 0.1 millisieverts of radiation, or a rate of 0.2 millisieverts per day; this is only one fifth the rate experienced by an astronaut in LEO. Additionally, airline passengers experience this level of radiation for a few hours of flight, while the ISS crew are exposed for their whole stay on board the station.[345]
Stress[edit]
There is considerable evidence that psychosocial stressors are among the most important impediments to optimal crew morale and performance.[346] Cosmonaut Valery Ryumin wrote in his journal during a particularly difficult period on board the Salyut 6 space station: «All the conditions necessary for murder are met if you shut two men in a cabin measuring 18 feet by 20 [5.5 m × 6 m] and leave them together for two months.»
NASA’s interest in psychological stress caused by space travel, initially studied when their crewed missions began, was rekindled when astronauts joined cosmonauts on the Russian space station Mir. Common sources of stress in early US missions included maintaining high performance under public scrutiny and isolation from peers and family. The latter is still often a cause of stress on the ISS, such as when the mother of NASA astronaut Daniel Tani died in a car accident, and when Michael Fincke was forced to miss the birth of his second child.
A study of the longest spaceflight concluded that the first three weeks are a critical period where attention is adversely affected because of the demand to adjust to the extreme change of environment.[347] ISS crew flights typically last about five to six months.
The ISS working environment includes further stress caused by living and working in cramped conditions with people from very different cultures who speak a different language. First-generation space stations had crews who spoke a single language; second- and third-generation stations have crew from many cultures who speak many languages. Astronauts must speak English and Russian, and knowing additional languages is even better.[348]
Due to the lack of gravity, confusion often occurs. Even though there is no up and down in space, some crew members feel like they are oriented upside down. They may also have difficulty measuring distances. This can cause problems like getting lost inside the space station, pulling switches in the wrong direction or misjudging the speed of an approaching vehicle during docking.[349]
Medical[edit]
The physiological effects of long-term weightlessness include muscle atrophy, deterioration of the skeleton (osteopenia), fluid redistribution, a slowing of the cardiovascular system, decreased production of red blood cells, balance disorders, and a weakening of the immune system. Lesser symptoms include loss of body mass, and puffiness of the face.[59]
Sleep is regularly disturbed on the ISS because of mission demands, such as incoming or departing spacecraft. Sound levels in the station are unavoidably high. The atmosphere is unable to thermosiphon naturally, so fans are required at all times to process the air which would stagnate in the freefall (zero-G) environment.
To prevent some of the adverse effects on the body, the station is equipped with: two TVIS treadmills (including the COLBERT); the ARED (Advanced Resistive Exercise Device), which enables various weightlifting exercises that add muscle without raising (or compensating for) the astronauts’ reduced bone density;[350] and a stationary bicycle. Each astronaut spends at least two hours per day exercising on the equipment.[327][328] Astronauts use bungee cords to strap themselves to the treadmill.[351][352]
Microbiological environmental hazards[edit]
Hazardous molds that can foul air and water filters may develop aboard space stations. They can produce acids that degrade metal, glass, and rubber. They can also be harmful to the crew’s health. Microbiological hazards have led to a development of the LOCAD-PTS which identifies common bacteria and molds faster than standard methods of culturing, which may require a sample to be sent back to Earth.[353] Researchers in 2018 reported, after detecting the presence of five Enterobacter bugandensis bacterial strains on the ISS (none of which are pathogenic to humans), that microorganisms on the ISS should be carefully monitored to continue assuring a medically healthy environment for astronauts.[354][355]
Contamination on space stations can be prevented by reduced humidity, and by using paint that contains mold-killing chemicals, as well as the use of antiseptic solutions. All materials used in the ISS are tested for resistance against fungi.[356]
In April 2019, NASA reported that a comprehensive study had been conducted into the microorganisms and fungi present on the ISS. The results may be useful in improving the health and safety conditions for astronauts.[357][358]
Noise[edit]
Space flight is not inherently quiet, with noise levels exceeding acoustic standards as far back as the Apollo missions.[359][360] For this reason, NASA and the International Space Station international partners have developed noise control and hearing loss prevention goals as part of the health program for crew members. Specifically, these goals have been the primary focus of the ISS Multilateral Medical Operations Panel (MMOP) Acoustics Subgroup since the first days of ISS assembly and operations.[361][362] The effort includes contributions from acoustical engineers, audiologists, industrial hygienists, and physicians who comprise the subgroup’s membership from NASA, Roscosmos, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
When compared to terrestrial environments, the noise levels incurred by astronauts and cosmonauts on the ISS may seem insignificant and typically occur at levels that would not be of major concern to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration – rarely reaching 85 dBA. But crew members are exposed to these levels 24 hours a day, seven days a week, with current missions averaging six months in duration. These levels of noise also impose risks to crew health and performance in the form of sleep interference and communication, as well as reduced alarm audibility.
Over the 19 plus year history of the ISS, significant efforts have been put forth to limit and reduce noise levels on the ISS. During design and pre-flight activities, members of the Acoustic Subgroup have written acoustic limits and verification requirements, consulted to design and choose quietest available payloads, and then conducted acoustic verification tests prior to launch.[361]: 5.7.3 During spaceflights, the Acoustics Subgroup has assessed each ISS module’s in flight sound levels, produced by a large number of vehicle and science experiment noise sources, to assure compliance with strict acoustic standards. The acoustic environment on ISS changed when additional modules were added during its construction, and as additional spacecraft arrive at the ISS. The Acoustics Subgroup has responded to this dynamic operations schedule by successfully designing and employing acoustic covers, absorptive materials, noise barriers, and vibration isolators to reduce noise levels. Moreover, when pumps, fans, and ventilation systems age and show increased noise levels, this Acoustics Subgroup has guided ISS managers to replace the older, noisier instruments with quiet fan and pump technologies, significantly reducing ambient noise levels.
NASA has adopted most-conservative damage risk criteria (based on recommendations from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and the World Health Organization), in order to protect all crew members. The MMOP Acoustics Subgroup has adjusted its approach to managing noise risks in this unique environment by applying, or modifying, terrestrial approaches for hearing loss prevention to set these conservative limits. One innovative approach has been NASA’s Noise Exposure Estimation Tool (NEET), in which noise exposures are calculated in a task-based approach to determine the need for hearing protection devices (HPDs). Guidance for use of HPDs, either mandatory use or recommended, is then documented in the Noise Hazard Inventory, and posted for crew reference during their missions. The Acoustics Subgroup also tracks spacecraft noise exceedances, applies engineering controls, and recommends hearing protective devices to reduce crew noise exposures. Finally, hearing thresholds are monitored on-orbit, during missions.
There have been no persistent mission-related hearing threshold shifts among US Orbital Segment crewmembers (JAXA, CSA, ESA, NASA) during what is approaching 20 years of ISS mission operations, or nearly 175,000 work hours. In 2020, the MMOP Acoustics Subgroup received the Safe-In-Sound Award for Innovation for their combined efforts to mitigate any health effects of noise.[363]
Fire and toxic gases[edit]
An onboard fire or a toxic gas leak are other potential hazards. Ammonia is used in the external radiators of the station and could potentially leak into the pressurised modules.[364]
Orbit[edit]
Altitude and orbital inclination[edit]
Graph showing the changing altitude of the ISS from November 1998 until November 2018
Animation of ISS orbit from 14 September 2018 to 14 November 2018. Earth is not shown.
The ISS is currently maintained in a nearly circular orbit with a minimum mean altitude of 370 km (230 mi) and a maximum of 460 km (290 mi),[365] in the centre of the thermosphere, at an inclination of 51.6 degrees to Earth’s equator with an eccentricity of 0.007. This orbit was selected because it is the lowest inclination that can be directly reached by Russian Soyuz and Progress spacecraft launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome at 46° N latitude without overflying China or dropping spent rocket stages in inhabited areas.[366][367]
It travels at an average speed of 28,000 kilometres per hour (17,000 mph), and completes 15.5 orbits per day (93 minutes per orbit).[2][19] The station’s altitude was allowed to fall around the time of each NASA shuttle flight to permit heavier loads to be transferred to the station. After the retirement of the shuttle, the nominal orbit of the space station was raised in altitude (from about 350 km to about 400 km).[368][369] Other, more frequent supply spacecraft do not require this adjustment as they are substantially higher performance vehicles.[44][370]
Atmospheric drag reduces the altitude by about 2 km a month on average. Orbital boosting can be performed by the station’s two main engines on the Zvezda service module, or Russian or European spacecraft docked to Zvezda‘s aft port. The Automated Transfer Vehicle is constructed with the possibility of adding a second docking port to its aft end, allowing other craft to dock and boost the station. It takes approximately two orbits (three hours) for the boost to a higher altitude to be completed.[370] Maintaining ISS altitude uses about 7.5 tonnes of chemical fuel per annum[371] at an annual cost of about $210 million.[372]
Orbits of the ISS, shown in April 2013
The Russian Orbital Segment contains the Data Management System, which handles Guidance, Navigation and Control (ROS GNC) for the entire station.[373] Initially, Zarya, the first module of the station, controlled the station until a short time after the Russian service module Zvezda docked and was transferred control. Zvezda contains the ESA built DMS-R Data Management System.[374] Using two fault-tolerant computers (FTC), Zvezda computes the station’s position and orbital trajectory using redundant Earth horizon sensors, Solar horizon sensors as well as Sun and star trackers. The FTCs each contain three identical processing units working in parallel and provide advanced fault-masking by majority voting.
Orientation[edit]
Zvezda uses gyroscopes (reaction wheels) and thrusters to turn itself around. Gyroscopes do not require propellant; instead they use electricity to ‘store’ momentum in flywheels by turning in the opposite direction to the station’s movement. The USOS has its own computer-controlled gyroscopes to handle its extra mass. When gyroscopes ‘saturate’, thrusters are used to cancel out the stored momentum. In February 2005, during Expedition 10, an incorrect command was sent to the station’s computer, using about 14 kilograms of propellant before the fault was noticed and fixed. When attitude control computers in the ROS and USOS fail to communicate properly, this can result in a rare ‘force fight’ where the ROS GNC computer must ignore the USOS counterpart, which itself has no thrusters.[375][376][377]
Docked spacecraft can also be used to maintain station attitude, such as for troubleshooting or during the installation of the S3/S4 truss, which provides electrical power and data interfaces for the station’s electronics.[378]
Orbital debris threats[edit]
The low altitudes at which the ISS orbits are also home to a variety of space debris,[379] including spent rocket stages, defunct satellites, explosion fragments (including materials from anti-satellite weapon tests), paint flakes, slag from solid rocket motors, and coolant released by US-A nuclear-powered satellites. These objects, in addition to natural micrometeoroids,[380] are a significant threat. Objects large enough to destroy the station can be tracked, and are not as dangerous as smaller debris.[381][382] Objects too small to be detected by optical and radar instruments, from approximately 1 cm down to microscopic size, number in the trillions. Despite their small size, some of these objects are a threat because of their kinetic energy and direction in relation to the station. Spacewalking crew in spacesuits are also at risk of suit damage and consequent exposure to vacuum.[383]
Ballistic panels, also called micrometeorite shielding, are incorporated into the station to protect pressurised sections and critical systems. The type and thickness of these panels depend on their predicted exposure to damage. The station’s shields and structure have different designs on the ROS and the USOS. On the USOS, Whipple Shields are used. The US segment modules consist of an inner layer made from 1.5–5.0 cm-thick (0.59–1.97 in) aluminium, a 10 cm-thick (3.9 in) intermediate layers of Kevlar and Nextel (a ceramic fabric),[384] and an outer layer of stainless steel, which causes objects to shatter into a cloud before hitting the hull, thereby spreading the energy of impact. On the ROS, a carbon fibre reinforced polymer honeycomb screen is spaced from the hull, an aluminium honeycomb screen is spaced from that, with a screen-vacuum thermal insulation covering, and glass cloth over the top.[385]
Space debris is tracked remotely from the ground, and the station crew can be notified.[386] If necessary, thrusters on the Russian Orbital Segment can alter the station’s orbital altitude, avoiding the debris. These Debris Avoidance Manoeuvres (DAMs) are not uncommon, taking place if computational models show the debris will approach within a certain threat distance. Ten DAMs had been performed by the end of 2009.[387][388][389] Usually, an increase in orbital velocity of the order of 1 m/s is used to raise the orbit by one or two kilometres. If necessary, the altitude can also be lowered, although such a manoeuvre wastes propellant.[388][390] If a threat from orbital debris is identified too late for a DAM to be safely conducted, the station crew close all the hatches aboard the station and retreat into their spacecraft in order to be able to evacuate in the event the station was seriously damaged by the debris. This partial station evacuation has occurred on 13 March 2009, 28 June 2011, 24 March 2012 and 16 June 2015.[391][392]
In November 2021, a debris cloud from the destruction of Kosmos 1408 by an anti-satellite weapons test threatened the ISS, leading to the announcement of a yellow alert, leading to crew sheltering in the crew capsules.[393] A couple of weeks later, it had to perform an unscheduled maneuver to drop the station by 310 meters to avoid a collision with hazardous space debris.[394]
-
A 7-gram object (shown in centre) shot at 7 km/s (23,000 ft/s), the orbital velocity of the ISS, made this 15 cm (5.9 in) crater in a solid block of aluminium.
-
Example of risk management: A NASA model showing areas at high risk from impact for the International Space Station.
-
A blueprint of a typical debris «Whipple Shield» design.
Sightings from Earth[edit]
The ISS is visible to the naked eye as a slow-moving, bright white dot because of reflected sunlight, and can be seen in the hours after sunset and before sunrise, when the station remains sunlit but the ground and sky are dark.[395] The ISS takes about 10 minutes to pass from one horizon to another, and will only be visible part of that time because of moving into or out of the Earth’s shadow. Because of the size of its reflective surface area, the ISS is the brightest artificial object in the sky (excluding other satellite flares), with an approximate maximum magnitude of −4 when in sunlight and overhead (similar to Venus), and a maximum angular size of 63 arcseconds.[396] The ISS, like many satellites including the Iridium constellation, can also produce flares of up to 16 times the brightness of Venus as sunlight glints off reflective surfaces.[397][398] The ISS is also visible in broad daylight, albeit with a great deal more difficulty.
Tools are provided by a number of websites such as Heavens-Above (see Live viewing below) as well as smartphone applications that use orbital data and the observer’s longitude and latitude to indicate when the ISS will be visible (weather permitting), where the station will appear to rise, the altitude above the horizon it will reach and the duration of the pass before the station disappears either by setting below the horizon or entering into Earth’s shadow.[399][400][401][402]
In November 2012 NASA launched its «Spot the Station» service, which sends people text and email alerts when the station is due to fly above their town.[403] The station is visible from 95% of the inhabited land on Earth, but is not visible from extreme northern or southern latitudes.[366]
Under specific conditions, the ISS can be observed at night on five consecutive orbits. Those conditions are 1) a mid-latitude observer location, 2) near the time of the solstice with 3) the ISS passing in the direction of the pole from the observer near midnight local time. The three photos show the first, middle and last of the five passes on 5–6 June 2014.
-
Skytrack long duration exposure of the ISS
-
The ISS on its first pass of the night passing nearly overhead shortly after sunset in June 2014
-
The ISS passing north on its third pass of the night near local midnight in June 2014
-
The ISS passing west on its fifth pass of the night before sunrise in June 2014
Astrophotography[edit]
Using a telescope-mounted camera to photograph the station is a popular hobby for astronomers,[404] while using a mounted camera to photograph the Earth and stars is a popular hobby for crew.[405] The use of a telescope or binoculars allows viewing of the ISS during daylight hours.[406]
Composite of six photos of the ISS transiting the gibbous Moon
Transits of the ISS in front of the Sun, particularly during an eclipse (and so the Earth, Sun, Moon, and ISS are all positioned approximately in a single line) are of particular interest for amateur astronomers.[407][408]
International co-operation[edit]
A Commemorative Plaque honouring Space Station Intergovernmental Agreement signed on 28 January 1998
Involving five space programs and fifteen countries,[409] the International Space Station is the most politically and legally complex space exploration programme in history.[410] The 1998 Space Station Intergovernmental Agreement sets forth the primary framework for international cooperation among the parties. A series of subsequent agreements govern other aspects of the station, ranging from jurisdictional issues to a code of conduct among visiting astronauts.[411]
Following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, continued cooperation between Russia and other countries on the International Space Station has been put into question. British Prime Minister Boris Johnson commented on the current status of cooperation, saying «I have been broadly in favour of continuing artistic and scientific collaboration, but in the current circumstances it’s hard to see how even those can continue as normal.»[412] On the same day, Roscosmos Director General Dmitry Rogozin insinuated that Russian withdrawal could cause the International Space Station to de-orbit due to lack of reboost capabilities, writing in a series of tweets, «If you block cooperation with us, who will save the ISS from an unguided de-orbit to impact on the territory of the US or Europe? There’s also the chance of impact of the 500-ton construction in India or China. Do you want to threaten them with such a prospect? The ISS doesn’t fly over Russia, so all the risk is yours. Are you ready for it?»[413] Rogozin later tweeted that normal relations between ISS partners could only be restored once sanctions have been lifted, and indicated that Roscosmos would submit proposals to the Russian government on ending cooperation.[414] NASA stated that, if necessary, US corporation Northrop Grumman has offered a reboost capability that would keep the ISS in orbit.[415]
On 26 July 2022, Yury Borisov, Rogozin’s successor as head of Roscosmos, submitted to Russian President Putin plans for withdrawal from the programme after 2024.[20] However, Robyn Gatens, the NASA official in charge of the space station, responded that NASA had not received any formal notices from Roscosmos concerning withdrawal plans.[21]
Participating countries[edit]
End of mission[edit]
According to the Outer Space Treaty, the United States and Russia are legally responsible for all modules they have launched.[416] Several possible disposal options were considered: Natural orbital decay with random reentry (as with Skylab), boosting the station to a higher altitude (which would delay reentry), and a controlled targeted de-orbit to a remote ocean area.[417] In late 2010, the preferred plan was to use a slightly modified Progress spacecraft to de-orbit the ISS.[418] This plan was seen as the simplest, cheapest and with the highest margin of safety.[clarify][418]
OPSEK was previously intended to be constructed of modules from the Russian Orbital Segment after the ISS is decommissioned. The modules under consideration for removal from the current ISS included the Multipurpose Laboratory Module (Nauka), launched in July 2021, and the other new Russian modules that are proposed to be attached to Nauka. These newly launched modules would still be well within their useful lives in 2024.[419]
At the end of 2011, the Exploration Gateway Platform concept also proposed using leftover USOS hardware and Zvezda 2 as a refuelling depot and service station located at one of the Earth–Moon Lagrange points. However, the entire USOS was not designed for disassembly and will be discarded.[420]
On 30 September 2015, Boeing’s contract with NASA as prime contractor for the ISS was extended to 30 September 2020. Part of Boeing’s services under the contract related to extending the station’s primary structural hardware past 2020 to the end of 2028.[421]
There have also been suggestions in the commercial space industry that the station could be converted to commercial operations after it is retired by government entities.[422]
In July 2018, the Space Frontier Act of 2018 was intended to extend operations of the ISS to 2030. This bill was unanimously approved in the Senate, but failed to pass in the U.S. House.[423][424] In September 2018, the Leading Human Spaceflight Act was introduced with the intent to extend operations of the ISS to 2030, and was confirmed in December 2018.[27][28][425] Congress later passed similar provisions in its CHIPS and Science Act, signed into law by President Joe Biden on 9 August 2022.[426][427]
In January 2022, NASA announced a planned date of January 2031 to de-orbit the ISS using a deorbit module and direct any remnants into a remote area of the South Pacific Ocean.[428]
Cost[edit]
The ISS has been described as the most expensive single item ever constructed.[429] As of 2010, the total cost was US$150 billion. This includes NASA’s budget of $58.7 billion ($89.73 billion in 2021 dollars) for the station from 1985 to 2015, Russia’s $12 billion, Europe’s $5 billion, Japan’s $5 billion, Canada’s $2 billion, and the cost of 36 shuttle flights to build the station, estimated at $1.4 billion each, or $50.4 billion in total. Assuming 20,000 person-days of use from 2000 to 2015 by two- to six-person crews, each person-day would cost $7.5 million, less than half the inflation-adjusted $19.6 million ($5.5 million before inflation) per person-day of Skylab.[430]
In film[edit]
Beside numerous documentaries such as the IMAX documentaries Space Station 3D from 2002,[431] or A Beautiful Planet from 2016,[432] the ISS is subject of feature films such as The Day After Tomorrow (2004),[433] Life (2017),[434] Love (2011),[435] or – together with the Chinese station Tiangong space station – in Gravity (2013).[436]
See also[edit]
- A Beautiful Planet – 2016 IMAX documentary film showing scenes of Earth, as well as astronaut life aboard the ISS
- Center for the Advancement of Science in Space – operates the US National Laboratory on the ISS
- List of commanders of the International Space Station
- List of space stations
- List of spacecraft deployed from the International Space Station
- Politics of outer space
- Science diplomacy
- Space Station 3D – 2002 Canadian documentary
Notes[edit]
- ^ Temporary docking adapter used till Prichal module arrival
- ^ «Zarya» can have a lot of meanings: «daybreak», «dawn» (in the morning) or «afterglow», «evening glow», «sunset» (in the evening). But usually it means «dawn».
- ^ temporary docking adapter is the grey ring surrounding the docking probe of Progress MS 17
- ^ The port had the temporary docking adapter before the SSVP-M or «Hybrid» standard, consisting of the traditional SSVP-G probe‑and‑drogue soft-dock mechanism and an APAS-95 hard-dock collar before Prichal arrival
- ^ Privately funded travellers who have objected to the term include Dennis Tito, the first such traveller,[260] Mark Shuttleworth, founder of Ubuntu,[261] Gregory Olsen and Richard Garriott.[262][263] Canadian astronaut Bob Thirsk said the term does not seem appropriate, referring to his crewmate, Guy Laliberté, founder of Cirque du Soleil.[264] Anousheh Ansari denied being a tourist[265] and took offence at the term.[266]
- ^ ESA director Jörg Feustel-Büechl said in 2001 that Russia had no right to send ‘amateurs’ to the ISS. A ‘stand-off’ occurred at the Johnson Space Center between Commander Talgat Musabayev and NASA manager Robert Cabana who refused to train Dennis Tito, a member of Musabayev’s crew along with Yuri Baturin. Musabayev argued that Tito had trained 700 hours in the last year and was as qualified as any NASA astronaut, and refused to allow his crew to be trained on the USOS without Tito. Cabana would not allow training to begin, and the commander returned with his crew to their hotel.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e Garcia, Mark (9 May 2018). «About the Space Station: Facts and Figures». NASA. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g Peat, Chris (21 May 2021). «ISS – Orbit». Heavens-Above. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
- ^ a b Holman, Joseph (12 October 2022). «ISS (ZARYA)». Satellite Tracking. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ «celestrak».
- ^ a b c NASA (18 February 2010). «On-Orbit Elements» (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- ^ «STS-132 Press Kit» (PDF). NASA. 7 May 2010. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- ^ «STS-133 FD 04 Execute Package» (PDF). NASA. 27 February 2011. Retrieved 27 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Gary Kitmacher (2006). Reference Guide to the International Space Station. Apogee Books Space Series. Canada: Apogee Books. pp. 71–80. ISBN 978-1-894959-34-6. ISSN 1496-6921.
- ^ «Human Spaceflight and Exploration – European Participating States». European Space Agency (ESA). 2009. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- ^ «International Space Station legal framework». European Space Agency (ESA). 19 November 2013. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ a b c «International Space Station Overview». ShuttlePressKit.com. 3 June 1999. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f «Fields of Research». NASA. 26 June 2007. Archived from the original on 23 January 2008.
- ^ a b
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Getting on Board». NASA. 26 June 2007. Archived from the original on 8 December 2007.
- ^ a b «ISS Research Program». NASA. Archived from the original on 13 February 2009. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- ^ Roberts, Jason (19 June 2020). «Celebrating the International Space Station (ISS)». NASA.
- ^ «Central Research Institute for Machine Building (FGUP TSNIIMASH) Control of manned and unmanned space vehicles from Mission Control Centre Moscow» (PDF). Russian Federal Space Agency. Retrieved 26 September 2011.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «NASA Sightings Help Page». Spaceflight.nasa.gov. 30 November 2011. Archived from the original on 5 September 2016. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «NASA – Higher Altitude Improves Station’s Fuel Economy». nasa.gov. 14 February 2019. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ a b
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Current ISS Tracking data». NASA. 15 December 2008. Archived from the original on 25 December 2015. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
- ^ a b c Harwood, William (26 July 2022). «Russia says it will withdraw from the International Space Station after 2024». CBS News. ViacomCBS. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ a b c Roulette, Joey (26 July 2022). «Russia signals space station pullout, but NASA says it’s not official yet». Reuters. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ de Selding, Peter B. (25 February 2015). «Russia – and Its Modules – To Part Ways with ISS in 2024». Space News. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ Bodner, Matthew (17 November 2014). «Russia May Be Planning National Space Station to Replace ISS». The Moscow Times. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ «First crew starts living and working on the International Space Station». European Space Agency. 31 October 2000.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Oct. 31, 2000, Launch of First Crew to International Space Station». NASA. 28 October 2015.
- ^ «Biden-Harris Administration Extends Space Station Operations Through 2030 – Space Station». blogs.nasa.gov.
- ^ a b Nelson, Senator Bill (20 December 2018). «The Senate just passed my bill to help commercial space companies launch more than one rocket a day from Florida! This is an exciting bill that will help create jobs and keep rockets roaring from the Cape. It also extends the International Space Station to 2030!».
- ^ a b «House joins Senate in push to extend ISS». SpaceNews. 27 September 2018. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ a b c Catchpole, John E. (2008). The International Space Station: Building for the Future. Springer-Praxis. ISBN 978-0-387-78144-0.
- ^ «Northrop Grumman Announces Realigned Operating Sectors – WashingtonExec». 25 September 2019. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ ESA — Columbus
- ^ «International Space Station». Astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 9 April 2002. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Heivilin, Donna (21 June 1994). «Space Station: Impact of the Expanded Russian Role on Funding and Research» (PDF). Government Accountability Office. Retrieved 3 November 2006.
- ^ Dismukes, Kim (4 April 2004). «Shuttle–Mir History/Background/How «Phase 1″ Started». NASA. Archived from the original on 16 November 2001. Retrieved 12 April 2007.
- ^ a b «Russia to decide on pullout from ISS since 2025 after technical inspection». TASS. 18 April 2021. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ Dobrovidova, Olga (20 April 2021). «Russia mulls withdrawing from the International Space Station after 2024». Science. American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). doi:10.1126/science.abj1005. ISSN 0036-8075. S2CID 235542488.
- ^ Harwood, William (26 July 2022). «Russia says it will withdraw from the International Space Station after 2024». CBS News. ViacomCBS. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ Roulette, Joey (26 July 2022). «Russia signals space station pullout, but NASA says it’s not official yet». Reuters. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ «Russia is likely to take part in International Space Station until 2028 -RIA». Reuters. 21 September 2022. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Memorandum of Understanding Between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States of America and the Russian Space Agency Concerning Cooperation on the Civil International Space Station». NASA. 29 January 1998. Retrieved 19 April 2009.
- ^ Payette, Julie (10 December 2012). «Research and Diplomacy 350 Kilometers above the Earth: Lessons from the International Space Station». Science & Diplomacy. 1 (4).
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «National Space Policy of the United States of America» (PDF). White House; USA Federal government. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Nations Around the World Mark 10th Anniversary of International Space Station». NASA. 17 November 2008. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ a b c Oberg, James (2005). «International Space Station». World Book Online Reference Center. Retrieved 3 April 2016.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image (MAXI)». JAXA. 2008. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ ESA via SPACEREF «SOLAR: three years observing and ready for solar maximum», 14 March 2011
- ^ «The International Space Station: life in space». Science in School. 10 December 2008. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: NASA – AMS to Focus on Invisible Universe. Nasa.gov (18 March 2011). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: In Search of Antimatter Galaxies – NASA Science. Science.nasa.gov (16 May 2011). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ Aguilar, M. et al. (AMS Collaboration) (3 April 2013). «First Result from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station: Precision Measurement of the Positron Fraction in Primary Cosmic Rays of 0.5–350 GeV» (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 110 (14): 141102. Bibcode:2013PhRvL.110n1102A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.141102. PMID 25166975.
- ^ Staff (3 April 2013). «First Result from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Experiment». AMS Collaboration. Archived from the original on 8 April 2013. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Heilprin, John; Borenstein, Seth (3 April 2013). «Scientists find hint of dark matter from cosmos». Associated Press. Archived from the original on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Amos, Jonathan (3 April 2013). «Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer zeroes in on dark matter». BBC News. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Perrotto, Trent J.; Byerly, Josh (2 April 2013). «NASA TV Briefing Discusses Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Results». NASA. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (3 April 2013). «Tantalizing New Clues Into the Mysteries of Dark Matter». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 August 2017. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ Horneck, Gerda; Klaus, David M.; Mancinelli, Rocco L. (March 2010). «Space Microbiology» (PDF). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. American Society for Microbiology. 74 (1): 121–156. Bibcode:2010MMBR…74..121H. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00016-09. PMC 2832349. PMID 20197502. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 August 2011. Retrieved 4 June 2011. (see Space Environment on page 122)
- ^ Amos, Jonathan (23 August 2010). «Beer microbes live 553 days outside ISS». BBC News. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ^ Ledford, Heidi (8 September 2008). «Spacesuits optional for ‘water bears’«. Nature. doi:10.1038/news.2008.1087.
- ^ a b c Buckey, Jay (23 February 2006). Space Physiology. Oxford University Press USA. ISBN 978-0-19-513725-5.
- ^ Grossman, List (24 July 2009). «Ion engine could one day power 39-day trips to Mars». New Scientist. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Boen, Brooke (1 May 2009). «Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity (ADUM)». NASA. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- ^ Rao, Sishir; et al. (May 2008). «A Pilot Study of Comprehensive Ultrasound Education at the Wayne State University School of Medicine». Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 27 (5): 745–749. doi:10.7863/jum.2008.27.5.745. PMID 18424650. S2CID 30566494.
- ^ Fincke, E. Michael; et al. (February 2005). «Evaluation of Shoulder Integrity in Space: First Report of Musculoskeletal US on the International Space Station». Radiology. 234 (2): 319–322. doi:10.1148/radiol.2342041680. PMID 15533948.
- ^ Strickland, Ashley (26 August 2020). «Bacteria from Earth can survive in space and could endure the trip to Mars, according to new study». CNN News. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ Kawaguchi, Yuko; et al. (26 August 2020). «DNA Damage and Survival Time Course of Deinococcal Cell Pellets During 3 Years of Exposure to Outer Space». Frontiers in Microbiology. 11: 2050. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.02050. PMC 7479814. PMID 32983036. S2CID 221300151.
- ^ «Earth Science & Remote Sensing Missions on ISS». NASA. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: May, Sandra, ed. (15 February 2012). «What Is Microgravity?». NASA Knows! (Grades 5-8). Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- ^ «European Users Guide to Low Gravity Platforms». European Space Agency. 6 December 2005. Archived from the original on 2 April 2013. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Materials Science 101». Science@NASA. 15 September 1999. Archived from the original on 14 June 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ^ «Mars500 study overview». ESA. 4 June 2011.
- ^ «Space station may be site for next mock Mars mission». New Scientist. 4 November 2011. Archived from the original on 11 July 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ^ «The Sustainable Utilisation of the ISS Beyond 2015» (PDF). International Astronautical Congress. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- ^ de Selding, Peter B. (3 February 2010). «ESA Chief Lauds Renewed U.S. Commitment to Space Station, Earth Science». Space News.
- ^ «Charlie Bolden». space.com. 4 June 2011.
- ^ Seitz, Virginia A. (19 September 2011). «Memorandum Opinion for the General Counsel, Office of Science and Technology Policy» (PDF). justice.gov. US Justice Department. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ^ Sandal, Gro M.; Manzey, Dietrich (December 2009). «Cross-cultural issues in space operations: A survey study among ground personnel of the European Space Agency». Acta Astronautica. 65 (11–12): 1520–1529. Bibcode:2009AcAau..65.1520S. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2009.03.074. ISSN 0094-5765.
- ^ «Online Materials». European Space Agency. Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ «ISS 3-D Teaching Tool: Spaceflight Challenge I». European Space Agency. 24 May 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ Building Peace in Young Minds through Space Education (PDF). Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space, 53rd Session. June 2010. Vienna, Austria. JAXA. June 2010.
- ^ «JAXA Spaceflight Seeds Kids I : Spaceflight Sunflower seeds – Let’s make them flower! and learn freshly the Earth environment just by contrast with the Space one». JAXA. 2006. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012.
- ^ «JAXA Seeds in Space I : Let’s Cultivate Spaceflight Asagao (Japanese morning glory), Miyako-gusa (Japanese bird’s foot trefoil) Seeds and Identify the Mutants!». JAXA. 2006. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012.
- ^ Murakami, Keiji (14 October 2009). «JEM Utilization Overview» (PDF). JAXA. Steering Committee for the Decadal Survey on Biological and Physical Sciences in Space. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ^ Tanaka, Tetsuo. «Kibo: Japan’s First Human Space Facility». JAXA. Archived from the original on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ «Amateur Radio on the International Space Station». 6 June 2011. Archived from the original on 27 May 2011. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- ^ Riley, Christopher (11 April 2011). «What Yuri Gagarin saw: First Orbit film to reveal the view from Vostok 1». The Guardian. London.
- ^ «Yuri Gagarin’s First Orbit – FAQs». Firstorbit.org. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Warr, Philippa (13 May 2013). «Commander Hadfield bids farewell to ISS with Reddit-inspired Bowie cover». wired.co.uk. Archived from the original on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ «Astronaut bids farewell with Bowie cover version (inc. video)». BBC News. 13 May 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ Davis, Lauren (12 May 2013). «Chris Hadfield sings «Space Oddity» in the first music video in space». Gizmodo.
- ^ Mabbett, Andy (29 November 2017). «Close encounters of the Wikipedia kind: Astronaut is first to specifically contribute to Wikipedia from space – Wikimedia Blog». Wikimedia foundation. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ Petris, Antonella (1 December 2017). «Primo contributo ‘extraterrestre’ su Wikipedia: è di Nespoli». Meteo Web (in Italian). Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ Pearlman, Robert Z. (23 November 2021). «‘The Infinite’ VR space station tour to premiere spacewalk in Houston». Space.com. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ Harbaugh, Jennifer, ed. (19 February 2016). «Manufacturing Key Parts of the International Space Station: Unity and Destiny». NASA. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- ^ «ISS Zvezda». Archived from the original on 20 August 2016. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ «Europe’s Airbus-built Columbus orbital outpost: 10 years in space». Airbus. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ^ «Ten years in perfect «Harmony»! – Thales Group». thalesgroup.com. October 2017.
- ^ «Building ISS». U.S. National Archives & DVIDS. Retrieved 28 October 2021.
- ^ «KSC-08pd0991». 22 April 2008. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
Cape Canaveral, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module toward the payload canister (lower right). The canister will deliver the module, part of the payload for space shuttle Discovery’s STS-124 mission, to Launch Pad 39A. On the mission, the STS-124 crew will transport the Kibo module as well as the Japanese Remote Manipulator System to the International Space Station to complete the Kibo laboratory. The launch of Discovery is targeted for May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
- ^ a b «The ISS to Date». NASA. 9 March 2011. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ Dismukes, Kim (1 December 2002). «Mission Control Answers Your Questions: STS-113 Q17». spaceflight.nasa.gov. NASA. Archived from the original on 24 July 2020. Retrieved 14 June 2009.
- ^ «NASA Facts. The Service Module: A Cornerstone of Russian International Space Station Modules» (PDF). spaceflight.nasa.gov. NASA. January 1999. IS-1999-09-ISS019JSC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 August 2020.
- ^ «STS-88». Science.ksc.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ Liston, Brad (2 November 2000). «Upward Bound: Tales of Space Station Alpha». Time. Archived from the original on 2 April 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2010.
- ^ «Space Station – Impact on the expanded Russian role of funding and research» (PDF). United States General Accounting Office. 21 June 1994. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ^ a b Ladwig, Alan (3 November 2000). «Call Bill Shepherd the Alpha Male of the International Space Station». Space.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2009. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ^ Halvorson, Todd (2 November 2000). «Expedition One Crew Wins Bid To Name Space Station Alpha». Space.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2009. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ^ «Interview with RSC Energia’s Yuri Semenov». Space.com. 3 September 2001. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- ^ «Interview with Yuri Semenov, general designer of Space Rocket corporation Energy». Voice of Russia. 21 March 2001. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- ^ «STS-92». Science.ksc.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 5 March 2011. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (26 July 2005). «Discovery launches – The Shuttle is back». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ «Mini-Research Module 1 (MIM1) Rassvet (MRM-1)». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ «STS-133». NASA. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- ^ «STS-134». NASA. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- ^ «Russia works on a new-generation space module». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 8 April 2016. Retrieved 29 November 2015.
- ^ «Crewed spacecraft docked to ISS’s module Nauka first time». TASS. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ «Rogozin confirmed that the module ‘Science’ placed the tanks from the upper stage ‘Frigate’«. TASS. 25 March 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ «Новости. Новый модуль вошел в состав российского сегмента МКС». roscosmos.ru. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ «NASA – The ISS to Date (03/09/2011)». NASA. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ NASA, International Space Station, Zarya (accessed 19 Apr. 2014)
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (15 October 2008). «Russian Segment: Enterprise». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
- ^ «NASA — NSSDCA — Spacecraft — Details». nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ Loff, Sarah (15 November 2018). «Unity». NASA. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ «Space Station Science Picture of the Day: Speed Limit». www.spaceref.com. 23 April 2003. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ Williams, Suni (presenter) (3 July 2015). Departing Space Station Commander Provides Tour of Orbital Laboratory (video). NASA. Event occurs at 17.46-18.26. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ Roylance, Frank D. (11 November 2000). «Space station astronauts take shelter from solar radiation». The Baltimore Sun. Tribune Publishing. Archived from the original on 1 September 2019. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ Stofer, Kathryn (29 October 2013). «Tuesday/Wednesday Solar Punch». NASA. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ «Service Module | RuSpace». suzymchale.com. Archived from the original on 21 September 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ a b Boeing (2008). «Destiny Laboratory Module». Boeing. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ a b NASA (2003). «U.S. Destiny Laboratory». NASA. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ a b NASA (2001). «STS-98». NASA. Archived from the original on 30 August 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ «August 28, 2009. S.P.Korolev RSC Energia, Korolev, Moscow region». RSC Energia. 28 August 2009. Archived from the original on 21 September 2020. Retrieved 3 September 2009.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (10 November 2009). «Poisk launches to add new room for space station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ^ «Mir close calls». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Pirs Docking Compartment». NASA. 10 May 2006. Retrieved 28 March 2009.
- ^ Williams, Suni (presenter) (19 May 2013). Station Tour: Harmony, Tranquility, Unity (video). NASA. Event occurs at 0.06-0.35. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
So this is Node 2 … this is where four out of six of us sleep.
- ^ NASA (23 October 2007). «STS-120 MCC Status Report #01». NASA.
- ^ Johnson Jr., John (24 October 2007). «Space Shuttle Discovery lifts off». Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ^ William Harwood (2007). «Harmony module pulled from cargo bay». CBS News. Retrieved 26 October 2007.
- ^ Schwartz, John (26 October 2007). «New Room Added to Space Station». The New York Times. Retrieved 26 October 2007.
- ^ NASA (2007). «PMA-3 Relocation». NASA. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ «NASA – NASA Receives Tranquility». Nasa.gov. 23 October 2010. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ^ Harwood, William (11 February 2008). «Station arm pulls Columbus module from cargo bay». Spaceflightnow.com. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2009.
- ^ Kamiya, Setsuko (30 June 2009). «Japan a low-key player in space race». Japan Times. p. 3. Archived from the original on 3 August 2009.
- ^ «Thales Alenia Space and ISS modules – Cupola: a window over the Earth». 26 July 2010. Archived from the original on 26 July 2010.
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris (9 April 2009). «STS-132: PRCB baselines Atlantis’ mission to deliver Russia’s MRM-1». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 12 November 2009.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «STS-132 MCC Status Report #09». NASA. 18 May 2010. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «STS-132 MCC Status Report #13». NASA. 20 May 2010. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^ Ray, Justin (28 June 2010). «Station Crew Takes Soyuz for ‘Spin around the Block’«. SpaceFlight Now. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^ a b «Многоцелевой лабораторный модуль «Наука»«. roscosmos.ru. Archived from the original on 14 July 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ «European Robotic Arm Brochure» (PDF). European Space Agency. p. 9.
- ^ «Sredstva Krepleniya Krupnogabaritnykh Obyektov, SKKO».
- ^ «The Russian Nauka/Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM) General Thread». forum.nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ^ «Schedule of ISS flight events (part 2)». forum.nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ «The Russian Nauka/Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM) General Thread». forum.nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ^ «Russia to bump its ISS crew back to three». www.russianspaceweb.com. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ^ Anatoly Zak [@RussianSpaceWeb] (17 November 2022). «More than 5 hours into the VKD-55 spacewalk, cosmonauts are finishing installation of the large payload platform on the Nauka module, before returning to the ISS» (Tweet). Retrieved 5 December 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ Pearlman, Robert (10 April 2016). «SpaceX Dragon Arrives at Space Station, Delivers Inflatable Room Prototype». Space.com. Retrieved 11 April 2016.
- ^ Harwood, William. «Spacewalkers attach docking adapter to space station for commercial vehicles – Spaceflight Now». Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (21 August 2019). «Spacewalkers Complete Installation of Second Commercial Docking Port». NASA Space Station. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ «Thales Alenia Space reaches key milestone for NanoRacks’ airlock module». Thales Alenia Space (Press release). 20 March 2019. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (2 August 2019). «SpaceX to begin flights under new cargo resupply contract next year». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ «NanoRacks, Boeing to Build First Commercial ISS Airlock Module». NanoRacks. 6 February 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (6 February 2017). «Progress Underway for First Commercial Airlock on Space Station». NASA. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (9 February 2021). «Progress MS-17 lifts off to prepare Prichal module arrival». RussianSpaceWeb.com. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- ^ «В РКК «Энергия» утвердили эскиз нового узлового модуля МКС». Roskosmos. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (25 July 2019). «New docking port, spacesuit and supplies en route to space station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- ^ a b Zak, Anatoly (22 June 2020). «Prichal Node Module, UM». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ S.P. Korolev RSC Energia – News Archived 2 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Energia.ru (13 January 2011). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ a b Atkinson, Ian (19 August 2020). «Russia’s Nauka ISS module arrives at Baikonur for final launch preparations». NASA Spaceflight. Retrieved 20 August 2020.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Spread Your Wings, It’s Time to Fly». NASA. 26 July 2006. Retrieved 21 September 2006.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: NASA (2008). «Consolidated Launch Manifest». NASA. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «EXPRESS Racks 1 and 2 fact sheet». NASA. 12 April 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ «Soyuz TMA-03M docks to ISS, returns station to six crewmembers for future ops». NASASpaceFlight.com. 23 December 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Welsch, L. D. (30 October 2009). «EVA Checklist: STS-129 Flight Supplement» (PDF). NASA.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Space Shuttle Mission: STS-131» (PDF). NASA. February 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Space Shuttle Mission: STS-134» (PDF). NASA. April 2011.
- ^ «HTV2: Mission Press Kit» (PDF). Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. 20 January 2011.
- ^ «Exposed Facility:About Kibo». JAXA. 29 August 2008. Archived from the original on 3 August 2009. Retrieved 9 October 2009.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «NASA–European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF)». NASA. 6 October 2008. Archived from the original on 19 October 2008. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
- ^ «ESA–Columbus–European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF)». ESA. 13 January 2009. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
- ^ «Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES)». ESA. Archived from the original on 9 June 2009. Retrieved 9 October 2009.
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris (10 March 2017). «SpaceX science – Dragon delivers experiments for busy science period». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ Graham, William (3 June 2017). «Falcon 9 launches with CRS-11 Dragon on 100th 39A launch». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ «The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Experiment». CERN. 21 January 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (4 April 2013). «Endeavour’s ongoing legacy: AMS-02 proving its value». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ «ESA and Airbus sign partnership agreement for new ISS commercial payload platform Bartolomeo». SpaceDaily. 9 February 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ^ «Airbus and ESA to partner on Bartolomeo platform». Aerospace Technology. 8 February 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ^ «ISS: Bartolomeo». eoPortal. European Space Agency. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ^ «Canadarm2 and the Mobile Servicing System». NASA. 8 January 2013. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ «Dextre, the International Space Station’s Robotic Handyman». Canadian Space Agency. 18 April 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ «Mobile Base System». Canadian Space Agency. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ a b «Space Shuttle Mission STS-134: Final Flight of Endeavour – Press Kit» (PDF). NASA. April 2011. pp. 51–53. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ «Remote Manipulator System: About Kibo». JAXA. 29 August 2008. Archived from the original on 20 March 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ «International Space Station Status Report #02-03». NASA. 14 January 2002. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ «Russia postpones launch of Nauka research module to orbital outpost to 2021». TASS. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (28 January 2020). «Axiom wins NASA approval to attach commercial habitat to space station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ «NASA taps startup Axiom Space for the first habitable commercial module for the Space Station». TechCrunch. 27 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ «NASA clears Axiom Space to put commercial habitat on space station, with Boeing on the team». GeekWire. 28 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ «Axiom Station Assembly Sequence – Axiom Space Axiom Space». Axiom Space. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ «CAM – location?». NASA Spaceflight Forums. Retrieved 12 October 2009.
- ^ Malik, Tariq (14 February 2006). «NASA Recycles Former ISS Module for Life Support Research». Space.com. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ^ «ICM Interim Control Module». U.S. Naval Center for Space Technology. Archived from the original on 8 February 2007.
- ^ «Russian Research Modules». Boeing. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly. «Russian segment of the ISS». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 3 October 2009.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (22 June 2020). «Russian space program in 2024». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ «Роскосмос примет решение о пути развития российской орбитальной станции до конца июля» [Roscosmos to decide development path of Russian orbital station by end of July]. TASS (in Russian). 19 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (16 April 2021). «Russian Orbital Service Station, ROSS». RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ «Научно-энергетический модуль запустят на «Ангаре» с Восточного» [The Science Power Module will be launched on an Angara from Vostochny]. Roscosmos (in Russian). 24 April 2021. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ Freudenrich, Craig (20 November 2000). «How Space Stations Work». Howstuffworks. Archived from the original on 12 December 2008. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ «5–8: The Air Up There». NASAexplores. NASA. Archived from the original on 18 December 2004. Retrieved 31 October 2008.
- ^ Anderson, Clinton P.; 90th Congress, 2nd Session; et al. (30 January 1968). Apollo 204 Accident: Report of the Committee on Aeronautical and Space Sciences, United States Senate (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: US Government Printing Office. p. 8. Report No. 956.
- ^ Davis, Jeffrey R.; Johnson, Robert & Stepanek, Jan (2008). Fundamentals of Aerospace Medicine. Vol. XII. Philadelphia PA, USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 261–264.
- ^ Malik, Tariq (15 February 2006). «Air Apparent: New Oxygen Systems for the ISS». Space.com. Retrieved 21 November 2008.
- ^ a b Barry, Patrick L. (13 November 2000). «Breathing Easy on the Space Station». NASA. Archived from the original on 21 September 2008. Retrieved 21 November 2008.
- ^ «RuSpace | ISS Russian Segment Life Support System». Suzymchale.com. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ Breathing Easy on the Space Station – NASA Science. Science.nasa.gov (13 November 2000). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ «The early history of bifacial solar cell_百度文库». Wenku.baidu.com. 25 October 2010. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (28 April 2016). «Facts and Figures». NASA. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- ^ G. Landis; C-Y. Lu (1991). «Solar Array Orientation Options for a Space Station in Low Earth Orbit». Journal of Propulsion and Power. 7 (1): 123–125. doi:10.2514/3.23302.
- ^ Miller, Thomas B. (24 April 2000). «Nickel-Hydrogen Battery Cell Life Test Program Update for the International Space Station». grc.nasa.gov. Research & Technology. NASA / Glenn Research Center. Archived from the original on 25 August 2009. Retrieved 27 November 2009.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (13 December 2016). «Japanese HTV makes battery delivery to International Space Station». Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 29 January 2017.
- ^ Patterson, Michael J. (18 June 1999). «Cathodes Delivered for Space Station Plasma Contactor System». grc.nasa.gov. Research & Technology. NASA / Lewis Research Center. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011.
- ^ Price, Steve; Phillips, Tony; Knier, Gil (21 March 2001). «Staying Cool on the ISS». NASA. Retrieved 22 July 2016.
- ^ ATCS Team Overview. (PDF). Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ a b «Communications and Tracking». Boeing. Archived from the original on 11 June 2008. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ Mathews, Melissa; James Hartsfield (25 March 2005). «International Space Station Status Report: SS05-015». NASA News. NASA. Retrieved 11 January 2010.
- ^ Harland, David (2004). The Story of Space Station Mir. New York: Springer-Verlag New York Inc. ISBN 978-0-387-23011-5.
- ^ Harvey, Brian (2007). The rebirth of the Russian space program: 50 years after Sputnik, new frontiers. Springer Praxis Books. p. 263. ISBN 978-0-387-71354-0.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (4 January 2010). «Space exploration in 2011». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 26 June 2010. Retrieved 12 January 2010.
- ^ «ISS On-Orbit Status 05/02/10». NASA. 2 May 2010. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- ^ «Memorandum of Understanding Between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States of America and the Government of Japan Concerning Cooperation on the Civil International Space Station». NASA. 24 February 1998. Retrieved 19 April 2009.
- ^ «Operations Local Area Network (OPS LAN) Interface Control Document» (PDF). NASA. February 2000. Retrieved 30 November 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «ISS/ATV communication system flight on Soyuz». EADS Astrium. 28 February 2005. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (10 November 2009). «STS-129 ready to support Dragon communication demo with ISS». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ Heath, Nick (23 May 2016). «From Windows 10, Linux, iPads, iPhones to HoloLens: The tech astronauts use on the ISS». TechRepublic. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- ^ «April 2019 – ISS On-Orbit Status Report». blogs.nasa.gov. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ Bilton, Nick (22 January 2010). «First Tweet From Space». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 November 2010. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Smith, Will (19 October 2012). «How Fast is the ISS’s Internet? (and Other Space Questions Answered)». Tested.com. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Williams, Matt (25 August 2019). «Upgraded ISS Now Has a 600 Megabit per Second Internet Connection». Universe Today. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ Williams, Matt (25 August 2019). «The ISS Now Has Better Internet Than Most of Us After Its Latest Upgrade». Universe Today. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ Zell, Martin; Suenson, Rosita (13 August 2013). «ESA ISS Science & System – Operations Status Report #150 Increment 36: 13-26 July 2013». European Space Agency. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Burt, Julie (1 June 2001). «Computer problems overcome during STS-100» (PDF). Space Center Roundup. NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Malik, Tariq (14 June 2007). «NASA: Space Station Computer Crash May Extend Shuttle Mission». Space.com. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Klotz, Irene (13 June 2007). «NASA battles failure of space station computer». Reuters. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Klotz, Irene (22 May 2017). «NASA Plans Emergency Spacewalk To Replace Key Computer On International Space Station». Huffpost. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- ^ Thomson, Iain (10 May 2013). «Penguins in spa-a-a-ce! ISS dumps Windows for Linux on laptops». The Register. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- ^ Gunter, Joel (10 May 2013). «International Space Station to boldly go with Linux over Windows». The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- ^ An, David (5 June 2019). «US-Taiwan Space Cooperation: Formosat, AMS, and the ISS computer». globaltaiwan.org. Global Taiwan Institute. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- ^ Chin, Jonathan; Tien-pin, Lo (12 June 2017). «Taiwan-designed computer now part of an ISS mission». taipeitimes.com. Taipei Times. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- ^ a b c Kuksov, Igor. «Internet in space: Is there Net on Mars?». Kaspersky. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ «The ISS Now Has Better Internet Than Most of Us After Its Latest Upgrade». ScienceAlert. 26 August 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ Creamer, T.J. [@Astro_TJ] (22 January 2010). «Hello Twitterverse! We r now LIVE tweeting from the International Space Station — the 1st live tweet from Space! 🙂 More soon, send your ?s» (Tweet). Earth orbit. Retrieved 5 December 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ «International Space Station Expeditions». NASA. 10 April 2009. Retrieved 13 April 2009.
- ^ NASA (2008). «International Space Station». NASA. Retrieved 22 October 2008.
- ^ «SpaceX completes emergency crew escape manoeuvre». BBC News. 19 January 2020.
- ^ Morring, Frank (27 July 2012). «ISS Research Hampered By Crew Availability». Aviation Week. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
A commercial capability would allow the station’s crew to grow from six to seven by providing a four-seat vehicle for emergency departures in addition to the three-seat Russian Soyuz capsules in use today.
- ^ Hoversten, Paul (1 May 2011). «Assembly (Nearly) Complete». Air & Space Magazine. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
In fact, we’re designed on the U.S. side to take four crew. The ISS design is actually for seven. We operate with six because first, we can get all our work done with six, and second, we don’t have a vehicle that allows us to fly a seventh crew member. Our requirement for the new vehicles being designed is for four seats. So I don’t expect us to go down in crew size. I would expect us to increase it.
- ^ «Biographies of USSR/Russian Cosmonauts: Padalka». Spacefacts. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ «Biographies of U.S. Astronauts: Whitson». Spacefacts. Archived from the original on 28 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Associated Press, 8 May 2001
- ^ Associated Press, The Spokesman Review, 6 January 2002, p. A4
- ^ Schwartz, John (10 October 2008). «Russia Leads Way in Space Tourism With Paid Trips into Orbit». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 July 2016.
- ^ Boyle, Alan (13 September 2005). «Space passenger Olsen to pull his own weight». NBC News.
- ^ «Flight to space ignited dreams | St. Catharines Standard». Stcatharinesstandard.ca. Archived from the original on 12 September 2012. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «ESA – Human Spaceflight and Exploration – Business – «I am NOT a tourist»«. Esa.int. 18 September 2006. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Interview with Anousheh Ansari, the First Female Space Tourist». Space.com. 15 September 2006. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Harwood, William (12 January 2011). «Resumption of Soyuz tourist flights announced». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Maher, Heather (15 September 2006). «U.S.: Iranian-American To Be First Female Civilian in Space». Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Space Tourists | A Film By Christian Frei». Space-tourists-film.com. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Geocaching – The Official Global GPS Cache Hunt Site». www.geocaching.com.
- ^ Cook, John (29 August 2011). «From outer space to the ocean floor, Geocaching.com now boasts more than 1.5 million hidden treasures». Geekwire.com. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ^ «American game designer follows father into orbit». ABC News. 12 October 2008. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- ^ Thompson, Amy (10 August 2021). «Antares rocket launches heaviest Cygnus cargo ship ever to space station for NASA». Space.com. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ Cook, John; Aksamentov, Valery; Hoffman, Thomas; Bruner, Wes (1 January 2011). «ISS Interface Mechanisms and their Heritage» (PDF). ntrs.nasa.gov (Conference paper). Houston, Texas: The Boeing Company. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
Docking is when one incoming spacecraft rendezvous with another spacecraft and flies a controlled collision trajectory in such a manner so as to align and mesh the interface mechanisms. The spacecraft docking mechanisms typically enter what is called soft capture, followed by a load attenuation phase, and then the hard docked position which establishes an air-tight structural connection between spacecraft. Berthing, by contrast, is when an incoming spacecraft is grappled by a robotic arm and its interface mechanism is placed in close proximity of the stationary interface mechanism. Then typically there is a capture process, coarse alignment and fine alignment and then structural attachment.
- ^
just for Nauka Experimental Airlock Module, that will be berthed to the forward port at its aft docking port by ERA, thereby being attached permanently to it. - ^ Garcia, Mark (8 December 2021). «Visitors to the Station by Country». NASA. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ «ESA;– ATV;– Crew role in mission control». ESA.int. 2 March 2011. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ «ESA – Human Spaceflight and Exploration;– International Space Station;– Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV)». ESA.int. 16 January 2009. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ «Acquisition of Orbital ATK approved, company renamed Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems». SpaceNews. 6 June 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n «Complete ISS flight events». NasaSpaceFlight.com Forum. 10 November 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e «Pirs undocking and deorbit date set». Roscosmos. 22 July 2021. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «Microgravity Research Flights». Glenn Research Center. 10 November 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ Berger, Eric (1 July 2022). «Yes, Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft really could fly astronauts this year». Ars Technica. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ Davenport, Christian (6 April 2020). «After botched test flight, Boeing will refly its Starliner spacecraft for NASA». The Washington Post. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (14 August 2019). «Cargo Dream Chaser solidifies ULA deal by securing six Vulcan Centaur flights». NASASpaceFlight. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ «ESA – ATV – Crew role in mission control». Esa.int. 2 March 2011. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ «ESA – Human Spaceflight and Exploration – International Space Station – Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV)». Esa.int. 16 January 2009. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ Woffinden, David C.; Geller, David K. (July 2007). «Navigating the Road to Autonomous Orbital Rendezvous». Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets. 44 (4): 898–909. Bibcode:2007JSpRo..44..898W. doi:10.2514/1.30734.
- ^ «ISS EO-6». Astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 18 June 2012. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Live listing of spacecraft operations». NASA. 1 December 2009. Archived from the original on 3 August 2008. Retrieved 8 December 2009.
- ^ Memi, Ed. «Space Shuttle upgrade lets astronauts at ISS stay in space longer». Boeing. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ «Human Space Flight Transition Plan» (PDF). NASA.gov. Space Operations Mission Directorate. 30 August 2006.
- ^ «NASA Seeks Proposals for Crew and Cargo Transportation to Orbit». SpaceRef.com (Press release). NASA. 18 January 2006. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- ^ «NASA proposes Soyuz photo op; shuttle launch readiness reviewed (UPDATED)». CBS. Retrieved 11 February 2011.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (25 May 2012). «First Private Craft Docks With Space Station». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 June 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ^ Trinidad, Katherine; Thomas, Candrea (22 May 2009). «NASA’s Space Shuttle Landing Delayed by Weather». NASA. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- ^ Oberg, James (11 January 2004). «Crew finds ‘culprit’ in space station leak». NBC News. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- ^ Harwood, William (18 September 2006). «Oxygen Generator Problem Triggers Station Alarm». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ «University of Toledo alumnus had role in rescue of space station». Toledo Blade. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ^ Peterson, Liz Austin (30 October 2007). «Astronauts notice tear in solar panel». Associated Press. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Stein, Rob (4 November 2007). «Space Station’s Damaged Panel Is Fixed». The Washington Post. Retrieved 4 November 2007.
- ^ Harwood, William (25 March 2008). «Station chief gives detailed update on joint problem». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- ^ Harik, Elliot P.; et al. (2010). The International Space Station Solar Alpha Rotary Joint Anomaly Investigation (PDF). 40th Aerospace Mechanisms Symposium. 12–14 May 2010. Cocoa Beach, Florida. JSC-CN-19606.
- ^ «Crew Expansion Prep, SARJ Repair Focus of STS-126». NASA. 30 October 2008. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- ^ Harwood, William (18 November 2008). «Astronauts prepare for first spacewalk of shuttle flight». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- ^ a b Bergin, Chris (1 April 2009). «ISS concern over S1 Radiator – may require replacement via shuttle mission». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 3 April 2009.
- ^ a b Harwood, William (31 July 2010). «Spacewalks needed to fix station cooling problem». Spaceflight Now for CBS News. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «NASA ISS On-Orbit Status 1 August 2010 (early edition)». Spaceref.com. 31 July 2010. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «International Space Station Active Thermal Control System». boeing.com. 21 November 2006. Archived from the original on 30 March 2010. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ Harwood, William (10 August 2010). «Wednesday spacewalk to remove failed coolant pump». Spaceflight Now for CBS News.
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris (11 August 2010). «Large success for second EVA as failed Pump Module is removed». NASA Spaceflight.
- ^ Harwood, William (11 August 2010). «Station’s bad pump removed; more spacewalking ahead». Spaceflight Now for CBS News.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (18 August 2010). «ISS cooling configuration returning to normal confirming ETCS PM success». NASASpaceFlight.com. Archived from the original on 24 October 2010.
- ^ Chow, Denise (2 August 2010). «Cooling System Malfunction Highlights Space Station’s Complexity». Space.com.
- ^ Harding, Pete (30 August 2012). «Astronaut duo complete challenging first post-Shuttle US spacewalk on ISS». NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ Boucher, Marc (5 September 2012). «Critical Space Station spacewalk a Success». SpaceRef.
- ^ «Astronauts Complete Rare Christmas Eve Spacewalk». Leaker. Associated Press. 24 December 2013. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ^ «ISS Crew Timeline» (PDF). NASA. 5 November 2008. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- ^ «What time zone do they use on the International Space Station? – BBC Science Focus Magazine». Science Focus. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ «NASA – Time in Space, A Space in Time». nasa.gov. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ «A Slice of Time Pie». 17 March 2013. Archived from the original on 17 March 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ «Human Space Flight (HSF) – Crew Answers». spaceflight.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ «Новости. Космонавт рассказал, кто может первым заселиться в модуль «Наука» на МКС». www.roscosmos.ru. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ «At Home with Commander Scott Kelly (Video)». International Space Station: NASA. 6 December 2010. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ «Nauka module prelaunch booklet» (PDF). Roscosmos.
- ^ Broyan, James Lee; Borrego, Melissa Ann; Bahr, Juergen F. (2008). «International Space Station USOS Crew Quarters Development» (PDF). SAE International. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ a b c d e «Daily life». ESA. 19 July 2004. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f Mansfield, Cheryl L. (7 November 2008). «Station Prepares for Expanding Crew». NASA. Retrieved 17 September 2009.
- ^ a b c d «Living and Working on the International Space Station» (PDF). CSA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 April 2009. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ a b Malik, Tariq (27 July 2009). «Sleeping in Space is Easy, But There’s No Shower». Space.com. Retrieved 29 October 2009.
- ^ Bedtime in space. youtube.com. Event occurs at[time needed]. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
- ^ «STEMonstrations: Sleep Science» (AV media). images.nasa.gov. NASA. 13 December 2018. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- ^ Benson, Charles Dunlap and William David Compton. Living and Working in Space: A History of Skylab. NASA publication SP-4208.
- ^ Portree, David S. F. (March 1995). Mir Hardware Heritage (PDF). NASA. p. 86. OCLC 755272548. Reference Publication 1357.
- ^ Nyberg, Karen (12 July 2013). Karen Nyberg Shows How You Wash Hair in Space. YouTube.com. NASA. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- ^ Lu, Ed (8 September 2003). «Greetings Earthling». NASA. Archived from the original on 1 September 2012. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- ^ Pesquet, Thomas (18 August 2021). Thomas tours the MLM module (in French with English subtitles available). YouTube.com. ESA. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 29 August 2021.
- ^ Zimmer, Carl (11 April 2019). «Scott Kelly Spent a Year in Orbit. His Body Is Not Quite the Same». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 May 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
NASA scientists compared the astronaut to his earthbound twin, Mark. The results hint at what humans will have to endure on long journeys through space.
- ^ Garrett-Bakeman, Francine E.; et al. (12 April 2019). «The NASA Twins Study: A multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight». Science. 364 (6436): eaau8650. doi:10.1126/science.aau8650. PMC 7580864. PMID 30975860.
- ^ Strickland, Ashley (15 November 2019). «Astronauts experienced reverse blood flow and blood clots on the space station, study says». CNN News. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ Marshall-Goebel, Karina; et al. (13 November 2019). «Assessment of Jugular Venous Blood Flow Stasis and Thrombosis During Spaceflight». JAMA Network Open. 2 (11): e1915011. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.15011. PMC 6902784. PMID 31722025.
- ^ Than, Ker (23 February 2006). «Solar Flare Hits Earth and Mars». Space.com.
- ^ «A new kind of solar storm». NASA. 10 June 2005.
- ^ «How Much Radiation Are ISS Astronauts Exposed To?». Forbes. 13 November 2018. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ «Galactic Radiation Received in Flight». FAA Civil Aeromedical Institute. Archived from the original on 29 March 2010. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- ^ Suedfeld, Peter; Wilk, Kasia E.; Cassel, Lindi (2011). «Flying with Strangers: Postmission Reflections of Multinational Space Crews». In Vakoch, Douglas A. (ed.). Psychology of Space Exploration, Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. pp. 143–176. ISBN 978-1-46999770-4.
- ^ Manzey, D.; Lorenz, B.; Poljakov, V. (1998). «Mental performance in extreme environments: Results from a performance monitoring study during a 438-day spaceflight». Ergonomics. 41 (4): 537–559. doi:10.1080/001401398186991. PMID 9557591.
- ^ «Behind the Scenes: The Making of an Astronaut». NASA. 23 August 2004. Archived from the original on 19 July 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- ^ Robson, David. «Why astronauts get the ‘space stupids’«. bbc.com.
- ^ Schneider, S. M.; Amonette, W. E.; Blazine, K.; Bentley, J.; c. Lee, S. M.; Loehr, J. A.; Moore, A. D.; Rapley, M.; Mulder, E. R.; Smith, S. M. (2003). «Training with the International Space Station Interim Resistive Exercise Device». Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 35 (11): 1935–1945. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000093611.88198.08. PMID 14600562.
- ^ «Bungee Cords Keep Astronauts Grounded While Running». NASA. 16 June 2009. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ^ Kauderer, Amiko (19 August 2009). «Do Tread on Me». NASA. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ^ Bell, Trudy E. (11 May 2007). «Preventing «Sick» Spaceships». NASA. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ^ Korn, Anne (23 November 2018). «ISS microbes should be monitored to avoid threat to astronaut health». BioMed Central (Press release). Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ Singh, Nitin K.; et al. (23 November 2018). «Multi-drug resistant Enterobacter bugandensis species isolated from the International Space Station and comparative genomic analyses with human pathogenic strains». BMC Microbiology. 18 (1): 175. doi:10.1186/s12866-018-1325-2. PMC 6251167. PMID 30466389.
- ^ Barry, Patrick L. (2000). «Microscopic Stowaways on the ISS». Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ^ Korn, Anne (7 April 2019). «NASA researchers catalogue all microbes and fungi on the International Space Station». BioMed Central (Press release). Retrieved 30 August 2021.
- ^ Sielaff, Aleksandra Checinska; et al. (8 April 2019). «Characterization of the total and viable bacterial and fungal communities associated with the International Space Station surfaces». Microbiome. 7 (50): 50. doi:10.1186/s40168-019-0666-x. PMC 6452512. PMID 30955503.
- ^ Limardo, José G.; Allen, Christopher S.; Danielson, Richard W. (14 July 2013). «Assessment of Crewmember Noise Exposures on the International Space Station». 43rd International Conference on Environmental Systems. Vail, CO: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. doi:10.2514/6.2013-3516. ISBN 978-1-62410-215-8.
- ^ Nakashima, Ann; Limardo, José; Boone, Andrew; Danielson, Richard W. (31 January 2020). «Influence of impulse noise on noise dosimetry measurements on the International Space Station». International Journal of Audiology. 59 (sup1): S40–S47. doi:10.1080/14992027.2019.1698067. ISSN 1499-2027. PMID 31846378. S2CID 209407363.
- ^ a b «International Space Station Medical Operations Requirements Documents (ISS MORD), SSP 50260 Revision B» (PDF). emits.sso.esa.int. NASA. May 2003. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 February 2020.
- ^ Allen, Christopher S.; Denham, Samuel A. (17 July 2011). «International Space Station Acoustics – A Status Report» (PDF). ntrs.nasa.gov (Conference paper). NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX (JSC-CN-24071 / JSC-CN-22173). hdl:2060/20150010438. Archived from the original on 16 February 2015.
- ^ «Safe in Sound Winners». safeinsound.us. 2020. Archived from the original on 25 June 2020.
- ^ Williams, Suni (presenter) (3 July 2015). Departing Space Station Commander Provides Tour of Orbital Laboratory (video). NASA. Event occurs at 18.00-18.17. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
And some of the things we have to worry about in space are fire … or if we had some type of toxic atmosphere. We use ammonia for our radiators so there is a possibility that ammonia could come into the vehicle.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (28 April 2016). «International Space Station Overview». NASA. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ^ a b Cooney, Jim. «Mission Control Answers Your Questions». Houston, TX. Archived from the original on 27 June 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2011.
Jim Cooney ISS Trajectory Operations Officer
- ^ Pelt, Michel van (2009). Into the Solar System on a String : Space Tethers and Space Elevators (1st ed.). New York, NY: Springer New York. p. 133. ISBN 978-0-387-76555-6.
- ^ «Europe’s ATV-2 departs ISS to make way for Russia’s Progress M-11M». NASASpaceFlight.com. 20 June 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Simberg, Rand (29 July 2008). «The Uncertain Future of the International Space Station: Analysis». Popular Mechanics. Archived from the original on 31 March 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ a b «ISS Environment». Johnson Space Center. Archived from the original on 13 February 2008. Retrieved 15 October 2007.
- ^ «Rocket company tests world’s most powerful ion engine». Newscientist.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ^ «Executive summary» (PDF). Ad Astra Rocket Company. 24 January 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 March 2010. Retrieved 27 February 2010.
- ^ «DMS-R: ESA’s Data Management System». www.esa.int.
- ^ «Exercising Control 49 months of DMS-R Operations» (PDF).
- ^ «Russian / US GNC Force Fight» (PDF). pims.grc.nasa.gov. Glenn Research Center. 7 October 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2012. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «International Space Station Status Report #05-7». NASA. 11 February 2005. Archived from the original on 17 March 2005. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ Roithmayr, Carlos (2003). Dynamics and Control of Attitude, Power, and Momentum for a Spacecraft Using Flywheels and Control Moment Gyroscopes (PDF). Langley Research Center: NASA. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (14 June 2007). «Atlantis ready to support ISS troubleshooting». NASASPaceflight.com. Retrieved 6 March 2009.
- ^ Hoffman, Michael (3 April 2009). «National Space Symposium 2009: It’s getting crowded up there». Defense News. Retrieved 7 October 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Whipple, F. L. (1949). «The Theory of Micrometeoroids». Popular Astronomy. Vol. 57. p. 517. Bibcode:1949PA…..57..517W.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (28 June 2011). «STS-135: FRR sets 8 July Launch Date for Atlantis – Debris misses ISS». NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 28 June 2011.
- ^ Nahra, Henry (24–29 April 1989). «Effect of Micrometeoroid and Space Debris Impacts on the Space Station Freedom Solar Array Surfaces» (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 7 October 2009.
- ^ «Space Suit Punctures and Decompression». The Artemis Project. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- ^ Plain, Charlie (16 July 2004). «Superhero Ceramics!». NASA.gov. Archived from the original on 23 January 2008.
- ^ «State space corporation ROSCOSMOS |». en.roscosmos.ru.
- ^ «Microsoft PowerPoint – EducationPackage SMALL.ppt» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2008. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ Courtland, Rachel (16 March 2009). «Space station may move to dodge debris». New Scientist. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ^ a b «ISS Maneuvers to Avoid Russian Fragmentation Debris» (PDF). Orbital Debris Quarterly News. 12 (4): 1&2. October 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ^ «Avoiding satellite collisions in 2009» (PDF). Orbital Debris Quarterly News. 14 (1): 2. January 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ^ «ATV carries out first debris avoidance manoeuvre for the ISS». ESA. 28 August 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2010.
- ^ «ISS crew take to escape capsules in space junk alert». BBC News. 24 March 2012. Retrieved 24 March 2012.
- ^ «Station Crew Takes Precautions for Close Pass of Space Debris». NASA Blog. 16 June 2015. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Grush, Loren (15 November 2021). «Russia blows up a satellite, creating a dangerous debris cloud in space». The Verge.
- ^ «International Space Station swerves to dodge space junk». Reuters. 3 December 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ Price, Pat (2005). The Backyard Stargazer: An Absolute Beginner’s Guide to Skywatching With and Without a Telescope. Gloucester, MA: Quarry Books. p. 140. ISBN 978-1-59253-148-6.
- ^ «Problem 346: The International Space Station and a Sunspot: Exploring angular scales» (PDF). Space Math @ NASA !. 19 August 2018. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ «Artificial Satellites > (Iridium) Flares». Calsky.com. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «How to Spot the International Space Station (and other satellites)». Hayden Planetarium. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ NASA (2 July 2008). «International Space Station Sighting Opportunities». NASA. Archived from the original on 21 December 2015. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
- ^ «ISS – Information». Heavens-Above.com. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ^ Weaver, Harold F. (1947). «The Visibility of Stars Without Optical Aid». Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 59 (350): 232. Bibcode:1947PASP…59..232W. doi:10.1086/125956. S2CID 51963530.
- ^ «ISS visible during the daytime». Spaceweather.com. 5 June 2009. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
- ^ «Get notified when the International Space Station is in your area». 3 News NZ. 6 November 2012. Archived from the original on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2013.
- ^ «Satellite Watching». HobbySpace. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Space StationAstrophotography – NASA Science». Science.nasa.gov. 24 March 2003. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «[VIDEO] The ISS and Atlantis shuttle as seen in broad daylight». Zmescience.com. 20 July 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ «Space Station Transiting 2017 ECLIPSE, My Brain Stopped Working – Smarter Every Day 175». youtube.com. 22 August 2017. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021.
- ^ Grossman, Lisa. «Moon and Space Station Eclipse the Sun». Wired.
- ^ «International Cooperation». NASA. 25 March 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ Garcia, Mark (25 March 2015). «International Cooperation». NASA. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ Farand, Andre. «Astronauts’ behaviour onboard the International Space Station: regulatory framework» (PDF). International Space Station. UNESCO.
- ^ «Boris Johnson to Announce New Russia Sanctions After Ukraine Invasion» – via www.youtube.com.
- ^ «The Russian invasion of Ukraine will have myriad impacts on spaceflight». Ars Technica. 25 February 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ Berger, Eric (2 April 2022). «Russia asked NASA to end sanctions to save the ISS, but the West didn’t blink». Ars Technica.
- ^ «Nasa explores how to keep international space station in orbit without Russian help». the Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 1 March 2022. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ United Nations Treaties and Principles on Outer Space. (PDF). United Nations. New York. 2002. ISBN 92-1-100900-6. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: «Tier 2 EIS for ISS» (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ a b
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Suffredini, Michael (October 2010). «ISS End-of-Life Disposal Plan» (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 7 March 2012.
- ^ Zak, Anatoly (22 May 2009). «Russia ‘to save its ISS modules’«. BBC News. Retrieved 23 May 2009.
- ^ «DC-1 and MIM-2». RussianSpaceWeb. Archived from the original on 10 February 2009. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Maass, Ryan (30 September 2015). «NASA extends Boeing contract for International Space Station». Space Daily. UPI. Retrieved 2 October 2015.
- ^ Grush, Loren (24 January 2018). «Trump administration wants to end NASA funding for the International Space Station by 2025». The Verge. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- ^ «Commercial space bill dies in the House». SpaceNews.com. 22 December 2018. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ Cruz, Ted (21 December 2018). «S.3277 – 115th Congress (2017–2018): Space Frontier Act of 2018». United States Congress. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ Babin, Brian (26 September 2018). «H.R.6910 – 115th Congress (2017-2018): Leading Human Spaceflight Act». United States Congress. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ Johnson, Lamar (9 August 2022). «Biden ends slog on semiconductor bill with signature». Politico. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- ^ Errick, Kirsten (4 August 2022). «NASA Authorization Act Aims to Strengthen U.S. Space Exploration». Nextgov.com. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- ^ «NASA plans to take International Space Station out of orbit in January 2031 by crashing it into ‘spacecraft cemetery’«. Sky News. 1 February 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ Zidbits (6 November 2010). «What Is The Most Expensive Object Ever Built?». Zidbits.com. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ Lafleur, Claude (8 March 2010). «Costs of US piloted programs». The Space Review. Retrieved 18 February 2012. See author correction in comments.
- ^ «Space Station 3D». IMDb. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ «A Beautiful Planet — Experience Earth Like Never Before». abeautifulplanet.imax.com. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ Shaw, Debra Benita (2008). Technoculture: The Key Concepts. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 67. ISBN 978-1-84520-298-9.
- ^ «Life». Sony Pictures. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ «Love». IMDb. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ «Gravity». IMDb. Retrieved 21 March 2022.
Attribution:
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Further reading[edit]
- Reference Guide to the International Space Station (PDF) (Utilization ed.). NASA. September 2015. NP-2015-05-022-JSC.
- Reference Guide to the International Space Station (PDF) (Assembly Complete ed.). NASA. 2010. ISBN 978-0-16-086517-6. NP-2010-09-682-HQ.
- O’Sullivan, John. European Missions to the International Space Station: 2013 to 2019 (Springer Nature, 2020).
- Ruttley, Tara M., Julie A. Robinson, and William H. Gerstenmaier. «The International Space Station: Collaboration, Utilization, and Commercialization.» Social Science Quarterly 98.4 (2017): 1160–1174. online
External links[edit]
- Official website
- ISS Location
Agency ISS websites[edit]
Research[edit]
- NASA: Daily ISS Reports
- NASA: Station Science
- ESA: Columbus
- RSC Energia: Science Research on ISS Russian Segment Archived 11 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine
Live viewing[edit]
- Live ISS webcam by NASA at uStream.tv
- Live HD ISS webcams by NASA HDEV at uStream.tv
- Sighting opportunities at NASA.gov
- Complete Orbital Position at KarhuKoti.com
- Real-time position at Heavens-above.com
- Real-time tracking and position at uphere.space
Multimedia[edit]
- Johnson Space Center image gallery at Flickr.com
- ISS tour with Sunita Williams by NASA at YouTube.com
- Journey to the ISS by ESA at YouTube.com
- The Future of Hope, Kibō module documentary by JAXA at YouTube.com
- Seán Doran’s compiled videos of orbital photography from the ISS: Orbit – Remastered, Orbit: Uncut; The Four Seasons, Nocturne – Earth at Night, Earthbound, The Pearl (see Flickr album for more)